ASUS TX97-X User Manual

R
TX97-X
Pentium® A TX Motherboard
USER’S MANUAL

USER’S NOTICE
No part of this manual, including the products and softwares described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
in any form or by any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
W ARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS,
EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DAT A, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL
OR PRODUCT.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or
explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
• Intel, LANDesk, and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
• IBM and OS/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines.
• Symbios is a registered trademark of Symbios Logic Corporation.
• Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
• Sound Blaster AWE32 and SB16 are trademarks of Creative Technology Ltd.
• Adobe and Acrobat are registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
The product name and revision number are both printed on the board itself. Manual revisions
are released for each board design represented by the digit before and after the period of the
manual revision number. Manual updates are represented by the third digit in the manual
revision number.
For previous or updated manuals, BIOS, drivers, or product release information, contact ASUS
at http://www.asus.com.tw or through any of the means indicated on the following page.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT
ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBLITY OR LIABILITY FOR
ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MA Y APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARES DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 1997 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
Product Name: ASUS TX97-X
Manual Revision: 3.00
Release Date: August 1997
2
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

ASUS CONTACT INFORMATION
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC.
Marketing Info
Address: 150 Li-Te Road, Peitou, Taipei, Taiwan 112, ROC
Telephone: +886-2-894-3447
Fax: +886-2-894-3449
Email: info@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
Fax: +886-2-895-9254
BBS: +886-2-896-4667
Email: tsd@asus.com.tw
WWW: www.asus.com.tw
Gopher: gopher.asus.com.tw
FTP: ftp.asus.com.tw/pub/ASUS
ASUS COMPUTER INTERNATIONAL
Marketing Info
Address: 721 Charcot Avenue, San Jose, CA 95131, USA
Telephone: +1-408-474-0567
Fax: +1-408-474-0568
Email: info-usa@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
BBS: +1-408-474-0569
Email: tsd-usa@asus.com.tw
WWW: www.asus.com
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH
Marketing Info
Address: Harkort Str. 25, 40880 Ratingen, BRD, Germany
Telephone: 49-2102-445011
Fax: 49-2102-442066
Email: info-ger@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
BBS: 49-2102-448690
Email: tsd-ger@asus.com.tw
Hotline: 49-2102-499712
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 3

CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION...........................................................................7
How this Manual is Organized ........................................................7
Item Checklist ..................................................................................7
II. FEATURES ....................................................................................8
Features of the ASUS TX97-X Motherboard ..................................8
Introduction to ASUS TX97 Series of Motherboards ................9
Parts of the ASUS TX97-X Motherboard ................................ 11
III. INSTALLATION ........................................................................12
ASUS TX97-X Motherboard Layout ............................................12
Installation Steps............................................................................14
1. Jumpers ......................................................................................14
Jumper Settings ..................................................................15
Compatible Cyrix CPU Identification ................................19
2. System Memory (DIMM) .........................................................19
DIMM Memory Installation Procedures: ...........................20
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU).................................................22
4. Expansion Cards .......................................................................23
Expansion Card Installation Procedure: .............................23
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards.................................23
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards...........................24
ISA Cards and Hardware Monitor ......................................24
5. External Connectors..................................................................25
Power Connection Procedures .................................................33
IV. BIOS SOFTWARE .....................................................................34
Support Software ...........................................................................34
Flash Memory Writer Utility....................................................34
Main Menu .........................................................................35
Advanced Features Menu ...................................................35
Managing and Updating Your Motherboard’s BIOS................36
6. BIOS Setup ...............................................................................37
Load Defaults .....................................................................38
Standard CMOS Setup .............................................................38
Details of Standard CMOS Setup:......................................38
BIOS Features Setup ................................................................41
Details of BIOS Features Setup..........................................41
Chipset Features Setup .............................................................44
Details of Chipset Features Setup.......................................44
Power Management Setup........................................................47
Details of Power Management Setup .................................47
4
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

CONTENTS
PNP and PCI Setup ..................................................................50
Details of PNP and PCI Setup ............................................50
Load BIOS Defaults .................................................................52
Load Setup Defaults .................................................................52
Supervisor Password and User Password ................................53
IDE HDD Auto Detection ........................................................54
Save & Exit Setup ....................................................................55
Exit Without Saving .................................................................55
V. SUPPORT SOFTWARE ..............................................................56
ASUS TX97 Motherboard Series Support CD ..............................56
LANDesk Client Manager (LDCM)..............................................56
Desktop Management Interface (DMI)..........................................58
Introducing the ASUS DMI Configuration Utility .............58
System Requirements .........................................................58
Using the ASUS DMI Configuration Utility ......................59
VI. ASUS PCI SCSI Cards ..............................................................61
Symbios SCSI BIOS and Drivers ..................................................61
ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860 SCSI Cards ..............................61
Setting Up the ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860 .....................62
Setting the INT Assignment for the ASUS PCI-SC200 ...........62
Terminator Requirements for SCSI Devices ............................62
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC860 ........................63
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC200 ........................63
SCSI ID Numbers for SCSI Devices .......................................64
SCSI ID Priority .......................................................................64
16-bit Audio (Section included with optional onboard audio).......65
ASUS Installation CD ..............................................................67
ASUS Audio Driver CD Contents ......................................67
Audio Drivers Installation ................................................................67
Win95 Audio Drivers.........................................................................68
Win3.x Audio Drivers........................................................................69
Configuration Manager ............................................................69
Creative PnP Configuration Manager (CTCM) .......................69
Audio Software ........................................................................71
Environment Variables .............................................................75
SOUND Environment variable...........................................75
BLASTER Environment Variable ......................................75
MIDI Environment Variable ...............................................76
Maximum Recording Rates for the Audio Hardware.........76
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 5
FCC & DOC COMPLIANCE
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
WARNING! The use of shielded cables for connection of the monitor to the
graphics card is required to assure compliance with FCC regulations. Changes
or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions
from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
6
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

I. INTRODUCTION
How this Manual is Organized
This manual is divided into the following sections:
I. Introduction Manual information and checklist
II. Features Information and specifications concerning this product
III. Installation Instructions on setting up the motherboard.
IV. BIOS Software Instructions on setting up the BIOS software
V. Support Software Information on the included support software
VI. ASUS SCSI Cards Installation of ASUS SCSI cards (optional)
Item Checklist
Please check that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or missing
items, please contact your retailer.
þ ASUS TX97-X motherboard
I. INTRODUCTION
(Manual / Checklist)
þ 1 IDE ribbon cable
þ 1 floppy ribbon cable
þ Support Drivers & Utilities
• Flash Memory Writer utility to update the FLASH BIOS
• Desktop Management Interface (DMI) utility
®
• LANDesk
• Readme files for descriptions and use of the files
• Technical Support Form
þ This user’s manual
¨ Infrared module (optional)
¨ ASUS PCI-SC200 Fast-SCSI or PCI-SC860 Ultra-Fast SCSI card (optional)
¨ ASUS audio onboard and audio driver CD with online help (optional)
Client Manager (LDCM) Software (with optional onboard LM78)
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 7

