Avaya BSG8ew, BSG12ew User Manual

Administration Guide
BSG8ew and BSG12aw/ew/tw 1.0
Business Services Gateway
Document Status: Standard
Document Number: NN47928-600
Document Version: 02.01
Date: May 2008

Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Trademarks
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Document status: Standard
Document version: 02.01
Document date: 14 May 2008
Copyright
All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada and the United States of America
LEGAL NOTICE
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly agreed to in
writing, NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT “AS-IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY
KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. This information and/or products described in this document are subject to
change without notice.
© 2008, Nortel Networks

Contents
New in this release. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Network Address Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
WiFi support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
SIP support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
VoIP gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
IP phone Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Quality of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Power over Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Ethernet connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
ADSL interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
FXO/FXS ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to Get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Contents 3
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Using the BSG Web UI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Logging on to the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Modifying system information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Deleting system information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
BSG security policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configuring LAN resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configuring MAC filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Enabling Network Address Translation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Configuring dynamic NAT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Firewall configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Defining management access to the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Enabling RMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Enabling SSH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuring authorized clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Configuring remote access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configuring the NAT virtual server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Enabling SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring SNMP community settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Administration Guide

4 Contents
Configuring authorization and authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
BSG users and groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Manage users and groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Manage passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
BSG fault management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Modifying SNMP community settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configuring an SNMPv3 user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Adding SNMPv3 users to groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Configuring SNMPv3 group privileges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring the SNMPv3 view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring digital certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Configuring user authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Creating a group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Adding privileges to a group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Creating a user account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Changing a user password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Changing the administrator password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Configure SNMP alarms and events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Enabling alarms and events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Configuring SNMP trap settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Viewing T1/E1 alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Configuring RMON events and alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Configuring RMON events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Configuring RMON alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
BSG performance management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Bridge information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Viewing bridge information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Interface statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Viewing interface statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Viewing Ethernet statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Viewing wireless statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
VLAN Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Viewing VLAN FDB Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Viewing VLAN Multicast Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
MSTP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Viewing MSTP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Viewing CIST port statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Viewing MSTI port statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
RSTP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Viewing RSTP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Viewing RSTP port statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
NN47928-600NN47928-600

Contents 5
802.1x statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Viewing 802.1x port based session statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Viewing 802.1x MAC based statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Viewing 802.1x authenticator statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Viewing 802.1x supplicant statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Viewing 802.1x MAC session statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
IP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Viewing IP interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Viewing ARP Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Viewing IP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Viewing ICMP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Viewing DHCP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Viewing DHCP binding statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Viewing DHCP server statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Viewing DHCP relay statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Viewing RIP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
OSPF Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Viewing OSPF statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Viewing OSPF Interface statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Viewing VRRP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
IGMP Snooping Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Viewing IGS V1/V2 statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Viewing IGS V3 statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Configuring and viewing RMOM statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Configuring RMON Ethernet statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Configuring RMON history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Viewing RMON Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Viewing NAT statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Viewing firewall statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Viewing VPN statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
VPN Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
VPN IKE Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
VPN IPSEC Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Viewing DSL Line statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Viewing T1/E1 statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Viewing T1/E1 current statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Viewing T1/E1 interval statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Viewing T1/E1 total statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
SIP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Viewing SIP summary statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Viewing SIP methods statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Viewing SIP response statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Administration Guide

6 Contents
Viewing QoS statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Viewing TACACS statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
BSG system logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Configuring logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Viewing logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Transferring logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
BSG backup and restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Backing up BSG configuration data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Restoring the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
BSG software upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Viewing policer statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Viewing queue statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Enabling system logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Configuring the syslog IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Configuring e-mail notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Viewing system logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Viewing the VPN log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Viewing the firewall log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Transferring a log file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Backing up configuration files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Restoring from a backup file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Restoring factory defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Upgrading the BSG software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Viewing system information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Viewing the system summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Viewing system files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Viewing PoE information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Viewing the IP interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Viewing the Interface status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Viewing the DHCP bindings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Viewing the ARP cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Viewing the MAC address table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Viewing the WLAN stations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Common operating procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Saving configuration files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Updating system information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Configuring the date and time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Rebooting the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Downloading files to the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Uploading files from the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
NN47928-600NN47928-600

