REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
CMOS 220 MHz True-Color Graphics
Triple 10-Bit Video RAM-DAC
ADV7150
© Analog Devices, Inc., 1996
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
@ 85 MHz
8-Bit Pseudo Color
15-Bit True Color
APPLICATIONS
High Resolution, True Color Graphics
Professional Color Prepress Imaging
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV7150 (ADV®) is a complete analog output, Video
RAM-DAC on a single CMOS monolithic chip. The part is specifically designed for use in high performance, color graphics
workstations. The ADV7150 integrates a number of graphic
functions onto one device allowing 24-bit direct True-Color operation at the maximum screen update rate of 220 MHz. The
ADV7150 implements 30-bit True Color in 24-bit frame buffer
designs. The part also supports other modes, including 15-bit
True Color and 8-bit Pseudo or Indexed Color. Either the Red,
Green or Blue input pixel ports can be used for Pseudo Color.
(Continued on page 12)
ADV is a registered trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
FEATURES
220 MHz, 24-Bit (30-Bit Gamma Corrected) True Color
Triple 10-Bit “Gamma Correcting” D/A Converters
Triple 256 3 10 (256 3 30) Color Palette RAM
On-Chip Clock Control Circuit
Palette Priority Select Registers
RS-343A/RS-170 Compatible Analog Outputs
TTL Compatible Digital Inputs
Standard MPU l/O Interface
10-Bit Parallel Structure
8+2 Byte Structure
Programmable Pixel Port: 24-Bit, 15-Bit and
Programmable Pixel Port: 8-Bit (Pseudo)
Pixel Data Serializer
Multiplexed Pixel Input Ports; 1:1, 2:1, 4:1
+5 V CMOS Monolithic Construction
160-Lead Plastic Quad Flatpack (QFP)
Thermally Enhanced to Achieve u
JC
< 1.08C/W
MODES OF OPERATION
24-Bit True Color (30-Bit Gamma Corrected)
@ 220 MHz
@ 170 MHz
@ 135 MHz
@ 110 MHz
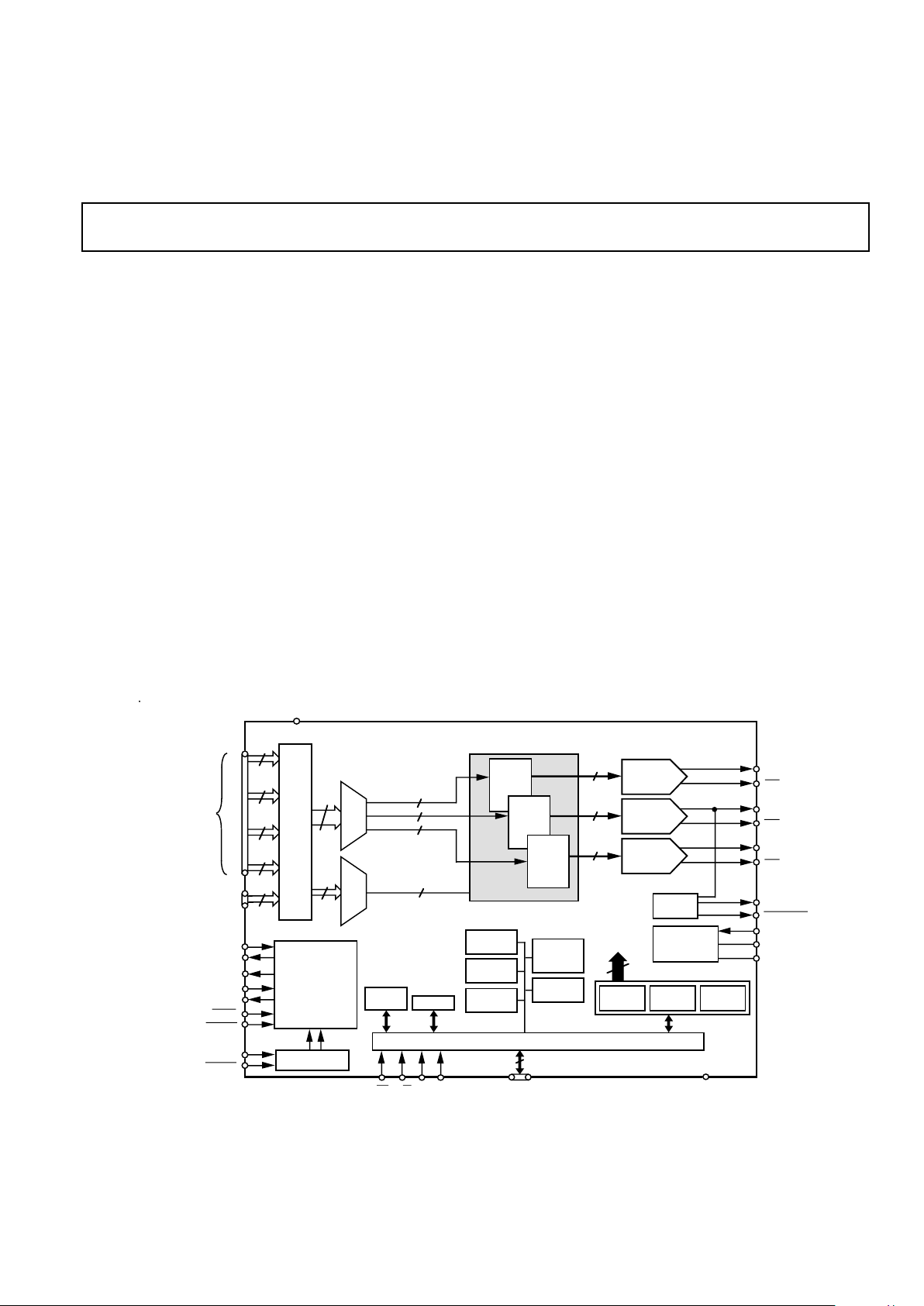
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
256-COLOR/GAMMA
PALETTE RAM
10
10-BIT
RED DAC
10-BIT
BLUE DAC
IOR
96
C
D
A
B
24
24
24
24
P
I
X
E
L
P
O
R
T
MUX
4:1
30
RED
256 x 10
MPU PORT
D9 – D0
10 (8+2)
CE R/W C0 C1
LOADIN
CLOCK
LOADOUT
PRGCKOUT
SCKIN
SCKOUT
CLOCK DIVIDE
&
SYNCHRONIZATION
CIRCUIT
÷32 ÷16, ÷8, ÷4, ÷2
ADDR
(A7–A0)
REVISION
REGISTER
COMMAND
REGISTERS
(CR1–CR3)
TEST
REGISTERS
(MR1)
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
CIRCUIT
ECL TO CMOS
ADV7150
V
REF
R
SET
COMP
SYNC
OUTPUT
I
PLL
RED (R7–R0),
GREEN (G7–G0),
BLUE (B7–B0)
COLOR DATA
V
AA
GND
DATA TO
PALETTES
CONTROL REGISTERS
COLOR REGISTERS
CLOCK CONTROL
MODE
REGISTER
ADDRESS
REGISTER
GREEN
256 x 10
BLUE
256 x 10
PALETTE
SELECTS
(PS0, PS1)
ID
REGISTER
GREEN
REGISTER
PIXEL MASK
REGISTER
8
IOR