II. FEATURES
(Features)
II. FEATURES
Features of the ASUS TX97-X Motherboard
The ASUS TX97-X is carefully designed for the demanding PC user who wants
many features in a small package. This motherboard:
• Intel Chipset: Features Intel’s 430TX PCIset with I/O subsystems.
®
• V ersatile Processor Support: Intel Pentium
P54CS), IBM®/Cyrix® 6x86-PR166+ (Rev 2.7 or later), IBM®/Cyrix® 6x86MX
(PR166 & faster), AMD-K5™ (PR75-PR133), AMD-K6™ (PR166 & faster).
• Versatile Memory Support: Is equipped with three DIMM sockets to support
(8, 16, 32, 64, or 128MB) 168-pin SDRAM memory modules up to 256MB.
• Easy Installation: Is equipped with BIOS that supports auto detection of hard
drives, PS/2 mouse, and Plug and Play devices to make setup of hard drives,
expansion cards, and other devices virtually automatic.
• ISA & PCI Expansion: Provides expansion for three 16-bit ISA cards, three
32-bit PCI cards, and 1 shared expansion for either a PCI or an ISA card.
75-233MHz (P55C-MMX™, P54C/
™
• Super Multi-I/O: Provides two high-speed UART-compatible serial ports and
one parallel port with EPP and ECP capabilities.
• Desktop Management Interface (DMI): Supports DMI through BIOS which
allows hardware to communicate within a standard protocol creating a higher
level of compatibility. (Requires DMI-enabled components.) (See section V)
• PCI Bus Master IDE Controller: Comes with an onboard PCI Bus Master
IDE controller with two connectors that supports four IDE devices in two channels, supports PIO Modes 3 and 4 and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2, and
supports Enhanced IDE devices such as Tape Backup and CD-ROM drives.
Supports two drives of either 5.25-inch (360KB or 1.2MB) or 3.5-inch (720KB,
1.44MB, or 2.88MB) disk drives. Supports Japanese “Floppy 3 mode” (3.5inch disk drive: 1.2MB) and LS-120 floppy disk drives (3.5-inch disk drive: 120
MB, 1.44MB, 720K). BIOS supports IDE CD-ROM or SCSI device boot-up.
• Level 2 Cache: 512KB Pipelined Burst SRAM onboard.
• Optional IrDA: Supports and optional IrDA receiver/transmitter device.
• Symbios SCSI BIOS: Has onboard firmware to support optional ASUS SCSI
controller cards.
• Optional Audio: Has optional onboard Creative Labs
®
Audio with 3D sound.
8 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

II. FEATURES
Introduction to ASUS TX97 Series of Motherboards
Performance
• SDRAM Optimized Performance - ASUS TX97 series of motherboards sup-
port the new generation memory - Synchronous Dynamic Random Access
Memory (SDRAM) which increases the data transfer rate from 264MB/s max
using EDO memory to 528MB/s max using SDRAM.
• Double the IDE Transfer Speed - ASUS TX97 series of motherboards with
Intel 430TX PCIset improves IDE transfer rate using Bus Master UltraDMA/33
IDE which can handle data transfer up to 33MB/s. The best of all is that this
new technology is compatible with existing ATA-2 IDE specs so there is no
need to upgrade current hard drives or cables.
• Concurrent PCI - Concurrent PCI allows multiple PCI transfers from PCI master
busses to memory to CPU.
• ACPI Ready - ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) is also
implemented on all ASUS 430TX series of motherboards. ACPI provide more
Energy Saving Features for the future operating systems (OS) supporting OS
Direct Power Management (OSPM) functionality. With these features implemented in the OS, PCs can be ready around the clock everyday, yet satisfy all
the energy saving standards. To fully utilize the benefits of ACPI, an ACPIsupported OS such as in the next release of Windows 95 must be used.
(TX97 Series)
II. FEATURES
• PC ’97 Compliant - Both the BIOS and hardware levels of ASUS TX97 series
of motherboards meet PC ’97 compliancy. The new PC 97 requirements for
systems and components are based on the following high-level goals: Support
for Plug and Play compatibility and power management for configuring and
managing all system components, and 32-bit device drivers and installation procedures for both Windows 95 and Windows NT.
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 9

