Page 1
Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-259
a
Technical notes on using Analog Devices DSPs, processors and development tools
Contact our technical support at dsp.support@analog.com and at dsptools.support@analog.com
Or vi sit our o n-li ne r esou rces htt p:/ /www.analog.com/ee-notes and http://www.analog.com/processors
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors
Contributed by Aseem Vasudev Prabhugaonkar and Jagadeesh Rayala Rev 1 – December 17, 2004
Introduction
This application note explains how to interface
parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC®
processors. The parallel ADC considered in this
application note is AD7865. This application
note also provides example code to demonstrate
how the SHARC processor’s external port can be
programmed to receive data from the AD7865 in
core and DMA modes.
About AD7865 ADCs
The AD7865 is a fast, low-power, four-channel
simultaneous sampling 14-bit A/D converter that
operates from a single 5 V supply. The device
contains a 2.4 µs successive approximation
ADC, four track/hold amplifiers, 2.5 V reference,
on-chip clock oscillator, signal conditioning
circuitry, and a high-speed parallel interface. The
input signals on four channels are sampled
simultaneously, thus preserving the relative
phase information of the signals on the four
analog inputs.
The AD7865 allows any subset of the four
channels be converted, maximizing the
throughput rate on the selected sequence. The
channels to be converted can be selected via
hardware (channel select input pins) or via
software (programming the channel select
register).
The high-speed parallel interface also allows
interfacing to 3 V processors.
AD7865 Product Highlights
The AD7865 features four track/hold
amplifiers and a fast (2.4 µs) ADC, allowing
simultaneous sampling and then conversion
of any subset of the four channels.
The AD7865 operates from a single 5 V
supply and consumes only 115 mW (typical),
making it ideal for low-power and portable
applications.
The AD7865 offers a high-speed parallel
interface for easy connection to
microprocessors, microcontrollers, and
digital signal processors.
The AD7865 is offered in three versions,
each with different analog input ranges. The
AD7865-1 offers the standard industrial
ranges of ±10 V and ±5 V; the AD7865-2
offers a unipolar range of 0 V to 2.5 V (or
0 V to 5 V); and the AD7865-3 offers the
common signal processing input range of
±2.5 V.
The AD7865 features very tight aperture
delay matching between the four input
sample-and-hold amplifiers.
AD7865 ADC Applications
AD7865 applications include:
AC motor control
Uninterruptible power supplies
Industrial power meters/monitors
Copyright 2004, Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Analog Devices assumes no responsibility for customer product design or the use or application of
customers’ products or for any infringements of patents or rights of others which may result from Analog Devices assistance. All trademarks and logos are property
of their respective holders. Information furnished by Analog Devices applications and development tools engineers is believed to be accurate and reliable, however
no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices regarding technical accuracy and topicality of the content provided in Analog Devices’ Engineer-to-Engineer Notes.
Page 2
a
Data acquisition systems
Communications
About ADSP-21161 Processors
The ADSP-21161 is the second member of the
SHARC processor family of 32-bit floating-point
programmable processors to be based on a SIMD
core architecture optimized for digital signal
processing performance. This processor is
capable of 600 million math operations per
second (MFLOPs). Like all SHARC processors,
the ADSP-21161 is code-compatible with the
other members of the SHARC family and
supports both fixed- and floating-point data
types. The ADSP-21161 lowers the price for
SIMD SHARC processing performance and is an
outstanding solution for many price-sensitive
applications.
ADSP-21161 Processor Features
ADSP-21161 processor features include:
100 MHz (10 ns) SIMD SHARC DSP core
600 MFLOPS (32-bit floating-point data),
600 MOPS (32-bit fixed-point data)
Code-compatible with all SHARC processors
Supports IEEE-compatible 32-bit floating-
point, 40-bit floating-point, and 32-bit fixedpoint math
Single-cycle instruction execution, including
SIMD operations in both computational units
One Mbit on-chip dual-ported SRAM
2.4 Gbyte/second on-chip data bandwidth
14 zero-overhead DMA channels
Four synchronous serial ports with I2S
support
Integrated support for SDRAM and
SBSRAM external memories
Support for single-cycle, 100 MHz
instruction execution from 48-bit-wide
external memories
ADSP-21161 Applications
ADSP-21161 applications include:
Speech recognition
Professional and high-end consumer audio
Automotive entertainment
Fingerprint recognition
Digital audio broadcast
Wireless communications
Motor control
Global positioning systems
Medical equipment
Telephony
Test equipment
AD7865-to-ADSP-21161 Interface
This application note employs a high-speed
parallel 14-bit ADC for the interface. A single
conversion start signal (
the track/holds into hold mode simultaneously
and initiates conversion sequence for the selected
channels. The /EOC signal indicates the end of
each individual conversion in the selected
conversion sequence. The
the end of the conversion sequence. Data is read
from the part via a 14-bit parallel data bus using
the standard /CS and /RD signals.
