Page 1

AP-4, AP-5, and AP-6
Page 2
Copyrights
• Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
• Microsoft Windows is a registered trademark of the Microsoft
Corporation.
• All trademarks mentioned herein belong to their respective
owners.
Publication Information
Copyright © 2004 Avaya, Inc. All rights reserved.
Part Number: 66221/B
Document Number: 555-301-708, Release 2.4.11
Date: April 2004
Page 3

Regulatory Information
See the Regulatory Flyer that came with your AP-3 unit or go to the CDROM to view the information.
Warranty
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your
sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In addition,
Avaya’s standard warranty language as well as information regarding
support for this product, while under warranty, is available through the
following Web site: www.avaya.com/support
Notice
While reasonable efforts were made to ensure that the information in this
book was complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya can
assume no responsibility for any errors. Changes and corrections to the
information contained in this document may be incorporated into future
reissues.
Page 4
How to Get Help
For additional support telephone numbers, go to the Avaya support Web
site: http://www.avaya.com/support. If you are:
• Within the United States, click the Escalation Management link.
Then click the appropriate link for the type of support you need.
• Outside the United States, click the Escalation Management link.
Then click the International Services link that includes telephone
numbers for the international Centers of Excellence.
TCP/IP Facilities
Customers may experience differences in product performance, reliability
and security depending upon network configurations/design and
topologies, even when the product performs as warranted.
To order copies of this and other documents
For the most current versions of documentation, go to the Avaya support
Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support.
Page 5

Page 6

Page 7

AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide Table of Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Introduction to Wireless Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Site Survey . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Guidelines for Roaming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
IEEE 802.11 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
802.11b . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
802.11a . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
802.11g . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Management and Monitoring Capabilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
HTTP/HTTPS Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
SNMP Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
2 Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Prerequisites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Product Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
MiniPCI Upgrade Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Hardware Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
ScanTool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Setup Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Download the Latest Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-45
Setup your TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-45
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1
Page 8

Download Updates from a TFTP Server using the Web Interface 2-46
Download Updates from a TFTP Server using the CLI Interface 2-47
Additional Hardware Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-47
Mounting Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-48
Installing the AP in a Plenum. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-54
Kensington Security Slot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-54
Power over Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-56
LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-57
Related Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-61
3 Status Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Logging into the HTTP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
System Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
4 Advanced Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Configuring the AP Using the HTTP/HTTPS Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Dynamic DNS Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
IP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
DHCP Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
Link Integrity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-18
Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-21
Operational Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-22
Wireless (802.11a) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-24
Wireless (802.11b) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-31
Wireless (802.11b/g) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-45
Wireless (802.11a/g) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-51
2 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 9

Wireless Distribution System (WDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-59
Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-64
Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-64
Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-65
IP Access Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-67
Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-68
Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-82
Ethernet Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-82
Static MAC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-84
Advanced. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-93
TCP/UDP Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-94
Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-96
Groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-97
Alarm Host Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-108
Syslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-109
Bridge. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-113
Spanning Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-114
Storm Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-114
Intra BSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-115
Packet Forwarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-116
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-118
Authentication and Encryption Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-118
Authentication Protocol Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-130
SSID, VLAN, and Security Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-130
VLAN Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-131
VLAN Workgroups and Traffic Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-135
Typical User VLAN Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-136
Configure Multiple SSID/VLAN/Security Mode Entries . . . . . . . . . . 4-137
Typical VLAN Management Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-146
MAC Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-147
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 3
Page 10

Rogue Access Point Detection (RAD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-149
RADIUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-155
MAC Access Control by Means of RADIUS Authentication . . . 4-156
RADIUS Authentication with 802.1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-161
RADIUS Accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-164
5 Monitor Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Logging into the HTTP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Version. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
ICMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
IP/ARP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Learn Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
IAPP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
RADIUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
Link Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
Station Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
Enabling and Viewing Station Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
Refreshing Station Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-20
6 Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Logging into the HTTP Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Introduction to File Transfer via TFTP or HTTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
TFTP File Transfer Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
HTTP File Transfer Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Image Error Checking during File Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Update AP by Using TFTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Update AP by Using HTTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
4 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 11

Upload File by Using TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
Upload File by Using HTTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-16
Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-19
Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
Help Link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
7 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
In This Chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Troubleshooting Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
Symptoms and Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Connectivity Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Basic Software Setup and Configuration Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Client Connection Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
VLAN Operation Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Power over Ethernet (PoE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
Recovery Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
Reset to Factory Default Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
Forced Reload Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
Setting IP Address using Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-24
Related Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-28
RADIUS Authentication Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-28
TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-28
A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1
A The Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1
In This Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
General Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Prerequisite Skills and Knowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Notation Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 5
Page 12

Important Terminology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-4
Navigation and Special Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-6
CLI Error Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-7
Bootloader CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-8
CLI Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-11
Command Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-11
Entering Text Strings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-13
CLI Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-14
The Question Mark . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-14
The Help Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-19
Accessing the AP CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-21
Using HyperTerminal to Log in to the AP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-21
Using Telnet to Log in to the AP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-22
CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-24
done. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-25
download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-25
exit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-26
help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-26
history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-29
passwd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-29
quit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-30
reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-30
search . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-31
set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-32
show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-36
upload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-39
Parameter Tables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-40
Auto Configuration Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-41
Auto Configuration Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-42
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-42
6 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 13

DHCP Server Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-43
DHCP Server Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-43
IP Address Pool Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-44
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-45
DNS Client Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-46
DNS Client for RADIUS Name Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-46
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-46
Ethernet Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-48
Ethernet Interface Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-48
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-48
Filtering Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-50
Ethernet Protocol Filtering Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-50
Ethernet Protocol Filtering Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-50
Static MAC Address Filter Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-51
Proxy ARP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-52
IP ARP Filtering Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-53
Broadcast Filtering Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-53
TCP/UDP Port Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-54
TCP/UDP Port Filtering Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-54
HTTP and HTTPS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-57
HTTP (Web browser) Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-57
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-58
IAPP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-60
IAPP Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-60
Intra BSS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-61
Intra BSS Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-61
Syntax Example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-61
Inventory Management Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-62
Inventory Management Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-62
IP Access Table Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-62
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 7
Page 14

IP Access Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-62
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-63
IP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-64
IP Configuration Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-64
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-65
Link Integrity Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-65
Link Integrity Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-65
IP Target Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-66
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-67
MAC Access Control Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-68
MAC Access Control Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-68
MAC Access Control Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-68
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-69
Monitoring Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-70
Packet Forwarding Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-71
Packet Forwarding Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-71
RAD Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-72
Rogue Access Point Detection (RAD) Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . A-73
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-73
RADIUS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-74
General RADIUS Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-74
RADIUS Authentication Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-75
RADIUS Accounting Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-77
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-78
Secure Management Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-82
Secure Management Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-82
Serial Port Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-83
Serial Port Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-83
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-84
SNMP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-84
8 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 15

SNMP Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-84
SNMP Trap Host Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-86
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-87
Spanning Tree Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-88
Spanning Tree Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-88
Spanning Tree Priority and Path Cost Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-89
SpectraLink VoIP Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-90
SpectraLink VoIP Parameters (802.11b and bg Modes Only). . . A-90
Storm Threshold Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-91
Storm Threshold Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-91
Storm Threshold Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-91
Syslog Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-92
Syslog Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-92
Syslog Host Table Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-94
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-94
System Information Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-95
System Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-95
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-96
Telnet Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-97
Telnet Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-97
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-98
TFTP Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-99
TFTP Server Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-99
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-100
WDS Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-102
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . A-102
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Security Table Parameters . . A-
102
802.11a Wireless Interface Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-103
802.11a Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-103
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 9
Page 16

Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-105
802.11b Wireless Interface Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-107
802.11b Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-108
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-111
802.11b/g Wireless Interface Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-115
802.11b/g Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-115
Wireless Interface SSID/VLAN/Security Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . A-121
Wireless Interface SSID Table Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-121
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-123
VLAN/SSID Pair Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-125
VLAN/SSID Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-125
VLAN ID Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-126
Syntax Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-127
B ASCII Character Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
C Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .C-1
In This Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
Software Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
Number of Stations per BSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-2
Management Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-2
Advanced Bridging Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Medium Access Control (MAC) Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Security Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Network Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-7
Advanced Wireless Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-8
Hardware Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
10 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 17

Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-10
Radio Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-11
802.11a Channel Frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-12
802.11b Channel Frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-14
802.11g Channel Frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-16
Wireless Communication Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-18
D Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .D-1
Before You Seek Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . D-1
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 11
Page 18

12 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 19

Introduction
In This Chapter
The following topics are covered in this section:
• Document Conventions
• Introduction to Wireless Networking
• IEEE 802.11 Specifications
• Management and Monitoring Capabilities
Document Conventions
• The term, AP, refers to an Access Point.
• The term, 802.11, is used to describe features that apply to the
802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g wireless standards.
• A Single-radio AP is an Access Point that supports one IEEE radio
standard. The AP-4, AP-5, and AP-6 are Single-radio APs.
• An 802.11a AP is an Access Point that supports the IEEE 802.11a
standard.
• An 802.11b AP is an Access Point that supports the IEEE 802.11b
standard.
1
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-1
Page 20
Introduction to Wireless Networking
• An 802.11b/g AP is an Access Point that supports the IEEE 802.11g
standard.
• An 802.11a/g AP is an Access Point that supports the IEEE
802.11a/g standards.
• Blue text indicates a link to a topic or Web address. If you are
viewing this documentation on your computer, click the blue text to
jump to the linked item.
NOTE:
A Note indicates important information that helps you make better
use of your computer.
!
CAUTION:
A Caution indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data
and tells you how to avoid the problem.
Introduction to Wireless Networking
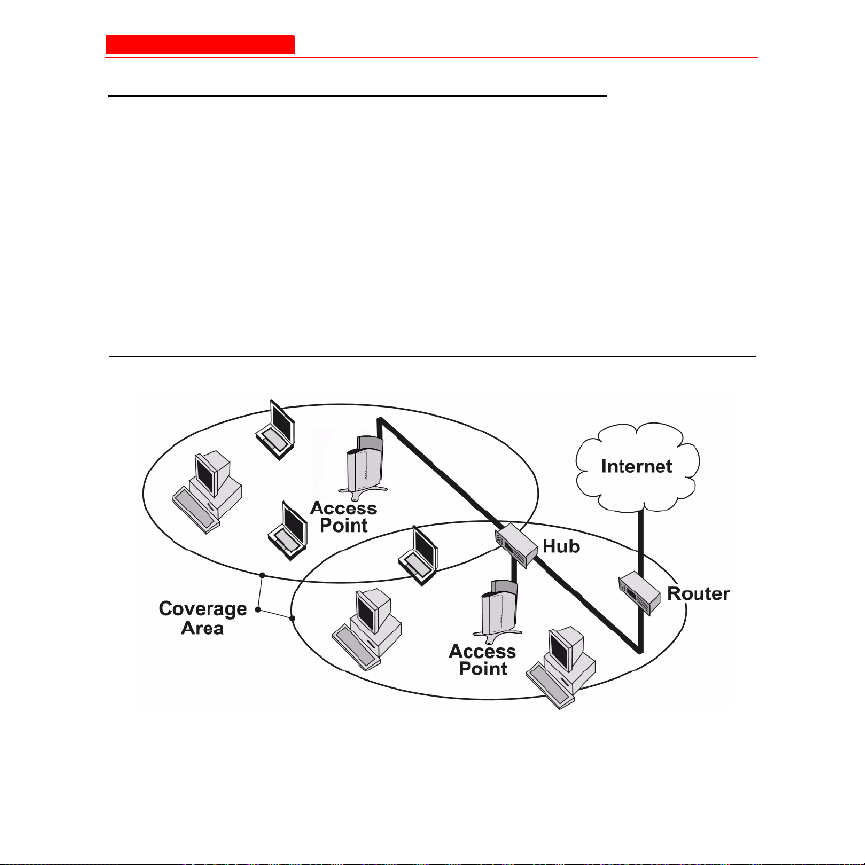
An AP extends the capability of an existing Ethernet network to devices
on a wireless network. Wireless devices can
• connect to a single Access Point, or
• move between multiple Access Points located within the same
vicinity. As wireless clients move from one coverage cell to another,
the devices maintain network connectivity.
1-2 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 21
Introduction to Wireless Networking
Site Survey
To determine the best location for an Access Point, Avaya recommends
conducting a Site Survey before placing the device in its final location. For
information about how to conduct a Site Survey, contact your local
reseller.
Before an Access Point can be configured for your specific networking
requirements, it must first be initialized. See Getting Started for details.
Figure 1-1. Typical wireless network access infrastructure
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-3
Page 22

Introduction to Wireless Networking
Once initialized, the network administrator can configure each unit
according to the network’s requirements. The AP functions as a wireless
network access point to data networks. An AP network provides:
• Seamless client roaming
• Easy installation and operation
• Over-the-air encryption of data
• High speed network links
To be fully operational, the AP-3 needs at least one wireless card
installed.
Guidelines for Roaming
Wireless Standard Support
An AP can only communicate with client devices that support its wireless
standard. For example, an 802.11a client cannot communicate with an
802.11b AP and an 802.11b client cannot communicate with an 802.11a
AP. However, both 802.11b and 802.11g clients can communicate with an
802.11b/g AP.
1-4 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 23

Introduction to Wireless Networking
Network Names
• All Access Points must have the same Network Name to support
client roaming.
• All workstations with an 802.11 client adapter installed must use
either a Network Name of “any” or the same Network Name as the
Access Points that they will roam between. If an AP has Closed
System enabled, a client must have the same Network Name as the
Access Point to communicate (see Interfaces).
Security Settings
All Access Points and clients must have the same security settings to
communicate.
Cell Coverage
• The Access Points’ cells must overlap to ensure that there are no
gaps in coverage and to ensure that the roaming client will always
have a connection available.
• The coverage area of an 802.11b or 802.11b/g AP is larger than the
coverage area of an 802.11a AP. The 802.11b and 802.11b/g APs
operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band; the 802.11a AP operates in
the 5 GHz band. Products that operate in the 2.4 GHz band offer
greater range than products that operate in the 5 GHz band.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-5
Page 24
IEEE 802.11 Specifications
Data Rates
An 802.11a or 802.11b/g AP operates at faster data rates than the
802.11b AP. 802.11a and 802.11g products operate at speeds of up to 54
Mbits/sec; 802.11b products operate at speeds of up to 11 Mbits/sec.
Channels
• All Access Points in the same vicinity should use a unique,
independent Channel. By default, the AP automatically scans for
available Channels during boot-up but you can also set the Channel
manually (see Interfaces for details).
• Access Points that use the same Channel should be installed as far
away from each other as possible to reduce potential interference.
IEEE 802.11 Specifications
In 1997, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
adopted the 802.11 standard for wireless devices operating in the 2.4
GHz frequency band. This standard includes provisions for three radio
technologies: direct sequence spread spectrum, frequency hopping
spread spectrum, and infrared. Devices that comply with the 802.11
standard operate at a data rate of either 1 or 2 Megabits per second
(Mbits/sec).
1-6 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 25

