Asus SL500, SL1000 FAQ

INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
address
Release date: 5/4/2004
1 Introduction
This document contains the frequently asked questions (FAQ) for SL-series Internet Security Router including SL1000, SL-500 and possibly the future SL- models.
2 FAQ
2.1 General
2.1.1 Why can’t I login to the Internet Security Router? How do I know what is wrong?
There are several reasons that you cannot login to the Internet Security Router, e.g. power not connected,
Ethernet cable not connected, your PC and the Internet Security Router not in the same subnet or incorrect
username and/or password. Please follow the steps below to connect back to the Internet Security Router:
1. Make sure that the Internet Security router is powered on. The color of the POWER LED is solid green. If the
POWER LED is not lit, make sure that the AC adapter is connected to a power source and the connector is
firmly attached to the power connector on the Internet Security Router.
2. Make sure that the Ethernet cable connecting your PC and the Internet Security Router is firmly inserted on
one of the LAN ports of the Internet Security Router and the network card on your PC. You may pull the
Ethernet cable to check if the cable is firmly connected. You should also verify that the LED of the
corresponding LAN port is lit in solid or flashing green.
3. Check if PC’s IP and LAN IP of SL-series are in the same subnet. Please see “How do I know if my PC and
the LAN of my Internet Security Router are in the same subnet?” and “How to configure my PC and the
Internet Security Router to reside in the same subnet?” for instructions.
4. Check if the username and login password that you entered are correct.
2.1.2 How to find out the IP address of my PC?
For Windows PC:
1. From the Start menu, select Run.
2. Enter cmd in the text field, and then click in “OK” button.
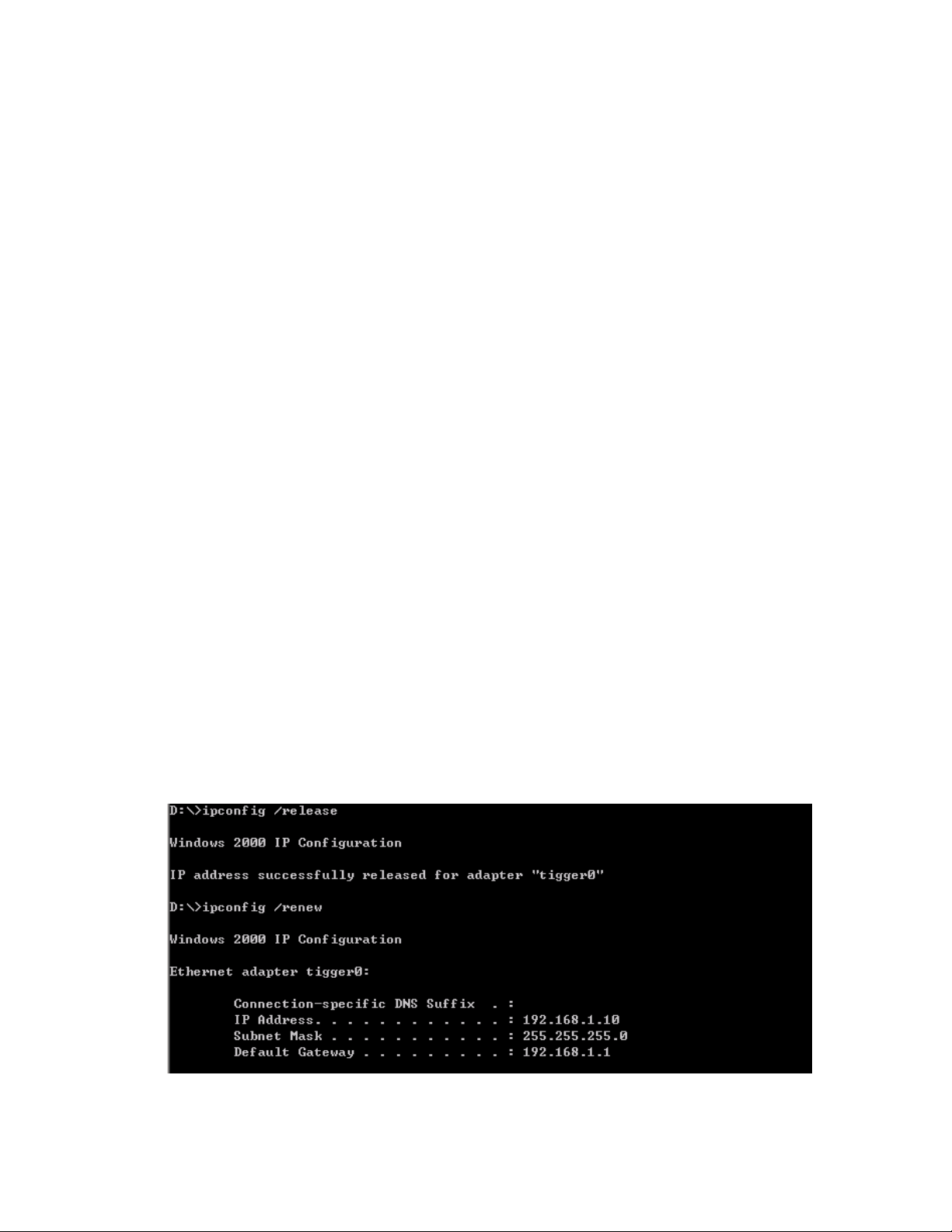
3. Enter ipconfig in the Command Prompt window. The following figure shows where the IP address of your
network card is displayed. Note that if you have more than one network card installed on your computer,
make sure you get the IP address from the correct network card.
