www.BDTIC.com/ADI
JPEG2000 Video Codec
FEATURES
Complete single-chip JPEG2000 compression and
decompression solution for video and still images
Patented SURF® (spatial ultra-efficient recursive filtering)
echnology enables low power and low cost wavelet-
t
based compression
Supports both 9/7 and 5/3 wavelet transforms with up to
vels of transform
6 le
Programmable tile/image size with widths up to 2048 pixels in
component 4:2:2 interleaved mode, and up to 4096 pixels
3-
in single-component mode
Maximum tile/image width: 4096 pixels
Video interface directly supporting ITU.R-BT656,
SMPTE125M P
ITU.R-BT1358 (625p) or any video format with a maximum
input rate of 65 MSPS for irreversible mode or 40 MSPS for
reversible mode
Two or more ADV202s can be combined to support full-
fr
ame SMPTE274M HDTV (1080i) or SMPTE296M (720p)
Flexible asynchronous SRAM-style host interface allows
glueless
and ASICs
2.5 V to 3.3 V I/O and 1.5 V core supply
12 mm × 12 mm 121-lead CSPBGA, speed grade 115 MHz, or
13 mm × 13 mm 144-lead CSPBGA, speed grade 135 MHz, or
13 mm × 13 mm 144-lead CSPBGA, speed grade 150 MHz
AL/ NTSC, SMPTE274M, SMPTE293M (525p),
connection to most 16-/32-bit microcontrollers
ADV202
APPLICATIONS
Networked video and image distribution systems
Wireless video and image distribution
Image archival/retrieval
Digital CCTV and surveillance systems
Digital cinema systems
Professional video editing and recording
Digital still cameras
Digital camcorders
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADV202 is a single-chip JPEG2000 codec targeted for
video and high bandwidth image compression applications that
can benefit from the enhanced quality and feature set provided
by the JPEG2000 (J2K)—ISO/IEC15444-1 image compression
standard. The part implements the computationally intensive
operations of the JPEG2000 image compression standard as well
as providing fully compliant code-stream generation for most
applications.
The ADV202’s dedicated video port provides glueless connection
o common digital video standards such as ITU.R-BT656,
t
SMPTE125M, SMPTE293M (525p), ITU.R-BT1358 (625p),
SMPTE274M (1080i), or SMPTE296M (720p). A variety of other
high speed, synchronous pixel and video formats can also be supported using the programmable framing and validation signals.
(continued on Page 4)
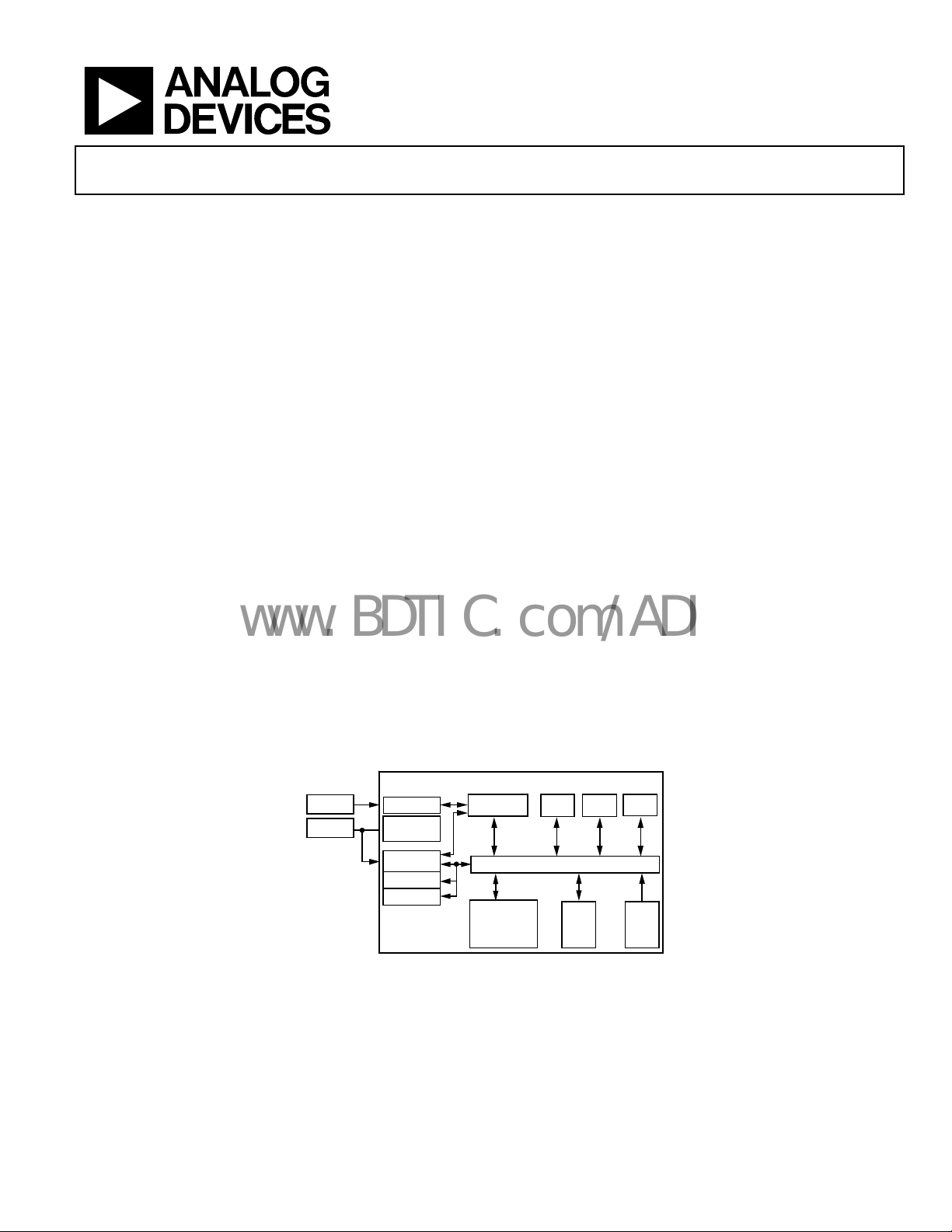
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PIXEL I/F
HOST I/F
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PIXEL I/F
EXTERNAL
DMA CTRL
PIXEL FIFO
CODE FIF O
ATTR FIFO
ADV202
WAVELET
ENGINE
INTERNAL BUS AND DM A ENGINE
EMBEDDED
RISC
PROCESSOR
SYSTEM
Figure 1.
EC1 EC2
RAM ROM
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
EC3
04723-001

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
Applications....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 3
General Description ......................................................................... 4
JPEG2000 Feature Support.......................................................... 4
Specifications..................................................................................... 5
Supply Voltages and Current ...................................................... 5
Input/Output Specifications........................................................ 5
Clock and
Normal Host Mode—Read Operation ...................................... 7
Normal Host Mode—Write Operation ..................................... 8
DREQ
DREQ
External DMA Mode—FIFO Write, Burst Mode .................. 13
External DMA Mode—FIFO Read, Burst Mode ................... 14
Streaming Mode (JDATA)—FIFO Read/Write...................... 16
VDATA Mode Timing............................................................... 17
Raw Pixel Mode Timing............................................................ 18
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 19
Thermal Resistance .................................................................... 19
ESD Caution................................................................................ 19
Pin BGA Assignments and Function Descriptions ................... 20
Pin BGA Assignments ...............................................................20
Pin Function Descriptions ........................................................ 23
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 26
Wavelet Engine ...........................................................................26
Entropy Codecs........................................................................... 26
RESET
Specifications................................................ 6
DACK
/
DMA Mode—Single FIFO Write Operation.. 9
/
DMA Mode—Single FIFO Read Operation. 11
DACK
Embedded Processor System.................................................... 26
Memory System.......................................................................... 26
Internal DMA Engine................................................................ 26
ADV202 Interface .......................................................................... 27
Video Interface (VDATA Bus).................................................. 27
Host Interface (HDATA Bus) ................................................... 27
Direct and Indirect Registers.................................................... 27
Control Access Registers........................................................... 27
Pin Configuration and Bus Sizes/Modes ................................ 28
Stage Register.............................................................................. 28
JDATA Mode............................................................................... 28
External DMA Engine ............................................................... 28
Internal Registers............................................................................ 29
Direct Registers........................................................................... 29
Indirect Registers........................................................................ 30
PLL ............................................................................................... 31
Hardware Boot............................................................................ 31
Video Input Formats...................................................................... 32
Applications..................................................................................... 34
Encode—Multichip Mode......................................................... 34
Decode—Multichip Master/Slave ............................................ 35
Digital Still Camera/Camcorder .............................................. 35
Encode/Decode SDTV Video Application............................. 36
ASIC Application (32-Bit Host/32-Bit ASIC)......................... 37
HIPI (Host Interface—Pixel Interface) ................................... 38
JDATA Interface ......................................................................... 38
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 39
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 40
Rev. C | Page 2 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REVISION HISTORY
11/06—Rev. B to Rev. C
Deleted ANC FIFO References ........................................Universal
Changes to Features..........................................................................1
Changes to Figure 1...........................................................................1
Changes to JPEG2000 Feature Support Section............................4
Changes to Figure 8.........................................................................10
Changes to Figure 10 ......................................................................11
Changes to Figure 12 ......................................................................12
Changes to External DMA Mode—FIFO Write,
Burst Mode Section.........................................................................13
Changes to External DMA Mode—FIFO Read,
Burst Mode Section.........................................................................13
Changes to Table 11 ........................................................................17
Changes to Figure 22 ......................................................................18
Deleted SPI Port Timing Section ..................................................18
Added Absolute Maximum Ratings Section ...............................19
Changes to Pin BGA Assignments and Function
Descriptions Section .......................................................................20
Changes to ADV202 Interface Section.........................................27
Changes to Table 19........................................................................29
Changes to Indirect Registers Section..........................................30
Changes to PLL Section..................................................................31
Changes to Table 23........................................................................31
Changes to Video Input Formats Section .................................... 32
Changes to Figure 24 ......................................................................34
Changes to Figure 26 ......................................................................35
Changes to Ordering Guide...........................................................40
1/05—Rev. A to Rev. B
U
pdated Outline Dimensions........................................................39
12/04—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
hanges to Features .......................................................................... 1
C
Changes to Table 2............................................................................ 4
Changes to Table 16........................................................................24
Changes to Table 23........................................................................32
7/04—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. C | Page 3 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
(continued from Page 1)
The ADV202 can process images at a rate of 40 MSPS in
r
eversible mode and at higher rates when used in irreversible
mode. The ADV202 contains a dedicated wavelet transform
engine, three entropy codecs, an on-board memory system, and
an embedded RISC processor that can provide a complete
JPEG2000 compression/decompression solution.
The wavelet processor supports the 9/7 irreversible wavelet
t
ransform and the 5/3 wavelet transform in reversible and
irreversible modes. The entropy codecs support all features in
the JPEG2000 Part 1 specification, except Maxshift ROI.
The ADV202 operates on a rectangular array of pixel samples
cal
led a tile. A tile can contain a complete image, up to the
maximum supported size, or some portion of an image. The
maximum horizontal tile size supported depends on the wavelet
transform selected and the number of samples in the tile.
Images larger than the ADV202’s maximum tile size can be
broken into individual tiles and then sent sequentially to the
chip while still maintaining a single, fully compliant JPEG2000
code stream for the entire image.
JPEG2000 FEATURE SUPPORT
The ADV202 supports a broad set of features that are included
in Part 1 of the JPEG2000 standard (ISO/IEC 15444). See
Getting Started with ADV202 for information on the JPEG2000
eatures that the ADV202 currently supports.
f
Depending on the particular application requirements, the
AD
V202 can provide varying levels of JPEG2000 compression
support. It can provide raw code-block and attribute data
output, which allow the host software to have complete control
over the generation of the JPEG2000 code stream and other
aspects of the compression process such as bit-rate control.
Otherwise, the ADV202 can create a complete, fully compliant
JPEG2000 code stream (.j2c) and enhanced file formats such as
.jp2 and .j2c. See
on the formats that the ADV202 currently supports.
Application notes and other ADV202 support documents can
be ac
cessed over the ADV202 product page at:
• http://www.analog.com/ADV202Notes or from
• ftp://ftp.analog.com/pub/Digital_Imaging/ADV202_FTP_s
te_contents_3.html
i
Getting Started with ADV202 fo
r information
Rev. C | Page 4 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
SUPPLY VOLTAGES AND CURRENT
Table 1.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
VDD DC Supply Voltage, Core 1.425 1.5 1.575 V
IOVDD DC Supply Voltage, I/O 2.375 3.3 3.63 V
PLLVDD DC Supply Voltage, PLL 1.425 1.5 1.575 V
V
Input Range −0.3 V
INPUT
Temp Operating Ambient Temperature Range in Free Air −40 +25 +85 °C
IDD Static Current
Dynamic Current, Core (JCLK Frequency = 150 MHz)
1
2
300 mA
570 mA
Dynamic Current, Core (JCLK Frequency = 108 MHz) 420 mA
Dynamic Current, Core (JCLK Frequency = 81 MHz) 325 mA
Dynamic Current, I/O 20 mA
Dynamic Current, PLL 2.6 mA
1
No clock or I/O activity.
2
ADV202-150 only.
INPUT/OUTPUT SPECIFICATIONS
+ 0.3 V
DDI/O
Table 2.
