
Configuration Guide
BSG8ew and BSG12ew/aw/tw 1.0
Business Services Gateway
Document Status: Standard
Document Number: NN47928-500
Document Version: 02.02
Date: October 2008

Copyright © 2008 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data, and
recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or implied
warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this document. The
information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Trademarks
Nortel, the Nortel logo, and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

Contents
How to Get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Configuration fundamentals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Wide area network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Local area network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Virtual local area network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Wireless network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
IP routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Dynamic host control protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Multicast/IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Quality of Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Virtual private network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Session initiation protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Port management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Contents 3
WAN configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
WAN configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Ethernet WAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Prerequisites for WAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Ethernet WAN configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
PPPoE WAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Prerequisites for WAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
PPPoE WAN configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
DSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Prerequisites for DSL configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
DSL configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
T1/E1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Prerequisites for T1/E1 configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
T1/E1 configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
VLAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
VLAN configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Wireless network configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Prerequisites to wireless network configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuration Guide

4 Contents
Wireless network configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
SIP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Prerequisites to SIP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
VPN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Prerequisites for VPN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Client tunnel configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Branch office tunnel configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
QoS configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Prerequisites for QoS configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
QoS configuration procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
WAN advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Prerequisites for WAN advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
WAN advanced configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
DSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
T1/E1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
LAN advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Client tunnel configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Branch office tunnel configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
QoS configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Ethernet WAN configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
PPPoE WAN configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Rate limit configuration parameters (Ethernet) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Renewing or releasing the WAN lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
DSL Basic Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
PPP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Rate limit configuration parameters (DSL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
T1/E1 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Alarms Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
T1/E1 Channel Group Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
PPP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Multilink Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Virtual interface configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Prerequisites for virtual interface configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Virtual interface configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Virtual interface configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Renewing or releasing the LAN lease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Ethernet LAN configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
NN47928-500NN47928-500

Contents 5
Wireless LAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Prerequisites for LAN configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Wireless LAN configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
WLAN settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
SSID configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
WLAN radio configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
MAC filtering configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
WLAN security configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
WEP configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Wireless multimedia configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
VLAN advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
VLAN settings configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
VLAN settings configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
VLAN basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
VLAN port settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Static VLAN configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Dynamic VLAN configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
VLAN protocol group configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
VLAN port protocol configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
VLAN database display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
VLAN STP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
STP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
MSTP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Prerequisites to MSTP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
MSTP configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
MSTP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
CIST configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
MSTP VLAN mapping configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
MSTP port settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
CIST port status display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
RSTP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Prerequisites to RSTP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
RSTP configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
RSTP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
RSTP timers configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
RSTP port settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
RSTP port status display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
IP routing advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Static ARP configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Static routes configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
RIP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Configuration Guide

6 Contents
OSPF configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
RRD configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
VRRP configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
DHCP advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
RIP configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
RIP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Adding a RIP interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
RIP interface configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
RIP neighbor setting configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
RIP security settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Prerequisites for OSPF configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
OSPF configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
OSPF basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
OSPF area configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
OSPF interface configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
OSPF virtual interface configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
OSPF route information display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
OSPF link state database display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
RRD configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
RRD basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
RRD RIP settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
RRD OSPF settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
VRRP configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
VRRP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
VRRP settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
DHCP server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
DHCP server configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
DHCP basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
DHCP global options configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
DHCP pool settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
DHCP pool options configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
DHCP host option configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
DHCP host IP settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
DHCP client access configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
DHCP relay settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Multicast advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Dynamic multicast configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
IGMP snooping configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Prerequisites to IGMP snooping advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
IGMP snooping configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
IGMP snooping basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
NN47928-500NN47928-500

Contents 7
IGMP snooping timer configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
IGMP snooping interface configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
IGMP snooping VLAN router ports mapping information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
IGMP snooping multicast forwarding group information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
QoS advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
QoS basic settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Policy map settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Class maps configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Marking configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Port based QoS configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
QoS queue settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
VPN advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
VPN settings configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
VPN settings configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
VPN global settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
VPN policy configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
VPN IPsec configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
IKE pre-shared secret configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Users configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Users configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
User database configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
IP address pool configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
VPN client termination configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
SIP advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
SIP server management configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
SIP system configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
SIP system configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Central SIP server configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Call admission control (CAC) configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Call detail recording (CDR) configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
SIP diagnostics (detailed traces) configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
SIP protocol configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
SIP protocol configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Header settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Transport settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Registrar settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
SIP proxy server configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Timers configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Routing rules configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Routing rules configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Configuration Guide

8 Contents
Provisioning users configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
FXO/FXS configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
NAT ALG display parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Port management advanced configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Ethernet ports configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Viewing rules configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Adding rules configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Advanced dial plan configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
FXO/FXS configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Global information configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Codec information configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
FXS information configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
FXO information configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Rebooting VoIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Ethernet ports configuration navigation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Basic port settings configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Port control configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
NN47928-500NN47928-500