Contents 7
Initial troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Network configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Site network map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Logical connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Device configuration information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Other important data about your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Normal behavior on your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Useful troubleshooting links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Partner Bulletins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Knowledge and Solution Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Using the Knowledge and Solution Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Diagnostic tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
SIP diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
T1/E1 loopbacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Advanced troubleshooting on the BSG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Switching and routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Layer 2 switching is not functioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Layer 3 forwarding is not functioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
LAN host does not receive an automatic IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
WAN and VPN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
WAN access failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Firewall issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
No traffic between WAN and LAN host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Verifying site-to-site VPN connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
DNS does not resolve the domain name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
PPP link does not start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
PPP link fails when the WAN interface is DSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Determining whether Telnet is operational . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Verifying a Telnet session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Determining whether SSH connects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
BSG subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Determining whether VOIP/SafeNet/SIP/ Wireless is operational . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Troubleshooting SIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Troubleshooting WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Firmware upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Administration Guide

8 Contents
NN47928-600NN47928-600

New in this release
The following sections detail what is new in Administration Guide for the Business Services
Gateway 8-port (BSG) and the BSG 12ew/aw/tw for Release 1.0.
Features
See the following sections for information about feature changes:
• Security
• Network Address Translation
• WiFi support
• SIP support
• Vo I P g a t e wa y
• IP phone Support
• Quality of Service
• Power over Ethernet
• Ethernet connectivity
• ADSL interface
• FXO/FXS ports
9
Security
The BSG provides several security features to protect your network.
Stateful firewall
The BSG stateful firewall monitors the connections on all of its interfaces. The BSG uses this
monitoring process to filter traffic and to apply security policies established on your network. The
stateful firewall also provides protection against port scanning by closing ports until a connection
request for a specific port is received.
RADIUS and TACACS authentication
By default, users are authenticated on the local BSG system. Alternately, you can choose to
authenticate users on a centralized server using Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
(RADIUS) or Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS).
VPN with IPSec
Private networking with IPSec ensures that only authorized users can access the network and that
data is protected.
Administration Guide

10 New in this release
Network Address Translation
Network Address Translation (NAT) enables the LAN to use one set of IP addresses for internal
traffic and one set of IP addresses for external traffic. This translation allows computers on a
private network to access the internet without requiring their own global (public) internet address.
The BSG supports three types of NAT: many-to-one, static, and dynamic.
WiFi support
The BSG provides connectivity for an 802.1 WLAN interface.
SIP support
The BSG supports Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) applications. SIP is a signalling protocol for
VoIP calls. It is also used for other media types, such as white board sessions and voice-data
integration.
VoIP gateway
The BSG provides gateway services for Voice over IP (VoIP) applications, such as the conversion
of voice and fax calls between the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) and the IP
network.
IP phone Support
The BSG supports IP phones that are connected to your network.
Quality of Service
You can configure and monitor Quality of Service (QoS) levels on your network.
Power over Ethernet
The Power over Ethernet (PoE) ports on the BSG provide power for connected devices. PoE ports
help minimize the number of electrical outlets and cables needed at the installation site.
Ethernet connectivity
The BSG provides Ethernet connectivity. The number of Ethernet ports available depends on the
model of BSG that you use. The BSG8ew provides 8 ports.
ADSL interface
The BSG12aw provides connections for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) equipment.
NN47928-600NN47928-600

New in this release 11
FXO/FXS ports
The BSG provides connections for Analog Telephony Adapter (ATA), fax, or an analog voice
trunk. When you connect an analog voice trunk to the Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) or Foreign
Exchange Subsciber (FXS) ports, the analog trunk can be used to connect your network with the
PSTN if the digital connections to your ISP fail.
Administration Guide

12 New in this release
NN47928-600NN47928-600

How to Get Help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel Technical Support
Web site:
http://www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to address issues
with Nortel products. More specifically, the site enables you to:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base for answers to
technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for Nortel equipment
13
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you don’t find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support Web site, and have a
Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the phone number for your region:
http://www.nortel.com/callus
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express Routing Code (ERC)
to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel product or service. To locate the ERC for
your product or service, go to:
http://www.nortel.com/erc
Administration Guide

14 How to Get Help
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchase a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or authorized reseller,
contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
NN47928-600NN47928-600

Introduction
This guide describes how to manage and maintain BSG 8ew and the BSG 12ew/aw/tw systems.
The concepts, operations, and tasks described in the guide relate to the fault, configuration,
performance, and security management features of the BSG system. This guide also describes
additional administrative tasks, such as log management, backups, and software updates.
The tasks described in this guide are based on the assumption that you use the BSG with full
administrative privileges. If you do not have full administrative privileges, you may see only a
subset of the tasks and panels described in this guide.
Navigation
• Using the BSG Web UI (page 17)
• BSG security policies (page 19)
• BSG users and groups (page 53)
• BSG fault management (page 59)
• BSG performance management (page 67)
• BSG system logs (page 113)
• BSG backup and restore (page 119)
• BSG software upgrades (page 123)
• Viewing system information (page 125)
• Common operating procedures (page 133)
• Initial troubleshooting (page 139)
• Advanced troubleshooting on the BSG (page 145)
15
Administration Guide

