Page 1

Intel
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700
Desktop Processor Series and
LGA1156 Socket
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
September 2009
®
Document Number:322167-002
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or
life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future
changes to them.
The Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 desktop processor series and Intel
defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized
errata are available on request.
®
5 Series Chipset and LGA1156 socket may contain design
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Intel, Core and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S and other countries.
* Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2009 Intel Corporation.
2 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 3

Contents
1Introduction..............................................................................................................9
1.1 References .........................................................................................................9
1.2 Definition of Terms ............................................................................................ 10
2 Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications....................................................... 11
2.1 Package Mechanical Specifications ....................................................................... 11
2.1.1 Package Mechanical Drawing.................................................................... 12
2.1.2 Processor Component Keep-Out Zones...................................................... 12
2.1.3 Package Loading Specifications ................................................................ 13
2.1.4 Package Handling Guidelines.................................................................... 13
2.1.5 Package Insertion Specifications............................................................... 13
2.1.6 Processor Mass Specification.................................................................... 13
2.1.7 Processor Materials................................................................................. 14
2.1.8 Processor Markings................................................................................. 14
2.1.9 Processor Land Coordinates ..................................................................... 15
2.2 Processor Storage Specifications ......................................................................... 16
3 LGA1156 Socket ...................................................................................................... 17
3.1 Board Layout .................................................................................................... 19
3.2 Attachment to Motherboard ................................................................................ 20
3.3 Socket Components........................................................................................... 20
3.3.1 Socket Body Housing .............................................................................. 20
3.3.2 Solder Balls ........................................................................................... 21
3.3.3 Contacts ............................................................................................... 21
3.3.4 Pick and Place Cover............................................................................... 21
3.4 Package Installation / Removal ........................................................................... 22
3.4.1 Socket Standoffs and Package Seating Plane.............................................. 23
3.5 Durability ......................................................................................................... 23
3.6 Markings .......................................................................................................... 24
3.7 Component Insertion Forces ............................................................................... 24
3.8 Socket Size ...................................................................................................... 24
4 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)................................................................... 25
4.1 Design Concept................................................................................................. 25
4.1.1 ILM Cover Assembly Design Overview ....................................................... 25
4.1.2 ILM Back Plate Design Overview............................................................... 26
4.1.3 Shoulder Screw and Fasteners Design Overview ......................................... 27
4.2 Assembly of ILM to a Motherboard....................................................................... 28
4.3 ILM Interchangeability ....................................................................................... 29
4.4 Markings .......................................................................................................... 29
5 LGA1156 Socket and ILM Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Specifications .31
5.1 Component Mass............................................................................................... 31
5.2 Package/Socket Stackup Height .......................................................................... 31
5.3 Socket Maximum Temperature............................................................................ 32
5.4 Loading Specifications........................................................................................ 32
5.5 Electrical Requirements...................................................................................... 33
5.6 Environmental Requirements .............................................................................. 34
6 Thermal Specifications ............................................................................................ 35
6.1 Thermal Specifications ....................................................................................... 35
6.1.1 Intel
6.1.2 Processor Specification for Operation Where Digital
®
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Thermal Profile ..... 37
Thermal Sensor Exceeds T
CONTROL
............................................................ 39
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 3
Page 4

6.1.3 Thermal Metrology..................................................................................40
6.2 Processor Thermal Features ................................................................................40
6.2.1 Processor Temperature............................................................................40
6.2.2 Adaptive Thermal Monitor ........................................................................41
6.2.3 THERMTRIP# Signal................................................................................44
6.3 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) ......................................................44
6.3.1 Introduction...........................................................................................44
6.3.2 PECI Client Capabilities............................................................................45
6.3.3 Temperature Data ..................................................................................45
7 Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance ..............................................47
7.1 Sensor Based Specification Overview....................................................................47
7.2 Sensor Based Thermal Specification .....................................................................49
7.2.1 TTV Thermal Profile.................................................................................49
7.2.2 Specification When DTS value is Greater than T
CONTROL
...............................50
7.3 Thermal Solution Design Process .........................................................................51
7.3.1 Boundary Condition Definition ..................................................................51
7.3.2 Thermal Design and Modelling ..................................................................52
7.3.3 Thermal Solution Validation......................................................................52
7.4 Fan Speed Control (FSC) design process...............................................................54
7.4.1 Fan Speed Control Algorithm without T
7.4.2 Fan Speed Control Algorithm with T
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Data ....................................54
Data.........................................55
7.5 System Validation..............................................................................................57
7.6 Thermal Solution Characterization........................................................................58
8 ATX Reference Thermal Solution ..............................................................................59
8.1 Heatsink Thermal Solution ..................................................................................59
8.2 Geometric Envelope for the Intel Reference ATX Thermal Mechanical Design..............60
8.3 Heatsink Mass and Center of Gravity ....................................................................60
8.4 Thermal Interface Material ..................................................................................60
9 Thermal Solution Quality and Reliability Requirements ............................................61
9.1 Reference Heatsink Thermal Verification ...............................................................61
9.2 Mechanical Environmental Testing........................................................................61
9.2.1 Recommended Test Sequence ..................................................................62
9.2.2 Post-Test Pass Criteria.............................................................................62
9.2.3 Recommended BIOS/Processor/Memory Test Procedures .............................62
9.3 Material and Recycling Requirements....................................................................63
10 Boxed Processor Specifications................................................................................65
10.1 Introduction......................................................................................................65
10.2 Mechanical Specifications....................................................................................66
10.2.1 Boxed Processor Cooling Solution Dimensions.............................................66
10.2.2 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Weight .......................................................68
10.2.3 Boxed Processor Retention Mechanism and Heatsink Attach Clip Assembly .....68
10.3 Electrical Requirements ......................................................................................68
10.3.1 Fan Heatsink Power Supply ......................................................................68
10.4 Thermal Specifications........................................................................................69
10.4.1 Boxed Processor Cooling Requirements......................................................69
10.4.2 Variable Speed Fan .................................................................................71
A Component Suppliers...............................................................................................73
B Mechanical Drawings ...............................................................................................75
C Socket Mechanical Drawings ....................................................................................89
D Package Mechanical Drawings .................................................................................95
E Heat Sink Back Plate Drawings ................................................................................99
4 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 5

Figures
2-1 Processor Package Assembly Sketch ........................................................................ 11
2-2 Package View ....................................................................................................... 12
2-3 Processor Top-Side Markings .................................................................................. 14
2-4 Processor Package Lands Coordinates ...................................................................... 15
3-1 LGA1156 Socket with Pick and Place Cover ............................................................... 17
3-2 LGA1156 Socket Contact Numbering (Top View of Socket).......................................... 18
3-3 LGA1156 Socket Land Pattern (Top View of Board) .................................................... 19
3-4 Attachment to Motherboard .................................................................................... 20
3-5 Pick and Place Cover.............................................................................................. 22
3-6 Package Installation / Removal Features................................................................... 23
4-1 ILM Cover Assembly .............................................................................................. 26
4-2 Back Plate ............................................................................................................ 26
4-3 Shoulder Screw..................................................................................................... 27
4-4 ILM Assembly ....................................................................................................... 28
4-5 Pin 1 and ILM Lever............................................................................................... 29
5-1 Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology .............................. 34
6-1 Thermal Test Vehicle Thermal Profile for Intel
Processor Series.................................................................................................... 37
6-2 TTV Case Temperature (TCASE) Measurement Location .............................................. 40
6-3 Frequency and Voltage Ordering.............................................................................. 42
6-4 Temperature Sensor Data Format............................................................................ 45
7-1 Comparison of Case Temperature versus Sensor Based Specification............................ 48
7-2 Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Thermal Profile .................... 49
7-3 Thermal solution Performance................................................................................. 50
7-4 Required YCA for Various T
AMBIENT
Conditions ........................................................... 52
7-5 Thermal Solution Performance versus Fan Speed ....................................................... 53
7-6 Fan Response Without T
7-7 Fan Response with T
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Data ....................................................................... 55
Aware FSC.................................................................... 56
8-1 ATX Heatsink Reference Design Assembly................................................................. 59
8-2 ATX KOZ 3-D Model Primary (Top) Side.................................................................... 60
10-1 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink................................................................................. 65
10-2 Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (side view)............................................ 66
10-3 Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (top view)............................................. 67
10-4 Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (overall view) ........................................ 67
10-5 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Power Cable Connector Description ............................... 68
10-6 Baseboard Power Header Placement Relative to Processor Socket ................................ 69
10-7 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Airspace Keepout Requirements (top view) .................... 70
10-8 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Airspace Keepout Requirements (side view) ................... 70
10-9 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Set Points.................................................................. 71
B-1 Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top) .......................................... 76
B-2 Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom) ................................. 77
B-3 Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top)......................................... 78
B-4 Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom) ................................ 79
B-5 Reference Design Heatsink Assembly ....................................................................... 80
B-6 Reference Fastener (Sheet 1 of 4) ........................................................................... 81
B-7 Reference Fastener (Sheet 2 of 4) ........................................................................... 82
B-8 Reference Fastener (Sheet 3 of 4) ........................................................................... 83
B-9 Reference Fastener (Sheet 4 of 4) ........................................................................... 84
B-10 Reference Clip (Sheet 1 of 2) .................................................................................. 85
B-11 Reference Clip (Sheet 2 of 2) .................................................................................. 86
B-12 Thermocouple Attach Drawing................................................................................. 87
C-1 Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4) ................................................................ 90
®
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 5
Page 6

C-2 Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4).................................................................91
C-3 Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4).................................................................92
C-4 Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4).................................................................93
D-1 Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 2) ................................................................96
D-2 Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 2) ................................................................97
E-1 Heat Sink Back Plate Keep In Zone ........................................................................100
E-2 Heat Sink Back Plate ............................................................................................101
6 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 7

Tables
1-1 Reference Documents ..............................................................................................9
1-2 Terms and Descriptions.......................................................................................... 10
2-1 Processor Loading Specifications ............................................................................. 13
2-2 Package Handling Guidelines................................................................................... 13
2-3 Processor Materials................................................................................................ 14
2-4 Storage Conditions ................................................................................................ 16
5-1 Socket Component Mass ........................................................................................ 31
5-2 1156-land Package and LGA1156 Socket Stackup Height ............................................ 31
5-3 Socket & ILM Mechanical Specifications .................................................................... 32
5-4 Electrical Requirements for LGA1156 Socket ............................................................. 33
6-1 Processor Thermal Specifications............................................................................. 36
6-2 Thermal Test Vehicle Thermal Profile for Intel
Processor Series.................................................................................................... 38
6-3 Thermal Solution Performance above TCONTROL for the Intel
i5-700 Desktop Processor Series ............................................................................. 39
6-4 Supported PECI Command Functions and Codes ........................................................ 45
6-5 Error Codes and Descriptions .................................................................................. 46
7-1 Thermal Solution Performance above T
8-1 Reference Thermal Solutions................................................................................... 59
9-1 Use Conditions (Board Level) .................................................................................. 61
10-1 Fan Heatsink Power and Signal Specifications............................................................ 69
10-2 Fan Heatsink Set Points.......................................................................................... 71
A-1 Reference Heatsink Enabled Components ................................................................. 73
A-2 LGA1156 Socket and ILM Components ..................................................................... 73
A-3 Supplier Contact Information .................................................................................. 74
B-1 Mechanical Drawing List ......................................................................................... 75
C-1 Mechanical Drawing List ......................................................................................... 89
D-1 Mechanical Drawing List ......................................................................................... 95
E-1 Mechanical Drawing List ......................................................................................... 99
E-2 Supplier Contact Information .................................................................................. 99
CONTROL
®
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop
®
Core™ i7-800 and
.......................................................... 58
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 7
Page 8

Revision History
Revision
Number
-001 • Initial release
-002
• Updated Tables A-2 and A-3.
• Updated Chapters 3, 4, 8, and Appendix B
Description Revision Date
September
2009
September
2009
§
8 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 9

Introduction
1 Introduction
This document differs from previous Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines. In this
document, mechanical and thermal specifications for the processor and the associated
socket are now included. The usual design guidance has been retained.
The components described in this document include:
• The thermal and mechanical specifications for the
— Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 desktop processor series
• The LGA1156 socket and the Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) and back
plate.
• The reference design thermal solution (heatsink) for the processors and associated
retention hardware.
Note: When the information is applicable to all products, the this document will use
“processor” or “processors” to simplify the document.
1.1 References
Material and concepts available in the following documents may be beneficial when
reading this document.
Table 1-1. Reference Documents
®
Intel
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Datasheet, Volume 1
®
Intel
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Datasheet, Volume 2
®
Intel
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Specification Update
®
Intel
5 Series Chipset and Intel® 3400 Chipset Datasheet
®
Intel
5 Series Chipset and Intel® 3400 Chipset Specification Update
®
5 Series Chipset and Intel® 3400 Chipset – Thermal Mechanical
Intel
Specifications and Design Guidelines
4-Wire Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controlled Fans
Document Location
http://download.intel.com/
design/processor/datashts/
322164.pdf
http://download.intel.com/
design/processor/datashts/
322165.pdf
http://download.intel.com/
design/processor/
specupdt/322166.pdf
www.intel.com/Assets/
PDF/datasheet/322169.pdf
www.intel.com/Assets/
PDF/specupdate/
322170.pdf
www.intel.com/Assets/
PDF/designguide/
322171.pdf
http://
www.formfactors.org/
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 9
Page 10
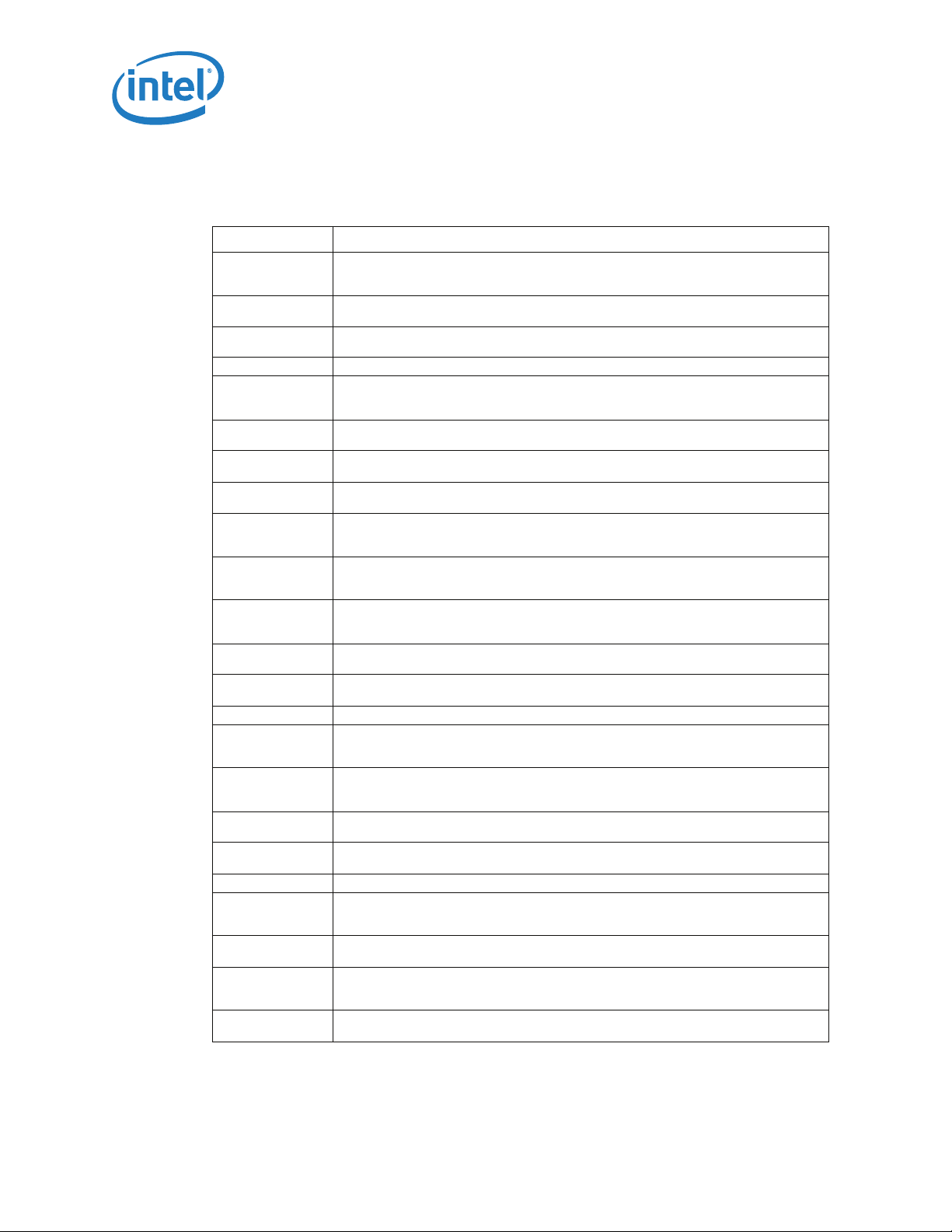
1.2 Definition of Terms
Table 1-2. Terms and Descriptions
Term Description
Bypass
CTE
DTS
FSC Fan Speed Control
IHS
ILM
PCH
LGA1156 socket
PECI
Ψ
CA
Ψ
CS
Ψ
SA
T
CASE or TC
T
CASE_MAX
TCC
T
CONTROL
TDP
Thermal Monitor
Thermal Profile Line that defines case temperature specification of the TTV at a given power level.
TIM
TTV
T
LA
T
SA
Bypass is the area between a passive heatsink and any object that can act to form a
duct. For this example, it can be expressed as a dimension away from the outside
dimension of the fins to the nearest surface.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion. The relative rate a material expands during a thermal
event.
Digital Thermal Sensor reports a relative die temperature as an offset from TCC
activation temperature.
Integrated Heat Spreader: a component of the processor package used to enhance the
thermal performance of the package. Component thermal solutions interface with the
processor at the IHS surface.
Independent Loading Mechanism provides the force needed to seat the 1156-LGA land
package onto the socket contacts.
Platform Controller Hub. The PCH is connected to the processor via the Direct Media
Interface (DMI) and Intel
The processor mates with the system board through this surface mount, 1156-land
socket.
The Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) is a one-wire interface that provides
a communication channel between Intel processor and chipset components to external
monitoring devices.
Case-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter (psi). A measure of thermal
solution performance using total package power. Defined as (T
Package Power. The heat source should always be specified for Ψ measurements.
Case-to-sink thermal characterization parameter. A measure of thermal interface
material performance using total package power. Defined as (T
Power.
Sink-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter. A measure of heatsink thermal
performance using total package power. Defined as (T
The case temperature of the processor, measured at the geometric center of the topside
of the TTV IHS.
The maximum case temperature as specified in a component specification.
Thermal Control Circuit: Thermal monitor uses the TCC to reduce the die temperature by
using clock modulation and/or operating frequency and input voltage adjustment when
the die temperature is very near its operating limits.
T
trigger point for fan speed control. When DTS > T
with the TTV thermal profile.
Thermal Design Power: Thermal solution should be designed to dissipate this target
power level. TDP is not the maximum power that the processor can dissipate.
is a static value that is below the TCC activation temperature and used as a
CONTROL
A power reduction feature designed to decrease temperature after the processor has
reached its maximum operating temperature.
Thermal Interface Material: The thermally conductive compound between the heatsink
and the processor case. This material fills the air gaps and voids, and enhances the
transfer of the heat from the processor case to the heatsink.
Thermal Test Vehicle. A mechanically equivalent package that contains a resistive heater
in the die to evaluate thermal solutions.
The measured ambient temperature locally surrounding the processor. The ambient
temperature should be measured just upstream of a passive heatsink or at the fan inlet
for an active heatsink.
The system ambient air temperature external to a system chassis. This temperature is
usually measured at the chassis air inlets.
®
Flexible Display Interface (Intel® FDI).
– TLA) / Total Package Power.
S
, the processor must comply
CONTROL
Introduction
– TLA) / Total
CASE
– TS) / Total Package
CASE
§
10 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 11

Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
2 Package Mechanical and
Storage Specifications
2.1 Package Mechanical Specifications
The processor is packaged in a Flip-Chip Land Grid Array package that interfaces with
the motherboard via the LGA1156 socket. The package consists of a processor
mounted on a substrate land-carrier. An integrated heat spreader (IHS) is attached to
the package substrate and core and serves as the mating surface for processor thermal
solutions, such as a heatsink. Figure 2-1 shows a sketch of the processor package
components and how they are assembled together. Refer to Chapter 3 and Chapter 4
for complete details on the LGA1156 socket.
The package components shown in Figure 2-1 include the following:
1. Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS)
2. Thermal Interface Material (TIM)
3. Processor core (die)
4. Package substrate
5. Capacitors
Figure 2-1. Processor Package Assembly Sketch
IHS
Substrate
System Board
Note:
1. Socket and motherboard are included for reference and are not part of processor package.
2. For clarity the ILM is not shown.
Core (die)
TIM
Capacitors
LGA1156 Socket
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 11
Page 12
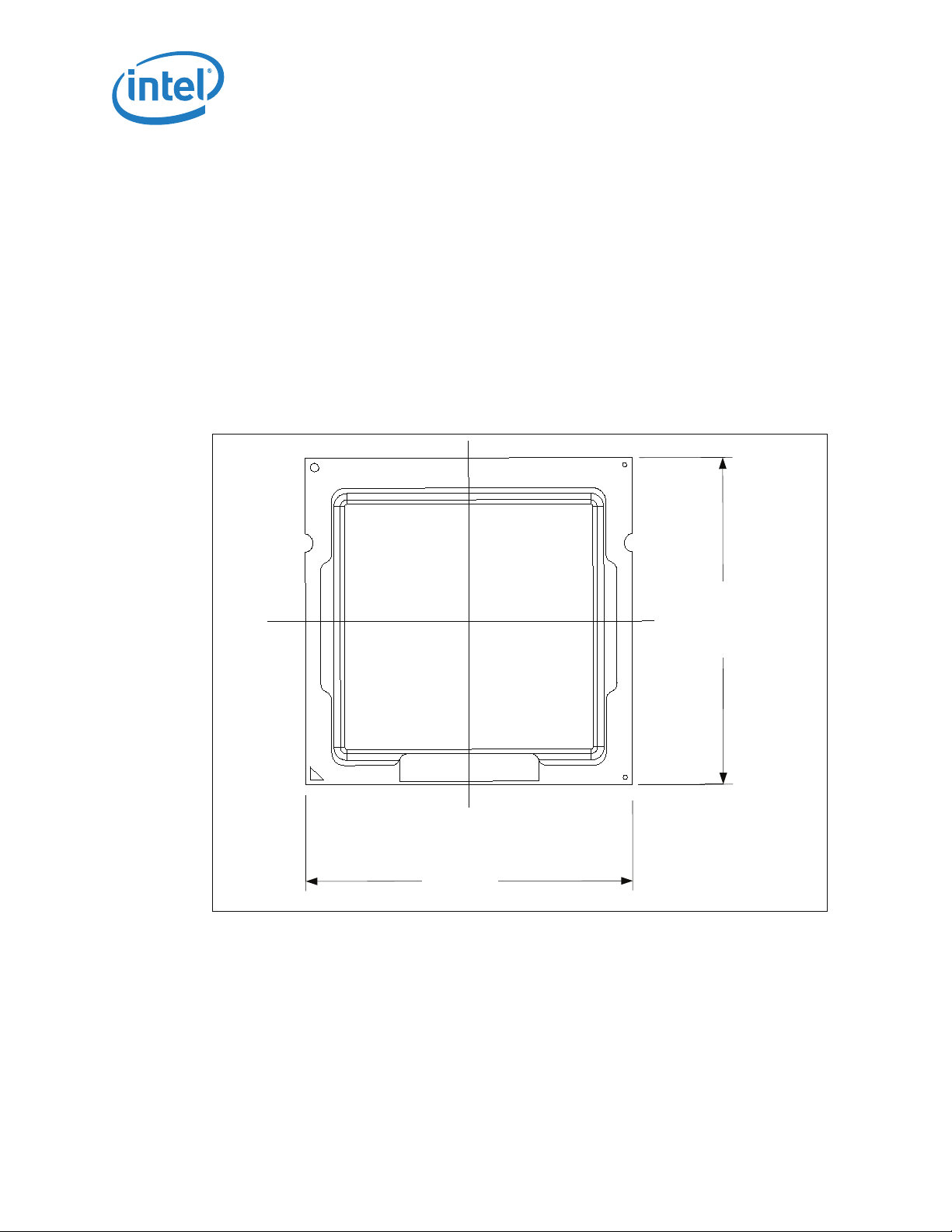
2.1.1 Package Mechanical Drawing
Figure 2-2 shows the basic package layout and dimensions. The detailed package
mechanical drawings are in Appendix D. The drawings include dimensions necessary to
design a thermal solution for the processor. These dimensions include:
1. Package reference dimensions with tolerances (total height, length, width, and so
forth.)
2. IHS parallelism and tilt
3. Land dimensions
4. Top-side and back-side component keep-out dimensions
5. Reference datums
6. All drawing dimensions are in mm
Figure 2-2. Package View
Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
37.5
2.1.2 Processor Component Keep-Out Zones
The processor may contain components on the substrate that define component keepout zone requirements. A thermal and mechanical solution design must not intrude into
the required keep-out zones. Decoupling capacitors are typically mounted to either the
topside or land-side of the package substrate. See Figure B-3 and Figure B-4 for keepout zones. The location and quantity of package capacitors may change due to
manufacturing efficiencies but will remain within the component keep-in. This keep-in
zone includes solder paste and is a post reflow maximum height for the components.
37.5
12 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 13
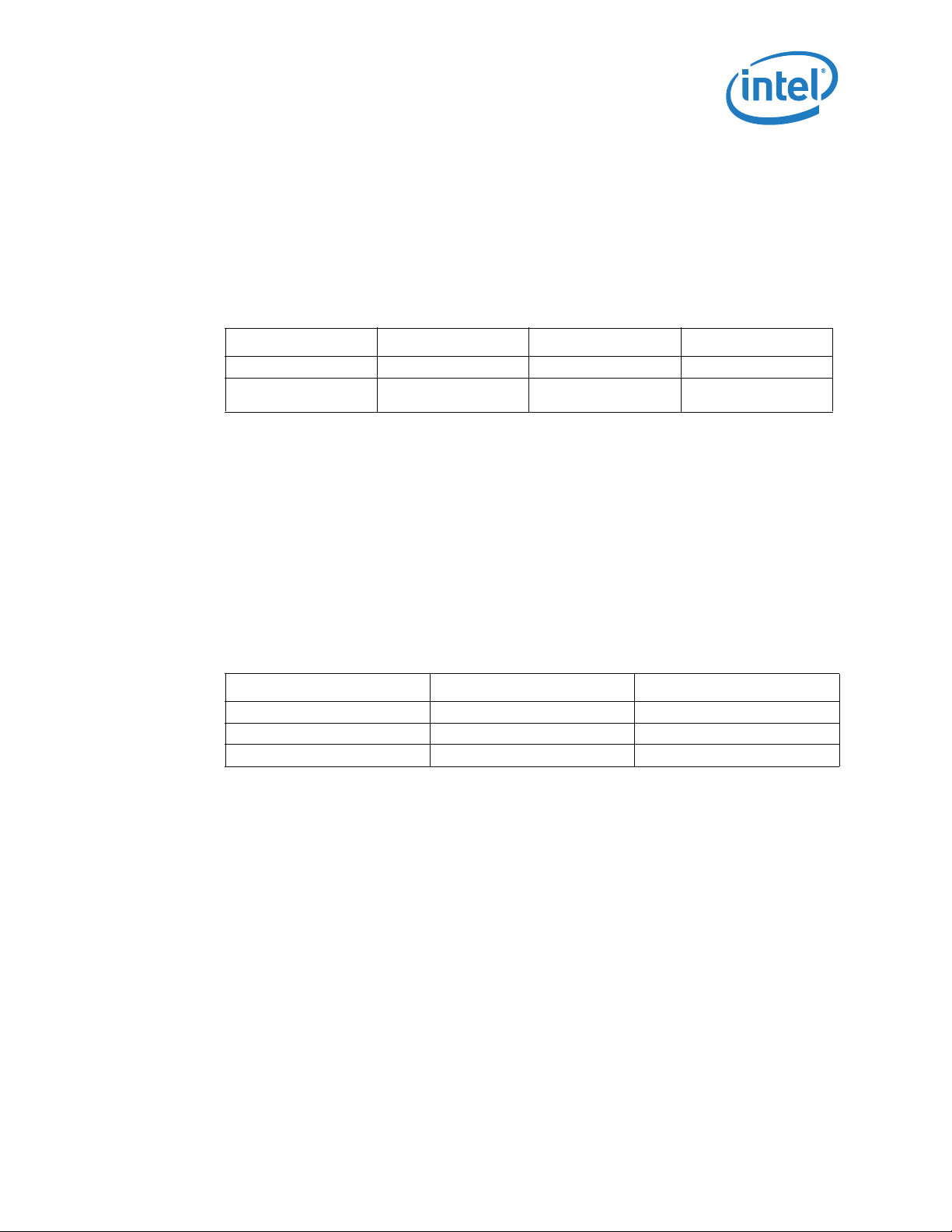
Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
2.1.3 Package Loading Specifications
Ta b le 2 - 1 provides dynamic and static load specifications for the processor package.
These mechanical maximum load limits should not be exceeded during heatsink
assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use condition. Also, any mechanical system
or component testing should not exceed the maximum limits. The processor package
substrate should not be used as a mechanical reference or load-bearing surface for
.
Table 2-1. Processor Loading Specifications
thermal and mechanical solution.
Parameter Minimum Maximum Notes
Static Compressive Load — 600 N [135 lbf] 1, 2, 3
Dynamic Compressive
Load
Notes:
1. These specifications apply to uniform compressive loading in a direction normal to the processor IHS.
2. This is the maximum static force that can be applied by the heatsink and retention solution to maintain the
heatsink and processor interface.
3. These specifications are based on limited testing for design characterization. Loading limits are for the
package only and do not include the limits of the processor socket.
4. Dynamic loading is defined as an 50g shock load, 2X Dynamic Acceleration Factor with a 500g maximum
thermal solution.
— 712 N [160 lbf] 1, 3, 4
2.1.4 Package Handling Guidelines
Ta b le 2 - 2 includes a list of guidelines on package handling in terms of recommended
maximum loading on the processor IHS relative to a fixed substrate. These package
handling loads may be experienced during heatsink removal.
Table 2-2. Package Handling Guidelines
Parameter Maximum Recommended Notes
Shear 311 N [70 lbf] 1, 4
Tensile 111 N [25 lbf] 2, 4
Torque 3.95 N-m [35 lbf-in] 3, 4
Notes:
1. A shear load is defined as a load applied to the IHS in a direction parallel to the IHS top surface.
2. A tensile load is defined as a pulling load applied to the IHS in a direction normal to the IHS surface.
3. A torque load is defined as a twisting load applied to the IHS in an axis of rotation normal to the IHS top
surface.
4. These guidelines are based on limited testing for design characterization.
2.1.5 Package Insertion Specifications
The processor can be inserted into and removed from an LGA1156 socket 15 times. The
socket should meet the LGA1156 socket requirements detailed in Chapter 5.
2.1.6 Processor Mass Specification
The typical mass of the processor is 21.5g (0.76 oz). This mass [weight] includes all
the components that are included in the package.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 13
Page 14
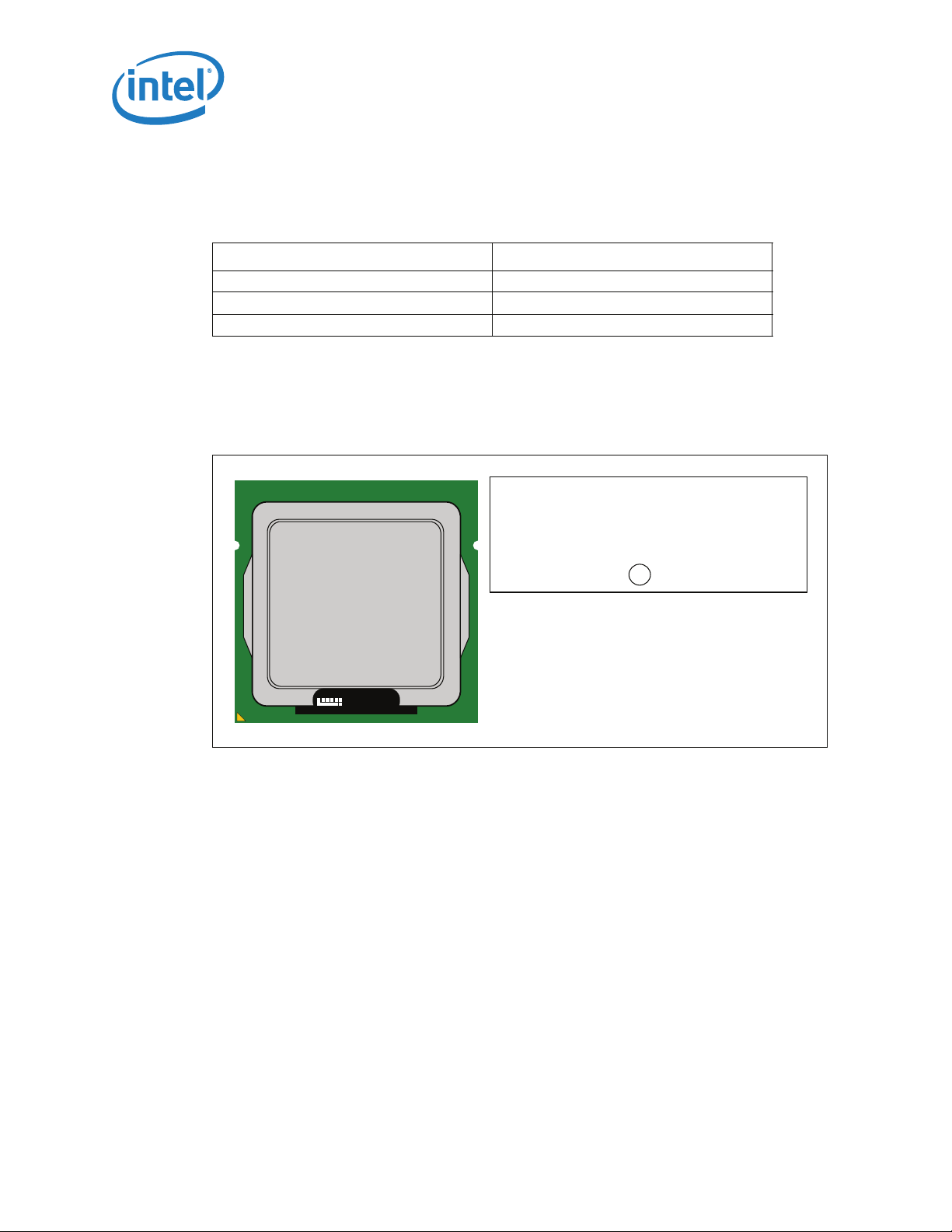
2.1.7 Processor Materials
Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
Tab l e 2- 3 lists some of the package components and associated materials.
Table 2-3. Processor Materials
Component Material
Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) Nickel Plated Copper
Substrate Fiber Reinforced Resin
Substrate Lands Gold Plated Copper
2.1.8 Processor Markings
Figure 2-3 shows the topside markings on the processor. This diagram is to aid in the
identification of the processor.
Figure 2-3. Processor Top-Side Markings
GRP1LINE1
GRP1LINE1
GRP1LINE2
GRP1LINE2
GRP1LINE3
GRP1LINE3
GRP1LINE4
GRP1LINE4
GRP1LINE5
GRP1LINE5
LOT NO S/N
Legend:
GRP1LINE1
GRP1LINE2
GRP1LINE3
GRP1LINE4
GRP1LINE5
Legend:
GRP1LINE1
GRP1LINE2
GRP1LINE3
GRP1LINE4
GRP1LINE5
Mark Text (Production Mark):
INTEL{M}{C}'08 PROC#
BRAND
SLxxx C00
SPEED/CACHE/F MB
e4
FPO
Mark Text (Engineering Mark):
INTEL{M}{C}'08
INTEL CONFIDENTIAL
Qxxx ES C00
PRODUCT CODE
e4
FPO
14 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 15
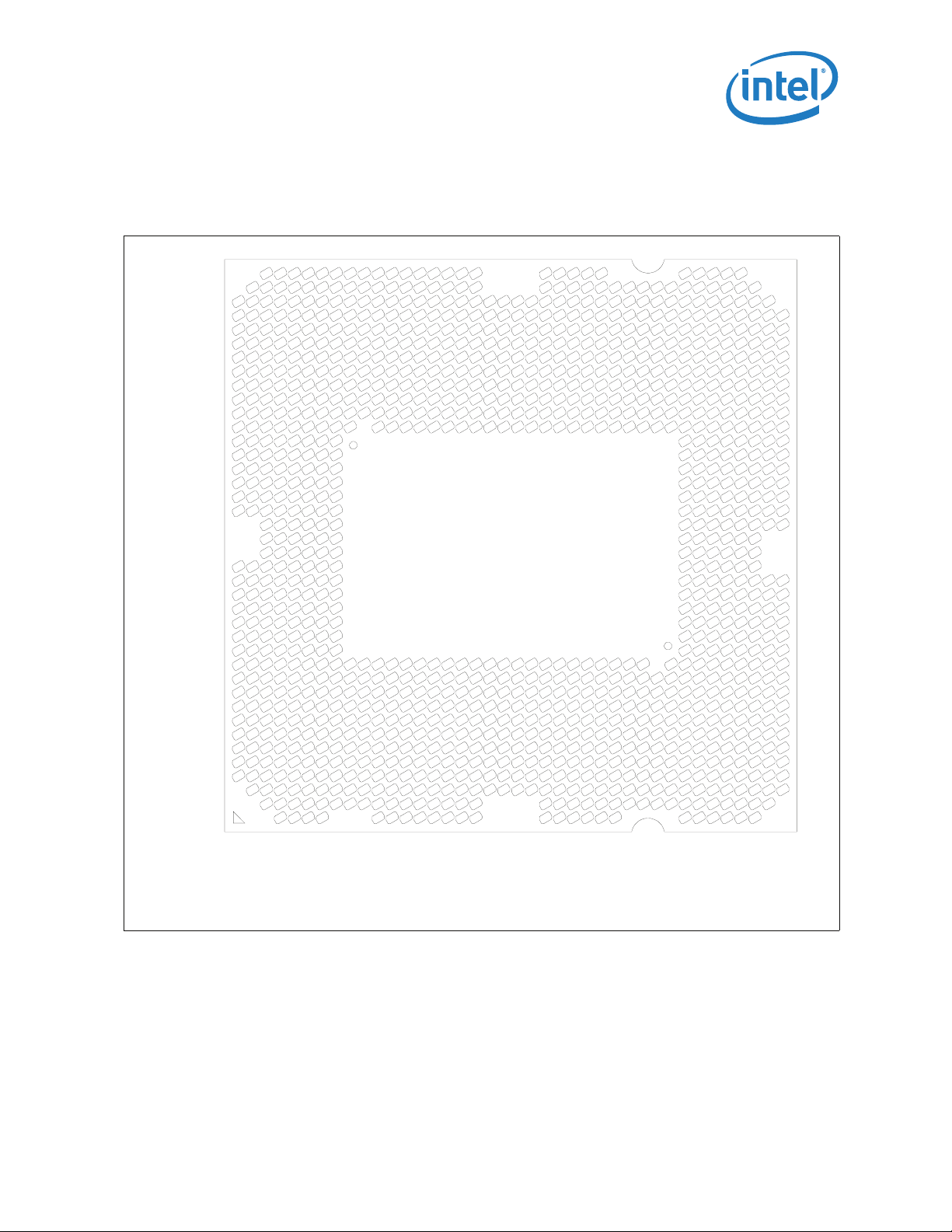
Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
2.1.9 Processor Land Coordinates
.
Figure 2-4. Processor Package Lands Coordinates
Figure 2-4 shows the bottom view of the processor package.
AY
AW
AV
AU
AT
AR
AP
AN
AM
AL
AK
AJ
AH
AG
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
U
P
R
T
N
M
K
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 15
33 35 37 39
34 36 38 40
Page 16
Package Mechanical and Storage Specifications
2.2 Processor Storage Specifications
Tab l e 2- 4 includes a list of the specifications for device storage in terms of maximum
and minimum temperatures and relative humidity. These conditions should not be
.
Table 2-4. Storage Conditions
exceeded in storage or transportation.
Parameter Description Min Max Notes
The non-operating device storage
T
ABSOLUTE STORAGE
T
SUSTAINED STORAGE
RH
SUSTAINED STORAGE
TIME
SUSTAINED STORAGE
Notes:
1. Refers to a component device that is not assembled in a board or socket that is not to be electrically
connected to a voltage reference or I/O signals.
2. Specified temperatures are based on data collected. Exceptions for surface mount reflow are specified in
applicable JEDEC standard and MAS document. Non-adherence may affect processor reliability.
3. T
ABSOLUTE STORAGE
moisture barrier bags or desiccant.
4. Intel
5. The JEDEC, J-JSTD-020 moisture level rating and associated handling practices apply to all moisture
6. Nominal temperature and humidity conditions and durations are given and tested within the constraints
®
branded board products are certified to meet the following temperature and humidity limits that are
given as an example only (Non-Operating Temperature Limit: -40 °C to 70 °C, Humidity: 50% to 90%,
non-condensing with a maximum wet bulb of 28 °C). Post board attach storage temperature limits are not
specified for non-Intel branded boards.
sensitive devices removed from the moisture barrier bag.
imposed by T
SUSTAINED
temperature. Damage (latent or otherwise)
may occur when subjected to for any length of
time.
The ambient storage temperature limit (in
shipping media) for a sustained period of time.
The maximum device storage relative humidity
for a sustained period of time.
A prolonged or extended period of time;
typically associated with customer shelf life. 0 Months6 Months
applies to the unassembled component only and does not apply to the shipping media,
and customer shelf life in applicable Intel box and bags.
-55 °C 125 °C 1, 2, 3
-5 °C 40 °C 4, 5
60% @ 24 °C 5, 6
6
§
16 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 17
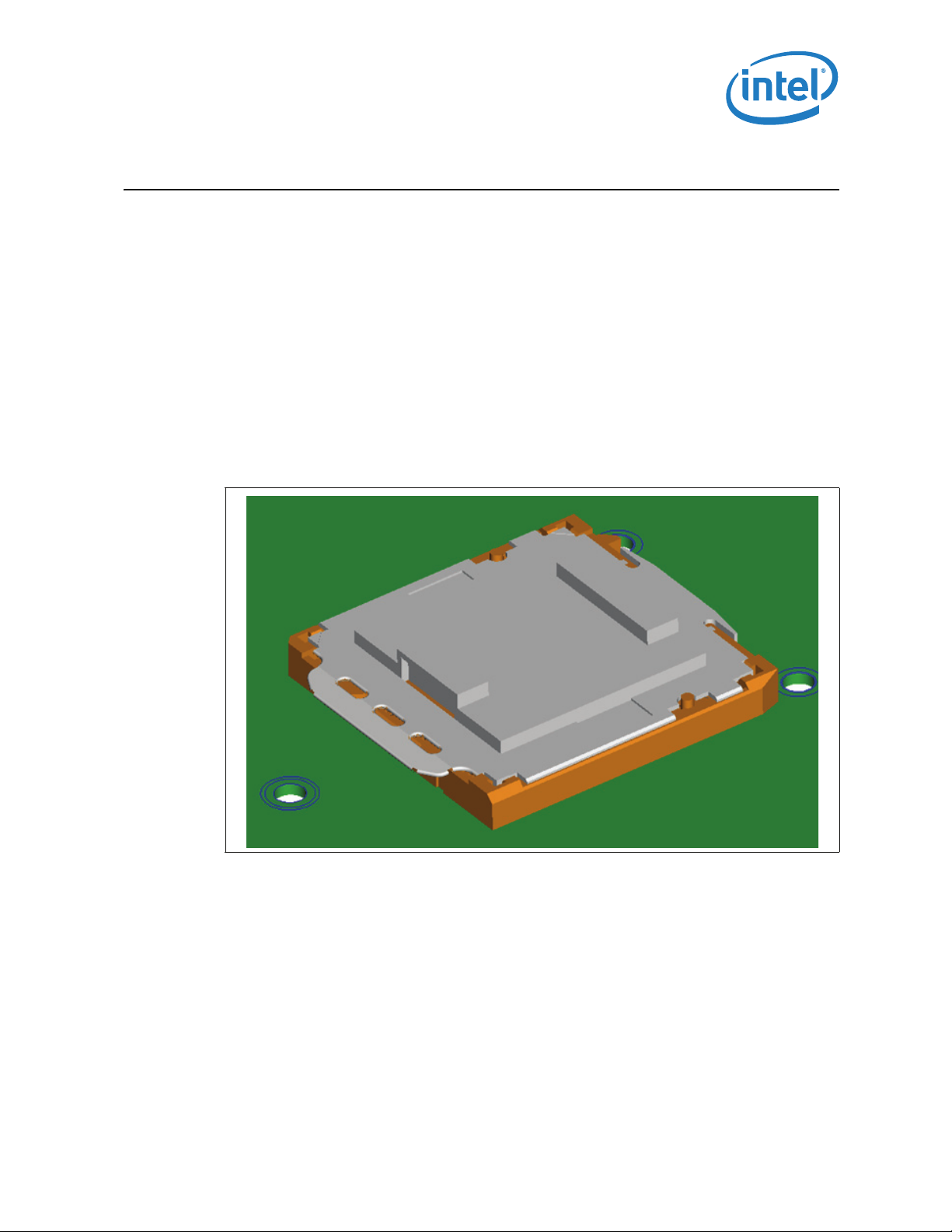
LGA1156 Socket
3 LGA1156 Socket
This chapter describes a surface mount, LGA (Land Grid Array) socket intended for the
processors. The socket provides I/O, power, and ground contacts. The socket contains
1156 contacts arrayed about a cavity in the center of the socket with lead-free solder
balls for surface mounting on the motherboard.
The contacts are arranged in two opposing L-shaped patterns within the grid array. The
grid array is 40 x 40 with 24 x 16 grid depopulation in the center of the array and
selective depopulation elsewhere.
The socket must be compatible with the package (processor) and the Independent
Loading Mechanism (ILM). The ILM design includes a back plate that is integral to
having a uniform load on the socket solder joints. Socket loading specifications are
listed in Chapter 5.
Figure 3-1. LGA1156 Socket with Pick and Place Cover
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 17
Page 18
Figure 3-2. LGA1156 Socket Contact Numbering (Top View of Socket)
30
30
30
30
29
29
29
29
28
28
28
28
27
27
27
27
26
26
26
26
25
25
25
25
24
24
24
24
23
23
23
23
22
22
22
22
21
21
21
21
20
20
20
20
19
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
17
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
LGA1156 Socket
40
40
40
40
39
39
39
39
38
38
38
38
37
37
37
37
36
36
36
36
35
35
35
35
34
34
34
34
33
33
33
33
32
32
32
32
31
31
31
31
30
30
30
30
29
29
29
29
28
28
28
28
27
27
27
27
26
26
26
26
25
25
25
25
24
24
24
24
23
23
23
23
22
22
22
22
21
21
21
21
20
20
20
20
19
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
17
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AWA C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF
18 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
AM AP AT AV AY
AM AP AT AV AY
AM AP AT AV AY
AM AP AT AV AY
AH AK
AH AK
AH AK
AH AK
Page 19
LGA1156 Socket
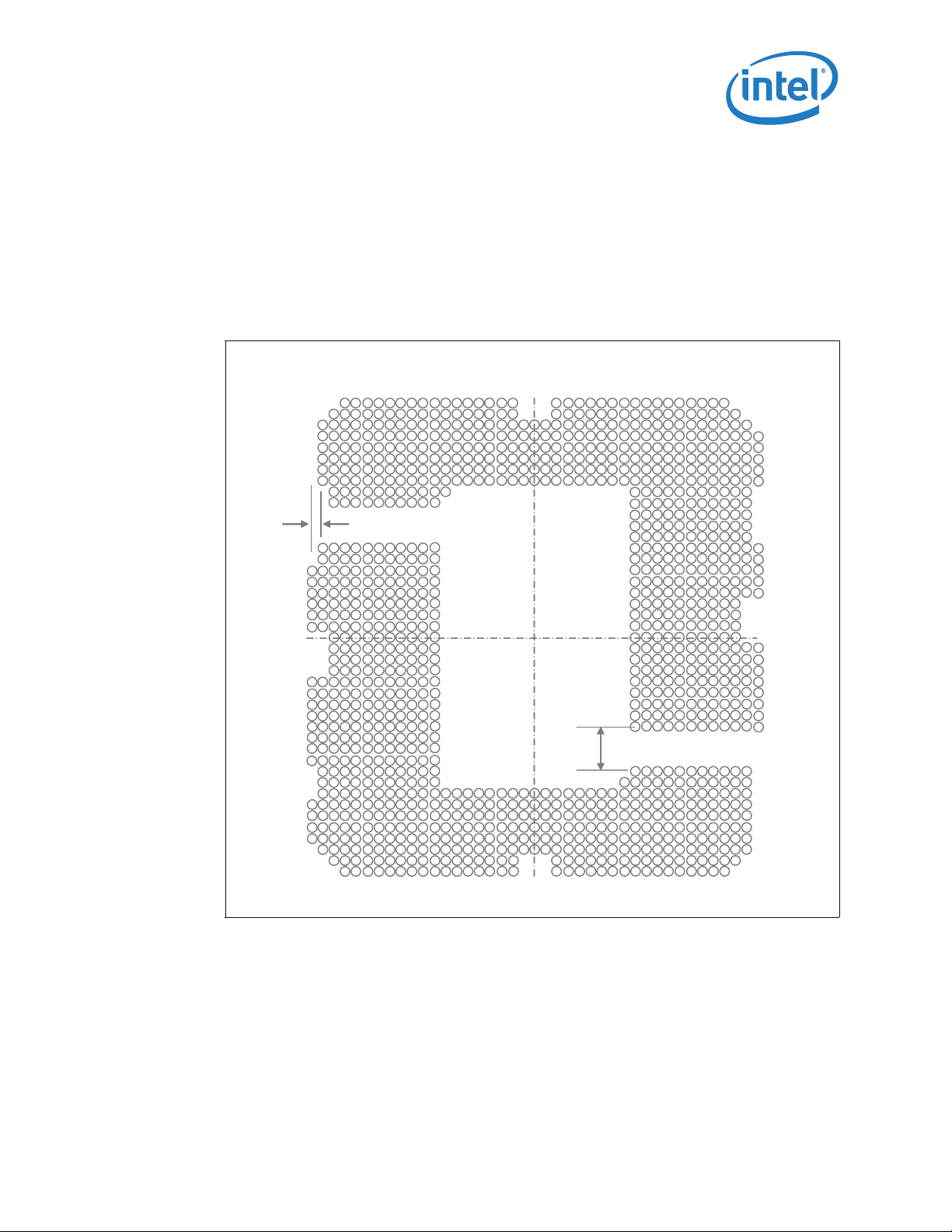
3.1 Board Layout
The land pattern for the LGA1156 socket is 36 mils X 36 mils (X by Y) within each of the
two L-shaped sections. Note that there is no round-off (conversion) error between
socket pitch (0.9144 mm) and board pitch (36 mil) as these values are equivalent. The
two L-sections are offset by 0.9144 mm (36 mil) in the x direction and 3.114 mm
(122.6 mil) in the y direction (see Figure 3-3). This was to achieve a common package
land to PCB land offset that ensures a single PCB layout for socket designs from the
multiple vendors.
Figure 3-3. LGA1156 Socket Land Pattern (Top View of Board)
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF AH AK AM AP AT AV AY
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF AH AK AM AP AT AV AY
36mil (0.9144 mm)
36mil (0.9144 mm)
30
30
30
29
29
29
28
28
28
27
27
27
26
26
26
25
25
25
24
24
24
23
23
23
22
22
22
21
21
21
20
20
20
19
19
19
18
18
18
17
17
17
16
16
16
15
15
15
14
14
14
13
13
13
12
12
12
11
11
11
10
10
10
9
9
9
8
8
8
7
7
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
2
2
2
1
1
1
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
A C E G J L N R U W AA AC AE AG AJ AL AN AR AU AW
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF AH AK AM AP AT AV AY
B D F H K M P T V Y AB AD AF AH AK AM AP AT AV AY
122.6 mil (3.1144mm)
122.6 mil (3.1144mm)
40
40
39
39
38
38
37
37
36
36
35
35
34
34
33
33
32
32
31
31
30
30
29
29
28
28
27
27
26
26
25
25
24
24
23
23
22
22
21
21
20
20
19
19
18
18
17
17
16
16
15
15
14
14
13
13
12
12
11
11
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 19
Page 20
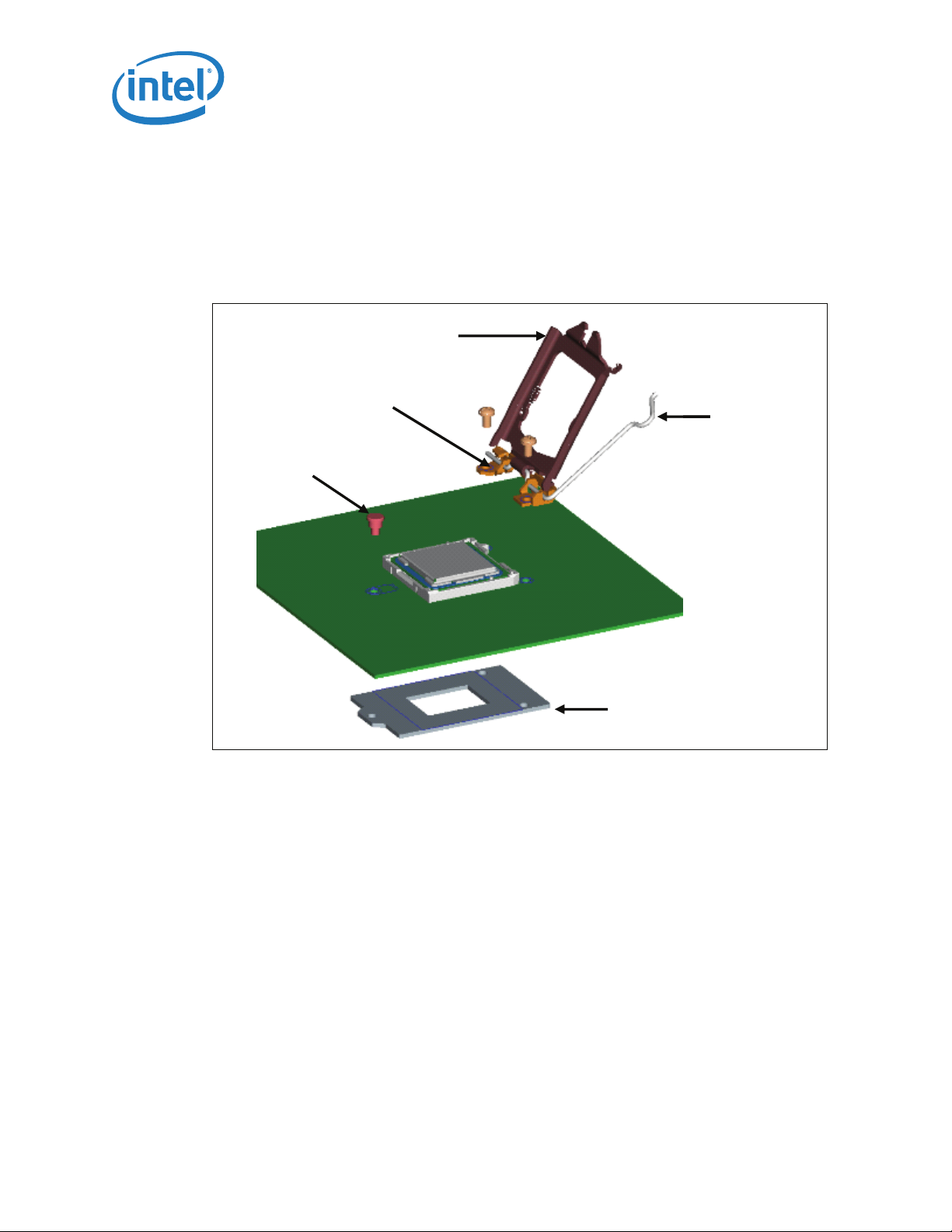
3.2 Attachment to Motherboard
The socket is attached to the motherboard by 1156 solder balls. There are no additional
external methods (that is, screw, extra solder, adhesive, etc.) to attach the socket.
As indicated in Figure 3-1, the Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) is not present
during the attach (reflow) process.
Figure 3-4. Attachment to Motherboard
Load plate
Load plate
Frame
Frame
Shoulder
Shoulder
Screw
Screw
LGA1156 Socket
Load Lever
Load Lever
Back Plate
Back Plate
3.3 Socket Components
The socket has two main components, the socket body and Pick and Place (PnP) cover,
and is delivered as a single integral assembly. Refer to Appendix C for detailed
drawings.
3.3.1 Socket Body Housing
The housing material is thermoplastic or equivalent with UL 94 V-0 flame rating capable
of withstanding 260 °C for 40 seconds, which is compatible with typical reflow/rework
profiles. The socket coefficient of thermal expansion (in the XY plane), and creep
properties, must be such that the integrity of the socket is maintained for the
conditions listed in Chapter 5.
The color of the housing will be dark as compared to the solder balls to provide the
contrast needed for pick and place vision systems.
20 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 21

