Page 1

Multi-turn actuators
SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1
Control unit: electromechanic
with actuator controls
AUMATIC AC 01.1 Intrusive
Control
Parallel
Profibus DP
→ Modbus
DeviceNet
Foundation Fieldbus
Assembly, operation, commissioningOperation instructions
Page 2

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Table of contents AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Read operation instructions first.
●
Observe safety instructions.
●
These operation instructions are part of the product.
●
Preserve operation instructions during product life.
●
Pass on instructions to any subsequent user or owner of the product.
Purpose of the document:
This document contains information for installation, commissioning, operation and maintenance staff . It is intended
to support device installation and commissioning.
Reference documents:
●
Manual (Operation and setting) AUMATIC AC 01.1/ACExC 01.1 Modbus
●
Manual (Device integration Fieldbus) AUMATIC AC 01.1/ACExC 01.1 Modbus
Reference documents can be downloaded from the Internet (www.auma.com) or ordered directly from AUMA
(refer to <Addresses>).
Table of contents Page
51. Safety instructions.................................................................................................................
51.1. Basic information on safety
51.2. Range of application
61.3. Applications in Ex zone 22 (option)
61.4. Warnings and notes
71.5. References and symbols
82. Identification...........................................................................................................................
82.1. Name plate
92.2. Short description
103. Transport, storage and packaging........................................................................................
103.1. Transport
103.2. Storage
103.3. Packaging
114. Assembly................................................................................................................................
114.1. Mounting position
114.2. Handwheel fitting
124.3. Multi-turn actuator: mount to valve/gearbox
124.3.1 Output drive types B, B1 – B4 and E
124.3.1.1 Multi-turn actuator (with output drive types B1 – B4 or E): mount to valve/gearbox
134.3.2 Output drive type A
134.3.2.1 Stem nut: finish machining
144.3.2.2 Multi-turn actuator (with output drive type A): mount to valve
154.4. Accessories for assembly
154.4.1 Stem protection tube for rising valve stem
154.5. Mounting positions of local controls
164.5.1 Mounting positions: modify
175. Electrical connection.............................................................................................................
175.1. Basic information
195.2. Connection with AUMA plug/socket connector
195.2.1 Terminal compartment: open
205.2.2 Cable connection
2
Page 3

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Table of contents
215.2.3 Terminal compartment: close
215.2.4 Bus terminal compartment: open
225.2.5 Bus cables: connect
255.2.6 Bus terminal compartment: close
255.3. Accessories for electrical connection
255.3.1 Controls mounted to wall bracket
265.3.2 Parking frame
275.3.3 Protection cover
275.3.4 Double sealed intermediate frame
275.3.5 Earth connection, external
286. Operation................................................................................................................................
286.1. Manual operation
286.1.1 Manual operation: engage
286.1.2 Manual operation: disengage
296.2. Motor operation
296.2.1 Local operation
306.2.2 Operation from REMOTE
306.3. Menu navigation via push buttons (for settings and indications)
316.3.1 Short overview: Functions of the push buttons
316.3.2 Structural design and navigation
326.4. Password entry
326.5. Language change in the display
347. Indications..............................................................................................................................
347.1. Status indications in the display
347.1.1 Status indication S0/S6 - operation
357.1.2 Torque indication: edit
357.2. Indication lights/LEDs
367.3. Mechanical position indicator/running indication
378. Signals.....................................................................................................................................
378.1. Signals via fieldbus
378.2. Feedback signals via output contacts (binary)
378.3. Feedback signals (analogue)
389. Commissioning (basic settings)...........................................................................................
389.1. Heat-up time for low temperature version
389.2. Type of seating: check/edit for end positions
429.3. Baud rate, parity and bus addres (slave addess): set
459.4. Further parameters of the Modbus interface
459.5. Switch compartment: open
469.6. Torque switching: set
469.7. Limit switching: set
479.7.1 End position CLOSED (black section): set
479.7.2 End position OPEN (white section): set
489.8. Intermediate positions: set
489.8.1 Running direction CLOSE (black section): set
489.8.2 Running direction OPEN (white section): set
499.9. Test run
499.9.1 Direction of rotation: check
509.9.2 Limit switching: check
509.9.3 Reference operation position feedback: perform
3
Page 4

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Table of contents AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
519.10. Potentiometer setting
519.11. Electronic position transmitter RWG: set
529.12. Mechanical position indicator: set
539.13. Switch compartment: close
5410. Corrective action....................................................................................................................
5410.1. Faults during commissioning
5410.2. Fault indications and warning indications
5510.2.1 Status indication S0 - faults and warnings
5510.2.2 Status indication S1 - faults
5610.2.3 Status indication S2 - warnings
5710.2.4 Status indication S3 - causes for not ready remote
5710.3. Fuses
5710.3.1 Fuses within the actuator controls
5810.3.2 Motor protection (thermal monitoring)
6011. Servicing and maintenance...................................................................................................
6011.1. Preventive measures for servicing and safe operation
6011.2. Maintenance
6111.3. Disposal and recycling
6212. Technical data.........................................................................................................................
6212.1. Features and functions of actuator
6312.2. Features and functions of actuator controls
6612.3. Modbus interface
6712.4. Service conditions
6812.5. Accessories
6812.6. Further information
6913. Spare parts.............................................................................................................................
6913.1. Multi-turn actuators SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1
7113.2. Actuator controls AUMATIC AC 01.1 with AUMA plug/socket connector (SD bus)
7314. Certificates..............................................................................................................................
7314.1. Declaration of Incorporation and EC Declaration of Conformity
7615. Index........................................................................................................................................
78Addresses...............................................................................................................................
4
Page 5

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Safety instructions
1. Safety instructions
1.1 Basic information on safety Standards/directives
Safety instructions/war-
nings
Qualification of staff
Commissioning
AUMA products are designed and manufactured in compliance with recognised
standards and directives.This is certified in a Declaration of Incorporation and an
EC Declaration of Conformity.
The end user or the contractor must ensure that all legal requirements, directives,
guidelines, national regulations and recommendations with respect to assembly,
electrical connection, commissioning and operation are met at the place of installation.
They include among others applicable configuration guidelines for fieldbus
applications.
All personnel working with this device must be familiar with the safety and warning
instructions in this manual and observe the instructions given. Safety instructions
and warning signs on the device must be observed to av oid personal injury or property
damage.
Assembly, electrical connection, commissioning, operation, and maintenance must
be carried out exclusively by suitab ly qualified personnel ha ving been authorised by
the end user or contractor of the plant only.
Prior to working on this product, the staff must have thoroughly read and understood
these instructions and, furthermore, know and observe officially recognised rules
regarding occupational health and safety.
Prior to commissioning, it is important to check that all settings meet the requirements
of the application. Incorrect settings might present a danger to the application, e.g.
cause damage to the valve or the installation.The manufacturer will not be held
liable for any consequential damage. Such risk lies entirely with the user.
Operation
Protective measures
Prerequisites for safe and smooth operation:
●
●
●
●
●
●
The end user or the contractor are responsible for implementing required protective
measures on site, such as enclosures, barriers, or personal protective equipment
for the staff.
Maintenance
T o ensure saf e device operation, the maintenance instructions included in this manual
must be observed.
Any device modification requires prior consent of the manufacturer.
1.2 Range of application
AUMA multi-turn actuators are designed for the operation of industrial valves, e.g.
globe valves, gate valves, butterfly valves, and ball valves.
Other applications require explicit (written) confirmation by the manufacturer.
Correct transport, proper storage, mounting and installation, as well as careful
commissioning.
Only operate the device if it is in perf ect condition while observing these instructions.
Immediately report any faults and damage and allow for corrective measures.
Observe recognised rules for occupational health and safety.
Observe the national regulations.
During operation, the housing warms up and surface temperatures > 60 °C may
occur.To prevent possible burns, we recommend checking the surface temperature using an appropriate thermometer and wearing protective gloves, if required, prior to working on the device.
The following applications are not permitted, e.g.:
●
Industrial trucks according to EN ISO 3691
●
Lifting appliances according to EN 14502
5
Page 6

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Safety instructions AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
●
Passenger lifts according to DIN 15306 and 15309
●
Service lifts according to EN 81-1/A1
●
Escalators
●
Continuous duty
●
Buried service
●
Permanent submersion (observe enclosure protection)
●
Potentially explosive areas, with the exception of zone 22
●
Radiation exposed areas in nuclear power plants
No liability can be assumed for inappropriate or unintended use.
Observance of these operation instructions is considered as part of the device's
designated use.
Information
These operation instructions are only valid for the "clockwise closing" standard
version, i.e. driven shaft turns clockwise to close the valve.
1.3 Applications in Ex zone 22 (option)
Actuators of the indicated series basically meet the requirements for applications in
dust hazardous locations of ZONE 22 in compliance with the A TEX directiv e 94/9/EC.
The actuators are designed to meet enclosure protection IP 67 or IP 68 and fulfil the
requirements of EN 50281-1-1:1998 section 6 - Electrical apparatus for use in
presence of combustible dust, requirements for category 3 electrical equipment protected by enclosures.
To comply with all requirements of EN 50281-1-1:1998, it is imperative that the
following points are observed:
●
In compliance with the A TEX directiv e 94/9/EC, the actuators must be equipped
with an additional identification – II3D IP6X T150 °C.
●
The maximum surface temperature of the actuators, based on an ambient
temperature of +40 °C in accordance with EN 50281-1-1 section 10.4, is +150
°C. In accordance with section 10.4, an increased dust deposit on the equipment
was not considered for the determination of the maximum surface temper ature.
●
The correct connection of the thermoswitches or the PTC thermistors as well
as fulfilling the requirements of the duty type and the technical data are prerequisites for compliance with the maximum surface temperature of devices.
●
The connection plug may only be plugged in or pulled out when device is disconnected from the mains.
●
The cable glands used also have to meet the requirements of category II3 D
and must at least comply with enclosure protection IP 67.
●
The actuators must be connected by means of an external ground connection
(accessory part) to the potential compensation or integrated into an earthed
piping system.
●
The threaded plug (part no. 511.0) or the stem protection tube with protective
cap (part nos. 568.1 and 568.2) for sealing the hollow shaft must imperatively
be mounted to guarantee tightness and therefore the combustible dust hazard
protection.
●
As a general rule, the requirements of EN 50281-1-1 must be respected in dust
hazardous locations. During commissioning, service, and maintenance, special
care as well as qualified and trained personnel are required for the saf e oper ation of actuators.
1.4 Warnings and notes
The following warnings draw special attention to saf ety-rele v ant procedures in these
operation instructions, each marked by the appropriate signal word (DANGER,
WARNING, CAUTION, NOTICE).
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation with a high level of risk. Failure
to observe this warning could result in death or serious injury.
6
Page 7

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Safety instructions
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation with a medium level of risk. F ailure
to observe this warning could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation with a low level of risk. Failure to
observe this warning may result in minor or moderate injury . Ma y also be used
with property damage.
Potentially hazardous situation. Failure to observe this warning may result in
property damage. Is not used for personal injury.
Arrangement and typographic structure of the warnings
Type of hazard and respective source!
Potential consequence(s) in case of non-observance (option)
→
Measures to avoid the danger
→
Further measure(s)
Safety alert symbol warns of a potential personal injury hazard.
The signal word (here: DANGER) indicates the level of hazard.
1.5 References and symbols
The following references and symbols are used in these instructions:
Information The term Information preceding the text indicates important notes and information.
Symbol for CLOSED (valve closed)
Symbol for OPEN (valve open)
Important information before the next step.This symbol indicates what is required
for the next step or what has to be prepared or observed.
Via the menu to parameter
Describes the path within the menu to the parameter. By using the push buttons of
the local controls you may quickly find the desired parameter in the display.
Step by step
Provides a detailed description of each step for setting/viewing the parameter.
Description of the parameter settings/indications
Describes the setting/viewing possibilities of a parameter.
< > Reference to other sections
T erms in brack ets shown abov e refer to other sections of the document which provide
further information on this topic.These terms are either listed in the index, a heading
or in the table of contents and may quickly be found.
7
Page 8

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Identification AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
2. Identification
2.1 Name plate
Each device component (actuator, controls, motor) is equipped with a name plate.
Figure 1: Arrangement of name plates
[1] Actuator name plate
[2] Controls name plate
[3] Motor name plate
[4] Additional plate, e.g. KKS plate (Power Plant Classification System)
Data for identification Figure 2: Actuator name plate
[1] Type and size of actuator
[2] Commission number
Figure 3: Controls name plate
[1] Type and size of the controls
[2] Commission number
[3] Wiring diagram
[4] Control
Type and size
8
These instructions apply to the following devices:
Multi-turn actuators for open-close duty: SA 07.1, 07.5, 10.1, 14.1, 14.5, 16.1
Multi-turn actuators for modulating duty: SAR 07.1, 07.5, 10.1, 14.1, 14.5, 16.1
AC 01.1 = Stellantriebs-Steuerung AUMATIC
Page 9

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Identification
Commission number
Wiring diagram
Control
2.2 Short description
Multi-turn actuator
Actuator controls
Local controls/COM-AC
Intrusive - Non-Intrusive
An order-specific commission number is assigned to each device.This commission
number can be used to directly download the wiring diagram, inspection records and
further information regarding the device from the Internet: http://www.auma.com.
The 7th position in the ACP wiring diagram indicates the type of feedback signals
from the actuator:
P = Potentiometer
R = RWG (electronic position transmitter)
Modbus RTU = Control via Modbus RTU interface.
Definition in compliance with EN ISO 5210:
A multi-turn actuator is an actuator which transmits to the valve a torque for at least
one full revolution. It is capable of withstanding thrust.
AUMA multi-turn actuators are driven by an electric motor and are capable of
withstanding thrust in combination with output drive type A. For manual operation,
a handwheel is provided. Switching off in end positions may be either by limit or
torque seating. Controls are required to operate or process the actuator signals.
The AUMATIC actuator controls are used to operate AUMA actuators and are supplied
ready for use.The controls may be mounted directly to the actuator or separately
on a wall bracket.
The functions of the AUMATIC controls include standard valve control in OPEN CLOSE duty, positioning, process control, logging of operating data, diagnostic
functions right through control via fieldbus.
Operation, setting, and display can be performed on site directly at the controls or
alternatively from REMOTE via a fieldbus interface.
On site it is possible to
●
Operate the actuator via the local controls (push buttons and display) and perform settings (contents of these instructions).
●
Read in or out data or modify and save settings via the COM-A C softw are (option), using a computer (laptop or PC). Depending on the version, the connection between computer and AUMATIC can be made with cable (infra-red interface) or without cable (Bluetooth interf ace) (not included in these instructions).
●
Intrusive version (control unit: electromechanical):
Limit and torque setting is performed via switches in the actuator.
●
Non-Intrusive version (control unit: electronic):
Limit and torque setting is performed via the controls, actuator and controls
housings do not have to be opened. For this purpose, the actuator is equipped
with an MWG (magnetic limit and torque transmitter), also supplying analogue
torque feedback signals/torque indication and analogue position feedback signals/position indication.
9
Page 10

