Page 1

ArubaActivate
User Guide
Page 2

Copyright Information
© Copyright 2018 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP.
Open Source Code
This product includes code licensed under the GNU General Public License, the GNU Lesser General Public
License, and/or certain other open source licenses. A complete machine-readable copy of the source code
corresponding to such code is available upon request. This offer is valid to anyone in receipt of this information and
shall expire three years following the date of the final distribution of this product version by Hewlett Packard
Enterprise Company. To obtain such source code, send a check or money order in the amount of US $10.00 to:
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company
Attn: General Counsel
3000 Hanover Street
Palo Alto, CA 94304
USA
0511311-1 | October 2018 Activate | User Guide
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents 3
Welcome to Aruba Activate! 5
Get started here... 5
...see what's new... 5
...or find the information you need 5
Basic Provisioning Workflow 6
Rules Overview 6
Troubleshooting 8
Device Setup and Provisioning 10
Create and Manage Folders 10
Define Rules 13
Assign Devices to Folders 19
Manually Add Devices 20
Managing Users 23
View User Information 23
Manage User Accounts 25
Managing Device Data 27
Monitor all Devices 27
Monitor Individual Devices 31
Create Whitelists 33
Export Device Data 34
ArubaActivate APIs 35
Inventory API-Update Example 36
Inventory API-Query Example 37
File API-Query Example 42
Folder API-Update Example 44
Folder API-Query Example 45
Rule API-Update Example 46
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Table of Contents | 3
Page 4

Rule API-Query Example 47
Customer API-Query Example 49
Whitelist Query API 50
Firmware API-Query Example 52
Device History API-Query Example 53
Sample Curl Code 54
Client.java Sample 55
Request.java Sample 55
What's New in Activate 62
Known Issues 62
Improvements and Modifications 62
64
4 | Table of Contents Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 5

Chapter 1
Welcome to Aruba Activate!
ArubaActivate is a cloud-based service that helps provision your Aruba devices and maintain your inventory.
For network administrators with experience deploying Aruba infrastructure, installing and configuring one or two
individual access points (APs) is a relatively simple and straightforward process. Provisioning APs in a large
corporate network is also a straightforward process, accomplished through ArubaOS Layer-2 discovery, DHCPor
DNS. But what if you want to install an AP at a branch office or remote site where no network administrator is
available? Or what if you need to deploy several APs all at once? A simple solution for this type of deployment is
ArubaActivate.
Activate automates the provisioning process, allowing a single IT technician to easily and rapidly deploy devices
throughout a distributed enterprise. When your company orders a new access point (AP) from Aruba, that device is
automatically added to your inventory in Activate. Once a device is in your inventory it can be automatically or
manually associated to a folder and provisioning rule. A remote technician only needs to connect the Instant AP to
the Internet, and that device will securely connect to Activate, retrieve its provisioning information, then use the
provisioning information to connect to its configuration master (controller or AMP) and update its configuration. This
entire process takes less than ten minutes and requires no human intervention, allowing for true zero-touch
provisioning.
Get started here...
The Basic Provisioning Workflow section of this guide provides a general overview of each step required to configure
your Aruba Instant points for remote deployment. If you are new to ArubaActivate, this is a good place to start.
...see what's new...
The What's New in Activate section of this guide describes the latest changes and improvements to the Aruba
Activate Release 6 service.
...or find the information you need
Other sections of this guide include detailed information on how to set up, monitor, and manage your devices and
device data. Select any of the headings in the navigation bar or click any of the following links for step-by-step
instructions on how to accomplish a specific task using ArubaActivate.
l Device Setup and Provisioning on page 10: Create and manage device folders, configure provisioning and
notification rules, and assign devices to a specific folder.
l Managing Users on page 23: View and manage your company's user accounts, and set folder permission levels
for each account.
l Managing Device Data on page 27: Review configuration details for a specific device, or view and sort an
inventory list of all your Instant or Remote AP devices. You can create and export whitelists of Arubadevices
that can be input into your controller or an external database.
l The Rules Overview on page 6 provides detailed information about the different rule types that supply
provisioning information to Instant APs, auto-assign devices to folders, and trigger notification events.
l Troubleshooting on page 8 provides suggestions for troubleshooting and fixing common issues.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Welcome to Aruba Activate! | 5
Page 6
Basic Provisioning Workflow
Activate enables zero-touch auto-configuration of Instant APs by associating the devices to the configuration master
(your AirWave server) from which they can retrieve their configurations. Before you begin setting up ArubaActivate
to provision your APs, though, you should be able to answer the following questions:
l Will all my devices have similar configuration requirements?
l Do I know which configuration I want to assign to my device? An Instant AP must be assigned to an organization-
specific configuration (folder/group) on an AirWave server. If your distributed APs have different requirements,
you may want to identify multiple configurations for different AP types or deployment locations.
Step 1: Identify Configurations
Before you can provision new Instant APs, you must identify the AirWave Management Platform (AMP) or Aruba
controller information you want to push to new devices.
Step 2: Create Folders
Folders allow you to group devices based on common provisioning scenarios. Each folder may contain one or more
rules. Create a new folder for each AMP, or AMP group policy. You may also find it useful to create groups of folders
for different device types or branch office locations, then add subfolders with Instant AP provisioning rules under
those higher-level folders.
Step 3: Define Rules
Create custom rules to supply provisioning information to Instant APs. You can also use rules to automatically
assign devices to folders, and identify events that will trigger email notifications.
Step 4: Select Devices
Sort and filter the device list to display just those devices you want to assign to a new folder. If you want to assign
new, unprovisioned devices, consider sorting the list by the "Last Seen" or "Ship Date" table columns to display the
newest entries at the top of the list.
To convert an instant AP to a remote AP, you must first create a rule that will supply provisioning information to the
AP and add the remote AP's MAC address to the remote AP whitelist on the controller. ArubaActivate allows you to
create a remote AP whitelist that you can input into Aruba controller.
Step 5: Assign Devices to Folders
All new devices are assigned to the default folder. When you assign devices to a different folder, the device will
immediately inherit the rules within the folder.
Rules Overview
ArubaActivate supports three categories of rules:
l Provisioning Rule: Provision devices with configuration master information.
l Move to Folder Rule: Move all devices matching certain criteria to the specified folder. You can move devices
based on shipping info, device category, part number, or customer PO.
l Notification Rule: Notify recipients when a device ships to your company, or when a specific provisioning or
"move to folder" rule has run, or the device requests a new firmware version.
Each rule category is described in detail in the sections below.
6 | Welcome to Aruba Activate! Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 7

Provisioning Rules
When a device in factory-default mode sends its MAC address, serial number, and mode to ArubaActivate, Activate
will respond with proper provisioning information based on the device's operating mode and rule definition within a
folder. Activate will only respond to a device when the device is associated with a customer that has enabled
Activate by configuring a provisioning rule.
Table 1:
Provisioning Rule Types
Rule Type Description
IAPto AirWave An IAP-to-AirWave rule instructs Activate to send a device operating in Instant AP
mode the IP address of the AirWave (AMP) server that will act as the device's
configuration master, and the AMP organization and shared secret. AMP uses
the organization information to segregate the AP into configuration and reporting
groups. The shared secret sent by Activate acts as the trust mechanism between
the Instant AP and AMP.
NOTE: The first device added to a new organization within an AMP must be
manually authorized using the AMP user interface. All subsequent APs in that
organization with the proper shared secret will be auto-authorized without human
intervention into the AMP.
IAP to RAP This rule instructs Activate to send a device operating in Instant mode the IP
address of the remote AP's configuration master, and instructions to convert the
device to operate in remote AP mode. IAP-to-RAP rules require you to specify an
APgroup for the device, but this information is not sent directly to the AP. When
you use Activate to generate a remote APwhitelist to upload into the controller,
the device's AP group is included in that whitelist information. The AP group
instructions tell the controller how to configure the remote AP. For more
information on creating a remote APwhitelist, see Create Whitelists.
IAP to CAP This rule converts an Instant AP to a campus AP, and provisions the campus AP
to communicate with its configuration master controller.
Switch to AirWave A Switch-to-AirWave rule instructs Activate to send an Aruba Mobility Access
Switch (MAS) or a HPE ArubaOS Switch, the IP address of the AirWave (AMP)
server that will act as the device's configuration master, and the shared secret for
the server. AirWave uses the group and folder information in the rule to
segregate the switch into configuration and reporting groups. The shared secret
sent by Activate acts as the trust mechanism between the switch and the AirWave
server.
Controller to AirWave A Controller-to-AirWave rule instructs Activate to send the controller the IP
address of the AirWave (AMP) server that will act as the device's configuration
master, the Activate folder and group to which the controller should be
associated, and the AMP shared secret, which acts as the trust mechanism
between the controller and AMP server.
Branch to Master Controller Provision an Aruba branch controller to communicate with its configuration
master controller.
Managed Device to Master
Controller
Provision a managed device to communicate with its configuration master
controller.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Welcome to Aruba Activate! | 7
Page 8

Move-to-Folder Rules
A move-to-folder rule automatically moves a device to a chosen folder based upon specific device criteria. A
Category move-to-folder rule moves devices to a selected folder based upon the category of that device. Activate
allows you to define category move-to-folder rules for each of the following category types:
l Instant AP
l Remote AP
l controller
l Switch
Part Number move-to-folder rules move APs to specific folders according to the device's part number. Customer
PO and Shipping Info rules move APs that match a specified string contained within customer PO or shipping data
for that device.
Notification Rules
A Shipment notification rule sends an email notification when Activate receives information that devices are being
shipped to your company. (Note, however, that Activate may not receive shipment information until up to a day after
the equipment has actually left Aruba or your device reseller.) A shipment notification rule can only be assigned to
the default folder, because that the folder to which all new devices are assigned.
Provisioning rules send email notifications when a device requests provisioning information from Activate, and FW
Check rules notify users when the device requests a firmware upgrade from Activate. The Move-to-folder
notification rule alerts users when devices are automatically or manually moved to another folder.
See also:
Creating a New Rule
Modifying an Existing Rule
Troubleshooting
Use the following steps to troubleshoot problems using ArubaActivate.
Connectivity Issues
Ensure that the Instant AP can access
l Verify that the AP has a valid IP address by associating the AP with the SSID and viewing the IP address.
l Verify that the network does not have a proxy server. (An Instant AP does not support auto-detection of proxy
servers.)
l Verify that the subnet does not contain another Instant AP.
l Make sure the local DHCP or DNS servers are not providing provisioning data to the Instant AP.
l Verify that the AP is in factory- default mode. You can reset an Instant AP back to factory-default mode by
pushing the factory reset button or clearing the configuration from the Instant AP’s WebUI.
l Check to make sure the Instant AP is running ArubaOS 3.0 or later. If the Instant AP is running an earlier version
of ArubaOS, click Check for New Firmware in the the Instant AP’s WebUI. Upgrade to the recommended
version, and the Instant AP should auto-connect to Activate for provisioning.
device.arubanetworks.com:443
by verifying the following:
Activate Issues
The device must be included in the Activate inventory and properly associated with folder and rule.
l Make sure the device shows up in your device inventory. You can validate this by searching for the MAC or serial
number in the Devices list.
8 | Welcome to Aruba Activate! Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 9

l Make sure the AP resides in a folder with proper rule.
l Make sure there are no historical communication history records with an error status.
AMP Configuration Master Issues
Ensure the AP is retrieving the proper configuration by checking the following issues:
l Verify AMP has an IP address that is exposed to the Internet port 443.
l Verify AMP is not handing back an internal IP address to the device in the template. You can see the IP address
that the Instant AP uses to communicate with AMP in the Instant AP’s WebUI. You may need to change the
template variable ams-ip %manager_ip_address% to hardcode the external IP address. The new setting
would be in the format
l Make sure AMP contains a group and folder that correlates to the organization name configured in the
provisioning rule in Activate.
l Verify that template exists for the AMP group that correlates to the organization name configured in the
provisioning rule in Activate.
l Check to make sure this device is not the first AP that has been added for this organization. If it is the first AP for
this organization, it will show up in APs/Devices > New list in the AMP and will need to be manually added.
l Set the Automatically Authorize Virtual Controller Mode setting in the the AMP Setup > General >
Automatic Authorization section to Manage Read/Write.
l Set the Add New Thin APs Location setting in the Groups > Basic > Automatic Authorization section to
Same Group/Folder as Discovering Device.
l Set the Audit Configuration on Devices setting in the Groups > Basic > Basic section to Yes.
ams-ip xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
.
Browser Compatibility
The Activate application has been designed to work best with Google Chrome Browser version 40+. You may
experience issues while using other browsers.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Welcome to Aruba Activate! | 9
Page 10

