Page 1

Integration Guide
AudioCodes One Voice Operation Center (OVOC)
OVOC
Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Version 8.0
Page 2
Notice
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Notice
Information contained in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable at the time
of printing. However, due to ongoing product improvements and revisions, AudioCodes
cannot guarantee accuracy of printed material after the Date Published nor can it accept
responsibility for errors or omissions. Updates to this document can be downloaded from
https://www.audiocodes.com/library/technical-documents.
This document is subject to change without notice.
Date Published: March-11-2021
WEEE EU Directive
Pursuant to the WEEE EU Directive, electronic and electrical waste must not be disposed of
with unsorted waste. Please contact your local recycling authority for disposal of this product.
Customer Support
Customer technical support and services are provided by AudioCodes or by an authorized
AudioCodes Service Partner. For more information on how to buy technical support for
AudioCodes products and for contact information, please visit our website at https://www.au-
diocodes.com/services-support/maintenance-and-support.
Documentation Feedback
AudioCodes continually strives to produce high quality documentation. If you have any
comments (suggestions or errors) regarding this document, please fill out the Documentation
Feedback form on our website at https://online.audiocodes.com/documentation-feedback.
Stay in the Loop with AudioCodes
Document Name
OVOC Documents
Migration from EMS and SEM Ver. 7.2 to One Voice Operations Center
One Voice Operations Center IOM Manual
One Voice Operations Center Product Description
- ii -
Page 3

Notice
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Document Name
One Voice Operations Center User’s Manual
Device Manager Pro Administrator's Manual
One Voice Operations Center Alarms Monitoring Guide
One Voice Operations Center Performance Monitoring Guide
One Voice Operations Center Security Guidelines
One Voice Operations Center Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Device Manager for Third-Party Vendor Products Administrator's Manual
Device Manager Agent Installation and Configuration Guide
ARM User’s Manual
Documents for Managed Devices
Mediant 500 MSBR User's Manual
Mediant 500L MSBR User's Manual
Mediant 500Li MSBR User's Manual
Mediant 500L Gateway and E-SBC User's Manual
Mediant 800B Gateway and E-SBC User’s Manual
Mediant 800 MSBR User’s Manual
Mediant 1000B Gateway and E-SBC User’s Manual
Mediant 1000B MSBR User’s Manual
Mediant 2600 E-SBC User's Manual
Mediant 3000 User’s Manual
Mediant 4000 SBC User's Manual
Mediant 9000 SBC User's Manual
Mediant Software SBC User's Manual
- iii -
Page 4
Notice
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Document Revision Record
LTRT Description
19226 Update to Section:MGs Topology List; Alarm Forwarding Data Formats; OVOC
Server Backup and Restore; Data Analytics API
Section:Step 6 Configuring AudioCodes Azure Active Directory (Operator
Authentication) moved to IOM
- iv -
Page 5

Content
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Table of Contents
1 Overview 1
2 OVOC Integration 2
OVOC Integration Elements 2
OVOC Topology File 2
Alarms 2
Gateway Status 3
Security 3
Configuration and Maintenance 3
MIB Folder 3
NBIF Folder 3
3 Topology Files 6
MGs Topology List 6
Topology.xml File 7
4 Managing PM Files 9
Saving PM Filter Queries 9
Creating PM Data File 10
5 Fault Management 11
Alarms and Events Forwarding to the NMS 11
Forwarding Alarms from OVOC Server to the NMS 12
Forwarding Alarms Directly from Devices to NMS 20
Alarm Aggregation 20
Examples of Aggregated Alarms 20
Alarm Forwarding Data Formats 22
OVOC Server Alarm Settings 28
Alarms Automatic Clearing (on Startup) 28
Alarms Automatic Clearing Period (Days) 29
Events Clearing Mechanism 29
Alarm Suppression Mechanism 29
Alarms Sequence Numbering 29
SNMP Alarms Synchronization 32
Resynchronization (Resync) Mechanism 32
OVOC Keep-alive 34
Status / State Management via Devices SNMP Interface 37
6 Voice Quality Reports 38
7 OVOC Server Backup and Restore 41
8 Data Analytics API 44
9 Security 47
Network Communication Protocols 47
OVOC User Identity Management 48
- v -
Page 6

Content
Authentication and Authorization using a Radius Server 48
Configuring Radius Server Client 49
Configuring RADIUS Server 50
Authentication and Authorization using an LDAP Server 51
Authentication and Authorization using Microsoft Azure 52
Step 6 Configuring AudioCodes Azure Active Directory (Operator Authentication) 53
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
HTTPS Connection 60
10 Data Analytics API Database Tables 61
Main Table Views 61
Type Views 75
- vi -
Page 7

Content
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
This page is intentionally left blank.
- vii -
Page 8

CHAPTER1 Overview
1 Overview
AudioCodes One Voice Operations Center OVOC delivers a comprehensive management tools
suite comprising of base platform and add-on modular applications for the management,
monitoring and operation of converged VoIP and data networks implemented in large-scale
cloud or premise-based unified communications deployments using AudioCodes devices. The
products that are managed by the OC include the Session Border Controllers (SBC), Media
Gateways, Microsoft Survivable Branch Appliances (SBA), Multi Service Business Router
(MSBR), residential gateways and devices .OVOC also integrates with the Microsoft Skype for
Business environment platforms.
The Network Operations Center's core product, the Operations Center OC manages these
products in a centralized device inventory via a Web client, enabling integrative network
operations. The following describes the key products in the OC suite:
■ The One Voice Operations Center: The OVOC is an advanced solution for remote
standards-based management of AudioCodes products within VoP networks, covering all
areas vital for their efficient operation, administration, management and security. A single
user interface provides real time information including network and device component
status, activity logs and alarms. Complete End-to-End network control includes data on all
devices, all locations, all sizes, all network functions and services and full control over the
network, including services, updates, upgrades, and operations. The OVOC is in
AudioCodes’ assessment, the best tool to manage AudioCodes devices. However, it does
not replace the NMS and OSS management systems, which displays to operators a
comprehensive view of the network, including other vendors’ equipment. After defining
and initially provisioning a device via the device's embedded Web server tool, operators
will usually work with an NMS / OSS for day-to-day maintenance. Only in the event of
problems with a device or when significant maintenance tasks must be performed, will
operators open the OVOC and work directly with it. Consequently, the OVOC provides
APIs for faults monitoring (alarms) and security integration with a higher level
management system.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ Voice Quality Management: Voice Quality Management involves the analyze of real-time
Voice Quality statistics, which enables the rapid identification of the metrics responsible
for degradation in the quality of any VoIP call made over the network nodes including
AudioCodes devices and links. It provides an accurate diagnostic and troubleshooting tool
for analyzing quality problems in response to VoIP user criticism. It proactively prevents
VoIP quality degradation and optimizes quality of experience for VoIP users. In addition, it
integrates with Microsoft Skype for Business monitoring server to provide end-to-end
VoIP quality monitoring on Microsoft Skype for Business deployments. In addition, Voice
Quality integrates and monitors with endpoints reporting RFC 6035 SIP PUBLISH packets.
■ The Device Manager Pro: Enables enterprise network administrators to effortlessly and
effectively set up, configure and update up to 30000 400HD Series IP phones in globally
distributed corporations. These phones can upload configuration files from the OVOC
server and send status updates over the REST protocol.
- 1 -
Page 9

CHAPTER2 OVOC Integration
2 OVOC Integration
This document describes how to integrate the network elements of AudioCodes One Voice
Operation Center (OVOC) with northbound interfaces. This includes the integration of alarms
and events that are generated by the managed elements, the XML files polling and the
Topology file. The figure below illustrates this integration.
Figure 2-1: OVOC Integration Overview
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
OVOC Integration Elements
This section describes the integration elements.
OVOC Topology File
The OVOC Topology file includes a snapshot of all the devices that are defined in the OVOC
application. This file is located on the OVOC server and is available for the higher level
management system (see Topology Files).
Alarms
Alarms are forwarded to the NMS as SNMP notifications (traps). These alarms can be
forwarded using one of the following methods:
■ Forwarded by the OVOC application to the NMS server (for all the network elements and
the OVOC itself).
- 2 -
Page 10
CHAPTER2 OVOC Integration
■ Sent directly by each one of the network elements directly to the NMS server. In this case,
there is the possibility to enable OVOC alarms. For example, when a connection between
the OVOC server and device is established or lost, traps are forwarded to the NMS server.
For detailed information, see Fault Management.
Gateway Status
The status of a device can be determined based on the set of supported IETF Management
Information Base (MIB-II) tables (described in the SNMP Reference Guide).
Security
Security integration covers two main areas: Users Management and Network Communication
protocols.
■ OVOC Users Management (Authentication and Authorization) locally in the OVOC
database or via a centralized RADIUS server or LDAP server.
■ Network Communication Protocols:
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
● HTTP/HTTPS:
◆ NBIF Client- OVOC server connection is secured by default over HTTPS port 443
using AudioCodes default certificates or custom certificates
◆ File transfer
● SNMPv2 and SNMPv3: For Maintenance actions and Faults
● SSH/SFTP/SCP: used for File transfer
For detailed information, see OVOC Server Backup and Restore
Configuration and Maintenance
A REST API will be available in a future release for performing configuration and maintenance
actions from the NMS and running automation scripts using REST API URLs. For more
information, contact your AudioCodes representative.
MIB Folder
AudioCodes MIB files are located under the following folder:
/opt/ACEMS/server_<server.version>/externals/mibs/
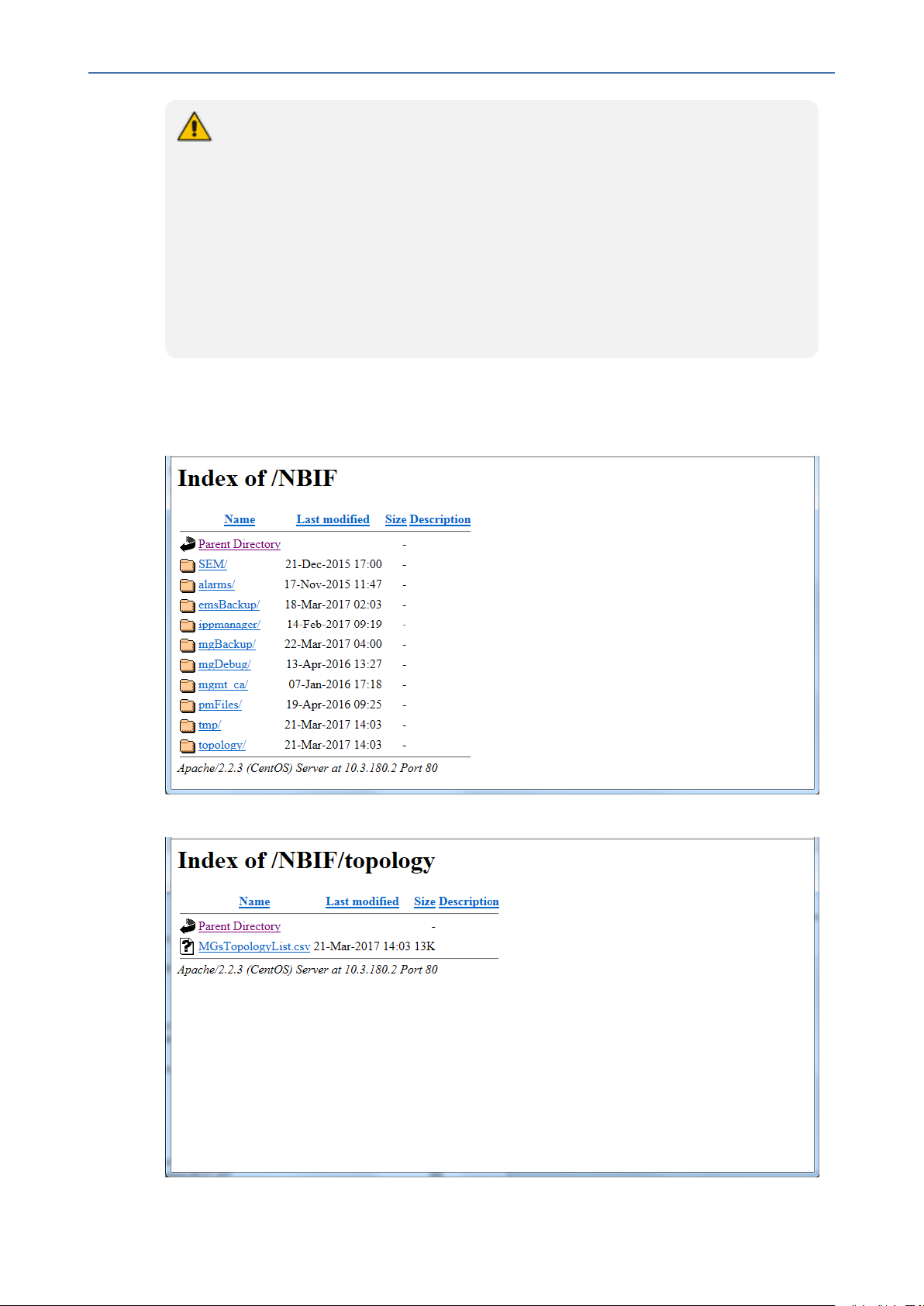
NBIF Folder
All OVOC and device information available for the NMS and other Northbound interfaces
including Topology and Backup data is located in the OVOC server machine under the folder
/NBIF. This folder can be accessed using HTTPS browsing by entering the URL https://<OVOC
server IP>/NBIF in your Web browser.
- 3 -
Page 11
CHAPTER2 OVOC Integration
● The customer’s Web browser must have installed the appropriate X.509
certificates signed by the same Certificate Authority (CA) as the OVOC server
web browser certificates. Choose the appropriate certificate, and then click OK.
● For more information on the implementation of X.509 certificates, refer to the
OVOC Security Guidelines.
● HTTP/S access to the NBIF folder requires a user name and password. This is
required for multi-tenancy support where only authorized tenants should be able to
access the NBIF folder. The Default user name is “nbif” and the default password
“pass_1234”. This password can be changed using the OVOC server Manager, for
more information, refer to Section Change HTTP/S Authentication Password for
NBIF Directory in the OVOC Server IOM.
The 'NBIF' folder content opens; double-click each one of the folders to list its contents.
Double-click each file to open its contents.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 2-2: NBIF Parent Directory
Figure 2-3: NBIF Topology Directory
- 4 -
Page 12
CHAPTER2 OVOC Integration
The 'NBIF' folder contains the following sub-folders:
■ SEM: this folder contains Scheduled Reports. For more information, see Voice Quality
Reports
■ alarms: this folder contains a file saved by the OVOC user (Actions > Save Alarms To File'
which is available in the Active Alarms/History Alarms and Journal pages) where the action
result displays no less than 1500 records. This file is created for local user requests and
must not be collected by higher level Management or Backup systems.
■ emsBackup: this folder contains the daily and weekly backup of the OVOC server. For
more information, see OVOC Server Backup and Restore.
■ ippmanager (Device Manager): this folder contains the following folders:
● generate: contains the device firmware files
● regioncache: contains the device global cfg files
● sess: contains system folder for sessions management
● templates: contains the device cfg template files
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
● tmp: contains system folder for temporary files
■ mgBackup: this folder contains the backed up device INI and CLI configuration files.
■ mgDebug: this folder contains Syslog and Packets debug information.
■ Mgmt_ca: this folder contains the default certificate files for the OVOCManaged devices
and the OVOC Root CA file.
■ pmFiles:this folder contains the output XMLfile for Performance Monitoring data that is
collected per polling interval according to the PMProfile and output to XMLfile according
to the filter settings.
■ topology: A Summary file of all the devices and their basic properties defined in the OVOC
application. The summary file is located under the 'topology' folder and is always named
MGsTopologyList.csv. For more information, see Topology Files.
- 5 -
Page 13