IOG
IOG
IOB
IOB
10-BIT
GREEN DAC
10
10
BLUE
REGISTER
RED
REGISTER
8
8
2
8
8
SYNC
BLANK
CLOCK
SYNCOUT
MUX
4:1
REV. A
–2–
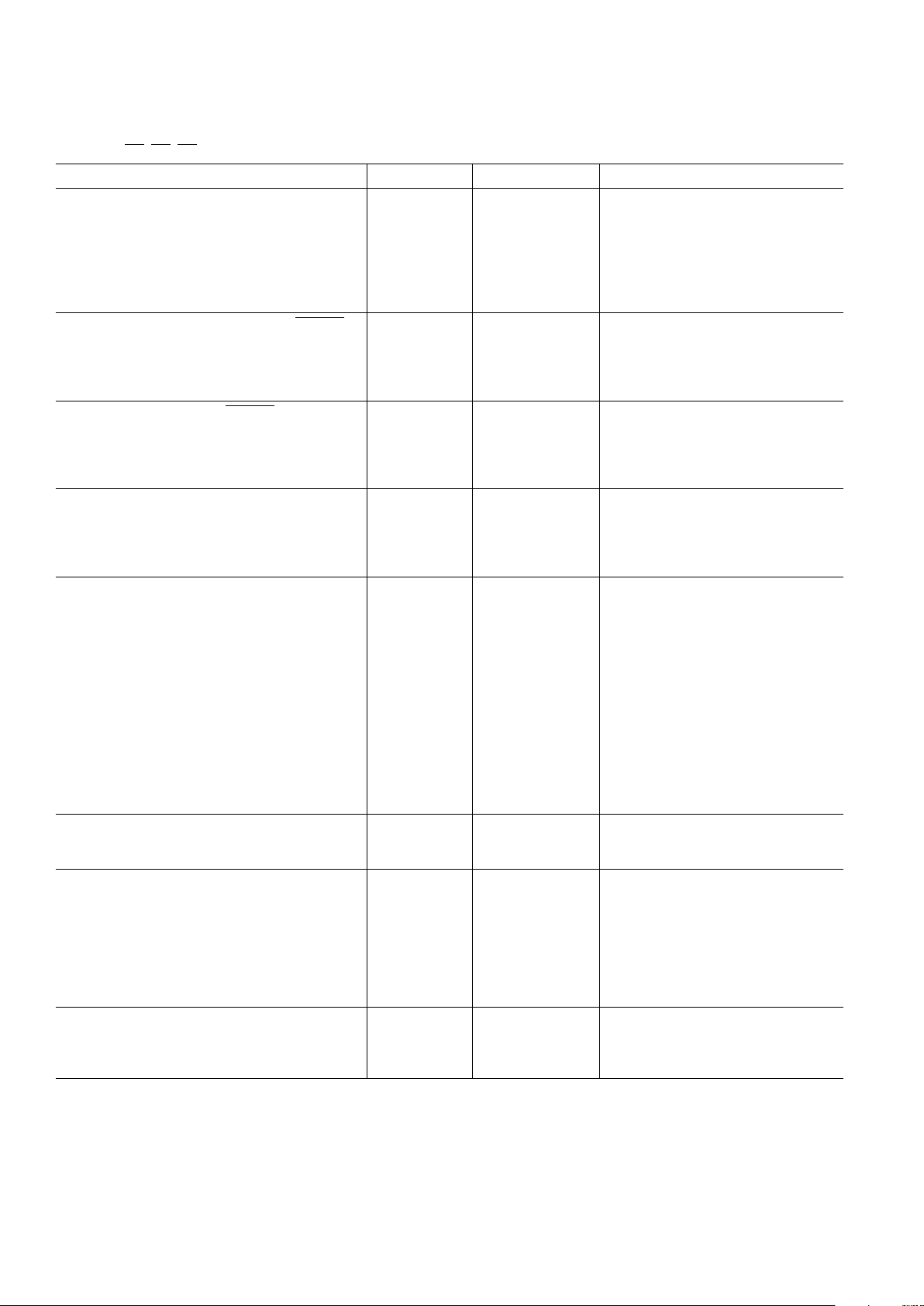
ADV7150–SPECIFICA TIONS
(V
AA
1
= +5 V; V
REF
= +1.235 V; R
SET
= 280 V. IOR, IOG, IOB (RL = 37.5 V,
CL = 10 pF); IOR, IOG, IOB = GND. All specifications T
MIN
to T
MAX
2
unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter All Versions Unit Test Conditions/Comments
STATIC PERFORMANCE
Resolution (Each DAC) 10 Bits
Accuracy (Each DAC)
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB max
Differential Nonlinearity ±1 LSB max Guaranteed Monotonic
Gray Scale Error ±5 % Gray Scale max
Coding Binary
DIGITAL INPUTS (Excluding CLOCK, CLOCK)
Input High Voltage, V
INH
2 V min
Input Low Voltage, V
INL
0.8 V max
Input Current, I
IN
±10 µA max VIN = 0.4 V or 2.4 V
Input Capacitance, C
IN
10 pF max
CLOCK INPUTS (CLOCK, CLOCK)
Input High Voltage, V
INH
VAA – 1.0 V min
Input Low Voltage, V
INL
VAA – 1.6 V max
Input Current, I
IN
±10 µA max VIN = 0.4 V or 2.4 V
Input Capacitance, C
IN
10 pF typ
DIGITAL OUTPUT
Output High Voltage, V
OH
2.4 V min I
SOURCE
= 400 µA
Output Low Voltage, V
OL
0.4 V max I
SINK
= 3.2 mA
Floating-State Leakage Current 20 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance 20 pF typ
ANALOG OUTPUTS
Gray Scale Current Range 15/22 mA min/max
Output Current
White Level Relative to Blank 17.69/20.40 mA min/max Typically 19.05 mA
White Level Relative to Black 16.74/18.50 mA min/max Typically 17.62 mA
Black Level Relative to Blank 0.95/1.90 mA min/max Typically 1.44 mA
Blank Level on IOR, IOB 0/50 µA min/max Typically 5 µA
Blank Level on IOG 6.29/8.96 mA min/max Typically 7.62 mA
Sync Level on IOG 0/50 µA min/max Typically 5 µA
LSB Size 17.22 µA typ
DAC-to-DAC Matching 3 % max Typically 1%
Output Compliance, V
OC
0/+1.4 V min/V max
Output Impedance, R
OUT
100 kΩ typ
Output Capacitance, C
OUT
30 pF max I
OUT
= 0 mA
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Voltage Reference Range, V
REF
1.14/1.26 V min/V max V
REF
= 1.235 V for Specified Performance
Input Current, I
VREF
+5 µA typ
POWER REQUIREMENTS
V
AA
5 V nom
I
AA
3
400 mA max 220 MHz Parts
I
AA
3
370 mA max 170 MHz Parts
I
AA
350 mA max 135 MHz Parts
I
AA
330 mA max 110 MHz Parts
I
AA
315 mA max 85 MHz Parts
Power Supply Rejection Ratio 0.5 %/% max Typically 0.12%/%: COMP = 0.1 µF
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Clock and Data Feedthrough
4, 5
–30 dB typ
Glitch Impulse 50 pV secs typ
DAC-to-DAC Crosstalk
6
–23 dB typ
NOTES
1
±5% for all versions.
2
Temperature range (T
MIN
to T
MAX
): 0°C to +70°C; TJ (Silicon Junction Temperature) ≤ 100°C.