How to Get Help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel Technical Support
Web site:
http://www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to address issues
with Nortel products. More specifically, the site enables you to:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base for answers to
technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for Nortel equipment
9
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you don’t find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support Web site, and have a
Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the phone number for your region:
http://www.nortel.com/callus
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express Routing Code (ERC)
to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel product or service. To locate the ERC for
your product or service, go to:
http://www.nortel.com/erc
Configuration Guide

10 How to Get Help
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or authorized
reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
NN47928-500NN47928-500

Configuration fundamentals
Wide area network
Wide area network (WAN) configuration includes configuring Ethernet ports. For more
information, see WAN configuration (page 15) and WAN advanced configuration (page 83).
Local area network
Local area network (LAN) configuration includes configuring the virtual interface, Ethernet LAN
settings, and wireless LAN settings. For more information, see VLAN configuration (page 37) and
LAN advanced configuration (page 97).
Virtual local area network
11
Virtual local area network (VLAN) configuration includes configuring basic VLAN settings,
VLAN port settings, static VLAN, and VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). For more
information, see VLAN configuration (page 37) and VLAN advanced configuration (page 111).
Wireless network
Wireless network (WLAN) configuration includes configuring the access point, radio, MAC
filtering, security, and wireless multi media. For more information, see Wireless network
configuration (page 43) and LAN advanced configuration (page 97).
IP routing
IP routing configuration includes configuring routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First
(OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Route Redistribution (RRD), and Virtual Router
Redundancy Protocol (VRRP). For more information, see IP routing advanced configuration
(page 127).
Dynamic host control protocol
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) configuration includes configuring DHCP server and
DHCP relay settings. For more information, see DHCP advanced configuration (page 145).
Configuration Guide

12 Configuration fundamentals
Multicast/IGMP
Multicast configuration includes configuring Dynamic Multicast and Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP) snooping. For more information, see Multicast advanced configuration
(page 153).
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) configuration includes configuring basic QoS settings, policy map
settings, class map settings, and queue settings. For more information, see QoS configuration
(page 71) and QoS advanced configuration (page 159).
Virtual private network
Virtual Private Network (VPN) configuration includes configuring VPN IP security (IPsec), traffic
selector table, IPsec Security Authentication (SA) table, and Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
pre-shared secret. For more information, see VPN configuration (page 55) and VPN advanced
configuration (page 165).
Session initiation protocol
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) configuration includes configuring the SIP server, SIP system,
SIP protocol, routing rules, user provisioning, and Foreign Exchange Office (FXO)/Foreign
Exchange Subscriber (FXS). For more information, see SIP configuration (page 47) and SIP
advanced configuration (page 177).
Port management
Port management configuration includes configuring Ethernet and (Power of Ethernet) PoE ports.
For more information, see Port management advanced configuration (page 197).
NN47928-500NN47928-500

Introduction
This document describes how to configure the Business Service Gateway (BSG) using the Web
user interface.
Navigation
• WAN configuration (page 15)
• VLAN configuration (page 37)
• Wireless network configuration (page 43)
• SIP configuration (page 47)
• VPN configuration (page 55)
• QoS configuration (page 71)
• Advanced configuration (page 81)
• WAN advanced configuration (page 83)
• LAN advanced configuration (page 97)
• VLAN advanced configuration (page 111)
• IP routing advanced configuration (page 127)
• DHCP advanced configuration (page 145)
• Multicast advanced configuration (page 153)
• QoS advanced configuration (page 159)
• VPN advanced configuration (page 165)
• SIP advanced configuration (page 177)
• Port management advanced configuration (page 197)
13
Configuration Guide

