Avaya Integrated Management User Manual

Avaya Integrated Management
Release 5.0
Network Management Console
14-300169
Issue 7
January 2008

© 2008 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the infor mation in this
document was complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya Inc. can
assume no liability for any errors. Changes and corrections to the information
in this document may be incorporated in future releases.
For full legal page information, please see the complete document, A vaya
Legal Page for Software Documentation, Document number 03-600758.
To locate this document on the website, simply go to
http://www.avaya.com/support
search box.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for any modifications, addition s, or deletions to
the original published version of this documentation unless such modifications,
additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya. Customer and/or End User
agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents, servants and
employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of,
or in connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this
documentation to the extent made by the Customer or End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web
sites referenced elsewhere within this documentation, and Avaya does not
necessarily endorse the products, services, or informa tion described or o ff ered
within them. We cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time and
we have no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales
agreement to establish the terms of the limited warran ty. In addition, Avaya’s
standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support for this
product, while under warranty, is available through the following Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, the Product is protected by copyrigh t
and other laws respecting proprietary rights. Unauthorized reproduction,
transfer, and or use can be a criminal, as well as a civil, offense un der the
applicable law.
Avaya support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report pro blems or t o ask
questions about your product. The support telephone number
is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support telephone
numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support
and search for the document number in the

Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
The Purpose of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Who Should Use This Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Organization of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Chapter 1: Avaya Network Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Avaya Network Management Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Avaya Network Management Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
What is Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
What is Avaya Network Management Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
What is a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
What is Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
What is Event Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
What’s New in This Release. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 2: Avaya Network Management Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Starting Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Stopping Avaya Network Management Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Chapter 3: Avaya Network Management Console Introduction . . . . . 25
Starting Avaya Network Management Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Remote Access and Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Licensing Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Changing Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Avaya Network Management Console User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Interfaces Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Alarms Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Modules Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Dialog Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Using Tooltips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Requesting Write Permission. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Issue 7 January 2008 3

Contents
Avaya Network Management Console Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
SNMP Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Default SNMP Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Setting SNMP Access Parameters for IP Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Setting Specific IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Setting Connectivity Polling Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Selecting a Default Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Setting Read/Write Defaults. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Setting CM Server Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Using Avaya Network Management Console Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Using Avaya Network Management Console Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Opening the Help to the Contents Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Opening the Help to a Topic of Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Chapter 4: Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree . . . . . 47
Introduction to the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Using the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
The Subnet View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
The Device Type View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
The VoIP System View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Creating Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Modifying Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Deleting Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Adding Branches in Custom Views. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Modifying Branches in Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Deleting Branches in Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Printing the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Searching the Tree. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Chapter 5: Launching Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Launching Device Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
IP Office Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
IP Office System Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Web Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
PING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Avaya Site Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Avaya MultiSite Administration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
4 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Avaya Fault and Performance Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Avaya Voice Announcement Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Extreme EPICenter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Polycom GMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Launching Network-wide Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Chapter 6: Avaya Network Management Console Tables. . . . . . . . . 69
The Network Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Network Table Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Network Table Colors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Viewing and Searching the Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Choosing Table Parameters to Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Filtering the Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
The Alarms Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Alarms Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
The Modules Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Modules Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Managing Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Contents
Manually Adding Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Modifying Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Device Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Deleting Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
The Port Connections Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Port Connections Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
The Registered Endpoints Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Registered Endpoints Table Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
The Inventory Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Inventory Table Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Inventory Table Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Inventory Table Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Choosing Inventory Table Parameters to Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Chapter 7: Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Introduction to Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Managing Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Creating a Network Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Opening a Network Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Saving a Network Map to a Different Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Printing a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Issue 7 January 2008 5

Contents
Importing Devices into the Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Exporting the Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
CSV File Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Chapter 8: Configuration Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Configuration Wizard Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Using the Configuration Wizard Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Step 1 - Welcome Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Step 2 - Identify CM Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Add/Edit CM Servers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Create or Add SNMPv3 User . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Server Certificate Verification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Provide SNMPv3 Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Step 3 - Define SNMP Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Configure User SNMP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Step 4 - Specify IP Networks to be Managed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Configure Subnet Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Step 5 - Start Network Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Chapter 9: Introduction to the Discovery Window . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Opening the Discovery Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
The Discovery User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Discovery Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Subnets Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Discovery Dialog Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Discovery Log Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Discovery Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Closing the Discovery Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Chapter 10: Discovering Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Setting Discovery Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Configuring Discovery Method and Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Configuring Discovery’s Naming Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Selecting Device Types to Discover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Using the Discovery Scheduler. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Discovering Subnets and Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Discovering All Subnets and Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Discovering Nodes on Specific Subnets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Manually Adding Subnets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
6 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Modifying Subnets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Subnet Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Deleting Subnets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Using the Discovery Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Configuring Router Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Saving the Discovery Log. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Deleting Log Entries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Clearing the Discovery Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Chapter 11: Introduction to the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Event Manager Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Viewing the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
The Event Manager User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
The Event Log Browser User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Event Log Browser Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
The Trap Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Status Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
The Event Configuration User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Event Configuration Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
The Event Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Assign Action Form Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Event Configuration Form Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
The Action List User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Action List Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
The Action Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Action Form Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Closing the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Contents
Chapter 12: Managing Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Managing Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Event Log Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Filtering Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Filtering by Severity Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Filtering by Category . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Filtering by IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Filtering by Device Type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Filtering by Acknowledged . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Viewing All Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Acknowledging Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Deleting Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Issue 7 January 2008 7

