Page 1

Page 2

2
Page 3

3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Safety Summary......................................4
Safety Information..................................4
Shock Hazards ......................................5
Flash Hazards ........................................5
Fire Hazards ..........................................6
Fume Hazards........................................7
Compressed Gasses
and Equipment Hazards ......................7
Additional Safety Information ................8
Welder Specifications ............................9
Description ............................................9
Welder Operating Characteristics ..........9
Duty Cycle ..........................................9
Internal Thermal Protection ....................9
Know Your Welder..................................10
Welder Installation ................................11
Power Source Connection ......................11
Power Requirements ............................11
Connect to Power Source ....................11
Extension Cords ..................................11
Assembling the Welder ..........................11
Unpacking the Welder ........................11
Packing List..........................................11
Assemble the Face Shield ....................11
Installing the Handle............................12
Selecting Shielding Gas........................12
Install the Shielding Gas ......................13
Check the Gas Flow ..............................13
Align and Set the Drive Roller ................13
Install the Welding Wire ........................14
Set the Wire Drive Tension ....................16
Installing Aluminium Wire ......................16
Change Polarity......................................16
Operation................................................17
Controls and Indicators ..........................17
Power Switch ......................................17
Voltage Selector ..................................17
Wire Speed Control ............................17
Tuning in the Wire Speed ..........................17
Learning to Weld ......................................18
Holding the Gun ....................................18
Welding Techniques................................19
Moving the Gun ..................................19
Types of Weld Beads ............................20
Welding Positions ................................20
Multiple Pass Welding ..........................21
Special Welding Methods ....................22
Spot Welding ....................................22
Maintenance ..........................................23
General ................................................23
Consumable Maintenance......................23
Maintaining the Contact Tip ..................23
Maintaining the Nozzle ..........................24
Testing for a Shorted Nozzle ..................24
Replace a Gun Liner ..............................24
Preventive Maintenance..........................26
Troubleshooting ....................................26
Wiring Diagram......................................28
Parts List..................................................29
Suggested Settings ................................33
Page 4

4
The warnings, cautions and instructions discussed in this instruction manual can not cover
all possible conditions or situations that could
occur. It must be understood by the operator
that common sense and caution are factors
which can not be built into this product, but
must be supplied by the operator. Reading this
operator’s manual before using the welder
will enable you to do a better, safer job. Learn
the welder’s applications and limitations as
well as the specific potential hazards peculiar
to welding.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
The following safety information is provided
as guidelines to help you operate your new
welder under the safest possible conditions.
Any equipment that uses electrical power
can be potentially dangerous to use when
safety or safe handling instructions are not
known or not followed. The following safety
information is provided to give the user the
information necessary for safe use and
operation.
A procedure step preceded by a WARNING is
an indication that the next step contains a procedure that might be injurious to a person if
proper safety precautions are not heeded.
A procedure preceded by a CAUTION is an
indication that the next step contains a procedure that might damage the equipment
being used.
A NOTE may be used before or after a procedure step to highlight or explain something in that step.
READ ALL SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY before attempting to install, operate,
or service this welder. Failure to comply with
these instructions could result in personal
injury and/or property damage.
RETAIN THESE INSTRUCTIONS FOR
FUTURE REFERENCE.
Note:
• The following safety alert symbols identify
important safety messages in this manual.
• When you see one of the symbols shown
here, be alert to the possibility of personal injury and carefully read the message
that follows.
This symbol indicates that the possibility of electric shock hazard
exists during the operation of the
step(s) that follow.
This symbol indicates that the possibility of fire hazard exists during
the operation of the step(s) that
follow.
This symbol indicates that the helmet must be worn during the
step(s) that follow to protect
against eye damage and burns
due to flash hazard.
This symbol indicates that the possibility of toxic gas hazard exists
during operation of the step(s)
that follow.
This symbol indicates that the possibility of being burned by hot slag
exists during operation of the
step(s) that follow.
This symbol indicates that the eye
protection should be worn to protect against flying debris in the following step(s).
This symbol indicates that the possibility of injury or death exists due
to improper handling and maintenance of compresses gas cylinders
or regulators.
• Published standards on safety are avail-
able. They are listed in ADDITIONAL
SAFETY INFORMATION at the end of this
SAFETY SUMMARY.
The National Electrical Code, Occupation
Safety and Health Act regulations, local
industrial codes and local inspection
requirements also provide a basis for equipment installation, use, and service.
SAFETY SUMMARY
Page 5

5
SHOCK HAZARD
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! To reduce the
risk of death or serious injury from shock,
read, understand, and follow the following
safety instructions. In addition, make certain
that anyone else who uses this welding
equipment, or who is a bystander in the
welding area understands and follows these
safety instructions as well.
• IMPORTANT! TO REDUCE THE RISK OF
DEATH, INJURY, OR PROPERTY DAMAGE, DO NOT ATTEMPT OPERATION of
this welding equipment until you have
read and understand the following safety summary.
• Do not, in any manner, come into physical contact with any part of the welding
current circuit. The welding current circuit includes:
a. the work piece or any conductive
material in contact with it,
b. the ground clamp,
c. the electrode or welding wire,
d. any metal parts on the electrode
holder, or wire feed gun.
• Do not weld in a damp area or come in
contact with a moist or wet surface.
• Do not attempt to weld if any part of
clothing or body is wet.
• Do not allow the welding equipment to
come in contact with water or moisture.
• Do not drag welding cables, wire feed
gun, or welder power cord through or
allow them to come into contact with
water or moisture.
• Do not touch welder, attempt to turn
welder on or off if any part of the body
or clothing is moist or if you are in physical contact with water or moisture.
• Do not attempt to plug the welder into
the power source if any part of body or
clothing is moist, or if you are in physical
contact with water or moisture.
• Do not connect welder work piece clamp
to or weld on electrical conduit.
• Do not alter power cord or power cord
plug in any way.
• Do not attempt to plug the welder
into the power source if the ground
prong on power cord plug is bent over,
broken off, or missing.
• Do not allow the welder to be connected
to the power source or attempt to weld if
the welder, welding cables, welding site,
or welder power cord are exposed to any
form of atmospheric precipitation, or salt
water spray.
• Do not carry coiled welding cables
around shoulders, or any other part of
the body, when they are plugged into the
welder.
• Do not modify any wiring, ground
connections, switches, or fuses in this
welding equipment.
• Wear welding gloves to help insulate
hands from welding circuit.
• Keep all liquid containers far enough
away from the welder and work area so
that if spilled, the liquid can not possibly
come in contact with any part of the
welder or electrical welding circuit.
• Replace any cracked or damaged parts
that are insulated or act as insulators
such as welding cables, power cord, or
electrode holder IMMEDIATELY.
FLASH HAZARDS
WARNING
ARC RAYS CAN INJURE EYES AND BURN
SKIN! To reduce the risk of injury from arc
rays, read, understand, and follow the following safety instructions. In addition, make
certain that anyone else that uses this welding equipment, or is a bystander in the
welding area understands and follows these
safety instructions as well. Headshields and
filter should conform to ANSI Z87.1 standards.
• Do not look at an electric arc without
proper protection. A welding arc is
extremely bright and intense and, with
inadequate or no eye protection, the
retina can be burned, leaving a permanent dark spot in the field of vision. A
shield or helmet with a number 10 shade
filter lens (minimum) must be used.
• Do not strike a welding arc until all
bystanders and you (the welder) have
Page 6