CHAPTER3 Topology Files
3 Topology Files
Topology files are created and maintained by the OVOC application. These file includes
updated information on the OVOC topology. The following files are generated by the OVOC
server:
■ MGsTopologyList.csv (see below)
■ Topology.xml file (see Topology.xml File)
Both the 'MGsTopologyList.csv' and the Topology.xml file can be retrieved using one of the
following methods:
■ Using the ‘Collect Logs’ option in the EMS Server Manager
■ By FTP or SFTP protocol
■ Via Telnet or SSH using 'nbif' user with user nbif, pass_1234
The Topology.xml must be generated manually using the Topology Export procedure
(described below in Topology.xml File).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
MGs Topology List
The MGsTopologyList.csv file is used by the NMS system to synchronize the list of devices that
are currently managed by the OVOC for the purposes of Alarms Forwarding integration. For
example, if a specific device has not been receiving alarms, you can verify in the topology file,
whether the relevant device is displayed in the list of connected gateways.
The Topology file is automatically updated upon the addition /removal of a device or upon
updates to the device's properties, such as name, IP address or region modification. The OVOC
sends 'acEMSTopologyUpdateEvent' (Topology Update) for changes in the definition or update
of a device and sends 'acEMSTopologyFileEvent (Topology File Generated) for a topology file
update. These events are displayed in the OVOC Alarm Browser and in the NMS Alarm Browser
when the 'OVOC Events Forwarding' check box is selected in the Trap Configuration
'Destination Rule Configuration' dialog.
When multiple devices are added, the Topology file is updated approximately once per minute
as the entire operation may take more than a few minutes. For detailed information on the
exact event fields, refer to the OVOC Alarms Guide.
The file header is composed of two lines commencing with “;” file format version, and column
names. Each row in the file represents a device in the OVOC tree and includes the following
information:
■ Device Serial Number (displays either 32-bit and 64-bit serial numbers for SBC devices)
according to the device firmware version and configuration settings in the externals/configurationProperties/generalConfig file for the include_serial_string.
■ IP Address
■ FQDN
- 6 -
Page 14

CHAPTER3 Topology Files
■ Node Name
■ Region Name
■ Description
■ Product Type
■ Software Version
■ Connection Status – Connected / Not Connected – represent the ability of OVOC
application to communicate with the device
■ Administrative State – Locked / Unlocked / Shutting Down
■ Operational State – Enabled / Disabled
■ Mismatch State – No Mismatch / Software Version Unsupported / Software Mismatch /
Hardware Mismatch.
■ Last Change Time
■ Protocol Type –SIP
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ Reset Needed
■ SBA FQDN Name
■ SBA IP Address
■ SNMP Version – options are SNMPv2/SNMPv3
■ SNMP Read – encrypted SNMP read community
■ SNMP Write – encrypted SNMP write community
■ SNMP User Profile - SNMP v3 user credentials in format: (EnginID;Se-
curityName;SecurityLevel;AuthProtocol;PrivacyKey)
■ Gateway User – user name for MG web access
■ Gateway Password– user password for device web access
■ HTTPS Enabled – 0-disabled/1-enabled HTTPS access to the device
■ Tenant Name
See an example Excel file view in the figure below.
Figure 3-1: Topology File-Excel View
Topology.xml File
The Topology.xml file backs up the following data:
- 7 -
Page 15
CHAPTER3 Topology Files
■ Tenants/Regions/Sites
■ AudioCodes devices
■ Skype for Business devices
■ Generic devices
■ Links
■ SBAs/CloudBond/CCE Appliances
■ License Pool configuration for each managed device
➢ To export the OVOC topology xml file:
1. Log in to the OVOC server platform as 'root' user with password root (default password is
root):
su – root
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
2. Change directory to /ACEMS/server_7.4.xxx:
cd /ACEMS/server_7.4.xxx
3. Execute topologyExport.pl script:
./topologyExport.pl
- 8 -
Page 16
CHAPTER4 Managing PM Files
4 Managing PM Files
Performance Monitoring data can be retrieved as follows:
■ Data files can be generated for polled data according to PM profile for each polling interval
(see Creating PM Data File)
■ Filter queries can be saved to an XMLfile which you can save to an external location (see
Saving PM Filter Queries)
Performance Monitoring parameters can be managed using SNMP and REST API.
Saving PM Filter Queries
You can save PMfilter queries to a CSVfile by selecting the option Save Device PM Data.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
➢ To save PMfilter queries:
1. In the OVOC Web, open the Network Devices page (Network tab >Devices menu).
2. Select the device whose data you wish to extract and click Show.
3. Verify that the device is currently being polled.
4. Click the Statistics tab and add a new filter.
5. Click Save Device PMData.
Filter output is saved to a CSV file; save the file to the desired external location. See
example file below.
Figure 4-1: PMData File
- 9 -
Page 17

CHAPTER4 Managing PM Files
Creating PM Data File
A PM data file can be automatically generated when the option "Create Data File" is selected in
the PM Profile in the OVOC Web. The data file is generated for polled data for each polling
interval for all parameters that are defined in the profile. These files can be retrieved from the
NBIF directory (see NBIF Folder).
➢ To create a PM data file:
1. In the OVOC Web, open the Add PMProfile screen (Statistics > PM Profiles > Add).
2. Select the 'Create Data File' check box.
See example XML format in XML editor below.
Figure 4-2: Performance Monitoring XMLOutput
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
- 10 -
Page 18

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
5 Fault Management
AudioCodes devices report their faults (alarms and events) and state changes
(Administrative/Operative state) via SNMP notification traps. Both standard and proprietary
traps are supported. AudioCodes proprietary traps have the same variable bindings set. Each
alarm includes information required by the ITU- T X.733 standard. Operative and
Administrative states are managed according to the ITU-T X.731 standard. See the OVOC
Alarms Guide for the exact list of standard, MG proprietary and OVOC proprietary traps that
are supported for each device. For each trap description, it’s indicated whether the trap is
defined as an alarm or an event.
Alarms and Events Forwarding to the NMS
Alarms can be forwarded to the NMS using one of the following methods:
■ Alarms and events are forwarded by the OVOC application to the NMS for all network
elements (devices, IP Phones and endpoints (purple-colored path in the figure below) or
only Management alarms and events are forwarded (green-colored path in the figure
below).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ Each one of the network elements (devices and devices) sends its own alarms directly to
the NMS (blue-colored path in the figure below). The device can send alarms to several
destinations (the exact number of destinations depends on the device type). For example,
the device can send alarms to the OVOC and NMS. You can configure each destination
with a different trap port.
Traps are forwarded to the NMS as SNMPv2 or SNMPv3 Notifications. The SNMPv3 protocol
provides more sophisticated security mechanisms than SNMPv2c. It implements a user-based
security model (USM), allowing both authentication and encryption of the requests sent
between the OVOC Manager and their agents, as well as user-based access control. SNMP can
be configured in the OVOC at the global level using an SNMP Connectivity template, at the
tenant level (Tenant SNMP Profile). You must configure identical SNMP settings on all managed
devices.
Although the OVOC can forward alarms and events in several formats (SNMP Notifications, Mail and Syslog), alarms and events are always sent to an NMS as SNMP
notifications for purposes of NMS integration.
- 11 -
Page 19