3
Pixel Port is continuously clocked with data corresponding to a linear ramp. TJ = 100°C.
4
Clock and data feedthrough is a function of the amount of overshoot and undershoot on the digital inputs. Glitch impulse includes clock and data feedthrough.
5
TTL input values are 0 to 3 volts, with input rise/fall times ≤ 3 ns, measured the 10% and 90% points. Timing reference points at 50% for inputs and outputs.
6
DAC-to-DAC crosstalk is measured by holding one DAC high while the other two are making low-to-high and high-to-low transitions.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
ADV7150
–3–
REV. A
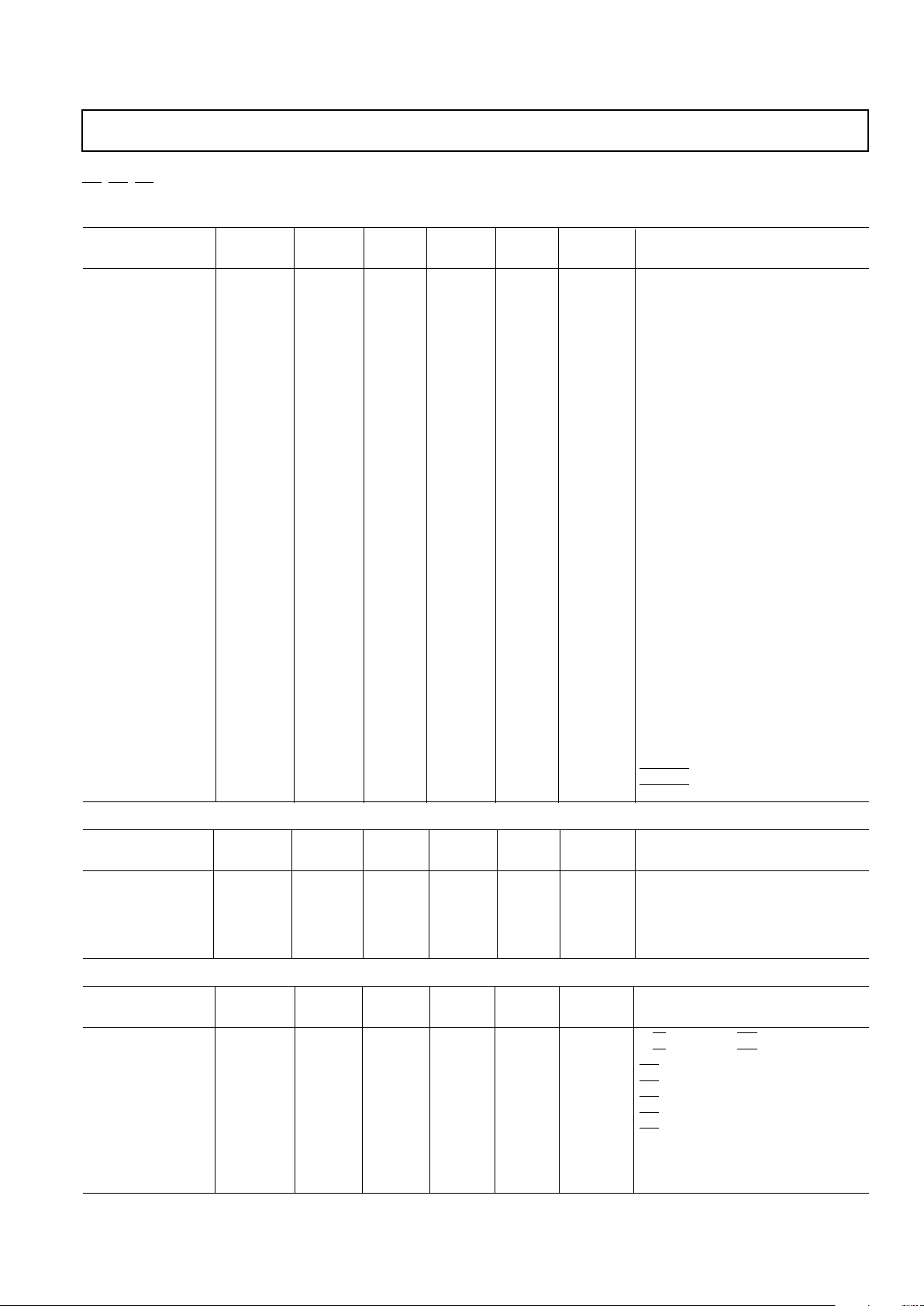
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
1
CLOCK CONTROL AND PIXEL PORT
4
220 MHz 170 MHz 135 MHz 110 MHz 85 MHz
Parameter Version Version Version Version Version Units
Conditions/Comments
f
CLOCK
220 170 135 110 85 MHz max Pixel CLOCK Rate
t
1
4.55 5.88 7.4 9.1 11.77 ns min Pixel CLOCK Cycle Time
t
2
2 2.5 3.2 4 4 ns min Pixel CLOCK High Time
t
3
2 2.5 3 4 4 ns min Pixel CLOCK Low Time
t
4
10 10 10 10 10 ns max Pixel CLOCK to LOADOUT Delay
f
LOADIN
LOADIN Clocking Rate
1:1 Multiplexing 110 110 110 110 85 MHz max
2:1 Multiplexing 110 85 67.5 55 42.5 MHz max
4:1 Multiplexing 55 42.5 33.75 27.5 21.25 MHz max
t
5
LOADIN Cycle Time
1:1 Multiplexing 9.1 9.1 9.1 9.1 9.1 ns min
2:1 Multiplexing 9.1 11.76 14.8 18.18 23.53 ns min
4:1 Multiplexing 18.18 23.53 29.63 36.36 47.1 ns min
t
6
LOADIN High Time
1:1 Multiplexing 44444ns min
2:1 Multiplexing 45689ns min
4:1 Multiplexing 8 9 12 15 18 ns min
t
7
LOADIN Low Time
1:1 Multiplexing 44444ns min
2:1 Multiplexing 45689ns min
4:1 Multiplexing 8 9 12 15 18 ns min
t
8
00000ns minPixel Data Setup Time
t
9
55555ns minPixel Data Hold Time
t
10
00000ns minLOADOUT to LOADIN Delay
τ–t
11
5
τ–5 τ–5 τ–5 τ–5 τ–5 ns max LOADOUT to LOADIN Delay
t
PD
6
Pipeline Delay
1:1 Multiplexing 55555CLOCKs (1 × CLOCK = t
1
)
2:1 Multiplexing 66666CLOCKs
4:1 Multiplexing 88888CLOCKs
t
12
10 10 10 10 10 ns max Pixel CLOCK to PRGCKOUT Delay
t
13
55555ns maxSCKIN to SCKOUT Delay
t
14
55555ns minBLANK to SCKIN Setup Time
t
15
11111ns minBLANK to SCKIN Hold Time
ANALOG OUTPUTS
7
220 MHz 170 MHz 135 MHz 110 MHz 85 MHz
Parameter Version Version Version Version Version Units Conditions/Comments
t
16
15 15 15 15 15 ns typ Analog Output Delay
t
17
11111ns typAnalog Output Rise/Fall Time
t
18
15 15 15 15 15 ns typ Analog Output Transition Time
t
SK
22222ns maxAnalog Output Skew (IOR, IOG, IOB)
00000ns typ
MPU PORTS
8, 9
220 MHz 170 MHz 135 MHz 110 MHz 85 MHz
Parameter Version Version Version Version Version Units Conditions/Comments
t
19
33333ns minR/W, C0, C1 to CE Setup Time
t
20
10 10 10 10 10 ns min R/W, C0, C1 to CE Hold Time
t
21
45 45 45 45 45 ns min CE Low Time
t
22
25 25 25 25 25 ns min CE High Time
t
23
8
55555ns minCE Asserted to Databus Driven
t
24
9
45 45 45 45 45 ns max CE Asserted to Data Valid
t
25
9
20 20 20 20 20 ns max CE Disabled to Databus Three-Stated
55555ns min
t
26
20 20 20 20 20 ns min Write Data (D0–D9) Setup Time
t
27
55555ns minWrite Data (D0–D9) Hold Time
(V
AA
2
= +5 V; V
REF
= +1.235 V; R
SET
= 280 V. IOR, IOG, IOB (RL = 37.5 V, CL = 10 pF);
IOR, IOG, I0B = GND. All specifications T
MIN
to T
MAX
3
unless otherwise noted.)