• Voltage Monitoring and Alert - System voltage levels are monitored to ensure
• System Resources Alert - T oday’ s operating systems such as W indows 95, W in-
II. FEATURES
(TX97 Series)
• Virus Write Protection - Normally, viruses can destroy data on storage media
II. FEATURES
stable current to critical motherboard components. Voltage specifications are
more critical for future processors, so monitoring is necessary to ensure proper
system configuration and management.
dows NT , and OS/2, require much more memory and hard drive space to present
enormous user interfaces and run large applications. The system resource monitor will warn the user before the system resources are used up to prevent possible application crashes. Suggestions will give the user information on managing their limited resources more efficiently.
such as hard drivers, floppy diskettes, and MO. Some new-generation viruses
will not only destroy data on storage media, but also clear BIOS data which is
usually unprotected. ASUS TX97 series of motherboards were designed to cooperate with BIOS, chipset, and flash EPROM to disable write permission when
the system’s initialization stage is completed upon boot-up.
• CPU Slow Down - When CPU fans or system fans are malfunctioning, the
system will deactivate the CPU Clock line to decrease CPU utilization to the
speed upon detection of system overheat. This will prevent CPU damage from
system overheat. The CPU utilization will restore normal operations when temperature falls below a safe level.
• Auto Fan Off - The system fans will power off automatically even in sleep
mode. This function reduces both energy consumption and system noise, and
is a important feature to implement silent PC systems.
• Dual Function Power Button (requires A TX power supply) - The system can
be in one of two states, one is Sleep mode and the other is the Soft-Off mode.
Pushing the power button for less than 4 seconds places the system into Sleep
mode. When the power button is pressed for more than 4 seconds, it enters the
Soft-Off mode.
• Remote Ring On (requires ATX power supply) - This allows a computer to be
turned on remotely through a modem. With this benefit on-hand, any user can
access vital information from their computer from anywhere in the world!
• Message LED - Chassis LEDs now act as information providers. Through the
way a particular LED illuminates, the user can determine the stage the computer
is in. A simple glimpse provides useful information to the user.
10 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual
II. FEATURES
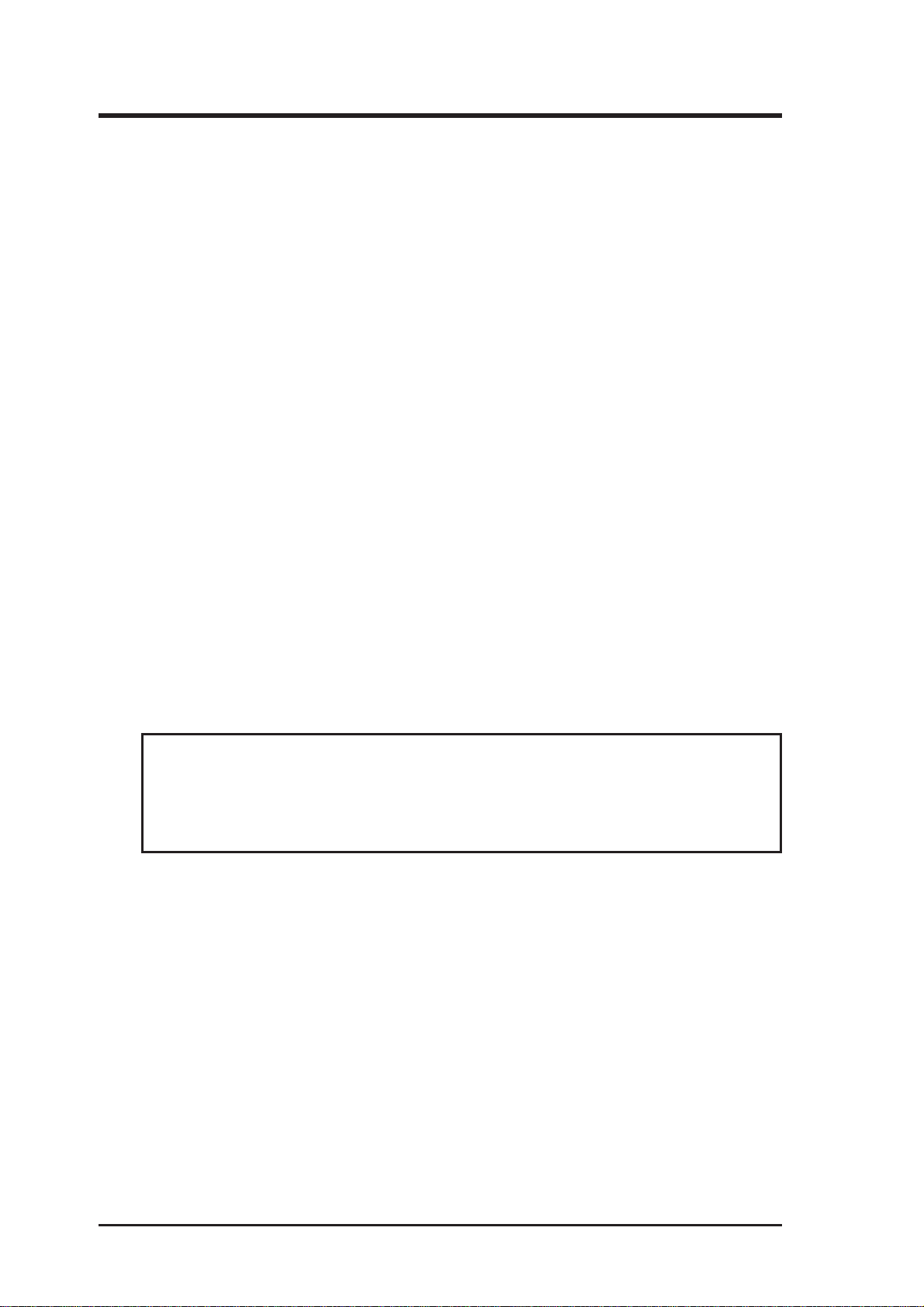
Parts of the ASUS TX97-X Motherboard
T: PS/2 Mouse
B: PS/2 Keyboard
T: USB Port 1
B: USB Port 2
COM 1
T: Parallel Conn.
B: Serial Conn.
COM 2
Intel’s 430TX
PCIset
(Optional)
T:Joystick/Midi
B:Out/In/Mic
2 DIMM
Sockets
CPU ZIF
Socket 7
CPU Thermal
Sensor (optional)
512KB Pipelined
Burst L2 Cache
II. FEATURES
(Motherboard Parts)
3 PCI Slots
Creative Labs
Audio (optional)
1 PCI/ISA
shared Slot
3 ISA Slots
LM78 Hardware
Monitor (optional)
Programmable
Flash ROM
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 11
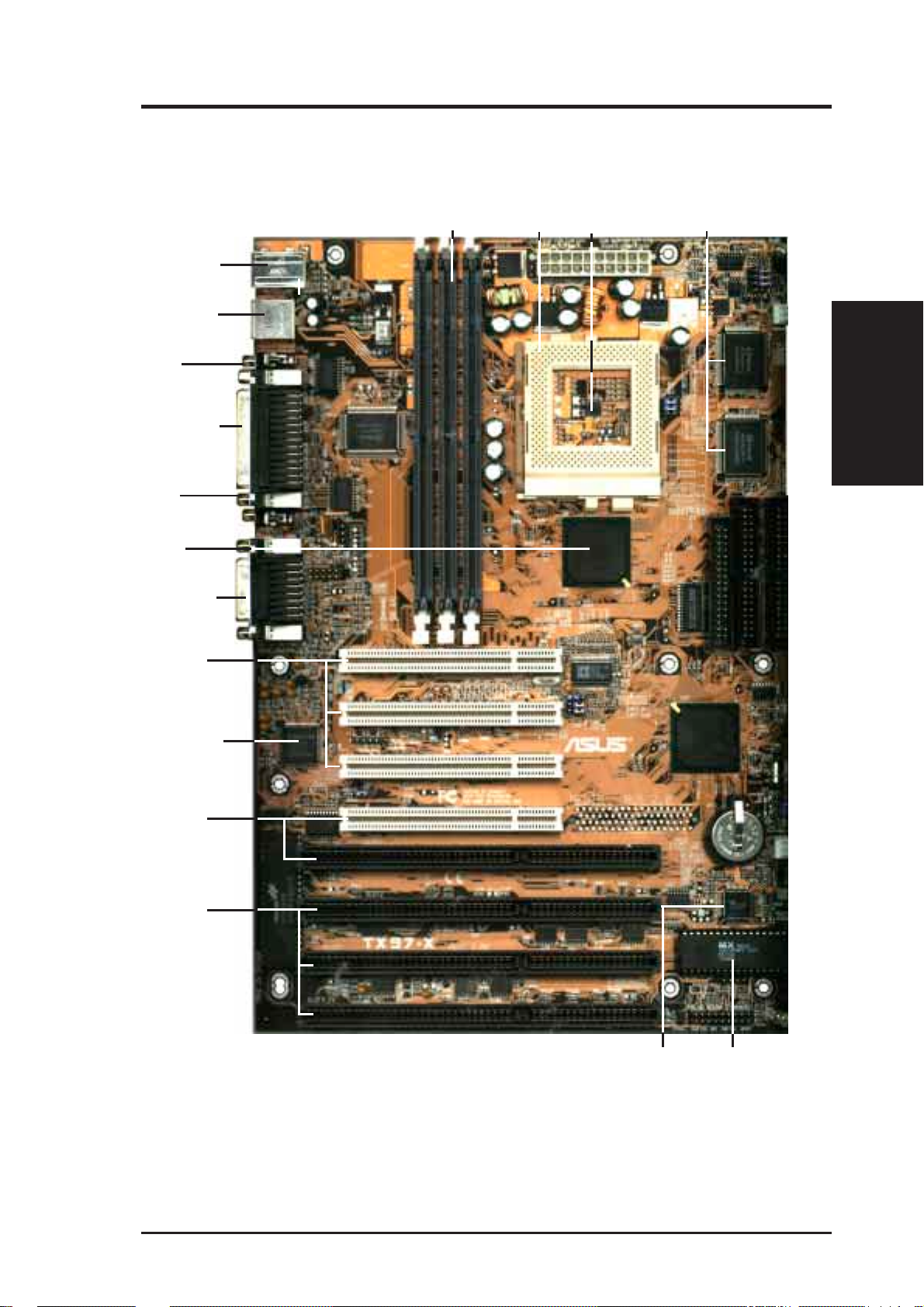
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS TX97-X Motherboard Layout
PS/2
USB
Parallel Port
(Motherboard Layout)
III. INSTALLATION
Game/Midi Port
Top: Mouse
Bottom: Keyboard
Top: USB 1
Bottom: USB 2
COM 1
COM 2
Sony CD In
Line
Out
Creative® Modem
Line
In
Connector
Mic
In
FANPWR3
Multi-I/O (En/Dis)
SIO
Row
PCI Slot 1
Board Power Input
for ATX Power Supply
CPU Thermal Sensor
(Hardware Monitor)
LM75
CPU ZIF Socket 7
DIMM Socket 1 (64-bit, 168-pin module)
DIMM Socket 2 (64-bit, 168-pin module)
DIMM Socket 3 (64-bit, 168-pin module)
Intel
430TX
PCIset
32
54
10
BUS Freq.
BF0
BF1
BF2
CPU Voltage
VID0
VID1
VID2
VID3
CPU Fan
Floppy Drives
Secondary IDE
Primary IDE
512KB Onboard L2 Cache
BUS FREQ
FS0
FS1
FS2
Intel PIIX4
R
PCIset
Creative
Labs
Audio
®
PCI Slot 2
Volume Control
VOLCTL
Wake on LAN
PCI Slot 3
AUDIO (Dis/En)
PCI Slot 4
ISA Slot 1
ISA Slot 2
Keyboard BIOS
ISA Slot 3
ISA Slot 4
Programmable
BIOS EEPROM
Panel Connections
IDE LED
NOTE: The items in outline are optional and may not be present.
CR2032
3 Volt
Lithium Cell
Chasis open
alarm lead
Hardware Monitor
LM78
Infrared Con. (IrDA)
RTCLR
RTC (Test/Clear)
FANPWR1
12 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