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 5-1: Alarm and Event Forwarding
Forwarding Alarms from OVOC Server to the NMS
This section describes how to configure alarms forwarding from the OVOC server to the NMS.
➢ To forward alarms from the OVOC to the NMS:
1. Open the Alarms Forwarding page (Alarms > Forwarding).
- 12 -
Page 20
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
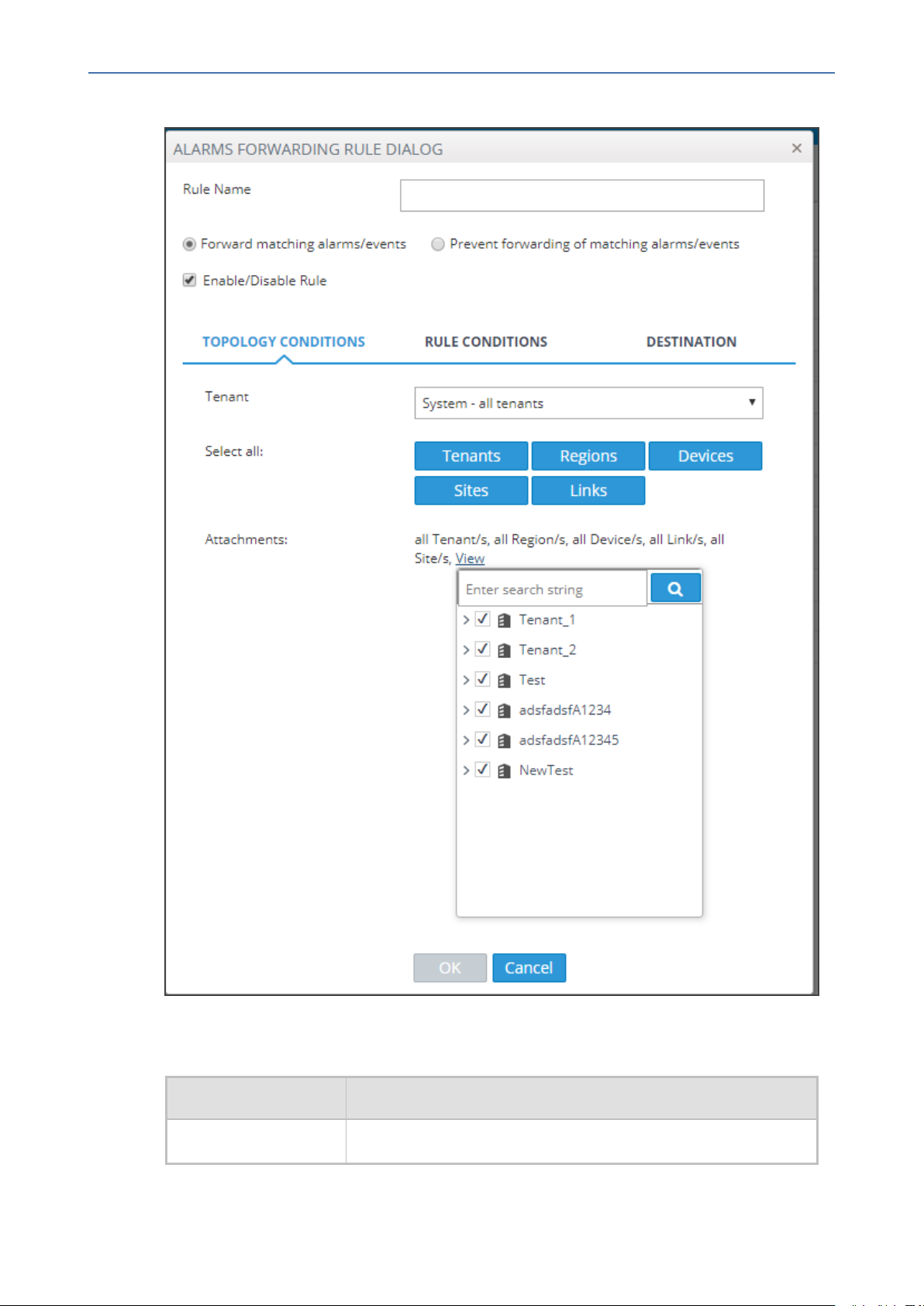
Figure 5-2: Alarms – Forwarding – Topology Conditions
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
2. Configure using the table below as a reference:
Table 5-1: Forwarding Alarms – Topology Conditions - Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Rule Name Define an intuitive name, to be displayed in the alarm summary
- 13 -
Page 21
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Parameter Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
screen.
Forward matching
alarms/events -or-
Prevent forwarding
matching
alarms/events
Allows or prevents forwarding alarms as Emails or Syslog
depending on the option you select from the 'Destination Type'
dropdown under the Destination tab. If for example you select
Prevent forwarding matching alarms/events and then select
Minor Alarms from the 'Severities' dropdown under the Rule
Conditions tab, then minor alarms are not forwarded.
Enable/Disable Rule Enables or disables the rule if the parameters and conditions
configured under this tab as well as under Rule Conditions and
Destinations are met.
Tenant From the dropdown, select System – all tenants; the rule will
then apply to all tenants and to all regions/links/devices/sites
under all tenants.
Next to 'Attachments', you'll then view:
all Tenant/s, all Region/s, all Device/s, all Link/s, all Site/s
Click View to view all tenants in a collapsed tree; expand the
branches to view and select specific regions/links/devices/sites
to apply the rule to.
Alternatively: Select from the dropdown a specific tenant; the
rule will be applied only to regions/links/devices/sites under
that specified tenant.
Tenants|Regions
Devices|Sites|Links
Click View to view only that specified tenant displayed in the
tree. You can expand the tenant to view and select specific
regions/links/devices/sites under it.
Click a button to apply the rule to that entity and the entities
under it. The buttons filter the System – all tenants option
described above. For example, if you want the rule to be applied
to all tenants but only to devices under all tenants, click the
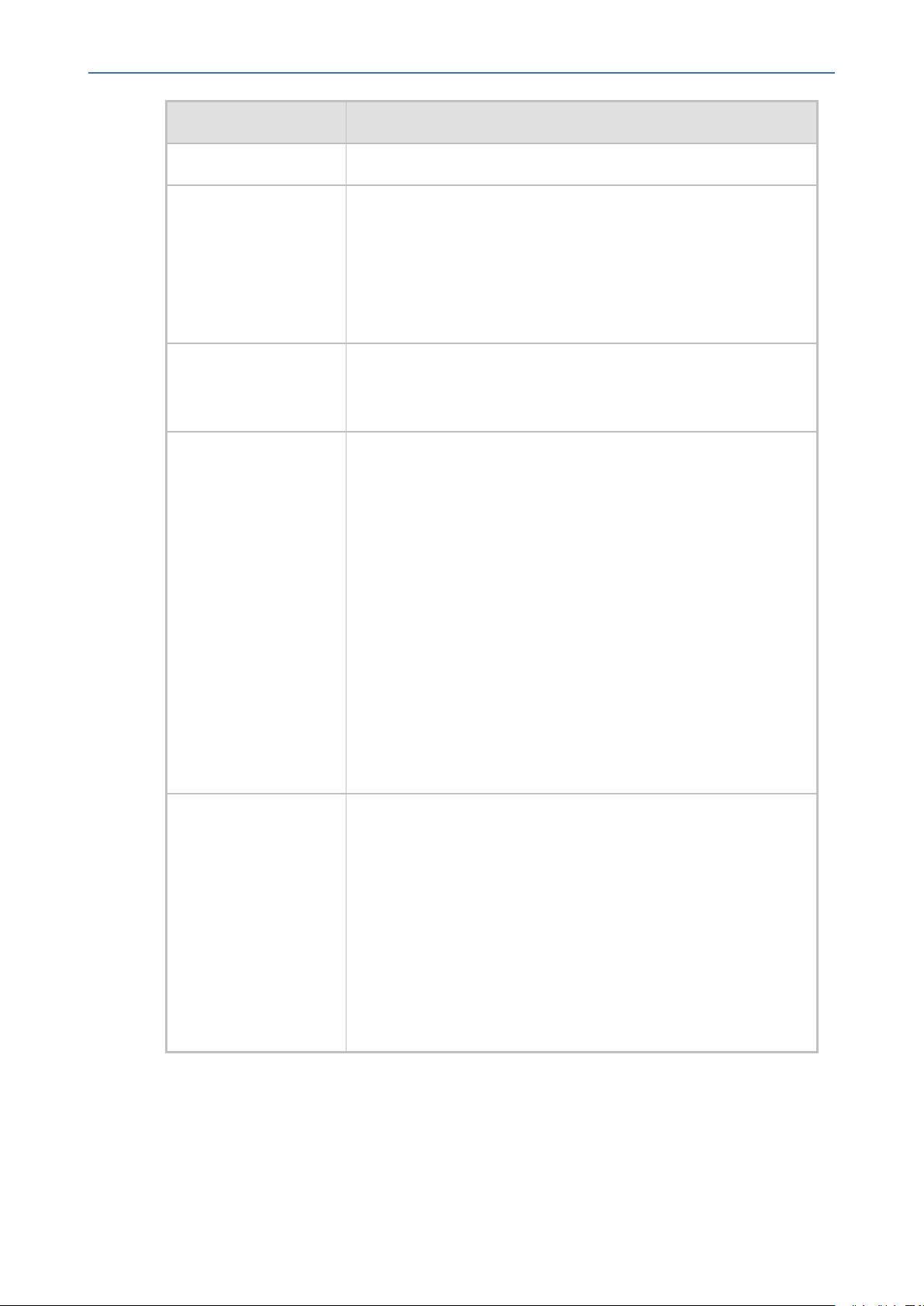
Devices button. Next to 'Attachments' you'll then view:
0 Tenant/s, 0 Region/s, all Device/s, 0 Link/s, 0 Site/s
If you click the View link, you'll view all tenants and all devices
under them displayed in a collapsed tree. After expanding the
tree and selecting specific entities, 'All Devices' will change to n
devices as follows:
- 14 -
Page 22
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Parameter Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
3. Click OK or optionally click the Rule Conditions tab.
- 15 -
Page 23
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Figure 5-3: Alarms – Forwarding – Rule Conditions
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
4. Configure using the table below as a reference:
Table 5-2: Forwarding Alarms – Rule Conditions - Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
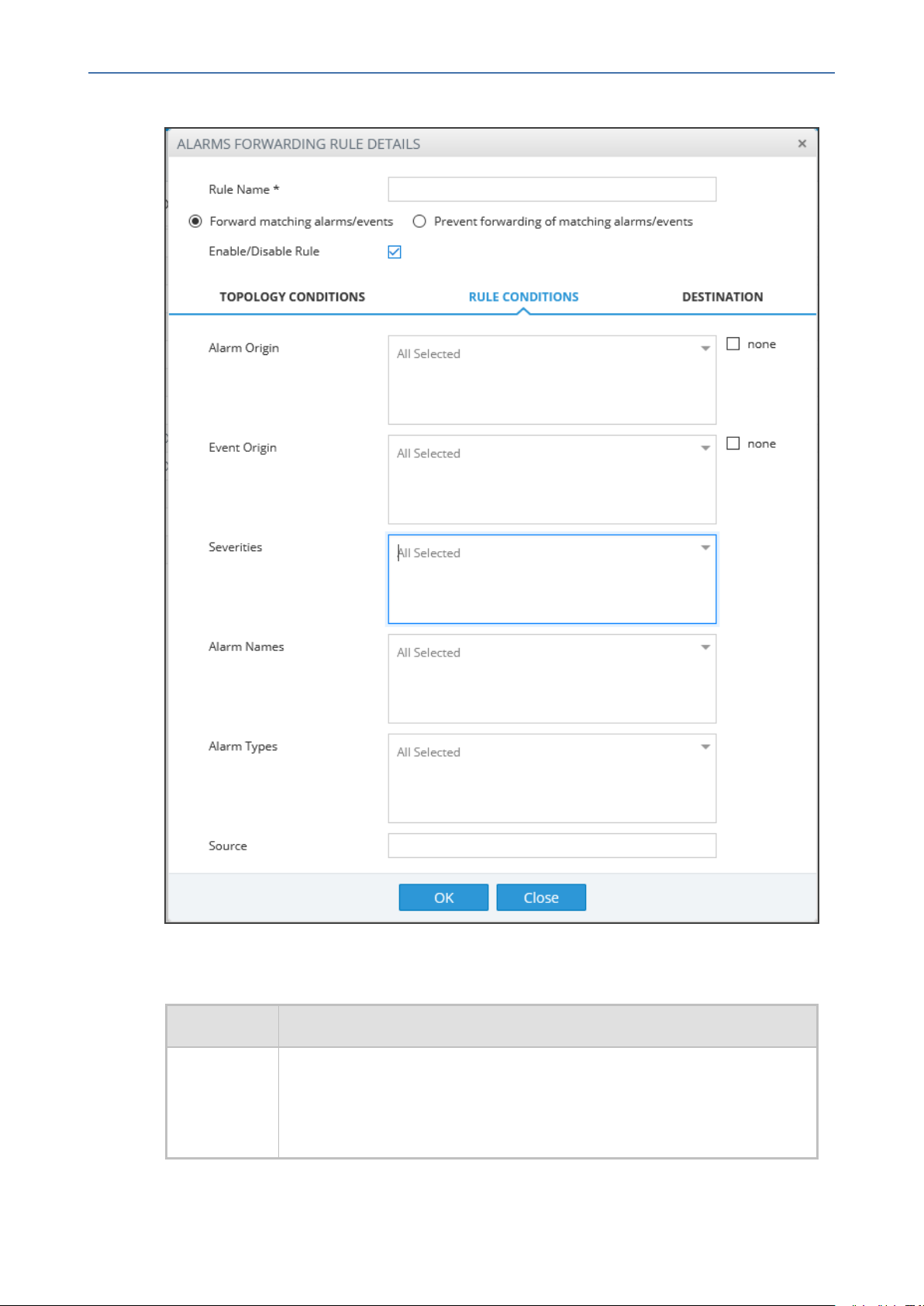
Alarm Origin Select the origin from which alarms will be forwarded:
■ Management
■ QoE
- 16 -
Page 24

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Parameter Description
Event Origin Select the origin from which events will be forwarded:
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ Devices
■ Endpoints
■ ARM
■ VIP Endpoint Users
■ Management
■ QoE
■ Devices
■ Endpoints
■ ARM
■ VIP Endpoint Users
Severities From the 'Severities' dropdown, select the severity level of the alarms you
want to receive:
■ Warning
■ Minor
■ Major
■ Critical
■ Indeterminate
Default: All Selected.
Alarm Names Allows forwarding alarms according to specific alarm names. For example, if
you select Power Supply Failure then only this alarm will be forwarded.
Default: All Selected.
Alarm Types Allows forwarding alarms according to specific alarm types. For example, if
you select communicationsAlarm then only this alarm type will be
forwarded.
Default: All Selected.
5. Click OK or - optionally - click the Destination tab.
- 17 -
Page 25
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Figure 5-4: Alarms – Forwarding – Destination SNMPv3
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
6. Configure using the tables below as reference:
Table 5-3: Forwarding Alarms – Destination
Parameter Description
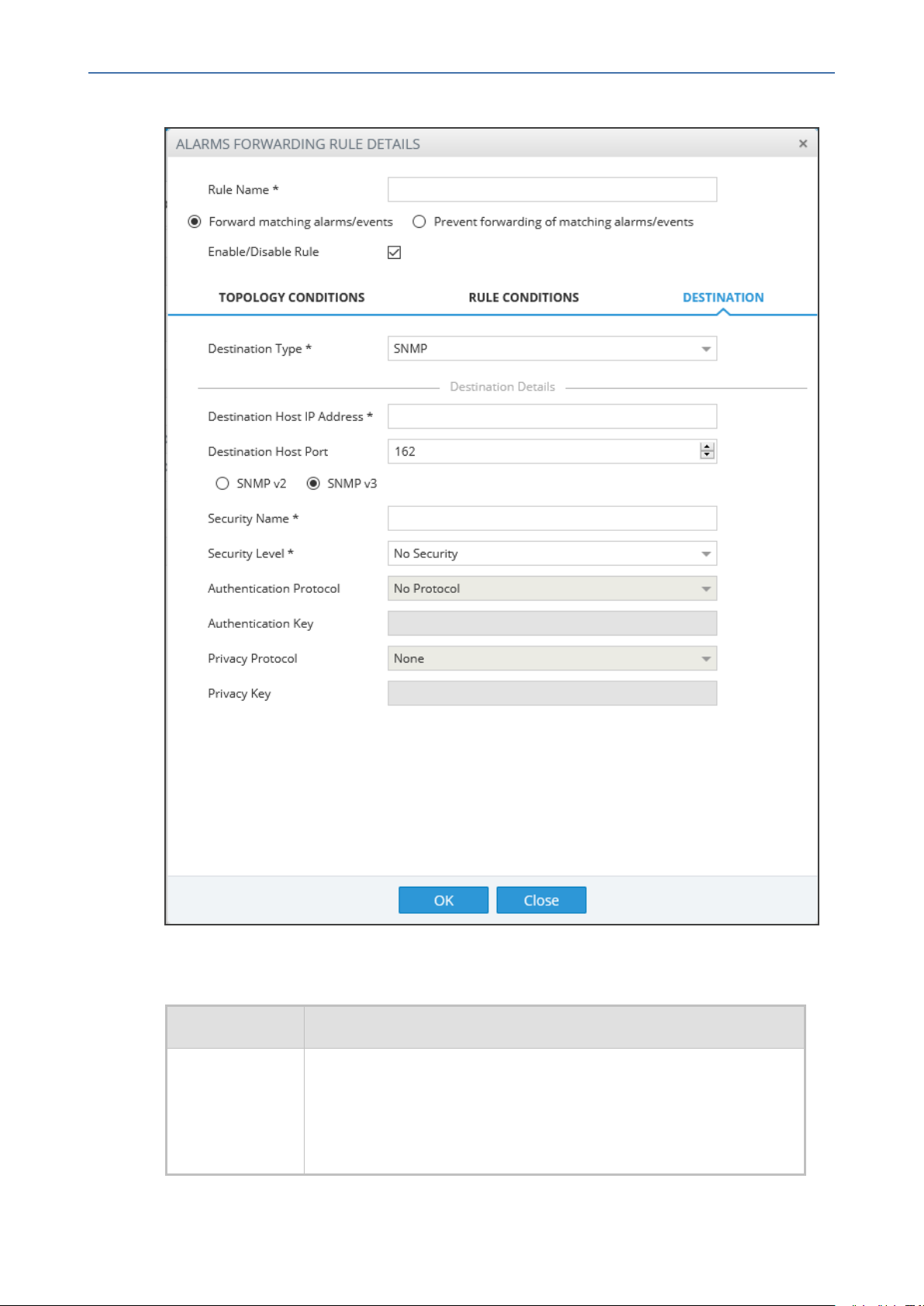
Destination
Type
Determines the format in which the alarm or event will be
forwarded.
From the dropdown, select
■ SNMP
- 18 -
Page 26

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Parameter Description
7. Select SNMP. Configure the parameters that are displayed using the table below as a
reference.
Table 5-4: Forwarding Alarms - Destination - SNMP
Parameter Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ MAIL
■ SYSLOG
Destination Host
IP Address
Enter the destination NMS host IP address to which to forward
alarms. Make sure you receive the alarms and events in the specified
IP address on the port specified below.
Destination Host
Port
Enter the destination host port to which to forward alarms. Make
sure you receive the alarms and events on the specified port in the IP
address specified above.
In the 'Destination Host port' field, enter the port number of the
destination host (the default SNMP port for trap reception is 162).
SNMP v2/SNMP
v3
Select either SNMP v2 or SNMP v3. Default: SNMP v3. Forwards only
those alarms that are in the format of the SNMP version you select.
Note: ensure that you configure identical SNMPv2 or SNMPv3
account details on the NMS.
Trap Community [Only available if SNMP v2 is selected above].
Note: OVOC by default sends SNMPv2c traps with the field 'SNMPv2c
Trap Community' set to public.
Security Name Enter the name of the operator.
Security Level From the dropdown select either:
■ No security
■ Authentication
■ Authentication & Privacy
See the table below for OVOC-Syslog mapping.
Authentication
Protocol
Only available if you select Authentication or Authentication &
Privacy from the list above. Select either:
■ No Protocol
■ MD5
■ SHA
- 19 -
Page 27
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Parameter Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Authentication
Key
Privacy Protocol From the drop-down list, select the SNMP v3 operator's privacy
Only available if you select MD5 or SHA from the list above.
protocol.
■ None
■ DES
■ AES-128
Privacy Key Enter the privacy key. Keys can be entered in the form of a text
password or long hex string. Keys are always persisted as long hex
strings and keys are localized.
Forwarding Alarms Directly from Devices to NMS
Alarms are forwarded directly from the network element to the NMS over SNMPv2 or SNMPv3.
On the managed devices, configure the NMS Trap Destination and identical SNMPv2 or
SNMPv3 account settings. On the NMS, also configure identical SNMPv2 or SNMPv3 account
settings. If you wish to forward alarms directly from devices to the NMS; however, forward
alarms from the other network elements via the OVOC server, then you can configure the
alarm forwarding rules accordingly as described in Alarms and Events Forwarding to the NMS.
Alarm Aggregation
An aggregated list of alarm notifications can be forwarded from OVOC in a batch in a single
email with the alarm filter settings according to the Forwarding rule. "Max number of alarms to
aggregate in single Email" sets the maximum number of alarms to aggregate into a single mail
and "Email alarms aggregation time interval (seconds)" sets the time interval between sending
the batch of alarms. For example, if the number of alarms to aggregate is set to 10, the time
interval is set to 60 seconds and then after 60 seconds there are only 5 alarms raised according
to the forwarding rule, then 5 alarms are forwarded.
Examples of Aggregated Alarms
The following shows examples of alarm alerts that are sent from OVOCto an NMS.
Alarms are separated by ***** Info****
Subject: OVOC received 10 new alarms
***** Event Info *****
Alarm Name: OVOC server Started
Date & Time: 1:12:54 PM Aug 8, 2018
- 20 -
Page 28

