Page 1
Engineer To Engineer Note EE-184
a
Technical Notes on using Analog Devices' DSP components and development tools
Contact our technical support by phone: (800) ANALOG-D or e-mail: dsp.support@analog.com
Or vi sit ou r on-l ine re sourc es ht tp:// www.analog.com/dsp and http://www.analog.com/dsp/EZAnswer
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin®
Processors
Contributed by Michael Hennerich May 20, 2003
Introduction
The Blackfin® Processor family of products are
based on an architecture that combines a dualMAC, state-of-the-art signal processing engine,
with an orthogonal RISC-like processor
instruction set, and single-instruction, multipledata (SIMD) multimedia capabilities into a single
instruction set architecture. By integrating a rich
set of industry leading system peripherals and
memory, Blackfin Processors are the platform of
choice for next generation applications that
require RISC like programmability, multimedia
support and leading edge signal processing in
one integrated Processor.
Typical Blackfin Processor applications such as
video Tele-conferencing systems, digital imaging
products or Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs)
all have a general for a display capability.
This EE-Note describes the hardware and
software environment necessary to provide an
interface between the EPSON S1D13806
Embedded Memory Display Controller and the
ADSP-BF535 High Performance 300 MHz,
Blackfin Processor.
The designs described in this document are
presented only as examples of how such
interfaces might be implemented.
S1D13806 Embedded Memory Display Controller
embedded memory supporting a wide range of
CPUs and display devices. The S1D13806
architecture is designed to meet the low cost, low
power requirements of the embedded markets,
such as Mobile Communications. The S1D13806
supports all LCD panel types, CRT, TV, and
additionally provides a number of differentiating
features.
• 1280K bytes of embedded DRAM
• Resolutions up to:
• 800x600 at a color depth of 16 bpp.
• 1024x768 at a color depth of 8 bpp.
Overview
The ADSP-BF535 System Bus
The External Bus Interface Unit (EBIU) on the
ADSP-BF535 provides a high performance
interface to a wide variety of industry-standard
memory and I/O devices. The asynchronous
memory controller provides a configurable
interface for up to four separate banks of
memory or I/O devices. Each bank occupies a
64M-byte window in the processor’s address
space bus system. The banks can also be
configured for either 16-bit wide or 32-bit wide