LGA1156 Socket
3.3.2 Solder Balls
A total of 1156 solder balls corresponding to the contacts are on the bottom of the
socket for surface mounting with the motherboard. The socket solder ball has the
following characteristics:
• Lead free SAC (SnAgCu) 305 solder alloy with a silver (Ag) content between 3%
and 4% and a melting temperature of approximately 217 °C. The alloy must be
compatible with immersion silver (ImAg) and Organic Solderability Protectant
(OSP) motherboard surface finishes and a SAC alloy solder paste.
The co-planarity (profile) and true position requirements are defined in Appendix C.
3.3.3 Contacts
Base material for the contacts is high strength copper alloy.
For the area on socket contacts where processor lands will mate, there is a 0.381 μm
[15 μinches] minimum gold plating over 1.27 μm [50 μinches] minimum nickel
underplate.
No contamination by solder in the contact area is allowed during solder reflow.
3.3.4 Pick and Place Cover
The cover provides a planar surface for vacuum pick up used to place components in
the Surface Mount Technology (SMT) manufacturing line. The cover remains on the
socket during reflow to help prevent contamination during reflow. The cover can
withstand 260 °C for 40 seconds (typical reflow/rework profile) and the conditions
listed in Chapter 5 without degrading.
As indicated in Figure 3-5, the cover remains on the socket during ILM installation, and
should remain on whenever possible to help prevent damage to the socket contacts.
Cover retention must be sufficient to support the socket weight during lifting,
translation, and placement (board manufacturing), and during board and system
shipping and handling. Covers can be removed without tools.
The socket vendors have a common interface on the socket body where the PnP cover
attaches to the socket body. This should allow the PnP covers to be compatible between
socket suppliers.
As indicated in Figure 3-5, a Pin1 indicator on the cover provides a visual reference for
proper orientation with the socket.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 21
Page 22
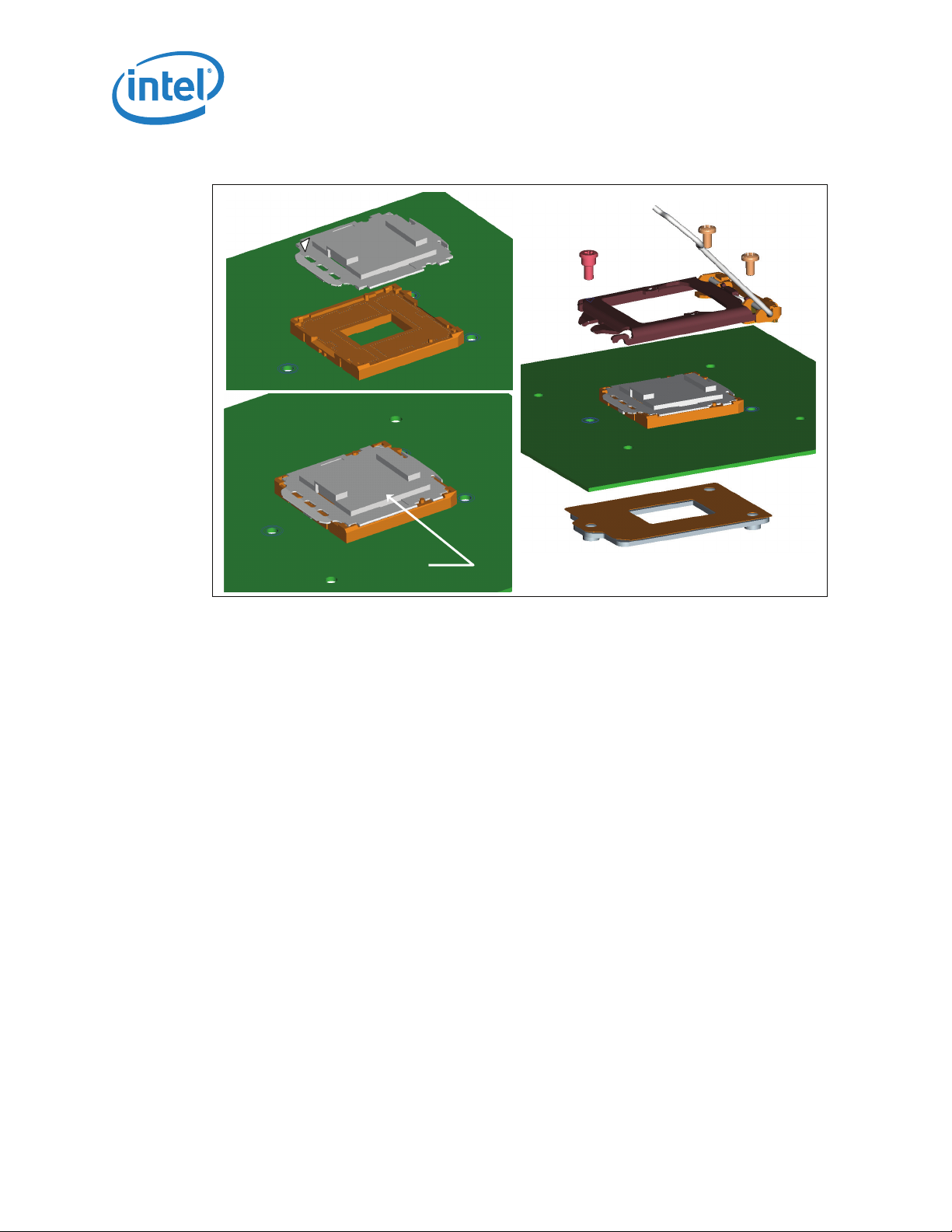
Figure 3-5. Pick and Place Cover
Pin 1
Pin 1
LGA1156 Socket
Pick & Place Cover
Pick & Place Cover
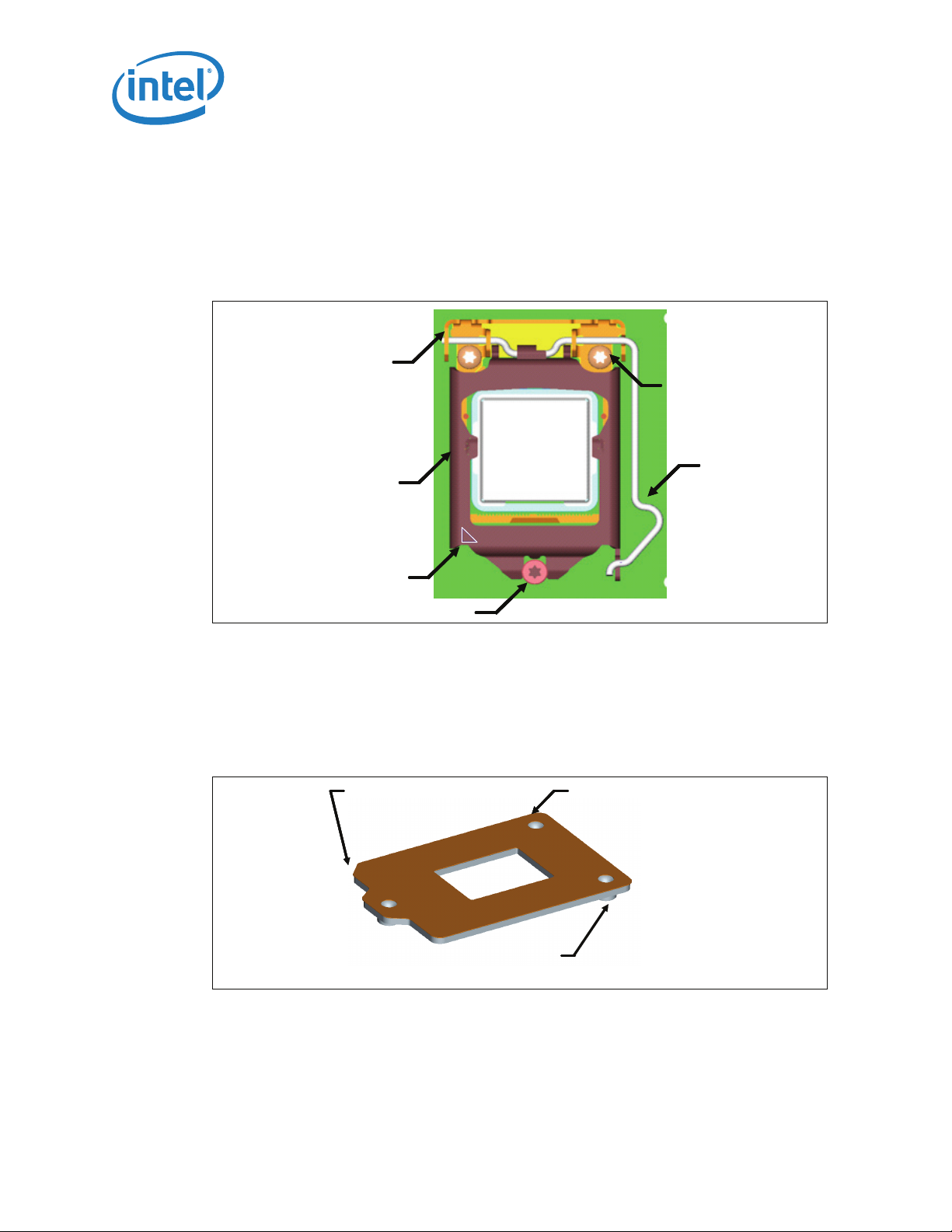
3.4 Package Installation / Removal
As indicated in Figure 3-6, access is provided to facilitate manual installation and
removal of the package.
To assist in package orientation and alignment with the socket:
• The package Pin 1 triangle and the socket Pin1 chamfer provide visual reference for
proper orientation.
• The package substrate has orientation notches along two opposing edges of the
package, offset from the centerline. The socket has two corresponding orientation
posts to physically prevent mis-orientation of the package. These orientation
features also provide initial rough alignment of package to socket.
• The socket has alignment walls at the four corners to provide final alignment of the
package.
ILM Installation
ILM Installation
22 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 23
LGA1156 Socket
(
)
.
Figure 3-6. Package Installation / Removal Features
Package
Pin 1
Indicator
Orientation
Notch
(2 Places)
Alignment
Post
2 Places
3.4.1 Socket Standoffs and Package Seating Plane
Pin 1
Chamfer
Finger
Access
(2 Places)
Standoffs on the bottom of the socket base establish the minimum socket height after
solder reflow and are specified in Appendix C.
Similarly, a seating plane on the top-side of the socket establishes the minimum
package height. See Section 5.2 for the calculated IHS height above the motherboard.
3.5 Durability
The socket must withstand 20 cycles of processor insertion and removal. The max
chain contact resistance from Tab l e 5 - 4 must be met when mated in the 1st and 20th
cycles.
The socket Pick and Place cover must withstand 15 cycles of insertion and removal.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 23
Page 24

3.6 Markings
There are three markings on the socket:
• LGA1156: Font type is Helvetica Bold - minimum 6 point (2.125 mm).
• Manufacturer's insignia (font size at supplier's discretion).
• Lot identification code (allows traceability of manufacturing date and location).
All markings must withstand 260°C for 40 seconds (typical reflow/rework profile)
without degrading, and must be visible after the socket is mounted on the
motherboard.
LGA1156 and the manufacturer's insignia are molded or laser marked on the side wall.
3.7 Component Insertion Forces
Any actuation must meet or exceed SEMI S8-95 Safety Guidelines for Ergonomics/
Human Factors Engineering of Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment, example Table
R2-7 (Maximum Grip Forces). The socket must be designed so that it requires no force
to insert the package into the socket.
LGA1156 Socket
3.8 Socket Size
Socket information needed for motherboard design is given in Appendix C.
This information should be used in conjunction with the reference motherboard keepout drawings provided in Appendix B to ensure compatibility with the reference thermal
mechanical components.
§
24 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 25

Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
4 Independent Loading
Mechanism (ILM)
The Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) provides the force needed to seat the
1156-LGA land package onto the socket contacts. The ILM is physically separate from
the socket body. The assembly of the ILM to the board is expected to occur after wave
solder. The exact assembly location is dependent on manufacturing preference and test
flow. See the Manufacturing Advantage Service collateral for this platform for additional
guidance.
Note: The ILM has two critical functions: deliver the force to seat the processor onto the
socket contacts and distribute the resulting compressive load evenly through the socket
solder joints.
Note: The mechanical design of the ILM is integral to the overall functionality of the LGA1156
socket. Intel performs detailed studies on integration of processor package, socket and
ILM as a system. These studies directly impact the design of the ILM. The Intel
reference ILM will be “build to print” from Intel controlled drawings. Intel recommends
using the Intel Reference ILM. Custom non-Intel ILM designs do not benefit from Intel's
detailed studies and may not incorporate critical design parameters.
4.1 Design Concept
The ILM consists of two assemblies that will be procured as a set from the enabled
vendors. These two components are ILM cover assembly and back plate. To secure the
two assemblies, two types of fasteners are required a pair (2) of standard 6-32 thread
screws and a custom 6-32 thread shoulder screw. The reference design incorporates a
T-20 Torx* head fastener. The Torx* head fastener was chosen to ensure end users do
not inadvertently remove the ILM assembly and for consistency with the LGA1366
socket ILM. The Torx* head fastener is also less susceptible to driver slippage. Once
assembled the ILM is not required to be removed to install / remove the motherboard
from a chassis.
4.1.1 ILM Cover Assembly Design Overview
The ILM Cover assembly consists of three major pieces: load lever, load plate and the
hinge frame assembly.
All of the pieces in the ILM cover assembly except the hinge frame and the screws used
to attach the back plate are fabricated from stainless steel. The hinge frame is plated.
The frame provides the hinge locations for the load lever and load plate. An insulator is
pre-applied to the bottom surface of the hinge frame.
The cover assembly design ensures that once assembled to the back plate the only
features touching the board are the shoulder screw and the insulated hinge frame
assembly. The nominal gap of the load plate to the board is ~1 mm.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 25
Page 26
When closed, the load plate applies two point loads onto the IHS at the “dimpled”
r
r
features shown in Figure 4-1. The reaction force from closing the load plate is
transmitted to the hinge frame assembly and through the fasteners to the back plate.
Some of the load is passed through the socket body to the board inducing a slight
compression on the solder joints.
A pin 1 indicator will be marked on the ILM cover assembly.
Figure 4-1. ILM Cover Assembly
Hinge /
Hinge /
Frame
Frame
Assy
Assy
Load
Load
Plate
Plate
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
Fasteners
Fasteners
Load
Load
Leve
Leve
Pin 1 Indicator
Pin 1 Indicator
Shoulder Screw
Shoulder Screw
4.1.2 ILM Back Plate Design Overview
The back plate (see Figure 4-2) is a flat steel back plate with pierced and extruded
features for ILM attach. A clearance hole is located at the center of the plate to allow
access to test points and backside capacitors if required. An insulator is pre-applied. A
notch is placed in one corner to assist in orienting the back plate during assembly.
Figure 4-2. Back Plate
Assembly
Assembly
Orient ation
Orient ation
Featur e
Featur e
Pierced & Extruded
Pierced & Extruded
Thread Features
Thread Features
Die Cut
Die Cut
Insulator
Insulator
26 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 27
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
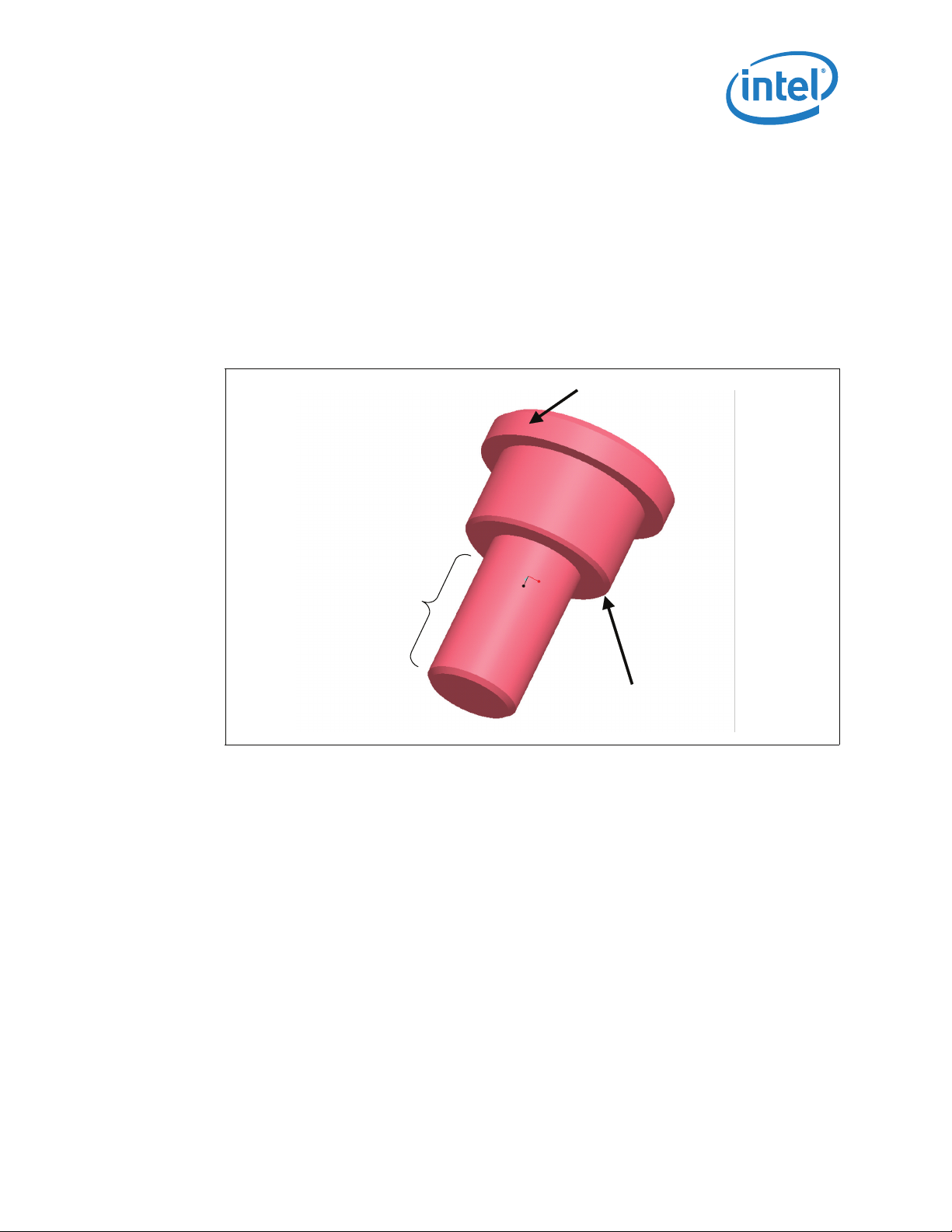
4.1.3 Shoulder Screw and Fasteners Design Overview
The shoulder screw is fabricated from carbonized steel rod. The shoulder height and
diameter are integral to the mechanical performance of the ILM. The diameter provides
alignment of the load plate. The height of the shoulder ensures the proper loading of
the IHS to seat the processor on the socket contacts. The design assumes the shoulder
screw has a minimum yield strength of 235 MPa.
Note: The reference design incorporates a T-20 Torx* head fastener. The Torx* head fastener
was chosen to ensure end users do not inadvertently remove the ILM assembly and for
consistency with the LGA1366 socket ILM.
Figure 4-3. Shoulder Screw
Cap
6-32 thread
Shoulder
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 27
Page 28
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
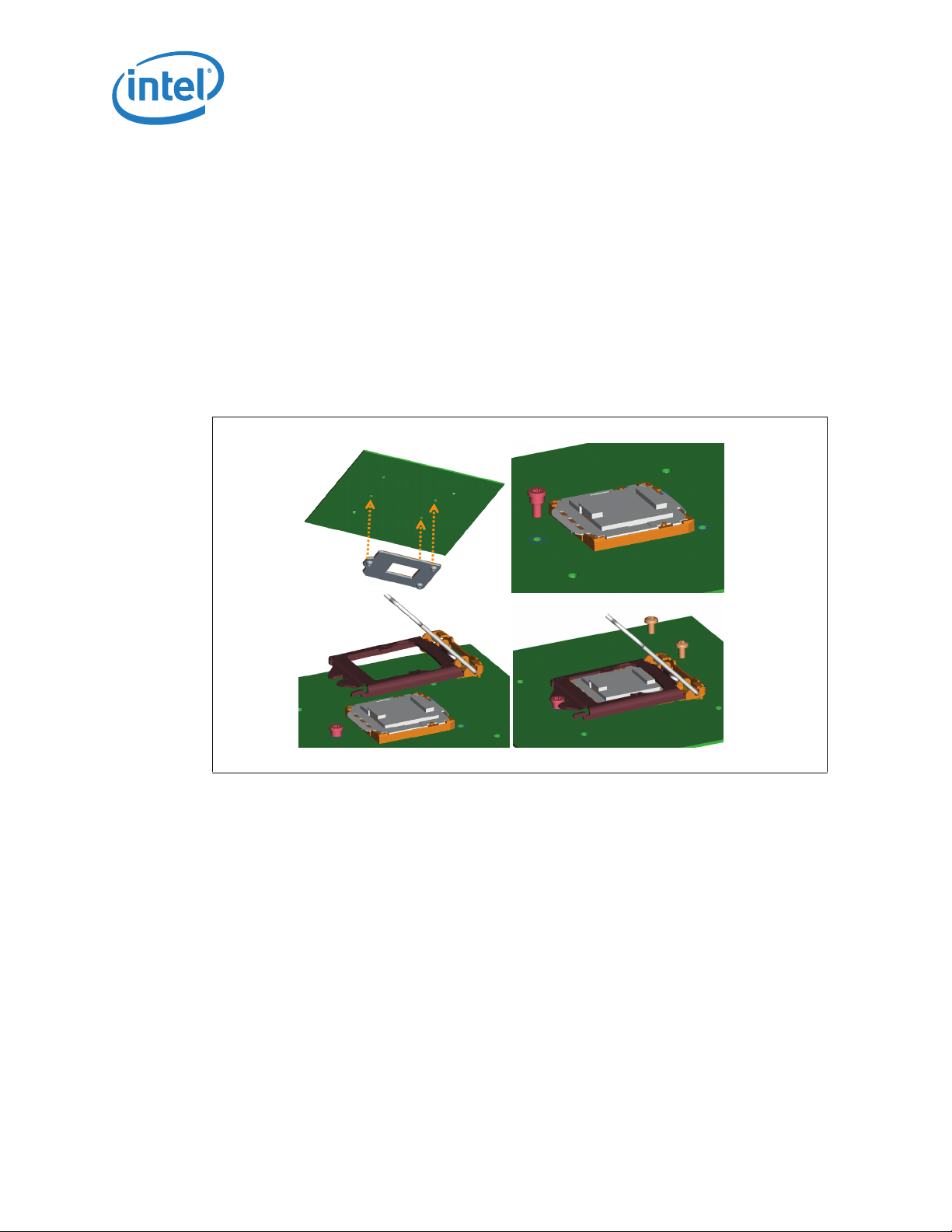
4.2 Assembly of ILM to a Motherboard
The ILM design allows a bottoms up assembly of the components to the board. See
Figure 4-4 for step by step assembly sequence.
1. Place the back plate in a fixture. The motherboard is aligned with the fixture.
2. Install the shoulder screw in the single hole near Pin 1 of the socket. Torque to a
minimum and recommended 8 inch-pounds, but not to exceed 10 inch-pounds.
3. Align and place the ILM cover assembly over the socket.
4. Install two (2) 6-32 fasteners. Torque to a minimum and recommended 8 inchpounds, but not to exceed 10 inch-pounds.
The thread length of the shoulder screw accommodates a nominal board thicknesses of
.
Figure 4-4. ILM Assembly
0.062”.
Step 1 Step 2
Step 1 Step 2
Step 1 Step 2
Step 4
Step 4
Step 3
Step 3
Step 3
28 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Step 4
Page 29
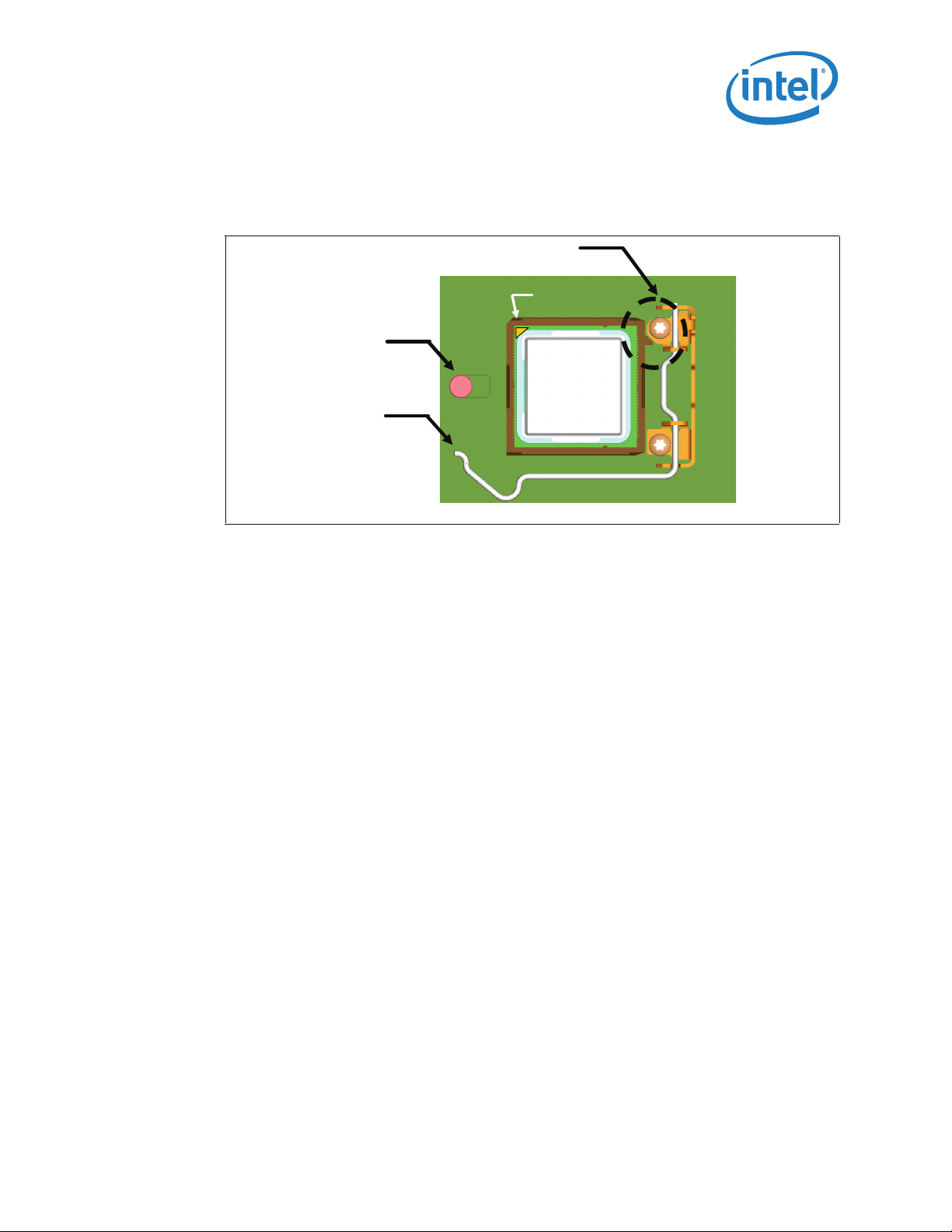
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
Alignment
As indicated in Figure 4-5, the shoulder screw, socket protrusion and ILM key features
prevent 180 degree rotation of ILM cover assembly with respect to socket. The result is
a specific Pin 1 orientation with respect to ILM lever.
Figure 4-5. Pin 1 and ILM Lever
Shoulder
Screw
Load
Lever
Features
Pin 1
Load plate not
shown for
clarity
4.3 ILM Interchangeability
ILM cover assemblies and ILM back plates built from the Intel controlled drawings are
intended to be interchangeable. Interchangeability is defined as an ILM from Vendor A
that will demonstrate acceptable manufacturability and reliability with a socket body
from Vendor A, B, or C. ILM covers assemblies and ILM back plates from all vendors
that are also interchangeable.
The ILMs are an integral part of the socket validation testing. ILMs from each vendor
have been tested with the socket bodies from each of the current vendors. The tests
include manufacturability, bake and thermal cycling.
See Appendix A for vendor part numbers that were tested.
Note: Desktop and Server ILM backplate/screws are NOT interchangeable.
Note: ILMs that are not compliant with the Intel controlled ILM drawings can not be assured
to be interchangeable.
4.4 Markings
There are four markings on the ILM:
• 115XLM: Font type is Helvetica Bold - minimum 6 point (2.125 mm).
• Manufacturer's insignia (font size at supplier's discretion).
• Lot identification code (allows traceability of manufacturing date and location).
• Pin 1 indicator on the load plate.
All markings must be visible after the ILM is assembled on the motherboard.
115XLM and the manufacturer's insignia can be ink stamped or laser marked on the
side wall.
§
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 29
Page 30

Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
30 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 31

LGA1156 Socket and ILM Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Specifications
5 LGA1156 Socket and ILM
Electrical, Mechanical, and
Environmental Specifications
This chapter describes the electrical, mechanical, and environmental specifications for
the LGA1156 socket and the Independent Loading Mechanism.
5.1 Component Mass
Table 5-1. Socket Component Mass
Component Mass
Socket Body, Contacts and PnP Cover 10 g
ILM Cover 29 g
ILM Back Plate 38 g
5.2 Package/Socket Stackup Height
Ta b le 5 - 2 provides the stackup height of a processor in the 1156-land LGA package and
LGA1156 socket with the ILM closed and the processor fully seated in the socket.
Table 5-2. 1156-land Package and LGA1156 Socket Stackup Height
Component Stackup Height Note
Integrated Stackup Height
From Top of Board to Top of IHS
Socket Nominal Seating Plane Height 3.4 ± 0.2 mm 1
Package Nominal Thickness (lands to top of IHS) 4.381 ± 0.269 mm 1
Notes:
1. This data is provided for information only, and should be derived from: (a) the height of the socket seating
plane above the motherboard after reflow, given in Appendix C, (b) the height of the package, from the
package seating plane to the top of the IHS, and accounting for its nominal variation and tolerances that
are given in the corresponding processor datasheet.
2. The integrated stackup height value is a RSS calculation based on current and planned processors that will
use the ILM design.
(mm)
7.781 ± 0.335 mm 2
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 31
Page 32

LGA1156 Socket and ILM Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Specifications
5.3 Socket Maximum Temperature
The power dissipated within the socket is a function of the current at the pin level and
the effective pin resistance. The key temperature limit for the LGA1156 socket is:
• Socket contact interface with package < 100 °C.
5.4 Loading Specifications
The socket will be tested against the conditions listed in Chapter 9 with heatsink and
the ILM attached, under the loading conditions outlined in this section.
Tab l e 5- 3 provides load specifications for the LGA1156 socket with the ILM installed.
The maximum limits should not be exceeded during heatsink assembly, shipping
conditions, or standard use condition. Exceeding these limits during test may result in
component failure. The socket body should not be used as a mechanical reference or
load-bearing surface for thermal solutions.
Table 5-3. Socket & ILM Mechanical Specifications
Parameter Min Max Notes
ILM static compressive load on processor IHS 356 N [80 lbf] 600 N [135 lbf] 3, 4, 7, 8
Heatsink static compressive load 0 N [0 lbf] 222 N [50 lbf] 1, 2, 3
Total static compressive Load
(ILM plus Heatsink)
Dynamic Compressive Load
(with heatsink installed)
Pick & Place cover insertion force N/A 10.2 N [2.3 lbf] -
Pick & Place cover removal force 2.2N [0.5 lbf] 7.56 N [1.7 lbf] 9
Load lever actuation force N/A 38.3 N [8.6 lbf] in the
Maximum heatsink mass N/A 500g 10
356 N [80 lbf] 822 N [185 lbf] 3, 4, 7, 8
N/A 712 N [160 lbf] 1, 3, 5, 6
vertical direction
10.2 N [2.3 lbf] in the
lateral direction.
-
Notes:
1. These specifications apply to uniform compressive loading in a direction perpendicular to the IHS top
surface.
2. This is the minimum and maximum static force that can be applied by the heatsink and it’s retention
solution to maintain the heatsink to IHS interface. This does not imply the Intel reference TIM is validated
to these limits.
3. Loading limits are for the LGA1156 socket.
4. This minimum limit defines the static compressive force required to electrically seat the processor onto the
socket contacts. The minimum load is a beginning of life load.
5. Dynamic loading is defined as a load a 4.3 m/s [170 in/s] minimum velocity change average load
superimposed on the static load requirement.
6. Test condition used a heatsink mass of 500gm [1.102 lb] with 50 g acceleration (table input) and an
assumed 2X Dynamic Acceleration Factor (DAF). The dynamic portion of this specification in the product
application can have flexibility in specific values. The ultimate product of mass times acceleration plus static
heatsink load should not exceed this limit.
7. The maximum BOL value and must not be exceeded at any point in the product life.
8. The minimum value is a beginning of life loading requirement based on load degradation over time.
9. The maximum removal force is the flick up removal upwards thumb force (measured at 45
to SMT operation for system assembly. Only the minimum removal force is applicable to vertical removal in
SMT operation for system assembly.
10. The maximum heatsink mass includes the core, extrusion, fan and fasteners. This mass limit is evaluated
using the refence heatsink attach to the PCB.
32 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
o
), not applicable
Page 33

LGA1156 Socket and ILM Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Specifications
5.5 Electrical Requirements
LGA1156 socket electrical requirements are measured from the socket-seating plane of
the processor to the component side of the socket PCB to which it is attached. All
specifications are maximum values (unless otherwise stated) for a single socket
contact, but includes effects of adjacent contacts where indicated.
Table 5-4. Electrical Requirements for LGA1156 Socket
Parameter Value Comment
Mated loop inductance, Loop <3.6nH The inductance calculated for two contacts,
Socket Average Contact Resistance
(EOL)
Max Individual Contact Resistance
(EOL)
Bulk Resistance Increase ≤
Dielectric Withstand Voltage 360 Volts RMS
Insulation Resistance 800 MΩ
19 mOhm The socket average contact resistance target is
100 mOhm The specification listed is at room temperature
3 mΩ The bulk resistance increase per contact from
considering one forward conductor and one
return conductor. These values must be satisfied
at the worst-case height of the socket.
calculated from the following equation:
sum (Ni X LLCRi) / sum (Ni)
• LLCRi is the chain resistance defined as the
resistance of each chain minus resistance of
shorting bars divided by number of lands in
the daisy chain.
• Ni is the number of contacts within a chain.
• I is the number of daisy chain, ranging from
1 to 119 (total number of daisy chains).
The specification listed is at room temperature
and has to be satisfied at all time.
and has to be satisfied at all time.
Socket Contact Resistance:
the socket contact, solderball, and interface
resistance to the interposer land; gaps included.
25 °C to 100 °C.
The resistance of
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 33
Page 34

LGA1156 Socket and ILM Electrical, Mechanical, and Environmental Specifications
5.6 Environmental Requirements
Design, including materials, shall be consistent with the manufacture of units that meet
the following environmental reference points.
The reliability targets in this section are based on the expected field use environment
for these products. The test sequence for new sockets will be developed using the
knowledge-based reliability evaluation methodology, which is acceleration factor
dependent. A simplified process flow of this methodology can be seen in Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-1. Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology
Establish the
market/expected use
environment for the
technology
Develop Speculative
stress conditions based on
historical data, content
experts, and literature
search
Freeze stressing
requirements and perform
additional data turns
Perform stressing to
validate accelerated
stressing assumptions and
determine acceleration
factors
A detailed description of this methodology can be found at: ftp://download.intel.com/
technology/itj/q32000/pdf/reliability.pdf.
§
34 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 35