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Source: OVOC Mgmt
Source Description:
Severity: major
Unique ID: 0
Alarm Type: communicationsAlarm
Alarm Probable Cause : other
Description: Server Startup
Additional Info 1:
Additional Info 2:
Additional Info 3:
***** System Info *****
System Name: OVOC Mgmt
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
System IP Address: 172.17.118.148
******************************
***** Alarm Info *****
Alarm Name: License Pool Infra Alarm
Date & Time: 12:13:03 PM Aug 6, 2018
Source: Board#1
Source Description:
Severity: clear
Unique ID: 12
Alarm Type: communicationsAlarm
Alarm Probable Cause : keyExpired
Description: Alarm cleared: License Pool Alarm. Device was unable to access the License Server.
Additional Info 1:
Additional Info 2:
Additional Info 3:
***** Device Info *****
Device Name: 172.17.118.51
Device Tenant: Eran
Device Region: Tel Aviv
Device IP Address: 172.17.118.51
- 21 -
Page 29
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Device Type: Mediant 500 MSBR
Device Serial: 5856696
Device Description:
Alarm Forwarding Data Formats
The table below describes the data format for the MIBfields that are forwarded to Northbound destinations.
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Table 5-5: Data Fields for Alarm Forwarding
Name (1)
TextualDescription(2)
Source (3)
Severity (4)
■ Integer 0..1000
■ The Alarm/event number as listed by product (usually
matches the last digit in the trap OID)
■ OCTET STRING 0..200
■ Summary of the reported issue that is sent in acEMSTrapG-
lobalsTextualDescription varbind
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ (Devices + OVOC: currently defined as 0..100)
■ The entity source of the problem, usually in the following
format:
✔ Trunk#1
✔ SEM/Link#2
✔ Entity1#x/Entity2#y/Entity3#z
■ cleared(0)
UniqID (5)
■ indeterminate(1)
■ warning(2)
■ minor(3)
■ major(4)
■ critical(5)
■ Integer 0..32000
■ The running number of alarms since the installation of the
OVOC instance.
■ The value of this number should be managed by the
- 22 -
Page 30
CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
system separately for alarms and events.
■ The OVOC application uses this number to recognize if
alarms were missed and to retrieve them using the Carriergrade system.
■ The forwarded information includes OVOC alarms
sequencing for NMS carrier-grade alarms: where the
running number events: always -1
Type (6)
ProbableCause (7)
■ other(0)
■ communicationsAlarm(1)
■ qualityOfServiceAlarm(2)
■ processingErrorAlarm(3)
■ equipmentAlarm(4)
■ environmentalAlarm(5)
■ integrityViolation(6)
■ operationalViolation(7)
■ physicalViolation(8)
■ securityServiceOrMechanismViolation(9)
■ timeDomainViolation(10)
■ other(0)
■ adapterError(1)
■ applicationSubsystemFailure(2)
■ bandwidthReduced(3)
■ callEstablishmentError(4)
■ communicationsProtocolError(5)
■ communicationsSubsystemFailure(6)
■ configurationOrCustomizationError(7)
■ congestion(8)
■ corruptData(9)
■ cpuCyclesLimitExceeded(10)
■ dataSetOrModemError(11)
- 23 -
Page 31

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ degradedSignal(12)
■ dteDceInterfaceError(13)
■ enclosureDoorOpen(14)
■ equipmentMalfunction(15)
■ excessiveVibration(16)
■ fileError(17)
■ fireDetected(18)
■ floodDetected(19)
■ framingError(20)
■ heatingVentCoolingSystemProblem(21)
■ humidityUnacceptable(22)
■ inputOutputDeviceError(23)
■ inputDeviceError(24)
■ lanError(25)
■ leakDetected(26)
■ localNodeTransmissionError(27)
■ lossOfFrame(28)
■ lossOfSignal(29)
■ materialSupplyExhausted(30)
■ multiplexerProblem(31)
■ outOfMemory(32)
■ ouputDeviceError(33)
■ performanceDegraded(34)
■ powerProblem(35)
■ pressureUnacceptable(36)
■ processorProblem(37)
■ pumpFailure(38)
■ queueSizeExceeded(39)
■ receiveFailure(40)
■ receiverFailure(41)
- 24 -
Page 32

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ remoteNodeTransmissionError(42)
■ resourceAtOrNearingCapacity(43)
■ responseTimeExecessive(44)
■ retransmissionRateExcessive(45)
■ softwareError(46)
■ softwareProgramAbnormallyTerminated(47)
■ softwareProgramError(48)
■ storageCapacityProblem(49)
■ temperatureUnacceptable(50)
■ thresholdCrossed(51)
■ timingProblem(52)
■ toxicLeakDetected(53)
■ transmitFailure(54)
■ transmitterFailure(55)
■ underlyingResourceUnavailable(56)
■ versionMismatch(57)
■ authenticationFailure(58)
■ breachOfConfidentiality(59)
■ cableTamper(60)
■ delayedInformation(61)
■ denialOfService(62)
■ duplicateInformation(63)
■ informationMissing(64)
■ informationModificationDetected(65)
■ informationOutOfSequence(66)
■ intrusionDetection(67)
■ keyExpired(68)
■ nonRepudiationFailure(69)
■ outOfHoursActivity(70)
■ outOfService(71)
- 25 -
Page 33

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ proceduralError(72)
■ unauthorizedAccessAttempt(73)
■ unexpectedInformation(74)
AdditionalInfo1 (8)
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ (Devices + OVOC: currently defined as 0..100)
This field is used by the system to provide additional
information regarding the reported alarm/event.
AdditionalInfo2 (9)
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ (Devices + OVOC: currently defined as 0..100)
This field is used by the system to provide additional
information regarding the reported alarm/event.
AdditionalInfo3 (10)
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ This field is used be the system to provide additional
information regarding the reported alarm/event
■ The forwarded information is filled in the following format:
GW_IP: <Device IP>, GW_TRAP_ID: <device’s alarm unique ID>
DateAndTime (11) DateAndTime SNMP Object
SystemSeverity (12)
DeviceName(13)
■ cleared(0)
■ indeterminate(1)
■ warning(2)
■ minor(3)
■ major(4)
■ critical(5)
Each value represents the entire system severity when a specific
alarm/event is issued.
This varbind is not sent for system alarms (alarms that
were generated by OVOC such as OVOC Disk Space
alarm).
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
- 26 -
Page 34

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ (Devices+ OVOC: currently defined as 0..250)
■ This field should not be filled by any of the products, as its
reserved for OVOC when an alarm/event is forwarded.
The information is filled in the following format:
■ Until Version 7.4:
MG Region:<EMS Region Name>, MG Name:<EMS MG Name>
■ Until Version 7.6:
<Entity Type> Name:<Entity Name>, Tenant:<Tenant Name>,
Region:<Region Name>
Where entity type can be one of the following:
■ Tenant, Region, Site, Device, Link, System etc.
DeviceInfo(14)
■ Tenant: <Tenant Name> - exists only when the entity has
tenant
■ Region: <Region Name> - exists only when the entity has
region
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ (Devices + OVOC: currently defined as 0..100)
■ This field should not be filled by any of the products, as its
reserved for OVOC when the alarm/event is forwarded.
The information is filled in the following format:
■ Until Version 7.4:
MG Type: <Device Type>, MG Serial: <primary device serial number>, <secondary device serial number>
<secondary device serial number> is applicable for HA devices
only
■ Until Version 7.6:
DeviceDescription(15)
Device Type: <Device Type>
Empty if entity not a device
■ OCTET STRING 0..255
■ This field should not be filled by any of the products, as its
reserved for OVOCwhen the alarm/event is forwarded.
The information is filled in the following format:
- 27 -
Page 35

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
MIB Name Description
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
<Device Description> OR <SBA Description>
<SBA Description> is provisioned in the device details under SBA
definition rubric.
A free text description field can also be globally configured in
the OVOCServer Configuration page (System > Administration
> OVOC Server > Configuration)for all OVOC System alarms.
This text is then sent to trap destinations in alarm forwarding in
the varbind acEMSTrapGlobalsDeviceDescription field for all
system alarms. For example, OVOC Disk Space alarm.
The hard-coded text description of the alarm that is
sent in the TextualDescription (2) acEMSTrapGlobalsTextualDescription varbind (see above) is a
separate description field that is different for each
alarm OID.
SystemSerialNumber
(16)
From Version 7.6:
OCTET STRING 0..255
The information is filled in the following format:
■ For Stand-alone systems:<Device serial number>
■ For HASystems:format <device serial #1>_<device serial
#2>)
Device Serial Number (displays either 32-bit and 64-bit serial
numbers for SBC devices) according to the device's firmware
version and configuration settings in the
externals/configurationProperties/generalConfig file for the
include_serial_string.
OVOC Server Alarm Settings
This section describes the global alarm settings on the OVOC server.
Alarms Automatic Clearing (on Startup)
The Active Alarms page is cleared of all the current alarms for a specific device upon system GW
startup (cold start event). Critical, Major, Minor, Warning or Info alarms are automatically
cleared from the Active Alarms Page (and transferred to the Alarms History page) when a Clear
alarm is generated by the same entity (source) and the same device. This feature prevents
older alarms from congesting the Active Alarms page. This feature is configured in the Alarms
page (System tab > Configuration > Alarms).
- 28 -
Page 36

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
Alarms Automatic Clearing Period (Days)
The operator can also configure the automatic clearing of Active alarms (disabled by default)
according to a time period. When the Automatic Clearing feature is enabled, alarms are cleared
by default every 30 days.
When the OVOC application performs automatic clearing, it moves the cleared Alarms to the
Alarms History page with the text indication 'Automatic Cleared'. This feature is configured in
the Alarms page (System tab > Configuration > Alarms).
Events Clearing Mechanism
Events are informative messages for OVOC and device actions (usually with low severity).
Device events (originating from the device) are automatically cleared from the Active Alarms
page upon GW startup (cold start event); however, device events originating in the OVOC (e.g.
adding a gateway) are not cleared upon device reset. The OVOC consequently employs a
mechanism to automatically clear these events from the Alarms page (by default this feature is
enabled and events are cleared every three days). This feature prevents old events from
congesting the Active Alarms page. When automatic clearing is performed, the cleared Events
are moved to the Alarm History page with the text indication 'Automatic Cleared'. This feature
is configured in the Alarms page (System tab > Configuration > Alarms).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Alarm Suppression Mechanism
This option enables the generating of the 'Alarm Suppression' alarm when the OVOC server
identifies that the number of alarms of the same type and from the same source, generated in
a time period, is greater than the number defined in the threshold. At this point, these alarms
are not added to the database and are not forwarded to configured destinations. This feature
is configured in the Alarms page (System tab > Configuration > Alarms).
Alarms Sequence Numbering
1. When receiving alarms directly from the devices and endpoints:
● These alarms and events have a different scala of sequence numbers. These sequence
numbers are placed at 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' varbindings (respectively
'tgTrapGlobalsUniqID', 'acBoardTrapGlobalsUniqID').
● OVOC alarms have a sequence number scala. Events are always sent with
'acEMSTrapGlobalsUniqID -1'.
2. When the OVOC server forwards device and OVOC alarms:
● Cold Start Trap is the only standard event that is forwarded by the OVOC application.
All other standard events are not forwarded.
● Each one of the alarms and events are forwarded with the original Notification OID
and variable bindings OIDs.
- 29 -
Page 37

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
● The original content of 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' varbinding (respectively
'tgTrapGlobalsUniqID', 'acBoardTrapGlobalsUniqID' and 'acEMSTrapGlobalsUniqID') is
updated as follows:
◆ For all the forwarded events, the 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' is set to -1.
◆ For all the forwarded alarms, the original 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' is replaced with the
OVOC sequence number, allowing the NMS to follow the forwarded alarms
sequencing. The original device 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' is applied to
'TrapGlobalsAdditionalInfo3' varbinding.
◆ For all the forwarded alarms and events, 'TrapGlobalsAdditionalInfo3' varbinding
(respectively 'tgTrapGlobals AdditionalInfo3', 'acBoardTrapGlobals
AdditionalInfo3' and 'acEMSTrapGlobals' 'AdditionalInfo3') is updated as follows:
original device IP address and device 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' in the following format:
GATEWAY_IP:x ,GATEWAY_TRAP_ID:y
A carrier-grade alarm system is characterized by the following:
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
■ Active Alarms
The device can determine which alarms are currently active by maintaining an Active
Alarms table. When an alarm is raised, it is added to the active alarms list. Upon alarm
clearing, it is removed from the active alarms list.
The maximal size of the active alarms for each of the product is shown in the table below:
Table 5-6: Maximum Active Alarms according to Device
Maximum Size of
Product
Active Alarms
Table
MP-1xx 40
MP-124 100
MP-1288 200
Mediant 500 MSBR, Mediant 500 SBC, Mediant 500L MSBR, Mediant
300
500L SBC, Mediant 800 MSBR, Mediant 800 SBC and Mediant 1000
SBC
Mediant 3000 500
Mediant 2600 E-SBC and Mediant 4000 SBC 600
Mediant 9000 SBC and Mediant Software SBC 1000
When the active alarms list exceeds its maximum size, an enterprise Active Alarms
Overflow alarm is sent to the Management system.
- 30 -
Page 38

