Page 1

ARTS PDF
Split Pro™
Version 2.0
Page 2

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Contents
Contents
1. INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................. 5
1.1. New to version 2.0 .................................................................................... 5
1.2. Demo Limitations...................................................................................... 5
2. SETUP .......................................................................................................... 6
2.1. System Requirements................................................................................ 6
2.2. Installation............................................................................................... 6
2.3. Activation................................................................................................. 7
2.4. Registration.............................................................................................. 8
2.5. Uninstall .................................................................................................. 8
3. SPLITTING METHODS ...................................................................................... 9
3.1. Split by Bookmarks ................................................................................... 9
3.2. Split by Control File ................................................................................... 9
3.3. Split by Control File - Full Path ...................................................................10
3.4. Split by File Size ......................................................................................10
3.5. Split into Single Pages ..............................................................................11
3.6. Split by Coordinate File .............................................................................11
4. WATCHED FOLDERS....................................................................................... 12
5. ARTS PDF SPLIT PRO™ ASSISTANT................................................................ 13
5.1. What is a Coordinate File? .........................................................................14
5.1.1. Inside a Coordinate File................................................................................. 14
5.2. Managing Coordinate Files.........................................................................16
5.2.1. Creating a New Coordinate File ...................................................................... 16
5.2.2. Activating the Rectangle Tool......................................................................... 16
5.2.3. Editing a Coordinate File................................................................................ 18
5.2.4. Opening a Coordinate File.............................................................................. 18
5.2.5. Saving a Coordinate File................................................................................ 19
5.2.6. Closing a Coordinate File............................................................................... 19
5.2.7. Viewing Text ............................................................................................... 19
5.2.8. Viewing Text Runs........................................................................................ 20
5.2.9. Viewing Commands...................................................................................... 21
6. ARTS PDF SPLIT PRO™ GUI ........................................................................ 23
6.1. Splitting Methods .....................................................................................23
6.1.1. Split by Bookmarks ...................................................................................... 23
6.1.2. Split by Control File ...................................................................................... 24
6.1.3. Split by Control File – Full Path....................................................................... 24
6.1.4. Split by Coordinate File ................................................................................. 24
6.1.5. Split by File Size .......................................................................................... 25
6.1.6. Split into Single Pages .................................................................................. 25
6.2. Watched Folders ......................................................................................26
6.2.1. Setting up a Watched Folder.......................................................................... 26
6.2.2. Watched Folder Splitting Methods................................................................... 27
| CONTENTS | Page 2 of 58
Page 3

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Contents
6.3. Options...................................................................................................28
6.3.1. Logging enabled........................................................................................... 29
6.3.2. Silent Mode................................................................................................. 30
6.3.3. Overwrite output file..................................................................................... 30
6.3.4. Update navigational elements ........................................................................ 30
6.3.5. Output subfolders......................................................................................... 31
7. ARTS PDF SPLIT PRO™ CL........................................................................... 32
7.1. Splitting Methods .....................................................................................32
7.1.1. Split by Bookmarks ...................................................................................... 32
7.1.2. Split by Control File ...................................................................................... 32
7.1.3. Split by Coordinate File ................................................................................. 32
7.1.4. Split into Single Pages .................................................................................. 33
7.1.5. Split by Page Range..................................................................................... 33
7.2. Parsing Methods.......................................................................................33
7.2.1. Parse a page ............................................................................................... 33
7.2.2. Parse a page range....................................................................................... 33
7.3. Watched Folders ......................................................................................34
7.3.1. Watched Folder Splitting Methods................................................................... 34
7.4. Options...................................................................................................34
7.4.1. Overwrite.................................................................................................... 34
7.4.2. Update navigational elements ........................................................................ 35
7.4.3. Run in the background.................................................................................. 35
8. ARTS PDF SPLIT PRO™ COM........................................................................ 36
8.1. Registering the COM object........................................................................36
8.2. Class Strings/Namespaces.........................................................................37
8.2.1. Visual Basic................................................................................................. 37
8.2.2. ASP............................................................................................................ 37
8.2.3. VB.NET....................................................................................................... 37
8.2.4. C#............................................................................................................. 37
8.2.5. Delphi ........................................................................................................ 38
8.2.6. PHP............................................................................................................ 38
8.3. Permissions for Web Applications................................................................38
8.3.1. ASP............................................................................................................ 38
8.3.2. ASP.NET ..................................................................................................... 38
8.4. Object ARTSSplitPro .................................................................................39
8.4.1. GetErrorMessage.......................................................................................... 39
8.4.2. GetVersionNumber ....................................................................................... 39
8.4.3. SetLicenceKey ............................................................................................. 39
8.4.4. SetOverwriteMode........................................................................................ 40
8.4.5. SetUpdateMode ........................................................................................... 40
8.4.6. SplitByBookmarks ........................................................................................ 40
8.4.7. SplitByControlFile......................................................................................... 41
8.4.8. SplitByCoordFile........................................................................................... 41
8.4.9. SplitByFileSize ............................................................................................. 41
8.4.10. SplitIntoSinglePages..................................................................................... 42
8.5. COM Examples.........................................................................................43
8.5.1. Visual Basic................................................................................................. 43
| CONTENTS | Page 3 of 58
Page 4

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Contents
8.5.2. ASP............................................................................................................ 44
9. APPENDIX A – RECTANGLE COMMANDS............................................................. 46
10. APPENDIX B – COMMAND LINE SWITCHES ........................................................ 51
11. TROUBLESHOOTING....................................................................................... 55
11.1. Frequently Asked Questions....................................................................55
11.2. Forum .................................................................................................56
11.3. Updates...............................................................................................56
11.4. Maintenance.........................................................................................57
11.5. Technical Support .................................................................................58
| CONTENTS | Page 4 of 58
Page 5

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Introduction
1. Introduction
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ is an industrial grade, stand-alone PDF split ter that allows you to split large
PDF files into smaller PDF files, in many different ways. The available
- Split by Bookmarks
- Split by Control File
- Split by Control File – full path
- Split by File Size
- Split into Single Pages
- Split by Coordinate File
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ is made up of four components:
• with the first being
actual file splitting;
• the
• the
• and lastly
Server based usage is supported by ARTS PDF Split Pro™. The
on a network to drop PDF files into a directory, and then use ARTS PDF Split Pro’s engine to
perform the file splitting.
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant is used to create coordinate files and gives the user the
power to perform advanced splitting operations;
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Command Line Interface (CLI or CL) allows splitting to be utilized
from the command-line;
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ COM Object (COM) enables developers to create customized
applications to accommodate PDF splitting in their workflow.
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Graphical User Interface (GUI) which performs the
watched folder function allows users
splitting methods include:
1.1. New to version 2.0
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ version 2.0 includes:
• support for Unicode documents.
• retains bookmarks and links in output files.
1.2. Demo Limitations
An ‘ARTS PDF Split Pro’ watermark will appear on each page of every output file when
using the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ demo version.
Note: No limitations are present in the full retail version. See section 2.3 of this document,
Activation, for information on how to activate the full version.
| CONTENTS | Page 5 of 58
Page 6

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Setup
2. Setup
2.1. System Requirements
Windows
• Intel® Pentium® processor or equivalent
• Microsoft® Windows NT® Workstation 4.0 with Service Pack 6, Windows® 2000
with Service Pack 2, Windows XP Professional or Home Edition, or Windows XP
Tablet PC Edition
• 64MB of RAM (128MB recommended)
• 50MB of available hard-disk space
• 1,024x768 screen resolution
Note: ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant requires Adobe® Acrobat® 5.0 or later.
For technical support queries, please consult the
or visit our website at
http://www.artspdf.com/support.asp.
Troubleshooting section of this manual
2.2. Installation
You may have received this software on either CD-ROM or as a downloaded file.
Windows (CD-ROM)
To install from a CD-ROM:
1. Verify that Adobe Acrobat is not running.
2. Insert the CD-ROM.
3. If the CD-ROM does not automatically start, navigate to the CD in Windows
Explorer and execute the Windows Installer.exe file.
4. Navigate to ARTS PDF Split Pro™.
5. Click Install.
6. Follow the prompts to install ARTS PDF Split Pro™.
Windows (.exe)
If you downloaded ARTS PDF Split Pro™, to install:
1. Verify that Adobe Acrobat is not running.
2. Execute the installation file provided.
3. Follow the prompts to install ARTS PDF Split Pro™.
| CONTENTS | Page 6 of 58
Page 7

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Setup
2.3. Activation
If you have the demo version of ARTS PDF Split Pro™ installed, you can activate the full
version using the following steps:
1. Open ARTS PDF Split Pro by going to ‘Start > Programs > ARTS PDF > ARTS PDF
Split Pro > ARTS PDF Split Pro 2.0’.
2. Click the ‘About’ button.
3. Ensure you have a valid serial. A valid serial can only be obtained by purchasing
the product. To purchase ARTS PDF Split Pro™:
a. Select the ‘Register’ tab page and click on ‘Buy Now’ to purchase the full
version.
b. After your purchase has been confirmed, you will receive an email containing
your serial number.
4. Select the ‘Register’ tab page and click on ‘Activate’.
5. Enter your license details, including your serial number, and click “OK”.
Alternatively you can do the following to activate t he full version using ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant:
1. In Acrobat select ‘Help > About 3
Assistant’.
2. Ensure you have a valid serial. A valid serial can only be obtained by purchasing
the product. To purchase ARTS PDF Split Pro™:
a. Select the ‘Register’ tab page and click on ‘Buy Now’ to purchase the full
version.
b. After your purchase has been confirmed, you will receive an email containing
your serial number.
3. Select the ‘Register’ tab page and click on ‘Activate’.
4. Enter your license details, including your serial number, and click “OK”.
rd
Party Plug-Ins > ARTS PDF Split Pro
| CONTENTS | Page 7 of 58
Page 8

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Setup
2.4. Registration
ARTS PDF provide the option of registering your copy of ARTS PDF Split Pro™ online.
Online registration allows you to protect your serial number. In the event you lose or
misplace your serial, we can locate and provide your serial to you on request.
Registered customers will also receive important upgrade information and notification of
product updates.
1. After activating your copy of ARTS PDF Split Pro™ you will be prompted to
register online. Do one of the following:
• Click “Now” to register your product online
• Click “Later” to register at a later stage. After entering your license details,
you can register your product anytime by clicking on the “Register Now”
button of the Register tab.
2. When registering your product, complete th e online form and click “Submit
Registration”.
3. You only need register your product with us once.
To manually register your ARTS PDF product, please visit our online registration page,
http://www.artspdf.com/register.asp.
1
.
2.5. Uninstall
Windows
To uninstall on a Windows platform:
1. Verify that Adobe Acrobat is not running.
2. Click Start > Settings > Control Panel.
3. Open Add/Remove Programs.
4. Select ‘ARTS PDF Split Pro 2.0’ from the menu.
5. Click ‘Add/Remove’.
1
You must be connected to the Internet.
| CONTENTS | Page 8 of 58
Page 9