Contents
Editing Severity Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Saving the Event Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Defining Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Actions Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Adding Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Modifying Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Action Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Action Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Action Audio Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Deleting Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Applying Changes to the Action List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Action Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Configuring Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Assigning Actions to Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Configuring Event Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Event Forwarding Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Configuring Forwarding Recipients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Appendix A: Network Management Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Avaya Network Management Console Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Avaya Network Management Console File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Avaya Network Management Console Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Avaya Network Management Console View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Avaya Network Management Console Actions Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Avaya Network Management Console Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Avaya Network Management Console Help Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Discovery Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Discovery File Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Discovery Edit Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Discovery View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Discovery Actions Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Discovery Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Event Log Browser Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Event Log Browser File Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Event Log Browser Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Event Log Browser View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Event Log Browser Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Event Configuration Menus. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Event Configuration File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Event Configuration Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
8 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Event Configuration Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Event Configuration Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Action List Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Action List File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Action List Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Action List Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Action List Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Contents
Issue 7 January 2008 9

Contents
10 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
Preface
Welcome to Avaya Network Management. This chapter provides an introductio n to the structure
and assumptions of this manual. It includes the following sections:
● The Purpose of This Manual - A description of the goals of this manual.
● Who Should Use This Manual - The intended audience of this manual.
● Organization of This Manual - The structure of this manual.
The Purpose of This Manual
This manual contains information needed to use Avaya Network Management, efficiently and
effectively.
Who Should Use This Manual
This manual is intended for network managers familiar with network management and its
fundamental concepts.
Organization of This Manual
This manual is structured to reflect the following conceptual divisions:
● Preface - A description of the manual’s purpose, intended audience, and organization.
● Avaya Network Management - An overview of Avaya Network Management, including a
discussion of basic network management concepts.
● Avaya Network Management Server - An overview of Avaya Network Management Server
including instructions on starting Avaya Network Management Server from your computer.
● Avaya Network Management Console Introduction - An introduction to Avaya Network
Management Console, including instructions on starting Avaya Network Management
Console, a detailed description of Avaya Network Management Console’s user interface,
and instructions on how to use Avaya Network Management Console’s on-line help.
Issue 7 January 2008 11

Preface
● Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree - A description of the Avaya Network
Management Console network tree including its default views - the Subnet View and
Device Type View - and the VoIP System View for networks containing VoIP devices. It
also includes instructions on how to create custom views and search the tree.
● Launching Applications - Instructions on how to launch device-specific and network-wide
applications from Avaya Network Management Console.
● Avaya Network Management Console Tables - A description of the contents of the Avaya
Network Management Console network table in different views, and instructions on how to
add, delete, and modify objects in the table.
● Network Maps - An explanation of Network Maps, instructions on how to create, open,
save, and print Network Maps, and instructions on importing devices into Network Maps
and exporting devices from Network Maps.
● Configuration Wizard - Information and instructions for using the Configuration Wizard.
● Introduction to the Discovery Window - Instructions on how to open and close the
Discovery window and a description of the Discovery window.
● Discovering Your Network - Instructions on how to use Avaya Network Management to
discover the subnets, nodes, and VoIP devices on your network. It also includes an
explanation of the Discovery Log and how to configure a router’s access p arameters using
SNMP V1 or SNMP V3 protocol.
● Introduction to the Event Manager - Instructions on how to open and close the Event
Manager and a description of the Event Manager.
● Managing Events - Instructions on how to use the Event Manager to view, filter, and delete
events from the Event Log Browser, define event actions, and assign actions to events.
● Network Management Menus - A description of the structure of the menus in the Network
Management Console.
12 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Chapter 1: Avaya Network Management
This chapter provides an overview and general description of Avaya Network Management. It
includes the following sections:
● Avaya Network Management Overview - A general description of Avaya Network
Management.
● Avaya Network Management Terms - Definitions of terms used in this documentation.
● What is Avaya Network Management Server - A description of the Avaya Network
Management Server and its functions.
● What is Avaya Network Management Console - A description of Avaya Network
Management Console and its functions.
● What is a Network Map - A description of Network Maps and their functions.
● What is Discovery - A description of Network Management’s Discovery feature.
● What is Event Handling - A description of events and how to view them using the Event
Manager.
More detailed information about each of these topics can be found in subsequent chapters.
Issue 7 January 2008 13