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
● The device sends a cold start trap to indicate that it is starting up. This allows the
management system to synchronize its view of the device's active alarms.
● Two views of active alarms table are supported by devices:
◆ Standard MIB: alarmActiveTable and alarmActiveVariableTable in the IETF ALARM
MIB for all the devices.
◆ Enterprise MIB:
n acActiveAlarmTable in the AC-ALARM-MIB mib for devices products.
n AudioCodes.acProducts.acEMS.acEMSConfiguration.acFaults (see SNMP
■ History Alarms
The device allows the recovery of lost alarm raise and clear notifications by maintaining a
log history alarms table. Each time an alarm-type trap (raise or clear) is sent, the CarrierGrade Alarm System adds it to the alarms history list. The trap contains a unique
Sequence Number. Each time a trap is sent, this number is incremented. The device allows
detection of lost alarms and clear notifications by managing an alarm sequence number
and displaying the current number.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Alarms Synchronization below).
The maximal size of the history alarms table is defined as follows:
Table 5-7: Maximum Active Alarms according to Device
Maximum Size of
Product
History Alarms
MP-1xx 100
MP-1288 1000
Mediant 500 MSBR, Mediant 500 SBC, Mediant 500L MSBR, Mediant
1000
500L SBC, Mediant 800 MSBR, Mediant 800 SBC and Mediant 1000
SBC
Mediant 3000 500
Mediant 2600 E-SBC and Mediant 4000 SBC 1000
Mediant 9000 SBC and Software SBC 2000
Table
When the history alarm list exceeds its maximum size, it starts overriding the oldest
alarms in the list in cyclic order.
● The following views of log history alarms table are supported by the devices:
◆ Standard MIB: 'nlmLogTable' and 'nlmLogVariableTable' in the NOTIFICATION-
LOG-MIB for all the devices.
◆ Enterprise MIB:
- 31 -
Page 39

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
n acAlarmHistoryTable in the 'AC-ALARM-MIB mib' for CPE and MP products.
SNMP Alarms Synchronization
A carrier-grade alarm system provides a reliable alarm reporting mechanism that takes into
account Operations Center system or network layer outages, and transport layer outages,
such as SNMP over UDP. During such outages, alarms may be raised, however not forwarded.
This mechanism is implemented at SNMP agent level, and serves OVOC, NMS, or higher level
management system synchronization. During the OVOC server synchronization process, the
OVOC server can recover such missed alarms from its database (events are not synchronized)
and then forward them to the NMS according to the following:
■ History alarms: By default, synchronization is performed with the Alarms History table.
When only a partial Alarms History table is retrieved from the OVOC server database, the
OVOC server notifies the user with one of the following events: 'Synchronizing Alarms
Event' and 'Synchronizing Active Alarms Event'. For more information, see the OVOC
Alarms Guide.
■ Active alarms: By default, synchronization is not performed with the Active Alarms table;
however, a mechanism can be implemented to perform random synchronization of this
table (see below).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Resynchronization (Resync) Mechanism
The Resync mechanism enables you to perform random requests to retrieve the Active alarms
table when there are network problems (as described above) or a discontinuation of the alarm
sequence is detected.
This feature implements an SNMP agent on the OVOC server with the MIB AudioCodes.acProducts.acEMS.acEMSConfiguration.acFaults with the following fields:
Table 5-8: Faults MIBs
Name Type OID
acFaultsFwdHostIp IpAddress 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.1.1.1
acFaultsFwdHostPort Integer 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.1.1.2
acFaultsFwdUpdate Integer (0-1) 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.1.1.3
Each SNMP message should be processed in the order shown in the table above
When the acFaultsFwdUpdate field is set to 1, the SNMP agent reads the acFaultsFwdHostIp &
acFaultsFwdHostPort fields and searches for all active SNMP Alarm Forwarding rules according
to the configured ‘Destination Host IP Address’ and ‘Destination Host Port’. It then resends all
the current Active alarms according to SNMPv2/SNMPv3 account credentials and the other
- 32 -
Page 40

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
criteria defined in the rule. If a specific rule is not active (Enable/Disable check box is clear),
then alarms are not sent to this destination.
● The acFaultsFwdHostIp & acFaultsFwdHostPort parameters should be re-set
each time after the Resync action is performed (they are set to default after each
Resync action).
● The OVOC SNMP agent supports only SNMPv2 get/set commands. However,
alarms can still be forwarded when configured with either SNMPv2 or SNMPv3
credentials in the alarm forwarding rule definition.
● The SNMP port used for this SNMP agent may be configured using the EMS
Server Manager (Network Configuration > SNMP Agent > SNMP Agent Listener
Port), instead of using the standard SNMP port number (161).
● When the SNMP agent is restarted, the acFaultsFwdHostIp &
acFaultsFwdHostPort parameters need to be reset.
● The Resync feature is applicable only for alarms and is not relevant for events.
The figure below illustrates the Resync flow process:
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 5-5: Resync Flow
The following steps describe the flow illustrated in the figure above:
1. The NMS executes SNMP SET to acFaultsFwdHostIp & acFaultsFwdHostPort
2. The NMS executes SNMP SET to acFaultsFwdUpdate to 1 (acFaultsFwdHostIp &
acFaultsFwdHostPort & acFaultsFwdUpdate are & set back to 0 automatically).
3. The OVOC server responds confirming successful SNMP SET.
4. The OVOC server finds all relevant Alarm Forwarding rules by acFaultsFwdHostIp &
acFaultsFwdHostPort.
5. The OVOC server sends an event regarding the start of re-sending of all active alarms
(acOvocReSyncEvent 1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.58) with Severity Indeterminate and
'TrapGlobalsUniqID' set to -1.
6. The OVOC server resends all active alarms according to the configured forwarding rules.
7. The OVOC server sends an event informing the end of resynchronization with Severity
clear and 'TrapGlobalsUniqID' set to -1.
- 33 -
Page 41

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
● Alarms are not cleared from the Active alarms table when the OVOC server is
reset.
● When a device is deleted or removed from the OVOC Web client, its active alarms
are also removed from the Active Active alarms table.
● Alarms are forwarded in the sequence order that they were received on the OVOC
server.
● SNMP traps are sent from source port 1164-1174 on the OVOC server.
● The Resync operation can be performed on up to three simultaneously active
SNMP forwarding rules.
● The Resync operation can send up to 5000 of the last received alarms.
● New alarms raised during the Resync operation are also forwarded.
● There can be up to two concurrent Resync processes. If more than two processes
are simultaneously active i.e. more than two users are concurrently attempting to
perform this operation, then all the additional attempts (greater than two) fail and an
error is sent to the log file (see below).
● Resync operation log failures are written to the log ‘alarmsReSync.csv’
(/var/log/ems).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
OVOC Keep-alive
You can configure the OVOC to generate SNMP Keep-alive traps toward the SNMP destination.
When the “OVOC Keep-Alive” check box is checked, this trap is sent from the OVOC to a
configured destination according to a configured interval (default 60 seconds). You can send
the Keep-alive trap to the desired SNMP destination, according to an existing configured
forwarding destination rule.
➢ To configure OVOC Keep-alive:
1. In the OVOC Web menu, open the Alarms page (System > Configuration > Alarms).
- 34 -
Page 42

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 5-6: OVOC Keep-alive
2. Select the OVOC Keep-Alive check box.
3. Open the Alarm Forwarding Rule page (Alarms > Forwarding); the Alarm Forwarding Rules
Configuration window is displayed:
Figure 5-7: Alarm Forwarding Configuration
4. Select the SNMP forwarding rule and then click Edit.
- 35 -
Page 43

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 5-8: Alarms Forwarding Rule Dialog
5. Ensure that the ‘Enable/Disable Rule’ check box is selected for each destination that you
wish to forward the OVOC Keep-alive trap.
6. In the Alarm Names pane, click the Alarms Filter and ensure that the "OVOC Keep-Alive"
alarm is selected.
- 36 -
Page 44

CHAPTER5 Fault Management
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 5-9: Destination Rule Configuration
Status / State Management via Devices SNMP Interface
For details regarding supported SNMP MIBs, refer to the SNMP Reference Guide for Gateways-
SBCs-MSBRs.
- 37 -
Page 45

CHAPTER6 Voice Quality Reports
6 Voice Quality Reports
Both template and custom Voice Quality reports can be generated for devices, links and URIs
for Tenants, Regions and Elements. You can export the report's definitions to JSONformat
from the Reports screen in the OVOC Web interface. The figure below shows an example of an
exported JSONfile.
The generation of customized Voice Quality Reports requires a license. For more
information, contact your AudioCodes representative.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
- 38 -
Page 46

CHAPTER6 Voice Quality Reports
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 6-1: Voice Quality Reports
- 39 -
Page 47

CHAPTER6 Voice Quality Reports
You can also save the output of the run reports to a CSV or PDF file.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 6-2: Run Report
- 40 -
Page 48

CHAPTER7 OVOC Server Backup and Restore
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
7 OVOC Server Backup and Restore
There are four main backup processes that run on the OVOC server:
■ Weekly backup: runs once a week at a pre-configured date & time (default is Saturday
02:00). In this process, the whole database is backed up into several “RMAN” files that are
located in /data/NBIF/emsBackup/RmanBackup directory. In addition, several other
configuration and software files are backed up to the archive file emsServerBackup_
<version>_<time&date>.tar in the /data/NBIF/emsBackup directory. In general, this TAR
file contains the entire /data/NBIF directory’s content, with the exception of the
'emsBackup' directory, OVOC Software Manager content and server_xxx directory
content.
To change the weekly backup’s time and date, refer to Section "Change Schedule Backup
Time" in the OVOC IOM.
■ Daily backup: runs daily except on the day scheduled for the weekly backup (see above).
The daily backup process backs up the last 24 hours. There are no changes in the TAR file
in this process.
■ Cassandra backup: runs daily (runs prior to the above) and backs up the last 24 hours to
the archive file cassandraBackup_<version>_<date>_<snapshotId>_<Role>_
numberOfNodes.tar.gz. When working in Service Provider Cluster, backup of the cluster
node servers (VQMand PM) is performed on the Management server. Cassandra backup
files are generated separately for both the VQM and PMserver and must be copied
separately to the respective server node machine (see below
■ Configuration backup: runs daily and backs up to the archive file ovocConfigBackup_
<version>_<time&date>.tar.gz
Daily and weekly backups run one hour after the Cassandra backup. For example, if the
backup time is 2:00, the Cassandra backup runs at 2:00 and the Weekly/Daily and Configuration backups runs at 3:00.
● The Backup process does not backup configurations performed using EMS Server
Manager, such as networking and security.
● RmanBackup files are deleted during the OVOC server upgrade.
● It is highly recommended to maintain all backup files on an external machine.
These files can be transferred outside the server directly from their default location
by SCP or SFTP client using 'acems' user.
Backup OVOC Server
➢ to backup the OVOCserver:
1. Copy the following backup files to an external machine:
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/emsServerBackup_<version>_<time&date>.tar
● /data/NBIF/ovocConfigBackup_<version>_<time&date>.tar.gz
- 41 -
Page 49

CHAPTER7 OVOC Server Backup and Restore
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/cassandraBackup_<version>_<date>_<snapshotId>_
<MGMT>_numberOfNodes.tar.gz
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/daily_dbems_<time&date>
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/weekly_dbems_<time&date>
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/control.ctl
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/init.ora
where:
● <time&date> is an example; replace this path with your filename.
● <version> is the version number of the OVOC server release
2. In addition, when operating in Service Provider Cluster,copy Cassandra backup files to
the /data/NBIF directory on the Cluster node of the respective server:
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/cassandraBackup__<version>_<date>_<snapshotId>_
<VQM>_numberOfNodes.tar.gz
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
● /data/NBIF/emsBackup/cassandraBackup__<version>_<date>_<snapshotId>_<PM>_
numberOfNodes.tar.gz
Restore the OVOC Server
➢ To restore the OVOC server:
1. In the EMS Server Manager, choose the Restore option.
2. Install (or upgrade) OVOC to the same version from which the backup files were created.
The Linux version must also be identical between the source and target machines.
3. Use the EMS Server Manager to perform all the required configurations, such as
Networking and Security, as was previously configured on the source machine.
4. Make sure all server processes are up in EMS Server Manager / Status menu and the
server functions properly.
5. Copy all the files you backed up to /data/NBIF directory by SCP or SFTP client using the
'acems' user. Overwrite existing files if required.
6. Choose one of the following options:
● Configuration Restore:Restores OVOC topology and OVOC Web configuration
● Full Restore: Restores OVOC topology, OVOCWeb configuration and data that is
retrieved from managed devices.
For more information, refer to Section "OVOC Server Restore"in the OVOC IOMmanual.
When operating in Service Provider Cluster:
● The restore cluster should be with identical system specifications as the backed
up server i.e. the same number of VQM/PM servers.
- 42 -
Page 50

CHAPTER7 OVOC Server Backup and Restore
● Following restore, restart slaves and then wait up to 24 hours for Cassandra DB
data(call details and PM details) to synchronize on all servers.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
- 43 -
Page 51

CHAPTER8 Data Analytics API
8 Data Analytics API
The Analytic API Voice Quality license enables access to specially designed views with selected
data from the OVOC database for the purpose of integration with Northbound third-party
interfaces. Customers can connect to the OVOC database using third-party DB access clients
and retrieve topology and statistics. This data can then be used in management interfaces
such as Power BI and Splunk to generate customized dashboards, reports and other
representative management data. Customers can combine data from AudioCodes OVOC and
enterprise voice or third-party data monitoring tools such as HPOpenView for data such as the
following:
■ Receive Alerts from HPOpenView
■ Calls tariffs
■ Data layer statistics
■ User information from corporate directory
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
The following data is accessible from OVOC (details of retrieved DB tables are shown below):
■ Network Topology including Tenants, Regions, Devices, Non-ACL Devices, Links
■ QoE Statistics including Calls, Nodes and Links Summaries
■ Active and History Alarms
Adedicated DBoperator("Analytics")is used for securing connection to the OVOC server over
port 1521. This port must be open on the customer firewall once this feature is enabled (for
more details, refer to the OVOC IOM).
● Multi-Tenancy is not supported for this feature.
● All data is read-only.
● Data is retrieved for the last 24 hours; it's recommended to synchronize daily with
the OVOC database, save this data to an external server and then run the
Analytics tool on this server.
● Backup and restore is not applicable for this feature.
➢ To connect to the OVOC server:
1. Open your DBaccess client.
2. Configure the following parameters:
● OVOC server IPaddress
● OVOC server port: 1521
● Username:Analytics
● Service Name:DBEMS
An example databaseschema retrieved from an access client is displayed below:
- 44 -
Page 52