ADV7150
–4–
REV. A
NOTES
1
TTL input values are 0 to 3 volts, with input rise/fall times ≤ 3 ns, measured between the 10% and 90% points. ECL inputs (CLOCK, CLOCK) are
VAA–0.8 V to VAA–1.8 V, with input rise/fall times ≤ 2 ns, measured between the 10% and 90% points. Timing reference points at 50% for inputs and outputs. Analog output load ≤ 10 pF. Databus (D0–D9) loaded as shown in Figure 1. Digital output load for LOADOUT, PRGCKOUT, SCKOUT, I
PLL
and
SYNCOUT ≤ 30 pF.
2
±5% for all versions.
3
Temperature range (T
MIN
to T
MAX
): 0°C to +70°C; TJ (Silicon Junction Temperature) ≤ 100°C.
4
Pixel Port consists of the following inputs: Pixel Inputs: RED [A, B, C, D]; GREEN [A, B, C, D]; BLUE [A, B, C, D], Palette Selects: PS0 [A, B, C, D]; PS1
[A, B, C, D]; Pixel Controls: SYNC, BLANK; Clock Inputs: CLOCK, CLOCK, LOADIN, SCKIN; Clock Outputs: LOADOUT, PRGCKOUT, SCKOUT.
5
τ is the LOADOUT Cycle Time and is a function of the Pixel CLOCK Rate and the Multiplexing Mode: 1:1 multiplexing; τ = CLOCK = t1 ns. 2:1 Multi-
plexing; τ = CLOCK × 2 = 2 × t1 ns. 4:1 Multiplexing; τ = CLOCK × 4 = 4 × t1 ns.
6
These fixed values for Pipeline Delay are valid under conditions where t10 and τ-t11 are met. If either t10 or τ-t11 are not met, the part will operate but the Pipe line De-
lay is increased by 2 additional CLOCK cycles for 2:1 Mode and is increased by 4 additional CLOCK cycles for 4:1 Mode, after calibration is performed.
7
Output delay measured from the 50% point of the rising edge of CLOCK to the 50% point of full-scale transition. Output rise/fall time measured between the 10%
and 90% points of full-scale transition. Transition time measured from the 50% point of full-scale transition to the output remaining within 2% of the final output
value (Transition time does not include clock and data feedthrough).
8
t23 and t24 are measured with the load circuit of Figure 1 and defined as the time required for an output to cross 0.4 V or 2.4 V.
9
t25 is derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change by 0.5 V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 1. The measured number is then extrapo-
lated back to remove the effects of charging the 100 pF capacitor. This means that the time, t25, quoted in the Timing Characteristics is the true value for the device
