Page 1

Reference Guide
AudioCodes Multi-Service Business Router Series
Simple Network
Management Protocol
MSBR
Version 7.2
Page 2
Notice
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Notice
Information contained in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable at the time
of printing. However, due to ongoing product improvements and revisions, AudioCodes
cannot guarantee accuracy of printed material after the Date Published nor can it accept
responsibility for errors or omissions. Updates to this document can be downloaded from
https://www.audiocodes.com/library/technical-documents.
This document is subject to change without notice.
Date Published: September-01-2020
WEEE EU Directive
Pursuant to the WEEE EU Directive, electronic and electrical waste must not be disposed of
with unsorted waste. Please contact your local recycling authority for disposal of this product.
Customer Support
Customer technical support and services are provided by AudioCodes or by an authorized
AudioCodes Service Partner. For more information on how to buy technical support for
AudioCodes products and for contact information, please visit our website at
https://www.audiocodes.com/services-support/maintenance-and-support.
Documentation Feedback
AudioCodes continually strives to produce high quality documentation. If you have any
comments (suggestions or errors) regarding this document, please fill out the Documentation
Feedback form on our website at https://online.audiocodes.com/documentation-feedback.
Stay in the Loop with AudioCodes
Related Documentation
MSBR Series Release Notes
Mediant 500 MSBR User's Manual
Mediant 500L MSBR User's Manual
Document Name
- ii -
Page 3
Notice
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Document Name
Mediant 800 MSBR User's Manual
MSBR CLI Reference Guide
Document Revision Record
LTRT Description
52374 Initial document release for Ver. 7.2.
52378 Typos.
52380 MP-1288 added; number of trap varbinds (13);
acBoardTrapGlobalsSystemSerialNumber (new); acLicensePoolInfraAlarm
(updated); acLicensePoolApplicationAlarm (updated);
acLicensePoolOverAllocationAlarm (updated); acTrackIdStateChangeAlarm (new);
acModuleServiceAlarm; acClusterBandwidthAlarm (new);
acSBAServicesStatusAlarm (updated); acKeepAlive (updated); acProxyConnectivity
(updated)
52381 SBA-related SNMP removed (added to SBA documents).
52383 Typos; varbinds increased to 16 (new - acBoardTrapGlobalsDeviceName,
acBoardTrapGlobalsDeviceInfo, acBoardTrapGlobalsDeviceDescription);
acLicensePoolInfraAlarm (description updated); acLicensePoolApplicationAlarm
(description updated); acLicenseKeyHitlessUpgradeAlarm (new)
52384 Source names added for PM MIB names; event source added to
acPerformanceMonitoringThresholdCrossing; description updated for
entConfigChange
52385 Source name for acPMSBCIPGroupInCallEstablishedDurationTable; Media
Transcoding Cluster removed
52386 Updated descriptions: acPowerSupplyAlarm; acHwFailureAlarm;
acHASystemFaultAlarm; acHASystemSwitchOverAlarm
New alarm -acHANetworkMonitorAlarm
52389 Updated to Ver. 7.20A.200.019
New traps: acHAEthernetGroupAlarm; acHANetworkMismatchAlarm;
acNGINXConfigurationIsInvalidAlarm; acNGINXPprocessIsNotRunningAlarm
Updated traps: acHwFailureAlarm; acHASystemFaultAlarm;
acHANetworkMonitorAlarm (OID); acHTTPProxyServiceAlarm
- iii -
Page 4
Notice
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
LTRT Description
52391 Updated to Ver. 7.20A.202.112
Updated traps: AcPowerSupplyAlarm; acBoardTemperatureAlarm;
acCertificateExpiryNotification changed to acCertificateExpiryAlarm;
acLicensePoolApplicationAlarm; acIpGroupNoRouteAlarm; acIDSPolicyAlarm;
acKeepAlive
New traps: acCloudLicenseManagerAlarm; acFloatingLicenseAlarm
Performance Monitoring - updated
52392 Updated to Ver. 7.20A.204.115
acAWSSecurityRoleAlarm
52393 acDataInterfaceStatus removed; acNATTraversalAlarm removed
52394 OIDs of performance monitoring MIBs; acProxyConnectionLost updated
(severity); SNMPSysName updated
52395 Updated for Ver. 7.20A.252
Configuring performance monitoring thresholds; coder enums for
acPMChannelsPerCoderTable; new acAnalogLineLeftOffhookAlarm;
acIpGroupNoRouteAlarm (description updated); new PM MIBs
(acPMActiveContextCountTable, acPMSBCInAttemptedCallsTable,
acPMSBCOutAttemptedCallsTable, acPMSBCInEstablishedCallsTable,
acPMSBCOutEstablishedCallsTable, acPMSBCMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable,
acPMSBCInShortCallsTable, acPMSBCOutShortCallsTable,
acPMSBCInAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupInShortCallsTable, acPMSBCIPGroupOutShortCallsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupInAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCIPGroupOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCSRDInAttemptedCallsTable, acPMSBCSRDOutAttemptedCallsTable,
acPMSBCSRDInEstablishedCallsTable, acPMSBCSRDOutEstablishedCallsTable,
acPMSBCSRDMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable, acPMSBCSRDInShortCallsTable,
acPMSBCSRDOutShortCallsTable, acPMSBCSRDInAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCSRDOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCSRDInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable,
acPMSBCSRDOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable, acPMSBCInUserDefinedFailures<126>Table, acPMSBCOutUserDefinedFailures<1-26>Table,
cPMSBCSRDInUserDefinedFailures<1-26>Table,
- iv -
Page 5

Notice
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
LTRT Description
acPMSBCSRDOutUserDefinedFailures<1-26>Table,
acPMSBCIPGroupInUserDefinedFailures<1-26>Table,
acPMSBCIPGroupOutUserDefinedFailures<1-26>Table, acPMSBCInCapsTable,
acPMSBCOutCapsTable, acPMSBCSrdInCapsTable, acPMSBCSrdOutCapsTable
52396 acCDRServerAlarm alarm added
52397 Updated to Ver. 7.20A.254
AcFanTrayAlarm and acBoardTemperatureAlarm updated for Mediant 90xx; CLI
command added to acBoardOverloadAlarm
52398 Typo fixed for acPMSIPSBCEstablishedCallsTable
52399 Updated to Ver. 7.20A.256.024
New PM MIB - acPMChannelsPerCoderG711Table; AcDSPFarmsMismatchAlarm
(new); acRemoteMonitoringAlarm (new); acBoardEvResettingBoard (text
updated); acMtcmClusterHaAlarm (updated); acMtceNetworkFailureAlarm
(updated); acMtceSwUpgradeFailureAlarm (updated); acMediaClusterAlarm
(new).
52428 Updated to Ver. 7.20M1.256.029; acFloatingLicenseAlarm (new);
acCloudLicenseManagerAlarm (new); acWirelessCellularModemStatusChanged
(updated for LTE)
Miscellaneous typos; acBoardEthernetLinkAlarm (description);
acEthernetGroupAlarm (description); acFeatureKeyError (not supported note
removed).
52429 AcDChannelStatus moved to alarms and description updated
- v -
Page 6

Content
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Table of Contents
1 Introduction 1
2 SNMP Overview 2
SNMP Standards and Objects 2
SNMP Message Standard 2
SNMP MIB Objects 3
SNMP Extensibility Feature 4
Supported MIBs 4
SNMP Interface Details 8
SNMP Community Names 8
Configuring Community Strings via the Web 9
Configuring Community Strings via the ini File 9
Configuring Community Strings via SNMP 9
SNMPv3 USM Users 11
Configuring SNMPv3 Users via ini File 12
Configuring SNMPv3 Users via SNMP 13
Trusted Managers 14
Configuring Trusted Managers via ini File 14
Configuring Trusted Managers via SNMP 14
SNMP Ports 16
Multiple SNMP Trap Destinations 16
Configuring Trap Managers via Host Name 16
Configuring Trap Managers via ini File 17
Configuring SNMP EngineID 18
Configuring Trap Managers via SNMP 18
3 Carrier-Grade Alarm System 20
Active Alarm Table 20
Alarm History 20
4 Topology MIB Objects 21
Physical Entity (RFC 2737) 21
IF-MIB (RFC 2863) 21
Ethernet Interface 21
DS1 Interface 23
BRI Interface 24
ADSL/VDSL Interface 25
VLAN Interface 26
MIB-II Counters 27
5 File Management 30
Downloading a File to the Device 30
Uploadingand Deleting a File 30
6 Performance Monitoring 32
- vi -
Page 7

Content
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
SNMP Performance Monitoring MIBs 37
Performance Monitoring MIBs for IP Network Interfaces 38
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Media Realms 40
Performance Monitoring MIBs for VoIP Calls 44
Performance Monitoring MIBs for SIP Messages 49
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Calls per IP Group 50
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Gateway Application 55
IP-to-Tel and Tel-to-IP Calls 55
Trunks 60
Trunk Groups 63
Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Application 67
SBC Sessions 67
SBC Calls per IP Group 71
SBC Calls per SRD 80
SBC Calls Per Second 83
Performance Monitoring MIB for DSP Resource Utilization 85
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Data-RouterNetworking 85
7 SNMP Traps 88
Standard Traps 88
Proprietary Traps 88
Trap Varbinds 89
Customizing Trap's Enterprise OID 94
SNMP Alarms in Syslog 94
SNMP Alarms 95
Trunk Alarms 95
Trunk Near-End LOS Alarm 95
Trunk Near-End LOF Alarm 96
Trunk AIS Alarm 97
Trunk Far-End LOF Alarm 97
DS1 Line Status Alarm 98
B-Channel Alarm 99
D-Channel Status Alarm 100
NFAS Group Alarm 101
Board Alarms 102
Fatal Error Alarm 102
ConfigurationError Alarm 103
Software Reset Alarm 104
Software UpgradeAlarm 104
Call Resources Alarm 105
All SIP Proxies Connection Lost per Proxy Set Alarm 106
Controller Failure Alarm 109
Board Overload Alarm 111
Administration Status Change Alarm 112
Operational Status Change Alarm 113
- vii -
Page 8

Content
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Remote Monitoring Alarm 113
TLS Certificate Expiry Alarm 114
License Key Alarms 116
Feature Key Error Alarm 116
License Pool Application Alarm 116
License Pool Over-Allocation Alarm 118
License Pool Infrastructure Alarm 120
Cloud License Manager Alarm 121
Network Alarms 124
Clock Configuration Alarm 125
NTP Server Status Alarm 125
Ethernet Link Alarm 126
WAN Link Alarm 127
Wireless Cellular Modem Alarm 128
LDAP Lost Connection Alarm 129
OCSP Server Status Alarm 129
Track ID Alarm 130
Active Alarm Table Alarm 131
Analog Port Alarms 132
Analog Port SPI Out-of-Service Alarm 132
Analog Port High Temperature Alarm 132
Analog Port Ground Fault Out-of-Service Alarm 133
Analog LineLeft Off-hook Alarm 134
Media Alarms 135
Media Process Overload Alarm 135
Media Realm Bandwidth Threshold Alarm 135
Call Quality Alarms 136
Answer-Seizure Ratio Threshold Alarm 136
Average Call Duration Threshold Alarm 137
Network Effectiveness Ratio Threshold Alarm 138
No Route to IP Group Alarm 139
Network Quality Monitoring 140
NQM Connectivity Alarm 140
NQM High RTT Alarm 141
NQM High Jitter Alarm 142
NQM High Packet Loss Alarm 143
NQM Low Conversational MOS Alarm 143
NQM Low Listening MOS Alarm 145
Intrusion Detection Alarms 146
IDS Policy Alarm 146
SNMP Event Traps (Notifications) 147
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) 147
IDS Threshold Cross Notification Trap 147
IDS Blacklist Notification Trap 148
Web User Access Denied due to Inactivity Trap 149
- viii -
Page 9

Content
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Web User Activity Log Trap 150
Power-Over-Ethernet Status Trap 150
Keep-Alive Trap 151
Performance Monitoring Threshold-Crossing Trap 152
HTTP Download Result Trap 153
Wireless Cellular Modem Status Changed Trap 153
Dial Plan File Replaced Trap 154
SecureShell (SSH) Connection Status Trap 154
SIP Proxy Connection Lost per Proxy Set Trap 155
Cold Start Trap 156
Authentication Failure Trap 157
Board Initialization Completed Trap 157
ConfigurationChange Trap 158
Link Up Trap 158
Link Down Trap 158
Enhanced BIT Status Trap 158
8 Advanced SNMP Features 160
SNMP NAT Traversal 160
Systems 160
SNMP Administrative State Control 161
9 Getting Started with SNMP 162
Basic SNMP Configuration Setup 162
Configuring SNMP Port 162
Configuring Trap Managers (Trap Destination) 162
Configuring Trap Destination Port 164
Configuring Trusted Managers 164
Getting Acquainted with AudioCodes MIBs 166
Traps and Alarms 168
Device Configuration 168
Carrier GradeAlarm (CGA) 169
- ix -
Page 10
CHAPTER1 Introduction
1 Introduction
This document provides you with supplementary information on Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) based management for your AudioCodes device. This
information complements the information provided by the device's User's Manual, and
includes SNMP configuration, SNMP traps (events and alarms), and SNMP performance
monitoring MIBs.
● The SNMP MIB manual is supplied in the Software Release Package delivered
with the device.
● For large deployments (for example, multiple devices in globally distributed
enterprise offices) that need to be managed by central personnel, it is
recommended to use AudioCodes One Voice Operations Center (OVOC). OVOC
is not included in the device's supplied package. Contact AudioCodes formore
information onits OVOC solution for large VoIP deployments.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
- 1 -
Page 11

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
2 SNMP Overview
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standards-based network control protocol
for managing elements in a network. The SNMP Manager, usually implemented by a thirdparty Network Management System (NMS) or AudioCodes One Voice Operations Center
(OVOC), connects to an SNMP Agent (embedded on a remote Network Element (NE) to
perform network element Operation, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning (OAMP).
Both the SNMP Manager and the NE refer to the same database to retrieve information or
configure parameters. This database is referred to as the Management Information Base
(MIB), and is a set of statistical and control values. Apart from the standard MIBs documented
in IETF RFCs, SNMP additionally enables the use of proprietary MIBs, containing non-standard
information set (specific functionality provided by the Network Element).
Directives, issued by the SNMP Manager to an SNMP Agent, consist of the identifiers of SNMP
variables (referred to as MIB object identifiers or MIB variables) along with instructions to
either get the value for that identifier, or set the identifier to a new value (configuration). The
SNMP Agent can also send unsolicited events towards an EMS, called SNMP traps.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The definitions of MIB variables supported by a particular agent are incorporated in descriptor
files, written in Abstract Syntax Notation (ASN.1) format, made available to EMS client
programs so that they can become aware of MIB variables and their usage.
The device contains an embedded SNMP Agent supporting both general network MIBs (such
as the IP MIB), VoP-specific MIBs (such as RTP) and proprietary MIBs (acGateway, acAlarm,
acMedia, acControl, and acAnalog MIBs) enabling a deeper probe into the interworking of the
device. All supported MIB files are supplied to customers as part of the release.
SNMP Standards and Objects
This section discusses the SNMP standards and SNMP objects.
SNMP Message Standard
Four types of SNMP messages are defined:
■ Get: A request that returns the value of a named object.
■ Get-Next: A request that returns the next name (and value) of the "next" object supported
by a network device given a valid SNMP name.
■ Set: A request that sets a named object to a specific value.
■ Trap: A message generated asynchronously by network devices. It notifies the network
manager of a problem apart from the polling of the device.
Each of these message types fulfills a particular requirement of network managers:
■ Get Request: Specific values can be fetched via the "get" request to determine the
performance and state of the device. Typically, many different values and parameters can
- 2 -
Page 12