III. INSTALLATION
Jumpers
1) RTCLR p. 15 Real Time Clock RAM (Operation/Clear Data)
2) AUDIO (optional) p. 15 Onboard Audio (Disable/Enable)
3) M/IO p. 16 Multi-I/O Selection (Enable/Disable)
4) FS0, FS1, FS2 p. 16 CPU External Clock (BUS) Frequency Selection
5) BF0, BF1, BF2 p. 16 CPU:BUS Frequency Ratio
6) VID0, 1, 2, 3 p. 18 CPU Voltage Regulator Output Selection
Expansion Slots
1) System Memory p. 19 System Memory Upgrade
2) CPU ZIF Socket 7 p. 22 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Socket
3) SLOT 1, 2, 3, 4 p. 23 16-bit ISA Bus Expansion Slots
4) PCI 1 , 2, 3, 4 p. 23 32-bit PCI Bus Expansion Slots
Connectors
1) PS2KEYBOARD p. 25 PS/2 Keyboard Connector (6-pin Female)
2) PS2MOUSE p. 25 PS/2 Mouse Connector (6-pin Female)
3) PRINTER p. 26 Parallel (Printer) Port Connector (25-pin Female)
4) COM1, COM2 p. 26 Serial Port COM1 & COM2 (T wo 9-pin Female)
5) FLOPPY p. 2 6 Floppy Drive Connector (34-pin Block)
6) AUDIO (optional) p. 27 Audio Port -Line Out, Line In, Mic (Three 1/8” Female)
7) GAME (optional) p. 27 Joystick/Midi Connector (15-pin Female)
8) USB p. 27 Universal Serial BUS Ports 1 & 2 (Two 4-pin Female)
9) Primary / Second IDE p. 28 Primary / Secondary IDE Connector (40-pin Blocks)
10) IDELED p. 28 IDE LED Activity Light
11) FANPWR1, 2, 3 p. 29 1 Chassis, 2 CPU, 3 Power Supply Fan Power Lead (3-pin Block)
12) CHASSIS p. 29 Chassis Open Alarm Lead (4-1pin Block)
13) IR p. 30 Infrared Port Module Connector
14) ATXPWR p. 30 A TX Motherboard Power Connector (20-pin Block)
15) VOLCTL (optional) p. 31 Digital Volume Level Control (Up/Down)
16) WOL p. 31 Wake on LAN (3 pins) (RESERVED)
17) MSG LED (PANEL) p. 32 System Message LED (2 pins)
18) SMI (PANEL) p. 32 SMI Switch Lead (2 pins)
19) PWR SW (PANEL) p. 32 ATX Power & Soft-Off Switch Lead (2 pins)
20) RESET (PANEL) p. 32 Reset Switch Lead (2 pins)
21)
PWR LED (
22)
KEYLOCK (
23) SPEAKER (PANEL) p. 32 Speaker Output Connector (4 pins)
PANEL)p. 32 System Power LED Lead (3 pins)
PANEL)p. 32 Keyboard Lock Switch Lead (2 pins)
*
†
(Map of Board)
III. INSTALLATION
*
The onboard hardware monitor uses the address 290H-297H so legacy ISA cards must not
use this address or else conflicts will occur.
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 13