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Splitting Methods
3. Splitting Methods
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ can split PDFs into smaller P DF files (or fragments) using a number of
different methods. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ can split PDFs by bookmarks, by control file
into single pages and by coordinate file. These splitting methods are explained in detail below.
3.1. Split by Bookmarks
This method will split a PDF file by its bookmarks. Each page that is bookmarked will be
the start of a new fragment, and the title of the bookmark w ill be used as the name of
the file.
All subsequent pages are added to that fragment, stopping at the next bookmarked
page. You will be given a chance to choose the level of bookmarks to use. Top-level
bookmarks are level 1.
You can Split By Bookmarks using either of the following ARTS PDF Split Pro™
components:
GUI
•
CLI
•
COM
•
2
, by file size,
3.2. Split by Control File
This method will split a PDF file as specified in a pre-defined control f ile. A control file is
a text file that specifies which pages will be split from the document, and the names of
each PDF file that will be split from the document.
An example of this is:
12 introduction.pdf
23-29 chapter3.pdf
80 conclusion.pdf
Using the above control file page 12 will be split and named introduction.pdf, pages 23
to 29 will be split and named chapter3.pdf and page 80 will be named conclusion.pdf. An
error will occur if the page number specified is out of range. To avoid such errors, put
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ in silent mode.
2
With control files you also have the option to specify full pathnames.
| CONTENTS | Page 9 of 58
Page 10

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Splitting Methods
You can Split By Control File (not full path ) using either of the following ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ components:
GUI
•
CLI
•
COM
•
3.3. Split by Control File - Full Path
This method of splitting will split a PDF file as specified in a control file, with each output
file (or fragment) being stored in the directory indicated by the full pat h in the control
file. A control file with the full path is a text file that specifies which pages will be split
from the document, and the storage location and name of the pdf file that will be split
from the document.
An example of this is:
23,25,55 c:\splitpdf_files\project\introduction.pdf
23-30 c:\splitpdf_files\project\sports.pdf
81 c:\splitpdf_files\media\movies.pdf
Using the above example page 23, 25 and 55 will be split and named introduction.pdf
and saved to “c:\splitpdf_files\project\”. Pages 23 to 30 will be split and named
sports.pdf in the “c:\splitpdf_files\project\” directory whilst page 81 will be named
conclusion.pdf and saved to the “c:\splitpdf_files\media” directory.
You can Split By Control File (fu ll path) using either of the following ARTS PDF Split Pro™
components:
GUI
•
COM
•
3.4. Split by File Size
This method of splitting allows PDFs to be split based on a file siz e value (in kilobytes)
specified by the user.
The way this works is that split pro will scan through you r pdf document/s one page at a
time, and check at the end of each page to see if the current fragment is equal to or
greater than the specified file size.
| CONTENTS | Page 10 of 58
Page 11

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Splitting Methods
If the fragment size is equal to or greater than the file size specified then at that point
the PDF will be split. Otherwise ARTS PDF Split Pro™ will move onto the next page and
perform the same check again.
You can Split By File Size using either of the follow ing ARTS PDF Split Pro™ components:
GUI
•
COM
•
3.5. Split into Single Pages
This method of splitting will split a PDF file into fragments containing one page each in
the destination folder specified by the user.
You can Split Into Single Pages using either of the following ARTS PDF Split Pro™
components:
GUI
•
CLI
•
3.6. Split by Coordinate File
This method of splitting will split a pdf file based on the text that is on each page.
Coordinate files are used to perform intelligent splitting of PDF files based on page
content. Coordinate files can be created using ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant.
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant for more detail.
See
You can Split By Coordinate using either of the follow ing ARTS PDF Split Pro™
components:
GUI
•
CLI
•
COM
•
| CONTENTS | Page 11 of 58
Page 12

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Watched Folders
4. Watched Folders
The watched folders function in ARTS PDF Split Pro™ GUI and CLI allows an automated splitting
solution to be set-up and accessible from the desktop or across a network. By selecting to use
Watched Folders, then specifying the folders where the files are stored during the splitting process;
PDF/s can be dropped in the specified input folder, split (either in to single pages, by coordinate file
or control file) and moved to the specified output folder.
Making the input and output directories accessible across a network results in having a high-speed
splitting solution available across a network.
GUI Watched Folder feature allows you to perform the following splitting methods using
The
watched folders:
• split into single pages
• split by control file
• split by control file full path
• split by coordinate file
CLI Watched Folder feature allows you to perform following splitting methods using watched
The
folders:
• split into single pages
• split by coordinate file
| CONTENTS | Page 12 of 58
Page 13
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
5. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant
The ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant is a plug-in for Adobe Acrobat that assists the user to create
coordinate files of which are utilized when splitting with ARTS PDF Split Pro™. It has been
designed to allow the user to create coordinate files quickly and easily without the need to directly
create or edit coordinate (text) files. The ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant can be accessed via the
toolbar, or Plug-ins menu.
Figure 1. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant menu-item
Figure 2. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant menu-item
| CONTENTS | Page 13 of 58
Page 14

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
5.1. What is a Coordinate File?
A coordinate file must be used when performing a ‘Split By Coordinate File’ split method.
Coordinate files use a .crd file extension but they are plain text files that can be viewed
or edited with any text editor. The contents of a coordinate file may contain a single line
or multiple lines of commands. An example of a coordinate file is shown below:
splitontextchange 507.406555 56.816055 535.184265 24.408707
addtofilename 507.406555 56.816055 535.184265 24.408707 "pageno "
providefilename 504.628784 67.001236 543.517578 21.630936
5.1.1. Inside a Coordinate File
A single line within a coordinate file st ar ts with a rectangle command, followed by
rectangle coordinates and a string parameter. The structure of a line within a coordinate
file is as shown below:
rectangle command [space] left rectangle coordinate [space] top rectangle coordinate
[space] bottom rectangle coordinate [space] right rectangle coordinate [space] “string“
An example of this is:
splitiftextcontainedinbox 70.093918 736.859451 141.122421 703.214371 "arts"
Where:
Rectangle Command = splitiftextcontainedinbox
Left coordinate = 70.093918
Top coordinate = 736.859451
Bottom coordinate = 141.122421
Right coordinate = 703.214371
String parameter = arts
Rectangle command
Each command line within the coordinate file has a rectangle comman d related to it,
which indicates what is required when splitting a PDF f ile. Rectangle commands give the
option to:
• split a PDF file if the page contains specific text.
• provide output filenames.
• exclude or include pages from output files.
• read text on a PDF file and export it to a text file.
A full list of available
Rectangle Commands can be found in Appendix A of this document.
| CONTENTS | Page 14 of 58
Page 15

