ANALOG DEVICES ADSP-2106x Service Manual

ADSP-2106x SHARC® Processor
User’s Manual
Analog Devices, Inc.
One Technology Way
Norwood, Mass. 02062-9106
Revision 2.1, March 2004
Part Number
82-000795-03
a

Copyright Information
© 2004 Analog Devices, Inc., ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. This
document may not be reproduced in any form without prior, express
written consent from Analog Devices, Inc.
Printed in the USA.
Disclaimer
Analog Devices, Inc. reserves the right to change this product without
prior notice. Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog
Devices for its use; nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of
third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by
implication or otherwise under the patent rights of Analog Devices, Inc.
Trademark and Service Mark Notice
The Analog Devices logo, EZ-ICE, EZ-LAB, SHARC, and the SHARC
logo are registered trademarks of Analog Devices, Inc.
All other brand and product names are trademarks or service marks of
their respective owners.
Errata Correction Notice
This revision is published to incorporate corrections to errata in the
Second Edition (May 1997). Please refer to Appendix H for more
information.

Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................1-1
1.2 ADSP-21000 FAMILY FEATURES & BENEFITS ................................................1-5
1.2.1 System-Level Enhancements ..........................................................................1-6
1.2.2 Why Floating-Point DSP? ................................................................................1-7
1.3 ADSP-2106X ARCHITECTURE...........................................................................1-8
1.3.1 Core Processor ................................................................................................ 1-8
1.3.1.1 Computation Units .......................................................................................1-8
1.3.1.2 Data Register File........................................................................................1-8
1.3.1.3 Program Sequencer & Data Address Generators .......................................1-9
1.3.1.4 Instruction Cache.......................................................................................1-10
1.3.1.5 Interrupts....................................................................................................1-10
1.3.1.6 Timer..........................................................................................................1-10
1.3.1.7 Core Processor Buses...............................................................................1-10
1.3.1.8 Internal Data Transfers..............................................................................1-11
1.3.1.9 Context Switching......................................................................................1-11
1.3.1.10 Instruction Set............................................................................................1-12
1.3.2 Dual-Ported Internal Memory.........................................................................1-12
1.3.3 External Memory & Peripherals Interface ......................................................1-13
1.3.4 Host Processor Interface ...............................................................................1-13
1.3.5 Multiprocessing ..............................................................................................1-14
1.3.6 I/O Processor .................................................................................................1-14
1.3.6.1 Serial Ports ................................................................................................1-14
1.3.6.2 Link Ports...................................................................................................1-15
1.3.6.3 DMA Controller ..........................................................................................1-15
1.3.6.4 Booting.......................................................................................................1-16
1.4 DEVELOPMENT TOOLS ...................................................................................1-16
1.5 MESH MULTIPROCESSING .............................................................................1-18
1.6 ADDITIONAL LITERATURE .............................................................................. 1-18
CHAPTER 2 COMPUTATION UNITS
2.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................2-1
2.2 IEEE FLOATING-POINT OPERATIONS .............................................................2-2
2.2.1 Extended Floating-Point Precision...................................................................2-3
2.2.2 Short Word Floating-Point Format ...................................................................2-3
2.2.3 Floating-Point Exceptions ................................................................................2-4
2.3 FIXED-POINT OPERATIONS .............................................................................. 2-4
2.4 ROUNDING..........................................................................................................2-4
iii

Contents
2.5 ALU ......................................................................................................................2-5
2.5.1 ALU Operation .................................................................................................2-6
2.5.2 ALU Operating Modes .....................................................................................2-6
2.5.2.1 Saturation Mode ..........................................................................................2-7
2.5.2.2 Floating-Point Rounding Modes ..................................................................2-7
2.5.2.3 Floating-Point Rounding Boundary.............................................................. 2-7
2.5.3 ALU Status Flags .............................................................................................2-7
2.5.3.1 ALU Zero Flag (AZ) .....................................................................................2-8
2.5.3.2 ALU Underflow Flag (AZ, AUS) ...................................................................2-8
2.5.3.3 ALU Negative Flag (AN) ..............................................................................2-8
2.5.3.4 ALU Overflow Flag (AV, AOS, AVS) ...........................................................2-8
2.5.3.5 ALU Fixed-Point Carry Flag (AC) ................................................................2-9
2.5.3.6 ALU Sign Flag (AS) .....................................................................................2-9
2.5.3.7 ALU Invalid Flag (AI) ...................................................................................2-9
2.5.3.8 ALU Floating-Point Flag (AF) ......................................................................2-9
2.5.3.9 Compare Accumulation....................................................................................2-9
2.5.4 ALU Instruction Summary ..............................................................................2-10
2.6 MULTIPLIER ......................................................................................................2-11
2.6.1 Multiplier Operation........................................................................................2-11
2.6.2 Fixed-Point Results........................................................................................2-12
2.6.2.1 MR Registers.............................................................................................2-12
2.6.3 Fixed-Point Operations ..................................................................................2-13
2.6.3.1 Clear MR Register .....................................................................................2-13
2.6.3.2 Round MR Register ...................................................................................2-14
2.6.3.3 Saturate MR Register On Overflow ...........................................................2-14
2.6.4 Floating-Point Operating Modes ....................................................................2-15
2.6.4.1 Floating-Point Rounding Modes ................................................................2-15
2.6.4.2 Floating-Point Rounding Boundary............................................................2-15
2.6.5 Multiplier Status Flags....................................................................................2-15
2.6.5.1 Multiplier Underflow Flag (MU) ..................................................................2-16
2.6.5.2 Multiplier Negative Flag (MN) ....................................................................2-17
2.6.5.3 Multiplier Overflow Flag (MV) ....................................................................2-17
2.6.5.4 Multiplier Invalid Flag (MI) .........................................................................2-17
2.6.6 Multiplier Instruction Summary.......................................................................2-18
2.7 SHIFTER............................................................................................................2-19
2.7.1 Shifter Operation............................................................................................2-19
2.7.2 Bit Field Deposit & Extract Instructions..........................................................2-20
2.7.3 Shifter Status Flags........................................................................................2-24
2.7.3.1 Shifter Zero Flag (SZ)................................................................................2-24
2.7.3.2 Shifter Overflow Flag (SV).........................................................................2-24
2.7.3.3 Shifter Sign Flag (SS)................................................................................2-24
2.7.4 Shifter Instruction Summary...........................................................................2-25
iv