and as such is independent of external databus loading capacitances.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
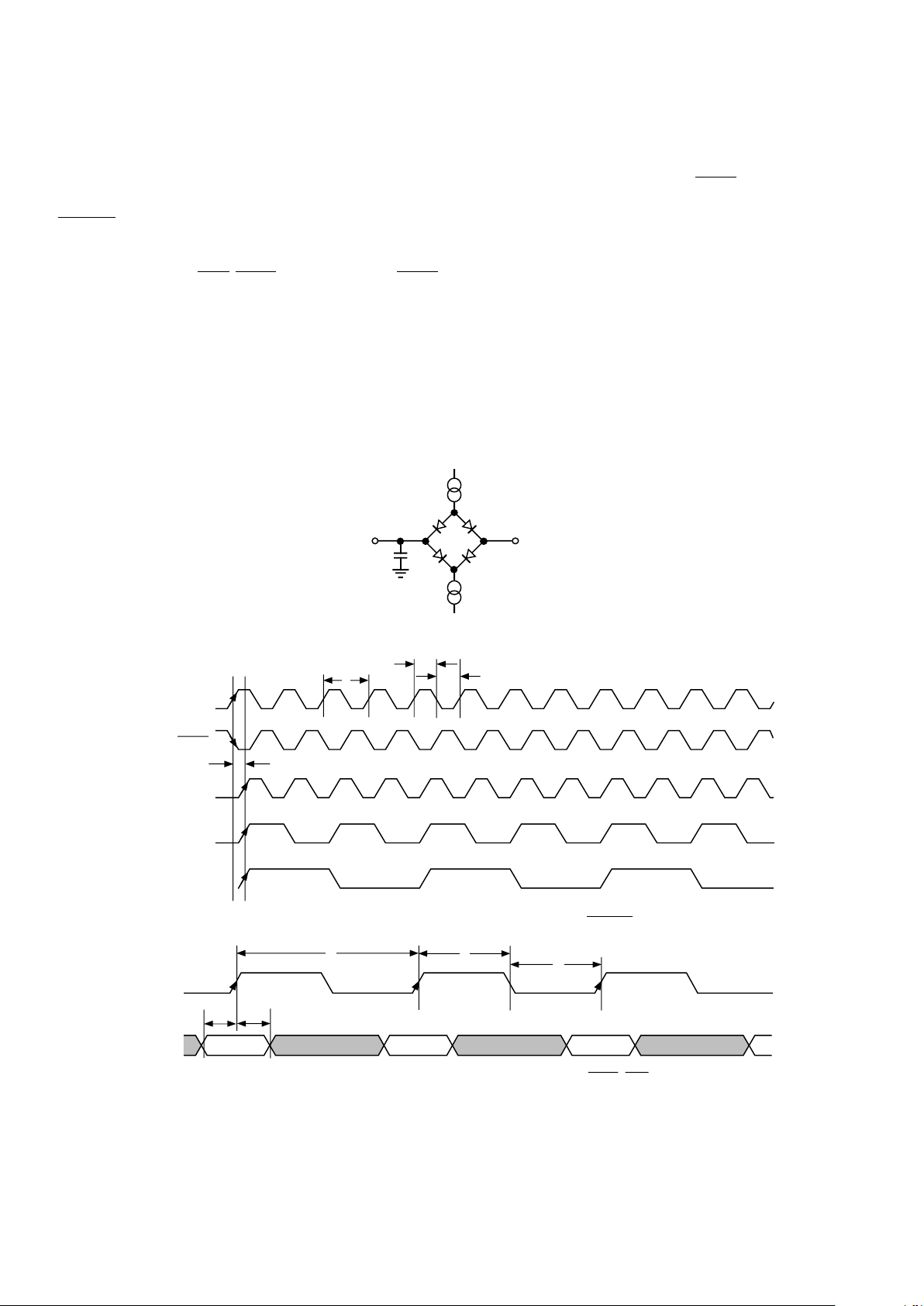
I
SINK
+2.1V
TO
OUTPUT
PIN
I
SOURCE
100pF
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Databus Access and Relinquish Times
t
3
t
2
CLOCK
LOADOUT
(1:1 MULTIPLEXING)
LOADOUT
(2:1 MULTIPLEXING)
LOADOUT
(4:1 MULTIPLEXING)
CLOCK
t
4
t
1
Figure 2. LOADOUT vs. Pixel Clock Input (CLOCK,
CLOCK
)
PIXEL INPUT
DATA*
LOADIN
t8t
9
VALID
DATA
VALID
DATA
VALID
DATA
t
5
t
6
*INCLUDES PIXEL DATA (R0–R7, G0–G7, B0–B7); PALETTE SELECT INPUTS (PS0–PS1); BLANK; SYNC
t
7
Figure 3. LOADIN vs. Pixel Input Data
ADV7150
–5–
REV. A
PIXEL INPUT
DATA*
A
N+2 BN+2
C
N+2 DN+2
CLOCK
LOADOUT
LOADIN
ANALOG
OUTPUT
DATA
t
10
t
PD
DIGITAL INPUT TO ANALOG
OUTPUT PIPELINE
A
N
B
N
C
N
D
N
*INCLUDES PIXEL DATA (R0–R7, G0–G7, B0–B7); PALETTE SELECT INPUTS (PS0–PS1); BLANK; SYNC
A
N+1 BN+1
C
N+1DN+1
ANBNCNDNA
N+1BN+1CN+1DN+1
A
N–1
B
N–1CN–1DN–1
A
N+2BN+2CN+2DN+2
IOR, IOR
IOG, IOG
IOB, IOB
I
PLL, SYNCOUT
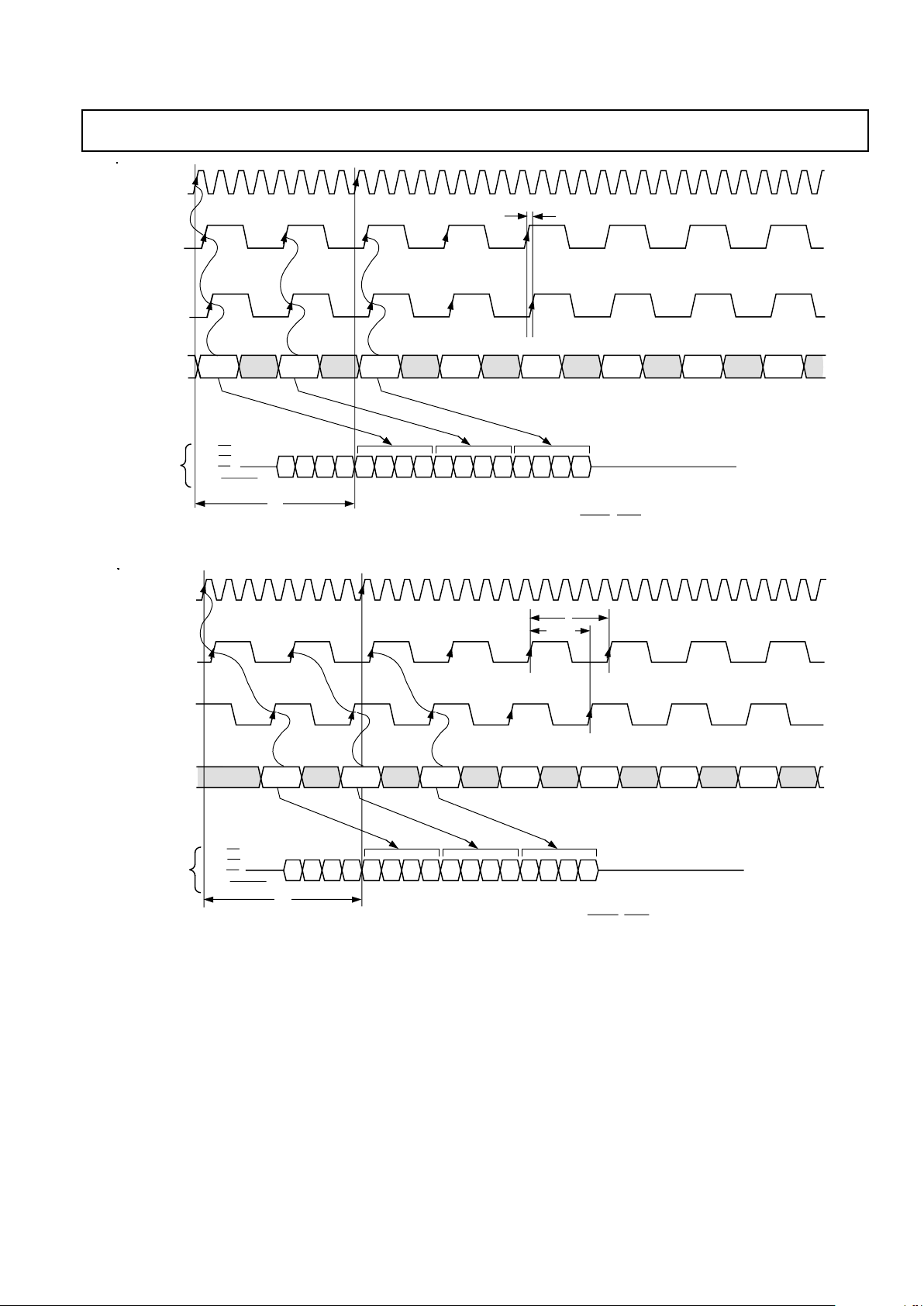
Figure 4. Pixel Input to Analog Output Pipeline with Minimum LOADOUT to LOADIN Delay (4:1 Multiplex Mode)
DIGITAL INPUT
TO ANALOG
OUTPUT
PIPELINE
A
N+2 BN+2
C
N+2 DN+2
CLOCK
LOADOUT
PIXEL INPUT
DATA*
LOADIN
ANALOG
OUTPUT
DATA
ANBNCND
N
A
N
B
N
C
N
D
N
A
N+1BN+1CN+1DN+1
A
N–1
B
N–1CN–1DN–1
A
N+2BN+2CN+2DN+2
t
PD
τ
τ– t
11
*INCLUDES PIXEL DATA (R0–R7, G0–G7, B0–B7); PALETTE SELECT INPUTS (PS0–PS1); BLANK; SYNC
IOR, IOR
IOG, IOG
IOB, IOB
I
PLL, SYNCOUT
A
N+1 BN+1
C
N+1DN+1
Figure 5. Pixel Input to Analog Output Pipeline with Maximum LOADOUT to LOADIN Delay (4:1 Multiplex Mode)
ADV7150
–6–
REV. A
PIXEL INPUT
DATA*
A
N
B
N
t
PD
A
N
B
N
A
N-1BN-1
A
N+1BN+1AN+2BN+2
*INCLUDES PIXEL DATA (R0–R7, G0–G7, B0–B7); PALETTE SELECT INPUTS (PS0–PS1); BLANK; SYNC
CLOCK
LOADOUT
LOADIN
ANALOG
OUTPUT
DATA
t
10
DIGITAL INPUT TO ANALOG
OUTPUT PIPELINE
A
N+1 BN+1
A
N+2 BN+2
IOR, IOR
IOG, IOG
IOB, IOB
I
PLL, SYNCOUT
Figure 6. Pixel Input to Analog Output Pipeline with Minimum LOADOUT to LOADIN Delay (2:1 Multiplex Mode)
CLOCK
LOADOUT
PIXEL INPUT
DATA*
LOADIN
ANALOG
OUTPUT
DATA
t
PD
DIGITAL INPUT TO ANALOG
OUTPUT PIPELINE
A
N
B
N
A
N+1 BN+1
A
N
B
N
A
N-1BN-1
A
N+1BN+1AN+2
B
N+2