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
Rectangle coordinates
Rectangle coordinates (left, top, bottom and right) are used to view the rectangle using
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant. The rectangle is used to look at text on a PDF page for
the splitting of PDFs. Text within a rectangle area can be compared against the
specified string parameter passed.
Example:
splitiftextcontainedinbox 70.093918 736.859451 141.122421 703.214371 "arts"
The coordinates, 70.093918 736.859451 141.122421 703.214371, form a rectangle.
The rectangle area is viewable on a PDF page using ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant. A
rectangle can be viewed on each page of the PDF document. Depending on where the
text run begins on the page, this rectangle may have text inside it. Using the
splitIfTextContainedInBox command, if ARTS PDF Split Pro™ finds that the “arts” string
is found inside the rectangle area then the PDF will split at t hat page i.e. PDF will split if
the word “arts” is found within the text inside the rectangle.
String parameter
When creating coordinate files, particular rectangle commands may require a user
specified text string to be entered in order to split PDFs the way the particular command
is expected to. There is a text box in the rectangle tool properties window named
‘Parameters for command’ where these text strings can be entered.
An example for a parameter is when utilizing the ‘split if t ext contained in box’ command
when creating a coordinate file. This command checks if the parameter specified by the
user within the parameter text box is present within the related ARTS PDF Split Pro™
rectangle in the PDF file. If this string is present , then the file is split.
Commands that do not require a specified text string are:
• SplitOnTextChange
• SkipHeader
• provideFilename
• provideFilenameFromFirstWord
• addToFilenameTextInBox
• excludeIfNoTextContainedInBox
• extractText
Note: Version 2 users will find that coordinate files created by ARTS PDF Split Pro™
Assistant have numeric values instead of a text string as the last parameter. This is to support
Unicode. Version 2 is backwards compatible and can still support string parameters if coordinate
files have been created or edited manually.
| CONTENTS | Page 15 of 58
Page 16
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
5.2. Managing Coordinate Files
5.2.1. Creating a New Coordinate File
To create a coordinate file:
1. Open a PDF document in Adobe Acrobat.
2. Click the 'Create a new CRD file' button on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant
toolbar. You can alternatively go to 'Plug-ins > ARTS PDF Split Pro Assistant >
New' in the Adobe Acrobat plug-ins menu.
The ‘Rectangle Tool’ button is now automatically activated enabling you to draw a
rectangle on your PDF page.
3. With the ‘Rectangle Tool’ button activated, drag a box over the area on the page
that contains the text you wish to apply a command to.
4. The 'Rectangle Tool Properties' window will now appear. Select the command you
wish to use for the rectangle and enter any parameters required. A full list of
available
5. Click ‘OK’. This command is now set to the rectangle currently selected.
6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 for every command you wish to add to the coordinate file.
7. Save the coordinate file.
Rectangle Commands can be found in Appendix A of this document.
Figure 3. ‘Create a new CRD file’ toolbar button
Note: There is no limit to the number of rectangle commands within a coordinate file. If you wish
to apply several commands to the same text on a page you can do so by creating another
rectangle over the top of the existing one.
5.2.2. Activating the Rectangle Tool
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ allows the user to split PDF files based on the text that appears on
the pages throughout a PDF document. The rectangle tool is used to select which text on
the page will be used for splitting the file.
Figure 4. ‘Activate Rectangle Tool’ toolbar button
To activate or deactivate the rectangle tool, do one of the following:
• Select ‘Activate Rectangle Tool’ from the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant menuitem,
• Click on the ‘Activate the Rectangle Tool’ button locat ed in the ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
| CONTENTS | Page 16 of 58
Page 17
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
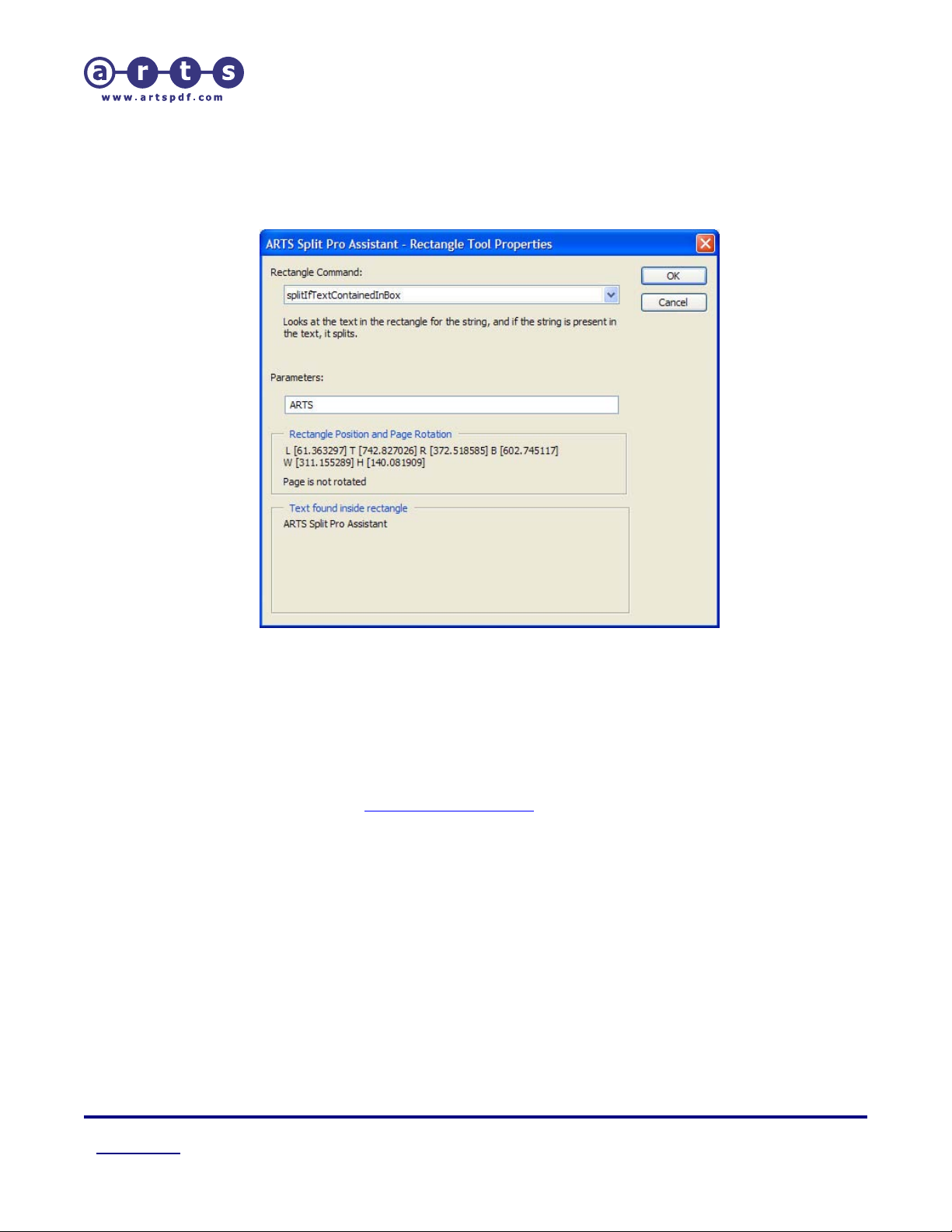
The rectangle tool will open the Rectangle Tool Properties window allowing you to:
• Create a new command
• Edit an existing command
Figure 5. ‘Rectan gle Tool Properties’ dialog
• Rectangle Command
The default command is ‘noop’ which means there is no active command selected for
this rectangle. Select the command you wish to use for the rectangle you just
created on your page.
A full list of available
Rectangle Commands can be found in the Appendix A of this
document.
• Parameters
Enter any parameter that is required for your command in the ‘parameters for
command‘ text box. This is where you enter the text when you wish to see if a
particular/literal string is present on the page.
• Rectangle Position and Page Rotation
Displays the rectangle coordinates for size and position on the page. If the page is
rotated the text cannot be extracted by ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant but ARTS PDF
Split Pro™ will function as normal.
• Text found inside rectangle
Displays the text that the rectangle reads off the current PDF page.
| CONTENTS | Page 17 of 58
Page 18

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
5.2.3. Editing a Coordinate File
To edit a rectangle command or string parameter:
1. Open a PDF document in Adobe Acrobat.
2. Open a coordinate file to edit if one is not yet open.
3. Open the ‘Rectangle Tool Properties’ dialog by doing one of the following:
• Activate the Rectangle Tool and then double click on the rectangle you
wish to edit.
• Open the View Commands dialog, select the command you wish to modify
and click ‘Edit’.
4. Select the new rectangle command you wish to use and/or modify any
parameters required.
5. Click ‘OK’.
6. Save the coordinate file.
To edit the size of a rectangle box (or rectangle coordinates):
1. Open a PDF document in Adobe Acrobat.
2. Open a coordinate file to edit if one is not yet open.
3. Activate the Rectangle Tool.
4. Click on a rectangle and move to the corner of the blue rectangle box until a
double-headed arrow appears. Drag the box to the desired size.
5. Save the coordinate file.
To edit a the position of a rectangle box (or rectangle coordinates):
1. Open a PDF document in Adobe Acrobat.
2. Open a coordinate file to edit if one is not yet open.
3. Activate the Rectangle Tool.
4. Click on the rectangle and drag it to a different position.
5. Save the coordinate file.
5.2.4. Opening a Coordinate File
To open a coordinate file:
1. Open a PDF document in Adobe Acrobat.
2. Select ‘Open’ from the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant menu or click on the open
button located on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
3. Select the coordinate file (.crd) to open.
4. Click ‘Open’.
Figure 6. ‘Open’ toolbar button
| CONTENTS | Page 18 of 58
Page 19

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
5.2.5. Saving a Coordinate File
To save the active coordinate file:
1. Select ‘Save’ from the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant menu or click on the save
button located on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
2. Enter a filename for your coordinate file and select the directory you wish to save
to, ensuring that the file exte nsion is of .crd type (it will be .crd by default).
3. Click ‘Save’.
Figure 7. ‘Save’ toolbar button
5.2.6. Closing a Coordinate File
To close the active coordinate file, select ‘Close’ from the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant
menu, or click on the close button located on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
Figure 8. Close’ toolbar button
5.2.7. Viewing Text
To view text as ARTS PDF Split Pro™ does, select ‘Show Text’ from the ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant menu, or click on the show text button located on the ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
Figure 9. ‘Show Text’ toolbar button
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant recognizes text on pages differently to how the human
eye does. This must be taken into consideration when us ing ARTS PDF Split Pro™
Assistant as it could affect the accuracy of the users pdf splitting. It is recommended to
use the ‘show text’ tool when using the rectangle to ensure that the rectangle is
positioned correctly around the text you wish to apply a command to.
| CONTENTS | Page 19 of 58
Page 20

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
Figure 10. How the human eye sees the text
Figure 11. How ARTS PDF Split Pro™ sees the text (zoomed to 200%)
Figure 10 and 11 show the difference between how the human eyes sees text on the
page, and how ARTS PDF Split Pro™ sees it. In figure 11, the red text is what ARTS PDF
Split Pro™ sees, and the text behind in and in figure 10 is how it appears to the user on
the page.
5.2.8. Viewing Text Runs
To view text runs, select ‘Show Run Start’ from the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant
menu, or click on the close button located on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
Figure 12. ‘Show Run Start’ toolbar button
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant allows the user to see where the start of each text run
starts on the page. A small red cross represents the start of each text run. This can be
seen in the diagram below (displaying text runs in ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant).
Figure 13. Displaying text runs in split pro assistant
Within a PDF file, text is drawn by moving to a specific location on the page and drawing
a line of text, which is formally known as a run of text. What appears to be one line of
text can actually be made of a number of runs of text put together.
In ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant, if a line of text begins inside a rectangle that you
have created on your screen then the entire run of text is considered inside that
rectangle. The rectangle that has been drawn in figure 13 contains two runs of text
| CONTENTS | Page 20 of 58
Page 21
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
inside it, and as mentioned earlier the red crosses denote these runs of text.
The text that ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant would recognize from this triangle and the
two runs of text inside it are:
• r in the list o
• down menu
Note: if a line of text begins inside a rectangle, the entire run of text is considered "inside" that
rectangle. The end of the rectangle in the figure 13 does not denote where ARTS PDF Split Pro™
Assistant will stop reading the text, rather the end of the text runs that begin within the rectangle
will.
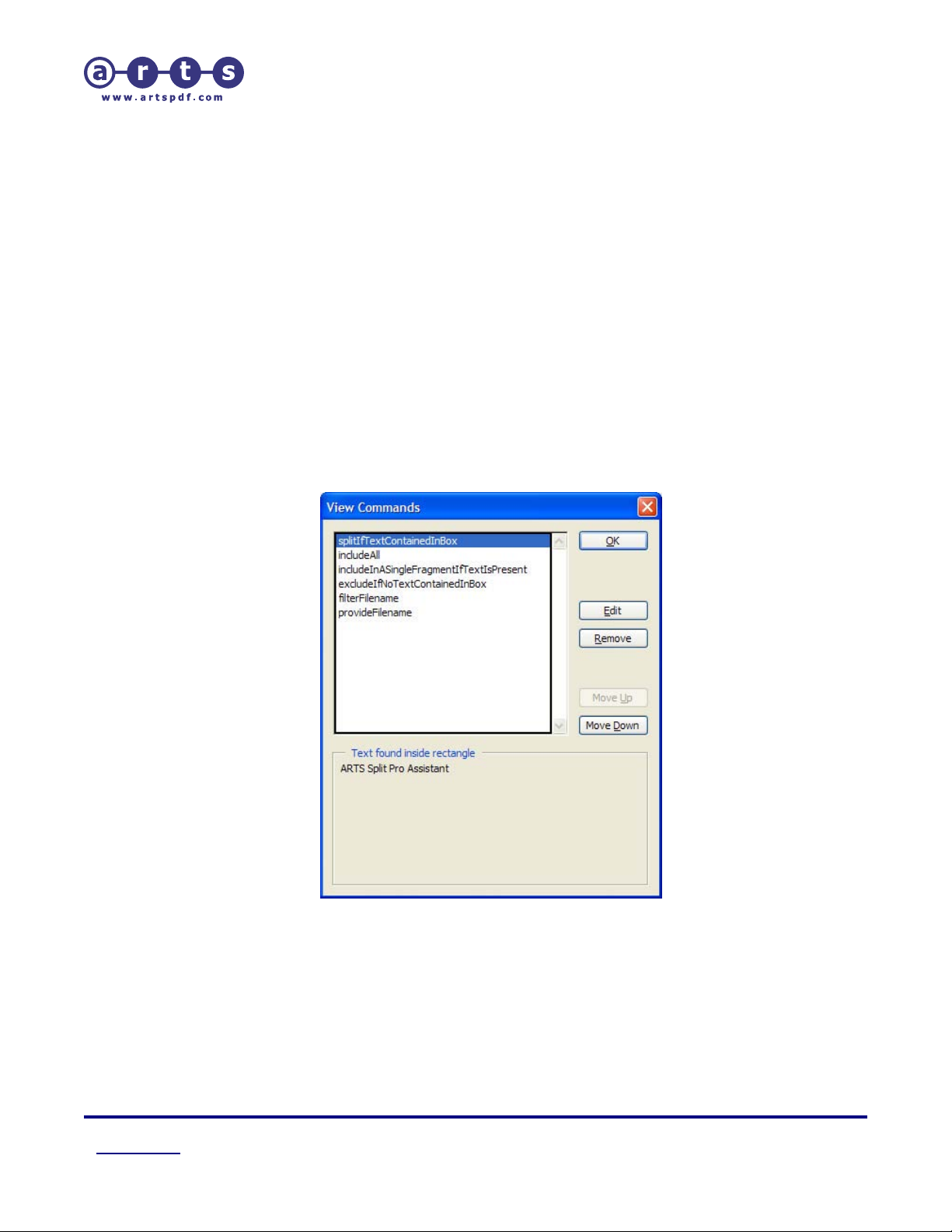
5.2.9. Viewing Commands
The View Commands dialog is used for managing all the commands found within a
coordinate file.
Figure 14. ‘View Commands’ dialog
To open the View Commands dialog, select ‘View Commands’ from the ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant menu, or click on the ‘Display and reorder commands’ button on the
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant toolbar.
| CONTENTS | Page 21 of 58
Page 22

