U2008B
Rev. A4, 12-Jan-01 1 (10)
Low-Cost Phase-Control IC with Soft Start
Description
The U2008B is designed as a phase-control circuit in
bipolar technology. It enables load-current detection as
well as mains-compensated phase control. Motor control
with load-current feedback and overload protection are
preferred applications.
Features
Full wave current sensing
Mains supply variation compensated
Variable soft-start or load-current sensing
Voltage and current synchronization
Automatic retriggering switchable
Triggering pulse typ. 125 mA
Internal supply-voltage monitoring
Current requirement 3 mA
Applications
Low-cost motor control
Domestic appliance
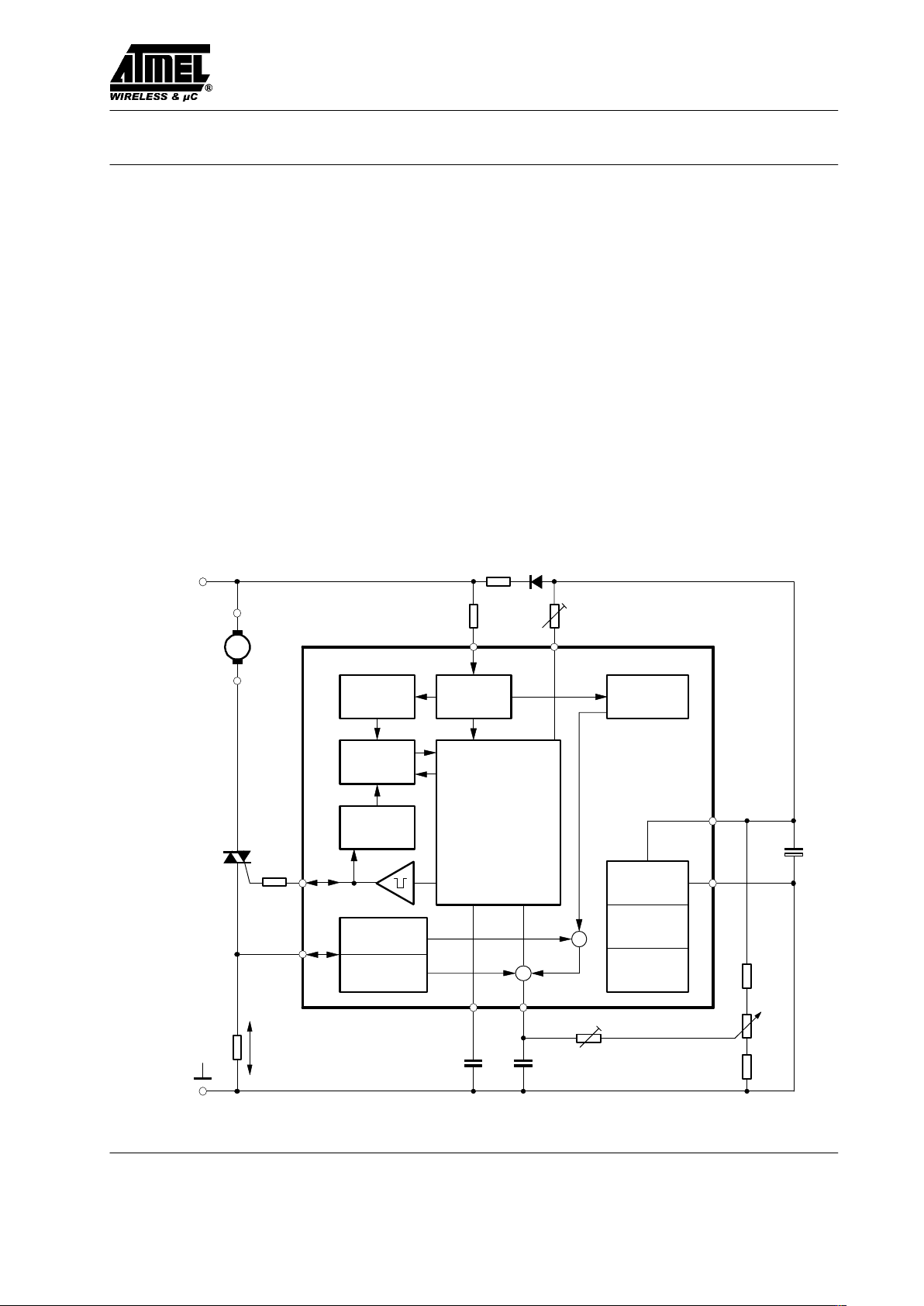
Block Diagram
Automatic
retriggering
Limiting
detector
Current
detector
Full wave load
current detector
Soft start
Voltage
detector
7
Phase
control unit
= f (V
3
)
6
Mains voltage
compensation
Supply
voltage
limiting
Reference
voltage
Voltage
monitoring
23
5
4
1
8
R
2
330 k
22 k/2W
BYT51K
R
1
D
1
R
8
1 M
180
R
3
TIC
226
Load
100 k
R
10
Load current
compensation
C
4
Set point
100 nF
C
3
3.3 nF
R
6
230 V ~
R
14
47 k
P
1
R
7
GND
–V
S
C
1
25 V
+
–
^
V
(R6)
= ±250 mV
U2008B
max
22 F/
Figure 1. Block diagram with typical circuit: Load current sensing

U2008B
Rev. A4, 12-Jan-012 (10)
Ordering Information
Extended Type Number Package Remarks
U2008B-x DIP8 Tube
U2008B-xFP SO8 Tube
U2008B-xFPG3 SO8 Taped and reeled
Automatic
retriggering
Limiting
detector
Current
detector
Full wave load
current detector
Soft start
Voltage
detector
7
Phase
control unit
= f (V
3
)
6
Mains voltage
compensation
Supply
voltage
limiting
Reference
voltage
Voltage
monitoring
23
5
4
1
8
R
2
680 k
22 k/2W
BYT51K
R1D
1
max
R
8
470 k
180
R
3
TIC
226
Load
68 k
R
10
C
4
Set point
100 nF
C
3
10 nF
230 V ~
P
1
50 k
R
7
220 k
GND
–V
S
C
1
100 F/
25 V
+
–
L
C
5
Soft start
4.7F/ 25 V
N
U2008B
Figure 2. Block diagram with typical circuit: Soft start

U2008B
Rev. A4, 12-Jan-01 3 (10)
Pin Description
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
I
sense
Cϕ
Control
GND
Output
V
sync.
Rϕ
V
S
U2008B
Figure 3. Pinning
Pin Symbol Function
1 I
sense
Load current sensing
2 Cϕ Ramp voltage
3 Control Control input / compensation
output
4 GND Ground
5 –V
S
Supply voltage
6 Rϕ Ramp current adjustment
7 V
sync.
Voltage synchronization
8 Output Trigger output
Mains Supply, Pin 5, Figure 2
The integrated circuit U2008B, which also contains
voltage limiting, can be connected via D1 and R1 via the
mains supply. Supply voltage between Pin 4 (pos.
,
)
and Pin 5 is smoothed by C1.
Series resistance R1 can be calculated as follows:
R
1max
0.85 x
VM–V