*INCLUDES PIXEL DATA (R0–R7, G0–G7, B0–B7); PALETTE SELECT INPUTS (PS0–PS1); BLANK; SYNC
τ
τ– t
11
A
N+2 BN+2
IOR, IOR
IOG, IOG
IOB, IOB
I
PLL, SYNCOUT
Figure 7. Pixel Input to Analog Output Pipeline with Maximum LOADOUT to LOADIN Delay (2:1 Multiplex Mode)
ADV7150
–7–
REV. A
t
12
CLOCK
PRGCKOUT
(CLOCK/4)
PRGCKOUT
(CLOCK/8)
PRGCKOUT
(CLOCK/16)
PRGCKOUT
(CLOCK/32)
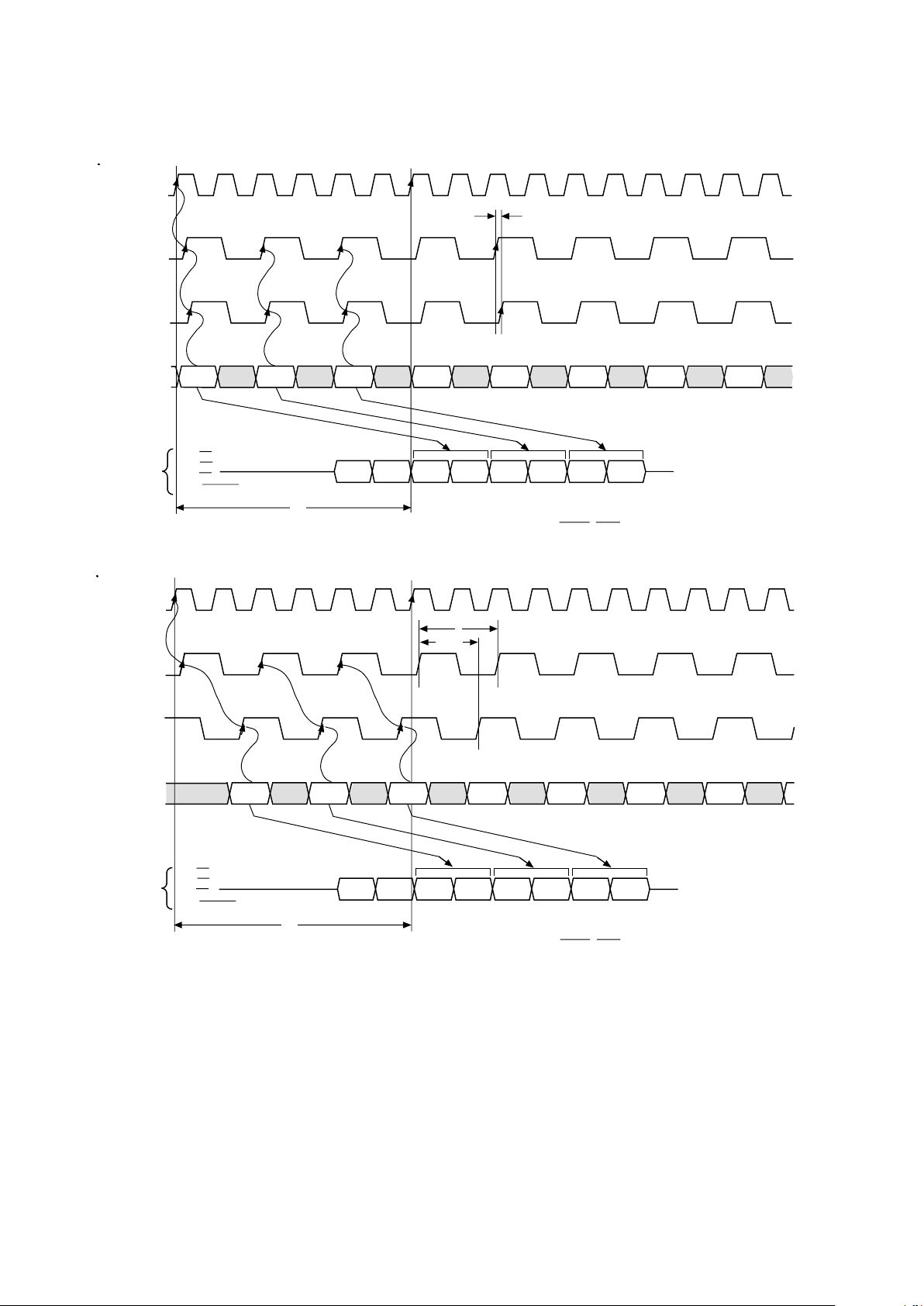
Figure 8. Pixel Clock Input vs. Programmable Clock Output (PRGCKOUT)
SCKIN
END OF SCAN LINE (N)
t
13
SCKOUT
START OF SCAN LINE (N+1)
BLANKING
PERIOD
t
15
t
14
BLANK
Figure 9. Video Data Shift Clock Input (SCKIN) & BLANK vs. Video Data Shift Clock Output (SCKOUT)
CLOCK
t
16
ANALOG
OUTPUTS
t
17
t
18
10 %
50 %
90 %
FULL-SCALE
TRANSITION
WHITE LEVEL
BLACK LEVEL
IOR, IOR
IOG, IOG
IOB, IOB
I
PLL, SYNCOUT
NOTE:
THIS DIAGRAM IS NOT TO SCALE. FOR THE PURPOSES OF
CLARITY, THE ANALOG OUTPUT WAVEFORM IS MAGNIFIED IN
TIME AND AMPLITUDE W.R.T THE CLOCK WAVEFORM.
I
PLL
AND SYNCOUT ARE DIGITAL VIDEO OUTPUT SIGNALS.
t
16
IS THE ONLY RELEVENT OUTPUT TIMING SPECIFICATION
FOR I
PLL
AND SYNCOUT.
Figure 10. Analog Output Response vs. CLOCK
ADV7150
–8–
REV. A
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITION
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Units
Power Supply V
AA
4.75 5.00 5.25 Volts
Ambient Operating Temperature T
A
0 +70 °C
Reference Voltage V
REF
1.14 1.235 1.26 Volts
Output Load R
L
37.5 Ω
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the ADV7150 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
VAA to GND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 V
Voltage on Any Digital Pin . . . . GND – 0.5 V to V
AA
+ 0.5 V
Ambient Operating Temperature (T
A
) . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature (T
S
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature (T
J
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 secs) . . . . . . . . . . . +260°C
Vapor Phase Soldering (1 minute) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +220°C
Analog Outputs to GND
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . GND – 0.5 to V
AA
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the
operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Analog Output Short Circuit to any Power Supply or Common can be of an
indefinite duration.
