Page 1

PRODUCTS
AUT OMATION
Operator’s Manual
GROUP, INC.
FLR
Series
Magnetic Float Sensors
9003284
Rev. A5, 10/09
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www.apgsensors.com • E-mail: sales@apgsensors.com
Automation Products Group, Inc.
Page 2

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
Table of Contents
Warranty ......................................................................................... 3
Description...................................................................................... 4
Installation ................................................................................... 5-6
Wiring.............................................................................................. 7
Circuit Pr otection ........................................................................... 8
Field Adjustment of Actuation Point.........................................9-21
Inspection & Maintenance ............................................................ 22
Technical Notes............................................................................. 22
Specifications ................................................................................ 23
Automation Products Group, Inc.
2
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 3

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
• Warranty and W arranty Restrictions
APG warrants its products to be free from defects of material and workmanship
and will, without charge, replace or repair any equipment found defective upon
inspection at its factory, provided the equipment has been returned,
transportation prepaid, within 24 months from date of shipment from factory .
THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF AND EXCLUDES ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES NOT EXPRESSL Y SET FOR TH HEREIN, WHETHER
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED BY OPERATION OF LAW OR OTHER WISE
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED T O ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANT ABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PAR TICULAR PURPOSE.
No representation or warranty, express or implied, made by any sales
representative, distributor, or other agent or representative of APG which is not
specifically set forth herein shall be binding upon APG. APG shall not be liable
for any incidental or consequential damages, losses or expenses directly or
indirectly arising from the sale, handling, improper application or use of the
goods or from any other cause relating thereto and APG’s liability hereunder, in
any case, is expressly limited to the repair or replacement (at APG’s option) of
goods.
Warranty is specifically at the factory. Any on site service will be provided at
the sole expense of the Purchaser at standard field service rates.
All associated equipment must be protected by properly rated electronic/
electrical protection devices. APG shall not be liable for any damage due to
improper engineering or installation by the purchaser or third parties. Proper
installation, operation and maintenance of the product becomes the
responsibility of the user upon receipt of the product.
Returns and allowances must be authorized by APG in advance. APG will
assign a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number which must appear on
all related papers and the outside of the shipping carton. All returns are subject
to the final review by APG. Returns are subject to restocking charges as
determined by APG’s “Credit Return Policy”.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
3
Page 4

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
Permanent Magnet
Float Travel-Stop
Float
Stem
Reed Switch
• Description
The FLR series instruments contain reed switches in the stem and permanent
magnets in the floats. As the float rises or falls with the level of the liquid, the
magnet inside the float act on the reed switch inside the stem to provide the
SPST switching action.
4
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 5

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
• Installation
- Unpacking -
When unpacking the instrument, exercise care not to subject the instrument to
mechanical shock. After unpacking, visually inspect the instrument for
damage.
- Environment -
The FLR series sensors should be installed in an areas indoor or outdoor
which meets the following conditions:
1. Non-hazardous area.
2. The medium temperature does not exceed -400F to 1850F (-140C to 850C).
NOTE: It is recommended that a sun shield be installed over the housing if
exposed to direct sunlight.
3. Relative humidity up to 100%
4. Pollution Degree 2
5. Measurment Category II
6. Altitude 2000 m or less.
7. Locate the sensor away from strong magnetic fields such as those
produced by motors, transformers, solenoid valves, etc.
8. The medium is free from metallic substances and other foreign matter.
9. No corrosive gases such as NH3, SO2, Cl2, etc.
10. No excessive vibration
11. Ample space for maintenance and inspection.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
5
Page 6

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
Stilling Tube
Inflow Inflow
Spacer
• Installation
- Location -
Do not locate the FLR series sensor near inlets/outlets.
If there is surface wave action, then use a time-delay relay or stilling tube. If a
stilling tube is used, drill vent holes in the tube and use a spacer to assure the
float has free travel inside the tube.
Wave action may cause switch to chatter. Use a stilling tube or time-delay
- Mounting -
The FLR can be mounted up to 300 from vertical.
1. Flange Mounting
Provide the compatible mating flange on the tank and install using a suitable
gasket.
2. Plug Mounting
Provide the compatible female boss on the tank and install the FLR with a
suitable gasket, O-ring, or thread tape.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
6
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
relay to prevent switch chatter.
Page 7