buses. Word or byte accesses can be controlled
by the Asynchronous Byte Enable signals
(
/ABE[x]).
s
The S1D13806 is a highly integrated color
LCD/CRT/TV graphics controller with
Copyright 2003, Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Analog Devices assumes no responsibility for customer product design or the use or application of
customers’ products or for any infringements of patents or rights of others which may result from Analog Devices assistance. All trademarks and logos are property
of their respective holders. Information furnished by Analog Devices Applications and Development Tools Engineers is believed to be accurate and reliable, however
no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices regarding technical accuracy and topicality of the content provided in Analog Devices’ Engineer-to-Engineer Notes.
Page 2
a
This section provides an overview of the
operation of the CPU bus in order to establish
interface requirements.
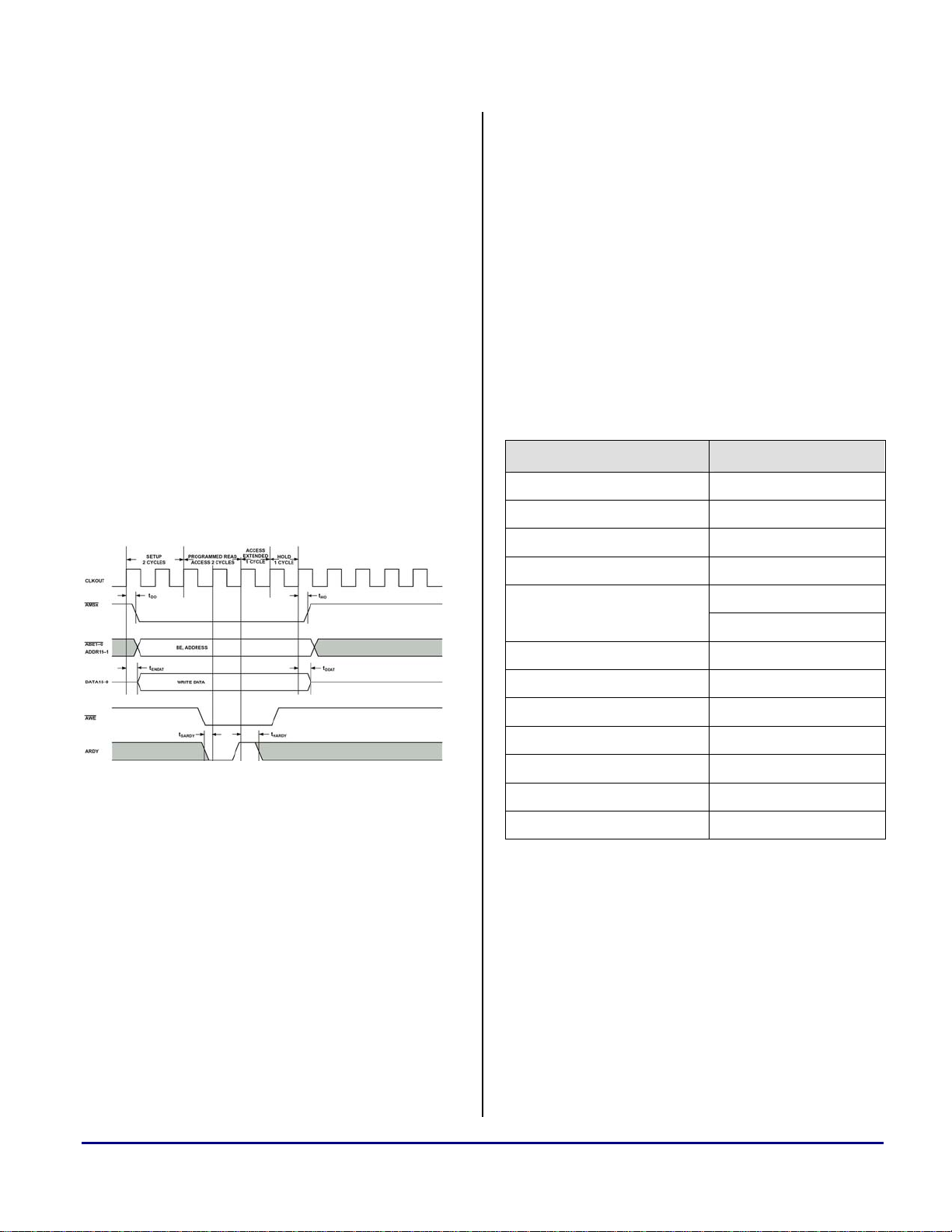
Asynchronous Memory Access Cycles
Once an address in the LCD block of memory is
placed on the external address bus
(
ADD[2:25], /ABE3), the LCD chip select (/CS) is
driven low by
signals (
appropriate cycle and
insert wait states into the cycle.
conjunction with
/WE0 (write low byte) and /WE1 (write high byte)
/AMS[x]. The read or write enable
/ARE or /AWE) are driven low for the
ARDY is driven low to
/ABE0 in
/ABE1 allows an external logic
byte steering.
Figure 1 illustrates a typical Blackfin
asynchronous memory write cycles to the LCD
controller interface.
Note: At reset, the Register/Memory Select bit in
the Miscellaneous Register (
REG[001h] bit 7) is
set to 1. This means that only REG[000h] (readonly) and REG[001h] are accessible until a write
to REG[001h] sets bit 7 to 0 making all registers
accessible. When debugging a new hardware
design, this can sometimes give the appearance
that the interface is not working, so it is
important to remember to clear this bit before
proceeding with debugging.
Host Bus Interface Pin Mapping
Table 1 shows the functions of each Host Bus
Interface signal.
ADSP-BF535 Pin Name S1D13806 Pin Name
ADDR[2:20], /ABE3 AB[1:20]
DATA[0:15] DB[0:15]
f
(/AWE, /ABE0, A20,A21)
f
(/AWE, /ABE1, A20,A21)
/ARE
/WE0
/WE1
/RD
RD/WR
Figure 1: ADSP-BF535 Write Cycle
S1D13806 Host Bus Interface
The S1D13806 directly supports multiple
processors. The S1D13806 implements a 16-bit
generic little endian Host Bus Interface which is
most suitable for direct connection to the ADSPBF535 microprocessor.