ORDERING GUIDE
1, 2, 3
Speed
220 MHz ADV7150LS220 110 MHz ADV7150LS110
170 MHz ADV7150LS170 85 MHz ADV7150LS85
135 MHz ADV7150LS135
NOTES
1
ADV7150 is packaged in a 160-pin plastic quad flatpack, QFP.
2
All devices are specified for 0°C to +70°C operation.
3
Contact sales office for latest information on package design.
16-Lead QFP Configuration
ROW D
PIN NO. 1
IDENTIFIER
ROW A
ROW C
ADV7150 QFP
TOP VIEW
(NOT TO SCALE)
ROW B
160 121
41 80
1
40
120
81
t
19
t
20
VALID
CONTROL DATA
t
21
t
22
t
23
t
26
t
25
t
27
D0–D9
(READ MODE)
D0–D9
(WRITE MODE)
CE
R/W, C0, C1
R/W = 1
R/W = 0
t
24
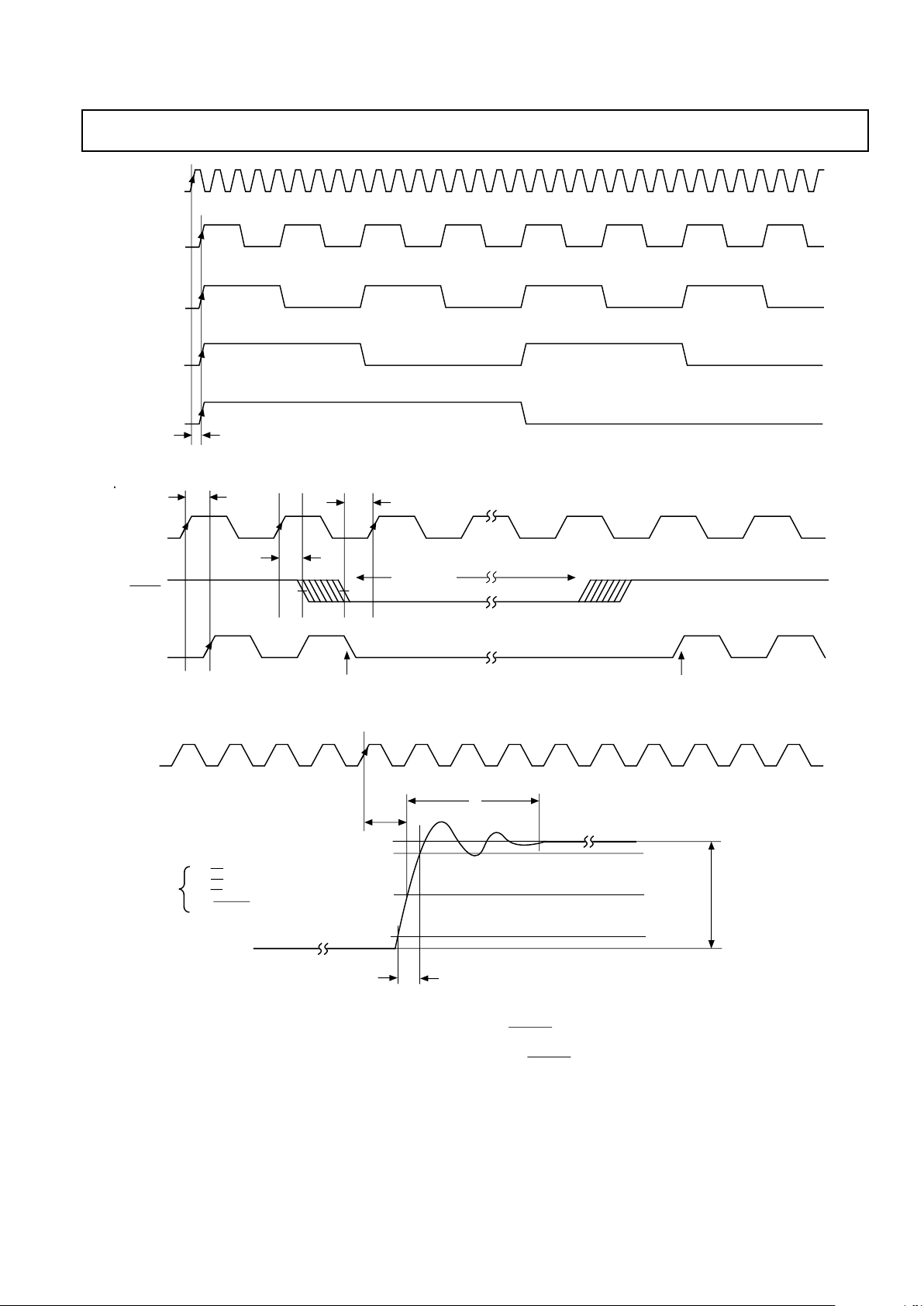
Figure 11. Microprocessor Port (MPU) Interface Timing
ADV7150
–9–
REV. A
ADV7150 PIN ASSIGNMENTS
Pin Pin Pin Pin
Number Mnemonic Number Mnemonic Number Mnemonic Number Mnemonic
1G3
A
41 PS1
D
81 NC 121 R1
A
2G3
B
42 B0
A
82 D2 122 R1
B
3G3
C
43 B0
B
83 NC 123 R1
C
4G3
D
44 B0
C
84 GND 124 R1
D
5G4
A
45 B0
D
85 GND 125 R2
A
6G4
B
46 B1
A
86 GND 126 R2
B
7G4
C
47 B1
B
87 D3 127 R2
C
8G4
D
48 B1
C
88 D4 128 R2
D
9G5
A
49 B1
D
89 D5 129 R3
A
10 G5
B
50 B2
A
90 V
AA
130 R3
B
11 G5
C
5 1 B2
B
91 D6 131 R3
C
12 G5
D
52 B2
C
92 D7 132 R3
D
13 CLOCK 53 B2
D
93 D8 133 R4
A
14 CLOCK 54 B3
A
94 D9 134 R4
B
15 LOADIN 55 B3
B
95 GND 135 R4
C
16 LOADOUT 56 B3
C
96 GND 136 R4
D
17 V
AA
57 B3
D
97 GND 137 R5
A
18 V
AA
58 B4
A
98 IOB 138 R5
B
19 PRGCKOUT 59 B4
B
99 IOR 139 R5
C
20 SCKIN 60 B4
C
100 IOG 140 R5
D
21 SCKOUT 61 B4
D
101 IOB 141 R6
A
22 SYNCOUT 62 B5
A
102 IOG 142 R6
B
23 GND 63 B5
B
103 V
AA
143 R6
C
24 GND 64 B5
C
104 V
AA
144 R6
D
25 GND 65 B5
D
105 V
AA
145 R7
A
26 G6
A
66 B6
A
106 IOR 146 R7
B
27 G6
B
67 B6
B
107 COMP 147 R7
C
28 G6
C
68 B6
C
108 V
REF
148 R7
D
29 G6
D
69 B6
D
109 R
SET
149 G0
A
30 G7
A
70 B7
A
110 I
PLL
150 G0
B
31 G7
B
71 B7
B
111 GND 151 G0
C
32 G7
C
72 B7
C
112 V
AA
152 G0
D
33 G7
D
73 B7
D
113 V
AA
153 G1
A
34 PS0
A
74 CE 114 V
AA
154 G1
B
35 PS0
B
75 R/W 115 SYNC 155 G1
C
36 PS0
C
76 C0 116 BLANK 1 56 G1
D
37 PS0
D
77 C1 117 R0
A
157 G2
A
38 PS1
A
78 D0 118 R0
B
158 G2
B
39 PS1
B
79 D1 119 R0
C
159 G2
C
40 PS1
C
80 GND 120 R0
D
160 G2
D
NC = No Connect.