16 Introduction
NN47928-600

Using the BSG Web UI
The Web User Interface (Web UI) is the primary management application that you use to
configure and administer BSG system. This chapter provides basic procedures for using the Web
UI, such as logging in, and modifying and deleting system information.
Navigation
• Logging on to the BSG (page 17)
• Modifying system information (page 18)
• Deleting system information (page 18)
Logging on to the BSG
The Web UI uses standard Internet browsers like Internet Explorer or Firefox to connect to BSG
devices over an IP network. Use the following procedure to access the BSG through the Web UI.
You can access the Web UI by using any of the following browsers:
17
• Internet Explorer 6.0
• Internet Explorer 7.0
• Mozilla Firefox
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 Open the Web browser such as Internet Explorer.
2 In the browser, type the IP address of the BSG.
3 Press Enter.
The BSG LOGIN page appears.
4 In the User Name field, type the user name.
5 In the Password field, type the password.
6 Click Login.
On successful validation of the user name and password, the System
Information page appears.
End
Administration Guide

18 Using the BSG Web UI
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to use the fields in the login page.
Variable Val ue
User Name Specifies the user name. The
default logon name is
nnadmin.
Password Specifies the password. The
default password is
PlsChgMe!.
Modifying system information
Many panels on the Web UI have two distinct areas: one area where you can configure new
settings, and a second area that lists existing settings in tabular format. For example, on the panel
Configuration > System > User Management > Users tab, the area at the top of the screen allows
you to enter the information for a new user account, while the table below lists the existing users.
When you want to modify an existing setting on the BSG, you can do so using the table provided.
Use the following procedure to modify existing system information on the BSG.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select the appropriate path for the information
that you want to modify.
2 In the table, select the row that you want to modify.
3 Modify the settings as needed.
4 Click Apply.
End
Deleting system information
Perform the following procedure to delete existing settings on the BSG.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select the appropriate path for the information
that you want to delete.
2 In the table, select the row that you want to delete.
3 Click Delete.
NN47928-600NN47928-600
End