Chapter 2
Device Setup and Provisioning
When an APin factory-default mode powers on and connects to the Internet, it will automatically check into Aruba
Activate. Activate supplies provisioning data to the Instant AP, which will then communicate with its configuration
master (controller or AirWave Management Platform). The AP's configuration master will push the configuration and
any required firmware update to the AP.
If the requirements for these devices ever change and you need to reprovision an AP, move the AP to another folder
within Activate, then set the APback to its factory-default setting by pushing the factory reset button. The AP will
repeat the provisioning process, applying the provisioning rules in its new folder.
Devices are grouped into folders that can contain a set of provisioning and email notification rules. If you want to
group your devices by unique provisioning requirements, you can create separate folders that each contain different
provisioning rules. You can also group devices by location or device type by creating folders or subfolders for each
device type or installation site.
For information on setting up ArubaActivate to provision your devices, refer to the following sections of this user
guide:
l Create and Manage Folders: Define folders for your devices, then view and manage the list of folders.
l Define Rules: Create and edit provisioning, folder, or notification rules to supply provisioning information to Aruba
devices, auto-assign devices to folders, and trigger notification events.
l Assign Devices to Folders : Filter and sort the Devices list to select the devices you want to move to a different
folder. After the move, the devices will inherit the rules in the new folder. You can automatically move devices
into a folder by configuring a move-to-folder rule based on shipping info, purchase order, device category, or part
number.
Create and Manage Folders
Each folder can have one or more rules that assign provisioning information to Instant APs, and identify events that
will trigger email notifications. When you move a device into a folder, the device will inherit the rules in the folder. A
users' access to ArubaActivate depends upon the folder to which the user account is assigned. Users cannot
assign devices to a folder to which they do not have access.
When the first user for your company accesses ArubaActivate, the system shows only one folder, the top-level
default
and notification rules, then you need to create additional folders. You must create at least one unique folder for each
configuration master. A folder can have both an Instant AP provisioning rule and a IAP-to-remote AP provisioning
rule, but cannot have more than one provisioning rule of each type. You may also find it useful to create groups of
folders for different device types or branch office locations, then add subfolders with provisioning rules under those
higher-level folders.
folder. If you want to use the Activate to provision your network devices with different configuration policies
Creating a New Folder
To add a new folder to the Folders list:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Click the New link in the title bar of the Folders list. The Create a New Folder window appears.
3. Enter the following information for the folder:
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 10
Page 11

l Name: Name of the new folder. The folder name must be 100 characters or less, and cannot include the
characters ?, # or &.
l Parent: The new folder's parent folder. The new folder will be created under the selected parent.
l Notes: (Optional) Use this field to add any additional notes about the folder.
4. Click Done to save the new folder.
Sort and Filter the Folders List
The Folders list displays the following information types for each folder.
Table 2:
Folders List
Column Description
Name Name of the folder
Parent Name of the parent folder. A top level folder will have the Default parent folder. Lower-level sub-
folders will display their immediate parent folder in this column.
Devices Number of devices in the selected folder. If a folder contains subfolders with their own devices, this
column will still only show the devices assigned to that folder, not its subfolders.
By default, the Setup page displays aggregate information for all folders. When you select an individual entry in the
Folders list, the Folder Detail section at the bottom of the window displays information about the user that created
the folder, the date it was created, and any folder notes. The Rules and Users tables on the Setup page
automatically filter to display just those rules and users associated to the selected folder.
ArubaActivate allows you to sort and filter folder data to display just the information you need. By default, the
Folders list displays the all folders, sorted by folder name. Click any of the Folders list column headings to sort the
information in the list by that column criteria. You can also click the filter icon ( ) and select which entries to
display. The filter mechanism for each heading depends upon the type of column, and number of unique entries in
that column.
Filtering Small to Medium-Sized Folders Lists by Folder Name, Parent or Customer
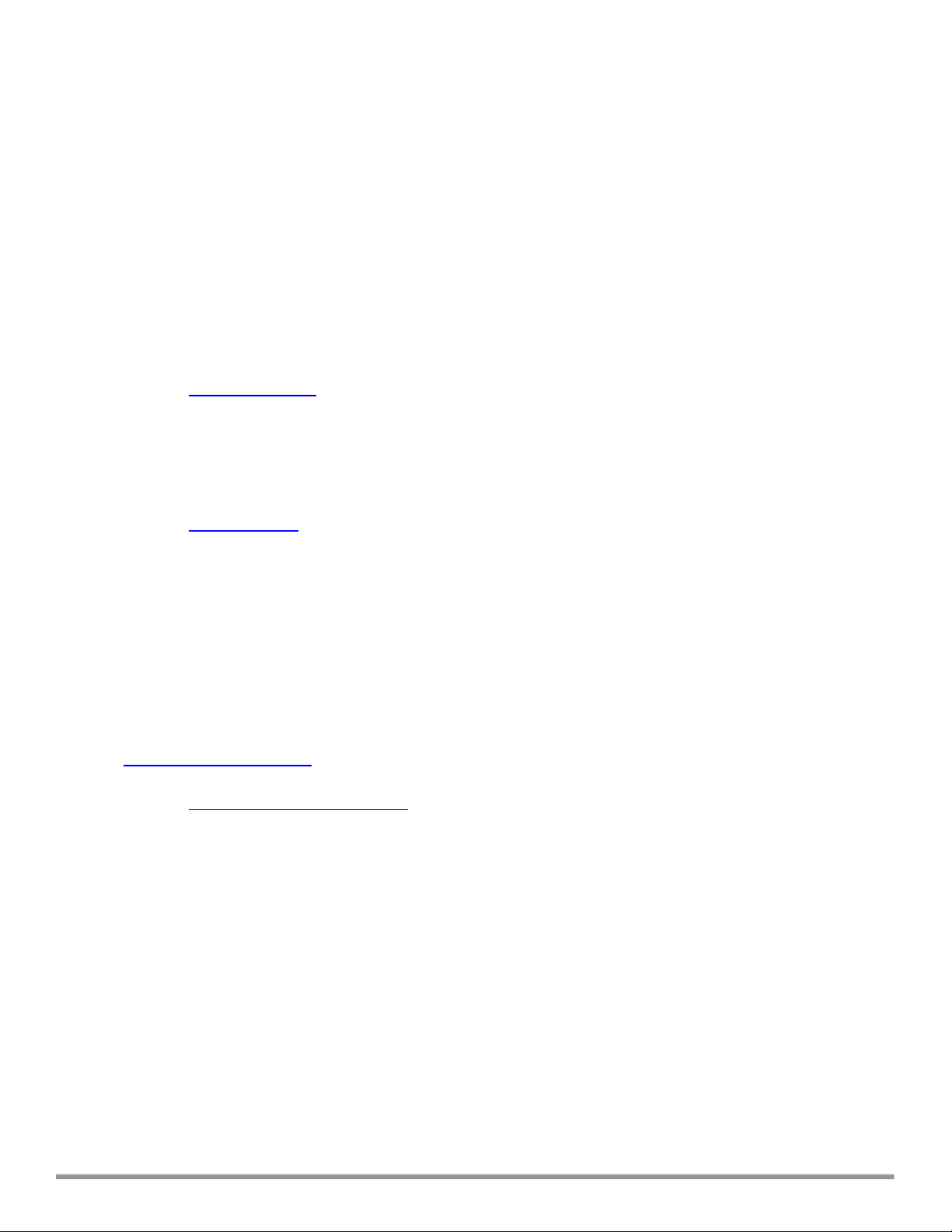
To filter data in a Folders list with fewer than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Folder Name, Parent or Customer column heading. The filter displays a
checkbox for each entry type.
3. To select an individual entry, uncheck the select all option and select the entry you want to display.
4. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
11 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 12
To remove a filter:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a column heading with an active filter.
2. Click the clear filter icon ( ) in the filter header to clear the current filter settings.
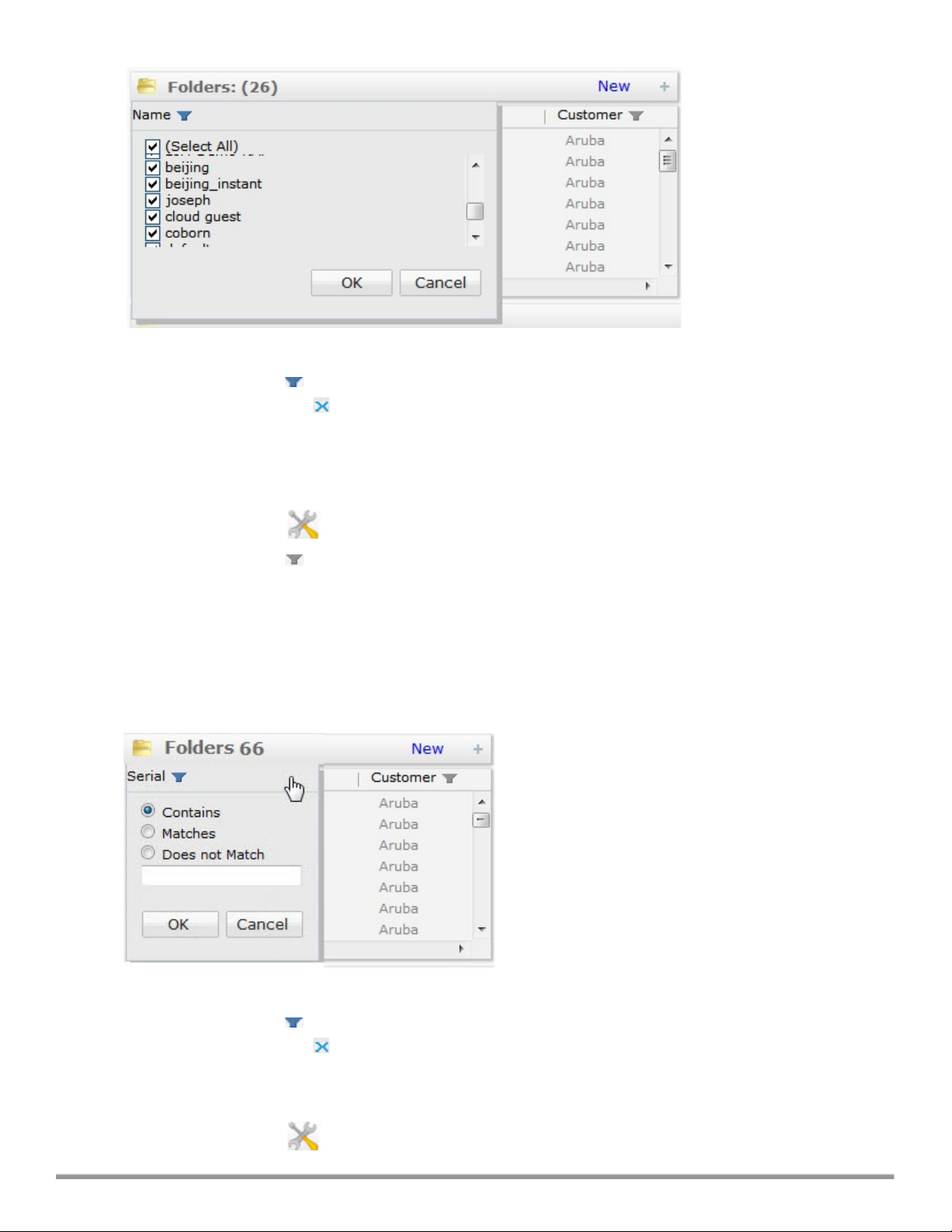
Filtering Large Folders Lists with 50+ Unique Entries by Folder Name, Parent or Customer
Columns with more than fifty unique entries allow you to search within that column for a specific text string.
To filter data in a column with more than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Folder Name, Parent or Type column heading.
3. Select one of the following search types:
l Contains: Search for entries that contain the search string.
l Matches: Search for entries that exactly match the search string
l Does not Match: Search for entries that do not exactly match the text string
4. Enter the search string into the search field.
5. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
To remove a filter:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a column heading with an active filter.
2. Click the clear filter icon ( ) in the header to clear the current filter settings.
Filtering Folders Lists by Devices, Users or Rules
To filter the Folders list by the numbers of associated devices, users or rules:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 12
Page 13