Smax
2 xI
tot
where:
V
M
Mains voltage
V
Smax
Maximum supply voltage
I
tot
I
Smax
I
x
= Total current compensation
I
Smax
= Maximum current consumption of the IC
I
x
= Current consumption of the external
components
An operation with external stabilized DC voltage is not
recommended.
Voltage Monitoring
When the voltage is built up, uncontrolled output pulses
are avoided by internal voltage monitoring. Apart from
that, all latches in the circuit (phase control, load limit
regulation) are reset and the soft-start capacitor is short
circuited. This guarantees a specified start-up behavior
each time the supply voltage is switched on or after short
interruptions of the mains supply. Soft start is initiated
after the supply voltage has been built up. This behavior
guarantees a gentle start-up for the motor and
automatically ensures the optimum run-up time.
Phase Control, Pin 6
The function of the phase control is largely identical to
that of the well-known IC U211B. The phase angle of the
trigger pulse is derived by comparing the ramp voltage V
2
at Pin 2 with the set value on the control input, Pin 3. The
slope of the ramp is determined by C
and its charging
current I .
The charging current can be regulated, changed, altered
using R at Pin 6. The maximum phase angle, α
max,
(minimum current flow angle
min
) can also be adjusted
by using R
(see figure 5).
When the potential on Pin 2 reaches the set point level of
Pin 3, a trigger pulse is generated whose pulse width, tp,
is determined from the value of C (tp = 9 s/nF, see
figure 7). At the same time, a latch is set with the output
pulse, as long as the automatic retriggering has not been
activated, then no more pulses can be generated in that
half cycle. Control input at Pin 3 (with respect to Pin 4)
has an active range from –9 V to –2 V. When V3 = –9 V,
then the phase angle is at its maximum α
max,
i.e., the
current flow angle is minimum. The minimum phase
angle α
min
is set with V3 –1 V.
Automatic Retriggering
The current-detector circuit monitors the state of the triac
after triggering by measuring the voltage drop at the triac
gate. A current flow through the triac is recognized when
the voltage drop exceeds a threshold level of typ. 40 mV.
If the triac is quenched within the relevant half wave after
triggering (for example owing to low load currents before
or after the zero crossing of current wave, or for commutator motors, owing to brush lifters), the automatic
retriggering circuit ensures immediate retriggering, if
necessary with a high repetition rate, tpp/tp, until the triac
remains reliably triggered.
 Loading...
Loading...