Parameter Description Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
High Level Input Voltage VDD = max 2.2 V
IH (3.3 V)
V
High Level Input Voltage VDD = max 1.9 V
IH (2.5 V)
V
IL (3.3 V, 2.5 V)
V
OH (3.3 V)
V
OH (2.5 V)
V
OL (3.3 V, 2.5 V)
Low Level Input Voltage VDD = min 0.6 V
High Level Output Voltage VDD = min, IOH = −0.5 mA 2.4 V
High Level Output Voltage VDD = min, IOH = −0.5 mA 2.0 V
Low Level Output Voltage VDD = min, IOL = 2 mA 0.4 V
IIH High Level Input Current VDD = max, VIN = VDD 1.0 μA
IIL Low Level Input Current VDD = max, VIN = 0 V 1 μA
I
High Level Three-State Leakage Current VDD = max, VIN = VDD 1.0 μA
OZH
I
Low Level Three-State Leakage Current VDD = max, VIN = 0 V 1.0 μA
OZL
CI Input Pin Capacitance 8 pF
CO Output Pin Capacitance 8 pF
Rev. C | Page 5 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
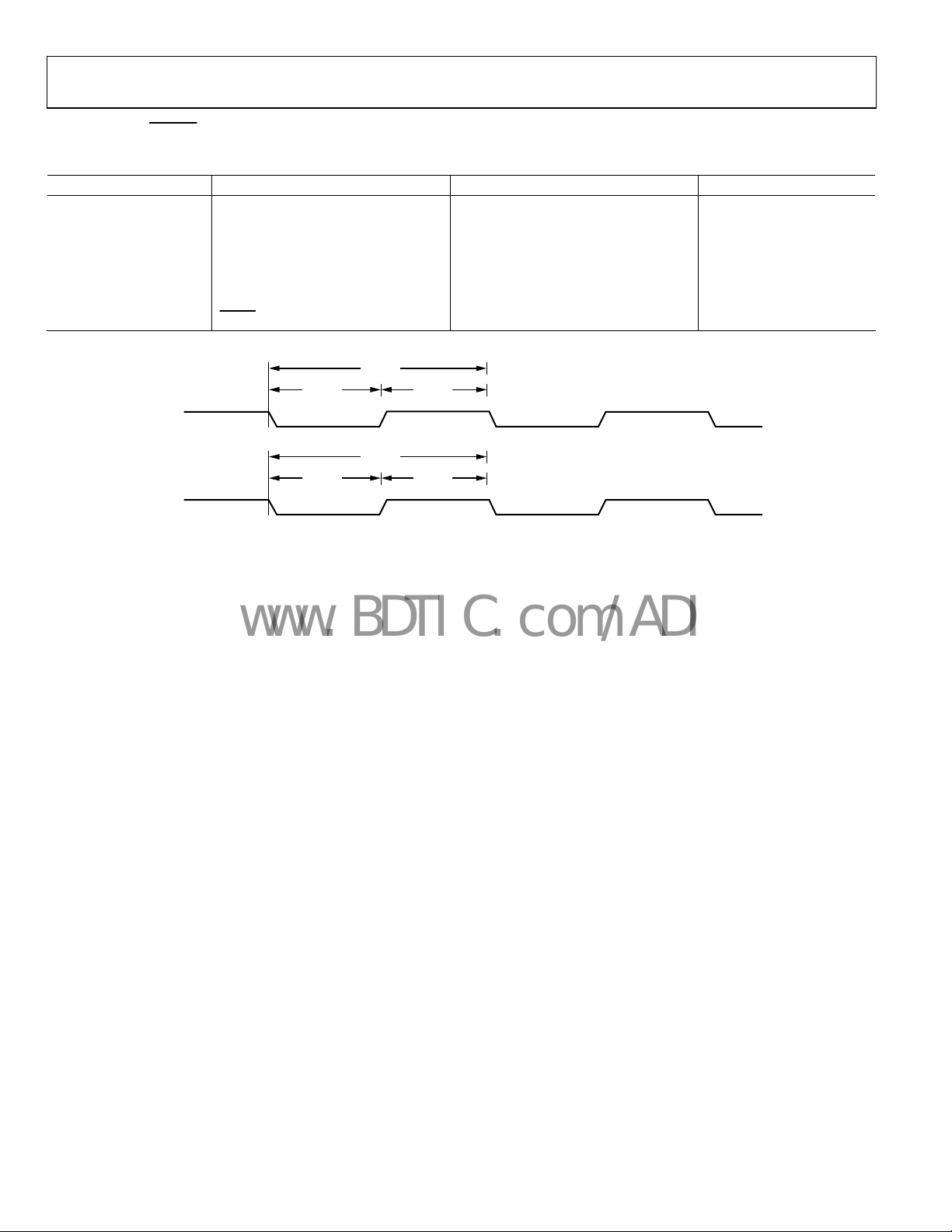
CLOCK AND RESET SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
MCLK1 Period 13.3 100 ns
MCLK
t
MCLK Width Low 6 ns
MCLKL
t
MCLK Width High 6 ns
MCLKH
t
VCLK Period 13.4 50 ns
VCLK
t
VCLK Width Low 5 ns
VCLKL
t
VCLK Width High 5 ns
VCLKH
t
RST
1
For a definition of MCLK, see the PLL section.
MCLK
RESET
Width Low
t
MCLKL
t
VCLKL
t
MCLK
t
VCLK
5 MCLK cycles
t
MCLKH
t
VCLKH
VCLK
Figure 2. Input Clock
04723-010
Rev. C | Page 6 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
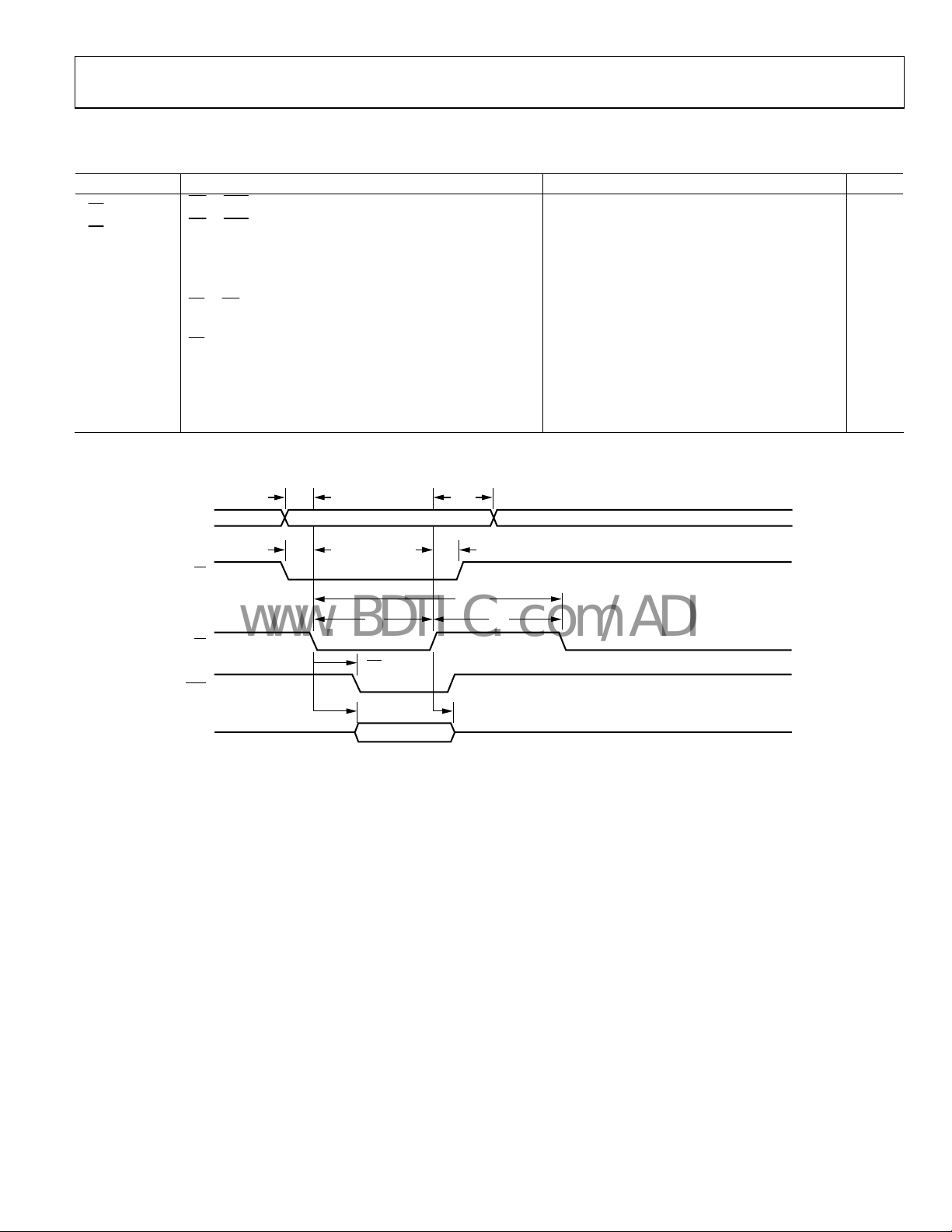
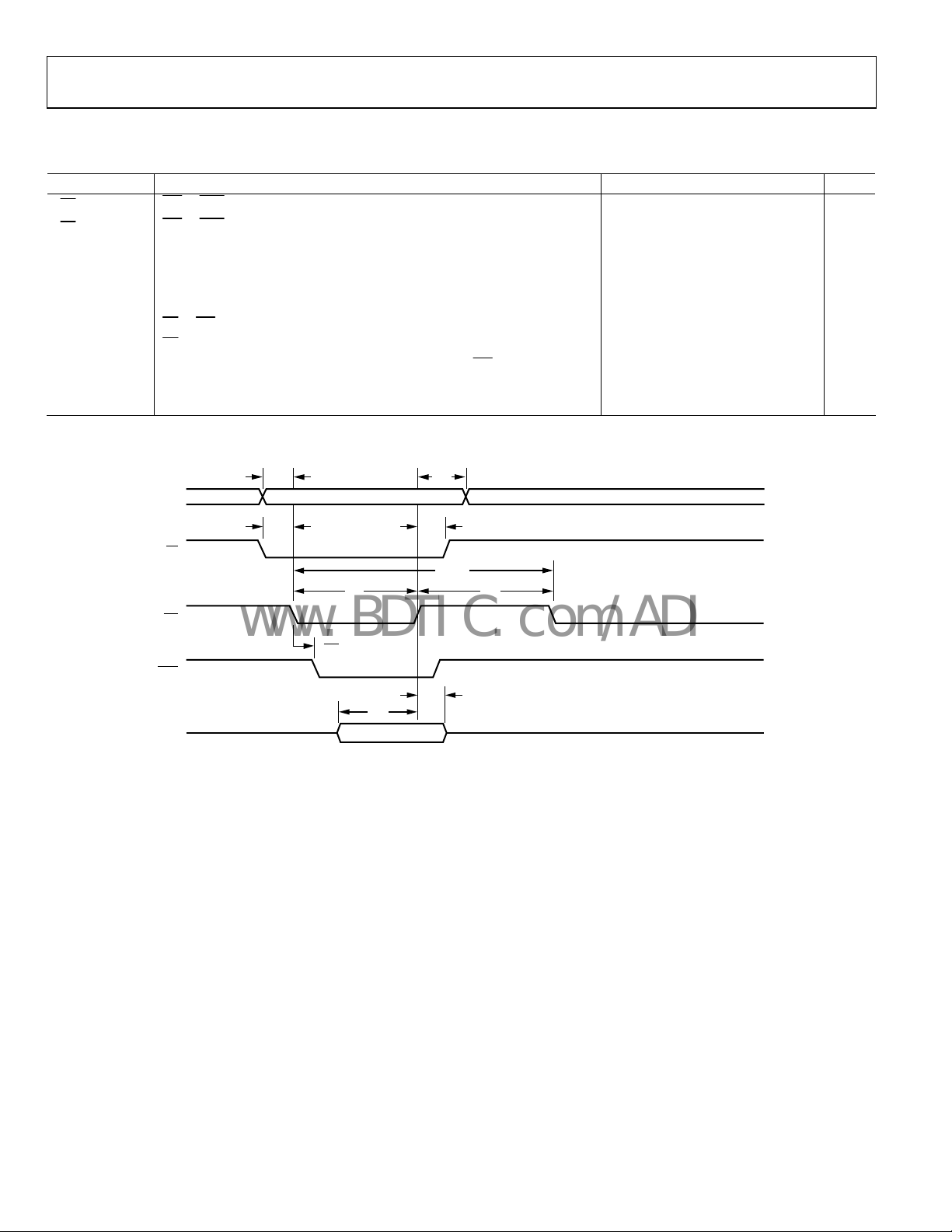
NORMAL HOST MODE—READ OPERATION
Table 4.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
[dir]
ACK
t
[indir]
ACK
t
[dir] Read Access Time, Direct Registers 5 1.5 × JCLK + 7.0 ns
DRD
t
[indir] Read Access Time, Indirect Registers 10.5 × JCLK 15.5 × JCLK + 7.0 ns
DRD
t
Data Hold 2 8.5 ns
HZRD
tSC
to ACK, Direct Registers and FIFO Accesses
RD
to ACK, Indirect Registers
RD
to RD Setup
CS
5 1.5 × JCLK
10.5 × JCLK 15.5 × JCLK + 7.0 ns
0 ns
tSA Address Setup 2 ns
tHC
CS
Hold
0 ns
tHA Address Hold 2 ns
tRH Read Inactive Pulse Width 2.5 JCLK
tRL Read Active Pulse Width 2.5 JCLK
t
Read Cycle Time, Direct Registers 5.0 JCLK
RCYC
1
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
1
+ 7.0 ns
ADDR
CS
RD
ACK
HDATA
t
SA
t
SC
t
RL
t
ACK
t
DRD
VALID
t
HA
t
HC
t
RCYC
t
RH
t
HZRD
04723-011
Figure 3. Normal Host Mode—Read Operation
Rev. C | Page 7 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
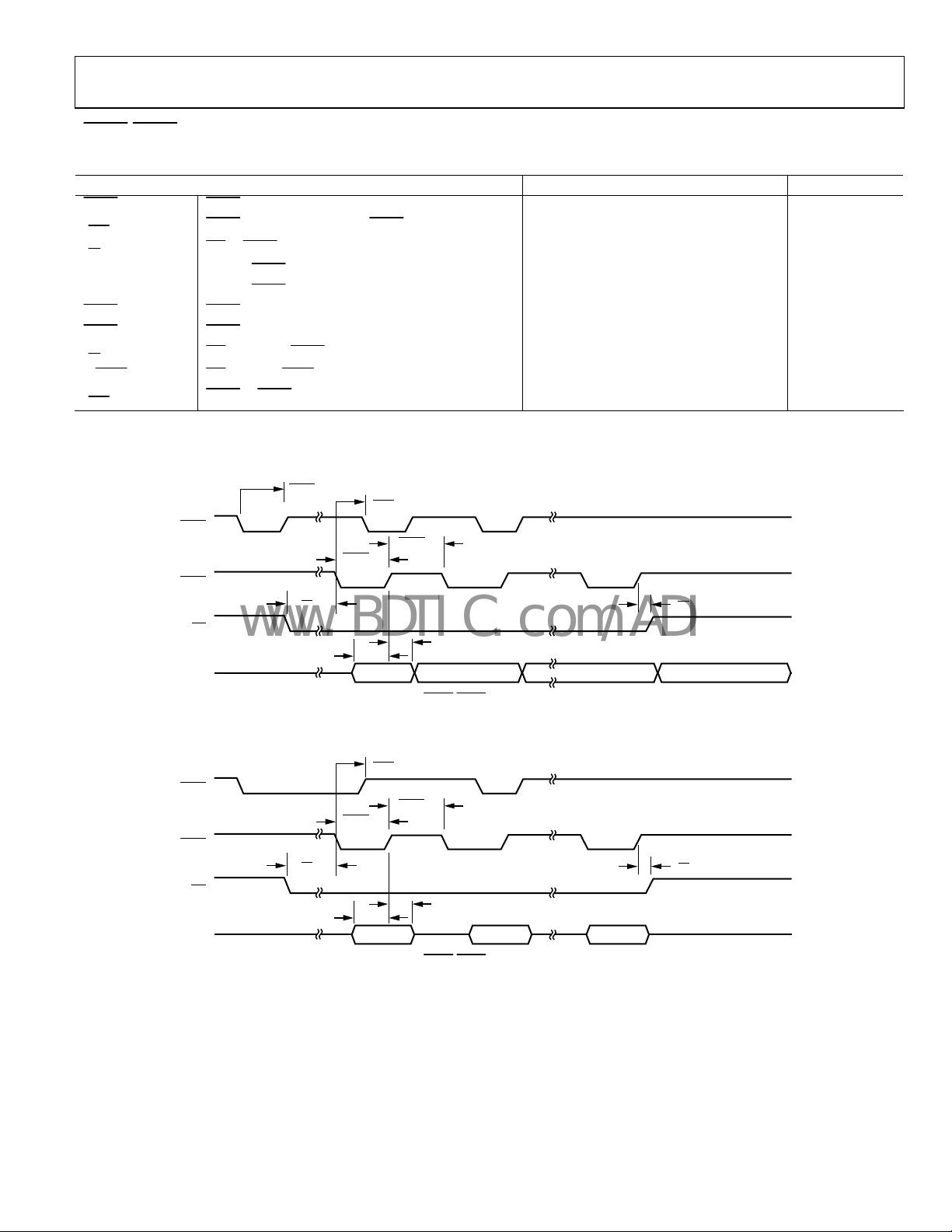
NORMAL HOST MODE—WRITE OPERATION
Table 5.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
t
(Direct)
ACK
t
(Indirect)
ACK
to ACK, Direct Registers and FIFO Accesses
WE
to ACK, Indirect Registers
WE
5 1.5 × JCLK
5 2.5 × JCLK + 7.0 ns
tSD Data Setup 3.0 ns
tHD Data Hold 1.5 ns
tSA Address Setup 2 ns
tHA Address Hold 2 ns
tSC
tHC
t
WH
