Page 1

Business Communication Manager Interoperability with
Communication Server 1000 and Meridian 1 IP Trunk
Document issue: 5.2
Document status: Standard
Product release: BCM 4.0 / BCM50R2
Date : June 2007
Page 2

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Revision History
Version
1.0 Dec 2003 Introduction of BCM 3.5 and Communication Server 1000Rls 3.0
2.0 June 2004 Introduction of BCM 3.6
3.0 March 2005 Update to include Communication Server 1000 Rls 4.0
4.0 May 2005 Update to include BCM 3.7 and BCM50
5.0 Nov 2006 Update to include BCM 4.0, BCM50R2, Communication Server 1000 Rls 4.5
5.1 Dec 2006 Corrected Table 1 to reflect SRG 1.5 support with Succession 3.0.
5.2 June 2007 Corrected Tables 6 and 7 to reflect the correct operation and support level of
Date Reason for Release
TRO-CM functionality from a BCM perspective.
List of Tables
Table 1: H.323 Interoperability by Software Release 3
Table 2: SIP Interoperability by Software Release 4
Table 3: Interoperability Patch Reference Table 5
Table 4: Supported H.323 Functionality - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5 6
Table 5: Supported H.323 Functionality between BCM and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk 3.0x 8
Table 6: Known H.323 Interop Issues Between BCM and CS1000 Release 4.5 and 4.0 11
Table 7: Known H.323 Interop Issues between BCM and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk 3.0x 14
Table 8: Succession and Meridian 1with IP Trunk Codec Configuration Rules 16
Table 9: Supported SIP Functionality - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5 18
Table 10: Known SIP Interop Issues - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5 19
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 2 OF 20
V
Page 3
BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Business Communications Manager Interoperability with
Communication Server 1000 and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk
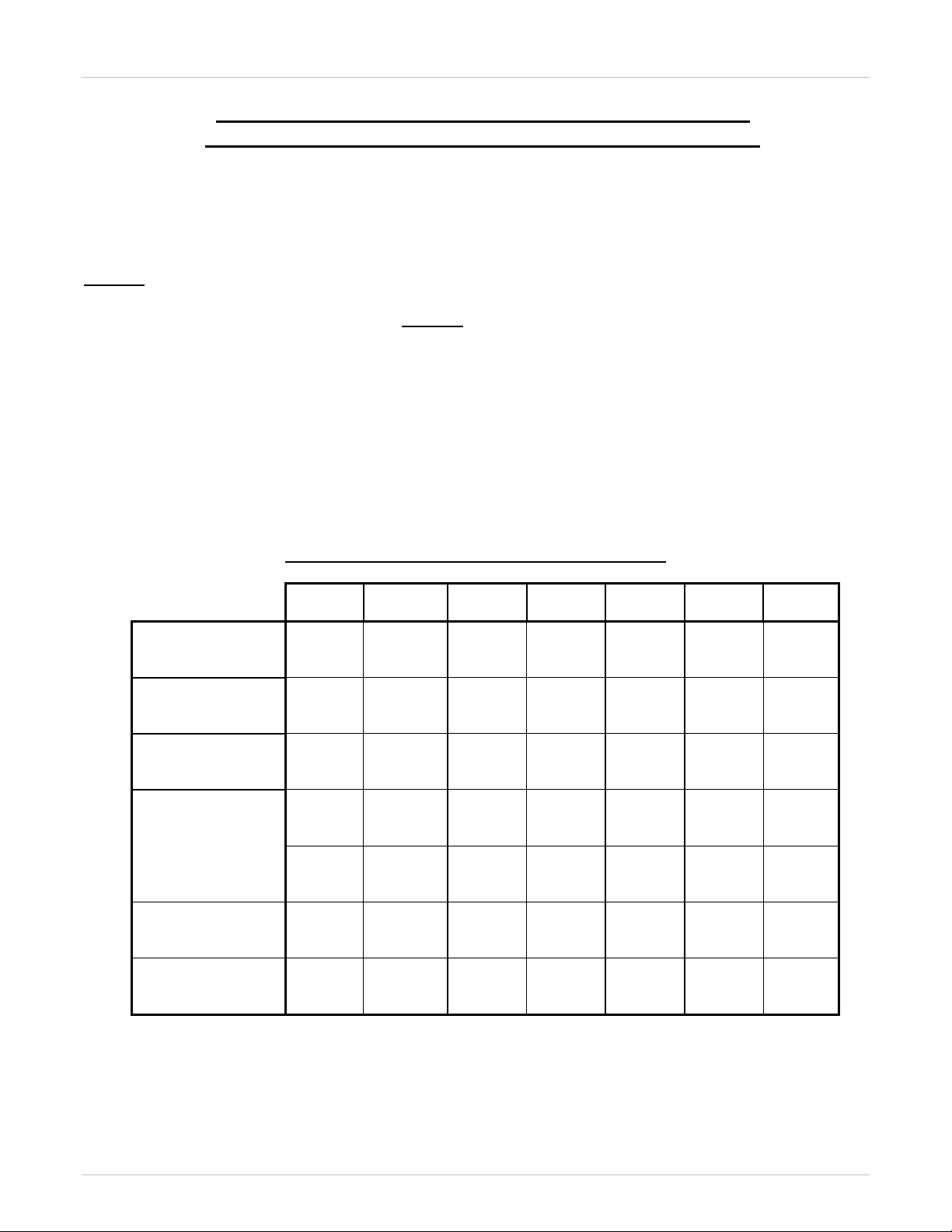
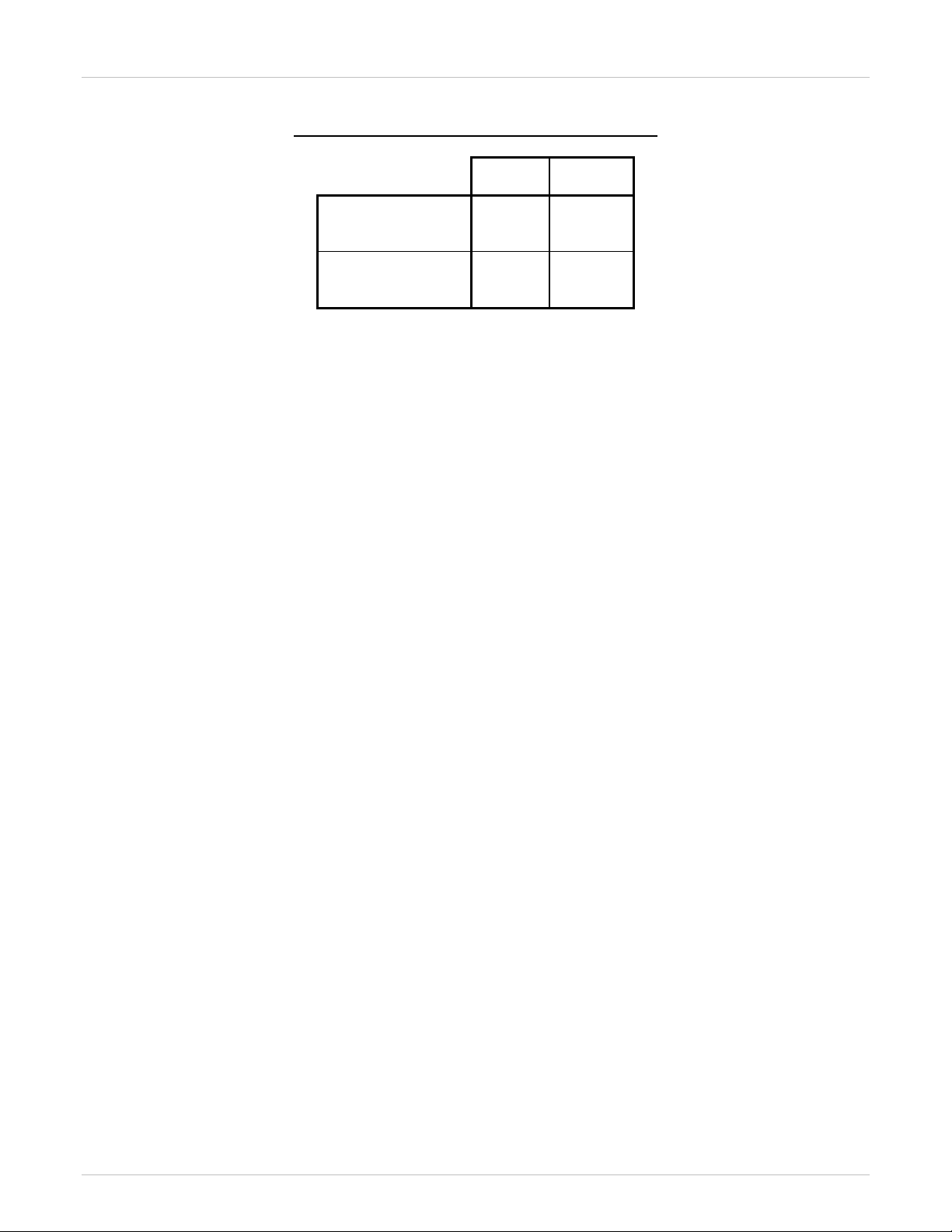
Table 1 and Table 2 represent the H.323 and SIP trunk interoperability, respectively, between various software
releases of the Business Communications Manager (BCM), the Communication Server 1000, and Meridian 1 IP
Trunk (formerly known as ITG Trunk) products. Blank cells indicate an unsupported configuration.
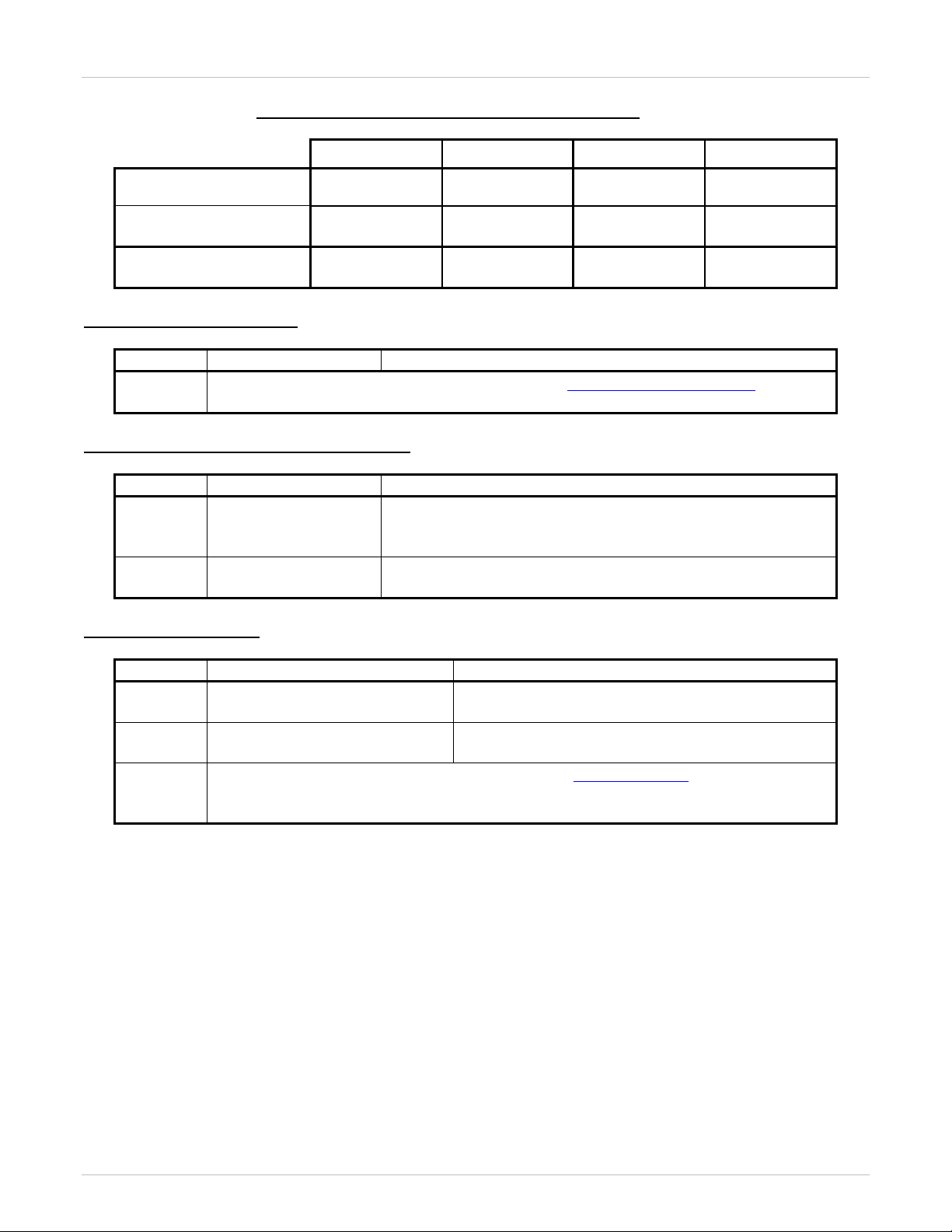
provides a summary of the PEPs and BCM Patches that are applicable to interoperability between the products.
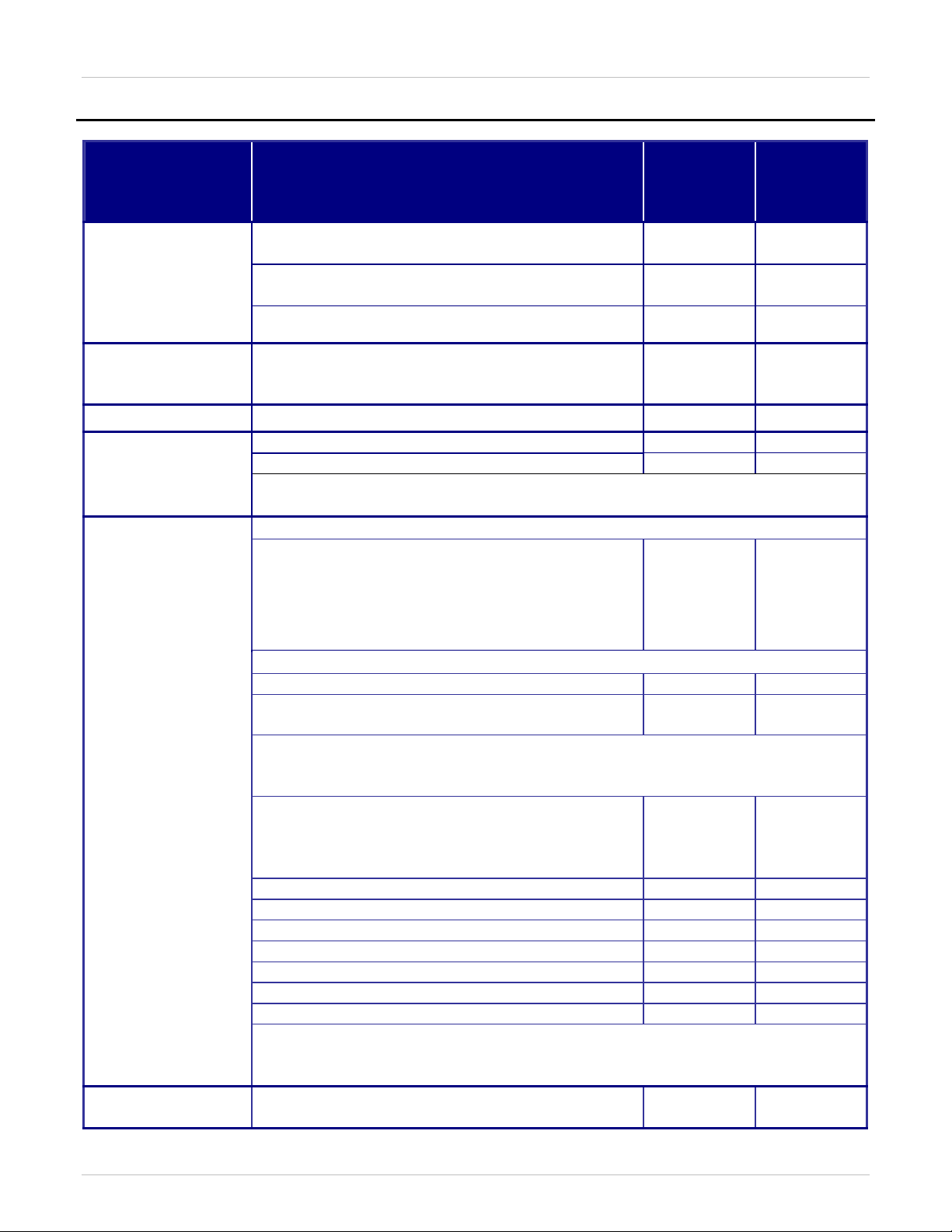