6
welding shields and/or helmets in place.
• Do not wear a cracked or broken
helmet and replace any cracked or broken filter lenses IMMEDIATELY.
• Do not allow the uninsulated portion
of the wire feed gun to touch the ground
clamp or grounded work to prevent an
arc flash from being created on contact.
• Provide bystanders with shields or helmets fitted with a #10 shade filter lens.
• Wear protective clothing. The intense light
of the welding arc can burn the skin in
much the same way as the sun, even
through light-weight clothing. Wear dark
clothing of heavy material. The shirt worn
should be long sleeved and the collar kept
buttoned to protect chest and neck.
• Protect against REFLECTED ARC RAYS. Arc
rays can be reflected off shiny surfaces
such as a glossy painted surface, aluminum, stainless steel, and glass. It is
possible for your eyes to be injured by
reflected arc rays even when wearing a
protective helmet or shield. If welding
with a reflective surface behind you, arc
rays can bounce off the surface, then off
the filter lens on the inside of your helmet
or shield, then into your eyes. If a reflective background exists in your welding
area, either remove it or cover it with
something non-flammable and nonreflective. Reflective arc rays can also
cause skin burn in addition to eye injury.
FIRE HAZARDS
WARNING
FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAN CAUSE DEATH,
INJURY, AND PROPERTY DAMAGE! To
reduce the risk of death, injury, or property
damage from fire or explosion, read, understand, and follow the following safety
instructions. In addition, make certain that
anyone else that uses this welding equipment, or is a bystander in the welding area,
understands and follows these safety
instructions as well. REMEMBER! Arc welding
by nature produces sparks, hot spatter,
molten metal drops, hot slag, and hot metal
parts that can start fires, burn skin, and
damage eyes.
• Do not wear gloves or other clothing that
contains oil, grease, or other flammable
substances.
• Do not wear flammable hair preparations.
• Do not weld in an area until it is checked
and cleared of combustible and/or flammable materials. BE AWARE that sparks
and slag can fly 35 feet and can pass
through small cracks and openings. If
work and combustibles cannot be separated by a minimum of 35 feet, protect
against ignition with suitable, snug-fitting, fire resistant, covers or shields.
• Do not weld on walls until checking for
and removing combustibles touching the
other side of the walls.
• Do not weld, cut, or perform other such
work on used barrels, drums, tanks, or
other containers that had contained a
flammable or toxic substance. The techniques for removing flammable substance and vapors, to make a used container safe for welding or cutting, are
quite complex and require special education and training.
• Do not strike an arc on a compressed
gas or air cylinder or other pressure vessel. Doing so will create a brittle area
that can result in a violent rupture immediately or at a later time as a result of
rough handling.
• Do not weld or cut in an area where the
air may contain flammable dust (such as
grain dust), gas, or liquid vapors (such as
gasoline).
• Do not handle hot metal, such as the
work piece or electrode stubs, with bare
hands.
• Wear leather gloves, heavy long sleeve
shirt, cuffless trousers, high-topped
shoes, helmet, and cap. As necessary,
use additional protective clothing such as
leather jacket or sleeves, fire resistant
leggings, or apron. Hot sparks or metal
can lodge in rolled up sleeves, trouser
cuffs, or pockets. Sleeves and collars
should be kept buttoned and pockets
eliminated from the shirt front.
• Have fire extinguisher equipment handy
for immediate use! A portable chemical
fire extinguisher, type ABC, is recommended.
• Wear ear plugs when welding overhead to
Page 7
7
prevent spatter or slag from falling into ear.
• Make sure welding area has a good,
solid, safe floor, preferably concrete or
masonry, not tiled, carpeted, or made of
any other flammable material.
• Protect flammable walls, ceilings, and
floors with heat resistant covers or
shields.
• Check welding area to make sure it is free
of sparks, glowing metal or slag, and
flames before leaving the welding area.
FUME HAZARDS
WARNING
FUMES, GASSES, AND VAPORS CAN
CAUSE DISCOMFORT, ILLNESS, AND
DEATH! To reduce the risk of discomfort, ill-
ness, or death, read, understand, and follow
the following safety instructions. In addition,
make certain that anyone else that uses this
welding equipment or is a bystander in the
welding area, understands and follows
these safety instructions as well.
• Do not weld in an area until it is checked
for adequate ventilation as described in
ANSI standard #Z49.1. If ventilation is
not adequate to exchange all fumes and
gasses generated during the welding
process with fresh air, do not weld unless
you (the welder) and all bystanders are
wearing air-supplied respirators.
• Do not heat metals coated with, or that
contain, materials that produce toxic
fumes (such as galvanized steel), unless
the coating is removed. Make certain the
area is well ventilated, and the operator
and all bystanders are wearing air-supplied respirators.
• Do not weld, cut, or heat lead, zinc, cadmium, mercury, beryllium, or similar
metals without seeking professional
advice and inspection of the ventilation
of the welding area. These metals produce EXTREMELY TOXIC fumes which can
cause discomfort, illness, and death.
• Do not weld or cut in areas that are near
chlorinated solvents. Vapors from chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as
trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene,
can be decomposed by the heat of an
electric arc or its ultraviolet radiation.
These actions can cause PHOSGENE, a
HIGHLY TOXIC gas to form, along with
other lung and eye-irritating gasses. Do
not weld or cut where these solvent
vapors can be drawn into the work area
or where the ultraviolet radiation can
penetrate to areas containing even very
small amounts of these vapors.
• Do not weld in a confined area unless it
is being ventilated or the operator (and
anyone else in the area) is wearing an
air-supplied respirator.
• Stop welding if you develop momentary
eye, nose, or throat irritation as this indicates inadequate ventilation. Stop work
and take necessary steps to improve ventilation in the welding area. Do not
resume welding if physical discomfort
persists.
COMPRESSED GASSES AND
EQUIPMENT HAZARDS
WARNING
IMPROPER HANDLING AND
MAINTENANCE OF COMPRESSED GAS
CYLINDERS AND REGULATORS CAN
RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH!
To reduce the risk of injury or death from
compressed gasses and equipment hazards,
read, understand, and follow the following
safety instructions. In addition, make certain
that anyone else who uses this welding
equipment or a bystander in the welding
area understands and follows these safety
instructions as well.
• Do not use flammable gasses with MIG
welders. Only inert or nonflammable
gasses are suitable for MIG welding.
Examples are Carbon Dioxide, Argon,
Helium, etc. or mixtures of more than
one of these gasses.
• Do not attempt to mix gasses or refill a
cylinder yourself. Do not expose cylinders to excessive heat, sparks, slag and
flame, etc. Cylinders exposed to temperatures above 130°F will require water
spray cooling.
Page 8

8
• Do not expose cylinders to electricity of
any kind.
• Do not use a cylinder or its contents for
anything other than its intended use. Do
not use as a support or roller.
• Do not locate cylinders in passageways
or work area where they may be struck.
• Do not use a wrench or hammer to open
a cylinder valve that cannot be opened
by hand. Notify your supplier.
• Do not modify or exchange gas cylinder
fittings.
• Do not deface or alter name, number or
other markings on a cylinder. Do not rely
on cylinder color to identify the contents.
• Do not connect a regulator to a cylinder
containing gas other than that for which
the regulator was designed.
• Do not attempt to make regulator repairs.
Send faulty regulators to manufacturer’s
designated repair center for repair.
• Do not attempt to lubricate a regulator.
• Always change cylinders carefully to prevent leaks and damage to their walls,
valves, or safety devices.
• Always secure cylinders with a steel chain
so that they cannot be knocked over.
• Always protect a cylinder, especially the
valve, from bumps, falls, falling objects
and weather. Remember that gasses in
the cylinders are under pressure and
damage to a regulator can cause the
regulator or portion of the regulator to
be explosively ejected from the cylinder.
• Always make certain the cylinder cap is
securely in place on the cylinder, whenever the cylinder is moved.
• Always close the cylinder valve and
immediately remove a faulty regulator
from service, for repair, if any of the following conditions exist.
• Gas leaks externally.
• Delivery pressure continues to rise with
down stream valve closed.
• The gauge pointer does not move off the
stop pin when pressurized or fails to
return to the stop pin after pressure is
released.
WARNING
This product contains chemicals, including
lead, or otherwise produces chemicals
known to the State of California to cause
cancer, birth defects and other reproductive
harm. Wash hands after Handling.
(California Health & Safety Code Sec.
25249.5 et seq.)
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION
For additional information concerning welding safety, refer to the following standards
and comply with them as applicable.
• ANSI Standard Z49.1 – SAFETY IN
WELDING AND CUTTING – obtainable
from the American Welding Society, 550
NW Le Jeune Road, Miami, FL 33126
Telephone (800) 443-9353, Fax (305)
443-7559 – www.amweld.org or
www.aws.org
• ANSI Standard Z87.1 – SAFE PRACTICE
FOR OCCUPATION AND EDUCATIONAL EYE AND FACE PROTECTION –
obtainable from the American National
Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd St.,
New York, NY 10036 Telephone (212)
642-4900,
Fax (212) 398-0023 – www.ansi.org
• NFPA Standard 51B – CUTTING AND
WELDING PROCESS – obtainable from
the National Fire Protection Association,
1 Batterymarch Park, P.O. Box 9101,
Quincy, MA 02269-9101 Telephone
(617) 770-3000
Fax (617) 770-0700 – www.nfpa.org
• OSHA Standard 29 CFR, Part 1910,
Subpart Q., WELDING, CUTTING AND
BRAZING – obtainable from your state
OSHA office or U.S. Dept. of Labor
OSHA, Office of Public Affairs, Room
N3647, 200 Constitution Ave.,
Washington, DC 20210 –
www.osha.gov
• CSA Standard W117.2 – Code for
SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING. –
obtainable from Canadian Standards
Association, 178 Rexdale Blvd.,
Etobicoke, Ontario M9W 1R3 –
www.csa.ca
• American Welding Society Standard
A6.0. WELDING AND CUTTING CONTAINERS WHICH HAVE HELD COMBUSTIBLES. – obtainable from the
American Welding Society, 550 NW Le
Jeune Road, Miami, FL 33126
Telephone (800) 443-9353, Fax (305)
443-7559 – www.amweld.org or
www.aws.org
Page 9

