Page 1

MGETM GalaxyTM 6000
50, 60 Hz
250 - 600 kVA
User manual
Single-unit UPS
Modular UPS
Parallel UPS with SSC
Frequency converter
Static Switch Cubicle
6739380EN/JC - Page 1
Page 2

Page 2 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 3

Contents
Introduction
System performance ................................................................................................. 5
System description .................................................................................................... 5
Different types of MGE
Isolation and protection devices ................................................................................ 8
Main operating modes .............................................................................................. 9
Description of MGETMGalaxyTM 6000 cubicles
Inverter cubicle ........................................................................................................ 13
Battery cubicle ........................................................................................................ 14
Static Switch Cubicle .............................................................................................. 15
External maintenance bypass cubicle ..................................................................... 15
Control panel
Visible control panel ................................................................................................ 16
Hidden control panel ............................................................................................... 18
Start-up
System start-up ....................................................................................................... 20
Start-up of a unit ..................................................................................................... 22
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 systems ................................................... 6
Shutdown
Shutdown of a unit .................................................................................................. 24
System shutdown .................................................................................................... 25
Buzzer reset ............................................................................................................ 26
Alarms
Maintenance bypass ............................................................................................... 27
Environment information
Standard information "Media Contacts 9" ............................................................... 28
"LED" signalling box ................................................................................................ 29
Additional information "Media Contacts 15" ............................................................ 29
Maintenance
Maintenance configuration ...................................................................................... 31
Battery maintenance ............................................................................................... 33
Autodiagnostics ....................................................................................................... 34
Visual check ............................................................................................................ 34
Functional check ..................................................................................................... 34
Training center ........................................................................................................ 34
"Monitor" alphanumeric display
General ................................................................................................................... 36
Control panel ........................................................................................................... 36
Lights 1 to 8 ............................................................................................................ 37
Alarm display and buzzer reset ............................................................................... 38
Measurement system .............................................................................................. 41
Voltage measurements ........................................................................................... 42
Current measurements ........................................................................................... 42
Frequency and power measurements .................................................................... 43
Battery measurements ............................................................................................ 43
Inverter "On/Off" commands ................................................................................... 45
Language, display contrast and buzzer volume settings ........................................ 45
Display system configuration .................................................................................. 46
6739380EN/JC - Page 3
Page 4

Contents (cont.)
Options
"LED" signalling box ................................................................................................ 47
Media Contacts 15 additional auxiliary transmission .............................................. 47
"Tele Monitor" remote indications unit..................................................................... 47
"GTC link" communications system ........................................................................ 47
"Vision" display........................................................................................................ 48
"Remote vision" display........................................................................................... 48
Insulating and Mains 1, 2, and load voltage matching transformer ......................... 48
Harmonics filter and power factor improvement ..................................................... 48
Double bridge rectifier-charger ............................................................................... 49
Battery "Temperature Monitor"................................................................................ 49
Empty cubicles ........................................................................................................ 49
Page 4 - 6739380EN/JC
TM
All MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 products are protected by patents. They implement original APC by Schneider Electric technology
not available to other manufacturers.
To take into account evolving standards and technology, equipment may be modified without notice. Indications concerning
technical characteristics and dimensions are not binding unless confirmed by APC by Schneider Electric.
This document may be copied only with the written consent of APC by Schneider Electric. Authorized copies must be marked
"APC by Schneider Electric MGE
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 User Manual N° 6739380EN.
Page 5
System performance
TM
A MGE
uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
delivers 3-phase power with the
following characteristics:
◗ stable voltage (+/-0.5% under steady
state conditions and +/-5% under
transient conditions for load step
changes of 25 to 100% or of 100 to
25%);
◗ stable frequency (+/-0.05Hz without
Mains 2);
◗ or frequency synchronized with
Mains 2 to 50/60Hz +/-2Hz (value may
be configured in 0.25 HZ steps);
◗ free of micro-breaks and outages for
the duration of the battery time (10, 15
or 30 minutes);
◗ less than 4% distortion in all system
configurations with linear loads;
◗ less than 5% distortion for a 100%
non-linear load with a peak factor of up
to 3.5.
The acoustic noise level of a
MGE
70dBA.
GalaxyTM 6000
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS is under
Single-line diagram of the MGE
B
mains 2
(bypass input)
mains 1
(normal input)
isolation
isolation
and
protection
A
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 system
maintenance
bypass
emergency
bypass
AC/DC
conversion
isolation and
protection
battery
DC/AC
conversion
Introduction
isolation
and
protection
load
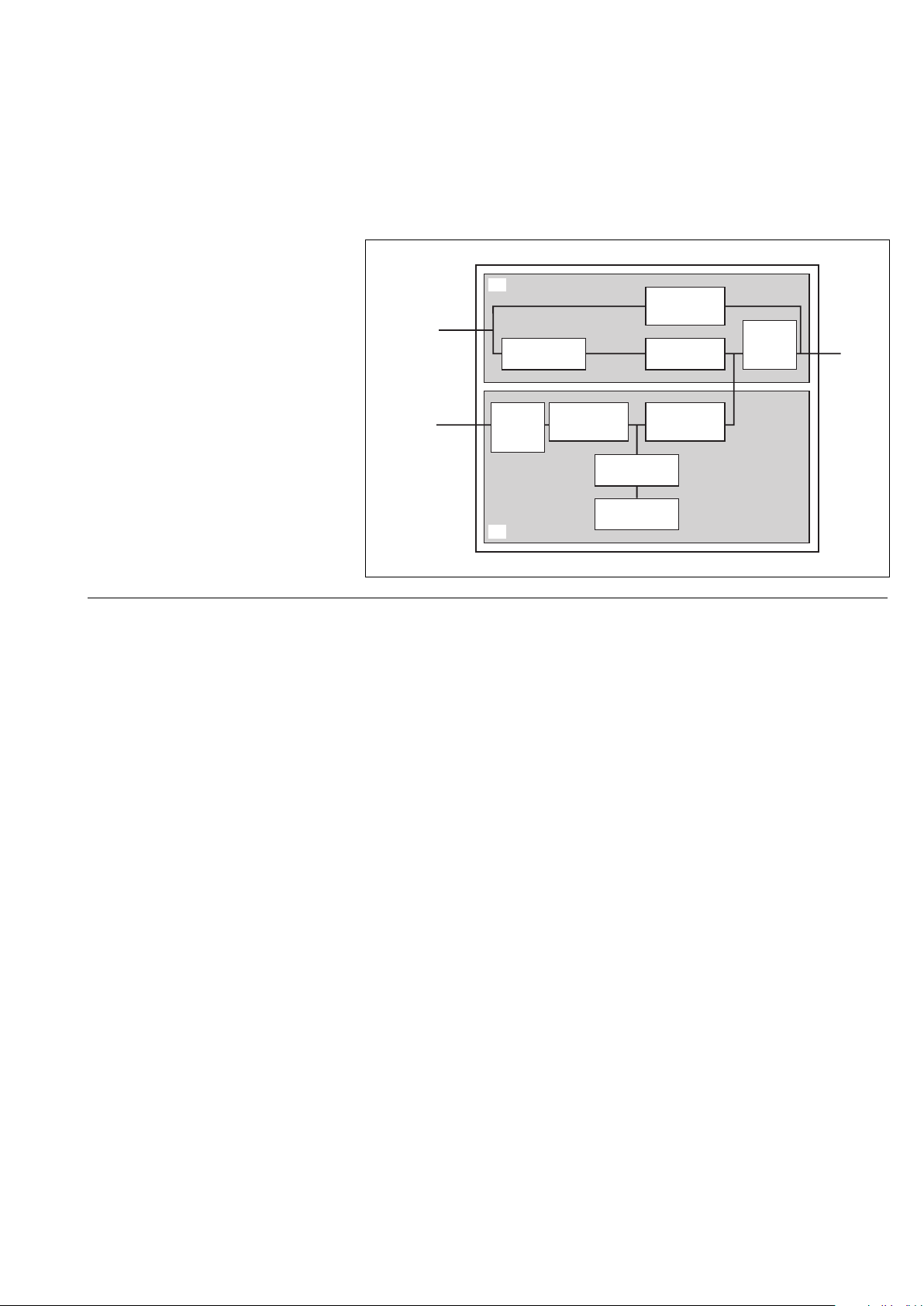
System description
◗ a rectifier-charger (RC) module
converts 3-phase AC power from the
Mains 1 supply into DC power for the
normal inverter input and float charges
or recharges the batteries;
◗ a battery unit provides backup power
for the inverter in the event of a voltage
drop or a Mains 1 failure;
◗ an inverter module converts the DC
power supplied by the rectifier-charger
module or the battery unit into 3-phase
AC power for the load;
◗ an emergency bypass module
ensures the instantaneous transfer of
the load via the static switch to the
Mains 2 bypass line in the event of an
inverter shutdown (initiated by the user
or by a protective device) or a sudden
overload;
◗ a maintenance bypass which isolates
the UPS for maintenance and transfers
the load without interrupting the supply
of power. The maintenance bypass is
made up of three manual switches.
Note:
◗ the Mains 1 normal input and the
Mains 2 bypass input have different
functions and, depending on the
installation, may be protected
differently upstream and/or come from
different sources;
◗ frequency converters are available
without backup batteries;
◗ the emergency bypass line and the
maintenance bypass line do not exist in
installations where the load frequency
and the Mains 2 frequency are different
(for example in frequency converters);
◗ for reasons of redundancy and/or
increased power, the rectifier-charger,
inverter and battery modules (the UPS,
part A in the MGE
TM
GalaxyTM 6000
schematic diagram above) may be
arranged in parallel lines. In this case,
an isolation function is added to the
output of each UPS for maintenance
without disrupting the load.
In this type of system, the components
of part B in the diagram are located in a
separate cubicle referred to as the
"Static Switch Cubicle".
The system may also include:
◗ an isolating transformer on the
Mains 2 line;
◗ a harmonics filter on the Mains 1
input;
◗ different remote control, indication
and display systems;
◗ a double bridge rectifier-charger
module.
6739380EN/JC - Page 5
Page 6

Introduction (cont.)
Different types of MGETMGalaxyTM 6000 systems
◗ Single-unit or modular UPS:
(figure 1)
mains 2
mains 1
Fig. 1
◗ Multi-bypass modular UPSs:
(figure 2)
Note:
2 modular UPSs (identical ratings) can
be parallel-connected in this way.
mains 2
mains 1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
Q3BP
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
load
battery
static switch
inverter
◗ Modular UPSs with external
maintenance bypass: (figure 3)
Note:
Up to 4 UPS (identical ratings) can be
parallel-connected.
Fig. 2
mains 2
mains 1
mains 2
mains 1
mains 2
rectifiercharger
Q3BP
rectifiercharger
battery
battery
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
battery
static switch
static switch
inverter
load
load
Q5N
Page 6 - 6739380EN/JC
Fig. 3
mains 1
rectifiercharger
inverter
battery
Page 7

Introduction (cont.)
◗ Frequency converter with battery
backup power: (figure 4)
◗ Frequency converter without backup
power: (figure 5)
◗ Frequency converters with backup
power: (figure 6)
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
mains 1
mains 1
mains 1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
inverter
load
battery
inverter
load
inverter
battery
inverter
load
◗ Parallel UPSs with SSC: (figure 7)
Note:
Up to 6 UPS (identical ratings) can be
parallel-connected in this way.
Fig. 6
mains 2
mains 1
rectifiercharger
Q3BP
Static Switch Cubicle
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
battery
battery
battery
inverter
inverter
inverter
load
Fig. 7
battery
6739380EN/JC - Page 7
Page 8
Introduction (cont.)
Isolation and protection devices
UPS or converter cubicles
(figure 8)
◗ Q1 (switch):
◗◗ isolation from Mains 1,
◗◗ RC start-up;
◗ QF1 (circuit breaker):
◗◗ battery protection and isolation;
◗ Q5N (switch):
◗◗ isolation of the inverter, frequency
converter or static switch module from
the load;
◗ Q4S (switch):
◗◗ isolation of the static switch from
Mains 2;
◗ Q3BP (switch):
◗◗ bypass switch for maintenance;
◗ FU1-2-3 (fuses):
◗◗ protection of the RC from Mains 1;
◗ FU5-6-7 (fuses):
◗◗ protection of the inverter from the
load.
Note:
◗◗ switches Q4S and Q3BP do not exist
on frequency converters,
◗◗ circuit breaker QF1 does not exist on
frequency converters without a battery.
Example of a single-unit UPS or single modular UPS
static switch
mains 2
mains 1
rectifier-
Q1
FU1-2-3 FU5-6-7
charger
Q4S
inverter
QF1
battery
Fig. 8
Q3BP
Q5N
load
Static Switch Cubicle
(figure 9)
◗ Q4S (switch):
◗◗ isolation of the static switch (and
mechanical contactor K2S) from
Mains 2;
◗ Q3BP (switch):
◗◗ bypass switch for maintenance;
◗ Q5N (switch):
◗◗ isolation of the load from the parallel
UPSs;
◗ Q1 (fuse switch):
◗◗ protection of the cubicle control
electronics from the parallel-connected
inverter outputs;
◗ Q2 (fuse switch):
◗◗ protection of the cubicle control
electronics from Mains 2.
External maintenance bypass
cubicle (figure 10)
◗ Q3BP (switch):
◗◗ bypass switch for maintenance;
◗ Q5N (switch):
◗◗ isolation of the load from the parallel-
connected UPSs.
Fig. 9
mains 2
parallel
UPSs
maintenance
bypass line
parallel
modular UPSs
Q2
Q1
Q4S
Q3BP
Q5N
static switch
control
electronics
Q3BP
Q5N
load
load
Page 8 - 6739380EN/JC
Fig. 10
Page 9