Table 4 and Table 5 provide a list of specific features that are supported between the latest releases of the BCM
(i.e. 4.0 / BCM50R2, and 3.7 / BCM50) with the Communication Server 1000 Rls 4.5 / 4.0, and Meridian 1 IP
Trunk 3.01 releases, respectively. Similarly,
the latest BCM releases and the Communication Server 1000 Rls 4.5 and 4.0, and IP Trunk 3.01 releases,
respectively.
Table 8 provides additional detail into codec configuration rules and diagnostic information.
Note: In this document, “CS1000 4.0” or “CS1000 4.5” refers to Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 or
4.5 respectively.
Note: Except where otherwise specifically noted in the document, the Survivable Remote Gateway (SRG)
interoperability is the same as the corresponding BCM 3.7, BCM 4.0, BCM50R1 or BCM50R2 release.
Table 1: H.323 Interoperability by Software Release
Table 6 and Table 7 identify the known issues that exist between
Table 3
BCM3.5 BCM 3.6 SRG 1.0 BCM 3.7
Succession 1000
Rls 2
Meridian 1
IP Trunk 3.0
Meridian 1 or
Succession 1000M
w/ IP Trunk 3.01
Succession 3.0
(using Signaling
Server 2.10.81)
Succession 3.0
(using Signaling
Server 2.11.03)
Communication
Server 1000 Rls 4.0
Communication
Server 1000 Rls 4.5
BCM50
R1
Supported
Supported
Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported Supported
BCM 4.0
Supported
on
SRG 1.5
Supported
on
SRG 1.5
BCM50
R2
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 3 OF 20
V
Page 4
BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 2: SIP Interoperability by Software Release
BCM 4.0
Communication
Server 1000 Rls 4.0
Communication
Server 1000 Rls 4.5
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
BCM50
R2
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 4 OF 20
V
Page 5
BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 3: Interoperability Patch Reference Table
Meridian 1 or Succession
1000M IP Trunk 3.01
Communication Server
1000 Rls 4.0
Communication Server
1000 Rls 4.5
BCM 3.7 BCM50R1 BCM 4.0 BCM50R2
T1, T2, B1, B3 T1, T2, B2, B3 T1, T2, B3 T1, T2, B3
S1, B1, B3 S1, B2, B3 S1, B3 S1, B3
S1, B1, B3 S1, B2, B3 S1, B3 S1, B3
Succession Patch References:
Reference Patch ID Status
S1 Refer to Nortel Enterprise Solutions PEP Library (http://www.nortel.com/espl) for Core
and Interop DepLists
Meridian 1 with IP Trunk Patch References:
Reference Patch Name Status
T1 MPLR18316 Optional (Required to allow V.34 fax machines to revert to G3
operation for T.38)
Note: This has been fixed in IP Trunk upissue 3.01.52
T2 MPLR17721 Required when MCDN not configured on BCM
Note: This has been fixed in IP Trunk upissue 3.01.09