IEEE 802.11 Specifications
802.11b
In 1999, the IEEE modified the 802.11 standard to support direct
sequence devices that can operate at speeds of up to 11 Mbits/sec. The
IEEE ratified this standard as 802.11b. 802.11b devices are backwards
compatible with 2.4 GHz 802.11 direct sequence devices (that operate at
1 or 2 Mbits/sec). Available Frequency Channels vary by regulatory
domain and/or country. See 802.11b Channel Frequencies for details.
802.11a
Also in 1999, the IEEE modified the 802.11 standard to support devices
operating in the 5 GHz frequency band. This standard is referred to as
802.11a. 802.11a devices are not compatible with 2.4 GHz 802.11 or
802.11b devices. 802.11a radios use a radio technology called
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) to achieve data
rates of up to 54 Mbits/sec. Available Frequency Channels vary by
regulatory domain and/or country. See 802.11a Channel Frequencies for
details.
802.11g
In 2003, the IEEE introduced the 802.11g standard. 802.11g devices
operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band using OFDM to achieve data rates
of up to 54 Mbits/sec. In addition, 802.11g devices are backwards
compatible with 802.11b devices. Available Frequency Channels vary by
regulatory domain and/or country. See 802.11g Channel Frequencies for
details.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-7
Page 26
Management and Monitoring Capabilities
Management and Monitoring Capabilities
There are three management and monitoring interfaces available to the
network administrator to configure and manage an AP on the network:
• HTTP/HTTPS Interface
• Command Line Interface
• SNMP Management
HTTP/HTTPS Interface
The HTTP Interface (also known as the Web browser Interface) provides
easy access to configuration settings and network statistics from any
computer on the network. You can access the Web or HTTP Interface:
• over your LAN (switch, hub, etc.),
• over the Internet, or
• with a “crossover” Ethernet cable connected directly to your
computer’s Ethernet Port.
HTTPS provides an HTTP connection over a Secure Socket Layer.
HTTPS is one of two available secure management options on the AP;
the other secure management option is SNMPv3. Enabling HTTPS allows
you to access the AP in a secure fashion using Secure Socket Layer
(SSL) over port 443. The AP supports SSLv3 with a 128-bit encryption
certificate maintained by the AP for secure communications between the
AP and the HTTP client. All communications are encrypted using the
server and the client-side certificate.
1-8 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 27

Management and Monitoring Capabilities
The AP comes pre-installed with all required SSL files: default certificate,
private key and SSL Certificate Passphrase installed.
Command Line Interface
The Command Line Interface (CLI) is a text-based configuration utility
that supports a set of keyboard commands and parameters to configure
and manage an AP.
Users enter Command Statements, composed of CLI Commands and
their associated parameters. Statements may be issued from the
keyboard for real time control, or from scripts that automate configuration.
For example, when downloading a file, administrators enter the
download CLI Command along with IP Address, file name, and file type
parameters.
How To Access the CLI
You access the CLI over a HyperTerminal serial connection or via Telnet.
During initial configuration, you can use the CLI over a serial port
connection to configure an Access Point’s IP address.
When accessing the CLI via Telnet, you can communicate with the
Access Point from over your LAN (switch, hub, etc.), from over the
Internet, or with a “crossover” Ethernet cable connected directly to your
computer’s Ethernet Port.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-9
Page 28

Management and Monitoring Capabilities
See The Command Line Interface for more information on the CLI and for
a list of CLI commands and parameters.
SNMP Management
You can also manage and configure an AP using the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP).
NOTE:
This requires an SNMP manager program, like HP Openview or
Castlerock’s SNMPc.
The AP supports several Management Information Base (MIB) files that
describe the parameters that can be viewed and/or configured over
SNMP:
• MIB-II (RFC 1213)
• Bridge MIB (RFC 1493)
• Ethernet-like MIB (RFC 1643)
• 802.11 MIB
• Avaya Wireless Enterprise MIB
Avaya provides these MIB files on the CD included with each
Access Point. You need to compile one or more of the above MIBs into
your SNMP program’s database before you can manage an Access Point
using SNMP. Refer to the documentation that came with your SNMP
manager for instructions on how to compile MIBs.
1-10 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 29

Management and Monitoring Capabilities
The Enterprise MIB defines the read and read-write objects that can be
viewed or configured using SNMP. These objects correspond to most of
the settings and statistics that are available with the other management
interfaces. Refer to the Enterprise MIB for more information; the MIB can
be opened with any text editor, such as Microsoft Word, Notepad, or
WordPad.
SNMPv3 Secure Management
SNMPv3 is one of two available secure management options on the AP;
the other secure management option is HTTPS (HTTP connection over
Secure Socket Layer). SNMPv3 is based on the existing SNMP
framework, but addresses security requirements for device and network
management.
The security threats addressed by Secure Management are:
• Modification of information: An entity could alter an in-transit
message generated by an authorized entity in such a way as to
effect unauthorized management operations, including the setting of
object values. The essence of this threat is that an unauthorized
entity could change any management parameter, including those
related to configuration, operations, and accounting
• Masquerade: Management operations that are not authorized for
some entity may be attempted by that entity by assuming the identity
of an authorized entity.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 1-11
Page 30

Management and Monitoring Capabilities
• Message stream modification: SNMP is designed to operate over a
connectionless transport protocol. There is a threat that SNMP
messages could be reordered, delayed, or replayed (duplicated) to
effect unauthorized management operations. For example, a
message to reboot a device could be copied and replayed later.
• Disclosure: An entity could observe exchanges between a manager
and an agent and thereby learns the values of managed objects and
learn of notifiable events. For example, the observation of a set
command that changes passwords would enable an attacker to
learn the new passwords.
To address the security threats listed above, SNMPv3 provides the
following when secure management is enabled:
• Authentication: Provides data integrity and data origin
authentication.
• Privacy (a.k.a Encryption): Protects against disclosure of message
payload.
• Access Control: Controls and authorizes access to managed objects
NOTE:
The remainder of this guide describes how to configure an AP using
the HTTP Web interface or the CLI interface. For information on how
to manage devices using SNMP, refer to the documentation that
came with your SNMP program. Also, refer to the MIB files for
information on the parameters available via SNMP.
1-12 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 31

Getting Started
2
In This Chapter
• Prerequisites
• Product Package
• System Requirements
• Hardware Installation
• Initialization
• Download the Latest Software
• Additional Hardware Features
Prerequisites
Before installing an AP, you need to gather certain network information.
The following section identifies the information you need.
NOTE:
Passwords must be configured with at least 6 characters in length.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-1
Page 32

Prerequisites
Information Description
Network Name
(SSID of the
wireless cards)
Assign the Access Point a Primary Network
Name before wireless users can
communicate with it. The clients also need
the same Network Name. This is not the
same as the System Name, which applies
only to the Access Point. The network
administrator typically provides the Network
Name.
AP’s IP Address If you do not have a DHCP server on your
network, then you need to assign the
Access Point an IP address that is valid on
your network.
HTTP (Web)
Interface Password
Each Access Point requires a read/write
password to access the Web interface. The
default password is “public”.
CLI Interface
Password
Each Access Point requires a read/write
password to access the CLI interface. The
default password is “public”.
SNMP Read
Password
Each Access Point requires a password to
allow get requests from an SNMP manager.
The default password is “public”.
1 of 3
2-2 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 33