14 Introduction
NN47928-500NN47928-500

WAN configuration
This section describes the procedures to configure the Wide Area Network (WAN) setup for the
Business Services Gateway (BSG) system.
WAN configuration navigation
The following sections provide information for configuring the WAN:
• Ethernet (page 15)
• DSL (page 23)
• T1/E1 (page 26)
Ethernet
The following sections describe WAN Ethernet configuration.
15
• “Ethernet WAN configuration” on page 15
• “PPPoE WAN configuration” on page 19
Ethernet WAN configuration
This section describes Ethernet WAN configuration. Ethernet appears under WAN configuration
if you are connected to a BSG8ew or BSG12ew.
Prerequisites for WAN configuration
• You must have SYSTEM - READ WRITE permission.
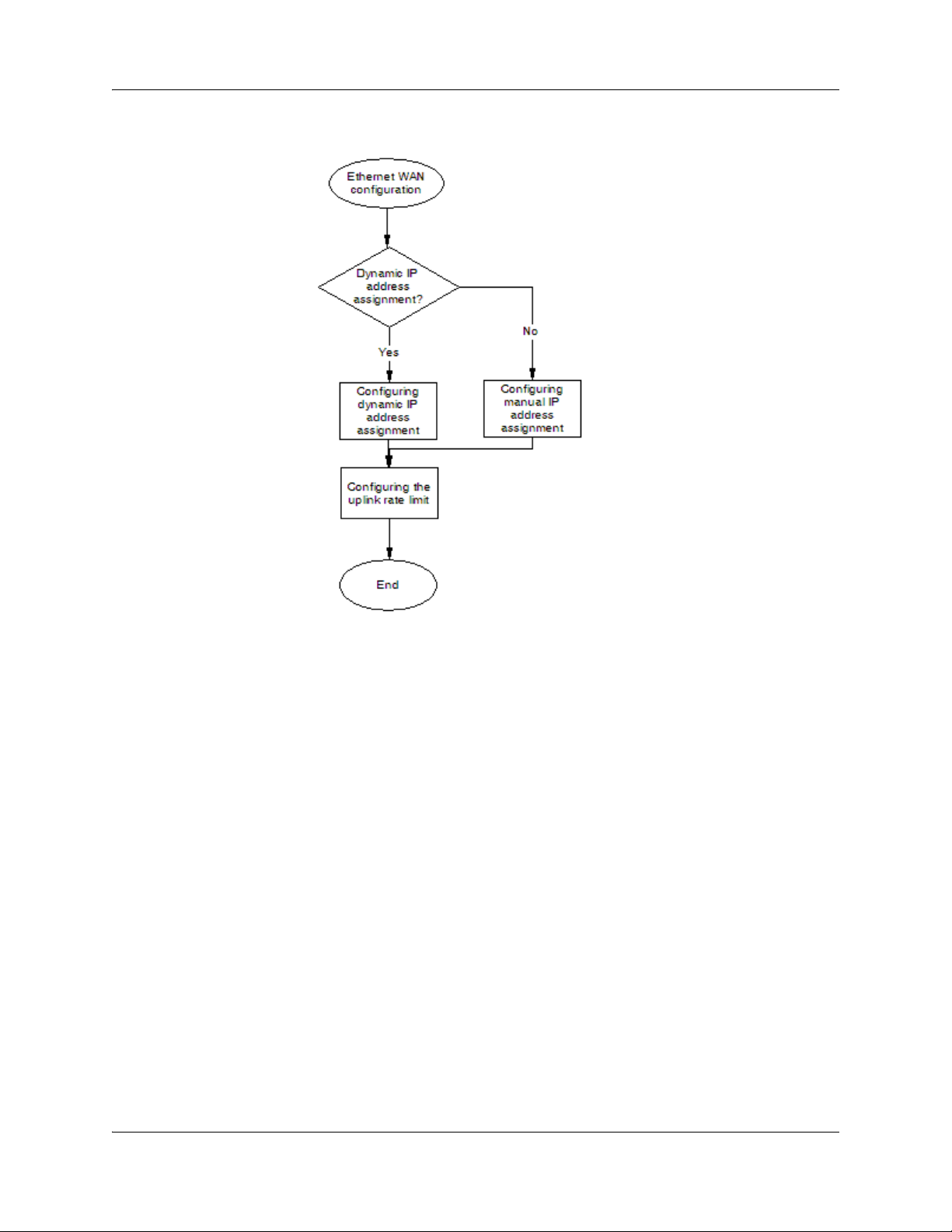
Ethernet WAN configuration procedures
The following task flow shows the sequence of procedures to perform to configure the Ethernet
WAN.
Configuration Guide
16 WAN configuration
Figure 1 Ethernet WAN configuration procedures
Configuring dynamic IP address assignment
Complete this procedure to configure the Ethernet WAN for dynamic IP address assignment.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Ethernet.
The WAN Configuration pane appears.
2 From the Interface list, select the required interface.
3 From the Encapsulation Mode list, select Ethernet.
4 From the MAC Cloning list, select Enable.
5 In the MAC Address field, type the MAC Address.
6 For IP Address Assignment, select Dynamic.
7 Click Apply.
End
NN47928-500NN47928-500
WAN configuration 17
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values for configuring Ethernet WAN.
Variabl e Val ue
Interface Select an Interface to be configured.
Encapsulation Mode Set the encapsulation mode to Ethernet. The WAN interface operates as a
normal Ethernet interface.
MAC Cloning Select the MAC cloning status.
Enable - the BSG uses the configured MAC address as the source of
Ethernet frames instead of the MAC address of the BSG WAN port.
Disable - disables MAC Cloning.
You can enable MAC cloning only if the Encapsulation Mode is Ethernet.
The default value is Disable.
MAC Address Type the MAC address, if the MAC cloning is enabled.
IP Address Assignment Select Dynamic for the system to assign the IP address for the specified
VLAN from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.
Configuring manual IP address assignment
Complete this procedure to configure the Ethernet WAN for manual IP address assignment. The IP
Address Assignment field has a default value of Manual.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Ethernet.
The WAN Configuration pane appears.
2 From the Interface list, select the required interface.
3 From the Encapsulation Mode list, select Ethernet.
4 In the WAN IP Address field, type the IP address.
5 In the Subnet Mask field, type the subnet mask.
6 In the Gateway IP Address field, type the Gateway IP Address.
7 In the Primary DNS field, type the Primary Domain Name System (DNS) IP
address.
8 In the Secondary DNS field, type the Secondary DNS IP address.
9 Click Apply.
End
Configuration Guide
18 WAN configuration
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values for configuring Ethernet WAN.
Variabl e Val ue
Interface Select an Interface to be configured.
Encapsulation Mode Set the encapsulation mode to Ethernet. The WAN interface operates as a
WAN IP Address Type the WAN IP address, if the IP Address Assignment is manual.
Subnet Mask Type the subnet mask, if the IP Address Assignment is manual.
Gateway IP Address Type the gateway IP Address, if the IP Address Assignment is manual.
Configurable
Primary DNS Type the primary DNS server IP address, if the IP Address Assignment is
Secondary DNS Type the secondary DNS server IP address, if the IP Address Assignment
Configuring the uplink rate limit
normal Ethernet interface.
manual.
is manual.
Certain downstream devices cannot handle the high traffic rate from the BSG. This feature allows
you to limit the rate of traffic sent on the WAN interface. You should limit the uplink speed only if
your WAN bandwidth is less than 100 Mbps and the device in front of the BSG does not support
pause frame.
Complete this procedure to configure the uplink rate limit.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Rate Limit.
The Rate Limit Configuration pane appears.
2 From the Rate Limit Status list, select Enabled.
3 In the Uplink Rate Limit field, type the uplink rate limit provided by your ISP.
4 Click Apply.
End
NN47928-500NN47928-500