Contents
2.8 MULTIFUNCTION COMPUTATIONS ................................................................2-26
2.9 REGISTER FILE ................................................................................................2-27
2.9.1 Alternate (Secondary) Registers....................................................................2-28
CHAPTER 3 PROGRAM SEQUENCING
3.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................3-1
3.1.1 Instruction Cycle ..............................................................................................3-2
3.1.2 Program Sequencer Architecture.....................................................................3-3
3.1.2.1 Program Sequencer Registers & System Registers....................................3-5
3.2 PROGRAM SEQUENCER OPERATIONS ..........................................................3-6
3.2.1 Sequential Instruction Flow..............................................................................3-6
3.2.2 Program Memory Data Accesses ....................................................................3-6
3.2.3 Branches..........................................................................................................3-6
3.2.4 Loops ...............................................................................................................3-6
3.3 CONDITIONAL INSTRUCTION EXECUTION .....................................................3-7
3.4 BRANCHES (CALL, JUMP, RTS, RTI) ................................................................3-9
3.4.1 Delayed & Nondelayed Branches ..................................................................3-10
3.4.2 PC Stack ........................................................................................................3-12
3.5 LOOPS (DO UNTIL)...........................................................................................3-13
3.5.1 Restrictions & Short Loops ............................................................................3-14
3.5.1.1 General Restrictions ..................................................................................3-14
3.5.1.2 Counter-Based Loops................................................................................3-15
3.5.1.3 Non-Counter-Based Loops........................................................................3-16
3.5.2 Loop Address Stack.......................................................................................3-18
3.5.3 Loop Counters And Stack ..............................................................................3-19
3.5.3.1 CURLCNTR...............................................................................................3-19
3.5.3.2 LCNTR.......................................................................................................3-20
3.6 INTERRUPTS ....................................................................................................3-21
3.6.1 Interrupt Latency ............................................................................................3-22
3.6.2 Interrupt Vector Table ....................................................................................3-24
3.6.3 Interrupt Latch Register (IRPTL)....................................................................3-26
3.6.4 Interrupt Priority..............................................................................................3-27
3.6.5 Interrupt Masking & Control ...........................................................................3-27
3.6.5.1 Interrupt Mask Register (IMASK)...............................................................3-27
3.6.5.2 Interrupt Nesting & IMASKP ......................................................................3-28
3.6.6 Status Stack Save & Restore.........................................................................3-29
3.6.7 Software Interrupts.........................................................................................3-29
3.6.8 Clearing The Current Interrupt For Reuse .....................................................3-30
3.6.9 External Interrupt Timing & Sensitivity ...........................................................3-31
v

Contents
3.6.9.1 Asynchronous External Interrupts .............................................................3-32
3.6.10 Multiprocessor Vector Interrupts (VIRPT) ......................................................3-32
3.7 TIMER ................................................................................................................3-33
3.7.1 Timer Enable/Disable.....................................................................................3-34
3.7.2 Timer Interrupts..............................................................................................3-35
3.7.3 Timer Registers..............................................................................................3-36
3.8 STACK FLAGS...................................................................................................3-36
3.9 IDLE & IDLE16...................................................................................................3-37
3.10 INSTRUCTION CACHE .....................................................................................3-38
3.10.1 Cache Architecture ........................................................................................3-38
3.10.2 Cache Efficiency ............................................................................................3-39
3.10.3 Cache Disable & Cache Freeze.....................................................................3-41
CHAPTER 4 DATA ADDRESSING
4.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................4-1
4.2 DAG REGISTERS................................................................................................4-1
4.2.1 Alternate DAG Registers..................................................................................4-3
4.3 DAG OPERATION ...............................................................................................4-4
4.3.1 Address Output & Modification ........................................................................4-4
4.3.1.1 DAG Modify Instructions..............................................................................4-5
4.3.1.2 Immediate Modifiers ....................................................................................4-6
4.3.2 Circular Buffer Addressing ...............................................................................4-6
4.3.2.1 Circular Buffer Operation.............................................................................4-7
4.3.2.2 Circular Buffer Registers .............................................................................4-8
4.3.2.3 Circular Buffer Overflow Interrupts ..............................................................4-8
4.3.3 Bit-Reversal ...................................................................................................4-10
4.3.3.1 Bit-Reverse Mode......................................................................................4-10
4.3.3.2 Bit-Reverse Instruction ..............................................................................4-10
4.4 DAG REGISTER TRANSFERS .........................................................................4-11
4.4.1 DAG Register Transfer Restrictions...............................................................4-12
CHAPTER 5 MEMORY
5.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................5-1
5.1.1 Dual Data Accesses.........................................................................................5-3
5.1.2 Instruction Cache & PM Bus Data Accesses ...................................................5-4
5.1.3 On-Chip Memory Buses & Address Generation ..............................................5-5
5.1.4 Bus Exchange (PX Registers) .........................................................................5-6
5.1.5 Memory Block Accesses & Conflicts................................................................5-8
vi

Contents
5.2 ADSP-2106X MEMORY MAP .............................................................................. 5-9
5.2.1 ADSP-21060 Internal Memory Space............................................................ 5-11
5.2.2 ADSP-21062 Internal Memory Space............................................................ 5-14
5.2.3 ADSP-21061 Internal Memory Space............................................................ 5-16
5.2.4 Porting Code from ADSP-21060 to ADSP-21062 or ADSP-21061................5-18
5.2.5 Multiprocessor Memory Space ......................................................................5-18
5.2.6 External Memory Space.................................................................................5-19
5.2.7 Memory Space Access Restrictions ..............................................................5-19
5.3 INTERNAL MEMORY ORGANIZATION & WORD SIZE ...................................5-20
5.3.1 32-Bit Words & 48-Bit Words .........................................................................5-20
5.3.2 Mixing 32-Bit & 48-Bit Words In One Memory Block .....................................5-23
5.3.3 Basic Examples Of Mixed 32-Bit & 48-Bit Words ..........................................5-24
5.3.4 16-Bit Short Words.........................................................................................5-27
5.3.5 Mixing 32-Bit & 48-Bit Words With Finer Granularity .....................................5-28
5.3.5.1 Low-Level Physical Mapping Of Memory Blocks.......................................5-29
5.3.5.2 Placement Restrictions For Mixed 32-Bit & 48-Bit Words .........................5-30
5.3.5.3 Shadow Write FIFO ................................................................................... 5-33
5.3.6 Configuring Memory For 32-Bit or 40-Bit Data...............................................5-34
5.4 EXTERNAL MEMORY INTERFACING..............................................................5-35
5.4.1 External Memory Banks.................................................................................5-38
5.4.2 Unbanked Memory.........................................................................................5-38
5.4.3 Boot Memory Select (BMS) ...........................................................................5-39
5.4.4 Wait States & Acknowledge...........................................................................5-39
5.4.4.1 WAIT Register ...........................................................................................5-40
5.4.4.2 Multiprocessor Memory Space Wait States & Acknowledge.....................5-44
5.4.5 DRAM Page Boundary Detection ..................................................................5-44
5.4.5.1 Suspend Bus Tristate (SBTS) ...................................................................5-47
5.4.5.2 Normal SBTS Operation: HBR Not Asserted ............................................5-47
5.5 EXTERNAL MEMORY ACCESS TIMING..........................................................5-48
5.5.1 External Memory............................................................................................5-48
5.5.1.1 External Memory Read – Bus Master........................................................5-48
5.5.1.2 External Memory Write – Bus Master........................................................5-49
5.5.2 Multiprocessor Memory..................................................................................5-50
CHAPTER 6 DMA
6.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................6-1
6.1.1 DMA Controller Features .................................................................................6-5
6.1.2 Setting Up DMA Transfers ...............................................................................6-6
6.2 DMA CONTROL REGISTERS .............................................................................6-7
vii

