AURORA OPERATING MANUAL
Application
Mode
Mode
Indicator
Operation
Calculation Mode
Normal calculations
COMP - MODE 1
Standard deviation
calculations
SD
SD
MODE 2
Regression calculations
REG
REG
MODE 3
Angle Unit Modes
Degrees
DEG D MODE MODE 1
Radians
RAD R MODE MODE 2
Grads
GRA G MODE MODE 3
Display Modes
Exponential notation
(canceling FIX and SCI
specification)
NORM1 - MODE MODE MODE 3 1
NORM2
-
MODE MODE MODE 3 2
Number of decimal
place specification
FIX
Fix
MODE MODE MODE 1
Number of significant
digit specification
SCI
Sci
MODE MODE MODE 2
Operation
Display
Instruction
MODE
COMP 1 SD 2 REG
3
Press1~3 key to select
the status of Normal
Calculation, Standard
Deviation or
Regression.
MODE 3
Lin 1 Log 2 Exp
3
Press 1~3 key to select
the status of Linear
regression, Logarithmic
regression or
exponential regression.
MODE 3
Pwr 1 Inv 2 Quad
3
Press 1~3 key to select
the status of Power
regression, Inverse
regression or Quadratic
regression.
MODE MODE
Deg 1 Rad 2 Gra
3
Press 1~3 key to select
current calculating
angle unit: Degrees,
radians or grads.
MODE MODE MODE
Fix 1 Sci 2 Norm
3
Press 1~3 key to settle
No. of Decimal Place
specification, No. of
significant Digit
Specification or
Exponential Notation.
MODE MODE MODE 1
Fix 0~9 ?
Press 0~9 to select
Decimal Place
specification.
MODE MODE MODE 2
Sci 0~9 ?
Press 0~9 to select No.
of significant digital
specification.
MODE MODE MODE 3
Norm 1~2 ?
Press 1~2 to select
exponential display
status and exit
Decimal Place
Specification and
Significant Digital
Specification status.
MODE MODE MODE
MODE 1
ab/c 1 d/c
2
Press 1~2 to select and
make sure the display
mode when the
calculating result is
more than 1.
MODE MODE MODE
MODE 1
Dot 1 Comma
2
Press 1~2 to select the
display status of
Separator Symbols.
D
2+3 ▲
5.
Disp
D
Ans×4 ▲
20.
For use with AX-582
Twin-line scientific calculator.
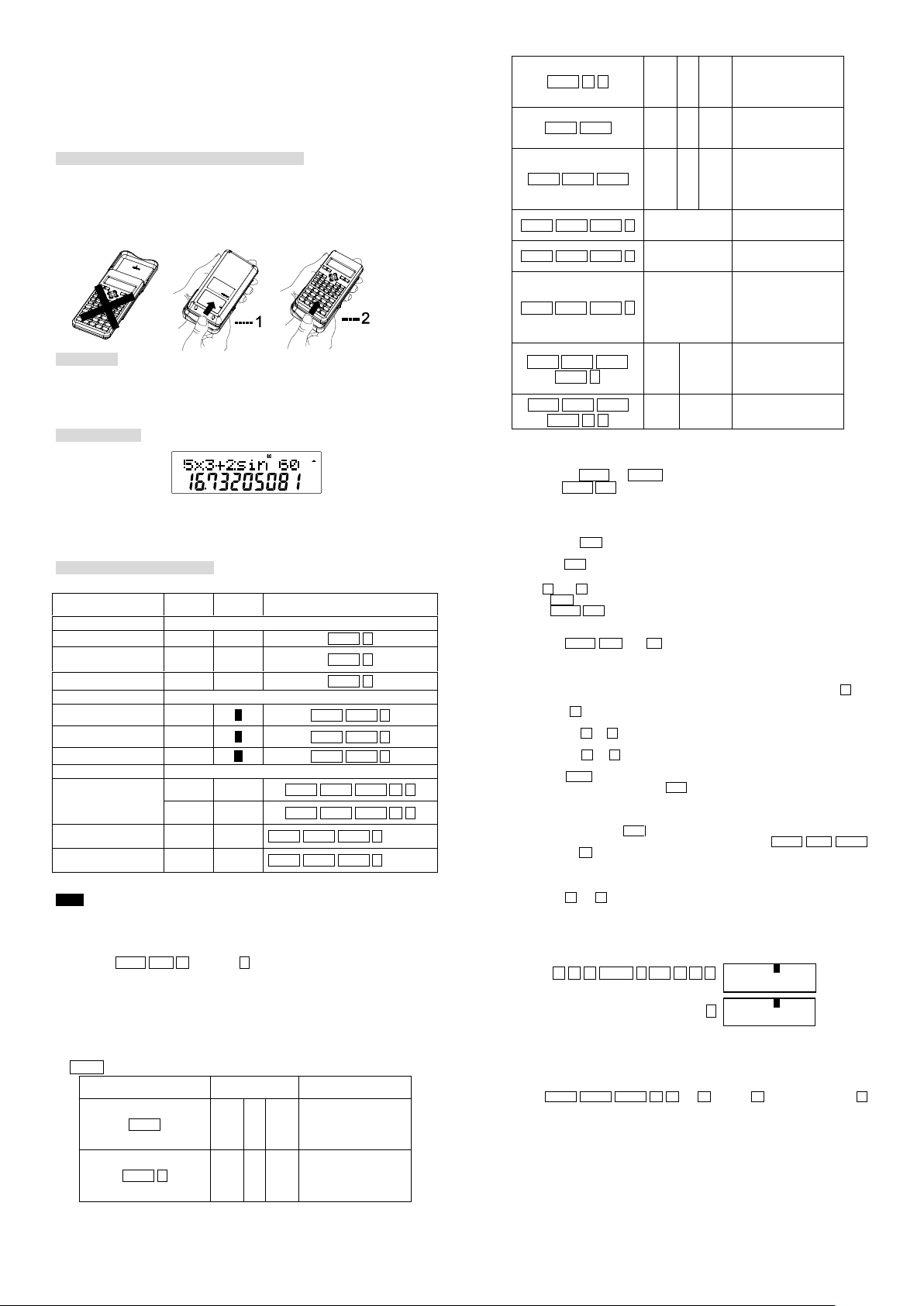
Removing and Replacing the Calculator’s Cover
Always slide the keyboard end of the unit into the cover first. Never slide the
display end of the unit into the cover.
Holding the cover as shown in the illustration, slide the unit out of the cover
before use. Picture………1
Holding the cover as shown in the illustration, slide the unit out of the cover
after use. Picture………2
Precautions
Don’t expose the machine to water, direct sunlight, extremely hot or cold
temperatures or dusty environments.
Don’t drop the machine or subject it to heavy impact.