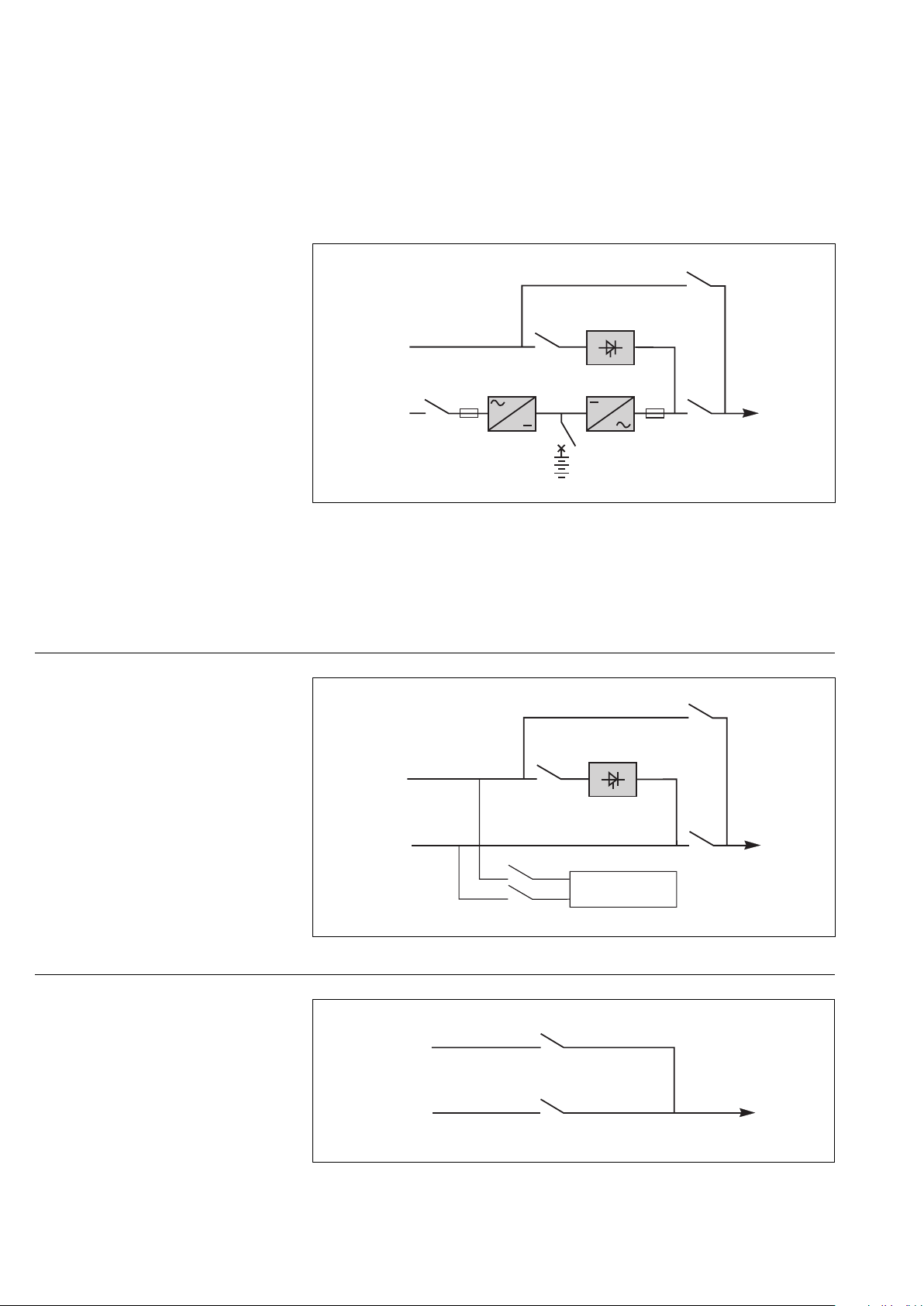
Main operating modes
Normal operation
Mains 1 power is available:
(see figure 11).
The green "load protected" light 5 on
the control panel is on.
!
+–
!
I
Introduction (cont.)
static switch
mains 2
rectifiercharger
O
mains 1
inverter
load
5
légend :
off on
The power necessary for the load is
provided by Mains 1 through the
rectifier-charger and the inverter.
The rectifier-charger also supplies the
power to float charge and recharge the
battery (1). The rectifier-charger output
voltage (DC) is regulated for the
different battery types and charging
modes:
◗ vented lead-acid or Ni/Cd batteries:
two different voltages, one for float
charging and one for recharging;
◗ sealed lead-acid batteries: a single
voltage for both charge functions.
Operation with Mains 1 down
(figure 12)
In the event of a Mains 1 failure or
Mains 1 voltage outside specified
tolerance of –10% in amplitude (–15%
optionally), the rectifier-charger stops
and the battery supplies the necessary
backup power to the load via the
inverter. The battery, float-connected
between the rectifier-charger and the
inverter, discharges during this
operating mode.
The green "load protected" light 5 on
the control panel is on.
The user is warned of battery operation
by a buzzer and the orange "load on
battery" light 4 on the control panel.
beep...beep...
!
+–
!
I
Fig. 11
The voltages depend on the number of
battery cells and the battery
manufacturer. They can be factory set
and are adjustable by the after-sales
support technicians.
An optional electronic board may be
used to continuously measure the
battery temperature and automatically
adjust the voltages.
mains 2
mains 1
Fig. 12
This information is also available via
volt-free changeover contacts for
remote control devices.
In this case, there is a 30 seconds
delay.
O
rectifiercharger
battery
Parallel UPS systems:
the power drawn by the load is equally
shared between the different UPSs.
(1) Except for frequency converters without a
battery
static switch
inverter
load
battery
Note:
In the event of a Mains 1 failure,
frequency converters without a battery
shut down and the load is no longer
supplied.
5
4
6739380EN/JC - Page 9
Page 10
Introduction (cont.)
Battery time
The available battery time during a
Mains 1 outage depends on the:
◗ rated capacity of the battery;
◗ power consumed by the load;
◗ temperature of the battery;
◗ age of the battery.
The specified battery time corresponds
to a minimum duration at full rated load.
The actual backup time can therefore
be greater if the system operates below
its full rated load during the Mains 1
outage. Operation on battery power can
be extended beyond the specified time
by reducing the load power
consumption (by disconnecting noncritical loads).
A "low battery shutdown" warning
signal is sent via volt-free changeover
contacts for remote control devices
when the battery voltage reaches a
level slightly above the minimum level.
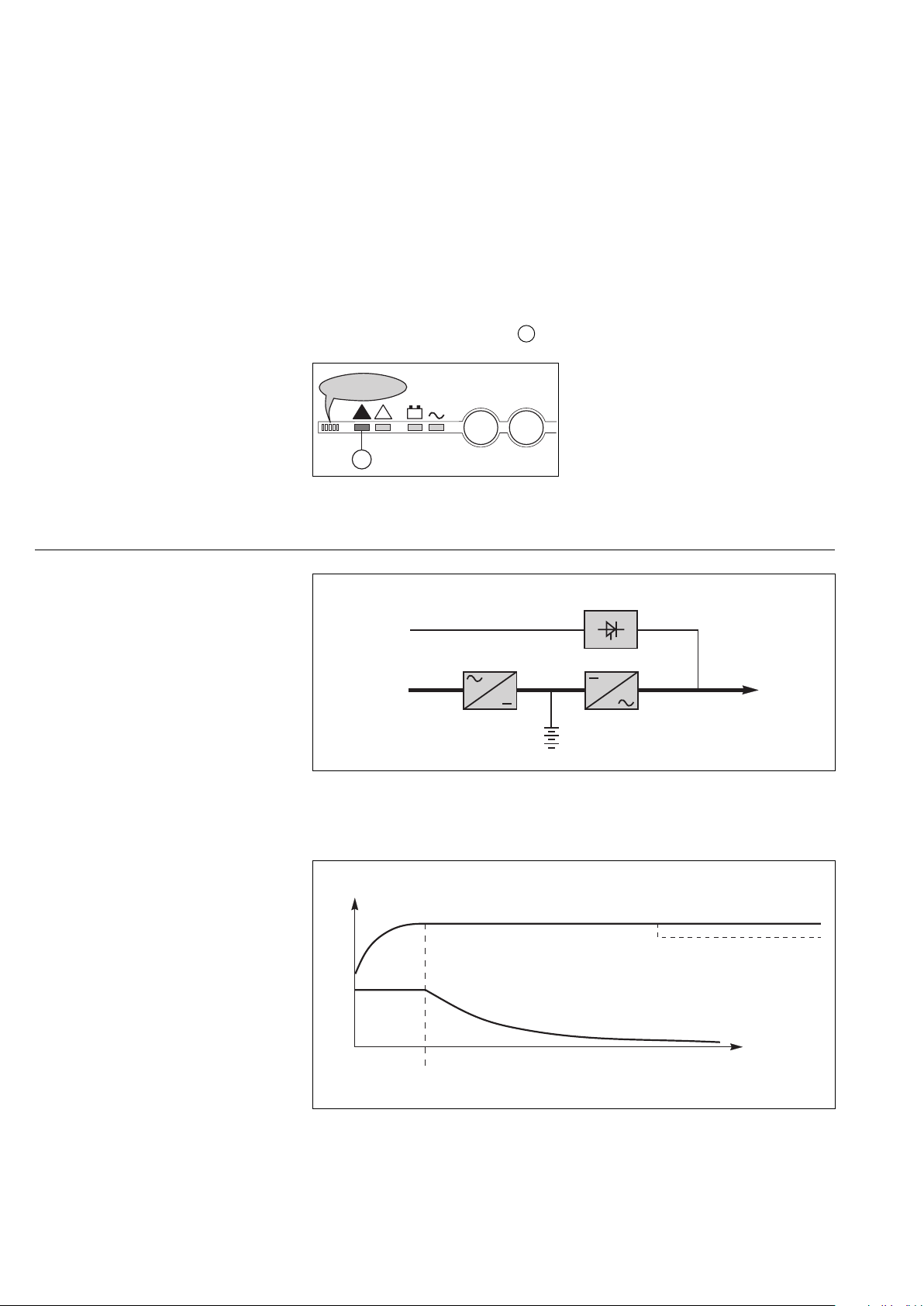
Operation with Mains 1 restored
(figure 13)
When Mains 1 power is restored or its
voltage returns to within specified
tolerances, the system automatically
returns to its normal operating mode
described above (on the condition it did
not reach the end of battery power).
If the end of battery power was reached
(with the resulting inverter shutdown),
the RC restarts automatically, but the
inverter must be restarted manually,
either locally or remotely in systems
equipped with a remote-control unit.
The rectifier-charger recharges the
battery which was discharged during
the Mains outage.
Note:
In frequency converters without battery
power, the return of Mains 1 power
results in the automatic restart of the
RC and the inverter.
The battery charge cycle takes place in
two steps (see figure 14):
◗ step 1: the battery is recharged at a
constant current limited to 0.1C10
(i.e. 1/10th of the battery capacity
specified for a 10 hour discharge).
The DC voltage increases with the
battery charge until the charge level is
reached;
◗ step 2: the battery is recharged at
constant voltage equal to the charge
level (maximum value 463V).
The charging current gradually
decreases until reaching a specified
low value (floating current).
For vented lead-acid batteries, the
rectifier-charger supplies the charging
voltage for 0 to 255 hours (parameter
defined by the after-sales support
department) and then the floating
voltage. For sealed lead-acid batteries,
This signal warns the user of the
imminent end of battery power. On the
device itself, the buzzer beeps
increasingly rapidly and loudly.
Battery power stops when the voltage
supplied by the battery reaches the
voltage minimum (340V). This results in
inverter shutdown and transfer of the
load without interruption to Mains 2.
The red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel is on.
beep...beep...
!
2
mains 2
mains 1
+–
!
rectifiercharger
I
O
Fig. 13
Battery charge cycle
U/I
current
limiting
0.1 C10
constant voltage
decreasing current
voltage
current
Fig. 14
the charging and floating voltages are
the same.
Note:
If the Mains 1 failure is shorter than 0 to
255 seconds (parameter defined by the
after-sales support department), the
If Mains 2 also fails, the load is no
longer supplied. Normally, the inverter
shuts down when the time on the
battery power exceeds three times the
specified backup time.
Note:
As an optional function (battery time
estimator), the "low battery shutdown"
warning signal can be sent with an
adjustable time delay prior to the
effective end of battery power.
static switch
inverter
load
battery
U charge/floating
(sealed batteries)
U "floating"
(vented batteries)
t
charger does not initiate a complete
charge cycle but automatically supplies
the floating voltage.
Page 10 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 11
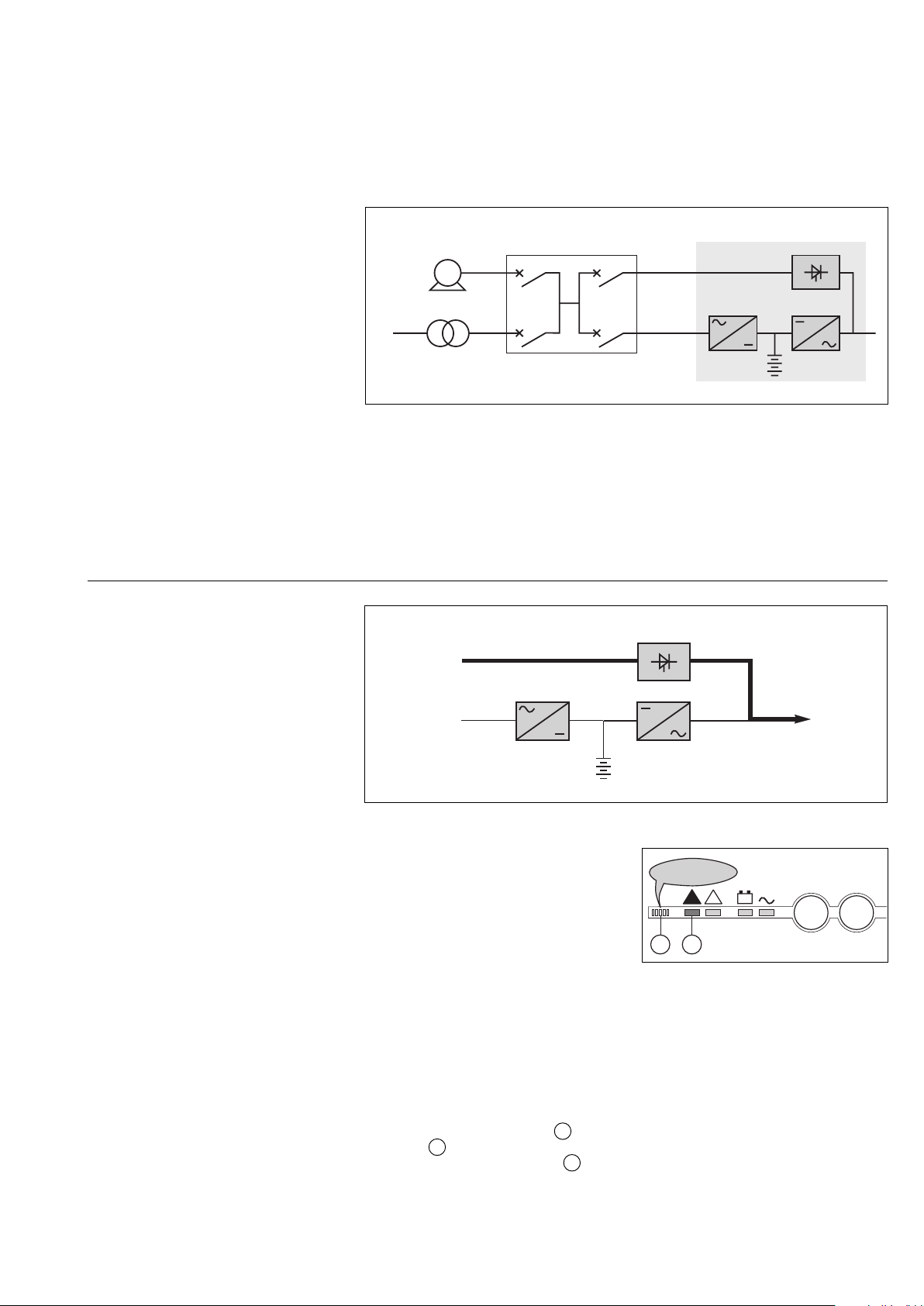
Introduction (cont.)
Installation with an engine
generator set
(figure 15)
If a stand-by generator is included in
the installation, it is generally started
automatically in the event of a
Mains failure and connected to the
main low voltage switchboard.
It is disconnected when Mains power is
restored.
With such a system, the required
battery time may be reduced to the
time necessary for starting and bringing
on line the stand-by generator.
The battery supplies power to the
inverter during the transfers:
Mains ➔ generator and
generator ➔ Mains.
The transfer sequences described:
Mains ➔ battery ➔ generator and
generator ➔ battery ➔ Mains are fully
automatic. They in no way affect the
load and require no manual operation
by the user.
UPS shutdown or overload
(systems with a static switch
module)
(figure 16)
Single-unit UPSs, modular UPSs or
UPSs with an SSC:
◗ in the event of a UPS shutdown
(initiated by the user or by an internal
protective device), the load is
automatically transferred to the Mains 2
bypass line. If transfer conditions are
correct, transfer takes place instantly,
without interruption to the load.
Note:
Transfer conditions are not correct
when Mains 2 characteristics are
outside tolerances (voltage: +/-10%;
frequency as per personalization;
phase sync with inverter +/-3°);
◗ in the event of a major transient
overload (greater than 160% of the full
load), immediate transfer takes place
as above, without interruption to the
load.
When the overload disappears, the
load is automatically returned to the
inverter depending on the configured
value of the re-transfer counter: no
return to inverter, or 1 to 255
(personalized value) overloads
accepted before the load is
permanently transferred to Mains 2.
This operating mode allows start-up of
load devices causing high inrush
currents.
Example of an installation with an engine generator set
Galaxy
HV
network
generator
G
main LV
switchboard
mains 2
mains 1
Fig. 15
Note:
To avoid load surges on the generator,
the rectifier/charger is started with a 10
second maximum current consumption
walk-in.
static switch
mains 2
mains 1
rectifiercharger
inverter
battery
Fig. 16
This system requires correct transfer
conditions. If the conditions are not
correct, the inverter will current limit to
160% of its rated current for 1 second
beep...beep...
!
!
before stopping;
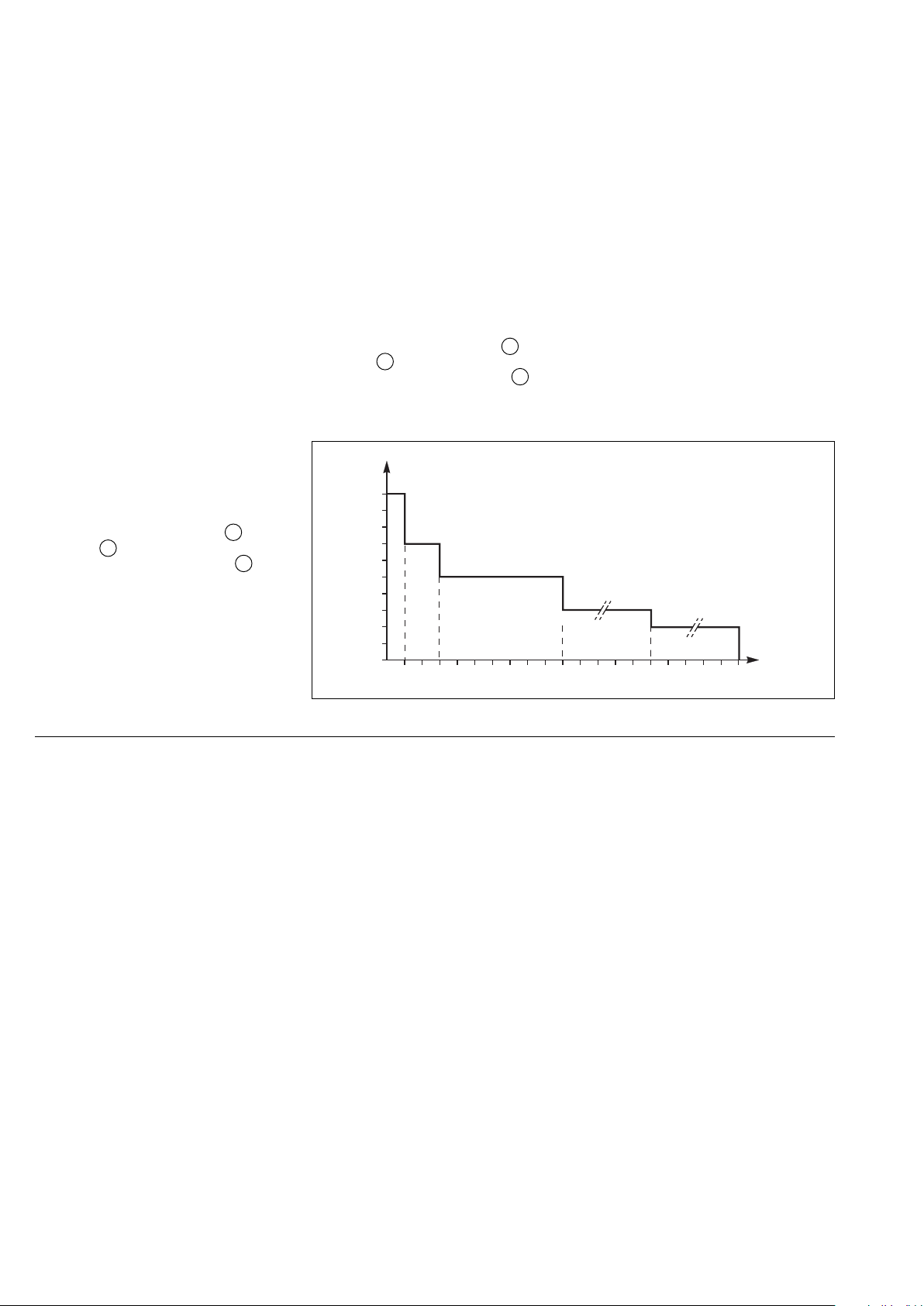
◗ in the event of a small but extended
overload (i.e. a continuous level of
2
1
power exceeding the full rated load),
the inverter will continue to supply
power for a period depending on the
magnitude of the overload (10 minutes
for a 125% overload, 1 minute for a
150% overload). See figure 17
(Overload curve);
◗ in all three of the above cases, the
inverter shutsdown and supplies the
load via Mains 2 with the following
information on the control panel:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 off,
◗◗ buzzer 1 on,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on.
+–
load
I
O
6739380EN/JC - Page 11
Page 12
Introduction (cont.)
Frequency converters without
redundancy
◗ in the event of a shutdown, the load
is no longer supplied with power;
◗ in the event of a major transient
overload (greater than 160% of the
rated load), the inverters will current
limit to 160% of their rated current for 1
second before stopping;
◗ in the event of a small but extended
overload (i.e. a continuous level of
power exceeding the full rated load),
the inverters will continue to supply
power for a period depending on the
magnitude of the overload (10 minutes
for a 125% overload, 1 minute for a
150% overload, see figure 17), and
then stop;
◗ in all three of the above cases,
inverter shutdown results in the
following on the control panel of the
concerned unit:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 off,
◗◗ buzzer 1 on,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on.
Frequency converters with
redundancy
◗ the shutdown of one unit is of no
consequence for the load. The other
lines each take up an equal amount of
load power and the load continues to
be supplied normally;
Inverter shutdown results in the
following on the control panel of the
concerned unit:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 off,
◗◗ buzzer 1 on,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on.
Overload curve
I
1,5 In
1,35 In
1,25 In
1,15 In
1,10 In
1,05 In
In
12345678910
◗ in the event of an overload, the
system only loses its redundancy as
long as the overload is less than the
total rated power of the functioning
units. If the overload is greater, the
operating mode is that previously
described for systems without
redundancy.
t
30 120
(minutes)
Output voltage quality and
continuity
The output voltage is stable in
amplitude and frequency and is free of
interruptions or transients outside
specified tolerances, irrespective of
Mains 1 or load disturbances (outages,
load step changes, etc.).
Steady state voltage regulation:
For stable or slowly varying load
conditions, the inverter output voltage is
regulated to within +/-0.5% in
amplitude.
The frequency of the output voltage can
theoretically be regulated to within
0.1% of the rated value, however the
output frequency range may be
intentionally extended to a maximum of
+/-2Hz so that the inverter can remain
synchronized with Mains 2 and its
inherent frequency fluctuations, thus
enabling transfer of the load to the
bypass line at any time.
Fig. 17
Note:
The output frequency range can be
personalized and if necessary modified
on the customer site by a qualified
support technician from +/-0.25Hz
to +/-2Hz in 0.25Hz steps.
When the Mains 2 voltage moves
outside this frequency range, the
inverter is desynchronized and
operates in "free running" mode, with
the output frequency regulated to a
high level of accuracy by a quartz
oscillator.
When the Mains 2 frequency returns to
within the specified tolerances, the
inverter is gradually re-synchronized to
the bypass line at a rate of 0.5Hz to
2Hz/s (as per the value personalized by
the after-sales support department),
thus avoiding exposing the load to
sudden frequency variations.
Transient voltage regulation:
The inverter output voltage is not
notably affected by instantaneous
major variations in load characteristics.
This is due to the PWM (Pulse Width
Modulation) chopping technique and
the microprocessor-based regulation
system that instantly compensates for
any variation. In particular, the inverter
output voltage remains within +/-5% of
the rated voltage for load step changes
of 25 to 100% or of 100 to 25%.
Page 12 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 13