Contents
6.2.1 External Port DMA Control Registers ..............................................................6-9
6.2.2 Serial Port DMA Control.................................................................................6-14
6.2.3 Link Port DMA Control ...................................................................................6-15
6.2.4 Port Selection For Shared DMA Channels ....................................................6-17
6.2.5 DMA Channel Status Register (DMASTAT) ..................................................6-18
6.3 DMA CONTROLLER OPERATION....................................................................6-20
6.3.1 DMA Channel Parameter Registers...............................................................6-21
6.3.2 Internal Request & Grant ...............................................................................6-24
6.3.3 DMA Channel Prioritization............................................................................6-25
6.3.3.1 Rotating Priority For Ext. Port Channels....................................................6-26
6.3.4 DMA Chaining................................................................................................6-28
6.3.4.1 Transfer Control Blocks & Chain Loading .................................................6-30
6.3.4.2 Setting Up & Starting The Chain ...............................................................6-31
6.3.4.3 Chain Insertion ..........................................................................................6-32
6.3.5 DMA Interrupts...............................................................................................6-33
6.3.6 Starting & Stopping DMA Sequences ............................................................6-35
6.4 EXTERNAL PORT DMA ....................................................................................6-36
6.4.1 External Port FIFO Buffers (EPBx) ................................................................6-36
6.4.1.1 External Port DMA Data Packing ..............................................................6-36
6.4.1.2 Packing Status...........................................................................................6-38
6.4.2 Internal & External Address Generation ........................................................6-38
6.4.3 External Port DMA Modes .............................................................................6-38
6.4.3.1 Master Mode..............................................................................................6-40
6.4.3.2 Paced Master Mode ..................................................................................6-40
6.4.3.3 Slave Mode................................................................................................6-40
6.4.3.4 Handshake Mode ......................................................................................6-42
6.4.3.5 External Handshake Mode ........................................................................6-46
6.4.4 System Configurations For ADSP-2106x Interprocessor DMA......................6-47
6.4.5 DMA Hardware Interfacing.............................................................................6-47
6.5 DMA THROUGHPUT .........................................................................................6-48
6.6 TWO-DIMENSIONAL DMA ................................................................................6-52
6.6.1 2-D DMA Channel Organization ....................................................................6-52
6.6.2 2-D DMA Operation .......................................................................................6-53
viii
CHAPTER 7 MULTIPROCESSING
7.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................7-1
7.2 MULTIPROCESSING SYSTEM ARCHITECTURES ...........................................7-4
7.2.1 Data Flow Multiprocessing...............................................................................7-4
7.2.2 Cluster Multiprocessing.................................................................................... 7-5

Contents
7.2.2.1 Link Port Data Transfers In A Cluster..........................................................7-7
7.2.3 SIMD Multiprocessing ...................................................................................... 7-8
7.3 MULTIPROCESSOR BUS ARBITRATION ..........................................................7-9
7.3.1 Bus Arbitration Protocol .................................................................................7-10
7.3.2 Bus Arbitration Priority (RPBA) ......................................................................7-14
7.3.3 Bus Mastership Timeout ................................................................................7-15
7.3.4 Core Priority Access ......................................................................................7-16
7.3.5 Bus Synchronization After Reset ...................................................................7-19
7.4 SLAVE DIRECT READS & WRITES..................................................................7-21
7.4.1 Direct Writes ..................................................................................................7-22
7.4.1.1 Direct Write Latency ..................................................................................7-22
7.4.2 Direct Reads ..................................................................................................7-23
7.4.3 Broadcast Writes............................................................................................7-23
7.4.4 Shadow Write FIFO .......................................................................................7-25
7.5 DATA TRANSFERS THROUGH THE EPBX BUFFERS ...................................7-26
7.5.1 Single-Word Transfers ...................................................................................7-26
7.5.1.1 Interrupts For Single-Word Transfers ........................................................7-27
7.5.2 DMA Transfers...............................................................................................7-28
7.5.2.1 DMA Transfers To Internal Memory ..........................................................7-28
7.5.2.2 DMA Transfers To External Memory ......................................................... 7-29
7.6 BUS LOCK & SEMAPHORES ...........................................................................7-29
7.6.1 Example: Sharing A DMA Channel With Reflective Semaphores .................7-31
7.7 INTERPROCESSOR MESSAGES & VECTOR INTERRUPTS .........................7-32
7.7.1 Message Passing (MSGRx)..........................................................................7-32
7.7.2 Vector Interrupts (VIRPT) .............................................................................7-33
7.8 SYSTAT REGISTER STATUS BITS.................................................................. 7-34
CHAPTER 8 HOST INTERFACE
8.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................8-1
8.2 HOST PROCESSOR CONTROL OF THE ADSP-2106X ....................................8-5
8.2.1 Acquiring The Bus............................................................................................8-6
8.2.2 Asynchronous Transfers ..................................................................................8-8
8.2.2.1 Asynchronous Transfer Timing..................................................................8-10
8.2.3 Synchronous Transfers..................................................................................8-12
8.2.4 Host Interface Deadlock Resolution With SBTS ............................................8-13
8.3 SLAVE DIRECT READS & WRITES..................................................................8-13
8.3.1 Direct Writes ..................................................................................................8-14
8.3.1.1 Direct Write Latency ..................................................................................8-14
8.3.2 Direct Reads ..................................................................................................8-15
8.3.3 Broadcast Writes............................................................................................8-15
ix