BCM Patch References:
Reference Patch Name Status
B1 BCM370.175-FEPS (FEPS
37.222.0.33)
B2 BCM050.108-FEPS (FEPS:
40.330.0.33)
B3 Refer to the BCM Software Downloads web site at www.nortel.com (by following
Support and Training, Technical Support, Software Downloads) for latest BCM patch
information.
Generally Available.
Generally Available.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 5 OF 20
V
Page 6
BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 4: Supported H.323 Functionality - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5
Supported
Functionality
(with CS1000 4.0 and
4.5)
CS1000 4.0/45
Network Routing
Server (NRS)
Succession 4.0/4.5
IP Peer Gateway
(Signaling Server)
H.323 Basic Call
Private Dial Plan
MCDN Networking
Description BCM 3.7
and
BCM50R1
Registration:
Supported Supported
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
• Registers as an H.323 Endpoint
Signaling method:
Supported Supported
• Gatekeeper Resolved
Alternate Gatekeeper
H.225 Call Signaling (using Nortel Interoperability
Supported
(Programmable)
Supported
(Programmable)
Supported Supported
format)
H.245 Media Channel Signaling
Call connection with Calling Line ID
CDP dial plan
UDP dial plan
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
• BCM private dial plan can only be configured for either CDP or UDP, not both
simultaneously.
Applications:
The following are typical applications that can be
supported using MCDN features:
Supported
Supported
• Centralized Voicemail,
• Central Attendant (Basic),
• Centralized Trunking
T.38 Fax
MCDN Features:
Private Name/Number
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
* Refer to
Table 6
Supported Supported
Supported*
Supported
(See note)
Notes:
• BCM 4.0 and BCM50R2 have enhanced the BCM TAT implementation to enable
TAT support on CTI based calls (eg. calls using BCM AutoAttendant functionality).
Trunk Route Optimization:
• Before Answer (TRO-BA)
• Call Modification (TRO-CM)
* Refer to
Table 6
Network Call Redirection
Message Waiting Indication (MWI)
Message Indicator Key (MIK)
Message Cancel Key (MCK)
Station Camp-on
Barge-In
ISDN Call Connection Limit (ICCL)
Not Supported*
Supported*
Not Supported*
Supported*
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Notes:
• On the BCM, these capabilities are enabled via the Nortel Voice Networking
(MCDN) keycode. The BCM Gateway Protocol must be set to “CSE”.
Fax detection during H.323 call; renegotiation to T.38
* Refer to
Table 6
Supported* Supported*
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 6 OF 20
V
Page 7