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
be determined via SNMP without the overhead associated with logging into the device, or
establishing a TCP connection with the device.
■ Get Next Request: Enables the SNMP standard network managers to "walk" through all
SNMP values of a device (via the "get-next" request) to determine all names and values
that a device supports.
■ Get-Bulk: Extends the functionality of GETNEXT by allowing multiple values to be returned
for selected items in the request. This is accomplished by beginning with the first SNMP
object to be fetched, fetching the next name with a "get-next", and repeating this
operation.
■ Set Request: The SNMP standard provides a action method for a device (via the "set"
request) to accomplish activities such as disabling interfaces, disconnecting users, clearing
registers, etc. This provides a way of configuring and controlling network devices via
SNMP.
■ Trap Message: The SNMP standard furnishes a mechanism for a device to "reach out" to a
network manager on their own (via the “trap" message) to notify or alert the manager of a
problem with the device. This typically requires each device on the network to be
configured to issue SNMP traps to one or more network devices that are awaiting these
traps.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The above message types are all encoded into messages referred to as "Protocol Data Units"
(PDUs) that are interchanged between SNMP devices.
SNMP MIB Objects
The SNMP MIB is arranged in a tree-structure, similar to a disk directory structure of files. The
top-level SNMP branch begins with the ISO "internet" directory, which contains four main
SNMP branches:
■ "mgmt": Contains the standard SNMP objects usually supported (at least in part) by all
network devices.
■ “private": Contains those "extended" SNMP objects defined by network equipment
vendors.
■ "experimental" and "directory": Also defined within the "internet" root directory, are
usually devoid of any meaningful data or objects.
The "tree" structure described above is an integral part of the SNMP standard, though the
most pertinent parts of the tree are the "leaf" objects of the tree that provide actual
management data regarding the device. Generally, SNMP leaf objects can be partitioned into
two similar but slightly different types that reflect the organization of the tree structure:
■ Discrete MIB Objects: Contain one precise piece of management data. These objects are
often distinguished from "Table" items (below) by adding a “.0" (dot-zero) extension to
their names. The operator must merely know the name of the object and no other
information.
- 3 -
Page 13

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
■ Table MIB Objects: Contain multiple pieces of management data. These objects are
distinguished from "Discrete" items (above) by requiring a "." (dot) extension to their
names that uniquely distinguishes the particular value being referenced. The "." (dot)
extension is the "instance" number of an SNMP object. For "Discrete" objects, this
instance number is zero. For "Table" objects, this instance number is the index into the
SNMP table. SNMP tables are special types of SNMP objects, which allow parallel arrays of
information to be supported. Tables are distinguished from scalar objects, such that
tables can grow without bounds. For example, SNMP defines the "ifDescr" object (as a
standard SNMP object) that indicates the text description of each interface supported by a
particular device. Since network devices can be configured with more than one interface,
this object can only be represented as an array.
By convention, SNMP objects are always grouped in an "Entry" directory, within an object with
a "Table" suffix. (The "ifDescr" object described above resides in the "ifEntry" directory
contained in the "ifTable" directory).
SNMP Extensibility Feature
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
One of the principal components of an SNMP manager is a MIB Compiler, which allows new
MIB objects to be added to the management system. When a MIB is compiled into an SNMP
manager, the manager is made "aware" of new objects that are supported by agents on the
network. The concept is similar to adding a new schema to a database.
Typically, when a MIB is compiled into the system, the manager creates new folders or
directories that correspond to the objects. These folders or directories can typically be viewed
with a "MIB Browser", which is a traditional SNMP management tool incorporated into
virtually all network management systems.
The act of compiling the MIB allows the manager to know about the special objects supported
by the agent and access these objects as part of the standard object set.
Supported MIBs
The device contains an embedded SNMP agent supporting the MIBs listed below. A description
in HTML format for all supported MIBs can be found in the MIBs directory in the release
package.
■ Standard MIB (MIB-2): The various SNMP values in the standard MIB are defined in RFC
1213. The standard MIB includes various objects to measure and monitor IP activity, TCP
activity, UDP activity, IP routes, TCP connections, interfaces, and general system
description.
● The standard icmpStatsTable and icmpMsgStatsTable under MIB-2 support ICMP
statistics for both IPv4 and IPv6.
● The inetCidrRouteTable (from the standard IP-FORWARD-MIB) supports both IPv4 and
IPv6.
- 4 -
Page 14

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
■ System MIB (under MIB-2): Standard system group: sysDescr, sysObjectID, sysUpTime,
sysContact, sysName, sysLocation, and sysServices. You can replace the value of
sysObjectID.0 with a variable value using the ini file parameter SNMPSysOid. This
parameter is polled during startup and overwrites the standard sysObjectID.
SNMPSysName is an administratively assigned name for this managed node. By
convention, this is the node's fully-qualified domain name (FQDN). If the name is
unknown, the value is the zero-length string. If the [HostName] ini file parameter is
configured, its' value overwrites the value of SNMPSysName.
■ Host Resources MIB (RFC 2790): The Host Resources MIB is used for managing host
systems. The term host is any computer that communicates with other similar computers
connected to the Internet and that is directly used by one or more human beings. The
following are the Host Resources MIB objects:
● hrSystem group
● hrStorage group (basic only)
● hrDevice group (CPU, RAM, Flash - basic only)
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● hrSWRunPerf (basic only)
● hrSWInstalled (OS only)
The Host Resources MIB is applicable only to data-routing functionality.
■ RTP MIB: The MIB is supported according to RFC 2959. It contains objects relevant to the
RTP streams generated and terminated by the device and to the RTCP information related
to these streams.
The inverse tables arenot supported.
■ Notification Log MIB: Standard MIB (RFC 3014 - iso.org.dod.internet.mgmt.mib-2)
supported for implementation of Carrier Grade Alarms.
■ Alarm MIB: IETF MIB (RFC 3877) Supported as part of the implementation of Carrier Grade
Alarms.
■ SNMP Target MIB: (RFC 2273) Allows for configuration of trap destinations and trusted
managers.
■ SNMP MIB: (RFC 3418) Allows support for the coldStart and authenticationFailure traps.
■ SNMP Framework MIB: (RFC 3411).
■ SNMP Usm MIB: (RFC 3414) Implements the user-based Security Model.
■ SNMP Vacm MIB: (RFC 3415) Implements the view-based Access Control Model.
■ SNMP Community MIB: (RFC 3584) Implements community string management.
■ ipForward MIB: (RFC 2096) Fully supported.
- 5 -
Page 15

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
■ RTCP-XR: (RFC) implements the following partial support:
● The rtcpXrCallQualityTable is fully supported.
● In the rtcpXrHistoryTable, support of the RCQ objects is provided only with no more
than 3 intervals, 15 minutes long each.
● Supports the rtcpXrVoipThresholdViolation trap.
■ ds1 MIB: supports the following:
● dsx1ConfigTable: partially supports the following objects with SET and GET applied:
◆ dsx1LineCoding
◆ dsx1LoopbackConfig
◆ dsx1LineStatusChangeTrapEnable
◆ dsx1CircuitIdentifier
All other objects in this table support GET only.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● dsx1CurrentTable
● dsx1IntervalTable
● dsx1TotalTable
● dsx1LineStatusChange trap
■ acPSTN MIB:
● acSonetSDHTable: currently has one entry (acSonetSDHFbrGrpMappingType) for
selecting a low path mapping type. Relevant only for PSTN applications. (Refer to the
MIB for more details.)
In addition to the standard MIBs, the complete product series contains proprietary MIBs:
■ AC-TYPES MIB: lists the known types defined by the complete product series. This is
referred to by the sysObjectID object in the MIB-II.
■ AcBoard MIB: includes the acTrap group.
Each proprietary MIB contains a Configuration subtree for configuring the related parameters.
In some, there also are Status and Action subtrees.
■ AcAnalog MIB
■ acControl MIB
■ acMedia MIB
■ acSystem MIB
■ acSysInterfaceStatusTable: supports the networking multiple interfaces feature status.
This table reflects all the device's active interfaces. The lines indices consist of both the
Entry Index and the Type Index. The table contains the following columns:
- 6 -
Page 16

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
● Entry Index - related Interface index in the interface configuration table (if the table is
empty,i.e., there is only single IP address, the index appears with 0)
● Type Index - 1 for IP Address and 2 for IPv6 Link-Local Address
● Application Types - type assigned to the interface
● Status Mode - interface configuration mode
● IP Address - IP address (either IPv4 or IPv6) for this interface
● Prefix Length - number of ‘1’ bits in this interface’s net mask
● Gateway - default gateway
● Vlan ID - VLAN ID of this interface
● Name - interface’s name
● Primary DNS Server IP Address - IP address of primary DNS server for this interface
● Secondary DNS Server IP Address - IP address of secondary DNS server for this
interface
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
■ acSysModuleTable
■ acPSTN MIB
■ acGateway MIB: This proprietary MIB contains objects related to configuration of the SIP
device. This MIB complements the other proprietary MIBs. The acGateway MIB includes
the following groups:
● Common: parameters common to both SIP and H.323.
● SIP: SIP only parameters.
■ AcAlarm: This is a proprietary carrier-grade alarm MIB. It is a simpler implementation of
the notificationLogMIB and the IETF suggested alarmMIB (both supported).
The acAlarm MIB has the following groups:
● ActiveAlarm: straight forward (single indexed) table listing all currently active Alarms
together with their bindings (the Alarm bindings are defined in acAlarm.
acAlarmVarbinds and also in acBoard.acTrap. acBoardTrapDefinitions. oid_1_3_6_1_
4_1_5003_9_10_1_21_2_0).
● acAlarmHistory: straight forward (single indexed) table listing all recently sent Alarms
together with their bindings (the Alarm bindings are defined in acAlarm.
acAlarmVarbinds and also in acBoard.acTrap. acBoardTrapDefinitions. oid_1_3_6_1_
4_1_5003_9_10_1_21_2_0).
The table size can be altered by one of the following:
● notificationLogMIB.notificationLogMIBObjects.nlmConfig.nlmConfigGlobalEntryLimit
● noti-
- 7 -
Page 17