2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Devices, Users or Rules column heading.
3. Select All to view all entries, or select and click the drop-down list to search the list using one of the following
options:
l >: Display entries with a value greater than the search value.
l >=: Display entries with a value greater than or equal to the search value.
l <: Display entries with a value less than the search value.
l <=:Display entries with a value less than or equal to the search value.
4. Enter a number into the search field.
5. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
To remove an filter:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a column heading with an active filter.
2. Click the clear filter icon ( ) to clear the current filter settings.
Modifying an Existing Folder
Any folder created by a user can be deleted or modified. Note that you cannot edit or delete the default folder, or
delete any folder that contains a subfolder, or has associated users, rules or devices.
To delete or modify the description and settings of an existing folder:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select any folder entry from the Folders list.
3. Click the Edit button below the Folder Detail section at the bottom of the page.
4. Change the folder name, folder parent or note fields as desired, then click Done to save your settings.
Define Rules
ArubaActivate uses rules to supply provisioning information to Aruba devices, auto-assign devices to folders, and
trigger notification events. A provisioning rule supplies provisioning information when a device in factory-default
mode communicates with the cloud. When Activate receives information about a device's current operating mode,
Activate responds with proper provisioning information based on the devices operating mode and folder rule
definitions.
Refer to the Rules Overview for detailed information about of the different provisioning, notification and move-to-folder
rule types supported by ArubaActivate.
Creating a New Rule
To create a new provisioning rule:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Click the New link in the title bar of the Rules list. The Create a New Rule window appears at the bottom of the
page. The individual configuration settings displayed in this window vary, depending upon the type of rule you
configure.
l Table 3 describes Provisioning rule settings.
l Table 4 describes Move to Folder rule settings
l Table 5 describes Notification rule settings.
3. Enter a value in each field for the selected rule type, then click Done to save your settings.
13 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 14
Table 3:
Provisioning Rule Configuration Settings
Provisioning Rule Type Provisioning Rule Settings
IAP to AirWave Provision an Instant AP (IAP) to communicate with its configuration master AirWave
(AMP) server. To create an IAP-to-AirWaverule, configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select IAP to AirWave.
l AMP IP: The IP address of an AirWave server that will act as the device's
configuration master. This field does not support DNSnames.
l Shared Secret: The shared secret sent by Activate acts the trust mechanism
between the Instant AP and AMP.
l Organization: AMP uses this organization information to segregate the AP into
a configuration policy.
l AMP-CN: Specify the common name of the AirWave server.
l Controller: IP address of the controller that will manage the IAP.
l Controller-MAC: MAC address of the controller that will manage the IAP.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule.
IAP to RAP Convert an Instant AP to a remote AP (RAP), and provision the remote AP to
communicate with its configuration master controller. To create an IAP-to-RAPrule,
configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select IAP to RAP(Controller).
l AP Group: Name of the AP group to which the device will be associated.
l Controller: IP address of the controller that will manage the RAP.
l Controller-MAC: MAC address of the controller that will manage the RAP.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule.
IAP to CAP Convert an Instant AP to a campus AP, and provision the campus AP to
communicate with its configuration master controller. To create an IAP-to-CAPrule,
configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select IAP to CAP(Controller).
l AP Group: The AP group defines a group of configuration settings for a campus
AP. Enter the name of the AP group to specify the group into which the device
will be placed.
l Controller: IP address of the controller that will manage the campus AP..
l Persist Controller IP: Select this check box if you want the controller IPto
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 14
Page 15
Table 3:
Provisioning Rule Configuration Settings
Provisioning Rule Type Provisioning Rule Settings
persist.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule.
Switch to AirWave Provision an Aruba Mobility Access Switch (MAS) or an HPE ArubaOS Switch to com-
municate with its configuration master AirWave (AMP) server. To create a Switch-toAirWave rule, you must configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select Switch to AirWave.
l AMP IP: The IP address of an AirWave server that will act as the device's
configuration master. This field does not support DNSnames.
l Shared Secret: The shared secret sent by Activate acts the trust mechanism
between the Instant AP and AMP.
l AMP Group: The AMP group defines a group of configuration settings for an
Aruba switch. Enter the name of the AMP group to specify the group into which
the device will be placed.
l AMP Folder: An AMP folder defines permissions for devices placed within that
folder. Enter the name of an AMP folder to specify the folder into which the
device will be placed.
l Controller: If your deployment requires a site-to-site tunnel between the Mobility
Access Switch or HPE ArubaOS Switch and AirWave, select the MAC address
of the controller that will act as a VPN concentrator for the AirWave server side
of the VPNtunnel.
l Backup Ctrl IP: If your deployment has a backup controller, specify the
IPaddress of the backup controller.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule.
Branch to Master Controller Provision a branch controller to communicate with the master controller from which
the branch will download its configuration. To create abranch-to-master-controller
rule, configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select Branch to Master Controller.
l Primary Controller: MAC address of the primary master controller. Activate
sends a branch controller whitelist with information about the controllers in this
folder to the master controller with this MAC address.
l Primary Ctrl IP: IP address of the primary master controller.
l Backup Controller: (Optional) MAC address of a backup master controller, for
deployments that require Layer-3 redundancy.
l Backup Ctrl IP: (Optional) Enter the IP address of the secondary (backup)
master controller.
15 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 16
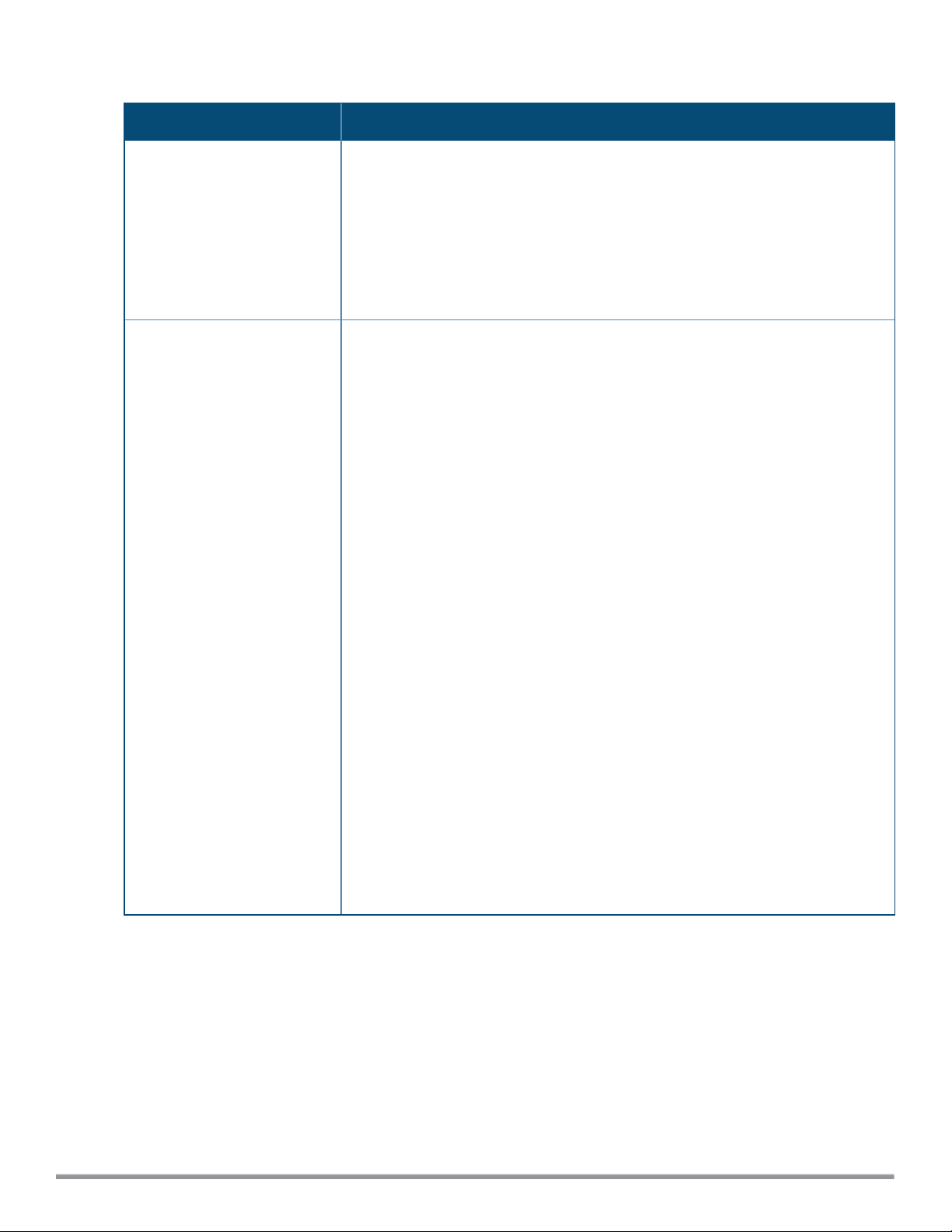
Table 3:
Provisioning Rule Configuration Settings
Provisioning Rule Type Provisioning Rule Settings
l Count ry Code: Select a country code to be assigned to the branch controllers in
the specified folder.
l Branch Config Group: Enter the name of a branch config group to assign that
group of branch configuration settings to the branch controllers in the specified
folder.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule
Managed Device to Master
Controller
Provision a Managed Device to communicate with the master controller from which
the managed device can download its configuration. To create aManaged Deviceto-Master-controller rule, configure the following settings:
l Rule Type: Select Provisioning Rule from this drop-down list.
l Parent Folder: The rule applies to devices within this folder.
l Provision Type: Select Managed Device to Master Controller.
l Redundancy Level: There are two available options—No redundancy and L2.
l Config Node Path: The configuration node path for the managed device.
l Master Controller: MAC address of the primary master controller.
l Master Controller IP: IP address of the primary master controller.
l VPNConcentrator MAC: MAC address of a VPN concentrator. This parameter
is only required for network topologies where the managed device creates a
VPN tunnel to a VPN concentrator which lies outside the firewall containing the
master controller.
l VPN Concentrator IP: IP address of a VPN concentrator, This parameter is only
required for network topologies where the managed device creates a VPN
tunnel to a VPN concentrator which lies outside the firewall containing the
master controller.
l Backup VPN Concentrator MAC: MAC address of a secondary VPN
concentrator. This parameter is only required for network topologies where the
managed device creates a VPN tunnel to a secondary VPN concentrator which
lies outside the firewall containing the master controller.
l Count ry Code: Select a country code to be assigned to the managed device in
the specified folder.
l Rule Name: Activate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule
type and folder. You can use this suggested name, or create your own custom
name for the rule.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 16
Page 17

Table 4:
Move to Folder Rule Configuration Setting
Move to Folder Rule
Setting
Description
Rule Type Click the Rule Type drop-down list, and select Move to Folder.
Move to Folder Select the destination folder into which the AP will be moved.
Move by Click the Move By drop-down list and specify one of the following filtering criteria:
l Device Category: Filter by device type (AP, Instant AP, controller, or switch).
l Part Number: Move devices with a specific model number.
l PO Number: Move devices whose purchase order contains a specified string.
l Billing Info: Move devices whose billing data contains a specified string.
l External IPaddress range: Move devices within an specific IP address range.
Rule Name ArubaActivate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule type and folder. You
can use this suggested name, or create your own custom name for the rule.
Table 5:
Notification
Rule Settings
Notification Rule Configuration Settings
Description
Rule Type Click the Rule Type drop-down list, and select Notification.
Email on Select the event type that will trigger the notification:
l Shipment: Notify when a device is shipped to your company by Arubaor a reseller
l Provisioning: Notify when a device requests provisioning information.
l Firmware Update: Notify when a device requests the latest firmware
l Move to Folder: Notify when a device has been moved to a new folder.
For Rule
For Provisioning and Move to Folder rules only
Specify the name of the rule that triggers the email notification.
Parent Folder
For Firmware Upgrade rules only
Specify folder of the devices whose firmware upgrade triggers the notification event.
Email To Enter a comma-separated list of email addresses to be sent a notification message when the
specified event is triggered.
Rule Name ArubaActivate suggests a name for the new rule, based upon the rule type and folder. You can
use this suggested name, or create your own custom name for the rule.
Sort and Filter the Rules List
The rules list displays the following information types for each folder.
17 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 18
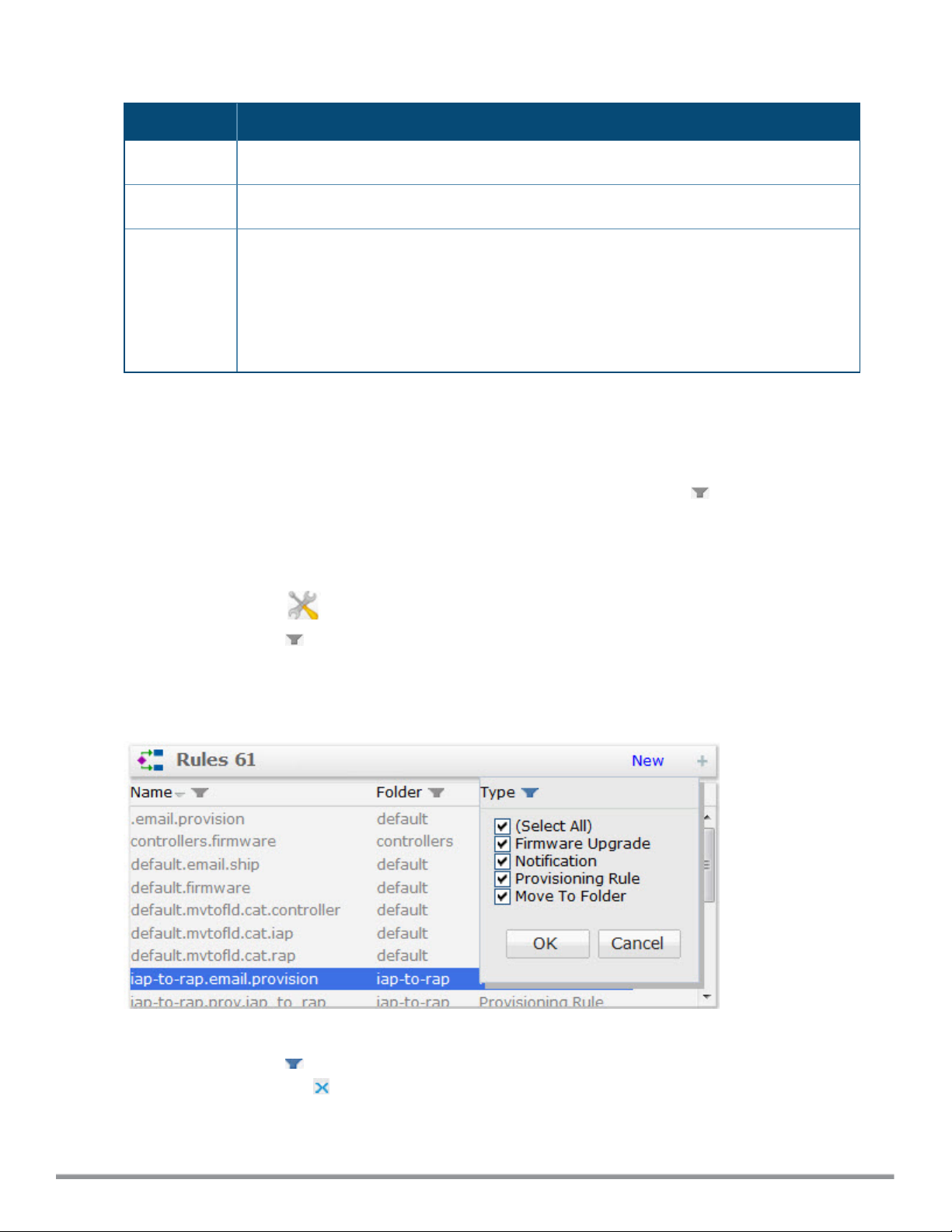
Table 6:
Rules List Information
Column Description
Folder Folder to which the rule is assigned
Name Name of the rule
Type
The rule is one of the following rule types:
l Notification
l Provisioning
l Firmware Upgrade
l Move to Folder
When you select an individual entry in the Rules list, the Rule Detail section at the bottom of the page also displays
information about the user that created the rule, and the date it was created.
ArubaActivate allows you to sort and filter folder data in every column to display just the information you need. By
default, the rules table displays the entire Rules list, sorted by rule name. Click any of the list's column headings to
sort the information in the list by that column criteria. You can also click the filter icon ( ) and filter the list of entries
to display. The filter mechanism for each heading depends upon the number of unique entries in that column.
Filtering Small to Medium-Sized Rules Lists
To filter data in Rules lists with fewer than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Rules list column heading. The filter displays a checkbox for each entry type.
3. To select an individual rule, uncheck the Select All checkbox and then click the checkbox next to the rule you
want to display.
4. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
To remove a filter:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a column heading with an active filter.
2. Click the clear filter icon ( ) in the filter header to clear the current filter settings.
Filtering Large Rules Lists with 50+ unique entries
Rules list columns with more than fifty unique entries allow you to search within that column for a specific text string.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 18
Page 19
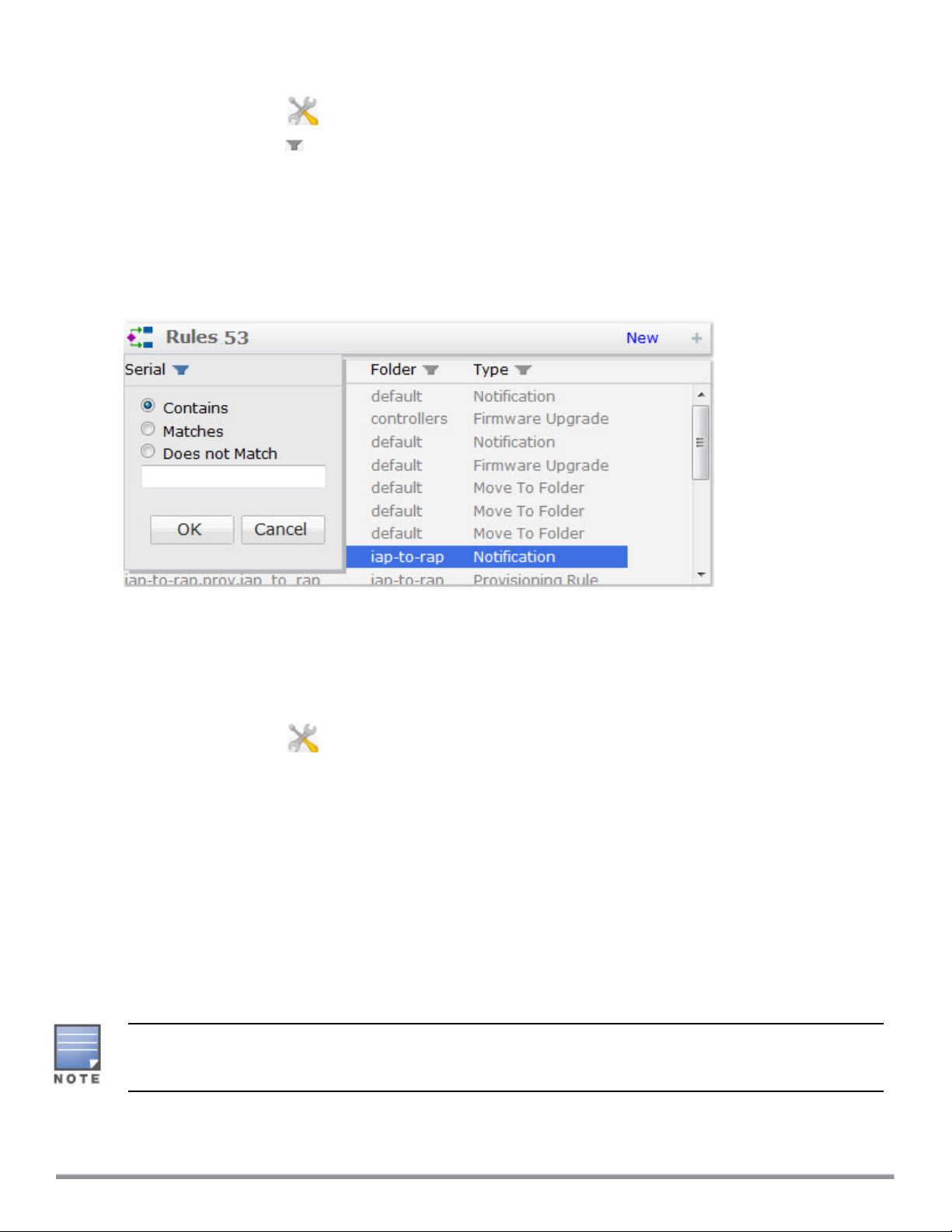
To filter data in columns with more than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Rules list column heading.
3. Select one of the following search types:
l Contains: Search for entries that contain the search string.
l Matches: Search for entries that exactly match the search string
l Does not Match: Search for entries that do not exactly match the text string
4. Enter the search string into the search field.
5. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
Modifying an Existing Rule
Any rule can be deleted or modified by a user with access to the folder in which the rule resides.
To delete or modify the description and settings of an existing folder:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the rule you want to edit from the Rules list.
3. Click the Edit button below the Rules Detail section at the bottom of the page.
4. Change the rule name, email addresses, or rule and folder settings as desired, or click Delete to delete the rule.
5. Click Done to save your settings.
Assign Devices to Folders
Each folder can contain one or more rules that supply provisioning information to Instant APs, auto-assign devices to
folders, and trigger notification events. When a device moves into a folder, the device immediately inherits all the
rules in the folder. A users' access privileges within ArubaActivate depends upon the folder to which the user
account is assigned. Users cannot assign devices to a folder to which they do not have access.
When you click the Move to Folder button, Activate re-assigns all devices currently appearing in the Devices list, so
make sure to filter the table until it displays only those devices you want to move. If you do not filter the table to display a
subset of devices, the folder assign process will move the entire device list into the selected folder.
To assign a device or group of devices to a folder:
19 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 20

