Page 1

Hunter Industrial
Pentium Processor™
Motherboard
Installation Guide
Page 2

Introduction
Contents
Introduction ...................................... V
Hunter Industrial - An Overview....................................... V I
Chapter 1 Pre-Configuration ............ 2
Handling Precautions ............................................................ 2
Static W arning ...................................................................... 2
Step 1 - Setting the Jumpers ............................ 4
Jumper Locations ................................................................. 5
Standard I/O Enable ............................................................. 6
Mouse IRQ Enable............................................................... 6
CMOS Reset ....................................................................... 6
I/O Port IRQ Selection ......................................................... 7
IDE Drives Selection ............................................................ 7
Clock Speed Selection ......................................................... 8
Display Selection .................................................................. 9
Cache Size ........................................................................... 9
Step 2 - DRAM, CPU and Cables Installation......10
Hunter Industrial Memory Configuration........................... 10
Installing Memory Modules ................................................. 10
CPU Installation ................................................................. 12
Installing Cables.................................................................. 14
Power and Control Panel Cables ........................................ 14
Installing Peripheral Cables ................................................. 17
Chapter 2 - W inBIOS Setup ............ 18
Starting WinBIOS Setup..................................................... 18
Using a Mouse with WinBIOS Setup .................................. 18
Using the Keyboard with WinBIOS Setup........................... 18
I
Page 3

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
W inBI OS Se tup Ma in Me nu ............................................... 19
Default Settings................................................................... 19
Section 1 - Setup............................................... 2 0
Standard Setup ................................................................ 20
Date/Time........................................................................... 20
Floppy Drive A, B .............................................................. 20
Pri Master/Pri Slave............................................................ 20
Sec Master/Sec Slave......................................................... 20
Configuring an MFM Drive ................................................. 20
User-Defined Drive ............................................................ 21
Configuring IDE Drives ....................................................... 21
Configuring a CD-ROM Drive ............................................ 22
Advanced Setup ............................................................... 22
Quick Boot ........................................................................ 22
BootUp Sequence .............................................................. 22
BootUp NumLock ............................................................. 22
Floppy Drive Swap ............................................................ 22
Floppy Drive Seek ............................................................. 23
Mouse Support .................................................................. 23
T ypematic Rate................................................................... 23
System Keyboard............................................................... 23
Primary Display .................................................................. 23
Password Check ................................................................ 23
OS/2 Compatible Mode ..................................................... 23
W ait For F1 if Error............................................................ 24
Press <F1> to continue....................................................... 24
Hit Del Message Display..................................................... 24
Hit <DEL> if you want to run Setup .................................... 24
Internal Cache .................................................................... 24
External Cache ................................................................... 24
System BIOS Shadow Cacheable....................................... 24
Chipset Setup................................................................... 25
Memory Hole ..................................................................... 25
DRAM Speed .................................................................... 25
IRQ12/M Mouse Function ................................................. 26
II
Page 4

Introduction
8-Bit I/O Recovery Time (SYSCLK).................................. 26
16-Bit I/O Recovery Time (SYSCLK)................................ 26
Power Management Setup............................................... 26
Power Management/APM .................................................. 26
Timeout (Minute) ................................................................ 26
Green PC Monitor Power State .......................................... 27
V ideo Power Down Mode.................................................. 27
Hard Disk Power Down Mode ........................................... 27
Hard Disk Timeout (Minute) ............................................... 27
Standby Timeout (Minute)................................................... 27
Suspend Timeout (Minute) .................................................. 28
Slow Clock Ratio ............................................................... 28
Display Activity .................................................................. 28
PCI/PnP Setup................................................................. 29
Plug and Play A ware OS .................................................... 29
PCI Burst Mode................................................................. 29
PCI Concurrency / PCI Latency Timer (in PCI Clocks)....... 29
PCI Streaming / PCI VGA Palette Snoop ........................... 30
PCI IDE Bus Master .......................................................... 30
Offboard PCI IDE Card ..................................................... 30
Offboard PCI IDE Primary IRQ ......................................... 30
Offboard PCI IDE Secondary IRQ..................................... 30
Reserved Memory Size....................................................... 31
Reserved Memory Address ................................................ 32
Peripheral Setup.............................................................. 32
Onboard FDC.................................................................... 32
Onboard Serial Port1 ......................................................... 32
Onboard Serial Port2 ......................................................... 32
On-board Parallel Port ....................................................... 32
Parallel Port Mode ............................................................. 33
Parallel Port DMA.............................................................. 33
Onboard PCI IDE .............................................................. 33
Section 2 - Utility .............................................. 3 4
Section 3 - Security .......................................... 3 4
Setting a Password ............................................................. 35
III
Page 5

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Changing a Password ......................................................... 35
Anti-V irus........................................................................... 36
Section 4 Default .............................................. 37
Original .............................................................................. 37
Optimal .............................................................................. 37
Fail-Safe ............................................................................ 37
Chapter 3 - Upgrading..................... 38
Upgrading the System Memory ........................................... 38
Upgrading the Microprocessor............................................ 38
Upgrading the Cache Memory ............................................ 38
Appendix A - Tech. Specifications .. 40
Appendix B - Flash Bios.................. 58
Appendix C - Troubleshooting ........ 60
Appendix D - Glossary of Terms..... 62
IV
Page 6

Introduction
Introduction
Thank you for your purchase of the Hunter Industrial system board. The
Hunter Industrial system board design was based on the Intel Triton™
chipset providing the ideal platform for getting the most power of the Intel
Pentium™ processor. With proper installation and maintenance, your
Hunter Industrial will provide years of high performance and trouble free
operation.
This manual provides a detailed explanation into the installation and use of
the Hunter Industrial system board. This manual is written for the novice
PC user/installer. However, as with any major computer component
installation, previous experience is helpful and should you not have prior
experience, it would be prudent to have someone assist you in the
installation. This manual is broken down into 3 chapters and 4 appendix.
Chapter 1 - System Board Pre-Configuration
This chapter provides all the necessary information for installing
the Hunter Industrial. Topics discussed include: Installing the
CPU (if necessary), DRAM installation, jumper settings for CPU,
cache and standard I/O. Connecting all the cables from the system
board to the chassis and peripherals.
Chapter 2 - BIOS Configuration
This chapter discusses the final step in getting your system up and
running - running the BIOS SETUP program.
Chapter 3 - Upgrading
The Hunter Industrial provides a number of expansion options
including memory and cache. All aspects of the upgrade possibilities are covered.
Appendix A - Technical Specifications
A complete listing of all the major technical specifications of the
Hunter Industrial is provided.
Appendix B - Flash BIOS Programming
Provides all the information necessary to program your optional
AMIBIOS Flash BIOS.
V
Page 7

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Appendix C - Troubleshooting
This Chapter lists the solutions for the most common questions
on the Hunter Industrial operation.
Appendix D - Glossary Of Terms
Static Electricity Warning!
The Hunter Industrial has been designed as rugged as possible but can still
be damaged if jarred sharply or struck. Handle the motherboard with care.
The Hunter Industrial also contains delicate electronic circuits that can be
damaged or weakened by static electricity. Before removing the Hunter
Industrial from its protective packaging, it is strongly recommended that
you use a grounding wrist strap. The grounding strap will safely discharged
any static electricity built up in your body and will avoid damaging the
motherboard. Do not walk across a carpet or linoleum floor with the bare
board in hand.
Hunter Industrial - An Overview
The Hunter Industrial represents the ultimate in system board technology.
No other system board available today provides such impressive list of
features:
CPU Support
Intel P54C Pentium™ Processor
AMD K5 Pentium™ Processor
CPU Clock Speeds
75, 90, 100, 120, 133, 150, 166 and 200MHz.
Supported Bus Clocks
50, 60 and 66 MHz.
VI
Page 8

Memory
32 or 36-bit JEDEC standard FPM or EDO SIMMS - 70ns minimum
access speed Memory capacity: 1 to 128MB.
High Speed DRAM Cache
256K of write-back direct-mapped asynchronous cache.
ROM BIOS
AMI© WinBIOS™ BIOS with optional FLASH ROM for easy
field upgrades.
On-Board I/O
• Up to 4 enhanced IDE drives: two PCI IDE controllers
• 2 Floppies up to 2.88 Mb
• Two high speed RS-232 serial ports 16Byte FIFO (16550)
• One Centronics™ compatible bidirectional parallel port
EPP/ECP mode compatible
• PS/2 mouse port
Introduction
Conventions Used in this Manual
When instructed to enter keyboard keystrokes, the text will be noted by:
Enter Keystroke
Information displayed on the screen other than figure is displayed as:
Enter Password
Information presented in a text box denotes special interest. There are two
types:
Important Information - such as static warnings, or
very important instructions
Notes - Such as a brief discussion of memory
types.
VII
Page 9

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Chapter 1
This chapter provides all the necessary information for installing the Hunter
Industrial into a standard PC chassis. The topics discussed ar: installing
the CPU (if necessary), DRAM installation, jumper settings for CPU, cache
and standard I/O.
Pre-Configuration
Handling Precautions
The Hunter Industrial has been designed to be as rugged as possible but
it can be damaged if dropped, jarred sharply or struck. Damage may also
occur by using excessive force in performing certain installation procedures
such as forcing the system board into the chassis or placing too much
torque on a mounting screw.
Take special care when installing or removing the system memory SIMMs.
Never force a SIMM into a socket. Screwdrivers slipping off a screw and
scraping the board can break a trace or component leads, rendering the
board unusable. Always handle the Hunter Industrial with care.
Special Warranty Note:
Products returned for warranty repair will be inspected for damaged caused by improper installation and misuse as described in the previous section and the static warning below. Should the board
show signs of abuse, the warranty will become void
and the customer will be billed for all repairs and
shipping and handling costs.
Static Warning
The Hunter Industrial contains delicate electronic semiconductors that are
highly sensitive to static electricity. These components, if subjected to a
static electricity discharge, can be weakened thereby reducing the serviceable life of the system board. BEFORE THE BOARD IS REMOVED FROM
ITS PROTECTIVE ANTISTATIC PACKAGING TAKE PROPER PRECAUTIONS! Work on a conductive surface that is connected to ground.
Before touching any electronic device, ground yourself by touching an
unpainted metal object or, and highly recommended, use a grounding strap.
1
Page 10

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Figure 1-1 Hunter Industrial System Board
Step 1 - Setting the Jumpers
Serial Ports
IDE
Interface
ISA Slots
Intel
Triton
Chipset
PS/2
Keyboard
Power
Connector
Parallel
Port
Floppy
Controller
Memory
Modules
AMIBIOS
2
Microprocessor
External
Cache
Auxiliary
Keyboard
Page 11