III. INSTALLATION
III. INSTALLATION
Installation Steps
Before using your computer, you must complete the following steps:
1. Set Jumpers on the Motherboard
2. Install System Memory
3. Install the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
4. Install Expansion Cards
5. Connect Ribbon Cables, Cabinet Wires, and Power Supply
6. Setup the BIOS Software
1. Jumpers
Several hardware settings are made through the use of jumper caps to connect jumper
pins (JP) on the motherboard. See “Motherboard Layout” for locations of jumpers.
The jumper settings will be described numerically such as [----], [1-2], [2-3] for no
(Jumpers)
connection, connect pins 1&2, and connect pins 2&3 respectively . Pin 1 for our motherboards is always on top
the keyboard connector away from yourself. A “1” is written besides pin 1 on jumpers
with three pins. The jumpers will also be shown graphically such as to connect
pins 1&2 and to connect pins 2&3. Jumpers with two pins will be shown as
for Short (On) and for Open (Off). For manufacturing simplicity, the jumpers may be sharing pins from other groups. Use the diagrams in this manual instead of
following the pin layout on the board. Settings with two jumper numbers require that
both jumpers be moved together. To connect the pins, simply place a plastic jumper
cap over the two pins as diagramed.
WARNING! Computer motherboards, baseboards and components, such as SCSI
cards, contain very delicate Integrated Circuit (IC) chips. To protect them against
damage from static electricity , you should follow some precautions whenever you
work on your computer.
Pin 1
or on the left
Pin 1
when holding the motherboard with
1. Unplug your computer when working on the inside.
2. Use a grounded wrist strap before handling computer components. If you do
not have one, touch both of your hands to a safely grounded object or to a
metal object, such as the power supply case.
3. Hold components by the edges and try not to touch the IC chips, leads or
connectors, or other components.
4. Place components on a grounded antistatic pad or on the bag that came with
the component whenever the components are separated from the system.
14 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual
III. INSTALLATION
Jumper Settings
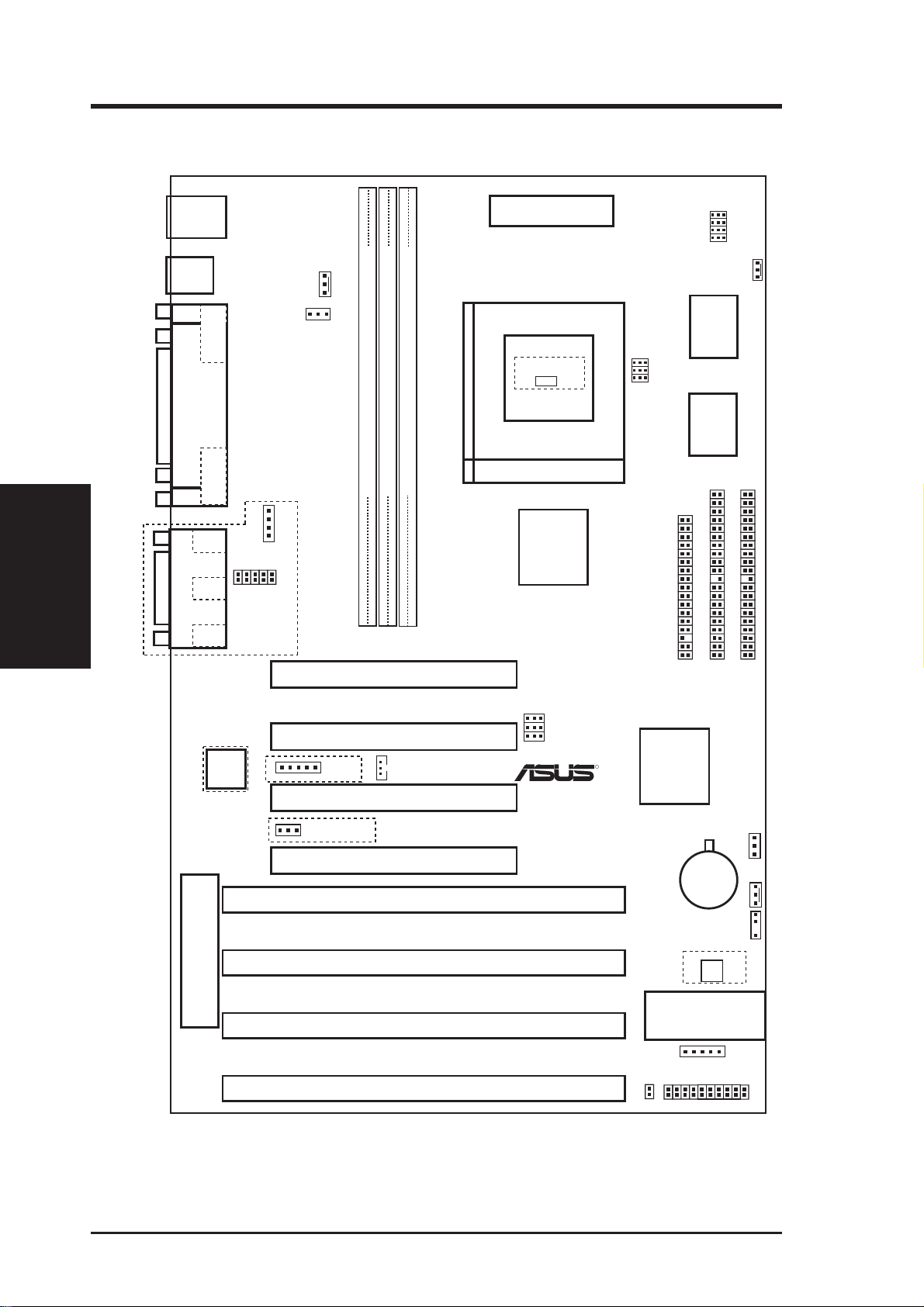
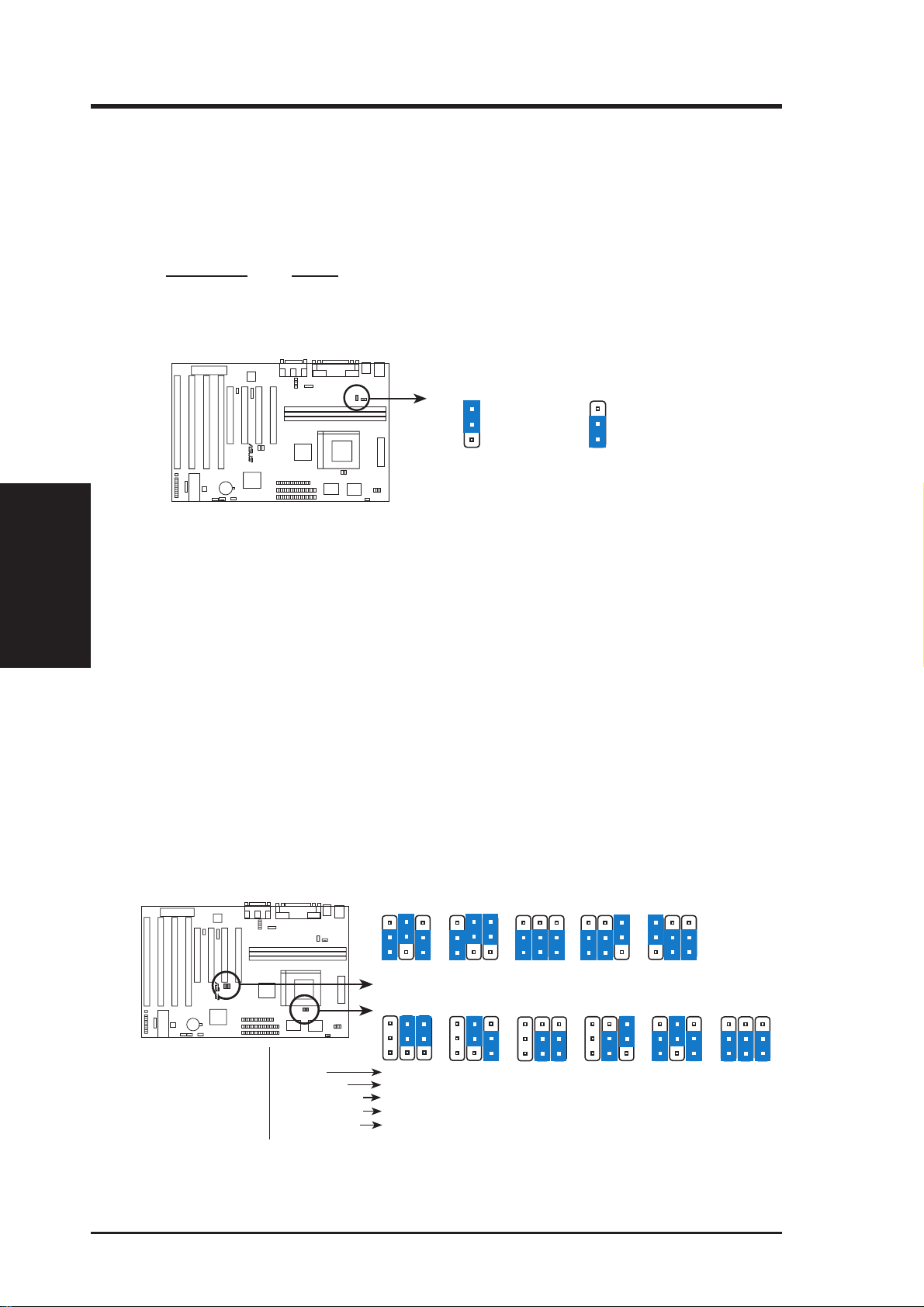
1. Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM (RTCLR)
The CMOS RAM is powered by the onboard button cell battery. To clear the
R TC data: (1) T urn of f your computer and remove the AC power , (2) Move this
jumper to “Clear Data,” (3) Move the jumper back to “Operation,” (4) T urn on
your computer, (5) Hold down <Delete> during bootup and enter BIOS setup to
re-enter user preferences.
Battery Test Jumper (RTCLR)
You can test the battery’s current by removing this jumper and attaching a current meter to pins 1&2. WARNING: You must unplug the power cord to
your power supply to ensure that there is no power to your motherboard.
The CMOS RAM containing BIOS setup information may be cleared by
this action. You should enter BIOS to “Load Setup Defaults” and re-enter
any user information after removing and reapplying this jumper.
RTC RAM RTCLR
Operation [1-2] (Default)
Clear Data [2-3] (momentarily)
RTCLR
Battery Test
R
Operation (Default)
RTC RAM (Operation / Clear Data)
RTCLR
Clear Data
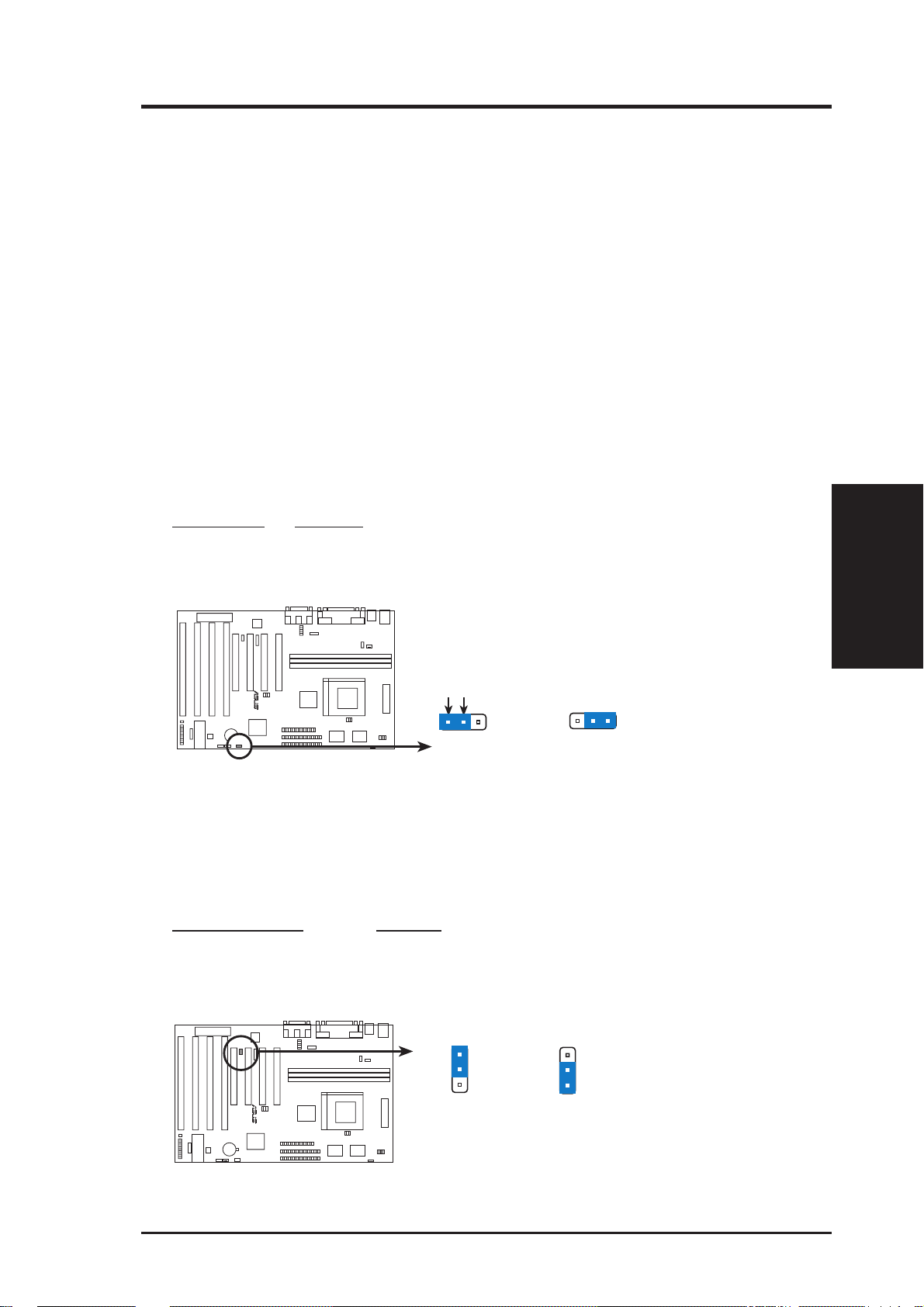
2. Onboard Audio Selection (AUDIO) (with optional onboard Audio)
This jumper allows you to Disable the onboard audio chipset inorder to use your
own audio card. Otherwise, leave on default of Enabled.
Onboard Audio AUDIO
Enabled [2-3] (Default)
Disabled [1-2]
AUDIO
1
2
3
Disable
R
AUDIO
1
2
3
Enable
(Default)
(Jumpers)
III. INSTALLATION
Onboard Audio (Disable / Enable)
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 15
III. INSTALLATION
3. Onboard Multi-I/O Selection (M/IO)
You can selectively disable each onboard Multi-I/O item (floppy, serial, parallel, and IrDA) through Chipset Features Setup of BIOS SOFTWARE or disable all Multi-I/O items at once with the following jumper in order to use your
own Multi-I/O card.
Multi-I/O M/IO
Enable [1-2] (Default)
Disable [2-3]
III. INSTALLATION
(Jumpers)
M/IO
1
2
3
Disabled
R
Multi I/O Setting (Enable / Disable)
M/IO
1
2
3
Enable (Default)
4. CPU External (BUS) Frequency Selection (FS0, FS1, FS2)
These jumpers tell the clock generator what frequency to send to the CPU. These
allow the selection of the CPU’ s External frequency (or BUS Clock). The BUS Clock
times the BUS Ratio equals the CPU’ s Internal frequency (the advertised CPU speed).
5. CPU to BUS Frequency Ratio (BF0, BF1, BF2)
These jumpers set the frequency ratio between the Internal frequency of the
CPU and the External frequency (called the BUS Clock) within the CPU. These
must be set together with the above jumpers CPU External (BUS) Frequency
Selection.
FS1
FS0
R
Complete Names:
Intel Pentium P54C
Pentium P55C-MMX
AMD K5, K6
IBM/Cyrix 6x86(L) (M1)
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX(M2)
P54C/K5
P55C/K6/MX
IBM/Cyrix 6x86
IBM/Cyrix 6x86L
AMD-K6 (.25µ)
FS2
50MHz
CPU External Clock (BUS) Frequency Selection
BF0
BF2
BF1
1.5x(3/2)
3.5x(7/2)
3.0x(3/1)
3.0x(3/1)
----
CPU : BUS Frequency Ratio
1
2
3
1
2
3
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
2.0x(2/1)
FS1
FS2
55MHz
BF2
BF1
----
FS0
BF0
1
2
3
1
2
3
FS1
FS2
FS0
60MHz
BF2
BF1
2.5x(5/2)
2.5x(5/2)
1.0x(1/1)
2.0x(2/1)
----
1
2
3
BF0
FS2
66MHz
1
2
3
3.0x(3/1)
3.0x(3/1)
16 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual
FS1
BF2
BF1
----
----
----
FS0
BF0
1
2
3
1
2
3
FS1
FS2
FS0
75MHz
BF2
BF1
----
----
----
----
4.0x(4/1)
1
2
3
BF0
1
2
3
BF2
BF1
----
----
----
----
4.5x(9/2)
BF0
1
2
3