1. Click the Devices icon ( ) at the top of the page to display the Devices page
2. Click the filter icon ( ) by any Devices list column heading and choose which entries to display. (For more
information, see Sort and Filter Device Data.) You can repeat this step and filter the list by multiple criteria types
until the list shows just those devices you want to move to a new folder.
3. Click the Move to Folder button at the top of the Devices page. A drop-down window with all folder names
appears.
4. Select the destination folder for the devices.
5. A confirmation window appears, showing the total number of devices that will be moved.
6. Click OK to confirm the change, or click Cancel to cancel the move.
You can also assign an individual device to a new folder by selecting that device from the Devices list and manually
changing its parent folder in the Device Details window.
Manually Add Devices
Instant APs running Instant versions 6.2.1.0-3.3.0.3 and later , Mobility Access Switches running ArubaOS 7.3 and
later, or HPE ArubaOS Switch versions 16.02.0012 and later can be manually added to your Activate account using
the device's cloud activation key and MAC address.
The IAP, Mobility Access Switch, or the HPE ArubaOS Switch must establish an HTTPS connection to
device.arubanetworks.com to learn the Cloud Activation Key. If the key does not appear on a device running a
supported version of Instant or ArubaOS, check to ensure that the device can securely connect to
device.arubanetworks.com.
Locate the Cloud Activation Key
The cloud activation key for an Instant device appears in the Instant WebUI. For a Mobility Access Switch or HPE
ArubaOS Switch, the key is displayed in the Mobility Access Switch or the HPEArubaOS Switch command-line
interface, respectively.
To locate the cloud activation key for an Instant device:
1. Log in to the IAP WebUI interface.
2. Select the Maintenance link in the upper right corner of the window. The Maintenance pop-up window appears.
3. Select the About tab. The key appears at the bottom of the tab.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 20
Page 21

To locate the cloud activation key for a Mobility Access Switch:
1. Log in to the Mobility Access Switch command-line interface.
2. Enter the enable mode, and then issue the show version command. The activation key appears at the bottom of
the command output.
(Aruba_MAS_S1500) #show version
Aruba Operating System Software.
ArubaOS (MODEL: ArubaS1500-12P), Version 7.3.2.2
Website: http://www.arubanetworks.com
Copyright (c) 2002-2014, Aruba Networks, Inc.
Compiled on 2014-07-09 at 11:48:15 PDT (build 44718) by p4build
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version CPBoot 1.0.42.0 (build 39779)
Built: 2013-09-09 07:19:55
Built by: p4build@re_client_39779
Switch uptime is 12 minutes 58 seconds
Reboot Cause: User reboot.
Processor XLS 208 (revision A1) with 1023M bytes of memory.
959M bytes of System flash
Activation Key: HLJRK869
To locate the cloud activation key for an HPEArubaOS Switch:
1. Log in to ArubaOS switch command- line interface (CLI).
2. Execute the show activate provision command. The cloud activation key is displayed at the end of the
command output.
(Aruba-XXXF-Central)# show activate provision
Configuration and Status - Activate Provision Service
Activate Server Address : device.arubanetworks.com
Activate Provision Service : Enabled
Activation Key : VMQF7EYA
Add the Activation Key to Activate
1. Log in to your Activate account.
2. Click the add devices link in the upper right corner of the window. The Manually Add Devices popup window
opens.
3. In the Activation Key field, enter the cloud activation key for the device.
4. In the MAC address field, enter thedevice MAC address.
21 | Device Setup and Provisioning Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 22

5. Click Done.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide DeviceSetup and Provisioning | 22
Page 23

Chapter 3
Managing Users
The Aruba Product Activation Service allows you to create multiple users and define what level of access each user
has to the system. The initial user account for your company will be assigned to the default folder, giving that user
full access to your company's inventory. The default level of access allows users to create and edit folders, manage
other users accounts, define provisioning and notification rules, and assign devices to any folder. You can edit a user
account to limit that user's access to just those devices within a specific subfolder, or give them read-only access at
any level, allowing them to view data but not make any changes.
For information on viewing and sorting user data or managing user accounts, refer to the following sections of this
user guide:
l View User Information: View and manage the list of users allowed to access the product activation service.
l Manage User Accounts: Create or edit users, and define the authorization levels to be assigned to each user
account.
View User Information
The user list can display two different tables of user information, the default Standard View and the expanded Details
View. You can toggle between the two different views by clicking the User list title bar.
User Information
The expanded Details View displays the following types of information for each user:
Table 7:
Column Name Information
Details View
Name Name assigned to the user.
Folder
Customer Your company name. This field is defined by Activate and cannot be
Role Role assigned to the users in your company. Users with full access
The parent folder (or highest-level access) for the user.
Users with access to the top-level default folder can view device
data and rules for all folders. Users with access to a lower-level
folder will only be able to see information for that folder and any of its
subfolders.
changed.
have the
customer-ro
customer
.
role. Users with read-only access have the role
Activated This field shows if the user has activated the account. If the Activated
value is true, then the user has clicked the embedded email URL
and configured a password. If the Activated value is false, the user
has not configured a password.
The Standard View displays username, folder permissions and user role data only.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing Users | 23
Page 24

Click on any entry in the User list to display detailed account information in the window below, including the user that
created the account, the date the account was created, and any account description or notes.
Sort and Filter User Data
ArubaActivate allows you to sort and filter the Users list to display just the users you want to view. By default, the
user table displays the entire user list, sorted by the Name column. To display just those users whose access is
limited to a specific parent folder, click that folder name in the Folders list.
Click any of the user list column headings to sort the information in the table by that column criteria, in ascending
order. You can also click the filter icon ( ) and choose which table entries to display. The filter mechanism for each
heading depends upon the number of unique entries in that column.
Filtering Small to Medium-Sized User Lists
To filter data in a table with fewer than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a User list column heading. The filter displays a checkbox for each entry in that
column.
3. To select an individual user, uncheck the Select All checkbox and then click the checkbox next to the user you
want to display.
4. Click OK.
To remove a filter:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a column heading with an active filter.
2. Click the clear filter icon ( ) in the filter header to clear the current filter settings.
Filtering User Lists with 50+ Unique Entries
Table columns with more than fifty unique entries allow you to search within that column for a specific text string. To
filter data in a table columns with more than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a user table column heading.
3. Select one of the following search types:
l Contains: Search for entries that contain the search string.
l Matches: Search for entries that exactly match the search string
24 | Managing Users Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 25

l Does not Match: Search for entries that do not exactly match the text string
4. Enter the search string into the search field.
5. Click OK.
Manage User Accounts
Each user is assigned either a standard (read-write) account that allows the user to view and edit device, user, rule
and folder settings, or a read-only account that lets a user view but not modify settings. A user with regular read-write
access to ArubaActivate can create and edit other users at or below their parent folder level. For example, a user
with the top-level (default) folder permissions can create other users with the same default folder accessordefine
users with access limited to a specific subfolder. A user with read-write permissions for just a subfolder can only
create users with access to that subfolder (or other lower-level folders below that subfolder.)
When users log into ArubaActivate with their unique user name and password, they can only view those devices
and users associated with their folder access level, and can perform only those operations allowed by their standard
or read-only account type.
Create a New User
To add a new user account:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) display the Setup page.
2. Click the New link in the title bar of the User Table. The Create a New User window appears at the bottom of
the page.
3. Enter the following information for the new user:
l Name: Unique login name for the new account. Best practice is to use an email address as the user's login
name.
l Email: User's email address.
l Folder: Select the parent folder for the user from the folder list. The default folder gives the user access to all
company devices and folders. Select a subfolder to limit the user's access to a subset of folders and devices.
l Read Only: (Optional) Select this checkbox to grant the user read-only access. The user will be able to view
devices, rules, folders and users, but not make any changes.
l Notes: (Optional) Use this field to add any additional information about the user account.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing Users | 25
Page 26

4. Click Done. ArubaActivate will send new users an email message prompting them activate their new account by
logging to the service and creating an account password. Note that both user names and passwords are casesensitive. Activate will send a confirmation email once the user account is activated.
Edit an Existing User
To edit or delete an existing user account:
1. Click the Setup icon ( ) to display the Setup page.
2. Click any entry in the User list to edit that account. The User Detail window appears at the bottom of the page.
3. Click Edit below the User Detail window to display the Edit User dialog.
4. Edit the fields as desired.
5. Click Done to save your changes.
26 | Managing Users Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 27

Chapter 4
Managing Device Data
Click the Device( ) icon to display the Device list and monitor and manage all APs, controllers and switches
purchased from Aruba. Activate allows you to sort and filter any list to display just the records you want to view. You
can also use this filtering capability to generate a whitelist or inventory report of devices.
If no individual devices are selected in the Device list, the Device page displays a summary of devices, as well as
pie charts showing the percentages of each Aruba device model and firmware type in your network inventory. Select
a single device on this page to drill down and view information specific to that individual device.
For information on viewing and managing device data, refer to the following sections of this user guide:
l Monitor all Devices: View and sort a complete list of all Aruba devices on your network.
l Monitor Individual Devices: Display a detailed summary of an individual device, or edit device details and folder
assignments.
l Create Whitelists: Generate whitelist CLI commands that you can copy and paste into your Aruba controller's
command-line interface.
l Export Device Data: Generate an inventory report in CSV format for export to an external database.
Monitor all Devices
The Devices list displays information about the devices in your network inventory. If your inventory includes less
than 1000 devices, the Devices list displays information for all devices on a single page. If your inventory includes
more than 1000 devices, the Devices list is divided into multiple pages of up to 1000 devices each. Use the scroll
bar on the right side of the Devices list to scroll through the list of devices on each page, or click the down arrow ( )
in theDevice Summary titlebar (located directly below the Devices list) to expand the Devices list to fill the entire
window.
If your Devices list appears on multiple pages, click the page forward ( ) or page back ( ) icons in the list titlebar
display additional pages. To disable automatic pagination and view all 1000+ devices on a single page, click the
Devices per page link on the Devices titlebar, and select the All option.
Disabling pagination for large network inventories may greatly increase the load time for the Devices list.
Table 8 describes the information displayed for each Arubadevice in your network inventory. By default, the Device
page displays the full device list, a summary of your inventory, and the Devices by Part Number and Devices by
Firmware graphs.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing DeviceData | 27
Page 28