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Your Hunter Industrial is equipped with a large number of peripherals and
has the ability to run at a variety of speeds without the need to change any
crystals or oscillators. As such, there is a large number of configuration
jumpers on the board. Taken step by step, setting these jumpers is easy.
We suggest you review each section and follow the instructions.
Jumper Types
Jumpers are small copper pins attached to the system board. Covering two
pins with a shunt closes the connection between them. The Hunter
Industrial examines these jumpers to determine specific configuration
information. There are three different categories of jumpers on the Hunter
Industrial.
A. Two pin jumpers are used for binary selections such as enable,
disable. Instructions for this type of jumper are open, for no shunt
over the pins or closed, when the shunt covers the pins.
B . Three or four pin jumpers are used for multiple selection. Instruc-
tions for these jumpers will indicate which two pins to cover. For
example: for JPx 2-3 the shunt will be covering pins 2 and 3 leaving
pins 1 and 4 exposed.
C . Grouped Jumpers are used when a certain function has multiple
selections. There are two grouped jumpers on the board and
careful attention should be given when setting these jumpers.
Instructions for grouped jumpers are similar to those above Jumper Location and Pin Numbers.
3
Page 12

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Jumper Locations
Use the diagram below and the tables on the following pages to locate and
set the on-board configuration jumpers.
JP18
JP21
JP22
JP13 JP17
JP19
JP20
JP7
JP9
JP16
JP14
JP10
4
JP28
JP2
JP26
Page 13

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Standard I/O Enable
The Hunter Industrial standard I/O consists of the two serial ports, the
parallel port and floppy disk controller. Jumper JP17 is used to enable
or disable these ports.
Table 1-1 Standard I/O Enable
I/O Enable Disable
JP17 1-2* 2-3
Mouse IRQ Enable
The PS/2 type mouse port on your Hunter Industrial uses IRQ 12 as its
interrupt request line. To enable the interrupt (default) leave Jumper
JP10 on pins 2-3. To disable the interrupt and subsequently the mouse
controller, move the jumper to pins 1-2.
Table 1-2 Mouse IRQ Enable
IRQ12 Disable Enable
JP10 1-2 2-3*
CMOS Reset
This option is provided as a convenience for those who need to reset the
CMOS registers. It should always be set to “Normal” for standard
operation. If the CMOS needs to be reset turn off the system, move JP9
to 2-3, turn the system on, move JP9 back to 1-2 and reset the motherboard.
Table 1-3 CMOS Reset
RTC Normal Reset
JP9 1-2 2-3*
5
Page 14

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
I/O Port IRQ Selection
The parallel port and both serial ports must have their IRQs. Normally,
these settings can be left in their default settings and only when conflicts
arise should they be changed. Jumper JP20 is used to select the parallel
port IRQ. Jumper JP19 is used to select the first serial port's IRQ. Jumper
JP18 is used to select the second serial port's IRQ. Use Table 1-8 to select
the IRQs for these options.
Table 1-4 I/O Port IRQ Selection
Port Jumper 1-2 2-3 Open
Parallel Port JP20 IRQ 7* IRQ 5 Disable
First Serial
Port
Second Serial
Port
JP19 IRQ 4* IRQ 5 Disable
JP18 IRQ 3* IRQ 9 Disable
IDE Drives Selection
The Hunter Industrial supports up to 4 IDE drives:
2 IDE drives on the primary PCI IDE controller
2 IDE drives on the secondary PCI IDE controller
The IDE interfaces can be configured in the BIOS.
6
Page 15

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Clock Speed Selection
The jumpers JP2, JP7 and JP 26 allow you to choose the appropriate CPU
speed, without changing crystals and oscillators.
Table 1-5 Clock Frequency
Clock Frequency JP7
50MHz 1-2
60MHz 3-4
66MHz 5-6*
Table 1-6 Clock Speed Selection
50 MHz 60MHz 66Mhz JP2 JP26
75 90 100 1-2 1-2 1.5x
100 120 133 2-3 1-2 2.0x
150 180 200 1-2 2-3 3.0x
N/A 150 166 2-3 2-3 2.5x
Table 1-7 DMA Configuration for ECP Parallel Port
Port Jumper 1-2* 3-4 5-6 7-8
JP21 Disabled DMA 3 DMA 5 DMA 6
ECP
DMA
JP22 Disabled DMA 3 DMA 5 DMA 6
Always move Both jumpers (JP21 and JP22) together.
Multiplier
7
Page 16

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Display Selection
Select the type of display trough JP14, 1-2 for color and 2-3 for
monochrome.
Table 1-8 Display Selection
Display 1-2 2-3
JP14 Mono Color*
Cache Size
The jumper JP28 allows you to choose the cache size desired.
Table 1-9 Cache Size Selection
Cache Size 256K 512K
JP28 1-2* 2-3
Flash BIOS
The jumper JP13 allows you to choose the Flash BIOS setup.
Table 1-10 Flash BIOS Selection
Flash BIOS Intel 5V Flash
JP13 1-2* 2-3
8
Page 17

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Step 2 - DRAM, CPU and Cables
Installation
Depending upon how your Hunter Industrial is configured you may need
to install the following:
• DRAM (SIMMs)
• CPU
Hunter Triton Configuration
The Hunter Industrial uses standard or EDO 70ns access speed
or faster SIMMs. It is very important that the quality of the
SIMMs is good. Undesirable operation of the system may result
if poor quality SIMMs are used. Always purchase your memory
from a reliable source.
The Hunter Industrial uses standard 32 or 36-Bit
SIMMs. They are slight larger than other 9-Bit
SIMMs that are also commonly used on systems
boards. They are configured into four, 8-Bit (or 1
Byte) sections. Thus, a total of 32 Bits ( no parity)
or 36 Bits (with parity) are stored. This is often
confusing because these SIMMs are commonly
referred to as 256K by 32 or 36 or 1MB by 32 or 36.
To determine the actual capacity of the SIMM,
simply multiply the 256K, 512K or 1MB by 4. Thus
the actual SIMMS capacity is 1MB, 2MB and 4MB
respectively.
Installing Memory Modules
The Hunter Industrial has 4 memory module sockets. The order in wich
they should be populated is from the inside of the board outward. Note that
each socket is labeled: SM1, SM2, SM3, SM4. Refer to figure 1.3.
At least TWO memory modules MUST be installed
at a time.
9
Page 18

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
When inserting the memory modules, note the notch on the edge of each
module. This notch is designed to permit insertion in only one way. This
notch must be pointed towards the keyboard connector.
Start with the innermost socket (SM1). Gently place the module into the
desired socket at a 30-45° angle. Then gently rotate or rock the module
into an upright position. Never force a memory module into its
socket. Rather, double check the notch and gently rock it into place.
When the module has been properly installed, the metal latches on either
side of the memory module will “click” into place. (See figure 1-2).
Repeat the mentioned steps until all memory modules are installed. No
jumpers are involved in DRAM configuration.
Figure 1-2 SIMM Insertion
10
Gently place the SIMM into the desired socket
at 30°- 45° angle.
Then gently rotate or rock the SIMM into an
upright position. Never force a SIMM into
its socket.
Double check the notch and gently rock it into
place if properly installed the SIMM will "click".
Page 19

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
Figure 1-3 Memory Modules Socket Locations
SM1
SM2
SM3
SM4
Bank 0
Bank 1
CPU Installation
The Hunter Industrial currently supports the following CPUs:
• Intel P54C Pentium 75, 90, 100, 120, 150, 166 and 200MHz.
• AMD K5 75, 90, 100 and 133MHz.
1. Improper installation of the CPU may cause
permanent damage to both the system board and
the CPU. -- Void of warranty
2. Always handle the CPU by the edges, never
touch the pins.
3. Always use a heatsink and CPU fan.
11
Page 20

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Using Figure 1-4, locate the diagonal notch on the CPU chip. This notch
represents pin one. The Pentium processor also has small dot as well
indicating pin 1. DO NOT USE THE CHIP LOGO OR LETTERING
TO LOCATE PIN ONE.
Locate the CPU socket on your Hunter Industrial system board. Pin 1 on
the socket is located in the lower left hand corner of the socket.
Figure 1-4 CPU Alignment
To install the Pentium processor lift the lever of the ZIF socket and gently
insert the CPU. Make sure the CPU is inserted all the way. Lower the
lever. See figure 1-5.
Figure 1-5 CPU Socket alignment
Pin # 1 Lever
12
Page 21

Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
This completes the installation of the CPU. Now is a good time to double
check both the CPU and SIMM installation to make sure that these devices
have been properly installed.
Installing Cables
Power and Control Panel Cables
Figure 1-6 Power and Control Panel Cables
Orange - Power good
Red +5V
P8
P9
Yellow +12V
Blue -12V
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
White -5V
Red +5V
Red +5V
Red +5V
Connect the power supply cables to the system board. There is no formal
convention for color coding the wires on power supplies except for ground
wires which are black. Use figure above to determine the proper cable
locations.
Next install the control panel cables for each of the control panel headers.
These headers are located along the bottom of the board. Again, there is
no standard convention for color coding these cables. However, the
connectors for “Key lock/Power LED” and “Speaker” are keyed. While
the actual connector on the cable harness may not be keyed, there will
probably be a wire missing.
13
Page 22

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Figure 1-7 On-Board Connectors Location
J10 - Serial 2
IDE 2
PCI IDE 2
IDE1
PCI IDE 1
J11 - Serial 1
J5 - PS/2 Mouse
J6
Keyboard
P1
Power AT
J9
Floppy
J16
Speaker
J18
Power LED/
Kbd lock
J17
IDE LED
J15
Reset
J13
IR (optional)
J12
Parallel
J7
Aux.Keyboard
J19
CPU Fan +12V
14
Page 23

Table 1-11 Control Panel Connectors
Connector Description
J5 PS/2 mouse
J6 Keyboard
J7 Aux. Keyboard
J9 Floppy
J10 Serial 2
J11 Serial 1
J12 Parallel
J13 Infra Red Interface
J15 Reset
Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
J16
J17 IDE LED 1-positive/2-signal
J18
J19 CPU Fan 1&3-GND/2-12V
P1 AT Power
IDE 1 PCI IDE
IDE 2 PCI IDE
1-SPK/2-key/3-GND/4-VCC
Speaker
1-LED/2-key/3-GND/
4&5-keylock
15
Page 24