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Transport, storage and packaging AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
3. Transport, storage and packaging
3.1 Transport
For transport to place of installation, use sturdy packaging.
Hovering load!
Risk of death or serious injury.
→
Do NOT stand below hovering load.
→
Attach ropes or hooks for the purpose of lifting by hoist only to housing and NOT
to handwheel.
→
Actuators mounted on valves: Attach ropes or hooks for the purpose of lifting
by hoist to valve and NOT to actuator.
→
Actuators mounted to gearboxes: Attach ropes or hooks f or the purpose of lifting
by hoist only to the gearbox using eyebolts and NOT to the actuator.
→
Actuators mounted to controls: Attach ropes or hooks for the purpose of lifting
by hoist only to the actuator and NOT to the controls.
3.2 Storage
Long-term storage
3.3 Packaging
Danger of corrosion due to inappropriate storage!
→
Store in a well-ventilated, dry room.
→
Protect against floor dampness by storage on a shelf or on a wooden pallet.
→
Cover to protect against dust and dirt.
→
Apply suitable corrosion protection agent to uncoated surfaces.
Damage on display caused by temperatures below permissible level!
→
The AUMATIC actuator controls must NOT be stored below –30 °C.
If the device must be stored for a long period (more than 6 months) the following
points must be observed in addition:
1. Prior to storage:
Protect uncoated surfaces, in particular the output drive parts and mounting
surface, with long-term corrosion protection agent.
2. At an interval of approx. 6 months:
Check for corrosion. If first signs of corrosion show , apply ne w corrosion protection.
Our products are protected by special packaging for transport when leaving the
factory .The packaging consists of environmentally friendly materials which can easily
be separated and recycled.We use the following packaging materials: wood,
cardboard, paper, and PE foil. For the disposal of the packaging material, we
recommend recycling and collection centres.
10
Page 11

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Assembly
4. Assembly
4.1 Mounting position
AUMA actuators and actuator controls can be operated without restriction in any
mounting position.
4.2 Handwheel fitting
Information For transport purposes, handwheels from a diameter of 400 mm are supplied sepa-
rately.
Damage at the change-over mechanism due to incorrect assembly!
→
Only pivot change-over lever manually.
→
Do NOT use extensions as lever for operation.
→
First engage manual operation correctly, then mount handwheel.
1. Manually lift the red change-over lev er while slightly turning the shaft back and
forth until manual operation engages.
The manual operation is correctly engaged if the change-over le ver can be lifted
➥
by approx. 85°.
2. Attach handwheel over the red change-over lever then on to the shaft.
3. Release change-over lever (should snap back into initial position by spring action, if necessary, push it back manually).
4. Secure handwheel using the circlip supplied.
11
Page 12

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Assembly AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
4.3 Multi-turn actuator: mount to valve/gearbox
Danger of corrosion due to damage to paint finish and condensation!
→
Touch up damage to paint finish after work on the device.
→
After mounting, connect the device immediately to electrical mains to ensure
that heater minimises condensation.
4.3.1 Output drive types B, B1 – B4 and E
●
Application
Design
For rotating, non-rising valve stem
●
Not capable of withstanding thrust
Output drive bore with keyway:
●
Types B1 – B4 with bore according to ISO 5210
●
Types B and E with bore according to DIN 3210
●
Later change from B1 to B3, B4, or E is possible.
Figure 6: Output drives
[1] Output drive types B1/B2 and B
[2] Hollow shaft with keyway
[3] Output drive types B3/B4 and E
[4] Output drive sleeve/output drive plug sleve with bore and keyway
Information Spigot at flanges should be loose fit.
4.3.1.1 Multi-turn actuator (with output drive types B1 – B4 or E): mount to valve/gearbox
1. Check if mounting flanges fit together.
2. Check whether bore and keyway match the input shaft.
3. Apply a small quantity of grease to the input shaft.
4. Place multi-turn actuator.
Information: Ensure that the spigot fits uniformly in the recess and that the
mounting faces are in complete contact.
5. Fasten multi-turn actuator with screws according to table.
Information: We recommend applying liquid thread sealing material to the
screws to avoid contact corrosion.
12
Page 13

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Assembly
6. Fasten screws crosswise to a torque according to table.
Table 1: Tightening torques for screws
Tightening torque TA [Nm]Screws
Strength class 8.8Threads
25M8
51M10
87M12
214M16
431M20
4.3.2 Output drive type A
●
Application
Output drive for rising, non-rotating valve stem
●
Capable of withstanding thrust
4.3.2.1 Stem nut: finish machining
This working step is only required if stem nut is supplied unbored or with pilot
✔
bore.
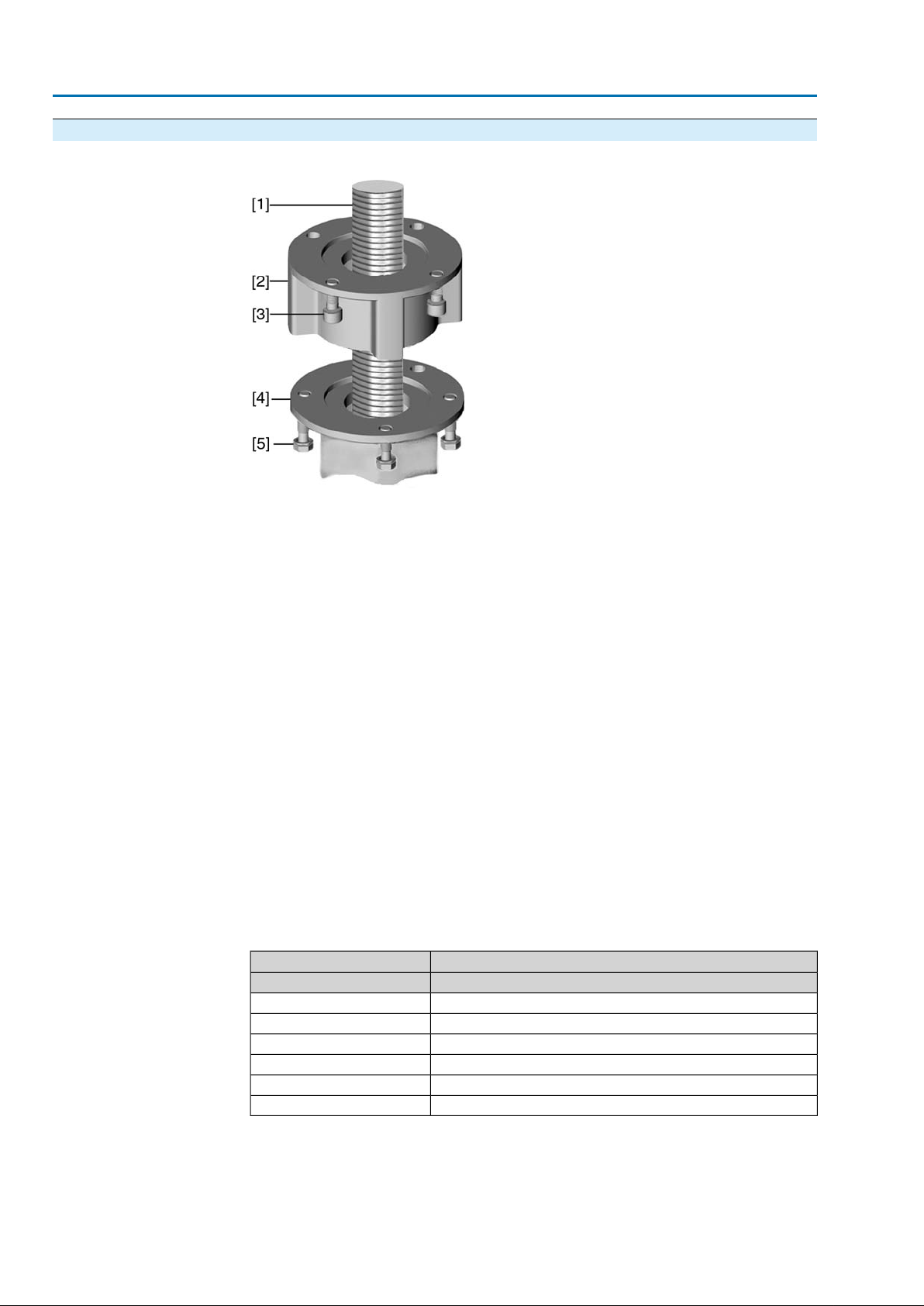
Figure 7: Design of output drive type A
[1] Stem nut
[2] Bearing
[2.1] Bearing race
[2.2] Bearing rim
[3] Spigot ring
1. Remove spigot ring [3] from output drive.
2. Remove stem nut [1] together with bearings [2].
3. Remove bearing races [2.1] and bearing rims [2.2] from stem nut [1].
4. Drill and bore stem nut [1] and cut thread.
Information: When fixing in the chuck, make sure stem nut runs true!
5. Clean the machined stem nut [1].
6. Apply sufficient Lithium soap EP multi-purpose grease to bearing rims [2.2] and
bearing races [2.1], ensuring that all hollow spaces are filled with grease.
7. Place greased bearing rims [2.2] and bearing races [2.1] onto stem nut [1].
8. Re-insert stem nut [1] with bearings [2] into output drive.
Information:Ensure that dogs or splines are placed correctly in the keyway of
the hollow shaft.
9. Screw in spigot ring [3] until it is firm against the shoulder.
13
Page 14
SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Assembly AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
4.3.2.2 Multi-turn actuator (with output drive type A): mount to valve
Figure 8: Assembly with output drive type A
[1] Valve stem
[2] Output drive type A
[3] Screws to actuator
[4] Valve flange
[5] Screws to output drive
1. If the output drive type A is already mounted to the multi-turn actuator: Loosen
screws [3] and remove output drive type A [2].
2. Check if the flange of output drive type A matches the valve flange [4].
3. Apply a small quantity of grease to the valve stem [1].
4. Place output drive type A on valve stem and turn until it is flush on the valve
flange.
5. Turn output drive type A until alignment of the fixing holes.
6. Screw in fastening screws [5], however do not completely tighten.
7. Fit multi-turn actuator on the valve stem so that the stem nut dogs engage into
the output drive sleeve.
The flanges are flush with each other if properly engaged.
➥
8. Adjust multi-turn actuator until alignment of the fixing holes.
9. Fasten multi-turn actuator with screws [3].
10. Fasten screws [3] crosswise with a torque according to table.
Table 2: Tightening torques for screws
Tightening torque TA [Nm]Screws
Strength class 8.8Threads
11M6
25M8
51M10
87M12
214M16
431M20
14
11. Turn multi-turn actuator with handwheel in direction OPEN until valve flange
and output drive A are firmly placed together.
12. Tighten fastening screws [5] between valve and output drive type A crosswise
applying a torque according to table.
Page 15

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Assembly
4.4 Accessories for assembly
4.4.1 Stem protection tube for rising valve stem — Option —
Figure 9: Assembly of the stem protection tube
[1] Cap for stem protection tube
[2] Stem protection tube
[3] Sealing ring
1. Seal thread with hemp, Teflon tape, or thread sealing material.
2. Screw stem protection tube [2] into thread and tighten it firmly.
3. Push down the sealing ring [3] onto the housing.
4. Check whether cap for stem protection tube [1] is available and in perfect con-
dition.
4.5 Mounting positions of local controls
The mounting position of the local controls is selected according to the order. If , after
mounting the actuator to the valve or the gearbox on site, the local controls are in
an unfav ourable position, the mounting position can be changed at a later date . F our
mounting positions are possible.
Figure 10: Mounting positions A and B
15
Page 16

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Assembly AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Figure 11: Mounting positions C and D
4.5.1 Mounting positions: modify
Hazardous voltage!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Disconnect device from the mains before opening.
1. Loosen screws and remove the local controls.
2. Check whether O-ring is in good condition, correctly insert O-ring.
3. Turn local controls into new position and re-place.
Cable damage due to twisting or pinching!
Risk of functional failures.
→
Turn local controls by a maximum of 180°.
→
Carefully assemble local controls to avoid pinching the cables.
4. Fasten screws evenly crosswise.
16
Page 17

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
5. Electrical connection
5.1 Basic information
Danger due to incorrect electrical connection
Failure to observe this warning can result in death, serious injury , or property damage.
→
The electrical connection must be carried out exclusively by suitably qualified
personnel.
→
Prior to connection, observe basic information contained in this chapter.
→
After connection but prior to applying the voltage, observe the <Commissioning>
and <Test run> chapters.
Wiring diagram/terminal
plan
Protection on site
The pertaining wiring diagram/terminal plan (in German and English language) is
attached to the device in a weather-proof bag, together with these operation
instructions. It can also be obtained from A UMA (state commission no ., refer to name
plate) or downloaded directly from the Internet (www.auma.com).
For short-circuit protection and for disconnecting the actuator from the mains, fuses
and disconnect switches have to be provided by the customer.
The current values for respective sizing is derived from the current consumption of
the motor (refer to electrical data sheet) plus the current consumption of the controls.
Table 3: Current consumption controls
Max. current consumptionMains voltage
650 mA100 to 120 V AC (±10 %)
325 mA208 to 240 V AC (±10 %)
190 mA380 to 500 V AC (±10 %)
500 mA, filter capacitor 2,200 µF24 V DC (+10 %/-15 %) and AC motor
750 mA, filter capacitor 2,200 µF24 V DC (+10 %/–10 %) and DC motor
Table 4: Maximum permissible protection
max. protectionRated powerSwitchgear
16 A (gL/gG)up to 1.5 kWReversing contactor A1
32 A (gL/gG)up to 7.5 kWReversing contactor A2
63 A (gL/gG)up to 11 kWReversing contactor A3
16 A (g/R) I²t<1,500A²sup to 1.5 kWThyristor
32 A (g/R) I²t<1,500A²sup to 3 kWThyristor
63 A (g/R) I²t<5,000A²sup to 5.5 kWThyristor
Power supply for the
controls (electronics)
Safety standards
Cable installation in ac-
cordance with EMC
If controls are mounted separately from actuator (controls on wall brack et): Consider
length and cross section of connecting cable when defining the protection required.
If the controls (electronics) are supplied externally with 24 V DC and DC motors (24
V DC, 48 V DC, 60 V DC, 110 V DC, 220 V DC) are used simultaneously, the 24 V
DC voltage supply for the controls should be ensured via the XK25/26 terminals,
separately from the power supply (U1, V1). In case of common supply using a single
cable (links from U1, V1 with XK25/26, for 24 V DC only !!!), short-term excess or
falling below the permissible voltage limits can be the consequence during s witching
(24 V DC +10 %/–10 %). Any possibly incoming operation commands are not
executed outside the admissible limit values.The controls briefly signal a fault
condition.
All externally connected devices shall comply with the relevant safety standards.
Signal and bus cables are susceptible to interference.
Motor cables are interference sources.
17
Page 18