Core Mode Interface
/CONVST) places all of
BUSY signal indicates
Serial ports support 128 channels TDM
frames with selection of companding on a
per-channel basis
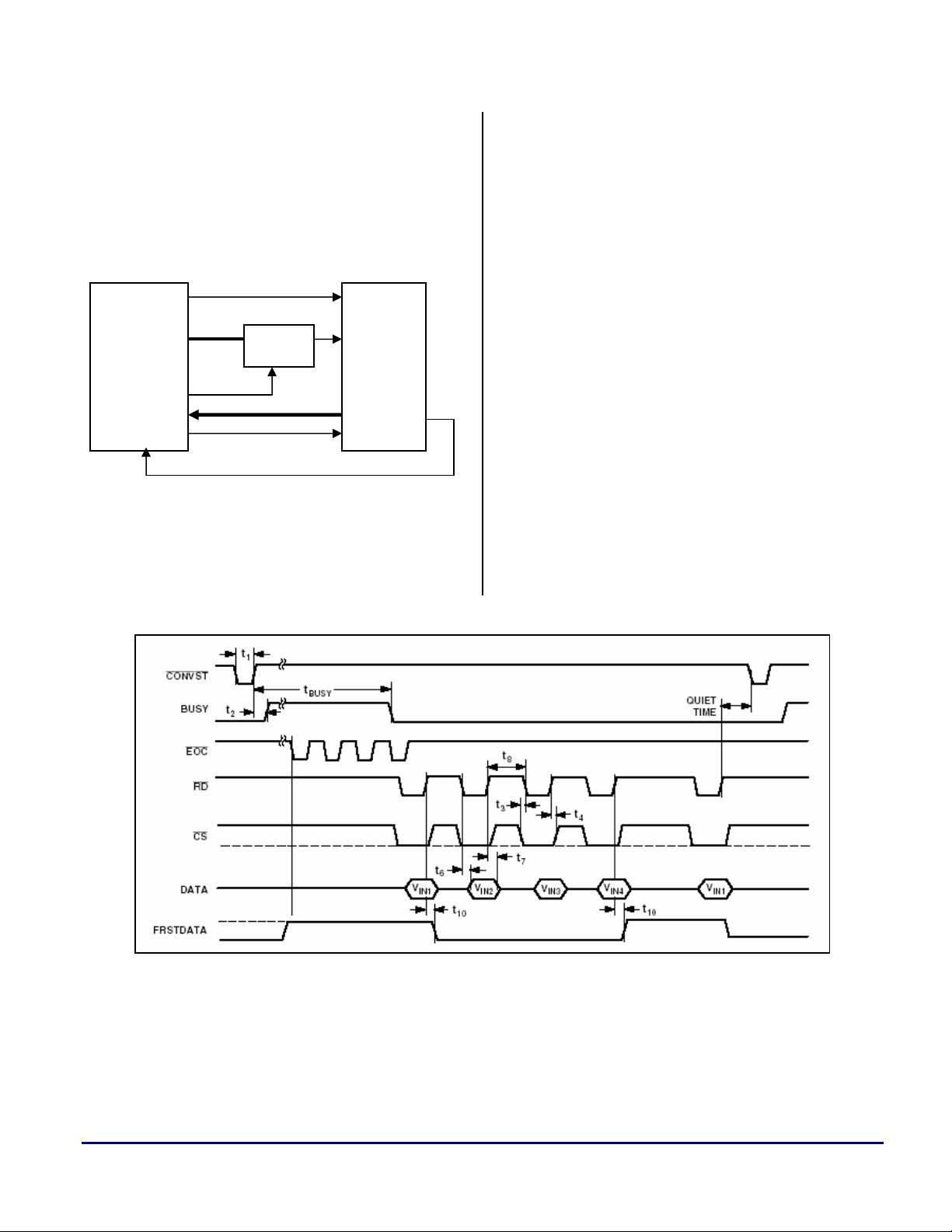
Refer to the functional block diagram in Figure 1
for details on the ADSP-21161-to-AD7865 ADC
interface. This interface scheme is used to
receive data from the ADC in processor core
mode. Note that all of the four ADC channels are
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 2 of 7
Page 3
a
selected in hardware. When the H#/S SEL pin is
at logic 0, the AD7865 conversion sequence
selection is controlled via the SL1–SL4 input
pins and uses an internal clock. The AD7865's
data bus (
DATA29
DB0-DB13) is interfaced with DATA16-
of the ADSP-21161 processor.