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Installing Peripheral Cables
Begin with the top of the Hunter Industrial system working left to right.
Refer Figure 1-1 for the locations of each of the peripheral connectors.
Now it is a good time to install the internal peripherals such as floppy and
hard disk drives. Do not connect the power cable to these peripherals as it
is easier to attach the bulky ribbon cables before the smaller power
connectors. If you are installing more than one IDE drive double check your
master/slave jumpers on the drives. Review the information supplied with
your drive for more information on this subject.
Connect the floppy cable (not included) to the system board. Then connect
remaining ends of the ribbon cable to the appropriate peripherals.
Finally, connect the IDE cable (not included) to the system. Then connect
remaining ends of the ribbon cable to the appropriate peripherals. This
concludes the hardware installation of your Hunter Industrial system.
Now it is a good time to re-check all of the cable connections to make
sure they are correct. It is also a good idea to label each of the external
peripheral connectors - COM1, COM2, Mouse and Parallel.
16
Page 25

User's Notes:
Chapter 1: Pre-Configuration
17
Page 26

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Chapter 2
WinBIOS Setup
Your Hunter Industrial features an AMI BIOS with available a new type of
system BIOS Setup utility. WinBIOS Setup has a graphical user interface
that permits mouse access, and is so compact that it can reside on the
same ROM as the system BIOS. The system configuration parameters are
set via WinBIOS Setup. Since WinBIOS Setup resides in the ROM BIOS,
it is available each time the computer is turned on.
Starting WinBIOS Setup
As POST executes, the following appears:
Hit <DEL> if you want to run SETUP
Using a Mouse with WinBIOS Setup
WinBIOS Setup has a built-in mouse driver and can be accessed
by either a serial or PS/2-type mouse.
Using the Keyboard with WinBIOS Setup
18
WinBIOS Setup has a built-in keyboard driver that uses simple
keystroke combinations:
Keystroke Function
<Tab> Move to the next window or field.
, , , Move to the next field to the right, left, above, or
below.
<Enter> Select in the current field.
+ Increments a value.
- Decrements a value.
<Esc> Closes the current operation and return to previous
level.
<PgUp> Returns to the previous page.
<PgDn> Advances to the next page.
<Home> Returns to the beginning of the text.
<End> Advances to the end of the text.
<Alt> <H> Access a help window.
<Alt> <Spacebar> Exit WINBIOS Setup.
Alphabetic keys A to Z are used in the Virtual Keyboard, and are not
case-sensitive.
Numeric keys 0 to 9 are used in the Virtual Keyboard and Numeric
Keypad.
Page 27

WinBIOS Setup Main Menu
The WinBIOS Setup main menu is organized into four windows.
Each window corresponds to a section in this chapter.
Each section contains several icons. Clicking on each icon
activates a specific function. The WinBIOS Setup icons and
functions are described in this chapter. Some options may not be
available in your BIOS. The sections are:
Setup: Described in Section 1. This section has five
icons that permit you to set system configura-
tions: standard setup, advanced setup, chipset
setup, power management setup and periph
eral setup.
Utilities: Described in Section 2. This section has two
icons that perform system functions.
Security: Described in Section 3. This section has three
icons that control WinBIOS security features.
Default: Described in Section 4. This section has
three icons that permit you to select a group of
settings for all WinBIOS Setup options.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Default Settings
Original: Returns settings to previous settings.
Optimal: These settings provide the best performance
Fail-Safe: These settings are more likely to configure a
characteristics.
workable computer when something is wrong.
If you cannot boot the computer successfully,
select the Fail-Safe WinBIOS Setup options
and try to diagnose the problem after the com-
puter boots. These settings do not provide
optimal performance.
19
Page 28

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Section 1Setup
WINBIOS Setup can have up to six separate screens. Different types of
system configuration parameters are set on each screen.
Standard Setup
Standard Setup options are displayed by choosing the Standard
icon from the WINBIOS Setup menu. All Standard Setup options
are described below.
Date/Time
Select the Date/Time option to change the date or time. The current
date and time are displayed. Enter new values through the displayed window.
Floppy Drive A, B
Choose the Floppy Drive A or B icon to specify the floppy drive
type. The settings are 360 KB 5¼”, 1.2 MB 5¼”, 720 KB 3½”,
1.44 MB 3½”, or 2.88 MB 3½”.
Pri Master Pri Slave
Sec Master Sec Slave
Choose these icons to configure the hard disk drive named in the
option. When you click on an icon, the following parameters are
listed: Type, LBA/Large Mode, Block Mode, 32Bit Mode, and PIO
Mode. All parameters relate to IDE drives except Type.
Configuring an MFM Drive
If configuring an old MFM hard disk drive, you must know the
drive parameters (number of heads, number of cylinders, number
of sectors, the starting write precompensation cylinder, and drive
capacity). Choose Type and choose the appropriate hard disk
drive type (1 - 46). If the drive parameters of your MFM drive do
not match any drive type listed, select User in the Type field and
enter the drive parameters on the screen that appears.
20
Page 29

User-Defined Drive
If you are configuring a SCSI drive or an MFM, RLL, ARLL, or ESDI
drive with drive parameters that do not match drive types 1-46, you
can select the User in the Type field. You must then enter the drive
parameters on the screen that appears. The drive
parameters include:
Cylinder (number of cylinders),
Hd (number of heads),
WP (starting write precompensation cylinder),
Sec (number of sectors),
Size (drive capacity).
Configuring IDE Drives
If the hard disk drive to be configured is an IDE drive, select the
appropriate drive icon (Pri Master, Pri Slave, Sec Master, or Sec
Slave). Select the IDE Detect icon to automatically detect all drive
parameters.
The BIOS automatically detects the IDE drive parameters (including ATAPI CD-ROM drives) and displays them. Click on the OK
button to accept these parameters Or you can set the parameters
manually if you are absolutely certain that you know the correct
IDE drive parameters.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
• Click on LBA/Large Mode and choose On to enable support
for IDE drives with capacities greater than 528 MB.
• Click on Block Mode and choose On to support IDE drives
that use Block Mode.
• Click on 32Bit Mode and click on On to support IDE drives
that permit 32-bit accesses.
• Click on PIO Mode to select the IDE Programmed I/O mode.
PIO programming also works with ATAPI CD-ROM drives.
The settings are Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5. Click on Auto to allow
the BIOS to automatically find the PIO mode that the IDE drive
being configured uses. If you select 0-5 you must make
absolutely certain that you are selecting the PIO mode
supported by the IDE drive being configured.
21
Page 30

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Configuring a CD-ROM Drive
Select the appropriate drive icon (Pri Master, Pri Slave, Sec Master,
or Sec Slave). Choose the Type parameter and select CDROM. You
can boot the computer from a CD-ROM drive. You can also choose
Auto and let the BIOS automatically set the correct drive parameters.
Advanced Setup
Advanced Setup options are displayed by choosing the Advanced icon from the WINBIOS Setup main menu. All Advanced
Setup options are described in this section.
Quick Boot
Set this option to Enabled to instruct the BIOS to boot quickly
when the computer is powered on. This option replaces the old
Above 1 MB Memory Test Advanced Setup option. The settings
are: enabled and disabled.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
BootUp Sequence
This option sets the sequence of boot drives (floppy drive A:, hard
disk drive C:, or a CD-ROM drive) that the BIOS attempts to boot
from after AMIBIOS POST completes. The settings are
C:,A:,CDROM, CDROM,A:,C:, or A:,C:, CDROM.
The default settings are C:,A:,CDROM.
BootUp NumLock
Set this option to Off to turn the Num Lock key off when the
computer is booted so you can use the arrow keys on both the
numeric keypad and the keyboard. The settings are On or Off. The
default settings are On.
Floppy Drive Swap
Set this option to Enabled to permit drives A: and B: to be
swapped. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The default
settings are Disabled.
22
Page 31

Floppy Drive Seek
Set this option to Enabled to specify that floppy drive A: will
perform a Seek operation at system boot. The settings are Dis-
abled or Enabled. The optimal and fail-safe default settings are
Disabled.
Mouse Support
When this option is set to Enabled, the BIOS supports a PS/2-type
mouse. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The default settings are Enabled.
Typematic Rate
This option specifies the speed at which a keyboard keystroke is
repeated. The settings are Fast or Slow. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Fast.
System Keyboard
This option specifies that a keyboard is attached to the computer.
The settings are Present or Absent. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Present.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Primary Display
This option specifies the type of display monitor and adapter in
the computer. The settings are Mono, CGA40, CGA80, EGA/VGA,
or Absent. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are EGA/
VGA.
Password Check
This option enables password checking every time the computer
is powered on or every time WINBIOS Setup is executed. If Always
is chosen, a user password prompt appears every time the computer is turned on. If Setup is chosen, the password prompt
appears if WINBIOS is executed.
The Optimal and Power-On defaults are Setup.
OS/2 Compatible Mode
Set this o ption to Enabled to permit the BIOS to run with IBM OS/
2. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The default settings are
Disabled.
23
Page 32

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Wait For F1 if Error
The BIOS POST error messages are followed by:
Press <F1> to continue
If this option is set to Disabled, the BIOS does not wait for you
to press the <F1> key after an error message. The settings are
Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are Enabled.
Hit Del Message Display
Set this option to Disabled to prevent the message
Hit <DEL> if you want to run Setup
from appearing on the first BIOS screen when the computer boots.
The settings are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Enabled.
Internal Cache
This option specifies the caching algorithm used for L1 internal
cache memory. The settings are: Disabled or Write Back (default).
External Cache
This option specifies the caching algorithm used for L2 secondary
(external) cache memory. The settings are:Disabled or Enabled
(default).
System BIOS Shadow Cacheable
When this option is set to Enabled, the contents of the F0000h
system memory segment can be read from or written to L2
secondary cache memory. The contents of the F0000h memory
segment are always copied from the BIOS ROM to system RAM
for faster execution. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The
Optimal default setting is Enabled. The Fail-Safe default is Dis-
abled.
24
Page 33

C000,16K Shadow
C400,16K Shadow
C800,16K Shadow
CC00,16K Shadow
D000,16K Shadow
D400,16K Shadow
D800,16K Shadow
C000,16K Shadow
These options control the location of the contents of the 16KB of
ROM beginning at the specified memory location. If no adaptor
ROM is using the named ROM area, this area is made available to
the local bus. The settings are: Enabled, Disabled and Cached.
In the BIOS for the Intel Triton chipset, the E000h page is used as
ROM during POST, but shadowing is disabled and the ROM CS#
signal is disabled to make the E000h page available on the local
bus.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Chipset Setup
Memory Hole
Use this option to specify an area in memory that cannot be
addressed on the ISA bus. The settings are Disabled, 512-640K
or 15-16MB. The default setting is Disabled.
DRAM Speed
Specify the RAS access speed of the SIMMs installed in the
motherboard as system memory. The settings are 60ns or 70 ns.
The default is 70ns.
25
Page 34