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Electrical connection AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
●
Lay cables being susceptible to interference or sources of interference at the
highest possible distance from each other.
●
The interference immunity of signal and bus cables increases if the cables are
laid close to the earth potential.
●
If possible, avoid laying long cables and make sure that they are installed in
areas being subject to low interference.
●
Avoid long par allel paths with cab les being either susceptible to interf erence or
interference sources.
●
For the connection of remote position transmitters, screened cables must be
used.
Type of current, mains
voltage and mains fre-
quency
Type of current, mains voltage and mains frequency must match the data on the
motor name plate.
Figure 12: Motor name plate (example)
Connecting cables
Bus cables
[1] Type of current
[2] Mains voltage
[3] Mains frequency (for 3-ph and 1-ph AC motors)
●
For device insulation, appropriate (v oltage-proof) cables must be used. Specify
cables for the highest occurring rated voltage.
●
Use connecting cable with appropriate minimum rated temperature.
●
For connecting cables exposed to UV radiation (outdoor installation), use UV
resistant cables.
Only cables complying with the recommendations of EIA 485 specifications should
be used for Modbus wiring.
Cable recommendation:
Impedance:
135 to 165 Ohm, at a measurement frequency between 3 and 20 MHz
Cable capacity:
Wire diameter
Wire cross section:
Loop resistance:
Screening:
< 30 pF per metre
> 0.64 mm
0.34 mm², corresponds to AWG 22
< 110 Ohm per km
CU shielding braid or shielding braid and shielding
foil
18
Prior to installation, please note:
●
Connect maximum 32 devices to one segment.
●
If more devices are to be connected:
- Connect several segments using repeaters.
●
Respect a distance of minimum 20 cm between the bus cable and other cab les.
●
If possible, bus cables should be laid in a separate, conductive, and earthed
cable tray.
●
Make sure to avoid potential differences between the individual devices on the
bus (perform an equipotential earth bonding).
Page 19

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
5.2 Connection with AUMA plug/socket connector Cross sections AUMA plug/socket connector:
●
Power terminals (U1, V1, W1, U2, V2, W2): max. 6 mm² flexible/10 mm² solid
●
PE connection : max. 6 mm² flexible/10 mm² solid
●
Control contacts (1 to 50): max. 2.5 mm²
Information For some special motors, the connection of the power terminals (U1, V1, W1, U2,
V2, W2) is not performed via the AUMA plug/socket connector but via a terminal
board at the motor.
5.2.1 Terminal compartment: open
Information The bus connection can be separately accessed from the mains connection (refer
to <Bus terminal compartment: open>).
Figure 13: Mains connection AUMA plug/socket connector SD bus
[1] Connection housing
[2] Screws for connection housing
[3] O-ring
[4] Screws for socket carrier
[5] Socket carrier
[6] Cable entry for mains
[7] Blanking plug
[8] Cable gland (not included in delivery)
Information Bus operation is not interrupted when removing the connection housing [1].
Hazardous voltage!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Disconnect device from the mains before opening.
1. Loosen screws [2] and remove connection housing [1].
2. Loosen screws [4] and remove socket carrier [5] from connection housing [1].
19
Page 20

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Electrical connection AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
3. Insert cable glands [8] suitable for connecting cables.
The enclosure protection IP... stated on the name plate is only ensured if suitab le
➥
cable glands are used. Example: Name plate shows enclosure protection IP
68.
4. Seal unused cable entries [6] with suitable blanking plugs [7].
5. Insert the cables into the cable glands [8].
5.2.2 Cable connection
Observe permissible cross sections.
✔
1. Remove cable sheathing.
2. Strip wires.
3. For flexible cables: Use end sleeves according to DIN 46228.
4. Connect cables according to order-related wiring diagram.
In case of a fault: Hazardous voltage while protective earth conductor is NOT
connected!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Connect all protective earth conductors.
→
Connect PE connection to external protective earth conductor of connecting
cables.
→
Start running the device only after having connected the protective earth conductor.
5. Tighten PE conductors firmly to PE connection using ring lugs (flexible cab les)
or loops (rigid cables).
Figure 15: PE connection
[1] Socket carrier
[2] Screw
[3] Washer
[4] Lock washer
[5] Protective earth with ring lugs/loops
[6]
PE connection, symbol:
20
Danger of corrosion: Damage due to condensation!
→
After mounting, commission the device immediately to ensure that heater minimises condensation.
Page 21

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
Information Some actuators are equipped with an additional motor heater.The motor heater
minimises condensation within the motor and improves the start-up behaviour for
extremely low temperatures.
5.2.3 Terminal compartment: close
Figure 16: AUMA plug/socket connector SD bus
[1] Connection housing
[2] Screws for connection housing
[3] O-ring
[4] Screws for socket carrier
[5] Socket carrier
[6] Cable entry for mains
[7] Blanking plug
[8] Cable gland (not included in delivery)
Short-circuit due to pinching of cables!
Risk of electric shock and functional failures.
→
Carefully fit socket carrier to avoid pinching the cables.
1. Insert the socket carrier [5] into the cover [1] and fasten with screws [4].
2. Clean sealing faces of connection housing [1] and housing.
3. Check whether O-ring [3] is in good condition, replace if damaged.
4. Apply a thin film of non-acidic grease (e.g. petroleum jelly) to the O-ring and
insert it correctly.
5. Fit connection housing [1] and fasten screws [2] evenly crosswise.
6. Fasten cable glands [8] applying the specified torque to ensure the required
enclosure protection.
5.2.4 Bus terminal compartment: open
The AUMA plug/soc ket connector (SD bus) is equipped with a connection board for
connecting the bus cables.When removing the cover [1] the connection board is
easily accessible.
21
Page 22

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Electrical connection AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Figure 17: AUMA plug/socket connector SD bus
[1] Cover (bus terminal compartment)
[2] Screws for cover
[3] O-ring
[4] Cable entries for bus cables
[5] Blanking plug
Hazardous voltage!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Disconnect device from the mains before opening.
Electrostatic discharge ESD!
Risk of damage to electronic components.
→
Earth both operators and devices.
1. Loosen screws [2] and remove cover [1].
2. Insert cable glands suitable for bus cables.
The enclosure protection IP… stated on the name plate is only ensured if suita-
➥
ble cable glands are used.
Example: Name plate shows enclosure protection IP 68.
➥
3. Seal unused cable entries [4] with suitable blanking plugs [5].
4. Insert the wires into the cable glands.
5.2.5 Bus cables: connect Versions
The bus connection described in this chapter applies to the following v ersions of the
connection board:
●
●
●
Information For loop redundancy, automatic termination is performed as soon as the AUMATIC
is connected to the power supply. When interrupting the power supply, e.g. after removing the AUMA plug/socket connector, both RS-485 loop segments are automatically connected to each other.
22
Standard version (1-channel)
Versions with overvoltage protection (up to 4 kV)
Versions for redundancy (2-channel)
Page 23

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
Figure 19: Connection board (standard version)
[S1] Bus termination channel 1
[X1]
Channel 1, ↑ from the previous device
[X2]
Channel 1, ↓ to the next device
[X3] Shielding clamp
Figure 20: Connection boards (versions with overvoltage protection)
[A] Board for line topology
[B] Board for loop topology (loop redundancy)
[S1] Bus termination channel 1
[S2] Bus termination channel 2
[S3] Redundancy
[X1]
Channel 1: ↑ from the previous device ↓ to the next device
[X2]
Channel 2: ↑ from the previous device ↓ to the next device
[X3] Shielding clamps
23
Page 24

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Electrical connection AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Figure 21: Connection baords (versions for redundancy)
[A] Board for line topology
[B] Board for loop topology (loop redundancy)
[S1] Bus termination channel 1
[S2] Bus termination channel 2
[S3] Redundancy
[X1]
Channel 1: ↑ from the previous device
[X2]
Channel 1: ↓ to the next device
[X3] Shielding clamps
[X4]
Channel 2: ↑ from the previous device
[X5]
Channel 2: ↓ to the next device
Table 5: Functions for switches S1 – S3
Bus termination channel 1 ONONS1
Bus termination channel 1 OFFOFF
Bus termination channel 2 ON (option)ONS2
Bus termination channel 2 OFF (option)OFF
one fieldbus board1SPCS3
two fieldbus boards (redundancy, option)2SPC
Information Switches S1 and S2 are supplied in OFF position.
Connecting bus cables:
1. Connect cables.
Table 6: Assignment of fieldbus cables
Fieldbus cables
AUMA labelling at the
connection
fieldbus devices)
2. If the actuator is the final device in the bus segment:
2.1 Switching on the termination resistor for channel 1 using switch S1 (ON
position).
2.2 For component redundancy: Switching on the termination resistor for
channel 2 using switch S2 (ON position). Refer to table <Functions for
switches S1 – S3>.
Information: As soon as the termination resistors are switched on, the
connection to the next Fieldbus device is automatically interrupted to avoid
multiple terminations (not applicable for overvoltage protection).
3. Connect cable shield largely to shielding clamp [X3].
ColourSUB-D 9 plug pin (for other
green8N/AA
red3P/BB
24
Page 25

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
5.2.6 Bus terminal compartment: close
Figure 22: AUMA plug/socket connector SD bus
[1] Cover
[2] Screws for cover
[3] O-ring
[4] Cable entries for bus cables
[5] Blanking plug
1. Clean sealing faces of cover [1] and housing.
2. Apply a thin film of non-acidic grease (e.g. petroleum jelly) to the sealing f aces.
3. Check whether O-ring [3] is in good condition, correctly insert O-ring.
4. Fit cover [1] and fasten screws [2] evenly crosswise.
5. Fasten cable glands with the specified torque to ensure the required enclosure
protection.
5.3 Accessories for electrical connection — Option —
5.3.1 Controls mounted to wall bracket
The wall bracket allows separate mounting of controls and actuator.
●
Application
If the actuator cannot be accessed.
●
If the actuator is subject to high temperatures.
●
In case of heavy vibration of the valve.
25
Page 26

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Electrical connection AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Design Figure 23: Design principle with wall bracket
[1] Wall bracket
[2] Connecting cables
[3] Electrical connection of wall bracket (XM)
[4] Electrical connection of actuator (XA)
[5] Electrical connection/bus connection of controls (XK) - customer plug
Observe prior to
connection
5.3.2 Parking frame Application
●
Permissible length of connecting cables: max. 100 m.
●
If the actuator is equipped with a position transmitter (RWG): Connecting cables
must be available as shielded version.
●
Versions with potentiometer in the actuator are not suitable.
●
We recommend: AUMA cable set LSW1.
●
If the AUMA cab le set is not used: Use suitab le flexib le and screened connecting
cables.
●
When using connecting cables, e.g. of the heater or s witch, requiring direct wiring
from the actuator to the XK customer plug (XA-XM-XK, refer to wiring diagram),
these connecting cables must be subject to an insulation test in compliance
with EN 50178. Connecting cab les of position tr ansmitters (R WG, IWG, potentiometer) do not belong to this group.They may not be subject to an insulation
test.
Parking frame for safe storage of a disconnected plug.
For protection against touching the bare contacts and against environmental
influences.
Figure 24: Parking frame
26
Page 27

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Electrical connection
5.3.3 Protection cover
Protection cover for plug compartment when plug is removed.
The open terminal compartment can be closed using a protective cover (not
illustrated).
5.3.4 Double sealed intermediate frame
When removing the electrical connection or due to leaky cable glands, ingress of
dust and water into the housing may occur.This is prevented effectiv ely b y inserting
the double sealed intermediate frame [2] between the plug/socket connector [1] and
the housing of the device.The enclosure protection of the device (IP 68) will not be
affected, even if the electrical connection [1] is removed.
Figure 25: Electrical connection with double sealed intermediate frame
[1] Electrical connection
[2] Double sealed intermediate frame
5.3.5 Earth connection, external
As an option, the housing is equipped with an external earth connection (U-bracket)
to connect the device to the equipotential earth bonding.
Figure 26: Earth connection
27
Page 28

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Operation AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
6. Operation
6.1 Manual operation
For purposes of setting and commissioning, in case of motor failure or power f ailure,
the actuator may be operated manually. Manual operation is engaged b y an internal
change-over mechanism.
6.1.1 Manual operation: engage Information When using brake motors, note that the motor is disengaged during manual operation.
For this reason, the brake motor cannot sustain any load during manual operation.
The load must be sustained via the handwheel.
Damage at the change-over mechanism due to faulty operation!
→
Engage manual operation only during motor standstill.
→
Only pivot change-over lever manually.
→
Do NOT use extensions as lever for operation.
1. Pivot change-over lever manually to approx. 85° while slightly turning the
handwheel back and forth until manual operation engages.
2. Release change-over lever (should snap back into initial position by spring action, if necessary, push it back manually).
3. Turn handwheel in desired direction.
→
To close the valve, turn handwheel clockwise:
➥
6.1.2 Manual operation: disengage
Manual operation is automatically disengaged when motor is started again.The
handwheel does not rotate during motor operation.
Drive shaft (valve) turns clockwise in direction CLOSE.
28
Page 29

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Operation
6.2 Motor operation
Perform all commissioning settings and the test run prior to motor operation.
✔
6.2.1 Local operation
The local operation of the actuator is performed using the push buttons of the local
controls.
Figure 30: Local controls
[1] Push button OPEN
[2] Push button STOP
[3] Push button CLOSE
[4] Push button Reset
[5] Selector switch
[6] Indication lights/LEDs
Hot surfaces, e.g. possibly caused by high ambient temperatures or strong
direct sunlight!
Danger of burns
→
Check surface temperature and wear protective gloves, if required.
→
Set selector switch [5] to position Local control (LOCAL).
The actuator can now be operated using the push buttons [1 – 3].
➥
- Run actuator in direction OPEN: Press push button OPEN [1].
- Stop actuator: Press push button STOP [2].
- Run actuator in direction CLOSE: Press push button CLOSE [3].
Information The OPEN - CLOSE operation commands can be given either in push-to-run opera-
tion mode or in self-retaining mode. In self-retaining mode, the actuator runs to the
defined end position after pressing the button, unless another command has been
received beforehand. For further information, please refer to the Manual (Operation
and setting).
29
Page 30

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Operation AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
6.2.2 Operation from REMOTE
→
Set selector switch to Remote control (REMOTE).
Now, the actuator can be remote-controlled via fieldbus.
➥
Information For actuators equipped with a positioner , it is possible to select between open-c lose
control (Remote OPEN-CLOSE) and setpoint control (Remote SETPOINT). For
further information, please refer to the Manual (Operation and setting).
6.3 Menu navigation via push buttons (for settings and indications)
The push buttons of the local controls are used to view, edit, and show various
indications on the display.
Figure 33: Local controls
[1]
Push button
[2]
Push button
[3]
Push button
[4]
Push button C
[5] Selector switch
[6] Display
→
Set selector switch [5] to position 0 (OFF).
Now, settings and indications can be performed via the push buttons [1 – 4].
➥
30
Page 31

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Operation
6.3.1 Short overview: Functions of the push buttons
tons
C
FunctionsPush but-
Scrolling within a group
(The triangles in the display show which direction of scrolling is possible)
Change values
Enter figures from 0 to 9
Confirm the selection to go to a new menu/subgroup
Cancel process
Return to previous display: press briefly
Change to another group (S, M, D):
●
●
6.3.2 Structural design and navigation
The indications on the display are divided into 3 groups:
●
Group S = Status indications
●
Group M = Menu (settings)
●
Group D = Diagnostic indications
The active group is displayed in the top right corner of the display.
hold down for approx. 3 seconds until group M0 is displayed.
hold down for longer than 3 seconds until group D0 is displayed (thereby,
group M is skipped).
Change from group S to group M:
1.
Press push button C and hold it down for approx. 3 seconds until group M0
appears.
Change from group S to group D:
2.
Press push button C and hold it down until group D0 is displayed.
(Thereby, group M is skipped.)
➥
Return from group M or group D to group S:
3.
Briefly press C .
Scrolling within a group:
4.
Press or .
The triangles in the top left corner of the display indicate which direction of
➥
scrolling (within one group) is possible.
31
Page 32