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Supported
Functionality
(with CS1000 4.0 and
4.5)
Overlap Signaling
H.245 Tunneling
Description BCM 3.7
and
BCM50R1
Ability for the CS1000 to be configured to use
Supported Supported
Overlap Signaling on call setup.
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
Notes:
• The BCM will interoperate with the CS1000 when the CS1000 has been configured
to use Overlap Signaling. However, the BCM rejects the Overlap Signaling call
setup attempts and requires Enbloc Signaling to be used.
H.245 messages use existing H.225 connection
Supported Supported
(instead of new TCP connection)
Notes:
• By default, CS1000 4.0 will attempt to use H.245 tunneling. If the BCM is
configured for its’ default setting (H.245 Tunneling: Off), then it negotiates with the
CS1000 to turn H.245 tunneling off.
• The BCM data services (NAT and Firewall) do not support H.323 when H.245
Tunneling is configured.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 7 OF 20
V
Page 8

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
b
Table 5: Supported H.323 Functionality between BCM and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk 3.0x
Supported
Functionality
(with IP Trunk 3.0x)
Network Routing
Server (NRS)
Note that NRS can
refer to the NRS on
CS1000 Rls 4.5 or 4.0
IP Trunk 3.01 Node
Registered with
NRS as
H323 Endpoint
Not Registered with
NRS
Description
Registration:
BCM 3.7
and
BCM50R1
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
Supported Supported
• Stand-alone or Co-resident GK
Signaling method (to IP Trunk 3.01 nodes registered
Supported Supported
with the NRS)
• Gatekeeper Resolved
Alternate NRS (Stand-alone or Co-resident):
• IP Address received during the registration process
H.225 Call Signaling using:
Supported
(Programmable)
Supported
(Programmable)
Supported Supported
• Direct routed to standard UDP port (15000)
• NRS to resolve destination telephone number
• Nortel Networks Interoperability format
capability, including GK-resolved MCDN Non-CallAssociated Signaling (NCAS).
Notes:
• The BCM H.323 Gatekeeper Settings tab should have the Gateway Protocol set to
“CSE”.
• BCM supports the Redirect FACILITY message that IP Trunk 3.01 Node Leader uses
to redirect all incoming calls to a reserved trunk resource in the node.
• BCM supports codec negotiation with IP Trunk 3.01 using Fast Start signaling
elements and H.245 Media Path signaling.
• BCM side (Node B) initiates H.245 Media Channel Signaling for direct media path
etween IP Trunk 3.01 nodes (A and C) that have a tandem IP Trunk call signaling
connection via the BCM (Node B).
• IP Trunk 3.01 side (Node B) never initiates H.245 Media Channel Signaling for direct
media path between BCM nodes (A and C) that have a tandem IP Trunk call signaling
connection via IP Trunk 3.01 (Node B).
H.225 Call Signaling using:
Supported Supported IP Trunk 3.01 Node
• Direct routed to standard TCP port
• Local BCM and IP Trunk dialing plan to resolve the
destination telephone number,
• ITG ISDN IP Trunk format.
MCDN NCAS using:
• Direct routed to a proprietary TCP port
• Local BCM and IP Trunk dialing plan to resolve the
destination telephone number.
Notes:
• The BCM should be configured to use “CSE” as the Gateway Protocol in the BCM
Remote Gateway Table. The IPT should be configured to use “CSE” mode in the dial
plan table.
• BCM supports the Redirect FACILITY message that IP Trunk 3.01 Node Leader uses
to redirect all incoming calls to a reserved trunk resource in the node.
• BCM supports codec negotiation with IP Trunk 3.01 using Fast Start signaling
elements and H.245 Media Path signaling.
• BCM side (Node B) initiates H.245 Media Channel Signaling for direct media path
between IP Trunk 3.01 nodes (A and C) that have a tandem IP Trunk call signaling
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 8 OF 20
V
Page 9