Inverter cubicle
Description of MGETMGalaxyTM 6000 cubicles
The rated outputs for
TM
MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS’s (without
parallel connection) or frequency
converters are 160, 200, 250, 300, 400,
500, 600 kVA.
Legend for figures 18 to 21:
1-rectifier-charger (RC) module
2-inverter stack modules
3-rack for electronic control boards
4-static switch module (Single-unit or
modular UPS)
4' - output static switch module
(modular UPS, frequency converter or
parallel UPS with SSC)
5-RC input fuses FU1-2-3
6-Mains 1 input switch Q1
7-protection fuses FU8 for the
Mains 2 resistance/capacitance voltage
surge protection network
8-Mains 2 input switch Q4S (Singleunit or modular UPS)
9-maintenance bypass switch Q3BP
(Single-unit or modular UPS)
10 - output switch Q5N
11 - inverter output fuses FU 5-6-7
12 - "Media Contacts 9" remote
indications board
13 - additional "Media Contacts 15"
remote indications board (optional).
250 to 400kVA UPS or frequency converter
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
1
3
5
6
12
2
13
7
4
8 9 10
Fig. 18
450 to 500kVA UPS or frequency converter
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
1
2
3
4
13
12
7
5
22
4'
11
22
4'
11
6
Fig. 19
600kVA UPS or frequency converter
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
22 2
1
5
6
2
Fig. 20
8 9 10
4'
11
7
4
22
3
1312
8
9
10
6739380EN/JC - Page 13
Page 14
Description of MGETMGalaxyTM 6000 cubicles (cont.)
800 kVA UPS
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
1
5
6
Fig. 21
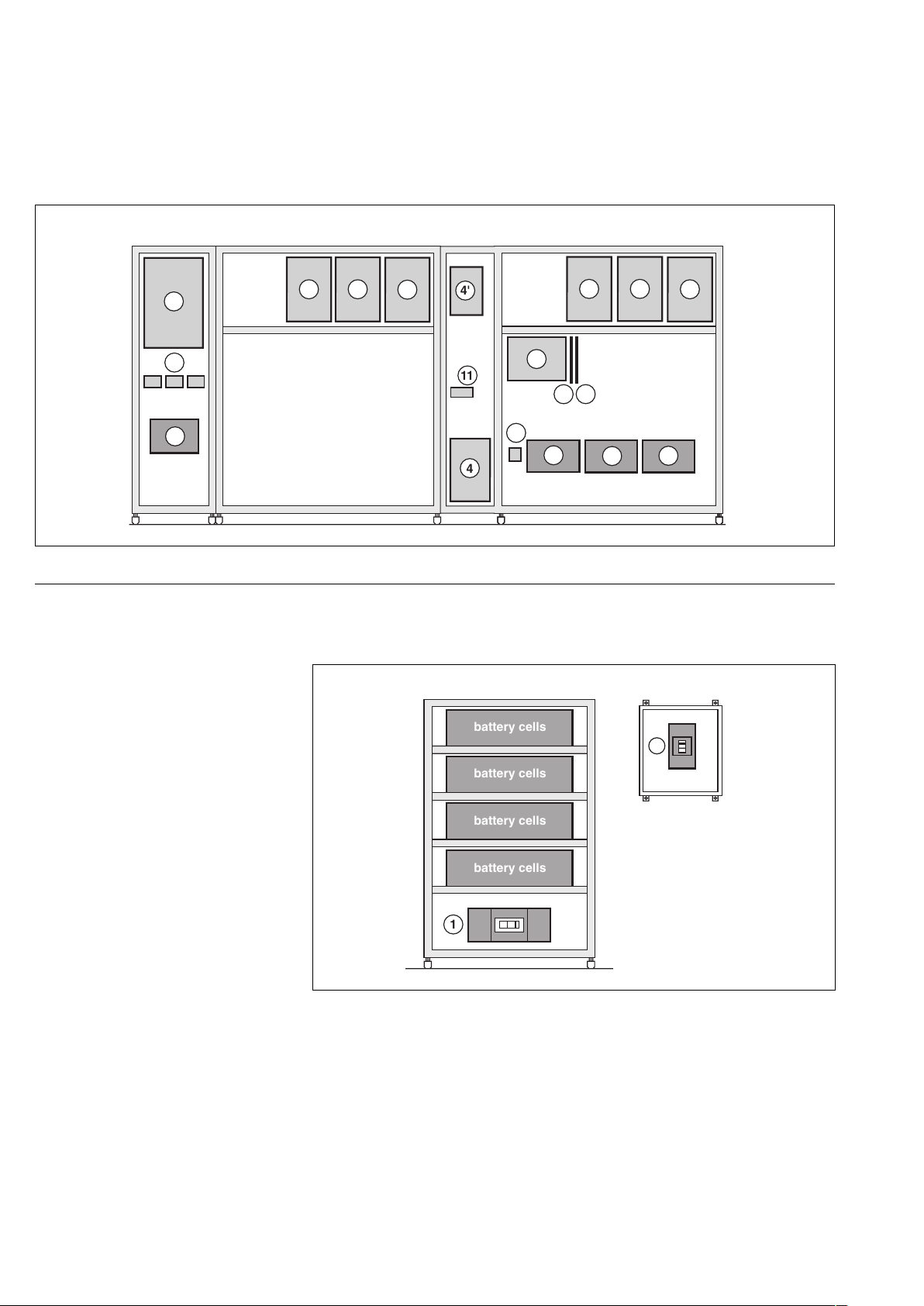
Battery cubicle
(for a 250 to 300kVA UPS)
Figure 22 is an example of component
layout in a battery cubicle and a battery
circuit breaker enclosure.
Legend for figure 22:
1-battery isolation and protection
circuit breaker QF1.
22 2
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
2
4'
11
4
battery cells
battery cells
3
1312
7
8
9
22
10
1
Fig. 22
battery cells
battery cells
1
battery circuit breaker
enclosure: front view,
door open
Page 14 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 15

Description of MGETMGalaxyTM 6000 cubicles (cont.)
Static Switch Cubicle
Static Switch Cubicles are rated 500,
800, 1200 and 2000 kVA. Figure 23
presents the layout of components in
these cubicles.
Legend for figure 23:
2-Mains 2 input switch Q4S,
3-maintenance bypass switch Q3BP,
4-output switch Q5N,
5-static switch module,
6-electronic control boards for the
backup function,
7-protection fuses FU1 for the
Mains 2 resistance/capacitance voltage
surge protection network,
8-fuse switch Q1 (protection of the
control electronics power supply
against Mains 1),
9-fuse switch Q2 (protection of the
control electronics power supply
against Mains 2),
10 - "Media Contacts 9" remote
indications board,
11 - additional "Media Contacts 15"
remote indications board (optional).
front view, doors open, protective covers removed
6
8
10
11
500 or 800kVA cubicle
5
97
2
3
4
5
7
5
1200kVA cubicle
2
5
897
6
11 10
2
3
4
External maintenance
bypass cubicle
Legend for figure 24:
1-connection of auxiliary wires to
indicate the positions of switches Q5N
and Q3BP,
2-maintenance bypass switch Q3BP,
3-output switch Q5N.
Fig. 23
2000kVA cubicle
6
89
10
11
3
4
2
1
3
Fig. 24
1200kVA cubicle
6739380EN/JC - Page 15
Page 16

Control panel
TM
MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 control panels
(see figure 25) are made up of:
◗ a visible panel with the basic controls
and indications required to check the
general status of the system;
◗ a hidden panel with more detailed
indications and more sophisticated
control functions including an
autodiagnostic system.
Note:
The information on the Mains 2
provided below does not concern
frequency converters. Information on
batteries does not concern frequency
converters without batteries.
MGE
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 control panel
visible
panel
Monitor
hidden
panel
cover
A
V
k
5
%
2
0
1
2
1
.
in
M
%
0
0
0
1
r 5
u
%
o
0
0
H
1
0
%
0
8
%
0
5
A
V
k
00
%
0
4
5
0
0
0
6
Y
X
A
L
A
G
0
IQ
E
L
L
l
e
A
S
ev
l
d
a
o
L
0
e
im
T
p
u
k
c
a
B
d
le
e
t
b
c
ila
te
a
v
ro
p
A
d
a
o
L
N
5
d
Q
a
e
o
t
m
L
n
o
e
H
m
ip
u
q
e
s
m
r
la
A
1
Q
e
in
l
n
O
1
F
d
Q
en
r
T
C
A
l
a
m
r
s
o
ic
t
N
is
t
ta
S
r
ie
if
t
c
e
R
S
y
r
4
te
Q
t
a
B
5
0
0
/2
5
/0
0
r
3
te
2
r
3
e
C
:
v
4
n
A
I
:2
s
5
s
1
a
p
y
B
P
B
3
s
Q
s
a
p
y
B
t
u
p
t
u
O
p
u
t
e
S
Visible control panel
Located in the upper left part of the
cubicle front, the visible panel is
designed to provide an easy and rapid
overview of system status (see figures
26 and 27).
Interpretation of symbols is very simple
and requires no particular training.
The information concerns only the
cubicle on which the panel is located.
The panel indicates:
◗ normal operation (load protected);
◗ abnormal situations (operating
problem);
◗ dangerous situations (load not
protected);
◗ operation with load on battery power.
The control panel on the Static Switch
Cubicle provides important information
for the load:
◗ normal operation (load protected and
supplied by the UPSs);
◗ abnormal situations (system
malfunction);
◗ dangerous situations (load not
protected).
Fig. 25
Visible control panel
(Inverter or frequency converter cubicle)
!
+–
!
5
4321 6 7
I
Fig. 26
Visible control panel
(Static Switch Cubicle)
!
!
321
5
Fig. 27
Legend for figure 26:
1-buzzer
2-"load not protected" light
O
3-"operating problem" light
4-"load on battery" light
5-"load protected" light
6-"inverter on" button
7-"inverter off" button
Legend for figure 27:
1-buzzer
2-"load not protected" light
3-"operating problem" light
5-"load protected" light
Page 16 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 17