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Operation AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
6.4 Password entry
In the menu (group M), the settings are password protected.To change the
parameters, a password m ust be entered first.The following def ault password is set
in the factory: 0000.
After selecting EDIT, the following is displayed:
ENTER PASSWORD
0 * * *
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
Step by step:
1.
Select figures 0 to 9: Press .
2.
Move to the next position: Press .
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for all four digits.
4. To cancel a process: Press C.
Information If no input is received over a longer period of time (approx. 10 min.), the controls
automatically return to status indication S0.
6.5 Language change in the display Via the menu to parameter:
MAIN MENU (M0)
LANGUAGE/CONTRAS (M00)
VIEW (M00)
EDIT (M01)
LANGUAGE (M010)
Default value:ENGLISH
Setting range: ENGLISH, GERMAN, MAGYAR, POLSKI, TUERKCE,
PORTUGUESE, ITALIAN, SPANISH, FRENCH
Step by step:
1. Set selector switch to position 0 (OFF).
2. Press C and hold it down for approx. 3 seconds.
Display indicates:
➥
MAIN MENU M0
LANGUAGE/CONTRAST
SETTINGS
OPERATIONAL DATA
32
3.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
LANGUAGE/CONTRAS M00
VIEW
EDIT
Page 33

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Operation
4.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
LANGUAGE/CONTRAS M01
VIEW
EDIT
5.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
ENTER PASSWORD
0 * * *
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
6. Enter password:
→
Press 4 x = 0000 (default factory password).
Display indicates:
➥
EDIT M010
LANGUAGE
LCD CONTRAST
7.
Press .
Display shows the set value:
➥
EDIT M010
LANGUAGE
ENGLISH
:EDIT C:ESC
8.
Press again to enter the edit mode.
Display indicates:
➥
EDIT M010
LANGUAGE
ENGLISH
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
9. Set new value:
→
Press .
10. Accept value or cancel?
→
→
Accept value: Press .
Cancel process without accepting the value: Press C .
33
Page 34

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Indications AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
7. Indications
7.1 Status indications in the display
The status indications in the display locally indicate the current operation states as
well as faults and warnings.
This section describes the indications for the operation states. Faults and warnings
are described in the <Fault indications and warning indications> chapter.
7.1.1 Status indication S0/S6 - operation Information
Operation mode display
Operation command/set-
point display
Valve position display
For actuators equipped with process controllers, status indication S6 is displayed
instead of status indication S0 in selector switch position REMO TE.The description
below applies to both indications (S0 and S6).
Line 1 indicates the current operation mode (LOCAL MODE, OFF, REMOTE MODE,
…).
LOCAL MODE S0
OPEN
E2 100 %
RUNNING OPEN
Line 2 indicates currently incoming operation commands (OPEN, STOP, CLOSE)
or the setpoints E1 or E7 (for actuators equipped with positioner/process controller)
in % of the total travel.
LOCAL MODE S0
OPEN
E2 100 %
RUNNING OPEN
Line 3 indicates the valve position in % of the travel.This indication is only available
if the actuator is equipped with a position transmitter.
End position/running in-
dication
LOCAL MODE S0
OPEN
E2 100 %
RUNNING OPEN
0 % = Actuator is in end position CLOSED
100 % = Actuator is in end position OPEN
Line 4 indicates the current actuator status.
LOCAL MODE S0
OPEN
E2 100 %
RUNNING OPEN
Description of indications in line 4:
RUNNING OPEN
Actuator runs logically OPEN (remains set during operation pauses).
RUNNING CLOSE
Actuator runs logically CLOSE (remains set during operation pauses).
OPEN POSITION
34
Page 35

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Indications
End position OPEN reached.
CLOSED POSITION
End position CLOSED reached.
SETPOINT POSITION
Setpoint (modulating actuators only).
7.1.2 Torque indication: edit
The torque value can be displayed in percent, Newtonmeter (Nm) or in Lbs/ft.
Via the menu to parameter:
MAIN MENU (M0)
SETTINGS (M1)
LOCAL CONTROLS (M13)
TORQUE INDICATION (M1317)
EDIT M1317
TORQUE INDICATION
NEWTONMETER
:EDIT
↵
:OK C:ESC
Description of the parameter settings:
PERCENT
Indication of the nominal torque in percent
NEWTONMETER
Indication in Nm
LBS.FT.
Indication in Lbs/ft.
7.2 Indication lights/LEDs
The indication lights/LEDs locally display the different operation states as optical
signals.The signals can be freely assigned.
Figure 38: Indication lights/LEDs on local controls
[1] Marking with symbols (standard)
[2] Marking with figures (option)
Table 7: Meaning of signals
LED 1 ( )
blinking
LED 5 ( )
blinking
Meaning of signalBehaviour (default)Indication light
Actuator is in end position CLOSEDilluminated
Running indication: Actuator runs in direction
CLOSE
Torque fault CLOSEilluminatedLED 2 (T)
Motor protection trippedilluminatedLED 3 (Th)
Torque fault OPENilluminatedLED 4 (T)
Actuator is in end position OPENilluminated
Running indication: Actuator runs in direction
OPEN
Bluetooth connection availableilluminatedLED 6 (BT) (option)
35
Page 36

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Indications AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Information
The behaviour (blinking/illuminated) can be changed via the BLINKER (M1311)
parameter.
7.3 Mechanical position indicator/running indication
— Option —
Mechanical position indicator:
●
Continuously indicates the valve position
(For complete travel from OPEN to CLOSED or vice versa, the indicator disc
[2] rotates by approximately 180° to 230°.)
●
Indicates whether the actuator is running (running indication)
●
Indicates that the end positions are reached (via indicator mark [3])
Figure 39: Mechanical position indicator
[1] Cover
[2] Indicator disc
[3] Mark
[4] Symbol for position OPEN
[5] Symbol for position CLOSED
36
Page 37

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Signals
8. Signals
8.1 Signals via fieldbus
The feedback signals via Modbus RTU can be read using the appropriate Modbus
function codes.
For further information, please refer to the Manual (Device integration fieldbus).
8.2 Feedback signals via output contacts (binary) — (Option) —
Feedback signals via output contacts are only available if a parallel interface is
provided in addition to the fieldbus interface.
The output contacts can be used to indicate operation modes of the actuator or the
controls as binary signals.The signals can be freely assigned. Example:
Output contact open = no thermal fault
Output contact closed = thermal fault in actuator
The output contacts are denominated in the wiring diagram as follows:
●
Output contacts 1 to 5: DOUT1 to DOUT5
●
Alarm contacts: NC fault/NO ready
Signal assignment is made via the parameters:OUTPUT CONTACT 1 to OUTPUT
CONTACT 5 and ALARM CONTACT.
Alarm contact default value:
FAULT GROUP 3 = fault signal (includes: torque fault, thermal fault, phase failure
and internal faults)
Default values OUTPUT CONTACT 1 to OUTPUT CONTACT 5:
OUTPUT CONTACT 1 = CLOSED POSITION
OUTPUT CONTACT 2 = OPEN POSITION
OUTPUT CONTACT 3 = REMOTE SW. POSITION
OUTPUT CONTACT 4 = TORQUE FAULT (CLOSE)
OUTPUT CONTACT 5 = TORQUE FAULT (OPEN)
8.3 Feedback signals (analogue) — (Option) —
Analogue feedback signals are only available if the following conditions are met:
●
In addition to the fieldbus interface, the AUMATIC is equipped with a parallel
interface.
●
The actuator is equipped with a position transmitter (potentiometer or RWG).
Valve position
Signal: E2 = 0/4 – 20 mA (galvanically isolated)
Designation in the wiring diagram:
ANOUT1 (position)
For further information to this topic, please refer to the Manual (Operation and setting).
37
Page 38

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
9. Commissioning (basic settings)
1. Set selector switch to position 0 (OFF).
Information: The selector switch is not a mains switch.When positioned to 0
(OFF), the actuator cannot be operated.The controls' power supply is
maintained.
2. Switch on the power supply.
Information:Please consider the heat-up time for ambient temperatures below
–20 °C.
3. Perform basic settings.
9.1 Heat-up time for low temperature version
Please note that for low temperature versions, the controls require a heat-up time.
This heat-up time is applicable in case the actuator and the controls are not live and
have cooled down to ambient temperature. Under these conditions and after
connection to the voltage supply, the following heat-up times must be complied with
prior to commissioning:
For –40 °C = 30 min.
For –50 °C = 60 min.
For –60 °C = 100 min.
Figure 41: Sketch illustrating the heat-up time
[t] Heat-up time in minutes
Ambient temperature in °C
[ϑ]
9.2 Type of seating: check/edit for end positions
Valve damage due to incorrect setting!
→
The torque must suit the valve.
→
Only change the setting with the consent of the valve manufacturer.
38
Limit seating
Torque seating
The limit switching is set in such a way that the actuator switches off at the desired
switching points.The torque switching acts as overload protection for the valve.
The torque switching is set to the desired tripping torque. After reaching the tripping
torque the actuator is turned off.
Page 39

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
The limit seating is used to signal that the limit switching will trip shortly before
reaching the set tripping torque. If this is not the case, one of the following fault
signals is displayed:TSO FAULTS or TSC FAULTS (menu S1).
Via the menu to parameter:
MAIN MENU (M0)
SETTINGS (M1)
SEATING MODE (M11)
VIEW (M110)
EDIT (M111)
OPEN POSITION (M11_0)
CLOSED POSITION (M11_1)
Default value:LIMIT
Step by step:
1. Set selector switch to position 0 (OFF).
2.
Press C and hold it down for approx. 3 seconds.
Display indicates:
➥
MAIN MENU M0
LANGUAGE/CONTRAST
SETTINGS
OPERATIONAL DATA
3.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
MAIN MENU M1
LANGUAGE/CONTRAST
SETTINGS
OPERATIONAL DATA
4.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
SETTINGS M11
SEATING MODE
TORQUE
LOCAL CONTROLS
5.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
SEATING MODE M110
VIEW
EDIT
Use and to select between VIEW and EDIT.
39
Page 40

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
6. View or edit?
Display seating mode: continue with 7.
Change seating mode: continue with 10.
7.
Display type of seating:
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
VIEW M1100
OPEN POSITION
CLOSED POSITION
VIEW M1101
OPEN POSITION
CLOSED POSITION
Use and to select between OPEN POSITION and CLOSED POSITION.
8.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
Change seating mode:
VIEW
OPEN POSITION
LIMIT
C:ESC
VIEW
CLOSED POSITION
LIMIT
C:ESC
Use and to also select here between OPEN POSITION and CLOSED
POSITION.
9.
Return to the VIEW/EDIT menu:
→
Press C twice.
10.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
SEATING MODE M111
VIEW
EDIT
40
11.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
ENTER PASSWORD
0 * * *
Page 41

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
12. Enter password:
→
Press 4 x = 0000 (default factory password).
➥
EDIT M1110
OPEN POSITION
CLOSED POSITION
EDIT M1111
OPEN POSITION
CLOSED POSITION
Use and to select between OPEN POSITION and CLOSED POSITION.
13.
Press .
Display shows the set value:
➥
EDIT M1110
OPEN POSITION
LIMIT
↵
:EDIT C:ESC
EDIT M1111
CLOSED POSITION
LIMIT
:EDIT C:ESC
Use and to select between OPEN POSITION and CLOSED POSITION.
14.
Press again to enter the edit mode.
Display indicates:
➥
EDIT M1110
OPEN POSITION
LIMIT
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
EDIT M1111
CLOSED POSITION
LIMIT
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
15. Set new value:
→
Press .
41
Page 42

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
16. Accept value or cancel?
→
→
Display indicates:
➥
Accept value: Press .
Cancel process without accepting the value: Press C .
EDIT M1110
OPEN POSITION
LIMIT
:EDIT C:ESC
AENDERN M1111
CLOSED POSITION
LIMIT
:EDIT C:ESC
Use and to select between OPEN POSITION and CLOSED POSITION.
17. Return to status display:
→
Press C several times until S0 is displayed.
9.3 Baud rate, parity and bus addres (slave addess): set Via the menu to parameter:
MAIN MENU (M0)
SETTINGS (M1)
MODBUS 1 (M1F)
BAUDRATE (M1F11)
PARITY (M1F12)
SLAVEADDRESS (M1F14)
Setting ranges and default values:
BAUDRATE: 300 – 38 400 BAUD (4 800 BAUD)
PARITAET: (EVEN, 1 STOPBIT)
ODD, 1 STOPBIT
NO, 2 STOPBITS
SLAVEADRESSE: 1 – 247 (247)
Step by step:
1. Set selector switch to position 0 (OFF).
2.
Press C and hold it down for approx. 3 seconds.
Display indicates:
➥
42
MAIN MENU M0
LANGUAGE/CONTRAST
SETTINGS
OPERATIONAL DATA
Page 43

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
3.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
MAIN MENU M1
LANGUAGE/CONTRAST
SETTINGS
OPERATIONAL DATA
4.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
SETTINGS M11
SEATING MODE
TORQUE
LOCAL CONTROLS
5.
Select MODBUS 1 (M1F): Press several times.
Display indicates:
➥
SETTINGS M1B
MONITOR TRIGGERS
POSITIONER ENABLED
MODBUS 1
Check settings (view):
6.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
MODBUS 1 M1F0
VIEW
EDIT
7. View or edit?
Check settings (view): continue with 8.
Change settings: continue with 11.
8.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
MODBUS 1 M1F01
BAUDRATE
PARITY
CONNECT-CONTROL TIME
9.
Use to select BAUDRATE, PARITY or SLAVEADDRESS and confirm selection with .
Display shows the selected value. Example SLAVEADDRESS:
➥
VIEW
SLAVEADDRESS
1
C:ESC
43
Page 44

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
10.
Return to the VIEW/EDIT menu:
→
Press C twice.
11.
Change settings:
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
MODBUS 1 M1F1
VIEW
EDIT
12.
Press .
Display indicates:
➥
ENTER PASSWORD
0 * * *
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
13. Enter password:
→
Press 4 x = 0000 (default factory password).
Display indicates:
➥
EDIT M1F11
BAUDRATE
PARITY
CONNECT-CONTROL TIME
14.
Use to select BAUDRATE, PARITY or SLAVEADDRESS and confirm selection with .
Display shows the selected value. Example SLAVEADDRESS:
➥
EDIT M1F14
SLAVEADDRESS
1
:EDIT C:ESC
15.
Press again to enter the edit mode.
Display indicates:
➥
EDIT M1F14
SLAVEADDRESS
1
:EDIT :OK C:ESC
44
16. Set new value:
→
Press .
Page 45