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Assistant
Figure 15. ‘Display and reorder command’ toolbar button
View Commands dialog lists all commands within a coordinate file. It is possible to
change the order of commands within the coordinate file simply by clicking on the ‘Move
Up’ or ‘Move Down’ button. With the dialog open, scroll through the PDF document to
see what text on the page is recognized by the rectangle coordinates.
| CONTENTS | Page 22 of 58
Page 23

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ GUI
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ is referred to as the component that performs the actual PDF splitting. This is
accessed through the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Graphical User Interface (GUI).
You can open ARTS PDF Split Pro™ from the Windows Start menu by going to ‘Start > Programs >
ARTS PDF > ARTS PDF Split Pro > ARTS PDF Split Pro 2.0’ or if you are a Windows XP user go to
‘Start > All Programs > ARTS PDF > ARTS PDF Split Pro > ARTS PDF Split Pro 2.0’
6.1. Splitting Methods
The splitting methods available can be selected in the listbox shown below:
Figure 16. Splitting methods found on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ dialog
6.1.1. Split by Bookmarks
To split by bookmarks:
1. Select ‘Split PDF by Bookmarks’ as the method of splitting.
2. Select the source PDF file to be split.
3. Enter the bookmark level in ‘Split by bookmark level’
4. Select the destination folder where th e PDF files will be stored following splitting.
This can be set to the same as the source folder, or in the folder of the users
choice.
5. Click the ‘Split’ button to begin the process.
| CONTENTS | Page 23 of 58
Page 24

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6.1.2. Split by Control File
To split by a control file:
1. Select ‘Split PDF by Control F ile’ as the method of splitting.
2. Select the source pdf file to be split.
3. Select the control file that will det ermine the split files. This control file should not
contain full pathnames.
4. Select the destination folder where the pdf file s will be stored following splitting.
This can be set to the same as the source folder, or in the folder of the users
choice.
5. Click the ‘Split’ button to begin the process.
The file will be split, and each output file (fragment) will be given a file name as
specified in the control file and placed in the selected folder.
6.1.3. Split by Control File – Full Path
To split by control file - full path:
1. Select ‘Split PDF by Control File – fu ll path’ as the method of splitting.
2. Select the source pdf file to be split.
3. Select the control file that will det ermine the split pdf files. This control file should
specify full pathnames.
4. Click the ‘Split’ button.
The file will be split, and each fragment will be saved with the specified location and
name. If the full path specifies a directory that does not exist, the directory will be
created.
6.1.4. Split by Coordinate File
To split by a coordinate file:
1. Select ‘Split PDF by Coordinate File’.
2. Select the source pdf file to be split.
3. Select the coordinate file to be used to determine the split pdf files.
4. Select the destination folder where the pdf file s will be stored following splitting.
This can be set to the same as the source folder, or in the folder of the users
choice.
5. Click the ‘Split’ button.
The file will be split based on the coordinate file command/s, and each fragment will be
saved to the specified directory.
| CONTENTS | Page 24 of 58
Page 25

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6.1.5. Split by File Size
To split by file size:
1. Select ‘Split PDF by File Size’.
2. Select the source PDF file to be split.
3. Select the destination folder where th e PDF files will be stored following splitting.
This can be set to the same as the source folder, or in the folder of the users
choice.
4. Enter the base name for each split fragments. All fragmen ts will use the name
you choose as a base name, and they will be saved in the directory you have
chosen. Ascending numeric values will be appended to the base name to name
every output file. If the user enters ‘order.pdf’ or ‘order’, the fragments will be
named order1.pdf, order2.pdf, and order3.pdf
5. Enter the file size value in KB.
6. Click the ‘Split’ button.
6.1.6. Split into Single Pages
To split into single pages:
1. Select ‘Split PDF into Single Pages’.
2. Select the source pdf file to be split.
3. Select the destination folder where the pdf file s will be stored following splitting.
This can be set to the same as the source folder, or in the folder of the users
choice.
4. Enter the base name for each split fragments. All fragmen ts will use the name
you choose as a base name, and they will be saved in the directory you have
chosen. Ascending numeric values will be appended to the base name to name
every output file. If the user enters ‘invoice.pdf’ or ‘invoice’, the fragments will be
named invoice1.pdf, invoice2.pdf, and invoice3.pdf
5. Click the ‘Split’ button.
| CONTENTS | Page 25 of 58
Page 26

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6.2. Watched Folders
6.2.1. Setting up a Watched Folder
Figure 17. Setting up watched folders
To set-up watched folders:
1. Click the ‘Watch Folder’ button on the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ GUI.
2. Select whether to ‘Split into Single Pa ges’ , ‘Split by Control File’ or ‘Split by
Coordinate File’. More information on this can be seen in the following sections.
3. Leave the processing folders (input, busy, done, error, output) as default, or
specify your own folders where the PDF files will be processed.
Input: folder to place the source PDF ready for splitting.
Busy: folder where the PDF in process is temporarily stored.
Done: folder to store the source PDF that has been successfully
processed.
Error: folder to store the source PDF where the split process was
incomplete due to an error.
Output: folder to store split output PDF f iles.
| CONTENTS | Page 26 of 58
Page 27
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
4. It is optional to select the ‘overwrite the original file’ checkbox that will overwrite
existing output files.
5. It is optional to add a suffix after the filename (but before number) for each split
PDF.
6. Select to have the split PDFs placed directly into the output folder or within a
subdirectory that would be created within the output directory. The subdirectory
will be named by the name of the PDF file dropped into the input folder.
6.2.2. Watched Folder Splitting Methods
Figure 18. Watched folder splitting methods
6.2.2.1. Split into single pages
By selecting this option, the watched folder will split each PDF placed in the input
directory into fragments with one page in each fragment. That is, when a PDF is
dropped into the input folder, the PDF will be split into sin gle pages and saved to the
output directory.
6.2.2.2. Split by control file
By selecting this option, the watched folder will split each PDF into fragments based
on a control file the user selects. Control files go in to the input folder, and the first
line of the control file should be a full path to the PDF file to be split.
For example:
C:\pdfsplit\reporting\annual_report.pdf
1,3,8 firstfewpages.pdf
15-20 bobloseshisjob.pdf
30-45 personnelplanning.pdf
| CONTENTS | Page 27 of 58
Page 28

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6.2.2.3. Split by control file – full path
If splitting by ‘control file - full path’ using watched folders, select the control file
option and leave the output directory blank.
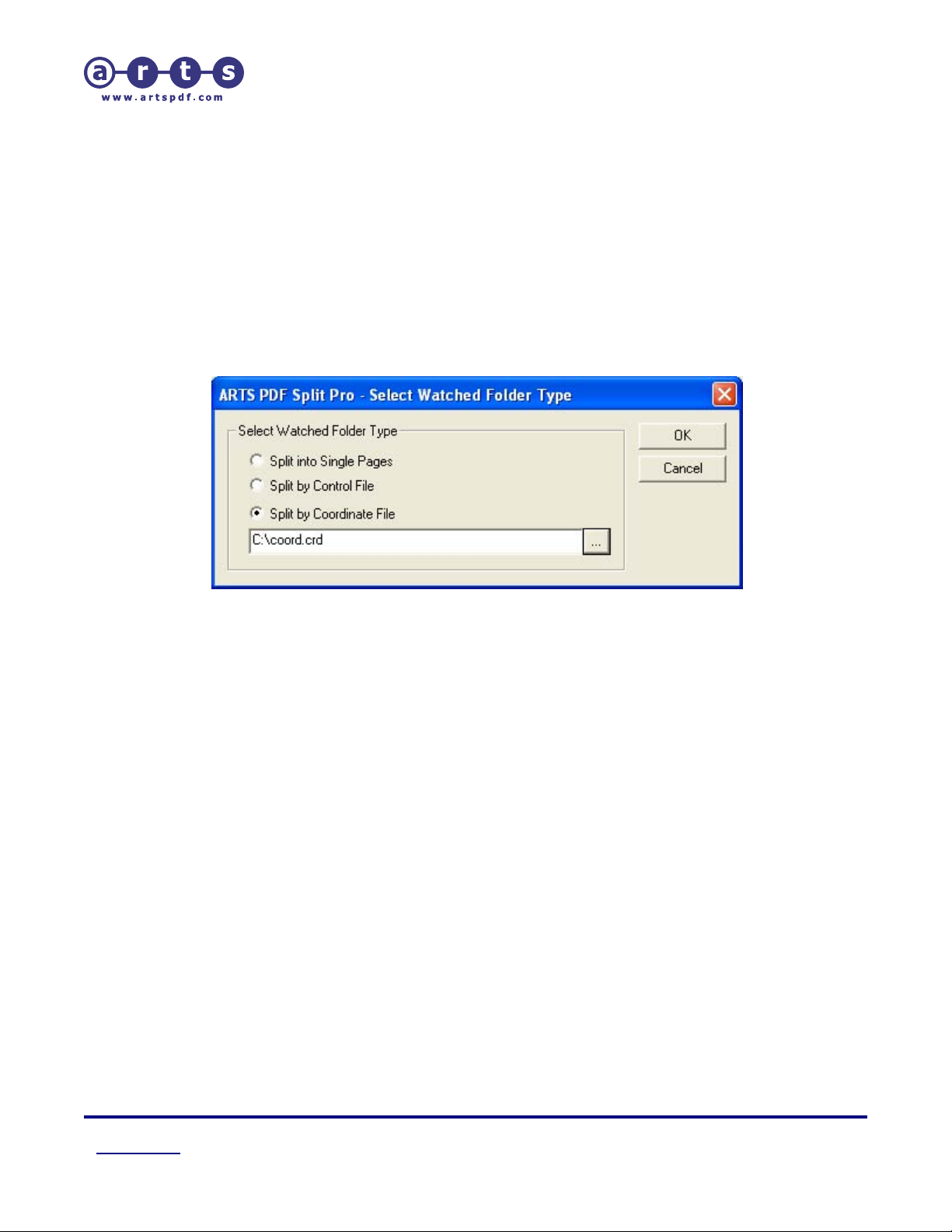
6.2.2.4. Split by coordinate file
By selecting this option, the watched folder will split each pdf into fragment s based
on a coordinate file the user must select. Upon selecting to split by coordinate file
with Watched folders, the user must specify the location of the coordinate file to be
used.
6.3. Options
Using ARTS PDF Split Pro™ you have the option to log the status of split processes, run
the application in silent mode, overwrite original output files and update navigational
elements. These options are also available for the GUI watched folders.
To access the Options dialog, click on the ‘Options’ button on the main ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ dialog.
Figure 19. Options dialog
| CONTENTS | Page 28 of 58
Page 29