9
WELDER SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION
Your new MIG (GMAW) flux core (FCAW)
wire feed welder is designed for maintenance and sheet metal fabrication. The
welder consists of a single-phase power
transformer, stabilizer, rectifier, and a
unique built-in control/feeder.
Now you can weld sheet metal from 24
gauge up to 1/4 inch thick with a single
pass. You can weld thicker steel with beveling and multiple pass techniques. Table 1
lists your MIG welder specifications.
Table 1. Welder Specifications
Primary (input) Volts 230 VAC
Primary (input) Amps 22.5
Phase Single
Frequency 60Hz
Secondary (output) volts 20
CSA rated output amps 120
Open Circuit Volts (Max.) 30 VDC
Duty Cycle Rating 25%
MIG welders equipped with gas are capable
of welding with 0.023 (0.6mm) and 0.030
(0.8mm) solid steel wire on DC reverse polarity and with 0.030 (0.8mm) self-shielding fluxcore wire on DC straight polarity. Larger,
0.035 inch (0.9mm) diameter solid steel wire,
on dc reverse polarity may also be used on
this welder. The use of larger diameter wire
makes welding difficult and the results cannot
be guaranteed. Use of larger than .035 diameter wire is not recommended.
WELDER OPERATING
CHARACTERISTICS
DUTY CYCLE
The duty cycle rating of a welder defines how
long the operator can weld and how long the
welder must be rested and cooled. Duty cycle is
expressed as a percentage of 10 minutes and
represents the maximum welding time allowed.
The balance of the 10-minute cycle is required
for cooling. Your new welder has a duty cycle
rating of 25% at the rated output. This means
that you can weld for two-and-a-half (2.5) minutes out of 10 with the remaining seven-and-ahalf (7.5) minutes required for cooling. (See
Table 2).
Table 2. Duty Cycle Ratings
Duty Maximum Required
Cycle Welding Resting
Rating Time Time
20% 2 minutes 8 minutes
25% 2.5 minutes 7.5 minutes
40% 4 minutes 6 minutes
60% 6 minutes 4 minutes
80% 8 minutes 2 minutes
100% 10 minutes 0 minutes
INTERNAL THERMAL PROTECTION
CAUTION
Do not constantly exceed the duty cycle or
damage to the welder can result. If you
exceed the duty cycle of the welder, an internal thermal protector will open, shutting off
all welder functions except the cooling fan. If
this happens, DO NOT SHUT OFF THE
WELDER. Leave the welder turned on with
the fan running. After cooling, the thermal
protector will automatically reset and the
welder will function normally again.
However you should wait at least ten minutes after the thermal protector opens
before resuming welding. You must do this
even if the thermal protector resets itself
before the ten minutes is up or you may
experience less than specified duty cycle
performance.
If you find that the welder will not weld for
two minutes without stopping, reduce the
wire speed slightly and tune in the welder at
the lowest wire speed setting that still produces a smooth arc. Welding with the wire
speed set too high causes excessive current
draw and shortens the duty cycle.
Page 10
10
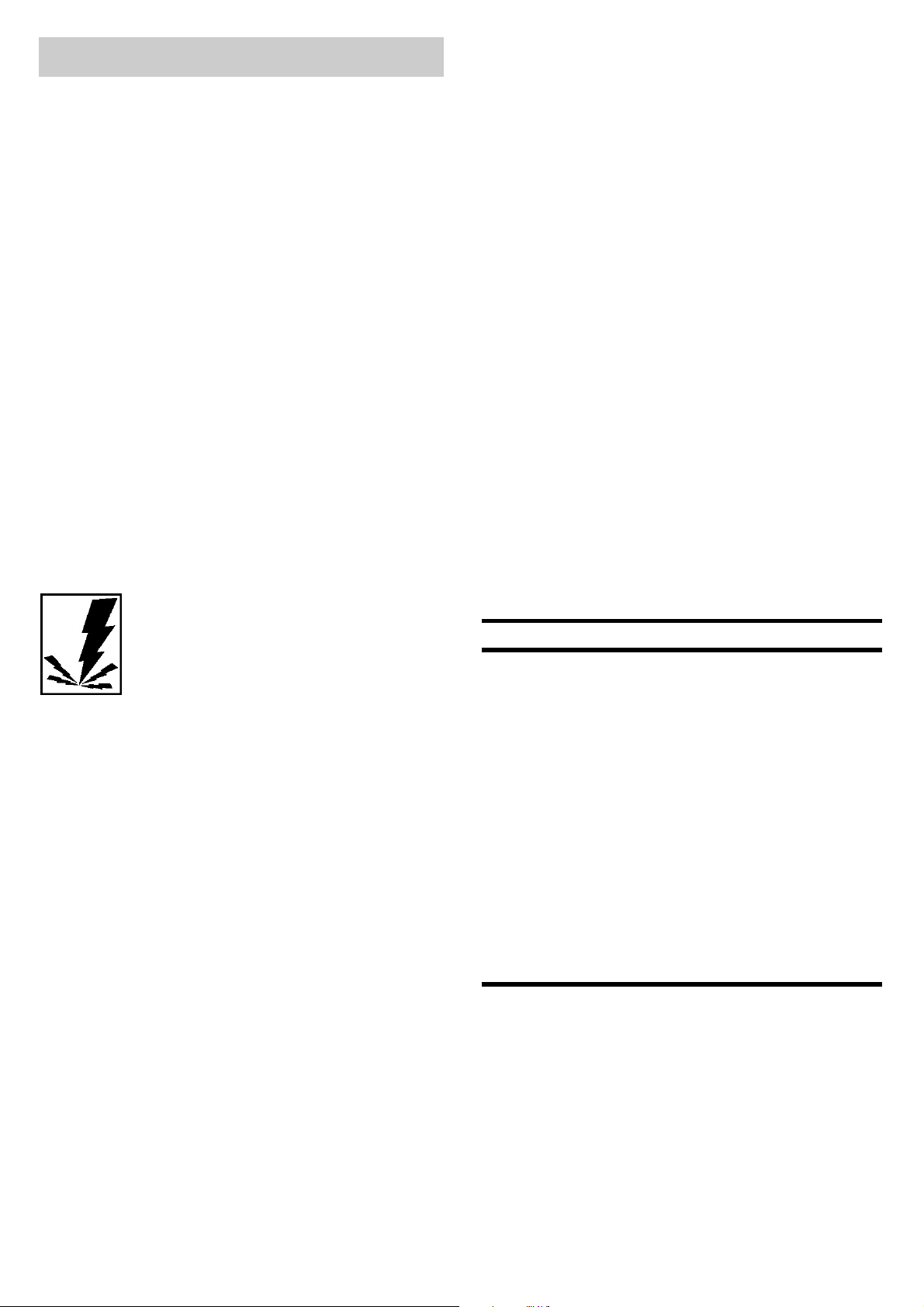
KNOW YOUR WELDER
Handle – Rugged, top mounted handle
allows for easy transport of your welder.
Wire Speed Control – Use this dial to adjust
the speed at which the welder feeds wire to the
gun. 1 is the slowest wire feed speed, 10 is the
highest. You will need to adjust or “tune-in”
your wire speed for different welding conditions
(thickness of metals, gas -vs- gasless welding,
metal type, wire size, etc.). When the wire speed
is properly “tuned-in” the welding wire will melt
into the material you are welding as quickly as
it is fed through the welding gun.
Voltage Selector – The voltage selectors
control the weld heat. There are six voltage
heat selections available on this welder. Lower
voltage (less heat) is achieved by setting the
Voltage Selector Switch to the MIN position
and/or the Voltage Selector Dial to a lower
number. Higher voltage (more heat) is
achieved by setting the Voltage Selector
Switch to the MAX position and/or the
Voltage Selector Dial to a higher number.
Different materials and material thickness will
require different voltage settings. You will
need to adjust your voltage accordingly for
different welding conditions. By properly
adjusting your voltage settings and wire feed
speed, you will enable clean, precision welds.
(Refer to the Suggested Settings Chart on p.33
of this manual OR on the inside of the door of
the welder.)
Power Switch – This switch turns the welder
ON and OFF. (Make sure the power switch is
in the OFF position before performing any
maintenance on the welder.)
Power Cord – This is a standard, 230 volt
power cord with a NEMA 6-50P 50 amp
plug. (Make sure you are using a properly
grounded 230 VAC, 60Hz, single phase, 50
amp power source.)
Ground Clamp – Attaching the ground
clamp to your work piece “completes” the
welding current circuit. You must attach the
ground clamp to the metal you are welding.
If the ground clamp is not connected to the
metal work piece you intend to weld, the
welder will not have a completed circuit and
you will be unable to weld. A poor connection at the ground clamp will waste power
and heat. Scrape away dirt, rust, scale, oil or
paint before attaching the ground clamp.
Ground Cable – The ground cable connects
the ground clamp to the internal workings of
the welder.
Welding Gun and Cable – The welding gun
controls the delivery of the welding wire to the
material to be welded. The welding wire is fed
through the welding cable and welding gun
when the welding gun trigger is pulled. You will
need to install a contact tip and welding nozzle
to the end of the welding gun, as described
later in this manual, prior to welding.
Welding Terms
Now that you are familiar with the main
parts of the welder, make note of the following terms. You will see them used throughout this manual.
weld puddle: The localized volume of molten
metal in a weld prior to its solidification.
weld angle: The angle of the welding wire,
as it extends from the welding gun, in relation to the item being welded.
slag: The protective coating that forms on
the surface of molten metal.
arc: A sustained luminous discharge of electricity across a gap in a circuit.
welding bead: The extended build up of a weld,
made by pushing or pulling the weld puddle.
Figure 1. Model Cat. 3175
Welding Gun
Ground
Clamp
Power
Cable
Ground
Cable
Voltage
Selector
Dial
Power
Switch
Wire
Speed
Gun
Cable
Handle
Voltage Selector Switch
Page 11
11
POWER SOURCE CONNECTION
POWER REQUIREMENTS
This welder is designed to operate on a properly grounded 230 volt, 60Hz, single-phase alternating current (AC) power source fused with a
50 amp time delayed fuse or circuit breaker. It
is recommended that a qualified electrician verify the ACTUAL VOLTAGE at the receptacle into
which the welder will be plugged and confirm
that the receptacle is properly fused and
grounded. The use of the proper circuit size can
eliminate nuisance circuit breaker tripping
when welding.
DO NOT OPERATE THIS WELDER if the
ACTUAL power source voltage is less than 198
volts AC or greater than 240 volts AC. Contact
a qualified electrician if this problem exists.
Improper performance and/or damage to the
welder will result if operated on inadequate or
excessive power.
CONNECT TO POWER SOURCE
WARNING
High voltage danger from power source!
Consult a qualified electrician for proper installation of receptacle at the power source.
This welder must be grounded while in use to
protect the operator from electrical shock. If you
are not sure if your outlet is properly grounded,
have it checked by a qualified electrician. Do not
cut off the grounding prong or alter the plug in
any way and do not use any adapters between
the welder’s power cord and the power source
receptacle. Make sure the POWER switch is OFF
then connect your welder’s power cord to a
properly grounded 230 VAC, 60 Hz, single
phase, 50 amp power source.
EXTENSION CORDS
For optimum welder performance, an extension cord should not be used unless absolutely
necessary. If necessary, care must be taken in
selecting an extension cord appropriate for use
with your specific welder.
Select a properly grounded extension cord that
will mate directly with the power source receptacle and the welder power cord without the
use of adapters. Make certain that the extension is properly wired and in good electrical
condition. Extension cords must be a #12
gauge cord at the smallest. Do not use an
extension cord over 25 ft. in length.
ASSEMBLING THE WELDER
The following procedures describe the process
required to assemble, install, maintain, and prepare to weld with your new wire feed welder.
UNPACKING THE WELDER
1. Remove any cartons or bags containing
parts/accessories. (Most parts are shipped
INSIDE the welder door.)
2. Open the cartons or bags packed with your
welder and inspect their contents for damage.
3. Layout the parts and compare them to the
the packing list in Table 3 to familiarize yourself with the parts and what they are called.
This will help you when reading the manual.
PACKING LIST
Table 3 contains a list of the items you will find
packed in the carton.
Table 3. Packing List
ITEM QTY.
Welder 1
Face Shield 1
Face Shield Handle 1
Face Shield Handle Cover 1
Face Shield Retaining Clips 2
Shaded Lens 1
Welder Handle 1
Wire Brush/Hammer 1
Parts Bag 1
Handle Screws 2
Contact Tip .023-.030-.040 1 ea.
Nozzle 1
Wire .030 Flux Core 1/2 lb.
Wire .023 Solid Core 1/2 lb.
Manual, Instruction 1
ASSEMBLE THE FACE SHIELD
1. Insert the upper tongue of the handle
into the upper slot on the face shield.
2. Align the second tab on the handle with
the second slot in the face shield by pushing the bottom of the handle in towards
the face mask, while at the same time
pushing upwards. (Alignment of the second tab is made easier by applying pressure to the point shown below.)
WELDER INSTALLATION
Page 12