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
17. Accept value or cancel?
→
→
Display indicates: Example SLAVEADDRESS:
➥
Accept value: Press .
Cancel process without accepting the value: Press C .
EDIT M1F14
SLAVEADDRESS
1
:EDIT C:ESC
18. Return to status display:
→
Press C several times until S0 is displayed.
Information:For component redundancy (option), the bus address for the 2nd
fieldbus interface can be set in the same way as the 1st field interface.The
menu for the second fieldbus interf ace has to be selected from the descriptions
Via the menu to parameter, e.g.MODBUS 2 instead MODBUS 1.
9.4 Further parameters of the Modbus interface Connection monitoring
time
Parameters for cable
redundancy
Parameter:CONNECT-CONTROL TIME (M1F_3)
Default value:3.0
This time should exceed the cycle time of the Modbus data transmission to all
connected devices. If no valid Modbus telegram was received within this time, the
“DATA EX” status is left and the failure behaviour or the change-over of the
communication channel is initiated, if applicable.
Parameters:
CABLE REDUNDANCY (M1F_5)
CHANNEL CHECK TIME (M1F_6)
Default values:
CABLE REDUNDANCY = OFF
CHANNEL CHECK TIME = 5.0 S
These parameters define the behaviour for cab le redundancy . For further information
to this topic, please refer to the Manual (Operation and setting).
9.5 Switch compartment: open
The switch compartment must be opened to perform the following settings (options).
1. Loosen screws [2] and remove cover [1] from the switch compartment.
Figure 44:
45
Page 46

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
2. If indicator disc [3] is available:
Remove indicator disc [3] using a spanner (as lever).
Information:T o a v oid damage to paint finish, use spanner in combination with
soft object, e.g. fabric.
Figure 45:
9.6 Torque switching: set
Once the set torque is reached, the torque switches will be tripped (overload protection
of the valve).
Information The torque switches may also trip during manual operation.
Valve damage due to excessive tripping torque limit setting!
→
The tripping torque must suit the valve.
→
Only change the setting with the consent of the valve manufacturer.
Figure 46: Torque switching heads
[1] Torque switching head black in direction CLOSE
[2] Torque switching head white in direction OPEN
[3] Lock screws
[4] Torque dials
1. Loosen both lock screws [3] at the indicator disc.
2. Turn torque dial [4] to set the required torque (1 da Nm = 10 Nm).
3. Fasten lock screws [3] again.
Information: Maximum tightening torque: 0.3 – 0.4 Nm
9.7 Limit switching: set
46
The torque switch setting is complete.
➥
Example:The figure above shows the following settings:
●
3.5 da Nm = 35 Nm for direction CLOSE
●
4.5 da Nm = 45 Nm for direction OPEN
The limit switching records the travel.When reaching the preset position, switches
are operated.
Page 47

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
Figure 47: Setting elements for limit switching
Black section:
[1] Setting spindle: End position CLOSED
[2] Pointer: End position CLOSED
[3] Mark: End position CLOSED is set
White section:
[4] Setting spindle: End position OPEN
[5] Pointer: End position OPEN
[6] Mark: End position OPEN is set
9.7.1 End position CLOSED (black section): set
1. Engage manual operation.
2. Turn handwheel clockwise until valve is closed.
3. T urn handwheel by approximately half a turn (overrun) in the opposite direction.
4. Press down and turn setting spindle [1] with screw driver in direction of the
arrow and observe the pointer [2]:While a ratchet click is felt and heard, the
pointer [2] moves 90° every time.
5. If the pointer [2] is 90° from mark [3]: Continue turning slowly.
6. If the pointer [2] moves to mark [3]: Stop turning and release setting spindle.
The end position CLOSED setting is complete.
➥
7. If you override the tripping point inadvertently (ratchet click is heard after the
pointer has snapped): Continue turning the setting spindle in the same direction
and repeat setting process.
9.7.2 End position OPEN (white section): set
1. Engage manual operation.
2. Turn handwheel counterclockwise until valve is open.
3. T urn handwheel by approximately half a turn (overrun) in the opposite direction.
4. Press down and turn setting spindle [4] with screw driver in direction of the
arrow and observe the pointer [5]:While a ratchet click is felt and heard, the
pointer [5] moves 90° every time.
5. If the pointer [5] is 90° from mark [6]: Continue turning slowly.
6. If the pointer [5] moves to mark [6]: Stop turning and release setting spindle.
The end position OPEN setting is complete.
➥
7. If you override the tripping point inadvertently (ratchet click is heard after the
pointer has snapped): Continue turning the setting spindle in the same direction
and repeat setting process.
47
Page 48

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
9.8 Intermediate positions: set — Option —
Actuators equipped with DUO limit switching contain two intermediate position
switches. One intermediate position may be set for each running direction.
Figure 48: Setting elements for limit switching
Black section:
[1] Setting spindle: Running direction CLOSE
[2] Pointer: Running direction CLOSE
[3] Mark: Intermediate position CLOSED is set
White section:
[4] Setting spindle: Running direction OPEN
[5] Pointer: Running direction OPEN
[6] Mark: Intermediate position OPEN is set
Information After 177 turns (control unit for 1 – 500 turns/stroke) or 1,769 turns (control unit for
1 – 5,000 turns/stroke), the intermediate switches release the contact.
9.8.1 Running direction CLOSE (black section): set
1. Move valve in direction CLOSE to desired intermediate position.
2. If you override the tripping point inadvertently:Turn valve in opposite direction
and approach intermediate position again in direction CLOSE.
Information: Always approach the intermediate position in the same direction
as in later electrical operation.
3. Press down and turn setting spindle [1] with screw driver in direction of the
arrow and observe the pointer [2]:While a ratchet click is felt and heard, the
pointer [2] moves 90° every time.
4. If the pointer [2] is 90° from mark [3]: Continue turning slowly.
5. If the pointer [2] moves to mark [3]: Stop turning and release setting spindle.
The intermediate position setting in running direction CLOSE is complete.
➥
6. If you override the tripping point inadvertently (ratchet click is heard after the
pointer has snapped): Continue turning the setting spindle in the same direction
and repeat setting process.
9.8.2 Running direction OPEN (white section): set
1. Move valve in direction OPEN to desired intermediate position.
2. If you override the tripping point inadvertently: Mov e v alv e in opposite direction
and approach intermediate position again in direction OPEN (always approach
the intermediate position in the same direction as in later electrical operation).
48
Page 49

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
3. Press down and turn setting spindle [4] with screw driver in direction of the
arrow and observe the pointer [5]:While a ratchet click is felt and heard, the
pointer [5] moves 90° every time.
4. If the pointer [5] is 90° from mark [6]: Continue turning slowly.
5. If the pointer [5] moves to mark [6]: Stop turning and release setting spindle.
The intermediate position setting in running direction OPEN is complete.
➥
6. If you override the tripping point inadvertently (ratchet click is heard after the
pointer has snapped): Continue turning the setting spindle in the same direction
and repeat setting process.
9.9 Test run
Perform test run only once all settings previously described have been performed.
9.9.1 Direction of rotation: check
Valve damage due to incorrect direction of rotation!
→
If the direction of rotation is wrong, switch off immediately (press STOP).
→
Eliminate cause, i.e. correct phase sequence for cable set wall bracket.
→
Repeat test run.
1. Move actuator manually to intermediate position or to sufficient distance from
end position.
2. Set selector switch to position Local control (LOCAL).
3. Switch on actuator in running direction CLOSE and observe the direction of
rotation:
with indicator disc: step 4
without indicator disc: step 5 (hollow shaft)
→
Switch off before reaching the end position.
4. With indicator disc:
→
Observe direction of rotation.
The direction of rotation is correct, if actuator runs in direction
➥
CLOSE and indicator disc turns counterclockwise.
49
Page 50

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
5. Without the indicator disc:
→
Unscrew threaded plug [1] and seal [2] or cap for stem protection tube [4]
and observe direction of rotation at hollow shaft [3] or the stem [5].
The direction of rotation is correct, if actuator runs in direction CLOSE and
➥
hollow shaft or stem turn clockwise.
Figure 51: Hollow shaft/stem
[1] Threaded plug
[2] Seal
[3] Hollow shaft
[4] Cap for stem protection tube
[5] Stem
[6] Stem protection tube
9.9.2 Limit switching: check
1. Set selector switch to position Local control (LOCAL).
2. Operate actuator using push buttons OPEN - STOP - CLOSE.
➥
- The yellow indication light/LED1 is illuminated in end position CLOSED
- The green indication light/LED5 is illuminated in end position OPEN
- The indication lights go out after travelling into opposite direction.
➥
- The actuator comes to a standstill before reaching the end position
- One of the red indication lights/LEDs is illuminated (torque fault), or the follo wing
3. If the end position setting is incorrect: Reset limit switching.
4. If the end position setting is correct and no options (e.g. potentiometer , position
The limit switching is set correctly if (default indication):
The limit switching is set incorrectly, if:
fault signals are displayed:
-
Status indication S0: FAULT IND.
-
Status indication S1: TORQUE FAULT (OPEN) or TORQUE FAULT
(CLOSE)
transmitter) are available: Close switch compartment.
9.9.3 Reference operation position feedback: perform
For actuators with position feedback (RWG, potentiometer), a reference operation
has to be performed once the limit switching setting was changed to ensure that the
position feedback (0/4 – 20 mA) supplies correct values:
50
Page 51

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
→
Operate actuator electrically (via the push buttons OPEN and CLOSE of the local
controls) once to the end position OPEN and once to the end position CLOSED .
If no reference operation is perf ormed after changing the limit switching, the feedbac k
signal via the bus is not correct.The bus signals the missing reference operation as
a warning.
9.10 Potentiometer setting — Option —
The potentiometer as travel sensor records the valve position.
Information This setting is only required if the potentiometer is directly wired to the customer
connection XK (refer to wiring diagram).
Information Due to the ratio of the reduction gearing the complete resistance range/stroke is not
always passed.Therefore, external adjustment (setting potentiometer) must be provided.
Figure 53: View of control unit
[1] Potentiometer
1. Move valve to end position CLOSED.
2. Turn potentiometer [1] clockwise to the stop.
End position CLOSED corresponds to 0 %
➥
End position OPEN corresponds to 100 %
➥
3. Turn potentiometer [1] slightly in opposite direction.
4. Perform fine-tuning of the zero point at external setting potentiometer (f or remote
indication).
9.11 Electronic position transmitter RWG: set — Option —
The electronic position transmitter RWG records the valve position. On the basis of
the actual position value measured by the potentiometer (tra vel sensor), it generates
a current signal between 0 – 20 mA or 4 – 20 mA.
Table 8: Technical data RWG 4020
Output current
Power supply
tion
Max. load
A
R
3- or 4-wire systemWiring
TP_ _4/ _ _ _KMSTerminal plan
0 – 20 mA, 4 – 20 mAI
V
B
24 V DC, ±15 % smoothedU
24 mA at 20 mA output currentIMax. current consump-
600 Ω
51
Page 52

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Commissioning (basic settings) AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Figure 54: View of control unit
[1] Potentiometer (travel sensor)
[2] Potentiometer min. (0/4 mA)
[3] Potentiometer max. (20 mA)
[4] Measuring point (+) 0/4 – 20 mA
[5] Measuring point (–) 0/4 – 20 mA
1. Connect voltage to electronic position transmitter.
2. Move valve to end position CLOSED.
3. Connect ammeter for 0 – 20 mA to measuring points [4 and 5].
4. Turn potentiometer [1] clockwise to the stop.
5. Turn potentiometer [1] slightly in opposite direction.
6. Turn potentiometer [2] clockwise until output current starts to increase.
7. T urn potentiometer [2] in opposite direction until the follo wing v alue is reached:
- for 0 – 20 mA approx. 0.1 mA
- for 4 – 20 mA approx. 4.1 mA
This ensures that the signal remains above the dead and live zero point.
➥
8. Move valve to end position OPEN.
9. Set potentiometer [3] to end value 20 mA.
10. Approach end position CLOSED again and check minimum value (0.1 mA or
4.1 mA). If necessary, correct the setting.
Information If the maximum value cannot be reached, the selection of the reduction gearing must
be checked. (The max. possible turns/stroke are indicated on the order-related
technical data sheet for the actuator.)
9.12 Mechanical position indicator: set — Option —
1. Place indicator disc on shaft.
2. Move valve to end position CLOSED.
3.
Turn lower indicator disc until symbol (CLOSED) is in alignment with the
mark on the cover.
4. Move actuator to end position OPEN.
52
Page 53

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Commissioning (basic settings)
5.
Hold lower indicator disc in position and turn upper disc with symbol (OPEN)
until it is in alignment with the mark on the cover.
6. Move valve to end position CLOSED again.
7. Check settings:
If the symbol (CLOSED) is no longer in alignment with mark on the cover:
7.1 Repeat setting procedure.
7.2 Check whether the appropriate reduction gearing has been selected, if
required.
9.13 Switch compartment: close
Danger of corrosion due to damage to paint finish!
→
Touch up damage to paint finish after work on the device.
1. Clean sealing faces of housing and cover.
2. Check whether O-ring [3] is in good condition, replace if damaged.
3. Apply a thin film of non-acidic grease (e.g. petroleum jelly) to the O-ring and
insert it correctly.
4. Place cover [1] on switch compartment.
5. Fasten screws [2] evenly crosswise.
53
Page 54

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Corrective action AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
10. Corrective action
10.1 Faults during commissioning
Table 9: Faults during commissioning
RemedyPossible causesFault description
Mechanical position indicator
cannot be set.
Fault in end position
Actuator runs to end stop although the limit switches work
properly.
Position transmitter RWG
Measurement range 4 – 20 mA
or maximum value 20 mA cannot
be set.
Limit and/or torque switches do
not trip.
Push buttons do not react
The controls may not be operated
via the local controls.
Display indicates:RESTRIC-
TED or EMERGENCY STOP.
turns/stroke of the actuator.
The overrun was not considered when setting
the limit switching.
The overrun is generated by the inertia of
both the actuator and the valve and the dela y
time of the controls.
turns/stroke of the actuator.
Switch is defective or switch setting is incorrect.
RESTRICTED signifies that the local con-
trols of the AUMATIC have not been released
yet.
EMERGENCY STOP signifies that the
EMERGENCY STOP mode has been activated via the EMERGENCY STOP button (option),
Exchange reduction gearing.Reduction gearing is not suitable for
Determine overrun: Ov errun = trav el cov ered
from switching off until complete standstill.
Set limit switching again considering the
overrun (turn handwheel back by the amount
of the overrun).
Exchange reduction gearing.Reduction gearing is not suitable for
Check setting, if required, reset end positions.
→ Check switches and replace them, if requi-
red.
For RESTRICTED: A release must be initiated externally via bus or input signal. Refer
to parameter Enable LOCAL MODE.
For EMERGENCY STOP: Release EMERGENCY STOP button.
Switch check
The red test buttons [1] and [2] are used for manual operation of the switches:
1. T urn test button [1] in direction of the TSC arrow:Torque switch CLOSED trips.
The indication light for torque fault CLOSED on the local controls is illuminated.
2. Press push button OPEN to reset the fault (indication light) by operating the
device in the opposite direction.
3. Turn test button [2] in direction of the TSO arrow:Torque switch OPEN trips.
The indication light for torque fault OPEN on the local controls is illuminated.
4. Press push button CLOSE to reset the fault (indication light) by operating the
device in the opposite direction.
If the actuator is equipped with a DUO limit switching (option), the intermediate
position switches (LSA and LSB) will be operated at the same time as the torque
switches.
1. Turn test button [1] in direction of the LSC arrow: Limit switch CLOSED trips.
2. Turn test button [2] in direction of the LSO arrow: Limit switch OPEN trips.
10.2 Fault indications and warning indications
54
Faults interrupt or prevent the electrical actuator operation.
Warnings have no influence on the electrical actuator operation.They only serve
for information purposes.
Fault and warning indications are shown in the display.
Page 55