Avaya Network Management
Avaya Network Management Overview
Avaya Network Management includes A vaya Network Management Server and A vaya Network
Management Console, an application that allows you to view the devices in your network.
Avaya Network Management Console also provides a platform from which you can launch
applications to manage network devices and monitor the traffic on your network. In addition,
Avaya Network Management provides a Discovery service that can search your network for
devices and an Event Log that reports network events.
Avaya Network Management uses a client/server architecture, enabling multiple users to
access the Avaya Network Management Server simultaneously. Web based technology
provides a method for accessing and managing your network from any computer with Internet
access.
The figure below illustrates the flow of information between the different components that
comprise Avaya Network Management and Avaya Network Management applications.
Figure 1: Network Management Overview
Postgres
User Input User Input
Avaya Network
Management
Console Server
Avaya Network
Management Console
Local Access
Device Managers
Daem ons
Network-wide
Application s
Database
I
nt
er
ne
t
Avaya Network
Management
Console
Rem ote Access
i40
AM110
i120
Network
Devices
Device Managers
Network-wide
Application s
When Avaya Network Management Server is launched, it runs a number of daemons, which
poll the network devices listed in the default Network Map to determine their st atus and updates
their colors in the Avaya Network Manageme nt Console View Area. Users can manage devices
or launch network-wide applications via Avaya Network Management Console. Avaya Network
14 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
Management Console communicates these requests to Avaya Network Management Server,
which launches the correct applications. When run remotely, these applications are uploaded
from Avaya Network Management Server to the remote station.
Avaya Network Management Terms
The following table provides a list of terms used in Avaya Network Management documentation
with their descriptions.
Table 1: Network Management Terms
Term Description
Best Name The best name for a device known to Network Management. For
information on defining the method used by Network Management to
arrive at the Best Name, refer to Configuring Discovery’s Naming
Method on page 116.
Avaya Network Management Terms
Branch An intermediate level in the Network Tree. Branches include device t ypes,
subnets, and user defined branches in custom views of the network.
Postgres
Database
Network Map The set of devices that are known to Avaya Network Management Server.
Node A network device. Nodes include (but are not limited to) switches, hubs,
Object A branch or node in the network.
Poll A request by an application for information from a device.
A database where information about the devices in the Network Map is
stored.
routers, network printers, and computers.
What is Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server communicates with the devices in the network via Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP) V1 or V3. It receives user input via Avaya Network
Management Console and updates Avaya Network Management Console with information from
the network devices. Avaya Network Management Server runs in the background as a
Windows Vista/2003/2000/XP service. The server provides a central address for event
reporting. It passes traps to Avaya Network Management Console for display in the Event Log
Browser. For more information about event handling and traps, refer to What is Event
Handling on page 18.
Issue 7 January 2008 15
Avaya Network Management
In addition, Avaya Network Management Server enables you to operate Avaya Network
Management Console from a remote location. This feature provides a method for managing
your network from any computer connected to the Internet. By pointing your web browser to
Avaya Network Management Server’s IP address, you can access Avaya Network
Management Console and manage your network. For more information on running Avaya
Network Management Console from a remote location, refer to Starting Avaya Network
Management Console on page 26.
What is Avaya Network Management Console
Avaya Network Management Console is the user interface to Avaya Network Management
Server. It receives information from Avaya Network Management Server and sends the server
information input by the user. Avaya Network Management Console displays the devices in the
current Network Map using a hierarchical tree. The tree can be organized by subnet or device
type, or logically by voice system hierarchy. Additionally, you can create custom views of the
network.
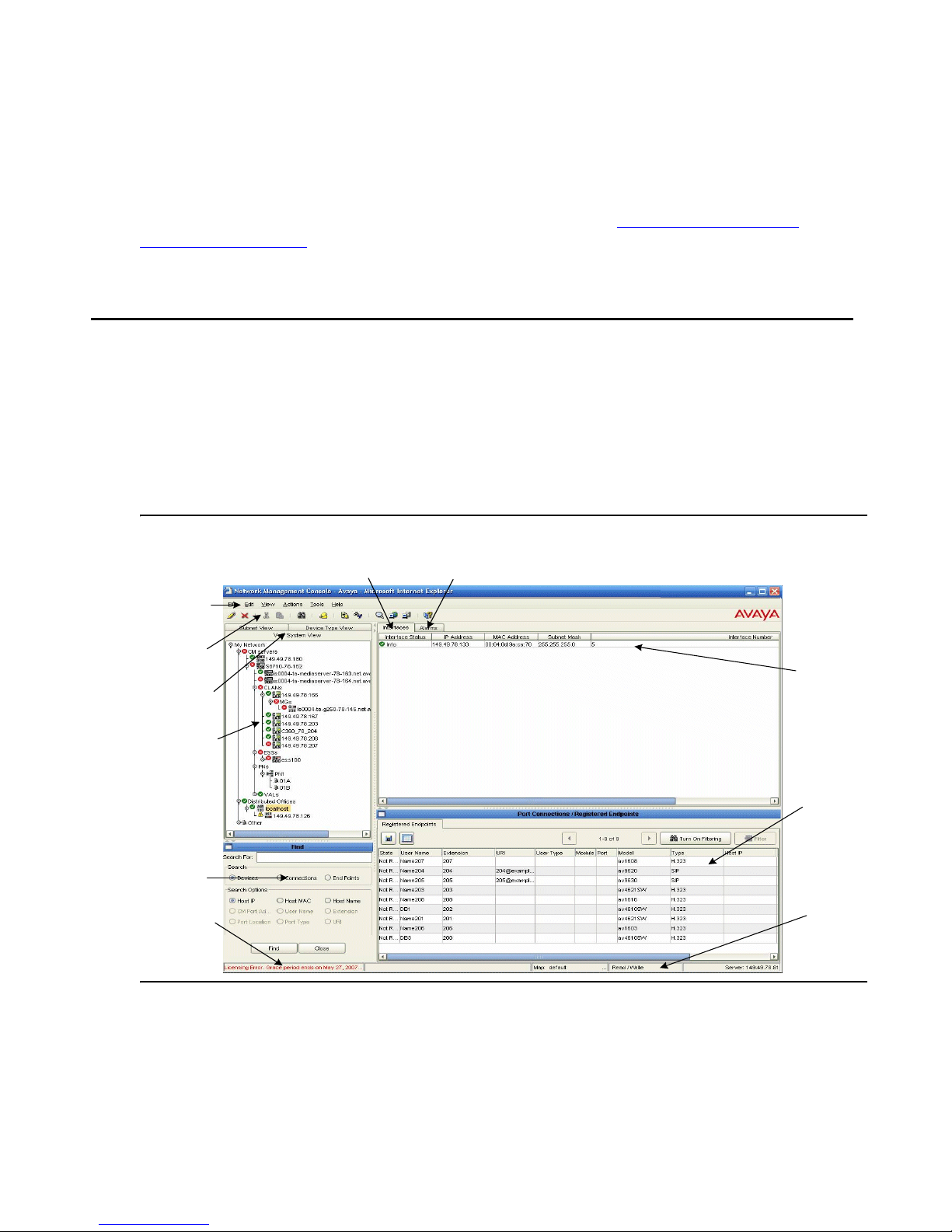
Figure 2: Avaya Network Management Console
Menu Bar
Toolbar
View Tabs
Network Tree
Search
Area
Licensing
Inform a tio n
Interface s
Tab
Alarms
Tab
Network
Table
Dialog
Area
Status
Bar
When a device in the Network Tree is selected, information about the selected device appears
in the Network Table. You can then modify the device’s parameters. Avaya Network
Management Console also provides the ability to launch applications that communicate directly
16 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
with the device. These applications allow you to manage the device via its Command Line
Interface (CLI) or Device Manager, and monitor the traffic on the device. For example, if you
select an Avaya G350 Device in the Network Table, you can launch Telnet to configure the
device via its CLI, or launch Avaya G350 Device Manager to configure and monitor the device
via its management application. In addition, Avaya Network Man agement Console allows you to
launch network-wide applications such as, Avaya Software Update Manager for updating
embedded software.
What is a Network Map
A Network Map consists of all of the devices known to Avaya Network Management Server,
their physical connectivity to ports, and their relationship in the voice hierarchy. The list of
devices is stored in the database, along with basic information about each device. When
Avaya Network Management Console opens, Avaya Network Management Server extracts
information about the devices in the Network Map from the database. These devices are
displayed in the Network Tree.
What is a Network Map
Devices can be added to the current Network Map using Discovery or the Add Device dialog
box. Devices in the Network Map can also be modified. All changes to the Network Map are
stored in the database.
You can maintain multiple Network Maps by saving individual maps with unique names. The
Network Map whose devices are visible in Avaya Network Management Console is the current
Network Map.
Note:
Note: Changing the map affects all open network-wide applications.
You can also create a text file that contains the necessary information about each device you
want to add to the current Network Map and import the devices listed in the file into the Network
Map. For more information on importing devices into the Network Map, refer to Importing
Devices into the Network Map on page 95.
Avaya Network Management Server can also export the information in th e current Network Map
to a CSV file. For more information on exporting the device information from the current
Network Map, refer to Exporting the Network Map
on page 95.
Issue 7 January 2008 17