ADV7150
–10–
REV. A
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Mnemonic Function
RED (R0A . . . R0D–R7A . . . R7D), Pixel Port (TTL Compatible Inputs): 96 pixel select inputs, with 8 bits each for Red, 8
GREEN (G0
A
. . . G0D–G7A. . . G7D), bits for Green and 8 bits for Blue. Each bit is multiplexed [A-D] 4:1, 2:1 or 1:1. It can
BLUE (B0
A
. . . B0D–B7A . . . B7D) be configured for 24-Bit True-Color Data, 8-Bit Pseudo-Color Data and 15-Bit True-Color
Data formats. Pixel Data is latched into the device on the rising edge of LOADIN.
PS0
A
. . . PS0D, PS1A . . . PS1
D
Palette Priority Selects (TTL Compatible Inputs): These pixel port select inputs determine whether or not the device’s pixel data port is selected on a pixel by pixel basis.
The palette selects allow switching between multiple palette devices. The device can be
preprogrammed to completely shut off the DAC analog outputs. If the values of PS0
and PS1 match the values programmed into bits MR16 and MR17 of the Mode Register, then the device is selected. Each bit is multiplexed [A-D] 4:1, 2:1 or 1:1. PS0 and
PS1 are latched into the device on the rising edge of LOADIN.
LOADIN Pixel Data Load Input (TTL Compatible Input). This input latches the multiplexed
pixel data, including PS0–PS1,
BLANK and SYNC into the device.
LOADOUT Pixel Data Load Output (TTL Compatible Output). This output control signal runs at
a divided down frequency of the pixel CLOCK input. Its frequency is a function of the
multiplex rate. It can be used to directly or indirectly drive LOADIN
f
LOADOUT
= f
CLOCK
/M
where M = 1 for 1:1 Multiplex Mode
where M = 2 for 2:1 Multiplex Mode
where M = 4 for 4:1 Multiplex Mode.
PRGCKOUT Programmable Clock Output (TTL Compatible Output). This output control signal
runs at a divided down frequency of the pixel CLOCK input. Its frequency is user
programmable and is determined by bits CR30 and CR31 of Command Register 3
f
PRGCKOUT
= f
CLOCK
/N
where N = 4, 8, 16 and 32.
SCKIN Video Shift Clock Input (TTL Compatible Input). The signal on this input is internally
gated synchronously with the
BLANK signal. The resultant output, SCKOUT, is a
video clocking signal that is stopped during video blanking periods.
SCKOUT Video Shift Clock Output (TTL Compatible Output). This output is a synchronously
gated version of SCKIN and
BLANK. SCKOUT, is a video clocking signal that is
stopped during video blanking periods.
CLOCK,
CLOCK Clock Inputs (ECL Compatible Inputs). These differential clock inputs are designed to
be driven by ECL logic levels configured for single supply (+5 V) operation. The clock
rate is normally the pixel clock rate of the system.
BLANK Composite Blank (TTL Compatible Input). This video control signal drives the analog
outputs to the blanking level.
SYNC Composite-Sync Input (TTL Compatible Input). This video control signal drives the
IOG analog output to the
SYNC level. It is only asserted during the blanking period.
CR22 in Command Re
gister 2 must be set if SYNC is to be decoded onto the analog
output, otherwise the
SYNC input is ignored.
SYNCOUT Composite-Sync Output (TTL Compatible Output). This video output is a delayed
version of
SYNC. The delay corresponds to the number of pipeline stages of the device.
D0–D9 Databus (TTL Compatible Input/Output Bus). Data, including color palette values and
device control information is written to and read from the device over this 10-bit, bidirectional databus. 10-bit data or 8-bit data can be used. The databus can be configured
for either 10-bit parallel data or byte data (8+2) as well as standard 8-bit data. Any unused bits of the databus should be terminated through a resistor to either the digital
power plane (V
CC
) or GND.
CE Chip Enable (TTL Compatible Input). This input must be at Logic “0,” when writing
to or reading from the device over the databus (D0–D9). Internally, data is latched on
the rising edge of CE.

ADV7150
–11–
REV. A
Mnemonic Function
R/
W Read/Write Control (TTL Compatible Input). This input determines whether data is
written to or read from the device’s registers and color palette RAM. R/
W and CE must
be at Logic “0” to write data to the part. R/
W must be at Logic “1” and CE at Logic
“0” to read from the device.
C0, C1 Command Controls (TTL Compatible Inputs). These inputs determine the type of read
or write operation being performed on the device over the databus (see Interface Truth
Table). Data on these inputs is latched on the falling edge of
CE.
IOR;
IOR, IOG; IOG, IOB; Red, Green and Blue Current Outputs (High Impedance Current Sources). These RGB
IOB video outputs are specified to directly drive RS-343A and RS-170 video levels into dou-
bly terminated 75 Ω loads.
IOR, IOG and IOB are the complementary outputs of IOR, IOG and IOB. These out-
puts can be tied to GND if it is not required to use differential outputs.
V
REF
Voltage Reference Input (Analog Input). An external 1.235 V voltage reference is required to drive this input. An AD589 (2-terminal voltage reference) or equivalent is recommended. (Note: It is not recommended to use a resistor network to generate the
voltage reference.)
R
SET
Output Full-Scale Adjust Control (Analog Input). A resistor connected between this pin
and analog ground controls the absolute amplitude of the output video signal. The value
of R
SET
is derived from the full-scale output current on IOG according to the following
equations:
R
SET
(Ω) = C1 × V
REF
/IOG (mA); SYNC on GREEN
R
SET
(Ω) = C2 × V
REF
/IOG (mA); NO SYNC on GREEN.
Full-Scale output currents on IOR and IOB for a particular value of R
SET
are given by:
IOR (mA)= C2 × V
REF
(V)/R
SET
(Ω)
and
IOB (mA) = C2 × V
REF
(V)/R
SET
(Ω)
where C1 = 6,050; PEDESTAL = 7.5 IRE
where C1 = 5,723; PEDESTAL = 0 IRE
and
where C2 = 4,323; PEDESTAL = 7.5 IRE
where C1 = 3,996; PEDESTAL = 0 IRE.
COMP Compensation Pin. A 0.1 µF capacitor should be connected between this pin and VAA.
I
PLL
Phase Lock Loop Output Current (High Impedance Current Source). This output is
used to enable multiple ADV7150s along with ADV7151s to be synchronized together
with pixel resolution when using an external PLL. This output is triggered either from
the falling edge of
SYNC or BLANK as determined by bit CR21 of Command Register
2. When activated, it supplies a current corresponding to:
I
PLL
(mA) = 1,728 × V
REF
(V)/R
SET
(Ω)
When not using the I
PLL
function, this output pin should be tied to GND.
V
AA
Power Supply (+5 V ± 5%). The part contains multiple power supply pins, all should be
connected together to one common +5 V filtered analog power supply.
GND Analog Ground. The part contains multiple ground pins, all should be connected
together to the system’s ground plane.
 Loading...
Loading...