to WE Setup
CS
Hold
CS
Write Inactive Pulse Width (Minimum Time Until Next WE
Pulse)
0 ns
0 ns
2.5 JCLK
tWL Write Active Pulse Width 2.5 JCLK
t
Write Cycle Time 5 JCLK
WCYC
1
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
ADDR
t
SA
t
HA
1
+ 7.0 ns
CS
WE
ACK
HDATA
t
SC
t
WL
t
ACK
t
SD
Figure 4. Normal Host Mode—Write Operation
VALID
t
HC
t
WCYC
t
WH
t
HD
04723-012
Rev. C | Page 8 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
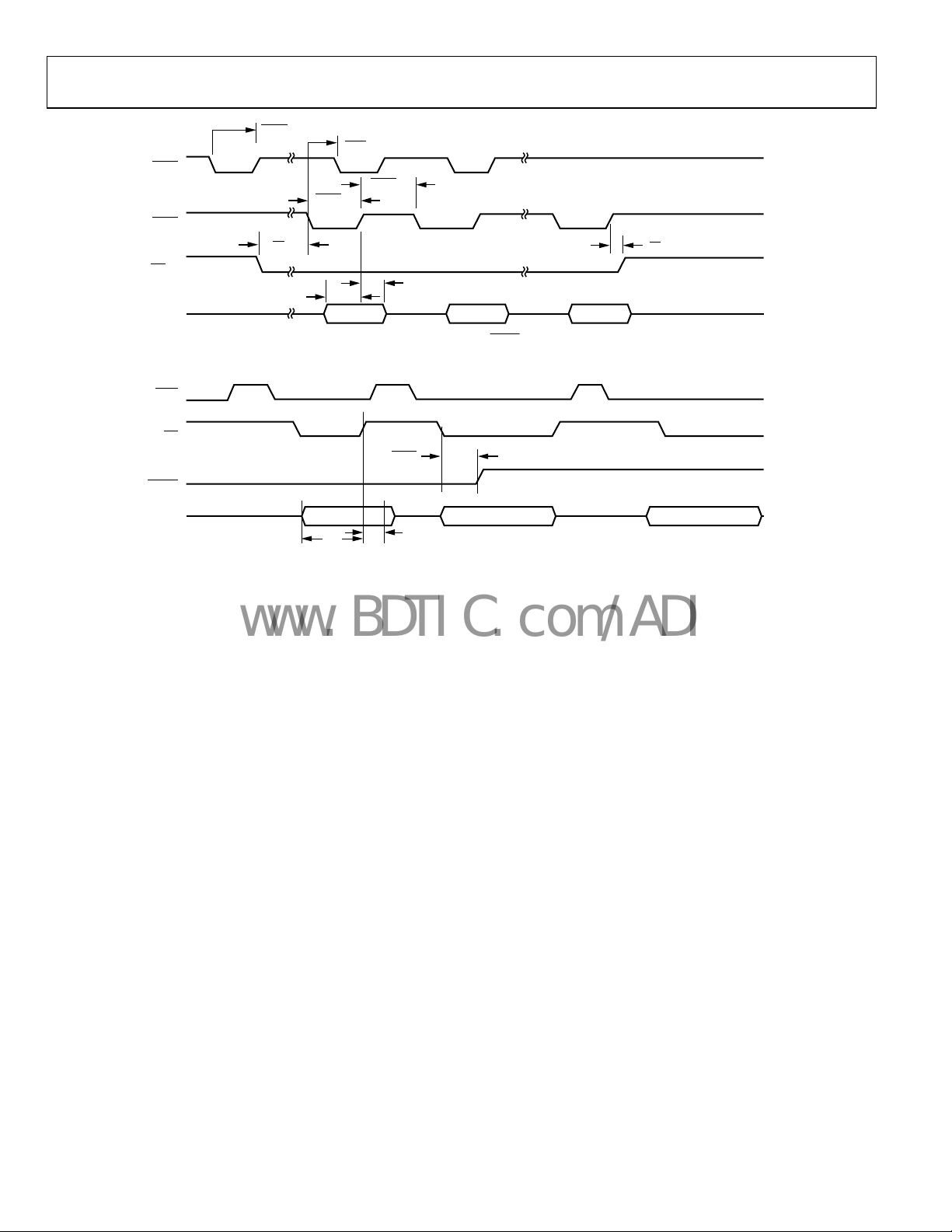
DREQ/DACK DMA MODE—SINGLE FIFO WRITE OPERATION
Table 6.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
DREQ
t
DREQ
t
WE
tSU
tHD
1
DREQ Pulse Width
PULSE
DACK Assert to Subsequent DREQ Delay
SU
WE
Data to DACK
Data to DACK
to DACK Setup
Deassert Setup
Deassert Hold
DACKLO DACK Assert Pulse Width
DACKHI DACK Deassert Pulse Width
t
HD
WE
Hold After DACK Deassert
WE
WFSRQ WE Assert to FSRQ Deassert (FIFO Full)
t
RTN
DREQ
1
Applies to assigned DMA channel, if EDMOD0 or EDMOD1[14:11] is programmed to a value that is not 0. Pulse width depends on the value programmed
2
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
to DREQ Deassert (DR × PULS = 0)
DACK
1 15 JCLK cycles
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
0 ns
2 ns
2 ns
2 JCLK cycles
2 JCLK cycles
0 ns
1.5 2.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
DREQ
DREQ
DACK
WE
HDATA
PULSE
t
WESU
Figure 5. Single Write for
DACK
t
t
DREQ
LO
SU
DACK
t
HD
HI
DREQ
DACK
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
t
WEHD
3210
04723-013
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] NOT Programmed to a Value of 0000)
t
DREQRTN
DREQ
DACK
HI
t
HD
0 1 2
DACK
DREQ
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
t
WEHD
04723-014
DACK
WE
HDATA
DACK
LO
t
WESU
t
SU
Figure 6. Single Write for
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] Programmed to a Value of 0000)
2
Rev. C | Page 9 of 40
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DREQ
DREQ
DACK
WEFB
HDATA
PULSE
t
WESU
Figure 7. Fly-By DMA Mode—Single Write Cycle (
t
DREQ
DACK
DACK
LO
t
SU
HI
t
HD
0 1 2
DREQ
t
WEHD
Pulse Width Is Programmable)
04723-015
FSC0
WE
WFSRQ
FSRQ0
HDATA
FIFO NOT FULL
0 1 2
t
HD
t
SU
Figure 8. DCS DMA Mode—Single Write Access (Rev. 0.1 and Higher)
FIFO FULL
NOT WRITTENTO FIFO
04723-016
Rev. C | Page 10 of 40
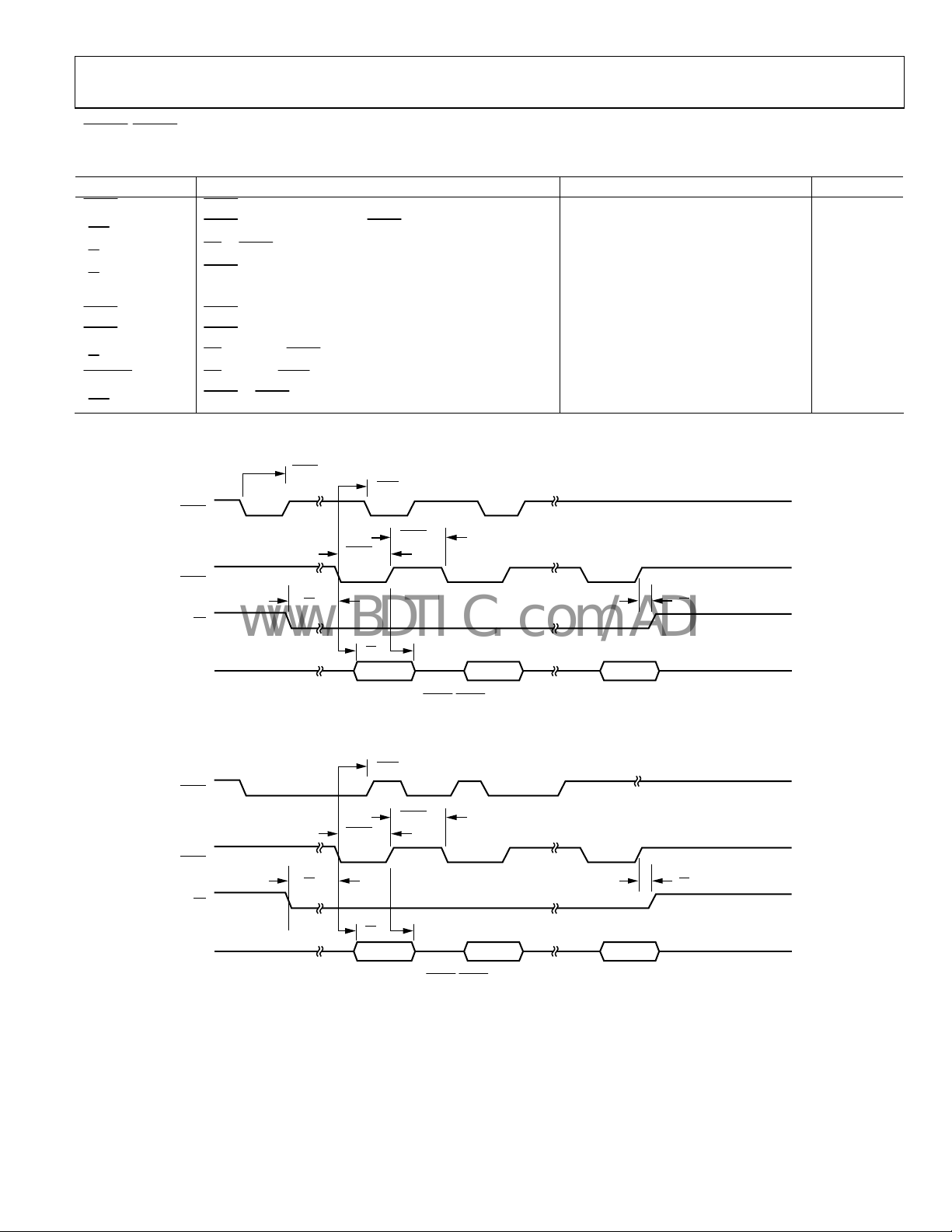
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
/
DREQ
Table 7.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
DREQ
PULSE
t
DREQ
t
SU
RD
tRD
t
Data Hold 1.5 ns
HD
DACKLO DACK Assert Pulse Width
DACKHI DACK Deassert Pulse Width
t
HD
RD
FSRQ RD Assert to FSRQ Deassert (FIFO Empty)
RD
RTN
DREQ
1
Applies to assigned DMA channel, if EDMOD0 or EDMOD1[14:11] is programmed to a nonzero value.