Avaya Network Management
What is Discovery
Avaya Network Management uses Discovery to detect or ’discover’ your network. The
Discovery tool discovers subnets and nodes, the physical port location of the devices, the
Avaya VoIP hierarchy, phone information and phone locations for IP, analo g and digit al ph ones.
The Discovery tool uses SNMP MIB-II on network nodes to search your network. In addition,
you can instruct Discovery to use ICMP Echo (ping) to search the network. You can instruct
Discovery to search your entire network, limit the search to selected subnets, or update
information about the objects in the Network View.
The Discovery window displays the results of your search. You can apply the results of a
Discovery to the current Network Map.
What is Event Handling
Events are unexpected or extraordinary occurrences in your network. Examples of events
include the loss of a port’s connection, the insertion or removal of a module from a device, and
the failure of a fan or power supply. Network Management provides a method of reporting
network events.
Note:
Note: For the purposes of this document, the terms ‘event’ and ‘trap’ are used
interchangeably.
Network Management communicates with device agents using SNMP. Device agent s can send
traps to Avaya Network Management Server reporting on the st atus of their po rts, modules, etc.
The server then passes traps to the relevant managers of the device involved and updates the
Event Manager.
To receive traps using Avaya Network Management, network devices must be configured to
send traps to the Avaya Network Management Server. For information on configuring Avaya
LAN and backbone devices to send traps to Avaya Network Management Server, refer to the
User Guide or Device Manager User Guide for the devices in your network. The Event Manager
maintains a log of all traps received from the devices in the networ k. These traps can be viewed
in the Event Log Browser.