Information Description
Prerequisites
SNMPv3
Authentication
Password
If Secure Management is enabled, each
Access Point requires a password for
sending authenticated SNMPv3 messages.
The default password is “public”.
SNMPv3 Privacy
Password
If Secure Management is enabled, each
Access Point requires a password when
sending encrypted SNMPv3 data. The default
password is “public”.
SNMP Read-Write
Password
Each Access Point requires a password to
allow get and set requests from an SNMP
manager. The default password is “public”.
This password must be at least 6 characters
in length.
Security Settings You need to determine what security features
you will enable on the Access Point.
Authentication
Method
A primary authentication server may be
configured; a backup authentication server is
optional. The network administrator typically
provides this information.
2 of 3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-3
Page 34

Prerequisites
Information Description
Authentication
Server Shared
Secret
Authentication
Server
Authentication Port
Client IP Address
Pool Allocation
Scheme
DNS Server IP
Address
This is a password shared between the
Access Point and the RADIUS authentication
server (so both passwords must be the
same), and is typically provided by the
network administrator.
This is a port number (default is 1812) and is
typically provided by the network
administrator.
The Access Point can automatically provide
IP addresses to clients as they sign on. The
network administrator typically provides the
IP Pool range.
The network administrator typically provides
this IP Address.
3 of 3
2-4 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 35

Product Package
Product Package
Each Single-radio AP comes with the following:
• One metal base for ceiling or desktop mounting (includes two
screws)
• Mounting hardware
— Four 3.5 mm x 40 mm screws
— Four 6 mm x 35 mm plugs
• One power supply
• One Installation CD-ROM that contains the following:
— Software Installation Wizard
— ScanTool
— Solarwinds TFTP software
— HTML Help
— this user’s guide in PDF format
• One Access Point Quick Start Guide
If any of these items are missing or damaged, please contact your reseller
or Technical Support (see Technical Support for contact information).
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-5
Page 36

System Requirements
MiniPCI Upgrade Kits
Single-radio APs can be fitted with different radio types. MiniPCI upgrade
kits are available for 802.11a /b/g and 802.11b/g wireless cards. Each kit
is composed of a single miniPCI board with an integral antenna attached.
The type of radio is indicated on the label on the antenna and instructions
on how to open your AP to replace the radio are provided with the kit.
System Requirements
The following are the minimum requirements to begin using an AP:
• A 10Base-T Ethernet or 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet switch or hub
• At least one of the following IEEE 802.11-compliant devices:
You will need an: If you have an:
802.11a client device 802.11a AP
802.11b or 802.11b/g client device 802.11b AP
802.11b/g client device 802.11b/g AP
802.11a/g client device 802.11a/g AP
2-6 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 37

Hardware Installation
• A computer that is connected to the same IP network as the AP and
has one of the following Web browsers installed:
— Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later and
patch Q323308
— Netscape 6.1 or later
(The computer is required to configure the AP using the Web or
HTTP interface.)
Hardware Installation
Follow these steps to install a Single-radio AP:
1. Unpack the Access Point and accessories from the shipping box.
2. If you intend to install the unit free-standing or if you intend to
mount it to the ceiling, use a Phillips screwdriver to attach the
metal base to the underside of the unit. The metal base and
screws are provided. See Mounting Options for additional
information.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-7
Page 38

Hardware Installation
Figure 2-1. Attach the Metal Base
2-8 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 39

Hardware Installation
3. Press down on the cable-cover lock located in the front-center of
the unit to release the cable cover.
Figure 2-2. Unlock the Cable Cover
cable-cover lock
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-9
Page 40

Hardware Installation
4. Remove the cable cover from the unit.
Figure 2-3. Remove Cable Cover
2-10 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 41

Hardware Installation
5. Remove the front cover (the side with the LED indicators) from the
unit.
Figure 2-4. Remove the Front Cover
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-11
Page 42

Hardware Installation
6. Remove the back cover from the unit.
Figure 2-5. Remove the Back Cover
2-12 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 43

Hardware Installation
7. Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the Access Point’s
Ethernet port. The other end of the cable should not be connected
to another device until after the installation is complete.
— Use a straight-through Ethernet cable if you intend to connect
the Access Point to a hub, switch, patch panel, or Power over
Ethernet power injector.
— Use a cross-over Ethernet cable if you intend to connect the
Access Point to a single computer.
8. If you are not using Power over Ethernet (or you want to connect
the Access Point to Power over Ethernet and AC power
simultaneously), attach the AC power cable to the Access Point’s
power port.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-13
Page 44

Hardware Installation
Figure 2-6. Attach Ethernet Cable and Power Cable
Power Cable
Ethernet Cable
NOTE:
Once attached, the power cable locks into place. To disconnect the
power cable, slide back the black plastic fitting and gently pull the
cable from the connector.
2-14 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 45

Hardware Installation
9. Connect the free end of the Ethernet cable to a hub, switch, patch
panel, Power over Ethernet power injector, or an Ethernet port on a
computer.
10. If using AC power, connect the power cord to a power source (such
as a wall outlet) to turn on the unit.
11. Configure and test the unit. See Initialization for details.
12. Download the latest software to the unit, if necessary. See
Download the Latest Software for details.
13. Place the unit in the final installation location. See Mounting
Options for mounting options and instructions.
NOTE:
Avaya recommends that you perform a Site Survey prior to
determine the installation location for your AP units. For information
about how to conduct a Site Survey, contact your local reseller.
14. Replace the back cover, front cover, and cable cover. Be careful to
avoid trapping the power and Ethernet cables when replacing the
cable cover.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-15
Page 46

Hardware Installation
Figure 2-7. Assembled Unit
15. If desired, you can attach a Kensington lock to secure the cable
cover into place. This will protect the unit from unauthorized
tampering. See Kensington Security Slot for details.
2-16 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 47

Initialization
Initialization
Avaya provides two tools to simplify the initialization and configuration of
an AP:
• ScanTool
• Setup Wizard
ScanTool is included on the Installation CD; the Setup Wizard launches
automatically the first time you access the HTTP interface.
NOTE:
These initialization instructions describe how to configure an AP
over an Ethernet connection using ScanTool and the HTTP
interface. If you want to configure the unit over the serial port, see
Setting IP Address using Serial Port for information on how to
access the CLI over a serial connection and The Command Line
Interface for a list of supported commands.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-17
Page 48

Initialization
ScanTool
ScanTool is a software utility that is included on the installation CD-ROM.
ScanTool allows you to find the IP address of an Access Point by
referencing the MAC address in a Scan List, or to assign an IP address if
one has not been assigned.
ScanTool automatically
• detects the Access Points installed on your network, regardless of
IP address,
• lets you configure each unit’s IP settings, and
• allows you to download new software to an AP that does not have a
valid software image installed (see Client Connection Problems).
To access the HTTP interface and configure the AP, the AP must be
assigned an IP address that is valid on its Ethernet network. By default,
the AP is configured to obtain an IP address automatically from a network
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server during boot-up. If
your network contains a DHCP server, you can run ScanTool to find out
what IP address the AP has been assigned.
Default IP Address
If your network does not contain a DHCP server, the Access Point’s IP
address defaults to 169.254.128.132. In this case, you can use ScanTool
to assign the AP a static IP address that is valid on your network.
2-18 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 49