2
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
DMA MODE—SINGLE FIFO READ OPERATION
DACK
DREQ Pulse Width
1
DACK Assert to Subsequent DREQ Delay
RD to DACK Setup
DACK to Data Valid
RD Hold After DACK Deassert
DACK to DREQ Deassert (DR × PULS = 0)
DREQ
PULSE
DREQ
DACK
t
DREQ
LO
DACK
1 15 JCLK cycles
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
0 ns
2.5 11 ns
2 JCLK cycles
2 JCLK cycles
0 ns
1.5 2.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles t
HI
2
DACK
t
RDSU
RD
t
RD
HDATA 0 1 2
Figure 9. Single Read for
t
HD
DREQ
DACK
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
t
RDHD
04723-018
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] Not Programmed to a Value of 0000)
t
DREQRTN
DREQ
DACK
DACK
LO
DACK
t
RDSU
RD
t
RD
HDATA 0 1 2
Figure 10. Single Read for
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] Programmed to a Value of 0000)
HI
t
HD
DREQ
DACK
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
t
RDHD
4723-019
Rev. C | Page 11 of 40
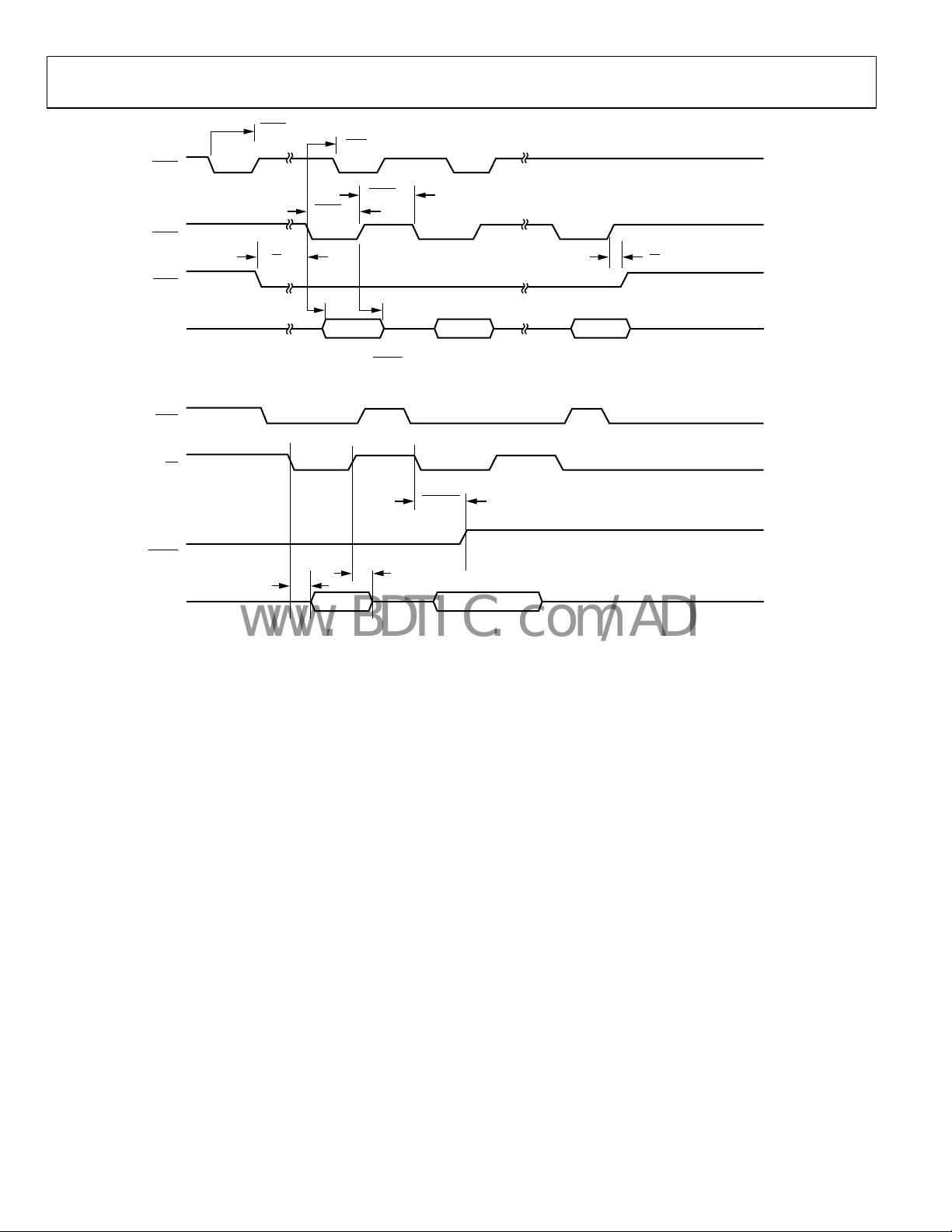
ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DREQ
DACK
RDFB
HDATA
DREQ
t
RDSU
PULSE
t
DREQ
DACK
DACK
LO
t
RD
HI
t
HD
0 1 2
t
RDHD
04723-020
Figure 11. Fly-By DMA Mode—Single Read Cycle
DREQ
(
Pulse Width Is Programmable)
FCS0
RD
RDFSRQ
FSRQ0
HDATA
FIFO NOT EMPTY
t
t
RD
HD
0 1
Figure 12. DCS DMA Mode—Single Read Access (Rev. 0.1 and Higher)
FIFO EMPTY
04723-021
Rev. C | Page 12 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
EXTERNAL DMA MODE—FIFO WRITE, BURST MODE
Table 8.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
DREQ
t
DREQ
t
DACK
t
SU
DREQ Pulse Width
PULSE
RTN
SU
WE to DREQ Deassert (DR × Pulse = 0)
DACK
to WE Setup
Data Setup 2.5 ns
tHD Data Hold 2 ns
WELO WE Assert Pulse Width
WEHI WE Deassert Pulse Width
WAIT
DREQ
1
Applies to assigned DMA channel, if EDMOD0 or EDMOD1[14:11] is programmed to a value that is not 0. Pulse width depends on the value programmed.
2
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
3
If sufficient space is available in FIFO.
Last Burst Access to Next DREQ
DREQ
DACK
1
DREQ
PULSE
1 15 JCLK2 cycles
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
0 ns
1.5 JCLK cycles
1.5 JCLK cycles
t
DREQWAIT
3
JCLK cycles t
2.5 4.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns
t
WE
HDATA
DACKSU
t
HD
t
SU
0 1 13 14 15
Figure 13. Burst Write Cycle for
WE
LO
DREQ
/DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
WE
HI
04723-022
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] NOT Programmed to a Value of 0000)
DREQ
DACK
WE
HDATA
t
DREQRTN
t
DACKSU
t
HD
t
SU
0 1 13 14 15
Figure 14. Burst Write Cycle for
WE
LO
DREQ
/DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
(EDMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] Programmed to a Value of 0000)
WE
HI
t
DREQWAIT
04723-023
Rev. C | Page 13 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
t
DREQ
DACK
WEFB
HDATA
DREQRTN
t
DACKSU
t
HD
t
SU
0 1 13 14 15
WE
LO
WE
HI
t
DREQWAIT
04723-024
Figure 15. Burst Write Cycle for Fly-By DMA Mode
DREQ
(
Pulse Width Is Programmable)
EXTERNAL DMA MODE—FIFO READ, BURST MODE
Table 9.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
DREQ
t
DREQ
t
DACK
tRD
t
HD
RD
RD
DREQ
1
Applies to assigned DMA channel, if EDMOD0 or EDMOD1[14:11] is programmed to a value that is not 0. Pulse width depends on the value programmed.
2
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
3
If sufficient space is available in FIFO.
DREQ Pulse Width
PULSE
RTN
SU
RD to DREQ Deassert (DR × PULS = 0)
DACK to RD Setup
RD to Data Valid
Data Hold 2.5 ns
LO
HI
WAIT
RD Assert Pulse Width
RD Deassert Pulse Width
Last Burst Access to Next DREQ
DREQ
1
DREQ
PULSE
1 15 JCLK cycles2
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns JCLK cycles
0 ns
2.5 9.7 ns
1.5 JCLK cycles
1.5 JCLK cycles
t
DREQWAIT
3
JCLK cycles t
2.5 3.5 × JCLK + 7.5 ns
DACK
t
RD
HDATA
DACKSU
t
HD
0 1 13 14 15
t
RD
Figure 16. Burst Read Cycle for
DREQ
RD
LO
DACK
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
RD
HI
04723-025
(EMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] NOT Programmed to a Value of 0)
Rev. C | Page 14 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
t
DREQWAIT
DREQ
DACK
RD
t
DREQRTN
t
DACKSU
t
RD
LO
HD
RD
HI
HDATA
Figure 17. Burst Read Cycle for
0 1 13 14 15
t
RD
DACK
DREQ
/
DMA Mode for Assigned DMA Channel
04723-026
(EMOD0/EDMOD1[14:11] Programmed to a Value of 0000)
t
DREQRTN
DREQ
DACK
RDFB
HDATA
t
DACKSU
t
HD
0 1 13 14 15
t
RD
Figure 18. Burst Read Cycle, Fly-By DMA Mode
DREQ
(
Pulse Width Is Programmable)
t
DREQWAIT
04723-027
Rev. C | Page 15 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
STREAMING MODE (JDATA)—FIFO READ/WRITE
Table 10.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
JDATATD MCLK to JDATA Valid 1.5 2.5 × JCLK + 7.0 ns JCLK cycles1
VALIDTD MCLK to VALID Assert/Deassert 1.5 2.5 × JCLK + .7.0 ns JCLK cycles
HOLDSU HOLD Setup to Rising MCLK 3 ns
HOLDHD HOLD Hold from Rising MCLK 3 ns
JDATASU JDATA Setup to Rising MCLK 3 ns
JDATAHD JDATA Hold from Rising MCLK 3 ns
1
For a definition of JCLK, see the PLL section.