Contents
8.3.4 Shadow Write FIFO .......................................................................................8-17
8.4 DATA TRANSFERS THROUGH THE EPBX BUFFERS ...................................8-18
8.4.1 Single-Word Transfers ...................................................................................8-18
8.4.1.1 Interrupts For Single-Word Transfers ........................................................8-19
8.4.2 DMA Transfers...............................................................................................8-20
8.4.2.1 DMA Transfers To Internal Memory ..........................................................8-20
8.4.2.2 DMA Transfers To External Memory .........................................................8-21
8.5 DATA PACKING.................................................................................................8-21
8.5.1 Packing Control Bits In SYSCON ..................................................................8-21
8.5.2 Data Bus Lines Used For Different Packing Modes.......................................8-25
8.5.3 32-Bit Data Packing .......................................................................................8-26
8.5.4 48-Bit Instruction Packing ..............................................................................8-28
8.6 SYSTAT REGISTER STATUS BITS..................................................................8-29
8.7 INTERPROCESSOR MESSAGES & VECTOR INTERRUPTS .........................8-31
8.7.1 Message Passing (MSGRx)..........................................................................8-32
8.7.2 Host Vector Interrupts (VIRPT) .....................................................................8-33
8.8 SYSTEM BUS INTERFACING...........................................................................8-34
8.8.1 Access To The ADSP-2106x Bus—Slave ADSP-2106x................................8-34
8.8.2 Access To The System Bus—Master ADSP-2106x ......................................8-36
8.8.2.1 Core Processor Access To System Bus....................................................8-36
8.8.2.2 Deadlock Resolution..................................................................................8-38
8.8.2.3 ADSP-2106x DMA Access To System Bus...............................................8-39
8.8.3 Multiprocessing With Local Memory ..............................................................8-40
8.8.4 ADSP-2106x To Microprocessor Interface ....................................................8-41
CHAPTER 9 LINK PORTS
9.1 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................................9-1
9.1.1 Link Port To Link Buffer Assignment................................................................9-3
9.1.2 Link Port DMA Channels..................................................................................9-4
9.1.3 Link Port Interrupts...........................................................................................9-5
9.1.4 Link Port Booting..............................................................................................9-5
9.2 LINK PORT CONTROL REGISTERS ..................................................................9-5
9.2.1 Link Buffer Control Register (LCTL).................................................................9-6
9.2.2 Link Common Control Register (LCOM) ..........................................................9-9
9.2.3 Link Assignment Register (LAR)....................................................................9-12
9.3 HANDSHAKE CONTROL SIGNALS..................................................................9-13
9.4 LINK BUFFERS..................................................................................................9-15
9.4.1 Core Processor Access To Link Buffers ........................................................9-16
9.4.2 Host Processor Access To Link Buffers.........................................................9-16
9.5 LINK PORT DMA CHANNELS...........................................................................9-16
x

Contents
9.5.1 DMA Chaining For Link Ports ........................................................................9-18
9.6 LINK PORT INTERRUPTS ................................................................................9-18
9.6.1 Link Port Interrupts With DMA Disabled ........................................................9-18
9.6.2 Link Port Interrupts With DMA Enabled .........................................................9-19
9.6.3 Link Port Service Request Interrupts (LSRQ) ................................................9-19
9.7 TRANSMISSION ERROR DETECTION ............................................................9-23
9.8 TOKEN PASSING ..............................................................................................9-23
9.9 LINK TRANSMISSION LINES............................................................................9-26
9.10 SYSTEM DESIGN EXAMPLE: LOCAL DRAM INTERFACE .............................9-27
9.11 PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES ...........................................................................9-28
9.11.1 Core-Driven Single-Word Transfers...............................................................9-28
9.11.2 DMA Transfers...............................................................................................9-28
CHAPTER 10 SERIAL PORTS
10.1 OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................10-1
10.1.1 SPORT Interrupts ..........................................................................................10-4
10.2 SPORT RESET ..................................................................................................10-4
10.3 SPORT CONTROL REGISTERS & DATA BUFFERS.......................................10-5
10.3.1 Register Writes & Effect Latency ...................................................................10-6
10.3.2 Transmit & Receive Data Buffers (TX, RX)....................................................10-7
10.3.2.1 Reading & Writing RX, TX .........................................................................10-8
10.3.3 Transmit & Receive Control Registers (STCTL, SRCTL) ..............................10-8
10.3.4 Clock & Frame Sync Frequencies (TDIV, RDIV) .........................................10-13
10.3.4.1 Maximum Clock Rate Restrictions...........................................................10-15
10.4 DATA WORD FORMATS.................................................................................10-16
10.4.1 Word Length ................................................................................................10-16
10.4.2 Endian Format ............................................................................................. 10-16
10.4.3 Data Packing & Unpacking ..........................................................................10-16
10.4.4 Data Type ....................................................................................................10-17
10.4.5 Companding.................................................................................................10-18
10.5 CLOCK SIGNAL OPTIONS..............................................................................10-19
10.5.1 Internal vs. External Clocks ......................................................................... 10-19
10.6 FRAME SYNC OPTIONS.................................................................................10-20
10.6.1 Framed vs. Unframed ..................................................................................10-20
10.6.2 Internal vs. External Frame Syncs ...............................................................10-21
10.6.3 Active Low vs. Active High Frame Syncs.....................................................10-22
10.6.4 Sampling Edge For Data & Frame Syncs ....................................................10-22
10.6.5 Early vs. Late Frame Syncs .........................................................................10-23
10.6.6 Data-Independent Transmit Frame Sync.....................................................10-24
10.7 MULTICHANNEL OPERATION .......................................................................10-25
xi

Contents
10.7.1 Frame Syncs In Multichannel Mode.............................................................10-26
10.7.2 Multichannel Control Bits In STCTL, SRCTL ...............................................10-27
10.7.2.1 Multichannel Enable ................................................................................10-27
10.7.2.2 Number Of Channels...............................................................................10-27
10.7.2.3 Current Channel Indicator .......................................................................10-27
10.7.2.4 Multichannel Frame Delay.......................................................................10-28
10.7.3 Channel Selection Registers........................................................................10-28
10.7.4 SPORT Receive Comparison Registers ......................................................10-29
10.8 TRANSFERRING DATA BETWEEN SPORTS AND MEMORY ......................10-31
10.8.1 DMA Block Transfers ...................................................................................10-32
10.8.1.1 SPORT DMA Channel Setup .................................................................. 10-33
10.8.1.2 SPORT DMA Parameter Registers .........................................................10-33
10.8.1.3 SPORT DMA Chaining ................................................................................ 10-35
10.8.2 Single-Word Transfers .................................................................................10-36
10.9 SPORT LOOPBACK ........................................................................................10-36
10.10 SPORT PIN DRIVER CONCERNS..................................................................10-37
10.11 SPORT PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES............................................................10-37
10.11.1 Single-Word Transfers Without Interrupts....................................................10-37
10.11.2 Single-Word Transfers With Interrupts.........................................................10-39
10.11.3 DMA Transfers With Interrupts ....................................................................10-41
CHAPTER 11 SYSTEM DESIGN
11.1 OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................11-1
11.2 ADSP-2106X PINS.............................................................................................11-1
11.2.1 Pin Definitions................................................................................................11-2
11.2.2 Pin States At Reset........................................................................................11-9
11.2.3 RESET & CLKIN ..........................................................................................11-10
11.2.3.1 Input Synchronization Delay ........................................................................11-11
11.2.4 Interrupt & Timer Pins ..................................................................................11-11
11.2.5 Flag Pins ......................................................................................................11-11
11.2.5.1 Flag Inputs ...................................................................................................11-12
11.2.5.2 Flag Outputs ................................................................................................11-13
11.2.6 JTAG Interface Pins.....................................................................................11-13
11.3 EZ-ICE EMULATOR.........................................................................................11-14
11.3.1 Target Board Connector For EZ-ICE Probe.................................................11-14
11.4 INPUT SIGNAL CONDITIONING.....................................................................11-17
11.4.1 Glitch Rejection Circuits...............................................................................11-17
11.4.2 Link Port Input Filter Circuits........................................................................11-17
11.4.3 RESET Input Hysteresis ..............................................................................11-18
11.5 HIGH FREQUENCY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS.........................................11-18
xii