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
L1
L2
L3
L4
BlackBlack White White Red Red Green Green
Wiring Color
L1
L1
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L7
L2
L3
L4
L5
L6
L7 Com.
Blk x 2
Blk x 2
Blk x 2
Blk x 2
Black
Black
Black
Wh x 2
Wh x 2
Wh x 2
White
White
White
Red x 2
Red x 2
Red
Red
Red
Grn x 2
Green
Green
Green
Yellow
Yellow
Yellow
Brown
Brown
Grey
Grey
GreyBlue
Number
of
Levels
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7
Common
Black White Red Green GreyBlueBrownYellow
• Wiring
- Wiring for 1 to 4 switches
- Wiring for greater than 4 switches
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Automation Products Group, Inc.
7
7
Page 8

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
L
C
R
E
C = I
R = Approx.
10 x I (I + 50/E)
E
Protecting Circuit Using CR
Protecting Circuit Using Varistor
Protecting Circuit Using Diode
2
/10 (uF)
• Circuit Protection
W ARNING!
DO NOT EXCEED CONT ACT RA TINGS! When an inductive load is used
(e.g. a motor, a coil, or an electromagnetic relay), a back electromotive
force of several hundred volts (energy stored in the inductance) arises
when the contacts are opened. This results in considerable decrease in
contact life. The same result arises even when a resistive load is used
with a high voltage or a large current. The figures below show circuits for
protecting the reed switch(s) from the back electromotive force.
Code A & B Switches
Max. contact capacity 70 VA AC,
Max. switching current 220 V AC 0.5 A, 120 VDC 0.5 A
Code C Switches
Max. contact capacity 110 VA AC,
Max. switching current 220 VAC 0.5 A, 115 VDC 0.5 A
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
8
Automation Products Group, Inc.
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 9

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
• Field Adjustment Of Actuation Point(s)
The FLR sensors are designed to allow field adjustments of the actuation
points by moving the floats and reed switches. This section contains two
procedures for making field adjustments.
NOTE: FLR units without housings are hermetically sealed and cannot be
field adjusted.
Procedure one should be used under the following conditions:
a. You want to move the actuation point relative to the factory settings.
b. Their will be
closed).
Procedure two should be used under the following conditions:
a. The float stops have been loosened and moved without marking their
previous stem location.
b. The switching logic needs to be reversed (normally open/normally
closed).
c. You want to move the actuation point independant of the factory settings
no change to the switching logic (normally open/normally
Procedure One:
1. Before making any adjustments to the FLR, mark the stem location of the
float stops that will need to be moved.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
9
Page 10

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
85 mm
85 mm
Marks of previous
stop locations
New
Actuation
Point
2. Determine the location of the new actuation point. The actuation point is
located at the center point between the float stops.
3. Loosen the retaining hex screws on the float stops and slide the stops
exactly the same distance along the stem to their new locations. Re-secure the
stops to the stem.
For example (refer to drawing above): Suppose the actuation point needs to be
adjusted 85 mm lower on the stem. The first step is to mark the location of
both float stops that will need to be moved. Next, move the float stops (and
float) exactly 85 mm down the stem from your marks. Re-secure the stops to
the stem and continue to step 4.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
10
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 11

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
4. Once the stops and float are set in the desired location, the reed switch
assembly inside the stem needs to be adjusted to match the new actuation
point. To access the reed assembly, you will need to remove the two screws
that secure the terminal mounting plate to the housing.
5. Carefully remove the terminal mounting plate along with the wiring and
internal reed switch assembly from the stem of the FLR. Keep the assembly
straight and take care not to bend or put stress on the reed switches.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
11
Page 12