WAN configuration 19
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values for configuring the uplink rate limit.
Variabl e Val ue
Rate Limit Status Select the rate limit status.
• Enabled - enables uplink rate limiting feature
• Disabled - disables uplink rate limiting feature
The default value is Disabled.
Uplink Rate Limit Specifies the maximum uplink rate limit over the WAN interface (in bps).
The range is 100,000 to 100,000,000 bps.
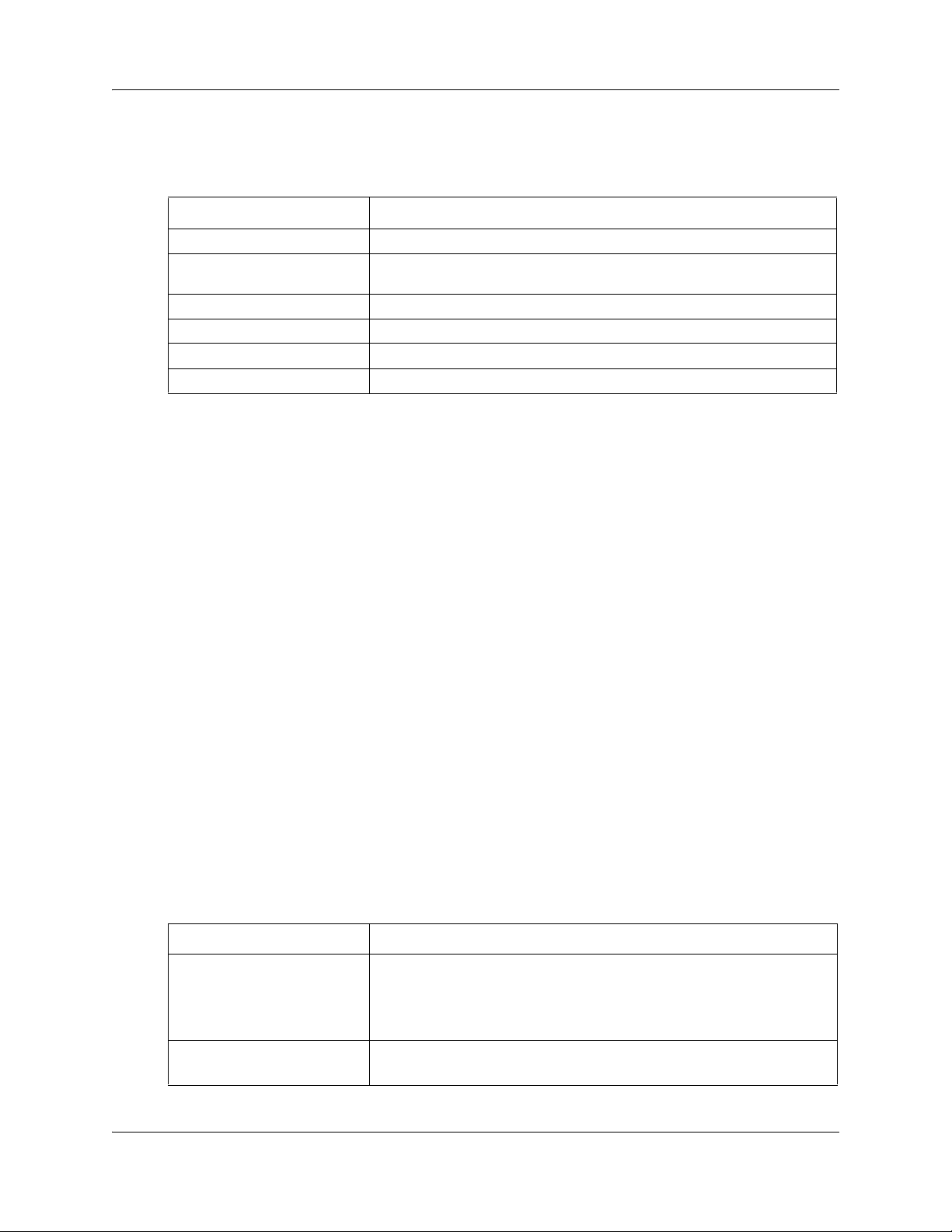
PPPoE WAN configuration
This section describes PPPoE WAN configuration. You can configure PPPoE WAN if you are
connected to a BSG8ew or BSG12ew.
Prerequisites for WAN configuration
• You must have SYSTEM - READ WRITE permission.
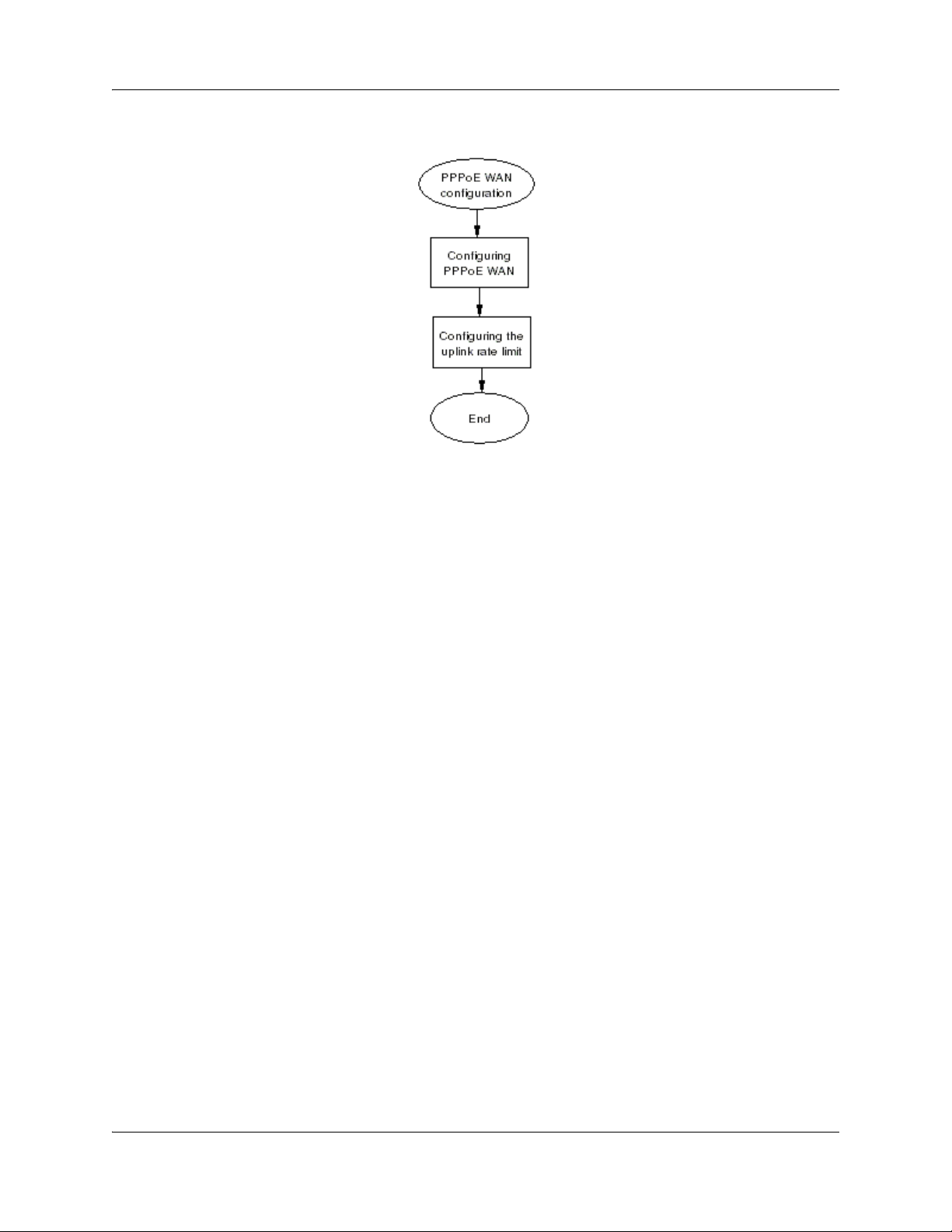
PPPoE WAN configuration procedures
The following task flow shows the sequence of procedures to perform to configure the PPPoE
WAN.
Configuration Guide
20 WAN configuration
Figure 2 PPPoE WAN configuration procedures
Configuring the PPPoE WAN
Complete this procedure to configure the PPPoE WAN.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Ethernet.
The WAN Configuration pane appears.
2 From the Interface list, select the required interface.
3 From the Encapsulation Mode list, select PPPoE.
4 In the ISP Name field, type the Internet Service Provider name.
5 In the User Name field, type the PPPoE user name supplied by your ISP.
6 In the Password field, type the PPPoE password supplied by your ISP.
7 In the Host Name field, type the Host name.
8 Click Apply.
End
NN47928-500NN47928-500