12
3. Once the handle tabs are properly seated in the face shield slots, install the
handle cover by firmly pushing it into the
recessed area on the face shield.
4. Install the dark glass by sliding it into
place behind the glass retaining tabs.
Note: if your face shield was supplied with a
3” x 3.8” dark glass you may choose to
remove the extra material from the face
shield to allow a larger field of vision when
welding. To remove the extra material,
remove the glass from the face shield and
carefully cut the material out of the face
shield with a utility knife.
5. Once protective dark glass has been
installed into face shield, secure it in
place with the retaining clips. Align the
holes on each of the retaining clips with
the pins on the retaining tabs and firmly
press into place.
INSTALLING THE HANDLE
1. Insert the tabs of the welder handle into
the slots provided on the top of the welder.
2. Insert a large flat head screw (included
in the accessories bag) into each hole on
the top of the welder handle.
3. With a flat tip screwdriver, securely tighten both screws. (see Figure 3)
SELECTING SHIELDING GAS
The shielding gas plays an extremely important role in the MIG welding process. It is critical that the molten weld puddle be shielded
from the atmosphere. The shielding gas creates a protective pocket around the weld puddle which keeps impurities in the air from contaminating the weld. Inadequate shielding will
result in porous, brittle welds.
Although there are many gasses and gas mixtures available for MIG welding, the following
recommendations are based on the electrical
output characteristics and metal thickness
capabilities of this specific MIG welder.
Gas Selection For Steel Welding With
Steel Wire
For either mild or low carbon (High Strength
Structural) steel, use a gas mixture of 75%
Argon and 25% Carbon Dioxide. DO NOT
USE Argon gas concentrations higher than
75% on steel. The result will be extremely poor
penetration, porosity, and brittleness of weld.
This gas mixture helps to prevent burn
through and distortion on very thin steel yet
provides good penetration on thicker steel. Its
ability to minimize spatter results in clean,
smooth weld appearances. In addition, it provides good puddle control when welding vertically or overhead.
Gas Selection For Stainless Steel Welding
The best shielding gas for stainless steel welding is
a mixture of 90% Helium, 7.5% Argon, and 2.5%
Carbon Dioxide. However, the 100% Argon, can
also be used, but an increase in the area being
heated by the arc will be experienced causing
slightly greater distortion of the base metal.
Gas Selection For Steel Welding With
Silicon Bronze Wire
Use only pure Argon when welding steel with
Silicon-Bronze wire.
Figure 2. Face Shield Assembly
Face Shield
Handle
Handle
Cover
Retaining
Tabs
Retaining
Clip
Retaining
Clip
Dark
Glass
Extra
Material
Figure 3. Handle Installation
Page 13

13
Gas Selection For Aluminium Welding
with Aluminium Wire
Use only pure Argon when welding
Aluminium.
INSTALL THE SHIELDING GAS
WARNING
IMPROPER HANDLING AND MAINTENANCE OF COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERS AND REGULATORS CAN RESULT IN
SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH! Always
secure gas cylinders to the welding cart, a
wall, or other fixed support to prevent the
cylinder from falling over and rupturing.
Read, understand, and follow all the COMPRESSED GASSES AND EQUIPMENT HAZARDS in the SAFETY SUMMARY at the front
of this manual. Secure your gas cylinder to
the welding cart, or other fixed support.
1. Remove the protective cap from the cylinder
and inspect the regulator connecting
threads for dust, dirt, oil, and grease.
Remove any dust or dirt with a clean cloth.
DO NOT ATTACH YOUR REGULATOR IF
OIL, GREASE, OR DAMAGE ARE PRESENT.
2. Open the cylinder valve FOR JUST AN
INSTANT to blow out any foreign matter
inside the valve port. Never aim the open
valve cylinder port at yourself or bystanders.
3. Screw the regulator into the cylinder valve
and tighten with a wrench.
4. Firmly push the gas hose over barbed fittings on back of welder and regulator.
5. Secure both ends of hose onto barbed fittings with hose clamps.
CHECK THE GAS FLOW
WARNING
IMPROPER HANDLING AND MAINTENANCE OF COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERS
AND REGULATORS CAN RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. To reduce the risk of
injury or death, always stand to the side of the
cylinder opposite the regulator when opening
the cylinder valve, keeping the cylinder valve
between you and the regulator. Never aim the
open cylinder valve port at yourself or
bystanders. Failure to comply with this warning
could result in serious personal injury.
Note: If the cylinder you have is equipped with
male regulator connecting threads instead of
female, you will need to obtain a special compressed gas cylinder adaptor from your gas
supplier to install between your gas cylinder
and regulator.
-The gas control function does not require
the welder to be turned on or plugged in.
-To avoid damage to your regulator, make
sure you have the regulator valve closed
before opening the cylinder valve.
1. Slowly crack open the cylinder valve, then
turn open ALL THE WAY.
2. Pull the trigger on the gun to allow the gas to
flow. KEEP THE TRIGGER PULLED. Listen and
feel for gas flowing from the end of the welding gun. If your regulator has no adjustment,
it has been preset at the factory for a flow of
20 cubic feet per hour. If your gas regulator
has an adjustment to control the gas flow
rate, turn the adjustment key clockwise to
increase gas flow; counterclockwise to
reduce flow. For most welding, the gas flow
should be set at 15-20 cubic feet per hour. If
no gas is heard or felt, verify all steps
involved in connecting the gas.
3. Release the trigger.
Note: If welding outside or in a draft, it may
become necessary to set up a wind break to
keep the shielding gas from being blown from
the weld area.
-MAKE SURE TO TURN OFF THE GAS
CYLINDER VALVE WHEN DONE WELDING.
ALIGN AND SET THE DRIVE ROLLER
Before installing any welding wire into the unit,
the proper sized groove must be placed into
position on the wire drive mechanism.
Figure 4. Feed Motor
Page 14

14
Change the drive roller according to the following steps:
1. Open the door to the welder drive compartment.
2. Remove the drive tension by loosening the
tension adjusting screw and lifting the Drive
Tension Adjustor up, away from the Drive
Tension Arm. Pull the drive tension arm
away from the drive roller.
3. If there is wire already installed in welder,
roll it back onto the wire spool hand-turning
the spool counterclockwise. Be careful not
to allow the wire to come out of the rear
end of the inlet guide tube without holding
onto it or it will unspool itself. Put the end of
the wire into the hole on the outside edge
of the wire spool and bend it over to hold
the wire in place. Remove the spool of wire
from the drive compartment of the welder.
4. Rotate the Drive Roller Cap counterclockwise and remove it from the Drive Roller.
5. Pull the Drive Roller off of the Drive Roller
Shaft.
Note: The drive roller has two wire size grooves
built into it. When installing the drive roller, the
number stamped on the drive roller for the wire
size you are using should be facing you. Use
only the proper size drive roller when using
your welder.
Table 4 indicates which drive roller groove
should be used with each wire diameter size.
Wire Diameter Drive Roller Groove:
.023 inch 0.6
.030 inch 0.8
.035 inch 0.8
Table 4. Drive Roller Sizing
6. Find the side of the drive roller that is
stamped with the same wire diameter as
that of the wire being installed (see Figure
6). Push the drive roller onto the drive roller
shaft, with the side stamped with the
desired wire diameter facing you.
7. Reinstall the Drive Roller Cap and lock in
place by turning it clockwise.
8. Close the door to the welder drive compartment.
INSTALL THE WELDING WIRE
WARNING
Electric shock can kill! Always turn the
POWER switch OFF and unplug the power cord
from the ac power source before installing wire.
1. Remove the nozzle and contact tip from
the end of the gun assembly.
2. Make sure the proper groove on the
drive roller is in place for the wire being
installed. If the proper groove is not in
place, change the drive roller as
described above.
3. Unwrap the spool of wire and then find
the leading end of the wire (it goes
through a hole in the outer edge of the
spool and is bent over the spool edge to
prevent the wire from unspooling), BUT
DO NOT UNHOOK IT YET.
4. Place the spool on the spindle in such a
manner that when the wire comes off the
spool, it will look like the top illustration
in Figure 7. The welding wire should
always come off the top of the spool into
the drive mechanism.
5. If you are installing a four-inch spool of
wire, install the drive brake hardware on
the top of the spool of wire according to
Figure 6. Drive Roller
Figure 5. Drive Roller Adjustments
Page 15