The Generic Host Bus Interface is selected by the
S1D13806 on the rising edge of
/RESET. After
releasing reset the bus interface signals assume
their selected configuration. For details on
S1D13806 configuration, refer to the
“S1D13806 Technical Manual”.
/AMS[x] /CS
ADDR21 M/R
+VDD AB0
ARDY /WAIT
+VDD /BS
CLKOUT BUSCLK
/RESET /RESET
Table 1: Host Bus Interface Pin Mapping
Host Bus Interface Signal Descriptions
The S1D13806 Generic Host Bus Interface
requires the following signals.
•
BUSCLK is a clock input which is required by
the S1D13806 Host Bus Interface. It is separate
from the input clock (
CLKI) and is typically
driven by the host CPU system clock (CLKOUT).
• The address inputs
DB[0:15], connect directly to the ADSP-BF535
AB[1:20], and the data bus
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 2 of 13
Page 3
a
address (ADDR[2:20], /ABE3) and data bus
(
DATA[0:15]), respectively. CONF[3:0] must be set
to select the Generic Host Bus Interface with
little endian mode.
•
M/R (memory/register) selects between memory
or register access. It may be connected to an
address line, allowing system address
be connected to the
• Chip Select (
M/R line.
/CS) must be driven low by /AMS[x]
ADDR21 to
whenever the S1D13806 is accessed by the
ADSP-BF535.
•
/WE0 (the low byte write enable signal) is
connected to an external decode logic
conjunction with address bit 0
. /AWE, in
(/ABE0), allow
byte steering of write operations to register
memory space. All other accesses are 16-bits
wide (
•
connected to an external decode logic
conjunction with address bit 0
/WE1 and /WE0 asserted simultaneously).
/WE1 (the high byte write enable signal) is
. /AWE, in
(/ABE1), allow
byte steering of write operations to register
memory space. All other accesses are 16-bits
wide
(/WE1 and /WE0 asserted simultaneously).
the S1D13806 internal registers and/or display
buffer. The
/WAIT line resolves these contentions
by forcing the host to wait until the resource
arbitration is complete.
• The
/BS and AB0 signals are not used for the
Generic Host Bus Interface and should be
connect to V
Hardware Description
DD
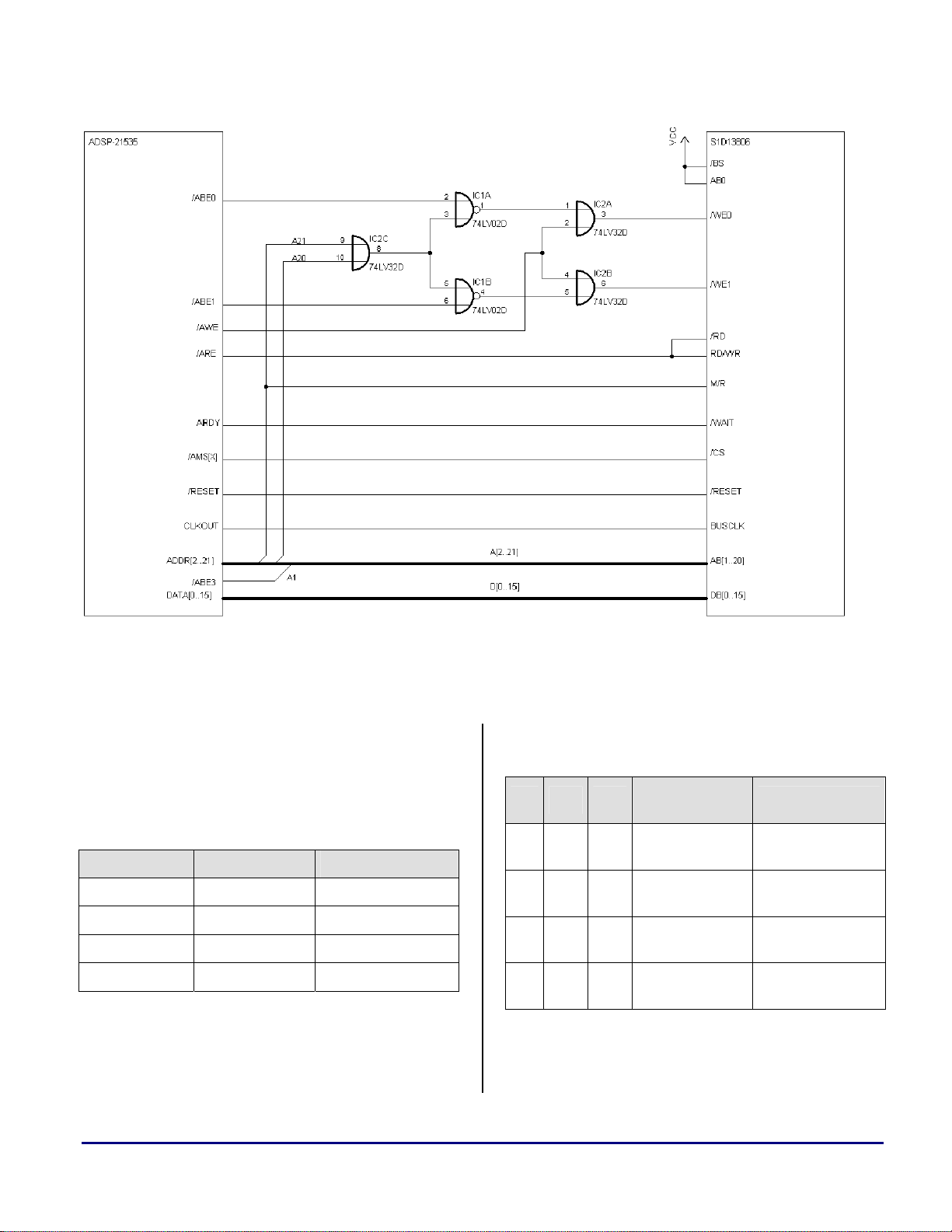
Figure 2 shows a typical implementation
utilizing the S1D13806 memory mapped into the
ADSP-BF535 address space.
S1D13806 Hardware Configuration
The S1D13806 latches CONF7 through CONF0 to
allow selection of the bus mode and other
configuration data on the rising edge of /RESET.