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Supported
Functionality
(with IP Trunk 3.0x)
IP Trunk 3.01 Node
Not Registered with
NRS
(cont’d)
Description
BCM 3.7
and
BCM50R1
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
connection via the BCM (Node B).
• IP Trunk 3.01 side (Node B) never initiates H.245 Media Channel Signaling for direct
media path between BCM nodes (A and C) that have a tandem H.323 Trunk call
signaling connection via IP Trunk 3.01 (Node B).
• IPT 3.0x systems require a PEP (reference
T2 in Table 3) when networked with BCMs
that do not have MCDN functionality activated.
QoS Monitor for Fallback to PSTN
Supported Supported
Notes:
• In direct call signaling mode on the BCM, remote gateway table entries in the Element
Manger give the options to enable QoS and set thresholds. For BCM50R1, BCM50R2
and BCM 4.0 systems, in order for any calls to the IP Trunk 3.01 to succeed when
QoS is enabled on a remote gateway entry, a second remote gateway row may be
required. The first remote gateway entry is provisioned with the IPT’s Node IP. If the
Node IP is different from the Card IP, a second remote gateway table row must be
added containing the Card IP of the IPT card. QoS must be enabled for this new entry.
(This additional entry is not required for BCM 3.7.) Note that this requires using
different Destination Digits in the second remote gateway entry, which will in turn
require the routing tables to be modified to include these digits as well.
H.323 Basic Call Supported Supported
Private Dial Plan
Call connection w/ Calling Line ID
CDP dial plan
UDP dial plan
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
• BCM private dial plan can only be configured for either CDP or UDP, not both
simultaneously.
MCDN Networking
Applications:
The following are typical applications that can be
Supported Supported
supported using MCDN features:
• Centralized Voicemail,
• Central Attendant (Basic),
• Centralized Trunking
Features supported:
Private Name/Number
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
* Refer to
Table 7
Supported Supported
Supported*
Supported
(See note)
Notes:
• BCM 4.0 and BCM50R2 have enhanced the BCM TAT implementation to enable
TAT support on CTI based calls (eg. calls using BCM AutoAttendant functionality).
Trunk Route Optimization:
• Before Answer (TRO-BA)
• Call Modification (TRO-CM)
* Refer to
Table 7
Network Call Redirection
Message Waiting Indication (MWI)
Not Supported*
Supported*
Supported*
Not Supported*
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
(Using call server RCAP of MWI)
Message Indicator Key (MIK)
Message Cancel Key (MCK)
Station Camp-on
Barge-In
ISDN Call Connection Limit (ICCL)
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
Supported Supported
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 9 OF 20
V
Page 10

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Supported
Functionality
(with IP Trunk 3.0x)
T.38 Fax Supported Supported
Description
Fax detection during H.323 call and renegotiation to
BCM 3.7
and
BCM50R1
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
T.38
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 10 OF 20
V
Page 11

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 6: Known H.323 Interop Issues Between BCM and CS1000 Release 4.5 and 4.0
Known Issues with
CS1000 4.5 and 4.0
Multiple Codecs,
Payload Sizes
Description BCM 3.7 and BCM 4.0 and
BCM50R1 BCM50R2
Advertised Codec Payload Configuration Supported Supported Support for
Notes:
• As per the previous release(s) of BCM, CS1000, and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk, for
optimum BCM to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 interoperability,
the codec settings must be coordinated for all H.323 and Unistim endpoints in the
network, particularly if H.323 tandem call scenarios are anticipated (such as blind
transfers). Payload sizes must match across the network.
• Refer to
Table 8 for details on codec configuration rules and diagnostic information.
T. 38 Fax detection & renegotiation Supported Supported T.38 Fax over IP
Notes:
• Note that BCM and IP Trunk 3.01 allow the use of V.34 based faxed machines,
(although they do reject V.34 negotiation attempts) while CS1000 does not.
TRO - BA (Before Answer):
Supported Supported MCDN Networking:
(Pre -Succession 3.0 feature)
TRO - CM (Call modification)
(New Succession 3.0 feature)
Not
Supported
Not
Supported
Notes:
• TRO-CM works as follows in a mixed Succession 4.5/4.0 and BCM VoIP
environment:
o When BCM is a transferring party node (B), TRO-CM does not work; the Media is
direct (A to C), but a tandem Signaling path is maintained (A to B to C).
o If BCM is originating or terminating node (A or C), TRO-CM does not work; the
Media is direct (A to C), but a tandem Signaling path is maintained (A to B to C).
o TRO-CM does not work in Succession 4.0/3.0 for Blind Transfer calls to a station
that is Call Forward No-Answer. The transferring user must remain on the
transferred call until it is answered to ensure that TRO-CM will optimize the call
when the Call Transfer is completed.
o TRO – BA and TRO – CM depend on implementation of a perfectly coordinated
(CDP) and/or uniform (UDP) dialing plan across all nodes in the private IP
Telephony network.
o All Succession 4.0/3.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 routes must be configured to enable
automatic insertion of UDP access codes (INAC = YES) in order for UDP Location
Codes to work with TRO. All nodes must send TRO-BA Offer and TRO-CM
Invoke messages with the correct NPI/TON values for the destination telephone
number.
o In Succession 4.0/3.0 and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk, all network translations where
TRO is required must point to a Route List Block (RLB) with an ENTR 0 that
contains an IP Peer Virtual Trunk or IP Trunk 3.01 route with idle trunk members
o
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
Supported Supported
(Pre -Succession 3.0 implementation)
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT) BCM 3.7:
(Succession 3.0 enhancement)
Supported
BCM50R1:
Supported
Not directly
Supported
(See notes)
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 11 OF 20
V
Page 12

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Known Issues with
CS1000 4.5 and 4.0
MCDN Networking:
(cont’d)
Description BCM 3.7 and BCM 4.0 and
BCM50R1 BCM50R2
Notes:
• BCM50R1 does not support the TAT and NAS enhancement of the Nortel Networks
H.323 Interoperability format that was introduced in Succession 3.0 and IP Trunk
3.01 to accurately validate the trombone condition by comparing the unique gateway
id (MAC address or IP address) in the extended TAT information element in the nonstandard data of the H.225 Setup, Alerting, and Facility messages. The following
text describes what is necessary for TAT to function between these versions of BCM
and the Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and/or IP Trunk 3.01 call servers.
• In the absence of the extended TAT IE in H.225 messages received from BCM,
Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 D-Channel/H.323 Gateway falls
back to comparing the Called and Calling numbers on the outgoing and incoming
side of the tromboned trunk connection.
• If the Called and Calling numbers on the two sides of the call don’t match, then the
TAT Invoke message from BCM is discarded regardless of matching Call Reference.
This prevents wrong connections that can occur due to false TAT optimization when
Call References assigned by different Gateways across the network randomly
matched for unrelated calls.
• Incoming calls to BCM that are answered and transferred within the BCM before
being routed in a trombone connection back to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 or IP
Trunk 3.01 will not be optimized by TAT because the Called and Calling numbers do
not match on the two sides of the tromboned call.
• In a private IP telephony voice network with mixed CDP Steering Codes and UDP
Location Codes, incoming calls to BCM that are forwarded using a different type of
number in a trombone connection back to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 or IP Trunk
3.01 will not be optimized by TAT because the Called and Calling numbers do not
match on the two sides of the tromboned call.
• BCM sets up a direct media path between the two ends of the tromboned connection,
but this can still result in multiple transcoding and voice quality degradation due to
media path loopback via Communication Server 4.5/4.0 Voice Gateway Media Cards
or IP Trunks.
Interop with ESN5 Signaling
Not Supported
Not Supported
Notes:
• Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk use ESN5 signaling
with MCDN to signal the Network Class of Service (NCOS) of the originating
terminal among Succession 4.0/3.0 nodes in order to control access to PSTN trunk
facilities at a remote Call Server and Media Gateway.
• The Nortel Networks Interoperability format introduced in Succession 2.0 supports
an extended ESN5 Information Element in the Non-standard data of the H.225 Call
Setup message, but BCM does not send optional ESN5 Information Element in the
H.225 Call Setup message.
• If ESN5 signaling is enabled on a Succession 4.0/3.0 IP Peer virtual trunk route, you
must configure an appropriate default NCOS value for incoming calls in Element
Manager from BCM to a Virtual Trunk route that has ESN5 signaling enabled.
• Succession 4.0/3.0 IP Peer H.323 Gateways insert a default NCOS value in the ESN5
prefix for calls received from BCM without the extended ESN5 information element.
VPNI IE for Bandwidth Management Zone
signaling
BCM:
Not Supported
SRG:
Partially
Supported
Not Supported
Partially
Supported
BCM:
SRG:
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 12 OF 20
V
Page 13