ADSP21161
FSx
ADDR
/MSx
/CONVST
Addr
decoder
AD7865-3
/CS
Data Data
/RD /RD
BUSY
Figure 1. Interface Block Diagram in Core Mode
/IRQx
A low-to-high transition on the /CONVST input
places all of the track/holds into hold mode and
starts the conversion on the selected channels.
Frame sync of SPORT0 is used to generate the
/CONVST signal for the ADC. The serial port is
configured to transmit with frame sync as data
independent frame sync. The SPORT frame sync
frequency is determined by the value loaded in
the DIV0 register. An initial dummy write to the
SPORT TX0A register is required to start
continuous frame sync on the
FS0 signal. A BUSY
signal from the AD7865 indicates the end of
conversion on all the selected ADC channels.
The falling edge of BUSY triggers an interrupt.
The interrupt is configured to be edge sensitive.
The ADC FIFO is read with four consecutive
core read operations in the interrupt service
routine. The AD7865, in this case, is a memorymapped device for the ADSP-21161 processor.
Refer to the timing diagram in Figure 2 for
reading after the conversion sequences.
The screen captures in Figure 3 and Figure 4
were taken with a logic analyzer while receiving
data from the AD7865 in core mode.
Figure 2. Timing Diagram, Reading After the Conversion Sequences
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 3 of 7
Page 4

a
Figure 3. Timing Diagram 1, Reading After the Conversion Sequences
Figure 4. Timing Diagram 2, Reading After the Conversion Sequences
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 4 of 7
Page 5

a
DMA Mode Interface
Refer to the functional block diagram in Figure 5
for details on the ADSP-21161-to-AD7865 ADC
interface scheme to receive data from the ADC
in DMA mode. The ADC channel selection is
performed in hardware.
ADSP21161
FSx
Addr
/MSx
/RD
/COVNST
Addr
deoder
/CS
Data Data
/RD
AD7865-3
/EOC
Figure 5. Interface Block Diagram in Paced Master
DMA Mode
/DMARx
The /EOC (end of conversion) signal is activated
after the conversion of each channel. /EOC is
connected to DMAR1 of the processor. The end-ofconversion pulses act as DMA requests for the
SHARC. In this scenario, paced master mode for
DMA seems appropriate. In this mode, the
processor attempts the internal memory DMA
transfers indicated by the DMA counter (CEPx),
making transfers based on external DMA request
inputs. The processor generates a DMA request
whenever the external device asserts the DMARx
pin. To read data from the ADC, the processor
controls the data transfer using the /RD signal
and by applying the selected number of wait
states. The /CONVST start signal is generated
using the SPORT0 frame sync.
Refer to the timing diagram in Figure 6 for
reading between conversion sequences. The
screen captures in Figure 7 and Figure 8 were
taken with a logic analyzer while receiving data
in paced master DMA mode.
Figure 6. Timing Diagram for Reading During Conversion Sequences
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 5 of 7
Page 6

a
Figure 7. Timing Diagram 1 for Reading During Conversion Sequences
Figure 8. Timing Diagram 2 for Reading During Conversion Sequences
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 6 of 7
Page 7

a
Conclusion
This application note shows that parallel ADCs
like the AD7865 can be interfaced gluelessly
with an ADSP-21161 processor. Also, the data
from such ADCs can be read in core mode or
DMA mode.
Appendix
Project files are included in a ZIP file attached to
this application note.
References
[1] ADSP-21161 SHARC DSP Hardware Reference. Third Edition, May 2002. Analog Devices, Inc.
[2] ADSP-21161 Evaluation System Board Schematics, Analog Devices, Inc.
[3] AD7865 Technical Data Sheet, Rev B. Analog Devices, Inc.
Document History
Revision Description
Rev 1 – December 17, 2004
by Aseem Vasudev Prabhugaonkar
Initial Release
Interfacing AD7865 Parallel ADCs to ADSP-21161 SHARC® Processors (EE-259) Page 7 of 7
 Loading...
Loading...