BSG security policies
You can configure the BSG to apply security to incoming and outgoing traffic on your network.
This chapter describes how to configure the system-wide security policies that control network
access.
Navigation
• Configuring LAN resources (page 19)
• Defining management access to the BSG (page 31)
• Configuring authorization and authentication (page 44)
Configuring LAN resources
This section provides procedures for configuring the policies that control access to and from the
LAN.
19
Navigation
• Configuring MAC filters (page 20)
• Enabling Network Address Translation (page 22)
• Firewall configuration (page 25)
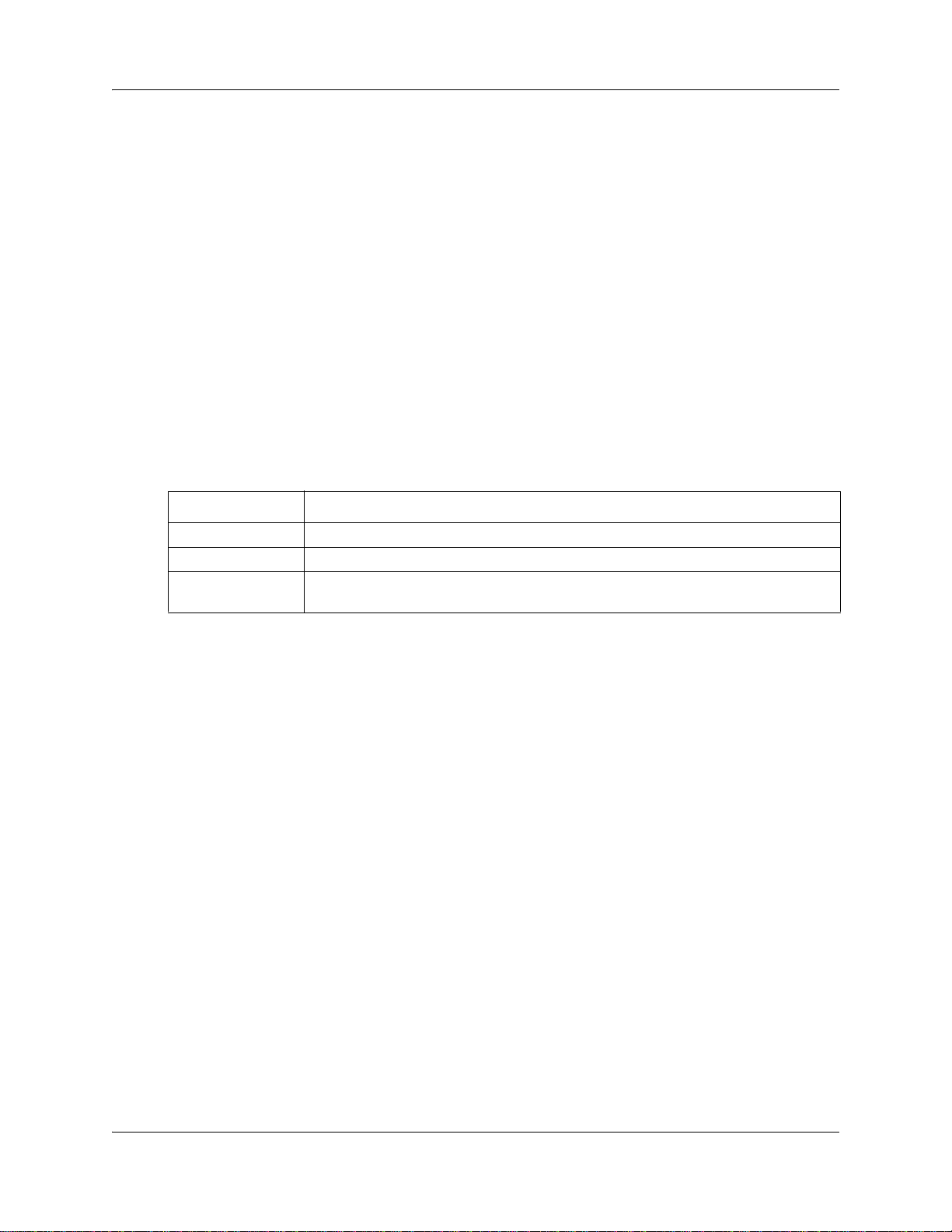
Use the following flowchart to determine which procedures to perform to define access to the
LAN.
Administration Guide
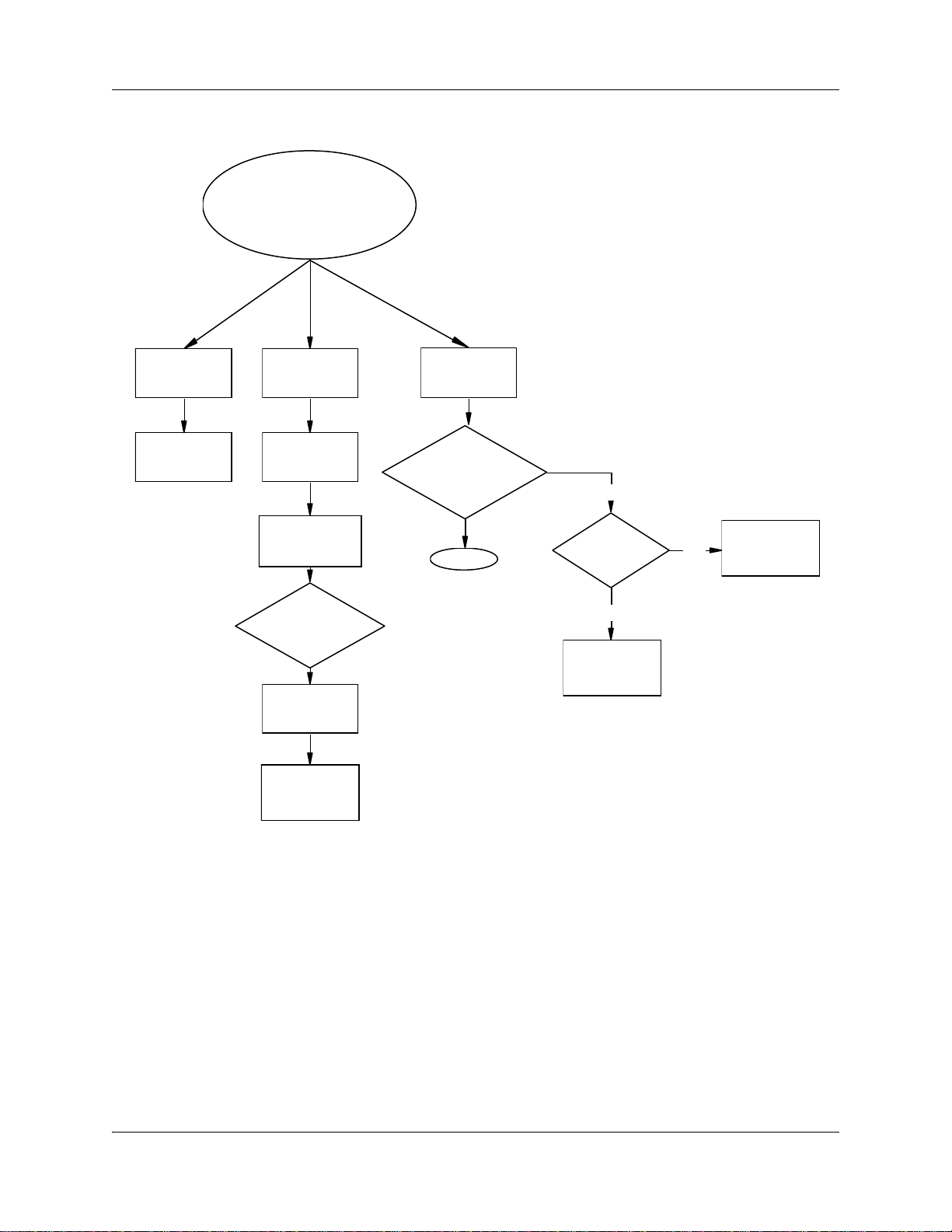
20 BSG security policies
Figure 1 Procedures for configuring LAN resources
Configuring LAN resources
Configuring MAC
unicast filters
Configuring MAC
multicast filters
Configuring the
firewall
Configuring
firewall filters
Associating filters
with access lists
Configure
optional firewall
settings?
Configuring URL
filters
Configuring the
DMZ
Enable NAT
Use default NAT
settings? (many-
to-one NAT)
Done
NO
Use static
NAT?
YES
Configuring
static NAT
NO
Configuring
dynamic NAT
Configuring MAC filters
This section describes how to configure MAC unicast filters, and MAC multicast filters.
Configuring MAC unicast filters
Use the following procedure to configure Media Access Control (MAC) filters. You can define the
MAC addresses of hosts and the LAN ports from which they are allowed to access a configured
VLAN on the BSG.
NN47928-600NN47928-600