WAN configuration 21
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values for configuring PPPoE WAN.
Variabl e Val ue
Interface Select an Interface to be configured.
Encapsulation Mode Set the encapsulation mode PPPoE. The WAN interface operates as a
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP).
ISP Name Type the name of the Internet Service Provider.
User Name Type the PPPoE user name.
Password Type the PPPoE password.
Host Name Type the host name.
Configuring the uplink rate limit
Certain downstream devices cannot handle the high traffic rate from the BSG. This feature allows
you to limit the rate of traffic sent on the WAN interface. You should limit the uplink speed only if
your WAN bandwidth is less than 100 Mbps and the device in front of the BSG does not support
pause frame.
Complete this procedure to configure the uplink rate limit.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Rate Limit.
The Rate Limit Configuration pane appears.
2 From the Rate Limit Status list, select Enabled.
3 In the Uplink Rate Limit field, type the uplink rate limit provided by your ISP.
4 Click Apply.
End
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values to configure the uplink rate limit.
Variabl e Val ue
Rate Limit Status Select the rate limit status:
• Enabled - enables uplink rate limiting feature
• Disabled - disables uplink rate limiting feature
The default value is Disabled.
Uplink Rate Limit Specifies the maximum uplink rate limit over the WAN interface (in bps).
The range is 100,000 to 100,000,000 bps.
Configuration Guide