18 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
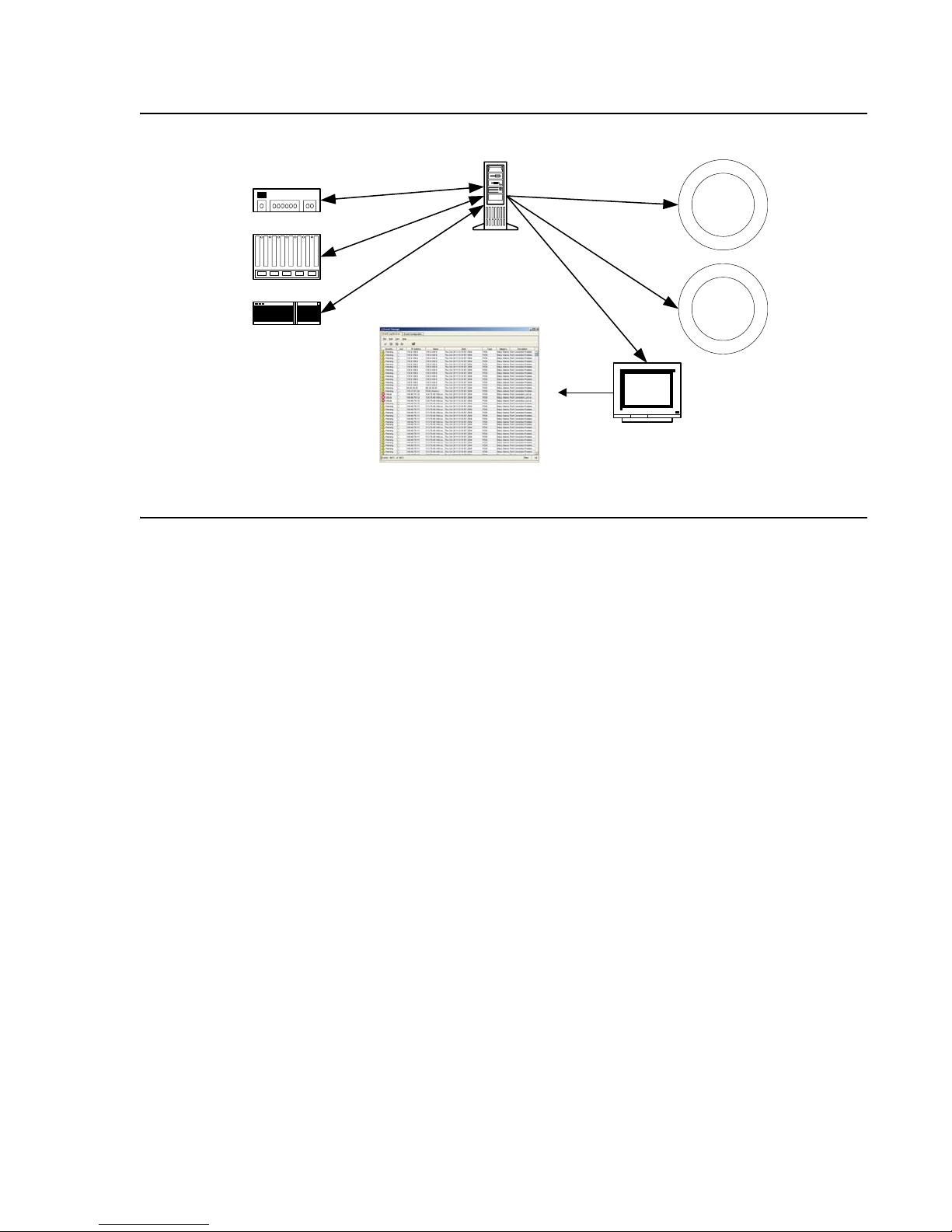
Figure 3: Event Handling Flow
g
Network Devices
SNMP
Avaya
Network
Managem ent
Server
What is Event Handling
Device
Managers
Network
Appli-
cations
Avaya Network
Managem ent Console
Avaya Network Management Console
Event Lo
Browser
Traps are categorized by their severity. Some traps report events that are not problems. An
example of this type of trap is the insertion of a module into a device. These traps have a
severity level of Info. Other traps require more attention, such as the loss of a regular port’s
connection. Traps of this type have a severity level of Warning. Finally, there are traps, such as
the failure of a backbone link, which require immediate attention. These traps have a severity
level of Minor, Major, or Critical.
Issue 7 January 2008 19
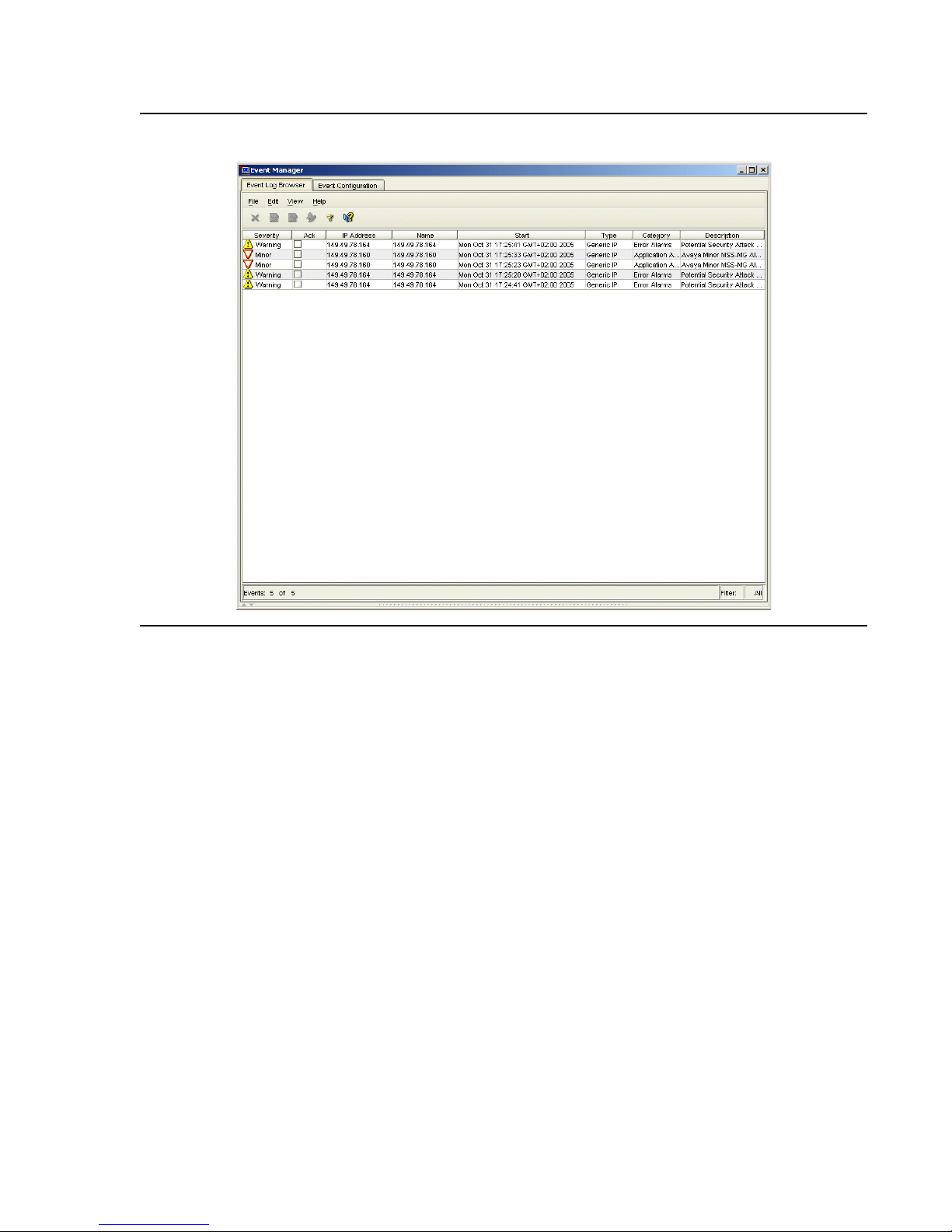
Avaya Network Management
Figure 4: Event Log Browser
The Event Manager displays all of the traps sent by A vaya Net work Management Server. In the
Event Manager you can:
● Sort the Event Log Browser by any of its fields.
● Filter the traps displayed and change the severity of selected traps.
● Acknowledge traps to help you remember which traps you have already seen.
● Define the format of the description field.
● Delete traps, signifying that the problem causing the trap was resolved.
In addition, the Event Manager allows you to define event actions. Event actions can include
notification via a pop-up, audible, or e-mail message or the running of a script. Actions can be
assigned to any network events. You can also limit the action to events from specified sources.
This feature enables you to receive immediate notification of important network events.
The Event Manager can also act as a trap surrogate, forwarding all, or selected, traps to other
devices.
20 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