III. INSTALLATION
WARNING! Frequencies above 66MHz exceed the specifications for the on-
board Intel Chipset and are not guaranteed to be stable.
Set the jumpers by the Internal speed of the Intel, AMD, IBM, or Cyrix CPU as follows:
(BUS Freq.) (Freq. Ratio)
CPU Model Freq. Ratio BUS Freq. FS2 FS1 FS0 BF2 BF1 BF0
Intel Pentium 233MHz 3.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium 200MHz 3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [1-2]
Intel Pentium 166MHz 2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [2-3]
Intel Pentium 150MHz 2.5x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [2-3] [2-3]
Intel Pentium 133MHz 2.0x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [2-3]
Intel Pentium 120MHz 2.0x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [2-3]
Intel Pentium 100MHz 1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium 90MHz 1.5x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
Intel Pentium 75MHz 1.5x 50MHz [2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K6-PR233 233MHz 3.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K6-PR200 200MHz 3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [1-2]
AMD-K6-PR166 166MHz 2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [2-3]
AMD-K5-PR133 100MHz 1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5-PR120 90MHz 1.5x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5-PR100 100MHz 1.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5-PR90 90MHz 1.5x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
AMD-K5-PR75 75MHz 1.5x 50MHz [2-3] [1-2] [2-3] [----] [1-2] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR233 200MHz 3.0x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [1-2]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR200 166MHz 2.5x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [2-3] [2-3]
IBM/Cyrix 6x86MX-PR166 150MHz 2.5x 60MHz [2-3] [2-3] [2-3] [----] [2-3] [2-3]
*IBM/Cyrix 6x86-PR166+ 133MHz 2.0x 66MHz [2-3] [2-3] [1-2] [----] [1-2] [2-3]
*NOTE: The only IBM or Cyrix 6x86 (M1) Rev 2.7 or later is supported on this motherboard (see
next page). Bootup screen will show 6x86-P166+ with the Cyrix PR166+ installed on this motherboard.
(Jumpers)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 17