Contents
11.5.1 Clock Specifications & Jitter.........................................................................11-19
11.5.2 Clock Distribution .........................................................................................11-19
11.5.3 Point-To-Point Connections .........................................................................11-21
11.5.4 Signal Integrity .............................................................................................11-22
11.5.5 Other Recommendations & Suggestions.....................................................11-24
11.5.6 Decoupling Capacitors & Ground Planes ....................................................11-25
11.5.7 Oscilloscope Probes ....................................................................................11-26
11.5.8 Recommended Reading ..............................................................................11-26
11.6 BOOTING.........................................................................................................11-27
11.6.1 Selecting The Booting Mode........................................................................11-27
11.6.2 EPROM Booting...........................................................................................11-29
11.6.2.1 Bootstrapping (256 Instructions) ..................................................................11-29
11.6.2.2 Loading The Remaining EPROM Data ........................................................11-31
11.6.2.3 Writing to BMS Memory Space....................................................................11-32
11.6.3 Host Booting ................................................................................................ 11-32
11.6.4 Link Port Booting..........................................................................................11-34
11.6.5 Multiprocessor Booting ................................................................................11-35
11.6.5.1 Multiprocessor Host Booting ........................................................................11-35
11.6.5.2 Multiprocessor EPROM Booting ..................................................................11-35
11.6.5.3 Multiprocessor Link Port Booting .................................................................11-37
11.6.5.4 Multiprocessor Booting From External Memory...........................................11-37
11.6.6 “No Boot” Mode............................................................................................11-37
11.6.7 Interrupt Vector Table Location....................................................................11-37
11.7 IMPORTANT PROGRAMMING REMINDERS.................................................11-38
11.7.1 Extra Cycle Conditions.................................................................................11-38
11.7.1.1 Nondelayed Branches.................................................................................. 11-38
11.7.1.2 Program Memory Data Access With Cache Miss ........................................11-38
11.7.1.3 Program Memory Data Access In Loops .....................................................11-39
11.7.1.4 One- & Two-Instruction Loops .....................................................................11-40
11.7.1.5 DAG Register Writes....................................................................................11-40
11.7.1.6 Wait States...................................................................................................11-40
11.7.2 Delayed Branch Restrictions........................................................................11-40
11.7.3 Circular Buffer Initialization ..........................................................................11-41
11.7.4 Disallowed DAG Register Transfers ............................................................11-41
11.7.5 Two Writes To Register File.........................................................................11-42
11.7.6 Computation Units ....................................................................................... 11-42
11.7.7 Memory Space Access Restrictions ............................................................ 11-42
11.7.8 Mixing 32-Bit & 48-Bit Words In A Memory Block........................................11-43
11.7.9 16-Bit Short Words.......................................................................................11-43
11.7.10 Dual Data Accesses.....................................................................................11-43
11.8 DATA DELAYS, LATENCIES, & THROUGHPUT............................................11-44
11.9 EXECUTION STALLS ......................................................................................11-44
xiii

Contents
APPENDIX A INSTRUCTION SET REFERENCE
A.1 OVERVIEW..........................................................................................................A-1
A.2 INSTRUCTION SET SUMMARY .........................................................................A-2
A.3 OPCODE NOTATION .........................................................................................A-8
A.4 UNIVERSAL REGISTER CODES .....................................................................A-12
GROUP I. COMPUTE AND MOVE INSTRUCTIONS.......................................A-15
÷
Compute / dreg
Compute ........................................................................................................A-17
Compute / ureg
Compute / dreg
Compute / ureg
Immediate shift / dreg
Compute / modify .......................................................................................... A-26
GROUP II. PROGRAM FLOW CONTROL .......................................................A-27
Direct jump|call ..............................................................................................A-28
Indirect jump|call / compute...........................................................................A-30
Indirect jump or compute / dreg
Return from subroutine|interrupt / compute...................................................A-34
Do until counter expired.................................................................................A-36
Do until ..........................................................................................................A-38
DM / dreg÷PM....................................................................A-16
÷
DM|PM , register modify.....................................................A-18
÷
DM|PM , immediate modify ................................................A-20
÷
ureg ....................................................................................A-22
÷
DM|PM......................................................................A-24
÷
DM.............................................................A-32
xiv
GROUP III. IMMEDIATE MOVE .......................................................................A-39
÷
DM|PM (direct addressing) .................................................................A-40
ureg
÷
DM|PM (indirect addressing) ..............................................................A-41
ureg
Immediate data ’ DM|PM ...............................................................................A-42
Immediate data ’ ureg....................................................................................A-43
GROUP IV. MISCELLANEOUS........................................................................A-45
System register bit manipulation ................................................................... A-46
I register modify / bit-reverse .........................................................................A-48
Push|Pop stacks /flush cache........................................................................A-50
nop.................................................................................................................A-51
idle .................................................................................................................A-52
idle16 .............................................................................................................A-53
cjump / rframe................................................................................................A-54

Contents
APPENDIX B COMPUTE OPERATION REFERENCE
B.1 OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................B–1
B.2 SINGLE-FUNCTION OPERATIONS...................................................................B–1
B.2.1 ALU Operations .............................................................................................. B–2
Rn = Rx + Ry..............................................................................................B–4
Rn = Rx – Ry..............................................................................................B–5
Rn = Rx + Ry + CI ......................................................................................B–6
Rn = Rx – Ry + CI – 1 ................................................................................B–7
Rn = (Rx + Ry)/2 ........................................................................................B–8
COMP(Rx, Ry) ...........................................................................................B–9
Rn = Rx + CI.............................................................................................B–10
Rn = Rx + CI – 1.......................................................................................B–11
Rn = Rx + 1 ..............................................................................................B–12
Rn = Rx – 1 ..............................................................................................B–13
Rn = –Rx ..................................................................................................B–14
Rn = ABS Rx ............................................................................................B–15
Rn = PASS Rx..........................................................................................B–16
Rn = Rx AND Ry ......................................................................................B–17
Rn = Rx OR Ry........................................................................................ B–18
Rn = Rx XOR Ry ......................................................................................B–19
Rn = NOT Rx............................................................................................B–20
Rn = MIN(Rx, Ry) .....................................................................................B–21
Rn = MAX(Rx, Ry)....................................................................................B–22
Rn = CLIP Rx BY Ry ................................................................................B–23
Fn = Fx + Fy .............................................................................................B–24
Fn = Fx – Fy .............................................................................................B–25
Fn = ABS (Fx + Fy) ..................................................................................B–26
Fn = ABS (Fx – Fy)...................................................................................B–27
Fn = (Fx + Fy)/2........................................................................................B–28
COMP(Fx, Fy) ..........................................................................................B–29
Fn = –Fx ...................................................................................................B–30
Fn = ABS Fx .............................................................................................B–31
Fn = PASS Fx...........................................................................................B–32
Fn = RND Fx ............................................................................................B–33
Fn = SCALB Fx BY Ry .............................................................................B–34
Rn = MANT Fx..........................................................................................B–35
Rn = LOGB Fx..........................................................................................B–36
Rn = FIX Fx BY Ry / Rn = FIX Fx.............................................................B–37
xv