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
ficationLogMIB.notificationLogMIBObjects.nlmConfig.nlmConfigLogTable.nlmConfigLogEntry.nlmConfigLogEntryLimit.
The table size (i.e., number of contained alarms) can be any value between 10 and 1,000
(default is 500)
● A detailed explanation of each parameter can beviewedin theMIB Description
● A detailed description in HTML format of all MIBs can be found in the MIBs
● Not all groups in theMIB are implemented.
● MIB Objects that are marked as 'obsolete' are not implemented.
● When a parameter is Set to a new value via SNMP, the change may affect device
● The current (updated) device configurationparameters are configuredon the device
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
field.
directory (included in the Release package).
functionality immediately or may requirethat the device be soft reset for the
change to take effect. This depends on the parameter type.
provided the user doesn't load an ini file to the device after reset. Loading an ini file
after reset overrides the updated parameters.
SNMP Interface Details
This subsection describes details of the SNMP interface needed when developing an Element
Management System (EMS) for any AudioCodes devices, or to manage a device with a MIB
browser.
There are several alternatives for SNMP security:
■ SNMPv2c community strings
■ SNMPv3 User-based Security Model (USM) users
■ SNMP encoded over IPSec
■ Various combinations of the above
Currently, both SNMP and ini file commands and downloads are not encrypted. For ini file
encoding, refer to the device's User's Manual.
SNMP Community Names
By default, the device uses a single, read-only community string of "public" and a single readwrite community string of "private". Up to five read-only community strings and up to five
- 8 -
Page 18
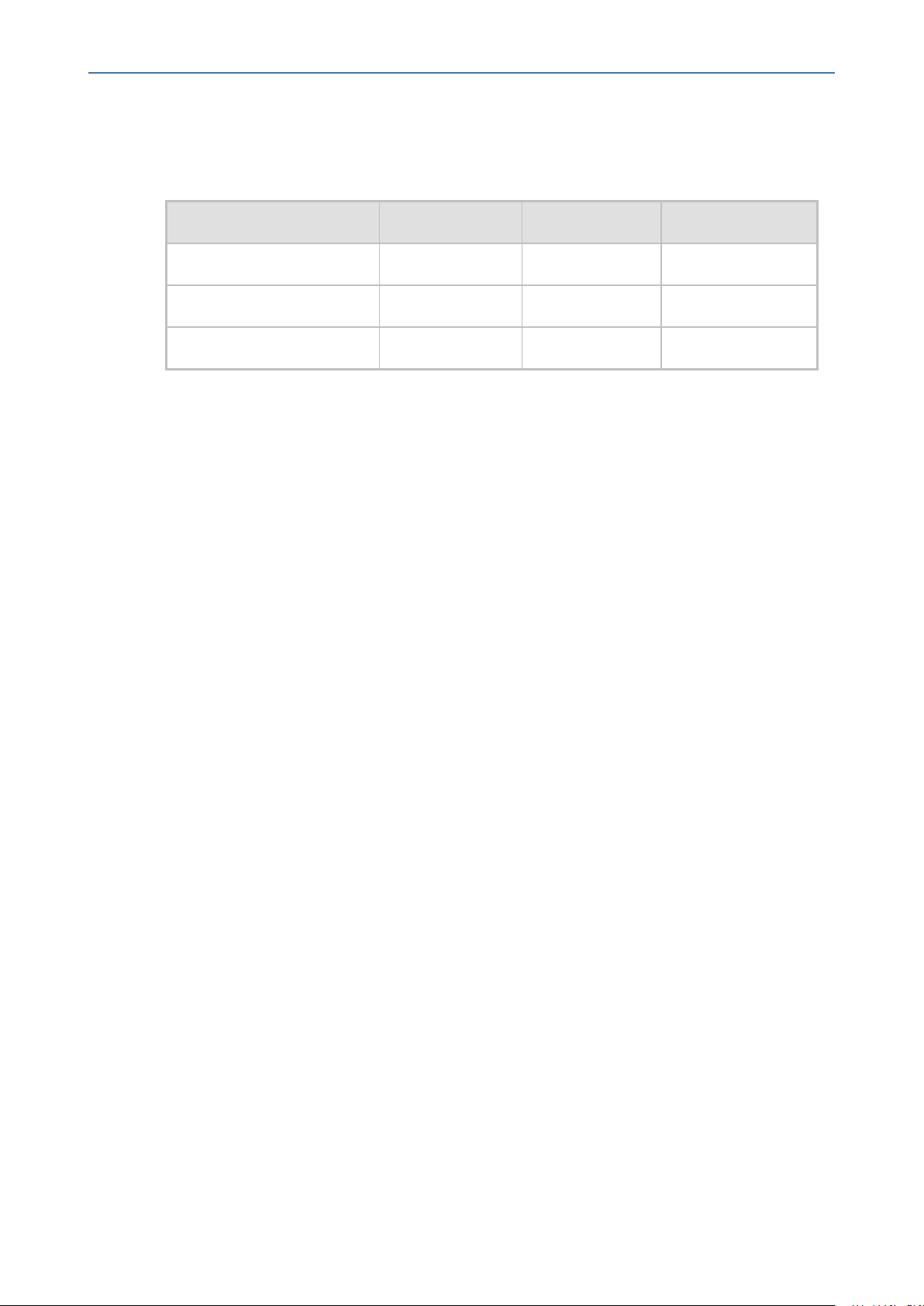
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
read-write community strings, and a single trap community string can be configured. Each
community string must be associated with one of the following predefined groups:
ReadGroup Yes No Yes
ReadWriteGroup Yes Yes Yes
TrapGroup No No Yes
Configuring Community Strings via the Web
For detailed information on configuring community strings through the Web interface, refer to
the device's User's Manual.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
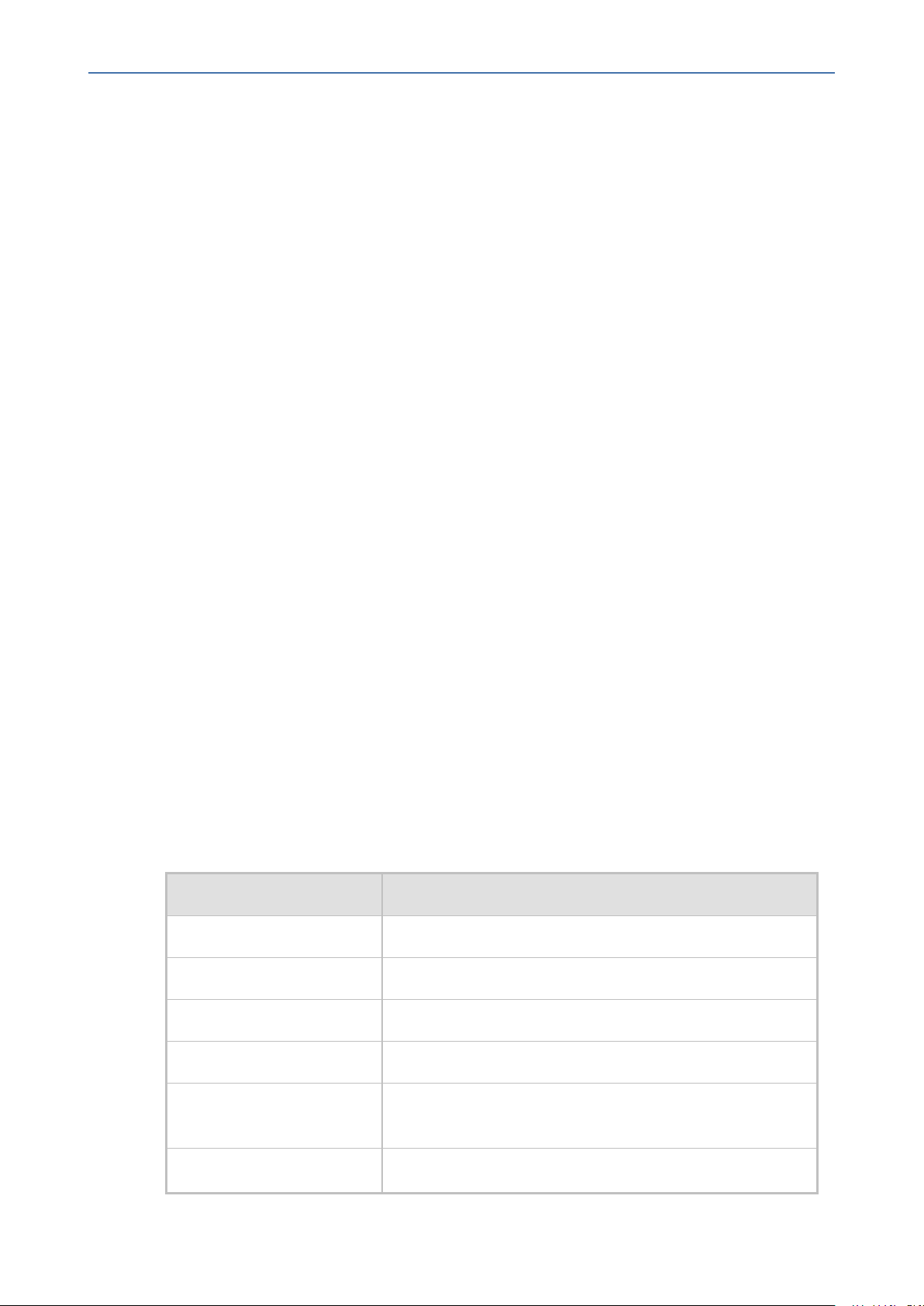
Table 2-1: SNMP Predefined Groups
Group Get Access Set Access Sends Traps
Configuring Community Strings via the ini File
The following ini file parameters are used to configure community strings:
■ SNMPREADONLYCOMMUNITYSTRING_<x> = '#######'
■ SNMPREADWRITECOMMUNITYSTRING_<x> = '#######'
Where <x> is a number from 0 through 4. Note that the '#' character represents any
alphanumeric character. The maximum length of the string is 19 characters that can include
only the following:
■ Upper- and lower-case letters (a to z, and A to Z)
■ Numbers (0 to 9)
■ Hyphen (-)
■ Underline (_)
Configuring Community Strings via SNMP
To configure community strings, the EMS must use the standard snmpCommunityMIB. To
configure the trap community string, the EMS must also use the snmpTargetMIB.
➢ To add a read-only v2user community string:
1. Add a new row to the snmpCommunityTable with CommunityName v2user.
2. Add a row to the vacmSecurityToGroupTable for SecurityName v2user, GroupName
ReadGroup and SecurityModel snmpv2c.
- 9 -
Page 19
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
➢ To delete the read-only v2user community string:
1. If v2user is being used as the trap community string, follow the procedure for changing
the trap community string. (See below.)
2. Delete the snmpCommunityTable row with CommunityName v2user.
3. Delete the vacmSecurityToGroupTable row for SecurityName v2user, GroupName
ReadGroup and SecurityModel snmpv2c.
➢ To add a read-write v2admin community string:
1. Add a new row to the snmpCommunityTable with CommunityName v2admin.
2. Add a row to the vacmSecurityToGroupTable for SecurityName v2admin, GroupName
ReadWriteGroup and SecurityModel snmpv2c.
➢ To delete the read-write v2admin community string:
1. If v2admin is being used as the trap community string, follow the procedure for changing
the trap community string. (See below.)
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
2. Delete the snmpCommunityTable row with a CommunityName of v2admin and
GroupName of ReadWriteGroup.
➢ To change the only read-write community string from v2admin to v2mgr:
1. Follow the procedure above to add a read-write community string to a row for v2mgr.
2. Set up the EM such that subsequent set requests use the new community string, v2mgr.
3. If v2admin is being used as the trap community string, follow the procedure to change the
trap community string. (See below.)
4. Follow the procedure above to delete a read-write community name in the row for
v2admin.
The following procedure assumes that a row already exists in the snmpCommunityTable for
the new trap community string. The trap community string can be part of the TrapGroup,
ReadGroup, or ReadWriteGroup. If the trap community string is used solely for sending traps
(recommended), then it should be made part of the TrapGroup.
➢ To change the trap community string:
1. Add a row to the vacmSecurityToGroupTable with these values: SecurityModel=2,
SecurityName=the new trap community string, GroupName=TrapGroup, ReadGroup or
ReadWriteGroup. The SecurityModel and SecurityName objects are row indices.
You must add GroupName and RowStatus on the same set.
2. Modify the SecurityName field in the appropriate row of the snmpTargetParamsTable.
- 10 -
Page 20
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
3. Remove the row from the vacmSecurityToGroupTable with SecurityName=the old trap
community string.
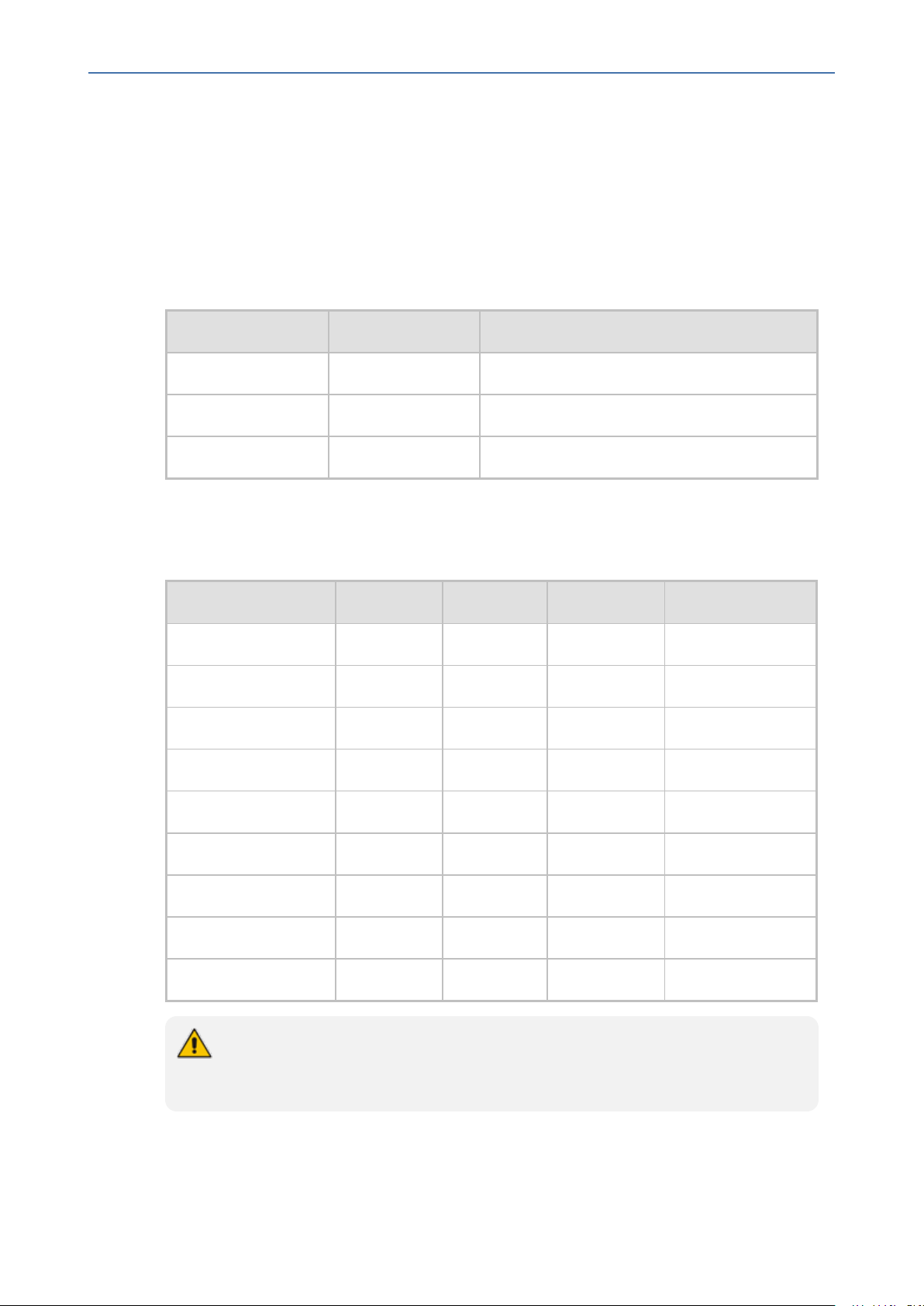
SNMPv3 USM Users
You can configure up to 10 User-based Security Model (USM) users (referred to as SNMPv3
user). Each SNMPv3 user can be configured to one of the following security levels:
Security Levels Authentication Privacy
noAuthNoPriv(1) none none
authNoPriv(2) MD5 or SHA-1 none
authPriv(3) MD5 or SHA-1 DES, 3DES, AES128, AES192, or AES256
Each SNMPv3 user must be associated with one of the predefined groups listed in the following
table:
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Table 2-2: SNMPv3 Security Levels
Table 2-3: SNMPv3 Predefined Groups
Group Get Access Set Access Sends Traps Security Level
ReadGroup1 Yes No Yes noAuthNoPriv(1)
ReadWriteGroup1 Yes Yes Yes noAuthNoPriv(1)
TrapGroup1 No No Yes noAuthNoPriv(1)
ReadGroup2 Yes No Yes authNoPriv(2)
ReadWriteGroup2 Yes Yes Yes authNoPriv(2)
TrapGroup2 No No Yes authNoPriv(2)
ReadGroup3 Yes No Yes authPriv(3)
ReadWriteGroup3 Yes Yes Yes authPriv(3)
TrapGroup3 No No Yes authPriv(3)
The first (initial) SNMPv3 user can only be configured through a management interface
other than SNMP (i.e., Web interface, configuration ini file, or CLI). Once configured,
additional users can be configuredthrough the SNMP interface as well.
- 11 -
Page 21

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
Configuring SNMPv3 Users via ini File
Use the [SNMPUsers] ini file table parameter to add, modify, and delete SNMPv3 users. The
[SNMPUsers] ini table is a hidden parameter. Therefore, when you load the ini file to the device
using the Web interface, the table is not included in the generated file.
Parameter Description Default
Row number Table index. Its valid range is 0 to 9. N/A
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Table 2-4: SNMPv3 Table Columns Description
SNMPUsers_Username Name of the v3 user. Must be unique. The maximum
N/A
length is 32 characters.
SNMPUsers_
AuthProtocol
SNMPUsers_
PrivProtocol
Authentication protocol to be used for this user.
Possible values are 0 (none), 1 (MD5), 2 (SHA-1)
Privacy protocol to be used for this user. Possible
values are 0 (none), 1 (DES), 2 (3DES), 3 (AES128), 4
(AES192), 5 (AES256)
SNMPUsers_AuthKey Authentication key. ""
SNMPUsers_PrivKey Privacy key. ""
SNMPUsers_Group The group that this user is associated with. Possible
values are 0 (read-only group), 1 (read-write group),
and 2 (trap group). The actual group will be
ReadGroup<sl>, ReadWriteGroup<sl> or
TrapGroup<sl> where <sl> is the SecurityLevel
(1=noAuthNoPriv, 2=authNoPriv, 3=authPriv)
0
0
0
Keys can be entered in the form of a text password or in the form of a localized key in hex
format. If using a text password, then it should be at least 8 characters in length. Below is an
example showing the format of a localized key:
26:60:d8:7d:0d:4a:d6:8c:02:73:dd:22:96:a2:69:df
The following sample configuration creates three SNMPv3 USM users.
[ SNMPUsers ]
FORMAT SNMPUsers_Index = SNMPUsers_Username, SNMPUsers_
AuthProtocol, SNMPUsers_PrivProtocol, SNMPUsers_AuthKey, SNMPUsers_
PrivKey, SNMPUsers_Group;
SNMPUsers 0 = v3user, 0, 0, -, -, 0;
SNMPUsers 1 = v3admin1, 1, 0, myauthkey, -, 1;
- 12 -
Page 22

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
SNMPUsers 2 = v3admin2, 2, 1, myauthkey, myprivkey, 1;
[ \SNMPUsers ]
The example above creates three SNMPv3 users:
■ The user v3user is set up for a security level of noAuthNoPriv(1) and is associated with
ReadGroup1.
■ The user v3admin1 is setup for a security level of authNoPriv(2), with authentication
protocol MD5. The authentication text password is “myauthkey” and the user is
associated with ReadWriteGroup2.
■ The user v3admin2 is setup for a security level of authPriv(3), with authentication protocol
SHA-1 and privacy protocol DES. The authentication text password is “myauthkey”, the
privacy text password is “myprivkey”, and the user is associated with ReadWriteGroup3.
Configuring SNMPv3 Users via SNMP
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
To configure SNMPv3 users, the EMS must use the standard snmpUsmMIB and the
snmpVacmMIB.
➢ To add a read-only, noAuthNoPriv SNMPv3 user, v3user:
1. Clone the row with the same security level. After the clone step, the status of the row will
be notReady(3).
2. Activate the row. That is, set the row status to active(1).
3. Add a row to the vacmSecurityToGroupTable for SecurityName v3user, GroupName
ReadGroup1 and SecurityModel usm(3).
A row with the same security level (noAuthNoPriv) must already exist in the
usmUserTable. (see the usmUserTable for details).
➢ To delete the read-only, noAuthNoPriv SNMPv3 user, v3user:
1. If v3user is associated with a trap destination, follow the procedure for associating a
different user to that trap destination. (See below.)
2. Delete the vacmSecurityToGroupTable row for SecurityName v3user, GroupName
ReadGroup1 and SecurityModel usm.
3. Delete the row in the usmUserTable for v3user.
➢ To add a read-write, authPriv SNMPv3 user, v3admin1:
1. Clone the row with the same security level.
2. Change the authentication key and privacy key.
3. Activate the row. That is, set the row status to active(1).
- 13 -
Page 23
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
4. Add a row to the vacmSecurityToGroupTable for SecurityName v3admin1, GroupName
ReadWriteGroup3 and SecurityModel usm(3).
A row with the same security level (authPriv) must already exist in the usmUserTable
(see the usmUserTable fordetails).
➢ To delete the read-write, authPriv SNMPv3 user, v3admin1:
1. If v3admin1 is associated with a trap destination, follow the procedure for associating a
different user to that trap destination. (See below.)
2. Delete the vacmSecurityToGroupTable row for SecurityName v3admin1, GroupName
ReadWriteGroup1 and SecurityModel usm.
3. Delete the row in the usmUserTable for v3admin1.
Trusted Managers
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
By default, the SNMP agent accepts Get and Set requests from any IP address, as long as the
correct community string is used in the request. Security can be enhanced implementing
Trusted Managers. A Trusted Manager is an IP address from which the SNMP agent accepts
and processes Get and Set requests. An element management can be used to configure up to
five Trusted Managers.
The concept of Trusted Managers is considered to be a weak form of security and therefore is
not a required part of SNMPv3 security, which uses authentication and privacy. Trusted
Managers for the devices' SNMP agent are applicable only for SNMPv2c users. An exception to
this is when the community string is not the default string (‘public’/’private’), at which time
Trusted Managers are applicable for SNMPV2c users alongside SNMPv3 users.
If Trusted Managers are defined, then all community strings work from all Trusted
Managers. In other words, there is no way to associate a community string with
specific Trusted Managers.
Configuring Trusted Managers via ini File
To set the Trusted Managers table from start up, write the following in the ini file:
SNMPTRUSTEDMGR_X = D.D.D.D
Where X is any integer between 0 and 4 (0 sets the first table entry, 1 sets the second and so
on), and D is an integer between 0 and 255.
Configuring Trusted Managers via SNMP
To configure Trusted Managers, the Element Management System (EMS) must use the SNMPCOMMUNITY-MIB and snmpCommunityMIB and the snmpTargetMIB.
- 14 -
Page 24