Thermal Specifications
6 Thermal Specifications
The processor requires a thermal solution to maintain temperatures within its operating
limits. Any attempt to operate the processor outside these operating limits may result
in permanent damage to the processor and potentially other components within the
system. Maintaining the proper thermal environment is key to reliable, long-term
system operation.
A complete solution includes both component and system level thermal management
features. Component level thermal solutions can include active or passive heatsinks
attached to the processor integrated heat spreader (IHS).
This chapter provides data necessary for developing a complete thermal solution. For
more information on ATX reference thermal solution design, refer to Chapter 8.
6.1 Thermal Specifications
To allow the optimal operation and long-term reliability of Intel processor-based
systems, the processor must remain within the minimum and maximum case
temperature (T
Thermal solutions not designed to provide this level of thermal capability may affect the
long-term reliability of the processor and system. For more details on thermal solution
design, refer to the Chapter 8.
) specifications as defined by the applicable thermal profile.
CASE
The processors implement a methodology for managing processor temperatures which
is intended to support acoustic noise reduction through fan speed control and to assure
processor reliability. Selection of the appropriate fan speed is based on the relative
temperature data reported by the processor’s Digital Temperature Sensor (DTS). The
DTS can be read using the Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) as described
in Section 6.3. Alternatively, when PECI is monitored by the PCH, the processor
temperature can be read from the PCH using the SMBus protocol defined in Embedded
Controller Support Provided by Platform Controller Hub (PCH). The temperature
report ed over PECI is always a neg ative value and represents a delta below the onset of
thermal control circuit (TCC) activation, as indicated by PROCHOT# (see Section 6.2,
Processor Thermal Features). Systems that implement fan speed control must be
designed to use this data. Systems that do not alter the fan speed only need to ensure
the case temperature meets the thermal profile specifications.
A single integer change in the PECI value corresponds to approximately 1 °C change in
processor temperature. Although each processors DTS is factory calibrated, the
accuracy of the DTS will vary from part to part and may also vary slightly with
temperature and voltage. In general, each integer change in PECI should equal a
temperature change between 0.9 °C and 1.1 °C.
Analysis indicates that real applications are unlikely to cause the processor to consume
maximum power dissipation for sustained time periods. Intel recommends that
complete thermal solution designs target the Thermal Design Power (TDP), instead of
the maximum processor power consumption. The Adaptive Thermal Monitor feature is
intended to help protect the processor in the event that an application exceeds the TDP
recommendation for a sustained time period. For more details on this feature, refer to
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 35
Page 36

Section 6.2. To ensure maximum flexibility for future processors, systems should be
designed to the Thermal Solution Capability guidelines, even if a processor with lower
power dissipation is currently planned.
Table 6-1. Processor Thermal Specifications
Thermal Specifications
Max
Power
8
(W)
exceeds V
CCP
Package
C1E
1,2,5,9
28 22 5.5 95 5
CC_MAX
Product Guidelines
Intel Core™ i7-800
and i5-700 desktop
processor series
(95 W)
Notes:
1. The package C-state power is the worst case power in the system configured as follows:
- Memory configured for DDR3 1333 and populated with 2 DIMM per channel.
- DMI and PCIe links are at L1.
2. Specification at DTS = -50 and minimum voltage loadline.
3. Specification at DTS = -50 and minimum voltage loadline.
4. Specification at DTS = -64 and minimum voltage loadline.
5. These DTS values (in Notes 2-4) are based on the TCC Activation MSR having a value of 100, see
Section 6.2.1.
6. These values are specified at V
Systems must be designed to ensure the processor is not to be subjected to any static V
combination wherein V
datasheet.
7. Thermal Design Power (TDP) should be used for processor thermal solution design targets. TDP is not the
maximum power that the processor can dissipate. TDP is measured at DTS = -1.
TDP is achieved with the Memory configured for DDR3 1333 and 2 DIMMs per channel.
8. The 2009B (09B) guidelines provide a design target for meeting all planned processor frequency
requirements. The 2009B (09B) is equivalent to the thermal requirements for the Intel
Q9000 processor series. The 2009A (09A) is equivalent to the thermal requirements for the Intel
Duo E8000 processor series. Reuse of those thermal solutions is recommended with the updated
mechanical attach to straddle the LGA1156 socket.
2009B
(09B)
Package
(W)
and V
CCP_MAX
Max
Power
C3
1,3,5,9
for all other voltage rails for all processor frequencies.
NOM
at specified I
Max
Power
Package
C6
1,4,5,9
(W)
. Refer to the loadline specifications in the
CCP
TTV
Thermal
Design
Power
6,7
(W)
Min
CASE
T
(°C)
CC
®
Core™ 2 Quad
and ICC
Maximum
TTV TCASE
Figure 6-1 &
9. Not 100% tested. Specified by design characterization.
(°C)
Table 6- 2
®
Core™ 2
36 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 37

Thermal Specifications
6.1.1 Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Thermal Profile
Figure 6-1. Thermal Test Vehicle Thermal Profile for Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700
Desktop Processor Series
TTV Thermal Profile
75.0
70.0
Y = Power x 0.29 + 45.1
65.0
60.0
55.0
50.0
TTV Case Temperature (°C)
45.0
40.0
0 20406080100
TTV Power (W)
Notes:
1. Please refer to Tab le 6- 2 for discrete points that constitute the thermal profile.
2. Refer to Chapter 8 and Chapter 9 for system and environmental implementation details.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 37
Page 38

Thermal Specifications
Table 6-2. Thermal Test Vehicle Thermal Profile for Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700
Desktop Processor Series
Power (W) T
0 45.1 50 59.6
2 45.7 52 60.2
4 46.3 54 60.8
6 46.8 56 61.3
8 47.4 58 61.9
10 48.0 60 62.5
12 48.6 62 63.1
14 49.2 64 63.7
16 49.7 66 64.2
18 50.3 68 64.8
20 50.9 70 65.4
22 51.5 72 66.0
24 52.1 74 66.6
26 52.6 76 67.1
28 53.2 78 67.7
30 53.8 80 68.3
32 54.4 82 68.9
34 55.0 84 69.5
36 55.5 86 70.0
38 56.1 88 70.6
40 56.7 90 71.2
42 57.3 92 71.8
44 57.9 94 72.4
46 58.4 95 72.7
48 59.0
CASE_MAX
(°C) Power (W) T
CASE_MAX
(°C)
38 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 39

Thermal Specifications
6.1.2 Processor Specification for Operation Where Digital
Thermal Sensor Exceeds T
When the DTS value is less than T
the speed of the thermal solution fan. This remains the same as with the previous
guidance for fan speed control.
CONTROL
CONTROL
, the fan speed control algorithm can reduce
During operation, when the DTS value is greater than T
algorithm must drive the fan speed to meet or exceed the target thermal solution
performance (ΨCA) shown in Tab l e 6 - 3 for the Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 desktop
processor series (95 W). To get the full acoustic benefit of the DTS specification,
ambient temperature monitoring is necessary. See Chapter 7 for details on
characterizing the fan speed to Ψ
and ambient temperature measurement.
CA
Table 6-3. Thermal Solution Performance above T
and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series
T
1
AMBIENT
45.1 0.290 0.290
44.0 0.310 0.301
43.0 0.328 0.312
42.0 0.346 0.322
41.0 0.364 0.333
40.0 0.383 0.343
39.0 0.401 0.354
38.0 0.419 0.364
37.0 0.437 0.375
36.0 0.455 0.385
35.0 0.473 0.396
34.0 0.491 0.406
33.0 0.510 0.417
32.0 0.528 0.427
31.0 0.546 0.438
30.0 0.564 0.448
29.0 0.582 0.459
28.0 0.600 0.469
27.0 0.618 0.480
26.0 0.637 0.491
25.0 0.655 0.501
24.0 0.673 0.512
23.0 0.691 0.522
22.0 0.709 0.533
21.0 0.727 0.543
20.0 0.746 0.554
ΨCA at
DTS = T
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
, the fan speed control
for the Intel® Core™ i7-800
2
ΨCA at
DTS = -1
3
Notes:
1. The ambient temperature is measured at the inlet to the processor thermal solution.
2. This column can be expressed as a function of T
3. This column can be expressed as a function of T
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 39
= 0.29 + (45.1 - T
Ψ
CA
= 0.29 + (45.1 - T
Ψ
CA
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
) x 0.0181
) x 0.0105
by the following equation:
AMBIENT
by the following equation:
AMBIENT
Page 40

6.1.3 Thermal Metrology
Thermal Specifications
The maximum TTV case temperatures (T
appropriate TTV thermal profile earlier in this chapter. The TTV T
geometric top center of the TTV integrated heat spreader (IHS). Figure 6-2 illustrates
the location where T
temperature measurements should be made. See Figure B-12
CASE
for drawings showing the thermocouple attach to the TTV package.
Figure 6-2. TTV Case Temperature (T
Measure T
the geometric
center of the
package
CASE
at
CASE-MAX
) Measurement Location
CASE
37.5
) can be derived from the data in the
is measured at the
CASE
37.5
Note: The following supplier can machine the groove and attach a thermocouple to the IHS.
The supplier is listed the table below as a convenience to Intel’s general customers and
the list may be subject to change without notice. THERM-X OF CALIFORNIA, 1837
Whipple Road, Hayward, Ca 94544. Ernesto B Valencia +1-510-441-7566 Ext. 242
ernestov@therm-x.com. The vendor part number is XTMS1565.
6.2 Processor Thermal Features
6.2.1 Processor Temperature
A new feature in the processors is a software readable field in the
IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET register that contains the minimum temperature at
which the TCC will be activated and PROCHOT# will be asserted. The TCC activation
temperature is calibrated on a part-by-part basis and normal factory variation may
result in the actual TCC activation temperature being higher than the value listed in the
register. TCC activation temperatures may change based on processor stepping,
frequency or manufacturing efficiencies.
40 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 41

Thermal Specifications
6.2.2 Adaptive Thermal Monitor
The Adaptive Thermal Monitor feature provides an enhanced method for controlling the
processor temperature when the processor silicon exceeds the Thermal Control Circuit
(TCC) activation temperature. Adaptive Thermal Monitor uses TCC activation to reduce
processor power via a combination of methods. The first method (Frequency/VID
control, similar to Intel
involves the processor reducing its operating frequency (using the core ratio multiplier)
and input voltage (using the VID signals). This combination of lower frequency and VID
results in a reduction of the processor power consumption. The second method (clock
modulation, known as Intel
processors) reduces power consumption by modulating (starting and stopping) the
internal processor core clocks. The processor intelligently selects the appropriate TCC
method to use on a dynamic basis. BIOS is not required to select a specific method (as
with previous-generation processors supporting TM1 or TM2). The temperature at
which Adaptive Thermal Monitor activates the Thermal Control Circuit is factory
calibrated and is not user configurable. Snooping and interrupt processing are
performed in the normal manner while the TCC is active.
When the TCC activation temperature is reached, the processor will initiate TM2 in
attempt to reduce its temperature. If TM2 is unable to reduce the processor
temperature then TM1 will be also be activated. TM1 and TM2 will work together (clocks
will be modulated at the lowest frequency ratio) to reduce power dissipation and
temperature.
®
Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2) in previous generation processors)
®
Thermal Monitor 1 or TM1 in previous generation
With a properly designed and characterized thermal solution, it is anticipated that the
TCC would only be activated for very short periods of time when running the most
power intensive applications. The processor performance impact due to these brief
periods of TCC activation is expected to be so minor that it would be immeasurable. An
under-designed thermal solution that is not able to prevent excessive activation of the
TCC in the anticipated ambient environment may cause a noticeable performance loss,
and in some cases may result in a T
temperature and may affect the long-term reliability of the processor. In addition, a
thermal solution that is significantly under-designed may not be capable of cooling the
processor even when the TCC is active continuously. Refer to the appropriate Thermal
Mechanical Design Guidelines for information on designing a compliant thermal
solution.
The Intel Thermal Monitor does not require any additional hardware, software drivers,
or interrupt handling routines. The following sections provide more details on the
different TCC mechanisms used by the processor.
6.2.2.1 Frequency/VID Control
When the Digital Temperature Sensor (DTS) reaches a value of 0 (DTS temperatures
reported using PECI may not equal zero when PROCHOT# is activated, see Section 6.3
for further details), the TCC will be activated and the PROCHOT# signal will be
asserted. This indicates the processors' temperature has met or exceeded the factory
calibrated trip temperature and it will take action to reduce the temperature.
Upon activation of the TCC, the processor will stop the core clocks, reduce the core
ratio multiplier by 1 ratio, and restart the clocks. All processor activity stops during this
frequency transition that occurs within 2 us. Once the clocks have been restarted at the
new lower frequency, processor activity resumes while the voltage requested by the
VID lines is stepped down to the minimum possible for the particular frequency.
that exceeds the specified maximum
CASE
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 41
Page 42

Thermal Specifications
V
V
Running the processor at the lower frequency and voltage will reduce power
consumption and should allow the processor to cool off. If after 1 ms the processor is
still too hot (the temperature has not dropped below the TCC activation point, DTS still
= 0, and PROCHOT# is still active), then a second frequency and voltage transition will
take place. This sequence of temperature checking and Frequency/VID reduction will
continue until either the minimum frequency has been reached or the processor
temperature has dropped below the TCC activation point.
If the processor temperature remains above the TCC activation point even after the
minimum frequency has been reached, then clock modulation (described below) at that
minimum frequency will be initiated.
There is no end user software or hardware mechanism to initiate this automated TCC
activation behavior.
A small amount of hysteresis has been included to prevent rapid active/inactive
transitions of the TCC when the processor temperature is near the TCC activation
temperature. Once the temperature has dropped below the trip temperature, and the
hysteresis timer has expired, the operating frequency and voltage transition back to
the normal system operating point using the intermediate VID/frequency points.
Transition of the VID code will occur first, to insure proper operation as the frequency is
increased. Refer to Tab l e 6 - 3 for an illustration of this ordering.
Figure 6-3. Frequency and Voltage Ordering
Temperature
Temperature
f
f
MAX
MAX
f
f
1
1
f
f
2
IDf
IDf
VIDf
VIDf
VIDf
VIDf
2
MAX
MAX
1
1
2
2
Frequency
Frequency
VID
VID
PROCHOT#
PROCHOT#
6.2.2.2 Clock Modulation
Clock modulation is a second method of thermal control available to the processor.
Clock modulation is performed by rapidly turning the clocks off and on at a duty cycle
that should reduce power dissipation by about 50% (typically a 30–50% duty cycle).
Clocks often will not be off for more than 32 microseconds when the TCC is active.
Cycle times are independent of processor frequency. The duty cycle for the TCC, when
activated by the Intel
It is possible for software to initiate clock modulation with configurable duty cycles.
®
Thermal Monitor, is factory configured and cannot be modified.
42 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 43

Thermal Specifications
A small amount of hysteresis has been included to prevent rapid active/inactive
transitions of the TCC when the processor temperature is near its maximum operating
temperature. Once the temperature has dropped below the maximum operating
temperature, and the hysteresis timer has expired, the TCC goes inactive and clock
modulation ceases.
6.2.2.3 Immediate Transition to combined TM1 and TM2
As mentioned above, when the TCC is activated, the processor will sequentially step
down the ratio multipliers and VIDs in an attempt to reduce the silicon temperature. If
the temperature continues to increase and exceeds the TCC activation temperature by
approximately 5 °C before the lowest ratio/VID combination has been reached, then
the processor will immediately transition to the combined TM1/TM2 condition. The
processor will remain in this state until the temperature has dropped below the TCC
activation point. Once below the TCC activation temperature, TM1 will be discontinued
and TM2 will be exited by stepping up to the appropriate ratio/VID state.
6.2.2.4 Critical Temperature Flag
If TM2 is unable to reduce the processor temperature, TM1 will also be activated. TM1
and TM2 will then work together to reduce power dissipation and temperature. It is
expected that only a catastrophic thermal solution failure would create a situation
where both TM1 and TM2 are active.
If TM1 and TM2 have both been active for greater than 20 ms and the processor
temperature has not dropped below the TCC activation point, then the Critical
Temperature Flag in the IA32_THERM_STATUS MSR will be set. This flag is an indicator
of a catastrophic thermal solution failure and that the processor cannot reduce its
temperature. Unless immediate action is taken to resolve the failure, the processor will
probably reach the Thermtrip temperature (see Section 6.2.3 Thermtrip Signal) within
a short time. In order to prevent possible permanent silicon damage, Intel
recommends removing power from the processor within ½ second of the Critical
Temperature Flag being set.
6.2.2.5 PROCHOT# Signal
An external signal, PROCHOT# (processor hot), is asserted when the processor core
temperature has exceeded its specification. If Adaptive Thermal Monitor is enabled
(note it must be enabled for the processor to be operating within specification), the
TCC will be active when PROCHOT# is asserted.
The processor can be configured to generate an interrupt upon the assertion or deassertion of PROCHOT#.
Although the PROCHOT# signal is an output by default, it may be configured as bidirectional. When configured in bi-directional mode, it is either an output indicating the
processor has exceeded its TCC activation temperature or it can be driven from an
external source (such as a voltage regulator) to activate the TCC. The ability to activate
the TCC using PROCHOT# can provide a means for thermal protection of system
components.
As an output, PROCHOT# (Processor Hot) will go active when the processor
temperature monitoring sensor detects that one or more cores has reached its
maximum safe operating temperature. This indicates that the processor Thermal
Control Circuit (TCC) has been activated, if enabled. As an input, assertion of
PROCHOT# by the system will activate the TCC for all cores. TCC activation when
PROCHOT# is asserted by the system will result in the processor immediately
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 43
Page 44

Thermal Specifications
transitioning to the minimum frequency and corresponding voltage (using Freq/VID
control). Clock modulation is not activated in this case. The TCC will remain active until
the system de-asserts PROCHOT#.
Use of PROCHOT# in bi-directional mode can allow VR thermal designs to target
maximum sustained current instead of maximum current. Systems should still provide
proper cooling for the VR, and rely on PROCHOT# only as a backup in case of system
cooling failure. The system thermal design should allow the power delivery circuitry to
operate within its temperature specification even while the processor is operating at its
Thermal Design Power.
6.2.3 THERMTRIP# Signal
Regardless of whether or not Adaptive Thermal Monitor is enabled, in the event of a
catastrophic cooling failure, the processor will automatically shut down when the silicon
has reached an elevated temperature. At this point, the THERMTRIP# signal will go
active and stay active as described in the datasheet. THERMTRIP# activation is
independent of processor activity. The temperature at which THERMTRIP# asserts is
not user configurable and is not software visible.
6.3 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)
6.3.1 Introduction
The Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) is a one-wire interface that provides
a communication channel between Intel processor and chipset components to external
monitoring devices. The processor implements a PECI interface to allow communication
of processor thermal and other information to other devices on the platform. The
processor provides a digital thermal sensor (DTS) for fan speed control. The DTS is
calibrated at the factory to provide a digital representation of relative processor
temperature. Instantaneous temperature readings from the DTS are available using the
IA32_TEMPXXXX MSR; averaged DTS values are read using the PECI interface.
The PECI physical layer is a self-clocked one-wire bus that begins each bit with a
driven, rising edge from an idle level near zero volts. The duration of the signal driven
high depends on whether the bit value is a logic '0' or logic '1'. PECI also includes
variable data transfer rate established with every message. The single wire interface
provides low board routing overhead for the multiple load connections in the congested
routing area near the processor and chipset components. Bus speed, error checking,
and low protocol overhead provides adequate link bandwidth and reliability to transfer
critical device operating conditions and configuration information.
The PECI bus offers:
• A wide speed range from 2 Kbps to 2 Mbps
• CRC check byte used to efficiently and automatically confirm accurate data delivery
• Synchronization at the beginning of every message minimizes device timing
accuracy requirements.
Generic PECI specification details are out of the scope of this document. What follows is
a processor-specific PECI client definition, and is largely an addendum to the PECI
Network Layer and Design Recommendations sections for the PECI 2.0 specification
document.
44 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 45

Thermal Specifications
For desktop system temperature monitoring and fan speed control management
purposes, the PECI 2.0 commands that are commonly implemented include Ping(),
GetDIB(), and GetTemp().
Table 6-4. Supported PECI Command Functions and Codes
Command Function
Ping() Yes 1
GetDIB() Yes 1
GetTemp() Yes 1
Note:
1. Thermal management related commands supported by the processor. Common command that will be
implemented for desktop system design.
6.3.2 PECI Client Capabilities
The processor PECI clients are designed to support processor thermal management.
Processor fan speed control is managed by comparing DTS temperature data against
the processor-specific value stored in the static variable, T
temperature data is less than T
speed of the thermal solution fan. This remains the same as with the previous guidance
for fan speed control. Refer to Section 6.1.2 for guidance where the DTS temperature
data exceeds T
CONTROL
.
The DTS temperature data is delivered over PECI, in response to a GetTemp()
command, and reported as a relative value to TCC activation target. The temperature
data reported over PECI is always a negative value and represents a delta below the
onset of thermal control circuit (TCC) activation, as indicated by PROCHOT#. Therefore,
as the temperature approaches TCC activation, the value approaches zero degrees.
CONTROL
Supported on the
processor
CONTROL
Note
. When the DTS
, the fan speed control algorithm can reduce the
6.3.3 Temperature Data
6.3.3.1 Format
The temperature is formatted in a 16-bit, 2’s complement value representing a number
of 1/64 degrees centigrade. This format allows temperatures in a range of ±512 °C to
be reported to approximately a 0.016 °C resolution.
Figure 6-4. Temperature Sensor Data Format
MSB
Upper nibble
S x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Sign Integer Value (0-511) Fractional Value (~0.016)
6.3.3.2 Interpretation
The resolution of the processor’s Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) is approximately 1 °C.
PECI temperatures are sent through a configurable low-pass filter prior to delivery in
the GetTemp() response data. The output of this filter produces temperatures at the full
1/64 °C resolution even though the DTS itself is not this accurate.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 45
MSB
Lower nibble
LSB
Upper nibble
LSB
Lower nibble
Page 46

Temperature readings from the processor are always negative in a 2’s complement
format, and imply an offset from the reference TCC activation temperature. As an
example, assume that the TCC activation temperature reference is 100 °C. A PECI
thermal reading of -10 indicates that the processor is running at approximately 10 °C
below the TCC activation temperature, or 90 °C. PECI temperature readings are not
reliable at temperatures above TCC activation (since the processor is operating out of
specification at this temperature). Therefore, the readings are never positive.
Note that changes in PECI data counts are approximately linear in relation to changes
in temperature in degrees centigrade. A change of ‘1’ in the PECI count represents
roughly a temperature change of 1 degree centigrade. This linearity is approximate and
cannot be ensured over the entire range of PECI temperatures, especially as the delta
from the maximum PECI temperature (zero) increases.
6.3.3.3 Processor Thermal Data Sample Rate and Filtering
The processor digital thermal sensor (DTS) provides an improved capability to monitor
device hot spots, which inherently leads to more varying temperature readings over
short time intervals. To reduce the sample rate requirements on PECI and improve
thermal data stability versus time the processor DTS implements an averaging
algorithm that filters the incoming data before reporting it over PECI.
6.3.3.4 Reserved Values
Thermal Specifications
Several values well out of the operational range are reserved to signal temperature
sensor errors. These are summarized in Tab l e 6- 5 .
Table 6-5. Error Codes and Descriptions
Error Code Description
8000h General Sensor Error (GSE)
8002h
Sensor is operational, but has detected a temperature below its operational range
(underflow)
§
46 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 47