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Known Issues with
CS1000 4.5 and 4.0
Network Routing
Server Functionality
(NRS)
Description BCM 3.7 and BCM 4.0 and
BCM50R1 BCM50R2
Notes:
• Communication Server 4.5/4.0 provides an optional MCDN Information Element that
signals the Virtual Private Network Identifier and the Bandwidth Management Zone
over IP Peer Virtual Trunk routes to allow Call Servers to coordinate codec selection
appropriately for different Internet Telephones depending on network location. This
VPNI IE is not generated or used on BCM systems. In SRG mode, this VPNI IE is
generated so that the Communication Server 4.5/4.0 can determine which zone calls
are originated or destined for bandwidth management. However, SRG does not
process any incoming VPNI IE and does not provide bandwidth management
capabilities.
Failover to Alternate Supported Supported
Maintenance switchover to Alternate
Not Supported Not Supported
Graceful recovery to Primary Supported Supported
Notes:
• BCM uses the Registration Time-To-Live (TTL) value in the BCM Gatekeeper
settings to establish the point at which re-registration is attempted. If no response is
received from the primary NRS, the BCM will send up to two additional registration
requests, each 12 seconds apart, at which point the alternate NRS registration process
is initiated, with a total elapsed time 24 seconds longer than the TTL setting.
• The Communication Server NRS also supports a mechanism to instruct gateways to
switch to the Alternate NRS for maintenance purposes. Communication Server
4.5/4.0 gateways and IP Trunk 3.01 nodes will re-register to the Alternate GK almost
immediately, while the BCM will treat the condition as a failure, and use the
Alternate NRS failover procedures identified above.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 13 OF 20
V
Page 14

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 7: Known H.323 Interop Issues between BCM and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk 3.0x
Known Issues with
Meridian 1 with
IP Trunk 3.0x
Multiple Codecs,
Payload Sizes
Description BCM 3.7 BCM 4.0
and and
BCM50R1 BCM50R2
Advertised Codec Payload Configuration Supported Supported Support for
Notes:
• As per the previous release(s) of BCM, CS1000, and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk, for
optimum BCM to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 interoperability,
the codec settings must be coordinated for all H.323 and Unistim endpoints in the
network, particularly if H.323 tandem call scenarios are anticipated (such as blind
transfers). Payload sizes must match across the network.
• Refer to
Table 8 for details on codec configuration rules and diagnostic information.
T. 38 Fax detection & renegotiation Supported Supported T.38 Fax over IP
Notes:
• Note that BCM and M1 with IP Trunk 3.01 allow the use of V.34 based faxed
machines, (although they do reject V.34 negotiation attempts) while Communication
Server 1000 does not.
TRO - BA (Before Answer):
Supported Supported MCDN Networking
(Pre -Succession 3.0 feature)
TRO - CM (Call modification) Not
(New Succession 3.0 feature)
Supported
Not
Supported
Notes:
TRO-CM feature works as follows in a mixed Meridian 1 with IP Trunk 3.0x and
BCM VoIP environment:
• When BCM is a transferring party node (B), not an originating or terminating node
(A or C), both the Media and Signaling are direct (A to C).
• When BCM is an originating or terminating node (A or C), the Media and the
Signaling path is maintained between the three sites.
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT) Supported Supported
(Pre -Succession 3.0 implementation)
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
(Succession 3.0 enhancement)
BCM 3.7:
Supported
BCM50:
Supported
Not directly
Supported
Notes:
• BCM50R1 does not support the TAT and NAS enhancement of the Nortel Networks
H.323 Interoperability format that was introduced in Communication Server 3.0 and
IP Trunk 3.01 to accurately validate the trombone condition by comparing the unique
gateway id (MAC address or IP address) in the extended TAT information element in
the non-standard data of the H.225 Setup, Alerting, and Facility messages. The
following text describes what is necessary for TAT to function between these
versions of BCM and the Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and/or IP Trunk 3.01 call
servers.
• In the absence of the extended TAT IE in H.225 messages received from BCM,
Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 D-Channel/H.323 Gateway falls
back to comparing the Called and Calling numbers on the outgoing and incoming
side of the tromboned trunk connection.
• If the Called and Calling numbers on the two sides of the call don’t match, then the
TAT Invoke message from BCM is discarded regardless of matching Call Reference.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 14 OF 20
V
Page 15

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Known Issues with
Meridian 1 with
IP Trunk 3.0x
Description BCM 3.7 BCM 4.0
and and
BCM50R1 BCM50R2
This prevents wrong connections that can occur due to false TAT optimization when
Call References assigned by different Gateways across the network randomly
matched for unrelated calls.
• Incoming calls to BCM that are answered and transferred within the BCM before
being routed in a trombone connection back to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 or IP
Trunk 3.01 will not be optimized by TAT because the Called and Calling numbers do
not match on the two sides of the tromboned call.
• In a private IP telephony voice network with mixed CDP Steering Codes and UDP
Location Codes, incoming calls to BCM that are forwarded using a different type of
number in a trombone connection back to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 or IP Trunk
3.01 will not be optimized by TAT because the Called and Calling numbers do not
match on the two sides of the tromboned call.
• BCM sets up a direct media path between the two ends of the tromboned connection,
but this can still result in multiple transcoding and voice quality degradation due to
media path loopback via Communication Server 4.5/4.0 Voice Gateway Media Cards
or IP Trunks.
Interop with ESN5 Signaling Not
Supported
Not
Supported
Notes:
• Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk use ESN5 signaling
with MCDN to signal the Network Class of Service (NCOS) of the originating
terminal among Communication Server 4.5/4.0 nodes in order to control access to
PSTN trunk facilities at a remote Call Server and Media Gateway.
• If BCM sends H.225 Call Setup with ITG ISDN IP Trunk format, IP Trunk 3.0x does
not recognize BCM as non-ESN5-signaling originating endpoint.
• The IP Trunk 3.0x must be configured with a Gatekeeper-resolved Network
Numbering.
• If ESN5 signaling is enabled on a IPT Trunk route or upgraded Succession 1000M,
you must configure an appropriate default NCOS value on the IP Trunk node for
incoming calls from BCM to a Virtual Trunk route that has ESN5 signaling enabled.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 15 OF 20
V
Page 16