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
The following procedure assumes the following: at least one configured read-write community;
currently no Trusted Managers; TransportTag for columns for all snmpCommunityTable rows
are currently empty.
➢ To add the first Trusted Manager:
1. Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrTable with these values: Name=mgr0, TagList=MGR,
Params=v2cparams.
2. Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrExtTable table with these values: Name=mgr0, snm-
pTargetAddrTMask=255.255.255.255:0. The agent does not allow creation of a row in this
table unless a corresponding row exists in the snmpTargetAddrTable.
3. Set the value of the TransportTag field on each non-TrapGroup row in the
snmpCommunityTable to MGR.
The following procedure assumes the following: at least one configured read-write community;
currently one or more Trusted Managers; TransportTag for columns for all rows in the
snmpCommunityTable are currently set to MGR. This procedure must be done from one of
the existing Trusted Managers.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
➢ To add a subsequent Trusted Manager:
1. Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrTable with these values: Name=mgrN, TagList=MGR,
Params=v2cparams, where N is an unused number between 0 and 4.
2. Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrExtTable table with these values: Name=mgrN, snm-
pTargetAddrTMask=255.255.255.255:0.
An alternative to the above procedure is to set the snmpTargetAddrTMask column while you
are creating other rows in the table.
The following procedure assumes the following: at least one configured read-write community;
currently two or more Trusted Managers; taglist for columns for all rows in the
snmpCommunityTable are currently set to MGR. This procedure must be done from one of
the existing trusted managers, but not the one that is being deleted.
➢ To delete a Trusted Manager (not the last one):
■ Remove the appropriate row from the snmpTargetAddrTable.
The change takes effect immediately. The deleted trusted manager cannot access the device.
The agent automatically removes the row in the snmpTargetAddrExtTable.
The following procedure assumes the following: at least one configured read-write community;
currently only one Trusted Manager; taglist for columns for all rows in the
snmpCommunityTable are currently set to MGR. This procedure must be done from the final
Trusted Manager.
- 15 -
Page 25
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
➢ To delete the last Trusted Manager:
1. Set the value of the TransportTag field on each row in the snmpCommunityTable to the
empty string.
2. Remove the appropriate row from the snmpTargetAddrTable.
The change takes effect immediately. All managers can now access the device. The agent
automatically removes the row in the snmpTargetAddrExtTable.
SNMP Ports
The SNMP Request Port is 161 and the SNMP Trap Port is 162. These port numbers for SNMP
requests and responses can be changed, by using the [SNMPPort] ini file parameter. The valid
value is any valid UDP port number. The default is 161 (recommended).
Multiple SNMP Trap Destinations
An agent can send traps to up to five managers. For each manager you need to define the
manager IP address and trap receiving port along with enabling the sending to that manager.
You can also associate a trap destination with a specific SNMPv3 USM user. Traps are sent to
this trap destination using the SNMPv3 format and the authentication and privacy protocol
configured for that user.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
To configure the Trap Managers table, use one of the following methods:
■ Web interface (refer to the device's User's Manual)
■ ini file (see Configuring Trap Managers via ini File on the next page)
■ SNMP (see Configuring Trap Managers via SNMP on page18)
Configuring Trap Managers via Host Name
One of the five available SNMP managers can be defined using the manager's host name (i.e.,
FQDN). This can be configured using the ini file parameter [SNMPTrapManagerHostName].
When this parameter value is defined for this trap, the device at start up tries to resolve the
host name. Once the name is resolved (i.e., the IP address is found), the resolved IP address
replaces the last entry of the trap manager table (defined by the parameter
[SNMPManagerTableIP_x]) and the last trap manager entry of snmpTargetAddrTable in the
snmpTargetMIB. The port is 162 (unless specified otherwise). The row is marked as 'used' and
the sending is 'enabled'.
When using 'host name' resolution, any changes made by the user to this row in either MIBs
are overwritten by the device when a resolving is redone (once an hour).
Some traps may be lost until the name resolving is complete.
- 16 -
Page 26

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
Configuring Trap Managers via ini File
In the ini file, the following parameters can be set to enable or disable the sending of SNMP
traps. Multiple trap destinations can be supported on the device by setting multiple trap
destinations in the ini file.
■ SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_<x>: indicates whether or not traps are to be sent to
the specified SNMP trap manager. A value of ‘1’ means that it is enabled, while a value of
‘0’ means disabled. The <x> represents a number 0, 1, or 2, which is the array element
index. Currently, up to five SNMP trap managers is supported.
■ SNMPManagerTrapUser_<x>: indicates to send an SNMPv2 trap using the trap user
community string configured with the SNMPTrapCommunityString parameter. You may
instead specify an SNMPv3 user name.
The following is an example of entries in the ini file regarding SNMP. The device can be
configured to send to multiple trap destinations.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
; SNMP trap destinations
; The device maintains a table of trap destinations containing 5
; rows. The rows are numbered 0..4. Each block of 5 items below
; applies to a row in the table.
;
; To configure one of the rows, uncomment all 5 lines in that
; block. Supply an IP address and if necessary, change the port
; number.
;
; To delete a trap destination, set ISUSED to 0.
;
;SNMPManagerTableIP_0=
;SNMPManagerTrapPort_0=162
;SNMPManagerIsUsed_0=1
;SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_0=1
;SNMPManagerTrapUser_0=’’
;
;SNMPManagerTableIP_1=
;SNMPManagerTrapPort_1=162
;SNMPManagerIsUsed_1=1
;SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_1=1
;SNMPMANAGERTRAPUSER_1=’’
;
;SNMPManagerTableIP_2=
;SNMPManagerTrapPort_2=162
;SNMPManagerIsUsed_2=1
;SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_2=1
;SNMPManagerTrapUser_2=’’
- 17 -
Page 27
CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
;
;SNMPManagerTableIP_3=
;SNMPManagerTrapPort_3=162
;SNMPManagerIsUsed_3=1
;SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_3=1
;SNMPManagerTrapUser_3=’’
;
;SNMPMANAGERTABLEIP_4=
;SNMPManagerTrapPort_4=162
;SNMPManagerIsUsed_4=1
;SNMPManagerTrapSendingEnable_4=1
;SNMPManagerTrapUser_4=’’
The ‘trap manager host name’ is configured via SNMPTrapManagerHostName. For example:
;SNMPTrapManagerHostName = 'myMananger.corp.MyCompany.com'
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The same information that is configurable in the ini file can also be configured via the
acBoardMIB.
Configuring SNMP Engine ID
The [SNMPEngineIDString] ini file parameter configures the SNMP engine ID. The ID can be a
string of up to 36 characters. Once defined, the device must be reset for the parameter to take
effect.
The default value is 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 (12 Hex characters). The provided key
must be set with 12 Hex values delimited by ‘:’.
If the supplied key does not pass validation of the 12 Hex values input or it is set with the
default value, the engine ID is then generated, according to RFC 3411.
Before setting this parameter, all SNMPv3 users must be deleted, otherwise the configuration
is ignored.
Configuring Trap Managers via SNMP
The snmpTargetMIB interface is available for configuring trap managers.
➢ To add an SNMPv2 trap destination:
■ Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrTable with these values: Name=trapN, TagList=AC_TRAP,
Params=v2cparams, where N is an unused number between 0 and 4
All changes to the trap destination configuration take effect immediately.
- 18 -
Page 28

CHAPTER2 SNMP Overview
➢ To add an SNMPv3 trap destination:
1. Add a row to the snmpTargetAddrTable with these values: Name=trapN, TagList=AC_TRAP,
Params=usm<user>, where N is an unused number between 0 and 4, and <user> is the
name of the SNMPv3 that this user is associated with.
2. If a row does not already exist for this combination of user and SecurityLevel, add a row to
the snmpTargetParamsTable with these values: Name=usm<user>, MPModel=3(SNMPv3),
SecurityModel=3 (usm), SecurityName=<user>, SecurityLevel=M, where M is either 1
(noAuthNoPriv), 2(authNoPriv) or 3(authPriv).
All changes to the trap destination configuration take effect immediately.
➢ To delete a trap destination:
■ Remove the appropriate row from the snmpTargetAddrTable.
■ If this is the last trap destination associated with this user and security level, you could
also delete the appropriate row from the snmpTargetParamsTable.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
➢ To modify a trap destination:
You can change the IP address and or port number for an existing trap destination. The same
effect can be achieved by removing a row and adding a new row.
■ Modify the IP address and/or port number for the appropriate row in the
snmpTargetAddrTable.
➢ To disable a trap destination:
■ Change TagList on the appropriate row in the snmpTargetAddrTable to the empty string.
➢ To enable a trap destination:
■ Change TagList on the appropriate row in the snmpTargetAddrTable to ‘AC_TRAP’.
■ Change TagList on the appropriate row in the snmpTargetAddrTable to "AC_TRAP".
- 19 -
Page 29

CHAPTER3 Carrier-Grade Alarm System
3 Carrier-Grade Alarm System
The basic alarm system has been extended to a carrier-grade alarm system. A carrier-grade
alarm system provides a reliable alarm reporting mechanism that takes into account EMS
outages, network outages, and transport mechanism such as SNMP over UDP.
A carrier-grade alarm system is characterized by the following:
■ The device allows an EMS to determine which alarms are currently active in the device.
That is, the device maintains an active alarm table.
■ The device allows an EMS to detect lost alarms and clear notifications [sequence number
in trap, current sequence number MIB object]
■ The device allows an EMS to recover lost alarm raise and clear notifications [maintains a
log history]
■ The device sends a cold start trap to indicate that it is starting. This allows the EMS to
synchronize its view of the device's active alarms.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
When the SNMP alarm traps are sent, the carrier-grade alarm system does not add or delete
alarm traps as part of the feature. This system provides the mechanism for viewing of history
and current active alarm information.
Active Alarm Table
The device maintains an active alarm table to allow an EMS to determine which alarms are
currently active in the device. Two views of the active alarm table are supported by the agent:
■ acActiveAlarmTable in the enterprise AcAlarm
■ alarmActiveTable and alarmActiveVariableTable in the IETF standard AcAlarm MIB (rooted
in the MIB tree)
The acActiveAlarmTable is a simple, one-row per alarm table that is easy to view with a MIB
browser.
Alarm History
The device maintains a history of alarms that have been sent and traps that have been cleared
to allow an EMS to recover any lost raise or clear traps. Two views of the alarm history table
are supported by the agent:
■ acAlarmHistoryTable in the enterprise AcAlarm - a simple, one-row per alarm table, that is
easy to view with a MIB browser.
■ nlmLogTable and nlmLogVariableTable in the standard NOTIFICATION-LOG-MIB
- 20 -
Page 30
CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
4 Topology MIB Objects
Physical Entity (RFC 2737)
The following groups are supported:
■ entityPhysical group: Describes the physical entities managed by a single agent.
■ entityMapping group: Describes the associations between the physical entities, logical
entities, interfaces, and non-interface ports managed by a single agent.
■ entityGeneral group: Describes general system attributes shared by potentially all types of
entities managed by a single agent.
■ entityNotifications group: Contains status indication notifications.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
IF-MIB (RFC 2863)
The following interface types are presented in the ifTable:
■ ethernetCsmacd(6): for all Ethernet-like interfaces, regardless of speed, as per RFC 3635
■ ds1(18): DS1-MIB
■ voiceFXO(101): Voice Foreign Exchange Office
■ voiceFXS(102): Voice Foreign Exchange Station
The numbers in the brackets above refer to the IANA's interface-number.
For each interface type, the following objects are supported:
Ethernet Interface
Table 4-1: Ethernet Interface
ifTable & ifXTable Value
ifIndex Constructed as defined in the device's Index format.
ifDescr Ethernet interface.
ifType ethernetCsmacd(6)
ifMtu 1500
ifPhysAddress 00-90-8F plus acSysIdSerialNumber in hex.Will be same for
both dual ports.
ifAdminStatus Always UP. [Read Only] - Write access is not required by the
- 21 -
Page 31

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable & ifXTable Value
ifOperStatus Up or Down corresponding to acAnalogFxsFxoType where
ifLastChange The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its
ifInOctets The number of octets in valid MAC frames received on this
ifInUcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifInDiscards As defined in IfMIB.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
standard. Support for 'testing' is not required.
Unknown is equal to Down.
current operational state.
interface, including the MAC header and FCS. This does
include the number of octets in valid MAC Control frames
received on this interface.
ifInErrors The sum for this interface of dot3StatsAlignmentErrors,
dot3StatsFCSErrors, dot3StatsFrameTooLongs, and
dot3StatsInternalMacReceiveErrors.
ifInUnknownProtos As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutOctets The number of octets transmitted in valid MAC frames on
this interface, including the MAC header and FCS. This
does include the number of octets in valid MAC Control
frames transmitted on this interface.
ifOutUcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutDiscards As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutErrors The sum for this interface of: dot3StatsSQETestErrors,
dot3StatsLateCollisions, dot3StatsExcessiveCollisions,
dot3StatsInternalMacTransmitErrors and
dot3StatsCarrierSenseErrors.
ifName Ethernet port #1 or# 2
ifInMulticastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifInBroadcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutMulticastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutBroadcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
- 22 -
Page 32

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable & ifXTable Value
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
ifHCInOctets
ifHCOutOctets
64-bit versions of counters. Required for ethernet-like
interfaces that are capable of operating at 20 Mb/s or
faster, even if the interface is currently operating at less
than 20 Mb/s.
ifHCInUcastPkts
ifHCInMulticastPkts
ifHCInBroadcastPkts
ifHCOutUcastPkts
ifHCOutMulticastPkts
64-bit versions of packet counters. Required for ethernetlike interfaces that are capable of operating at 640 Mb/s or
faster, even if the interface is currently operating at less
than 640 Mb/s.
Therefore, will be constant zero.
ifHCOutBroadcastPkts
ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable Set to disabled (2). Refer to [RFC 2863].
ifPromiscuousMode Constant False. [R/O]
ifConnectorPresent Constant True.
ifAlias An 'alias' name for the interface as specified by a network
manager (NVM)
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime As defined in IfMIB.
DS1 Interface
The DS1 interface is applicable only to digital PSTN interfaces.
Table 4-2: DS1 Digital Interface
ifTable Value
ifDescr Digital DS1 interface.
ifType ds1(18).
ifMtu Constant zero.
ifSpeed DS1 = 1544000, or E1 = 2048000, according to dsx1LineType
ifPhysAddress The value of the Circuit Identifier [dsx1CircuitIdentifier]. If
no Circuit Identifier has been assigned this object should
have an octet string with zero length.
ifAdminStatus Trunk’s Lock & Unlock during run time. In initialization
- 23 -
Page 33