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
In addition to the options found within the Options dialog, you can find options
applicable to watched folders in the Watched Folder dialog. See Figure 20.
Figure 20. Watched Folder options in red
6.3.1. Logging enabled
The option to enable logging can be found in the Options dialog. With ‘Logging enabled’
selected, ARTS PDF Split Pro™ will log successful and unsuccessful split events. The
error details for any unsuccessful processes will be recorded in the log file.
The log file is a text file that is stored in the same location as the ARTS PDF Split Pro™
GUI executable. By default, the log file can be found in ‘C:\Program Files\ARTS PDF
Split Pro’.
| CONTENTS | Page 29 of 58
Page 30

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
6.3.2. Silent Mode
The option to run ARTS PDF Split Pro™ in silent mode can be found in the Options dialog .
This will run ARTS PDF Split Pro™ with no visual output or required user interaction. It is
recommended that the ‘Logging enabled’ checkbox is selected if silent mode is checked.
Logging enabled will notify you of any errors or status messages by writing entries to a
log file. If running in silent mode and you wish to stop processing a file, you must exit
the application.
6.3.3. Overwrite output file
The option to overwrite existing files can be found in the Options dialog. By default,
ARTS PDF Split Pro will avoid overwriting an existing file by appending a number to the
new filename. Select this option to overwrite existing output files instead of appending a
number
3
.
For example:
• First split produces the following output files:
tax.pdf, invoice.pdf, order.pdf
• Second split does NOT have ‘Overwrite output file’ selected. Output files are:
tax_1.pdf, invoice_1.pdf, order_1.pdf
• Third split does have ‘Overwrite output file’ selected. Ou tput files of the third split
will overwrite the output files of the first split:
tax.pdf, invoice.pdf, order.pdf
Watched folders will ignore the ‘Overwrite output file’ option found in the Options dialog.
To set the overwrite mode for watched folders, select ‘Overwrite the original file’ in the
Watched Folder dialog.
6.3.4. Update navigational elements
The option to update navigational elements
the Watched Folder dialog. Select this option to update all links, bookmarks and named
destinations so that they remain connected to the proper page. To set ‘Update
navigational elements’ for watched folders, select the checkbox in the Watched Folder
dialog.
4
can be found in the Options dialog and in
3
The ‘Overwrite output file’ option will not affect control file split methods (‘By Control File’ and ‘By Control
File – full path). Any output files using a control file will always be overwritten because the filename is
specified within the control file.
4
Form fields and annotations other than links, such as comments, are not updated and are removed from all
output files.
| CONTENTS | Page 30 of 58
Page 31

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Graphical User Interface
GoTo5 links are adjusted to stay connected to the proper page, even if the pages end up
in a different order in the final document. GoTo links are changed into a GoToR
ensure that links are not broken should a linked page end up in different output file.
GoToR links or Launch actions, both of which reference an external file, use a relative
pathname that takes into account the difference if the files created by splitting are in a
different directory from the original file.
If you split a file with named destinations, the named destinations will be inserted into
the output files. Links that use named destinations within the original document will be
changed from GoTo to GoToR links as necessary. The links will still use named
destinations.
Bookmarks are copied into all files and are adjusted just as the links are.
6.3.5. Output subfolders
The option to place output files in subfolders is only applicable to watched folders and
can be found in the Watched Folder dialog. Select ‘Put fragments into subfolders’ to
place all output files in subfolders where the subfolder is named after the source file. The
other option is to select ‘Put fragments directly into the Output folder’ to place all output
files directly into the specified output folder rat her than into separate subfolders.
6
links to
5
GoTo links are links that go to another page in the same document.
6
GoToR links are links that goes from one file to another using a reference external.
| CONTENTS | Page 31 of 58
Page 32

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Command Line Interface
7. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ CL
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ can be launched from the command line using command line switches to
specify what type of splitting to process. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Command Line Interface (CLI or CL)
application can be found in the ARTS PDF Split Pro folder e.g. C:\Program Files\ARTS PDF Split
Pro\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe.
It is important that spaces are placed between each switch specified. Some switches are followed
by specific operands, and these operands must also be separated by a space. If a pathname
contains a space, then the path must be enclosed in quotes. An example of this can be seen below:
-i c:\artssplitpro.pdf correct
-i c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro.pdf wrong
-i "c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro.pdf" correct
A full list of available
Command Line Switches can be found in Appendix B of this document.
7.1. Splitting Methods
7.1.1. Split by Bookmarks
To split by bookmarks, you will need to use the split by bookmarks (-m), in put (-i) and
output (-o) switches.
For example to split by level 1 bookmarks:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -m 1-1 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf" -o "c:\outputfolder\"
7.1.2. Split by Control File
To split using a control file, you will need to use the control file (-c), input (-i) and
output (-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -i "c:\inp ut file.pdf" -o "c:\outputfolder\" -c
"c:\controlfile.txt"
7.1.3. Split by Coordinate File
To split using a coordinate file, you will need to use the coordinate file (-x), input (-i)
and ouput (-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -i "c:\inputfile.pdf" -o "c:\outputfolder\" -x
"c:\coordinatefile.crd"
| CONTENTS | Page 32 of 58
Page 33

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Command Line Interface
7.1.4. Split into Single Pages
To split by single pages, you will need to use the fragment size (-k), input (-i) and
output (-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -k 1 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf “ -o
"c:\outputfolder\basefilename"
In addition, you can use the serial number (-n) switch to add padded zeros to the suffix
and use the fragment numbering (-f) switch to specify the starting number.
For example, the following will add a suffix to all output filenames with an incrementing
3 digit value starting at 6:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -k 1 -f 6 -n 3 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf “ -o
"c:\outputfolder\basefilename"
7.1.5. Split by Page Range
To split by page range, you will need to use the page range (-r), input (-i) and output
(-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -r 5-10 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf “ -o
"c:\outputfolder\outputfile.pdf"
7.2. Parsing Methods
7.2.1. Parse a page
To parse a single page to a text file, you will need to use the parse (-pa), input
(-i) and output (-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -pa 2 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf “ -o "c:\outputfile.txt"
7.2.2. Parse a page range
To parse a range of pages of a PDF file to a text file, you will need to use the parse
debug (-pr), input (-i) and output (-o) switches.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -pr 1-5 -i "c:\inputfile.pdf “ -o "c:\outputfile.txt "
| CONTENTS | Page 33 of 58
Page 34

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Command Line Interface
7.3. Watched Folders
7.3.1. Watched Folder Splitting Methods
7.3.1.1. Split into single pages
7.3.1.2. Split by coordinate file
Use the watch folder (–w) switch, along with the done (-d), input (-i), output (-o),
busy (-b), error (-e), and fragment size (-k) switches, to split a file into single pages
using a watched folder.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -w -d "c:\donefolder\" -i "c:\inputfolder” -o
"c:\outputfolder“ -b "c:\busyfolder“ -e "c:\errorfolder“-k 1
Use the watched folder by coordinate file (–wc) switch, specifying the coordinate file,
input, output, busy, done and error folder, to run a coordinate watched folder.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -wc "c:\coordinatefile.crd" “c:\inputfolder”
“c:\outputfolder\” “c:\busyfolder\” “c:\donefolder\” “c:\errorfolder\”
By default, output files will be placed in subfolders named after the input file. Use the
subfolder (–ns) switch to place output files directly into the output folder.
For example:
“c:\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -ns -wc "c:\coordinatefile.crd" “c:\inputfolder\”
“c:\outputfolder\” “c:\busyfolder\” “c:\donefolder\” “c:\errorfolder\”
7.4. Options
7.4.1. Overwrite
Use the overwrite (/de) switch to overwrite existing output files when splitting by
coordinate file, by bookmarks or into single pages.
For example:
“c:\path\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -k 1 -f 6 -n 3 -i "c:\path\inputfile.pdf “ -o
"c:\path\basefilename" /de
| CONTENTS | Page 34 of 58
Page 35

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Command Line Interface
Use the overwrite (–ow) switch for watched folders to overwrite existing output files
when running a watched folder.
For example:
“c:\path\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -wc "c:\path\coordinatefil e .crd"
“c:\path\inputfolder\” “c:\path\outputfolder\” “c:\path\busyfolder\”
“c:\path\donefolder\” “c:\path\errorfolder\”] -ow
7.4.2. Update navigational elements
Use the update navigational elements switch (–ne) to update bookmarks and links within
output files.
For example:
“c:\path\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -ne -wc "c:\path\coordinatefile.crd"
“c:\path\inputfolder\” “c:\path\outputfolder\” “c:\path\busyfolder\”
“c:\path\donefolder\” “c:\path\errorfolder\”
Another example:
“c:\path\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -ne -k 1 -f 6 -n 3 -i "c:\path\inputfile.pdf “ -o
"c:\path\basefilename"
7.4.3. Run in the background
To run ARTS PDF Split Pro in the background and log errors in a log file use the headless
(–h) switch.
For example:
“c:\path\ARTS PDF Split Pro CL.exe" -w -d "c:\path\donefolder\" -i
"c:\path\inputfile.pdf” -o "c:\path\inputfile.pdf “ -b "c:\path\inputfile.pdf “ -e
"c:\path\inputfile.pdf “-k 1 –h "c:\path\statuslog.txt"
| CONTENTS | Page 35 of 58
Page 36