What’s New in This Release
Avaya Network Management Console Release 5.0 introduces the following enhancements:
● Support for Avaya Communication Manager Release 5.0:
- You can automatically configure Avaya Communication Manager Release 5.0 to work
with Avaya Network Management Console.
- All digital and analog phones that work with Avaya Communication Manager Release 5.0
are discovered and displayed in Avaya Network Management Console.
● Support for the S8300C (Avaya Communication Manager/SES co-residency):
- The S8300C is displayed in VoIP System View as a branch under the co-resident Avaya
Communication Manager.
- SIP phones registered to the SES are discovered and displayed in Avaya Network
Management Console. You can search for these phones in the Port Connection table.
● Support for the G450 branch gateway (including discovery, display in System View, trap
formatting, fault monitoring, administration, and port connections).
What’s New in This Release
● Support for the G860 high density trunk gateway.
● Support for the following routers with the IG550 Integrated Gateway (including discovery,
display in System View, trap formatting, fault monitoring, and administration):
- J2320
- J2350
● Support for the following media modules on the IG550 Integrated Gateway:
- TIM508 (8-port FXS Analog Telephony Interface Module)
- TIM516 (16-port FXS Analog Telephony Interface Module)
- TIM518 (8+8-port FXS/FXO Analog Telephony Interface Module)
● Support for the following new set types:
- 9630G IP Telephone
- 9640G IP Telephone
● The ability to manage IP Office devices. You can now run IP Office Manager R6.1 and
Avaya Provisioning and Installation Manager for IP Office from Network Management
Console.
Issue 7 January 2008 21