For details on configuration, refer to the
S1D13806 Hardware Functional Specification.
Table 2 shows the configuration settings
important to the Generic Host Bus Interface used
by the ADSP-BF535 .
•
/RD and RD/WR connected to /ARE (the read
enable signal from the ADSP-BF535) and must
be driven low when the ADSP-BF535 is reading
data from the S1D13806. This causes all read
accesses to be 16-bits wide.
•
/WAIT connected to ARDY and is a signal output
from the S1D13806 that indicates the ADSPBF535 must wait until data is ready (read cycle)
or accepted (write cycle) on the host bus. Since
ADSP-BF535 accesses to the S1D13806 may
occur asynchronously to the display update, it is
possible that contention may occur in accessing
S1D13806 Pin
Name
CONF[3:0]
CONF4
CONF5 0 = BUSCLK input not divided
CONF6 1 = /WAIT is always driven
Table 2: Summary of Power-On/Reset Options
state of this pin at rising
edge of /RESET
0000 = Generic Host Bus
Interface, little endian, active
low /WAIT selected
Reserved. Must be tied to
ground
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 3 of 13
Page 4
a
Figure 2: Typical Implementation of ADSP-BF535 to S1D13806 Interface
Register/Memory Mapping
The ADSP-BF535 supports four asynchronous
memory regions. Each has a unique memory
select (
AMS[x]) associated with it, shown in the
Table 3.
Memory Bank Address Start Address End
AMS[0]
AMS[1]
AMS[2]
AMS[3]
Table 3: Register/Memory Mapping
2000 0000 23FF FFFF
2400 0000 27FF FFFF
2800 0000 2BFF FFFF
2C00 0000 2FFF FFFF
The S1D13806 is a memory-mapped device. The
internal registers are mapped in the lower
requires 1.25M bytes and is mapped in the third
and fourth megabytes (0x20 0000 to 0x33 FFFF).
A21 A20 A12
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 x
1 X x
x = don’t care
Table 4: Typical Register/Memory Mapping
address space starting at zero. The display buffer
Physical
Address Range
0h2x00 0000 to
0h2x00 01FF
0h2x00 1000 to
0h2x00 1FFF
0h2x10 0000 to
0h2x1F FFFF
0h2x20 0000 to
0h2x33 FFFF
Function
Control Registers
Decoded
MediaPlug
Registers Decoded
BitBLT Registers
Decoded
Display Buffer
Decoded
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 4 of 13
Page 5

a
A typical implementation as shown in the
schematic has the Memory/Register select pin
(
M/R) connected to ADSP-BF535 address line
ADD21. ADD21 selects between the S1D13806
display buffer (
(
ADD21=0). This implementation decodes as
ADD21=1) and internal registers
shown in the Table 4.