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
IRQ12/M Mouse Function
Set this option to Enabled to specify that IRQ12 will be used for
the mouse. The settings are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
8-Bit I/O Recovery Time (SYSCLK)
This option specifies the length of the delay (in SYSCLKs)
inserted between consecutive 8-bit I/O operations. The settings
are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are 1.
16-Bit I/O Recovery Time (SYSCLK)
This option specifies the length of the delay (in SYSCLKs)
inserted between consecutive 16-bit I/O operations. The settings
are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are 1.
Power Management Setup
Power Management Setup options are displayed by choosing the
Power Mgmt icon from the WINBIOS Setup main menu. All Power
Management Setup options are described in this section.
Power Management/APM
Set this option to Enabled to enable the power management and
APM (Advanced Power Management) features. The BIOS uses
the RTC Alarm function to wake the computer at a pre-specified
time. The settings are Enabled or Disabled or Instant On. The
default settings are Disabled.
Inst-On Timeout (Minute)
This option allow the stand by feature. Set the time from Disabled
up to 15 minutes. The default setting is Disabled.
26
Page 35

Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Green PC Monitor Power State
This option specifies the power management state that the
Green PC-compliant video monitor enters after the specified
period of display inactivity has expired. The settings are Off,
Standby, or Suspend. The default setting is Standby.
Video Power Down Mode
This option specifies the power management state that the video
subsystem enters after the specified period of display inactivity
has expired. The settings are Disabled, Standby, or Suspend.
The default settings are Disabled.
Hard Disk Power Down Mode
This option specifies the power management state that the hard
disk drive enters after the specified period of display inactivity
has expired. The settings are Disabled, Standby, or Suspend.
The default settings are Disabled.
Hard Disk Timeout (Minute)
This option specifies the length of a period of hard disk inactivity. When this period expires, the hard disk drive enters the
power-conserving mode specified in the Hard Disk Power
Down Mode option described on the previous page. The settings are Disabled, 1 Min (minutes), and all one minute intervals
up to and including 15 Min. The default settings are Disabled.
Standby Timeout (Minute)
This option specifies the length of the period of system inactivity when the computer is in Full-On mode before the computer
is placed in Standby mode. In Standby mode, some power use is
curtailed. The settings are Disabled, 1 Min, 2 Min, and all one
minute intervals up to and including 15 Min. The default settings
are Disabled.
27
Page 36

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Suspend Timeout (Minute)
This option specifies the length of the period of system inactivity
when the computer is already in Standby mode before the computer is placed in Suspend mode. In Suspend mode, nearly all
power use is curtailed. The settings are Disabled, 1 Min, 2 Min,
and all one minute intervals up to and including 15 Min. The default
settings are Disabled.
Slow Clock Ratio
This option specifies the speed at which the system clock runs in
power saving modes. The settings are expressed as a ratio
between the normal clock speed and the power down clock speed.
The settings are 1:1, 1:2 (half as fast as normal), 1:4 , 1:8, 1:16,
1:32, 1:64, or 1:128. The default setting is 1:8.
Display Activity
This option specifies if the BIOS is to monitor activity on the
display monitor for power conservation purposes. When this
options set to Monitor and there is no display activity for the
length of time specifed in the value in the Full-On to Standby
Timeout (Min) option, the computer enters a power saving state.
The settings are Monitor or Ignore. The default settings are
Ignore.
IRQ 3 - Monitor
IRQ 4 - Monitor
IRQ 5 - Ignore
IRQ 7 - Monitor
IRQ 9 - Ignore
IRQ 10 - Ignore
IRQ 11 - Ignore
IRQ 12 - Monitor
IRQ 13 - Ignore
IRQ 14 - Monitor
28
Page 37

IRQ 15 - Monitor
These options enable event monitoring. When the computer is in
a power saving mode, activity on the named interrupt request line
is monitored by the BIOS. When any activity occurs, the computer
enters Full On mode.
Each of these options can be set to Monitor or Ignore. The default
setting for all options are as above indicated.
PCI/PnP Setup
PCI/PnP Setup options are displayed by choosing the PCI/PnP
Setup icon from the WINBIOS Setup main menu. All PCI/PnP
Setup options are described in this section
Plug and Play Aware OS
Set this option to Yes if the operating system installed in the
computer is Plug and Play-aware. The BIOS only detects and
enables PnP ISA adapter cards that are required for system boot.
The Windows 95 operating system detects and enables all other
PnP-aware adapter cards. Windows 95 is PnP-aware. Set this
option to No if the operating system (such as DOS, OS/2, Windows 3.x) does not use PnP. You must set this option correctly or
PnP-aware adapter cards installed in your computer will not be
configured properly. The settings are No or Yes. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are No.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
PCI Burst Mode
Set this option to Enabled to enable PCI burst mode. The settings
are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal default setting is Enabled.
The Fail-Safe default setting is Disabled.
PCI Concurrency
PCI Latency Timer (in PCI Clocks)
This option sets latency of all PCI devices on the PCI bus. The
settings are in units equal to PCI clocks. The settings are 32, 64,
96, 128, 160, 192, 224, or 248. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default
settings are 64.
29
Page 38

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
PCI Streaming
PCI VGA Palette Snoop
This option must be set to Enabled if any ISA adapter card
installed in the computer requires VGA palette snooping. The
settings are Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Disabled.
PCI IDE Bus Master
Set this option to Enabled to specify that the IDE controller on the
PCI local bus has bus mastering capability. The settings are
Disabled or Enabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are Disabled.
Offboard PCI IDE Card
This option specifies if an offboard PCI IDE controller adapter card
is used in the computer. You must also specify the PCI expansion
slot on the motherboard where the offboard PCI IDE controller
card is installed. If an offboard PCI IDE controller is used, the
onboard IDE controller on the motherboard is automatically
disabled. The settings are Erase, Auto, Slot1, Slot2, Slot3, or
Slot4.
If Auto is selected, AMIBIOS automatically determines the correct
setting for this option. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings
are Auto.
In the AMIBIOS for the Intel Triton chipset, this option forces IRQ
14 and 15 to a PCI slot on the PCI local bus. This is necessary to
support non-compliant PCI IDE adapter cards.
Offboard PCI IDE Primary IRQ
This option specifies the PCI interrupt used by the primary IDE
channel on the offboard PCI IDE controller. The settings are
Disabled, INTA, INTB, INTC, INTD, or Hardwired. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
Offboard PCI IDE Secondary IRQ
This option specifies the PCI interrupt used by the secondary IDE
channel on the offboard PCI IDE controller. The settings are
Disabled, INTA, INTB, INTC, INTD or Hardwired. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
30
Page 39

IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ7
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
IRQ14
IRQ15
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
These options specify the bus that the named interrupt request
lines (IRQs) are used on. These options allow you to specify IRQs
for use by legacy ISA adapter cards.
These options determine if the BIOS should remove an IRQ from
the pool of available IRQs passed to BIOS configurable devices.
The available IRQ pool is determined by reading the ESCD
NVRAM (Flash BIOS ROM only). If more IRQs must be removed
from the pool, the end user can use these PCI/PnP Setup options
to remove the IRQ by assigning the option to the ISA/EISA setting.
Onboard I/O is configurable by AMIBIOS. The IRQs used by
onboard I/O are configured as PCI/PnP.
The settings are PCI/PnP or ISA/EISA. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are ISA/EISA and IRQ14 and IRQ 15 PCI/PnP.
Reserved Memory Size
This option specifies the size of the memory area reserved for
legacy ISA adapter cards.
The settings are Disabled, 16K, 32K, or 64K. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
31
Page 40

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Reserved Memory Address
This option specifies the beginning address (in hex) of the
reserved memory area. The specified ROM memory area is reserved for use by legacy ISA adapter cards.
The settings are C0000, C4000, C8000, CC000, D0000, D4000,
D8000, or DC000. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are
C0000.
Peripheral Setup
Peripheral Setup options are displayed by choosing the Peripheral
Setup icon from the WINBIOS Setup main menu. All Peripheral
Setup options are described in this section.
Onboard FDC
This option enables the floppy drive controller on the motherboard.
The settings are Enabled, Disabled or Auto. The Optimal default
setting is Auto. The Fail-Safe default setting is Auto.
Onboard Serial Port1
This option enables serial port 1 on the motherboard and specifies
the base I/O port address for serial port 1.
The settings are Auto, 3F8h, 2F8, 3E8, 2E8 or Disabled. The
Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Auto.
Onboard Serial Port2
This option enables serial port 2 on the motherboard and specifies
the base I/O port address for serial port 2.
The settings are Auto, 3F8h, 2F8, 3E8, 2E8 or Disabled. The
Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Auto.
On-board Parallel Port
This option enables the parallel port on the motherboard and
specifies the parallel port base I/O port address. The settings are
Auto, 378h, 278h, 3BC, or Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default setting are Auto.
32
Page 41

Parallel Port Mode
This option specifies the parallel port mode. ECP and EPP are both
bi-directional data transfer schemes that adhere to the IEEE P1284
specifications. The settings are: Normal, Bi-Directional, EPP,
ECP.
Parallel Port DMA
This option is only available if the setting for the Parallel Port
Mode option is ECP.
The settings are Disabled, DMA CH (channel) 0, DMA CH 1, or
DMA CH 3. The default setting is Disabled.
Refer to Hardware Jumper settings on Chapter
one for JP 21 and JP22 when setting for these
options.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Onboard PCI IDE
This option specifies the onboard IDE controller channels that will
be used. The settings are Primary, Secondary, Both, or Disabled.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Primary.
33
Page 42

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Section 2Utility
The following icons appear in this section:
Detect IDE and
Language
Detect IDE
This option allows the detection of an IDE hard drive automatically.
Language
English support only.
Section 3Security
AMIBIOS Password Support
Three icons appear in this part of the WINBIOS Setup screen:
Supervisor,
User,
Anti-Virus.
Two Levels of Passwords
Both the Supervisor and the User icons configure password
support. If you use both, the Supervisor password must be set
first. The system can be configured so that all users must enter a
password every time the system boots or when WINBIOS Setup
is executed, using either or both the Supervisor password or User
password.
34
Page 43

Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
If You Do Not Want to Use a Password
Just press <Enter> when the password prompt appears.
Setting a Password
The password check option is enabled in Advanced Setup by
choosing either Always (the password prompt appears every time
the system is powered on) or Setup (the password prompt appears
only when WINBIOS is run). The password is stored in CMOS
RAM. The following screen appears when you select the password icon from the WINBIOS Setup main menu.
You can enter a password by:
Typing the password on the keyboard or
Selecting each letter via the mouse.
When you select Supervisor or User, the BIOS prompts for a
password. You must set the Supervisor password before you can
set the User password. Enter a 1 – 6 character password. The
password does not appear on the screen when typed. Make sure
you write it down. If you forget it, you must drain CMOS RAM and
reconfigure the system.
Changing a Password
Select the appropriate password icon (Supervisor or User) from
the Security section of the WINBIOS Setup main menu. Enter the
password and press <Enter>. The screen does not display the
characters entered. After the new password is entered, retype the
new password as prompted and press <Enter>.
If the password confirmation is incorrect, an error message appears. If the new password is entered without error, press <Esc>
to return to the WINBIOS Main Menu. The password is stored in
CMOS RAM after WINBIOS completes. The next time the system
boots, you are prompted for the password if the password
function is present and is enabled.
35
Page 44

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Remember the Password
Keep a record of the new password when the password is
changed. If you forget the password, you need to reset the CMOS
memory (refer to JP 9 on jumper settings - chapter 1)
Anti-Virus
When this icon is selected from the Security section of the
WINBIOS Setup main menu, the BIOS issues a warning when any
program (or virus) issues a Disk Format command or attempts to
write to the boot sector of the hard disk drive. The settings are
Enabled or Disabled. If enabled, the following appears when a
write is attempted to the boot sector. You may have to type N
several times to prevent the boot sector write.
Boot Sector Write!!!
Possible VIRUS: Continue (Y/N)? _
The following appears after any attempt to format any cylinder,
head, or sector of any hard disk drive via the BIOS INT 13 Hard Disk
Drive Service:
36
Format!!!
Possible VIRUS: Continue (Y/N)? _
Page 45

Section 4 Default
The icons in this section permit you to select a group of settings
for all WINBIOS Setup options. Not only can you use these icons
to quickly set system configuration parameters, you can choose
a group of settings that have a better chance of working when the
system is having configuration-related problems.
Original
Choose the Original icon to return to the system configuration
values present in WINBIOS Setup when you first began this
WINBIOS Setup session.
Optimal
You can load the optimal default settings for the WINBIOS by
selecting the Optimal icon. The Optimal default settings are bestcase values that should optimize system performance. If CMOS
RAM is corrupted, the Optimal settings are loaded automatically.
Chapter 2: Bios Configuration
Fail-Safe
You can load the Fail-Safe WINBIOS Setup option settings by
selecting the Fail-Safe icon from the Default section of the
WINBIOS Setup main menu.
The Fail-Safe settings provide far from optimal system performance, but are the most stable settings. Use this option as a
diagnostic aid if the system is behaving erratically.
37
Page 46

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Chapter 3: Upgrading
Upgrading the System Memory
The Hunter Industrial allows an upgrade of the system memory up to
128MB, using SIMMs memory modules. Please refer to chapter one for
proper memory installation.
Upgrading the Microprocessor
The Hunter Industrial currently supports the following CPUs:
-Intel P54C Pentium 75, 90, 100, 120, 150, 166 and 200MHz.
-AMD K5 Pentium Processor 75, 90, 100 and 133MHz
To upgrade the Microprocessor, please refer to Chapter 1 for proper
installation and jumper settings.
38
Page 47

User's Notes:
Chapter 3: Upgrading
39
Page 48

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Appendix A
Chip Sets
Core Logic
Intel Triton 430FX Chip-Set
Peripheral I/O
Chips & Technologies 735A or
Standard microsystems FDC37C665
Micro Processor Support
-Intel 3.3V Pentium processors 75, 90, 100, 120, 133, 150, 166,
and 200MHz
-AMD K5 Pentium processors 75, 90, 100, 120, 133, 166MHz
System Memory
Technical
Specifications
Memory Capacity
1 to 128MB of FPM or EDO DRAM memory.
Memory Type
Four sockets for JEDEC compatible (72 pin) 32 bit SIMMs, 70ns
access speed or faster. All memory configurations is automatic
through BIOS.
Supports FPM and EDO memories.
36 bit SIMMS can be used, but parity is not supported
Cache Memory
Cache on board with 256K asynchronous cache SRAMS.
40
Page 49

Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Bios
System BIOS
AMI WinBIOS with standard CMOS Setup, Peripheral Setup,
Power Management, Automatic Hard Disk Detection and Advanced Chip-set Setup.
Flash BIOS
Optional feature for System BIOS. Flash programming done
through BIOS
Embedded Interfaces
IDE
Two PCI EIDE controllers. Supports up to 4 devices
Floppy
Up to two floppy disk drives. Sizes supported are: 5.25" 360K and
1.2MB; 3.5" 720K, 1.44MB and 2.88MB. Floppy Tape and CD ROM
compatible. 34 pin header on-board.
Serial Ports
Two high speed 16550 compatible UARTS.
BIOS configurable as COM1 - 4.
Parallel Port
One Centronics compatible, bi-directional (PS/2 compatible).
Microsoft/HP EPC/EPP high speed.
Mouse Port
One PS/2 compatible mouse controller with 6 pin mini-din connector cable.
Expansion Slots
Seven 16 bit ISA slots.
41
Page 50

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Miscellaneous
CMOS/Battery
RTC with lithium battery. No external battery is required.
Control Panel Connections
Reset, Keylock, Speaker, CPU fan (12V). LEDs for power and IDE.
CPU Socket
Standard ZIF (Zero Insertion Force), socket 7.
Form Factor
Baby AT Size - 8.6" x 13"
PCB Construction
Four Layer, dry film mask.
Manufacturing Process
Automated surface mount.
Reliability
MTBF: Higher than 48.000 hours
Environmental Operating Non-Operating
Temperature 0 to +55 -40 to +65 C
Humidity
Shock 2.5G @ 10ms 10G 10ms
Vibration 0.25 @ 5-100Hz 5G @ 5-100Hz
5 to 95% @ 40 C
non-condensing
5 to 95% @ 40 C
non-condensing
42
Page 51
Appendix A: Technical Specifications
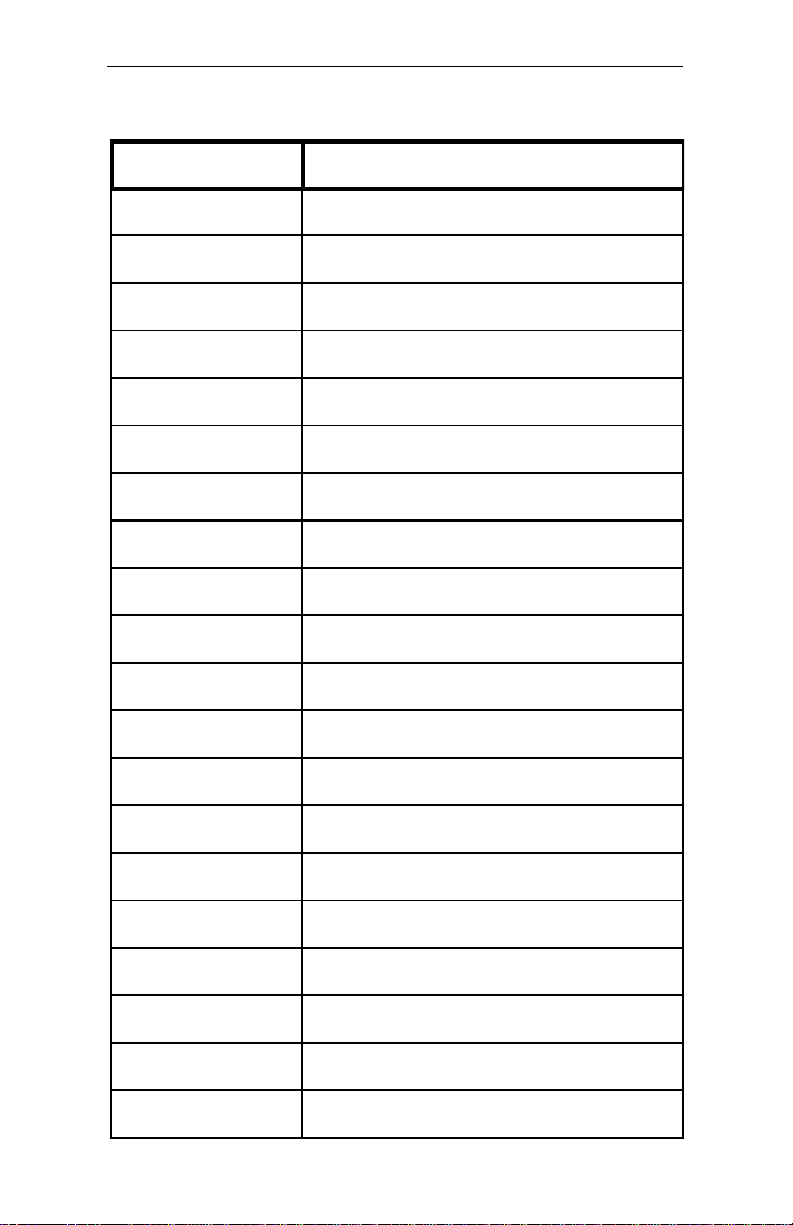
Table A-1 Standard PC-AT I/O Map
Address (HEX) Device
000-01F DMA Controller
020-03F Interrupt Controller 1
040-05F Timer
070-07F
080-09F DMA Page Registers
0A0-0BF Interrupt Controller 2
0C0-0DF DMA Controller 2
0F8-0FF Math co-processor
1F0-1FF Hard Disk Controller
200-207 Game I/O
278-27F Prototype Card
2F8-2FF Serial Port 2
300-31F Parallel Printer Port
380-38F SDLC Bisynchronous 2
3B0-3AF Bisynchronous 1
3B0-3BF Monochrome Display/Printer
Real Time Clock (non-maskable interrupt)
3C0-3CF (Reserved)
3D0-3DF Color Graphics Display Adapter
3F0-3F7 Floppy Disk
3F8-3FF Serial Port COM1
43
Page 52