IP
Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc. Page 1
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
2.1.3 How do I know if my PC and the LAN of my Internet Security Router are in the same subnet?
Follow the procedures below to check if your PC and the Internet Security Router are in the same subnet.
1. Get the network address of your PC and the Internet Security Router. To find out the network address, do
a binary “&” operation on the IP address and the subnet mask. For example, the IP address of your
Internet Security Router is 192.168.1.1 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, then the network address
is 192.168.1.0, which is calculated by (192.168.1.1) & (255.255.255.0).
2. If your PC and the Internet Security Router have the same network address, then they are in the same
subnet.
2.1.4 How to configure my PC and the Internet Security Router to reside in the same subnet?
The configuration procedure depends on whether the DHCP server is enabled or not and also the operating
system on your PC. We’ll only describe the procedures for the Windows 2000. For other operating systems,
please refer to the user manual for details.
Scenario 1: DHCP server is enabled:
On windows 2000 computer do the flowing:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <Start> button, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the Local Area Connection icon, and then
select Properties.
4. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click
<Properties> button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Obtain an IP
address automatically. Also click the radio button labeled Obtain DNS server address automatically
or enter IP addresses of your DNS servers.
6. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the Control Panel.
7. From the Start menu, select Run.
8. Enter cmd in the open field and then click on OK button. You’ll see the Command Window displays.
9. Enter ipconfig/release in the Command Window to release existing IP lease.
10. Enter ipconfig/renew in the Command Windows to obtain a new IP lease. The following figure shows the
information you’ll get after renewing an IP lease from the DNS server.
Scenario 2: DHCP server is disabled:
Page 2 Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc.

INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
On windows 2000 computer do the flowing:
1. In the Windows task bar, click the <Start> button, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network and Dial-up Connections icon.
3. In the Network and Dial-up Connections window, right-click the Local Area Connection icon, and then
select Properties.
4. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click
<Properties> button.
5. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click the radio button labeled Use the following
IP address and enter an IP address for your PC. Make sure that this IP address is in the same subnet as
that for the Internet Security Router LAN IP.
6. Enter the subnet mask. The value is the same as what is configured in the LAN IP configuration page on
the Internet Security Router.
7. Enter the Default Gateway IP address. This is the LAN IP of the Internet Security Router.
8. Enter IP addresses of the DNS servers provided by your ISP.
9. Click <OK> button twice to confirm and save your changes, and then close the Control Panel.
For example: LAN IP of your Internet Security Router is 192.168.1.1 and subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. You can
then set your PC’s IP address to192.168.1.10 and subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
2.2 WAN
2.2.1 Why can’t my Internet Security Router get an IP from my ISP?
Go through the following steps to eliminate the causes of failing to obtain an IP address from your ISP.
1. Check if the Internet Security Router and/or the ADSL or cable modem is powered on. Turn on the power
if necessary.
2. Check if the WAN LED is in solid or flashing green. If the WAN LED is off, make sure that the Ethernet
cable connecting the Internet Security Router and your modem is firmly attached to the Ethernet
connectors on both devices.
3. Check if the LED indicating the connection between your ADSL or cable modem and your ISP is lit. If this
LED is off, that means the connection is down. You may have to call your ISP to find out why the
connection is down.