Table 8:
Devices List
Column Name Information
Serial The device's nine-digit serial number.
MAC Address MAC address of the device's Eth0 interface.
Status Indicates if the device has shipped to the customer site, or if it has already been
received at the site and provisioned.
Part Device's part number or SKU number.
Part Description Description of the device to identify its type.
Folder Folder to which this device is assigned. The folder determines which provisioning and
notification rules are applied to the device.
Firmware The last known ArubaOS version on the device. If the device has checked into
ArubaActivate, it will show the ArubaOS version reported at that time. If the device has
not checked in, this column will show the ArubaOS version loaded on the device by
the manufacturing facility.
Mode
Shows the mode of the device the last time it checked into Activate.
l BRANCH: Device operates as a branch controller or managed device. Whether the
device works as a managed device or branch controller is set implicitly.
Note: The ‘Master Controller’ and ‘MD-VPNC’ modes are to be set explicitly
in the UI.
l CAP: Device operates as a Campus Access Point.
l CONT RO LLER: Device operates as controller.
l IAP-VC: Device operates as an Instant Virtual Controller.
l IAP-SUB: Device operates as a subordinate Aruba Instant Access Point
l MAS-PRI: Device operates as primary Mobility Access Switch.
l Other: This mode category is reserved for future use
First Seen Date and time that the device first checked into Activate.
AP/Device Name User-friendly name assigned to this device. If you use Activate to generate whitelist
CLI commands, the name is included in these commands. You can use Activate as a
master inventory and use Activate-generated whitelist commands to synchronize your
AP device inventory (name, full name, and description) to your controllers.
Ship Date Date that the device order shipped from Aruba or a reseller.
Sort and Filter Device Data
Click any of the Devices list column headings to all sort the information in the table by that column criteria, in
ascending order. You can also click the filter icon ( ) and choose which table entries to display. The filter
mechanism for each heading depends upon the type of column, and the number of unique entries in that column.
Filtering a Small to Medium-Sized Device List
28 | Managing Device Data Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 29

To filter data in a Devices list with fewer than fifty unique entries:
1. Click the Devices icon ( ) to display the Devices page.
2. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Devices list column heading. The filter displays a checkbox for each entry type.
3. To select an individual device, uncheck the Select All checkbox and then click the checkbox next to the entry
you want to display.
4. Click OK. The filter icon by the column heading will turn blue to indicate that column has an active filter.
Filtering a Large Devices List with 50+ unique entries
Devices List columns with more than fifty unique entries allow you to search within that column for a specific text
string. To filter data in a column with more than fifty unique entries:
1. Select the filter icon ( ) above a Devices list column heading. A search box appears below the heading title.
2. Select one of the following search types, then enter the search string into the search field.
l Contains: Search for entries that contain the search string.
l Matches: Search for entries that exactly match the search string.
l Does not Match: Search for entries that do not exactly match the text string.
3. To filter the list by Ship Date or Last Seen dates, enter a date in
MM/DD/YYYY
format, then select one of the
following options.
l >: Search for entries after the selected date.
l >=: Search for entries on or after the selected date.
l <: Search for entries before the selected date.
l <=:Search for entries on or before the selected date.
4. Click OK.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing DeviceData | 29
Page 30

Device Summary Information
When no devices are selected in the Devices list, the device summary information at the bottom of the page
displays a summary of device and order types, and the Devices by Part Number and Devices by Firmware
graphs.
Device Details
This section shows the total number of devices in the Device list, as well as the numbers of each of the following
device types:
l AP: Campus AP or access points not functioning as Instant APs
l Controller
l IAP: Instant APs
l RAP: Remote APs
l MAS: Aruba Switches
l HPE ArubaOS Switches
You can expand or hide this section at any time by clicking the Device Details heading.
Order Detail
This section shows summarized device totals in the following categories:
l Standard Direct: New devices with permanent (non-evaluation) licenses shipped directly to you from Aruba.
l Standard Indirect : New devices with permanent (non-evaluation) licenses shipped to you through an Aruba
reseller.
l Evaluation: The device was ordered as part of a equipment evaluation.
l Internal: This type of order is similar to an evaluation order, but the inventory is owned by a salesperson (either
from Aruba or reseller) and not by the customer.
You can expand or hide this section at any time by clicking the Order Detail heading.
Device Charts
The
Devices by Part Number
your device inventory. The
various versions of ArubaOS.
These pie charts can display up to ten different categories of data. If the chart needs to represent more than ten
different category types, the chart will display the top nine categories as separate sections, and group all others into
a tenth "other" category. Hover your mouse over any section of a pie chart to display a tooltip that shows the
percentage and number of devices represented by that section of the chart.
pie chart allows you to see, at a glance, the percentage each device part number in
Devices by Firmware
chart displays the percentage of devices in your inventory running
30 | Managing Device Data Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 31

Monitor Individual Devices
To view detailed information for a single Aruba device in your inventory, click the Devices icon ( ) at the top of
the page to display the
Devices
page, then select a entry in the Device List.
Individual Device Details
The
Device Details
pane in the
Devices
page displays physical characteristics, status, and order information for the
selected device, as well as a detailed history showing the device's latest provisioning and firmware check.
Device Details
The
Device Details
Table 9:
Device Details
Column Description
Serial Number The device's nine-digit serial number
MAC Eth0 The MAC address of the device's Eth0 interface.
Provisioning Image Software version of device's factory-installed boot image. This is not updated even when
Status Current device status
pane in the Devices page shows the following information for the selected device.
a device communicates with Activate.
l Shipped: Device has been shipped to a customer, but not yet provisioned.
l Provisioned: Device has shipped and been provisioned at least once by Activate.
First Seen Date and time the device was first seen by ArubaActivate.
Folder Folder to which the device was assigned. The folder determines which provisioning and
notification rules are applied to the device.
Device-Name (Optional) User-friendly name assigned to this device. If you use Activate to generate
whitelist CLI commands, the name is included in these commands. The name must be 50
characters or less, and cannot include a space or the characters ?, # or &.
Full Name (Optional) The full name you assigned to the device. If you use Activate to generate
whitelist CLI commands, the name is included in these commands. The full name must be
120 characters or less, and cannot include a space or the characters ?, # or &.
Description (Optional) The description you assigned to the device. If you use Activate to generate
whitelist CLI commands, the name is included in these commands. The full name must be
120 characters or less, and cannot include a space or the characters ?, # or &. The device
description must be 50 characters or less, and cannot include a space or the characters
?, # or &.
Click the Device Detail heading to expand or collapse this section for the selected device.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing DeviceData | 31
Page 32

Order Detail
Click the Order Detail heading to expand or collapse the
Order Detail
section. This section is hidden by default, and
Order Detail information cannot be edited.
Order details for each device include the following values.
l Purchase Order: This field shows the purchase order number for the device order in which the device was
purchased.
l Ship Date: Date that the device was shipped from Aruba or an Aruba reseller.
l Direct Order (Fulfilled by Aruba)
n Sold To: Your company name or company name alias.
n Ship To: Your company name or company name alias.
n End User: Your company name or company name alias.
l Indirect Order (Fulfilled by an Aruba reseller)
n Bill to: Your reseller
n End User: Your company name or company name alias.
Device History
The Device History window at the bottom of the Devices page shows a history of all communication between
Activate and a selected device for as long as your company has owned that device. The list is sorted on the date
column in descending order. This window supports a collapsed and expanded mode. Clicking the Device History
title bar expands the window to the left so it takes the full width of the browser window.
The device history window displays the following information:
Table 10:
Device History
Column Name Information
Date The date and time that the device communicated with Activate.
Type Type of communication with Activate:
l firmware-check: The device requested the latest firmware. Instant APs perform firmware
checks every seven days.
l provision-update: The device requested provisioning information.
Source IP Source IP address of the device when it checked into Activate. This is typically the company’s
external IP exposed to the Internet. The real (internal) IP of the device will be hidden by NAT.
Current
Version
Mode Shows the mode of the device the last time it checked into Activate.
The device's current version of ArubaOS or Instant, as reported by the device when it is checked
in.
l BRANCH: Device operates as a branch controller or managed device.
l CAP: Device operates as a Campus Access Point.
l CONT RO LLER: Device operates as a controller.
l IAP-VC: Device operates as an Instant Virtual Controller.
l IAP-SUB: Device operates as a subordinate Aruba Instant Access Point.
32 | Managing Device Data Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 33

Table 10:
Device History
Column Name Information
l MAS-PRI: Device operates as primary Mobility Access Switch.
l RAP: Device operates as a remote AP.
l Other: This mode category is reserved for future use.
Status Status of the communication exchange between the device and Activate. Activateuses the
following status codes:
l success: the communication exchange between the AP and Activate was successful
l fail-prov-no-rule: there is no provisioning rule defined for the device mode and folder
Description This column contains the data that Activate sent to the device during the communication
exchange.
The description column is hidden by default. To display description information, click the expand
(+)icon next to the View Device History link to expand this list. Clicking the collapse (-)icon
collapses the list back to its original size.
Device Info Contains the data the device sent to Activate during the communication exchange, including the
device's serial number, Eth0 MAC address and part number.
An IAP virtual controller sends data for all subordinate APs (e.g., AL0146305, 00:01:02:03:04:05,
AP-105, AL014777701:02:06:07:08:11, AP-135 ).
The Device Info column is hidden by default. To display the Device Info column, click the expand
(+)icon next to the View Device History link to expand this list. Clicking the collapse (-)icon
collapses the list back to its original size.
Create Whitelists
If you convert an Instant AP to a Remote AP, you must also ensure that the remote AP's MAC address is input into
the controller's
MAC address is not in the controller’s remote AP whitelist, the AP will not be able to successfully authenticate with
the controller and retrieve configuration policy.
ArubaActivate allows you to easily update your controller's remote AP whitelist by generating a script of CLI
commands that you can paste directly into the controller's command-line interface. If your devices are running
ArubaOS 6.1.4 or later and you are maintaining a whitelist on an external RADIUS server, you can use Activate to
create a remote AP whitelist in comma-separated value (CSV) format.
The commands to create or update the controller's internal remote AP whitelist can vary, depending upon the
controller's software version. When you generate a list of remote AP whitelist commands, you must specify whether
the controller is running an older ArubaOS version (6.1.3 or earlier), or ArubaOS 6.1.4 or later. Whitelists in CSV
format contain only the MAC addresses of each remote AP. To create a more detailed inventory report that includes
additional device information, see Export Device Data.
When ArubaActivate generates a whitelist, it includes an entry for each AP, (Campus AP, Instant AP or remote AP)
that appears in the Devices list. To generate a whitelist for a subset of device types, you first must filter the Devices
list to display only the target devices for your whitelist.
remote AP whitelist
, which is the controller's internal database of valid remote APs. If the device's
Before you generate a whitelist, you must create provisioning rules that identify the controller AP group to which the
remote APs will be associated. The whitelist CLI commands include the AP group of each device, as well as any
device names, full names, and descriptions configured in Activate. Whitelists generated by Activate provide both
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide Managing DeviceData | 33
Page 34

add
and
delete
commands for each device, so the commands can update the name, full name, and description if
needed. If you only want add commands, then filter these out before you input the commands into the controller's
command-line interface . If the remote AP is currently connected to the controller and you input both delete and add
commands, the delete command will temporarily bring down the remote AP, potentially causing a disruption of
service for clients associated with that remote AP.
To Generate and Upload a Controller Whitelist:
1. Click the Devices icon at the top of the page to display the
2. Click Whitelist CLI.
3. Select either Older AOS Format (for ArubaOS 6.1.3 and earlier) or 6.1.4 Format for controllers running ArubaOS
6.1.4 or later. Note that it may take up to a minute to generate the file containing the commands.
4. A prompt asks you if you want to open the generated file or save it on your computer. Specify whether you want
to open or save the file, then click OK.
5. Open the generated file, and copy the commands after the header.
6. Access the controller's command-line interface.
7. Enter config mode.
8. Paste the copied commands into the controller's command-line interface.
9. Press Enter on your keyboard to enter the commands.
10.Issue the write mem command to save your settings before exiting the CLI terminal session.
Best practices are to issue the command write mem to save your settings before closing the controller command
line interface.
Devices
page.
To Generate an External Database Whitelist:
1. Click the Devices icon ( ) at the top of the page to display the
2. Click the More drop-down list.
3. Select Whitelist CSV.A prompt asks you if you want to open the generated file or save it on your computer.
4. Specify whether you want to open or save the file, then click OK.
Devices
page.
Export Device Data
ArubaActivate can generate and export the contents of the Devices list into a report in comma-separated value
(CSV) format, for direct import into Microsoft Excel.
When ArubaActivate generates an inventory report, it includes an entry for each device that appears in the Devices
List. To generate an inventory report for a subset of devices, you must first filter the Device list to show just the
entries you want to include in the report.
To generate and export a device data report:
1. Click the Devices icon ( ) at the top of the page to display the Devices page.
2. Click the More drop-down list.
3. Select Inventory CSV. The system prompts you to specify if you want to open the generated file or save it on
your computer.
4. Specify whether you want to open or save the file, then click OK.
34 | Managing Device Data Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 35