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Corrective action
10.2.1 Status indication S0 - faults and warnings
Line 4 of status indication S0 displays faults and warnings.
LOCAL MODE S0
OPEN
E2 100 %
FAULT IND.
Table 10: Description of the fault indications
RemedyDescriptionSignal
FAULT IND.
WARNING IND.
FAULT + WARNING
NOT READY IND.
FLT + NR
WRN + NR
FLT + WRN + NR
A fault has occurred.
A warning has occurred.
Faults as well as warnings have occurred.
The actuator cannot be operated from REMOTE.The actuator can only be operated via
the local controls.
Faults and the NOT READY IND. signal
have occurred.
Warnings and the NOT READY IND. signal have occurred.
Faults, warnings, and the NOT READY
IND. signal have occurred.
For further information, press and go to
status indication S1.
For further information, press and go to
status indication S2.
For further information, press and go to
status indication S1 (faults) or S2 (warnings).
For further information, press and go to
status indication S3 (cause for fault indications).
For further information, press and go to
status indication S1 or S3.
For further information, press and go to
status indication S2 or S3.
For further information, press and go to
status indications S1 to S3.
10.2.2 Status indication S1 - faults
Faults are indicated within the status indication S1:
FAULT IND. S1
NO FAULT
Table 11: Description of the fault indications
NO FAULT
INTERNAL FAULT
No fault has occurred.
Internal fault has occurred.
TORQUE FAULT (CLOSE)
TORQUE FAULT (OPEN)
RemedyDescriptionSignal
For further information:
Go to group D0: Press C and hold it
1.
down until diagnostic indication D0 is
displayed.
Go to diagnostic indication D2: Press
2.
twice.
Operation command in direction OPEN.Torque fault in direction CLOSE.
Set selector switch to position Local control
(LOCAL) and reset fault indication via push
button Reset.
Or:
Perform reset command via fieldbus.
Operation command in direction CLOSE.Torque fault in direction OPEN.
Set selector switch to position Local control
(LOCAL) and reset fault indication via push
button Reset.
Or:
Perform reset command via fieldbus.
55
Page 56

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Corrective action AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
RemedyDescriptionSignal
LOSS OF PHASE
THERMAL FAULT
CONFIGURATION FAULT
The controls configuration is incorrect.
Test/connect phases.One phase is missing.
Cool down, wait.Motor protection tripped.
If the fault indication display persists after
cooling down:
Set selector switch to position Local control
(LOCAL) or reset fault indication via push
button Reset.
Or:
Perform reset command via fieldbus.
Check fuse F4.
For further information:
Go to group D0: Press C and hold it
1.
down until diagnostic indication D0 is
displayed.
Go to diagnostic indication D4: Press
2.
4 x.
10.2.3 Status indication S2 - warnings
Faults are indicated within the status indication S2:
WARNING IND. S2
Table 12: Description of the warnings
NO WARNINGS
WARNING OPER. TIME
No warnings have occurred.
Preset running time for a travel betw een end
position OPEN and end position CLOSED
has been exceeded.
WARNING STARTS/RUN
ning time/h have been exceeded.
INTERNAL FEEDBACK
INTERNAL WARNING
FEEDBACK E2 LOSS
Position transmitter (potentiometer or RWG)
is not standardised.
Internal warnings have occurred.
Signal loss of position transmitter
SETPOINT E1 LOSS
NO WARNINGS
RemedyDescriptionSignal
Set the operating time (MONITOR TRIG-
GERS parameter) in accordance with the
actual operating time.
Check tripping behaviour of end position
switches.
Verify actuator mechanics.
Check modulating behaviour.Preset values for max. starts/h or max. runIncrease dead time.
Reduce number of setpoint changes.
Operate actuator into both end positions
(OPEN and CLOSED).
For further information:
Go to group D0: Press C and hold it
1.
down until diagnostic indication D0 is
displayed.
Go to diagnostic indication D3: Press
2.
3 times.
Check position transmitter signal.
Go to group D0: Press C and hold it
1.
down until diagnostic indication D0 is
displayed.
Go to diagnostic indication D7, D8 or
2.
D9: Press either 7, 8 or 9 times.
Check position transmitter wiring.
Check POSITION E2 parameter.The
setting must correspond to the wiring diagram.
Check wiring.Signal loss of setpoint
56
Page 57

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Corrective action
RemedyDescriptionSignal
TORQUE E6 LOSS
I/O ANLOG IN1 LOSS
parallel interface (only for fieldbus/standard
interface combinations)
I/O ANLOG IN2 LOSS
parallel interface (only for fieldbus/standard
interface combinations)
P-FEEDBACK E4 LOSS
if PID controller is available and active)
FIBER OPTIC LOSS
topology only)
ANALOG IN1 BUS1 LOSS
ANALOG IN2 BUS1 LOSS
Check wiring.Signal loss of torque source
Check wiring.Signal loss of the analogue input 1 of the
Check wiring.Signal loss of the analogue input 2 of the
Check wiring.Signal loss of actual process value E4 (only
Check wiring.Signal loss of FO cable (for bus with FO loop
Check wiring.Signal loss of analogue input 1
Check wiring.Signal loss of analogue input 2
10.2.4 Status indication S3 - causes for not ready remote
The causes for the NOT READY IND. fault signals (from status indication S0) are
displayed within status indication S3.
NOT READY IND. S3
READY
Table 13: Description of the fault indications
DescriptionSignal
READY
NOT REMOTE
EMERGENCY MODE
EXTERNAL CONTROLS
EMCY STOP ACTIVE
ACTUATOR LOCKED
Actuator can be operated from REMOTE.
Actuator cannot be operated from REMOTE as the selector switch is in position LOCAL
or OFF.
The EMERGENCY operation mode is active.
For combination fieldbus/standard interface function:
Operation via parallel interface.
The EMERGENCY STOP button has been operated.
Actuator locked (only set for special applications e.g. for by-pass function).
10.3 Fuses
10.3.1 Fuses within the actuator controls
Fuses F1 and F2 can be accessed after removing the cover [1] on the rear side.
Fuses F3, F4, and F5 are located on the power supply unit and can be accessed
after removing the electrical connection [2].
Hazardous voltage!
Risk of electric shock.
→
Disconnect device from the mains before opening.
57
Page 58

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Corrective action AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Figure 59: Access to fuses
[1] Rear cover
[2] Electrical connection
F1/F2
F3
F4
F5
Primary fuses on power supply unit
AUMA Art. No.:F1/F2G fuses
6.3 x 32 mmSize
K002.2771 A T; 500 VReversing contactors
Power supply ≤ 500 V
K002.6652 A FF; 660 VReversing contactors
Power supply > 500 V
K001.18516 A FF; 500 VThyristor units for motor power up to 1.5 kW
K006.96530 A FF; 500 VThyristor units for motor power up to 3.0 kW
K002.2771 A T; 500 VThyristor units for motor power up to 5.5 kW
Internal 24 V DC supply
Internal 24 V AC supply (115 V AC) for:
●
Heater, switch compartment, reversing contactors control
●
PTC tripping device
●
for 115 V AC also control inputs OPEN - STOP - CLOSE
F4F3G fuse according to IEC 60127-2/III
5 x 20 mm5 x 20 mmSize
1.25 A T; 250 V1.0 A T; 250 VVoltage output (power supply unit) = 24 V
0.315 A T; 250 V1.0 A T; 250 VVoltage output (power supply unit) = 115 V
Automatic reset fuse as short-circuit protection for external 24 V DC supply for
customer (see wiring diagram)
Information After fuse replacement, replace and fasten cover.
10.3.2 Motor protection (thermal monitoring)
In order to protect against overheating and impermissibly high surface temper atures
at the actuator, PTC thermistors or thermoswitches are embedded in the motor
winding.The thermoswitch is tripped as soon as the max. permissible winding
temperature has been reached.
The actuator is switched off and the following signals are given:
●
LED 3 (thermal fault) on the local controls is illuminated.
●
Status indication S0: Operation mode OFF/LOCAL = FLT + NR
●
Status indication S0/S6: Operation mode REMOTE = FAULT IND.
●
Status indication S1: THERMAL FAULT
The motor has to cool down before the operation can be resumed. Depending on
the parameter setting, the fault signal is either automatically reset or the f ault signal
has to be acknowledged.
58
Page 59

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Corrective action
The acknowledgement is made:
●
via the Reset push button in selector switch position LOCAL.
●
or with the reset command via fieldbus.
For further information to this topic, please refer to the Manual (Operation and setting).
59
Page 60

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Servicing and maintenance AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
11. Servicing and maintenance
Damage caused by inappropriate maintenance!
→
Servicing and maintenance must be carried out exclusively by suitably qualified
personnel having been authorised by the end user or the contractor of the plant.
Therefore, we recommend contacting our service.
→
Only perform servicing and maintenance tasks when the device is switched off.
AUMA
Service & Support
AUMA off er extensiv e service such as servicing and maintenance as well as customer
product training. For the relevant contact addresses, please refer to <Addresses>
in this document or to the Internet (www.auma.com) .
11.1 Preventive measures for servicing and safe operation
The following measures are required to ensure safe device operation:
6 months after commissioning and then every year
●
Carry out visual inspection:
Cable entries, cable glands, b lanking plugs, etc. have to be checked for correct
tightness and sealing.
Respect torques according to manufacturer's details.
●
Check fastening screws between actuator and gearbox/valve for tightness. If
required, fasten screws while applying the tightening torques as indicated in
chapter <Assembly>.
●
When rarely operated: Perform test run.
●
For devices with output driv e A: Press in Lithium soap EP m ulti-purpose grease
on mineral oil base at the grease nipple with a grease gun.
●
Lubrication of the valve stem must be done separately.
Figure 60: Output drive type A
11.2 Maintenance Lubrication
60
[1] Output drive type A
[2] Grease nipple
Table 14: Grease quantities for bearing of output drive type A
A 16.2A 14.2A 10.2A 07.2Output drive
1)
For grease at density r = 0.9 kg/dm³1)
5321.5Quantity [g]
For enclosure protection IP 68
After continuous immersion:
●
Check actuator.
●
In case of ingress of water, locate leaks and repair, dry device correctly and
check for proper function.
●
In the factory, the gear housing is filled with grease.
Page 61

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Servicing and maintenance
●
Grease change is performed during maintenance
- Generally after 4 to 6 years for modulating duty.
- Generally after 6 to 8 years if operated frequently (open-close duty).
- Generally after 10 to 12 years if operated rarely (open-close duty).
●
We recommend exchanging the seals when changing the grease.
●
No additional lubrication of the gear housing is required during operation.
11.3 Disposal and recycling
Our devices have a long lifetime. However, they have to be replaced at one point in
time.The devices have a modular design and may, therefore, easily be separated
and sorted according to materials used, i.e.:
●
electronic scrap
●
various metals
●
plastics
●
greases and oils
The following generally applies:
●
Greases and oils are hazardous to water and must not be released into the
environment.
●
Arrange for controlled waste disposal of the disassemb led material or for separate recycling according to materials.
●
Observe the national regulations for waste disposal.
61
Page 62

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Technical data AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
12. Technical data
Information The following technical data includes standard and optional features. For detailed
information on the customer-specific version, refer to the order-relevant data sheet.
This data sheet can be downloaded from the Internet at http://www.auma.com in
German and English (indication of commission number required).
12.1 Features and functions of actuator
Type of duty
1)
Insulation class
Motor protection
Self-locking
Limit switching
Standard:
●
SA: Short-time duty S2 - 15 min
●
SAR: Intermittent duty S4 - 25 %
Options:
●
SA: Short-time duty S2 - 30 min
●
SAR: Intermittent duty S4 - 50 %
●
SAR: Intermittent duty S5 – 25 %
Refer to actuator name plateTorque range
Refer to actuator name plateOutput speed
Standard: 3-ph AC asynchronous motor, type IM B9 according to IEC 60034Motor
Standard: F, tropicalized
Option: H, tropicalized
Standard:Thermoswitches (NC)
Option: PTC thermistors (according to DIN 44082)
Self-locking: Output speeds up to 90 rpm (50 Hz), 108 rpm (60 Hz)
NOT self-locking: Output speeds up to 125 rpm (50 Hz), 150 rpm (60 Hz)
Multi-turn actuators are self-locking, if the valve position cannot be changed from standstill
while torque acts upon the output drive.
Counter gear mechanism for end positions CLOSED and OPEN
Turns per stroke: 1 to 500 (standard) or 1 to 5,000 (option)
Standard:
●
Single switches (1 NC and 1 NO; not galvanically isolated) for each end position
Options:
●
Tandem switches (2 NC and 2 NO) for each end position, switches galvanically isolated
●
Triple switches (3 NC and 3 NO) for each end position, switches galvanically isolated
●
Intermediate position switch (DUO limit switching), adjustable for any position
Torque switching
logue (option)
(option)
Motor heater (option)
Manual operation
Valve attachment
Torque switching adjustable for directions OPEN and CLOSE
Standard:
Single switches (1 NC and 1 NO; not galvanically isolated) for each direction
Option:
Tandem switches (2 NC and 2 NO) for each direction, switches galvanically isolated
Potentiometer or 0/4 – 20 mA (RWG)Position feedback signal, ana-
Continuous indication, adjustable indicator disc with symbols OPEN and CLOSEDMechanical position indicator
Blinker transmitter (standard for SA, option for SAR)Running indication
Voltages: 110 – 220 V AC, 220 – 240 V AC or 400 V AC
Power depending on the size 12.5 – 25 W
Manual drive for setting and emergency operation, handwheel does not rotate during electrical
operation.
Option: Handwheel lockable
AUMA plug/socket connector with screw-type connectionConnection to controls
Standard: B1 according to EN ISO 5210
Options:
A, B2, B3, B4 according to EN ISO 5210
A, B, D, E according to DIN 3210
C according to DIN 3338
Special output drive types: AF, B3D, ED, DD, IB1, IB3
A with stem lubrication
62
Page 63

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Technical data
For nominal voltage and 40 °C ambient temperature and an average load with running torque or modulating torque according to sepa-
1)
rate technical data.The type of duty must not be exceeded.
Technical data for limit and torque switches
2 x 106 startsMechanical lifetime
Silver plated contacts:
30 V AC/DCU min.
250 V AC/DCU max.
20 mAI min.
I max. AC current
I max. DC current
Gold plated contacts:
5 A at 250 V (resistive load)
3 A at 250 V (inductive load, cos phi = 0.6)
0.4 A at 250 V (resistive load)
0.03 A at 250 V (inductive load, L/R = 3 µs)
7 A at 30 V (resistive load)
5 A at 30 V (inductive load, L/R = 3 µs)
5 VU min.
30 VU max.
4 mAI min.
400 mAI max.
Technical data for blinker transmitter
107 startsMechanical lifetime
Silver plated contacts:
10 V AC/DCU min.
250 V AC/DCU max.
I max. AC current
3 A at 250 V (resistive load)
2 A at 250 V (inductive load, cos phi ≈ 0.8)
0.25 A at 250 V (resistive load)I max. DC current
12.2 Features and functions of actuator controls
Power supply, mains frequency
Current consumption
External supply of the electronics (option)
Switchgear
1) 2)
For mains voltage and mains frequency, refer to name plates at the controls and the motor
Permissible variation of the nominal voltage: ±10 %
Permissible variation of the mains frequency: ±5 %
Motor current consumption: Refer to motor name plate
Current consumption of the controls depending on the mains voltage:
100 to 120 V AC = max. 650 mA
208 to 240 V AC = max. 325 mA
380 to 500 V AC = max. 190 mA
24 V DC +20 %/–15 %
Current consumption: Basic version approx. 200 mA, with options up to 500 mA
The controls are designed for the rated power of the motor, refer to motor name plateRated power
Category III according to IEC 60364-4–443Overvoltage category
Standard:
Reversing contactors (mechanically and electrically interlocked) f or motor power up to po wer
class A1
Options:
●
Reversing contactors (mechanically and electrically interlocked) for motor power up to
power class A2
●
Thyristor unit for mains voltage up to 500 V AC (recommended f or modulating actuators)
for AUMA power classes B1, B2 and B3
Via fieldbus interfaceControl
Via fieldbus interfaceOutput signals
63
Page 64