4. Open the WAN configuration page and click on the Apply button to re-establish the connection to your
ISP.
2.2.2 What is Dial-on-Demand and Keep Alive? Which one shall I use?
Dial-on-demand and keep alive options are available only when the WAN connection mode is set to PPPoE. Dialon-demand can terminate and resume traffic at the PPPoE interface based on the data inactivity timeout period
configured for the interface, without any user intervention. It terminates a PPPoE session after the lapse of the
inactivity timeout period and automatically re-establishes a PPPoE session after traffic resumes. This option is
useful when your broadband service charge is based on the amount of time connected because the Internet
Security Router will maintain connection only when there is traffic. Note that the update interval setting for the
Internet time server must be greater than the inactivity timeout period configured for the dial-on-demand.
Keep alive can keep your service connected even when there is no traffic. This option will provide
2.2.3 MAC Cloning
2.2.3.1 What is MAC address?
The unique hardware address programmed into the Ethernet and Token Ring adapters that identify a network
card from all others.
Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc. Page 3
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
address
2.2.3.2 How to find out the MAC address of my network card?
For Windows PC:
1. From the Start menu, select Run.
2. Enter cmd in the text field, and then click in “OK” button.
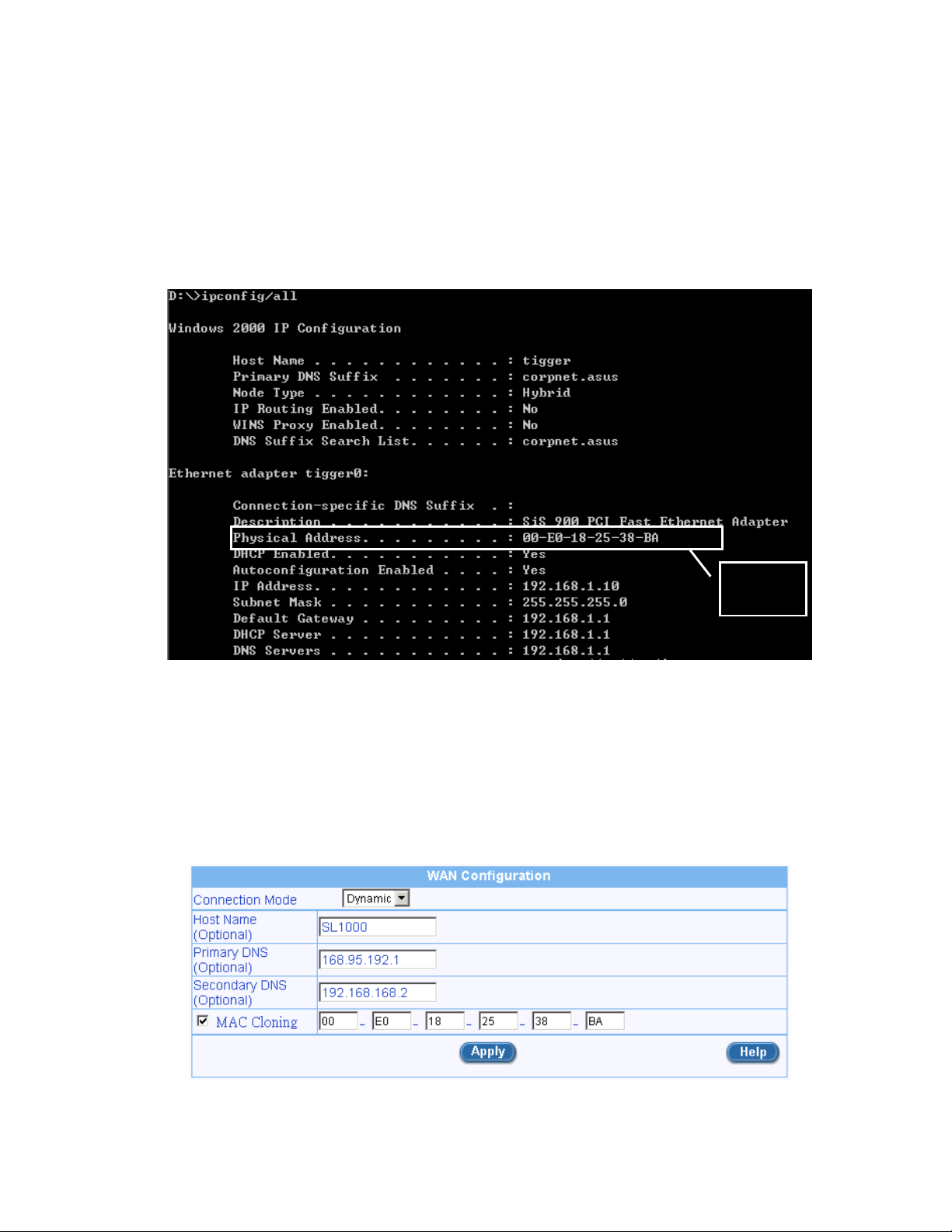
3. Enter ipconfig/all in the Command Prompt. The following figure shows where the MAC address of your
network card is displayed. Note that if you have more than one network card installed on your computer,
make sure you get the MAC address from the correct network card.