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
6. Carefully lay the reed switch assembly on a clean surface and remove the
tape securing the wires to the assembly rod. Do not cut into the wires!
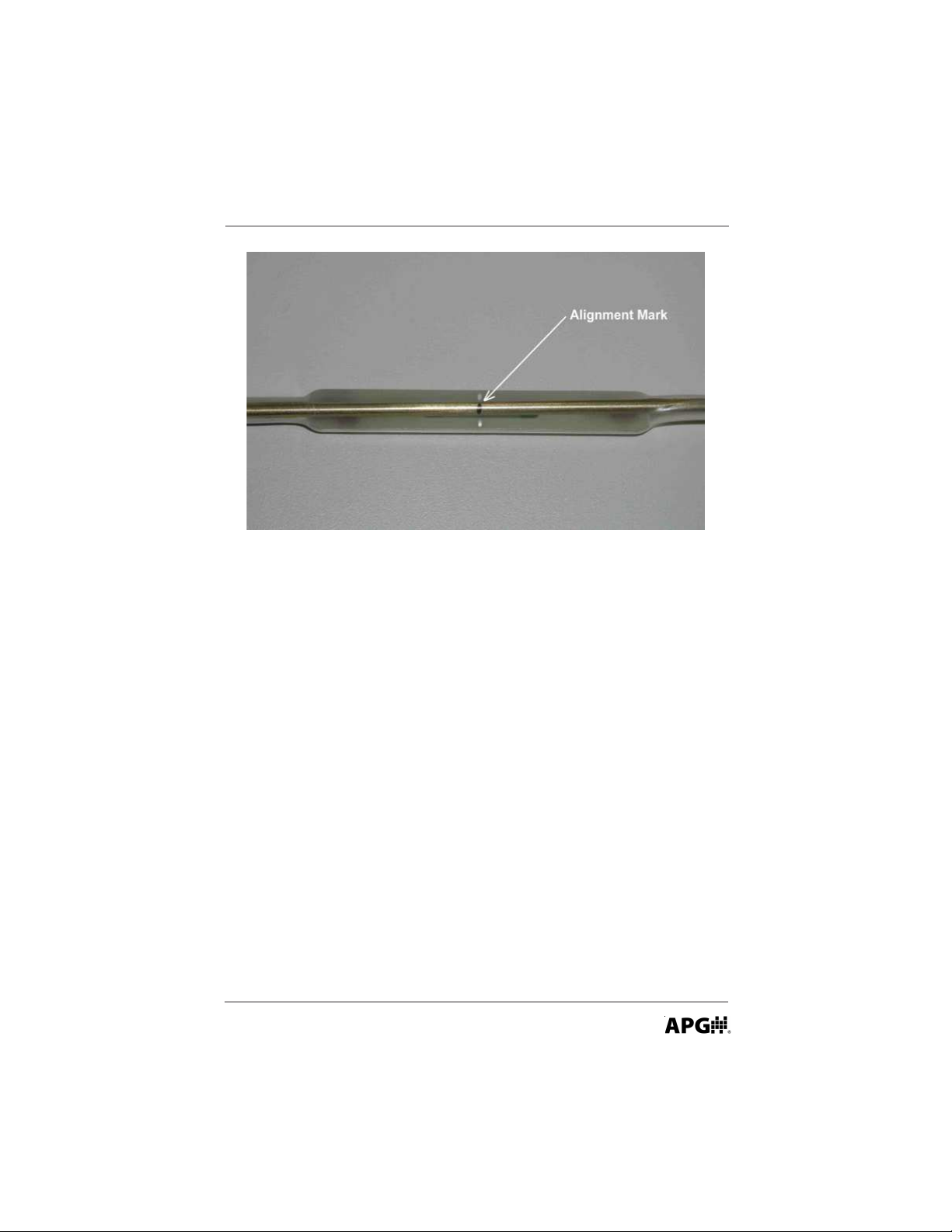
7. If you look closely at the reed switch assembly rod, you will notice a black
mark at each reed switch location. During factory calibration, these marks are
used to align the center of each reed switch with the desired actuation point.
To align the reed switch with the newly adjusted float position, simply move
the reed switch along the rod the same distance that you previously moved the
float stops on the stem. This distance is measured from the center of the reed
switch to the black mark on the rod.
8. Once the reed switches have been moved into the correct position, use
electrical tape to re-secure the wires to the assembly rod. You are now ready to
carefully reassemble the FLR and test the new actuation point.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
12
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 13