Use a soft cloth to clean the machine. Do not use detergents.
Two-line Display
The two-line display makes it possible to view both the calculation formula and
its result at the same time.
The upper line shows the calculation formula.
The lower line shows the result.
Before Starting Calculations ...
■ Modes
Note!
Mode indicators appear in the upper part of the display.
The COMP, SD, and REG modes can be used in combination with the angle
unit mode.
To return the calculation mode and setup to the initial defaults shown below,
press SHIFT CLR 2 (MODE) =
Calculation Mode: COMP
Angle Unit: Deg
Exponential Display Format: Norm 1
Fraction Display Format: a b/c
Decimal Point Character: Dot
Be sure to check the current calculation mode (SD, REG, COMP) and angle
unit setting (Deg, Rad, Gra) before calculating.
■ MODE Key Operation and Display
Printed in China
9220250
■ Input Capacity
The memory area used for calculation input can hold 79“steps”. One step
is taken up each time you press a number key or arithmetic operator key (+, , ×, ÷). A SHIFT or ALPHA key operation does not take up a step, so
inputting SHIFT 3√ takes up only one step.
You can input up to 79 steps for a single calculation. Whenever you input the
73rd step of any calculation, the cursor changes from “ _” to “■” to let you
know memory is running low. If you need to input more than 79 steps, you
should divide your calculation into two or more parts.
Pressing the Ans key recalls the last result obtained, which you can use in a
subsequent calculation. See “Answer Memory” for more information about
using the Ans key.
■ Making Corrections During Input
Use ► and ◄ to move the cursor to the location you want.
Press DEL to delete the number or function at the current cursor position.
Press SHIFT INS to change to an insert cursor □. Inputting something while
the insert cursor is on the display inserts the input at the insert cursor
position.
Pressing SHIFT INS , or = returns to the normal cursor from the insert
cursor.
■ Replay Function
Every time you perform a calculation, the replay function stores the
calculation formula and its result in replay memory. Pressing the ▲key
displays the formula and result of the calculation you last performed.
Pressing ▲again back steps sequentially (new-to-old) through past
calculations.
Pressing the ► or ◄ key while a replay memory calculation is on the display
changes to the editing screen.