Note: The ADSP-BF535 provides 64M byte of
address space. Since the ADSP-BF535 address
bits
ADDR[22:25] are ignored, the S1D13806
registers and display buffer are aliased within the
allocated address space. If aliasing is
undesirable, the address space must be fully
decoded.
ADSP-BF535 Configuration
In the ADSP-BF535 Asynchronous Memory Global
Control Register (EBIU_AMGCTL)
must be set to 1, in order to enable
, the AMCKEN bit
CLKOUT for
asynchronous memory region accesses. Enable
16-bit packing mode by setting the
BxPEN bit to
1, this sets the interface to operate using a 16-bit
data bus.
In the
(EBIU_AMBCTLx)
1 indicating that the state of
determine completion of access. The
polarity bit
Asynchronous Memory Bank Control x Register
, the BxRDYEN bit must be set to
ARDY is used to
ARDY
BxRDYPOL must be set to 1, to
complete transition if ARDY is sampled high. The
S1D13806 timing requirements can be
programmed using following bit fields and
initialization values:
BxWAT[3:0]=0011
BxRAT[3:0]=0011
BxHT[1:0]=00
BxST[1:0]=01
BxTT[1:0]=01.
The frequency of CLKOUT output is programmed
from the state of pins SSEL[1:0], MSEL[6:0] and DF
during reset, and from
PLL Control (PLL_CTL)
configuration registers of the ADSP-BF535,
which can be changed on the fly.
The S1D13806 maximum
(f
=50MHz) is detailed in the S1D13806
CLK
BUSCLK frequency
Technical Manual. Tests conducted as part of
this project have shown that the S1D13806 may
work reliably up to
BUSCLK frequencies <
70MHz, without dangerous overheating, but
users should consult the data sheet for the
S1D13806.
Software
A simple demo source on how to configure and
run the S1D13806 is attached to this document.
The sample source initializes ADSP-BF535
asynchronous memory configuration registers,
followed by the initialization of the S1D13806.
The code in this example will perform
initialization to the following specification: 640 x
480 CRT, 60Hz frame rate and 16bpp color
depth.
Configuring the S1D13806 demo program for
use with your target display is very easy. The
source has been written such that it can directly
use the information generated by the
13806cfg.exe utility program provided by Epson.
You simply use the Epson utility to define your
display device, and export the register values to a
file (C header file for S1D13806 generic drivers
s1d13806.h) which is then included by your
project.
The S1D13806 configuration utilities and 3
rd
party or sample display drivers are available on
the internet at
www.erd.epson.com.
References
1. Analog Devices, Inc, ADSP-BF535 Blackfin
Processor Hardware Reference
2. Analog Devices, Inc, ADSP-BF535 Blackfin
Processor Datasheet
3. Epson Research and Development, Inc., S1D13806
Hardware Functional Specification, Document
Number X28B-A-001-xx.
4. Epson Research and Development, Inc., S1D13806
Programming Notes and Examples, Document
Number X28B-G-003-xx.
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 5 of 13
Page 6

Source Code
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------//
// File generated by S1D13806CFG.EXE
//
// Copyright (c) 2000,2001 Epson Research and Development, Inc.
// All rights reserved.
//
// PLEASE NOTE: If you FTP this file to a non-Windows platform, make
// sure you transfer this file using ASCII, not BINARY mode.