Chapter 5
ArubaActivate APIs
The Activate APIs are designed to meet the needs of users who want to configure their folders and rules in the Cloud
just once, and then have their internal provisioning system integrate with Activate without further user interaction. All
Activate APIs are JSON-encoded, and user session-based authentication.
The following procedure describes an example use case using Activate APIs.
1. The customer configures provisioning rules and folders in Activate.
2. An internal Aruba application performs the following tasks:
a. Queries Activate each day for new inventory that has shipped to the customer.
b. Adds inventory into a configuration management database (CMDB).
c. Determines how to provision the new devices from a query or internal CMDB.
d. Uses APIs to add new inventory to its proper Activate folder.
3. Inventory is shipped directly to the customer location, without any preconfiguration.
4. The end user receives a device and connects it to the Internet.
5. The device connects to Activate and receives proper provisioning information.
6. The device leverages provisioning information to connect to its configuration master (AMP/controller) and receive
the appropriate security policy.
7. An Internal application queries Activate each day for status updates on provisioned devices and updates CMDB.
All APIs are JSON encoded and use session-based authentication. For detailed information on individual APIs, see
the following sections of this user guide:
l Inventory Update and Inventory Query APIs: Allow a customer to retrieve new inventory and update inventory in
Activate without interacting with the WebUI.
l File Query API: Provides a list of files posted to Activate from a controller, Instant AP, AirWave, Mobility Access
Switch, or ClearPass Policy Manager.
l Folder Update and Folder Query APIs: Provide a list of folders, and the folder ID required to move a device into a
new or different folder. This API also provides the ability to create and rename folders.
l Rule Update and Rule Query APIs: Provide a list of rules, and gives users the ability to create and update rules.
l Customer Query APIs: Provide a customer ID for submitted devices or purchase orders, so a service provider or
reseller can retrieve folders, devices, or rules by the Activate customer ID. Users with a single customer account
do not need to use this API.
l Whitelist Query API: Provides whitelist commands used to update your controller's whitelist.
l Firmware Query API: Provides a list of firmware files and URL locations on the Activate servers.
l Device History API: Retreives and provides the history of a device for admin user or the device owner.
The following code examples can also be downloaded from this site:
l Samples of Curl code to query all inventory, query a single MAC or update inventory
l Sample Client Javascript code
l Sample Request Javascript code
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 35
Page 36

Inventory API-Update Example
This API enables a customer to update inventory in Activate without accessing the WebUI. There are no URL
parameter filters for this API.
The URL for an inventory update is
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=update.
Table 11:
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Inventory API on a post
Nature of
HTML Body Filters
Parameter/
Subparameter
devices Mandatory
parameter
mac Mandatory
subparameter
Definition Sample
Device details for the
update action
MAC address of the
device to be updated.
"devices" : [
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:05",
"deviceName" : "steve-AP-105",
"deviceFullName" : "Steve's AP-105",
"deviceDescription" : "New Long
Description"
},
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:06",
"folderId" : "a301e0a5-a532-
11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0a001"
}
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:04",
"folderName": "Southwest APs"
}
]
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:05"
deviceName Optional
subparameter
deviceFullName Optional
subparameter
deviceDescription Optional
subparameter
folderId Optional
subparameter
folderName Optional
subparameter
Name of the device to
be updated.
Full name of the
device to be updated
Description of the
device to be
updated.
Folder ID to be
associated for the
device that is to be
updated.
Folder name to be
associated for the
device that is to be
updated.
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Update Inventory
"deviceName" : "steve-AP-105"
"deviceFullName" : "Steve's AP-105"
"deviceDescription" : "New Long
Description"
"folderId" : "a301e0a5-a532-11e19eaf-a4badbe0a001"
"folderName": "Southwest APs"
36 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 37

HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Update Inventory
The following example moves devices into a new folder:
json={
"devices" : [
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:05",
"deviceName" : "steve-AP-105",
"deviceFullName" : "Steve's AP-105",
"deviceDescription" : "New Long Description"},
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:06",
"folderId" : "a301e0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0a001" }
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:04",
"folderName": "Southwest APs" }
]
}
Sample Body of Response HTML for Inventory Update
{
"info" : {
"api" : "inventory",
"version" : "1.4"
},
"message" : {
"text" : "2 devices updated",
"code" : "0"
},
"errors" : [
{
"key" : "00:01:02:03:04:05",
"errMessage" : "DevNotFound"
}
]
}
Inventory API-Query Example
The Inventory API provides users with the ability to query for or update inventory.
The URL for an inventory query is:
[POST]www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query.
The following example is a sample URL to return basic data only for all devices added to Activate from 01/01/2012:
[POST]www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query&addDate=01-01-
2012&deviceFilter=basicData
The following example is a sample URLto return data with pagination parameters set for limit and offset:
[POST]www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query&limit=10&offset=2
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 37
Page 38

Table 12:
URL filters that can be passed to the Inventory API on a post
URLFilters
No filter — Returns all devices with all data
addDate Optional
shipDate Optional
deviceFilter Optional
limit
offset
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
parameter
parameter
Optional
parameters
Definition Sample
Returns all devices added to your inventory
from this date forward. This is not the ship
date, but the actual date a device is added to
Activate. For example, The device could
have shipped on 01/01/2012, but was added
to Activate on 01/02/2012.
Returns all devices that were shipped on this
date. Note this is different than addDate.
Determines what device content that will be
returned. If parameter is not present or
blank, it returns all device content including
basicData, orderData, additionalData.
These parameters setthe pagination. Both
parameters must be provided for pagination
to take effect.
l limit—accepts an integer value greater
than or equal to 1.
addDate=01/01/2012
shipDate=01/01/2012
deviceFilter=basicData
limit=10&offset=2
l offset—accepts an integer value greater
than or equal to 0.
Table 13:
HTML Body
Filters
No filter — Returns all devices
devices Optional parameter Return only the
folders Optional parameter Return only rules
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Inventory API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
with all data
devices specified.
Device must be
specified as the
MAC of Eth0
within folders
specified. Folders
must be specified
as the id of the
folder.
"devices" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06"
]
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
38 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 39

Table 13:
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Inventory API on a post
HTML Body
Filters
deviceNames Optional parameter Return only the
serialNumbers Optional parameter Return only the
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
"deviceNames" : [
device(s) that match
the input string
exactly. The query
is case sensitive, so
“ap-1” does not
match “AP-1”.
devices specified –
that match the serial
number elements
supplied. The query
is case sensitive, so
“al0000001” does
not match
“AL0000001”.
“ap-1",
"ap-2"
]
"serialNumbers" : [
“AL0000001",
"AL0000002" ,
]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Return Devices Related to Customer
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Return Specific MAC Addresses
json={
"devices" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06"
]
}
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Return only Device in Specific Folders
json={
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
}
Sample Request URLswith Response JSON Encoding that Includes the Total Count of Devices
The inventory data for a customer who has 75,555 devices can be fetched with two chain requests, as shown in the
following example:
Request 1
www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query&limit=50000&offset=0
Response JSONfor Request 1
{
"info": {
"api": "inventory",
"version": "1.4"
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 39
Page 40

},
"message": {
"text": "50000 devices returned",
"code": 0
},
"totalCount": 75555,
"devices": [
{
...data for first 50000 devices...
}
]
}
Request 2
www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query&limit=50000&offset=50000
Response JSONfor Request 2
{
"info": {
"api": "inventory",
"version": "1.4"
},
"message": {
"text": "25555 devices returned",
"code": 0
},
"totalCount": 75555,
"devices": [
{
...data for next 25555 devices...
}
]
}
Sample Body of Response JSON Encoding for Inventory Query
NOTE: If the body is empty, the API will respond with all devices. You can supply only one of the HTML body filters
mentioned earlier, and you cannot combine multiple filters within the body. You can, however, combine URL and HTML
body filters.
{
"info" : {
"api" : "inventory",
"version" : "1.4" },
"message" : {
"text" : "2 devices returned",
"code" : "0" },
"errors" : [
{
40 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 41

"key" : "00:01:02:03:04:05",
"errMessage" : "InvalidFormat" }
],
"totalCount": 220
"devices" : [
{
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:05" :
"basicData" : {
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:05",
"customerId" : "344ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f264"
"serialNumber" : "BE0000011",
"partNumber" : "IAP-105",
"folderId" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"firstSeen" : "01-15-2011",
"lasttSeen" : "02-15-2011",
"status" : "shipped", },
"orderData" : {
"shipDate" : "01-01-2012",
"custPo" : "zzz0101001",
"shipData1" : "Intel",
"shipData2" : "Intel",
"shipData3" : "Intel",
"orderType" : "STD", },
"additionalData" : {
"deviceName" : "paul-AP-105",
"deviceFullName" : "Paul's AP-105",
"deviceDescription" : "Long Description",
"apGroupName" : "north-ap",
"folder" : "North_APs",
"folderId" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"firstSeen" : "01-15-2011",
"lasttSeen" : "02-15-2011",
"lastAosVersion" : "6.0.1.0.1"
"lastBootVersion" : "6.0.1.0.1"
"sourceIpAddress" : "10.1.1.1" }
},
{
"mac" :"00:01:02:03:04:06" :
"basicData" : {
"serialNumber" : "BE0000012",
"customerId" : "344ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f264"
"partNumber" : "IAP-105", },
"orderData" : {
"shipDate" : "02-01-2012",
"custPo" : "xxx0101001",
"shipData1" : "Intel",
"shipData2" : "Intel",
"shipData3" : "Intel",
"orderType" : "STD", },
"additionalData" : {
"deviceName" : "john-AP-105",
"deviceFullName" : "John's AP-105",
"deviceDescription" : "Long Description",
"apGroupName" : "north-ap",
"folderName" : "North_APs",
"folderId" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"firstSeen" : "02-15-2011",
"lasttSeen" : "03-15-2011",
"lastAosVersion" : "6.0.1.0.1"
"lastBootVersion" : "6.0.1.0.1"
"sourceIpAddress" : "10.1.1.1" }
}
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 41
Page 42

]
}
File API-Query Example
This API provides a list of files posted to Activate. These files can originate from a controller, IAP, AMP, Mobility
Access Switch, HPE ArubaOS Switch, or CPPM. You can filter based on URL or HTML parameters.
The URL for a firmware query is
[POST]phonehomelogs.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/file.json?action=query.
Table 14:
HTML Body
FIlters
No filter — Returns all devices with all data. —
createDate Optional
Table 15:
HTML Body Filters
devices Optional
serialNumbers Optional
URL filters that can be passed to the File API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Returns all files added from this
date forward. This is the actual
date the file was added to
Activate.
HTML body filters that can be passed to the File API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Returns only the files for the
devices specified by their
primary key, the MAC of eth0.
Returns only the files for the
devices specified by their serial
number.
createDate=01-01-2012
"devices" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06"
]
"serialNumbers" : [
“AL0000001",
"AL0000002"
]
customerIds Optional
parameter
sourceIpAddress Optional
parameter
Returns only the files for the
customers specified.
Returns only the files for the
specified source IPaddress.
"customerIds" : [
“A323lDDEE433CABBAA398833",
"A323lDDEE433CABBAA398833"
]
"sourceIpAddress" : [
“10.1.1.1",
"10.1.2.1"
]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Return Specific MAC Addresses
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Return Specific MAC Addresses
json={
42 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 43

"devices" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06"
]
}
Sample URL to Return all Firmware Files Added to Activate from 01-01-2012
phonehomelogs.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/file.json?action=query&createDate=01-01-2012
Sample Body of Response JSON Encoding with No Folders Requested
{
"info" : {
"api" : "file",
"version" : "1.4" },
"message" : {
"text" : "Request successfully processed",
"code" : "0" },
"files" : [
{
"fileName" : "01-02-2013-11-02-54_CTR_CRASH_01:02:03:04:05:06.tar.gz",
"fileSize" : 4091164,
"checksum" : "AADE593772A3DE847DFD77ECAE2E1095A06C4EE1",
"fileType” : "crash",
"createDate" : "02-01-2013",
"createTimestamp" : 1385063003000,
"email" : "username@example.com",
"bugId" : "339-f444",
"caseNumber" : "AE43-BBED",
"version" : "5.0.3.0-1.0.0.1",
"build" : "28245",
"oem" : "aruba",
"mac" : "00:01:02:03:04:06",
"serialNumber" : “BE2430001",
"partNumber" : “7224-US",
"fileUrl" : "internal.activate.activate.com/file/dir/123",
"sourceIpAddress" : "10.1.1.1",
"customerId" : "344ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f264",
"customerName" : "Intel Inc."
},
"fileName" : "11-22-2013-01-15-33_CTR_RUN_02:04:AA:BB:CC:06.tar.gz",
"fileSize" : 3032233,
"checksum" : "BCAA69327AB3CAB47DFD77ECAE2E1095A06C4EE1",
"fileType” : "running",
"createDate" : "11-22-2013",
"createTimestamp" : 1385063003000,
"email" : "paul@arubanetworks.com",
"bugId" : "339-f444",
"caseNumber" : "AE43-BBED",
"version" : "6.3.0.0-1.0.0.1",
"build" : "45141",
"oem" : "aruba",
"mac" : "02:04:AA:BB:CC:06",
"serialNumber" : “CM0943802",
"partNumber" : “6500-US",
"fileUrl" : "internal.activate.activate.com/file/dir/123",
"sourceIpAddress" : "10.1.1.1",
"customerId" : "6534ab0c4-b141-11a1-9ab1-cc1a2be0f264",
"customerName" : "Starbucks Inc."
]
}
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 43
Page 44

Folder API-Update Example
This API allows you to update or create a folder in Activate without accessing the WebUI.
The URL for a folder update is
[POST] activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/folder.json?action=update.
Table 16:
HTML Body
Filters
folders Mandatory
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Folder API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
The folder name or folder
ID to be passed for
creating or renaming a
folder.
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post for Folder Update
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Update Folder
json={
"folders" : [
{
"folderName" : "Change Name of Folder"},
{
"parentId" : "22af3144-2abc-22e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f733",
"folderName" : "New Folder Name"},
{
"folderId" : "43be9844-eafd-22e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f7ee",
"parentId" : "fea32554-12ea-22e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f21a"}
]
}
Sample body of Response HTML for Folder Update
{
"info" : {
"api" : "folder",
"version" : "1.4"},
"message" : {
"text" : "3 folders updated or created",
"code" : "0"},
"folders" : [
{
"folderId" : "abced180-2562-22e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f786",
"folderName" : "New Folder Name" },
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
{
"folderId" : "123da0c4-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"folderName" : "Another New Folder" }
]
}
"errors" : [
{
"key" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Folder ID Not Found"},
44 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 45

{
"key" : "New Folder + b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Parent folder not found: …9eaf-a4badbe0f786"},
{
"key" : " b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Duplicate child folder (New Folder): for parent" }
]
}
Folder API-Query Example
This API provides a list of folders.
The URL for a folder query is
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/folder.json?action=query.
Table 17:
URL filters that can be passed to the Folder API on a post
HTML Body Filters Definition Sample
Blank body Returns all devices with all data —
Table 18:
HTML Body
FIlters
folders Optional
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Folder API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Return only devices within
folders specified. Folders
must be specified as the id
of the folder.
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Return Folders
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding to Return Only Specific Folders
json={
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
}
Sample Body of Response JSON Encoding for Folder Query
{
"info": {
"api": "folder",
"version": "1.4"
},
"message": {
"text": "Request successfully processed",
"code": "0"
},
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 45
Page 46