15
figure 8A. If you are installing an eightinch spool, install the spindle adapter
and drive brake hardware as shown in
Figure 8B. The purpose of the drive
brake is to cause the spool of wire to
stop turning at nearly the same moment
that wire feeding stops.
6. Once the drive brake hardware is
installed, set the spool tension. With one
hand, turn the wire spool and continue
turning it while adjusting the tension on
the spool. With your free hand, tighten
(turn clockwise) the knob that holds the
spool in place. Stop tightening when drag
is felt on the wire spool that you are turning, then stop hand-turning the wire spool.
Note: If TOO MUCH tension is applied to the
wire spool, the wire will slip on the drive roller
or will not be able to feed at all. If TOO LITTLE
tension is applied, the spool of wire will want
to unspool itself. Readjust the drive brake tension as necessary to correct for either problem.
7. After checking to make sure that your
welder is disconnected from the ac
power source, free the leading end of
the wire from the spool, but do not let go
of it until instructed to do so, or the wire
will unspool itself.
8. Use a wire cutter, cut the bent end off the
leading end of the wire so that only a
straight leading end remains.
9. Flip down the screw holding the drive
tension arm in place and lift the tension
arm up off the drive roller.
10.Insert the leading end of the wire into
the inlet guide tube. Then push it across
the drive roller and into the gun assembly about six inches.
CAUTION
Make certain that the welding wire is actually going into the gun liner. Be very sure it
has not somehow been accidentally routed
alongside the liner or even in some other
direction. If this should happen, the wire
could feed inside the cable casing or take a
right angle and follow the wires and gas
hose inside the welder. It could also feed
back on itself jamming up the mechanism.
11.Line the wire up in the inside groove of
the drive roller, then allow the drive tension arm to drop onto the drive roller.
12. Flip the quick release drive tensioner back
up into position on the drive tensioner arm.
13. Tighten (turn clockwise) the drive tension
adjusting screw until the tension roller is
applying enough force on the wire to prevent
it from slipping out of the drive assembly.
14. Let go of the wire.
15. Connect the welder power cord to the ac
power source. Turn the welder ON by setting the VOLTAGE switch to the voltage
(heat) setting recommended for the gauge
metal that is to be welded. Refer to the
label mounted on the cover, inside the
drive compartment, for recommended voltage (heat) settings for your welding job.
The VOLTAGE selector controls the weld
heat. There are six voltage heat selections
available on this welder. Placing the voltage switch in MIN position, and the voltage
dial in position 1 provides the lowest voltage (heat). Placing the voltage switch in
MAX position, and the voltage dial in position 3 provides the highest voltage (heat).
Figure 7. Wire Installation
Figure 8A. Drive
Brake Hardware
Installation
Figure 8B. Spindle
Adapter and Drive
Brake Installation
Page 16

16
16.Set the WIRE SPEED control to the middle
of the wire speed range.
16.Straighten the gun cable and pull the
trigger on the welding gun to feed the
wire through the gun assembly.
17. When at least an inch of wire sticks out past
the end of the gun, release the trigger.
18.Select a contact tip stamped with the
same diameter as the wire being used. If
stamped in metric see DESCRIPTION.
Note: Due to inherent variances in fluxcored welding wire, it may be necessary to
use a contact tip one size larger than your
flux core wire if wire jams occur.
19.Slide the contact tip over the wire (protruding from the end of the gun). Thread
the contact tip into the end of the gun
and hand-tighten securely.
20.Install the nozzle on the gun assembly.
For best results, coat the inside of the
nozzle with anti-stick spray or gel.
21.Cut off the excess wire that extends past
the end of the nozzle.
SET THE WIRE DRIVE TENSION
WARNING
To reduce the risk of arc flash, make certain
that the wire coming out of the end of the
gun does not come in contact with work
piece, ground clamp or any grounded material during the drive tension setting process
or arcing will occur.
1. Pull the trigger on the gun.
2. Turn the drive tension adjustment knob
clockwise, increasing the drive tension until
the wire seems to feed smoothly without
slipping.
When set correctly, there should be no slippage between the wire and the drive roller
under normal conditions. If an obstruction
occurs along the wire feed path, the wire
should then slip on the drive roller.
After the tension is properly adjusted, the
quick release drive tensioner may unlocked
and relocked and no radjustment of the
drive tension adjustment knob will be necessary (unless the diameter or type of wire is
changed).
INSTALLING ALUMINIUM WIRE
Install aluminium wire the same as steel
wire, but with the following exceptions:
1. Install a plastic liner (PN PRT 30900002)
in the welding gun.
2. Adjust the drive tension VERY carefully.
Aluminium wire is very sensitive to slight
changes in drive tension.
Note: For welding aluminium with this unit,
5356 alloy wire is recommended because of
its superior feedability. A plastic liner is needed. When welding with softer aluminium
alloys, you may experience feed problems.
CHANGE POLARITY
This welder allows you to change the welding
current polarity. Select straight polarity for
welding with flux core wire (FCAW). Select
reverse polarity for MIG welding (GMAW) when
using mild steel, stainless steel or silicon bronze
wire. Reverse polarity is also suggested with
some flux core wire used in hard facing.
Change the polarity of your welder according
to the following procedure steps. Figure 8
shows what the polarity block should look like
for each polarity setting.
WARNING
Electric shock can kill! Always turn the
power OFF and unplug the power cord from
the ac power source before changing polarity.
CAUTION
Do not use a ratchet, crescent or other lever
type wrench to tighten knobs on the polarity
block. The nuts must be hand tightened only.
Too much torque applied to one of the knobs
could cause the knob to break off.
1. Remove the retaining knobs from the +
and - mounting posts on the Gas/No
Gas Board, located just below the drive
motor on the inside of your welder.
A. For Gasless (FCAW) welding, mount
the Ground Clamp ring terminal to
the “+” mounting post and the Torch
ring terminal to the “-” mounting post.
Page 17

17
B. For MIG (GMAW) welding, mount the
Ground Clamp ring terminal to the “” mounting post and the Torch ring
terminal to the “+” mounting post.
See configuration shown in Figure 9.
2. Attach the ground clamp to the work
piece, making sure that it is cleaned of
dirt, oil, rust, scale, oxidation, and paint
at the point of connection.
Note: It is best to connect the ground clamp
directly to the work piece and as close to the
weld as possible. If it is impractical to connect the ground clamp directly to the work
piece, connect it to the metal that is securely attached to the work piece, but not electrically insulated from it. Make certain this
other metal is of equal or greater thickness
than that of the workpiece.
CAUTION
Risk of electric component damage! If
the ground clamp is being connected to an
automobile or other equipment with onboard computer systems, solid state electronic controls, solid state sound systems,
etc., do not weld until disconnecting the
battery that is attached to the chassis
ground. Failure to do so may result in electronic component damage.
Operation of this welder consists of selecting
and adjusting operating controls for optimum voltage (welding heat) and wire speed
settings.
Operation of this welder consists of selecting
and adjusting operating controls for optimum
voltage (welding heat) and wire speed settings.
CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
POWER SWITCH - The power switch supplies electrical current to the welder.
ALWAYS turn the power switch to the OFF
position and unplug the welder before performing any maintenance.
VOLTAGE SELECTOR - The voltage selector
switch and dial control the welding heat. The
voltage selector switch is label MIN/MAX,
referring to minimum and maximum voltage
output. The voltage selector dial is numbered 1-3. Number 1 is the lowest heat and
number 3 is the highest. Refer to the label
under the welder hood (or on page 33 of
this manual) for recommended heat settings
for your welding job.
WIRE SPEED CONTROL - The wire speed
control adjusts the speed at which the wire is
fed out of the welding gun. The wire speed
needs to be closely matched (tuned-in) to
the rate at which it is being melted off. Some
things that affect wire speed selection are
the type and diameter of the wire being
used, the heat setting selected, and the
welding position to be used.
Note: The wire will feed faster without an
arc. When an arc is being drawn, the wire
speed will slow down.
TUNING IN THE WIRE SPEED
This is one of the most important parts of MIG
welder operation and must be done before
starting each welding jobor whenever any of
the following variables are changed: heat setting wire diameter, or wire type.
1. Set up and ground a scrap piece of the
same type of material which you will be
welding. It should be equal to or greater
that the thickness of the actual work piece,
and free of oil, paint, rust, etc.
2. Select a heat setting.
3. Hold the gun in one hand, allowing the
nozzle to rest on the edge of the work-
OPERATION
Figure 9. Changing Polarity
Page 18