III. INSTALLATION
III. INSTALLATION
Compatible Cyrix CPU Identification
The only Cyrix CPU that is supported on this motherboard is
labeled Cyrix 6x86 PR166+ but must be Revision 2.7 or later .
Look on the underside of the CPU for the serial number . The
number should read G8DC6620A or later.
5. Voltage Regulator Output Selection (VID0, 1, 2, 3)
These jumpers set the voltage supplied to the CPU. VID1 for 3.4V(STD) is
ignored, therefore, the jumper setting for 2.8V(Dual) may work for both
3.4V(STD) and 2.8V(Dual).
(Jumpers)
Pentium MMX (P55C)
(150MHz-233MHz)
Intel Pentium (P54C)
(75MHz-200MHz)
AMD-K6
(PR166 and faster)
AMD-K5
(PR75-PR133)
IBM/Cyrix 6x86(MX)
(PR166 and faster)
IBM/Cyrix 6x86(M1)
(PR166 and faster)
WARNING! Because CPU designs change rapidly, the following chart is only
intended as a simple quideline and is not intended to be true for your CPU. Look
for the CPU voltage included with your CPU and follow the Voltage setting
diagramed below the chart.
Manufacturer CPU Type Single Plane Dual Plane VID3 VID2 VID1 VID0
Intel/AMD/IBM/Cyrix P54C/CS/K5/M1 3.5V(VRE) ---- [----] [2-3] [----] [1-2]
AMD/IBM/Cyrix K6-166,200/MX ---- 2.9V(Dual) [----] [2-3] [2-3] [1-2]
Intel/AMD P54C/CS/K5 3.4V(STD) ---- [----] [2-3] [2-3] [2-3]
Intel P55C ---- 2.8V(Dual) [----] [2-3] [2-3] [2-3]
AMD K6-PR233 ---- 3.2V(Dual) [----] [1-2] [2-3] [2-3]
AMD (.25micron) K6-233,266,300 ---- 2.1V(Dual) [----] [----] [2-3] [1-2]
VID1
VID2
VID0
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
VID3
2.5 Volts
VID0
1
2
3
R
Voltage Regulator Output Selection
VID2
VID3
1.8 Volts
3.2 Volts
VID1
VID0
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
VID0
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
VID3
2.1 Volts
2.9 Volts2.8 Volts2.7 Volts
3.5 Volts3.4 V
VID1
VID2
VID3
1.9 Volts
*
*3.4V VID1 may be [----] or [2-3]
VID1
VID2
18 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual
III. INSTALLATION
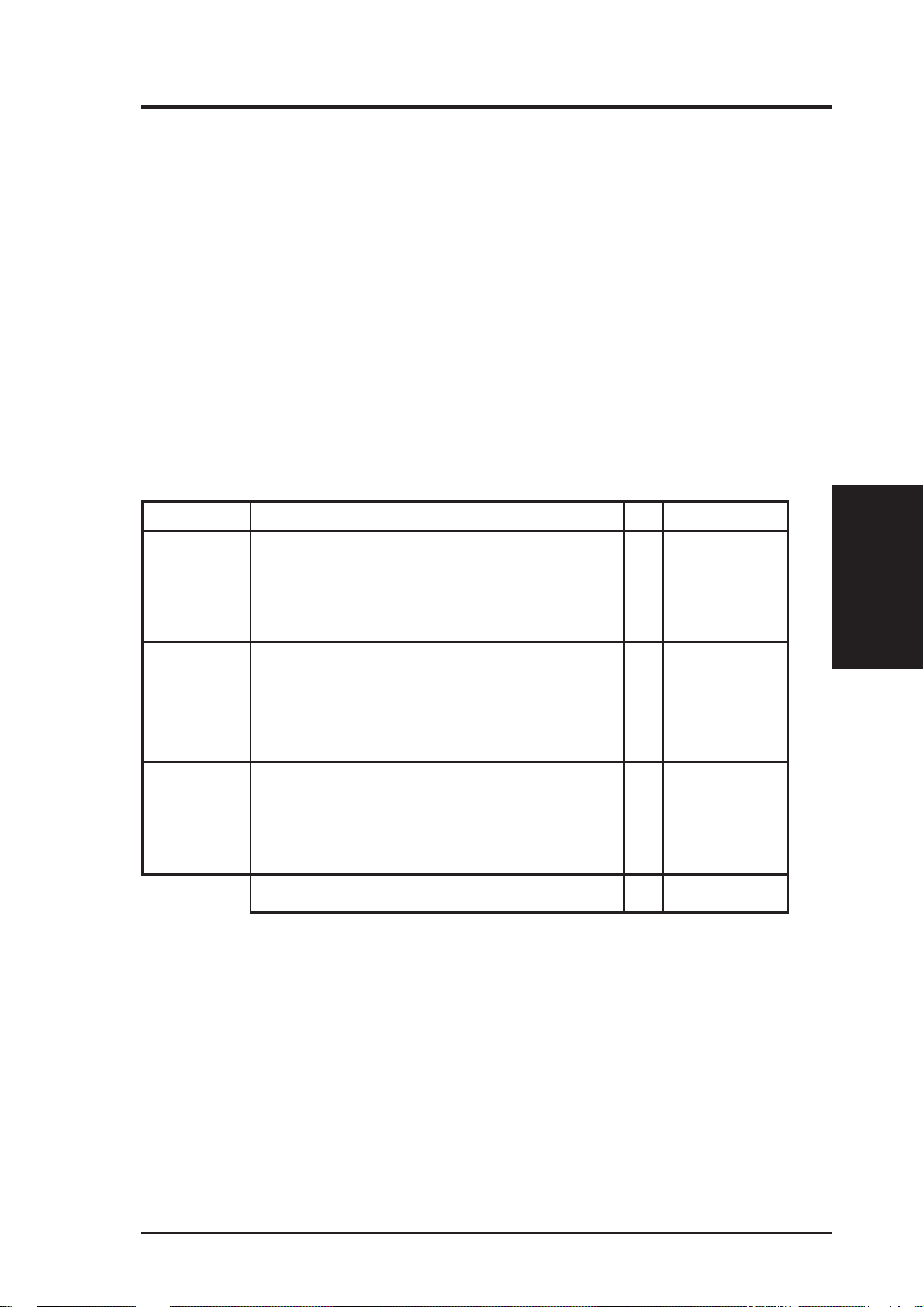
2. System Memory (DIMM)
Only Dual Inline Memory Modules (DIMM’s) can be used with this motherboard.
T wo sockets are available for 3.3V olt (power level) Unbuffered Synchronous DRAMs
(SDRAM) or EDO DRAM of either 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128MB to form a memory size
between 8MB to 256MB. One side (with memory chips) of the DIMM module
takes up one Row on the motherboard.
IMPORTANT: Memory speed setup is required through "Auto Configuration" in BIOS Chipset Setup of the BIOS SOFTWARE.
Install memory in any combination as follows:
DIMM Type 168-pin DIMM Memory Modules Total Memory
Socket 1 SDRAM 8MB, 16MB, 32MB x1
(Rows 0&1) SDRAM 64MB, 128MB - but
(Socket 3 must be empty)
EDO 8, 16, 32, 64, 128MB
Socket 2 SDRAM 8MB, 16MB, 32MB x1
(Rows 2&3) SDRAM 64MB, 128MB - but
(Socket 3 must be empty)
EDO 8, 16, 32, 64, 128MB
Socket 3 SDRAM 8MB, 16MB, 32MB - but
(Rows 4&5) Socket 1 or 2 must not have x1
64MB or 128MB SDRAM
EDO 8, 16, 32, 64, 128MB
Total System Memory (Max 256MB) =
NOTE:
• Maximum memory size is 256MB total for this motherboard.
• Socket 3 will not support 64MB or 128MB DIMMs with 64Mbit SDRAM cells.
• If Socket 1 and/or Socket 2 has 64MB or 128MB DIMM’ s with 64Mbit SDRAM
cells, Socket 3 must be empty.
(System Memory)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 19
III. INSTALLATION
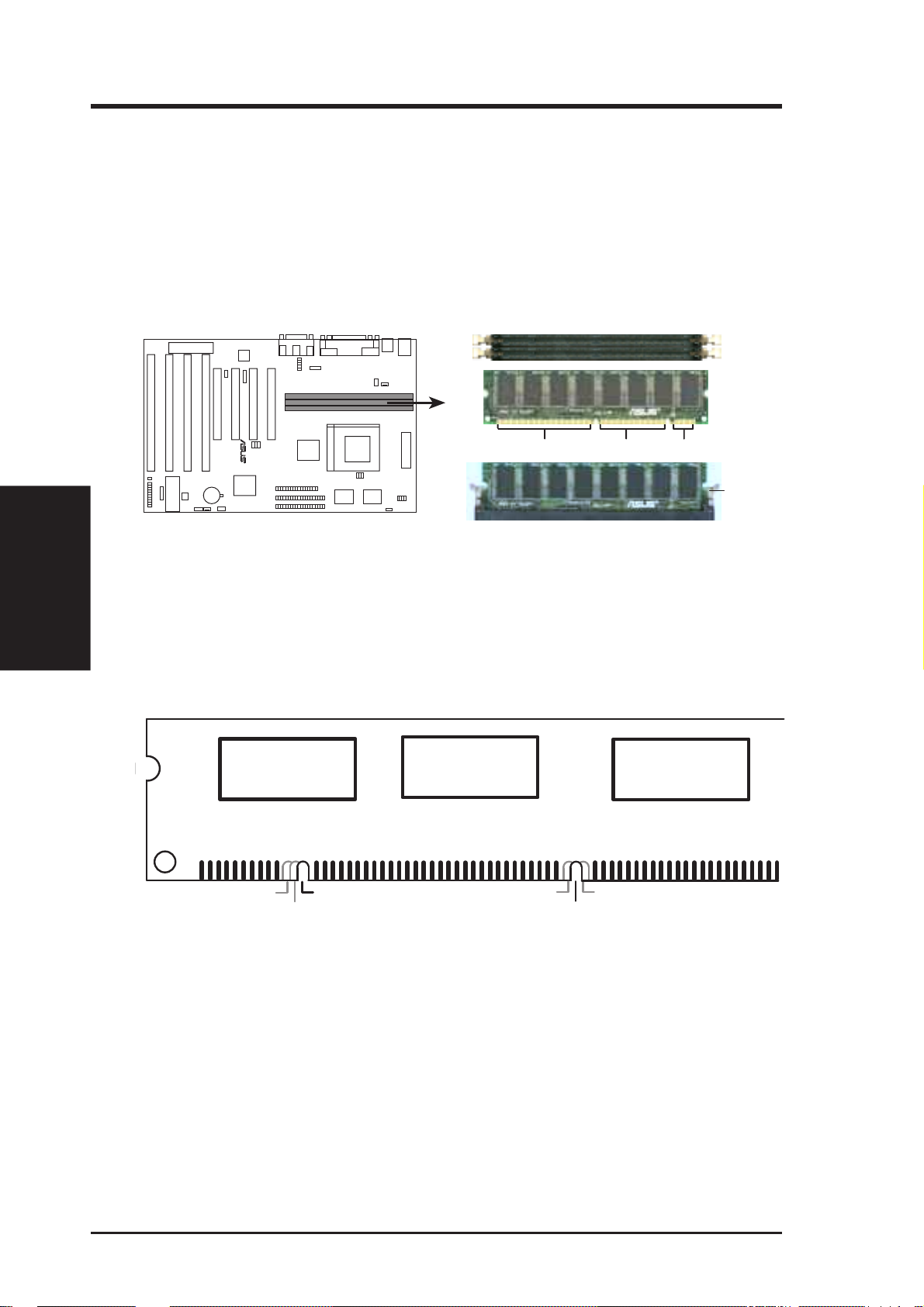
DIMM Memory Installation Procedures:
Insert the module(s) as shown. Because the number of pins are different on either
side of the breaks, the module will only fit in the orientation as shown. DRAM
SIMM modules have the same pin contact on both sides. SDRAM DIMM modules
have different pint contact on each side and therefore have a higher pin density.
III. INSTALLATION
(System Memory)
168 Pin DIMM Memory Sockets
The Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) memory modules must be 3.3Volt Unbuffered Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) or Extended Data Output (EDO) . You
can identify the type of DIMM module by the illustration below:
168-Pin DIMM Notch Key Definitions (3.3V)
R
DRAM Key Position
RFU
Buffered
Unbuffered
88 Pins 60 Pins 20 Pins
Voltage Key Position
5.0V
Reserved
3.3V
Lock
The notch on the DIMM module will shift between left, center, or right to identify
the type and also to prevent the wrong type to be inserted into the DIMM slot on the
motherboard. You must ask your retailer for the specifications before purchasing.
Four clock signals are supported on this motherboard.
20 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