Control panel (cont.)
Buzzer 1
beep...beep...
!
1
+–
!
I
O
The buzzer sounds in the following
situations:
◗ load supplied by Mains 2;
◗ load on battery;
◗ operating problems.
It beeps at a low decibel level and slow
rate for minor problems and when the
load is supplied from battery power.
When the "low battery shutdown
imminent" warning is received, the
beeps
increase in decibel level and rate.
Finally, if the inverter shuts down, the
beep is loud and continuous. A buzzer
reset button is located on the hidden
control panel. If the buzzer is reset, a
higher level alarm will set it on again.
"Load not protected" light
!
2
+–
!
I
O
This red light 2 signals that:
◗ the load is supplied by Mains 2
following inverter shutdown (initiated by
the user or by a protective device or a
sudden overload) or the opening of the
inverter output switch Q5N;
◗ battery circuit breaker QF1 has
opened, thus making battery power
unavailable.
Note:
In a parallel system, this light concerns
only the specific UPS. The load may still
be protected by the other lines.
"Operating problem" light
!
+–
!
3
I
This orange light 3 signals an
operating problem or an environment
fault, however the load is still supplied
by the inverter.
◗ operating problems:
◗◗ static switch ventilation fault,
◗◗ static switch control system fault;
◗ environment faults:
◗◗ battery temperature outside
tolerances,
◗◗ overload greater than 5%,
◗◗ Mains 2 up but with voltage,
frequency or phase characteristics
outside tolerances with regards to the
inverter.
"Battery operation" light
!
+–
!
4
I
This blinking orange light 4 signals
that the load is on battery power
following:
◗ a Mains 1 outage or voltage drop;
◗ insufficient power on Mains 1, for
example power supplied by an engine
generator set requiring additional
battery power;
◗ battery problem.
"Load protected" light
!
+–
!
I
Note:
In parallel systems, this light concerns
only the specific UPS.
The load may not be protected if it
O
depends on the other lines. It is
necessary to take into account all the
"load protected" lights 5 for the
different system lines or the light on the
control panel of the Static Switch
Cubicle, if it exists.
"Inverter on" button
!
+–
!
This green button 6 is used to locally
start the inverter. When it is pushed,
the green "load protected" light 5
blinks for 3 seconds, indicating that the
start-up order has been received. When
the inverter has synchronized with
Mains 2, it supplies the load and the
green "load protected" light 5
remains on. The load is supplied by the
O
UPS and the system is functioning
normally. If the transfer to Mains 2
conditions are not correct (Mains 2
voltage, frequency or phase conditions
outside tolerances), the inverter will not
start and the system awaits a special
order (see the "Hidden control panel"
section).
Note:
◗ for modular UPSs with external
maintenance bypass or parallel UPSs
with SSC, transfer of the load to the
inverters takes place only when the
number of operating lines required to
supply the load has been reached;
◗ for frequency converters, inverter
start-up must take place with the load
off or drawing a quantity of power equal
to or less than that supplied by a single
O
UPS.
I
O
6
5
This green light 5 signals that the
load is supplied by the inverter and that
the specified battery time is available
in the event of a Mains 1 outage. In
short, it signals that the system is
operating normally.
6739380EN/JC - Page 17
Page 18

Control panel (cont.)
"Inverter off" button
!
+–
!
I
7
This gray button 7 turns the inverter
off.
◗ press the "inverter off" button 7 for
3 seconds;
◗ if the transfer to Mains 2 conditions
are correct:
◗◗ the load is transferred without
interrupting to Mains 2,
◗◗ the inverter shuts down,
◗◗ the green "load protected" light 5
goes off and the red "load not
protected" light 2 goes on.
Hidden control panel
The hidden panel, located behind the
hinged cover, offers the following
indications and control functions:
◗ environment faults;
◗ general faults in system modules;
◗ special control buttons
(see figure 28).
This panel is identical for all types of
cubicles, however, the controls or
indications 8 that do not concern a
given cubicle are not activated.
◗ if the transfer to Mains 2 conditions
are not correct, the button produces no
effect. A special function on the hidden
panel may be used to force the
O
transfer.
Caution:
If the transfer is forced, the load will be
subjected to a 0.8 second interruption
in the supply of power.
Hidden control panel (Inverter and Static Switch Cubicles)
fault
12 345
Note:
◗ for Modular UPSs or parallel UPSs
with SSC, the shutdown of an inverter
may or may not result in the transfer of
the load to Mains 2, depending on
redundancy conditions;
◗ if the transfer to Mains 2 conditions
are not correct or if the system does not
have a Mains 2, the shutdown of a
single inverter will result in the
shutdown of the entire system if there is
no redundancy.
8
NMLKJIHGFEDCBA
Clear fault log
This button 10 clears the alarms stored
in memory. The memory may not be
cleared until the cause of the alarms
has ceased.
Buzzer reset
This button 11 stops the buzzer.
A new fault starts the buzzer again.
Battery charge cycle
This button 12 starts a battery charge
cycle (vented lead-acid batteries only).
The cycle duration may be
programmed (default value is 24
hours). Then the RC automatically
shifts to "floating" mode.
Return to float charge
This button 13 can be used during a
charge cycle to force the RC to return
to "floating" mode.
Security button
This button 14 avoids inadvertent
operation of the remaining three control
buttons:
◗ Mains 2 synchronization or
desynchronization;
◗ forced transfer to inverter with load
interruption;
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Fig. 28
◗ forced inverter shutdown with load
interruption;
When pressing one of the above three
buttons, the security button must also
be pressed at the same time.
Mains 2 synchronization or
desynchronization
This button 15 desynchronizes or
resynchronizes the inverter output
frequency with that of Mains 2.
Note:
◗ for parallel-connected modular
UPSs, this function must be carried out
on all the UPSs.
Forced transfer to inverter with load
interruption
This button 16 transfers the load to
the inverter. If the transfer conditions
(Mains 2 characteristics outside
tolerances) are not correct, the transfer
will result in a 0.8 second interruption in
the supply of power to the load.
Note:
◗ for parallel-connected modular
UPSs, forced transfer of the load will
not take place if the number of
operating UPSs required by the load is
greater than one;
◗ for parallel UPSs with centralised
SSC, this function is available only on
the SSC.
Forced inverter shutdown with load
interruption
This button 17 :
◗ transfers the load to Mains 2;
◗ shuts down the inverter.
It may be used if the transfer conditions
(Mains 2 characteristics outside
tolerances) are not correct, in which
case the "inverter off" button 7 on the
visible control panel produces no effect;
◗ is disabled on the SSC.
Page 18 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 19

Control panel (cont.)
Light A - emergency shutdown
This red light signals that the remote
"emergency shutdown" button was
pressed (external information received
and stored in memory).
Light B - rectifier-charger on
This green light indicates that the
rectifier-charger is on.
Light C - rectifier-charger fault
This red light is an alarm stored in
memory signaling a rectifier-charger
fault. It can signify one or several of the
following faults:
◗ input switch Q1 open;
◗ RC input protection fuse (FU1-2-3)
blown;
◗ RC internal over-temperature;
◗ battery charge over-current;
◗ battery over-voltage;
◗ RC electronic control board faulty,
not calibrated or not personalized;
◗ power supply board fault.
Light D - Mains 1 outside tolerances
This yellow light signals that the
Mains 1 voltage and/or frequency
characteristics are outside tolerances.
Light E - battery room ventilation
fault and/or harmonics filter
temperature outside tolerances
This yellow light is an alarm stored in
memory signaling a battery room
ventilation fault (external information
that must be supplied from the room).
If the installation includes a harmonics
filter, this light will also signal an
overtemperature of the filter’s inductor
(information supplied).
Light F - battery temperature outside
tolerances
This yellow light signals that the battery
temperature is outside tolerances
(external information supplied by
special board ("Temperature Monitor"
option).
Light G - battery charging
This yellow light signals that the battery
is being recharged (vented batteries
only). This light is deactivated in
systems with sealed lead-acid
batteries.
Light H - inverter fault
This red light is an alarm stored in
memory signaling an inverter fault. It
can signify one or several of the
following faults:
◗ inverter shutdown due to inverter
output voltage outside tolerances;
◗ inverter output protection fuse (FU5-
6-7) blown;
◗ inverter stack subassembly
protection fuse blown (parallel
systems);
◗ inverter leg fault;
◗ inverter output transformer over-
temperature;
◗ inverter leg over-temperature;
◗ phase or output voltage fault (parallel
systems only);
◗ internal clock fault;
◗ inverter control board faulty, not
calibrated or not personalized;
◗ power supply board fault.
Light I - battery discharged
This yellow light signals that the battery
has reached its minimum voltage level,
resulting in inverter shutdown.
Light J - inverter desynchronized
with Mains 2
This light signals that the inverter
output frequency has been voluntarily
desynchronized with that of Mains 2.
Light K - transfer to inverter function
fault
This red light is an alarm stored in
memory signaling a fault in the systems
for load transfer from Mains 2 to the
inverter. It can signify one or several of
the following faults:
◗ inverter output switch K3N fault;
◗ parallel-connection relay fault
(parallel systems only);
◗ static switch internal over-
temperature;
◗ static switch ventilation fault;
◗ static switch power supply fault;
◗ transfer function control board fault;
◗ inverter control board not calibrated
or not personalized;
◗ power supply board fault.
Light L - overload
This yellow light is an alarm signaling
one or several of the following faults:
◗ inverter stack current more than 5%
above rated current;
◗ inverter output current more than 5%
above rated current;
◗ Mains 2 line current more than 5%
above rated current;
◗ inverter shutdown due to current
limiting of output current.
Light M - Mains 2 outside tolerances
This yellow light signals that the
Mains 2 voltage or frequency
characteristics are outside tolerances.
N - maintenance position
Light
This yellow light signals that devices
QF1, Q4S, Q5N and Q3BP are set to
the maintenance configuration. The
UPS system is not available for load
protection.
Test connector
This 9-pin connector is reserved for
after-sales support technicians.
It is used for connection to a
microcomputer for:
◗ system calibration;
◗ personalization;
◗ computer-aided diagnostics.
6739380EN/JC - Page 19
Page 20

Start-up
System start-up
Single-unit or modular UPS
Proceed in the following order:
◗ close the upstream switches
supplying Mains 1 and 2 power (on the
LV switchboard);
◗ close Mains 1 input switch Q1.
The system powers up:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
ON
(0)
OFF
(0)
(I)
ON
(I)
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel goes on,
◗◗ the rectifier/chargers automatically
starts;
◗ close Mains 2 input Q4S:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
OFF
(0)
◗ close inverter output switch Q5N:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
◗ close battery circuit breaker QF1:
QF1
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
◗ open maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ press the inverter on button 6 on
the control panel:
!
+–
!
6
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 blinks
I
O
for 3 seconds,
◗◗ the inverter starts and if transfer to
Mains 2 conditions are correct, the load
is supplied by the inverter,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 goes
off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
remains on, without blinking.
Multi-bypass modular UPS
Proceed in the following order:
◗ check that switches Q1, Q4S, Q5N
and QF1 on the UPSs are open and
that switches Q3BP are closed,
otherwise set them to the required
position;
◗ close the upstream switches (on the
low-voltage switchboard) supplying
power to the Mains 1 and Mains 2
inputs on the UPSs, the load is
supplied with power;
◗ close the Mains 1 input switch Q1 on
the UPSs to supply them with power:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
ON
OFF
(0)
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
(0)
(I)
ON
(I)
the control panels of the UPSs goes on:
!
2
+–
!
OFF
(0)
I
O
◗◗ the rectifier/chargers automatically
start;
◗ close the Mains 2 input switch Q4S
on the UPSs:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ close inverter output switch Q5N on
OFF
(0)
the UPSs:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ close battery circuit breaker QF1 on
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
the UPSs:
QF1
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
◗ open maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP on the UPSs:
◗ the load is now supplied by the
Mains 2 input via the static switches of
the UPSs.
◗ press the "inverter on" button 6 on
the control panel of each UPSs:
!
+–
!
6
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
I
O
flashes for three seconds,
◗◗ the inverter starts and, if transfer
conditions with the Mains 2 input are
correct, the load is transferred to the
inverter,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 on
the control panel goes on.
Page 20 - 6739380EN/JC
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
Page 21

Start-up (cont.)
mains 2
mains 1
mains 2
mains 1
Galaxy UPS 1
rectifiercharger
Q1
Galaxy UPS 2
rectifiercharger
Q1
Q4S
QF1
Q4S
QF1
static switch
inverter
battery
static switch
inverter
battery
Q3BP
Q5N
load
Q3BP
Q5N
Modular UPS with external
maintenance bypass
Proceed in the following order:
◗ check that all lines supplying the load
are off or that the load is disconnected;
◗ in the maintenance bypass cubicle,
open output switch Q5N, then close
bypass switch Q3BP;
◗ close the upstream switch (on the
low-voltage switchboard) supplying
power to the Mains 1 inputs on the
UPSs;
◗ close the Mains 1 input switch Q1 on
the UPSs to supply them with power:
Q1 Q4S Q5N
OFF
ON
OFF
(0)
(0)
(I)
◗◗ the rectifier/chargers automatically
start;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panels of the UPSs goes on:
!
2
+–
!
I
OFF
(0)
O
◗ close battery circuit breaker QF1 on
the UPSs:
QF1
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
◗ close the upstream switches (on the
low-voltage switchboard) supplying
power to the Mains 2 inputs on the
UPSs, then close the Mains 2 input
switch Q4S on the UPSs:
Q1 Q4S Q5N
OFF
ON
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
◗ close inverter output switch Q5N on
the UPSs:
Q1 Q4S Q5N
OFF
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ close output switch Q5N in the
maintenance bypass cubicle;
◗ open bypass switch Q3BP in the
maintenance bypass cubicle;
◗ press the "inverter on" button 6 on
the control panel of a UPS:
!
+–
!
6
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
I
O
flashes for three seconds,
◗◗ the inverter starts and waits for the
start of the other units;
◗ proceed in the same manner for
each unit. When the number of running
units is sufficient, the inverter output
switches close and the load is supplied
by the inverters:
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 on
the control panel goes on.
6739380EN/JC - Page 21
Page 22

Start-up (cont.)
Frequency converters
Proceed in the following order:
◗ check that all lines supplying the load
are off or that the load is disconnected;
◗ close the upstream switch supplying
Mains 1 power (on the LV switchboard);
◗ close Mains 1 input switch Q1.
The system powers up:
Q1 Q5N
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel goes on,
◗◗ the rectifier-charger automatically
starts;
OFF
(0)
◗ close battery circuit breaker QF1
(systems equipped with a battery);
QF1
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
◗ close inverter output switch Q5N:
Q1 Q5N
OFF
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ press the "inverter on" button 6 on
the control panel:
!
+–
!
6
I
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 blinks
for 3 seconds,
◗◗ the inverter starts and awaits the
start of the other inverters;
◗ proceed in the same manner for
each line;
◗◗ when they are all on or enough have
been started to supply the rated load,
the output switch for each running line
closes. The load is supplied and the
connected devices can be started,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
remains constant, on the control panel
of each line supplying the load.
O
Parallel UPS systems with a
Static Switch Cubicle
Proceed in the following order:
◗ check that all lines supplying the load
are off or that the load is disconnected;
◗ close the upstream switches
supplying Mains 1 and 2 power (on the
LV switchboard);
◗ close fuse switch Q2 in the Static
Switch Cubicle (see figure 22);
◗ close Mains 2 input switch Q4S in
the Static Switch Cubicle;
◗ close switch Q5N in the Static Switch
Cubicle;
◗ open maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP in the Static Switch Cubicle;
Start-up of a unit
Start-up of a rectifier/charger
◗ it is recommended not to stop the
rectifier/charger because the battery
will no longer be charged. Rectifier/
charger start-up is automatic when
Mains 1 input switch Q1 is closed;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel goes on;
◗ close battery circuit breaker QF1.
◗ close fuse switch Q1 in the Static
Switch Cubicle;
◗ close input switch Q1 on an UPS
line.
The line powers up;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the line control panel goes on,
◗◗ the RC automatically starts;
◗ close the line battery circuit breaker
QF1;
◗ close inverter output switch Q5N for
the line;
◗ press the "inverter on" button 6 on
the line control panel;
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 blinks
for 3 seconds,
◗◗ the inverter starts and awaits the
start of the other inverters;
◗ proceed in the same manner for
each line;
◗◗ when they are all on or enough have
been started to supply the rated load
power, the output switch for each
running line closes and the load is
supplied with power;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 goes
off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
remains on, without blinking, on the
control panel of each line supplying the
load.
Page 22 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 23