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Technical data AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Fieldbus interface
Voltage output
Redundancy in loop structure
(option)
Standard:
Modbus RTU interface without additional inputs
Options:
Additional inputs.The following version are available:
●
4 free 24 V DC inputs (current consumption: approx. ca. 5 mA/input) and 2 free 0/4 – 20
mA inputs. Signal transmission is made via fieldbus interface.
●
24 V DC control inputs OPEN – CLOSE – EMERGENY, or alternatively OPEN – STOP
– CLOSE (current consumption: approx. 5 mA/input). Selection of control mode via 24
V DC BUS/REMOTE input
●
24 V DC control inputs OPEN - CLOSE (current consumption: approx. 5 mA/input) and
0/4 – 20 mA input for position setpoint (positioner). Selection of control mode via 24 V
DC inputs BUS/REMOTE and MODE
●
24 V DC (115 V AC as option) control inputs OPEN - STOP - CLOSE - EMERGENCY
(current consumption: approx. 5mA/input) and 0/4 – 20 mA input for position setpoint
(positioner)
Selection of control mode via 24 V DC (optional 115 V AC) B US/REMOTE and MODE
-
inputs
Status signals via 6 programmable output contacts, position feedback signal 0/4 –
-
20 mA
Standard:
Auxiliary voltage 24 V DC, max. 100 mA for supply of the control inputs, galvanically isolated
from internal voltage supply
Option:
Auxiliary voltage 115 V AC, max. 30 mA to supply the control inputs3), galvanically isolated
from internal voltage supply
Additional redundant Modbus RTU interfaceComponent redundancy (option)
AUMATIC is equipped with an additional redundant Modbus interface to form a redundant
loop when combined with the SIMA Master Station
●
Max. number of actuators equipped with AUMATIC actuator controls per redundant loop:
247 units. Max. possible cable length between the actuators equipped with AUMATIC
actuator controls without external repeater: 1,200 m
●
Max. possible total cable length per redundant loop: approx. 290 km
Local controls
Standard:
●
Selector switch LOCAL - OFF - REMOTE (lockable in all three positions)
●
Push buttons OPEN - STOP - CLOSE - RESET
●
5 indication lights:
End position CLOSED and running indication CLOSE (yellow), torque fault CLOSE
-
(red), motor protection tripped (red), torque fault OPEN (red), end position and running
indication OPEN (green)
●
LC display, illuminated
●
Programming interface (infra-red)
Options:
●
Bluetooth programming interface is equipped with a class II Bluetooth chip with a range
of up to 10 m.The interface supports the Bluetooth protocol SPP (Serial Port Profile).
●
Enabling the local controls using selector switch LOCAL - OFF - REMOTE via fieldbus
This way, actuator operation via push buttons of local controls can be either enabled or
disabled.
●
Special colours for the 5 indication lights:
End position CLOSED (green), torque fault CLOSE (blue), torque f ault OPEN (yellow),
-
motor protection tripped (white), end position OPEN
●
Protection cover, lockable
●
Protection cover with indicator glass, lockable
64
Page 65

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Technical data
Functions
Monitoring functions
Electronic name plate
Operating data logging
Motor protection evaluation
Standard:
●
Switch-off mode adjustable
Limit or torque seating for end position OPEN and end position CLOSED
-
●
Torque monitoring over the whole travel
●
Torque by-pass, adjustable up to 5 seconds (no torque monitoring during this time)
●
Phase failure monitoring4) with automatic phase correction
●
Running indication via indication lights/LEDs
●
Programmable behaviour in case of loss of bus communication
●
Positioner
-
-
-
-
Options:
●
Process controller, PID
-
-
-
-
-
●
Multiport valve function
-
●
Programmable monitoring of the max. number of starts, generates warning signal
●
Reaction monitoring for operation command (programmable from 1 to 15 seconds), ge-
5)
Position setpoint via fieldbus interface
Programmable behaviour on loss of signal
Automatic adaptation of the dead band (adaptive behaviour can be selected)
Change-over between open-close duty and modulating duty via fieldbus interface
6)
Process setpoint via fieldbus interface
Actual process value via 0/4 – 20 mA additional input
Programmable behaviour on loss of signal
Limitation of the control range
Change-over between open-close duty and modulating duty via fieldbus interface
7)
Direct approaching of up to 8 intermediate positions via fieldbus and local controls
nerates fault signal and results in switching off
●
Operating time monitoring (programmable from 4 to 1,800 seconds), generates warning
signal
●
Ordering data:
AUMATIC commission number, actuator commission number , KKS number (definition
-
system for power plants), valve number, plant number
●
Product data:
Product name, actuator works number, AUMATIC works number, logic software ver-
-
sion, logic hardware version, date of final test, wiring diagram, terminal plan
●
Project data:
Project name, 2 freely definable customer fields with a max. of 19 characters each
-
●
Service data:
Service telephone, Internet address, service text 1, service text 2
-
A resettable counter and a lifetime counter each for:
Motor running time, number of starts, torque switch trippings in end position CLOSED, limit
switch trippings in end position CLOSED , torque s witch trippings in end position OPEN, limit
switch trippings in end position OPEN, torque faults CLOSE, torque faults OPEN, motor
protection trippings
Standard:
Monitoring of the motor temperature in combination with thermoswitches in the motor
Options:
●
Additional thermal overload relay in the controls in combination with thermoswitches within
the motor
●
PTC tripping device in combination with PTC thermistors in the motor
Electrical connection
Overvoltage protection (option)
Standard:
AUMA plug/socket connector (S) with screw-type connection and M-threads
Options:
●
Pg-threads, NPT-threads, G-threads, special threads
●
Gold-plated control contacts (pins and sockets)
●
Parking frame for wall mounting of the disconnected plug
●
Protection cover for plug compartment (when plug is removed)
Protection of the actuator and control electronics against overvoltages on the fieldbus cab les
of up to 4 kV
Refer to name plateWiring diagram
65
Page 66

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Technical data AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
The reversing contactors are designed for a lifetime of 2 million starts.1)
For the assignment of AUMA power classes, please refer to electrical data on actuator.2)
Not possible in combination with PTC tripping device3)
During an adjustable period (factory setting 10 seconds), faults in the supply voltage (e.g. voltage drops) will not lead to a fault signal.4)
Requires position transmitter in actuator5)
Requires position transmitter in actuator6)
Requires position transmitter in actuator7)
Further options for version with potentiometer or RWG in the actuator
Timer
Start and end of stepping mode as well as ON and OFF time (1 up to 300 seconds) can be
programmed individually for the directions OPEN and CLOSE.
Intermediate positions
Any 8 intermediate positions between 0 and 100 %, reaction and signal behaviour programmable
12.3 Modbus interface
Settings/programming the Modbus interface
Baud rate, parity and Modbus address are set via the display of the AUMATIC.Setting the Modbus interface
Commands and signals of the fieldbus interface
(command signals)
Process representation input
(feedback signals)
OPEN, STOP, CLOSE, position setpoint1), RESETProcess representation output
●
End position OPEN, CLOSED
●
Actual position value
●
Actual torque value
●
Selector switch in position LOCAL/REMOTE
●
Running indication4) (directional)
●
Torque switch OPEN, CLOSE
●
Limit switch OPEN, CLOSED
●
Manual operation by handwheel5) or via local controls
●
2 analogue and 4 digital customer inputs
2)
3)
Process representation input
(fault signals)
Behaviour on loss of communication
Requires position transmitter in actuator1)
Requires position transmitter in actuator2)
Requires magnetic limit and torque transmitter (MWG) in actuator3)
Requires position transmitter in actuator4)
Requires position transmitter in actuator5)
Requires position transmitter in actuator6)
General fieldbus interface data
Network topology
●
Motor protection tripped
●
Torque switch tripped in mid-travel
●
One phase missing
●
Loss of the analogue customer inputs
The behaviour of the actuator is programmable:
●
Stops in current position
●
Travel to end position OPEN or CLOSED
●
Travel to any intermediate position
6)
Modbus RTUCommunication protocol
●
Line (bus) structure
●
Active bus termination at both ends
●
Coupling and uncoupling of devices during operation without affecting other devices is
possible
Twisted, screened copper cable according to IEC 61158Transmission medium
EIA-485 (RS485)Fieldbus interface
66
Page 67

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Technical data
General fieldbus interface data
●
Transmission speed/cable
length
Device types
Supported fieldbus functions
Baud rate and maximum cable length (segment length) without repeater:
between 300 and 38,400 bit/s: 1,200 m
●
Baud rate and possible cable length with repeater (total network cable length):
between 300 and 38,400 bit/s: approx. 10 km
Modbus slave, e.g. devices with digital and/or analogue inputs/outputs such as actuators,
sensors
32 devices in each segment without repeater, with repeaters expandable to 247Number of devices
Polling between master and slaves (query response)Bus access
01 Read Coil Status
02 Read Input Status
03 Read Holding Registers
04 Read Input Registers
05 Force Single Coil
15 (0FHex) Force Multiple Coils
06 Preset Single Register
16 (10Hex) Preset Multiple Registers
07 Read Exception Status
17 (11Hex) Report Slave ID
08 Diagnostics:
●
00 00 Loopback
●
00 10 (0AHex) Clear Counters and Diagnostic Register
●
00 11 (0BHex) Return Bus Message Count
●
00 12 (0CHex) Return Bus Communication Error Count
●
00 13 (0DHex) Return Bus Exception Error Count
●
00 14 (0EHex) Return Slave Message Count
●
00 15 (0FHex) Return Slave No Response Count
12.4 Service conditions
Enclosure protection according
to EN 60529
Corrosion protection
Installation altitude
Pollution degree
Ambient temperature
Any positionMounting position
Indoor and outdoor use permissibleUse
Standard:
●
IP 67 with AUMA 3-ph AC motor/1-ph AC motor
●
IP 55 with DC motor
For actual version, refer to actuator/controls name plate.
Standard:
KS: Suitable for installation in industrial units, in water or power plants with a low pollutant
concentration as well as for installation in occasionally or permanently aggressive atmosphere
with a moderate pollutant concentration (e.g. in wastew ater treatment plants, chemical industry)
Options:
●
KX: Suitable for installation in extremely aggressiv e atmospheres with high humidity and
high pollutant concentration
●
KX-G : same as KX, however aluminium-free version (outer parts)
Standard: ≤ 2,000 m above sea level
Option: > 2,000 m above sea level, please contact AUMA
Up to 100 % relative humidity over the entire permissible temperature rangeHumidity
Within controls: Pollution degree 2
Outside controls (when closed): Pollution degree 4
Standard: Paint based on polyurethane (powder coating)Finish coating
Standard: AUMA silver-grey (similar to RAL 7037)Colour
Standard:
●
–25 °C to +70 °C
For actual version, refer to actuator/controls name plate.
67
Page 68

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Technical data AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Vibration resistance according
to IEC 60068-2-6
1 g, from 10 to 200 Hz
Resistant to vibration during start-up or for failures of the plant. However, a fatigue strength
may not be derived from this. Not valid in combination with gearboxes.
Lifetime
Open-close duty (operating cycles (OPEN - CLOSE - OPEN):
SA 07.1/07.5 – SA 10.1: 20,000
SA 14.1/14.5 – SA 16.1: 15,000
Modulating duty:
1)
SAR 07.1/07.5 – SAR 10.1: 5.0 million modulating steps
SAR 14.1/14.5 – SAR 16.1: 3.5 million modulating steps
Refer to separate technical dataWeight
The lifetime depends on the load and the number of starts. A high starting frequency will rarely improve the modulating accuracy.To
1)
reach the longest possible maintenance and fault-free operating time, the n umber of starts per hour chosen should be as low as permissible for the process.
12.5 Accessories
Wall bracket
1)
EMERGENCY STOP button
Cable length between actuator and AUMATIC max. 100 m. Not suitable for version with potentiometer in the actuator. Instead of the
1)
potentiometer, an RWG has to be used.
Only in combination with reversing contactors and AUMATIC AC 01.1 in enclosure protection IP 67 or IP 682)
AUMATIC mounted separately from the actuator, including plug/socket connector . Connecting
cables on request. Recommended for high ambient temper atures, difficult access, or in case
of heavy vibration during service
2)
The control voltage of the rev ersing contactors is interrupted by operating the EMERGENCY
STOP button.
COM-AC. An interface cable is required for the standard infra-red programming interface.Programming software for PC
12.6 Further information
EU Directives
●
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): (2004/108/EC)
●
Low Voltage Directive: (2006/95/EC)
●
Machinery Directive: (2006/42/EC)
68
Page 69

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Spare parts
13. Spare parts
13.1 Multi-turn actuators SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1
69
Page 70