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 8: Succession and Meridian 1with IP Trunk Codec Configuration Rules
Communication Server 4.5/4.0 Element Manager IP Telephony Node VGW Profile:
Payload
Voice Activity
Detection (VAD)
IP Trunk 3.0x OTM 2.1 ITG ISDN IP Trunk Node Properties DSP Profile:
Payload
The following are the default values of the IP Trunk 3.0x:
• G.711 payload size defaults to 20 ms
• G.729A payload size defaults to 20 ms.
• G.723.1 payload size is fixed at 30 ms.
The BCM payload size is now configurable, but does not default to these same values.
For optimum interoperability of a BCM, Communication Server 4.5/4.0, and IP Trunk
3.01 network, the following rules should be adhered to:
• For each BCM/SRG and CS 1000 node in the network the codec list including
payload size must be identical, and the BCM/SRG should be provisioned to
advertise a list of CODECS (i.e. NOT a single CODEC with the biggest payload).
• BCM50 does not support G.723.1 codecs on calls terminating or originating on
TDM sets or circuit-switched trunks on the BCM50, but is supported calls with
two IP endpoints (H.323 to IP set or IP trunk tandem calls).
• Note that the advertised payload size for BCM H.323 negotiation when the BCM
endpoint is an IP set is the higher of the payload size assigned to IP Trunk codecs
or IP Set codec settings.
• G.711 Silence suppression or Voice Activity Detection (VAD) is disabled and
cannot be enabled.
• G.729A setting on the Communication Server 1000is equivalent to “G.729 Silence
suppression disabled” setting on the BCM (i.e. VAD is disabled). G.729AB
setting on the Communication Server 1000is equivalent to “G.729 Silence
suppression enabled” setting on the BCM (i.e. VAD is enabled). Both devices
must be configured with equivalent settings.
• G.723.1 Silence suppression or Voice Activity Detection (VAD) is disabled and
cannot be enabled.
• VAD was previously referred to as Silence Suppression on BCM but was renamed
to align with Communication Server 4.5/4.0 terminology.
The following are the default values of the IP Trunk 3.0x:
• G.711 payload size defaults to 10 ms
• G.729A payload size defaults to 30 ms.
• G.723.1 payload size is fixed at 30 ms.
• G.729A and G.723.1 cannot be selected together for IP Trunk 3.0x.
The BCM payload size is now configurable, but does not default to these same values.
For optimum interoperability of a BCM, Communication Server 4.5/4.0, and IP Trunk
3.01 network, the following rules should be adhered to:
• For each BCM/SRG and CS 1000 node in the network the codec list including
payload size must be identical, and the BCM/SRG should be provisioned to
advertise a list of CODECS (i.e. NOT a single CODEC with the biggest payload).
• BCM50 does not support G.723.1 codecs on calls terminating or originating on
TDM sets or circuit-switched trunks on the BCM50, but is supported calls with
two IP endpoints (H.323 to IP set or IP trunk tandem calls).
• Note that the advertised payload size for BCM H.323 negotiation when the BCM
endpoint is an IP set is the higher of the payload size assigned to IP Trunk codecs
or IP Set codec settings.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 16 OF 20
V
Page 17

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Voice Activity
• G.711 Silence suppression or VAD is disabled by default. Verify that it remains
Detection (VAD)
• G.729A Silence suppression (VAD) is enabled by default. Ensure that the VAD
• G.723.1 Silence suppression or VAD is enabled by default. Ensure that the VAD
• VAD was previously referred to as Silence Suppression on BCM but was renamed
Fax Setting
• T.38 FAX and V.21 FAX tone detection is enabled by default. Verify that V.21
Codec Mismatch Diagnostics:
BCM to Succession
Calls from BCM to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 with a codec mismatch are released
immediately by Communication Server 4.5/4.0 without ringing the terminating
telephone and without seizing an outgoing trunk for a tandem routed call. Succession
3.0 Overlay 96 D-Channel monitor shows the following diagnostic messages:
(For incoming calls from BCM that terminate to a station or an outgoing ISDN PRI)
DCH 10 IMSG SETUP REF 00008021 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:18:46
CALLING #:1405 NUM PLAN: PRIVATE/ABBREVIATED (CDP)
CALLED #:4015 NUM PLAN: PRIVATE/ABBREVIATED (CDP)
DCH 10 OMSG REL COMP REF 00008021 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:18:46
CAUSE :SWED EQIP CONGESTION
DIAG: 171
(For incoming calls from BCM that terminate to a non-ISDN PRI
trunk)
CH 10 IMSG SETUP REF 00008001 CH 83 0 0 0 TOD 18:33:18
CALLING #:1405 NUM PLAN: PRIVATE/ABBREVIATED (CDP)
CALLED #:5010 NUM PLAN: PRIVATE/ABBREVIATED (CDP)
DCH 10 OMSG REL COMP REF 00008001 CH 83 0 0 0 TOD 18:33:18
CAUSE :NO CHANNEL/CIRC AVAIL
DIAG: 095
Succession to BCM
Calls from S Communication Server 4.5/4.0 to BCM with a codec mismatch ring the
terminating telephone until the call is answered, then BCM disconnects the call.
Communication Server 4.5/4.0 Overlay 96 D-Channel monitor shows the following
diagnostic messages:
DCH 10 IMSG CONNECT REF 000001A1 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:30:36
DCH 10 OMSG CONN ACK REF 000001A1 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:30:36
DCH 10 IMSG DISC REF 000001A1 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:30:36
CAUSE :INCOMPATIBLE DEST
DCH 10 OMSG RELEASE REF 000001A1 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:30:36
DCH 10 IMSG REL COMP REF 000001A1 CH 84 0 0 0 TOD 17:30:36
disabled for interoperation with BCM.
setting on IP Trunk matches the Silence suppression setting on BCM.
setting on IP Trunk matches the Silence suppression setting on BCM. IPT 3.00
G.723.1 VAD is always enabled regardless of VAD setting. IPT 3.01 G.723.1
VAD is enabled or disabled according to the VAD setting.
to align with Communication Server 4.5/4.0 terminology.
FAX tone detection remains enabled for T.38 FAX. Group 3 T.38 FAX protocol is
wrongly identified as T.30 in OTM 2.1 ITG ISDN IP Trunk Node Properties DSP
Profile General tab. Don’t be misled -- the FAX protocol is T.38.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 17 OF 20
V
Page 18