MCLK
JDATA
JDATA
HD
SU
JDATA
VALID
JDATA
VALID
TD
TD
HOLD
HOLD
SU
HOLD
HD
04723-028
Figure 19. Streaming Mode Timing—Encode Mode JDATA Output
MCLK
JDATA
HD
HOLD
HOLD
SU
HD
Figure 20. Streaming Mode Timing—Decode Mode JDATA Input
04723-029
JDATA
VALID
HOLD
JDATA
VALID
SU
TD
Rev. C | Page 16 of 40

ADV202
V
V
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VDATA MODE TIMING
Table 11.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
VDATATD VCLK to VDATA Valid Delay (VDATA Output) 12 ns
VDATASU VDATA Setup to Rising VCLK (VDATA Input) 4 ns
VDATAHD VDATA Hold from Rising VCLK (VDATA Input) 4 ns
HSYNCSU HSYNC Setup to Rising VCLK 3 ns
HSYNC
HSYNCTD VCLK to HSYNC Valid Delay 12 ns
VSYNC
VSYNCHD VSYNC Hold from Rising VCLK 4 ns
VSYNCTD VCLK to VSYNC Valid Delay 12 ns
FIELDSU FIELD Setup to Rising VCLK 4 ns
FIELDHD FIELD Hold from Rising VCLK 3 ns
FIELDTD VCLK to FIELD Valid 12 ns
SYNC DELAY Decode Data Sync Delay for HD Input with EAV/SAV Codes 7 VCLK cycles
Decode Data Sync Delay for SD Input with EAV/SAV Codes 9 VCLK cycles
HSYNC Hold from Rising VCLK 4 ns
HD
VSYNC Setup to Rising VCLK 3 ns
SU
Decode Data Sync Delay for HVF Input (from First Rising VCLK after HSYNC Low to
irst Data Sample)
F
VCLK
VDATA(IN)
VCLK
Cr Y Cb Y FF EAV FF SAV Cb Y Cr
ENCODE CCIR-656 L INE
VDATA
VDATA
VDATA
HD
SU
TD
10 VCLK cycles
DATA(OUT)
VCLK
DATA(OUT)
VCLK
DATA(OUT)
HSYNC
VSYNC
VCLK
VDATA(IN)
HSYNC
VSYNC
Cr Y Cb Y FF EAV FF SAV Cb Y Cr
DECODE MASTE R CCIR-656 LINE
VDATA
TD
CrY Y Cb Y FF EAV FF SAV Cb Y
DECODE SLAVE CCIR-656 L INE
VDATA
TD
Cb Y Cr Y Cb CbY
DECODE SLAVE HVF MO DE
CrY Y Cb YCrYCbY YCrYCb Cb
ENCODE HVF MO DE
*HSYNC AND VSYNC DO NOT HAVE TO BE APPLIED S IMULTANEOUSLY
SYNC DELAY
SYNC DELAY
HSYNCHD*
VSYNCHD*
HSYNC
VSYNC
Cb Y Cr Y
SU
SU
HSYNC
VSYNC
HD
HD
Figure 21. Video Mode Timing
Rev. C | Page 17 of 40
4723-030

ADV202
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
RAW PIXEL MODE TIMING
Table 12.
Parameter Description Min Typ Max Unit
VDATATD VCLK to PIXELDATA Valid Delay (PIXELDATA Output) 12 ns
VDATASU PIXELDATA Setup to Rising VCLK (PIXELDATA Input) 4 ns
VDATA
VRDY
VFRM
VFRM
VFRM
VSTRB
VSTRB
PIXELDATA Hold from Rising VCLK (PIXELDATA Input) 4 ns
HD
VCLK to VRDY Valid Delay 12 ns
TD
VFRM Setup to Rising VCLK (VFRAME Input) 3 ns
SU
VFRM Hold from Rising VCLK (VFRAME Input) 4 ns
HD
VCLK to VFRM Valid Delay (VFRAME Output) 12 ns
TD
VSTRB Setup to Rising VCLK 4 ns
SU
VSTRB Hold from Rising VCLK 3 ns
HD
VCLK
VDATA
HD
VDATA
PIXEL
DATA(IN)
VFRM(IN)
N–1 N 0 1 2
VFRM
SU
VFRM
HD
SU
VRDY
TD
VRDY
VSTRB
HD
VSTRB
SU
VSTRB
RAW PIXEL MODE – ENCODE
VCLK
VDATA
VRFM
TD
TD
04723-031
RAW PIXEL MODE – DECODE
PIXEL
DATA
FRM(OUT)
NN 0 1 2
Figure 22. Raw Pixel Mode Timing
Rev. C | Page 18 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 13.
Parameter Rating
VDD (Supply Voltage, Core)
IOVDD (Supply Voltage, I/O)
PLLVDD (Supply Voltage, PLL)
Storage Temperature (TS) Range −65°C to 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
−0.3 V to +1.65 V
−0.3 V to +IOVDD + 0.3 V
−0.3 V to +1.65 V
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θ
is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
JA
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 14. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θ
ADV202 (144-Lead) 22.5° 3.8° C/W
ADV202 (121-Lead) 32.8° 7.92° C/W
θ
JA
Unit
JC
ESD CAUTION
Rev. C | Page 19 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN BGA ASSIGNMENTS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
PIN BGA ASSIGNMENTS
Table 15. Pin BGA Assignments for 121-Lead Package
Pin. No. Pin Location Pin Description
1 A1 DGND
2 A2 HDATA[2]
3 A3 VDD
4 A4 DGND
5 A5 HDATA[0]
6 A6 HDATA[1]
7 A7 VDATA[1]
8 A8 VDD
9 A9 DGND
10 A10 VDATA[0]
11 A11 DGND
12 B1 HDATA[3]
13 B2 HDATA[4]
14 B3 HDATA[5]
15 B4 HDATA[7]
16 B5 HDATA[8]
17 B6 IOVDD
18 B7 VDATA[6]
19 B8 VDATA[5]
20 B9 VDATA[4]
21 B10 VDATA[2]
22 B11 VDATA[3]
23 C1 DGND
24 C2 HDATA[6]
25 C3 HDATA[9]
26 C4 HDATA[10]
27 C5 HDATA[11]
28 C6 IOVDD
29 C7 VDATA[9]
30 C8 IOVDD
31 C9 VDATA[8]
32 C10 VDATA[7]
33 C11 DGND
34 D1 HDATA[12]
35 D2 HDATA[13]
36 D3 HDATA[14]
37 D4 HDATA[15]
38 D5 IOVDD
39 D6 DGND
40 D7 VDD
41 D8 VSYNC
42 D9 HSYNC
43 D10 VDATA[10]
44 D11 VDATA[11]
45 E1 DGND
46 E2 HDATA[18]_VDATA[14]
47 E3 HDATA[17]_VDATA[13]
48 E4 HDATA[16]_VDATA[12]
49 E5 DGND
Rev. C | Page 20 of 40
Pin. No. Pin Location Pin Description
50 E6 DGND
51 E7 DGND
52 E8 IOVDD
53 E9 VCLK
54 E10 FIELD
55 E11 DGND
56 F1 DGND
57 F2 HDATA[19]_VDATA[15]
58 F3 HDATA[20]
59 F4 HDATA[21]
60 F5 DGND
61 F6 DGND
62 F7 DGND
63 F8
64 F9
65 F10
66 F11 DGND
67 G1 DGND
68 G2 HDATA[22]
69 G3 HDATA[23]
70 G4 HDATA[24]_JDATA[0]
71 G5 DGND
72 G6 DGND
73 G7 DGND
74 G8 IOVDD
75 G9
76 G10
77 G11 DGND
78 H1 HDATA[28]_JDATA[4]
79 H2 HDATA[27]_JDATA[3]
80 H3 HDATA[26]_JDATA[2]
81 H4 HDATA[25]_JDATA[1]
82 H5 IOVDD
83 H6 DGND
84 H7 VDD
85 H8
86 H9
87 H10 ADDR[1]
88 H11 ADDR[3]
89 J1 DGND
90 J2 HDATA[31]_JDATA[7]
91 J3 HDATA[30]_JDATA[6]
92 J4 HDATA[29]_JDATA[5]
93 J5 IOVDD
94 J6 TEST1
95 J7
96 J8
97 J9 ADDR[0]
DREQ0
DACK0
DREQ1
DACK1
IRQ
ACK
RD
WE
CS

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin. No. Pin Location Pin Description
98 J10 TEST3
99 J11 DGND
100 K1 SCOMM[4]
101 K2 SCOMM[3]
102
103 K4 SCOMM[1]
104 K5 IOVDD
105 K6 IOVDD
106 K7 IOVDD
107 K8 ADDR[2]
108 K9 TEST2
109 K10 TEST5
K3 SCOMM[0]
Table 16. Pin BGA Assignments for 144-Lead Package
Pin No. Pin Location Pin Description
1 A1 DGND
2 A2 HDATA[2]
3 A3 HDATA[1]
4 A4 HDATA[0]
5 A5 DGND
6 A6 DGND
7 A7 DGND
8 A8 DGND
9 A9 VDATA[2]
10 A10 VDATA[1]
11 A11 VDATA[0]
12 A12 DGND
13 B1 HDATA[5]
14 B2 HDATA[4]
15 B3 HDATA[3]
16 B4 IOVDD
17 B5 DGND
18 B6 VDD
19 B7 VDD
20 B8 DGND
21 B9 IOVDD
22 B10 VDATA[5]
23 B11 VDATA[4]
24 B12 VDATA[3]
25 C1 HDATA[8]
26 C2 HDATA[7]
27 C3 HDATA[6]
28 C4 IOVDD
29 C5 DGND
30 C6 VDD
31 C7 VDD
32 C8 DGND
33 C9 IOVDD
34 C10 VDATA[8]
35 C11 VDATA[7]
36 C12 VDATA[6]
37 D1 HDATA[11]
Pin. No. Pin Location Pin Description
110 K11 DGND
111 L1 DGND
112 L2 SCOMM[7]
113 L3 SCOMM[6]
114 L4 SCOMM[5]
115 L5 SCOMM[2]
116 L6 TEST4
117 L7
118 L8 DGND
119 L9 MCLK
120 L10 PLLVDD
121 L11 DGND
Pin No. Pin Location Pin Description
38 D2 HDATA[10]
39 D3 HDATA[9]
40 D4 IOVDD
41 D5 DGND
42 D6 VDD
43 D7 VDD
44 D8 DGND
45 D9 IOVDD
46 D10 VDATA[11]
47 D11 VDATA[10]
48 D12 VDATA[9]
49 E1 HDATA[14]
50 E2 HDATA[13]
51 E3 HDATA[12]
52 E4 DGND
53 E5 DGND
54 E6 DGND
55 E7 DGND
56 E8 DGND
57 E9 FIELD
58 E10 VSYNC
59 E11 HSYNC
60 E12 VCLK
61 F1 HDATA[18]_VDATA[14]
62 F2 HDATA[17]_VDATA[13]
63 F3 HDATA[16]_VDATA[12]
64 F4 HDATA[15]
65 F5 DGND
66 F6 DGND
67 F7 DGND
68 F8 DGND
69 F9
70 F10
71 F11
72 F12
73 G1 HDATA[22]
74 G2 HDATA[21]
RESET
DACK1
DREQ1
DACK0
DREQ0
Rev. C | Page 21 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin No. Pin Location Pin Description
75 G3 HDATA[20]
76 G4 HDATA[19]_VDATA[15]
77 G5 DGND
78 G6 DGND
79 G7 DGND
80 G8 DGND
81 G9 DGND
82 G10
83 G11
84 G12
85 H1 HDATA[26]_JDATA[2]
86 H2 HDATA[25]_JDATA[1]
87 H3 HDATA[24]_JDATA[0]
88 H4 HDATA[23]
89 H5 DGND
90 H6 DGND
91 H7 DGND
92 H8 DGND
93 H9 DGND
94 H10
95 H11
96 H12 ADDR[0]
97 J1 HDATA[30]_JDATA[6]
98 J2 HDATA[29]_JDATA[5]
99 J3 HDATA[28]_JDATA[4]
100 J4 HDATA[27]_JDATA[3]
101 J5 DGND
102 J6 VDD
103 J7 VDD
104 J8 DGND
105 J9 DGND
106 J10 ADDR[1]
107 J11 ADDR[2]
108 J12 ADDR[3]
109 K1 SCOMM[1]
IRQ
ACK
RD
WR
CS
Pin No. Pin Location Pin Description
110 K2 SCOMM[0]
111 K3 HDATA[31]_JDATA[7]
112 K4 IOVDD
113 K5 DGND
114 K6 VDD
115 K7 VDD
116 K8 DGND
117 K9 IOVDD
118 K10 TEST3
119 K11 TEST2
120 K12 TEST1
121 L1 SCOMM[4]
122 L2 SCOMM[3]
123 L3 SCOMM[2]
124 L4 IOVDD
125 L5 DGND
126 L6 VDD
127 L7 VDD
128 L8 DGND
129 L9 IOVDD
130 L10 TEST5
131 L11
132 L12 MCLK
133 M1 DGND
134 M2 SCOMM[7]
135 M3 SCOMM[6]
136 M4 SCOMM[5]
137 M5 DGND
138 M6 DGND
139 M7 DGND
140 M8 DGND
141 M9 TEST4
142 M10 PLLVDD
143 M11 DGND
144 M12 DGND
RESET
Rev. C | Page 22 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Table 17.
Pins
Us
Mnemonic
MCLK 1 L9 L12 I
RESET
HDATA[15:0] 16
ADDR[3:0] 4 H11, K8, H10, J9 J12, J11, J10, H12 I Address Bus for the Host Interface.
CS
WE
RDFB
RD
WEFB
ACK
IRQ
DREQ0
FSRQ0
VALID
CFG[1] I
DACK0
ed
121-Lead Package 144-Lead Package I/O Description
System Input Clock. For details, see the PLL section.
aximum input frequency on MCLK is 74.25 MHz.
M
1 L7 L11 I
D4 to D1, C5 to C3,
B5, B4, C2, B3 to B1,
A2, A6 to A5
1 J8 H11 I
1 J7 H10 I Write Enable Used with the Host Interface.
1 H9 G12 I Read Enable. Used with the host interface.
1 H8 G11 O
1 G10 G10 O
1 F8 F12 O
O
O
1 F9 F11 I
F4, E1 to E3, D1 to D3,
C1 to C3, B1 to B3, A2,
A3, A4
Reset. Causes the ADV202 to immediately reset. CS
, DACK0, DACK1, DREQ0, and DREQ1 must be held
WE
high when a RESET
I/O
Host Data Bus. With HDATA[23:16], [27:24], [31:28], these
pins make up the 32-bit wide host data bus.