CHAPTER8 Data Analytics API
The following OVOC database tables are retrieved (for details, see Data Analytics API Database
Tables):
■ Main Table Views:
● View Name: NODES_VIEW
● View Name: LINKS_VIEW
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 8-1: Example Database schema
● View Name: CALLS_VIEW
● View Name: ALARMS_VIEW
● View Name: NODES_SUMMARY_VIEW
● View Name: LINKS_SUMMARY_VIEW
■ Type Views:
● Type Name: DisableEnableType
● Type Name: MGType
● Type Name: ItuPerceivedSeverity
● Type Name: ConnectionType
● Type Name: MismatchType
● Type Name: SemConnectionState
● Type Name: StatusType
● Type Name: VQThresholdStatus
● Type Name: SipMessageStatusType
● Type Name: NoYesType
● Type Name: NetworkState
● Type Name: ManagedType
● Type Name: FailSuccessType
● Type Name: BackupStatusType
● Type Name: ItuEntityAdministrativeState
- 45 -
Page 53

CHAPTER8 Data Analytics API
● Type Name: AlarmStatusType
● Type Name: AlarmNameType
● Type Name: QualityLevelType
● Type Name: CallCauseType
● Type Name: CallOriginatorType
● Type Name: TerminationReasonType
● Type Name: TerminationReasonDetailsType
● Type Name: MediaType
● Type Name: EndpointType
● Type Name: CallSourceType
● Type Name: PstnTermReasonType
● Type Name: LinkType
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
● Type Name: LinkDirection
- 46 -
Page 54

CHAPTER9 Security
9 Security
The following aspects are relevant for the NMS application when integrating the OVOC and the
managed device:
■ Network Communication Protocols (see below)
■ OVOC Users Management (Authentication and Authorization) (see OVOC User Identity
Management)
■ HTTPS Connection (see HTTPS Connection )
For detailed information, refer to the OVOC Security Guidelines document.
Network Communication Protocols
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
The following describes the different OVOC network communication protocols:
■ OVOC client - server communication is secured using an HTTPS tunnel with a single HTTPS
port.
■ OVOC server – managed devices communication can be secured as follows:
● Devices:
◆ SNMPv3 for Maintenance Actions and Faults Management
◆ HTTPS for file transfer and for Single Sign-to the managed device
■ OVOC server secure access:
● Secure access to the OVOC server machine is possible via SSH and SFTP protocols for
performing maintenance actions and accessing files.
● SNMPv3 traps can be forwarded from the OVOC server machine to another SNMP
Trap Manager.
● OVOC User Authentication and Authorization is performed either via the OVOC
Application local database, or via a centralized user database on RADIUS, LDAP or
Microsoft Azure (see OVOC User Identity Management) according to the Security
profile configured by the OVOC Administrator.
● Syslog messages and emails sent from the OVOC server to a northbound interface
are not secured.
● Single sign-on is not supported for devices located behind a NAT, unless the Cloud
Architecture feature is enabled, in which case, SBC device connections can be
secured over an HTTP/S Tunnel Overlay network (refer to the IOMmanual and the
Security Guidelines for more information).
● An SSH connection from the OVOC server to the device is not supported.
- 47 -
Page 55

CHAPTER9 Security
OVOC User Identity Management
By default, OVOC users are managed in the OVOC server's local database. Users can also be
managed via a centralized RADIUS or LDAP server or using Microsoft Azure. The figure below
illustrates these options.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-1: OVOC User Management
■ For information on the local OVOC users database, refer to the OVOC User’s Manual
■ For OVOC user authentication with RADIUS server, see Authentication and Authorization
using a Radius Server
■ For OVOC user authentication with LDAPserver, see Authentication and Authorization
using an LDAP Server
■ For OVOC user authentication with Microsoft Azure, see Authentication and Authorization
using Microsoft Azure
Authentication and Authorization using a Radius Server
Customers may enhance the security and capabilities of logging into the OVOC application by
using a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) to store numerous usernames,
passwords and access level attributes. This feature allows multiple user management on a
centralized platform. RADIUS (RFC 2865) is a standard authentication protocol that defines a
method for contacting a pre-defined server and verifying a given name and password pair
against a remote database in a secure manner.
- 48 -
Page 56

CHAPTER9 Security
When accessing the OVOC application, users must provide a valid username and password of
up to 128 Unicode characters. OVOC doesn’t store the username and password; however,
forwards them to the pre- configured RADIUS server for authentication (acceptance or
rejection). If the login attempt to the RADIUS server fails, OVOC attempts to connect with the
same credentials to the local database. An additional fallback mechanism 'Combined
Authentication Mode' can also be implemented (for information, refer to the OVOC User's
Manual)
OVOC supports the provisioning of up to three Radius servers for redundancy purposes.
When the first server does not respond, the OVOC proceeds to the second server, and then to
the third server. OVOC will always start working with the previously responded server that is
indicated as the Current Active Radius servers.
Configuring Radius Server Client
This section describes an example of a RADIUS server configuration. You must configure the
OVOC server as a RADIUS client to perform authentication and authorization of OVOC users
using the RADIUS server from the OVOC application.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
The example configuration is based on FreeRADIUS, which can be downloaded from the
following location: www.freeradius.org. Follow the directions on this site for information on
installing and configuring the server.
If you use a RADIUS server from a different vendor, refer to the appropriate vendor
documentation.
➢ To set up OVOC RADIUS client using FreeRADIUS:
1. Define the OVOC server as an authorized client of the RADIUS server with a predefined
'shared secret' (a password used to secure communication) and a 'vendor ID'. The figure
below displays an example of the file 'clients.conf' (FreeRADIUS client configuration).
Example of the File clients.conf (FreeRADIUS Client Configuration)
#
# clients.conf - client configuration directives
#
client 10.31.4.47 {
secret = FutureRADIUS
shortname = OVOC
}
2. If access levels are required, set up a VSA dictionary for the RADIUS server and select an
attribute ID that represents each user's access level. The following example shows a
dictionary file for FreeRADIUS that defines the attribute 'ACL-Auth-Level' with ID=35.
Example of a Dictionary File for FreeRADIUS (FreeRADIUS Client Configuration)
#
# AudioCodes VSA dictionary
#
- 49 -
Page 57

CHAPTER9 Security
VENDOR AudioCodes 5003
ATTRIBUTE ACL-Auth-Level 35 integer AudioCodes
VALUE ACL-Auth-Level ACL-Auth-Monitor 50
VALUE ACL-Auth-Level ACL-Auth-Operator 100
VALUE ACL-Auth-Level ACL-Auth-Admin 200
3. In the RADIUS server, define the list of users who are authorized to use the device, using
one of the password authentication methods supported by the OVOC server
implementation. The following example shows a user configuration file for FreeRADIUS
using a plain-text password.
Example of a User Configuration File for FreeRADIUS Using a Plain-Text Password
# users - local user configuration database
john Auth-Type := Local, User-Password == "qwerty"
larry Auth-Type := Local, User-Password == "123456"
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Service-Type = Login-User,
ACL-Auth-Level = ACL-Auth-Monitor
Service-Type = Login-User,
ACL-Auth-Level = ACL-Auth-Admin
4. Record and retain the IP address, port number, 'shared secret', vendor ID and VSA access
level identifier (if access levels are used) used by the RADIUS server.
5. Provision the relevant OVOC parameters according to the section below.
Configuring RADIUS Server
You can centrally configure authentication of OVOC operators using a RADIUS (Remote
Authentication Dial-In User Service) server. If you already have centralized user authentication
via a RADIUS server, it's recommended to implement it for OVOC operators as well. When the
RADIUS-authenticated operator logs into OVOC, they're assigned one of the OVOC security
levels, for example - 'Operator'. If it's not defined on the RADIUS server, OVOC by default
allows access for the RADIUS-authenticated operator, with 'Operator' permission.
➢ To configure using a RADIUS server.
1. In the OVOC Web, open the RADIUS Authentication Settings page (System tab > Security >
Authentication), and then from the Authentication Type drop-down list, select RADIUS.
- 50 -
Page 58

CHAPTER9 Security
Figure 9-3:
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-2: RADIUS Authentication and Authorization
2. For each one of the three RADIUS servers, define the IP address, port and Secret. Note,
that at least one RADIUS server must be provisioned.
3. Define the following parameters:
● RADIUS Auth Retransmit Timeout' (default-3000 milliseconds)
● RADIUS Auth Number of Retries (default-1)
These parameters will be used for each of the Radius Servers.
4. Configure other parameters as required according to your RADIUS server configuration.
For more information, refer to the OVOC User's Manual.
Authentication and Authorization using an LDAP Server
Authentication of OVOC operators can be centrally configured using a Lightweight Directory
Access Protocol (LDAP) server. If you already have centralized user authentication via an LDAP
server, it's recommended to implement it for OVOC operators as well. When an LDAPauthenticated operator logs into OVOC, they're assigned one of OVOC's security levels, e.g.,
'Operator'. The equivalent names for these security levels on the LDAP server are displayed in
the screen below. When one of these security levels is not defined on the LDAP server, OVOC
by default allows access to the LDAP-authenticated operator with 'Operator' permissions.
➢ To configure using an LDAP server.
1. In the OVOC Web, open the LDAP Authentication Settings page (System tab > Security >
Authentication), and then from the Authentication Type drop-down list, select LDAP.
- 51 -
Page 59

CHAPTER9 Security
2. Configure parameters as required (refer to the OVOC User's Manual).
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-4: LDAP Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and Authorization using Microsoft Azure
Authentication of OVOC operators can be centrally configured using the Microsoft Azure Active
Directory (AD). If you already have centralized user authentication via Azure AD, it's recommended to implement it for OVOC operators as well. When an Azure-authenticated operator
logs into the OVOC, they're assigned one of OVOC's security levels, e.g., 'Operator'. The equivalent names for these security levels in the Azure AD are displayed in the screen below . When
no security level is configured in the Azure AD, the parameter 'Default Operator Type and
Security Level' in OVOC's Authentication page (when 'Authentication Type' is AZURE) is applied.
➢ To configure authentication of OVOC operators using Azure AD:
1. Open the Authentication page (System > Administration > Security > Authentication), and
then from the 'Authentication Type' drop-down, select AZURE.
Figure 9-5: Azure Authentication
Figure 9-6:
2. Configure parameters are required (refer to OVOCUser's Manual).
- 52 -
Page 60

CHAPTER9 Security
Step 6 Configuring AudioCodes Azure Active Directory (Operator Authentication)
This procedure describes how to configure security permissions for OVOCoperators who are
authenticated with Azure Active Directory (when the "Azure" authentication type is configured
in the OVOCWeb (Security >Authentication settings page).
➢ To configure Microsoft Azure:
1. Add Service Providers Account Domain:
a. Open the Microsoft 365 Admin Center.
b. Login to AudioCodes with administrator privileges (via office.com).
c. In the Navigation pane, select Setup > Domains
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-7: Domains
2. Create a new Tenant in the Azure Portal: Sign into Azure portal as Global Administrator
and extract the Tenant ID of your directory (required for the OVOC Azure authentication
setup in OVOC Azure Configuration).
For details, see https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-
directory/develop/quickstart-create-new-tenant
3. Add Tenant Operators on AudioCodes Microsoft Azure:
● You must change passwords for new users upon first login via Azure portal sign-in
before logging in to OVOC.
● At this stage guest users you invite from another tenants/directories are not fully
supported by OVOC.
● For details, refer to the following:
✔ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-
directory/fundamentals/active-directory-groups-create-azure-portal#create-abasic-group-and-add-members
✔ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/add-
users-azure-active-directory#add-a-new-user
4. Add Security Groups:
- 53 -
Page 61

CHAPTER9 Security
a. Open AudioCodes Office 365.
b. Open the Admin page.
c. In the Navigation pane, select Groups.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-8: Add a Security Group
A list of existing groups are displayed. Note that there are several predefined custom
security groups that have been predefined for OVOC displayed in the screen below with
‘EMS_’ prefix.
d. Click Add a group.
e. Select the Security option and then click Next.
Figure 9-9: Choose a Group Type
f. Enter the Service Provider Domain account name and then click Next.
- 54 -
Page 62

CHAPTER9 Security
g. Review and finish adding group.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-10: Setup the Basics
Figure 9-11: Review and Finish
h. Click Create group. A confirmation screen is displayed:
Figure 9-12: New Group Created
- 55 -
Page 63

CHAPTER9 Security
5. Add New Users:
a. In the Navigation pane, select Active Users.
b. Click Add a User.
c. Enter the details of the Service Provider account user.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-13: Create New User
d. Assign Product License (Choose country).
Figure 9-14: Assign Product Licenses
e. Select option create user without product license and then click Next.
- 56 -
Page 64

CHAPTER9 Security
f. Click Finish adding.
g. Select option create user without product license and then click Next.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-15: Review and finish
Figure 9-16: Review and Finish
h. Click Finish adding
6. Add User Membership:add user membership to the predefined One Voice Live Security
groups and to the Security Group that you defined above.
a. In the Navigation pane, select Active Users and then select the new user that you
created above.
- 57 -
Page 65

CHAPTER9 Security
b. Click Manage groups and then Add Membership.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-17: Add User Membership
Figure 9-18: Add Membership
c. Select the checkboxes adjacent to the required OVOC group permissions :
◆ EMS_Tenant_Admin_Links
◆ EMS_Tenant_Operator_Links
◆ EMS_Tenant_Monitor_Links
d. Add membership to the Service Provider Account Group i.e. the Security Group that
you created above.
In the example below membership has been added to the ‘EMS_Operator’ and
‘SouthVoIP’ Group.
- 58 -
Page 66

CHAPTER9 Security
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Figure 9-19: Add Membership
This Group Name corresponds to the “AD Authentication: Group Name” that is configured for the OVOC Tenant created for this account in OVOC.
e. Click Save and close.
Figure 9-20: Successful Membership Assignment
7. Register new WEB Application: See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-
directory/develop/quickstart-register-app.
● The Redirect URI step should be configured like WEB and OVOC's login endpoint
should be specified as URI: https://<IP address>/ovoc/v1/security
● Generally for this step you should only keep the Client ID of your application that
you need to specify in OVOC Microsoft Azure authentication setup (see
Authentication and Authorization using Microsoft Azure
8. Create Client Secret for your Registered Application: See
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/quickstart-configureapp-access-web-apis#add-credentials-to-your-web-application. You must configure this
secret in Authentication and Authorization using Microsoft Azure.
- 59 -
Page 67