BSG security policies 21
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, MAC Filters.
The MAC Filter Configuration dialog box appears.
2 From the VLAN ID list, select the VLAN ID.
3 In the MAC Address field, type the MAC address.
4 In the Allowed Ports field, type the por t numbers a llowed to access this VLAN.
5 Select a Status from the drop-down menu.
6 Click Add.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the MAC Filter Configuration dialog
box.
Variable Val ue
VLAN ID The VLAN ID.
MAC Address The MAC address.
Allowed Ports The allowed port range.
Status The status:
Permanent
Delete on Reset
Delete on Timeout
Configuring MAC multicast filters
Use the following procedure to configure Media Access Control (MAC) filters. The MAC
addresses that you configure on this panel are allowed access to your network.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, MAC Filters,
Multicast.
The MAC Filter Configuration dialog box appears.
2 From the VLAN ID list, select the VLAN ID.
3 In the MAC Address field, type the MAC address.
4 In the Allowed Ports field, type the por t numbers a llowed to access this VLAN.
5 In the Forbidden Ports field, enter the range of ports that you want to prohibit
or prevent from accessing this VLAN.
Administration Guide
22 BSG security policies
6 Select a Status from the drop-down menu.
7 Click Add.
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the MAC Filter Configuration dialog
box.
Variable Val ue
VLAN ID The VLAN ID.
MAC Address The MAC address.
Allowed Ports The allowed port range.
Forbidden Ports The ports you want to prohibit or prevent.
Status The status:
End
Permanent
Delete on Reset
Delete on Timeout
Enabling Network Address Translation
The BSG supports Network Address Translation (NAT). This translation provides security for
your LAN by hiding the IP addresses of devices on your network from external computers. The
BSG supports many-to-one NAT, static NAT, and dynamic NAT.
Enabling NAT
Use the following procedure to enable NAT on the BSG. When you enable NAT, the system
defaults to many-to-one NAT; that is, the BSG translates many administered private IP addresses
to a single globally routable IP address.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, NAT.
The NAT Basic Settings dialog box appears.
2 In the NAT Status list, select the status of the NAT as Enabled or Disabled.
3 In the Idle Time Out (Seconds) field, type the time to wait before an idle session
times out.
4 In the TCP Time Out (Seconds) field, type the time to wait before a TCP
session times out.
5 In the UDP Idle Time Out (Seconds) field, type the time to wait before a UDP
session times out.
NN47928-600NN47928-600
BSG security policies 23
6 Click Apply.
7 Click Interface Settings tab.
The NAT Interface Settings dialog box appea rs.
8 In the Interface list, select the interface on which to enable NAT.
9 In the Address Translation list, select the status of address translation as
enabled or disabled on the interface.
10 In the Port Translation list, select the status of the port translation on the
interface.
11 Click Add.
12 Click Apply.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the NAT Basic Settings dialog box.
Variable Val ue
NAT status The status of the NAT as Enabled or Disabled.
If you select Enabled, the NAT translation is applied on the incoming and outgoing
traffic.
If you select Disabled, the NAT translation is not applied on the incoming and
outgoing traffic.
The default value is Enabled.
Idle Time Out The number of seconds to elapse before an idle session times out.
The configuring values ranges from 60 to 86400 seconds. The default value is 60
seconds.
TCP Time Out The number of seconds to elapse before a TCP session times out.
The configuring values ranges from 300 to 86400 seconds.
The default value is 86400 seconds.
UDP Time Out The number of seconds to elapse before a UDP session times out.
The configuring values ranges from 300 to 86400 seconds.
The default value is 300 seconds.
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the NAT Interface Settings dialog box.
Variable Val ue
Interface The interface on which to configure Network Address Translation and Network Port
Translation.
Administration Guide
24 BSG security policies
Variable Val ue
Address Translation The status of the Address Translation as Enabled or Disabled.
Port Translation The status of the Port Translation as Enabled or Disabled.
Configuring static NAT
Static NAT involves mapping a given local IP address to a unique global IP address. Perform the
procedure in this section to configure static NAT.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, NAT.
2 Click Static NAT.
The default value is Enabled.
If Port translation status is enabled, then the same global IP address is overloaded
and can be used for many local hosts by translating the port number.
The default value is Enabled.
The Static NAT d i alo g box ap pe a rs.
3 In the Interface list, select the interface.
4 In the Local IP Address field, type the IP address of the local computer.
5 In the Translated IP Address field, type the translated IP address of the local
computer.
6 Click Add.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the Static NAT dialog box.
Variable Val ue
Interface The interface for static NAT configuration.
Local IP Address The local IP address of the host present in the local network.
Translated Address The translated IP address used on the Internet.
Configuring dynamic NAT
The dynamic NAT involves mapping the internal IP address to an external IP address, which is
drawn from a pool of global IP addresses. The external address varies with each session. When
you choose dynamic NAT, you should have the same number of external IP addresses as local IP
addresses. Perform the procedure in this section to configure dynamic NAT.
NN47928-600NN47928-600
BSG security policies 25
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, NAT.
2 Click Dynamic NAT.
The Dynamic NAT dialog box appears.
3 In the Interface list, select the interface.
4 In the Global IP Address Translation field, type the global IP address.
5 In the Subnet Mask field, type the subnet mask.
6 Click Add.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the dynamic NAT dialog box.
Variable Val ue
Interface Specifies the Interface ID.
Global IP Address Specifies the global IP address.
Subnet Mask Specifies the Subnet mask which, combined with the IP address, provides the range
of global IP addresses.
Firewall configuration
The BSG stateful firewall monitors the connections on all interfaces. This monitoring process
allows the BSG to filter traffic and apply the security policies established in your network. The
firewall module blocks all packets that are not explicitly configured to be allowed into the
protected network, and provides a logging mechanism to track the IP address and port number of
the packets denied by the firewall filtering. The procedures in this section describe how to
configure the firewall.
Navigation
• Configuring the firewall (page 25)
• Configuring firewall filters (page 27)
• Configuring the firewall access control list (page 29)
• Configuring the firewall demilitarized zone (page 30)
• Configuring the URL filter (page 31)
Configuring the firewall
Perform the procedure in this section to configure firewall basic settings.
Administration Guide