Start-up (cont.)
Start-up of an inverter
When the rectifier/charger is on:
◗ press the "inverter on" button 6 on
the control panel;
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 blinks
for 3 seconds;
Single-unit or modular UPS system:
◗ the inverter starts and if the transfer
to Mains 2 conditions are correct, the
load is supplied by the inverter;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
becomes constant.
Frequency converter or multi-bypass
UPS:
◗ the inverter starts and awaits the
start of the other inverters;
◗ when they are all on or enough have
been started to supply the rated load
power, the output switch for each
running line closes and the load is
supplied with power;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
becomes constant, on the control panel
of each line supplying the load.
Modular UPS with external
maintenance bypass or parallel UPS
with SSC:
◗ the inverter starts and awaits the
start of the other inverters;
◗ when they are all on or enough have
been started to supply the rated load
power, the output switch for each
running line closes and the load is
supplied with power;
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
goes off,
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
remains on, without blinking, on the
control panel of each line supplying the
load and on the control panel of the
Static Switch Cubicle.
Frequency converter without a
battery:
◗ Start-up of the rectifier/charger
automatically leads to start-up of the
inverter.
6739380EN/JC - Page 23
Page 24

Shutdown
Shutdown of a unit
Shutdown of an inverter
◗ press the "inverter off" button 7 on
the control panel for 3 seconds;
!
+–
!
Single-unit UPS
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel goes on,
◗◗ the inverter stops;
◗ if transfer to Mains 2 conditions are
correct, the inverter shuts down and the
load is transferred to Mains 2;
◗ if transfer to Mains 2 conditions are
not correct, the inverter does not shut
down;
◗◗ special action on the hidden control
panel is required to force inverter
shutdown,
◗◗ to force inverter shutdown, press
simultaneously the security button 14
and button 5 "Forced inverter
shutdown" 17 on the hidden control
panel,
◗◗ the load is transferred to Mains 2
with a 0.8 second interruption in the
supply of power.
Multi-bypass modular UPS:
◗ the UPS shuts down (the other
parallel-connected unit can supply the
entire load):
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel goes on.
The load is not affected and continues
to be supplied by the other unit.
I
O
7
Modular UPS with external
maintenance bypass:
◗ all the UPSs shut down:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel of each unit goes on,
◗◗ orange "operating problem" light 3
on the other units goes on, all shut
down due to the overload.
Frequency converter:
◗ if the system is redundant, i.e. the
other parallel-connected inverters can
supply the load on their own, the
inverter shuts down:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
lights on the control panel of the line;
The load is not affected in that the other
inverters continue to supply it normally;
◗ if the system is not redundant, all the
inverters shut down;
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2 on
the control panel of each line goes on,
◗◗ orange "operating problem" light 3
on the control panel of the other lines
goes on, all shut down due to the
overload.
Parallel UPS with SSC:
◗ if the system is redundant, i.e. the
other parallel-connected inverters can
supply the load on their own, the
inverter shuts down:
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5 goes
off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
lights on the control panel of the line.
The load is not affected in that the other
inverters continue to supply it normally;
◗ if the system is not redundant and
the transfer to Mains 2 conditions are
correct, all the inverters shut down;
◗◗ green "load protected" light 5
goes off,
◗◗ red "load not protected" light 2
lights on the control panel of each line,
◗◗ orange "operating problem" light 3
on the control panel of the other lines
goes on (all shut down due to the
overload),
◗◗ the load is transferred to Mains 2
without an interruption in the supply of
power;
◗ if the system is not redundant and
the transfer to Mains 2 conditions are
not correct, the inverter does not shut
down;
◗◗ special action on the hidden control
panel is required to force inverter
shutdown,
◗◗ to force inverter shutdown, press
simultaneously the security button 14
and button 5 "Forced inverter
shutdown" 17 on the hidden control
panel,
◗◗ the load is transferred to Mains 2
with a 0.8 second interruption in the
supply of power.
Shutdown of an rectifier/charger
Except in frequency converters without
a battery, it is recommended not to stop
the rectifier/charger because the
battery will no longer be charged.
Except in the case of a test of the
inverter on battery power, the rectifier/
charger should be shutdown after the
inverter to avoid unnecessary battery
discharge.
Page 24 - 6739380EN/JC
Proceed in the following order:
◗ open battery circuit breaker QF1;
◗ open Mains 1 input switch Q1;
◗◗ the rectifier/charger shuts down,
◗◗ all control panel lights go off because
the device is powered down.
Note:
In a frequency converter without a
battery, rectifier/charger shutdown
automatically results in inverter
shutdown.
Page 25

System shutdown
Shutdown (cont.)
Single-unit or single modular
UPS
◗ shutdown the inverter (see the
"shutdown of a module" section);
◗ carry out operations in the following
order:
◗◗ close maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
◗◗ open output switch Q5N:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
(I)
Modular UPS with external
maintenance bypass
◗ shutdown each UPS (see section
"shutdown of a unit");
◗ transfer to the maintenance bypass
in the order indicated below (the load is
supplied directly by Mains 2 via bypass
switch Q3BP):
◗◗ in the maintenance bypass cubicle,
close switch Q3BP, then open switch
Q5N;
◗◗ open output switch Q5N for each
UPS;
◗◗ cut the Mains 2 supply to each UPS
by opening the upstream protection
devices;
◗◗ open battery circuit breaker QF1 on
each UPS;
◗◗ open input switch Q1 on each UPS;
◗ the UPSs are de-energised once the
capacitors have discharged.
◗◗ open Mains 2 input switch Q4S:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
ON
(I)
OFF
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
◗◗ open battery circuit breaker QF1:
QF1
OFF
ON
(0)
(I)
External maintenance bypass
Modular UPS 1
Q4S
mains 2
rectifiercharger
mains 1
Q1
Modular UPS 2
Q4S
mains 2
rectifiercharger
mains 1
Q1
QF1
QF1
◗◗ open Mains 1 input switch Q1:
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
ON
OFF
OFF
(0)
(0)
(I)
ON
(I)
◗ the UPS is powered down (except
the Mains cables upstream from
switches Q1, Q4S and Q3BP) and the
load is supplied by Mains 2. All the
lights on the control panel are off. A full
powering down requires load shutdown
and the opening of the upstream
protection devices on Mains 1 and 2.
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
battery
static switch
inverter
Q5N
Q5N
Q5N
OFF
(0)
load
battery
6739380EN/JC - Page 25
Page 26

Shutdown (cont.)
Multi-bypass modular UPS
◗ shutdown each UPS (see section
"shutdown of a unit");
◗ the load is supplied via the Mains 2
of each UPS;
◗ close switch Q3BP on each UPS, the
load is supplied by the Mains 2, via the
bypass lines (Q3BP) of each UPS;
◗ open switches Q5N, Q4S, Q1 and
QF1 on each UPS, the situation is that
shown in the figure opposite;
◗ the UPSs are de-energised once the
capacitors have discharged.
mains 1
mains 2
Modular UPS 1
rectifiercharger
Q1
Q4S
QF1
static switch
inverter
battery
Q3BP
Q5N
Frequency converters
(no Mains 2)
Shutdown of the inverters results in the
interruption of the load;
◗ shut down each inverter (see the
"shutdown of a unit" section);
◗ open battery circuit breaker QF1 and
Mains 1 input switch Q1 on each unit;
Modular UPS 2
rectifiercharger
ON
(I)
Q1
QF1
OFF
(0)
mains 1
Q1 Q5N
ON
OFF
(I)
(0)
ON
(I)
Q4S
QF1
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
battery
◗ the system is powered down (except
Q5N
the Mains 1 cables upstream from
switch Q1). A full powering down
requires the opening of the upstream
protection device on Mains 1.
load
Parallel UPSs with SSC
(with Mains 2)
◗ shut down each inverter (see the
"shutdown of a unit" section);
◗ carry out the maintenance bypass
operation in the Static Switch Cubicle
(the load will be directly supplied by
Mains 2 via maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP);
Buzzer reset
◗ first determine the cause of the
alarm;
◗ press the "buzzer reset" button 11
on the hidden control panel on the
concerned cubicle.
The buzzer stops, but a new alarm will
set it off again.
Page 26 - 6739380EN/JC
◗ close switch Q3BP and open
switches Q5N and Q4S in the "static
switch" cubicle;
◗ open fuse switches Q1 and Q2 in the
Static Switch Cubicle;
◗ open battery circuit breaker QF1 in
each UPS (except for frequency
converters without a battery);
◗ open input switch Q1 for each UPS;
◗ the UPSs are powered down (except
ABCDEFGH I JKLMN
12 3
11
4
5
the Mains cables upstream from
switches Q1, Q4S and Q3BP) and the
load is supplied by Mains 2.
All the lights on the control panel are
off. A full powering down requires load
shutdown and the opening of the
upstream protection devices on
Mains 1 and 2.
Page 27

Alarms
The autodiagnostic system considers
any system status other than normal as
a problem.
Prior to any other action, note any
lights (A to
N) on the hidden control
panel that may be on.
Also note any messages on the screen.
Certain problems may result in the
control panel not functioning.
Maintenance bypass
This operation is possible only if the
system includes a Mains 2. It results in
the load being directly supplied by
Mains 2 via maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP, thus ensuring a higher level of
security in the event of a malfunction.
Important:
Prior to beginning the bypass
operation, shut down all system
inverters (press the "inverter off" button
7 on each UPS control panel). If an
inverter remains operating and the
Mains 2 transfer conditions are not
correct, the load will suffer a 0.8 second
interruption.
Switching procedures are explained on
a drawing next to each switch. It is
imperative that the operation proceed in
the following order:
◗ shut down any inverters that may
still be running;
In this case, it is strongly
recommended to call the after-sales
support department.
◗ if the load is still correctly supplied
with power, it has probably been
transferred to Mains 2 (static switch)
and is therefore no longer protected;
◗ if the load is no longer supplied with
power, transfer it manually to the
maintenance bypass (see section
below).
◗ 1 : close maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP;
◗ 2 : open inverter output switch Q5N;
◗ 3 : open Mains 2 input switch Q4S:
bypass
Q1 Q4S Q3BP Q5N
OFF
ON
1
(I)
ON
2
(I)
ON
3
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
(0)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
ON
(I)
OFF
(0)
OFF
(0)
Note:
◗ in systems with a Static Switch
Cubicle, the above operation is carried
out in the Static Switch Cubicle;
◗ the operation with the three switches
is carried out in reverse order (3, 2, 1)
to return to normal status;
◗ in an installation comprising modular
UPSs with an external maintenance
bypass, the operation is carried out in
the external maintenance bypass. The
cubicle is not equipped with a Q4S
switch and it is therefore necessary to
open the protection devices upstream
on the maintenance-bypass line.
!
+–
!
I
O
7
6739380EN/JC - Page 27
Page 28

Environment information
Standard information Media Contacts 9
Terminals XR1, XR2, XR3 and XR4 on
the remote transmission board of each
type of unit can be used for the input of
data from the operating environment
and for the transmission of signals on
the operational status of the device
(see figures 18, 19, 20 and 22 for the
position of the board).
Signal reception
The signals should be provided by voltfree contacts.
◗ emergency shutdown. An NC
contact causes:
◗◗ rapid shutdown of the inverter and
the RC,
◗◗ opening of battery circuit breaker
QF1,
◗◗ transfer of the load to Mains 2
(generally without interruption in the
supply of power);
◗ battery room ventilation fault:
a NO contact causes the shutdown of
the RC;
Remote transmission board
XR1 XR2 XR3 XR4
◗ battery circuit breaker QF1 closed:
a NO contact inhibits inverter start-up
when the breaker is open;
◗ battery temperature: an optional
PC-board may be connected to the
remote transmission board. It supplies
information on the battery temperature,
thus enabling the RC to regulate the
battery voltage.
Note:
The Static Switch Cubicle does not
receive any of the above signals.
Signal transmission
◗ an auxiliary 24V power supply,
isolated and backed up, is used to
supply:
◗◗ the undervoltage coil release for the
battery circuit breaker(s) QF1,
◗◗ an optional board that measures the
temperature in the battery room;
◗ "general alarm" information
(2 volt-free changeover contacts) which
includes:
◗◗ internal faults,
◗◗ information on temperatures outside
tolerances in the battery room
(optional),
◗◗ overload information (I > In),
◗◗ static switch ventilation and power-
supply faults;
◗ "low battery shutdown" warning
signal (2 volt-free changeover
contacts) indicating that battery time is
about to run out. The warning threshold
may be personalized;
◗ "load on inverter" signal (2 volt-
free changeover contacts) indicating
that the load is supplied by the inverter.
In single-unit UPS systems, one voltfree changeover contact may be used
to indicate that the load is supplied by
Mains 2;
◗ "load on battery" signal (2 volt-free
changeover contacts) indicating that
the inverter is supplied by the battery in
the following cases:
◗◗ Mains 1 outage or voltage drop,
◗◗ RC shutdown,
◗◗ RC current limiting;
This signal, which may be used to
initiate process saving and shutdown
procedures, is time-delayed by 30
seconds to avoid unnecessary
operations following micro-breaks;
◗ "maintenance position" signal
(2 volt-free changeover contacts)
indicating that;
◗◗ maintenance bypass switch Q3BP is
closed,
◗◗ Mains 2 input switch Q4S is open,
◗◗ inverter output switch Q5N is open,
◗◗ battery circuit breaker QF1 is open;
◗ signal to open battery circuit
breaker(s) QF1 in the event the
"emergency shutdown" button being
pressed or to avoid an excessive
battery discharge (more than 3 rated
time).
Note:
◗ the maximum breaking capacity of
the changeover contacts is 5A at 250V;
◗ information on the battery is not
supplied to frequency converters
without a battery or to the Static Switch
Cubicle;
◗ in systems with a Static Switch
Cubicle, the "load on inverter" and
"maintenance position" signals must be
directed to the Static Switch Cubicle.
Page 28 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 29