Avaya Network Management
22 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Chapter 2: Avaya Network Management Server
This chapter provides a detailed description of Avaya Network Management Server. It includes
the following sections:
● Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server - An introduction to Avaya Network
Management Server.
● Starting Avaya Network Management Server - Detailed instructions on how to start Avaya
Network Management Server.
● Stopping Avaya Network Management Server - Detailed instructions on how to shut down
Avaya Network Management Server.
Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server communicates with network devices. It p asses informa tion
to Avaya Network Management Console and handles requests to launch applications. In
addition, Avaya Network Management Server enables remote sessions of Avaya Network
Management Console. Ensure that Avaya Network Management Server is running on the host
computer before starting Avaya Network Management Console locally, and that it is running on
the remote server before starting a remote session of Avaya Network Management Console.
Avaya Network Management Server can import devices from CSV (Comma Separated Value)
files into the Network Map. Avaya Network Management Server can also export the Network
Map to a CSV file, for use with other applications, such as a Microsoft Excel.
Issue 7 January 2008 23

Avaya Network Management Server
Starting Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server is a Windows Service. When Windows start s on the server
station, Avaya Network Management Server starts automatically. Using Windows’ Service
Manager, you can configure Avaya Network Management Server so that it does not start
automatically.
If Avaya Network Management Server is shut down, you will need to start it manually. To
manually start or stop Avaya Network Management Server, you must be logged in to Windows
with Administrator privileges. When you log off the computer, Avaya Network Management
Server continues running.
To start Avaya Network Management Server:
Select Start > Programs > Avaya > Start Avaya Services.
To view the status of Avaya Network Management Server:
Select St art > Programs > Avaya > Tools > A vaya Network Management Serve r Status.
Stopping Avaya Network Management Server
To stop Avaya Network Management Server:
Select Start > Programs > Avaya > Stop Avaya Services.
24 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Chapter 3: Avaya Network Management Console
Introduction
This chapter provides an introduction to Avaya Network Management Console. It includes the
following sections:
● Starting Avaya Network Management Console - Instructions on how to start Avaya
Network Management Console, information about security issues when accessing Avaya
Network Management Console from a web browser, and licensing information.
● Avaya Network Management Console User Interface - An introduction to Avaya Network
Management Console’s user interface, including instructions on how to use the toolbar
buttons.
● Requesting Write Permission - Instructions on how to request and release Read/Write
permissions for a specific Avaya Network Management Console session.
● Avaya Network Management Console Options - Instructions on how to set Avaya Network
Management Console’s options.
● Using Avaya Network Management Console Tables - An explanation of symbols used in
Avaya Network Management Console tables.
● Using Avaya Network Management Console Help - An explanation of the options for
accessing on-line help in Avaya Network Management Console.
Issue 7 January 2008 25