26 BSG security policies
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, Firewall.
2 In the Firewall Status list, select the firewall status as Enabled or Disabled.
3 In the URL Filtering Status list, select the URL filtering status as Enabled or
4 In the ICMP Error Generation list, select the status as Enabled or Disabled.
5 In the Filter NetBIOS Packets list, select the status as Enabled or Disabled.
6 In the Check IP Spoofing list, select the status as Enabled or Disabled.
7 In the Examine TCP SYN packets option list, select the status as Enabled or
8 In the Maximum Filters field, type the maximum number of filters.
9 In the Maximum Access-Lists field, type the maximum number of access list s.
10 In the Maximum TCP Open Handshaking Count field, type the number of TCP
11 In the SYN Time Out (secs) field, type the time interval after which the TCP
The Firewall Basic Settings dialog box appears.
Disabled.
Disabled.
connection requests entering the firewall module.
connection requests elapse.
12 Click Apply.
13 Click the Interface tab.
The Firewall Interface Configuration dialog box appears.
14 In the Interface list, select the interface on which to enable the firewall.
15 In the Type list, select the type as Trusted or Untrusted.
16 Click Add.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the Firewall Basic Settings dialog box.
Variable Val ue
Firewall Status The firewall status: Enabled or Disabled
URL Filtering Status The URL filtering status: Enabled or Disabled.
ICMP Error
Generation
Filter NetBIOS
Packets
Specifies the ICMP error generation status as Enabled or Disabled.
If you select enabled, the BSG will generate and send ICMP error messages.
If you select disabled, BSG will not generate and send ICMP error messages.
Specifies the filter NetBIOS packets status as Enabled or Disabled.
If you select enabled, the BSG will drop NetBIOS packets entering the BSG.
If you select disabled, the BSG permits NetBIOS packets to be sent.
NN47928-600NN47928-600
BSG security policies 27
Variable Val ue
Check IP Spoofing Specifies the check IP spoofing function as enabled or disabled.
If you select enabled, the BSG detects and prevents attempts to spoof trusted IP
addresses.
If you select disabled, the examining of IP spoofing attack is disabled.
Examine TCP SYN
packets option
Max Filters The maximum number of filters allowed. The default value is 100
Max Access-Lists Displays the maximum number of access lists. The default value is 100.
Maximum TCP
Open Handshaking
Count
SYN Time Out
(secs)
Specifies the the examine TCP SYN packets option as enabled or disabled.
If you select enabled, the examining of TCP SYN packets is enabled.
If you select disabled, the examining of TCP SYN packets is disabled.
Specifies the number of TCP connection requests entering in the firewall module.
The default value is 50.
Specifies the synchronizing timeout value, which represents the time interval after
which the TCP connection requests that exceed the threshold are discarded.
The default value is 1 second.
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the Firewall Interface Configuration
dialog box.
Variable Val ue
Interface Specifies the interface ID.
Type Specifies the type as trusted or untrusted.
Trusted indicates a LAN network.
Untrusted indicates a WAN network.
Configuring firewall filters
Perform the following procedure to configure firewall filters, which specify the parameters to be
checked against the packet.
After you have created firewall filters, you can associate the filters with an access control list. The
access control list specifies whether packets that match the configured filter should be permitted or
not. See Configuring the firewall access control list (page 29) for more information.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, Firewall.
2 Click Filters.
The Firewall Filter Configuration dialog box appears.
3 In the Filter Name field, type the name of the filter.
4 In the Source Range list, select the source range as Any or Subnet.
5
In the Source Address field, type the source address.
Administration Guide
28 BSG security policies
6 In the Source Mask list, select the source mask.
7 In the Destination Range list, select the destination range.
8 In the Destination Address field, type the destination address.
9 In the Destination Mask list, select the destination mask.
10 In the Protocol list, select the protocol.