MAC
2.2.3.3 How to configure MAC cloning?
MAC cloning option is available only when Dynamic mode (i.e. DHCP client) is selected for the WAN connection
mode. Follow the procedures below to configure MAC cloning. is configured Configured MAC Cloning(Only in
Dynamic Mode) using WAN→WAN→MAC Cloning.
1. Open the WAN configuration page.
2. Select “Dynamic” for the WAN connection mode.
3. Check the check box for MAC Cloning and enter the MAC address in the space provided (see the
following figure). To find the MAC address for your PC, please refer to “How to find out the MAC address
of my network card?” for instructions.
Page 4 Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc.

INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
2.2.4 Why can’t I see the default gateway IP after completing the configuration for the WAN port in DHCP or PPPoE connection mode?
Sometimes this may happen. Just lick on Apply button again to refresh the screen.
2.3 LAN
2.3.1 Why is there no response from the browser after the LAN IP of the Internet Security is changed?
This is because LAN IP was changed, and the browser still waits for the response from the old IP. You’ll have to
connect to the router using the new IP address. Note that you may have to change the IP of your PC if you had
configured its IP manually or renew the IP lease of your PC if you had configured it to receive IP from the DHCP
server. Please see “How to configure my PC and the Internet Security Router to reside in the same subnet?” for
instructions.
2.3.2 Why can’t I login into the Internet Security Router after its LAN IP is changed?
To reconnect your PC and the Internet Security Router after its LAN IP is changed, you need to make sure that
your PC’s IP address is in the same subnet as that of the Internet Security Router. Please see “How do I know if
my PC and the LAN of my Internet Security Router are in the same subnet?” and “How to configure my PC and
the Internet Security Router to reside in the same subnet?” for instructions.
2.4 Firewall and NAT
2.4.1 How to setup a virtual server?
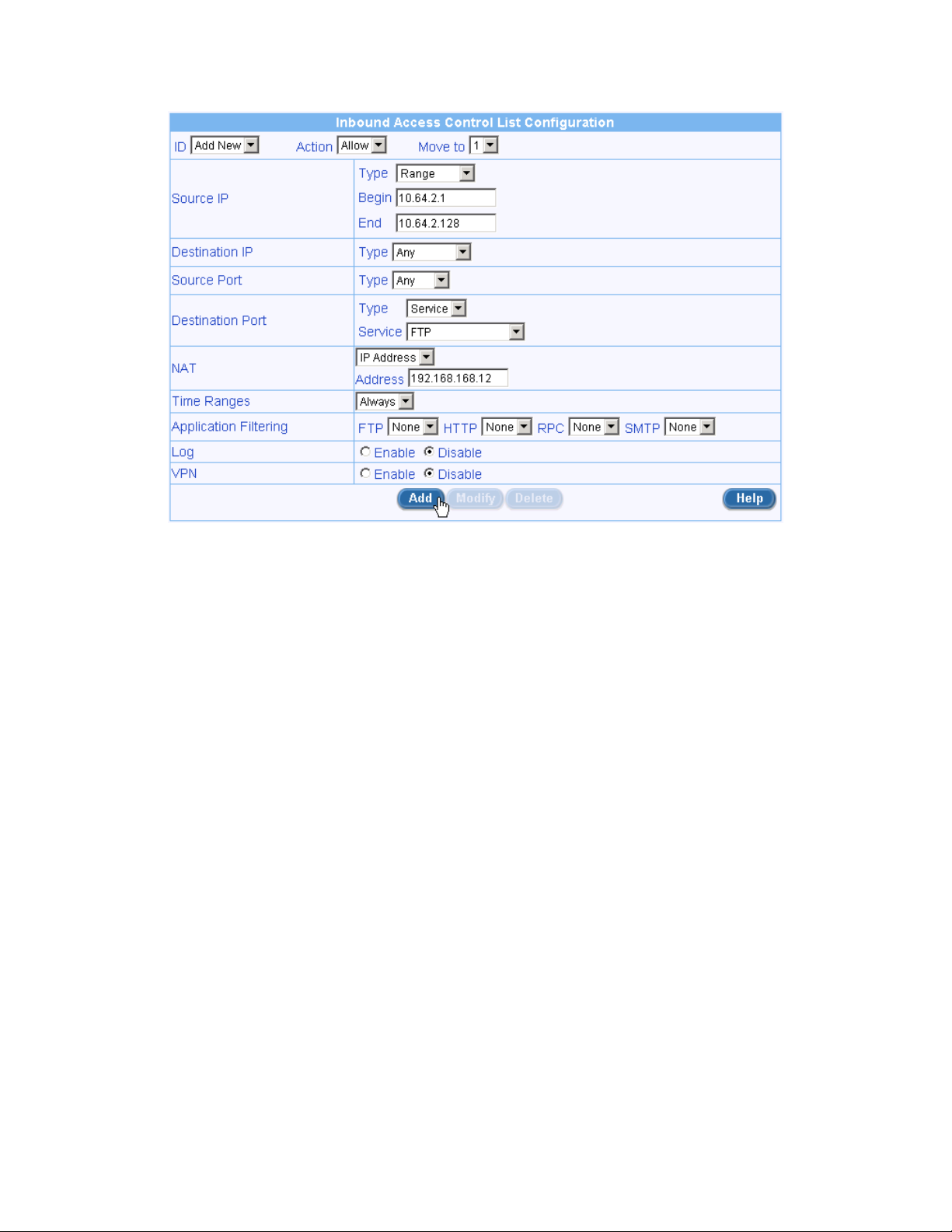
It is best explained using an example. Let’s say you want to set up a FTP server in your LAN and have the firewall