CHAPTER9 Security
9. Grant API Permissions: Extend default application's permissions set and give admin
consent to all the existing permissions. Add and provide admin consent to such delegated
Microsoft Graph API related permissions: Group.Read.All.
For more details, refer to the following:
● https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/quickstart-
● https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/quickstart-
HTTPS Connection
The connection between the NBIF client and the OVOC server is by default secured over HTTPS
(port 443). This security is managed by the EMS Server Manager option ‘IP Phone Manager Pro
and NBIF Web pages Secured Communication’. You can secure this connection either using
AudioCodes default self-signed certificates or by applying custom certificates signed by an
external CA. For more information, refer to the OVOC Security Guidelines document.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
configure-app-access-web-apis#add-permissions-to-access-web-apis
configure-app-access-web-apis#understanding-api-permissions-and-admin-consent-ui
- 60 -
Page 68

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
This chapter describes the database tables that are accessible using the Data Analytics API:
■ Main Table Views
■ Type Views
Main Table Views
This section describes the Main Table Views that are accessible in the OVOC database.
Table 10-1: View Name: NODES_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
NODE_ID x NUMBER(28)
NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
NODE_DESCRIPTION x NVARCHAR2(255)
FQDN x NVARCHAR2(255)
IP_ADDRESS x VARCHAR2(20)
SW_VERSION x VARCHAR2(100)
SERIAL_NUMBER x VARCHAR2(255)
SECOND_SERIAL_NUMBER x VARCHAR2(255)
DEFINED_AT x DATE
REGION_ID x NUMBER(28)
REGION_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
TENANT_ID x NUMBER(28)
TENANT_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
PRODUCT_TYPE x NUMBER(3)
PRODUCT_TYPE_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
ADMIN_STATE x VARCHAR2(20)
ADMIN_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
- 61 -
Page 69

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
MGMT_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
MGMT_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
SEVERITY_STATE x VARCHAR2(20)
SEVERITY x VARCHAR2(100)
CONNECTION_STATE x NUMBER(3)
CONNECTION_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
CONNECTION_LOST_TIME x DATE
MISMATCH_STATE x NUMBER
MISMATCH_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
RESET_NEEDED x NUMBER
RESET_NEEDED_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
BURN_NEEDED x NUMBER
BURN_NEEDED_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
NETWORK_STATE x NUMBER
NETWORK_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
SBA_CONNECTION_STATE x NUMBER
SBA_CONNECTION_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQM_CONNECTION_STATE x NUMBER
VQM_CONNECTION_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_CONTROL_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_CONTROL_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_MEDIA_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
- 62 -
Page 70

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
VQ_MEDIA_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
SIP_MESSAGE_STATUS x NUMBER
SIP_MESSAGE_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
MANAGED_STATE x NUMBER
MANAGED_STATE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
MANAGED_STATE_SEM x NUMBER
MANAGED_STATE_SEM_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LICENSE_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
LICENSE_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LICENSE_POOL_STATUS x NUMBER
CLM_STATUS x NUMBER
SNMP_PORT x NUMBER
SNMP_VERSION x NUMBER
HTTPS_PROXY_ENABLED x NUMBER
HTTPS_ENABLED_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LAST_BACKUP_STATUS x NUMBER
LAST_BACKUP_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LAST_PERFORMED_BACKUP_TIME x DATE
POLLING_ENABLED x NUMBER
POLLING_ENABLED_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LAST_POLLING_STATUS x NUMBER
LAST_POLLING_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LAST_POLLING_FAIL_REASON x NUMBER
- 63 -
Page 71

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
LAST_SUCCESFUL_POLLING x DATE
LAST_UNSUCCESFUL_POLLING x DATE
LAST_NUM_POLLING x NUMBER
NETWORK_X_LOCATION x FLOAT(126)
NETWORK_Y_LOCATION x FLOAT(126)
NETWORK_LATITUDE x VARCHAR2(25)
NETWORK_LONGITUDE x VARCHAR2(25)
REPORTED_NODE_ID x NUMBER
SQL_SERVRE_IP x NVARCHAR2(50)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
SQL_SERVER_PORT x NUMBER
SQL_SERVER_INSTANCE_NAME x VARCHAR2(50)
Table 10-2: View Name: LINKS_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
LINK_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(10)
LINK_NAME x VARCHAR2(50)
TENANT_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
SRC_TENANT_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
SECOND_TENANT_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
DEST_TENANT_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
REGION_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
REGION_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
SRC_NODE_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
SRC_NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
SRC_N_NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
- 64 -
Page 72

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
DEST_NODE_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
DEST_NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
DEST_N_NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
LINK_TYPE x NUMBER(3)
LINK_TYPE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
TYPE_IP_GROUP x NUMBER(10)
TYPE_TRUNK_GROUP x NUMBER(10)
TYPE_IP_PREFIX x VARCHAR2(250)
TYPE_PHONE_PREFIX x VARCHAR2(250)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
TYPE_MEDIA_REALM x NUMBER(10)
TYPE_MEDIA_IP_PREFIX x VARCHAR2(250)
TYPE_SRC_FQDN x NVARCHAR2(100)
TYPE_DEST_FQDN x NVARCHAR2(100)
SRC_PRODUCT_TYPE x NUMBER(3)
SRC_PRODUCT_TYPE_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
DEST_PRODUCT_TYPE x NUMBER(3)
DEST_PRODUCT_TYPE_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
LINK_DIRECTION x NUMBER(3)
LINK_DIRECTION_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
DEFINED_AT x NOT NULL
VQ_STATUS x NOT NULL
VQ_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_CONTROL_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_CONTROL_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
- 65 -
Page 73

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
VQ_MEDIA_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_MEDIA_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_CALL_DURATION_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_CALL_DURATION_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_MAX_CONCURRENT_CALLS_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_MAX_CONC_CALLS_STATUS_V x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_BANDWIDTH_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
VQ_BANDWIDTH_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Table 10-3: View Name: CALLS_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
CALL_INDEX NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
EMS_CALL_IDENTIFIER NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
NODE_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
NODE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
SESSION_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
CALL_START_TIME NOT NULL DATE
CALL_END_TIME NOT NULL DATE
CALL_DURATION x NUMBER(10)
CALL_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
CALL_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
VQ_COLOR x NUMBER(3)
VQ_COLOR_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
QUALITY_CAUSE x NUMBER(3)
- 66 -
Page 74

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
QUALITY_CAUSE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
RED_COLOR_PERCENT x NUMBER(10,2)
YELLOW_COLOR_PERCENT x NUMBER(10,2)
GREEN_COLOR_PERCENT x NUMBER(10,2)
TERMINATION_INITIATOR x NUMBER(3)
TERMINATION_INITIATOR_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
TERMINATION_REASON_CATEGORY x NUMBER(3)
TERM_REASON_CATEGORY_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
TERMINATION_REASON_DETAILS x VARCHAR2(100)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
TERM_REASON_DETAILS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
SIP_TERMINATION_REASON x VARCHAR2(50)
SIP_TERMINATION_DESC x VARCHAR2(100)
PSTN_TERMINATION_REASON x NUMBER(4)
PSTN_TERM_REASON_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
MEDIA_TYPE x NUMBER(3)
MEDIA_TYPE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
ENDPOINT_TYPE x NUMBER(10)
ENDPOINT_TYPE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
CALLER_URI x VARCHAR2(160)
CALLEE_URI x VARCHAR2(160)
NO_EVENT_FLAG x NUMBER(3)
CALL_NODES x VARCHAR2(300)
CALL_LINKS x VARCHAR2(300)
CALL_SOURCE_TYPE x NOT NULL
- 67 -
Page 75

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
CALL_SOURCE_TYPE_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
MOS x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER x NUMBER(10,2)
PLOSS x NUMBER(10,2)
DELAY x NUMBER(10,2)
RERL x NUMBER(10,2)
Table 10-4: View Name: ALARMS_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
ALARM_ID x NUMBER(28)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
IS_EVENT x NUMBER(8)
ALARM_REMOTE_HOST x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_UNIQUE_ID x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_DESCRIPTION x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_SEVERITY x NUMBER(3)
ALARM_SEVERITY_VALU x VARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_SOURCE x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_ADDITIONAL_INFO1 x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_ADDITIONAL_INFO2 x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_ADDITIONAL_INFO3 x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_REMOTE_PORT x NUMBER(8)
ALARM_SYSTEM_UP_TIME x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_SNMP_VERSION x NUMBER(3)
ALARM_OID x VARCHAR2(100)
- 68 -
Page 76

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
ALARM_STATUS x NUMBER(3)
ALARM_STATUS_VALUE x VARCHAR2(100)
LAST_ACTION_TIME x DATE
LAST_ACTION_OPERATOR x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_RECIEVED_TIME x DATE
ALARM_UNIT_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_REGION_ID x NUMBER(28)
ALARM_REGION_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_UNIT_ID x NUMBER(28)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
TENANT_ID x NUMBER(28)
TENANT_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
ALARM_SOURCE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(255)
ALARM_DATE_TIME x NVARCHAR2(255)
Table 10-5: View Name: NODES_SUMMARY_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
DEVICE_NAME x NVARCHAR2(100)
NODE_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
TIME_STAMP NOT NULL DATE
NODE_NAME x VARCHAR2(100)
REGION_ID x NUMBER(28)
CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
CALLS_DURATION_TOTAL x NUMBER(10)
CALLS_DURATION_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
SUCCESS_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
- 69 -
Page 77

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
FAILED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
RERL_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
MOS_MIN x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_MIN x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_MIN x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_MIN x NUMBER(10)
RERL_MIN x NUMBER(10)
MOS_MAX x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_MAX x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_MAX x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_MAX x NUMBER(10)
RERL_MAX x NUMBER(10)
MOS_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
PLOSS_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
DELAY_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
- 70 -
Page 78

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
RERL_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
MOS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
RERL_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
SNR_MIN x NUMBER(10)
SNR_MAX x NUMBER(10)
SNR_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
SNR_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
RX_KB_TOTAL x NUMBER(28)
TX_KB_TOTAL x NUMBER(28)
VOICE_CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
FAX_CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
MOS_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
- 71 -
Page 79

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
PLOSS_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
RERL_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MAX_CONCURRENT_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
INCOMING_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
OUTGOING_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
Table 10-6: View Name: LINKS_SUMMARY_VIEW
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
REAL_LINK_NAME x VARCHAR2(50)
LINK_ID NOT NULL NUMBER(28)
TIME_STAMP NOT NULL DATE
LINK_NAME x VARCHAR2(50)
REGION_ID x NUMBER(28)
CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
CALLS_DURATION_TOTAL x NUMBER(10)
CALLS_DURATION_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
SUCCESS_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
- 72 -
Page 80

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
FAILED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
RERL_CAUSE x NUMBER(10)
MOS_MIN x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_MIN x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_MIN x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_MIN x NUMBER(10)
RERL_MIN x NUMBER(10)
MOS_MAX x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_MAX x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_MAX x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_MAX x NUMBER(10)
RERL_MAX x NUMBER(10)
MOS_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
JITTER_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
PLOSS_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
DELAY_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
- 73 -
Page 81

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
RERL_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
MOS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
RERL_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
SNR_MIN x NUMBER(10)
SNR_MAX x NUMBER(10)
SNR_TOTAL x NUMBER(10,2)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
SNR_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
RX_KB_TOTAL x NUMBER(28)
TX_KB_TOTAL x NUMBER(28)
VOICE_CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
FAX_CALLS_COUNT x NUMBER(10)
MOS_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MOS_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
JITTER_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
- 74 -
Page 82

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Name Null? Supported Enumerator
PLOSS_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
PLOSS_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
DELAY_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_RED_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_YELLOW_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
RERL_GREEN_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
RERL_GRAY_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
MAX_CONCURRENT_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
INCOMING_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
OUTGOING_CALLS x NUMBER(10)
Type Views
This appendix describes the Type Views that are accessible in the OVOC database.
Table 10-7: Type Name: DisableEnableType
Type Values
(0) Disable
(1) Enable
The table below is divided into two columns for readability. In the database, there is a
single column for “MGType” e.g. (0) UNKNOWN.
- 75 -
Page 83

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Table 10-8: Type Name: MGType
Type Values MGType
(0) UNKNOWN
(1) Mediant 8000
(2) STRETTO 8000
(3) Mediant 5000
(4) STRETTO 5000
(5) Mediant 2000
(6) STRETTO 2000
(7) MP102
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(8) MP104 FXS
(9) MP104 FXO
(10) MP108 FXS
(11) MP108 FXO
(12) MP124
(13) IPAT 8000
(14) IPAT 5000
(15) IPAT 2000
(16) CA IPAT 8000
(17) CA IPAT 5000
(18) CA IPAT 2000
(20) UNKNOWN MP102
(21) UNKNOWN MP104 FXS
(22) UNKNOWN MP104 FXO
(23) UNKNOWN MP108 FXS
- 76 -
Page 84

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(24) UNKNOWN MP108 FXO
(25) UNKNOWN MP124
(26) UNKNOWN Mediant 2000
(27) UNKNOWN STRETTO 2000
(28) UNKNOWN Mediant 8000
(29) UNKNOWN STRETTO 8000
(30) UNKNOWN Mediant 5000
(31) UNKNOWN STRETTO 5000
(32) UNKNOWN IPAT 8000
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(33) UNKNOWN IPAT 5000
(34) UNKNOWN IPAT 2000
(35) UNKNOWN CA IPAT 8000
(36) UNKNOWN CA IPAT 5000
(37) UNKNOWN CA IPAT 2000
(38) IPMedia 2000
(39) UNKNOWN IPMEDIA 2000
(40) IPMedia 5000
(41) UNKNOWN IPMEDIA 5000
(42) IPMedia 8000
(43) UNKNOWN IPMEDIA 8000
(44) Mediant 1000
(45) UNKNOWN Mediant 1000
(46) Mediant 3000
(47) UNKNOWN Mediant 3000
- 77 -
Page 85

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(9) UNKNOWN MP118FXS
(50) MP114 FXS
(51) UNKNOWN MP114FXS
(52) MP112
(53) UNKNOWN MP112
(54) MP118 FXO
(55) UNKNOWN MP118FXO
(56) MP114 FXO
(57) UNKNOWN MP114FXO
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(58) IPMedia 3000
(59) UNKNOWN IPMEDIA 3000
(60) MP118 FXSFXO
(61) UNKNOWN MP118 FXS/FXO
(62) MP114 FXSFXO
(63) UNKNOWN MP114 FXS/FXO
(64) Mediant 260
(65) UNKNOWN Mediant 260
(66) IPMedia 260
(67) UNKNOWN IPMEDIA 260
(68) Mediant 3000 8410
(69) UNKNOWN Mediant 3000 8410
(70) IPMedia 3000 8410
(71) UNKNOWN IPMedia 3000 8410 8410
(72) Mediant 3000 8410 V5.2
- 78 -
Page 86