Initialization
ScanTool Instructions
Follow these steps to install ScanTool, initialize the Access Point, and
perform initial configuration:
1. Locate the unit’s Ethernet MAC address and write it down for future
reference. The MAC address is printed on the product label. Each
unit has a unique MAC address, which is assigned at the factory.
2. Confirm that the AP is connected to the same LAN subnet as the
computer that you will use to configure the AP.
3. Power up, reboot, or reset the AP.
— Result: The unit requests an IP Address from the network
DHCP server.
4. Insert the Installation CD into the CD-ROM drive of the computer
that you will use to configure the AP.
— Result: The installation program will launch automatically.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the Access Point
software and documentation.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-19
Page 50

Initialization
NOTE:
The Avaya Wireless Installation program supports the following
operating systems:
— Windows 98SE
— Windows 2000
— Windows NT
— Windows ME
— Windows XP
6. After the software has been installed, double-click the ScanTool
icon on the Windows desktop to launch the program (if the
program is not already running).
— Result: ScanTool scans the subnet and displays all detected
Access Points. The ScanTool’s Scan List screen appears, as
shown in the following example.
NOTE:
If your computer has more than one network adapter installed, you
will be prompted to select the adapter that you want ScanTool to use
before the Scan List appears. If prompted, select an adapter and
click OK. You can change your adapter setting at any time by
clicking the Select Adapter button on the Scan List screen.
The ScanTool Network Adapter Selection screen will not appear
if your computer only has one network adapter installed.
2-20 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 51

Initialization
Figure 2-8. Scan List
7. Locate the MAC address of the AP you want to initialize within the
Scan List.
NOTE:
If your Access Point does not show up in the Scan List, click the
Rescan button to update the display. If the unit still does not appear
in the list, see Troubleshooting for suggestions. Note that after
rebooting an Access Point, it may take up to five minutes for the unit
to appear in the Scan List.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-21
Page 52

Initialization
8. Do one of the following:
— If the AP has been assigned an IP address by a DHCP server
on the network, write down the IP address and click Cancel to
close ScanTool. Go to Setup Wizard for information on how to
access the HTTP interface using this IP address.
— If the AP has not been assigned an IP address (in other words,
the unit is using its default IP address, 169.254.128.132),
follow the steps in the table to assign it a static IP address that
is valid on your network:
2-22 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 53

Initialization
Step Action
1. Highlight the entry for the AP you want
to configure.
2. Click the Change button.
Result: The Change screen appears.
Scan Tool Change Screen
1 of 3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-23
Page 54

Initialization
Step Action
3. Set IP Address Type to Static.
4. Enter a static IP Address for the AP in
the field provided. You must assign the
unit a unique address that is valid on
your IP subnet. Contact your network
administrator if you need assistance
selecting an IP address for the unit.
5. Enter your network’s Subnet Mask in
the field provided.
6. Enter your network’s Gateway IP
Address in the field provided.
7. Enter the SNMP Read/Write password
in the Read/Write Password field (for
new units, the default SNMP Read/Write
password is “public”).
NOTE:
The TFTP Server IP Address and
Image File Name fields are only
available if ScanTool detects that
the AP does not have a valid
software image installed. See Client
Connection Problems.
2 of 3
2-24 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 55

Initialization
Step Action
8. Click OK to save your changes.
Result: The Access Point will reboot
automatically and any changes you
made will take effect.
9. When prompted, click OK a second time
to return to the Scan List screen.
10. Click Cancel to close the ScanTool.
11. Proceed to Setup Wizard for information
on how to access the HTTP interface.
3 of 3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-25
Page 56

Initialization
Setup Wizard
The first time you connect to an AP’s HTTP interface, the Setup Wizard
launches automatically. The Setup Wizard provides step-by-step
instructions for how to configure the Access Point’s basic operating
parameter, such as Network Name, IP parameters, system parameters,
and management passwords.
Setup Wizard Instructions
Follow these steps to access the Access Point’s HTTP interface and
launch the Setup Wizard:
1. Open a Web browser on a network computer.
The HTTP interface supports the following Web browser:
— Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later
— Netscape 6.1 or later
2. If necessary, disable the browser’s Internet proxy settings. For
Internet Explorer users, follow these steps:
a. Select Tools > Internet Options....
b. Click the Connections tab.
c. Click LAN Settings....
d. If necessary, remove the check mark from the Use a proxy
server box.
2-26 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 57

Initialization
e. Click OK twice to save your changes and return to Internet
Explorer.
3. Enter the Access Point’s IP address in the browser’s Address field
and press Enter.
This is either the
— dynamic IP address assigned by a network DHCP server or
— the static IP address you manually configured.
See ScanTool for information on how to determine the unit’s IP
address and manually configure a new IP address, if necessary.
— Result: The Enter Network Password screen appears.
4. Enter the HTTP password in the Password field. Leave the User
Name field blank. For new units, the default HTTP password is
“public”.
— Result: The Setup Wizard will launch automatically. An
example of the Password dialog and the Setup Wizard page
are shown next.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-27
Page 58

Initialization
Figure 2-9. Enter Network Password
2-28 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 59

Figure 2-10. Setup Wizard
5. Click Setup Wizard to begin. If you want to configure the AP
without using the Setup Wizard, click Exit and see Advanced
Configuration.
The Setup Wizard supports the following navigation options:
Initialization
— Save & Next Button: Each Setup Wizard screen has a Save
& Next button. Click this button to submit any changes you
made to the unit’s parameters and continue to the next page.
The instructions described next shown how to navigate the
Setup Wizard using the Save & Next buttons.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-29
Page 60

Initialization
— Navigation Panel: The Setup Wizard provides a navigation
panel on the left-hand side of the screen. Click the link that
corresponds to the parameters you want to configure to be
taken to that particular configuration screen. Note that clicking
a link in the navigation panel will not submit any changes you
made to the unit’s configuration on the current page.
— Exit: The navigation panel also includes an Exit option. Click
this link to close the Setup Wizard at any time.
!
CAUTION:
If you exit from the Setup Wizard, any changes you submitted (by clicking
the Save & Next button) up to that point will be saved to the unit but will
not take effect until it is rebooted.
6. Configure the System Configuration settings and click Save &
Next. See System for more information.
7. Configure the Access Point’s Basic IP address settings, if
necessary, and click Save & Next. See Basic IP Parameters for
more information.
2-30 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 61

Initialization
8. Assign the AP new passwords to prevent unauthorized access and
click Save & Next. Each management interface has its own
password:
— SNMP Read Password
— SNMP Read-Write Password
— SNMPv3 Authentication Password
— SNMPv3 Privacy Password
— CLI Password
— HTTP (Web) Password
By default, each of these passwords is set to “public”. See
Passwords for more information.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-31
Page 62

Initialization
9. Configure the basic wireless interface settings and click Save &
Next.
— The following options are available for an 802.11a AP:
Option Description
Primary Network
Name (SSID)
Enter a Network Name (between 2
and 31 characters long) for the
wireless network. You must configure
each wireless client to use this name
as well.
Additional Network
Names (SSIDs)
The AP supports up to 16 SSIDs and
VLANs per wireless interface (radio).
Refer to the Advanced Configuration
chapter for information on the
detailed rules on configuring multiple
SSIDs, VLANs, and security modes.
1 of 4
2-32 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 63

Initialization
Option Description
Auto Channel Select By default, the AP scans the area for
other Access Points and selects the
best available communication
channel, either a free channel (if
available) or the channel with the
least amount of interference.
Remove the check mark to disable
this option. Note that you cannot
disable Auto Channel Select for
802.11a products in Europe (see
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS)
for details).
2 of 4
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-33
Page 64