11 In the Protocol Number field, type the protocol number.
12 In the Source Port field, type the source port.
13 In the Destination Port field, type the destination port.
14 Click Add.
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the Firewall Filter Configuration
dialog box.
Variable Val ue
End
Filter Name Specifies the filter name.
Source Range Specifies the source range as Any or Subnet.
Source Address Specifies the source IP address, if you select the source range as Subnet.
The default value is 0.0.0.0/0.
Source Mask Specifies the Source mask, if you select the Source range Subnet.
Destination Range Specifies the destination range.
Destination Address Specifies the destination address., if you select the Destination range Subnet.
Destination Mask Specifies the destination mask, if you select the Destination range Subnet.
Protocol Specifies the protocol of the incoming packets. Select one of the following options:
•Any
•ICMP
•IGMP
•GGP
•IP
•TCP
•EGP
•IGP
•NVP
• UDP
•IRTP
•IDPR
• RSVP
• MHRP
•IGRP
• OSPF
•Other
NN47928-600NN47928-600
BSG security policies 29
Variable Val ue
Protocol Number Specifies the protocol number. If you set the Protocol list to Any, you do not need to
complete this field.
Source Port Specifies the source port that is to be checked against the packet. The source port
Destination Port Specifies the destination port that is to be checked. The destination port value
value ranges from 1 to 65536.
ranges from 1 to 65536.
Configuring the firewall access control list
The Access Control List (ACL) specifies rules that allow or block specific traffic. Use the
following procedure to enable and configure the firewall access control list.
Before you configure the access control list, you must create filters. See Configuring firewall
filters (page 27) for more information.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, Firewall.
2 Click Access List.
The ACL Configuration dialog box appears.
3 In the ACL Name field, type the name of the ACL.
4 In the Filter Name list, select the filter name.
5 In the Packet Direction list, select the direction for the transmission.
6 In the Action list, select the action as permit or deny.
7 In the Priority field, type the priority of the access rule.
8 In the Logs list, select the level of log to generate whenever this ACL is
executed.
9 Click Add.
End
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the fields in the ACL Configuration dialog box.
Variable Val ue
ACL Name The name of the new access rule. Maximum 32 characters.
Filter Name The name of the filter to be associated with the ACL.
Packet Direction The direction for transmission of packet as trusted to untrusted (outbound
packets) and untrusted to trusted (inbound packets).
Administration Guide
30 BSG security policies
Variable Val ue
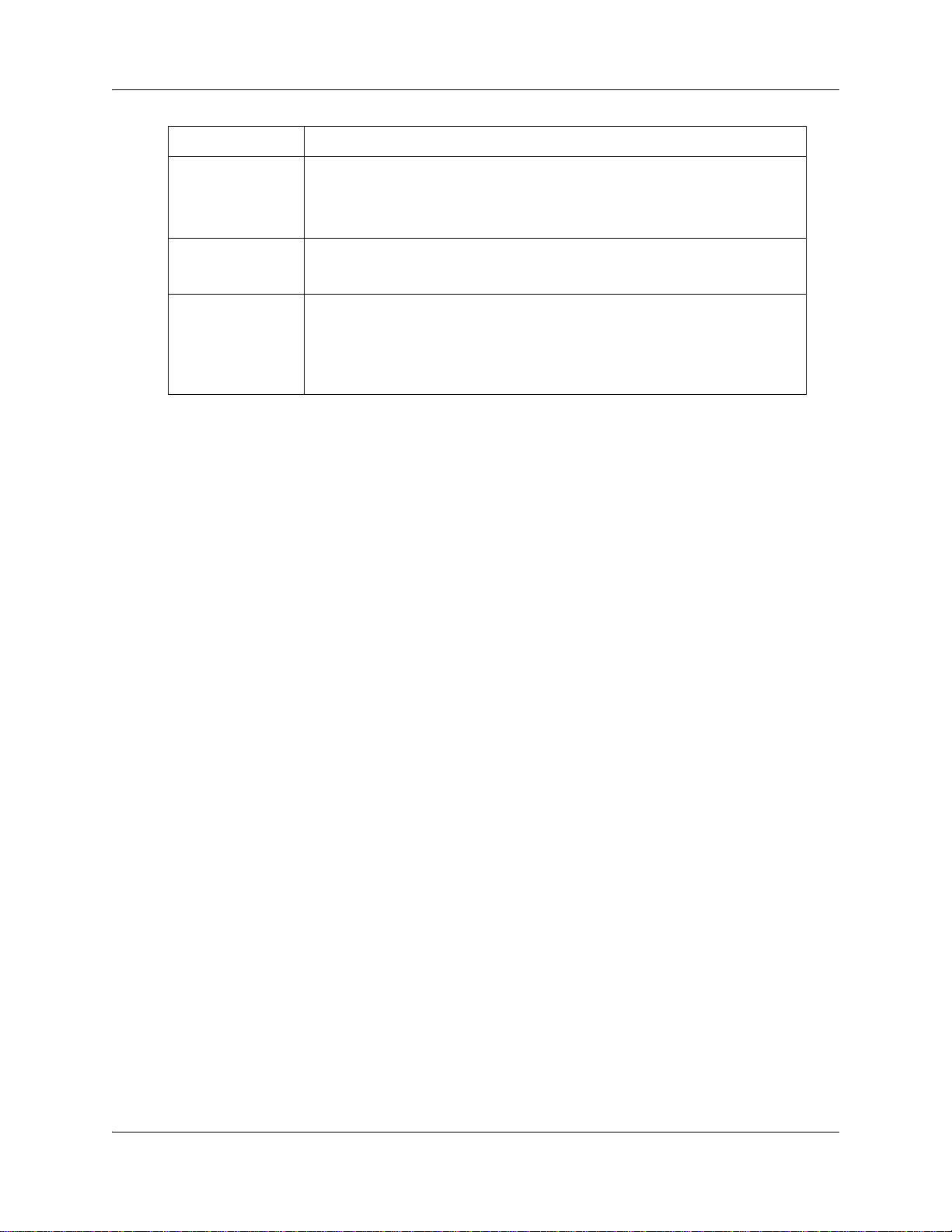
Action The action to be performed for the given access rule as permit or deny.
Priority The priority value for the access rule, ranging from 1 to 65535. A lower number
Logs Specifies when a packet is permitted or denied. You can select any one from the
Configuring the firewall demilitarized zone
The firewall demillitarized zone (DMZ) allows a computer on the LAN to be exposed on the
Internet. It allows the host configured as a DMZ to respond to requests only; the host cannot
generate requests. This prevents an attacker from using the DMZ as a launch point to attack other
hosts on the LAN. For example, you can use DMZ to allow internet users to access your web
server. Use the following procedure to configure the firewall demilitarized zone. You can
configure a maximum of 5 DMZ hosts.
If you select Permit, the packet is permitted if the filter matches.
If you select Deny, the packet is rejected and an ICMP message is sent as
response.
translates into a higher priority; therefore, and ACL with a priority of 1 will be
used over an ACL with a priority of 10 if both ACLs are applicable to a packet.
following options:
• None—Firewall logs are not required
• Brief—Firewall logs are included in brief
• Detail—Firewall logs are included in detail.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation panel, select Configuration, Security, Firewall.
2 Click DMZ.
The DMZ Host Configuration dialog box appears.
3 In the DMZ Host IP Address, type the DMZ host IP address.
4 Click Add.
End
NN47928-600NN47928-600
 Loading...
Loading...