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7 Sensor Based Thermal
Specification Design Guidance
The sensor based thermal specification presents opportunities for the system designer
to optimize the acoustics and simplify thermal validation. The sensor based
specification uses the Digital Thermal Sensor information accessed using the PECI
interface.
This chapter will review thermal solution design options, fan speed control design
guidance and implementation options and suggestions on validation both with the TTV
and the live die in a shipping system.
7.1 Sensor Based Specification Overview
Create a thermal specification that meets the following requirements:
• Use Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) for real-time thermal specification compliance.
• Single point of reference for thermal specification compliance over all operating
conditions.
• Does not require measuring processor power and case temperature during
functional system thermal validation.
• Opportunity for acoustic benefits for DTS values between T
CONTROL
and -1.
Thermal specifications based on the processor case temperature have some notable
gaps to optimal acoustic design. When the ambient temperature is less than the
maximum design point, the fan speed control system (FSC) will over cool the processor.
The FSC has no feedback mechanism to detect this over cooling, this is shown in the
top half of Figure 7-1.
The sensor based specification will allow the FSC to be operated at the maximum
allowable silicon temperature or T
acoustics for operation above T
for the measured ambient. This will provide optimal
J
CONTROL
. See lower half of Figure 7-1.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 47
Page 48

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
p
p)
p
p)
Figure 7-1. Comparison of Case Temperature versus Sensor Based Specification
T a = 4 5 .1 ° C
T a = 4 5 .1 ° C
Tcontrol
Tcontrol
Ta = 30 °C
Ta = 30 °C
Ψ -ca = 0.292
Ψ -ca = 0.292
TDP
Power
Power
Current Specification (C ase Tem p)
Current Specification (C ase Tem p)
Ψ -ca = 0.564
Ψ -ca = 0.564
TDP
Ψ -ca = 0.448
Ψ -ca = 0.448
Tcontrol
Tcontrol
Power
Power
Sensor Based S
Sensor Based S
Ta = 30 C
Ta = 30 C
TDP
TDP
ecification (DTS Tem
ecification (DTS Tem
48 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 49

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
TTV Th
fil
7.2 Sensor Based Thermal Specification
The sensor based thermal specification consists of two parts. The first is a thermal
profile that defines the maximum TTV T
thermal profile defines the boundary conditions for validation of the thermal solution.
as a function of TTV power dissipation. The
CASE
The second part is a defined thermal solution performance (Ψ
DTS value as reported over the PECI bus when DTS is greater than T
defines the operational limits for the processor using the TTV validated thermal
solution.
) as a function of the
CA
CONTROL
. This
7.2.1 TTV Thermal Profile
For the sensor-based specification the only reference made to a case temperature
measurement is on the TTV. Functional thermal validation will not require the user to
apply a thermocouple to the processor package or measure processor power.
Note: All functional compliance testing will be based on fan speed response to the reported
DTS values above T
will be necessary.
A knowledge of the system boundary conditions is necessary to perform the heatsink
validation. Section 7.3.1 will provide more detail on defining the boundary conditions.
The TTV is placed in the socket and powered to the recommended value to simulate the
TDP condition. See Figure 7-2 for an example of the Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-700
desktop processor series TTV thermal profile.
Figure 7-2. Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 Desktop Processor Series Thermal Profile
CONTROL
75.0
. As a result no conversion of TTV T
ermal Pro
e
to processor T
CASE
CASE
70.0
Y = Power x 0.29 + 45.1
65.0
60.0
55.0
50.0
TTV Case Temperature (°C)
45.0
40.0
0 20406080100
TTV Power (W)
Note: This graph is provided as a reference, the complete thermal specification is in Chapter 6.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 49
Page 50

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.2.2 Specification When DTS value is Greater than T
The product specification provides a table of ΨCA values at DTS = T
DTS = -1 as a function of T
AMBIENT
points, a linear interpolation can be done for any DTS value reported by the processor.
A copy of the specification is provided as a reference in Tab l e 7 - 1 of Section 7.6.
The fan speed control algorithm has enough information using only the DTS value and
T
AMBIENT
to command the thermal solution to provide just enough cooling to keep the
part on the thermal profile.
As an example the data in Tab l e 7 - 1 has been plotted in Figure 7-3 to show the
required Ψ
at 25, 30, 35, and 40°C T
CA
required ΨCA, which means lower fan speeds and reduced acoustics from the processor
thermal solution.
In the prior thermal specifications this region, DTS values greater than T
defined by the processor thermal profile. This required the user to estimate the
processor power and case temperature. Neither of these two data points are accessible
in real time for the fan speed control system. As a result the designer had to assume
the worst case T
AMBIENT
and drive the fans to accommodate that boundary condition.
Figure 7-3. Thermal solution Performance
0.700
0.650
(inlet to heatsink). Between these two defined
AMBIENT
. The lower the ambient, the higher the
CONTROL
CONTROL
and
CONTROL
, was
0.600
0.550
0.500
0.450
0.400
TTV Theta_ca [C/W]
0.350
0.300
TTV Ψ_ca @
DTS = Tcontrol DTS = -1
TTV Ψ_ca @
Ta = 40 °C
Ta = 35 °C
Ta = 30 °C
Ta = 25 °C
50 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 51

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.3 Thermal Solution Design Process
Thermal solution design guidance for this specification is the same as with previous
products. The initial design needs to take into account the target market and overall
product requirements for the system. This can be broken down into several steps:
• Boundary condition definition
• Thermal design / modelling
•Thermal testing
7.3.1 Boundary Condition Definition
Using the knowledge of the system boundary conditions such as inlet air temperature,
acoustic requirements, cost, design for manufacturing, package and socket mechanical
specifications and chassis environmental test limits the designer can make informed
thermal solution design decisions.
For the and Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 desktop processor series, the thermal
boundary conditions for an ATX tower system are as follows:
•T
•T
•T
EXTERNAL
RISE
AMBIENT
= 35 °C. This is typical of a maximum system operating environment
= 5 °C. This is typical of a chassis compliant to CAG 1.1 or TAC 2.0.
= 40 °C (T
AMBIENT
= T
EXTERNAL
+ T
RISE
)
Based on the system boundary conditions the designer can select a T
to use in thermal modelling. The assumption of a T
the required ΨCA needed to meet TTV T
assumed T
AMBIENT
Figure 7-4 shows a number of satisfactory solutions for the Intel Core™ i7-800 and i5-
700 desktop processor series.
Note: If the assumed T
thermal solution performance may not be sufficient to meet the product requirements.
The results may be excessive noise from fans having to operate at a speed higher than
intended. In the worst case this can lead to performance loss with excessive activation
of the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC).
and ΨCA
CASEMAX
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
has a significant impact on
at TDP. A system that can deliver lower
can utilize a design with a higher ΨCA, which can have a lower cost.
AMBIENT
is inappropriate for the intended system environment, the
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 51
Page 52

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
Figure 7-4. Required Ψ
for Various T
CA
Ψ-ca = 0.45
Ta = 30 °C
AMBIENT
Ψ-ca = 0.40
Ta = 35 °C
Conditions
80.0
70.0
60.0
50.0
40.0
30.0
TTV Tcase (°C)
20.0
10.0
0.0
0 20406080
TTV Power Dissipation (W)
Note: If an ambient of greater than 45.1 °C is necessary based on the boundary conditions a thermal solution
with a Ψ
lower than 0.29 °C/W will be required.
CA
7.3.2 Thermal Design and Modelling
Ψ-ca = 0.34
Ta = 40 °C
Ψ-ca = 0.29
Ta = 45.1 °C
Based on the boundary conditions the designer can now make the design selection of
the thermal solution components. The major components that can be mixed are the
fan, fin geometry, heat pipe or air cooled solid core design. There are cost and acoustic
trade-offs the customer can make.
7.3.3 Thermal Solution Validation
7.3.3.1 Test for Compliance with the TTV Thermal Profile
This step is the same as previously suggested for prior products. The thermal solution
is mounted on a test fixture with the TTV and tested at the following conditions:
• TTV is powered to the TDP condition
• Thermal solution fan operating at full speed
•T
AMBIENT
The following data is collected: TTV power, TTV T
calculate Ψ
This testing is best conducted on a bench to eliminate as many variables as possible
when assessing the thermal solution performance. The boundary condition analysis as
described in Section 7.3.1 should help in making the bench test simpler to perform.
at the boundary condition from Section 7.3.1
, and T
which is defined as:
CA
ΨCA = (TTV T
CASE
– T
AMBIENT
CASE
) / Power
AMBIENT
. This is used to
52 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 53

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.3.3.2 Thermal Solution Characterization for Fan Speed Control
The final step in thermal solution validation is to establish the thermal solution
performance,Ψ
allow the fan speed control algorithm developer to program the device. It also is
needed to asses the expected acoustic impact of the processor thermal solution in the
system.
The characterization data should be taken over the operating range of the fan. Using
the RCBF7-1156 (DHA-A) as the example the fan is operational from 900 to 3150 RPM.
The data was collected at several points and a curve was fit to the data see Figure 7-5.
Taking data at 6 evenly distributed fan speeds over the operating range should provide
enough data to establish an equation. By using the equation from the curve fitting a
complete set of required fan speeds as a function of Ψ
from the reference thermal solution characterization are provided in Tab le 7 -1 .
The fan speed control device may modulate the thermal solution fan speed (RPM) by
one of two methods. The first and preferred is pulse width modulation (PWM) signal
compliant with the 4-Wire Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controlled Fans specification.
the alternative is varying the input voltage to the fan. As a result the characterization
data needs to also correlate the RPM to PWM or voltage to the thermal solution fan. The
fan speed algorithm developer needs to associate the output command from the fan
speed control device with the required thermal solution performance as stated in
Ta b le 7 - 1. Regardless of which control method is used, the term RPM will be used to
indicate required fan speed in the rest of this document.
and acoustics as a function of fan speed. This data is necessary to
CA
be developed. The results
CA
Note: When selecting a thermal solution from a thermal vendor, the characterization data
should be requested directly from them as a part of their thermal solution collateral.
Figure 7-5. Thermal Solution Performance versus Fan Speed
Note: This data is taken from the preliminary evaluation of the validation of the RCBF7-1156 (DHA-A)
reference processor thermal solution. The Ψ
this chapter.
versus RPM data is available in Tab le 7 -1 at the end of
CA
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 53
Page 54

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.4 Fan Speed Control (FSC) design process
The next step is to incorporate the thermal solution characterization data into the
algorithms for the device controlling the fans.
As a reminder, the requirements are:
• When the DTS value is at or below T
CONTROL
as with prior processors.
• When DTS is above T
CONTROL
, FSC algorithms will use knowledge of T
ΨCA versus RPM to achieve the necessary level of cooling.
This chapter will discuss two implementations. The first is a FSC system that is not
provided the T
current T
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
information and a FSC system that is provided data on the
. Either method will result in a thermally compliant solution and some
acoustic benefit by operating the processor closer to the thermal profile. But only the
T
AMBIENT
aware FSC system can fully use the specification for optimized acoustic
performance.
, the fans can be slowed down — just
AMBIENT
and
In the development of the FSC algorithm it should be noted that the T
expected to change at a significantly slower rate than the DTS value. The DTS value will
be driven by the workload on the processor and the thermal solution will be required to
respond to this much more rapidly than the changes in T
An additional consideration in establishing the fan speed curves is to account for the
thermal interface material performance degradation over time.
7.4.1 Fan Speed Control Algorithm without T
In a system that does not provide the FSC algorithm with the T
designer must make the following assumption:
• When the DTS value is greater than T
CONTROL
derived in Section 7.3.1.
This is consistent past FSC guidance from Intel, to accelerate the fan to full speed when
the DTS value is greater than T
specification at DTS = T
CONTROL
CONTROL
can reduce some of the over cooling of the processor
. As will be shown below, the DTS thermal
and provide an acoustic noise reduction from the processor thermal solution.
In this example the following assumptions are made:
•T
AMBIENT
= 40 °C
• Thermal Solution designed / validated to a 40 °C environment
•T
CONTROL
= -20
• Reference processor thermal solution (RCFH7-1156 (DHA-A))
•Below T
CONTROL
the fan speed is slowed down as in prior products
, the T
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
.
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Data
information, the
is at boundary condition
is
For a processor specification based on a T
equal to or greater than T
CONTROL
, the fan speed must be accelerated to full speed. For
thermal profile, when the DTS value is
CASE
the reference thermal solution full speed is 3150 RPM (dashed line in Figure 7-6). The
DTS thermal specification defines a required Ψ
CA
at T
CONTROL
2300 RPM. This is much less than full speed even when assuming the T
and the fan speed is
AMBIENT
= 40 °C
(solid line in Figure 7-6). The shaded area displayed in Figure 7-6 is where DTS values
54 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 55

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
are less than T
from T
CONTROL
CONTROL
- 10 to T
. For simplicity, the graph shows a linear acceleration of the fans
CONTROL
control algorithms.
As the processor workload continues to increase, the DTS value will increase and the
FSC algorithm will linearly increase the fan speed from the 2300 RPM at DTS = -20 to
full speed at DTS value = -1.
Figure 7-6. Fan Response Without T
as has been Intel’s guidance for simple fan speed
AMBIENT
Data
7.4.2 Fan Speed Control Algorithm with T
In a system where the FSC algorithm has access to the T
capable of using the data the benefits of the DTS thermal specification become more
striking.
As will be demonstrated below, there is still over cooling of the processor, even when
compared to a nominally ambient aware thermal solution equipped with a thermistor.
An example of these thermal solutions are the RCFH7-1156 (DHA-A) or the boxed
processor thermal solutions. This over cooling translates into acoustic margin that can
be used in the overall system acoustic budget.
In this example the following assumptions are made:
•T
AMBIENT
• The same Thermal Solution designed / validated to a 40 °C environment as used in
the example in Section 7.4.1
•T
CONTROL
• FSC device has access to T
• Reference processor thermal solution (RCFH7-1156 (DHA-A))
•Below T
= 35 °C
= -20
CONTROL
AMBIENT
data
the fan speed is slowed down as in prior products
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Data
information and is
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 55
Page 56

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
For a processor specification based on a T
equal to or greater than T
for the T
AMBIENT
as controlled by the thermistor in thermal solution. For the RCFH71156 (DHA-A), this would be about 2150 RPM at 35 °C. This is graphically displayed as
the dashed line in Figure 7-7.
This is an improvement over the ambient unaware system but is not fully optimized for
acoustic benefit. The DTS thermal specification required Ψ
speed in this scenario is 1500 RPM. This is less than thermistor controlled speed of
2150 RPM — even if the assumption is a T
in Figure 7-7.
The shaded area displayed in Figure 7-7 is where DTS values are less than T
For simplicity, the graph shows a linear acceleration of the fans from T
T
CONTROL
as has been Intel’s guidance for simple fan speed control algorithms.
As the processor workload continues to increase the DTS value will increase and the
FSC algorithm will linearly increase the fan speed from the 1500 RPM at DTS = -20 to
2150 RPM at DTS value = -1.
Figure 7-7. Fan Response with T
CONTROL
AMBIENT
thermal profile, when the DTS value is
CASE
, the fan speed is accelerated to maximum fan speed
and therefore the fan
CA
AMBIENT
= 35 °C. This is graphically displayed
CONTROL
CONTROL
- 10 to
Aware FSC
.
56 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 57

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.5 System Validation
System validation should focus on ensuring the fan speed control algorithm is
responding appropriately to the DTS values and T
device being monitored for thermal compliance.
Since the processor thermal solution has already been validated using the TTV to the
thermal specifications at the predicted T
chassis is not expected to be necessary.
Once the heatsink has been demonstrated to meet the TTV Thermal Profile, it should be
evaluated on a functional system at the boundary conditions.
In the system under test and Power/Thermal Utility Software set to dissipate the TDP
workload confirm the following item:
• Verify if there is TCC activity by instrumenting the PROCHOT# signal from the
processor. TCC activation in functional application testing is unlikely with a
compliant thermal solution. Some very high power applications might activate TCC
for short intervals this is normal.
• Verify fan speed response is within expectations — actual RPM (Ψ
with DTS temperature and T
• Verify RPM versus PWM command (or voltage) output from the FSC device is within
expectations.
• Perform sensitivity analysis to asses impact on processor thermal solution
performance and acoustics for the following:
— Other fans in the system.
— Other thermal loads in the system.
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
.
AMBIENT
data as well as any other
, additional TTV based testing in the
) is consistent
CA
In the same system under test, run real applications that are representative of the
expected end user usage model and verify the following:
• Verify fan speed response vs. expectations as done using Power/Thermal Utility SW
• Validate system boundary condition assumptions: Trise, venting locations, other
thermal loads and adjust models / design as required.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 57
Page 58

Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
7.6 Thermal Solution Characterization
Tab l e 7- 1 is early engineering data on the RCBF7-1156 (DHA-A) thermal solution as a
reference for the development of thermal solutions and the fan speed control
algorithm.
Table 7-1. Thermal Solution Performance above T
T
AMBIENT
1
ΨCA at
DTS = T
CONTROL
45.1 0.290 N/A 0.290 N/A
44.0 0.310 N/A 0.301 N/A
43.0 0.328 N/A 0.312 N/A
42.0 0.346 2950 0.322 N/A
41.0 0.364 2600 0.333 N/A
40.0 0.383 2300 0.343 3150
39.0 0.401 2100 0.354 2750
38.0 0.419 1900 0.364 2600
37.0 0.437 1750 0.375 2400
36.0 0.455 1650 0.385 2250
35.0 0.473 1500 0.396 2150
34.0 0.491 1400 0.406 2050
33.0 0.510 1350 0.417 1900
32.0 0.528 1200 0.427 1850
31.0 0.546 1150 0.438 1750
30.0 0.564 1050 0.448 1650
29.0 0.582 1000 0.459 1600
28.0 0.600 1000 0.469 1550
27.0 0.618 1000 0.480 1450
26.0 0.637 1000 0.491 1400
25.0 0.655 1000 0.501 1350
24.0 0.673 1000 0.512 1300
23.0 0.691 1000 0.522 1250
22.0 0.709 1000 0.533 1200
21.0 0.727 1000 0.543 1150
20.0 0.746 1000 0.554 1100
RPM for ΨCA at
2
DTS = T
CONTROL
CONTROL
5
ΨCA at
DTS = -1
3
RPM for ΨCA at
DTS = -1
5
Notes:
1. The ambient temperature is measured at the inlet to the processor thermal solution
2. This column can be expressed as a function of T
3. This column can be expressed as a function of T
4. This table is provided as a reference please consult the product specification for current values.
5. Based on the testing performed a curve was fit to the data in the form
6. Full Speed of 3150 RPM the DHA-A thermal solution delivers a Ψ
7. Minimum speed is limited to 1000 RPM to ensure cooling of other system components
= 0.29 + (45.1 - T
Ψ
CA
= 0.29 + (45.1 - T
Ψ
CA
3
Psi_ca = a x RPM
a = -1.53 E-11, b = 1.41 E-07, c = -0.00048, d = 0.925782
+b x RPM2+c x RPM + d, where:
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
) x 0.0181
) x 0.0105
testing.
by the following equation:
AMBIENT
by the following equation:
AMBIENT
CA
= 0.335 °C /W based on preliminary
§
58 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 59

ATX Reference Thermal Solution
8 ATX Reference Thermal
Solution
Note: The reference thermal mechanical solution information shown in this document
represents the current state of the data and may be subject to modification.The
information represents design targets, not commitments by Intel.
The design strategy is to use the design concepts from the prior Intel
Bifurcated Fin Heatsink Reference Design (Intel® RCBFH Reference Design) designed
originally for the Intel
This chapter describes the overall requirements for the ATX heatsink reference thermal
solution supporting the processors including critical-to-function dimensions, operating
.
environment, and validation criteria.
®
Pentium® 4 processors.
8.1 Heatsink Thermal Solution
The reference thermal solutions are active fan solution similar to the prior designs for
the Intel® Pentium® 4 and Intel® Core™2 Duo processors. The RCFH7-1156 (DHA-A) is
a universal design supporting the Intel® Core™ i7-800 and i5-700 desktop processor
series processors.
®
Radial Curved
Table 8-1. Reference Thermal Solutions
Thermal Solution Name Guidelines Processor
RCFH7-1156 (DHA-A) 2009B (09B)
Figure 8-1 shows the reference thermal solution assembly. The heat sink attaches to
the motherboard with the push pin fastener design from previous reference designs,
see Figure B-6 through Figure B-9 for details on the push pin fastener design.
Figure 8-1. ATX Heatsink Reference Design Assembly
®
Intel
Core™ i7-800 and i5-700
desktop processor series (95W)
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 59
Page 60

ATX Reference Thermal Solution
26.00
26.00
8.2 Geometric Envelope for the Intel Reference ATX Thermal Mechanical Design
Figure 8-2 shows a 3-D representation of the board component keep out for the
reference ATX thermal solution. A fully dimensioned drawing of the keepout information
is available at Figure B-1 and Figure B-2 in Appendix B.
Figure 8-2. ATX KOZ 3-D Model Primary (Top) Side
mm Maximum
27.00mm Maximum
27.00mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(3 places)
(3 places)
mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(3 places)
(3 places)
10.10mm Maximum
10.10mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(5 places)
(5 places)
2.07mm Maximum
2.07mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(1 place)
(1 place)
1.20mm Maximum
1.20mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(1 place)
(1 place)
1.6 mm Maximum
1.6 mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(2 places)
2.50mm Maximum
2.50mm Maximum
Component Height
Component Height
(6 places)
(6 places)
Note: All maximum component heights are post reflow or assembly.
(2 places)
Note: The maximum height of the reference thermal solution (in Figure 8-1) above the
motherboard is 46.00 mm [1.81 inches], and is compliant with the motherboard
primary side height constraints defined in the ATX Specification and the microATX
Motherboard Interface Specification found at http://www.formfactors.org.
The reference solution requires a chassis obstruction height of at least 81.30 mm
[3.20 inches], measured from the top of the motherboard. This allows for appropriate
fan inlet airflow to ensure fan performance, and therefore overall cooling solution
performance. This is compliant with the recommendations found in both ATX
Specification and microATX Motherboard Interface Specification documents.
8.3 Heatsink Mass and Center of Gravity
• Total mass including plastic fan housing and fasteners <500 g.
• Assembly center of gravity ≤25.4 mm, measured from the top of the IHS.
8.4 Thermal Interface Material
A thermal interface material (TIM) provides conductivity between the IHS and heat
sink. The designs use Dow Corning TC-1996. The TIM application is 0.14 g, which will
be a nominal 20 mm diameter (~0.79 inches).
§§
60 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 61

Thermal Solution Quality and Reliability Requirements
9 Thermal Solution Quality and
Reliability Requirements
9.1 Reference Heatsink Thermal Verification
Each motherboard, heatsink and attach combination may vary the mechanical loading
of the component. Based on the end user environment, the user should define the
appropriate reliability test criteria and carefully evaluate the completed assembly prior
to use in high volume. The Intel reference thermal solution will be evaluated to the
boundary conditions in Chapter 5.
The test results, for a number of samples, are reported in terms of a worst-case mean
+ 3σ value for thermal characterization parameter using the TTV.
9.2 Mechanical Environmental Testing
Each motherboard, heatsink and attach combination may vary the mechanical loading
of the component. Based on the end user environment, the user should define the
appropriate reliability test criteria and carefully evaluate the completed assembly prior
to use in high volume. Some general recommendations are shown in Ta b l e 9 - 1 .
The Intel reference heatsinks will be tested in an assembled LGA1156 socket and
mechanical test package. Details of the environmental requirements, and associated
stress tests, can be found in Tab l e 9 - 1 are based on speculative use condition
assumptions, and are provided as examples only.
Table 9-1. Use Conditions (Board Level)
1
Test
3 drops each for + and - directions in each of 3
Mechanical Shock
Random Vibration
Notes:
1. It is recommended that the above tests be performed on a sample size of at least ten assemblies from
multiple lots of material.
2. Additional pass/fail criteria may be added at the discretion of the user.
perpendicular axes (i.e., total 18 drops)
Profile: 50 g, Trapezoidal waveform, 4.3 m/s [170 in/s]
minimum velocity change
Duration: 10 min/axis, 3 axes
Frequency Range: 5 Hz to 500 Hz
5 Hz @ 0.01 g
20 Hz to 500 Hz @ 0.02 g
Power Spectral Density (PSD) Profile: 3.13 g RMS
Requirement Pass/Fail Criteria
2
/Hz to 20 Hz @ 0.02 g2/Hz (slope up)
2
/Hz (flat)
Visual Check and
Electrical Functional
Test
Visual Check and
Electrical Functional
Test
2
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 61
Page 62