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Starting Avaya Network Management Console
Avaya Network Management Console is a java applet running in a browser. When you point
your browser to the Avaya Network Management Server’s IP address, a Java applet prepares
your browser to communicate with Avaya Network Management Server. A welcome screen
appears, followed by a password screen. Once you enter a valid user name and password,
Avaya Network Management Console opens in a special browser window.
To start a local session of Avaya Network Management Console from the server:
1. Double-click the Avaya Integrated Management link on the Windows desktop. Avaya
Integrated Management home page is launched.
2. From the Avaya Integrated Management home page, click the Network Management
Console link to launch Avaya Network Management Console.
To start a session of Avaya Network Management Console from a client machine:
1. Point your web browser to http://IP_Address/ where IP_Address is the IP address of the
Avaya Network Management Server. The Avaya Integrated Management entry page opens
(see Figure 5
).
26 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
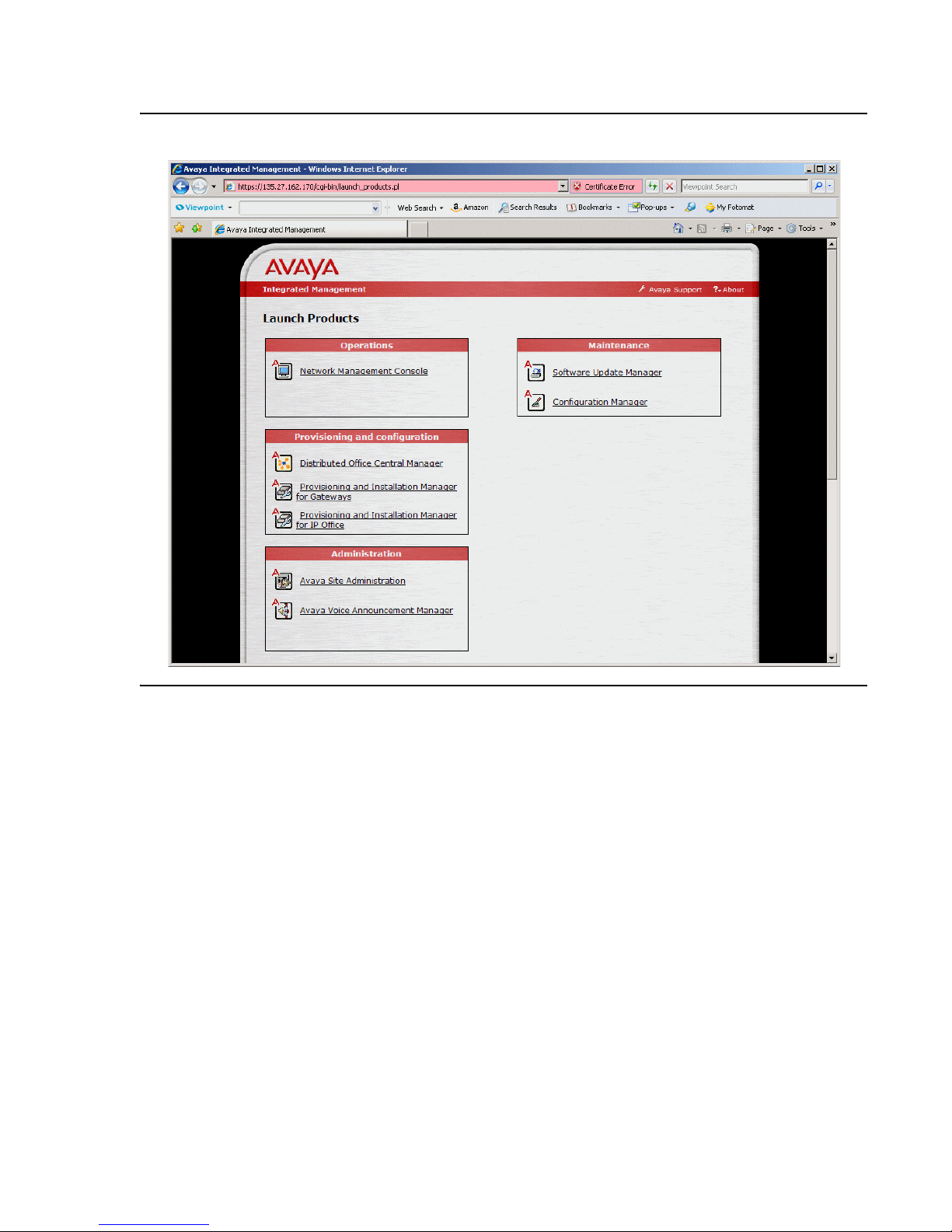
Starting Avaya Network Management Console
Figure 5: Avaya Integrated Management Home Page
2. Click Network Management Console. The Java applet starts.
3. A window opens requesting your user name and password.
4. Enter your user name and password, and click OK. After a few seconds, Avaya Network
Management Console opens.
Issue 7 January 2008 27

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Remote Access and Security
You can access Avaya Network Management Console from any computer, using a web
browser. Network Management’s files are secured by Windows NT’s NTFS file system. This
prevents unauthorized users from changing Network Management’s files. In addition, the web
server is configured to work with HTTPS, and login to Avaya Network Management Console
requires authentication. This enables only authorized users to access Avaya Network
Management Console remotely. For more information on NTFS, refer to your Microsoft
Windows user guide.
Avaya Network Management Console communicates with devices using SNMP. Only the
SNMPv3 protocol is encrypted and requires authentication. It is, therefore, highly recommended
that you use the SNMPv3 protocol.
Licensing Requirements
Avaya Network Management Console is a licensed product. Upon installation, you have 30
days to install a product license. Login will be disabled if your license is not installed after 30
days. A warning message displaying the product expiry date is shown during login and the
license expiry date is displayed in the status bar, until the license is installed. For further details
please refer to the Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Enterprise Network
Management Installation and Upgrade Guide 14-300444.
28 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console

Changing Passwords
You can change your password through Avaya Network Management Console.
To change your password:
1. Select Actions > Change Password. The Password Change window opens.
Figure 6: Password Change Window
Changing Passwords
2. Enter your old password in the Old Password field.
3. Enter your new password in the New Password field.
4. Enter your new password in the Confirm Password field.
5. Click .
Issue 7 January 2008 29

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Avaya Network Management Console User Interface
The user interface consists of the following elements:
● Menu Bar - Menus for accessing Avaya Network Management Console management
functions. For more information on menus, refer to Appendix A: Network Management
Menus.
● Toolbar - Toolbar buttons for accessing Avaya Network Management Console
management functions.
● Network Tree - A resizeable window containing a hierarchical representation of the
Network Map.
● View Tabs - Tabs for switching between the various views of the network.
● Interfaces Tab - Displays a table where details about the branches and nodes in the
Network Tree are displayed.
● Alarms Tab - Displays a table where alarms reported for devices on the network are
displayed.
● Modules T ab - Disp lays a table where a list of modules and the module type are displayed.
● Dialog Area - A resizeable window where all dialog boxes open.
● Status Bar - Displays information about the current Avaya Network Management Console
session and license expiry information.
The figure below shows the user interface, with its various parts labeled.
30 Avaya Integrated Management Release 5.0 Network Management Console
 Loading...
Loading...