Initialization
Option Description
Frequency Channel When Auto Channel Select is
enabled, this field is read-only and
displays the Access Point’s current
operating channel. When Auto
Channel Select is disabled, you can
specify the Access Point’s channel. If
you decide to manually set the unit’s
channel, ensure that nearby devices
do not use the same frequency.
Available Channels vary based on
regulatory domain. See 802.11a
Channel Frequencies. Note that you
cannot manually set the channel for
802.11a products in Europe (see
Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS)
for details).
Transmit Rate Use the drop-down menu to select a
specific transmit rate for the AP.
Choose between 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48, 54 Mbits/s, and Auto Fallback.
The Auto Fallback feature allows the
AP to select the best transmit rate
based on the cell size.
3 of 4
2-34 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 65

Option Description
WEP Encryption Place a check mark in the box
provided to enable WEP encryption.
See WEP Encryption for more
information.
Initialization
Set Encryption Key
1
If you enabled Encryption, configure
an Encryption Key. This key is used
to encrypt and decrypt data between
the AP and its wireless clients. Enter
the number of characters that
correspond to the desired key size,
as described below:
• Enter 10 hexadecimal
characters (0-9 and A-F) or 5
ASCII characters (see ASCII
Character Chart) to use 64-bit
encryption.
• Enter 26 hexadecimal
characters or 13 ASCII
characters to use 128-bit
encryption.
• Enter 32 hexadecimal
characters or 16 ASCII
characters to use 152-bit
encryption.
4 of 4
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-35
Page 66

Initialization
— The following options are available for an 802.11b AP:
Option Description
Primary Network
Name (SSID)
Enter a Network Name (between 2
and 31 characters long) for the
wireless network. You must configure
each wireless client to use this name
as well.
Additional Network
Names (SSIDs)
The AP supports up to 16 SSIDs and
VLANs per wireless interface (radio).
Refer to the Advanced Configuration
chapter for information on the
detailed rules on configuring multiple
SSIDs, VLANs, and security modes.
Auto Channel Select By default, the AP scans the area for
other Access Points and selects the
best available communication
channel, either a free channel (if
available) or the channel with the
least amount of interference.
Remove the check mark to disable
this option. If you are setting up a
Wireless Distribution System (WDS),
it must be disabled. See Wireless
Distribution System (WDS) for more
information.
1 of 4
2-36 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 67

Option Description
Frequency Channel When Auto Channel Select is
enabled, this field is read-only and
displays the Access Point’s current
operating channel. When Auto
Channel Select is disabled, you can
specify the Access Point’s operating
channel. If you decide to manually
set the unit’s channel, ensure that
nearby devices do not use the same
frequency (unless you are setting up
a WDS). Available Channels vary
based on regulatory domain. See
802.11b Channel Frequencies.
Initialization
Distance Between
APs
Set to Large, Medium, Small,
Microcell, or Minicell depending on
the site survey for your system. The
distance value is related to the
Multicast Rate (described next). In
general, a larger distance between
APs means that your clients operate
a slower data rates (on average).
See Distance Between APs for more
information.
2 of 4
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-37
Page 68

Initialization
Option Description
Multicast Rate Sets the rate at which Multicast
messages are sent. This value is
related to the Distance Between
APs parameter (described
previously). The table below displays
the possible Multicast Rates based
on the Distance between APs. See
Multicast Rate for more information.
Distance
between APs Multicast Rate
Large 1 and 2 Mbits/sec
Medium 1, 2, and 5.5
Mbits/sec
Small 1, 2, 5.5 and 11
Mbits/sec
Minicell 1, 2, 5.5 and 11
Mbits/sec
Microcell 1, 2, 5.5 and 11
Mbits/sec
3 of 4
2-38 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 69

Option Description
WEP Encryption Place a check mark in the box
provided to enable WEP encryption.
See WEP Encryption for more
information.
Initialization
Set Encryption Key
1
If you enabled Encryption, configure
an Encryption Key. This key is used
to encrypt and decrypt data between
the AP and its wireless clients. Enter
the number of characters that
correspond to the desired key size,
as described below:
• Enter 10 hexadecimal
characters (0-9 and A-F) or 5
ASCII characters (see ASCII
Character Chart) to use 64-bit
encryption.
• Enter 26 hexadecimal
characters (0-9 and A-F) or 13
ASCII characters to use 128-bit
encryption
4 of 4
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-39
Page 70

Initialization
— The following options are available for an 802.11b/g AP:
Option Description
Operational Mode An 802.11b/g wireless interface can
be configured to operate in the
following modes:
• 802.11b mode only
• 802.11g mode only
• 802.11g-wifi mode
• 802.11b/g mode (default)
Primary Network
Name (SSID)
Enter a Network Name (between 2
and 31 characters long) for the
wireless network. You must
configure each wireless client to use
this name as well.
Additional Network
Names (SSIDs)
The AP supports up to 16 SSIDs and
VLANs per wireless interface (radio).
Refer to the Advanced Configuration
chapter for information on the
detailed rules on configuring multiple
SSIDs, VLANs, and security modes.
1 of 5
2-40 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 71

Initialization
Option Description
Auto Channel Select By default, the AP scans the area for
other Access Points and selects the
best available communication
channel, either a free channel (if
available) or the channel with the
least amount of interference.
Remove the check mark to disable
this option.
Frequency Channel When Auto Channel Select is
enabled, this field is read-only and
displays the Access Point’s current
operating channel. When Auto
Channel Select is disabled, you can
specify the Access Point’s channel. If
you decide to manually set the unit’s
channel, ensure that nearby devices
do not use the same frequency.
Available Channels vary based on
regulatory domain. See 802.11g
Channel Frequencies.
2 of 5
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-41
Page 72

Initialization
Option Description
Transmit Rate Select a specific transmit rate for the
AP. The values available depend on
the Operational Mode. Auto Fallback
is the default setting; it allows the AP
to select the best transmit rate based
on the cell size.
• For 802.11b only -- Auto
Fallback, 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbits/sec
• For 802.11g only -- Auto
Fallback, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48, 54 Mbits/sec
• For 802.11b/g and
802.11g-wifi-- Auto Fallback, 1,
2, 5.5, 6, 9, 11, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48, 54 Mbits/sec
WEP Encryption Place a check mark in the box
provided to enable WEP encryption.
See WEP Encryption for more
information.
3 of 5
2-42 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 73

Initialization
Option Description
Set Encryption Key 1 If you enabled Encryption, configure
an Encryption Key. This key is used
to encrypt and decrypt data between
the AP and its wireless clients. Enter
the number of characters that
correspond to the desired key size,
as described below:
• Enter 10 hexadecimal
characters (0-9 and A-F) or 5
ASCII characters (see ASCII
Character Chart) to use 64-bit
encryption.
• Enter 26 hexadecimal
characters or 13 ASCII
characters to use 128-bit
encryption.
• Enter 32 hexadecimal
characters or 16 ASCII
characters to use 152-bit
encryption.
4 of 5
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-43
Page 74

Initialization
Option Description
Set Encryption Key 1
(continued)
NOTE:
Additional advanced settings
are available in the Wireless
Interface Configuration
screen. See Wireless (802.11a),
Wireless (802.11b), or Wireless
(802.11b/g) for details. See
Security for more information on
security features.
5 of 5
10. Review the configuration summary. If you want to make any
additional changes, use the navigation panel on the left-hand side
of the screen to return to an earlier screen. After making a change,
click Save & Next to save the change and proceed to the next
screen.
11. When finished, click Reboot on the Summary screen to restart the
AP and apply your changes.
2-44 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 75