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable Value
ifOperStatus Up or Down, according to the operation status.
ifLastChange The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its
ifXTable Value
ifName Digital# acTrunkIndex
ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable Set to disabled(2)
ifHighSpeed Speed of line in Megabits per second: 2
ifConnectorPresent Set to true(1) normally, except for cases such as DS1/E1
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
process we need to refer the Admin-Status parameter.
current operational state.
over AAL1/ATM where false(2) is appropriate
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime Always zero.
BRI Interface
This table is applicable only to BRI interfaces.
Table 4-3: BRI Interface
ifTable Value
ifDescr BRI interface
ifType isdns(75)
ifMtu Constant zero
ifSpeed 144000
ifPhysAddress Octet string with zero length
ifAdminStatus Trunk’s Lock & Unlock during run time. In initialization
process, refer to the Admin-Status parameter.
ifOperStatus Up or Down according to the operation status.
- 24 -
Page 34

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable Value
ifLastChange The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its
ifXTable Value
ifName BRI port no. #
ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable Set to disabled (2)
ifHighSpeed Speed of line in megabits per second.
ifPromiscuousMode Non promiscuous mode (1)
ifConnectorPresent Set to true (1) normally
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime Always zero
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
current operational state.
ADSL/VDSL Interface
Table 4-4: ADSL/VDSL Interface
ifTable & ifXTable Value
ifInOctets The number of octets in valid MAC frames received on this
interface, including the MAC header and FCS. Includes the number
of octets in valid MAC Control frames received on this interface.
ifInUcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifInDiscards As defined in IfMIB.
ifInErrors The sum for this interface of dot3StatsAlignmentErrors,
dot3StatsFCSErrors, dot3StatsFrameTooLongs, and
dot3StatsInternalMacReceiveErrors.
ifInUnknownProtos As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutOctets The number of octets transmitted in valid MAC frames on this
interface, including the MAC header and FCS. This does include the
number of octets in valid MAC Control frames transmitted on this
interface.
ifOutUcastPkts As defined in IfMIB.
ifOutDiscards As defined in IfMIB.
- 25 -
Page 35

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable & ifXTable Value
ifOutErrors The sum for this interface of: dot3StatsSQETestErrors,
VLAN Interface
ifTable Value
ifDescr CLI interface name.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
dot3StatsLateCollisions, dot3StatsExcessiveCollisions,
dot3StatsInternalMacTransmitErrors and
dot3StatsCarrierSenseErrors.
Table 4-5: VLAN Interface
If not exists - Virtual LAN Interface / WAN Virtual LAN
Interface
ifType ds1(136).
ifMtu Interface MTU [default 1500]
ifSpeed 0
ifPhysAddress The value of the Circuit Identifier [dsx1CircuitIdentifier]. If
no Circuit Identifier has been assigned this object should
have an octet string with zero length.
ifAdminStatus INTERFACE_STATUS_WORKING -> snmpIF_ifAdminStatus_
up_E/snmpIF_ifOperStatus_up_E
INTERFACE_STATUS_UNKNOWN)
INTERFACE_STATUS_DISABLED
INTERFACE_STATUS_INACTIVE ->
snmpIF_ifAdminStatus_down_E/snmpIF_ifOperStatus_
down_E
ifOperStatus
ifLastChange The value of sysUpTime at the time the interface entered its
current operational state.
ifXTable Value
ifName Interface name
ifLinkUpDownTrapEnable Set to disabled(2)
- 26 -
Page 36

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
ifTable Value
ifHighSpeed Speed of line in Megabits per second: 2
ifConnectorPresent Set to true(1) normally
ifCounterDiscontinuityTime Always zero.
MIB-II Counters
■ TCP (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.6):
● tcpRtoAlgorithm
● tcpRtoMin
● tcpRtoMax
● tcpMaxConn
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● tcpActiveOpens
● tcpPassiveOpens
● tcpAttemptFails
● tcpEstabResets
● tcpCurrEstab
● tcpInSegs
● tcpOutSegs
● tcpRetransSegs
● tcpInErrs
● tcpOutRsts
● tcpHCInSegs
● tcpHCOutSegs
■ UDP (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.7):
● udpInDatagrams
● udpNoPorts
● udpInErrors
● udpOutDatagrams
● udpHCInDatagrams
● udpHCOutDatagrams
■ IP (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.4):
- 27 -
Page 37

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
● ipForwarding
● ipDefaultTTL
● ipInReceives
● ipInHdrErrors
● ipInAddrErrors
● ipForwDatagrams
● ipInUnknownProtos
● ipInDiscards
● ipInDelivers
● ipOutRequests
● ipOutDiscards
● ipOutNoRoutes
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● ipReasmTimeout
● ipReasmReqds
● ipReasmOKs
● ipReasmFails
● ipFragCreate
■ ICMP (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.5):
● icmpInMsgs
● icmpInErrors
● icmpInDestUnreachs
● icmpInTimeExcds
● icmpInParmProbs
● icmpInSrcQuenchs
● icmpInRedirects
● icmpInEchos
● icmpInEchoReps
● icmpInTimestamps
● icmpInTimestampReps
● icmpInAddrMasks
● icmpInAddrMaskReps
● icmpOutMsgs
- 28 -
Page 38

CHAPTER4 Topology MIB Objects
● icmpOutErrors
● icmpOutDestUnreachs
● icmpOutTimeExcds
● icmpOutParmProbs
● icmpOutSrcQuenchs
● icmpOutRedirects
● icmpOutEchos
● icmpOutEchoReps
● icmpOutTimestamps
● icmpOutTimestampReps
● icmpOutAddrMasks
● icmpOutAddrMaskReps
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
■ IF (OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2):
● ifInOctets
● ifInUcastPkts
● ifInDiscards
● ifInErrors
● ifOutOctets
● ifOutUcastPkts
● ifOutErrors
● ifInMulticastPkts
● ifInBroadcastPkts
● ifOutMulticastPkts
● ifOutBroadcastPkts
- 29 -
Page 39

CHAPTER5 File Management
5 File Management
SNMP supports file download, upload, and removal.
Downloading a File to the Device
The file URL is set in the appropriate MIB object under the acSysHTTPClient subtree (refer to
the subtree objects description for the URL form). The download can be scheduled using the
acSysHTTPClientAutoUpdatePredefinedTime and acSysHTTPClientAutoUpdateFrequency
objects. It can also be a manual process using acSysActionSetAutoUpdate. In this case (only)
and as long as one URL is set at a time, the result can be viewed in acSysActionSetAutoUpdateActionResult. In both cases, the acHTTPDownloadResult trap is sent,
indicating the success or failure of the process.
acSysActionSetActionId can be set to any value and can be used to indicate an action
performed by a certain manager.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
A successful process also ends with the file name in the appropriate object under the acSysFile
subtree or in the acCASFileTable or the acAuxiliaryFiles subtree, along with the URL being
erased from the object under the acSysHTTPClient subtree.
● The action result (both in the acSysActionSetAutoUpdateActionResult object and
acHTTPDownloadResult trap) for the Voice Prompt andXML indicates only that
the file reached the device and has no indication on the application’s ability to parse
the file.
● The action result in acSysActionSetAutoUpdateActionResult is reliable as long as
only onefile is downloaded at a time.
Uploading and Deleting a File
File upload is the procedure of sending a file from the device to the manager. Deleting a file is
erasing it from the device, an offline action that requires a reset for it to be applied. The
acSysUpload subtree holds all relevant objects.
■ acSysUploadFileURI indicates the file name and location along with the file transfer
protocol (HTTP or NFS), for example, “http:\\server\filename.txt”.
■ acSysUploadFileType and acSysUploadFileNumber are used to determine the file to be
uploaded along with its instance when relevant (for CAS or Video Font).
■ acSysUploadActionID is at the disposal of the manager and can be used to indicate that a
certain manager has performed the action.
■ acSysUploadActionType determines the action that occurs and triggers it off at the same
time.
- 30 -
Page 40

CHAPTER5 File Management
File upload using SNMP is supported only for ini files; file removal using SNMP is
supportedfor all files except ini files.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
- 31 -
Page 41

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
6 Performance Monitoring
Performance measurements (performance monitoring) are available for third- party
performance monitoring systems through an SNMP interface. These can be polled at
scheduled intervals by an external poller or utility in the management server or other offboard systems.
The device provides performance measurements in the form of two types:
■ Gauges: Gauges represent the current state of activities on the device. Gauges, unlike
counters, can decrease in value and like counters, can increase. The value of a gauge is the
current value or a snapshot of the current activity on the device at that moment.
■ Counters: Counters always increase in value and are cumulative. Counters, unlike gauges,
never decrease in value unless the server is reset, which causes the counters to reset to
zero (0).
The device's performance measurements are provided by the following proprietary MIBs that
are located under the acPerformance subtree, iso (1).org (3).dod (6).internet (1).private
(4).enterprises(1).AudioCodes(5003).acPerformance(10):
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
■ acPMMedia: Media-related (voice) monitoring such as RTP and DSP. The MIB includes the
following parameters:
● Number of active DSP channels
● Channels used for each coder
● Discarded packets in robust RTP filter
● Media Networking subtree - an array of packet behavior parameters such as delay,
jitter, transmitted/received and lost RTP bytes and packets.
● Media Networking Aggregated subtree - displays similar data only for the entire device
and includes TDM-IP and IP-IP calls.
● Channel Utilization subtree - parameters regarding channel use by fax, modem, TDM-
IP calls, RTP, SRTP, multicast source and modem relay
● Streaming Cache subtree - hit count, miss count and server request count
■ acPMControl: Control protocol-related (SIP) monitoring such as connections, commands.
● CP Connection subtree – parameters include connection lifetime/state, counters for
commands, retransmissions, active contexts, command success/failure and process
time, transaction processing time and call attempts
● SIP subtree
■ acPMAnalog: Analog channels off-hook state (one table only).
■ acPMPSTN: PSTN-related monitoring such as channel use and trunk utilization. All
statistics in this MIB are per trunk:
● Number of active channels
- 32 -
Page 42

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
● Trunk activity
● Number of channels that are in/out of service and in maintenance
■ acPMSystem: General device monitoring:
● IP connection.
● Discarded UDP packets due to unknown port
● System Net Utils subtree – transmitted/received bytes/packets, discarded packets
● System Network subtree – DHCP response time/request count and STUN-related
statistics
● System Multicast subtree – multicast IP packets received, multicast IP packets
conveying UDP payload packets received/rejected, IGMP packets/generalqueries/specific-queries received, IGMP membership-report/leave-group sent
messages
● System Congestion subtree – congestion state for general resources, DSP resources,
IP resources, conference resources
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● System NFS subtree – NFS-related parameters
● System MSBR subtree – includes received good/bad octets, received under-
sized/oversized/discarded packets, received MAC errors, received FSC error packets,
transmitted octets/packets/collisions/late-packets
Performance monitoring MIBs all have an identical, fixed structure, which includes two major
subtrees:
■ Configuration subtree: Allows configuration of general attributes of the MIB and specific
attributes of the monitored objects. This subtree includes:
● Reset Total Counters: Resets the "total" (see below) objects in all the MIB’s tables, if
they are defined.
● Attributes subtrees: Number of subtrees in which scalars are used to configure high
and low thresholds for relevant tables.
■ Data subtree: Consists of monitored data and statistics, and includes:
● Time From Start Of Interval object: GETs the time in seconds from the beginning of the
current interval.
● Data tables: All have similar structure. Not all possible columns appear in all of them.
The specific structure of a table (i.e. what columns are defined) is parameter specific.
The only column that always appears is the interval column. The information in each
column is a statistical attribute of the parameter being measured.
The device measures performance at fixed intervals of 15 minutes. The device keeps a record
of the last two completed intervals. These intervals are used as a key in the MIB tables in which
the performance monitoring results are presented. There are one or two indices in each table.
- 33 -
Page 43

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
If there are two, the first is a sub-set in the table (e.g., trunk number) and the second (or the
single where there is only one) index represents the interval number:
■ 0: Current interval (not completed)
■ 1: Last completed interval
■ 2: Second last completed interval
When the current interval (Interval 0) completes (reaches 15 minutes), Interval 2 is discarded,
Interval 1 becomes Interval 2, Interval 0 becomes Interval 1, and a new Interval 0 is created.
● The interval’s start time is synchronizedwith the device’s clock so that the
intervals begin on the hour (e.g., 12:00). If you are using NTP, then it is likely that
the last interval within the first hour after device startup will be cut short to
accommodate for this synchronization.
● Some performance monitoring parameters support a history with more than two
intervals. These includeconference calls, trunk-test calls and digit-collect
requests.
● An attribute whose value is -1 means that the attribute isn’t relevant at that point of
time.
● If the device has just startedup and thefirst measuring interval has not elapsed,
intervals 1and 2 are not applicable and their data values are typically displayed as
"-1" or as empty cells.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The following figure shows an example of a monitored parameter, in this case, the number of
utilized B-channels in a single trunk:
The x-axis is the time within the interval; the y-axis is the number of used channels. The
parameter’s value is a gauge. While the interval index is 0 (i.e., current interval), any GET on
the parameter value will return a y-axis value at that moment. When the interval is complete
(index 1 or 2), the gauge value is no longer relevant and other attributes become relevant such
as the average (area in green divided by the interval length in seconds), which is called timebased statistics.
- 34 -
Page 44