"LED" signalling box (optional)
A basic "LED" signalling box with four
indication lights may be supplied as an
option with the MGE
system.
It supplies the following signals:
◗ load on battery;
◗ low battery shutdown warning;
◗ inverter stop;
◗ general alarm.
It connects to the terminals presented
on the preceding page and draws its
power from the external 220V AC,
50Hz or 60Hz power supply not
connected to a UPS.
TM
GalaxyTM 6000
Environment information (cont.)
erie
sur batt
t
men
Fonctionne
erie
tt
.ba
uto
d'a
test
e fin
larm
réa
P
rêt
duleur à l'ar
On
le
globa
Alarme
Additional information "Media Contacts 15" (optional)
An additional board may be installed in
all types of systems. Terminals XR5 to
XR9 on the board may be used to
receive additional information from the
environment and supply more precise
information on system status (see
figures 18, 19, 20 and 22 for the
position of the board).
Signal reception
The signals should be provided by voltfree contacts.
◗ "desynchronization with Mains 2"
signal inhibits the inverter from
synchronizing its output frequency with
that of Mains 2. The inverter supplies a
stable frequency and the load may no
longer be correctly transferred from the
inverter to Mains 2. In the event of a
malfunction or an overload, the transfer
will take place with a 0.8 second
interruption in the supply of power to
the load;
◗ "gradual rectifier/charger
shutdown" signal makes the rectifier/
charger shut down progressively to
avoid excessive step load variations in
the event of a low output engine
generator set replacing Mains 1;
◗ "generator current limiting" signal
makes the rectifier/charger current limit
the power drawn when a low output
engine generator set has replaced
Mains 1. The additional power required
for the inverter is supplied by the
battery;
◗ "battery charge current limiting"
signal reduces the battery charge
current (programmable parameter) in
the event a low output engine generator
set has replaced Mains 1;
Additional remote transmission
board
XR5 XR6 XR7XR9XR8
◗ "transfer to Mains 2 disabled"
signal blocks transfer of the load from
the inverter to Mains 2. In the event the
inverter shuts down (overload, etc.), the
load is no longer supplied (for modular
UPSs, this information is disabled and
transferred to an auxiliary output);
◗ "transfer to Mains 2 with
interruption disabled" signal blocks
transfer of the load from the inverter to
Mains 2 if it would result in an
interruption in the supply of power to
the load. Only no-break transfers are
allowed, i.e. transfer to Mains 2
conditions must be correct or the
transfer is disabled (for modular UPSs,
this information is disabled and
transferred to an auxiliary output);
◗ "auxiliary" signal can be used to
provoke (depending on
personalization):
◗◗ a forced shutdown of the inverter
(regardless of the status of Mains 2),
◗◗ a protected inverter shutdown
(transfer of the load to Mains 2 without
interruption only if it is within
tolerances),
◗◗ modification of the inverter output
frequency (50Hz or 60Hz);
◗ "remote inverter on" signal can be
used to remotely start the inverter;
◗ "remote inverter off" signal can be
used to remotely shut down the
inverter.
Note:
In a system with a Static Switch
Cubicle, the following signals must be
directed to the Static Switch Cubicle:
◗◗ desynchronization with Mains 2,
◗◗ transfer to Mains 2 disabled,
◗◗ transfer to Mains 2 with interruption
disabled.
6739380EN/JC - Page 29
Page 30

Environment information (cont.)
Signal transmission
These signals are each transmitted by
two volt-free changeover contacts with
a maximum breaking capacity of 5A
250V.
◗ "overload" signal indicates that an
overload has taken place (Pload >
Pnominal in kVA);
◗ "rectifier/charger function fault"
signal indicates that:
◗◗ a fault has taken place in the
rectifier/charger module,
◗◗ Mains 1 input switch Q1 is open;
◗ "inverter function fault" signal
indicates that a fault has taken place in
the inverter module;
◗ "transfer to inverter fault" signal
indicates that the load transfer
conditions from Mains 2 to the inverter
are incorrect;
◗ "transfer to Mains 2 fault" signal
indicates that the transfer to Mains 2
conditions (voltage, frequency or
phase) are incorrect and a forced
transfer will result in a 0.8 second
interruption in the supply of power to
the load;
◗ "rectifier/charger on" signal
indicates the status of the module.
Note:
A Static Switch Cubicle receives only
the following signals:
◗◗ overload,
◗◗ transfer to inverter fault,
◗◗ transfer to Mains 2 fault.
Page 30 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 31

Maintenance configuration
Single-unit or single modular
UPS (figure 29)
During maintenance, the UPS must be
isolated from Mains 1 and 2, the battery
and the load.
◗ inverter isolation
Proceed in the following order:
◗◗ shut down the inverter (press the
"inverter off" button 7 for 3 seconds),
◗◗ close bypass switch Q3BP,
◗◗ open isolating switches Q5N, Q4S,
QF1 and Q1.
The UPS is powered down once the
capacitors have discharged (a few
minutes);
◗ start-up
Following servicing, proceed in the
following order:
◗◗ close switch Q1, then after
approximately ten seconds, switches
QF1, Q5N and Q4S,
◗◗ open bypass switch Q3BP,
◗◗ start the inverter (press the "inverter
on" button 6 ).
mains 2
rectifier-
mains 1
Q1
charger
Fig. 29
Caution:
◗ work should be carried out in
accordance with applicable safety
regulations;
Q4S
QF1
Maintenance
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
battery
◗ to avoid interrupting the load, the
various switching operations must
be carried out in the correct order.
Operations are explained in
diagrams placed next to the
switches.
Q5N
load
Multi-bypass modular UPS
(figure 30)
Prior to servicing a given UPS, it must
be isolated from Mains 1, Mains 2, its
battery and the load outputs of the
other UPSs (in this case, never operate
the Q3BP switches in the units).
◗ isolate the UPS
Proceed in the following order:
◗◗ shut down the inverter (press the
"inverter off" button 7 for three
seconds);
◗◗ open isolating switches Q5N, QF1,
Q4S and Q1 in the unit.
The UPS is de-energised once the
capacitors have discharged (a few
minutes).
◗ start-up
Once servicing is completed, proceed
in the following order:
◗◗ close Q1, then QF1, Q4S and Q5N;
◗◗ start the inverter (press the “inverter
on” button 6 ).
Note. It is strongly advised to call on
our after-sales support department for
these operations.
mains 2
mains 1
mains 2
mains 1
Modular UPS 1
rectifiercharger
Q1
Modular UPS 2
rectifiercharger
Q1
Q4S
QF1
Q4S
QF1
static switch
inverter
battery
static switch
inverter
battery
Q3BP
Q5N
Q3BP
load
Q5N
Fig. 30
6739380EN/JC - Page 31
Page 32

Maintenance (cont.)
Modular UPS with external
maintenance bypass
(figure 31)
To service a number of modular UPSs
with an external maintenance bypass, it
is necessary to isolate them.
◗ isolate the UPSs
Proceed in the following order:
◗◗ shut down each inverter (press the
"inverter off" button 7 for three
seconds),
◗◗ switch to the maintenance bypass
whereby the load will be directly
supplied by Mains 2 via Q3BP (close
Q3BP, then open Q5 in the
maintenance bypass cubicle),
◗◗ open input switch Q4S on each UPS;
◗◗ isolate each UPS from Mains 2 by
opening the upstream protection
devices,
◗◗ open input switch Q1 on each UPS,
◗◗ open output switch Q5N on each
UPS.
The UPSs are de-energised (except the
Mains 1 cables upstream of the Q1
switches on each UPS), but the load is
supplied with Mains 2 power via the
maintenance bypass. Complete
isolation of the installation requires
opening of the upstream protection
devices on both Mains 1 and Mains 2.
◗ start-up
Once servicing is completed, proceed
in the following order:
◗◗ close the input switches Q1 and Q4S
on each UPS,
◗◗ close output switch Q5N on each
UPS,
◗◗ close output switch Q5N in the
maintenance bypass cubicle,
◗◗ open switch Q3BP in the
maintenance bypass cubicle,
◗◗ close battery circuit breaker Q1 on
each UPS,
External maintenance bypass
Modular UPS 1
Q4S
mains 2
rectifiercharger
mains 1
Q1
QF1
Modular UPS 2
Q4S
mains 2
rectifiercharger
mains 1
Q1
QF1
Fig. 31
◗◗ start all the inverters (press the
"inverter on" button 6 ).
The UPSs all come on line at the same
time if they are sufficient in number to
supply the load.
Q3BP
static switch
inverter
battery
static switch
inverter
battery
Q5N
Q5N
Q5N
Note. It is strongly advised to call on
our after-sales support department for
these operations.
load
Frequency converter or parallel
UPS with SSC
(figure 32)
During maintenance, the concerned
UPS or converter must be isolated from
Mains 1, its battery and the output
circuits of the other units.
◗ inverter isolation
Proceed in the following order:
◗◗ shut down the inverter (press the
"inverter off" button 7 for 3 seconds),
◗◗ open isolating switches Q5N, QF1
and Q1 for that line.
The unit is powered down once the
capacitors have discharged (a few
minutes).
In redundant systems with at least one
redundant UPS, the other UPSs (or
converters) ensure continuity of power
to the load.
Page 32 - 6739380EN/JC
mains 1
mains 1
mains 1
Q1
QF1
Q1
QF1
Q1
QF1
Fig. 32: frequency converter exemple
Q5N
Q5N
load
Q5N
Page 33

Maintenance (cont.)
In non-redundant systems with a
Mains 2, the load is supplied by the
Mains 2 and the Static Switch Cubicle.
In non-redundant systems without a
Mains 2, the entire system must be
shut down.
Static Switch Cubicle
During maintenance, the Static Switch
Cubicle must be isolated from Mains 2,
the load and the parallel UPSs.
◗ if work is required on the control
electronics alone, open cubicle switch
Q4S (but not Q5N) and cubicle fuse
switches Q1 and Q2. The load can then
remain supplied by the UPSs. After
servicing, reclose fuse switches Q1, Q2
and switch Q4S.
Caution:
When the Static Switch Cubicle is
powered down using the above
procedure, only the control electronics
are in fact powered down. The power
circuits remain energized. Maintenance
on the static switch power circuits
requires shutdown of the UPSs and
transfer of the load to the maintenance
bypass line.
◗ open switch Q5N, then the
disconnector-fuses Q1 and Q2 in the
SSC;
◗ open switches Q5N, then switch Q4S
on all the UPSs (figure 33).
Caution:
Even in the maintenance bypass
configuration, the cubicle is only
partially shut down and the supply
of power to the load continues via
switch Q3BP.
◗ more extensive maintenance work
on the Static Switch Cubicle requires
the entire system to be shut down.
◗ start-up
Following servicing, proceed in the
following order:
◗◗ close switch Q1, then switches QF1,
Q5N and Q4S,
◗◗ start the inverter (press the "inverter
on" button 6 ).
mains 2
mains 1
mains 1
Q1
QF1
Q1
QF1
Fig. 33
Note:
We recommend that you call on the
after-sales support department to carry
out these operations.
Q4S
Note:
We recommend that you call on the
after-sales support department to carry
out these operations.
Q3BP
Q5N
load
Q5N
Q5N
Battery maintenance
Consult the instructions supplied by the
battery manufacturer. Below are a few
general indications:
◗ sealed lead-acid batteries.
These batteries require no
maintenance:
◗◗ but check the terminals of each cell
from time to time and clean if
necessary;
◗ vented lead-acid batteries:
◗◗ check the electrolyte level regularly
and add water if necessary,
◗◗ check the voltage of each cell to
determine if it is necessary to equalize
the battery,
◗◗ check the terminals of each cell and
clean if necessary.
Caution:
Battery maintenance is undertaken with
the system powered up. Operations
must be carried out in accordance with
applicable safety regulations by
qualified personnel using insulated
tools, gloves and safety goggles.
Batteries contain dangerous
substances that will harm the
environment if thrown away. If you
change the batteries yourself, call on
qualified organizations for battery
disposal and recycling.
Pb Pb
6739380EN/JC - Page 33
Page 34

Maintenance (cont.)
Autodiagnostics
Note the indications supplied on the
hidden control panel (lights A to
See the "control panel" section.
In systems with one or several
alphanumeric displays, check the list of
alarms.
N 8 ).
Visual check
◗ after-sales support technicians will
power down the system prior to any
maintenance operations.
Note:
In redundant, parallel UPS systems and
frequency converters, the check may
be carried out successively on each
UPS or converter without interrupting
the load. In other configurations and for
the Static Switch Cubicle, the load must
be supplied via the maintenance
bypass (see the "Alarm" section).
Functional check
◗ check that lights J, K, M and N on the
hidden control panel are not on to avoid
an interruption in the supply of power to
the load due to incorrect transfer
conditions or a battery problem;
◗ press the "inverter off" button and
check that the buzzer and control panel
lights function correctly (see the "main
operating modes" section);
◗ press the "inverter on" button and
check again that the control panel lights
function correctly;
◗ run a transfer to battery test. With the
If there is a true malfunction, note the
indications and alarms and call the
after-sales support department.
◗ clean the system regularly,
particularly the air inlet and outlet grills.
Check that the air circulates freely in
the cubicles. Use a vacuum cleaner if
necessary;
◗ check that nothing hinders the
ventilation at the top of the system;
◗ check that all the fans operate
correctly.
inverter on, open input switch Q1.
The orange "battery" light on the control
panel should light. After two minutes on
battery power, close input switch Q1.
The rectifier/charger should
automatically restart and the orange
"battery" light on the control panel
should go off;
◗ in parallel systems, run these tests
on each UPS or converter.
Page 34 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 35

Training centers
To allow you to useAPC by Schneider Electric products effectively and carry out basic maintenance, we offer a complete range of
technical training courses in English and French.
Training centers
Schneider Critical Power & cooling services
50 Hz :
France Training Centre
140, Avenue Jean Kuntzmann
Innovallée
38334 - St Ismier Cedex
France
Tel: +33 (0)4 76 18 34 14
Fax: +33 (0)4 76 18 45 21
Singapore Training Centre
10 Ang MO Kio Street 65, #03-06/10
Techpoint Building
Singapore 569059
Singapore
Tel: +65 6389 6792
China Training Centre
No. 999, Shen Fu Road
Min Hang District
Shanghai 201108
P.R. China
Training center
Schneider Critical Power & cooling services
50-60 Hz :
United States Training Centre
132 Fairgrounds Road
West Kingston - RI02892
U.S.A
Tel: +1 877 800 4272
Tel: +86 21 3407 3365
Fax: +86 21 3407 4526
Internet : Http://powerlearning.apc.com
On-line catalogue and registration.
6739380EN/JC - Page 35
Page 36

"Monitor" alphanumeric display
General
◗ local operation. The "Monitor"
alphanumeric display (see figure 34)
may be installed behind the hinged
cover of the hidden panel (see figure
25) on the control panel in all types of
cubicles (UPS or Static Switch
Cubicle).
◗ remote operation. Installed in a
special enclosure, the "Tele Monitor"
provides the user with remote
indications on system status. Two "Tele
Monitor" units may be connected to the
same system, one as a master for
indications and remote control, the
other as a slave for indications only.
The "Monitor" can operate in two
different modes:
◗ mono-cubicle: the option monitors
only the cubicle in which it is installed;
◗ multi-cubicle: "Monitor" can monitor
all system cubicles (up to eight
maximum). In this mode, the system is
equipped with only one "Monitor" which
may be installed in any of the cubicles.
Display
A message indicating the general
status of the cubicle or system is
continuously displayed. If there is no
alarm or problem and the load is
normally supplied, the message on the
screen is:
Alphanumeric display screen and control panel
19
load protected
power supply OK
AV
Fig. 34
The alphanumeric display screen 18 is
made up of two lines with 20 characters
each. The control panel is made up of:
◗◗ nine display control buttons,
◗◗ eight selection lights for the
concerned cubicle,
◗◗ eight alarm lights for the cubicles.
LOAD PROTECTED
POWER SUPPLY OK
W.Hz
+–
24232221
2018
87654321
!
25 26 27
*
Control panel
"Settings" button 19 .
This button can be used to select the
display language, adjust screen
contrast to local conditions and, for the
"Tele Monitor" option, adjust the
volume level of the buzzer.
"V" button 21 .
Provides access to voltage
measurements:
◗ Mains 1 phase-to-phase voltages;
◗ Mains 2 phase-to-neutral and phase-
to-phase voltages;
◗ inverter output phase-to-neutral and
phase-to-phase voltages;
◗ load phase-to-neutral and phase-to-
phase voltages.
"A" button 22 .
Provides access to current
measurements:
◗ currents on the Mains 1 and 2 lines
and the load;
◗ percent current drawn by the load;
◗ percent load with regards to the
rated value;
◗ load current peak factor.
"W.Hz" button 23 .
Provides access to measurements:
◗ Mains 1 and 2 and inverter
frequency;
◗ active and apparent power drawn by
the load;
◗ load power factor.
"Battery" button 24 .
Provides access to battery
measurements:
◗ battery voltage (or DC voltage for
frequency converters without a battery);
◗ battery current (charge or discharge);
◗ battery temperature (optional);
◗ remaining battery time.
"Alarms" button 25 .
Displays current or logged alarms and
stops the buzzer for the "Tele Monitor"
option.
A blinking character ("!", "A" or "kW") at
the end of the line indicates that the
user must press the "alarms" 25 ,
"A" 22 or "W.Hz" 23 button
respectively to display the remaining
alarms or further information.
"I/O" button 26 .
Provides access to On/Off controls.
This button is active only on remote,
master "Tele Monitor" units.
"*" button 27 .
This button has a number of functions
depending on the displayed messages
(confirmation, positive response, etc.).
Pressing this button followed
immediately by the "V" button 21 (less
than one second) provides access to
the display configuration function. In
"Monitor" multi-cubicles mode, this
button can also be used to display the
type of cubicle concerned by the
displayed message. The information
disappears when the button is
released. For example:
CUBICLE NUMBER 1 =
STATIC SWITCH MODULE
Page 36 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 37