Contents
Rn = TRUNC Fx BY Ry / Rn = TRUNC Fx...............................................B–37
Fn = FLOAT Rx BY Ry / Fn = FLOAT Rx.................................................B–38
Fn = RECIPS Fx.......................................................................................B–39
Fn = RSQRTS Fx .....................................................................................B–40
Fn = Fx COPYSIGN Fy ............................................................................B–41
Fn = MIN(Fx, Fy) ......................................................................................B–42
Fn = MAX(Fx, Fy).....................................................................................B–43
Fn = CLIP Fx BY Fy .................................................................................B–44
B.2.2 Multiplier Operations .....................................................................................B–45
Rn|MR = Rx
Rn|MR = MR + Rx
Rn|MR = MR – Rx
Rn|MR = SAT MR.....................................................................................B–50
Rn|MR = RND MR....................................................................................B–51
MR = 0......................................................................................................B–52
MR=Rn / Rn=MR......................................................................................B–52
Fn = Fx * Fy ..............................................................................................B–53
B.2.3 Shifter Operations .........................................................................................B–54
Rn = LSHIFT Rx BY Ry|<data8> .............................................................B–55
Rn = Rn OR LSHIFT Rx BY Ry|<data8>..................................................B–56
Rn = ASHIFT Rx BY Ry|<data8> .............................................................B–57
Rn = Rn OR ASHIFT Rx BY Ry|<data8> .................................................B–58
Rn = ROT Rx BY RY|<data8>..................................................................B–59
Rn = BCLR Rx BY Ry|<data8> ................................................................B–60
Rn = BSET Rx BY Ry|<data8>.................................................................B–61
Rn = BTGL Rx BY Ry|<data8>.................................................................B–62
BTST Rx BY Ry|<data8> .........................................................................B–63
Rn = FDEP Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6>........................................................B–64
Rn = Rn OR FDEP Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6>............................................B–65
Rn = FDEP Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6> (SE) ...............................................B–66
Rn = Rn OR FDEP Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6> (SE) ...................................B–67
Rn = FEXT Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6>........................................................B–68
Rn = FEXT Rx BY Ry|<bit6>:<len6> (SE)................................................B–69
Rn = EXP Rx ............................................................................................B–70
Rn = EXP Rx (EX) ....................................................................................B–71
Rn = LEFTZ Rx ........................................................................................B–72
Rn = LEFTO Rx........................................................................................B–73
Rn = FPACK Fx........................................................................................B–74
Fn = FUNPACK Rx ..................................................................................B–75
Ry.......................................................................................B–47
*
Ry.............................................................................B–48
*
Ry .............................................................................B–49
*
xvi

Contents
B.3 MULTIFUNCTION COMPUTATIONS ............................................................... B–76
Dual Add/Subtract (Fixed-Pt.)...................................................................B–77
Dual Add/Subtract (Floating-Pt) ...............................................................B–78
Parallel Multiplier & ALU (Fixed-Pt.).........................................................B–79
Parallel Multiplier & ALU (Floating-Pt.).....................................................B–80
Parallel Multiplier & Dual Add/Subtract.....................................................B–82
APPENDIX C NUMERIC FORMATS
C.1 OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................C-1
C.2 IEEE SINGLE-PRECISION FLOATING-POINT DATA FORMAT .......................C-1
C.3 EXTENDED PRECISION FLOATING-POINT FORMAT .....................................C-2
C.4 SHORT WORD FLOATING-POINT FORMAT ....................................................C-3
C.5 FIXED-POINT FORMATS ...................................................................................C-5
APPENDIX D JTAG TEST ACCESS PORT
D.1 OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................D-1
D.2 TEST ACCESS PORT.........................................................................................D-2
D.3 INSTRUCTION REGISTER................................................................................. D-3
D.4 BOUNDARY REGISTER .....................................................................................D-5
D.5 DEVICE IDENTIFICATION REGISTER ............................................................ D-13
D.6 BUILT-IN SELF-TEST OPERATION (BIST)......................................................D-13
D.7 PRIVATE INSTRUCTIONS ............................................................................... D-13
D.8 REFERENCES ..................................................................................................D-13
APPENDIX E CONTROL/STATUS REGISTERS
E.1 OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................E–1
E.2 SYSTEM REGISTERS (CORE PROCESSOR) ..................................................E–2
E.2.1 Effect Latency & Read Latency ......................................................................E–2
E.2.2 System Register Bit Operations......................................................................E–3
E.2.2.1 Bit Test Flag ...............................................................................................E–3
E.2.3 User-Defined Status Registers ....................................................................... E–3
E.3 IOP REGISTERS (I/O PROCESSOR) ................................................................E–4
E.3.1 IOP Registers Summary .................................................................................E–4
E.3.2 IOP Register Access Restrictions ...................................................................E–8
E.3.3 IOP Register Group Access Contention ......................................................... E–8
E.3.4 IOP Register Write Latencies .........................................................................E–9
xvii