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
The following figure shows an example of the last three intervals. In this example, the device
was powered up at 11:24. The first interval (of 15 minutes) ended at 11:39 and the second
interval (of 15 minutes) ended at 11:54. The current interval (Interval 0) has not completed the
15 minutes. Typically, you would want the measured performance of the last completed
interval (i.e., Interval 1).
The performance monitoring MIB tables can include the following properties (columns):
■ Table specific index: This is a table key.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
■ Interval: Indicates the measured interval (0,1, or 2), which is a table key.
■ Val: Indicates the value of the gauge or counter. This is the snapshot view of the device's
current activity.
● Counter: Cumulative value (only increases).
● Gauge: Fluctuates in value (increases and decreases).
■ Average: Indicates the average value within the interval.
■ Max: Indicates the maximum gauge value during the interval.
■ Min: Indicates the minimum gauge value during the interval.
■ Volume: Indicates the number of times the gauge or counter was updated (i.e., the
volume of change), for example:
● For a trunk utilization element, the volume indicates how many calls were made and
released.
● For the Ethernet connection status element, the volume indicates how many network
connections and disconnections occurred.
■ Thresholds:
● TimeBelowLowThreshod: Indicates the percent (%) of the interval time for which the
gauge was below the low threshold (if defined).
● TimeAboveHighThreshod: Indicates the percent (%) of the interval time for which the
gauge was above the high threshold (if defined).
● TimeBetweenThresholds: Indicates the percent (%) of the interval time for which the
gauge was between the low and high thresholds (if defined).
- 35 -
Page 45
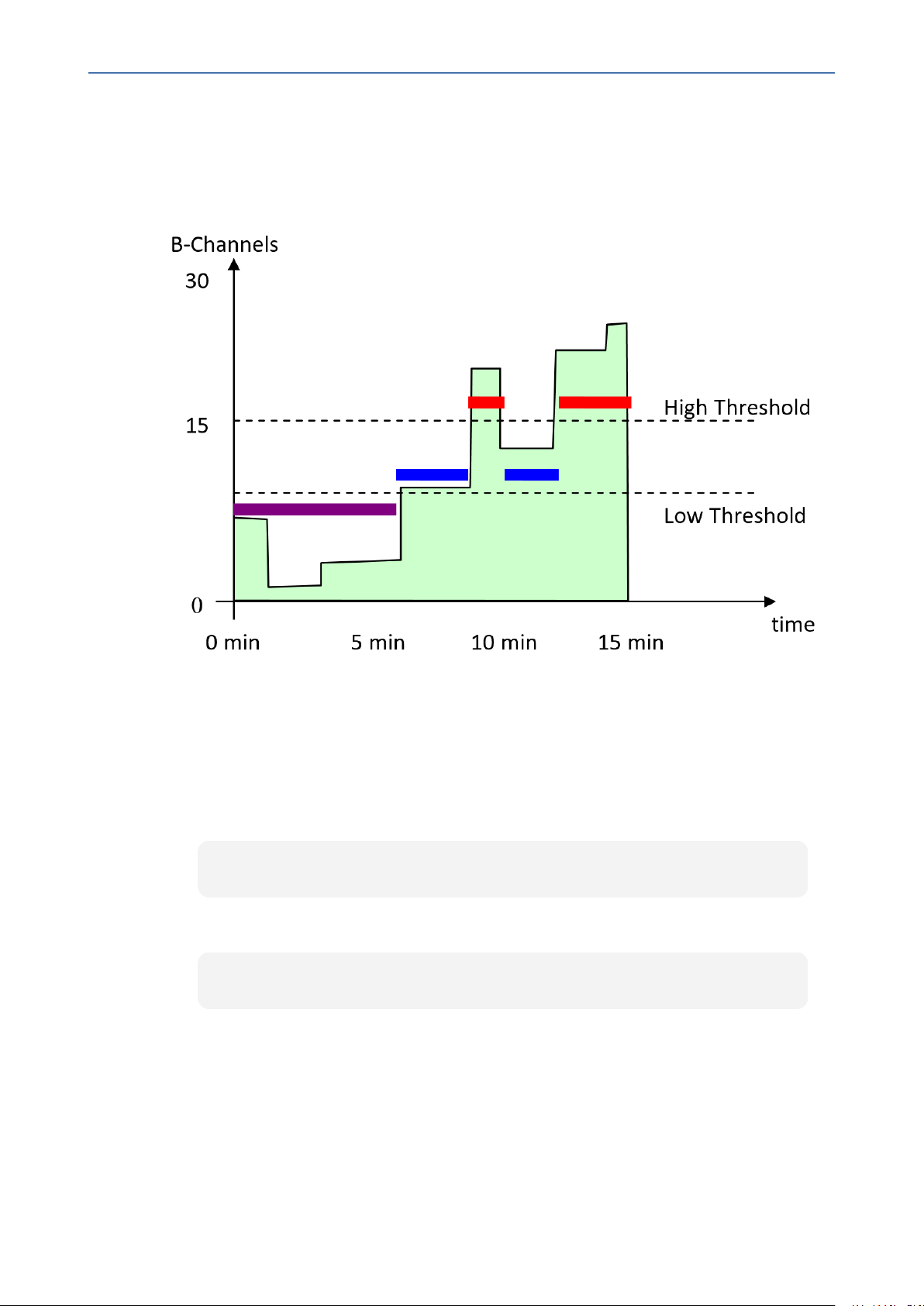
CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
The following figure shows an example of how the device calculates thresholds. The purple
bar indicates the time when the element was below the low threshold (about 40% of the
interval time), the blue bar indicates the time when the element was between the low and
high threshold (about 30%), and the red bar indicates the time when the element was
above the high threshold (about 30%).
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The SNMP trap event acPerformanceMonitoringThresholdCrossing is sent every time the
high or low threshold of a Performance Monitored MIB object is crossed (see Performance
Monitoring Threshold-Crossing Trap on page152). The severity field is 'indeterminate'
when the crossing is above the threshold and 'cleared' when it returns to below the
threshold. The trap's 'source varbind' indicates the object for which the threshold is
crossed. To enable this feature, load an ini file to the device with the following parameter
setting:
PM_EnableThresholdAlarms = 1
Once enabled, you can change the low and high threshold values from their default
values, through ini file by using the following syntax:
PM_<MIB Source Name> = '1,<Low Threshold>,<High Threshold>,15'
where:
● <MIB Source Name>: The source name of the MIB (e.g., PM_TrunkUtilization, PM_
NetUtilKBytes, and PM_gwIPGroupOutINVITEDialogs)
● <Low Threshold>: Defines the low-threshold value
● <High Threshold>: Defines the high-threshold value
- 36 -
Page 46

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
The value "15" in the syntax is the measuring interval, which is always fixed at 15 minutes.
The following is an example of an ini file that configures the acPMSIPIPGroupOutInviteDialogsTable performance monitoring MIB (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.35) with a
low threshold of 10 and a high threshold of 18:
PM_gwIPGroupOutINVITEDialogs = '1,10,18,15'
If you download (save) the device's ini file, it includes all SNMP performance
monitoring MIBs whose thresholds (low and/or high) you have changed from default. To
apply these same threshold values to other devices, load the file to the other devices.
■ FullDayAverage: Indicates the 24-hour average.
■ Total: (Applicable only to Counters) Indicates the summation of all counter values. In
other words, it does not reset to zero for each new interval. However, the total does reset
after a device reset. In addition, you can reset this property per MIB module, by setting
the ResetTotal object to the value 2:
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● PM-Analog: acPMAnalogConfigurationResetTotalCounters
● PM-Control: acPMControlConfigurationResetTotalCounters
● PM-Media: acPMMediaConfigurationResetTotalCounters
● PM-PSTN: acPMPSTNConfigurationResetTotalCounters
● PM-System: acPMSystemConfigurationResetTotalCounters
For example:
acPMMediaConfigurationResetTotalCounters.0 (integer) resetTotalCounters
(2)
■ StateChanges: Indicates the number of times a state (mostly active/non-active) was
toggled.
Not all the properties listed above are applicable to every Performance Monitoring MIB.
Properties that are not applicable are displayed as "-1" or as an empty cell.
SNMP Performance Monitoring MIBs
This section describes the Performance Monitoring SNMP MIBs.
- 37 -
Page 47

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
The tables in this section use check marks "√" and crosses "x" to indicate support for
the specific MIB property:
● "G/C": gauge / counter
● "Int": measured interval
● "Val": value of gauge or counter
● "Min": minimum gauge value
● "Max": maximum gauge value
● "Avg": average within the interval
● "TbLT": percentage of interval time that value was below low threshold
● "TbT": percentage of interval time that value was between low and high thresholds
● "TaHT": percentageof interval time that value was above high threshold
● "HT": configuredor default high threshold
● "LT": configured or default low threshold
Performance Monitoring MIBs for IP Network Interfaces
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for IP network interfaces.
Table 6-1: Performance Monitoring MIBs for IP Network Interface
G
I
Performance Monitoring MIB
V
/
n
C
t
a
l
MinM
ax
A
v
g
Tb
LT
T
TaHTHTL
b
T
■ MIB Name: acPMNetUtilKBytesTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.2.31.1
■ Source Name: PM_NetUtilKBytes
Indicates the number of Kbytes
(1000 bytes) received and
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü û û
5
transmitted on the interface (Index
0 is transmit; Index 1 is receive),
including those received in error,
from the beginning of the current
collection interval as indicated by
the time interval.
T
OVOC parameter name: Number of
Incoming / Outgoing Kbytes
■ High threshold:
acPMNetUtilsAttributesKBytesH
ighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.1.33.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetUtilsAttributesKBytesL
- 38 -
Page 48

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
owThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.1.33.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMNetUtilPacketsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.2.31.2
■ Source Name: PM_NetUtilPackets
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
C
t
a
l
MinM
ax
A
v
g
Tb
LT
T
TaHTHTL
b
T
T
Indicates the number of incoming
and outgoing packets from the
interface (Index 0 is transmit; Index
1 is receive), from the beginning of
the current collection interval as
indicated by time Interval.
OVOC parameter name: Number of
Outgoing / Incoming Pkts.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ High threshold:
acPMNetUtilsAttributesPackets
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.1.33.3)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetUtilsAttributesPackets
LowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.1.33.4)
■ MIB Name: acPMNetUtilDiscardedPacketsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.11.2.31.3
■ Source Name: PM_NetUtilDiscardedPackets
Indicates the number of
malformed IP packets received on
the interface during the last
interval. These are packets which
are corrupted or discarded due to
errors in their IP headers, including
bad checksums, version number
mismatch, other format errors,
time-to-live exceeded, errors
discovered in processing their IP
options, etc.
C 1
5
- 39 -
ü û û û û û û û û
Page 49

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
OVOC parameter name: Number of
Incoming Discarded Pkts.
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Media Realms
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for Media Realms.
Table 6-2: Performance Monitoring MIBs for Media Realms
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
C
t
a
l
MinM
ax
A
v
g
Tb
LT
T
TaHTHTL
b
T
T
G
I
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
n
C
t
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmPacketLossRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.10
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmPacketLossRx
Indicates the received RTP packet loss
(reported by RTCP) per Media Realm.
G 1
5
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmPacketLossTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.11
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmPacketLossTx
Indicates the transmitted RTP packet
loss (reported by RTCP) per Media
Realm.
G 1
5
V
M
M
a
i
a
l
n
x
T
A
v
g
T
b
b
L
T
T
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
T
a
H
T
HT LT
50 30
50 30
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmBytesTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.1
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmBytesTx
Indicates the number of bytes received
in RTCP data, per Media Realm.
G 1
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBytesTxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.1)
- 40 -
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
150
000
0
100
000
0
Page 50

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
C
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBytesTxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmBytesRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.2
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmBytesRx
Indicates the number of bytes received
in RTCP data, per Media Realm.
G 1
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBytesRxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.3)
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
T
T
a
b
T
H
T
HT LT
150
100
000
000
0
0
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBytesRxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.4)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmPacketsTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.3
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmPacketsTx
Indicates the number of media packets
sent in RTCP data, per Media Realm.
G 1
5
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmPacketsTxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.5)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmPacketsTxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.6)
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
7500600
0
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmPacketsRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.4
- 41 -
Page 51

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
M
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
n
a
i
C
t
l
n
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmPacketsRx
Indicates the number of media packets
received in RTCP data, per Media
Realm.
G 1
û ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmPacketsRxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.7)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmPacketsRxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.8)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmVERealmPacketDelayTable
M
T
A
a
x
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
H
T
HT LT
7500600
0
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.5
■ Source Name: PM_VERealmPacketDelay
Indicates the packet delay in RTCP
data, per Media Realm.
G 1
û ü ü ü û û û
5
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesVEReal
mPacketDelayHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.9)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesVEReal
mPacketDelayLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.10)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmVERealmPacketJitterTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.6
■ Source Name: PM_VERealmPacketJitter
150 120
Indicates the packet jitter in RTCP data,
per Media Realm.
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesVEReal
- 42 -
G 1
ü ü ü ü û û û
5
150 120
Page 52

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
Performance Monitoring MIB
mPacketJitterHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.11)
/
n
C
t
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesVEReal
mPacketJitterLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.12)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmRealmMOSTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.7
■ Source Name: PM_RealmMOS
Indicates the MOS quality in RTCP-XR
data, per Media Realm.
G 1
5
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesRealm
MOSHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.13)
V
M
M
a
i
a
l
n
x
T
A
v
g
T
b
b
L
T
T
ü ü ü ü û û û
T
a
H
T
HT LT
50 10
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesRealm
MOSLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.14)
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmBwRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.8
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmBwRx
Indicates the average bandwidth for Rx
bytes, per Media Realm.
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBwRxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.15)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBwRxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.16)
G 1
ü ü ü ü û û û
5
150
000
0
0
- 43 -
Page 53

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMMediaRealmBwTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.53.9
■ Source Name: PM_MediaRealmBwTx
Indicates the average bandwidth for Tx
bytes, per Media Realm.
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBwTxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.17)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaRealmAttributesMediaR
ealmBwTxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.35.18)
G
/
C
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
ü ü ü ü û û û
5
T
T
a
b
T
H
T
HT LT
150
000
0
0
Performance Monitoring MIBs for VoIP Calls
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for VoIP calls.
Table 6-3: Performance Monitoring MIBs for VoIP Calls
G
I
V
M
M
A
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMChannelsPerCoderTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.22
■ Source Name: PM_VEChannelsPerCoder
Indicates the number of active channels
per coder, where the Index denotes the
coder: 0 (G.711), 1 (G.723), 2 (G.728), 3
(G.729A), 4 (G.729E), 5 (AMR), 6 (G.729EV), 7
(EG.711), 8 (EVRC), 9 (Unknown Coder), 10
(G.726), 11 (RTA), 12 (SILK), 13 (AMR-WB),
14 (G.722), 15 (G.727), 16 (GSM), 17
(QCELP), 18 (VOX ADPCM), 19 (iLBC), 20
/
C
G 1
n
a
i
a
v
t
l
n
x
g
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
T
b
L
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
- 44 -
Page 54

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
C
(Speex).
■ High threshold:
acPMCodersAttributesChannelsPerCod
erHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.32.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMCodersAttributesChannelsPerCod
erLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.32.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMChannelsPerCoderG711Table
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.26
■ Source Name: PM_VeG711Channels
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the number of active channels
per G.711 A-law or G.711 U-law, where the
Index denotes the coder type: 0 (G.711 Alaw) and 1 (G.711 U-law).
G 1
■ High threshold:
acPMCodersAttributesChannelsPerCod
erHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.32.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMCodersAttributesChannelsPerCod
erLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.32.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPPacketLossRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.9
■ Source Name: PM_veModuleRTPPacketLossRx
Indicates the Rx RTP packet loss (reported
by RTCP), during the time Interval.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
OVOC parameter name: Rx RTP Packet
Loss.
■ High threshold:
- 45 -
Page 55

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
C
acPMNetworkingAttributesModuleRTP
PacketLossRxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.17)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesModuleRTP
PacketLossRxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.18)
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPPacketLossTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.10
■ Source Name: PM_veModuleRTPPacketLossTx
Indicates the Tx RTP packet loss (reported
by RTCP), during the time Interval.
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
H
T
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
HTL
T
OVOC parameter name: Tx RTP Packet
Loss.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesModuleRTP
PacketLossTxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.19)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesModuleRTP
PacketLossTxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.20)
■ MIB Name: acPMModulePacketDelayTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.1
■ Source Name: PM_veModulePacketDelay
Indicates the RTP packet delay during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: RTP delay.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesPacketDelay
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.1)
- 46 -
Page 56

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesPacketDelay
LowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMModulePacketJitterTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.2
■ Source Name: PM_veModulePacketJitter
Indicates the RTP packet jitter during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: RTP jitter.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesPacketJitter
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.3)
G
/
C
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
H
T
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
HTL
T
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesPacketJitter
LowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.4)
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPBytesRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.4
■ Source Name: PM_veModuleRTPBytesRx
Indicates the Tx RTP bytes during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: Rx RTP Bytes.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPBytesRx
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.7)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPBytesRx
LowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.8)
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
- 47 -
Page 57

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPBytesTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.3
■ Source Name: PM_veModuleRTPBytesTx
Indicates the Rx RTP bytes during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: Tx RTP Bytes.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPBytesTx
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.5)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPBytesTxL
owThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.6)
G
/
C
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
H
T
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
HTL
T
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPPacketsRxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.6
■ Source Name: PM_RTPModulePacketsRx
Indicates the Rx RTP packets during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: Rx RTP Packets.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPPackets
RxHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.11)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPPackets
RxLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.12)
■ MIB Name: acPMModuleRTPPacketsTxTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.31.21.5
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ Source Name: PM_RTPModulePacketsTx
- 48 -
Page 58

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring MIB
Indicates the Tx RTP Packets during the
collection time interval.
OVOC parameter name: Tx RTP Packets.
■ High threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPPacketsT
xHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.9)
■ Low threshold:
acPMNetworkingAttributesRTPPacketsT
xLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.33.10)
G
/
C
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
H
T
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
HTL
T
Performance Monitoring MIBs for SIP Messages
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for SIP messages.
Table 6-4: Performance Monitoring MIBs for SIP Messages
G
I
V
M
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
n
a
i
C
t
l
n
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPActiveSIPTransactionsPerSecondTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.41
■ Source Name: PM_gwActiveSIPTransacionsPerSecond
Indicates the number of active incoming
and outgoing SIP transactions (e.g.,
INVITE message) per second.
G 1
ü û û û û û û
5
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesActiveSIPTransactio
nsPerSecondHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.35)
M
a
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
0 0
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesActiveSIPTransactio
- 49 -
Page 59