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 9: Supported SIP Functionality - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5
Supported SIP
Functionality with
Communication
Description
BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
Server 1000 Release
4.0 and 4.5
Network Routing
Server (NRS)
SIP Basic Call Supported
Private Dial Plan
Static Registration
Dynamic Registration
Call connection with Calling Line ID
CDP dial plan
UDP dial plan
Supported
Not Supported
Supported
Supported
• BCM private dial plan can only be configured for either CDP or UDP, not both
simultaneously.
MCDN Networking:
Applications:
The following are typical applications that can be
supported using a combination of MCDN features and
Supported
information contained in SIP messages:
• Centralized Voicemail,
• Central Attendant (Basic),
• Centralized Trunking
Features:
Private Name/Number
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
* Refer to
Table 6
Supported
Supported
(See note)
Notes:
• BCM 4.0 and BCM50R2 have enhanced the BCM TAT implementation to enable
TAT support on CTI based calls (eg. calls using BCM AutoAttendant functionality).
Trunk Route Optimization:
• Before Answer (TRO-BA)
• Call Modification (TRO-CM)
* Refer to
Table 6
Network Call Redirection
Message Waiting Indication (MWI)
Message Indicator Key (MIK)
Message Cancel Key (MCK)
Station Camp-on
Barge-In
ISDN Call Connection Limit (ICCL)
Supported*
Not Supported*
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Supported
Notes:
• On the BCM, these capabilities are enabled via the Nortel Voice Networking
(MCDN) keycode. The BCM Gateway Protocol must be set to “CSE”.
T.38 Fax Supported*
Fax detection during SIP call; renegotiation to T.38
using UDP transport
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 18 OF 20
V
Page 19

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Table 10: Known SIP Interop Issues - BCM and Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 and 4.5
Known SIP Issues
with CS 1000
Release 4.0 and 4.5
SIP Transport
Protocol
Tandeming between
SIP and H.323
Multiple Codecs,
Payload Sizes
Description BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
• The BCM default is UDP transport. Although the Element Manager interface
displays a selection for TCP, this functionality is not currently supported.
• The Communication Server 1000 Rls 4.5/4.0 default is TCP.
• VAD must be enabled on all sites and codec and payload settings configured per
Nortel recommendation to be able to support tandeming between a SIP and H.323
trunk on BCM. Note that this requirement is also valid for MCS5100 Rls 3.5 and Rls
3.0 interoperability.
• When BCM is tandeming between SIP and H.323 IP trunks and TAT is attempted,
the TAT attempt will fail. Note that this does not impact the call; the call will remain
stable with direct media connection between the two endpoints but will use all of the
original signaling resources for the duration of the call.
Advertised Codec Payload Configuration Supported Support for
Notes:
• As per the previous release(s) of BCM, CS1000, and Meridian 1 with IP Trunk, for
optimum BCM to Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and IP Trunk 3.01 interoperability,
the codec settings must be coordinated for all SIP, H.323 and Unistim endpoints in
the network, particularly if H.323 tandem call scenarios are anticipated (such as blind
transfers). Payload sizes must match across the network.
T. 38 Fax detection & renegotiation Supported T.38 Fax over IP
Notes:
• Note that BCM allows the use of V.34 based faxed machines, (although it rejects
V.34 negotiation attempts) while CS1000 does not.
TRO - BA (Before Answer):
Supported MCDN Networking:
(Pre -Succession 3.0 feature)
TRO - CM (Call modification)
(New Succession 3.0 feature)
Partially
Supported
Notes:
• TRO-CM works as follows in a mixed Succession 4.5/4.0 and BCM SIP
environment:
o When BCM is a transferring party node (B), not an originating or terminating node
(A or C), TRO-CM works and both the Media and Signaling are direct (A to C).
o If BCM is originating or terminating node (A or C), TRO-CM does not work; the
Media is direct (A to C), but a tandem Signaling path is maintained (A to B to C).
o TRO-CM does not work in Succession 4.0/3.0 for Blind Transfer calls to a station
that is Call Forward No-Answer. The transferring user must remain on the
transferred call until it is answered to ensure that TRO-CM will optimize the call
when the Call Transfer is completed.
o TRO – BA and TRO – CM depend on implementation of a perfectly coordinated
(CDP) and/or uniform (UDP) dialing plan across all nodes in the private IP
Telephony network.
o All Succession 4.5/4.0 routes must be configured to enable automatic insertion of
UDP access codes (INAC = YES) in order for UDP Location Codes to work with
TRO. All nodes must send TRO-BA Offer and TRO-CM Invoke messages with the
correct NPI/TON values for the destination telephone number.
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT) Supported
(Pre -Succession 3.0 implementation)
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 19 OF 20
V
Page 20

BCM INTEROPERABILITY WITH COMMUNICATION SERVER 1000 AND MERIDIAN 1 WITH IP TRUNK
Known SIP Issues
with CS 1000
Release 4.0 and 4.5
(cont’d)
Description BCM 4.0
and
BCM50R2
Trunk Anti-Tromboning (TAT)
Supported MCDN Networking:
(Succession 3.0 enhancement)
Interop with ESN5 Signaling
Notes:
Not Supported
• Communication Server 4.5/4.0 and Meridian 1 with
IP Trunk use ESN5 signaling with MCDN to signal
the Network Class of Service (NCOS) of the
originating terminal among Succession 4.5/4.0 nodes
in order to control access to PSTN trunk facilities at
a remote Call Server and Media Gateway.
• The Nortel Networks Interoperability format
introduced in Succession 2.0 supports an extended
ESN5 Information Element in the Non-standard data
of the H.225 Call Setup message, but BCM does not
send optional ESN5 Information Element in the
H.225 Call Setup message.
• If ESN5 signaling is enabled on a Succession 4.5/4.0
IP Peer virtual trunk route, you must configure an
appropriate default NCOS value for incoming calls
in Element Manager from BCM to a Virtual Trunk
route that has ESN5 signaling enabled.
• Succession 4.5/4.0 IP Peer SIP Gateways insert a
default NCOS value in the ESN5 prefix for calls
received from BCM without the extended ESN5
information element.
VPNI IE for Bandwidth Management Zone signaling
Notes:
• Communication Server 4.5/4.0 provides an optional
MCDN Information Element that signals the Virtual
Private Network Identifier and the Bandwidth
Management Zone over IP Peer Virtual Trunk routes
to allow Call Servers to coordinate codec selection
BCM
Not Supported
SRG
Partially
Supported
:
:
appropriately for different Internet Telephones
depending on network location. This VPNI IE is not
generated or used on BCM systems. In SRG mode,
this VPNI IE is generated so that the
Communication Server 4.5/4.0 can determine which
zone calls are originated or destined for bandwidth
management. However, SRG does not process any
incoming VPNI IE and does not provide bandwidth
management capabilities.
ERSION 5.2 JUNE 2007 PAGE 20 OF 20
V
 Loading...
Loading...