Pressing the ► or ◄ key immediately after you finish a calculation displays
the editing screen for that calculation.
Pressing CA does not clear replay memory, so you can recall the last
calculation even after you press CA .
Replay memory capacity is 128 bytes for storage of both expressions and
results.
Replay memory is cleared by any of the following actions.
1. When you press the ON key.
2. When you initialize modes and settings by pressing SHIFT CLR 2
(Mode) = .
3. When you change from one calculation mode to another.
4. When you turn off the calculator.
■ Error Locator
Pressing ► or ◄ after an error occured displays the calculation with the
cursor positioned at the location where the error occurred.
■ Multi-statements
A multi-statement is an expression that is made up of two or more smaller
expressions, which are joined using a colon ( : ).
Example: To add 2 + 3 and then multiply the result by 4
2 + 3 ALPHA : Ans × 4 =
=
■ Exponential Display Formats
This calculator can display up to 10 digits. Larger values are automatically
displayed using exponential notation. In the case of decimal values, you can
select between two formats that determine at what point exponential notation is
used.
Pressing MODE MODE MODE 3 1 (or 2 ), press 1 to select Norm 1 or 2
for Norm 2.
Norm 1
With Norm 1, exponential notation is automatically used for integer values
with more than 10 digits and decimal values with more than two decimal
places.
Norm2
With Norm 2, exponential notation is automatically used for integer values
with more than 10 digits and decimal values with more than nine decimal
places.
All of the examples in this manual show calculation results using the Norm
1
1 format.
15
7
2
5
4
1
3
2
214
2
1.26.1
2
1
4
3
22.75
5.0
2
1
353
2
1
D
2」3+1」4」5 ▲
2」7」15.
D
2.75 ▲
2.75
D
2.75 ▲
2」3」4.
D
2.75 ▲
11」4.
D
1」2 ▲
1」2.
D
1」2 ▲
0.5
D
1」2」3 ▲
1」2」3.
D
1」2」3 ▲
5」3.
D
1」2」3 ▲
1」2」3.
D
2.258 ▲
2.258
D
2.258 ▲
2˚15˚28.8
D
2.258 ▲
2.258
D
12˚34˚56˚×3.
▲
→
43˚24˚31.2
D
200÷7×14
▲
400.
D FIX
200÷7×14
▲
400.000
D FIX
200÷7
▲
28.571
D FIX
Ans×14
▲
400.000
D FIX
200÷7
▲
28.571
D FIX
200÷7
▲
28.571
D FIX
Ans×14
▲
399.994
D SCI
1÷3
▲
3.3
×10
-01
D
3×5E–9 ▲
1.5
-08
D
5×(9+7) ▲
80.
D
2」4 ▲
1」2.
D
1」2+1.6 ▲
2.1
D
1500×12% ▲
180.
D
660÷880% ▲
75.
D
2500×15%+ ▲
2,875.
D
3500×25% - ▲
2,625.
D
300+500% ▲
160.
D
46-40% ▲
15.
D
48-40% ▲
20.
M D
23+9→M
▲
32.
M D
53-6M+
▲
47.
D
1」2 ▲
1」2.
■ Decimal Point and Separator Symbols
You can use the display setup (Disp) screen to specify the symbols you want for
the decimal point and 3-digit separator.
To change the decimal point and separator symbol setting, press the MODE
MODE MODE MODE 1 ► .
Press the number key( 1 or 2 )that corresponds to the setting you want to
use.
1 (Dot): Period decimal point, comma separator
2 (Comma): Comma decimal point, period separator
■ Initializing the Calculator
Perform the following key operation when you want to initialize the calculation
mode and setup, and clear replay memory and variables.
SHIFT CLR 3 (All) =
Basic Calculations
■ Arithmetic Calculations
● Use the COMP mode for basic calculations.
● Negative values inside of calculations must be enclosed within parentheses.
● It is not necessary to enclose a negative exponent within parentheses.
● Example 1:3×(5×10
● Example 2:5×(9+7)=80
● You can skip all ) operations before = .
■ Fraction Operations
● Fraction Calculations
● Decimal ↔ Fraction Conversion
SHIFT d/c
ab/c
ab/c
● Mixed Fraction ↔ Improper Fraction Conversion
■ Percentage Calculations
● Use the COMP mode for percentage calculations.