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
8. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ COM
ARTS PDF Split Pro™ COM allows developers to integrate the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ methods of
splitting in custom applications. The COM component comes as a DLL file containing methods that
can be called to split PDF files and can be utilized in environment s such as Visual Basic, Delphi,
ASP, ASP.NET and PHP. Examples of Visual Basic and ASP code can be found in section 8.2 of this
document,
8.1. Registering the COM object
COM Examples.
The ARTS PDF Split Pro COM Library is contained within the distributable file
APSplitPro.dll. This interface is automatically registered as an OLE server when installed
using the ARTS PDF Split Pro installer and can be located in the Windows System32
folder, typically C:\WINDOWS\system32\APSplitPro.dll
To redistribute applications built using this library to other mach ines, copy this file to the
target computer and register it using Windows’ REGSVR32 utility. Note that the
APSplitPro.dll file does not need to be located in the SYSTEM32 folder; however it is
recommended you copy it there to avoid any potential permissions problems.
To unregister the COM object, use the –u switch in the command line call, i.e. regsvr32
C:\WINDOWS\system32\APSplitPro.dll -u
| CONTENTS | Page 36 of 58
Page 37

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
8.2. Class Strings/Namespaces
Use the following class strings to instantiate the ARTS PDF Split Pro COM object. Please
note that we do not provide a native .NET assembly class. To use ARTS PDF Split Pro in
a .NET application you will need to utilize an Interop Assembly and include this within
the bin folder of the application, i.e. bin\Interop. ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.dll.
8.2.1. Visual Basic
ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
' Early Binding
Dim objAPSplitPro As ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
Set objAPSplitPro = New ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
' Early Binding
Dim objAPSplitPro As New ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
' Late Binding
Dim objAPSplitPro As Object
Set objAPSplitPro = New ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
8.2.2. ASP
ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro
' Late Binding
Dim objAPSplitPro
Set objAPSplitPro = Server.CreateObject("ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro")
8.2.3. VB.NET
ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib
Imports ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib
' Early Binding
Dim objAPSplit As ARTSSplitProClass
objAPSplit = New ARTSSplitProClass
' Early Binding
Dim objSplit As New ARTSSplitProClass
8.2.4. C#
ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib
| CONTENTS | Page 37 of 58
Page 38

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
Using ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib
ARTSSplitProClass objAPSplit;
8.2.5. Delphi
ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro
APSP: Variant;
APSP := CreateOleObject('ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro');
8.2.6. PHP
ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro
$APSplitPro = new COM("ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro")
8.3. Permissions for Web Applications
When using ARTS PDF Split Pro COM within a web application, certain permissions must
be granted to the designated output folder in order for these output files to be saved to
disk. If these permissions are not granted correctly, the splitting method will generally
return the error value 403 – I/O Error.
8.3.1. ASP
Both the Internet Guest (IUSR_MachineName) and Launch IIS Process
(IWAM_MachineName) accounts require sufficient privileges to write to the specified
output folder.
8.3.2. ASP.NET
The Internet Guest (IUSR_MachineName), Launch IIS Process (IWAM_MachineName)
and ASP.NET Machine (ASPNET) accounts require sufficient privileges to write to the
specified output folder.
If anonymous internet access is not permitted to your web application then substitute
the Internet Guest Account with that of the authorized user account(s).
| CONTENTS | Page 38 of 58
Page 39

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
y
COM Object
8.4. Object ARTSSplitPro
The ARTSSplitPro object carries informational properties as well as methods for the
functionality to split a PDF file. ARTSSplitPr o offers you the following methods:
METHOD DESCRIPTION
GetErrorMessage Returns error message
GetVersionNumber Returns ARTS PDF Split Pro™ version number
SetLicenceKey Sets the serial number
SetOverwriteMode Sets the overwrite mode
SetUpdateMode Sets the mode for updating navigational elements
SplitByBookmarks Splits a PDF by bookmark levels
SplitByControlFile Splits a PDF by control file
SplitByCoordFile Splits a PDF by coordinate file
SplitByFileSize Splits a PDF by file size
SplitIntoSinglePages Splits a PDF into single pages
8.4.1. GetErrorMessage
GetErrorMessage String GetErrorMessage(Long lErrorCode)
Description Returns an error message for unsuccessful split results.
Parameters
lErrorCode – the error value of the split result.
Return Value String of text describing the error that occurred.
Related methods SplitByBookmarks, SplitByControlFile, SplitByCoordF ile,
SplitByFileSize, SplitIntoSinglePages
8.4.2. GetVersionNumber
GetVersionNumber String GetVersionNumber( )
Description Returns the version number of ARTS PDF Split Pro COM.
Return Value Version number in the format of X.X[X].
8.4.3. SetLicenceKey
SetLicenceKey Long SetLicenceKey (String sSN, String sOldSN)
Description Sets the serial number to run COM in full versio n or demo
mode. COM will run in full version onl
if the serial is
| CONTENTS | Page 39 of 58
Page 40

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
accepted.
Parameters
sSN – Valid serial number or use ‘DEMO’ to run in demo
mode.
SOldSN – Optional parameter. Valid serial number of the
previous version. Only required if an upgrade serial is
used for sSN.
Return Value 0 if serial number is accepted, COM will run in full.
1 if serial is invalid, COM will run in demo mode.
8.4.4. SetOverwriteMode
SetOverwriteMode SetOverwriteMode (BOOL bOverwriteMode)
Description Sets the overwrite mode.
Parameters
bOverwriteMode – True will overwrite existing files.
8.4.5. SetUpdateMode
SetOverwriteMode SetUpdateMode (BOOL bUpdateMode)
Description Sets the mode for updating navigational elements.
Parameters
bUpdateMode – True will update navigational elements.
8.4.6. SplitByBookmarks
SplitByBookmarks Long SplitByBookmarks (String sInputFile, St ring
sOutputFolder, Long lLowestLevel, Long lHighestLevel)
Description This method splits a PDF using the split by bookmarks
method.
Parameters
sInputFile– Pathname of the source PDF.
sOutputFolder – Path of the destination folder where
output files are placed.
lLowestLevel – The lowest bookmark level to split.
lHighestLevel – The lowest bookmark level to split.
Return Value 0 if PDF split is successful otherwise returns an error
value.
Related methods GetErrorMessage
| CONTENTS | Page 40 of 58
Page 41

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
8.4.7. SplitByControlFile
SplitByControlFile Long SplitByControlFile (String sInputFile, String
sOutputFolder, String sControlFile, BOOL bFullPath)
Description This method splits a PDF using the split by control file
method.
Parameters
sInputFile – Pathname of the source PDF.
sOutputFolder – Path of the destination folder where
output files are placed.
SControlFile – Pathname of the control file.
bFullPath – Optional parameter. Set to True if control file
contains complete pathnames.
Return Value 0 if PDF split is successful otherwise returns an error
value.
Related methods GetErrorMessage
8.4.8. SplitByCoordFile
SplitByCoordFile Long SplitByCoordFile (String sInputFile, String
sOutputFolder, String sCoordFile)
Description This method splits a PDF using the split by coordinate file
method.
Parameters
sInputFile – Pathname of the source PDF.
sOutputFolder – Path of the destination folder where
output files are placed.
sCoordFile – Pathname of the coordinate file.
Return Value 0 if PDF split is successful otherwise returns an error
value.
Related methods GetErrorMessage
8.4.9. SplitByFileSize
SplitByFileSize Long SplitByFileSize (String sInputFile, St ring
sOutputFolder, Long lFileSize)
Description This method splits a PDF using the split by file size
method.
Parameters
sInputFile – Pathname of the source PDF.
sOutputFolder – Path of the destination folder where
output files are placed.
lFileSize – File size in kilobytes.
| CONTENTS | Page 41 of 58
Page 42

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
Return Value 0 if PDF split is successful otherwise returns an error
value.
Related methods GetErrorMessage
8.4.10. SplitIntoSinglePages
SplitIntoSinglePages Long SplitIntoSinglePages (String sInputFile, String
sOutputFolder, String sBaseName)
Description This method splits a PDF using the split into single pages
method.
Parameters
sInputFile – Pathname of the source PDF.
sOutputFolder – Path of the destination folder where
output files are placed.
sBaseName – Base filename for each fragment.
Return Value 0 if PDF split is successful otherwise returns an error
value.
Related methods GetErrorMessage
| CONTENTS | Page 42 of 58
Page 43

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
8.5. COM Examples
8.5.1. Visual Basic
Private Sub cmdSplit_Click()
Dim sMode As String ' version mode (demo or full)
Dim lMode As Long ' value of the version mode
Dim iCounter As Integer
Dim lOptionSelected As Long ' value of the split method selected
Dim lSplitResult As Long ' value of the split result
Dim SplitPro As New ARTSSPLITPROCOMLib.ARTSSplitPro
'Display version number
txtVersionNumber = SplitPro.GetVersionNumber
'Check if a serial number is entered
If txtSerialNo = "" Then
sMode = "Demo version"
Else
'Set the serial number and get the version mode value
lMode = SplitPro.SetLicenceKey(txtSerialNo)
'Assign the version mode value a text description
Select Case lMode
Case 0
sMode = "Full version"
Case 1
sMode = "Demo version"
End Select
End If
'If overwrite is selected then set the mode
If chkOverwriteMode = True Then
SplitPro.SetOverwriteMode (bOverwriteMode)
End If
'Check which option is selected on the form
For iCounter = 0 To 4
If optSplitOption(iCounter).Value = True Then
lOptionSelected = iCounter
End If
Next iCounter
'Perform the selected method to split
Select Case lOptionSelected
Case 0
lSplitResult = SplitPro.SplitByBookmarks(txtInput,
txtOutput, txtLowestBookmark, txtHighestBookmark)
Case 1
lSplitResult = SplitPro.SplitByControlFile(txtInput,
txtOutput, txtControlFile, chkFullPath)
Case 2
lSplitResult = SplitPro.SplitByCoordFile(txtInput,
| CONTENTS | Page 43 of 58
Page 44

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
txtOutput, txtCoordinateFile)
Case 3
lSplitResult = SplitPro.SplitByFileSize(txtInput, txtOutput,
txtFileSize)
Case 4
lSplitResult = SplitPro.SplitIntoSinglePages(txtInput,
txtOutput, txtBaseName)
End Select
'Check if an error occurred
If lSplitResult <> 0 Then
'If an error has occurred display the error message
MsgBox (SplitPro.GetErrorMessage(lSplitResult))
End If
Set SplitPro = Nothing
End Sub
8.5.2. ASP
<%
Dim ARTSSplitPro
Set ARTSSplitPro =server.CreateObject("ARTSSplitPro.ARTSSplitPro")
'Check to see if title has been entered or not
u_title=request.form("u_title")
if u_title = "" then
%>
<!-- Input form area - This will only display when no Title has been
entered -->
<form method="POST" action="<%=
request.servervariables("script_name")%>">
<p>Input File Name<br><input type="text" name="u_title"
size="30"></p>
<p>Page Range<br><input type ="text" name= "pagerange" size
="35"></p>
<p>Output File Name<br><input type="text" name="outputfilename"
size="35"><input type="submit" value="Submit" ></p>
</form>
<%
end if
%>
<%
if u_title <> "" then
' If there is a user inputted title
' get all of the user's input values
u_title=request.form("u_title")
pagerange=Request.form("pagerange")
outputfilename = Request.Form("outputfilename")
| CONTENTS | Page 44 of 58
Page 45