III. INSTALLATION
(This page was intentionally left blank)
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
(System Memory)
III. INSTALLATION
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 21

3. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The motherboard provides a 321-pin ZIF Socket 7 that is backwards compatible
with ZIF Socket 5 processors. The CPU that came with the motherboard should
have a fan attached to it to prevent overheating. If this is not the case then purchase
a fan before you turn on your system. Apply thermal jelly to the CPU top and then
install the fan onto the CPU.
WARNING! Without a fan circulating air on the CPU and heat sinks, the CPU
and/or heat sinks can overheat and cause damage to both the CPU and the motherboard. (See “CPU Cooling Fan Connector” at the end of this section.)
To install a CPU, first turn off your system and remove its cover. Locate the ZIF
(System Processor)
III. INSTALLATION
socket and open it by first pulling the lever sideways away from the socket then
upwards to a 90-degree right angle. Insert the CPU with the correct orientation as
shown. Use the notched corner of the CPU as your guide. The white dot should
point towards the end the of the lever. Notice that there is a blank area where one
hole is missing from that corner of the square array of pin holes and a “1” printed on
the motherboard next to that corner . Because the CPU has a corner pin for three of
the four corners, the CPU will only fit in the one orientation as shown. The picture
is for reference only; you should have a CPU fan that will cover the face of the CPU.
With the added weight of the CPU fan, no force is required to insert the CPU. Once
completely inserted, hold down on the fan and close the socket’s lever.
III. INSTALLATION
IMPORTANT: You must set jumpers for “CPU to BUS Frequency Ratio” and
jumpers for “BUS Frequency Selection” depending on the CPU that you install.
BlankLever Lock
1
R
ZIF Socket 7 with Pentium MMX Processor
Notch
1
22 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual

III. INSTALLATION
4. Expansion Cards
WARNING! Make sure that you unplug your power supply when adding or
removing expansion cards or other system components. Failure to do so may
cause severe damage to both your motherboard and expansion cards.
Expansion Card Installation Procedure:
1. Read your expansion card documentation on any hardware and software settings that may be required to setup your specific card.
2. Set any necessary jumpers on your expansion card.
3. Remove your computer system’s cover.
4. Remove the bracket on the slot you intend to use.
Keep the bracket for possible future use.
5. Carefully align the card’s connectors and press firmly.
6. Secure the card on the slot with the screw you removed in step 4.
7. Replace the computer system’s cover.
8. Edit the BIOS settings if necessary.
(such as “IRQ xx Used By ISA: Yes” in PNP AND PCI SETUP)
9. Install the necessary software drivers for your expansion card.
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards
Some expansion cards need to use an IRQ to operate. Generally an IRQ must be
exclusively assigned to one use. In an standard design there are 16 IRQs available
but most of them are already in use by parts of the system which leaves 6 free for
expansion cards.
Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may need to use IRQs. System IRQs are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus first, and any remaining IRQs are
then used by PCI cards. Currently, there are two types of ISA cards. The original
ISA expansion card design, now referred to as “Legacy” ISA cards, requires that
you configure the card’ s jumpers manually and then install it in any available slot on
the ISA bus. You may use Microsoft’s Diagnostic (MSD.EXE) utility included in
the Windows directory to see a map of your used and free IRQs. For Windows 95
users, the “Control Panel” icon in “My Computer,” contains a “System” icon which
gives you a “Device Manager” tab. Double clicking on a specific device gives you
the “Resources” tab, which shows the Interrupt number and address. Make sure that
no two devices use the same IRQs or your computer will experience problems when
those two devices are in use at the same time.
(Expansion Cards)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual 23

T o simplify this process this motherboard has complied with the Plug and Play (PNP)
specification which was developed to allow automatic system configuration whenever a PNP-compliant card is added to the system. For PNP cards, IRQs are assigned automatically from those available.
If the system has both Legacy and PNP ISA cards installed, IRQs are assigned to
PNP cards from those not used by Legacy cards. The PCI and PNP configuration of
the BIOS setup utility can be used to indicate which IRQs are being used by Legacy
cards. For older Legacy cards that does not work with the BIOS, you can contact
your vendor for an ISA Configuration Utility.
An IRQ number is automatically assigned to PCI expansion cards after those used
by Legacy and PNP ISA cards. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS automatically
assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that has a card in it that requires an IRQ. To install a
PCI card, you need to set something called the INT (interrupt) assignment. Since all
III. INSTALLATION
(Expansion Cards)
the PCI slots on this motherboard use an INTA #, be sure that the jumpers on your
PCI cards are set to INT A.
III. INSTALLATION
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards
Some ISA cards, both legacy and PnP, may also need to use a DMA (Direct Memory
Access) channel. DMA assignments for this motherboard are handled the same way
as the IRQ assignment process described earlier. You can select a DMA channel in
the PCI and PnP configuration section of the BIOS Setup utility.
IMPORTANT: To avoid conflicts, reserve the necessary IRQs and DMAs for legacy
ISA cards (under PNP AND PCI SETUP of the BIOS SOFTWARE, choose Yes in IRQ
xx Used By ISA and DMA x Used By ISA for those IRQs and DMAs you want to reserve).
ISA Cards and Hardware Monitor
The onboard hardware monitor uses the address 290H-297H so legacy ISA cards
must not use this address or else conflicts will occur.
24 ASUS TX97-X User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...