//
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CRT: (active) 640x480 60Hz (PCLK=CLKI2=25.175MHz)
// Memory: Embedded SDRAM (MCLK=CLKI3=50.000MHz) (BUSCLK=65.000MHz)
#define S1D_DISPLAY_WIDTH 640
#define S1D_DISPLAY_HEIGHT 480
#define S1D_DISPLAY_BPP 16
#define S1D_DISPLAY_SCANLINE_BYTES 1280
#define S1D_PHYSICAL_VMEM_ADDR 0x24200000L
#define S1D_PHYSICAL_VMEM_SIZE 0x140000L
#define S1D_PHYSICAL_REG_ADDR 0x24000000L
#define S1D_PHYSICAL_REG_SIZE 0x200
#define S1D_DISPLAY_PCLK 25175
#define S1D_PALETTE_SIZE 256
#define S1D_FRAME_RATE 60
#define S1D_POWER_DELAY_ON 0
#define S1D_POWER_DELAY_OFF 120
#define S1D_CRT
#define S1D_HWBLT
#define S1D_REGDELAYOFF 0xFFFE
#define S1D_REGDELAYON 0xFFFF
#define S1D_WRITE_PALETTE(p,i,r,g,b) \
{ \
((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E2/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)] = (S1D_VALUE)(i); \
((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)] = (S1D_VALUE)(r); \
((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)] = (S1D_VALUE)(g); \
a
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 6 of 13
Page 7

a
((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)] = (S1D_VALUE)(b); \
}
#define S1D_READ_PALETTE(p,i,r,g,b) \
{ \
((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E2/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)] = (S1D_VALUE)(i); \
r = ((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)]; \
g = ((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)]; \
b = ((volatile S1D_VALUE*)(p))[0x1E4/sizeof(S1D_VALUE)]; \
}
typedef unsigned short S1D_INDEX;
typedef unsigned char S1D_VALUE;
typedef struct
{
S1D_INDEX Index;
S1D_VALUE Value;
} S1D_REGS;
static S1D_REGS aS1DRegs[] =
{
{0x0001,0x00}, // Miscellaneous Register
{0x01FC,0x00}, // Display Mode Register
{0x0004,0x00}, // General IO Pins Configuration Register 0
{0x0005,0x08}, // General IO Pins Configuration Register 1
{0x0008,0x00}, // General IO Pins Control Register 0
{0x0009,0x00}, // General IO Pins Control Register 1
{0x0010,0x02}, // Memory Clock Configuration Register
{0x0014,0x00}, // LCD Pixel Clock Configuration Register
{0x0018,0x02}, // CRT/TV Pixel Clock Configuration Register
{0x001C,0x02}, // MediaPlug Clock Configuration Register
{0x001E,0x02}, // CPU To Memory Wait State Select Register
{0x0021,0x03}, // DRAM Refresh Rate Register
{0x002A,0x00}, // DRAM Timings Control Register 0
{0x002B,0x01}, // DRAM Timings Control Register 1
{0x0020,0x80}, // Memory Configuration Register
{0x0030,0x25}, // Panel Type Register
{0x0031,0x00}, // MOD Rate Register
{0x0032,0x4F}, // LCD Horizontal Display Width Register
{0x0034,0x12}, // LCD Horizontal Non-Display Period Register
{0x0035,0x01}, // TFT FPLINE Start Position Register
{0x0036,0x0B}, // TFT FPLINE Pulse Width Register
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 7 of 13
Page 8

a
{0x0038,0xDF}, // LCD Vertical Display Height Register 0
{0x0039,0x01}, // LCD Vertical Display Height Register 1
{0x003A,0x2C}, // LCD Vertical Non-Display Period Register
{0x003B,0x0A}, // TFT FPFRAME Start Position Register
{0x003C,0x01}, // TFT FPFRAME Pulse Width Register
{0x0040,0x05}, // LCD Display Mode Register
{0x0041,0x00}, // LCD Miscellaneous Register
{0x0042,0x00}, // LCD Display Start Address Register 0
{0x0043,0x00}, // LCD Display Start Address Register 1
{0x0044,0x00}, // LCD Display Start Address Register 2
{0x0046,0x80}, // LCD Memory Address Offset Register 0
{0x0047,0x02}, // LCD Memory Address Offset Register 1
{0x0048,0x00}, // LCD Pixel Panning Register
{0x004A,0x00}, // LCD Display FIFO High Threshold Control Register
{0x004B,0x00}, // LCD Display FIFO Low Threshold Control Register
{0x0050,0x4F}, // CRT/TV Horizontal Display Width Register
{0x0052,0x13}, // CRT/TV Horizontal Non-Display Period Register
{0x0053,0x01}, // CRT/TV HRTC Start Position Register
{0x0054,0x0B}, // CRT/TV HRTC Pulse Width Register
{0x0056,0xDF}, // CRT/TV Vertical Display Height Register 0
{0x0057,0x01}, // CRT/TV Vertical Display Height Register 1
{0x0058,0x2B}, // CRT/TV Vertical Non-Display Period Register
{0x0059,0x09}, // CRT/TV VRTC Start Position Register
{0x005A,0x01}, // CRT/TV VRTC Pulse Width Register
{0x005B,0x18}, // TV Output Control Register
{0x0060,0x05}, // CRT/TV Display Mode Register
{0x0062,0x00}, // CRT/TV Display Start Address Register 0