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
">" button 20
This button has a number of functions
depending on the displayed messages
(selection, negative response, etc.).
In "Monitor" multi-cubicles mode, this
button can also be used to select one
of the eight cubicles that may be
connected to the "Monitor" unit, in
which case any action on the control
panel and the messages or
measurements displayed concern only
the selected cubicle.
In the event the selected cubicle does
not respond, the following message is
displayed:
CUBICLE NUMBER XX
UNAVAILABLE
In the event of no reply from the display
screen, the following message appears:
DISPLAY NUMBER XX
UNAVAILABLE
Which corresponds to a communications
fault.
In the event of invalid data, the
following message is displayed:
General display function organization
Initial screen, display of general alarms
This is the normal display which systematically reappears
when the control panel has not been used for ten minutes.
!
V
A
W.Hz
+–
Alarm display and buzzer reset
Voltage measurements
Current measurements
Frequency and power measurements
Battery measurements
On/Off controls
Language, screen contrast and
buzzer volume settings
to
set
to
*
confirm
to
*
confirm
CUBICLE NUMBER XX
FAULT
Note:
◗ most functions may be directly
accessed. For example, when voltage
measurements are currently displayed,
it is possible to directly access current
measurements by pressing the "A"
button;
◗ in "Monitor" multi-cubicles mode, it is
possible to access the same
measurement in another cubicle by
simply pressing the ">" button. For
example, if the battery voltage of a
cubicle is currently displayed, it is
possible to directly display the battery
voltages of the other cubicles by
pressing the ">" button once for each
other cubicle.
Lights 1 to 8
These lights are useful particularly in
multi-cubicle mode.
Green lights
Only one of these lights is on at a time,
indicating the number of the cubicle
concerned by the current display.
Red lights
These lights provide an indication on
system status by signaling alarms and
problems in the concerned cubicles.
Cubicle selection for display of measurements
(multi-cubicle mode only)
*
V
*
Information on type of cubicle
(multi-cubicle mode only)
Display configuration
to select
or answer
no
They light if maintenance is carried out
on a cubicle or if the communication
link with a cubicle breaks down.
to confirm
or answer
*
yes
6739380EN/JC - Page 37
Page 38

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
Alarm display and buzzer reset
When the control panel has not been
used for ten minutes, the alphanumeric
display presents a general message
indicating the general status of the
cubicle or the system.
If there are no alarms or problems, and
the load is correctly supplied by the
inverter, the display indicates:
LOAD PROTECTED
POWER SUPPLY OK
If there is a problem, the screen first
displays a general alarm, then if
applicable, a list of secondary alarms
may be obtained by successively
pressing the "alarms" button ("!").
See the lists below.
For the local "Monitor" option,
button 11 on the hidden control panel
stops the buzzer.
For the remote "Monitor" option ("Tele
Monitor"), the "!" button stops the
buzzer.
Note:
The existence of another alarm in the
list is indicated by the blinking "!"
character at the end of a message.
The last alarm in the list is not followed
by the blinking "!" character at the end.
If the "alarms" button is pressed again,
the system returns to the initial screen.
Display of alarms
on the initial screen
(ALARM MESSAGE NUMBER 1)
(ALARM MESSAGE NUMBER 2)
(LAST ALARM MESSAGE)
general alarm
!
!
!
!
initial screen
This message is displayed only if the buzzer has
been activated. It is a prompt to consult the list of
!
current alarms by pressing the "alarms" ("!")
button after having read each message.
!
The last alarm message is not followed by the
blinking "!" character. If the "alarms" ("!") button
is pressed again, the system returns to the
initial screen.
List of general alarms
LOAD PROTECTED
POWER SUPPLY OK
This is the normal display when there
are no alarms or problems and the load
is correctly supplied by the inverter.
LOAD PROTECTED
PROBLEM... !
The load is supplied by the inverter, but
a minor problem requiring servicing has
occurred. The cause of the problem is
contained in the list of secondary
alarms (see next page).
MAINS 1 PROBLEM
LOAD ON BATTERY !
The load is supplied by the inverter, but
Mains 1 is down or outside tolerances
and power is supplied by the battery.
REMAINING BAT. TIME
__MN %KW LOAD =___
This message is automatically
displayed for five seconds, alternating
with the preceding. It indicates the
remaining battery time in minutes prior
to inverter shutdown. The calculation
takes into account:
◗ the percentage of full rated load
power being drawn;
◗ the type of battery;
◗ battery temperature;
◗ battery age.
LOW BATTERY
SHUTDOWN IMMINENT !
This message replaces the "Mains 1
problem, load on battery" message
when battery voltage reaches the "low
battery shutdown" warning level. It
alternates with the message described
above, "remaining battery time…".
The user must then rapidly take
measures to secure the load (load
shedding, file saves and shutdown,
etc.). In the next one to two minutes at
most, the inverter will shutdown and the
load will be interrupted.
Two low battery thresholds exist:
◗ a battery voltage threshold, which is
slightly above the threshold causing an
inverter shutdown (this threshold can
be disabled);
◗ a time threshold, which refers to an
adjustable value of the time remaining
before effective end of battery power.
ALARM ...
!
This message signifies that the battery
circuit breaker is open and the inverter
shut down. The cause of the alarm is in
the list of secondary alarms (see next
page).
Page 38 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 39

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
List of secondary alarms
These alarm messages may be
consulted by pressing the "alarms" ("!")
button when the "!" character appears
at the end of a general alarm message.
The "alarms" ("!") button can then be
used to read the other alarms from the
list.
EMERGENCY SHUTDOWN
AUXILIARY COMMAND !
The remote emergency-shutdown
button has been pressed with as a
result:
◗ shutdown of the inverter;
◗ shutdown of the rectifier/charger;
◗ opening of battery circuit breaker
QF1;
◗ transfer of the load to Mains 2.
To ensure full powering down of the
system, this button must also open the
external upstream circuit breakers
supplying Mains 1 and 2.
LOAD ON
MAINS 2 !
The load has been transferred to
Mains 2 and is no longer protected.
MAINS 2 PROBLEM
CHECK FREQUENCY !
Mains 2 frequency is outside tolerances
and the inverter, unable to synchronize,
has switched to free-running frequency
mode. Transfer of the load from the
inverter to Mains 2 or vice-versa will
result in an interruption of the supply of
power to the load.
MAINS 2 PROBLEM
CHECK VOLTAGE !
Mains 2 voltage is outside tolerances.
Transfer of the load from the inverter to
Mains 2 or vice-versa will result in an
interruption of the supply of power to
the load.
FREQUENCY IMPOSED
DESYNCH. COMMAND !
The inverter has received an external
command to desynchronize its output
frequency with that of Mains 2.
INVERTER IMPOSED
AUXILIARY COMMAND !
The inverter has received an auxiliary
command inhibiting transfer to Mains 2.
In the event of an inverter malfunction
and shutdown, the load will no longer
be supplied.
BATTERY OVERTEMP.
CHECK FANS !
This message is displayed only if the
"Temperature Monitor" option has been
installed. It signals that the battery
temperature is outside tolerances.
BATT. HOUSING VENT
OR HARM FILTER FAULT!
A fault requiring servicing has occurred
in the battery room ventilation system.
The rectifier-charger stops after
30 seconds.
If the installation includes a harmonics
filter, this light will also signal an
overtemperature of the filter’s inductor.
MAINS 1 PROBLEM
CHECK FREQUENCY !
Mains 1 frequency is outside tolerances
and the RC has shut down. The
inverter is on battery power.
MAINS 1 PROBLEM
CHECK VOLTAGE !
Mains 1 is down or its voltage is outside
tolerances and the rectifier/charger has
shut down. The inverter is on battery
power.
CHARGER SHUTDOWN
AUXILIARY COMMAND !
The rectifier/charger has received an
external command to progressively
shut down (for example, for a
progressive transfer to an engine
generator set).
INPUT KVA LIMITED
AUXILIARY COMMAND !
The rectifier/charger has received an
external command to limit the power
drawn on Mains 1. The remaining
power required for the load is supplied
by the battery. This situation is
encountered, for example, when the
system operates on power supplied by
an undersized engine generator set.
I BATTERY LIMITED
AUXILIARY COMMAND !
The rectifier/charger has received an
external command to limit the charge
current supplied to the battery. The
normal charge current will be supplied
when Mains 1 returns. This situation is
encountered, for example, when the
system operates on power supplied by
an undersized engine generator set.
Note:
The battery charge current limit value
may be programmed.
BATTERY BREAKER
QF1 OPEN !
QF1 battery circuit breaker has tripped
or is open. The load is no longer
protected because battery power in
unavailable in the event of a Mains 1
outage.
LOW BATTERY
... !
The inverter has shut down at the end
of battery power.
CHARGER OFF
... !
The rectifier/charger has shut down.
CHARGER FAULT
CALL SUPPORT DEPT.!
A fault has occurred in the rectifier/
charger module requiring servicing by
the after-sales support department.
MAINS 1 SWITCH
Q1 OPEN !
Mains 1 input switch Q1 is open. It
must be closed for rectifier/charger
start-up.
I INVERTER > IN
CHECK P.F. KW
An inverter overload has occurred due
to a load power factor greater than 0.9.
The blinking "kW" sign at the end of the
message is a prompt to read the load
power factor.
6739380EN/JC - Page 39
Page 40

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
INVERTER FAULT
CALL SUPPORT DEPT.!
A fault has occurred in the inverter
module requiring servicing by the aftersales support department.
INVERTER SHUTDOWN
OVERLOAD > IMAX !
An overload greater than 1.6 In has
occurred on the load, resulting in
inverter shutdown.
INVERTER SHUTDOWN
OVERLOAD > IN A
An overload between In and 1.6 In has
occurred on the load, resulting in
inverter shutdown. The blinking "A" at
the end of the message is a prompt to
read the load current measurement.
AUXILIARY CONTROL
SIGNAL RECEIVED !
An auxiliary "Media Contacts 15" option
signal has been received. The next
display will indicate which of the four
possible functions was set.
FORCED UPS SHUTDOWN
AUXILIARY CONTROL
The UPS has received a forced
shutdown command. This corresponds
to an auxiliary control signal received
via a "Media Contacts 15" option set for
this function.
PROTECT.UPS SHUTDOWN
AUXILIARY CONTROL
The UPS has received a shutdown
command. This command will only be
executed if load transfer conditions on
Mains 2 are satisfied. This corresponds
to an auxiliary signal received via a
"Media Contacts 15" option set for this
function.
FREQUENCY REVERSAL
AUXILIARY CONTROL
The UPS has received a command to
change its output frequency (50 or
60Hz).
This command is only executed if the
inverter is off. The frequency will be
changed the next time the inverter is
started. The command corresponds to
an auxiliary control signal received via
a "Media Contacts 15" option set for
this function
.
I LOAD > IN
CHECK LOAD A
The power drawn by the load is greater
than the rated value. The blinking "A" at
the end of the message is a prompt to
read the load current measurement.
TRANSFER FAULT
CALL SUPPORT DEPT.!
A fault has occurred in the static switch
which ensures transfer of the load
between the inverter and Mains 2.
Servicing by the after-sales support
department is required.
PHASE OUT OF LIMITS
!
For a single-unit UPS or Static Switch
Cubicle, the phase shift between the
inverter and Mains 2 is outside
tolerances. Transfer of the load
between the inverter and Mains 2 will
result in an interruption in the supply of
power to the load.
For a parallel UPS, the phase shift
between this inverter and the other
inverters is outside tolerances, and the
corresponding UPSs has therefore
been disconnected.
MAINS 2 SWITCH
Q4S OPEN !
Mains 2 input switch Q4S is open, i.e.
transfer of the load from the inverter is
impossible.
OUTPUT SWITCH
Q5N OPEN !
Inverter output switch Q5N is open, i.e.
the load cannot be supplied by the
inverter.
MAINT. BYPASS SWITCH
Q3BP CLOSED !
Maintenance bypass switch Q3BP is
closed. The system is in maintenance
configuration and the load is supplied
by Mains 2.
EMERGENCY OFF
OVERLOAD > IN !
The load is no longer supplied by
Mains 2 following an extended
overload.
BATTERY
CHARGING !
The battery is currently being
recharged.
INDEPENDENT
INVERTER FREQUENCY!
The inverter frequency is stable and
accurate to 0.05Hz, but no longer
synchronous with that of Mains 2.
NUMBER OF INVERTERS
READY INSUFFICIENT!
This message is valid only for parallel
UPS systems. The number of UPSs
ready for connection to the load is
insufficient for the required power level.
Another UPS must be started before all
the lines together may supply the load.
Until another line is started, the load will
remain supplied by Mains 2.
BATTERY MAINTENANCE
CALL AFTER-SALES
Indicates that the battery has probably
reached the end of its service life
(based on the estimated average
service life since its installation).
TRANSFER DISABLED
AUXILIARY CONTROL
Transfer of the load to Mains 2 is
inhibited due to:
◗ certain transfer conditions not
satisfied;
◗ "transfer to Mains 2 with interruption
disabled" auxiliary contact of the
"Media Contacts 15" option closed.
Page 40 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 41

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
UPS IMPOSED
TRANSFER DISABLE !
Cannot transfer the load to Main 2 due
to:
◗ transfer conditions not satisfied;
◗ UPS operating on an independent
frequency;
Measurement system
The "Monitor" system displays a
number of input and output
measurements at different points in the
system.
◗ Mains 1
◗◗ phase-to-phase voltages,
◗◗ currents of the three phases,
◗◗ frequency;
◗ Mains 2
◗◗ phase-to-neutral voltage,
◗◗ phase-to-phase voltages,
◗◗ frequency;
◗ battery
◗◗ voltage,
◗◗ charge or discharge current,
◗◗ remaining battery time (calculated for
each UPS);
◗ inverter output
◗◗ phase-to-neutral voltage,
◗◗ phase-to-phase voltages,
◗◗ currents of the three phases,
◗◗ frequency,
◗◗ active and apparent power,
◗◗ ratio peak current / rated current rms;
◗ total load
◗◗ phase-to-neutral voltage,
◗◗ phase-to-phase voltages,
◗◗ currents of the three phases,
◗◗ frequency,
◗◗ active and apparent power;
◗ option
◗◗ battery temperature.
Note:
Frequency converters without batteries
are not concerned by the battery
measurements. The displayed battery
voltage corresponds to the DC voltage
at the RC output.
◗ UPS operating with current limitation;
◗ internal fault;
◗ auxiliary control inhibits switching to
Mains 2.
Single-unit or modular UPS
Q3BP
mains 2
U - F
mains 2
mains 1
Q4S
Q1
QF1
charger
U - I - F
Frequency converter
mains 1
Q1
QF1
charger
U - I - F
Static Switch Cubicle
battery
U - I
battery
U - I
K3N
inverter
U - F
K3N
inverter
U - F
Q5N
inverter
I - P
Q5N
inverter
I - P
load
load
U - I - F - P
common
load
load
U - I - F - P
mains 2
RCIB line(s)
Q4S
mains 2
U - F
load
U - I - F - P
Q3BP
K2S
Q5N
load
6739380EN/JC - Page 41
Page 42