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
C
nsPerSecondLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.36)
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPIPGroupInviteDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.22
■ Source Name: PM_gwIPGroupINVITEDialogs
Indicates the number of INVITE dialogs
per IP Group.
G 1
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesIPGroupINVITEDial
ogsHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.25)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesIPGroupINVITEDial
ogsLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.26)
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
0 0
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Calls per IP Group
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for Gateway and SBC calls per IP
Group.
For additional performance monitoring MIBs for SBC calls per IP Group, see SBC Calls
perIP Groupon page71.
Table 6-5: Performance Monitoring MIBs for Call Sessions per IP Group
Performance
Monitoring
MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAttemptedCalls
Indicates the G 15
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
ü û û û û û û û û
- 50 -
Page 60

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
number of
attempted
incoming
calls per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.6
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
attempted
outgoing
calls per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.9
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
failed call
routing per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInNoResourcesCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.18
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInNoResourcesCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming call
resource
allocation
failures per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutNoResourcesCallsTable
- 51 -
Page 61

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.19
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutNoResourcesCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
outgoing call
resource
allocation
failures per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInNoMatchCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.20
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInNoMatchCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming call
media
negotiation
failures per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutNoMatchCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.21
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutNoMatchCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
outgoing call
media
negotiation
failures per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInBusyCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.22
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInBusyCalls
- 52 -
Page 62

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming
busy calls
per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutBusyCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.23
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutBusyCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
outgoing
busy calls
per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInNoAnswerCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.24
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInNoAnswerCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming
no-answer
calls per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutNoAnswerCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.25
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutNoAnswerCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
outgoing noanswer calls
per IP
Group.
- 53 -
Page 63

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInForwardedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.26
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInForwardedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming
forwarded
calls per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutForwardedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.29
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutForwardedCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
outgoing
forwarded
calls per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.32
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedCalls
Indicates the
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
number of
incoming
calls that
failed due to
general fail
reason per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.35
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedCalls
- 54 -
Page 64

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates the
number of
outgoing
calls that
failed due to
general fail
reason per
IP Group.
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.38
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInEstablishedCalls
Indicates the
number of
incoming
established
calls per IP
Group.
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.41
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedCalls
Indicates the
number of
outgoing
established
calls per IP
Group.
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Gateway Application
This section is applicable only to the Gateway application (i.e., Tel/PSTN interfaces).
IP-to-Tel and Tel-to-IP Calls
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for IP-to-Tel and Tel-to-IP calls.
- 55 -
Page 65

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
In the MIB tables, Index 0 indicates Tel-to-IP calls andIndex 1 indicates IP-to-Tel calls.
Table 6-6: Performance Monitoring MIBs for IP-to-Tel and Tel-to-IP Calls
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwAttemptedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
n
ValM
t
/
C
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
H
H
T
LT
T
Indicates the number of attempted
calls (Index 1) during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Call Attempts
C 1
5
■ MIB Name: acPMActiveContextCountTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.31.5
■ Source Name: PM_ActiveContextCount
Indicates the number of Gateway
calls.
G 1
5
■ High threshold:
acPMActiveContextCountTimeA
boveHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.31.5.1.9)
■ Low threshold:
acPMActiveContextCountTimeB
elowLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.31.5.1.7)
ü û û û û û û û û
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
0 0
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPCallDurationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwCallDuration
Indicates the call duration of
established calls during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Average Call Duration
[sec]calls.
G
/
C
- 56 -
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
1
5
Page 66

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesCallDurationH
ighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesCallDurationL
owThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.2)
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPNoMatchCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwNoMatchCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
n
ValM
t
/
C
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
H
H
T
LT
T
Indicates the number of calls that
failed due to mismatched media
server capabilities for calls, during
last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Failed Calls due
to No Matched Capabilities.
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPBusyCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.4
■ Source Name: PM_gwBusyCalls
Indicates the number of calls that
failed as a result of a busy line,
during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Calls Terminated
due to a Busy Line.
C 1
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPNoAnswerCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.5
■ Source Name: PM_gwNoAnswerCalls
Indicates the number of calls that
weren't answered during last
interval.
C 1
- 57 -
ü û û û û û û û û
5
Page 67

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Calls Terminated
due to No Answer.
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPNoRouteCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.6
■ Source Name: PM_gwNoRouteCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
n
ValM
t
/
C
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
H
H
T
LT
T
Indicates the number of calls whose
destinations weren't found during
last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Failed Calls due
to No Route.
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPFailCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.7
■ Source Name: PM_gwFailCalls
This counter is incremented as a
result of calls that fail due to
reasons not covered by the other
counters during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Failed Calls due
to Other reasons.
C 1
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.8
■ Source Name: PM_gwEstablishedCalls
Indicates the number of established
calls during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Established
Calls.
C 1
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPFaxAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.9
- 58 -
ü û û û û û û û û
Page 68

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ Source Name: PM_gwFaxAttemptedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
n
ValM
t
/
C
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
H
H
T
LT
T
Indicates the number of attempted
fax calls.
C 1
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPFaxSuccessCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.10
■ Source Name: PM_gwFaxSuccessCalls
Indicates the number of successfully
established fax calls.
C 1
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPForwardedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.11
■ Source Name: PM_gwForwardedCalls
Indicates the number of calls that
were terminated due to a call
forward during last interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Calls Terminated
due to Forward.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
ü û û û û û û û û
5
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPNoResourcesCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.12
■ Source Name: PM_gwNoResourcesCalls
Indicates the number of calls that
failed due to unavailable resources
or a media server lock during last
interval.
OVOC parameter name: IP to Tel /
Tel to IP Number of Failed Calls due
to No Resources.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTel2IPTrunkEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.13
■ Source Name: PM_gwTel2IPTrunkEstablishedCalls
- 59 -
Page 69

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
n
ValM
t
/
C
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
H
H
T
LT
T
Indicates the current number of
established calls pertaining to a
trunk for Tel-to-IP calls.
G 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPIP2TelTrunkEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.14
■ Source Name: PM_gwIP2TelTrunkEstablishedCalls
Indicates the current number of
established calls pertaining to a
trunk for IP-to-Tel calls.
G 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTel2IPTrunkGroupEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.15
■ Source Name: PM_gwTel2IPTrunkGroupEstablishedCalls
Indicates the current number of
established calls pertaining to a
Trunk Group for Tel-to-IP calls.
G 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPIP2TelTrunkGroupEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.16
■ Source Name: PM_gwIP2TelTrunkGroupEstablishedCalls
Indicates the current number of
established calls pertaining to a
Trunk Group for IP-to-Tel calls.
G 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
Trunks
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIB for trunks.
Table 6-7: Performance Monitoring MIBs for Trunks
Performance
Monitoring MIB
■ MIB Name: dsx1IntervalTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.2.1.10.18.8
G/CIntValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTaHTHTL
T
- 60 -
Page 70

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
The DS1 Interval
Table contains
various statistics
collected by each
DS1 Interface over
the previous 24
hours. The past 24
hours are broken
into 96 completed
15-minute intervals.
Each row in this
table represents
one such interval
(identified by
dsx1IntervalNumbe
r) for one specific
instance (identified
by
dsx1IntervalIndex:
G/CIntValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTaHTHTL
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
T
■ dsx1IntervalESs:
Number of
Errored Seconds
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Errored
Seconds)
■
dsx1IntervalCSS
s: Number of
Controlled Slip
Seconds (OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Controlled Slip
Seconds)
■
dsx1IntervalPCV
s: Number of
Path Coding
- 61 -
Page 71

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
Violations
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Path Coding
Violations)
■
dsx1IntervalBES
s: Number of
Bursty Errored
Seconds (OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Bursty Errored
Seconds)
■ dsx1TotalESs:
Call duration per
timeslot and E1
since last clear
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Calls Duration)
G/CIntValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTaHTHTL
T
■ dsx1TotalCSSs:
Number of
Controlled Slip
Seconds
encountered by
a DS1 interface
in the previous
24-hour interval
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Controlled Slip
Seconds)
■ dsx1TotalPCVs:
Number of Path
Coding
Violations
- 62 -
Page 72

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
encountered by
a DS1 interface
in the previous
24-hour interval
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Path Coding
Violations)
■ dsx1TotalBESs:
Number of
Bursty Errored
Seconds
encountered by
a DS1 interface
in the previous
24-hour interval
(OVOC
parameter
name: Trunk
Bursty Errored
Seconds)
G/CIntValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTaHTHTL
T
Trunk Groups
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for trunk groups.
Table 6-8: Performance Monitoring MIBs for Trunk Groups
G
I
V
M
M
A
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
n
a
C
t
l
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupNoResourcesCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.28
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupNoResourcesCalls
Indicates the number of calls that could
not be established due to unavailable
device resources (e.g., no free channels)
C 1
ü û û û û û û
5
i
a
n
x
b
v
g
T
L
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
0 0
- 63 -
Page 73

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
Performance Monitoring MIB
per Trunk Group.
/
n
C
t
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupNoReso
urcesCallsHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.7)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupNoReso
urcesCallsLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.8)
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupCallDurationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.29
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupCallDuration
V
M
M
a
i
a
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the average call duration (in
seconds) of calls per trunk group.
G 1
5
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesCallDurationHighTh
reshold (1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesCallDurationLowThr
eshold (1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.2
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupUtilizationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.26
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupUtilization
Indicates the number of channels
currently in use (busy) per trunk group.
For example, if the device has 240
channels and the threshold is set to 106, if
the number of concurrent busy channels
exceeds 106, this threshold alarm is sent.
Note that if a trunk is in LOF state, this
MIB counts only the channels that are
used.
G 1
5
ü ü ü ü û û û
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
0 0
2
0
1
6
0
■ High threshold:
- 64 -
Page 74

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
M
Performance Monitoring MIB
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupUtilizati
onHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.3)
/
n
a
i
C
t
l
n
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupUtilizati
onLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.4)
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupPercentageUtilizationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.27
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupPercentageUtilization
Indicates the percentage (%) of channels
currently in use (busy) per trunk group.
The device supports configuration of a
busy channel threshold per trunk group,
which when exceeded, sends an SNMP
alarm. For example, if a device has 200
voice channels and the threshold is set to
90%, if the number of concurrent busy
channels exceeds 90% (i.e., 180 channels),
this threshold alarm is sent.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
M
a
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
958
5
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupPercent
ageUtilizationHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.5)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupPercent
ageUtilizationLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.6)
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupAllTrunksBusyTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.25
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupAllTrunksBusy
Indicates the duration (in seconds) that all
channels of a specific trunk group were
G 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
- 65 -
Page 75
CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
M
M
Performance Monitoring MIB
concurrently busy, if this scenario occurs.
For example, if trunk group #3 has 200
channels and all these were concurrently
busy for 60 seconds, then this MIB will
display 60 for this trunk group. Note that
trunks that are out of service or not
configured (set to NONE) are considered
"busy" in this calculation.
/
n
a
i
a
C
t
l
n
x
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPTrunkGroupAllTrunksBusyPercentageTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.40
■ Source Name: PM_gwTrunkGroupAllTrunksBusyPercentage
Indicates the percentage (%) of time
within a 15-minute polling interval, that all
channels in a specific trunk group were
busy simultaneously. This measurement
is sent only at the end of the interval
(beginning of the current interval), so
each measurement reflects the previous
interval. For example, assume that all
trunks of a trunk group were busy for 6
minutes during an interval. The MIB will
send a measurement of 40% (i.e., 6
minutes / 15 minutes * 100). In other
words, all trunks of the trunk group were
simultaneously busy for 40% of the time
during this 15-minute interval.
G 1
ü û û û û û û
5
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
0 0
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupAllTrun
ksBusyPercentageHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.33)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesTrunkGroupAllTrun
ksBusyPercentageLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.34)
■ MIB Name: acPMTrunkUtilizationTable
- 66 -
Page 76
CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.10.2.21
■ Source Name: PM_TrunkUtilization
Indicates the number of busy channels on
a specific E1 / T1 trunk. A busy channel is
when the Physical DS0 Termination isn't in
Null context or OOS.
■ High threshold:
acPMTrunkUtilizationAttributesHighTh
reshold (1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.10.1.31.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMTrunkUtilizationAttributesLowTh
reshold (1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.10.1.31.2)
G
/
C
G 1
I
V
M
M
n
a
i
a
t
l
n
x
T
A
b
v
L
g
T
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
T
T
a
b
T
HTL
H
T
T
302
5
Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Application
This section describes the performance monitoring MIBs of the SBC application.
SBC Sessions
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for SBC sessions. For MIBs that
have low and high thresholds, if a threshold is crossed the device sends the acPerformanceMonitoringThresholdCrossing trap (see Performance Monitoring Threshold-Crossing
Trap on page152).
Table 6-9: Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Sessions
G
I
Performance Monitoring MIB
/
n
C
t
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPSBCAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.42
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCAttemptedCalls
V
a
l
M
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the number of attempted
SBC calls.
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesSBCAttempted
C 1
- 67 -
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
0 0
Page 77

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
CallsHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.37)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesSBCAttempted
CallsLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.38)
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.65
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInAttemptedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
a
C
t
l
M
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the total number of
attempted incoming SBC calls.
C 1
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.67
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutAttemptedCalls
Indicates the total number of
attempted outgoing SBC calls.
C 1
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSIPSBCEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.52.43
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCEstablishedCalls
Indicates the number of established
SBC calls.
C 1
5
■ High threshold:
acPMSipAttributesSBCEstablished
CallsHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.39)
ü û û û û û û û û
ü û û û û û û û û
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
0 0
■ Low threshold:
acPMSipAttributesSBCEstablished
CallsLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.34.40)
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.69
- 68 -
Page 78

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInEstablishedCalls
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
a
C
t
l
M
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the total number of
incoming established SBC calls.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.71
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutEstablishedCalls
Indicates the total number of
outgoing established SBC calls.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.151.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCMediaBrokenConnectionCalls
Indicates the total number of
established calls that were
disconnected because no RTP
packets (media) were received for a
user-defined period (configured by
the BrokenConnectionEventTimeout
parameter).
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInShortCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInShortCalls
Indicates the total number of
incoming calls whose duration was
less than the value configured by the
ShortCallSeconds parameter.
C 1
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutShortCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutShortCalls
Indicates the total number of
outgoing calls whose duration was
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
ü û û û û û û û û
5
- 69 -
Page 79

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
less than the value configured by the
ShortCallSeconds parameter.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInAttemptedRegistrations
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
a
C
t
l
M
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the number of incoming
attempted SBC registrations.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutAttemptedRegistrations
Indicates the number of outgoing
attempted SBC registrations.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number of incoming
successful registrations.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number of outgoing
successful registrations.
C 1
ü û û û û û û û û
5
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCMediaLegsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.47
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCMediaLegs
Indicates the number of media (RTP)
session resources currently utilized.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ High threshold:
- 70 -
0 0
Page 80

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance Monitoring MIB
acPMSbcMediaLegsHighThreshol
d (1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.36.50)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSbcMediaLegsLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.36.51)
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCTranscodingSessionsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.48
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCTranscodingSessions
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
a
C
t
l
M
in
M
A
T
T
Ta
a
v
b
b
x
g
LT
T
HTL
H
T
T
Indicates the number of transcoding
sessions.
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
■ High threshold:
acPMSbcSBCTranscodingSessions
HighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.36.52)
■ Low threshold:
acPMSbcSBCTranscodingSessions
LowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.1.36.53)
SBC Calls per IP Group
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for SBC calls per IP Group.
For additional performance monitoring MIBs for SBC calls per IP Group, see
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Calls per IP Group on page50.
Table 6-10: Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Calls per IP Group
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInCallEstablishedDurationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.1
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInCallEstablishedDuration
Indicates the call C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
- 71 -
HT
HT LT
Page 81