Thermal Solution Quality and Reliability Requirements
9.2.1 Recommended Test Sequence
Each test sequence should start with components (that is, baseboard, heatsink
assembly, and so forth) that have not been previously submitted to any reliability
testing.
Prior to the mechanical shock & vibration test, the units under test should be
preconditioned for 72 hours at 45 ºC. The purpose is to account for load relaxation
during burn-in stage.
The test sequence should always start with a visual inspection after assembly, and
BIOS/Processor/memory test. The stress test should be then followed by a visual
inspection and then BIOS/Processor/memory test.
9.2.2 Post-Test Pass Criteria
The post-test pass criteria are:
1. No significant physical damage to the heatsink and retention hardware.
2. Heatsink remains seated and its bottom remains mated flatly against the IHS
surface. No visible gap between the heatsink base and processor IHS. No visible tilt
of the heatsink with respect to the retention hardware.
3. No signs of physical damage on baseboard surface due to impact of heatsink.
4. No visible physical damage to the processor package.
5. Successful BIOS/Processor/memory test of post-test samples.
6. Thermal compliance testing to demonstrate that the case temperature specification
can be met.
9.2.3 Recommended BIOS/Processor/Memory Test Procedures
This test is to ensure proper operation of the product before and after environmental
stresses, with the thermal mechanical enabling components assembled. The test shall
be conducted on a fully operational baseboard that has not been exposed to any
battery of tests prior to the test being considered.
Testing setup should include the following components, properly assembled and/or
connected:
• Appropriate system baseboard.
• Processor and memory.
• All enabling components, including socket and thermal solution parts.
The pass criterion is that the system under test shall successfully complete the
checking of BIOS, basic processor functions and memory, without any errors. Intel PC
Diags is an example of software that can be used for this test.
62 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 63

Thermal Solution Quality and Reliability Requirements
9.3 Material and Recycling Requirements
Material shall be resistant to fungal growth. Examples of non-resistant materials
include cellulose materials, animal and vegetable based adhesives, grease, oils, and
many hydrocarbons. Synthetic materials such as PVC formulations, certain
polyurethane compositions (such as polyester and some polyethers), plastics that
contain organic fillers of laminating materials, paints, and varnishes also are
susceptible to fungal growth. If materials are not fungal growth resistant, then MILSTD-810E, Method 508.4 must be performed to determine material performance.
Material used shall not have deformation or degradation in a temperature life test.
Any plastic component exceeding 25 grams should be recyclable per the European Blue
Angel recycling standards.
The following definitions apply to the use of the terms lead-free, Pb-free, and RoHS
compliant.
Lead (Pb)-free: Lead has not been intentionally added, but lead may still exist as an
impurity below 1000 ppm.
RoHS compliant: Lead and other materials banned in RoHS Directive are either
(1) below all applicable substance thresholds as proposed by the EU or (2) an
approved/pending exemption applies.
Note: RoHS implementation details are not fully defined and may change.
§
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 63
Page 64

Thermal Solution Quality and Reliability Requirements
64 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 65

Boxed Processor Specifications
10 Boxed Processor Specifications
10.1 Introduction
The processor will also be offered as an Intel boxed processor. Intel boxed processors
are intended for system integrators who build systems from baseboards and standard
components. The boxed processor will be supplied with a cooling solution. This chapter
documents baseboard and system requirements for the cooling solution that will be
supplied with the boxed processor. This chapter is particularly important for OEMs that
manufacture baseboards for system integrators.
Note: Unless otherwise noted, all figures in this chapter are dimensioned in millimeters and
inches [in brackets]. Figure 10-1 shows a mechanical representation of a boxed
processor.
Note: The cooling solution that is supplied with the boxed processor will be halogen free
Note: Drawings in this chapter reflect only the specifications on the Intel boxed processor
Figure 10-1. Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink
compliant.
product. These dimensions should not be used as a generic keep-out zone for all
cooling solutions. It is the system designers’ responsibility to consider their proprietary
cooling solution when designing to the required keep-out zone on their system
platforms and chassis. Refer to the Appendix B for further guidance on keep in and
keep out zones.
Note: The airflow of the fan heatsink is into the center and out of the sides of the fan heatsink.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 65
Page 66

Boxed Processor Specifications
10.2 Mechanical Specifications
10.2.1 Boxed Processor Cooling Solution Dimensions
This section documents the mechanical specifications of the boxed processor. The
boxed processor will be shipped with an unattached fan heatsink. Figure 10-1 shows a
boxed processor fan heatsink.
Clearance is required around the fan heatsink to ensure unimpeded airflow for proper
cooling. The physical space requirements and dimensions for the boxed processor with
assembled fan heatsink are shown in Figure 10-2 (side view), and Figure 10-3 (top
view). The airspace requirements for the boxed processor fan heatsink must also be
incorporated into new baseboard and system designs. Airspace requirements are
shown in Figure 10-7 and Figure 10-8. Note that some figures have centerlines shown
(marked with alphabetic designations) to clarify relative dimensioning.
Figure 10-2. Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (side view)
66 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 67

Boxed Processor Specifications
Figure 10-3. Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (top view)
Note: Diagram does not show the attached hardware for the clip design and is provided only as a mechanical
representation.
Figure 10-4. Space Requirements for the Boxed Processor (overall view)
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 67
Page 68

Boxed Processor Specifications
10.2.2 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Weight
The boxed processor fan heatsink will not weigh more than 450 grams.
10.2.3 Boxed Processor Retention Mechanism and Heatsink Attach Clip Assembly
The boxed processor thermal solution requires a heatsink attach clip assembly, to
secure the processor and fan heatsink in the baseboard socket. The boxed processor
will ship with the heatsink attach clip assembly.
10.3 Electrical Requirements
10.3.1 Fan Heatsink Power Supply
The boxed processor's fan heatsink requires a +12 V power supply. A fan power cable
will be shipped with the boxed processor to draw power from a power header on the
baseboard. The power cable connector and pinout are shown in Figure 10-5.
Baseboards must provide a matched power header to support the boxed processor.
Tab l e 10 - 1 contains specifications for the input and output signals at the fan heatsink
connector.
The fan heatsink outputs a SENSE signal, which is an open-collector output that pulses
at a rate of 2 pulses per fan revolution. A baseboard pull-up resistor provides V
match the system board-mounted fan speed monitor requirements, if applicable. Use of
the SENSE signal is optional. If the SENSE signal is not used, pin 3 of the connector
should be tied to GND.
The fan heatsink receives a PWM signal from the motherboard from the 4th pin of the
connector labeled as CONTROL.
The boxed processor's fanheat sink requires a constant +12 V supplied to pin 2 and
does not support variable voltage control or 3-pin PWM control.
The power header on the baseboard must be positioned to allow the fan heatsink power
cable to reach it. The power header identification and location should be documented in
the platform documentation, or on the system board itself. Figure 10-6 shows the
location of the fan power connector relative to the processor socket. The baseboard
power header should be positioned within 110 mm [4.33 inches] from the center of the
processor socket.
Figure 10-5. Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Power Cable Connector Description
Signal
Pin
1
2
3
4
GND
+12 V
SENSE
CONTROL
Straight square pin, 4-pin terminal housing with
polarizing ribs and friction locking ramp.
0.100" pitch, 0.025" square pin width.
Match with straight pin, friction lock header on
mainboard.
OH
to
34
12
68 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 69

Boxed Processor Specifications
Table 10-1. Fan Heatsink Power and Signal Specifications
Description Min Typ Max Unit Notes
+12 V: 12 volt fan power supply 11.4 12.0 12.6 V —
IC:
• Maximum fan steady-state current draw
• Average steady-state fan current draw
• Maximum fan start-up current draw
• Fan start-up current draw maximum duration
SENSE: SENSE frequency — 2 — pulses per fan
CONTROL 21 25 28 kHz
—
—
—
—
1.2
0.5
2.2
1.0
—
—
—
—
Second
revolution
NOTES:
1. Baseboard should pull this pin up to 5 V with a resistor.
2. Open drain type, pulse width modulated.
3. Fan will have pull-up resistor for this signal to maximum of 5.25 V.
Figure 10-6. Baseboard Power Header Placement Relative to Processor Socket
R110
B
[4.33]
A
—
A
A
1
2, 3
C
10.4 Thermal Specifications
This section describes the cooling requirements of the fan heatsink solution used by the
boxed processor.
10.4.1 Boxed Processor Cooling Requirements
The boxed processor may be directly cooled with a fan heatsink. However, meeting the
processor's temperature specification is also a function of the thermal design of the
entire system, and ultimately the responsibility of the system integrator. The processor
temperature specification is found in Chapter 6 of this document. The boxed processor
fan heatsink is able to keep the processor temperature within the specifications (see
Ta b le 6 . 1) in chassis that provide good thermal management. For the boxed processor
fan heatsink to operate properly, it is critical that the airflow provided to the fan
heatsink is unimpeded. Airflow of the fan heatsink is into the center and out of the
sides of the fan heatsink. Airspace is required around the fan to ensure that the airflow
through the fan heatsink is not blocked. Blocking the airflow to the fan heatsink
reduces the cooling efficiency and decreases fan life. Figure 10-7 and Figure 10-8
illustrate an acceptable airspace clearance for the fan heatsink. The air temperature
entering the fan should be kept below 40 ºC. Again, meeting the processor's
temperature specification is the responsibility of the system integrator.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 69
Page 70

Boxed Processor Specifications
Figure 10-7. Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Airspace Keepout Requirements (top view)
Figure 10-8. Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Airspace Keepout Requirements (side view)
70 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 71

Boxed Processor Specifications
10.4.2 Variable Speed Fan
If the boxed processor fan heatsink 4-pin connector is connected to a 3-pin
motherboard header, it will operate as follows:
The boxed processor fan will operate at different speeds over a short range of internal
chassis temperatures. This allows the processor fan to operate at a lower speed and
noise level, while internal chassis temperatures are low. If internal chassis temperature
increases beyond a lower set point, the fan speed will rise linearly with the internal
temperature until the higher set point is reached. At that point, the fan speed is at its
maximum. As fan speed increases, so do fan noise levels. Systems should be designed
to provide adequate air around the boxed processor fan heatsink that remains cooler
then lower set point. These set points, represented in Figure 10-9 and Table 10-2, can
vary by a few degrees from fan heatsink to fan heatsink. The internal chassis
temperature should be kept below 40 ºC. Meeting the processor's temperature
specification (see Chapter 6) is the responsibility of the system integrator.
The motherboard must supply a constant +12 V to the processor's power header to
ensure proper operation of the variable speed fan for the boxed processor. Refer to
Table 10-1 for the specific requirements.
Figure 10-9. Boxed Processor Fan Heatsink Set Points
Table 10-2. Fan Heatsink Set Points
Boxed Processor Fan
Heatsink Set Point
Note:
1. Set point variance is approximately ± 1 °C from fan heatsink to fan heatsink.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 71
ºC)
(
X ≤ 30
Y = 35
Z ≥ 40
When the internal chassis temperature is below or equal to this set point,
the fan operates at its lowest speed. Recommended maximum internal
chassis temperature for nominal operating environment.
When the internal chassis temperature is at this point, the fan operates
between its lowest and highest speeds. Recommended maximum internal
chassis temperature for worst-case operating environment.
When the internal chassis temperature is above or equal to this set point,
the fan operates at its highest speed.
Boxed Processor Fan Speed Notes
1
-
-
Page 72

Boxed Processor Specifications
If the boxed processor fan heatsink 4-pin connector is connected to a 4-pin
motherboard header and the motherboard is designed with a fan speed controller with
PWM output (CONTROL see Table 10-1) and remote thermal diode measurement
capability, the boxed processor will operate as follows:
As processor power has increased the required thermal solutions have generated
increasingly more noise. Intel has added an option to the boxed processor that allows
system integrators to have a quieter system in the most common usage.
The 4th wire PWM solution provides better control over chassis acoustics. This is
achieved by more accurate measurement of processor die temperature through the
processor's Digital Thermal Sensors (DTS) and PECI. Fan RPM is modulated through the
use of an ASIC located on the motherboard that sends out a PWM control signal to the
4th pin of the connector labeled as CONTROL. The fan speed is based on actual
processor temperature instead of internal ambient chassis temperatures.
If the new 4-pin active fan heat sink solution is connected to an older 3-pin baseboard
processor fan header, it will default back to a thermistor controlled mode, allowing
compatibility with existing 3-pin baseboard designs. Under thermistor controlled mode,
the fan RPM is automatically varied based on the Tinlet temperature measured by a
thermistor located at the fan inlet.
§
72 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 73

Component Suppliers
A Component Suppliers
Note: The part numbers listed below identifies the reference components. End-users are
responsible for the verification of the Intel enabled component offerings with the
supplier. These vendors and devices are listed by Intel as a convenience to Intel's
general customer base, but Intel does not make any representations or warranties
whatsoever regarding quality, reliability, functionality, or compatibility of these devices.
Customers are responsible for thermal, mechanical, and environmental validation of
these solutions. This list and/or these devices may be subject to change without notice.
Table A-1. Reference Heatsink Enabled Components
Item Intel PN AVC Delta Foxconn ITW Nidec
2009B Heatsink
Assembly
RCFH7-1156
(DHA-A)
Clip E36830-001 A208000389 N/A N/A N/A N/A
Fasten er
E41759-002 N/A DTC-DAA07
Base:
C33389
Cap:
E63768-001
N/A N/A N/A
1A01C7T00DHA_XA02
N/A
Base:
C33389
Cap:
E63768-001
F90T12MS1Z
7-64A01A1
N/A
Table A-2. LGA1156 Socket and ILM Components
Item Intel PN Foxconn Molex Tyco Lotes
LGA1156 Socket E51948-002
LGA1156 ILM E36142-002 PT44L11-6401 475969910 2013882-3
Back Plate
(with Screws)
E36143-002 PT44P11-6401 475969930 2069838-2
PE1156274041-01F
475961132 2013092-1 N/A
ACA-ZIF-078T02
DCA-HSK-144T01
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 73
Page 74

Table A-3. Supplier Contact Information
Supplier Contact Phone Email
AVC
(Asia Vital
Components Co.,
Ltd.)
Delta
Foxconn Julia Jiang +1 408 919 6178 juliaj@foxconn.com
ITW Fastex Roger Knell +1 773 307 9035 rknell@itwfastex.com
Lotes Co., Ltd. Windy Wong +1 604 721 1259 windy@lotesconn.com
Molex Carol Liang +86 21 504 80889 x3301 carol.liang@molex.com
Nidec Karl Mattson +1 360 666 2445 karl.mattson@nidec.com
Tyco Billy Hsieh +81 44 844 8292 billy.hsieh@tycoelectronics.com
Kai Chang
William
Bradshaw
The enabled components may not be currently available from all suppliers. Contact the
supplier directly to verify time of component availability.
+86 755 3366 8888
x63588
+1 510 668 5570
+86 136 8623 1080
§
Component Suppliers
kai_chang@avc.com.tw
WBradshaw@delta-corp.com
74 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 75

Mechanical Drawings
B Mechanical Drawings
Ta b le B - 1 lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix.
Table B-1. Mechanical Drawing List
Drawing Description Figure Number
“Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top)” Figure B-1
“Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)” Figure B-2
“Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top)” Figure B-3
“Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)” Figure B-4
“Reference Design Heatsink Assembly” Figure B-5
“Reference Fastener (Sheet 1 of 4)” Figure B-6
“Reference Fastener (Sheet 2 of 4)” Figure B-7
“Reference Fastener (Sheet 3 of 4)” Figure B-8
“Reference Fastener (Sheet 4 of 4)” Figure B-9
“Reference Clip (Sheet 1 of 2)” Figure B-10
“Reference Clip (Sheet 2 of 2)” Figure B-11
“Thermocouple Attach Drawing” Figure B-12
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 75
Page 76

Figure B-1. Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top)
E21319_REV_L_PAE 1 L
DWG. NO SHT. REV
LEGEND
SOCKET/THERMAL/MECHANICAL COMPONENT KEEP-INS
10.10 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
1.6 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
1.2 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
BOARD ROUTING KEEP-OUT
27 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
BOARD ROUTING SURFACE TRACE KEEP-OUT
2.07 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
(95.00 )(36.00 )
(75.00 2X)
Mechanical Drawings
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
R
DEPARTMENT
2.5 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
26 MM MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 7
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
INTERPRET DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES
L
2
OF
1
SHEET
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
E21319_REV_L_PAE
LGA1156 & 1155 SOCKET ATX KEEP-INS
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1
TITLE
DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
IN ACCORDANCE WITH ASME Y14.5M-1994
SCALE: NONE
THIRD ANGLE PROJECTION
2X39.01
+0.05
-0.03
+0.05
-0.03
47.50
29.67
28.00
4X NO ROUTE6.00
4X NPTH4.03
2X38.40
37.54
2X36.89
33.80
28.46
25.79
21.25
18.90
( )95.0
+0.05
-0.03
3X NPTH3.80
2X38.12
20.13
27.02
29.69
35.03
35.21
38.18
39.63
40.10
BOARD PRIMARY SIDE
EAST
2X37.56
2X37.50
NORTH
SOUTH
2X39.49
29.08
34.42
WEST
26.00
26.40
25.70
26.11
23.70
21.25
+0.05
-0.03
18.00
6.00
PRIMARY & SECONDARY SIDES 6
3X NO ROUTE ON
PIN 1
6.15
7.62
()6.00
SILKSCREEN OUTLINE
ON PRIMARY SIDE
AS SHOWN
3 X 4.70 NO ROUTE ON
ALL OTHER LAYERS
0.00
2
6.15
2.54
7.00
NO ROUTE ON
PRIMARY SIDE 6
18.00
13.97
23.70
25.70
26.00
2X29.67
31.61
30.00
32.50
37.63
35.80
2X39.01
2X37.50
47.50
46.42
45.50
37.31
26.70
25.81
23.81
20.90
10.00
PACKAGE BOUNDRY
0.00
2
5.40
10.50
10.00
2X21.25
2X25.25
35.21
40.71
46.89
(95.00 )
(75.00 2X)
ILM BOUNDRY 5
LEVER UNHOOKED POSITION
40.71
48.12
2 GEOMETRIC CENTER OF SOCKET HOUSING CAVITY.
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
5 REFER TO INTEL PART DRAWING E21320 FOR ILM AND SOCKET KEEPIN VOLUME DIMENSIONS.
6 COPPER PAD ON PRIMARY SIDE, NON-GROUNDED.
3. BOARD COMPONENET KEEP-INS AND MECHANICAL COMPONENET KEEP-OUTS
TO BE UTILIZED WITH SUFFICIENT ALLOWANCES FOR PLACEMENT AND SIZE TOLERANCES,
ASSEMBLY PROCESS ACCESS, AND DYNAMIC EXCURSIONS.
7 COMBINED COMPONENT AND SOLDER PASTE HEIGHT INCLUDING TOLERANCES AFTER REFLOW.
4. ASSUME SYMMETRY FOR UNDIMENSIONED CORNERS AND EDGES.
COPPER PAD CAN INSET A MAXIMUM OF 0.127MM FROM THE NO ROUTE EDGE.
76 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 77

Mechanical Drawings
Figure B-2. Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)
SOCKET& PROCESSOR
VOLUMETRIC KEEP-IN OUTLINE
L
2
OF
2
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
E21319_REV_L_PAE
1.000
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1
SCALE:
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
DEPARTMENT
ROUTING KEEPOUTS
KEEPINS
COMPONENT VOLUMETRIC
4X 6.00
4X 10.00
25.81
(27.33 )
(61.02 )
(78.25 )
BOARD SECONDARY SIDE
35.21
SOUTH
EAST
WEST
NORTH
26.00
18.00
9.36
INTEL PN E21320
VOLUMETRIC KEEP-IN
18.00
(36.00 )
26.00
SOCKET& PROCESSOR
(18.72 )
37.54
13.67
2
4X R1.8
0.00
13.67
35.21
LEGEND
40.71
COMPONENT KEEP-OUT
ROUTING AND COMPONENT KEEP-OUT
0.00
2
(52.00 )
7.05
9.36
10.80
MAX COMPONENT HEIGHT 2.54MM
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 77
Page 78

Figure B-3. Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Primary Side (Top)
78.25
()15.16
4.00
6.55
()94.76
SECONDARY SIDE
COMPONENT CLEARANCE
PRIMARY SIDE COMPONENT
CLEARANCE
()42.50
C
B
()37.54
()2.50
()1.50
()42.50
3X 6.34
B
8.12
2
19.99
27.33
6
618.72
49.50
12.29
3.75
POSITION
LEVER UNLATCHED
Mechanical Drawings
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
LGA1156 & 1155 SOCKET,
PST-TMI
DEPARTMENT
TITLE
BOTTOM SIDE
11.75
J
2
OF
1
SHEET
E21320
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
ILM & PROCESSOR KEEPIN
1.000
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1
SCALE:
(R )65.21
(R )46.51
8
7
TO OPEN LID
TO LEVER STOP
CLEARANCE NEEDED
3.75
MIN LEVER MOTION SPACE
MAX LEVER MOTION SPACE
TOP SIDE
1
7170.0
FOR WIRE TRAVEL
9.26
9.26
C
1.25
6.76
6.76
13.00
37.54
7.00
1.50
()
TYP PCB THICKNESS
2.50
3.18
8.97
3.18
15.92
19.50
51.00
42.50
C
()49.50
3X 5.00
21.25
28.12
2.50
C
1.75
SECTION B-B
3X 2.58
SECTION A-A
1 SOCKET CENTER PLANES ARE REFERENCED FROM GEOMETRIC
2 SOCKET KEEP-IN VOLUME VERTICAL HEIGHT ESTABLISHES LIMIT OF SOCKET
NOTES:
CENTER OF SOCKET HOUSING CAVITY FOR CPU PACKAGE (ALIGNS
WITH DATUM REFERENCE GIVEN FOR BOARD COMPONENT KEEP-INS).
AND CPU PACKAGE ASSEMBLY IN THE SOCKET LOCKED DOWN POSITION.
IT ENCOMPASSES SOCKET AND CPU PACKAGE DIMENSIONAL TOLERANCES
5 NO COMPONENT BOUNDARY-FINGER ACCESS AREA
6 MOTHERBOARD BACKSIDE COMPONENT KEEP-IN
7 MAXIMUM OPEN ANGLE TO OPEN LOAD PLATE
AND DEFLECTION / SHAPE CHANGES DUE TO ILM LOAD.
3. SOCKET KEEP-IN VOLUME ENCOMPASS THE SOCKET NOMINAL VOLUME
AND ALLOWANCES FOR SIZE TOLERANCES. THERMAL/MECHANICAL COMPONENT
DEVELOPERS SHALL DESIGN TO THE OUTSIDE OF SOCKET KEEP IN VOLUME WITH
8 MINIMUM OPEN ANGLE TO CLEAR LOAD PLATE
CLEARANCE MARGINS. SOCKET DEVELOPERS SHALL DESIGN TO THE INSIDE VOLUME.
4.DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
8130.0
LOAD PLATE OPENING
MOTION SPACE
70.37
SEE DETAIL A
SEE DETAIL A
17.00
5
8.97
B
A
B
A
4.00
B
40.71
5.50
()78.25
78 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 79