{0x0063,0x00}, // CRT/TV Display Start Address Register 1
{0x0064,0x00}, // CRT/TV Display Start Address Register 2
{0x0066,0x80}, // CRT/TV Memory Address Offset Register 0
{0x0067,0x02}, // CRT/TV Memory Address Offset Register 1
{0x0068,0x00}, // CRT/TV Pixel Panning Register
{0x006A,0x00}, // CRT/TV Display FIFO High Threshold Control Register
{0x006B,0x00}, // CRT/TV Display FIFO Low Threshold Control Register
{0x0070,0x00}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Control Register
{0x0071,0x01}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Start Address Register
{0x0072,0x00}, // LCD Cursor X Position Register 0
{0x0073,0x00}, // LCD Cursor X Position Register 1
{0x0074,0x00}, // LCD Cursor Y Position Register 0
{0x0075,0x00}, // LCD Cursor Y Position Register 1
{0x0076,0x00}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Blue Color 0 Register
{0x0077,0x00}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Green Color 0 Register
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 8 of 13
Page 9

a
{0x0078,0x00}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Red Color 0 Register
{0x007A,0x1F}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Blue Color 1 Register
{0x007B,0x3F}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Green Color 1 Register
{0x007C,0x1F}, // LCD Ink/Cursor Red Color 1 Register
{0x007E,0x00}, // LCD Ink/Cursor FIFO Threshold Register
{0x0080,0x00}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Control Register
{0x0081,0x01}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Start Address Register
{0x0082,0x00}, // CRT/TV Cursor X Position Register 0
{0x0083,0x00}, // CRT/TV Cursor X Position Register 1
{0x0084,0x00}, // CRT/TV Cursor Y Position Register 0
{0x0085,0x00}, // CRT/TV Cursor Y Position Register 1
{0x0086,0x00}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Blue Color 0 Register
{0x0087,0x00}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Green Color 0 Register
{0x0088,0x00}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Red Color 0 Register
{0x008A,0x1F}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Blue Color 1 Register
{0x008B,0x3F}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Green Color 1 Register
{0x008C,0x1F}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor Red Color 1 Register
{0x008E,0x00}, // CRT/TV Ink/Cursor FIFO Threshold Register
{0x0100,0x00}, // BitBlt Control Register 0
{0x0101,0x00}, // BitBlt Control Register 1
{0x0102,0x00}, // BitBlt ROP Code/Color Expansion Register
{0x0103,0x00}, // BitBlt Operation Register
{0x0104,0x00}, // BitBlt Source Start Address Register 0
{0x0105,0x00}, // BitBlt Source Start Address Register 1
{0x0106,0x00}, // BitBlt Source Start Address Register 2
{0x0108,0x00}, // BitBlt Destination Start Address Register 0
{0x0109,0x00}, // BitBlt Destination Start Address Register 1
{0x010A,0x00}, // BitBlt Destination Start Address Register 2
{0x010C,0x00}, // BitBlt Memory Address Offset Register 0
{0x010D,0x00}, // BitBlt Memory Address Offset Register 1
{0x0110,0x00}, // BitBlt Width Register 0
{0x0111,0x00}, // BitBlt Width Register 1
{0x0112,0x00}, // BitBlt Height Register 0
{0x0113,0x00}, // BitBlt Height Register 1
{0x0114,0x00}, // BitBlt Background Color Register 0
{0x0115,0x00}, // BitBlt Background Color Register 1
{0x0118,0x00}, // BitBlt Foreground Color Register 0
{0x0119,0x00}, // BitBlt Foreground Color Register 1
{0x01E0,0x00}, // Look-Up Table Mode Register
{0x01E2,0x00}, // Look-Up Table Address Register
{0x01F0,0x10}, // Power Save Configuration Register
{0x01F1,0x00}, // Power Save Status Register
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 9 of 13
Page 10

a
{0x01F4,0x00}, // CPU-to-Memory Access Watchdog Timer Register
{0x01FC,0x02}, // Display Mode Register
};
Listing 1: Header file generated by the S1D13806CFG.EXE (EPSON)
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// FILE: S1D13806.c
//
// Analog Devices Inc. 2003
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <defBF535.h>
#include "S1D13806.h"
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// defines
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//first address of the display buffer memory
#define pMem ((volatile unsigned short *) (S1D_PHYSICAL_VMEM_ADDR))
//starting address of the S1D13806 registers.