"folders": [{
"folderId": "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"folderName": "South",
"folders": [{
"folderId": "e48c31a5-a532-44am-4cb2-a4badbe0f134",
"folderName": "Southwest APs"
},
{
"folderId": "a3fc71a5-a532-44am-4cb2-a4badbe0f555",
"folderName": "Southeast APs"
}],
"folderId": "14356a0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"folderName": "North",
"folders": [{
"folderId": "e48ff1a5-a532-44am-4cb2-a4badbe0f134",
"folderName": "Northwest APs"
},
{
"folderId": "443f1fa-a532-44am-4cb2-a4badbe0f5432",
"folderName": "Northeast APs"
}]
}]
}
Rule API-Update Example
This API enables a customer to update/create a rule in Activate without requiring interaction with the WebUI.
The URL for a rule update is
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/rule.json?action=update.
Table 19:
HTML
Body
Filters
rules Mandatory
There are no URL parameter filters for this API.
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Rule API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Updates the
specified rule
"rules": [{
"ruleName": "customer1.provision.rule",
"parentFolderId": "17c090a6-4ccb-4e3a
-beaa-00e4a54c61fe",
"ruleType": "provision",
"provisionType": "iap_to_rap",
"controller": "1.1.1.1",
"apGroup": "1231234",
"controllerMac": ""
}]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Update Rule
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
46 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 47

Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of JSON Encoding to Create an IAP to RAP Rule
json={
"rules": [{
"ruleName": "customer1.provision.rule",
"parentFolderId": "17c090a6-4ccb-4e3a-beaa-00e4a54c61fe",
"ruleType": "provision",
"provisionType": "iap_to_rap",
"controller": "1.1.1.1",
"apGroup": "1231234",
"controllerMac": ""
}]
}
Sample Body of Response HTML for Rule Update
{
"info" : {
"api" : "rule",
"version" : "1.4"},
"message" : {
"text" : "2 rules updated or created",
"code" : "0"},
"rules" : [
{
"ruleId" : "abced180-2562-22e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f786",
"ruleName" : "west.provision.rule" }
]
},
"errors" : [
{
"key" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-cc32adbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Rule ID Not Found"},
{
"key" : "New Rule + b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Parent folder not found: …9eaf-a4badbe0f786"},
{
"key" : " b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"errMessage" : "Duplicate rule name" }
]
}
Rule API-Query Example
This API provides a list of rules in your folder hierarchy. You can limit the scope of the query to a particular folder or
folders by including the required folder(s) in the body.
The URL for a rule query is
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/rule.json?action=query.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 47
Page 48

Table 20:
HTML
Body
Filters
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Rule API on a post
Definition Sample
folders Return only rules within folders specified.
Folders must be specified as the id of the
folder.
rules Return only rules specified. Rules must be
specified as the id of the rule.
There are no URL parameter filters for this API.
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
"rules" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
To view examples, click any of the following headings.
Sample Header Post to Return Rules
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length:
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample body of Response JSON Encoding to Return Specific Rules
json={
"rules" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
}
Sample Body of Response JSON Encoding with no Rules Requested
{
"info" : {
"api" : "rule",
"version" : "1.4" },
"message" : {
"text" : "Request successfully processed",
"code" : "0" },
"rules" : [
{
"ruleId" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ruleName" : "west.provision.rule",
"parentFolderid" : "433aa43-b432-0001-84323abcddd",
"ruleType" : "provision,
"provisionType" : "iap_to_athena",
"managementUrl" : "athena.arubanetworks.com"
},
{
"ruleId" : "aa03f0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0fa342",
"ruleName" : "east.provision.rule",
"parentFolderid" : "433aa43-b432-0001-84323abcddd",
"ruleType" : "provision",
48 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 49

"provisionType" : "iap_to_amp",
"ampIp" : "10.1.1.1",
"ampOrg" : "bww",
"ampSharedsecret" : "bww"
]
}
Customer API-Query Example
This APIprovides the customer details related to devices in Activate.
The URL for a customer query is:
[POST] activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/customer.json?action=query
Table 21:
URL Filters
No filter — Returns all devices relevant to all customers.
Table 22:
HTML Body
Filters
custPos Optional parameter Returns the customers related to
URL filters that can be passed to the Rule API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
HTML body filters that can be passed to the Customer API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
these purchase order and ship date
pairs.
—
"custPos" : [
{
"custPo" : "47320938",
"shipDate" : "05-14-2012"
}
]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post to Return Customer Details
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding for Returning Devices Related to Customer PO and Ship Date
json={
custPos" : [
{
"custPo" : "47320938",
"shipDate" : "05-14-2012"},
{
"custPo" : "xx-3201-44z3",
"shipDate" : "07-14-2012"},
]
}
Sample body of Response JSON Encoding for Customer PO & Ship Date Requests
{
"info" : {
"api" : "rule",
"version" : "1.3"},
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 49
Page 50

"message" : {
"text" : "Request successfully processed",
"code" : "0"},
"customers" : [
{
"cusomterId" : "b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"customerName" : "Intel Inc."
"custPo" : "47320938",
"shipDate" : "05-14-2012"},
{
"cusomterId" : "a33aaaaa-a444-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"customerName" : "Microsoft Inc."
"custPo" : "xx-3201-44z3",
"shipDate" : "07-14-2012"}
]
Whitelist Query API
This API provides the whitelist CLI commands that allow the controller to identify the remote APs allowed to connect
to the controller using Control Plane Security. These whitelist commands are used in a script which can access the
controller using SSH.
The URL for the whitelist query is
[POST]www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=whitelist.
The following example is a sample URL requesting both “add” and “delete” whitelist commands:
[POST]www.activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=whitelist&format=original&addOnly=false
Table 23:
URL Filters
No filter —
format Optional
URL filters that can be passed to the Whitelist API on a post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Returns only the add
commands (addOnly)
in original format.
Determines CLI
format of the whitelist
returned
l original – provides
command
formatted for
ArubaOS 6.1.3
and earlier. This is
the default value.
l new – provides
commands
formatted for
ArubaOS 6.1.4
and later.
—
format=original
format=new
addOnly Optional
parameter
50 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Determines which
whitelist commands
are returned
l false – returns both
(add and delete)
addOnly=false
addOnly=true
Page 51

URL Filters
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
commands.
l true – return only
(add) commands.
This is the default.
Table 24:
HTML
filters
devices
folders
HTMLparameters that can be passed to Whitelist Query Parameters
Nature of
Parameter
Optional
parameter
Optional
parameter
Definition Sample
Returns the
specified
devices
Returns the
devices within
the specified
folders
"devices" : [
"folders" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06" ]
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"]
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post for Whitelist Query
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding by Devices
json={
"devices" : [
"00:01:02:03:04:05",
"00:01:02:03:04:06" ]
}
Sample Body of Post JSON Encoding by Folder
json={
"folders" : [
"b40ef0a5-a532-11e1-9eaf-a4badbe0f786",
"ccef00bf-133a-22fa-9111-a333aaa0f786"
]
}
Note: You cannot mix folders and devices in the same body. If the body is empty, the API will respond with all
devices that are applicable for a whitelist.
Sample Body of Response with non-JSONEncoding
local-userdb-ap del mac-address 00:01:02:03:04:05 <CRLF>
local-userdb-ap add mac-address 00:01:02:03:04:05 ap-group “rap” ap name "steve-AP-105" fullname “Steve’s AP-105” description “New Long Description” <CRLF>
local-duserdb-ap del mac-address 00:01:02:03:04:06 <CRLF>
local-userdb-ap add mac-address 00:01:02:03:04:06 ap-group “rap” ap name "david-AP-105" fullname “David’s AP-105” description “New Long Description” <CRLF>
<EOF>
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 51
Page 52

Firmware API-Query Example
This API provides a list of firmware versions. You can filter on URL parameters, but there are no body parameter
filters forthis API.
The URL for a firmware query is
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/firmware.json?action=query.
Below is a sample URL that returns all firmware files added to Activate on 11-01-2016.
[POST]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/firmware.json?action=query&createDate=11-01-2016
Table 25:
URL Filters
No filter — Returns all devices with all data
createDate Optional
build Optional
Version Optional
There are no HTML parameter filters for this API.
URL Filters Passed to the Firmware APIon a Post
Nature of
Parameter
parameter
parameter
parameter
Definition Sample
Returns all firmware files added from this
date forward. This is not the release date
of the firmware, but the actual date the
firmware file was added to Activate.
Returns all firmware files equal to build.
This will return Aruba and all OEM
derivative files.
Returns all firmware files equal to
version. This will return Aruba and all
OEM derivatives files.
—
createDate=11-01-2016
build=28245
Version=5.0.3.0-1.0.0.1
Example Body of Postand Return JSONEncoding
Sample Header Post for Firmware Query
HTTP/1.1
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2012 16:11:12 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Connection: Keep-Alive
Sample Body of Response JSON Encoding with no Folders Requested
{
"info": {
"api": "firmware",
"version": "1.3"
},
"firmwareFiles": [{
"firmwareId": "77634c55-1400-4e74-97b1-f832b350fbab",
"fileName": "WB_16_02_0014.swi",
"fileSize": 15055657,
"version": "WB.16.02.0014",
"build": "783",
"platformId": "9d835ce3-c531-11e5-ac8f-22000aa8017b",
"platform": "ArubaOSSwitch",
52 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 53

"platformMode": "SWITCH",
"oem": "aruba",
"checksum": "4E989A39C8B4518B9C8DF1B7AE888063",
"track": "release",
"dependent": false,
"compliant": true,
"cBuild": false,
"createDate": "11-08-2016",
"createUser": "firmware-update",
"imageUrl": "http://d2vxf1j0rhr3p0.cloudfront.net/fwfiles/WB_16_02_0014.swi"
},
{
"firmwareId": "0fc0c697-d315-4b5d-b7dd-3fdd789895b0",
"fileName": "YC_16_02_0014.swi",
"fileSize": 19443082,
"version": "YC.16.02.0014",
"build": "910",
"platformId": "9d835ce3-c531-11e5-ac8f-22000aa8017b",
"platform": "ArubaOSSwitch",
"platformMode": "SWITCH",
"oem": "aruba",
"checksum": "24A228F56A5F16A87238A1BA992FD038",
"track": "release",
"dependent": false,
"compliant": true,
"cBuild": false,
"createDate": "11-08-2016",
"createUser": "firmware-update",
"imageUrl": "http://d2vxf1j0rhr3p0.cloudfront.net/fwfiles/YC_16_02_0014.swi"
} ],
"message": {
"text": "2 firmware returned",
"code": 0
}
}
Device History API-Query Example
The device history API provides the device communication history for devices. The following table provides
information about how this APIworks for admin and non-admin users.
Table 26:
User Role Functionality
Admin Activate retrieves the history of devices by using the MAC filter.
Non-Admin
The URL for a device history query is:
[GET]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/device.json?action=history&mac=XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX.
The following example is a sample URL to return device communication history for a specific MAC address (filter):
[GET]activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/device.json?action=history&mac=EA:EC:B8:30:43:80
Working of the API for Admin and Non-Admin Users
Activate retrieves the device history only if the customer ID of the device matches the
customer IDof the user who sends the query request.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 53
Page 54

Table 27:
URL filters that can be passed to the Device History API
URLFilters
mac Mandatory Returns device communication history for the
Nature of
Parameter
Definition Sample
specified MAC address.
Example Response Body of Return JSONEncoding
Sample Body of Return JSON Encoding for Device History
{
"devicehistory": [
{
"date": 1523988522183,
"type": "provision-update",
"source_ip": "104.36.250.11",
"current_version": "WC.16.03.0005",
"mode": "MAS-PRI",
"status": "success"
},
{
"date": 1523988222192,
"type": "provision-update",
"source_ip": "104.36.250.11",
"current_version": "WC.16.03.0005",
"mode": "MAS-PRI",
"status": "success"
}
]
}
mac=EA:EC:B8:30:43:80
Sample Curl Code
Sample code to query all inventory
The first line performs the authentication and creates a cookie, and the second line provides the query. Substitute
your own credentials forthe username and password in the example below.
curl -d 'credential_0=username&credential_1=password' -c Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/LOGIN
curl -b Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query
Sample code to query a single MAC address
The first line performs the authentication and creates a cookie, and the second line provides the query. Substitute
your own credentials forthe username and password in the example below.
curl -d 'credential_0=username&credential_1=password' -c Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/LOGIN
curl -d 'json={"devices" : ["6C:F3:7F:C3:54:42" ] }' -b Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query
Sample code to update inventory
The first line performs the authentication and creates a cookie, and the second line provides the update. Substitute
your own credentials forthe username and password in the example below.
54 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 55

curl -d 'credential_0=username&credential_1= password' -c Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/LOGIN
curl -d 'json={"devices" : [{"mac" : "6C:F3:7F:C3:54:42", "deviceName" : "steve-AP-105" } ]
}' -b Activate-cookie.txt
https://activate.arubanetworks.com/api/ext/inventory.json?action=update
Client.java Sample
public class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
Request request = null;
String username = null;
String password = null;
if (args.length < 2) {
System.out.println("usage: username password {apas host}");
System.exit(1);
} else if (args.length == 2) {
username = args[0];
password = args[1];
request = new Request();
} else if (args.length > 2) {
username = args[0];
password = args[1];
request = new Request(args[2], false);
}
int status = request.login(username, password);
if (status != 200)
System.out.println("login failed code[" + status + "]");
else {
request.sendRequest("/api/ext/folder.json?action=query", null);
System.out.println(request.getResponseBody());
String post = "json={\"folders\":[\"72ffcf7c-6242-415a-84a4-f64606af3c9c\"]}";
request.sendRequest("/api/ext/inventory.json?action=query", post);
System.out.println(request.getResponseBody());
}
request.close();
}
}
Request.java Sample
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSession;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier;
public class Request {
private boolean log = false;
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 55
Page 56

private Socket client;
private DataOutputStream out;
private InputStream in;
private String lf = "\r\n";
private String cl = "Content-Length:";
private Map<String,String> headers;
private Map<String,String> addHeaders = new HashMap<String,String>();
private String response;
private String session;
static HostnameVerifier hv = new HostnameVerifier() {
public boolean verify(String urlHostName, SSLSession session) {
System.out.println("Warning: URL Host: " + urlHostName + " vs. " + session.getPeerHost
());
return true;
}
};
/**
* ArubaActivate request constructor
**/
public Request() {
this ("activate.arubanetworks.com", false);
}
/**
* ArubaActivate request constructor
* @param server The Activate server activate.arubanetworks.com
* @param log System.out logging of HTTP responses
**/
public Request(String server, boolean log) {
this.log = log;
try {
HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultHostnameVerifier(hv);
// Create a trust manager that does not validate certificate chains
TrustManager[] trustAllCerts = new TrustManager[] {new X509TrustManager() {
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(final X509Certificate[] chain, final String authType )
{
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(final X509Certificate[] chain, final String authType )
{
}
@Override
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return null;
}
}};
// Install the all-trusting trust manager
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL" );
sslContext.init(null, trustAllCerts, new java.security.SecureRandom() );
// Create an ssl socket factory with our all-trusting manager
SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory();
client = sslSocketFactory.createSocket(server, 443);
// get th in/out streams
out = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream());
in = client.getInputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
/**
* Login to ArubaActivate server.
56 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 57