The async host interface is interfaced together with
ADDR[3:0], CS
should be pulled down via a 10 kΩ resistor.
Chip Select. This signal is used t
and write access to the ADV202 using the host interface.
Read Enable When Fly-By DMA Is Enabled.
te: Simultaneous assertion of WE
No
the HDATA bus, even if the DMA channels are disabled.
Write Enable When Fly-By DMA Is Enabled.
te: Simultaneous assertion of RD
No
the HDATA bus, even if the DMA channels are disabled.
Acknowledge. Used for direct register accesses. This signal
indicates that the last register access was successful.
Note: Due to synchronization issues, control and status
register accesses can incur an additional delay, so the host
software should wait for acknowledgment from the ADV202.
Accesses to the FIFOs (external DMA modes), on the other
hand, are guaranteed to occur immediately, if space is
available, and should not wait for ACK, if the timing
constraints are observed. If ACK is shared with more than
one device, ACK
(10 kΩ) and the PLL_HI register, Bit 4, must be set to 1.
Interrupt. This pin indicates that the ADV202 requires the
attention of the host processor. This pin can be
programmed to indicate the status of the internal
interrupt conditions within the ADV202. The interrupt
sources are enabled via bits in Register EIRQIE.
Data Request for External DMA Interface. Indicates that
the ADV202 is ready to send/receive data to/from the FIFO
assigned to DMA Channel 0.
Used in DCS-DMA Mode. Service request from the FIFO
assigned to Channel 0 (asynchronous mode).
Valid Indication for JDATA Input/Output Stream. Polarity
of this pin is programmable in the EDMOD0 register.
VALID is always an output.
Boot Mode Configuration. This pin is read on reset to
mine the boot configuration of the on-board
deter
processor. The pin should be tied to IOVDD or DGND
through a 10 kΩ resistor.
Data Acknowledge for External DMA Interface. Signal
from the host CPU, which indicates that the data transfer
request (DREQ0) has been acknowledged and data
transfer can proceed. This pin must be held high at all
times if the DMA interface is not used, even if the DMA
channels are disabled.
is applied.
, WE, RD, and ACK. Unused HDATA pins
o qualify addressed read
and DACK low activates
and DACK low activates
should be connected to a pull-up resistor
, RD,
Rev. C | Page 23 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pins
Mnemonic
HOLD
FCS0
DREQ1
FSRQ1
CFG[2] I
DACK1
FCS1
HDATA[31:28] 4 J2 to J4, H1 K3, J1 to J3 I/O Host Expansion Bus.
JDATA[7:4] I/O JDATA Bus (JDATA Mode).
HDATA[27:24] 4 H2 to H4, G4 J4, H1 to H3 I/O Host Expansion Bus.
JDATA[3:0] I/O JDATA Bus (JDATA Mode).
HDATA[23:16] 8
SCOMM[7] 8 L2 M2 I/O
SCOMM[6] L3 M3 I/O
SCOMM[5] L4 M4 I/O
SCOMM[4] K1 L1 O
SCOMM[3] K2 L2 O This pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ resistor.
SCOMM[2] L5 L3 O This pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ resistor.
SCOMM[1] K4 K1 I This pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ resistor.
SCOMM[0] K3 K2 O This pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ resistor.
VCLK 1 E9 E12 I
VDATA[11:0] 12
VSYNC 1 D8 E10 I/O Vertical Sync for Video Mode.
VFRM
HSYNC 1 D9 E11 I/O Horizontal Sync for Video Mode.
VRDY O Raw Pixel Mode Ready Signal.
U
sed 121-Lead Package 144-Lead Package I/O Description
I
I
1 F10 F10 O
O
1 G9 F9 I
I
G3, G2, F4, F3, F2 E2,
E3, E4
D11, D10, C7, C9,
C10, B7, B8, B9, B11,
B10, A7, A10
H4, G1 to G4, F1 to F3 I/O Host Expansion Bus.
D10 to D12,
C10 to C12,
to B12, A9 to A11
B10
External Hold Indication for JDATA Input/Output Stream.
olarity is programmable in the EDMOD0 register. This pin
P
is always an input.
Used in DCS-DMA Mode. Chip select for the FIFO assigned
to Channel 0 (asynchronous mode).
Data Request for External DMA Interface. Indicates that
the ADV202 is r
assigned to DMA Channel 1.
Used in DCS-DMA Mode. Service request from the FIFO
assigned to Channel 1 (asynchronous mode).
Boot Mode Configuration. This pin is read on reset to
mine the boot configuration of the on-board
deter
processor. The pin should be tied to IOVDD or DGND
through a 10 kΩ resistor.
Data Acknowledge for External DMA Interface. Signal
from the host CPU, which indicates that the data transfer
request (DREQ1
transfer can proceed. This pin must be held high at all
times unless a DMA or JDATA access is occurring. This pin
must be held high at all times if the DMA interface is not
used, even if the DMA channels are disabled.
Used in DCS-DMA Mode. Chip select for the FIFO assigned
to Channel 1 (asynchronous mode).
When not used, this pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ
esistor.
r
When not used, this pin should be tied low via a 10 kΩ
esistor.
r
This pin must be used in multiple chip mode to
outputs of two or more ADV202s. For details, see the
Applications section and AN-796 ADV202 Multichip
pplication application note. When not used, this pin
A
be tied low via a 10 kΩ resistor.
should
LCODE Output in Encode Mode. When LCODE is enabled,
the output on t
the last data-word for a field has been read from the FIFO.
For an 8-bit interface, such as JDATA, LCODE is asserted for
four consecutive bytes and is enabled by default.
Video Data Clock. Must be supplied if video data is
output on the VDATA bus.
input/
I/O
Video Data. Unused pins should be pulled down via a
10 kΩ resistor.
Raw Pixel Mode Framing Signal. Indicates first sample of a
tile when a
eady to send/receive data to/from the FIFO
) has been acknowledged and data
his pin indicates on a high transition that
sserted high.
align the
Rev. C | Page 24 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pins
Mnemonic
FIELD 1 E10 E9 I/O Field Sync for Video Mode.
VSTRB I Raw Pixel Mode Transfer Strobe.
TEST1 1 J6 K12 I
TEST2 1 K9 K11 I
TEST3 1 J10 K10 I
TEST4 1 L6 M9 I
TEST5 1 K10 L10 O No Connect.
VDD A3, A8, D7, H7
DGND
PLLVDD 1 L10 M10 V Positive Supply for PLL.
IOVDD
U
sed 121-Lead Package 144-Lead Package I/O Description
This pin should be connected to ground via a pull-down
esistor.
r
This pin should be connected to ground via a pull-down
esistor.
r
This pin should be connected to ground via a pull-down
esistor.
r
This pin should be connected to ground via a pull-down
esistor.
r
V Positive Supply for Core.
GND Ground.
V Positive Supply for I/O.
A1, A11, A4, A9, C1,
D6, E1, E5 to E7,
C11,
E11, F1, F5 to F7,
F11, G1, G5 to G7,
G11, H6, J1, J11,
K11, L1, L8, L11
B6, C6, C8, D5, E8,
8, H5, J5, K5, K6, K7
G
B6, B7, C6, C7, D6, D7,
J6, J7, K6, K7, L6,
A1, A5 to A8, A12, B5,
B8, C5, C8, D5, D8, E4
to E8, F5 to F8, G5 to
G9, H5 to H9, J5, J8 to
J9, K5, K8, L5, L8, M1,
M5 to M8, M11, M12
B4, B9, C4, C9, D4, D9,
K4, K9, L4, L9
L7
Rev. C | Page 25 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
THEORY OF OPERATION
The input video or pixel data is passed on to the ADV202’s pixel
interface, where samples are de-interleaved and passed on to the
wavelet engine, which decomposes each tile or frame into
subbands using the 5/3 or 9/7 filters. The resulting wavelet
coefficients are then written to internal memory. Next, the
entropy codecs code the image data so it conforms to the
JPEG2000 standard. An internal DMA provides high
bandwidth memory-to-memory transfers, as well as high
performance transfers between functional blocks and memory.
WAVELET ENGINE
The ADV202 provides a dedicated wavelet transform processor
based on Analog Devices’ proven and patented SURF
technology. This processor can perform up to six wavelet
decomposition levels on a tile. In encode mode, the wavelet
transform processor takes in uncompressed samples, performs
the wavelet transform and quantization, and writes the wavelet
coefficients in all frequency subbands to internal memory. Each
of these subbands is then further broken down into code blocks.
The code-block dimensions can be user-defined and are used
by the wavelet transform processor to organize the wavelet
coefficients into code blocks when writing to internal memory.
Each completed code block is then entropy coded by one of the
entropy codecs.
In decode mode, wavelet coefficients are read from internal
m
emory and recomposed into uncompressed samples.
ENTROPY CODECS
The entropy codec block performs context modeling and
arithmetic coding on a code block of the wavelet coefficients.
Additionally, this block performs the distortion metric
calculations during compression that are required for optimal
rate and distortion performance. Because the entropy coding
process is the most computationally intensive operation in the
JPEG2000 compression process, three dedicated hardware
entropy codecs are provided on the ADV202.
EMBEDDED PROCESSOR SYSTEM
The ADV202 incorporates an embedded 32-bit RISC processor.
This processor is used for configuration, control, and management of the dedicated hardware functions, as well as for parsing
and generating the JPEG2000 code stream. The processor
system includes memory for both program and data memory,
an interrupt controller, standard bus interfaces, and other
hardware functions such as timers and counters.
MEMORY SYSTEM
The memory system’s main function is to manage wavelet
coefficient data, interim code-block attribute data, and
temporary work space for creating, parsing, and storing the
JPEG2000 code stream. The memory system can also be used
for program and data memory for the embedded processor.
INTERNAL DMA ENGINE
The internal DMA engine provides high bandwidth memoryto-memory transfers, as well as high performance transfers
between memory and functional blocks. This function is critical
for high speed generation and parsing the code stream.
Rev. C | Page 26 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ADV202 INTERFACE
There are several possible modes to interface to the ADV202 using
the VDATA bus and t he HDATA bus or the HDATA bus alone.
VIDEO INTERFACE (VDATA BUS)
The video interface can be used in applications in which
uncompressed pixel data is on a separate bus from compressed
data. For example, it is possible to use the VDATA bus to input
uncompressed video while using the HDATA bus to output the
compressed data. This interface is ideal for applications
requiring very high throughput such as live video capture.
Optionally, the ADV202 can compress ITU.R-BT656 resolution
deo on a field-by-field basis or on a two-fields-combined
vi
basis, which yields significantly more efficient compression
performance. Additionally, high definition digital video such as
SMPTE274M (1080i) is supported using two or more ADV202
devices.
The video interface can support video data or still image data
input/output, 8-, 10-, and 12-bit single or multiplexed
components. The VDATA interface supports digital video in
YCbCr format or single component format. YCbCr data must
be in 4:2:2 format.
Video data can be input/output in several different modes on
e VDATA bus, as described in Tab l e 1 8 . In all these modes,
th
t
he pixel clock must be input on the VCLK pin.
Table 18. Video Input/Output Modes
Mode Description
EAV/SAV
HVF
Raw
Video
Accepts video with embedded EAV/SAV codes, where
YCbCr data is interleaved onto a single bus.
the
Accepts video data accompanied with separate H, V,
and F signals wher
single bus.
Used for still picture data and nonstandard video.
VFRM, VSTRB, and VRDY are used to program the
dimensions of the image.
e YCbCr data is interleaved onto a
HOST INTERFACE (HDATA BUS)
The ADV202 can connect directly to a wide variety of host
processors and ASICs using an asynchronous SRAM-style
interface, DMA accesses, or streaming mode (JDATA) interface.
The ADV202 supports 16- and 32-bit buses for control and
8-, 16-, and 32-bit buses for data transfer.
The control and data channel bus widths can be specified
endently, which allows the ADV202 to support applica-
indep
tions that require control and data buses of different widths.
The host interface is used for configuration, control, and status
f
unctions, as well as for transferring compressed data streams. It
can be used for uncompressed data transfers in certain modes.
The host interface can be shared by as many as four concurrent
data streams in addition to control and status communications.
The data streams are
ncompressed tile data (for example, still image data)
• U
• F
ully encoded JPEG2000 code stream (or unpackaged code
blocks)
• Cod
The ADV202 uses big endian byte alignment for 16- and 32-bit
tra
e-block attributes
nsfers. All data is left-justified (MSB).
Pixel Input on the Host Interface
Pixel input on the host interface supports 8-, 10-, 12-, 14-, and
16-bit raw pixel data formats. It can be used for pixel (still
image) input/output or compressed video output. Because there
are no timing codes or sync signals associated with the input
data on the host interface, dimension registers and internal
counters are used and must be programmed to indicate the start
and end of the frame. See the
de for details on how to use the ADV202 in this mode.
mo
technical note on using HIPI
Host Bus Configuration
For maximum flexibility, the host interface provides several
configurations to meet particular system requirements. The
default bus mode uses the same pins to transfer control, status,
and data to and from the ADV202. In this mode, the ADV202
can support 16- and 32-bit control transfers and 8-, 16-, and
32-bit data transfers. The size of these buses can be selected
independently, allowing, for example, a 16-bit microcontroller
to configure and control the ADV202 while still providing
32-bit data transfers to an ASIC or external memory system.