#define pRegs ((volatile unsigned char *) (S1D_PHYSICAL_REG_ADDR))
//starting address of the S1D13806 BitBLT_Data register
#define BitBLT_Data ((volatile unsigned short *) (S1D_PHYSICAL_REG_ADDR + 0x100000 ))
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// function prototypes
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
unsigned short S1D13806_init(void);
unsigned short S1D13806_clear_vmem(unsigned short color);
void S1D13806_plot_xy(unsigned short x,unsigned short y,unsigned short color);
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 10 of 13
Page 11

a
void S1D13806_plot_hline(unsigned short x1,unsigned short y1,unsigned short x2,unsigned short
color);
void S1D13806_plot_vline(unsigned short x1,unsigned short y1,unsigned short y2,unsigned short
color);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// void main()
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void main()
{
unsigned short lCnt,error=0;
// set Asynchronous Memory Control Registers
*((volatile unsigned short *) EBIU_AMGCTL) = 0x0025;
*((volatile int *) EBIU_AMBCTL0) = 0x33170000;
S1D13806_init();
S1D13806_clear_vmem(0);
S1D13806_plot_hline(0,239,639,0xFFFF);
S1D13806_plot_vline(0,0,479,0xFFFF);
for(lCnt=0 ; lCnt < 628 ; lCnt++) {
S1D13806_plot_xy(lCnt,(unsigned short)( 100*cos((float)lCnt/100) +240),0x001F);
S1D13806_plot_xy(lCnt,(unsigned short)( 80*sin((float)lCnt/50) +240),0xF100);
}
}
// Configure S1D13806 Registers
unsigned short S1D13806_init(void)
{
unsigned short i=0;
unsigned short error=0;
for( i=0; i<107; i++ )
{
*( pRegs + aS1DRegs[i].Index) = aS1DRegs[i].Value;
}
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 11 of 13
Page 12

a
return(error);
}
//Clear display memory
unsigned short S1D13806_clear_vmem(unsigned short color)
{
int lCnt;
unsigned short error=0;
for (lCnt = 0; lCnt < (S1D_PHYSICAL_VMEM_SIZE/2); lCnt++)
{
*(pMem+lCnt) = color;
}
return(error);
}
//One pixel at position (x,y)
inline void S1D13806_plot_xy(unsigned short x,unsigned short y,unsigned short color)
{
*(pMem + ( ( y * (S1D_DISPLAY_WIDTH ) ) + x )) = color;
}
//Horizontal line running to the right
// x1,y1--------------------x2,y1
void S1D13806_plot_hline(unsigned short x1,unsigned short y1,unsigned short x2,unsigned short
color)
{
unsigned short temp;
if (x1 > x2){ //SWOP
temp = x1;
x1 = x2;
x2 = temp;
}
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 12 of 13
Page 13

a
while(x1 <= x2)
S1D13806_plot_xy(x1++, y1,color);
}
//Vertical line running down
/*
* x1,y2
* |
* |
* x1,y1
*/
void S1D13806_plot_vline(unsigned short x1,unsigned short y1,unsigned short y2,unsigned short
color)
{
unsigned short temp;
if (y1 > y2){ //SWOP
temp = y1;
y1 = y2;
y2 = temp;
}
while(y1 <= y2)
S1D13806_plot_xy(x1, y1++,color);
}
Listing 2: Source file S1D13806.c
Document History
Version Description
May 20, 2003 Updated according to new Blackfin naming convention.
January 31, 2003 by M.Hennerich Initial Release
Interfacing EPSON S1D13806 memory display controller to Blackfin® Processors (EE-184) Page 13 of 13
 Loading...
Loading...