● Example 1: To calculate 12% of 1500(180)
● Example 2: To calculate what percentage of 880 is 660(75%)
Sin -1.23 → sin ( (-) 1.23 )
Sin 2.34×10-5 → sin 2.34 EXP (-) 5
3 × 5 EXP (-) 9 =
5 × ( 9 + 7 ) =
● Use the COMP mode for fraction calculations. Values are displayed in
decimal format automatically whenever the total number of digits of a
fractional value (integer + numerator + denominator + separator marks)
exceeds 10.
● Example 1:
● Example 2:
● Example 3:
● Results of calculations that mix fraction and decimal values are always
decimal.
● Example 1:
● Example 2:
-
9
)=1.5×10
2 ab/c 4 =
(Decimal ↔ Fraction)
(Fraction ↔ Decimal)
1 ab/c 2 =
-
8
2 ab/c 3 + 1 ab/c 4 ab/c 5 =
1 ab/c 2 + 1.6 =
2.75 =
ab/c
● Example:
1 ab/c 2 ab/c 3 =
SHIFT d/c
SHIFT d/c
● You can use the display setup (Disp) screen to specify the display format
when a fraction calculation result is greater than one. Pressing MODE
MODE MODE MODE 1 .
● Press the number key( 1 or 2 )that corresponds to the setting you
want to use.
1 (a
2 (d/c):Improper fraction
● An error occurs if you try to input a mixed fraction while the d/c display
format is selected.
b
/c):Mixed fraction
1500 × 12 SHIFT %
● Example 3: To add 15% onto 2500 (2875)
● Example 4: To discount 3500 by 25% (2625)
● Example 5: If 300 grams are added to a test sample originally weighing 500
grams, what is the percentage increase in weight ? (160%)
● Example 6: If the temperature changes from 40℃ to 46℃, what percentage did
it rise? How about to 48℃? (15%, 20%)
660 ÷ 880 SHIFT %
2500 × 15 SHIFT % +
3500 × 25 SHIFT % -
300 + 500 SHIFT %
46 - 40 SHIFT %
◄ ◄ ◄ ◄ ◄ ◄ 8 =
■ Degrees, Minutes, Seconds Calculations
● You can perform sexagesimal calculations using degrees (hours), minutes,
and seconds, and convert between sexagesimal and decimal values.
● Example 1: To convert the decimal value 2.258 to a sexagesimal value and
then back to a decimal value.
2.258 =
● Example 2: To perform the following calculation:
12°34′56″ ×3.45
12 ° ′ ″ 34 ° ′ ″ 56 ° ′ ″ × 3.45 =
■ FIX, SCI, RND
● Example 1: 200÷7×14 =
(Internal calculation 200 ÷ 7 =
continues using 12 digits.) × 14 =
The following performs the same calculation using the specified number of
decimal places.
( Internal rounding ) SHIFT Round
● Press MODE MODE MODE 3 1 to clear the Fix specification.
● Example 2: 1÷3, displaying result with two significant digits (Sci 2).
● Press MODE MODE MODE 3 1 to clear the Sci specification.
200 ÷ 7 × 14 =
MODE MODE MODE 1 3
MODE MODE MODE 2 2
1 ÷ 3 =
° ′ ″
° ′ ″
200 ÷ 7 =
× 14 =
Memory Calculations
■ Answer Memory
● Whenever you press = after inputting values or an expression, the calculated
result automatically updates Answer Memory contents by storing the result.
● In addition to = , Answer Memory contents are also updated with result
whenever you press SHIFT % , M+ , SHIFT M- or SHIFT STO followed by
a letter (A through F, or M, X, or Y).
● You can recall Answer Memory contents by pressing Ans .
● Answer Memory can store up to 12 digits for the mantissa and two digits for
the exponent.
● Answer Memory contents are not updated if the operation performed by any of
the above key operations results in an error.
■ Consecutive Calculations
● You can use the calculation result that is currently on the display (and also
stored in Answer Memory) as the first value of your next calculation. Noted
that pressing an operator key while a result is displayed causes the displayed
value to change to Ans, indicating it is the value that is currently stored in
Answer Memory.
● The result of a calculation can also be used with a subsequent Type A
function(x2, x3, x-1, x!), +, -, ^(xy), x√, ×,÷, nPr , nCr and ° ′ ″.
■ Independent Memory
● Values can be input directly into memory, added to memory, or subtracted
from memory. Independent memory is convenient for calculating cumulative
totals.
● Independent memory uses the same memory area as variable M.
● To clear independent memory (M), input 0 SHIFT STO M (M+).
● Example:
23 + 9 = 32 23 + 9 SHIFT STO M
2
 Loading...
Loading...