Contents
APPENDIX H DOCUMENTATION ERRATA
E.4 MODE1 REGISTER ..........................................................................................E–14
E.5 MODE2 REGISTER ..........................................................................................E–16
E.6 ARITHMETIC STATUS (ASTAT) ......................................................................E–18
E.7 STICKY STATUS (STKY) .................................................................................E–20
E.8 INTERRUPT LATCH (IRPTL) & INTERRUPT MASK
(IMASK).............................................................................................................E–22
E.9 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION (SYSCON)..........................................................E–24
E.10 SYSTEM STATUS (SYSTAT) ...........................................................................E–30
E.11 EXTERNAL MEMORY WAIT STATE CONTROL
(WAIT)...............................................................................................................E–32
E.12 EXTERNAL PORT DMA CONTROL
(DMAC6-DMAC9) .............................................................................................E–34
E.13 DMA CHANNEL STATUS (DMASTAT) ...........................................................E–38
E.14 LINK BUFFER CONTROL (LCTL) ....................................................................E–41
E.15 LINK BUFFER COMMON CONTROL (LCOM).................................................E–43
E.16 LINK ASSIGNMENT REGISTER (LAR)............................................................E–46
E.17 LINK SERVICE REQUEST (LSRQ) ..................................................................E–47
E.18 SPORT TRANSMIT CONTROL
(STCTL0, STCTL1) ...........................................................................................E–49
E.19 SPORT RECEIVE CONTROL (SRCTL0, SRCTL1) .........................................E–51
E.20 SPORT DIVISORS (TDIV, RDIV) .....................................................................E–53
E.21 SYMBOL DEFINITIONS FILE (DEF21060.H)...................................................E–54
xviii
APPENDIX F INTERRUPT VECTOR TABLE
APPENDIX G SHARC GLOSSARY
INDEX
FIGURES
Figure 1.1 Super Harvard Architecture.....................................................................1-2
Figure 1.2 ADSP-2106x SHARC Block Diagram .....................................................1-3
Figure 1.3 ADSP-2106x System ..............................................................................1-4
Figure 1.4 System Design and Development Process...........................................1-17
Figure 2.1 Computation Units...................................................................................2-2
Figure 2.2 Multiplier Fixed-Point Result Placement ...............................................2-12
Figure 2.3 MR Transfer Formats ............................................................................2-13

Contents
Figure 2.4 Register File Fields For Shifter Instructions ..........................................2-20
Figure 2.5 Register File Fields For FDEP, FEXT Instructions................................2-20
Figure 2.6 Bit Field Deposit Instruction ..................................................................2-21
Figure 2.7 Bit Field Deposit Example .....................................................................2-22
Figure 2.8 Bit Field Extract Example ......................................................................2-23
Figure 2.9 Input Registers For Multifunction Computations (ALU & Multiplier) ......2-27
Figure 3.1 Program Flow Variations.........................................................................3-2
Figure 3.2 Pipelined Execution Cycles .....................................................................3-3
Figure 3.3 Program Sequencer Block Diagram........................................................3-4
Figure 3.4 Nondelayed Branches...........................................................................3-10
Figure 3.5 Delayed Branches .................................................................................3-11
Figure 3.6 Loop Operation .....................................................................................3-14
Figure 3.7 One-Instruction Counter-Based Loops..................................................3-16
Figure 3.8 Two-Instruction Counter-Based Loops..................................................3-17
Figure 3.9 Pushing The Loop Counter Stack For Nested Loops............................3-20
Figure 3.10 Interrupt Handling..................................................................................3-23
Figure 3.11 Timer Block Diagram.............................................................................3-33
Figure 3.12 TIMEXP Signal...................................................................................... 3-34
Figure 3.13 Timer Enable & Disable ........................................................................3-35
Figure 3.14 Timer Interrupt Timing........................................................................... 3-36
Figure 3.15 Instruction Cache Architecture ..............................................................3-39
Figure 3.16 Cache-Inefficient Code..........................................................................3-40
Figure 4.1 Data Address Generator Block Diagram.................................................4-2
Figure 4.2 Alternate DAG Registers.........................................................................4-3
Figure 4.3 Pre-Modify & Post-Modify Operations.....................................................4-5
Figure 4.4 Circular Data Buffers...............................................................................4-7
Figure 4.5 DAG Register Transfers........................................................................4-11
Figure 5.1 ADSP-2106x Block Diagram ...................................................................5-2
Figure 5.2 PX Register .............................................................................................5-6
Figure 5.3 PX Register Transfers.............................................................................5-7
Figure 5.4 Memory Addresses (E = external, M = Multiprocessor, S = Internal)......5-9
Figure 5.5 ADSP-2106x Memory Map ...................................................................5-10
Figure 5.6 ADSP-21060 Internal Memory Space ...................................................5-12
Figure 5.7a ADSP-21062 Internal Memory Space ...................................................5-15
Figure 5.7b ADSP-21061 Internal Memory Space ...................................................5-17
Figure 5.8 Memory Organization vs. Address (ADSP-21060)................................5-22
Figure 5.9a Memory Organization vs. Address (ADSP-21062)................................5-22
Figure 5.9b Memory Organization vs. Address (ADSP-21061)................................5-23
Figure 5.10 Basic Examples of Mixed Instructions & Data In A Memory Block .......5-25
xix

Contents
Figure 5.11 Short Word Addresses ..........................................................................5-28
Figure 5.12 Preprocessing of 16-Bit Short Word Addresses...................................5-29
Figure 5.13 48-Bit Words & 32-Bit Words Mixed In A Memory Block
(ADSP-21060).......................................................................................5-31
Figure 5.14 48-Bit Words & 32-Bit Words Mixed In A Memory Block
(ADSP-21062 or ADSP-21061).............................................................5-32
Figure 5.a External Port Data Alignment................................................................5-35
Figure 5.15 WAIT Register.......................................................................................5-42
Figure 5.16 Bus Idle Cycle, Hold Time Cycle, Page Idle Cycle...............................5-43
Figure 5.17 Example DRAM Interface......................................................................5-46
Figure 5.18 External Memory Access Timing...........................................................5-49
Figure 5.19 Multiprocessor Memory Access Timing ................................................5-51
Figure 6.1 ADSP-2106x Block Diagram ...................................................................6-2
Figure 6.2 DMA Data Paths & Control .....................................................................6-3
Figure 6.3 DMACx Registers....................................................................................6-9
Figure 6.4 DMA Address Generation .....................................................................6-24
Figure 6.5 Rotating Priority Example (ADSP-21060 & ADSP-21062)....................6-27
Figure 6.6 Chain Pointer Register & PCI Bit ..........................................................6-29
Figure 6.7 TCB Setup In Memory (For External Port DMA Channel).....................6-31
Figure 6.8 DMA Handshake Timing With Asynchronous Requests.......................6-45
DMAR
Figure 6.9
Figure 6.10 System Configurations For ADSP-2106x-To-ADSP-2106x DMA .........6-49
Figure 6.11 Example DMA Hardware Interface........................................................6-50
Figure 6.12 DMARx/DMAGx Timing ........................................................................6-51
x Delay After Enabling Handshake DMA....................................6-47
Figure 7.1 ADSP-2106x Multiprocessor System ......................................................7-2
Figure 7.2 Data Flow Multiprocessing ......................................................................7-4
Figure 7.3 Cluster Multiprocessing...........................................................................7-5
Figure 7.4 Two-Dimensional SIMD Mesh Multiprocessing.......................................7-8
Figure 7.5 Bus Arbitration Timing...........................................................................7-12
Figure 7.6 Bus Request & Read/Write Timing .......................................................7-13
Figure 7.7 Core Priority Access Timing..................................................................7-18
Figure 7.8 Broadcast Write Timing Example..........................................................7-24
Figure 7.9 SYSTAT Register..................................................................................7-35
Figure 8.1 External Port & Host Interface.................................................................8-2
Figure 8.2 Example Timing For Bus Acquisition ......................................................8-7
Figure 8.3 Example Timing For Host Read & Write Cycles ...................................8-11
Figure 8.4 SYSCON Register.................................................................................8-22
Figure 8.a External Port Data Alignment................................................................8-26
Figure 8.5 Example Timing For Host Interface Data Packing ................................8-27
xx