18
piece farthest away from you, and at an
angle similar to that which will be used
when welding. (SEE HOLDING THE GUN
on page 18 if you are uncertain of the
angle at which you will be welding)
4. With your free hand, turn the Wire Speed
Dial to maximum and continue to hold
onto the knob.
WARNING
EXPOSURE TO A WELDING ARC IS
EXTREMELY HARMFUL TO THE EYES AND
SKIN! Prolonged exposure to the welding
arc can cause blindness and burns. Never
strike an arc or being welding until you are
adequately protected. Wear flameproof
welding gloves, a heavy long sleeved shirt,
cuffless trousers, high topped shoes and a
welding helmet.
5. Lower your welding helmet and pull the
trigger on the gun to start an arc, then
begin to drag the gun towards you while
simultaneously turning the Wire Speed
Dial counter-clockwise.
6. LISTEN! As you decrease the wire speed,
the sound that the arc makes will change
from a sputtering to a high-pitched
buzzing sound and then will begin sputtering again if you decrease the wire
speed too much. The wire speed that
creates a smooth high-pitched buzzing
sound will achieve the best quality weld.
You can use the wire speed control to slightly
increase or decrease the heat and penetration
for a given heat setting by selecting hugher or
lower wire speed settings. Repeat this tune-in
procedure if you select a new heat setting, a
different diameter wire, or a different type of
welding wire.
LEARNING TO WELD
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding is the process
of uniting metallic parts by heating and
allowing the metals to flow together through
the use of an electrical arc. The electrical arc
is created between a continuous consumable wire electrode (the welding wire) and
the work piece. An inert shielding gas is
used to protect the weld puddle from con-
tamination and enhance the welding capabilities of the electrical arc.
Whether you have welded before or not, it is
important that you become familiar with
your new welder, its controls, and the results
achieved at different settings. We strongly
recommend that you practice with your new
welder on scrap metal trying different heat
settings, base metal thicknesses, and welding positions for each type and size of wire
you will be using. By doing this you will gain
a feel for how changes in these welding
variables affect the weld.
Of course, if you have not welded before,
you will need to develop welding skills and
techniques as well.
The self-taught welder learns through a
process of trial and error. The best way to
teach yourself how to weld is with short periods of practice at regular intervals. All practice welds should be done on scrap metal
that can be discarded. Do not attempt to
make any repairs on valuable equipment
until you have satisfied yourself that your
practice welds are of good appearance and
free of slag or gas inclusions. What you fail
to learn through practice will be learned
through mistakes and re-welds later on.
HOLDING THE GUN
The best way to hold the welding gun is the
way that feels most comfortable to you.
While practicing to use your new welder,
experiment holding the gun in different
positions until you find the one that seems to
work best for you. Refer to WELDING POSITIONS - p.20.
Position the Gun to the Work Piece
There are two angles of the gun nozzle in
relation to the work piece that must be considered when welding.
1. Angle A (Figure 10) can be varied, but in
most cases the optimum angle will be 60
degrees. The point at which the gun
handle is parallel to the work piece. If
angle A is increased, penetration will
increase. If angle A is decreased, penetration will decrease also.
Page 19

19
2. Angle B (Figure 11) can be varied for two
reasons: to improve the ability to see the
arc in relation to the weld puddle and to
direct the force of the arc.
The force of the welding arc follows a
straight line out of the end of the nozzle.
If angle B is changed, so will the direction of
arc force and the point at which penetration
will be concentrated.
On a butt weld joint, the only reason to vary
angle B from perpendicular (straight up) to
the work piece would be to improve visibility of the weld puddle. In this case, angle B
can be varied anywhere from zero to 45
degrees with 30 degrees working about the
best.
On a fillet weld joint, the nozzle is generally
positioned in such a manner so as to split
the angle between the horizontal and vertical members of the weld joint. In most
cases, a fillet weld will be 45 degrees.
Distance from the Work Piece
The end of the welding gun is designed with
the contact tip recessed from the end of the
nozzle and the nozzle electrically insulated
from the rest of the gun. This permits the
operator to actually rest the nozzle on the
work piece and drag it along while welding.
This can be very helpful to beginning
welders to steady the gun, allowing the
welder to concentrate on welding technique.
If the nozzle is held off the work piece, the
distance between the nozzle and the work
piece should be kept constant and should
not exceed 1/4 inch or the arc may begin
sputtering, signaling a loss in welding performance.
WELDING TECHNIQUES
WARNING
EXPOSURE TO A WELDING ARC IS
EXTREMELY HARMFUL TO THE EYES AND
SKIN! Prolonged exposure to the welding
arc can cause blindness and burns. Never
strike an arc or begin welding until you are
adequately protected. Wear flameproof
welding gloves, a heavy long sleeved shirt,
cuffless trousers, high topped shoes and a
welding helmet.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! To prevent
ELECTRIC SHOCK, do not perform any welding while standing, kneeling, or lying directly on the grounded work.
MOVING THE GUN
Gun travel refers to the movement of the
gun along the weld joint and is broken into
two elements: Direction and Speed. A solid
weld bead requires that the welding gun be
moved steadily and at the right speed along
the weld joint. Moving the gun too fast, too
slow, or erratically will prevent proper fusion
or create a lumpy, uneven bead.
1. TRAVEL DIRECTION is the direction the
gun is moved along the weld joint in relation to the weld puddle. The gun is either
PUSHED (see Figure 12) into the weld
puddle or PULLED away from the weld
puddle
Angle A
Angle B
Figure 10. Gun Position, Angle A
Figure 11. Gun Position, Angle B
Page 20

20
For most welding jobs you will pull the gun
along the weld joint to take advantage of
the greater weld puddle visibility.
2. TRAVEL SPEED is the rate at which the
gun is being pushed or pulled along the
weld joint. For a fixed heat setting, the
faster the travel speed, the lower the penetration and the lower and narrower the
finished weld bead. Likewise, the slower
the travel speed, the deeper the penetration and the higher and wider the finished weld bead.
TYPES OF WELD BEADS
The following paragraphs discuss the most
commonly used welding beads.
Once you have the gun in position with the
wire lined up on the weld joint, lower your
helmet, pull the trigger and the arc will start.
In a second or two you will notice a weld
puddle form and the base of the bead
beginning to build. It is now time to begin to
move with the gun. If you are just learning
to weld, simply move the gun in a straight
line and at a steady speed along the weld
joint. Try to achieve a weld with the desired
penetration and a bead that is fairly flat and
consistent in width.
As you become more familiar with your new
welder and better at laying some simple
weld beads, you can begin to try some different weld bead types.
There are two basic types of weld beads, the
stringer bead and the weave bead.
1. The STRINGER BEAD (Figure 13) is formed
by traveling with the gun in a straight line
while keeping the wire and nozzle centered
over the weld joint. This is the easiest type of
bead to make.
2. The WEAVE BEAD (Figure 14) is used
when you want to deposit metal over a
wider space than would be possible with a
stringer bead. It is made by weaving from
side to side while moving with the gun. It is
best to hesitate momentarily at each side
before weaving back the other way.
WELDING POSITIONS
There are four basic welding positions: flat,
horizontal, vertical, and overhead.
1. The FLAT POSITION (Figure 15) is the
easiest of the welding positions and is most
commonly used. It is best if you can weld in
the flat position if at all possible as good
results are easier to achieve.
2. The HORIZONTAL POSITION (Figure 16)
is next in difficulty level. It is performed very
much the same as the flat weld except that
angle B (see HOLDING THE GUN - p.18) is
such that the wire, and therefore the arc
Figure 13. Stringer Bead
Figure 14. Weave Bead
Figure 15. Flat Position
Figure 12. Travel Direction
Page 21

21
force, is directed more toward the metal
above the weld joint. This is to help prevent
the weld puddle from running downward
while still allowing slow enough travel speed
to achieve good penetration. A good starting point for angle B is about 30 degrees
DOWN from being perpendicular to the
work piece.
3. The VERTICAL POSITION (Figure 17) is
the next most difficult position. Pulling the
gun from top to bottom may be easier for
many people, but in some instances it can
be difficult to prevent the puddle from running downward. Pushing the gun from bottom to top may provide better puddle control and allow slower rates of travel speed to
achieve deeper penetration. When vertical
welding, angle B (see HOLDING THE GUN p.18) is usually always kept at zero, but
angle A will generally range from 45 to 60
degrees to provide better puddle control.
WARNING
Hot slag can cause fires and serious injury
from burns! Be sure to wear protective clothing and eye gear when using the Overhead
Position.
4. The OVERHEAD POSITION (Figure 18) is
the most difficult welding position because
gravity is pulling at the weld puddle trying to
make it drip off the work piece. Angle A (see
HOLDING THE GUN - p.18) should be
maintained at 60 degrees, the same as in
the flat position. Maintaining this angle will
reduce the chances of molten metal falling
into the nozzle should it drip from the weld
puddle. Angle B should be held at zero
degrees so that the wire is aiming directly
into the weld joint. If you experience excessive dripping of the weld puddle, select a
lower heat setting. Also, the weave bead
tends to work better than the stringer bead
when welding overhead.
MULTIPLE PASS WELDING
Butt Weld Joints. When butt welding thick-
er materials, you will need to prepare the
edges of the material to be joined by grinding a bevel on the edge of one or both
pieces of the metal being joined. When this
is done, a V is created between the two
pieces of metal, that will have to be welded
closed. In most cases more than one pass or
bead will need to be laid into the joint to
close the V. Laying more than one bead into
the same weld joint is known as a multiplepass weld.
Figure 17. Vertical Position
Figure 16. Horizontal Position
Figure 18. Overhead Position
Page 22