Download the Latest Software
Download the Latest Software
Avaya periodically releases updated software for the AP on its Web site at
http://www.avaya.com/support. Avaya recommends that you check the
Web site for the latest updates after you have installed and initialized the
unit.
Three types of files can be downloaded to the AP from a TFTP server:
• image (AP software image or kernel)
• config (configuration file)
• bspBl (BSP/Bootloader firmware file)
Setup your TFTP Server
A Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server allows you to transfer files
across a network. You can
• upload files from the AP for backup or copying, and
• download the files for configuration and AP Image upgrades.
The Solarwinds TFTP server software is located on the Avaya Wireless
AP Installation CD-ROM. You can also download the latest TFTP
software from Solarwind’s Web site at http://www.solarwinds.net.
NOTE:
If a TFTP server is not available in the network, you can perform
similar file transfer operations using the HTTP interface.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-45
Page 76

Download the Latest Software
After the TFTP server is installed:
• Check to see that TFTP is configured to point to the directory
containing the AP Image.
• Make sure you have the proper TFTP server IP address, the proper
AP Image file name, and that the TFTP server is operational.
• Make sure the TFTP server is configured to both Transmit and
Receive files, with no automatic shutdown or time-out.
Download Updates from a TFTP Server using the Web Interface
1. Download the latest software from http://www.avaya.com/support.
2. Copy the latest software updates to your TFTP server.
3. In the Web Interface, click the Commands button and select the
Download tab.
4. Enter the IP address of your TFTP server in the field provided.
5. Enter the File Name (including the file extension). Enter the full
directory path and file name. If the file is located in the default
TFTP directory, you need enter only the file name.
6. Select the File Type from the drop-down menu (use Img for
software updates).
7. Select Download & Reboot from the File Operation drop-down
menu.
8. Click OK.
9. The Access Point will reboot automatically when the download is
complete.
2-46 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 77

Additional Hardware Features
Download Updates from a TFTP Server using the CLI Interface
1. Download the latest software from http://www.avaya.com/support.
2. Copy the latest software updates to your TFTP server.
3. Open the CLI interface via Telnet or a serial connection.
4. Enter the CLI password when prompted.
5. Enter the command: download <tftpaddr
— Result: The download will begin. Be patient while the image is
downloaded to the Access Point.
6. When the download is complete, type reboot 0 and press Enter.
NOTE:
See The Command Line Interface for more information.
> <filename> img
Additional Hardware Features
• Mounting Options
• Installing the AP in a Plenum
• Kensington Security Slot
• Power over Ethernet
• LED Indicators
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-47
Page 78

Additional Hardware Features
Mounting Options
There are three mounting options for the AP, described below.
Desktop Mount
This is the standard installation for the AP. See Hardware Installation for
instructions.
Wall Mount
Follow these steps to mount the AP on a wall:
1. Identify the location where you intend to mount the unit.
NOTE:
For best results, mount the unit vertically. In other words, the
antenna should be pointing up or down but not sideways.
2. Unplug the Access Point’s power supply, if necessary.
3. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the metal base from the
underside of the AP, if necessary.
4. Press down on the cable cover lock to release the cable cover.
See Unlock the Cable Cover for an illustration.
5. Remove the cable cover from the unit. See Remove Cable Cover
for an illustration.
2-48 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 79

Additional Hardware Features
6. Remove the front cover from the unit. See Remove the Front
Cover for an illustration.
7. Remove the back cover from the unit. See Remove the Back
Cover for an illustration.
8. Place the back cover on the mounting location and mark the center
of the three mounting holes.
9. Remove the cover from the wall and drill a hole at each of the
locations you marked above. Each hole should be wide enough to
hold a mounting plug (which is 6 mm x 35 mm).
10. Insert a plug into each hole. The AP comes with four 6 mm x 35
mm plugs; you only need to use three of these when wall mounting
the unit.
11. Insert a screw into each of the mounting holes molded into the
back cover. The AP comes with four 3.5 mm x 40 mm pan-head
screws; you only need to use three of these when wall mounting
the unit.
12. Insert the screws into the wall plugs. Use a screwdriver to tighten
the screws and attach the back cover to the wall. In the following
example, the back cover is mounted upside down (the two holes
are at the bottom).
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-49
Page 80

Additional Hardware Features
Figure 2-11. Attach the Back Cover to the Wall
13. Attach Ethernet and power cables to the AP unit, if necessary.
2-50 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 81

Additional Hardware Features
14. Snap the unit into the back cover. In the following example, the unit
is mounted upside down and its antenna is facing down.
Figure 2-12. AP Mounted on a Wall
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-51
Page 82

Additional Hardware Features
15. Replace the front cover.
16. Replace the cable cover.
17. Turn on the AP.
Ceiling Mount
Follow these steps to mount the AP to a ceiling:
1. Unplug the Access Point’s power supply, if necessary.
2. Use a Phillips screwdriver to attach the metal base to the
underside of the AP, if necessary. SeeAttach the Metal Base for an
illustration.
3. Feed a mounting screw through each of the four rubber feet. The
AP comes with four 3.5 mm x 40 mm pan-head screws.
4. Remove the screws from the rubber feet.
5. Turn the AP upside down position the base against the ceiling
where you want to mount the unit.
6. Mark the center of the four mounting holes in the rubber feet.
7. Set the AP aside and drill a hole at each of the locations you
marked above. Each hole should be wide enough to hold a
mounting plug (which is 6 mm x 35 mm).
8. Insert a plug into each hole. The AP comes with four 6 mm x 35
mm plugs.
9. Insert the screws into the holes you made previously in the rubber
feet.
2-52 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 83

Additional Hardware Features
10. Insert the screws into the wall plugs. Use a screwdriver to tighten
the screws and attach the Access Point’s metal base to the ceiling.
Figure 2-13. Mounting the AP to the Ceiling
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-53
Page 84

Additional Hardware Features
Installing the AP in a Plenum
In an office building, plenum is the space between the structural ceiling
and the tile ceiling that is provided to help air circulate. Many companies
also use the plenum to house communication equipment and cables.
However, these products and cables must comply with certain safety
requirements, such as Underwriter Labs (UL) Standard 2043: “Standard
for Fire Test for Heat and Visible Smoke Release for Discrete Products
and Their Accessories Installed in Air-Handling Spaces”.
The AP has been certified under UL Standard 2043 and can be installed
in the plenum only when the following conditions apply:
• The unit uses Power over Ethernet (PoE) to receive power over a
plenum-rated Category 5 Ethernet cable (the power cable must not
be connected to the unit).
• The unit’s plastic covers have been removed (this includes the cable
cover, the front cover, and the back cover).
Kensington Security Slot
The AP enclosure includes a Kensington Security Slot for use with a
Kensington locking mechanism. When properly installed, a Kensington
lock can prevent unauthorized personnel from stealing the AP. In
addition, the Kensington locks secures the cable cover in place, which
prevents tampering with the Ethernet and power cables.
2-54 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 85

Additional Hardware Features
The Kensington Security Slot is shown in the illustrations below (the
figure on the left shows the slot with the cable cover attached; the figure
on the right shows the slot with the cable cover removed). See
http://www.kensington.com for information on Kensington security
solutions.
Figure 2-14. Kensington Security Slot
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-55
Page 86