control the access and offer protection for the FTP server. The following figure illustrates how an inbound ACL
rule is created for the FTP server to control access of the server. This ACL rule only allows hosts with the IP in
the range of 10.64.2.1 to 10.64.2.128 to access the FTP server. Note that the IP address of the FTP server is
192.168.168.12, which is a private IP address.
1. Open the inbound ACL rule configuration page (Firewall è Inbound ACL).
2. Enter source IP to specify which hosts are allowed to access the FTP server – in this case, hosts w/ IP in
the range of 10.64.2.1 to 10.64.2.128.
3. Select “Service” for the destination port type and also select “FTP” service from the service drop-down list.
4. Enter the IP address of the FTP server
a) Select “IP Address” as the NAT type.
b) Enter FTP server IP address in the NAT Address field: in this case, 192.168.168.12.
5. You may enter additional options for access control, such as time range and application filtering for FTP.
Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc. Page 5
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
2.4.2 How to setup virtual DMZs?
The number of virtual DMZ hosts supported depends on the number of public IP addresses provided by your ISP.
2.4.2.1 Single DMZ
The following figure shows an example of a network supporting a DMZ, a web server as well as several local
hosts accessing the Internet via NAT. The address mapping for the DMZs and the web server are also illustrated
in the figure – DMZ: (192.168.1.11 ↔ 1.1.1.1), and the web server (192.168.1.12 ↔ 1.1.1.1). The local hosts,
host1 and host2, access the Internet using the WAN IP address: 1.1.1.1. This scenario is probably the most often
encountered scenario by most users having only one public IP address provided by ISPs.
Page 6 Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc.
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
address
Internet
Internet Security Router
LAN: 192.168.1.1
DMZ:
192.168.1.11
Pub: 1.1.1.1
WAN: 1.1.1.1
Web server
192.168.1.12
Pub: 1.1.1.1
Host1:
192.168.1.21
Host2:
192.168.1.22
Follow these steps to set up the Internet Security Router to support multiple DMZs.