DIRECT AND INDIRECT REGISTERS
To minimize pin count and cost, the number of address pins has
been limited to four, which yields a total direct address space of
16 locations. These locations are most commonly used by the
external controller and are, therefore, accessible directly. All
other registers in the ADV202 can be accessed indirectly
through the IADDR and IDATA registers.
CONTROL ACCESS REGISTERS
With the exception of the indirect address and data registers
(IADDR and IDATA), all control/status registers in the ADV202
are 16 bits wide and are half-word (16-bit) addressable only.
When 32-bit host mode is enabled, the upper 16 bits of the
HDATA bus are ignored on writes and return all 0s on reads of
16-bit registers.
Rev. C | Page 27 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN CONFIGURATION AND BUS SIZES/MODES
The ADV202 provides a wide variety of control and data
configurations, which allows it to be used in many applications
with little or no glue logic. The following modes are configured
using the BUSMODE register. In the following descriptions,
host refers to normal addressed accesses (
and data refers to external DMA accesses (
32-Bit Host/32-Bit Data
In this mode, the HDATA[31:0] pins provide full 32-bit wide data
accesses to PIXEL, CODE, and ATTR FIFOs. The expanded
video interface (VDATA) is not available in this mode.
16-Bit Host/32-Bit Data
This mode allows a 16-bit host to configure and communicate
with the ADV202 while still allowing 32-bit accesses to the
PIXEL, CODE, and ATTR FIFOs using the external DMA
capability.
All addressed host accesses are 16 bits and, therefore, use only
e HDATA[15:0] pins. The HDATA[31:16] pins provide the
th
additional 16 bits necessary to support the 32-bit external DMA
transfers to and from the FIFOs only. The expanded video
interface (VDATA) is not available in this mode.
16-Bit Host/16-Bit Data
This mode uses 16-bit transfers, if used for host or external
DMA data transfers. This mode allows for the use of the
extended pixel interface modes.
16-Bit Host/8-Bit Data (JDATA Bus Mode)
This mode provides separate data input/output and host
control interface pins. Host control accesses are 16 bits and use
HDATA[15:0], while the dedicated data bus uses JDATA[7:0].
JDATA uses a valid/hold synchronous transfer protocol. The
ection of the JDATA bus is determined by the mode of the
dir
ADV202. If the ADV202 is encoding (compression), JDATA[7:0]
is an output. If the ADV202 is decoding (decompression),
JDATA[7:0] is an input. Host control accesses remain
asynchronous (also refer to the
JDATA Mode section).
STAGE REGISTER
Because the ADV202 contains both 16-bit and 32-bit registers
and its internal memory is mapped as 32-bit data, a mechanism
has been provided to allow 16-bit hosts to access these registers
and memory locations using the stage register (STAGE).
CS
/RD/WR/ADDR)
DACK
DREQ
/
).
STAGE is accessed as a 16-bit register using HDATA[15:0].
Prior to writing to the desired register, the stage register must be
written with the upper (most significant) half-word.
When the host subsequently writes the lower half-word to the
esired control register, HDATA is combined with the previously
d
staged value to create the required 32-bit value that is written.
When a register is read, the upper (most significant) half-word
is returned immediately on HDATA and the lower half-word
can be retrieved by reading the stage register on a subsequent
access. For details on using the stage register, see the
Us
er’s Guide.
Note that the stage register does not apply to the three data
cha
nnels (PIXEL, CODE, and ATTR). These channels are
always accessed at the specified data width and do not require
the use of the stage register.
ADV202
JDATA MODE
JDATA mode is typically used only when the dedicated video
interface (VDATA) is also enabled. This mode allows code
stream data (compressed data compliant with JPEG2000) to be
input or output on a single dedicated 8-bit bus (JDATA[7:0]).
The bus is always an output during compression operations
and is an input during decompression.
A 2-pin handshake is used to transfer data over this synchrono
us interface. VALID is used to indicate that the ADV202 is
ready to provide or accept data and is always an output. HOLD
is always an input and is asserted by the host if it cannot accept/
provide data. For example, JDATA mode allows real-time
applications, in which pixel data is input over the VDATA bus
while the compressed data stream is output over the JDATA bus.
EXTERNAL DMA ENGINE
The external DMA interface is provided to enable high
bandwidth data I/O between an external DMA controller and
the ADV202 data FIFOs. Two independent DMA channels can
each be assigned to any one of the three data stream FIFOs
(PIXEL, CODE, or ATTR).
The controller supports asynchronous DMA using a data-
DREQ
re
quest/data-acknowledge (
single or burst access modes. Additional functionality is provided
for single address compatibility (fly-by) and dedicated chip
select (DCS) modes.
DACK
/
) protocol in either
Rev. C | Page 28 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
INTERNAL REGISTERS
This section describes the internal registers of the ADV202.
DIRECT REGISTERS
The ADV202 has 16 direct registers, as listed in Tab l e 1 9 .
The direct registers are accessed over the ADDR[3:0],
HDATA[31:0],
Table 19. Direct Registers
Address Name Description
0x00 PIXEL Pixel FIFO Access Register
0x01 CODE Compressed Code Stream Access Register
0x02 ATTR Attribute FIFO Access Register
0x03 Reserved Reserved
0x04 CMDSTA Command Stack
0x05 EIRQIE External Interrupt Enabled
0x06 EIRQFLG External Interrupt Flags
0x07 SWFLAG Software Flag Register
0x08 BUSMODE Bus Mode Configuration Register
0x09 MMODE Miscellaneous Mode Register
0x0A STAGE Staging Register
0x0B IADDR Indirect Address Register
0x0C IDATA Indirect Data Register
0x0D BOOT Boot Mode Register
0x0E PLL_HI PLL Control Register—High Byte
0x0F PLL_LO PLL Control Register—Low Byte
CS
, RD, WR, and
ACK
pins.
The host must first initialize the direct registers before any
pplication-specific operation can be implemented.
a
For additional information on accessing and configuring these
r
egisters, see the ADV202 User’s Guide.
Rev. C | Page 29 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
INDIRECT REGISTERS
In certain modes, such as custom-specific input format or HIPI
mode, indirect registers must be accessed by the user through
the use of the IADDR and IDATA registers. The indirect
register address space starts at Internal Address 0xFFFF0000.
Table 20. Indirect Registers
Address Name Description
0xFFFF0400 PMODE1 Pixel/Video Format
0xFFFF0404 COMP_CNT_STATUS Horizontal Count
0xFFFF0408 LINE_CNT_STATUS Vertical Count
0xFFFF040C XTOT Total Samples per Line
0xFFFF0410 YTOT Total Lines per Frame
0xFFFF0414 F0_START Start Line of Field 0 [F0]
0xFFFF0418 F1_START Start Line of Field 1 [F1]
0xFFFF041C V0_START Start of Active Video Field 0 [F0]
0xFFFF0420 V1_START Start of Active Video Field 1 [F1]
0xFFFF0424 V0_END End of Active Video Field 0 [F0]
0xFFFF0428 V1_END End of Active Video Field 1 [F1]
0xFFFF042C PIXEL_START Horizontal Start of Active Video
0xFFFF0430 PIXEL_END Horizontal End of Active Video
0xFFFF0440 MS_CNT_DEL Master/Slave Delay
0xFFFF0444 Reserved Reserved
0xFFFF0448 PMODE2 Pixel Mode 2
0xFFFF044C VMODE Video Mode
0xFFFF1408 EDMOD0 External DMA Mode Register 0
0xFFFF140C EDMOD1 External DMA Mode Register 1
0xFFFF1410 FFTHRP FIFO Threshold for Pixel FIFO
0xFFFF1414 Reserved Reserved
0xFFFF1418 Reserved Reserved
0xFFFF141C FFTHRC FIFO Threshold for CODE FIFO
0xFFFF1420 FFTHRA FIFO Threshold for ATTR FIFO
0xFFFF1428 to 0xFFFF14FC Reserved Reserved
Both 32-bit and 16-bit hosts can ac
32-bit hosts use the IADDR and IDATA registers, while the
16-bit hosts use IADDR, IDATA, and the stage register.
For additional information on accessing and configuring these
r
egisters, see the ADV202 User’s Guide.
cess the indirect registers.
Rev. C | Page 30 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PLL
The ADV202 uses the PLL_HI and PLL_LO direct registers to
co
nfigure the PLL. Any time the PLL_LO register is modified,
the host must wait at least 20 μs before reading or writing to any
other register. If this delay is not implemented, erratic behavior
could result.
The PLL can be programmed to have any possible final
ultiplier value as long as
m
CLK > 50 MHz and < 150 MHz (144-lead version).
• J
• J
CLK > 50 MHz and < 135 MHz (144-lead version).
• J
CLK > 50 MHz and < 115 MHz (121-lead version).
• HCLK < 108 MHz (144-lead, 150 MHz version).
• H
CLK < 100 MHz (144-lead, 135 MHz version).
• H
CLK < 81 MHz (121-lead version).
• J
CLK ≥ 2 × VCLK for single-component input.
• J
CLK ≥ 2 × VCLK for YCrCb [4:2:2] input.
• I
n JDATA mode (JDATA), JCLK must be 4 × MCLK or
higher.
• For de-interlaced modes, JCLK must be ≥ 4 × MCLK.
• The maximum burst frequency for external DMA modes is
≤0.36 JCLK.
• F
or MCLK frequencies greater than 50 MHz, the input
clock divider must be enabled, that is, IPD set to 1.
• IPD ca
nnot be enabled for MCLK frequencies below 20 MHz.
To achieve the lowest power consumption, an MCLK frequency
f 27 MHz is recommended for a standard definition CCIR656
o
input. The PLL circuit is recommended to have a multiplier of 3.
This sets JCLK and HCLK to 81 MHz.
MCLK
IPD
⎟
2
Figure 23. PLL Architecture and Control Functions
PHASE
DETECT
⎟
LFB
BYPASS
2
LPF
⎟
PLLMULT
VCO
⎟ 2
HCLKD
JCLK
HCLK
04723-009
Table 21. Recommended PLL Register Settings
IPD LFB PLLMULT HCLKD HCLK JCLK
0 0 N 0 N × MCLK N × MCLK
0 0 N 1 N × MCLK/2 N × MCLK
0 1 N 0 2 × N × MCLK
0 1 N 1 N × MCLK
1 0 N 0 N × MCLK/2
1 0 N 1 N × MCLK/4
1 1 N 0 N × MCLK
2 × N × MCLK
2 × N × MCLK
N × MCLK/2
N × MCLK/2
N × MCLK
1 1 N 1 N × MCLK/2 N × MCLK
Table 22. Recommended Values for PLL_HI and PLL_LO Registers
Video Standard CLKIN Frequency on MCLK PLL_HI PLL_LO
SMPTE125M or ITU-R.BT656 (NTSC or PAL) 27 MHz 0x0008 0x0004
SMPTE293M (525p) 27 MHz 0x0008 0x0004
ITU-R.BT1358 (625p) 27 MHz 0x0008
0x0004
SMPTE274M (1080i) 74.25 MHz 0x0008 0x0084
HARDWARE BOOT
ADV202 User’s GuideThe boot mode can be configured via hardware using the CFG pins or via software (see the ). The first boot mode
after power-up is set by the CFG pins. Only Boot Mode 2, Boot Mode 4, and Boot Mode 6, described in Tab l e 2 3, are available via hardware.
Table 23. Hardware Boot Modes
Boot Mode Settings Description
Hardware Boot
Mode 2
Hardware Boot
Mode 4
Hardware Boot
de 6
Mo
CFG[1] tied high,
CFG[2] tied low
CFG[1] tied low,
CFG[2] tied high
CFG[1] and CFG[2]
tied high
No-Boot Host Mode. ADV202 does not boot, but all internal registers and memory are accessible
through normal host I/O operations.
For details, see the and the application note. ADV202 User’s Guide Getting Started with the ADV202
SoC Boot Mode.
Reserved.
Rev. C | Page 31 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VIDEO INPUT FORMATS
The ADV202 supports a wide variety of formats for
uncompressed video and still image data. The actual interface
and bus modes selected for transferring uncompressed data
dictates the allowed size of the input data and the number of
samples transferred with each access.
The host interface can support 8-, 10-, 12-, 14-, and 16-bit data
f
ormats. The video interface can support video data or still image
data input/output. Supported formats are 8-, 10-, 12-, or 16-bit
Table 24. Maximum Pixel Data Input Rates
Compression
Interface
144-LEAD PACKAGE
HDATA Irreversible 8-bit data 45 [40] 130 200
Irreversible 10-bit data 45 [40] 130 200
Irreversible 12-bit data 45 [40] 130 200
Irreversible 16-bit data 45 [40] 130 200
Reversible 8-bit data 40 [36] 130 200
Reversible 10-bit data 32 [28] 130 200
Reversible 12-bit data 27 [24] 130 200
Reversible 14-bit data 23 [20] 130 200
VDATA Irreversible 8-bit data 65 [55] 130 200
Irreversible 10-bit data 65 [55] 130 200
Irreversible 12-bit data 65 [55] 130 200
Reversible 8-bit data 40 [34] 130 200
Reversible 10-bit data 32 [28] 130 200
Reversible 12-bit data 27 [23] 130 200
121-LEAD PACKAGE
HDATA Irreversible 8-bit data 34 98 150
Irreversible 10-bit data 34 98 150
Irreversible 12-bit data 34 98 150
Irreversible 16-bit data 34 98 150
Reversible 8-bit data 30 98 150
Reversible 10-bit data 24 98 150
Reversible 12-bit data 20 98 150
Reversible 14-bit data 17 98 150
VDATA Irreversible 8-bit data 48 98 150
Irreversible 10-bit data 48 98 150
Irreversible 12-bit data 48 98 150
Reversible 8-bit data 30 98 150
Reversible 10-bit data 24 98 150
Reversible 12-bit data 20 98 150
1
Input rate limits for HDATA can be less for certain applications depending on input picture size and content, host interface settings, and DMA transfer settings. Values
in brackets refer to the 135 MHz speed grade version of the ADV202.