Additional Hardware Features
Power over Ethernet
An Power over Ethernet-enabled AP is equipped with an
802.3af-compliant Power over Ethernet module. Power over Ethernet
(PoE) delivers both data and power to the access point over a single
Ethernet cable. If you choose to use Power over Ethernet, there is no
difference in operation; the only difference is in the power source.
• The Power over Ethernet (PoE) integrated module receives ~48
VDC over a standard Category 5 Ethernet cable.
• To use Power over Ethernet, you must have an PoE hub (also
known as a power injector) connected to the network.
• The cable length between the PoE hub and the Access Point should
not exceed 100 meters (approximately 325 feet).
• The PoE hub is not a repeater and does not amplify the Ethernet
data signal.
• If connected to an PoE hub and an AC power simultaneously, the
Access Point draws power from Power over Ethernet.
• Maximum power supplied to an Access Point is 11 Watts; the unit
typically draws approximately 10 Watts.
Also see Hardware Specifications.
NOTE:
The AP’s 802.3af-compliant Power over Ethernet module is
backwards compatible with all Avaya Wireless Power over Ethernet
hubs that do not support the IEEE 802.3af standard.
2-56 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 87

Additional Hardware Features
LED Indicators
The AP has four LED indicators. The LEDs are identified in LED
Indicators Illustrated and exhibit the following behavior:
Ethernet
Power
Solid
Green
Solid
Amber
Solid
Green
Solid Red Off Off Off SDRAM Test Failure
Link
Green
when link
exists
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Ethernet
Activity
Green
flash
with
data
activity
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Wireless
Activity Indication
Green
flash
with data
activity
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Normal Operation
Rebooting/Power on Self Test
(POST)
Reset to Factory Defaults
command issued
1 of 3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-57
Page 88

Additional Hardware Features
Ethernet
Power
Solid Red Green Off Off If the AP is configured to get
Blinking
Red
Blinking
Red
Solid Red Blinking
Solid Red Off Off Solid Red Wireless Test Failure
Blinking
Amber
Link
Blinking
Red or Off
Off Off Blinking
Red or Off
Blinking
Amber or
Off
Ethernet
Activity
Blinking
Red
Solid
Red
Blinking
Amber
or Off
Wireless
Activity Indication
an IP address from a DHCP
server, it may take up to two
minutes to obtain the
address. The Power LED will
be red and if there is an
Ethernet link the Ethernet
Link LED will be green during
the time the AP is trying to
obtain an address. Once an
address is obtained, the
Power LED will turn green.
Off Hardware Timer Test Failure
Flash Test Failure
Red
Off Ethernet Test Failure
Off Missing or bad AP image
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Solid
Amber
Missing or bad bootloader
image (all LEDs remain solid
amber)
2 of 3
2-58 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 89

Additional Hardware Features
Ethernet
Power
n/a n/a n/a Red Wireless radio is not working
n/a n/a Amber Amber Indicated interface in
Link
Ethernet
Activity
Wireless
Activity Indication
properly
administrative down state
3 of 3
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-59
Page 90

Additional Hardware Features
y
Figure 2-15. LED Indicators Illustrated
Power LED
Ethernet Link
LED
Ethernet Activit
LED
Wireless Activity
LED
2-60 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 91

Related Topics
Related Topics
The Setup Wizard helps you configure the basic AP settings required to
get the unit up and running. The AP supports many other configuration
and management options. The remainder of this user guide describes
these options in detail.
• See Advanced Configuration for information on configuration
options that are available within the Access Point’s HTTP interface.
• See Monitor Information for information on the statistics displayed
within the Access Point’s HTTP interface.
• See Commands for information on the commands supported by the
Access Point’s HTTP interface.
• See Troubleshooting for troubleshooting suggestions.
• See The Command Line Interface for information on the CLI
interface and for a list of CLI commands.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 2-61
Page 92

Related Topics
2-62 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User ’s Guide
Page 93

Status Information
3
In This Chapter
• Logging into the HTTP Interface
• System Status
Logging into the HTTP Interface
Once the AP has a valid IP Address and an Ethernet connection, you may
use your web browser to monitor the system status.
Follow these steps to monitor an AP’s operating statistics using the HTTP
interface:
1. Open a Web browser on a network computer.
NOTE:
The HTTP interface supports the following Web browser:
— Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later
— Netscape 6.1 or later
2. If necessary, disable the Internet proxy settings. For Internet
Explorer users, follow these steps:
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 3-1
Page 94

Logging into the HTTP Interface
— Select Tools > Internet Options....
— Click the Connections tab.
— Click LAN Settings....
— If necessary, remove the check mark from the Use a proxy
server box.
— Click OK twice to save your changes and return to Internet
Explorer.
3. Enter the Access Point’s IP address in the browser’s Address field
and press Enter.
— Result: The Enter Network Password screen appears.
4. Enter the HTTP password in the Password field and click OK.
Leave the User Name field blank. (By default, the HTTP password
is “public”).
— Result: The System Status screen appears.
3-2 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 95

System Status
Figure 3-1. Enter Network Password Screen
System Status
System Status is the first screen to appear each time you connect to the
HTTP interface. You can also return to this screen by clicking the Status
button.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 3-3
Page 96

System Status
Figure 3-2. System Status Screen
3-4 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 97

System Status
Each section of the System Status screen provides the following
information:
— System Status: This area provides system level information,
including the unit’s IP address and contact information. See
System for information on these settings.
— System Alarms: System traps (if any) appear in this area.
Each trap identifies a specific severity level: Critical, Major,
Minor, and Informational. See Alarms for a list of possible
alarms.
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 3-5
Page 98

System Status
3-6 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
Page 99

Advanced Configuration
In This Chapter
• Configuring the AP Using the HTTP/HTTPS Interface
• System: Configure specific system information such as system name
and contact information.
• Network: Configure IP settings, DNS client, DHCP server, and Link
Integrity.
• Interfaces: Configure the Access Point’s interfaces: Wireless and
Ethernet. Also describes configuring a Wireless Distribution System
(WDS).
• Management: Configure the Access Point’s management
Passwords, IP Access Table, and Services such as configuring
secure or restricted access to the AP via SNMPv3, HTTPS, CLI, or
Automatic Configuration.
• Filtering: Configure Ethernet Protocol filters, Static MAC Address
filters, Advanced filters, and Port filters.
• Alarms: Configure the Alarm (SNMP Trap) Groups, the Alarm Host
Table, and the Syslog features.
• Bridge: Configure the Spanning Tree Protocol, Storm Threshold
protection, Intra BSS traffic, and Packet Forwarding.
• Security: Configure security features such as MAC Access Control,
WPA, WEP Encryption, and 802.1x. Configure Rogue Access Point
4
Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide 4-1
Page 100

Configuring the AP Using the HTTP/HTTPS Interface
Detection (RAD) and define the Scan Interval. Configure up to 16
VLAN and SSID pairs per wireless interface, and define the security
mode for each pair.
• RADIUS: Configure RADIUS features such as RADIUS Access
Control and Accounting.
Configuring the AP Using the HTTP/HTTPS
Interface
Follow these steps to configure an Access Point’s operating settings
using the HTTP/HTTPS interface:
1. Open a Web browser on a network computer.
NOTE:
The HTTP interface supports the following Web browser:
— Microsoft Internet Explorer 6 with Service Pack 1 or later
— Netscape 6.1 or later
2. If necessary, disable the Internet proxy settings. For Internet
Explorer users, follow these steps:
— Select Tools > Internet Options....
— Click the Connections tab.
— Click LAN Settings....
4-2 Avaya Wireless AP-4/5/6 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...