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
COM Object
set fso = createobject("scripting.filesystemobject")
' create the text file
Set act = fso.CreateTextFile("C:\test\test.txt", true)
set filename = fso.GetFile("c:\test\test.txt")
' write all of the user input to the text file
act.WriteLine pagerange & vbTab & outputfilename
Response.Write "<br> "
' close the document
act.Close
%>
<p>Text file created using ARTS PDF Split Pro COM
v.<b><%=ARTSSplitPro.GetVersionNumber%></b></p>
Your page has been successfully create and can be viewed by clicking
<a href="c:\test\test.txt">here</a>
<br>
<br>
<%
end if
Dim InputFile
Dim OutputFolder
Dim ControlFile
InputFile = Request.Form("u_title")
Outputfolder = "C:\test"
ControlFile = filename
Response.write(ARTSSplitPro.SplitByControlFile(InputFile,OutputFolde
r, ControlFile, true))
%>
| CONTENTS | Page 45 of 58
Page 46

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix A - Rectangle Commands
9. Appendix A – Rectangle Commands
Rectangle commands are used in coordinate files. Contained in this appendix is a list of all the
commands that can be used in conjunction with the rectangle tool found in the ARTS PDF Split
Pro™ Assistant.
SplitIfTextIsPresent
If the specified parameter is contained in any run of text on the page, the PDF will be split and the
page will be the start of a new file. The comparison is case sensitive.
SplitIfTextContainedInBox
Text inside the rectangle on a page is searched to see if it contains the specified parameter. If the
string parameter is found inside the rectangle on a page, then the PDF will be split and that page
becomes the start of a new file.
SplitItTextIsInARun
If the specified parameter is found in any text run then the PDF will be split. Text that spans
multiple runs of text will not activate a split.
SplitOnTextChange
If text inside the rectangle on a page is different from the text inside the rectangle on the previous
page, the PDF will be split and that page becomes the start of a new file.
SplitOnTextChangeAfterString
If the text inside the rectangle after the string parameter is different from (the text inside the
rectangle after the string parameter of) the previous page, the PDF will be split and that page
becomes the start of a new file.
SplitOnTextChangeAfterStringOnly
The text inside the rectangle on a page is searched for the specified string parameter. If the
specified string is found, it will look if the text after th e specified parameter changes from page to
page. If the text does change the PDF will be split and a new file started. Ignores pages where the
string is not present.
SplitItThisTextRepeats
The text inside the rectangle on a page is searched to see if it contains the specified parameter. If
the string parameter is found inside the rectangle on two pages in a row, the PDF will split between
the two pages so that they end up in different fragments.
SkipHeader
Normally, the splitiftextcontainedinbox command causes a new fragment to be started whenever
the specified text is found within the box. The first fragment starts at page one and continues up to
the page before the first page that contains the text in the box. The
Skipheader command causes the first fragment to start with the first page that contai ns the text in
the box, leaving out any pages that came before it.
| CONTENTS | Page 46 of 58
Page 47

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix A - Rectangle Commands
ProvideBaseFilename
Takes the specified string parameter entered and uses it as the base filename of any split output
files.
ProvideFilename
Whatever text falls inside the rectangle (see runs of text) is used as the file name for the fragment.
If this command appears more than once in the coordinate file, the last provideF ilename command
will overwrite any other provideFilename commands.
ProvideFilenameIfStringInBox
The text inside the rectangle on a page is searched for the specified parameter. If the string
parameter is found inside the rectangle, then all the text inside the rectangle box on the first page
of the split output file is used as the output filename
ProvideFilenameFromFirstWord
The first word of the text inside the rectangle (or start of the text run) is appended to the output
filename. Any initial spaces are skipped, and the word continues until a space or the end of the run
of text.
ProvideFilenameFromSelectedWord
This looks at the text inside the rectangle and takes the word of text determined by the value
specified. The word is appended to the output filename.
ProvideFilenameFromRangeOfCharacters
This looks at the text inside the rectangle and takes a range of characters from that text and
appends the characters to the output filename. The range of characters is specified by two values,
firstNum and lastNum.
ProvideFilenameAfterString
This is similar to the providefilename command, except that the software searches the text inside
the rectangle for string, and if it finds the string, only the text inside the rectangle that comes after
string is used for the file name. If string is not found, nothing is appended to the file name.
ProvideFilenameAfterStringInBox
The text inside the rectangle on a page is searched for the specified parameter. If the string
parameter is found inside the rectangle, then the text after the string parameter and inside the
rectangle box on the first page of the split output file is used as the output filename.
AddToFilename
This command adds the string parameter to the output filename.
addToFilenameTextInBox
This command adds all text inside the rectangle box to the output filen ame.
addToFilenameIfStringInBox
This searches inside the rectangle for the string parameter. If the string parameter is found, it adds
the text within the rectangle box to the output filename.
| CONTENTS | Page 47 of 58
Page 48

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix A - Rectangle Commands
addToFileNameAfterStringInBox
This searches inside the rectangle for the string parameter. This command adds the text that
comes after the string parameter to the output filename.
DeleteCharactersFromFilename
If the specified character is found in the run of text for any of the providef ilename or addtofilename
commands, the character will be deleted as the text is added to the filename. The order of the
command matters as it will only delete characters from the filename that are added by commands
that come after this command in the coordinate file. This means that the
deletecharactersfromfilename command must come before any of the providefilename or
addtofilename commands that it will operate on.
FilterFilename
This filters characters from a filename so that the first character specified is replaced by the
character that follows. The order of the command matters as it will only filter characters from the
filename that are added by commands that come after this command in the coordinate file. This
means that the filterfilename command must come before any of the providefilename or
addtofilename commands that it will operate on.
GetFilenamesFromListInFile
This command opens a text file that lists the names given to each fragment created. The text file
should contain one file name per line.
IncludeAll
Normally, all pages go into one fragment or another, and the commands control where fragments
end and another fragment starts. Passing a false parameter to the includeall command causes all
pages to not be included in any fragment unless they are explicitly included by commands such as
includeiftextispresent and includeiftextcontainedinbox.
IncludeIfTextIsPresent
All text on the page is searched for the string parameter. If the string parameter is found
somewhere on the page, then the page will be included in the fragment . Since by default all pages
go into one fragment or another, this command is only effective if a false parameter is passed to
the includeall command.
IncludeInASingleFragmentIfTextIsPresent
If the literal string is found to occur in the text that is inside the rectangle, the page is added to the
list of pages to be included in a single fragment. This is meaningless unless you set includeall to
false.
IncludeIfTextContainedInBox
All text within the rectangle on the page is searched for the string parameter. If the string
parameter is found somewhere inside the rectangle, then the page will be included in the fragment.
Since by default all pages go into one fragment or another, this command is only effective if a false
parameter is passed to the includeall command.
| CONTENTS | Page 48 of 58
Page 49

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix A - Rectangle Commands
IncludeIfTextChangeAfterString
Looks at the text inside the rectangle for the string , if the string exists it will check if the text after
the string changes. If the text after the string changes from the previous page that contained the
string then the page will be included into the fragment. Since by default all pages go into one
fragment or another, this command is only effective if a false parameter is passed to the includeall
command.
ExcludeIfTextIsPresent
If the string parameter is found somewhere in the text on the page, then this command causes the
page to be excluded from all fragments.
ExcludeIfTextContainedInBox
If the string parameter is found somewhere in the text on the page inside the rectangle, then this
command causes the page to be excluded from all fragments.
ExcludeIfTextChangeAfterString
if the string parameter is found inside the rectangle it will check if the text after the string changes.
If the text after the string changes then t he page will be excluded from the fragment.
ExcludeIfNoTextContainted
This command looks inside the rectangle for text. If there is no text found within the rectangle box
then the page will be excluded. Useful wh en excluding blank pages from an output file.
ExtractFilename
This command opens a text extract file that will receive the text extracted by the various extract
commands.
ExtractText
This command extracts the run or runs of text that begin within the rectangle into the extract file
specified by the extractfilename command.
ExtractTextSelectedWords
This command works similarly to the extracttext command, but it extracts only the words indicated
by the range number-number. It looks at the run of text that falls within the rectangle, and takes
only the words that are number-number in order. For instance, if a run of text is text
15.839996,826.880005 (this is text on the page) and the extract command is
extracttextselectedword 12 829 18 823 2-4, then only the text is text on will be extracted. This
command uses the run or runs of text that begin within the rectangle into the extract file specified
by the extractfilename command.
ExtractTextSkipWords
This command works similarly to the extracttext command, but it skips over number words. If the
text in the run is text 15.839996,826.880005 (this is text on the page)and the extract command is
extracttextskipwords 12 829 18 823 2, then the text text on the page will be extracted, because
the first two words were skipped.
| CONTENTS | Page 49 of 58
Page 50

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix A - Rectangle Commands
ExtractTextSkipThisWord
This command works similarly to the extracttext command, bu t it skips over any initial
Whitespace and skips over the first occurance of text in the run of text. If text is not present, the
entire run of text inside the rectangle is extracted. If text is present, then the text that comes after
text in the run of text inside the rectangle is extracted.
ExtractTextSkipCharacters
This command works similarly to the extracttext command, bu t it skips over any initial
Whitespace and then skips over number characters. If the text in the run is text
15.839996,826.880005 (this is text on the page) and the extract command is
extracttextskipcharacters 12 829 18 823 2, then the text is text on the page will be extracted,
because the first two characters were skipped.
ExtractOnlyIfThisTextInRect
This command causes extracttext commands that follow it in the coordinate file to extract only if
the text is found inside the rectangle on a page. The order of the commands in the coordinate file
is important.
ExtractOnlyIfThisTextNotInRect
This command causes extracttext commands that follow it in the coorodinate file to extract only if
the text is not in the rectangle on a page. The order of the commands in the coordinate file is
important.
ExtractTextLineAfterString
If the parameter specified by the user is found on a visual line of text in the pdf, the rest of the
text on that line after the specified parameter is extracted.
ExtractTextLineAfterStringInRect
If the parameter specified by the user is found on a visual line of text using text runs within the
rectangle, the rest of the text within the rectangle on that line after the specified parameter is
extracted.
FillInfoDictEntry
Takes the text that is inside the rectangle and stores it within the specified key of the document
properties description i.e. title, author, subject or keywords.
| CONTENTS | Page 50 of 58
Page 51