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
Desired
Actuation
Point
9 mm
9 mm
• Field Adjustment Of Actuation Point(s)
Procedure Two:
1. Determine the desired actuation point.
2. Loosen the retaining screws on float stops that need to be repositioned.
3. Slide the float along the stem until the float’s center is aligned with the
desired actuation point.
4. Re-secure the float stops 9 mm above and below the new float position (refer
to drawing below).
NOTE: The 9 mm distance between the float and stops is critical for the switch
to operate reliably.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
13
Page 14

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
5. With the float and stops in place at the new actuation point, the internal reed
switch needs to be repositioned to match the new actuation point. Remove the
two screws that secure the terminal mounting plate to the housing (shown
above).
6. Carefully remove the terminal mounting plate along with the wiring and
internal reed switch assembly from the stem of the FLR. Keep the assembly
straight and take care not to bend or put stress on the reed switches.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
14
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 15

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
7. Measure the distance from the bottom of the stem to the new actuation point.
The actuation point is at the center position between the float stops. In the
example above, the actuation point is at 250 mm.
8. A brass rod inside the stem holds the reed switches in place. The location of
the switch needs to be adjusted to match the new actuation point. Determine
which switch type you are using and continue to the step indicated below.
CODE “A & B” (approx. 20 mm switch length)
Normally Open continue to step 8a
(page 15)
Normally Closed skip to step 8b
(page 16)
CODE “C” (approx. 30 mm switch length)
Normally Open skip to step 8c
(page 17)
Normally Closed skip to step 8d
(page 18)
NOTE: The float is considered in the “normal” position when it is at
rest against the lower stop.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
15
Page 16

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
Actuation
Point
Indention designates
top of float
ON
OFF
For normally open (NO) switching action
with a Code "A" or "B" switch, the center
point of reed switch assembly is set in line
with the float center.
9 mm
9 mm
Plug
Approx. 6 mm
Brass Rod
Normally Open Switching for Code “A” & “B” Switches
8a. For “normally open” (NO) switching (code A & B switches), subtract 6 mm
from the measurement taken in step 7 and record the result. This distance will
be used to adjust the reed switch along the internal brass rod. The 6 mm is
subtracted to compensate for the plug in the bottom of the stem. Refer to
drawings below.
16
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Automation Products Group, Inc.
Page 17

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
For normally closed (NC) switching
action with a Code "A" or "B" switch,
the center point of reed switch assembly
is set 12mm below the actuation point.
Indention designates
top of float
ON
OFF
12 mm
Actuation
Point
9 mm
9 mm
Plug
Approx. 6 mm
Brass Rod
Normally Closed Switching for Code “A” & “B” Switches
8b. For “normally closed” (NC) switching (code A & B switches), subtract 18
mm from the measurement taken in step 7 and record the result. This distance
will be used to adjust the reed switch along the internal brass rod. The 18 mm
is subtracted to compensate for both the offset of the reed switch from the
actuation point (-12 mm), and the plug in the bottom of the stem (-6 mm).
Refer to drawings below.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Automation Products Group, Inc.
17
Page 18

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
Indention designates
top of float
For normally open (NO)
switching action, the center
point of reed switch is set 3 mm
above the desired actuation point.
ON
OFF
3 mm
9 mm
9 mm
Actuation
Point
Plug
Approx. 6 mm
Brass Rod
Normally Open Switching for Code “C” Switches
8c. For “normally open” (NO) switching (code C switches), subtract 3 mm from
the measurement taken in step 7 and record the result. This distance will be
used to adjust the reed switch along the internal brass rod. The 3 mm is
subtracted to compensate for both the offset of the reed switch from the
actuation point (+3 mm), and the plug in the bottom of the stem (-6 mm). Refer
to drawings below.
18
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Automation Products Group, Inc.
Page 19