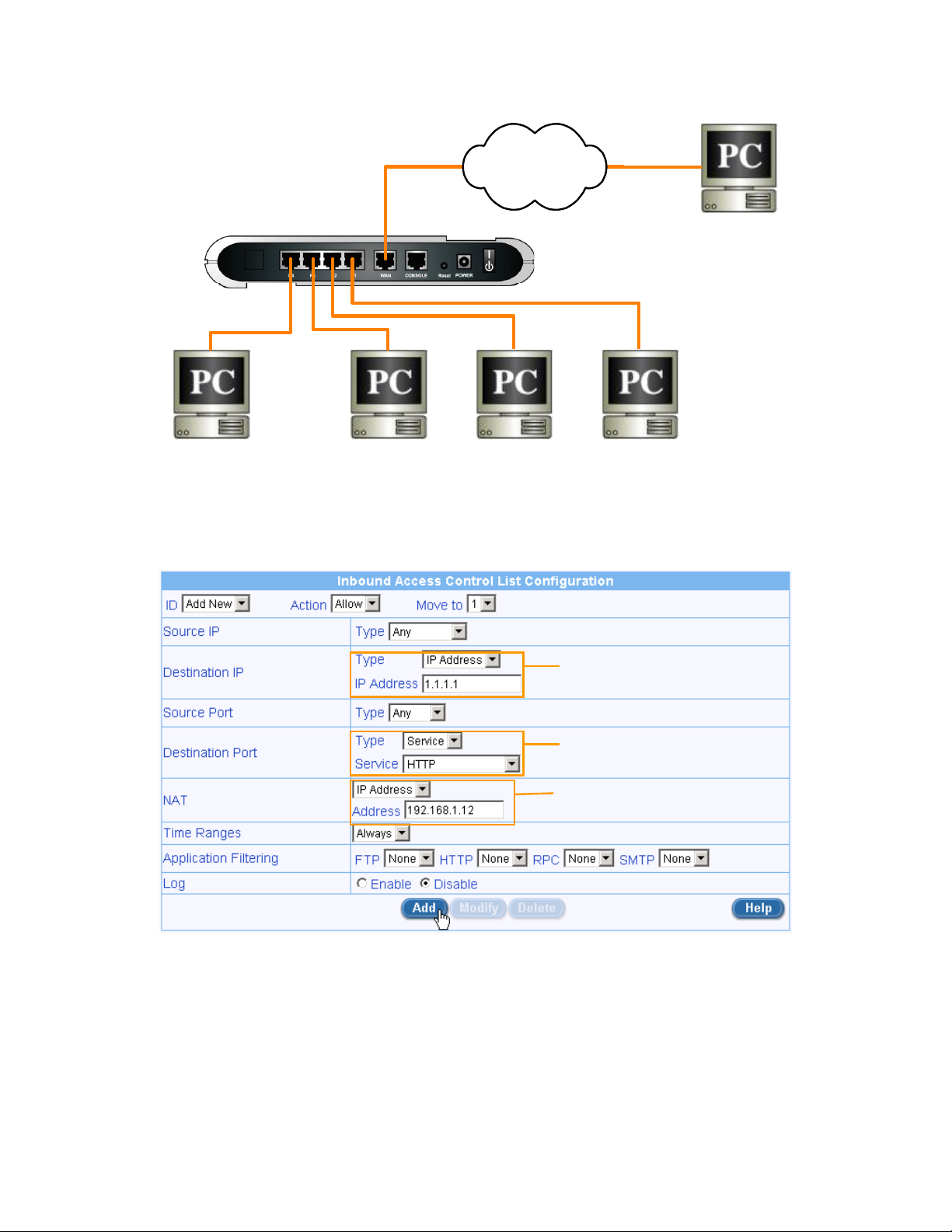
1. Create a firewall ACL rule for the web server
Enter the destination IP of
the inbound packets.