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Table A-2 DMA Page Register and I/O address
Channel Function
Page Register I/O Hex Address
Channel 0 87
Channel 1 83
Channel 2 81
Channel 3 82
Controller 2: 16-bit (at Only - ports 0C0-0DF)
Channel 5 8B
Channel 6 89
Channel 7 8A
Refresh (AT) 8F
Table A-3 DMA Assignments
Channel Function
0 Reserved
1 SDLC
2 Floppy Disk
3 Spare
4 Cascade for CTRL
5 Spare (Reserved)
6 Spare (Reserved)
7 Spare (Reserved)
44
Page 53
Appendix A: Technical Specifications
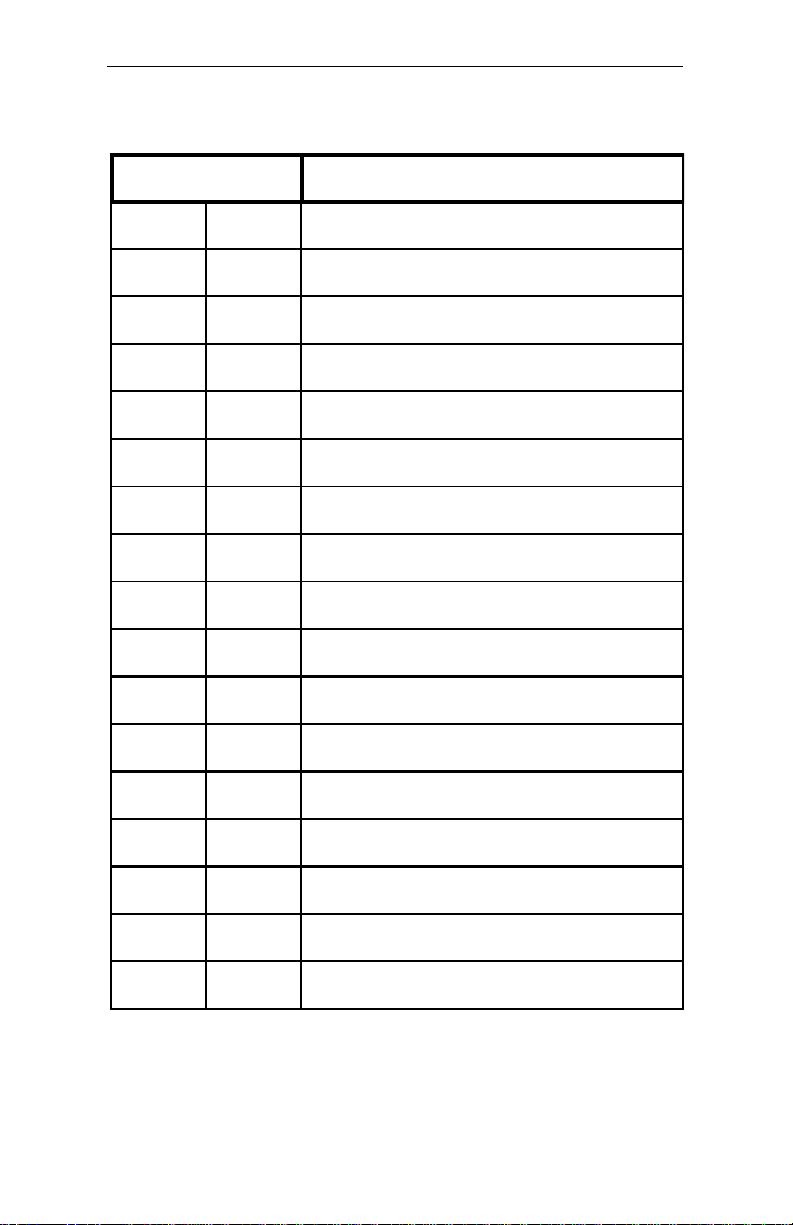
Table A-4 DMA Controller Register
DMA # Description
1 2
0 0C0 CH0 base and current address
1 0C2 CH0 base and current word count
2 0C4 CH0 base and current address
3 0C6 CH0 base and current word count
4 0C8 CH0 base and current address
5 0CA CH0 base and current word count
6 0CC CH0 base and current address
7 0CE CH0 base and current word count
8 0D0
9 0D2 Write request register
00A 0D4 Write single mask request register bit
00B 0D6 Write mode register
00C 0D8 Clear byte pointer Flip/Flop
00D 0DA
00E 0DC Clear mask register
00F 0DE Write all mask register bits
Read status register/write command register
Read temporary register / Write master clear
45
Page 54

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Table A-5 Interrupts
Channel Name Function
NMI NMI Parity
0 IRQ0 System Timer Output 0*
1 KYBIRQ Keyboard Output Buffer Full
2 IRQ2 CTRL2 Interrupt (IRQ8-IRQ15)
3 IRQ3 Serial Port 2 (COM2)
4 IRQ4 Serial Port 1 (COM1)
5 IRQ5 Parallel Port 2
6 IRQ6 Floppy Disk Controller
7 IRQ7 Parallel Port 1
8 RTCIRQ Real Time Clock
9 IRQ9
10 IRQ10
11 IRQ11
Available
Available
Available
12 IRQ12 PS/2 Mouse
13 IRQ13 Math Coprocessor
14 IRQ14 Primary IDE
15 IRQ15
Secondary IDE
46
Page 55

Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Connectors Pin Outs
Table A-6 Serial Connectors
Pin# Name
1 -DCD
2 -DSR
3 RXD
4 -RTS
5 TXD
6 -CTS
7 -DTR
8 -RI
9 GND
10 N/C
47
Page 56

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Table A-7 Floppy Disk Drive Connector
Pin# Name
2 RMP/LC
4 N/C
6 IDO
8 -INDEX
10 -MTRO
12 -DRV1
14 -DRVO
16 -MTR1
18 DIR
48
20 -STEP
22 -WDATA
24 -WGATE
26 -TRK0
28 -WPRT
29 ID0
30 -RDATA
32 HDSEL
33 ID1
34 DSKCHG
* GND
Page 57

Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Table A-8 Parallel DB25 Connector
Pin# Name
1 -STROBE
2 +DATA BIT 0
3 +DATA BIT 1
4 +DATA BIT 2
5 +DATA BIT 3
6 +DATA BIT 4
7 +DATA BIT 5
8 +DATA BIT 6
9 +DATA BIT 7
10 ACK1
11 BUSY
12 PAPER EMPTY
13 SLCT
14 AUTOFEED
15 ERROR
16 INIT
17 SLCT IN
18-25 GND
49
Page 58
Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
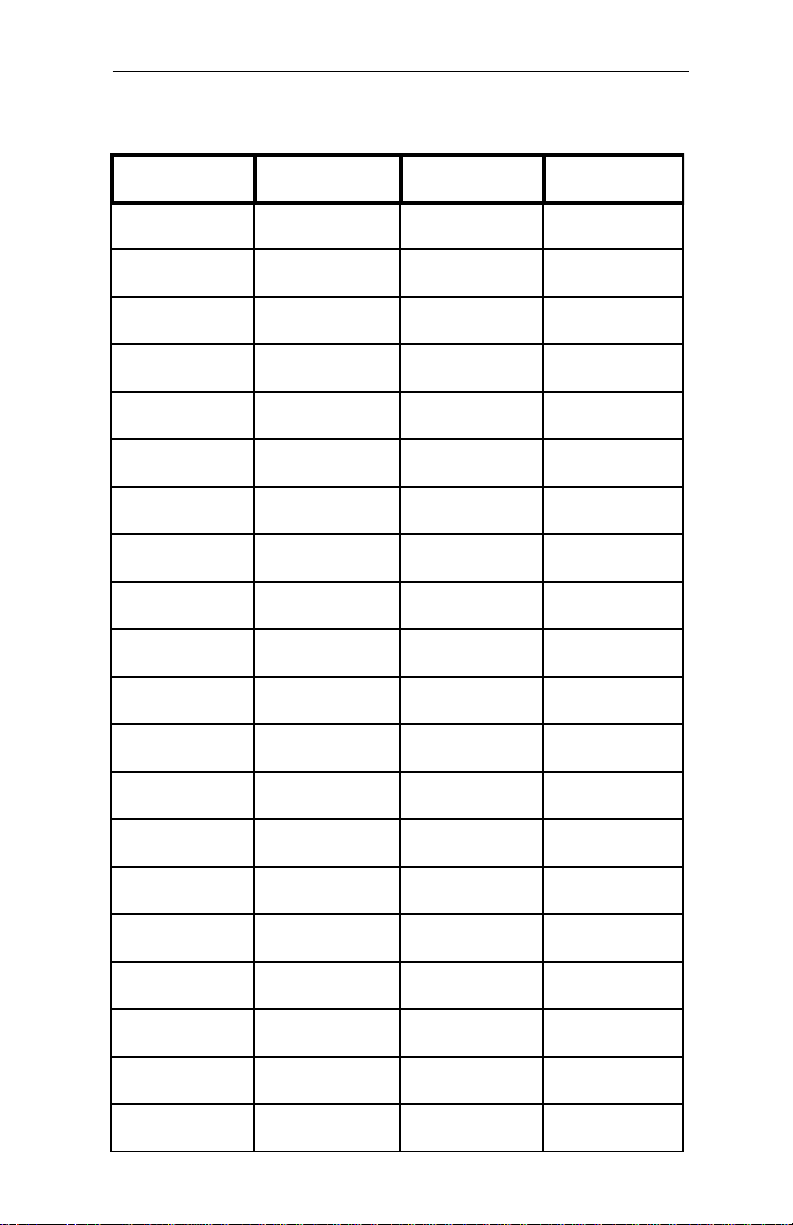
Table A-9 IDE Connector
Pin# Name Pin# Name
1 -RST 21 N/C
2 GND 22 GND
3 D7 2 IOW
4 D8 3 GND
5 D6 24 IOR
6 D9 25 GND
7 D5 26 N/C
8 D10 27 BALE
9 D4 28 N/C
50
10 D11 29 GND
11 D3 30 IRQ14
12 D12 31 IO16
13 D2 32 SAI
14 D13 34 N/C
15 D1 35 SA0
16 D14 36 SA2
17 D0 37 CS0
18 D15 38 CS1
19 GNC 39 HDIND
20 N/C 40 N/C
Page 59

Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Table A-10 PS/2 Mouse Connector
Pin# Name
1 DATA
2 N/C
3 GND
4 +5V
5 CLOCK
6 N/C
Table A-11 Serial Port Cable Wire List
Pin# Signal Pin# 9 Pin
1 -DCD 8 1
2 -DSR 6 6
3 RXD 3 2
4 -RTS 4 7
5 TXD 2 3
6 -CTS 5 8
7 -DTR 20 4
8 -RI 22 9
9 GND 7 5
10 N/C N/C N/C
51
Page 60
Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
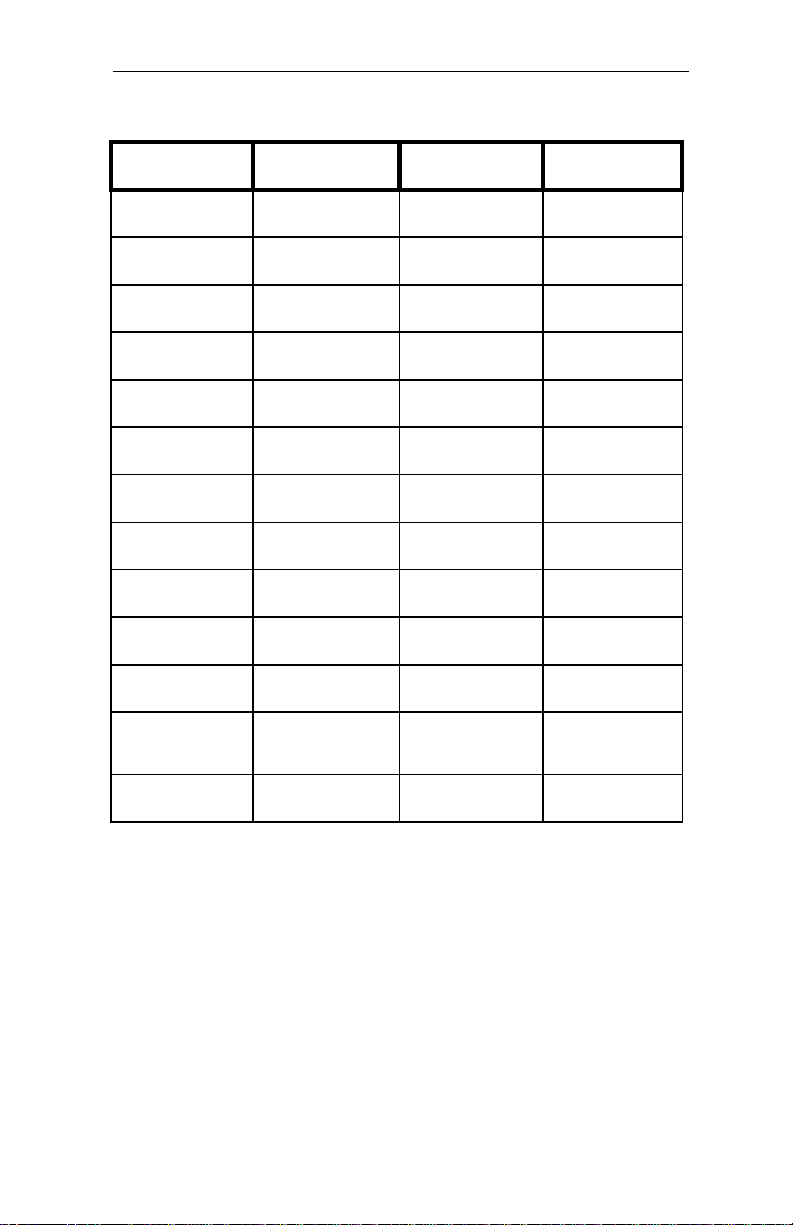
Table A-12 Parallel Port Connector
Pin# Name Pin# Name
1 -STROBE 2 AUTOFEED
3 +DATA BIT 0 4 ERROR
5 +DATA BIT 1 6 INIT
7 +DATA BIT 2 8 SLCT IN
9 +DATA BIT 3 10 GND
11 +DATA BIT 4 12 GND
13 +DATA BIT 5 14 GND
15 +DATA BIT 6 16 GND
17 +DATA BIT 7 18 GND
52
19 ACK 20 GND
21 BUSY 22 GND
23
25 SLCT 26 N/C
PAPER
EMPTY
24 GND
Page 61

Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Table A-13 PCI Connector Pin Assignments
Pin# Assign. Pin# Assign.
A01 TRST# A32 AD16
A02 +12V A33 --A03 TMS A34 FRAME#
A04 TDI A35 GND
A05 +5V A36 TRDY#
A05 INTA# A37 GND
A06 INTC# A38 STOP#
A07 +5V A39
A08 CLKC A40 SDONE
A09 +5V A41 SB0#
A10 CLCKD A42 GND B11 GNT3# B42 SERR#
A11 GND A43 PAR B12 GND B43 ---A12 GND A44 AD15 B13 GND B44 C/BE1#
A13 GNT1# A45 ---- B14 CLKA B45 AD14
A14 RST# A46 AD13 B15 GND B46 GND
A15 +5V (I/O) A47 AD11 B16 CLKB B47 AD12
Pin# Assign Pin# Assign.
B01 -12V B32 ad17
B02 TCK B33 C/BE2#
B03 GND B34 GND
B04 TDO B35 IRDY#
B05 +5V B36 ---B06 +5V B37 DEVSEL
B07 INTB# B38 GND
---- B08 INTD# B39 LOCK#
B09 REQ3# B40 PERR#
B10 REQ1#1 B41 ----
A16 GNT0# A48 GND B17 GND B48 AD10
A17 GND A49 AD09 B18 REQ0# B49 GND
A18 REQ2# A50 KEY B19 +5V(I/O) B50 KEY
A19 AD30 A51 KEY B20 AD31 B51 KEY
A20 ---- A52 C/BE0# B21 AD29 B52 AD08
A21 AD28 A53 ---- B22 GND B53 AD07
A22 AD26 A54 AD06 B23 AD27 B54 ---A23 GND A55 AD04 B24 AD25 B55 AD05
53
Page 62
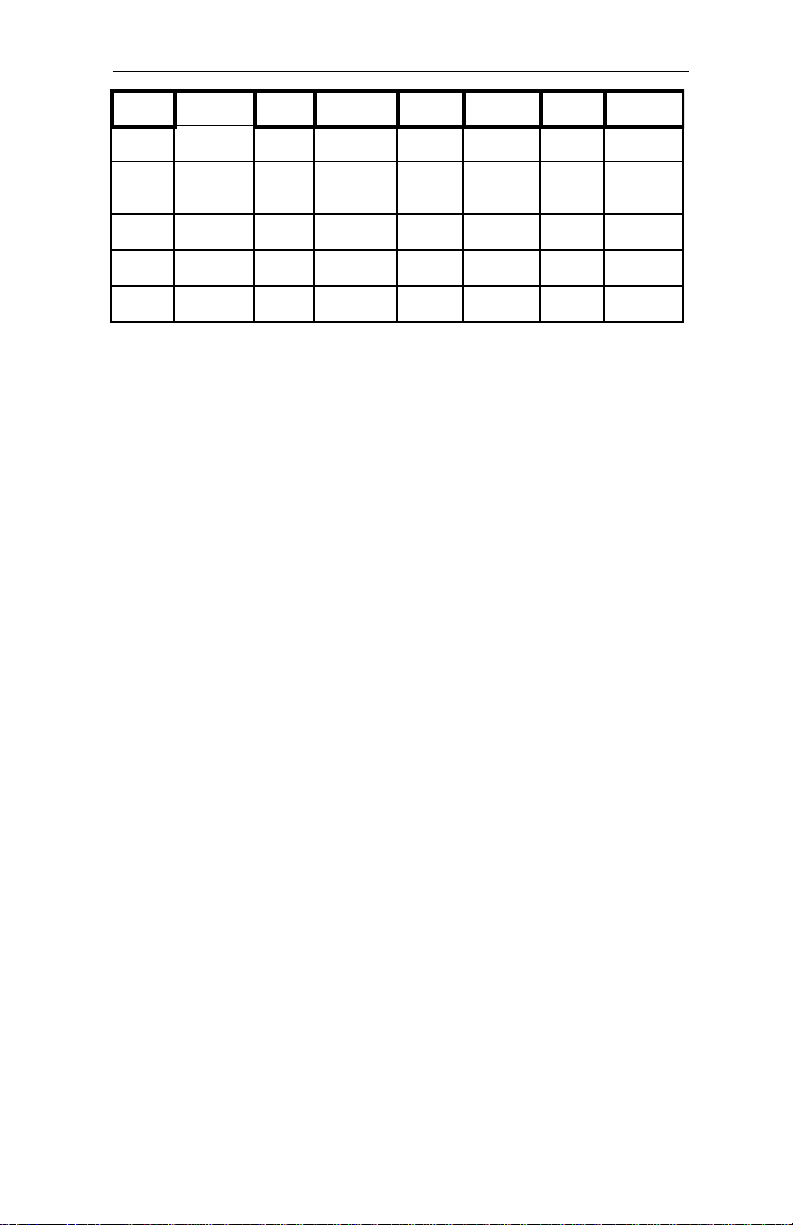
Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Pin# Assign. Pin# Assign. Pin# Assign Pin# Assign.
A26
----
A58 AD00 B27 AD23 B58 AD01
A27 AD22 A59 +5V (I/O) B28 GND B59
A29 AD20 A60 REQ64# B29 AD21 B60 ACK64#
A30 GND A61 +5V B30 AD19 B61 +5V
A31 AD18 A62 +5V B31
----
B62 +5V
+5V
(I/O)
54
Page 63
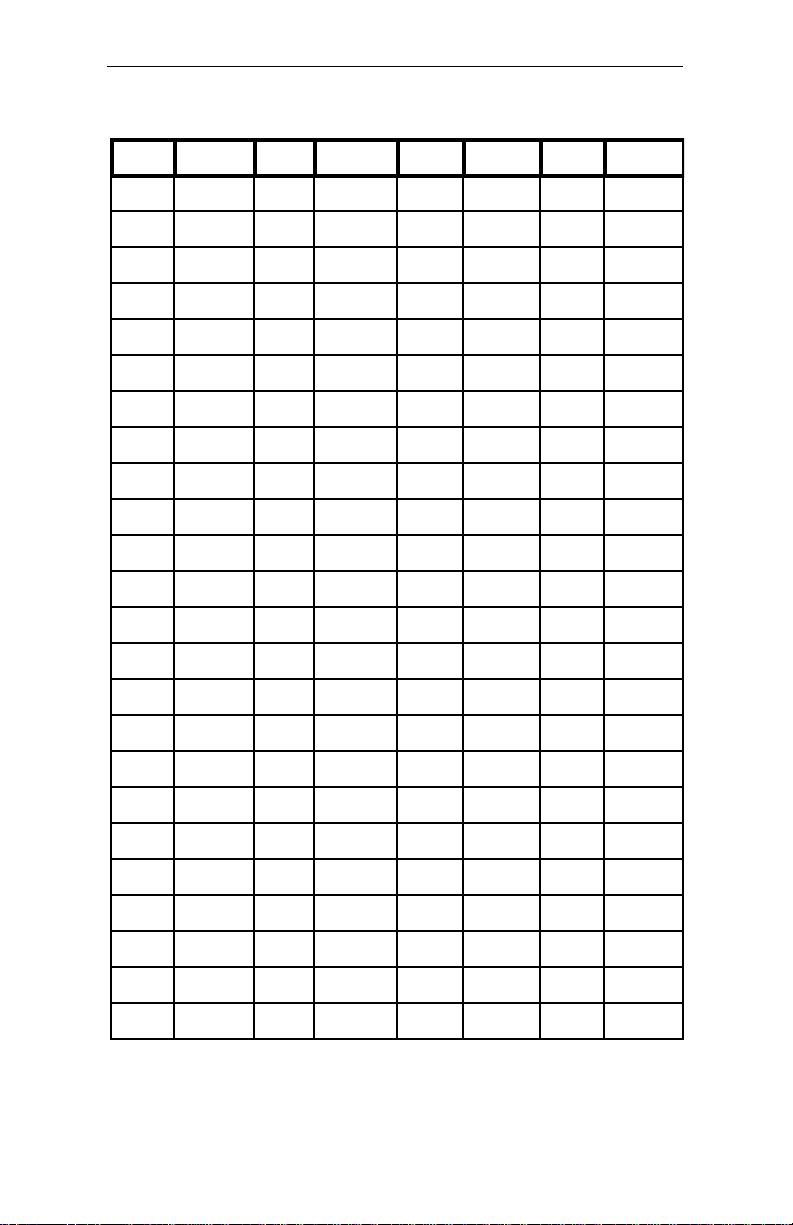
Appendix A: Technical Specifications
Table A-14 ISA Connector Pin Assignments
Pin# Assign. Pin#
IOCHCH
A01
B01
A02 SD7 B02
A03 SD6 B03
A04 SD5 B04
A05 SD4 B05
A05 SD3 B06
A06 SD2 B07
A07 SD1 B08
A08 SD0 B09
A09 IOCHR B10
A10 AEN B11
A11 SA19 B12
A12 SA18 B13
A13 SA17 B14
A14 SA16 B15
A15
SA15
B16
Assign.
GND
RESETD
+5V
IRQ9
+5V
DRQ2
-12V
ENDXFR
+12V
GND
SMEMW#
SMERW#
IOW#
IOR#
DACK3#
DRQ3
Pin# Assign Pin# Assign.
C01 SBHE# d01 EMCS1
C02 LA23 D02 IOCS16
C03 LA22 D03 IRQ10
C04 LA21 D04 IRQ11
C05 LA20 D05 IRQ12
C06 LA19 D06
IRQ15
C07 LA18 D07 IRQ14
C08 LA17 D08 DACK0
C09 MEMR D09 DRQ0
MEMW#
C10
D10 DACK5
C11 SD8 D11 DRQ5
C12 SD9 D12 DACK6
C13 SD10 D13 DRQ6
C14 SD11 D14 DACK7
C15 SD12 D15 DRQ7
C16 SD13 D16 +5V
A16 SA14 B17
A17 SA13 B18
A18 SA12 B19
A19 SA11 B20
A20 SA10 B21
A21 SA9 B22
A22 SA8 B23
A23 SA7 B24
DACK1#
DRQ1
REFRES
SYSCLK
IRQ7
IRQ6
IRQ5
IRQ4
C17 SD14 D17 MASTE
C18 SD15 D18 GND
55
Page 64