22 WAN configuration
NN47928-500NN47928-500
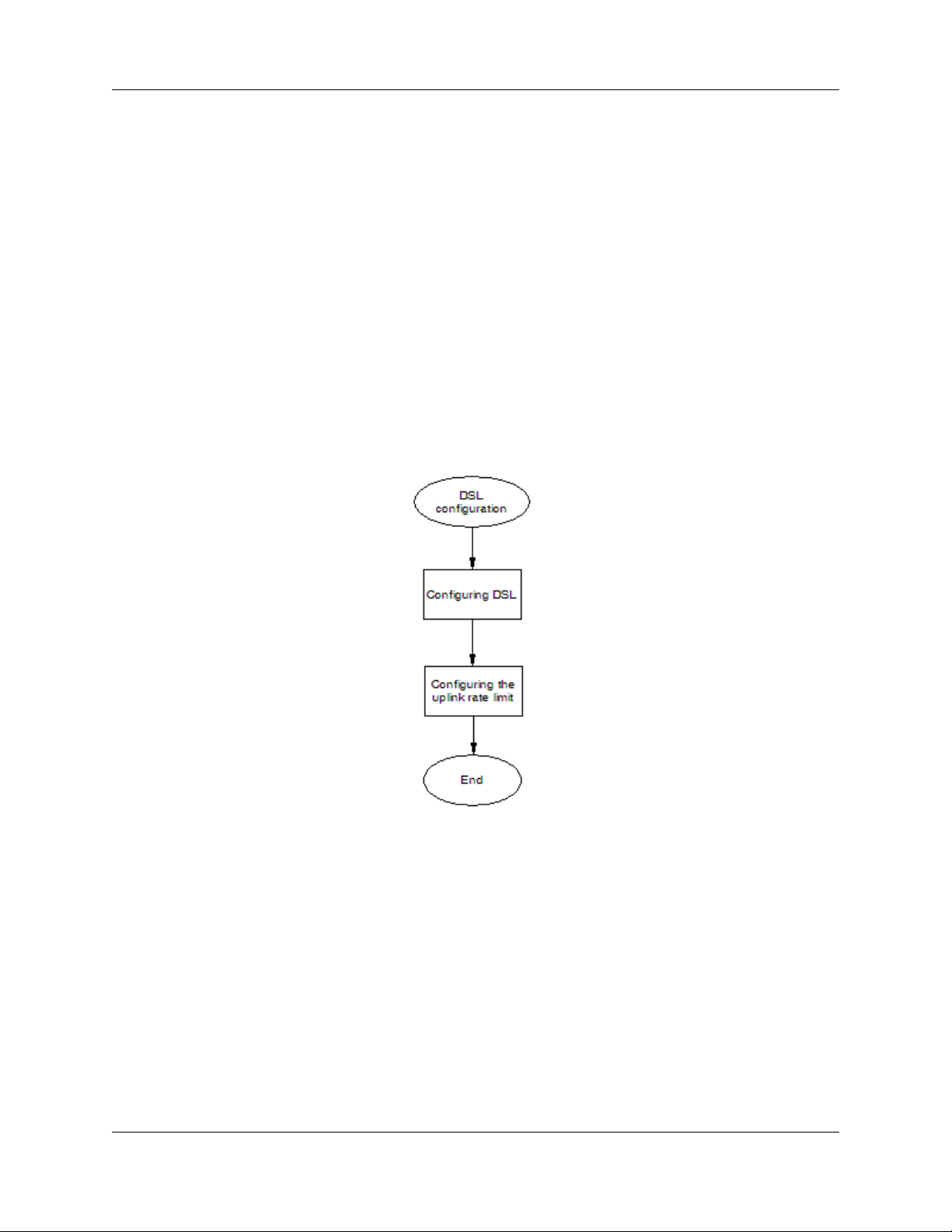
DSL
DSL appears under WAN configuration if you are connected to a BSG12aw.
On the Digital Subscribe Line (DSL) pages you can configure and control the DSL modem that
connects to the BSG. You can also configure the ATM parameters of the modem and access the
DSL modem statistics.
Prerequisites for DSL configuration
• You must have access read/write permission to configure DSL.
DSL configuration procedures
The following task flow shows the sequence of procedures to perform to configure DSL.
Figure 3 DSL configuration procedures
WAN configuration 23
Configuring DSL
Complete this procedure to configure DSL.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, DSL.
The Basic Configuration pane appears.
2 In the VPI / VCI field, type the VPI / VCI values.
Configuration Guide
24 WAN configuration
3 In the MRU field, type the value 1492.
4 Click Add.
5 Select the IP Configuration tab.
6 In the User Name field, type the User Name provided by your service provider.
7 In the Password field, type the Password provided by your service provider.
8 Click Apply.
Variable definitions
This table describes the variables to configure DSL.
Variabl e Val ue
Your service provider provides you with these values when you set up your
account.
The PPP Configuration pane appears.
End
VPI / VCI The Virtual Path Identifier/Virtual Channel Identifier (VPI/VCI) used by the
MRU The Maximum Receivable Unit (MRU) value. MRU specifies the maximum
User Name The user name for the specified PPP interface, used for authentication.
Password The password for the specified PPP interface, used for authentication. The
DSL modem to make a connection.
The range is 0 to 255.
The default value for VPI is 8 and VCI is 35. These default values do not
appear until you add a configuration.
number of bytes received on a link. The default value is 1492.
The user name is provided by your service provider.
password is provided by your service provider.
Configuring the uplink rate limit
Complete this procedure to enable the uplink rate limit. The rate limit value is based on the uplink
bandwidth of the ADSL service.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, Rate Limit.
The Rate Limit Configuration pane appears.
NN47928-500NN47928-500
2 From the Rate Limit Status list, select Enabled.
3 In the Uplink Rate Limit field, type the uplink rate limit provided by your ISP.
4 Click Apply.
WAN configuration 25
End
Variable definitions
The following table describes the variables and values to configure the uplink rate limit.
Variabl e Val ue
Rate Limit Status Select the rate limit status:
• Enabled - enables uplink rate limiting feature
• Disabled - disables uplink rate limiting feature
The default value is Disabled.
Uplink Rate Limit Specifies the maximum uplink rate limit over the WAN interface (in bps).
The range is 100,000 to 100,000,000 bps.
Configuration Guide