External PC
Select HTTP service for
the web server
Select “IP Address” and
enter the mapping private IP
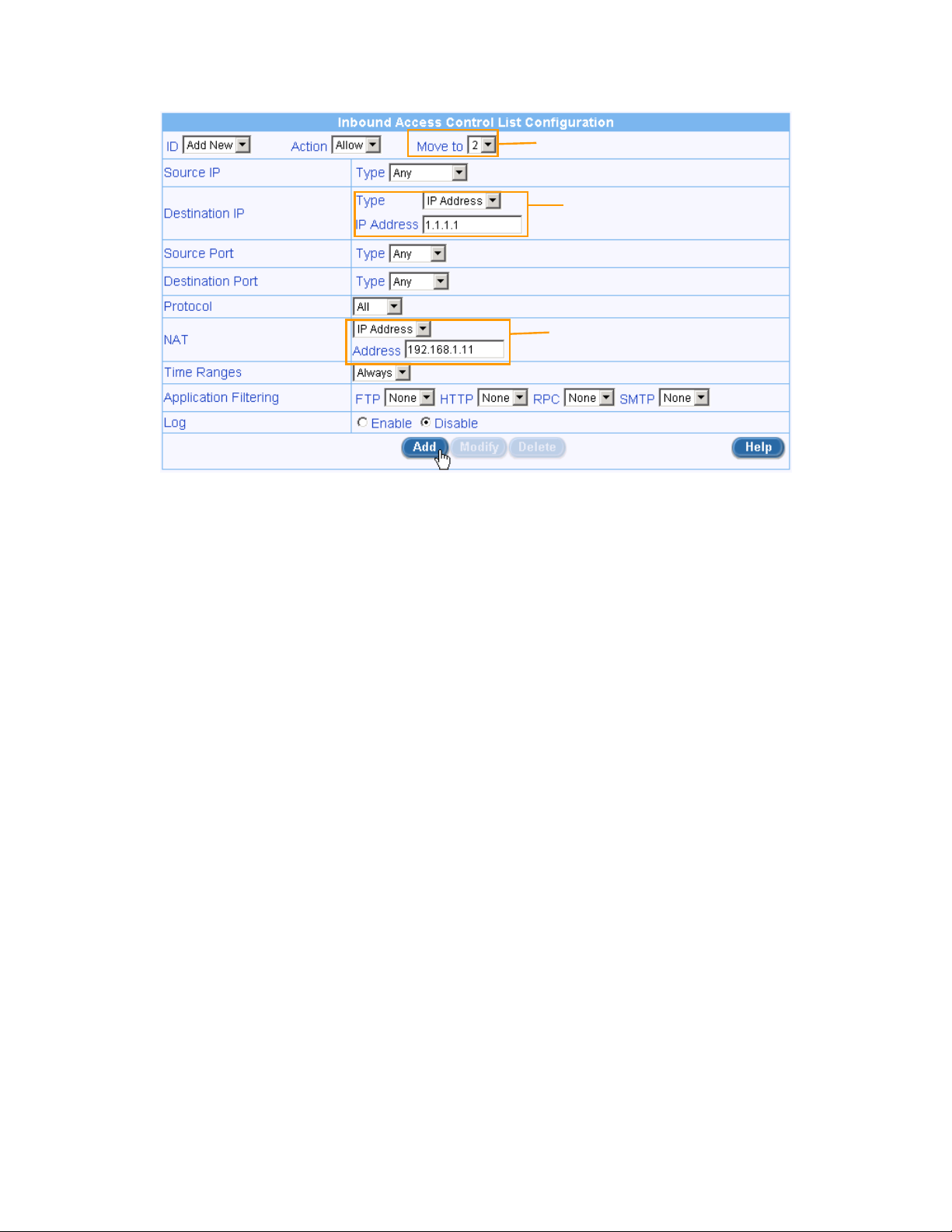
2. Create a firewall ACL rule for the DMZ
Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc. Page 7
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
address
Make sure the priority is lower
than that of the web server
Enter the destination IP of
the inbound packets.
Select “IP Address” and
enter the mapping private IP
3. Create an outbound policy for local hosts to access the Internet. This step may be skipped because the
Internet Security Router comes with a default firewall outbound ACL rule to allow all the outbound
packets to use NAT (using the WAN IP address) to access the Internet.