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
Voltage measurements
These measurements may be
accessed in two manners:
◗ pressing the "V" button displays the
series of screens in the figure opposite;
◗ in "Monitor" multi-cubicle mode,
pressing the ">" button when the
screen already displays the voltage
measurements of a cubicle.
The system shifts to the voltage
measurements of the next cubicle.
Note:
◗ Mains 2 measurements are not
displayed on converters and parallel
UPS with SSC;
◗ Mains 1 and inverter output
measurements are not displayed on
Static Switch Cubicles.
Caution:
For installations comprising a number
of modular UPSs connected in parallel,
the absence of load (UPS output)
voltage indicated on a display is only
valid if it also indicated on the displays
of all the other parallel-connected
UPSs. Before carrying out any work on
a UPS, always check the absence of
voltage using a method complying with
applicable safety rules for work on
electrical equipment.
Display of voltage measurements
V
MNS.1
V RMS
MNS.2
V RMS
MNS.2
V RMS
INV.
V RMS
INV.
V RMS
LOAD
V RMS
LOAD
V RMS
U12 U23 U31
V
V1 V2 V3
V
U12 U23 U31
V
V1 V2 V3
V
U12 U23 U31
V
V1 V2 V3
V
U12 U23 U31
V
Direct access to the function
by pressing the "V" button.
Mains 1 input phase-to-phase voltages in V rms
(RC input).
Mains 2 input phase-to-neutral voltage in V rms.
Mains 2 input phase-to-phase voltages in V rms.
Inverter output phase-to-neutral voltage in V rms.
Inverter output phase-to-phase voltages in V rms.
Load phase-to-neutral voltage in V rms.
Load phase-to-phase voltages in V rms.
Current measurements
These measurements may be
accessed in two manners:
◗ pressing the "A" button displays the
series of screens in the figure opposite;
◗ in "Monitor" multi-cubicle mode,
pressing the ">" button when the
screen already displays the current
measurements of a cubicle.
The system shifts to the current
measurements of the next cubicle.
Note:
◗ Mains 2 measurements are not
displayed on UPS cubicles in parallel
UPS systems;
◗ Mains 1 and inverter output
measurements are not displayed on
Static Switch Cubicles.
Display of current measurements
A
MNS.1
A RMS
MNS.2
A RMS
INV.
A RMS
LOAD
A RMS
I LOAD / IN
=
LOAD
PEAK F.
I1 I2 I3
A
I1 I2 I3
A
I1 I2 I3
A
I1 I2 I3
A
% (IN = A)
A
I1 I2 I3
A
Direct access to the function by pressing the "A"
button.
Currents of the three phases at Mains 1 input
in A rms (RC input).
Currents of the three phases at Mains 2 input
in A rms.
Currents of the three phases at inverter output
input in A rms.
Currents of the three load phases in A rms.
Percentage of the current drawn on the most
heavily loaded load phase with regards to the
rated current (in parentheses).
Peak factor for each phase of the load current
with regards to a sine current.
Page 42 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 43

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
Frequency and power measurements
These measurements may be
accessed in two manners:
◗ pressing the "W.Hz" button displays
the series of screens in the figure
opposite;
◗ in "Monitor" multi-cubicle mode,
pressing the ">" button when the
screen already displays the frequency
and power measurements of a cubicle.
The system shifts to the frequency and
power measurements of the next
cubicle.
Note:
◗ Mains 2 measurements are not
displayed on UPS cubicles in parallel
UPS systems;
◗ Mains 1 output measurements are
not displayed on Static Switch
Cubicles.
Display of power and frequency measurements
Direct access to the function by pressing the
W. Hz
FREQ.
MNS1 MNS2 INV.
HZ
W. Hz
LOAD
KW
P LOAD / Pn
= %
LOAD
KVA
P. TOTAL
LOAD
POWER FACTOR
LOAD P.F. =
P1 P2 P3
W. Hz
(PN= KW)
W. Hz
P1 P2 P3
W. Hz
P.KW P.KVA
W. Hz
W. Hz
"W.Hz" button.
Frequency value for Mains 1, Mains 2 and the
inverter output in Hz with one decimal figure
(values valid only for concerned cubicle).
Active power drawn by the load in kW on each
phase.
Percentage of the power drawn by the load with
regards to the rated unit output (in parentheses).
Apparent power drawn by the load in kVA on
each phase.
Active power (in kW) and apparent power (in
total kVA drawn by the load (total of the three
phases)).
Load power factor (active power / apparent
power).
Battery measurements
These measurements may be
accessed in two manners:
◗ pressing the "battery" button displays
the series of screens in the figure
opposite;
◗ in "Monitor" multi-cubicle mode,
pressing the ">" button when the
screen already displays the battery
measurements of a cubicle. The
system shifts to the battery
measurements of the next cubicle.
Note:
◗ these measurements do not concern
the Static Switch Cubicle. The "battery"
button on the Static Switch Cubicle will
display the following message for a few
seconds:
COMMAND INVALID
STATIC SWITCH MODUL
◗ the available battery time value
blinks to attract attention;
◗ the battery temperature is displayed
only if the "Temperature Monitor" option
is installed.
Display of battery measurements
+–
UBAT.
V
AVAILABLE BAT.TIME
MN %KW LOAD =
REMAINING BAT.TIME
MN %KW LOAD =
see figure on next page
IBAT.
A
*
+–
+–
T° BAT.
°C
ou
+–
Note:
Stars appear in the battery backup time
display if the battery time estimator
function has not been validated by the
after-sales support technicians.
Direct access to the function by pressing the
"battery" button.
Battery voltage, charge current (+ sign) or
discharge current (- sign), battery temperature
(optional).
If Mains 1 is up - available battery time in the
event of a Mains 1 outage.
If Mains 1 is down or outside tolerances remaining battery time in minutes (real time
calculation).
6739380EN/JC - Page 43
Page 44

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
Display of battery measurements (cont.)◗ battery test: see figure opposite.
+–
BATTERY CHARGE
LEVEL=_ _ _%
+–
BATTERY LIFE
EXPECTANCY=_ _YEAR(S)
+–
MANUAL TEST?
*=YES =NO
*
AUTOMATIC TEST?
*=YES =NO
✴✴The screen opposite is displayed when a
battery test is requested. It indicates the battery
charge status and the remaining service life. A
manual or automatic test may be requested.
*
LAST TEST _W _D _H
BATTERY OK
+–
PARAMETERS?
*=YES =NO
*
WEEKS=_ _
=CONTINU *=VALID
*
DAYS=_ _
=CONTINU *=VALID
*
HOURS=_ _
=CONTINU *=VALID
*
BATTERY TEST ON
U DC=_ _ _V
The screen opposite is displayed following a
positive, automatic battery test. It indicates the
time since the last test and provides access to
test settings.
The screen opposite is displayed when the
user requests access to the automatic test
settings. It is possible to modify the interval
between two automatic tests.
The screen opposite is displayed during a
battery test, whether manual or automatic.
Page 44 - 6739380EN/JC
BATTERY OK
BATTERY NON OK
TEST ABANDONNED
CHECK THE ALARMS
The screen opposite is displayed when the
battery test cannot be completed.
Page 45

Inverter On/Off commands
"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
These commands may be accessed
only via the master display. When the
"I/O" button is pressed, the series of
screens in the figure opposite is
displayed.
Note:
◗ these commands do not concern the
Static Switch Cubicle. The "I/O" button
on the "static switch" cubicle produces
the message:
COMMAND INVALID
STATIC SWITCH MODUL
◗ the "I/O" button on a slave display
monitor produces the message:
COMMAND INVALID
ON SLAVE DISPLAY
◗ if the On/Off commands have not
been validated (by the after-sales
support technicians), pressing the "I/O"
button produces the message:
COMMAND INVALID
CONFIGURATION
Display for the inverter On/Off commands
or
START INVERTER ?
=YES >=ESCAPE
*
*
initial screen
STOP INVERTER ?
=YES >=ESCAPE
*
*
initial screen
◗ if a "Soft Tunor" session is in
progress (initiated by after-sales
support technicians), pressing the "I/O"
button produces the message:
Direct access to the function by pressing
the "I/O" button .
This screen is displayed if the inverter is already
off. It is a prompt to press the "*" button to
confirm start-up. During start-up, the following
screen is displayed:
PROCESSING
…
This screen is displayed if the inverter is on. It is
a prompt to press the "*" button to confirm
shutdown.
If the transfer to Mains 2 conditions are not
correct, the following screen is displayed a few
seconds:
COMMAND REFUSED
TRANSFER IMPOSSIBLE
Following confirmation of the command, the
system automatically returns to the initial
screen.
COMMAND INVALID
SOFT TUNOR
Language, display contrast and buzzer volume settings
These settings may be accessed by
pressing the "settings" button.
The series of screens in the figure
opposite is displayed.
Display of the settings selection screens
LANGUAGE = ENGLISH
=CONFIRM.
*
*
DISPLAY CONTRAST
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
*
BUZZER VOLUME
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
*
initial screen
Direct access to the function by pressing the
"settings" button.
Selection of the display language: English,
French, German, Italian, Spanish, Dutch,
Swedish, Finnish, Portuguese.
This screen is a prompt to set the display
contrast by successively pressing the ">" button.
When the setting is confirmed by pressing the
"*" button, the system goes on to the buzzer.
When this screen is displayed, the buzzer
automatically turns on. Press the ">" button
several times to adjust the volume. After
confirmation of the buzzer volume by the "*"
button, the system automatically returns to the
initial screen.
6739380EN/JC - Page 45
Page 46

"Monitor" alphanumeric display (cont.)
Display system configuration
This function may be accessed from
the initial screen. Press the "*" button,
followed by the "V" button in less than
one second.
Note:
◗ ensure that two "Monitor" or "Tele
Monitor" units do not receive the same
number;
◗ only one master "Tele Monitor" may
be installed on the display network;
◗ this function may be accessed only
with a password.
Display system configuration
initial screen
V
*
PASSWORD ?
=
DISPLAY = LOCAL
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
DISPLAY = MASTER
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
if display
is master
*
*
if display
is slave
This function may be accessed from the initial
screen. Press the "*" button, followed by the "V"
button in less than one second.
Enter the password (a combination of four
buttons among the control panel buttons). If the
password is incorrect, the system displays the
following screen for a few seconds:
INCORRECT
PASSWORD
then automatically returns to the initial screen.
Selection of the type of display: local ("Monitor")
or distant ("Tele Monitor"). If the display is
distant, the local buzzer is deactivated.
Selection of display role on the network: master
(only one display may be the master) or slave.
DISPLAY NUMBER =
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
CUBICLE N° = YES
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
initial screen
DISPLAY N° = YES
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
CUBICLE N° = YES
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
*
GIANT DISPLAY =YES
>=SELECT =CONFIRM.
initial screen
*
Selection of the slave display number (multidisplay installation) from 1 to 10.
Selection of the numbers of the cubicles that the
display must control. Ten cubicle numbers are
successively presented. Select "yes" if the
display is to control the cubicle or "no" if it does
not control the cubicle or if the cubicle does not
exist. Confirm using the "*" button. The system
goes on to the next cubicle number. Following
confirmation of the last cubicle number, the
system automatically returns to the initial
screen.
Selection of the numbers of the slave displays
controlled by the master display. Ten display
number are successively presented. Select
"yes" if the master display is to control the slave
display or "no" if it does not control the display
or if the display does not exist. Confirm using
the "*" button. The system goes on to the next
display.
Selection of the numbers of the cubicles
controlled by the display. Eight cubicle number
are successively presented. Select "yes" if the
display is to control the cubicle or "no" if it does
not control the cubicle or if the cubicle does not
exist. Confirm using the "*" button. The system
goes on the next screen.
Confirmation as to whether the installation is
equipped with a giant screen. Following
confirmation using the "*" button, the system
automatically returns to the initial screen.
Page 46 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 47

"LED" signalling box
Options
This unit remotes the basic elements of
information on system status:
◗ load on battery;
◗ low battery shutdown warning;
◗ inverter stop;
rie
tte
a
r b
su
t
n
e
m
nne
io
ct
n
Fo
ie
atter
b
o.
t
d'au
test
fin
e
rm
la
a
Pré
êt
l'arr
r à
leu
u
nd
O
bale
e glo
larm
A
◗ general alarm.
"Media Contacts 15" additional auxiliary transmission
An additional board may be installed on
all types of devices for the reception of
additional environment information and
the transmission of additional
information on the device status.
XR5 XR6 XR7XR9XR8
For further details on the information
received and transmitted, see the
"Environment information" section).
The position of the board is indicated in
figures 18, 19, 20, 21 and 23.
Used for basic remote monitoring, it
includes a buzzer with a reset button
and an indication light test button.
It is also equipped with a battery to
ensure correct operation in the event of
a power supply problem.
"Tele-Monitor" remote indications unit
This unit is the remote version of the
optional alphanumeric display installed
on the UPS or Static Switch Cubicles.
It offers the same functions (see the
"Monitor alphanumeric display"
section).
Two units may be remotely installed, in
which case:
◗ one unit is the master with all the
indications and control functions;
◗ the other is the slave with only
indications functions.
"GTC link" communications system
The "GTC link" is a communications
system comprising both hardware and
software for transmission to a computer
system, such as a Building and Energy
Management (BEM) system, of
information on the
TM
MGE
and reception of the On/off and self-test
remote controls.
GalaxyTM 6000 operating status
6739380EN/JC - Page 47
Page 48

Options (cont.)
"Vision" display
125 kVA
MGE GALAXY 6000 400 kVA
SALLE IQ
Home
Alarms
Online
Trend
Statistics
Normal AC
Rectifier
Battery
Inverter
Bypass AC
Bypass
Output
Set up
Load protected
Q1 Q5N
Q4S
0 Hour 50 Min.
Available Backup Time Load level
QF1
Q3BP
100%
50%
0
15:24:32 30/05/2005
Load
equipment
120%
100%
80%
50%
0
"Remote vision" display
125 kVA
MGE GALAXY 6000 400 kVA
SALLE IQ
Home
Alarms
Online
Trend
Statistics
Normal AC
Rectifier
Battery
Inverter
Bypass AC
Bypass
Output
Set up
Load protected
Q1 Q5N
Q4S
0 Hour 50 Min.
Available Backup Time Load level
QF1
Q3BP
100%
50%
0
15:24:32 30/05/2005
Load
equipment
120%
100%
80%
50%
0
The "Vision" display may be installed
in all types of cubicles (UPS or Static
Switch Cubicle).
Installed in a special enclosure, the
"Remote vision" display provides the
user with remote indications on system
status.
The "Vision" display can operate in two
different modes:
◗ mono-cubicle: the "Vision" display
monitors only the cubicle in which it is
installed;
◗ multi-cubicle: "Vision" display can
monitor all system cubicles (up to eight
maximum). In this mode, the system is
equipped with only one "Vision" display
which may be installed in any of the
cubicles.
Insulating and Mains 1, Mains 2 and load voltage matching transformer
This transformer may be used to match
Mains 2 voltage to that of the inverter,
to create galvanic insulation between
the load and the Mains or to create the
appropriate neutral system.
Harmonics filter and power factor improvement
This option, placed on the Mains 1
input upstream from the inverter,
reduces the reinjection of harmonic
currents into the mains. Harmonic
reinjection, produced by the rectifier/
charger, increases distortion on the
mains.
The amount of the increase depends
on the source impedance. The
reduction in distortion reduces the risk
of disturbing other sensitive loads
connected to the mains. The filter can
also increase the power factor
upstream from the inverter.
Three types of filter are available:
◗ uncompensated filter for the
advantages listed above;
◗ compensated filter for the
advantages listed above and to limit the
capacitive current absorbed by the filter
(additional inductance), in the event the
UPS is supplied by an engine generator
set;
◗ phase shift filter, an economical
solution to limit the reinjection of
harmonics on the mains.
Page 48 - 6739380EN/JC
Page 49

Double bridge rectifier-charger
Battery "Temperature Monitor"
This option reduces the reinjection of
harmonic disturbances into Mains 1,
but to a lesser extent than the
harmonics filter.
The double bridge rectifier-charger
replaces the
TM
MGE
input rectifier-charger.
An electronic PC-board measures the
battery temperature. The rectifier/
charger uses this information to adjust
the battery charge current to the
temperature in view of:
◗ optimizing battery recharge;
◗ obtaining maximum battery time;
◗ ensuring maximum battery life.
GalaxyTM 6000UPS's standard
Options (cont.)
Empty cubicles
Cubicles may be supplied empty, thus
enabling users to make up their own
auxiliary cubicles (battery cubicles or
other) or panels and meet the particular
demands of each installation. In this
way, the entire electrical installation will
have a uniform appearance.
6739380EN/JC - Page 49
Page 50

Page 50 - 6739380EN/JC
6739380EN-JC
 Loading...
Loading...