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(73) UNKNOWN Mediant 3000 8410 V5.2
(74) IPMedia 3000 8410 VIDEO
(75) UNKNOWN IPMedia 3000 8410 8410 VIDEO
(76) Mediant 600
(77) UNKNOWN Mediant 600
(78) Mediant 800 MSBR
(79) UNKNOWN Mediant 800 MSBR
(80) Mediant 1000 MSBR
(81) UNKNOWN Mediant 1000 MSBR
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(82) Mediant 800 E-SBC
(83) UNKNOWN Mediant 800 E-SBC
(84) Mediant 1000 E-SBC
(85) UNKNOWN Mediant 1000 E-SBC
(86) Mediant 4000 E-SBC
(87) UNKNOWN Mediant 4000 E-SBC
(88) SW SBC
(89) UNKNOWN S
(90) Mediant 500 MSBR
(91) UNKNOWN Mediant 500 MSBR
(92) Mediant 500 E-SBC
(93) UNKNOWN Mediant 500 E-SBC
(94) Mediant 850 MSBR
(95) UNKNOWN Mediant 850 MSBR
(96) Mediant 850 E-SBC
- 79 -
Page 87

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(97) UNKNOWN Mediant 850 E-SBC
(98) Mediant 2600 E-SBC
(99) UNKNOWN Mediant 2600 E-SBC
(100) Mediant 500L MSBR
(101) UNKNOWN Mediant 500L MSBR
(102) Mediant 500L E-SBC
(103) UNKNOWN Mediant 500L E-SBC
(104) Mediant 800B MSBR
(105) UNKNOWN Mediant 800B MSBR
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(106) Mediant 800B E-SBC
(107) UNKNOWN Mediant 800B E-SBC
(108) SW SE SBC
(109) UNKNOWN SW SE SBC
(110) SW SE-H SBC
(111) UNKNOWN SW SE-H SBC
(112) SW VE SBC
(113) UNKNOWN SW VE SBC
(114) SW VE-H SBC
(115) UNKNOWN SW VE-H SBC
(116) Mediant 9000 SBC
(117) UNKNOWN Mediant 9000 SBC
(118) SW SBC CM
(119) UNKNOWN SW SBC CM
(120) Mediant 4000B E-SBC
- 80 -
Page 88

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(121) UNKNOWN Mediant 4000B E-SBC
(122) Mediant 9000 SBC CM
(123) UNKNOWN Mediant 9000 SBC CM
(124) SW VE SBC CM
(125) UNKNOWN SW VE SBC CM
(126) MP1288
(127) UNKNOWN MP1288
(128) SW SE SBC CM
(129) UNKNOWN SW SE SBC CM
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(19) MP124-E
(130) UNKNOWN MP124E
(131) Mediant 2600B E-SBC
(132) UNKNOWN Mediant 2600B E-SBC
(133) Mediant 500LI MSBR
(134) UNKNOWN Mediant 500LI MSBR
(200) Generic Device
(250) CloudBond 365 Standard Edition
(251) UNKNOWN CloudBond 365 Standard Edition
(252) CloudBond 365 Standard Plus Edition
(253) UNKNOWN CloudBond 365 Standard Plus Edition
(254) CloudBond 365 Pro Edition
(255) UNKNOWN CloudBond 365 Pro Edition
(256) CloudBond 365 Enterprise Edition
(257) UNKNOWN CloudBond 365 Enterprise Edition
- 81 -
Page 89

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(258) CloudBond 365 Virtualized Edition
(259) UNKNOWN CloudBond 365 Virtualized Edition
(260) User Management Pack
(261) UNKNOWN User Management Pack
(262) Mediant 800 CCE Appliance
(263) UNKNOWN Mediant 800 CCE Appliance
(264) Mediant Server CCE Appliance
(265) UNKNOWN Mediant Server CCE Appliance
(266) SmartTap
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(267) null
(268) User Management Pack Multi-Tenant
(269) UNKNOWN User Management Pack Multi-Tenant
(299) SBA
(300) Skype Front End Server
(301) Skype Mediation Server
(302) Skype Edge Server
(303) Skype SBA
(304) MP202 B
(305) UNKNOWN MP202 B
(306) MP204 B
(307) UNKNOWN MP204 B
(308) MP202
(309) UNKNOWN MP202
(310) MP204
- 82 -
Page 90

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Type Values MGType
(311) UNKNOWN MP204
(326) MP202 R
(327) UNKNOWN MP202 R
(328) MP204 R
(329) UNKNOWN MP204 R
(312) SW SE SBC SC
(313) UNKNOWN SW SE SBC SC
(314) SW SE-H SBC SC
(315) UNKNOWN SW SE-H SBC SC
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(316) SW VE SBC SC
(317) UNKNOWN SW VE SBC SC
(318) SW VE-H SBC SC
(319) UNKNOWN SW VE-H SBC SC
(320) SW ESBC SC
(321) UNKNOWN SW ESBC SC
(322) Mediant 800C MSBR
(323) UNKNOWN Mediant 800C MSBR
(324) Mediant 800C E-SBC
(325) UNKNOWN Mediant 800C E-SBC
Table 10-9: Type Name: ItuPerceivedSeverity
(0) cleared
(1) indeterminate
(2) warning
Values
- 83 -
Page 91

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
(3) minor
(4) major
(5) critical
Table 10-10:Type Name: ConnectionType
(0) Not Connected
(1) Connected
Table 10-11:Type Name: MismatchType
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Values
Type Values
Type Values
(0) No Mismatch
(1) Hardware Mismatch
(2) Sw Version Unsupported
(3) Configuration Mismatch
(4) Predefine Mismatch
(5) Predefine Mismatch with upload configuration
(6) Predefine Mismatch with Download configuration
Table 10-12:Type Name: SemConnectionState
Type Values
(0) Not defined
(1) Not defined not connected
(2) Not connected
(3) connected
(4) Not connected no resources
- 84 -
Page 92

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Table 10-13:Type Name: StatusType
(0) ERROR
(1) WARNING
(2) OK
(3) UNMONITORED
Table 10-14:Type Name: VQThresholdStatus
(0) CRITICAL
(1) MAJOR
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Type Values
Type Values
(2) CLEAR
(3) UNMONITORED
Table 10-15:Type Name: SipMessageStatusType
(0) UNDEFINED
(1) SBC_IND_START_SENDING_SIPM
(2) SBC_IND_STOP_SENDING_SIPM
Table 10-16:Type Name: NoYesType
(0) No
(1) Yes
Type Values
Type Values
(0) Regular
(1) NAT
Table 10-17:Type Name: NetworkState
Type Values
- 85 -
Page 93

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Table 10-18:Type Name: ManagedType
(0) Not Defined
(1) Managed
(2) Unmanaged
Table 10-19:Type Name: FailSuccessType
(0) Fail
(1) Success
Table 10-20:Type Name: BackupStatusType
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Type Values
Type Values
(0) No backup info
(1) File uploaded
(2) File not changed
(3) MG not connected
(4) Upload error
(5) Not enough disk space
(6) Backup error
Table 10-21:Type Name: ItuEntityAdministrativeState
(0) Locked
Type Values
Type Values
(1) ShuttingDown
(2) Unlocked
- 86 -
Page 94

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
Table 10-22:Type Name: AlarmStatusType
(0) New
(1) Acknowledged
(2) Cleared
(3) Automatically Cleared
(4) Coldstart Cleared
The table below is divided into two columns for readability. In the database, there is a
single column for “Type Values” e.g. (.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.41)
acSonetLineRDIAlarm.
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
Type Values
Table 10-23:Type Name: AlarmNameType
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.41) acSonetLineRDIAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.40) acSonetLineAISAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.43) acHwFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.42) acSonetIfHwFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.70) IPPhoneRequiresReset
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.30.2.2.0.5) acSbaCertificateExpiredAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.72) acAlarmsFwOverflow
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.30.2.2.0.4) acSBADiskSpaceAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.71) acAlarmsOverflow
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.74) acPmTimeOutEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.73) acEMSFQDNResolveEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.76) acDevicePmPollingEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.75) acTokenPoolIsEmpty
- 87 -
Page 95

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.78) acPmHasNoSnmpConnection
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.77) acPmBatchOverFlowAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.79) JabraFirmwareUpgradeFailed
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.49) acTrunksAlarmNearEndLOS
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.48) acHitlessUpdateStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.45) acDialPlanFileReplaced
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.44) acH248LostConnectionWithCA
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.47) acAnalogPortHighTemperature
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.46) acAnalogPortSPIOutOfService
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.52) acTrunksAlarmFarEndLOF
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.51) acTrunksAlarmRcvAIS
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.54) acAMSProcedureResult
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.53) acIPv6ErrorAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.50) acTrunksAlarmNearEndLOF
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.61) floatingLicenseExtended
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.60) acSEMSipMessageStatusAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.63) acClmRegisterSuccessfulEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.62) acClmDeviceReportAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.65) acClmFailToSendUsageReportAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.64) acClmRegisterFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.67) acClmServiceShutdownAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.66) acClmFailToSendUsageReportExtendedAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.69) acClmMaxDeviceCapacityAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.68) acClmMaxDeviceMismatchEvent
- 88 -
Page 96

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.59) acGWSASEmergencyModeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.56) acTMInconsistentRemoteAndLocalPLLStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.55) acWeakRedundancy
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.58) acTMReferenceChange
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.57) acTMReferenceStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.21) acSS7LinkBlockStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.20) acSS7LinkInhibitStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.50) acSEMLicenseKeyAlarmDevice
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.52) acEMSNotEnoughOracleSpaceAlarm
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.51) acEMSDiskSpaceAlarmCheck
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.54) IPPhoneSpeakerFirmDownloadFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.53) acLicenseAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.55) IPPhoneSpeakerFirmUpgradeFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.56) IPPhoneConferSpeakerConnectFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.58) acOvocReSyncEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.57) IPPhoneGeneralLocalEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.59) IPPhoneWebSuccessiveLoginFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.27) acPerformanceMonitoringThresholdCrossing
(.1.3.6.1.2.1.10.18.15.0.1) ds1LineStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.26) acSS7RedundancyAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.29) acFanTrayAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.28) acHTTPDownloadResult
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.23) acSS7LinkSetStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.22) acSS7LinkCongestionStateChangeAlarm
- 89 -
Page 97

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.25) acSS7SNSetStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.24) acSS7RouteSetStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.30) acPowerSupplyAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.32) acSAMissingAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.31) acPEMAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.41) IPPhoneLyncLoginFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.40) IPPhoneSurvivableModeStart
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.30.2.2.0.1) acSBAServicesStatusAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.43) acSEMRuleBandwidthAlarm
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.42) acEMSAlarmSuppression
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.30.2.2.0.3) acSBAMemoryStatusAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.45) acEMSKeepAliveAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.30.2.2.0.2) acSBACpuStatusAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.44) acSEMRuleMaxConcurrentCallsAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.47) acEndpointPublishAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.46) acEMSPreProvisioningAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.49) acEndpointServerOverloadAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.48) acEndpointLicenseAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.38) acSonetSectionLOFAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.37) acDChannelStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.39) acSonetSectionLOSAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.34) acHASystemConfigMismatchAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.33) acHASystemFaultAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.36) acUserInputAlarm
- 90 -
Page 98

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.35) acHASystemSwitchOverAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.3) acEMSNodeConnectionLostAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.9) acEMSNoMismatchNodeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.7) acEMSConfigurationMismatchNodeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.12) acARMTopologyReloaded
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.13) acARMRoutingRuleMatch
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.10) acBoardEthernetLinkAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.10) acARMLicenseMissing
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.11) acARMQualityChanged
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.2.1.47.2.0.1) entConfigChange
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.16) acARMRegistrationStatusResyncThreshold
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.17) acARMExternalWebService
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.5.2) resettingBoard
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.14) acARMRouterReloaded
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.70.1.2.2.0.15) acARMNoAvailableRouter
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.19) acSS7LinkStateChangeAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.1) acEMSSnmpCannotBindError
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.16) acKeepAlive
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.15) acOperationalStateChange
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.18) acEnhancedBITStatus
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.17) acNATTraversalAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.12) acActiveAlarmTableOverflow
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.11) acBoardOverloadAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.14) acAudioProvisioningAlarm
- 91 -
Page 99

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.13) acAtmPortAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.141) acAnalogLineLeftOffhookAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.142) acCDRServerAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.140) acInstallationFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.138) acFloatingLicenseAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.139) acAWSSecurityRoleAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.136) acHANetworkMonitorAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.137) acHAEthernetGroupAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.134) acMediaClusterRemoteInterfaceAlarm
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.135) acHANetworkMismatchAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.132) acCloudLicenseManagerAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.133) acMediaClusterAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.81) endpointVipDisconnected
(.1.3.6.1.2.1.255.3.1) rtcpXrVoipThresholdViolation
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.80) endpointVipUnregistered
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.83) acReportSchedulersLoadAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.82) acReportSchedulersTimeEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.85) acFlexPoolLicenseUsage
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.84) acReportSchedulersExecutionEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.20.3.2.0.86) acUMPUsersSchedulerAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.145) acRemoteMonitoringAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.143) acDSPFarmsMismatchAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.144) acFlexLicenseManagerAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.1) coldStart
- 92 -
Page 100

CHAPTER10 Data Analytics API Database Tables
OID Type Values
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.120) acMtcePsuFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.2) warmStart
(.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3) linkDown
(.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.4) linkUp
(.1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.5) authenticationFailure
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.50) acUmpEndUserAuthFailEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.116) acMtceNetworkFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.117) acMtceSwUpgradeFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.114) acIpGroupNoRouteAlarm
OVOC | Integration with Northbound Interfaces
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.115) acMtcmClusterHaAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.112) acACDThresholdAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.113) acNERThresholdAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.110) acResetNeededAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.111) acASRThresholdAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.40.3.2.0.13) acVaCallRecordingErrorEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.118) acMtceHwTemperatureFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.40.3.2.0.11) acVaResourceThresholdAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.10.1.21.2.0.119) acMtceHwFanTrayFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.40.3.2.0.12) acVaConnectionFailureAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.49) acUmpUserSettingsFailEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.48) acUmpO365CommandExEvent
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.45) acUmpAzureADSyncAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.44) acUmpEndUserLicThresholdAlarm
(.1.3.6.1.4.1.5003.9.80.3.2.0.47) acUmpSBCFailureAlarm
- 93 -
 Loading...
Loading...