* @return HTTP status code
**/
public int login(String username, String password) {
String post =
"credential_0=" + username + "&" +
"credential_1=" + password;
sendRequest("/LOGIN", post);
session = getSessionId();
return getHttpStatusCode();
}
/**
* Add an http header to the request
* @param name The header name
* @param value The header value
**/
public void addHttpHeader(String name, String value) {
addHeaders.put(name, value);
}
/**
* Send HTTP request to the ArubaActivate server.
* @param api The API to post to: for example /api/ext/inventory.json?action=query
* @param post Any post values to send: for example json={"folders":["72ffcf7c-6242-415a-
84a4-f64606af3c9c"]}
**/
public void sendRequest(String api, String post) {
response = null;
try{
String http =
(post != null ? "POST " : "GET ") + api + " HTTPS/1.1" + lf +
"Content-Length: " + (post != null ? String.valueOf(post.length()) : "0") + lf +
"Content-Type: " + (post != null ? "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;" :
"text/plain;") + " charset=utf-8" + lf +
"Connection: Keep-Alive" + lf;
if (session != null) http +=
"Cookie: session=" + String.valueOf(session) + lf;
for (String name : addHeaders.keySet())
http += name + ": " + addHeaders.get(name) + lf;
System.out.println(http);
out.writeBytes(http + lf);
if (post != null) out.writeBytes(post);
response = getResponse();
headers = new HashMap<String,String>();
String[] lines = response.split("\r\n");
for (String line : lines)
if (line.indexOf(":") > -1)
headers.put(line.substring(0, line.indexOf(":")), line.substring(line.indexOf(":")
+1).trim());
else if (line.startsWith("HTTP") && line.indexOf(" ") > -1)
headers.put("HTTP", line.split(" ")[1]);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.err.println("Don't know about host");
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Couldn't get I/O for the connection");
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
}
}
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 57
Page 58

private String getSessionId() {
session = null;
for (String header : headers.keySet()) {
if (header.equalsIgnoreCase("Set-Cookie")) {
String[] elements = headers.get(header).split(";");
for (String element : elements) {
if (element.startsWith("session")) {
return element.split("=")[1];
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
private int getHttpStatusCode() {
for (String header : headers.keySet()) {
if (header.startsWith("HTTP")) {
String value = headers.get(header);
try {return Integer.parseInt(value);} catch(NumberFormatException nfe) {return -1;}
}
}
return -1;
}
private String getResponse() throws Exception {
byte[] bytes;
int count = 0;
int total = 0;
int contentLength = -1;
int contentCount = 0;
int contentStart = -1;
String buffer = new String();
while(total > -1) {
bytes = new byte[64];
total = in.read(bytes);
if(total > 0) {
int offset = (count > 0 ? ((bytes.length * count) -1) : 0);
buffer += new String(bytes, 0, total);
}
if (contentLength < 0 && buffer.indexOf(cl) > -1) {
int start = buffer.indexOf(cl) + 16;
int end = buffer.indexOf("\r\n", start);
if (end > 0) {
contentLength = Integer.parseInt(buffer.substring(start, end));
if (log) System.out.print("\nSpecified " + cl + " " + contentLength + "\n");
}
}
// measure the content
contentStart = buffer.indexOf(lf + "\r\n");
if (contentStart > -1) {
contentStart += lf.length() + 2;
contentCount = buffer.length() - (contentStart);
if (contentCount >= contentLength) break; // got it all
}
count++;
}
if (log) {
System.out.println("-- response start --");
System.out.print(buffer);
System.out.println("-- response end --");
if (buffer.length() == 0)
System.out.println("Actual " + cl + " 0");
else
58 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 59

System.out.print("Actual " + cl + " " + buffer.substring(contentStart, contentStart +
contentCount).length() + "\n");
}
return buffer;
}
/**
* Provides the HTTP response body.
* @return The HTTP response body.
**/
public String getResponseBody() {
if (response != null && response.indexOf("\r\n\r\n") > -1)
return response.split("\\r\\n\\r\\n")[1];
else return "";
}
/**
* Close the request
**/
public void close() throws java.io.IOException {
// TODO: Perform an HTTP GET with a Connection: close header
in.close();
}
}
/**
* Login to APAS server.
* @return HTTP status code
**/
public int login(String username, String password) {
String post =
"credential_0=" + username + "&" +
"credential_1=" + password;
sendRequest("/LOGIN", post);
session = getSessionId();
return getHttpStatusCode();
}
/**
* Send HTTP request to the APAS server.
* @param api The API to post to: for example /api/ext/inventory.json?action=query
* @param post Any post values to send: for example json={"folders":["72ffcf7c-6242-415a-
84a4-f64606af3c9c"]}
**/
public void sendRequest(String api, String post) {
response = null;
try{
String http =
(post != null ? "POST " : "GET ") + api + " HTTPS/1.1" + lf +
"Content-Length: " + (post != null ? String.valueOf(post.length()) : "0") + lf +
"Content-Type: " + (post != null ? "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;" :
"text/plain;") + " charset=utf-8" + lf +
"Connection: Keep-Alive" + lf;
if (session != null) http +=
"Cookie: session=" + String.valueOf(session) + lf;
out.writeBytes(http + lf);
if (post != null) out.writeBytes(post);
response = getResponse();
headers = new HashMap<String,String>();
String[] lines = response.split("\r\n");
for (String line : lines)
if (line.indexOf(":") > -1)
headers.put(line.substring(0, line.indexOf(":")), line.substring(line.indexOf(":")
+1).trim());
else if (line.startsWith("HTTP") && line.indexOf(" ") > -1)
headers.put("HTTP", line.split(" ")[1]);
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 59
Page 60

} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.err.println("Don't know about host");
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Couldn't get I/O for the connection");
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
System.exit(1);
}
}
private String getSessionId() {
session = null;
for (String header : headers.keySet()) {
if (header.equalsIgnoreCase("Set-Cookie")) {
String[] elements = headers.get(header).split(";");
for (String element : elements) {
if (element.startsWith("session")) {
return element.split("=")[1];
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
private int getHttpStatusCode() {
for (String header : headers.keySet()) {
if (header.startsWith("HTTP")) {
String value = headers.get(header);
try {return Integer.parseInt(value);} catch(NumberFormatException nfe) {return -1;}
}
}
return -1;
}
private String getResponse() throws Exception {
byte[] bytes;
int count = 0;
int total = 0;
int contentLength = -1;
int contentCount = 0;
int contentStart = -1;
String buffer = new String();
while(total > -1) {
bytes = new byte[64];
total = in.read(bytes);
if(total > 0) {
int offset = (count > 0 ? ((bytes.length * count) -1) : 0);
buffer += new String(bytes, 0, total);
}
if (contentLength < 0 && buffer.indexOf(cl) > -1) {
int start = buffer.indexOf(cl) + 16;
int end = buffer.indexOf("\r\n", start);
if (end > 0) {
contentLength = Integer.parseInt(buffer.substring(start, end));
if (log) System.out.print("\nSpecified " + cl + " " + contentLength + "\n");
}
}
// measure the content
contentStart = buffer.indexOf(lf + "\r\n");
if (contentStart > -1) {
60 | ArubaActivate APIs Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 61

contentStart += lf.length() + 2;
contentCount = buffer.length() - (contentStart);
if (contentCount >= contentLength) break; // got it all
}
count++;
}
if (log) {
System.out.println("-- response start --");
System.out.print(buffer);
System.out.println("-- response end --");
if (buffer.length() == 0)
System.out.println("Actual " + cl + " 0");
else
System.out.print("Actual " + cl + " " + buffer.substring(contentStart, contentStart +
contentCount).length() + "\n");
}
return buffer;
}
/**
* Provides the HTTP response body.
* @return The HTTP response body.
**/
public String getResponseBody() {
if (response != null && response.indexOf("\r\n\r\n") > -1)
return response.split("\\r\\n\\r\\n")[1];
else return "";
}
/**
* Close the request
**/
public void close() throws java.io.IOException {
// TODO: Perform an HTTP GET with a Connection: close header
in.close();
}
}
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide ArubaActivate APIs | 61
Page 62

Chapter 6
What's New in Activate
The following tables describe known issues and recent improvements and modifications in Aruba Activate.
Known Issues
There are no known issues in this release of Activate.
Improvements and Modifications
Table 28:
Activate Release 4 Changes—July 2018
Change Description
UI change: Username
in the Activate WebUI
Devices table:
Truncation of records
UI change: Devices
page
New check box in the
IAP to CAP Rule
New text box (field) in
the Switch to AirWave
Rule
Device History table When a device is provisioned for the first time, the Device table in the Devices page
The logged-in username is now displayed at the header pane (see the top right corner) of
the Activate WebUI.
Any device data older than 2 years is deleted after a backup of the Devices table is taken.
In the Devices page, under the Devices table, the Last Modified, IPAddress, and
Controller/Primary columns are no longer available. Also, in the Device Detail section, the
controller information is not available anymore.
For any device, the Device History table provides information on the IPAddress and the
Last Modified date.
While setting the IAP to CAP rule, you can see a new Persist Controller I P check box. You
can select this check box if you want the controller IPto persist.
While setting the Switch to AirWave rule, you can now specify the IPaddress of the backup
controller in the Backup Ctrl IPtext box.
reflects the update in the Status column. For details on any further device updates through
APIs, users can see the Device History pane in the Devices page.
Table 29:
Changes—June 2018
Change Description
APIupdate: Device
History API
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide What's New in Activate | 62
A new API is now available that provides the device communication history for devices.
The admin users can retrieve the history of all devices by using the MAC filter. For nonadmin users, Activate retrieves the device history only if the customer ID of the device
matches the customer IDof the user who sends the query request. Bug Id:
Page 63

Table 30:
Changes—November 2016
Change Description
UIchange: Inclusion of
Part Description
column in the Device
page
A new Part Descript ion column is added in the Devices table. This is because HPEparts
naming convention does not allow us to understand the device name from the Part
column. To ease the effort of knowing the device name, the Part Description column is
included to display the device name.
For example, JL015A has
Point
Changes to the IAPto
Central provisioning
rule
Table 31:
Changes—September 2016
To restrict the rule creation for Instant APs to take place only through Central, the option
for the IAPto Central provisioning rule is made unavailable in the Activate UI.
Change Description
New query
parameters in
pagination
support for the
External
Inventory API
The following URLquery parameters are introduced for the Inventory Query API:
1. limit – optional parameter; takes an integer value that is greater than or equal to 1.
2. offset – optional parameter; takes an integer value greater than or equal to 0.
Both the parameters—limit and offset—must be specified for pagination specifications to take
effect.
The following key is added in the JSONresponse:
totalCount – returns the total count of inventory present for the customer irrespective of the
pagination specifications.
HP 365 Cloud Managed Dual Radio 802.11ac (WW) Access
as its part description.
See the Inventory API-Query Example section for information about applying the specifications
for pagination.
Locating the
cloud activation
key for ArubaOS
switches
Table 32:
Changes—July 2016
1. Access the command- line interface (CLI) of the ArubaOS switch.
2. Execute the show activate provision command. The cloud activation key is displayed at the
end of the command output.
(Central)# show activate provision
Configuration and Status - Activate Provision Service
Activate Server Address : device.arubanetworks.com
Activate Provision Service : Enabled
Activation Key : VMQF7EYA
Change Description
UIchange: MAS-to-
AMP Rule renamed to
Switch-to-AMP.
The MAS-to-AMP rule has been renamed, and appears as a Switch-to-AMP rule in the
Activate UI. Although the rule name has changed, it continues to allow you to provision an
Aruba Mobility Access Switch (MAS) to communicate with its configuration master AirWave
(AMP) server.
63 | What's New in Activate Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide
Page 64

Table 33:
Changes—May 2016
Change Description
Device History The View Device History will now show Device communication history with Activate only
for past two months limited to 1000 records.
Table 34:
Changes—October 2015
Change Description
UIchange: Pagination
added to the Devices
list.
UI change: Column
removed from
theDevices list
UI change: Columns
removed from the
Folder list
For users with more than 1000 devices, the Devices list is now automatically divided into
pages of 1000 devices each, dramatically improving the load time for large device
inventories.
Click the page forward ( ) or page back ( ) icons in the Devices list titlebar to display
other pages in the Device list. To disable the pagination feature and view all 1000+
devices on a single page, click the Devices per page link on the Devices list titlebar, and
select the All option.
The PO number column is removed from the devices table. To view purchase order (PO)
data for a specific device, select the device in the Devices list, then expand the Order
Detail section.
The Rule count and User count fields are removed from theFolder list on the Setup page.
To view the number of rules or users associated to a folder, select a folder in the Folders
list. The Rules and Users tables on that page will be automatically filtered to display data
for just that folder.
Aruba Activate Release 6| User Guide What's New in Activate | 64
 Loading...
Loading...