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Spare parts AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Information: Please state type and commission no. of the device (see name plate) when ordering spare parts.
Only original AUMA spare parts should be used. F ailure to use original spare parts voids the warranty and e xempts
AUMA from any liability. Delivered spare parts may slightly vary from the representation.
TypeDesignationNo.TypeDesignationNo.
Output drive shaft D516.1Sub-assemblyHousing001.0
Snap ring535.1Sub-assemblyBearing flange002.0
Screw plug539.0Sub-assemblyHollow shaft without worm wheel003.0
Sub-assemblyHandwheel with ball handle542.0Sub-assemblyWorm shaft005.0
Output drive sleeve B3/B4/E549.1Motor coupling005.1
Parallel key551.1Coupling pin005.2
Sub-assemblyMechanical position indicator553.0Manual drive coupling005.3
Sub-assemblySocket carrier with motor cable har-
Sub-assemblyPotentiometer for position transmitter556.0Worm wheel006.0
Sub-assemblyPotentiometer without slip clutch556.1Sub-assemblyPlanetary gear for manual drive009.0
Sub-assemblyHeater557.0Sub-assemblyRetaining flange010.0
Sub-assemblyBlinker transmitter including pins at
Sub-assemblyControl unit with torque switching
Sub-assemblyControl unit with magnetic limit and
Sub-assemblySwitch stack for direction OPEN560.0-1Sub-assemblySwing lever020.0
Sub-assemblySwitch stack for direction CLOSE560.0-2Sub-assemblyDrive pinion II for torque switching022.0
Sub-assemblyPosition transmitter RWG566.0Sub-assemblyLocking plate025.0
Sub-assemblyPotentiometer for RWG without slip
Sub-assemblyElectronic board RWG566.2Sub-assemblyTorque switching head061.0
Sub-assemblyWire harness for RWG566.3Sub-assemblyMotor (VD motor incl. no. 079.0)070.0
Sub-assemblySlip clutch for potentiometer/RWG567.1Sub-assemblyPlanetary gear for motor drive
SetSeal kit, smallS1Sub-assemblyPin for motor506.0
SetSeal kit, largeS2Sub-assemblyPlug cover507.0
079.0
080.0
(SA/SAR 07.1 – 14.1 for VD motor)
(SA/SAR 16.1 for AD90 motor)
554.0Pull rope005.4
558.0Sub-assemblyTorque lever017.0
559.0-1Gear segment018.0
559.0-2Sub-assemblyCrown wheel019.0
566.1Sub-assemblyWire for protective earth (pin)058.0
574.1Sub-assemblySocket for motor504.0
Sub-assemblyThreaded plug511.0
Sub-assemblyOutput drive form A (without stem nut)514.0
Sub-assemblyAxial needle roller bearing514.1
ness
wires (without impulse disc and insulation plate)
heads and switches
torque transmitter (MWG) for Non-intrusive version in combination with
AUMATIC integral controls
Switch for limit/torque switching560.1Sub-assemblyOutput drive wheel for limit switching023.0
Switch case560.2Sub-assemblyDrive wheel for limit switching024.0
clutch
Stem protection tube (without cap)568.1Sub-assemblyPlanetary gear for motor drive
Cap for stem protection tube568.2Sub-assemblyReduction gearing155.0
V-Seal568.3Sub-assemblyCover for switch compartment500.0
Change-over lever assy569.0Sub-assemblySocket carrier (complete with sockets)501.0
Change-over lever569.1Sub-assemb lyPin carrier without pins502.0
Notched pin569.2Sub-assemblySocket for controls503.0
Radial seal output drive A for ISO
flange
Stem nut type A575.1Sub-assemblyPin for controls505.0
70
Page 71

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Spare parts
13.2 Actuator controls AUMATIC AC 01.1 with AUMA plug/socket connector (SD bus)
71
Page 72

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Spare parts AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
Information: Please state type and commission no. of the device (see name plate) when ordering spare parts.
Only original AUMA spare parts should be used. F ailure to use original spare parts voids the warranty and e xempts
AUMA from any liability. Delivered spare parts may slightly vary from the representation.
TypeDesignationNo.
Sub-assemblyHousing001.0
Sub-assemblyLocal controls002.0
Local controls board002.3
Sub-assemblyPower supply006.0
Bus-Platine008.1
Sub-assemblyLogic board009.0
Relay board011.1
Bus connection board050.1
Sub-assemblyCover500.0
Sub-assemblySocket carrier (complete with sockets)501.0
Sub-assemblyPin carrier without pins502.0
Sub-assemblySocket for controls503.0
Sub-assemblySocket for motor504.0
Sub-assemblyPin for controls505.0
Sub-assemblyPin for motor506.0
Sub-assemblyElectrical connection for bus without connection board (050.0)507.0
Sub-assemblyFrame507.1
Sub-assemblySwitchgear508.0
Padlock509.1
SetFuse kit510.0
SetSeal kitS
72
Page 73

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Certificates
14. Certificates
14.1 Declaration of Incorporation and EC Declaration of Conformity
73
Page 74

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
74
Page 75

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
75
Page 76

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
Index AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU
I
Index
A
Accessories (electrical
connection)
Accessories for assembly 15
Actuator operation from remote
Ambient temperature 67
Applications 5
Assembly 11
B
Baud rate 42
Bus address 42
Bus cables 18 , 22
C
Cable redundancy 45
Cable set 25
Commission number 9
Commissioning 5
Connecting cable 25
Connection monitoring time 45
Control 9
Corrective action 54
Corrosion protection 10 , 67
Cross section 18
Cross sections 19
Current consumption 17
D
DUO limit switching 48
Declaration of Incorporation 73
Direction of rotation 49
Directives 5
Display (indications) 34
Disposal 61
Double sealed 27
E
EC Declaration of Conformity 73
EMC 17
Earth connection 27
Electrical connection 17
Electronic position transmitter 51
Enclosure protection 67
End position(s) reached display
End positions 38
F
Fault indications and warning
indications
Feedback signals (analogue) 37
H
Handwheel 11
Heat-up time 38
25
30
34
54
Identification 8
Indication lights 35
Indications 34
Indicator disc 36 , 52
Inspection record 9
Intermediate frame 27
Intermediate positions 48
Intrusive 9
L
LEDs 35
Language in the display 32
Limit switching 46 , 50
Local control 29
Local controls 29
Low temperature version 38
Lubrication 60
M
Mains frequency 18
Mains voltage 18
Maintenance 5 , 60 , 60
Manual operation 28
Mechanical position indicator 36 , 52
Menu navigation via push
buttons
Motor heater 21
Motor operation 29
N
Name plate 8 , 18
Non-Intrusive 9
O
Operation 5 , 28
Operation command/setpoint
display
Operation mode display 34
Output drive type A 13
Output drive types B, B1, B2,
B3, B4, and E
P
Packaging 10
Parity 42
Parking frame 26
Password entry 32
Position indicator 52
Position transmitter RWG 51
Potentiometer 51
Power supply 17 , 18
Protection cover 27
Protection on site 17
Protective measures 5
Push buttons 31
Q
Qualification of staff 5
30
34
12
76
Page 77

SA 07.1 – SA 16.1/SAR 07.1 – SAR 16.1 Control unit: electromechanic
AC 01.1 Intrusive Modbus RTU Index
R
RWG 51
Range of application 5
Recycling 61
Reference operation 50
Remote actuator operation 30
Running indication 35 , 36
Running indication (in display) 34
S
S0/S6 - operation 34
Safety instructions 5
Safety instructions/warnings 5
Service 60
Service conditions 67
Servicing 60
Short-circuit protection 17
Signals 37
Slave address 42
Spare parts 69
Standards 5
Status indications (in the dis-
34
play)
Stem nut 13
Stem protection tube 15
Storage 10
Support 60
Switch check 54
T
Technical data 62
Technical data for switches 63
Terminal plan 17
Test run 49
Torque indication 35
Torque switching 46
Transport 10
Tripping torque 38
Type and size 8
Type of current 18
Type of seating 38
V
Valve position display 34
Valve stem 15
W
Wall bracket 25
Wire diameter (bus cable) 18
Wiring diagram 9 , 17
77
Page 78

AUMA worldwide
Europe
AUMA Riester GmbH & Co. KG
Plant Müllheim
DE 79373 Müllheim
Tel +49 7631 809 - 0
Fax +49 7631 809 - 1250
riester@auma.com
www.auma.com
Plant Ostfildern - Nellingen
DE 73747 Ostfildern
Tel +49 711 34803 - 0
Fax +49 711 34803 - 3034
riester@wof.auma.com
Service-Center Köln
DE 50858 Köln
Tel +49 2234 2037 - 900
Fax +49 2234 2037 - 9099
service@sck.auma.com
Service-Center Magdeburg
DE 39167 Niederndodeleben
Tel +49 39204 759 - 0
Fax +49 39204 759 - 9429
Service@scm.auma.com
Service-Center Bayern
DE 85386 Eching
Tel +49 81 65 9017- 0
Fax +49 81 65 9017- 2018
Riester@scb.auma.com
AUMA ACTUATORS Ltd.
UK Clevedon, North Somerset BS21 6TH
Tel +44 1275 871141
Fax +44 1275 875492
mail@auma.co.uk
www.auma.co.uk
AUMA ITALIANA S.r.l. a socio unico
IT 20023 Cerro Maggiore (MI)
Tel +39 0331 51351
Fax +39 0331 517606
info@auma.it
www.auma.it
AUMA BENELUX B.V.
NL 2314 XT Leiden
Tel +31 71 581 40 40
Fax +31 71 581 40 49
office@benelux.auma.com
www.auma.nl
AUMA Polska Sp. z o.o.
PL 41-219 Sosnowiec
Tel +48 32 783 52 00
Fax +48 32 783 52 08
biuro@auma.com.pl
www.auma.com.pl
OOO Priwody AUMA
RU 124365 Moscow a/ya 11
Tel +7 495 221 64 28
Fax +7 495 221 64 38
aumarussia@auma.ru
www.auma.ru
Auma Endüstri Kontrol Sistemleri Limited
irketi
TR 06810 Ankara
Tel+90 312 217 32 88
Fax+90 312 217 33 88
Servis@auma.com.tr
www.megaendustri.com.tr
AUMA Technology utomations Ltd.
UA 02099 Kiyiv
Tel+38 044 586-53-03
Fax+38 044 586-53-03
auma-tech@aumatech.com.ua
Africa
AUMA South Africa (Pty) Ltd.
ZA 1560 Springs
Tel +27 11 3632880
Fax +27 11 8185248
aumasa@mweb.co.za
A.T.E.C.
EG Cairo
Tel +20 2 23599680 - 23590861
Fax +20 2 23586621
atec@intouch.com
CMR Contrôle Maintenance Régulation
TN 1002 Tunis
Tel +216 71 903 577
Fax +216 71 903 575
instrum@cmr.com.tn
www.cmr-tunisie.net
AUMA Armaturenantriebe GmbH
AT 2512 Tribuswinkel
Tel +43 2252 82540
Fax +43 2252 8254050
office@auma.at
www.auma.at
AUMA (Schweiz) AG
CH 8965 Berikon
Tel +41 566 400945
Fax +41 566 400948
RettichP.ch@auma.com
AUMA Servopohony spol. s.r.o.
CZ 250 01 Brandýs n.L.-St.Boleslav
Tel +420 326 396 993
Fax +420 326 303 251
auma-s@auma.cz
www.auma.cz
OY AUMATOR AB
FI 02230 Espoo
Tel +358 9 5840 22
Fax +358 9 5840 2300
auma@aumator.fi
www.aumator.fi
AUMA France S.A.R.L.
FR 95157 Taverny Cedex
Tel +33 1 39327272
Fax +33 1 39321755
info@auma.fr
www.auma.fr
ERICHS ARMATUR AB
SE 20039 Malmö
Tel +46 40 311550
Fax +46 40 945515
info@erichsarmatur.se
www.erichsarmatur.se
GRØNBECH & SØNNER A/S
DK 2450 København SV
Tel+45 33 26 63 00
Fax+45 33 26 63 21
GS@g-s.dk
www.g-s.dk
IBEROPLAN S.A.
ES 28027 Madrid
Tel+34 91 3717130
Fax+34 91 7427126
iberoplan@iberoplan.com
D. G. Bellos & Co. O.E.
GR 13671 Acharnai Athens
Tel+30 210 2409485
Fax+30 210 2409486
info@dgbellos.gr
SIGURD SØRUM AS
NO 1300 Sandvika
Tel+47 67572600
Fax+47 67572610
post@sigum.no
INDUSTRA
PT 2710-297 Sintra
Tel+351 2 1910 95 00
Fax+351 2 1910 95 99
industra@talis-group.com
MANZ INCORPORATED LTD.
NG Port Harcourt
Tel +234-84-462741
Fax +234-84-462741
mail@manzincorporated.com
www.manzincorporated.com
America
AUMA ACTUATORS INC.
US PA 15317 Canonsburg
Tel +1 724-743-AUMA (2862)
Fax +1 724-743-4711
mailbox@auma-usa.com
www.auma-usa.com
AUMA Argentina Representative Office
AR 1609 Boulogne
Tel/Fax +54 232 246 2283
contacto@aumaargentina.com.ar
AUMA Automação do Brasil Ltda.
BR São Paulo
Tel +55 11 8114-6463
bitzco@uol.com.br
AUMA Chile Representative Office
CL 9500414 Buin
Tel +56 2 821 4108
Fax +56 2 281 9252
aumachile@adsl.tie.cl
TROY-ONTOR Inc.
CA L4N 8X1 Barrie Ontario
Tel +1 705 721-8246
Fax +1 705 721-5851
troy-ontor@troy-ontor.ca
78
Page 79

AUMA worldwide
Ferrostaal de Colombia Ltda.
CO Bogotá D.C.
Tel +57 1 401 1300
Fax+57 1 416 5489
dorian.hernandez@ferrostaal.com
www.ferrostaal.com
PROCONTIC Procesos y Control
Automático
EC Quito
Tel +593 2 292 0431
Fax +593 2 292 2343
info@procontic.com.ec
Corsusa International S.A.C.
PE Miraflores - Lima
Tel +511444-1200 / 0044 / 2321
Fax +511444-3664
corsusa@corsusa.com
www.corsusa.com
PASSCO Inc.
PR 00936-4153 San Juan
Tel +18 09 78 77 20 87 85
Fax +18 09 78 77 31 72 77
Passco@prtc.net
Suplibarca
VE Maracaibo Estado, Zulia
Tel +58 261 7 555 667
Fax +58 261 7 532 259
suplibarca@intercable.net.ve
AUMA Actuators Middle East W.L.L.
AE 15268 Salmabad 704
Tel +973 17877377
Fax +973 17877355
Naveen.Shetty@auma.com
PERFECT CONTROLS Ltd.
HK Tsuen Wan, Kowloon
Tel +852 2493 7726
Fax +852 2416 3763
joeip@perfectcontrols.com.hk
DW Controls Co., Ltd.
KR 153-702 Seoul
Tel +82 2 2624 3400
Fax +82 2 2624 3401
sichoi@actuatorbank.com
www.actuatorbank.com
Sunny Valves and Intertrade Corp. Ltd.
TH 10120 Yannawa Bangkok
Tel +66 2 2400656
Fax +66 2 2401095
sunnyvalves@inet.co.th
www.sunnyvalves.co.th/
Top Advance Enterprises Ltd.
TW Jhonghe City Taipei Hsien (235)
Tel +886 2 2225 1718
Fax +886 2 8228 1975
support@auma-taiwan.com.tw
www.auma-taiwan.com.tw
Asia
AUMA Actuators (Tianjin) Co., Ltd.
CN 300457 Tianjin
Tel +86 22 6625 1310
Fax +86 22 6625 1320
mailbox@auma-china.com
www.auma-china.com
AUMA INDIA PRIVATE LIMITED
IN 560 058 Bangalore
Tel +91 80 2839 4656
Fax +91 80 2839 2809
info@auma.co.in
www.auma.co.in
AUMA JAPAN Co., Ltd.
JP 211–0016 Nakaharaku, Kawasaki-shi
Kanagawa
Tel +81 44 863 8371
Fax +81 44 863 8372
mailbox@auma.co.jp
www.auma.co.jp
AUMA ACTUATORS (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
SG 569551 Singapore
Tel +65 6 4818750
Fax +65 6 4818269
sales@auma.com.sg
www.auma.com.sg
Australia
BARRON GJM Pty. Ltd.
AU NSW 1570 Artarmon
Tel +61 294361088
Fax +61 294393413
info@barron.com.au
www.barron.com.au
79
Page 80

AUMA Riester GmbH & Co. KG
P.O.Box 1362
D 79373 Muellheim
Tel +49 7631 809 - 0
Fax +49 7631 809 - 1250
riester@auma.com
www.auma.com
For detailed information on AUMA products refer to the Internet: www.auma.com
Y004.639/003/en/4.12
 Loading...
Loading...