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix B - Command Line Switches
10. Appendix B – Command Line Switches
The following switches can be used with ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Command Line (CL).
Input switch
-i [c:\input.pdf]
The input switch specifies the pdf file to be split.
Output switch
-o [c:\input.pdf]
-o [c:\outputfolder]
The output switch specifies the name of the fragment created or the folder that will contain the
fragments, depending upon which other switches are used.
Control switch
-c [c:\control.txt]
The control switch specifies a control file that lists the page numbers to be split and the fragment
names. See the control files section for more information.
Done switch
-d [c:\done]
The done switch specifies the path of a folder that a pdf file will be moved to from a watched folder
after the file has been successfully split.
Error switch
-e [c:\error]
The error switch specifies the path of a folder that a pdf file will be moved to from a watched folder
if an attempt to split the file generates an error.
Busy switch
-b [c:\busy]
The busy switch specifies the path of a folder that a pdf file will be moved into from a watched
folder while the file is being split.
| CONTENTS |
Page 51 of 58
Page 52

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix B - Command Line Switches
Watched folder switch
-w [c:\done]
The watched folder switch starts a watched folder using the method of splitting specified by other
switches. This requires the -i, -o, -b, -d, and -e switches. For specifying what method of splitting to
use, only the -k 1 switch is currently supported for watched folders from the command line with the
-w flag.
Watching a folder for splitting based on a coordinate file is specified with the -wc flag, not the -w
flag. (note: for watched folders, the fragments are put into the output folder. On completion, the
file being split is put into the done or error folder.)
Watched folder by coordinate file switch
-wc [c:\coordinate.crd] [c:\input] [c:\output] [c:\busy] [c:\done] [c:\error]
The watched folder/coordinate file switch starts a watched folder, meaning that any pdf file
dropped into the input folder is split according to the specified coordinate file. Multiple watched
folders can be created using the -wc switch more than once. Each use of the - wc switch must be
followed by the six operands that specify the appropriate paths.
Overwrite switch for watched folder
-ow
The overwrite switch will overwrite the original output file using watch folders. To use the overwrite
switch the –wc or –w switch is required.
Overwrite switch
/de
This overwrite switch will overwrite the original output file. This switch can be used with the –k, –
m, or –x switch.
Update navigational elements switch
-ne
This switch will update all bookmarks and links in output files so th at pages remain linked. This
switch can be used with the –k, –m, –x, –wc or –w switch. When using the –wc switch, –ne must
be placed before the –wc switch.
Page range switch
-r [1-5]
The page range switch uses two numbers separated by a dash to specify a range of pages that are
split from the file specified by the -i input switch an d saved in a newly created file whose name is
specified by the -o output switch. The -i and -o switches are required.
| CONTENTS |
Page 52 of 58
Page 53

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix B - Command Line Switches
Split by bookmark switch
-m [1-1]
The split by bookmark switch uses two numbers separated by a dash to specify the level of
bookmarks that are used for splitting. See split by bookmarks for more information.
Coordinate file switch
-x [c:\coordinate.crd]
The -x switch specifies a coordinate file to be used in splitting a pdf file. The -i and –o switches are
required. See the coordinate files section for more information.
Serial number switch
-n [3]
The -n switch specifies the minimum number of digits in a serial number. If a serial number has
fewer digits than the number specified by the -n switch, zeros are added to the front of the serial
number to pad it to length. Since any number has a least one digit already, -n 1 does not cause
any padding. This flag is only relevant if you are us ing the - k flag.
No subfolders switch
-ns
The -ns switch results in ARTS PDF Split Pro™ putting the split fragments directly into the output
folder, rather than create subfolders for the fragments. By default, for each pdf placed into the
input folder there will be a subfolder created in which the fragments from each pdf will be stored
in. This switch must be used before the –wc switch.
Fragment numbering switch
-f [123]
The -f switch specifies the first number to use when serially numbering the fragments. This switch
is ignored unless the -n flag is present and specifies a number greater than zero. This flag is only
relevant if you are using the –k flag.
Fragment size switch
-k [1]
The -k switch splits files into chunks of the specified size. The number specifies the number of
pages that go into each fragment. Currently, only -k 1 is supported, which will split a file into
fragments of one page each. The -i and -o flags are required. A serial number (1,2,3,4...) Is added
to the file name specified by the -o flag. If you use the optional -n and -f flags may be used to
control the numbering of the fragments. -k 1 –i c:\big.pdf -o c:\files\tiny.pdf will produce files
named tiny1.pdf and tiny2.pdf inside the folder named files on the c drive.
| CONTENTS |
Page 53 of 58
Page 54

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Appendix B - Command Line Switches
Headless switch
-h [c:\statuslog.txt]
The headless switch causes the software to run without any visual output or user interaction. Any
error or status messages are written into the status log. The software also returns an error value,
with zero indicating success. If the specified status log already exists, it will be deleted an d
replaced with a new log.
Shared read switch
-sh [c:\coordinate.crd]
The shared read switch indicates that the file being split (usually specified wit h the –i switch)
should be opened with shared read access instead of the usual exclusive read access.
Parse switch
-pa [42]
The parse switch parses the selected page. The -i switch specifies the pdf file to be parsed, and the
-o switch specifies the name of the text file to be output.
Parse debug
-pr [42-45]
The parse debug switch parses the selected page range. This is similar to the -pa switch, except
that the -pr switch parses a range of pages. The -i switch specifies the pdf file to be parsed, and
the -o switch specifies the name of the text file t o be output.
| CONTENTS |
Page 54 of 58
Page 55

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Troubleshooting
11. Troubleshooting
11.1. Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides some answers to common questions and details on what to do if a
problem is encountered concerning the following:
Rectangle commands not working
•
Control File splits with overwritin g
•
Landscape documents
•
General
•
Rectangle commands not working
“I think some of the rectangle commands don’t work! I’ve tried ‘IncludeIfTextIsPresent’
and ‘DeleteCharactersFromFilename’ and they don’t seem to do anything.”
A number of rectangle commands are dependant on other rectangle commands and are
only effective if you set the rectangle commands in the correct order. Use the ARTS PDF
Split Pro™ Assistant’s ‘View Commands’ dialog to display and reorder commands. food
• ‘IncludeIf’ commands (e.g. IncludeIfTextIsPresent) require that the IncludeAll
command is set to false. IncludeIf commands must come after the IncludeAll
command.
• DeleteCharactersFromFilename and FilterFilename rectangle commands need to
come before a ‘ProvideFilename’ or ‘AddToFilename’ command.
Control File splits with overwriting
“I selected the Control File split method and the overwrite mode option is off but it
keeps on the overwriting the output files. Is this a bug?”
The split methods ‘Split PDF by Control File’ and ‘Split PDF by Control File – full path’ are
set to always overwrite output PDF files. The reason for this is because the filename
must always be specified within the control file. If you don ’t want it to overwrite existing
output files; rename the file within the cont rol file or change the destination folder.
Landscape documents
“Why can’t I use the ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Assistant on landscape documents?”
This is because the PDF is rotated. However, if you attempt to split the PDF, ARTS PDF
Split Pro™ will still work on the landscape document.
| CONTENTS |
Page 55 of 58
Page 56

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Troubleshooting
General
“I am having a problem with ARTS PDF Split Pro™ and it is not covered in this FAQ.
What can I do?”
• Visit our ARTS PDF Forum (
technical support and other ARTS PDF product users. Search the existing discussions
and/or post your own questions. Each ARTS PDF product has it own dedicated
discussion area.
• Visit our website at
ARTS PDF support.
http://www.artspdf.com/support.asp for more information on
http://forum.artspdf.com) to talk with ARTS PDF
11.2. Forum
Are you having a problem that you can’t find in the Frequently Asked Questions? Then
perhaps you’ll find it on the ARTS PDF Forum. Visit the ARTS PDF Forum at
http://forum.artspdf.com.
11.3. Updates
To ensure you are up-to-date with the most recently released bug fixes and new
features, check that you have the latest version of ARTS PDF Split Pro™ installed.
To check if your version is the latest:
1. Start ARTS PDF Split Pro™ GUI.
2. Click on the About button.
3. Choose Product Info and click Updates.
Or alternatively:
1. Start Adobe Acrobat.
2. Choose Help > About Third-Party Plug-In s > ARTS PD F Split Pro Assistant.
3. Choose Product Info and click Updates.
| CONTENTS |
Page 56 of 58
Page 57

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Troubleshooting
11.4. Maintenance
At times ARTS PDF will release updates that may include significant enhancements to
the product. It is recommended that you take up annual maintenance to be entitled to
free upgrades (whether it be minor or major release versions) over a period of 12
months from the initial purchase. Annual Maintenance also entitles you to priority phone
and email support.
Annual maintenance can be purchased at the same time you buy the associated product
from ARTS PDF or your ARTS PDF reseller. If you wish to renew a subscription, or if you
wish to purchase a subscription for a product you already own, please contact your
reseller or ARTS PDF directly at
info@artspdf.com
| CONTENTS |
Page 57 of 58
Page 58

ARTS PDF Split Pro™ Guide
Troubleshooting
11.5. Technical Support
Before contacting ARTS PDF please read the complete Troubleshooting section as the
answer to your problem may be found in the FAQs or on the ARTS PDF Forum. To
contact ARTS PDF Technical Support, submit your query using the support contact form
found on our website:
below will help us assist you with the problem you are experiencing.
a. The exact version of ARTS PDF Split Pro™ you are using (this is located by
running ARTS PDF Split Pro, and then clicking About > Product Info). Please also
specify whether you are using a demo or full registered version.
b. Whether or not you purchased Maintenance with ARTS PDF Split Pro™. If you did
purchase Maintenance, please supply your ARTS PDF Split Pro™ serial number.
c. The amount of free disk space remaining.
d. The CPU speed and amount of RAM for the system on which ARTS PDF Split Pro™
is running (e.g. Pentium 233 MMX, 32MB RAM).
e. Any other programs that are running at the time of the error (e.g. Outlook,
Internet Explorer, etc).
f. All error messages that were displayed when the error occurred.
g. The exact series of steps that led to the error.
h. Whether this error occurs on every PDF document or one specific file.
i. What program was used to create the PDF documents? E.g. Acrobat Distiller,
Crystal Reports, Zeon PDF Driver, etc.
Feedback If you have ideas and suggestions on how we could improve ARTS
PDF Split Pro™, we would love to hear your thoughts. Please send
them to
Legal Notes
Acrobat and Exchange are registered trademarks of Adobe
Systems Incorporated. ARTS PDF Split Pro™ is Copyright © 2005
ARTS PDF.
http://www.artspdf.com/support_contact.asp. The information
info@artspdf.com
| CONTENTS |
Page 58 of 58
 Loading...
Loading...