26 WAN configuration
T1/E1
T1/E1 appears under WAN configuration if you are connected to a BSG12tw.
T1/E1 is a digital WAN carrier facility. T1 transmits DS-1 formatted data at 1.544 MB/s and E1
transmits E1 formatted data at 2.048 MB/s through the telephone e-switching network.
Prerequisites for T1/E1 configuration
• You must have access read/write permission to configure T1/E1.
T1/E1 configuration procedures
The following task flow shows the sequence of procedures to perform to configure T1/E1.
NN47928-500NN47928-500
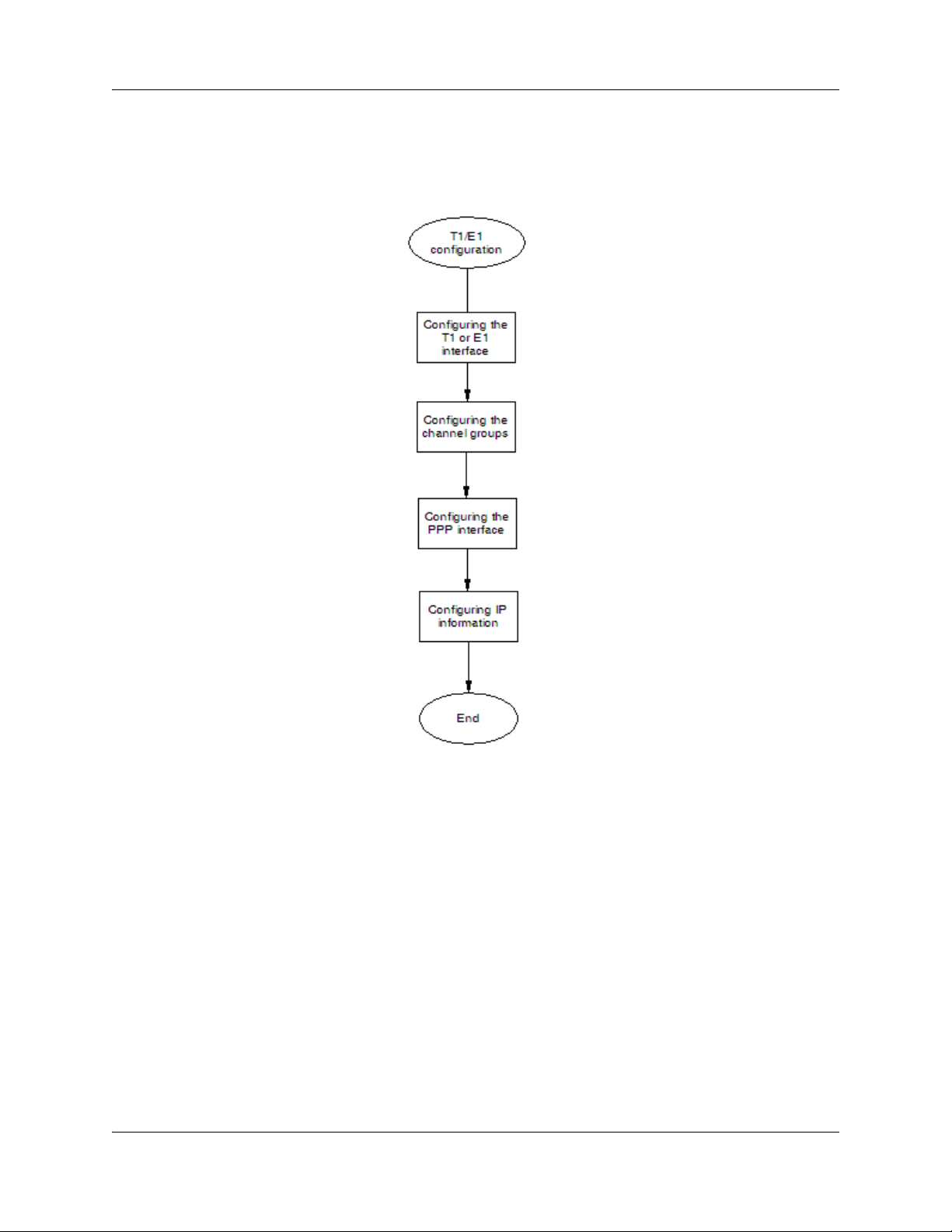
Figure 4 T1/E1 configuration procedures
WAN configuration 27
Configuring the T1 interface
If your BSG is located in North America, configure the T1 interface. This procedure guides you
through setting up one T1 interface.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, T1/E1.
Configuration Guide