22
The illustrations in Figure 19 show the
sequence for laying multiple pass beads into
a single V butt joint.
NOTE: WHEN USING SELF-SHIELDING
FLUX-CORE WIRE it is very important to thoroughly chip and brush the slag off each completed weld bead before making another
pass or the next pass will be of poor quality.
Fillet Weld Joints. Most fillet weld joints, on
metals of moderate to heavy thickness, will
require multiple pass welds to produce a
strong joint. The illustrations in Figure 20
show the sequence of laying multiple pass
beads into a T fillet joint and a lap fillet joint.
SPECIAL WELDING METHODS
SPOT WELDING
The purpose of a spot weld is to join pieces
of metal together with a spot of weld instead
of a continuous weld bead. There are three
methods of spot welding: Burn-Through,
Punch and Fill, and Lap (see Figure 21).
Each has advantages and disadvantages
depending on the specific application as
well as personal preference.
1. The BURN-THROUGH METHOD welds
two overlapped pieces of metal together
by burning through the top piece and into
the bottom piece.
With the burn-through method, larger wire
diameters tend to work better than smaller
diameters because they have greater current
carrying capabilities allowing the arc to burn
through very quickly while leaving a minimal
amount of filler metal build up. Wire diameters that tend to work best, with the burnthrough method, are 0.030 inch diameter
solid wire or 0.035 inch self-shielding fluxcorewire.
Do not use 0.023 inch diameter solid or
0.030 inch self-shielding flux-core wires
when using the burn-through method
unless the metal is VERY thin or excessive
filler metal build-up and minimal penetration is acceptable.
Always select the HIGH heat setting with the
burn-through method and tune in the wire
speed prior to making a spot weld.
2. The PUNCH AND FILL METHOD produces
a weld with the most finished appearance
of the three spot weld methods. In this
method, a hole is punched or drilled into
Figure 19. Butt Joints
Figure 20. Fillet Weld Joints
Figure 21. Spot Welding
Page 23

23
the top piece of metal and the arc is
directed through the hole to penetrate
into the bottom piece. The puddle is
allowed to fill up the hole leaving a spot
weld that is smooth and flush with the
surface of the top piece.
Select the wire diameter, heat setting, and
tune in the wire speed as if you were welding the same thickness material with a continuous bead.
3. The LAP SPOT METHOD directs the welding arc to penetrate the bottom and top
pieces, at the same time, right along each
side of the lap joint seam.
Select the wire diameter, heat setting, and
tune in the wire speed as if you were welding the same thickness material with a continuous bead.
SPOT WELDING INSTRUCTIONS
1. Select the wire diameter and heat setting
recommended above for the method of
spot welding you intend to use.
2. Tune in the wire speed as if you were
going to make a continuous weld.
3. Hold the nozzle piece completely perpendicular to and about 1/4 inch off the work
piece.
4. Pull the trigger on the gun and release it
when it appears that the desired penetration has been achieved.
5. Make practice spot welds on scrap metal,
varying the length of time you hold the
trigger, until a desired spot weld is made.
6. Make spot welds on the actual work piece
at desired locations.
GENERAL
This welder has been engineered to give
many years of trouble-free service providing
that a few very simple steps are taken to
properly maintain it.
1. Keep the wire drive compartment lid
closed at all times unless the wire needs
to be changed or the drive tension needs
adjusting.
2. Keep all consumables (contact tips, nozzles,
and gun liner) clean and replace when necessary. See CONSUMABLE MAINTENANCE
and TROUBLESHOOTING later in this section for detailed information.
3. Replace power cord, ground cable,
ground clamp, or gun assembly when
damaged or worn.
4. Periodically clean dust, dirt, grease, etc.
from your welder. Every six months, or as
necessary, remove the side panels from
the welder and air-blow any dust and
dirt that may have accumulated inside
the welder.
WARNING
Electric shock can kill! To reduce the risk of
electric shock, always unplug the welder
from its ac power source before removing
side panels.
CONSUMABLE MAINTENANCE
IT IS VERY IMPORTANT TO MAINTAIN THE
CONSUMABLES TO AVOID THE NEED FOR
PREMATURE REPLACEMENT OF THE GUN
ASSEMBLY.
The GUN LINER is intended to provide an
unrestricted path for the welding wire to flow
through the gun assembly. Over time the
liner will accumulate dust, dirt, and other
debris. Replacement is necessary when these
accumulations begin to restrict the free flow
of wire through the gun assembly.
MAINTAINING THE CONTACT TIP
The purpose of the CONTACT TIP is to transfer welding current to the welding wire while
allowing the wire to pass through it smoothly.
Always use a contact tip stamped with the
same diameter as the wire it will be used with.
MAINTENANCE
Page 24

24
Note: Due to inherent variances in fluxcored welding wire, it may be necessary to
use a contact tip one size larger than your
flux core wire if wire jams occur.
1. If the wire burns back into the tip, remove
the tip from the gun and clean the hole
running through it with an oxygen-acetylene torch tip cleaner or tip drill.
2. Over time, the hole in the contact tip will
become worn by the wire passing
through it. The more worn this hole
becomes, the less efficient is the transfer
of welding current to the wire and eventually arc breakage and difficult arc
starting will result. Replace contact tips
when signs of wear become apparent.
MAINTAINING THE NOZZLE
The nozzle directs the shielding gas to the
weld puddle, determines the size of the
shielding area, and prevents the electrically
hot contact tip from contacting the work piece.
CAUTION
KEEP THE NOZZLE CLEAN! During the
welding process, spatter and slag will build
up inside the nozzle and must be cleaned
out periodically. Failure to clean and/or
replace the nozzle in a timely fashion WILL
CAUSE DAMAGE TO THE FRONT-END OF
THE GUN ASSEMBLY.
For best results, coat the inside of a new, or
freshly cleaned nozzle with anti stick spray
or gel.
1. Stop welding and clean any accumulated
slag or spatter from the nozzle every 5 to
10 minutes of welding time.
2. When welding overhead, if any molten
metal drips from the weld puddle and
falls into the nozzle, STOP WELDING
IMMEDIATELY and clean the nozzle.
3. If the slag cannot be thoroughly cleaned
from the nozzle, REPLACE THE NOZZLE!
Failure to keep the nozzle adequately
cleaned can result in the following problems:
A SHORTED nozzle results when spatter
buildup bridges the insulation in the nozzle,
allowing welding current to flow through it
as well as the contact tip. When shorted, a
nozzle will steal welding current from the
wire whenever it contacts the grounded
work piece. This causes erratic welds and
reduced penetration. In addition, a shorted
nozzle overheats the end of the gun, which
can DAMAGE the front-end of the gun.
A RESTRICTED nozzle is created when
enough slag builds up in the nozzle to affect
the direction, concentration, and/or rate of
the shielding gas flow. This problem can cause
porous, brittle welds and reduce penetration.
TESTING FOR A SHORTED NOZZLE
Arcing between the nozzle and the work
piece ALWAYS means the nozzle is shorted,
but this can be hard to detect through the
lens of a welding helmet. The following testing method is another way to tell if a nozzle
is shorted.
With the welder unplugged from the ac
power source, touch the probes of an ohmmeter or continuity tester to the end of the
contact tip and the outside of the nozzle. If
there is any continuity at all, the nozzle IS
shorted. Clean or replace as needed.
REPLACE A GUN LINER
When installing a new gun liner, care must be
taken not to kink or otherwise damage the
gun liner. See Figure 22 for the drive assembly and Figure 23 for the gun assembly.
1. Turn OFF welder POWER SWITCH and
unplug welder from power supply.
2. Open the welder side panel.
3. Loosen the tension arm and lift it up off
the drive roller.
4. Turn the wire spool counter-clockwise (be
sure to hold onto the wire itself while turning the spool or the wire will unspool itself
when it becomes free of the gun liner),
and remove wire from gun assembly.
5. Lay gun cable and gun handle straight
out in front of unit.
6. Remove gun liner holding clamp by
removing the three screws.
7. Take gun handle halves apart by removing five phillips head screws.
8. Remove gas hose from fast coupler fitting on Gas Valve. Depress lip on fast
coupler fitting back towards fitting and
pull gas hose out.
9. Remove Fast Coupler Fitting from Gas
Valve using a 9 millimeter wrench.
10. Firmly hold the brass fitting on the end
Page 25

25
of the gun liner with a wrench and rotate
Gas Valve counterclockwise to unscrew
fitting.
Note: Rotate Gas Valve – Do not rotate
brass fitting or gun liner twist inside gun
cable and may cause damage to gun
cable.
11.The Live Wire Terminal is held in place
on the Gas Valve by the brass fitting on
the end of the gun liner. When the brass
fitting is removed , slide the Live Wire
Terminal off of the brass fitting.
12.Firmly grip the gun cable and pull the
gun liner all the way out.
13.Install the new gun liner into gun cable,
starting from the end where the welding
gun will be mounted, and feeding the
liner all the way through the gun cable to
the wire feed roller.
Note: It may be helpful to apply a small
amount of liquid soap to the end of the
gun liner to decrease resistance during
installation process.
14.Slide the eyelet of the Live Wire Terminal
onto the threaded end of the gun liner
brass fitting.
15. Firmly hold the brass fitting on the end
of the gun liner with a wrench and rotate
Gas Valve clockwise to screw it onto fitting.
Note: Rotate Gas Valve – Do not rotate
brass fitting or gun liner will twist inside
gun cable and may cause damage to
gun cable.
16.Return all components to the handle casing and realign them as they were origi-
nally.
17.With both halves of the handle case in
place, tighten the five phillips head screws.
18.Using wire cutters, trim the new gun liner
to approximately 3/16 inch beyond the
edge of the Cable Holding Clamp. ( The
goal is to make sure that the end of the
gun liner will be as close to the drive
roller as possible after the Cable Holding
Clamp is assembled. This will make
installing the welding wire much easier. )
19.Reinstall liner holding clamp at feeder.
20.Reinstall the welding wire according to
specifications in INSTALL THE WELDING
WIRE section.
21.Close side panel.
22.Plug welder into power supply and turn
POWER SWITCH to ON position.
Figure 23. Gun Assembly
Figure 22. Drive Assembly
Page 26

PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Except for internal and external cleaning,
cleaning the nozzle, and occasionally
retightening screws, there is no periodic
maintenance recommended for your welder.
TROUBLESHOOTING
The following TROUBLESHOOTING information is provided as a guide to help
resolve some of the more common problems
that could be encountered.
Table 5 is a troubleshooting table provided
to help you determine a possible remedy
when you are having a problem with your
welder. This table does not provide all possible solutions, only those possibilities considered to likely be common faults. The table
consists of a TROUBLE or symptom, a POSSIBLE CAUSE for the symptom, and a POSSIBLE REMEDY for that symptom.
26
Page 27

27
TABLE 5 – TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLE
Dirty, porous, brittle weld
Wire feed works but no arc
Arc works but no feeding wire
Nothing works except fan
Low output or nonpenetrating weld
Wire is jamming or “birdnesting” at
the drive roller
Wire burns back to contact tip
Ground clamp and/or ground cable
gets hot
Gun nozzle arcs to work surface
POSSIBLE CAUSE
1. Plugged welding nozzle
2. No shielding gas
3. Wrong type of gas
4. Dirty or rusty welding wire
1. Bad ground or loose connection
2. Bad connection to gun or faulty
gun
1. Faulty wire speed control
assembly
2. No tension on drive roller
3. Faulty drive motor ( RARE! )
1. Faulty trigger on gun
2. Exceeded duty cycle; thermal
protector opened
3. Faulty transformer ( RARE! )
1. Loose connection inside
machine
2. Too long improper extension
cord
3. Wrong type or size wire
4. Poor ground connection
5. Wrong size contact tip
6. Loose gun connection or faulty
gun assembly
7. Wrong welding polarity set
8. Dirty or rusty welding wire
1. Too much tension on drive roller
2. Gun liner worn damaged
3. Contact tip is clogged or damaged
4. Liner stretched or is too long
1. Gun liner worn or damaged
2. Liner stretched or is too long
3. Wrong size contact tip
4. Contact tip is clogged or damaged
5. Wire feed speed is too slow
Bad connection from cable to clamp
Slag building inside nozzle or nozzle is shorted
POSSIBLE REMEDY
1. Clean or replace nozzle.
2. Tank empty, flow restricted or
regulator set too low.
3. See SELECTING SHIELDING
gas section of manual.
4. Replace spool of wire.
1. Check ground and connections.
Tighten as necessary.
2. Check connection to gun or
replace gun.
1. Replace wire speed control
assembly.
2. Adjust the drive tension.
3. Replace drive motor.
1. Replace gun trigger.
2. Let welder cool at least 10 minutes ( observe and maintain proper
duty cycle. )
3. Replace transformer.
1. Blow inside of machine out with
compressed air. Clean and tighten
all connections.
2. See EXTENSION CORDS section of manual.
3. Use correct size wire.
4. Reposition clamp and check
cable to clamp connection.
5. Use correct size contact tip.
6. Tighten gun or replace gun.
7. Change to proper polarity.
8. Replace spool of wire.
1. Adjust drive tension. ( See
INSTALL THE WELDING WIRE )
2. Replace gun liner.
3. Replace contact tip.
4. Trim liner to proper length.
1. Replace gun liner.
2. Trim liner to proper length.
3. Use correct size contact tip.
4. Replace contact tip.
5. Increase wire feed speed.
Tighten connection or replace cable.
Clean or replace nozzle as needed.
Page 28

28
WIRE FEED WELDER WIRING DIAGRAM
Page 29

29
WIRE FEED WELDER PARTS LIST
01 PRT 22710076 E1292 P.C.BOARD "CSA" 1
02 PRT 04600146 JOHNSON MOTOR ø37 + PINION 1
03 PRT 21600035 HANDLE 1
04 PRT 22210014 THERMOSTAT 100° 10A 1
05 PRT 04600286 FAN&FAN MOTOR ASSY. 220V 1
06 PRT 21605036 CABLE CLAMP W/NUT 1
07 PRT 21690425 PLASTIC TRIM 1
08 PRT 21690422 TORCH GROMMET 1
09 PRT 22200038 VOLTAGE SELECTOR SWITCH 1
10 PRT 04600337 BLACK POTENTIOMETER KNOB ø38 1
11 PRT 22200035 YELLOW POWER SWITCH 16A-250V 1
12 PRT 04600002 COMPLETE SPOOL HOLDER 1
13 PRT 21910048 .023 (0.6MM) 1/2LB (0,225KG) SOLID CORE WIRE SPOOL 1
13 PRT 21910050 .030 (0,8MM) 1/2LB (0,225KG) FLUX CORE WIRE SPOOL 1
14 PRT 05000182 DIVIDING PANEL W/LABELS 1
15 PRT 44400019 PLASTIC WIRE FEEDER ø37 1
16 PRT 33805074 FEED ROLL ø7X25 0,6-0,8 1
17 PRT 21690424 ACCESS PANEL SUPPORTS+PINS 2
18 PRT 20220120 POWER CORD 3XAWG12 8' (2,5M) W/50A PLUG 1
19 PRT 05000177 FRONT PANEL 1
20 PRT 05000181 UPPER PANEL W/LABELS 1
21 PRT 04600257 BLACK SWITCH KNOB ø38 1
22 PRT 22205143 SWITCH 16A 1
23 PRT 44135018 CHOKE 40X40 AL 1
25 PRT 22400038 RECTIFIER PMS 8/4/1F 1
26 PRT 44120178 TRANSFORMER 220V 60HZ 40X85 AL 1
27 PRT 22210016 127° 16A THERMOSTAT 1
28 PRT 05000184 REAR PANEL W/LABELS 1
29 PRT 23000124 0/8 TORCH 10MM² 7'3' (2,2M) G-NG 1
30 PRT 04600234 CABLE CLAMP ø10 + SCREW 1
31 PRT 21690442 FRONT TRIM WITH LOUVER 1
32 PRT 21690443 TAP ø 36 1
33 PRT 43210161 EARTH CABLE 10MM² 6-1/2' (2M) CL.200/0.8 1
34 PRT 22110007 EARTH CLAMP 200A 1
35 PRT 21690426 BACK FRAME 1
36 PRT 33700242 9005 LOWER PANEL 1
37 PRT 21690226 DOOR LATCH 1
38 PRT 05000180 SIDE DOOR W/LABEL 1
39 PRT 04600114 KIT GAS/NO GAS CHANGE BOARD 1
40 PRT 21905041 FACE SHIELD 50X105-75X98 1
41 PRT 21905007 DARK GLASS 75X98 DIN 11 1
42 PRT 21905039 WIRE BRUSH / HAMMER 1
43 PRT 04600361 SCREWS SET FOR HANDLE AND CABINET 1
Page 30

30
Page 31

31
WIRE FEED WELDER GUN PARTS LIST
01 PRT 04600163 HANDLE ASSY., BLUE 1
02 PRT 23005332 GAS VALVE 1
03 PRT 23005145 SWAN NECK WITH INSULATING COVER 1
04 PRT 23005091 SWAN NECK LINER 1
05 PRT 23005285 ISOLATING COVER FOR NECK 2
06 PRT 23005146 TW1 TORCH DIFFUSER 1
07 PRT 23005018 0.023 CONTACT TIP 1
07 PRT 23005019 0.030 CONTACT TIP 1
07 PRT 23005020 0.040 CONTACT TIP 1
08 PRT 23005147 TORCH GAS NOZZLE 1
09 PRT 21200010 FAST-ON CONTACT 6,3X0,8 1
10 PRT 33800032 TORCH CONTACT SPRING 1
11 PRT 30900021 RUBBER OUTER SLEEVE ø17,5 + HOSES 1
12 PRT 23005254 STEEL LINER 1.4X4BLUE 2,2M W/END FITTING 1
12A PRT 30900002 PLASTIC LINER 1,5X4 2,5M 1
13 PRT 22910001 FAST CONNECTION FOR HOSE ø4 M6X0,75 1
13A PRT 22910001 PLASTIC LINER END FITTING ø4 M6X0,75 1
14 PRT 30900020 TORCH GAS HOSE ø2X4 4,6M 1
15 PRT 04600063 KIT 2 PINS MALE CONNECTOR + 2 CONTACTS 1
16 PRT 23005148 NECK+OUTER INSULATION+DIFFUSER 1
17 PRT 23005318 ALUMINIUM GAS VALVE + NECK + DIFFUSER 1
Page 32

32
Page 33

33
SUGGESTED SETTINGS
Page 34

34
NOTES
Page 35

35
Page 36

77611256
 Loading...
Loading...