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
duration of the last
incoming established
SBC call per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutCallEstablishedDurationTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutCallEstablishedDuration
Indicates the call
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
duration of the last
outgoing established
SBC call per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAttemptedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.4
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAttemptedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
HT
HT LT
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of attempted incoming
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAttemptedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.5
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAttemptedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of attempted incoming
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
dialogs per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.7
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
of attempted outgoing
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
- 72 -
Page 82

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.8
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of attempted outgoing
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
dialogs per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.10
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed call routing of
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.11
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupRoutingFailedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed call routing of
all dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.12
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedCalls
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed incoming
dialogs due to
Admission Control rules
per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedSubscribeDialogsTable
- 73 -
Page 83

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.13
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed incoming
SUBSCRIBE dialogs
pertaining to Admission
Control per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.14
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAdmissionFailedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed incoming
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE dialogs
pertaining to Admission
Control per IP Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.15
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedCalls
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed outgoing
dialogs pertaining to
Admission Control per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.16
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed outgoing
SUBSCRIBE dialogs
pertaining to Admission
Control per IP Group.
- 74 -
Page 84

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.17
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAdmissionFailedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of failed outgoing
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE dialogs
pertaining to Admission
Control per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInForwardedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.27
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInForwardedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming forwarded
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInForwardedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.28
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInForwardedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming forwarded
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
dialogs per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutForwardedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.30
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutForwardedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing forwarded
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutForwardedOtherDialogsTable
- 75 -
Page 85

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.31
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutForwardedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing forwarded
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
dialogs per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.33
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming SUBSCRIBE
dialogs that failed due
to general fail reason
per IP Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.34
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInGeneralFailedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming dialogs
other than SUBSCRIBE
and INVITE that failed
due to general fail
reason per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.36
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing SUBSCRIBE
dialogs that failed due
to general fail reason
per IP Group.
- 76 -
Page 86

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.37
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutGeneralFailedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing dialogs
other than SUBSCRIBE
and INVITE that failed
due to general fail
reason per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInEstablishedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.39
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInEstablishedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming established
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInEstablishedOtherDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.40
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInEstablishedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming established
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedSubscribeDialogsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.42
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedSUBSCRIBEDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing established
SUBSCRIBE dialogs per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedOtherDialogsTable
- 77 -
Page 87

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.43
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutEstablishedOtherDialogs
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing established
dialogs other than
SUBSCRIBE and INVITE
per IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAbnormallyTerminatedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.44
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAbnormallyTerminatedCalls
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming calls that
were abnormally
terminated per IP
Group.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAbnormallyTerminatedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.45
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAbnormallyTerminatedCalls
Indicates the number
G 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing calls that
were abnormally
terminated per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.151.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupMediaBrokenConnectionCalls
Indicates the number
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of established calls per
IP Group that were
disconnected because
no RTP packets (media)
were received for a
user-defined period
- 78 -
Page 88

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
(configured by the
BrokenConnectionEven
tTimeout parameter).
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInShortCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.5
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInShortCalls
Indicates the number
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming calls per IP
Group, whose duration
was less than the value
configured by the
ShortCallSeconds
parameter.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutShortCallsTable
HT
HT LT
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.6
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutShortCalls
Indicates the number
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of outgoing calls per IP
Group, whose duration
was less than the value
configured by the
ShortCallSeconds
parameter.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.5
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInAttemptedRegistrations
Indicates the number
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
of incoming attempted
user registrations per IP
Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.6
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutAttemptedRegistrations
- 79 -
Page 89

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance
Monitoring MIB
Indicates the number
of outgoing attempted
user registrations per IP
Group.
G/
C
C 15
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
ü û û û û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.5
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number
of successful incoming
registrations per IP
Group.
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.6
HT
HT LT
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number
of successful outgoing
registrations per IP
Group.
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
SBC Calls per SRD
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for SBC calls per SRD.
Table 6-11: Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Sessions per SRD
Performance Monitoring
MIB
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDInAttemptedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.66
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInAttemptedCalls,
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
HT
HT LT
Indicates the number of
incoming attempted calls
per SRD.
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDOutAttemptedCallsTable
- 80 -
Page 90

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring
MIB
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.68
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutAttemptedCalls
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
outgoing attempted calls
per SRD.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDInEstablishedCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.70
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInEstablishedCalls
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
incoming calls per SRD
that were established.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDOutEstablishedCallsTable
HT
HT LT
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.72
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutEstablishedCalls
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
outgoing calls per SRD
that were established.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDMediaBrokenConnectionCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.151.2
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDMediaBrokenConnectionCalls
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
established calls per SRD
that were disconnected
because no RTP packets
(media) were received for
a user-defined period
(configured by the
BrokenConnectionEventT
imeout parameter).
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDInShortCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInShortCalls
- 81 -
Page 91

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring
MIB
Indicates the number of
G/
C
C 15
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
ü û û û û û û û û
incoming calls per SRD,
whose duration was less
than the value configured
by the ShortCallSeconds
parameter.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDOutShortCallsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.152.4
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutShortCalls
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
outgoing calls per SRD,
whose duration was less
than the value configured
by the ShortCallSeconds
parameter.
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDInAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInAttemptedRegistrations
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
incoming attempted user
registrations per SRD.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDOutAttemptedRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.153.4
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutAttemptedRegistrations
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
outgoing attempted user
registrations per SRD.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDInSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.3
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number of
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
incoming successful
- 82 -
Page 92

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Performance Monitoring
MIB
registrations per SRD.
G/
C
ValMinMaxAvgTbLTTbTTa
Int
HT
HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSRDOutSuccessfulRegistrationsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.154.4
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutSuccessfulRegistrations
Indicates the number of
outgoing successful
registrations per SRD.
C 15
ü û û û û û û û û
SBC Calls Per Second
The following table lists the performance monitoring MIBs for SBC calls per second (CPS).
Table 6-12: Performance Monitoring MIBs for SBC Calls Per Second
Performance
Monitoring
MIB
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCInCapsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.59
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCInCPS
Indicates
the number
of CPS for
incoming
SBC calls.
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCOutCapsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.60
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCOutCPS
Indicates
the number
of CPS for
outgoing
SBC calls.
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSrdInCapsTable
- 83 -
Page 93
CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.63
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDInCPS
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Indicates
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
the number
of CPS for
incoming
SBC calls per
SRD.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCSrdOutCapsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.64
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCSRDOutCPS
Indicates
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
the number
of CPS for
outgoing
SBC calls per
SRD.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupInCapsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.61
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupInCPS
Indicates
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
the number
of CPS for
incoming
SBC calls per
IP Group.
■ MIB Name: acPMSBCIPGroupOutCapsTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.8.2.54.62
■ Source Name: PM_gwSBCIPGroupOutCPS
Indicates
G 15
ü ü ü ü û û û û û
the number
of CPS for
- 84 -
Page 94
CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
Performance
Monitoring
G/C Int Val Min Max Avg TbLT TbT TaHT HT LT
MIB
outgoing
SBC calls per
IP Group.
Performance Monitoring MIB for DSP Resource Utilization
The following table lists the SNMP MIB that reports the percentage of DSP resources utilized by
the device. Low and high thresholds can also be defined, which if crossed, the SNMP trap
event, acPerformanceMonitoringThresholdCrossing is sent by the device.
Table 6-13: Performance Monitoring MIB for DSP Utilization
Performance Monitoring MIB
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
G
I
V
/
n
C
t
a
l
MinM
ax
A
T
T
v
bL
g
T
b
T
TaHTH
LT
T
■ MIB Name: acPMDSPUsageTable
■ OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.2.25
■ Source Name: PM_VEDSPUsage
Indicates the percentage (%) of DSP
resources utilized by the device. A
value of 0% indicates that no DSP
resources have been used; a value
of 100% indicates that all DSP
resources have been used.
■ High threshold:
acPMMediaDSPUsageAttrDSPUs
ageHighThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.35.1)
■ Low threshold:
acPMMediaDSPUsageAttrDSPUs
ageLowThreshold
(1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.10.7.1.35.2)
G 1
ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü
5
(1
1)
ü
(1
0
0
1)
Performance Monitoring MIBs for Data-Router Networking
The acSysDataInterfaceStatusTable (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.10.2.6.4.22) table lists the
performance monitoring MIBs for Data Networking. This table contains a summary of the IP
status and configuration of the data interfaces. The interface types are: VLAN, loopback, sub
- 85 -
Page 95

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
interface, physical port, bridge, Dot11, GRE, IPIP, PPPoE, L2tp, PPTP, ATM, ATM VLAN, cellular,
serial, multilink. Every entry in the table represents a data/logic interface and contains the
following fields:
Table 6-14: Performance Monitoring MIBs for Data Networking
MIB Name Description
Name Interface name
IPAddress IPv4 address for this interface
Netmask Netmask for this interface
Info Status of interface can be one of the following: Unknown, Disabled,
Description Description of the interface
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Enabled, Connected or Disconnected
OperationalState Protocol is Up or Down
StateTime State Time (hh:mm:ss)
Uptime Uptime (hh:mm:ss)
MtuMode Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on the specified interface. Can
be: automatically, DHCP or value (in bytes)
DnsStatus The primary and secondary IP addresses
RxPackets Total packets received
RxBytes Total bytes received
RxDropped No space in Linux buffers
RxErrors Bad packets received
TxPackets Total packets transmitted
TxBytes Total bytes transmitted
TxDropped No space available in Linux
TxErrors Packet transmit problem
Minutes Determines the time interval (minutes) in which the rate sampling is
done. The value is relevant to the columns MinuteInputRate and
MinuteOutputRate. The value is 5 minutes.
- 86 -
Page 96

CHAPTER6 Performance Monitoring
MIB Name Description
MinuteInputRate Average value of packets and bits transmitted (per second units) in
MinuteOutputRate Average value of packets and bits received (per second units) in the
Seconds Determines the time interval (seconds) in which the rate sampling is
SecondInputRate Average value of packets and bits transmitted (per second units) in
SecondOutputRate Average value of packets and bits received (per second units) in the
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
the last x minutes.
last x minutes. The output rate is exponentially weighted averages
with a time of x minutes.
done. The value is relevant to the columns SecondInputRate and
SecondOutputRate. The value is 15 seconds.
the last x seconds.
last x seconds. The output rate is exponentially weighted averages
with a time of x seconds.
- 87 -
Page 97

CHAPTER7 SNMP Traps
7 SNMP Traps
This section describes the SNMP traps supported by the device.
Standard Traps
The device also supports the following standard traps:
■ authenticationFailure
■ coldStart: The device supports a cold start trap to indicate that the device is starting up.
This allows the OVOC to synchronize its view of the device's active alarms. In fact, two
different traps are sent at start-up:
● Standard coldStart trap: iso(1).org(3).dod(6).internet(1). snmpV2(6). snmpModules(3).
snmpMIB(1). snmpMIBObjects(1). snmpTraps(5). coldStart(1) sent at system
initialization.
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
● Enterprise acBoardEvBoardStarted: generated at the end of system initialization. This
is more of an "application-level" cold start sent after all the initializing process is over
and all the modules are ready
■ linkDown
■ linkup
■ entConfigChange
■ dsx1LineStatusChange (Applicable only to Digital Series)
Proprietary Traps
This section provides information on proprietary SNMP traps supported by the device. There is
a separation between traps that are alarms and traps that are not (i.e., logs). All traps have the
same structure made up of the same 16 varbinds (Variable Binding), i.e.,
1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.1. For a list of the varbinds, see Trap Varbinds on the next page.
The source varbind is composed of a string that details the device component from which the
trap is being sent (forwarded by the hierarchy in which it resides). For example, an alarm from
an SS7 link has the following string in its source varbind: acBoard#1/SS7#0/SS7Link#6. The SS7
link number is specified as 6 and is part of the only SS7 module in the device that is placed in
slot number 1 (in a chassis) and is the module to which this trap relates. For devices where
there are no chassis options, the slot number is always 1.
Full proprietary trap definitions and trap varbinds are found in AcBoard MIB and AcAlarm MIB.
All traps are sent from the SNMP port (default 161).
- 88 -
Page 98

CHAPTER7 SNMP Traps
Trap Varbinds
Trap varbinds are sent with each proprietary SNMP trap. Refer to the AcBoard MIB for more
information on these varbinds.
acBoardTrapGlobalsName (1) Alarm or event number. The number value is
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Table 7-1: Trap Varbinds for Proprietary SNMP Traps
Trap Varbind Description
obtained from the last digit(s) of the OID of
the sent trap, and then subtracted by 1. For
example, for the trap
acBoardEthernetLinkAlarm, which has an OID
of 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.10, the value
of the varbind is 9 (i.e., 10 – 1).
The value is an integer from 0 to 1000.
acBoardTrapGlobalsTextualDescription
(2)
Description of the reported issue.
The value is an octet string of up to 200
characters.
acBoardTrapGlobalsSource (3) The source of the issue. For example, Trunk#1
or Entity1#x.
The value is an octet string of up to 100
characters.
acBoardTrapGlobalsSeverity (4) Active alarm severity on the device:
■ noAlarm(0)
■ indeterminate(1)
■ warning(2)
■ minor(3)
■ major(4)
■ critical(5)
AcBoardTrapGlobalsUniqID (5) Consecutive number count of trap since
device was powered on. The number is
managed separately for alarms and events.
For example, you may have an alarm whose
value is 1 and an event whose value is 1.
The value is an integer from 0 to 32000.
acBoardTrapGlobalsType (6)
■ other(0)
- 89 -
Page 99

CHAPTER7 SNMP Traps
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Trap Varbind Description
■ communicationsAlarm(1)
■ qualityOfServiceAlarm(2)
■ processingErrorAlarm(3)
■ equipmentAlarm(4)
■ environmentalAlarm(5)
■ integrityViolation(6)
■ operationalViolation(7)
■ physicalViolation(8)
■ securityServiceOrMechanismViolation(9)
■ timeDomainViolation(10)
acBoardTrapGlobalsProbableCause (7)
■ other(0)
■ adapterError(1)
■ applicationSubsystemFailure(2)
■ bandwidthReduced(3)
■ callEstablishmentError(4)
■ communicationsProtocolError(5)
■ communicationsSubsystemFailure(6)
■ configurationOrCustomizationError(7)
■ congestion(8)
■ corruptData(9)
■ cpuCyclesLimitExceeded(10)
■ dataSetOrModemError(11)
■ degradedSignal(12)
■ dteDceInterfaceError(13)
■ enclosureDoorOpen(14)
■ equipmentMalfunction(15)
■ excessiveVibration(16)
■ fileError(17)
■ fireDetected(18)
- 90 -
Page 100

CHAPTER7 SNMP Traps
MSBR | SNMP Reference Guide
Trap Varbind Description
■ floodDetected(19)
■ framingError(20)
■ heatingVentCoolingSystemProblem(21)
■ humidityUnacceptable(22)
■ inputOutputDeviceError(23)
■ inputDeviceError(24)
■ lanError(25)
■ leakDetected(26)
■ localNodeTransmissionError(27)
■ lossOfFrame(28)
■ lossOfSignal(29)
■ materialSupplyExhausted(30)
■ multiplexerProblem(31)
■ outOfMemory(32)
■ ouputDeviceError(33)
■ performanceDegraded(34)
■ powerProblem(35)
■ pressureUnacceptable(36)
■ processorProblem(37)
■ pumpFailure(38)
■ queueSizeExceeded(39)
■ receiveFailure(40)
■ receiverFailure(41)
■ remoteNodeTransmissionError(42)
■ resourceAtOrNearingCapacity(43)
■ responseTimeExecessive(44)
■ retransmissionRateExcessive(45)
■ softwareError(46)
■ softwareProgramAbnormallyTerminated
(47)
- 91 -
 Loading...
Loading...