28 WAN configuration
2 Select interface 1.
3 From the Framing list, select ESF or SF.
4 From the Line Mode list, select CSU or DSU.
5 From the LineBuildOut list, select 0, -7.5, -15, or -22.5.
The T1/E1 Configuration pane appears.
The Interface Type field defaults to T1.
The framing you set here must agree with the framing used by the peer.
This setting depends upon the distance between the devices on either end of
the T1 line. For shorter distances, use DSU. For longer distances, use CSU.
This information should be provided by your service provider.
You can configure LineBuildOut if Line Mode is CSU.
You should contact your service provider for proper settings for the:
• type of framing
• line coding
• line mode
• line build out
• line length
• clock source
6 From the Line Length list, select the line length.
You can configure line length when Line Mode is DSU. This setting depends
upon the length of the cable connecting the devices on each end of a T1 line.
7 From the Transmit ClockSource list, select Loop Timing.
When you select Loop Tim ing, the remote end provides the clock source . Check
with your service provider.
8 Click Apply.
End
NN47928-500NN47928-500
Variable definitions
This table describes the variables used to configure the T1/E1 interface.
Variabl e Val ue
Interface The T1/E1 controller.
Framing The Framing Type for the T1/E1 data line.
Options for T1:
Extended Super Frame (ESF)— 24
consecutive 193-bit frames of data.
Super Frame (SF)—12 consecutive
193-bits of data.
Unframed—the non signaling or unframed
framing format is a simplified version of
the T1 super frame.
The default value is ESF.
Line Mode The Line Mode.
Options:
Channel Service Unit (CSU)—select if
cable length is equal to or more than 655
feet.
Data Service Unit (DSU)—select if cable
length is less than 655 feet.
The default value is CSU.
LineBuildOut The level of attentuation (in decibels)
required for the devices on each end of a
T1 line to communicate. Options are:
0 db
-7.5 db
-15 db
-22.5 db
You can configure this field only for T1
CSU mode.
WAN configuration 29
Configuration Guide
30 WAN configuration
Variabl e Val ue
Line Length The Line Length value.
Transmit ClockSource The clock source.
Line Length refers to the length of the
cable (in feet) that connects the devices
on each end of a T1 line.
Options:
0 - 133
134 - 266
267 - 399
400 - 533
534 - 655
The default value is 0 - 133.
You can configure the line length only
when the Line Mode is DSU.
Options:
Local Timing—A local clock source is
used or an external clock is attached to
the box containing the interface.
Loop Timing—Recovered received clock
is used to transmit the clock.
The default value is Loop Timing.
Configuring the E1 interface
If your BSG is located in Europe, configure the E1 interface. This procedure guides you through
setting up one E1 interface.
Procedure steps
Step Action
1 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, T1/E1.
The T1/E1 Configuration pane appears.
2 Select interface 1.
3 From the Interface Type list, select E1.
4 Reboot the system.
You must reboot the system before setting up the E1 parameters.
5 From the BSG navigation pane, select Configuration, WAN, T1/E1.
The T1/E1 Configuration pane appears.
6 Select interface 1.
7 From the Framing list, select E1 or E1CRC.
The framing you set here must agree with the framing used by the peer.
8 From the Line Mode list, select CSU or DSU.
NN47928-500NN47928-500