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Pin# Assign. Pin#
A24 SA6 B25
A25 SA5 B26
A26 SA4 B27
A27 SA3 B28
A29 SA2 B29
A30 SA1 B30
A31 SA0 B31
Assign.
DACK2#
TC
BALE
+5V
OSC
GND
Pin# Assign Pin# Assign.
56
Page 65

User's Notes:
Appendix A: Technical Specifications
57
Page 66

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Appendix B Flash BIOS
programming
If your board has the optional FLASH BIOS installed, you will be able to
update your BIOS without having to replace the EPROM. The WinBios will
read the new BIOS file from a floppy disk, replace the old BIOS and reboot
your computer.
When updating your BIOS, make sure you have a disk with the correct BIOS
file (it’s size should be 128K).
Rename the file to “AMIBOOT.ROM”. Turn your computer off. Insert the
disk in Drive A:, turn the computer on while pressing <CTRL><HOME>.
Your computer will show no screen, but will beep to indicate what is being
done.
If the programming is successful, you should hear the 4 beeps and your
computer will reboot with the new BIOS.
Please never turn the power off while reprogramming a FLASH BIOS. Refer
to the table on the next page for beep errors.
58
Page 67

Table B-1 Flash Bios Beep Erros
Beeps Description
1 Insert diskette in floppy A:
Appendix B: Flash BIOS
2
3 Base memory error
4 Flash program successfull
5 Floppy read error
6 Keyboard controller BAT command failed
7 No FLASH EPROM detected
8 Floppy controller failure
9 Boot Block BIOS checksum error
10 Flash erase error
The AMI BOOT.ROM file was not found
in the root directory of floppy drive A
11 Flash program error
12 AMIBOOT.ROM file size error
59
Page 68

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Appendix C Troubleshooting
Power-On Self Test
The BIOS featured in the Hunter Industrial provides all IBM
standard Power-On Self Test (POST) routines as well as enhanced
BIOS POST routines. The BIOS POST supports CPU internal
diagnostics. The BIOS POST checkpoint codes are accessible via
the manufacturing Test Port (I/O port 80h).
Post Phases:
Every time the system is powered on. The BIOS executes two
types of POST routines:
System Test and Initialization (test and initialize BIOS for
normal operations).
System Configuration Verification (compare defined configuration with hardware actually installed).
BIOS Error Reporting:
If the error occurs before the display device is initialized a series
of beeps sound. Beep codes indicate that a fatal error has occurred.
The BIOS beep codes are described on the next page.
If the error occurs after the display device is initialized the error
message is displayed. A prompt to press <F1> can also appear
power is on.
Fatal errors, which halt the boot process, are communicated
through a series of audible beeps.
60
Page 69

Appendix C: Troubleshooting
Table C-1 Beep Errors
Beeps Error Message Description
1 Refresh Failure
2 Parity Error
3
4 Timer Not Operational
5 Processor Error The CPU generated an error
6
7
8
9 ROM Checksum Error
Base 64 KB Memory
failure
8042 - Gate A20
failure
Processor Exception
Interrupt Error
Display Memory
Read/Write Error
The memory refresh circuitry is
faulty
Parity error in the base memory
(the first 64 KB block) of memory
Memory failure in the first 64 KB
A memory failure in the first 64
KB of memory, or timer 1 is not
functioning
Cannot switch to protect mode
The CPU on the CPU card
generated an exception interrupt
The system video adapter is
either missing or its memory is
faulty. This is not a fatal error.
The ROM checksum value does
not match the value encloded in
AMIBIOS
10
11
CMOS Shutdown
Register Read/Write
Error
Cache Memory Bad -Do not Enable Cache
The shutdown register for CMOS
RAM has failed
The cache memory test failed.
Cache memory is disabled. Do
not press <ctrl><alt><shift><+>
to enable cache memory
61
Page 70

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Appendix D Glossary of Terms
Bidirectional Parallel Port:
An eight-bit port that can be used for an input as well as an output
device.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output Systems):
The on-board firmware which communicates with the display,
keyboard, printers and other peripheral devices.
Bus:
One or more electrical conductors that transmit power or binary
data to the various sections of a computer.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor):
A technique of fabricating transistors which uses very low power.
CMOS RAM:
Random Access Memory made from CMOS transistors.
DMA (Direct Memory Access Channel):
A channel for transferring data from host main memory to and from
peripheraIs without direct involvement of the CPU resources.
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory):
The main memory in your computer. It needs to be refreshed by
a memory or it will lose its information.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)
A programmable device which stores information regardless of
power. The information can be erased and new information
written.
62
Page 71

Appendix D: Glossary of Terms
Floating Point Unit (FPU):
A device which can perform calculations on numbers in floating point
format as opposed to simple integers.
IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics):
A standard of signalling and communicating with a device.
Interleave
Multiple banks of memory that overlap to reduce the access time
and eliminate wait states.
Interrupt:
Temporarily halting the operation of a digital computer to respond
to service an external event.
Interval Timer:
A device that can generate a pulse at a defined interval for
background tasks.
IRQ (Interrupt Request):
A signal channel used to trigger the CPU to temporarily change
tasks
.
Kilobyte (KB):
1024 bytes
ns (nano seconds):
1x10-9 seconds. (There are one billion nanoseconds in one second)
Page Mode:
The ability to read a whole line (page) of memory to reduce access
time
Parity:
A way to detect corrupted data in DRAM.
63
Page 72

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
Parallel Port:
An eight-bit port usually used for connecting a printer.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect):
Local bus for PCs provide a high-speed data path between the CPU
and peripherals (video, disk, network, etc.). The PCI bus coexists
in the PC with the ISA or EISA bus. ISA and EISA boards still plug
into an ISA or EISA slot, while high- speed. PCI controllers plug
into a PCI slot, The PCI bus runs at 25, 30 or 33MHz, supports 32bit and 64-bit data paths and bus mastering. The first PCs with PCI
buses became available toward the end of 1993.
Port:
Ports are used to connect peripheral devices such as external
drives and printers to your computer.
RAM (Random Access Memory):
The memory used to execute applications while your computer is
turned ON. When you tum your computer OFF, all data stored in
RAM is lost.
Real-Time Clock (RTC):
A CMOS counter used to maintain local time.
Retaining Bracket:
The bracket on the end of the board that attaches to
the back of the chassis and contains connectors, usually key
board, mouse, serial port, and/or parallel port.
Serial Port:
A two channel port, one channel used for “In” transmis
sions and one for “Out” transmissions.
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface):
A high speed, general purpose interface to storage devices.
64
Page 73

Appendix D: Glossary of Terms
SRAM(Static Random Access Memory):
As opposed to DRAM, this memory does not need to be refreshed
by a controller and holds its information as long as the power is
on.
Tag Comparator:
A memory that tells whether an address is available in the cache.
Wait State:
Extra time inserted to allow access to slower devices (e.g. DRAM)
or EPROMs.
Write-Back Cache:
The process where the CPU updates the cache and the DRAM
simultaneously but does not wait for the DRAM to complete the
update.
Write-Thru Cache:
The process where the CPU updates the cache and the DRAM
simultaneously but the CPU waits for the DRAM to complete the
update, resulting in more time being consumed than in write-back.
65
Page 74

Hunter Industrial - Installation Guide
User's Notes
66
Page 75

MN - PNTHI - 02
 Loading...
Loading...