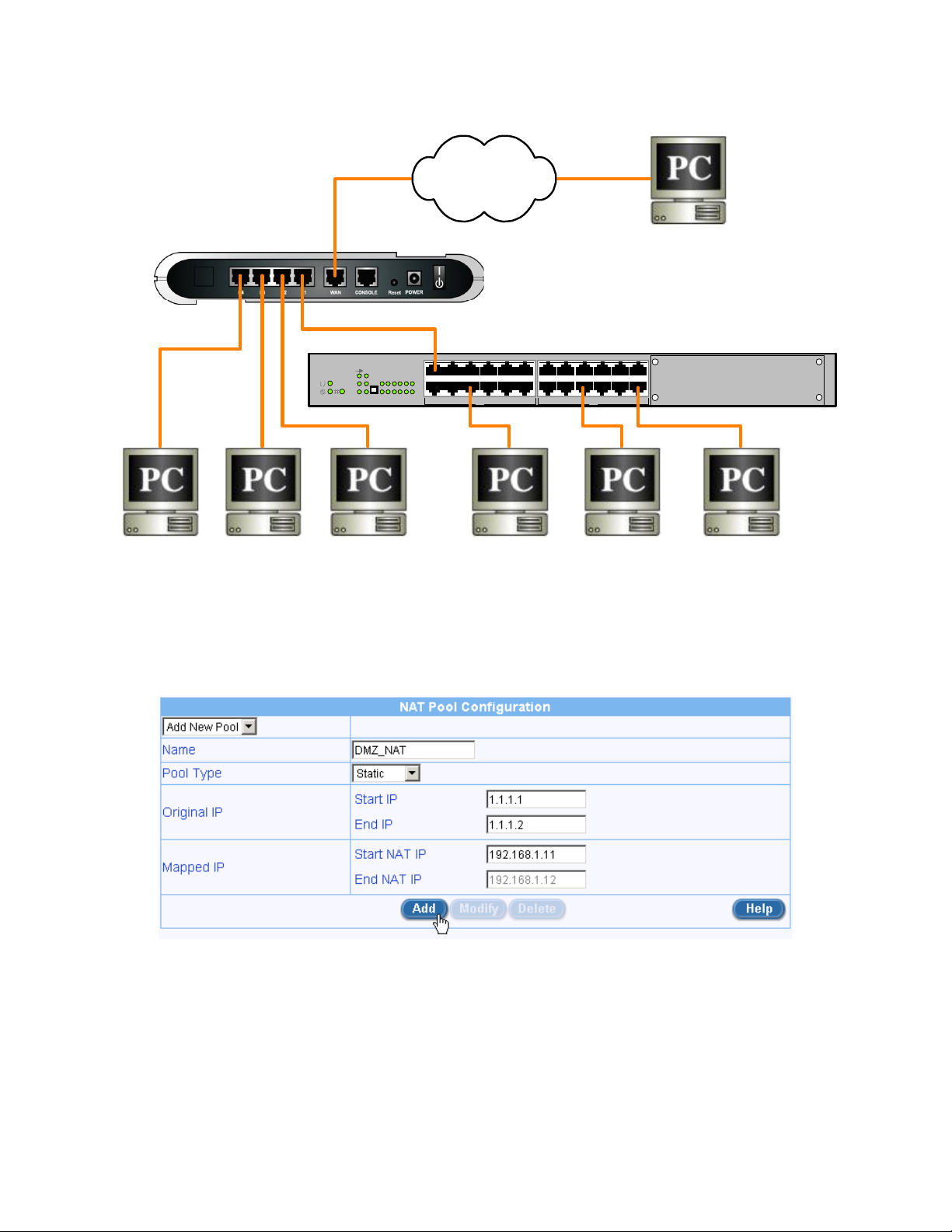
2.4.2.2 Multiple DMZs
The following figure shows an example of a complicated network supporting multiple DMZs, a web server as well
as several local hosts accessing the Internet via NAT. The address mapping for the DMZs and the web server are
also illustrated in the figure – DMZ1: (192.168.1.11 ↔ 1.1.1.1), DMZ2: (192.168.1.12 ↔ 1.1.1.2), and the web
server (192.168.1.13 ↔ 1.1.1.3). The local hosts, host1 to host3, access the Internet using the WAN IP address:
1.1.1.1.
Page 8 Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc.
INTERNET SECURITY ROUTER FAQ
Internet
Internet Security Router
WAN: 1.1.1.1 External PC
LAN: 192.168.1.1
12x
6x
5x
B
Host2:
192.168.1.22
DMZ1:
192.168.1.11
Pub: 1.1.1.1
DMZ2:
192.168.1.12
Pub: 1.1.1.2
C
Ethernet
A
Web server:
192.168.1.13
Pub: 1.1.1.3
789101112
123456
8x2x9x3x10x4x11x
7x
1x
7x
12x
1x
6x
5x
A
Host1:
192.168.1.21
8x2x9x3x10x4x11x
Follow these steps to set up the Internet Security Router to support multiple DMZs.
1. Setup an inbound policy for the DMZs
a) Create a “static” NAT address pool for the block of public IP addresses provided by your ISP.
Switch
Host3:
192.168.1.23
b) Create a firewall ACL rule for the DMZs
Copyright 2003-2004, ASUSTeK Computer, Inc. Page 9
 Loading...
Loading...