2
Minimum guaranteed sustained output rate or minimum sustainable compression rate (input rate/minimum peak output rate).
3
Maximum peak output rate, or output rate above this value is not possible .
Mode Input Format
Input Rate Limit Active
Resolution (MSPS)
single component or YCbCr 4:2:2 formats. See the
er’s Guide for details. All formats can support less precision
Us
t
han provided by specifying the actual data width/precision in
the PMODE register.
The maximum allowable data input rate is limited by using
reversible or reversible compression modes and the data width
ir
(or precision) of the input samples. Use
ermine the maximum data input rate.
det
1
Approx Min Output Rate,
Compressed Data
2
(Mbps)
Tabl e 24 and Tabl e 25 to
Approx Max Output Rate,
ompressed Data
C
(Mbps)
ADV202
3
Rev. C | Page 32 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Table 25. Maximum Supported Tile Width for Data Input on HDATA and VDATA Buses
Compression Mode Input Format Tile/Precinct Maximum Width
9/7i Single-component 2048
9/7i Two-component 1024 each
9/7i Three-component 1024 (Y)
5/3i Single-component 4096
5/3i Two-component 2048 (each)
5/3i Three-component 2048 (Y)
5/3r Single-component 4096
5/3r Two-component 2048
5/3r Three-component 1024
Rev. C | Page 33 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATIONS
This section describes typical video applications for the
ADV202 JPEG2000 video processor.
ENCODE—MULTICHIP MODE
Due to the data input rate limitation (see Tabl e 24 ), an 1080i
a
pplication requires at least two ADV202s to encode or decode
full-resolution 1080i video. In encode mode, the ADV202
accepts Y and CbCr data on separate buses. The input data must
be in EAV/SAV format. An encode example is shown in
Figure 24.
In decode mode, a master/slave configuration (as shown in
Figure 25) or a slave/slave configuration can be used to
syn
chronize the outputs of the two ADV202s. See AN-796
ADV202 Multichip Application application note for details on
how to configure the ADV202s in a multichip application.
Applications that have two separate VDATA outputs sent to an
FPGA or buffer before they are sent to an encoder do not
require synchronization at the ADV202 outputs
32-BIT HOST CP U
DATA[31:0] HDATA[31:0]
ADDR[3:0] ADDR[3:0]
CS CS
RD RD
WR WE
ACK ACK
IRQ
DREQ DREQ
DACK DACK
G I/O SCOMM[5]
CS
RD
WR
ACK
IRQ
DREQ
DACK
ADV202
_1_SLAVE
VCLK
MCLK
IRQ
HDATA[31:0]
ADDR[3:0]
CS
RD
WE
ACK
IRQ
DREQ
DACK
SCOMM[5]
VDATA[11:2]
ADV202
_2_SLAVE
VDATA[11:2]
FIELD
VSYNC
HSYNC
VCLK
MCLK
HSYNC
VSYNC
FIELD
Figure 24. Encode—Mult
Y
CbCr
CbCr
ichip Application
10-BIT SD/HD
VIDEO
DECODER
LLC
Y[9:0]
C[9:0]
1080i
VIDEO IN
04723-002
Rev. C | Page 34 of 40

ADV202
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DECODE—MULTICHIP MASTER/SLAVE
In a master/slave configuration, it is expected that the master HVF
o
utputs are connected to the slave HVF inputs and that each
SCOMM[5] pin is connected to the same GPIO on the host.
32-BIT HOST CPU
DATA[31:0] HDATA[31:0]
ADDR[3:0] ADDR[3:0]
CS CS
RD RD
WR WE
ACK ACK
IRQ
DREQ DREQ
DACK DACK
G I/O SCOMM[5]
CS
RD
WR
ACK
IRQ
DREQ
DACK
Figure 25. Decode—Multichip Master/Slave Application
ADV202
_1_MASTER
IRQ
ADV202
HDATA[31:0]
ADDR[3:0]
CS
RD
WE
ACK
IRQ
DREQ
DACK
SCOMM[5]
VDATA[11:2]
HSYNC
HSYNC
VSYNC
VDATA[11:2]
In a slave/slave configuration, the common HVF for both
ADV202s is generated by an external house sync, and each
SCOMM[5] is connected to the same GPIO output on the host.
SWIRQ1, Software Interrupt 1 in the EIRQIE register, must be
unmasked on both devices to enable multichip mode.
74.25MHz
OSC
VCLK
MCLK
YY
FIELD
VSYNC
VCLK
MCLK
FIELD
CbCr
CbCr
10-BIT SD/ HD
VIDEO
ENCODER
CLKIN
Y[9:0]
C[9:0]
1080i
IDEO OUT
04723-003
DIGITAL STILL CAMERA/CAMCORDER
Figure 26 is a typical configuration for a digital camera or camcorder.
AD9843A FPGA
10
D[9:0]
SDATA SERIAL DATA
SCK SERIAL CLK
SL SERIAL EN
Figure 26. Digital Still Camera/Camcorder Encode Application for 10-Bit Pixel Data Using Raw Pixel Mode
DATA INPUTS[9:0]
Rev. C | Page 35 of 40
ADV202
MCLK
VCLK
VFRM
VRDY
VSTRB
VDATA[15:6]
DATA[15:0]HDATA[15:0]
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
IRQIRQ
16-BIT
HOST CPU
04723-004

ADV202
V
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ENCODE/DECODE SDTV VIDEO APPLICATION
Figure 27 shows two ADV202 chips using 10-bit CCIR656 in normal host mode.
ENCODE MODE
32-BIT
HOST CPU
DECODE MODE
32-BIT
HOST CPU
HDATA[31:0]DAT A [31:0]
IRQINTR
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
HDATA[31:0]DAT A [31:0]
IRQINTR
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
ADV202
ADV202
VCLK
MCLK
MCLK
27MHz
OSC
P[19:10]VDATA[11:2]
LLC1
P[9:0]VDATA[11:2]
CLKINVCLK
10-BIT
VIDEO
DECODER
10-BIT
VIDEO
ENCODER
VIDEO IN
IDEO OUT
04723-005
Figure 27. Encode/Decode—SDTV Video Application
Rev. C | Page 36 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ASIC APPLICATION (32-BIT HOST/32-BIT ASIC)
Figure 28 shows two ADV202 chips using 10-bit CCIR656 in normal host mode.
ASIC
32-BIT
HOST CPU
DATA[31:0]
ASIC
31 -BIT
HOST CPU
DATA[31:0]
DREQ0DREQ0
DACK0DACK0
HDATA[31:0]DAT A[31:0]
IRQIRQ
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
DREQ0DREQ0
DACK0DACK0
HDATA[31:0]DAT A[31:0]
IRQIRQ
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
ADV202
VDATA[11:2]
ADV202
VCLK
MCLK
MCLK
27MHz
OSC
P[19:10]
LLC1
P[9:0]VDATA[11:2]
CLKINVCLK
10-BIT
VIDEO
DECODER
10-BIT
VIDEO
ENCODER
VIDEO IN
ENCODE MODE
VIDEO OUT
DECODE MODE
04723-006
Figure 28. Encode/Decode ASIC Application
Rev. C | Page 37 of 40

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
HIPI (HOST INTERFACE—PIXEL INTERFACE)
Figure 29 is a typical configuration using HIPI mode.
32-BIT HOS T
DATA [31:0]
CS
RD RD
WR WE
ACK ACK
IRQ IRQ
DREQ DREQ0
DACK DACK0
DREQ DREQ1
DACK DACK1
Figure 29. Host Interface—Pixel Interface Mode
74.25MHz
HDATA<31>Y0/G0<MSB>
HDATA<30>Y0/G0<6>
HDATA<29>Y0/G0<5>
HDATA<28>Y0/G0<4>
HDATA<27>Y0/G0<3>
HDATA<26>Y0/G0<2>
HDATA<25>Y0/G0<1>
HDATA<24>Y0/G0<0>
HDATA<23>Cb0/G1<MSB>
HDATA<22>Cb0/G1<6>
HDATA<21>Cb0/G1<5>
HDATA<20>Cb0/G1<4>
HDATA<19>Cb0/G1<3>
HDATA<18>Cb0/G1<2>
HDATA<17>Cb0/G1<1>
HDATA<16>Cb0/G1<0>
HDATA<15>Y1/G2<MSB>
HDATA<14>Y1/G2<6>
HDATA<13>Y1/G2<5>
HDATA<12>Y1/G2<4>
HDATA<1 1>Y1/G2<3>
HDATA<10>Y1/G2<2>
HDATA<9>Y1/G2<1>
HDATA<8>Y1/G2<0>
HDATA<7>Cr0/G3<MSB>
HDATA<6>Cr0/G3<6>
HDATA<5>Cr0/G3<5>
HDATA<4>Cr0/G3<4>
HDATA<3>Cr0/G3<3>
HDATA<2>Cr0/G3<2>
HDATA<1>Cr0/G3<1>
HDATA<0>Cr0/G3<0>
CS
MCLK
RAW PIXEL
DATAPATH
COMPRESSED
DATAPATH
04723-007
JDATA INTERFACE
Figure 30 shows a typical configuration using JDATA with a dedicated JDATA output, 16-bit host, and 10-bit CCIR656.
ASIC
16-BIT
HOST CPU
ADV202
JDATA[7:0]
HOLD
VALID
HSYNC
HDATA[15:0]DATA[15:0]
IRQIRQ
ADDR[3:0]ADDR[3:0]
CSCS
RDRD
WEWE
ACKACK
Figure 30. JDATA Application
Rev. C | Page 38 of 40
VCLK
MCLK
YCrCb
P[19:10]VDATA[11:2]
FIELDFIELD
VSVSYNC
HS
LLC1
VIDEO IN
04723-008

ADV202
A
R
*
A
R
*
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
1 CORNE
INDEX AREA
63
5
4
DETAILA
SEATING
PLANE
1 CORNE
INDEX AREA
9
5
BOTTOM VIEW
SEATING
PLANE
4
21
321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
*
1.31
1.21
1.11
0.20 NOM
COPLANARITY
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
*
1.32
1.21
1.11
COPLANARITY
0.20 MAX
021506-A
1.85
1.71
1.40
1.85
MAX
12.20
12.00 SQ
11.80
BALL A1
INDICATOR
TOP VIEW
DETAIL A
*
COMPLIANT WITH JEDEC S T ANDARDS MO-192-ABD-1 WITH
EXCEPTIO N TO PACKAGE HEI GHT AND THICKNESS.
10.00
BSC SQ
0.50 NOM
0.30 MIN
9
1087
11
1.00 BSC
BOTTOM VIEW
0.70
0.60
0.50
BALL DIAMETE R
Figure 31. 121-Lead Chip Scale Package Ball Grid Array [CSPBGA]
(BC-12
1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
13 .00
BSC SQ
BALL A1
INDICATOR
TOP VIEW
DETAIL A
BCS SQ
1.00 BSC
0.53
0.43
121110 876
11.00
0.70
0.60
0.50
BALL DIAMET E R
DETAILA
*
COMPLIANT WITH JEDEC S T ANDARDS M O-192-AAD-1 WI T H
EXCEPTIO N TO PACKAGE HEI GHT AND THICKNESS.
Figure 32. 144-Lead Chip Scale Package Ball Grid Array [CSPBGA]
Dimensions shown in millimeters
Rev. C | Page 39 of 40
(BC-14
4-3)
021506-A

ADV202
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature
Range
ADV202BBC-115 −40°C to +85°C 115 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 121-Lead CSPBGA BC-121
ADV202BBCZ-115 −40°C to +85°C 115 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 121-Lead CSPBGA BC-121
ADV202BBCZRL-115 −40°C to +85°C 115 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 121-Lead CSPBGA BC-121
ADV202BBC-135 −40°C to +85°C 135 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 144-Lead CSPBGA BC-144-3
ADV202BBCZ-135 −40°C to +85°C 135 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 144-Lead CSPBGA
ADV202BBC-150 −40°C to +85°C 150 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 144-Lead CSPBGA BC-144-3
ADV202BBCZ-150 −40°C to +85°C 150 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 144-Lead CSPBGA
ADV202BBCZRL-150 −40°C to +85°C 150 MHz 1.5 V Internal, 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O 144-Lead CSPBGA BC-144-3
ADV202-HD-EB High Definition Evaluation Board
ADV202-ASD-P160-EB Standard Definition Evaluation Board
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
1
1
1
1
Speed
Grade
Package
Option Model Operating Voltage Package Description
BC-144-3
BC-144-3
©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D04723-0-11/06(C)
Rev. C | Page 40 of 40
 Loading...
Loading...