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
For normally closed (NC)
switching action, the center
point of reed switch is set
6 mm below the desired
actuation point.
Indention designates
top of float
6 mm
9 mm
9 mm
ON
OFF
Actuation
Point
Plug
Approx. 6 mm
Brass Rod
Normally Closed Switching for Code “C” Switches
8d. For “normally closed” (NC) switching (code C switches), subtract 12 mm
from the measurement taken in step 7 and record the result. This distance will
be used to adjust the reed switch along the internal brass rod. The 12 mm is
subtracted to compensate for both the offset of the reed switch from the
actuation point (-6 mm), and the plug in the bottom of the stem (-6 mm). Refer
to drawings below.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
19
Page 20

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
9. Using the distance you derived in step 8, measure from the bottom of the
reed switch assembly and mark the center rod at that location.
10. Remove the tape securing the reed switch to the assembly rod. Be careful
not to cut any of the wires or to put pressure in the reed switch.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
20
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 21
Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
11. Slide the reed switch along the rod until the center lines up with the mark
you make on the rod in step 9. Re-secure the wires to the center rod with
electrical tape.
12. Carefully reinsert the reed switch assembly into the stem and test the switch
action.
13. If the actuation point needs fine tuning, remove the reed assembly from the
stem and make any necessary adjustments to the reed switch position.
14. Reassemble the unit.
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
21
Page 22

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
• Inspection and Maintenance
Periodic inspection is necessary to keep your FLR unit in good working
order.
CAUTION! Do not remove the housing cover until the power
supplied to the unit is turned off.
1. Keep the sensor clean.
Never leave the housing cover off. If the cover becomes
damaged or is misplaced, order a replacement immediately .
If sediment or other foreign matter is trapped between the stem
and the float, detection errors may be caused. Keep the float and
stem clean.
2. Inspect the switches and terminals.
• T echnical Notes
1. The float travel stop settings are based on how the magnetic field
influences the reed switch. Normally it is not necessary to move the
stop. If the stops are moved, check the switch action for float overrun.
2. Normally Open (NO) (switch closes as level rises) and Normally Closed
(NC) (switch closes as level falls).
Automation Products Group, Inc.
22
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 23

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
• FLR Specifications
Maximum Number Switching Points 7
Resolution +/- 1/16” (2mm)
Field Adjustable Actuation Levels Yes
Maximum Length 153 in.
Maximum Process Temperature -400 to 1850F
Housing Material Die Cast
Aluminium
Hazardous Rating None
Housing Rating NEMA 4
Contact Rating:
Code A & B Switch
Max. contact capacity 70 V A AC,
Max. switching current 200 V AC 0.5 A, 120 VDC 0.5 A
Code C Switch
Max. contact capacity 110 VA AC,
Max. switching current 220 V AC 0.5 A, 115 VDC 0.5 A
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
23
Page 24

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
24
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 25

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
25
Page 26

FLR Series Rev. A5, 10/09
26
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
Page 27

Rev. A5, 10/09 FLR Series
Automation Products Group, Inc.
APG...Providing tailored solutions for measurement applications
Tel: 1/888/525-7300 • Fax: 1/435/753-7490 • www .apgsensors.com • sales@apgsensors.com
27
Page 28

AUT OMATION
APG...Providing tailored solutions
for measurement applications
Automation Products Group, Inc.
T el: 1/888/525-7300
Fax: 1/435/753-7490
e-mail: sales@apgsensors.com
www.apgsensors.com
GROUP, INC.
1/435/753-7300
PRODUCTS
Automation Products Group, Inc.
1025 W. 1700 N.
Logan, UT 84321
 Loading...
Loading...