Mechanical Drawings
Figure B-4. Socket / Processor / ILM Keepout Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)
()18.12
17.00
LEVER UNLATCHED
10.97
()6.30
3.50
8.00
3.50
()11.78
()13.75
()15.83
TOP SIDE VIEW
DETAIL A
2
OF
2
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1 E21320 J
SCALE: NONE
TOP SIDE
PCB ILM SILKSCREEN
+0.05
-0.03
6.00
3X
NO ROUTE ON
PRIMARY & SECONDARY SIDES
3 X 4.70 NO ROUTE ON
ALL OTHER LAYERS
COPPER PAD ON PRIMARY SIDE,
37.31
25.70
0.00
ADD SILKSCREEN OUTLINE
ON PCB PRIMARY SIDE
AS SHOWN
25.70
+0.05
-0.03
0.1 B C
NON-GROUNDED.
COPPER PAD CAN INSET MAXIMUM
OF .127MM FROM THE NO ROUTE EDGE
18.00
0.00
18.00
3X NPTH3.80
23.81
B
()10.50
0.00
C
B
5 FINGER ACCESS
COMPONENT KEEPOUT
AREA
()47.50
R3.50
C
25.50
TOP SIDE
PCB ILM MOUNTING HOLES
25.81
0.00
PIN 1
35.21
40.71
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 79
Page 80

Figure B-5. Reference Design Heatsink Assembly
Mechanical Drawings
80 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 81

Mechanical Drawings
Figure B-6. Reference Fastener (Sheet 1 of 4)
(
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 81
Page 82

Figure B-7. Reference Fastener (Sheet 2 of 4)
Mechanical Drawings
82 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 83

Mechanical Drawings
(
Figure B-8. Reference Fastener (Sheet 3 of 4)
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 83
Page 84

Figure B-9. Reference Fastener (Sheet 4 of 4)
Mechanical Drawings
84 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 85

Mechanical Drawings
Figure B-10. Reference Clip (Sheet 1 of 2)
13
REVISION HISTORY
E36830 1 A
DWG. NO SHT. REV
4
ZONE REV DESCRIPTION DATE APPROVED
D
C
B
A
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119CORP.
R
01E36830D
REVDRAWING NUMBERCAGE CODESIZE
123
SHEET 1 OF 2DO NOT SCALE DRAWINGSCALE: 3:1
HEAT SINK CLIP
DESCRIPTIONPART NUMBERITEM NO
HAVENDALE POWER ON SAMPLE
PST
DEPARTMENT
TITLE
--
--
PARTS LIST
02/04/08KG TAN
04/02/03R. AOKI
DATEAPPROVED BY
DATECHECKED BY
DATEDRAWN BY
A RELEASE FOR PROTOTYPING 02/04/08 NA
5 PUNCH DIRECTION
7 CRITICAL TO FUNCTION DIMENSION
NOTES:
1. THIS DRAWING TO BE USED IN CONJUNTION WITH SUPPLIED 3D
DATABASE FILE. ALL DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES ON THIS
DRAWING TAKE PRECEDENCE OVER SUPPLIED FILE AND ARE
APPLICABLE AT PART FREE, UNCONSTRAINED STATE UNLESS
INDICATED OTHERWISE.
2. MATERIAL:
A) TYPE: AISI 1065 COLD DRAWN STEEL OR EQUIVALENT
1.6MM THICKNESS .02 [.063"]
B) CRITICAL MECHANICAL MATERIAL PROPERTIES
FOR EQUIVALENT MATERIAL SELECTION:
ELASTIC MODULUS > 206.8 GPA [29,900 KSI]
MIN TENSILE YIELD STRENGTH (ASTM D638) > 380 MPa [55KSI]
SEE DETAIL A
SEE DETAIL A
A
8 COINING REQUIRED AS SPECIFIED
C) MASS - 37.7 GRAMS (REF)
3. SECONDARY OPERATIONS:
A) FINISH: NICKEL PLATE REQUIRED AFTER FORMING
4. ALL DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES ARE SHOWN AFTER PLATING
6. BREAK ALL SHARP CORNERS AND BURRS
9. SECONDARY UNIT TOLERANCES SHOULD BE CALCULATED FROM PRIMARY
UNITS TO AVOID ROUND OFF ERROR.
DATEDESIGNED BY
CLIP, STEEL, STAMPEDE36830-001TOP
-001-002-003
QTY PER ASSY
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED:
DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS.
TOLERANCES: LINEAR .15
ANGLES: 1
.007[]
.079
2 0.2
SEE NOTES
SEE NOTES
FINISH:
MATERIAL:
THIRD ANGLE PROJECTION
INTERPRET DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES
PER ANSI Y14.5M-1994
74.22 0.2
.007[]
.166
4
5678
.007[]
.394
0.5 [.01] A B
4X 10 0.2
7
3.890[]
98.8
D
733.86 0.2
.007[]
1.333
A
REMOVE ALL BURRS OR SHARP EDGES AROUND PERIMETER OF PART.
SHARPNESS OF EDGES SUBJECT TO HANDLING ARE REQUIRED TO
MEET THE UL1439 TEST.
PERMANENTLY MARK PART
NUMBER AND REVISION LEVEL
APPROXIMATELY WHERE SHOWN
XXXXXX-XXX REV XX
B
.007[]
2.106
SQ 53.5 0.2
0.5 [.01] A B
7
3.890[]
98.8
C
B
1.643[]
41.73
SEE DETAIL B
SEE DETAIL B
SEE DETAIL D
SEE DETAIL D
.063[]
()1.60
A
5678
A
SECTION A-A
SEE DETAIL C
SEE DETAIL C
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 85
Page 86

Figure B-11. Reference Clip (Sheet 2 of 2)
13
.0177[]
R MIN0.45
Mechanical Drawings
01E36830D
REVDRAWING NUMBERSIZEDEPARTMENT
123
SHEET 2 OF 2DO NOT SCALE DRAWINGSCALE: 3:1
E36830 2 01
DWG. NO SHT. REV
0.4 [.01] A B
0.5 [.01] A B
WX 4X
4
.055[]
R1. 4
5678
.042[]
.065[]
1.65
1.06
.0118[]
R TYP0.3
.1417[]
2X R3.6
7
0.1 [.003] A B
DIMENSION ON SHEET 1 ZONE A7
THIS POINT CORRESPONDES TO THE 41.73
0.2 [.007] A B
BOUNDARY
A
A
X
.122[]
R3. 1
DETAIL B
SCALE 10:1
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119CORP.
R
TMD
.141[]
3.57
43.1
DETAIL D
SCALE 10:1
W
4
5678
45 X 0.25 0.05 8
[.010 .001]
DETAIL C
SCALE 10:1
TYP 4 PLACES
.289[]
7.34
135
.0197[]
2X R0.5
.2894[]
7.35
.2087[]
5.3
DETAIL A
SCALE 10:1
TYPICAL 4 PLACES
86 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 87

Mechanical Drawings
Figure B-12. Thermocouple Attach Drawing
':*12 6+ 5(9
%
$
'(7$,/'
6&$/(
5(9
6+((72)
(
&+$1'/(5$5,=21$
'(3$570(17
'(7$,/&
6&$/(
'(6,*1('%< '$7(
:&+$1'/(5%/9'
'21276&$/('5$:,1*
'5$:,1*180%(5
7+(502&283/($77$&+
/*$,+6*5229()2562/'(5
&$*(&2'(
%
6&$/(
'$7(
'$7(
$33529('%<
&+(&.('%<
6,=(
352-(&7,21
7+,5'$1*/(
7,7/(
'$7(
'5$:1%<
127(',5(&7,212)0,//('*5229(
5(/$7,9(72$/,*10(17127&+(6
;5
'(7$,/%
6&$/(
6(&7,21$$
3$&.$*(
&(17(5
%
',6&/26('
3$&.$*(
',63/$<('25
('*(6
1
&
3$&.$*(&(17(5
5()(5(1&(')520
3$&.$*(('*(6
$
$
,1*&217$,16,17(/&25325$7,21&21),'(17,$/,1)250$7,21,7,6
7+,6'5$:
,1&21),'(1&($1',76&217(1760$<127%(',6&/26('5(352'8&('
02',),(':,7+2877+(35,25:5,77(1&216(172),17(/&25325$7,2
'
%
$1*/(6
72/(5$1&(6
$60(<0
,17(535(7',0$1'72/3(5
',0(16,216$5(,1,1&+(6
81/(6627+(5:,6(63(&,),('
;;;
;;
72/;
0$7(5,$/
),1,6+
127(681/(6627+(5:,6(63(&,),('
1250$/$1'/$7(5$//2$'6217+(,+60867%(
0,1,0,=(''85,1*0$&+,1,1*
0$&+,1(:,7+&/($1'5<$,521/<12)/8,'625
2,/6
$//0$&+,1('685)$&(672%(0,//),1,6+25
%(77(5
,+60$7(5,$/,61,&.(/3/$7('&233(5
&87',5(&7,2125,(17$7,212)*5229(,6$66+2:1
$//0$&+,1('('*(6$5(72%()5((2)%8556
7+('(37+$77+(3$&.$*(&(17(5,6&5,7,&$/
$
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 87
Page 88

Mechanical Drawings
§
88 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 89

Socket Mechanical Drawings
C Socket Mechanical Drawings
Ta b le C - 1 lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix.
Table C-1. Mechanical Drawing List
Drawing Description Figure Number
“Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4)” Figure C-1
“Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4)” Figure C-2
“Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4)” Figure C-3
“Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4)” Figure C-4
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 89
Page 90

Figure C-1. Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 1 of 4)
Socket Mechanical Drawings
E27147 1 4
DWG. NO SHT. REV
REVISION HISTORY
ZONE REV DESCRIPTION DATE APPROVED
H
- 1 PRELIMINARY RELEASE 10/23/07 -
G
F
E
6
D
7
11
C
12
B
A
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
SOCKET LGA1156
-
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
DEPARTMENT
TITLE
--
--
DATECHECKED BY
02/28/07B. KNAPIK
DATEDRAWN BY
02/28/07L. YUPENG
DATEDESIGNED BY
THIRD ANGLE PROJECTION
4
OF
1
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
4
A1 E27147 4
SCALE:
SEE NOTESSEE NOTES
FINISHMATERIAL--DATEAPPROVED BY
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
NOTES:
1. THE PURPOSE OF THIS DRAWING IS TO ESTABLISH THE
MECHANICAL FORM FACTOR OF THE SOCKET. THIS DRAWING IS
NOT INTENDED TO SHOW INTERNAL DETAIL OF THE SOCKET
WHICH MAY VARY FROM SUPPLIER TO SUPPLIER.
2. MATERIAL:
BASE AND CAP: HIGH TEMPERATURE THERMOPLASTIC. UL94V-0
CONTACT: HIGH STRENGTH COPPER ALLOY
POSTS: HIGH TEMPERATURE THERMOPLASTIC UL94V-0
SOLDER BALL: LEAD FREE SAC
3. FINISH: NONE
4. CONTACT MUST REMAIN ON LAND THROUGHOUT ACTUATION STROKE.
5. REMOVE ALL BURRS AND SHARP EDGES R0.05 MAX.
6 SOCKET NAME TO BE INDICATED IN THIS AREA.
7 LOT NUMBER SHALL BE INDICATED IN THIS AREA.
8 CHAMFER INDICATES THE CORNER CLOSEST TO PACKAGE PIN A1
9 CONTACT MUST REMAIN OUTSIDE THE CENTRAL CAVITY THROUGHOUT THE ACTUATION STROKE.
10 PICK-AND-PLACE TOOLING KEEP-IN ZONE. NO THOUGH HOLES ALLOWED IN THIS ZONE.
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
H
G
11 SOCKET MANUFACTURER NAME SHOWN ON SIDEWALL. OPPOSITE SIDEWALL CAN BE USED IF NEEDED.
F
12 ONLY THE LGA CONTACTS/SOLDER BALLS ALONG THE BOUNDARIES OF THE TWO "L" ARRAYS ARE SHOWN
IN THE DRAWINGS.
13 THE DIMENSION MEASURED FROM THE TOP OF THE ILM KEY-IN FEATURE TO THE TOP OF THE SOCKET
ALIGNMENT FEATURE.
14 DO NOT TOOL THIS KEY-IN FEATURE. MOLD TOOLING SHALL ALLOW THIS FEATURE TO BE ADDED IN THE
FUTURE NO LARGER THAN THE AREA SPECIFIED.
15 SOCKET SEAT PLANES.
E
D
C
B
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
A
90 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 91

Socket Mechanical Drawings
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
Figure C-2. Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 2 of 4)
4
OF
2
SCALE 20
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
4
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1 E27147 4
SCALE:
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
-
DEPARTMENT
E27147 2 4
DWG. NO SHT. REV
F
F
6X 19.75
4X 15.5
0.1 A B
42.5 #0.2
F
DETAIL ON SHEET 3
DETAIL ON SHEET 3
6X 19.1
4X 15.5
E
E
16X 1 MIN
2
1.5
40 ROWS
39X 0.9144
2.35
16X 7
29X 0.9144
30X COLUMNS
D
DETAIL
0.5
C
SCALE 10
DETAIL
G
0.1 A C
42.5 #0.2
A
C
B2X 37.6
9
0 ABC
20.5 MIN THRU
2X 9
A
B
2X 1.6
4
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
H
G
16.25
2X 18.95
F
2.9
9
12.8 MIN THRU
2X 37.6
0 ACB
DETAIL ON SHEET 3
DETAIL ON SHEET 3
C
D
15.96
E
2X 2.1 #0.2
4X 1.7
8
2 X 2 PIN A1
A
2X 1X3 CHAMFER
6X 1
A
SECTION A-A
B
DETAIL
SCALE 10
29X 0.9144
30X COLUMNS
40X ROWS
39X 0.9144
1156X 0.6
SOLDER BALLS (LF)
3.4 #0.2 AFTER SMT
A
SCALE 10
DETAIL
A
1156X
CONTACT TIPS
D
C
0.65 MAX
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
B
A
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 91
Page 92

(
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
Figure C-3. Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 3 of 4)
Socket Mechanical Drawings
F
DETAIL
SCALE 10
4
OF
3
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
6
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1 E27147 4
SCALE:
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
-
DEPARTMENT
18.2878
18.2878
17.3738
A
8.2296
31 33 35 37 39
32 34 36 38 40
7.5868
(3.1144)
18.9308
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30
10.0584
8X 0.4X0.5 CHAMFER
(0.4 HORIZONTAL 0.5 VERTICAL)
29X 0.9144
30X COLUMNS
0.3 A F G
0.25 A
0.3 A F G
0.25 A
1156X SOLDER BALLS
39X 0.9144
40 ROWS
29X 0.9144
39X 0.9144
30X COLUMNS
E
SCALE 10
DETAIL
40X ROWS
13
0.75
E27147 3 4
DWG. NO SHT. REV
18.9308
7.5868
(3.1144)
8.2296
10.0584
AY AW AVAU ATAR APAN AMAL AKAJ AHAG AFAE ADAC ABAA Y W V U T R P N M L K J H G F E D C B
17.3738
15
SCALE 15
TOP VIEW
SCALE 5
0.75
DETAIL H
G
DETAIL
14
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
H
G
G
F
4
H
E
D
C
B
SCALE 15
A
92 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Page 93

Socket Mechanical Drawings
Figure C-4. Socket Mechanical Drawing (Sheet 4 of 4)
E27147 4 4
DWG. NO SHT. REV
22.55 MAX
2X 11.35 MAX
4
OF
4
SHEET
J
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
5
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1 E27147 4
SCALE:
39.6
2X 37.5
24.56 #0.1
(0.6)
MAX
2X 2.1
2X 37.5
J
2X 0.6
2X 4.45
30
2X 8
41.5
29
27
12
E
A
1.9 MAX
K
H
2.4
SECTION A-A
0.35
TOP VIEW
0
-0.1
2X 9
A
2X 2
0.3 MAX
H
SECTION E-E
H
DEPARTMENT
SCALE 20
DETAIL J
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
-
2X 6
20
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
10
E
0.1
18
2X 2.5
2X 18.95
2X 4.5 MAX
§
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 93
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Page 94

Socket Mechanical Drawings
94 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 95

Package Mechanical Drawings
D Package Mechanical
Drawings
Ta b le D - 1 lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix.
Table D-1. Mechanical Drawing List
Drawing Description Figure Number
“Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 2)” Figure D-1
“Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 2)” Figure D-2
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 95
Page 96

Figure D-1. Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 2)
Package Mechanical Drawings
H
E22526 1 6
DWG. NO SHT. REV
G
F
2
G
E
2
H
D
SUBSTRATE
C
B
C
2
F
A
2
OF
1
SHEET
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
5
PACKAGE MECHANICAL DRAWING
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
DEPARTMENT
A1 E22526 6
TITLE
SCALE:
B
FINISHMATERIAL
DATEAPPROVED BY
DATECHECKED BY
DATEDRAWN BY
DATEDESIGNED BY
SCALE 15
DETAIL
1
G
1
H
A
SEE DETAIL
J
2
J
0.05
0.203 C
IHS LID PACKAGE
1
0.203 C
COMMENTS
0.08
IHS SEALANT
4
F
ANGLES ±0.5
DIMENSIONS ±0
0.021 SOLDER RESIST
ALL UNTOLERANCED LINEAR
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
INTERPRET DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES
IN ACCORDANCE WITH ASME Y14.5M-1994
0.15 C D E
THIRD ANGLE PROJECTION
C
FIDICAL
SCALE 15
DETAIL
MILLIMETERS
SUBSTRATE ALIGNMENT
2
B
2
4
C
D
C
C
A
E
PIN #1
SYMBOL
MIN MAX
0.175
37.45 37.55
B
37.45 37.55
1
2
B
0.625
2.2 2.3
1.3 1.4
33.9 34.1 1 C D
4.112 4.602
31.72 31.92 1 C E
1
2
C
C
C
2.331 2.843
1
2
4
4
3
D
F
F
C
35.6616 BASIC
35.6616 BASIC
1
2
G
G
COMMENTS
17.8308 BASIC
17.8308 BASIC
1
2
H
H
0.9144 BASIC
0.9144 BASIC
1
2
J
J
0.2
0.1
0.13
0.52
MILLIMETERS
MIN MAX
1
1
2
3
M
M
M
1
1
D
1
C
B
A-A
SECTION
1
2X M
3
C
SYMBOL
RM
1
6X RM
2
2X M
DETAILASCALE 100
C
A
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
H
G
F
E
B
C
D
C
C
3
2X M
B
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
A
96 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 97

Package Mechanical Drawings
Figure D-2. Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 2)
.
H
E22526 2 6
DWG. NO SHT. REV
C
H
G
F
2
T
F
E
11.95
5.975
D
1
T
D
C
E
G
2
V
1
V
1.06 MAX ALLOWABLE
COMPONENT HEIGHT
COMMENTS
MILLIMETERS
R1.09 BASIC
MIN MAX
1
R
SYMBOL
B
R1.09 BASIC
2
R
T
0.2 BASIC
9.75 BASIC
1
2
T
9.75 BASIC
1
V
0.2 BASIC
2
V
A
2
OF
2
SHEET
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
6
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1 E22526 6
SCALE:
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
R
DEPARTMENT
19.68
9.84
F
H
JK
0.23 C F H
K
8 7 6 5 4 3 2
J
DETAILDSCALE 20
R1
G
H
DETAILESCALE 20
MN
0.23 C G H
R2
N
M
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
THIS DRAWING CONTAINS INTEL CORPORAT ION CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION. IT IS DISCLOSED IN CONFIDENCE AND ITS CONT ENTS
MAY NOT BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED, DI SPLAYED OR MODIFIED, WITHOUT THE PRI OR WRITTEN CONSENT OF INTEL CORPORAT ION.
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
§
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 97
Page 98

Package Mechanical Drawings
98 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
Page 99

Heat Sink Back Plate Drawings
E Heat Sink Back Plate
Drawings
This heat sink back plate design is intended to adapt as a reference for OEMs that use
threaded fasteners on customized thermal solution, to comply with the mechanical and
structural requirements for the LGA1156 socket. The heat sink back plate does not
have to provide additional load for socket solder joint protect. Structural design
strategy for the heat sink is to provide sufficient load for the Thermal Interface Material
(TIM) and to minimize stiffness impact on the motherboard.
Note: Design modifications for specific application and manufacturing are the responsibility of
Table E-1. Mechanical Drawing List
Table E-2. Supplier Contact Information
OEM and the listed vendors for customized system implementation and validation.
These vendors and devices are listed by Intel as a convenience to Intel's general
customer base, but Intel does not make any representations or warranties whatsoever
regarding quality, reliability, functionality, or compatibility of these devices. Customers
are responsible for thermal, mechanical, and environmental validation of these
solutions. This list and/or these devices may be subject to change without notice.
Please refer to the motherboard keep out zone listed in Appendix B to ensure compliant
with the heat sink back plate implementation. Figure E-1 is the heat sink back plate
keep in zone for the design implementation.
Ta b le E - 1 lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix. Ta b le E - 2 lists the
mechanical drawings.
Drawing Description Figure Number
“Heat Sink Back Plate Keep In Zone” Figure E-1
“Heat Sink Back Plate” Figure E-2
Supplier Contact Phone Email
CCI (Chaun Choung
Technology Corp.)
Monica Chih +886-2-29952666 x1131 monica_chih@ccic.com.tw
The enabled components may not be currently available from supplier. Contact the
supplier directly to verify time of component availability.
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 99
Page 100

Figure E-1. Heat Sink Back Plate Keep In Zone
34.21
27.81
Heat Sink Back Plate Drawings
B
1
OF
95
2200 MISSION COLLEGE BLVD.
P.O. BOX 58119
SANTA CLARA, CA 95052-8119
13.9
R
1
SHEET
E58389_REV_B_PAE
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
-
DEPARTMENT
TITLE
3X 5
95
36
C
1
1
B
35.22
A
5.08
4X 9.25
2X 25.81
72.75
2X 37.54
19.19
2.54
2
LGA 1156 & 1155 HS BACKPLATE KEEP IN
SIZE DRAWING NUMBER REV
A1
SCALE:
1
C
2X 75
4
4
38.12
1 SOCKET CENTER PLANES ARE REFERENCED FROM GEOMETRIC
NOTES:
CENTER OF SOCKET HOUSING CAVITY FOR CPU PACKAGE (ALIGNS
WITH DATUM REFERENCE GIVEN FOR BOARD COMPONENT KEEP-INS).
3. LGA 1156 & 1155 HS BACKPLATE KEEP-IN VOLUME ENCOMPASS THE BACKPLATE NOMINAL VOLUME
4 OUTLINE OF LGA 1156 & 1155 ILM BACKPLATE FOR REFERENCE ONLY.
AND ALLOWANCES FOR SIZE TOLERANCES. THERMAL/MECHANICAL COMPONENT
DEVELOPERS SHALL DESIGN TO THE OUTSIDE OF SOCKET H1 ILM BACKPLATE 4
WITH CLEARANCE MARGINS.
REFERENCE DRAWINGS:
E20847 - LGA 1156 & 1155 ILM BACKPLATE
E21320 - LGA 1156 & 1155 ILM & PROCESSOR KEEPIN
5. DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS
B
2X 75
78.25
26 MAX 26 MAX
1
100 Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
 Loading...
Loading...