Contents
Figure 8.6 SYSTAT Register..................................................................................8-30
Figure 8.7 Basic System Bus Interface ..................................................................8-35
Figure 8.8 Bidirectional System Bus Interface........................................................8-37
Figure 8.9 ADSP-2106x Subsystems On A System Bus .......................................8-41
Figure 9.a Link Port Pin Connections.......................................................................9-2
Figure 9.b Link Port Communication Examples .......................................................9-3
Figure 9.1 Link Ports & Buffers ................................................................................9-4
Figure 9.2 LCTL Register .........................................................................................9-8
Figure 9.3 LCOM Register .....................................................................................9-11
Figure 9.4 LAR Register.........................................................................................9-13
Figure 9.5 Link Port Handshake Timing .................................................................9-14
Figure 9.5a Logic For Link Port Interrupts................................................................9-20
Figure 9.6 LSRQ Register ...................................................................................... 9-22
Figure 9.7 Token Passing Flow Chart ....................................................................9-24
Figure 9.8 Local DRAM With Link Ports.................................................................9-27
Figure 10.1 Serial Port Block Diagram .....................................................................10-3
Figure 10.2 STCTL0, STCTL1 Transmit Control Registers....................................10-10
Figure 10.3 SRCTL0, SRCTL1 Receive Control Registers....................................10-12
Figure 10.4 TDIV0, TDIV1 Transmit Divisor Registers...........................................10-13
Figure 10.5 RDIV0, RDIV1 Receive Divisor Registers...........................................10-14
Figure 10.6 Framed vs. Unframed Data.................................................................10-21
Figure 10.7 Normal vs. Alternate Framing .............................................................10-24
Figure 10.8 Multichannel Operation .......................................................................10-26
Figure 11.1 Basic ADSP-2106x System...................................................................11-1
Figure 11.a External Port Data Alignment................................................................11-9
Figure 11.2 Flag Output Timing.............................................................................. 11-13
Figure 11.3 Target Board Connector For ADSP-2106x EZ-ICE Emulator
(Jumpers In Place) ..............................................................................11-15
Figure 11.4 JTAG Scan Path Connections For Multiprocessor
ADSP-2106x Systems.........................................................................11-16
Figure 11.5 Not Recommended Clock Distribution Method
(End-Of-Line Termination) ..................................................................11-20
Figure 11.6 Recommended Clock Distribution Method
(Source Termination) .......................................................................... 11-21
Figure 11.7 Source Termination For Long-Distance
Point-To-Point Connections ................................................................11-22
Figure 11.8 Star Connection Damping Resistors ...................................................11-23
Figure 11.9 Single Damping Resistor Between Processor Groups........................ 11-23
Figure 11.10 Single Transmission Line Terminated At Both Ends...........................11-24
Figure 11.11 Bypass Capacitor Placement ..............................................................11-25
xxi

Contents
Figure 11.12 Multiple SHARCs Booting From One EPROM,
Processors-Take-Turns.......................................................................11-36
Figure 11.13 Multiple SHARCs Booting From One EPROM,
One-Boots-Others ...............................................................................11-36
Figure A.1 Map 1 Universal Register Codes ..........................................................A-12
Figure A.2 Map 2 Universal Rgister Codes ............................................................A-13
Figure B.1 Allowed Input Registers For Multifunction Computations ..................... B-76
Figure C.1 IEEE 32-Bit Single-Precision Floating-Point Format ..............................C-1
Figure C.2 40-Bit Extended-Precision Floating-Point Format ...................................C-2
Figure C.3 16-Bit Floating-Point Format...................................................................C-3
Figure C.4 32-Bit Fixed-Point Formats.....................................................................C-6
Figure C.5 64-Bit Unsigned Fixed-Point Product .....................................................C-7
Figure C.6 64-Bit Signed Fixed-Point Product .........................................................C-8
Figure D.1 Serial Scan Paths ...................................................................................D-4
TABLES
Table 3.1 Program Sequencer Registers & System Registers ...............................3-5
Table 3.2 Condition & Loop Termination Codes .....................................................3-8
Table 3.3 Interrupt Vectors & Priority ....................................................................3-25
xxii
Table 5.1 ADSP-21060 Internal Memory Addresses ............................................5-13
Table 5.2a ADSP-21062 Internal Memory Addresses............................................5-14
Table 5.2b ADSP-21061 Internal Memory Addresses............................................5-16
Table 5.3 Address Ranges For Instructions & Data (ADSP-21060) .....................5-26
Table 5.4 Address Ranges For Instructions & Data (ADSP-21062) .....................5-26
Table 5.5 Starting Address for Contiguous 32-Bit Data (ADSP-21060)................5-30
Table 5.6 Starting Address for Contiguous 32-Bit Data
(ADSP-21062 or ADSP-21061).............................................................5-33
Table 5.7 External Memory Interface Signals .......................................................5-36
Table 5.8 WAIT Register Bit Definitions................................................................5-41
Table 6.1a ADSP-2106x DMA Channels & Data Buffers..........................................6-4
Table 6.1b ADSP-2106x DMA Channels & Data Buffers..........................................6-4
Table 6.2 DMA Control, Buffer, & Parameter Registers..........................................6-8
Table 6.3 External Port DMA Control Registers (DMACx)....................................6-10
Table 6.4 Serial Port DMA Channels ....................................................................6-14

Contents
Table 6.5 STCTLx/SRCTLx Control Bits For Serial Port DMA..............................6-14
Table 6.6 SPORT DMA Interrupts.........................................................................6-15
Table 6.7 Link Port DMA Channels.......................................................................6-15
Table 6.8 LCTL Control Bits For Link Port DMA ...................................................6-16
Table 6.9 Link Buffer DMA Interrupts....................................................................6-17
Table 6.10 DMASTAT Register...............................................................................6-19
Table 6.11 DMA Parameter Registers ....................................................................6-23
Table 6.12 Parameter Registers For Each DMA Channel ......................................6-23
Table 6.13 Internal Memory I/O Bus Access Priority ..............................................6-25
Table 6.14 TCB Chain Loading Sequence..............................................................6-30
Table 6.15 DMA Interrupt Vectors & Priority...........................................................6-33
Table 6.16 2-D Register Mapping ...........................................................................6-52
Table 7.1 Pin Connections For Cluster Multiprocessor System..............................7-1
Table 7.2 ADSP-2106x Multiprocessor Signals ......................................................7-9
Table 7.3 Rotating Priority Arbitration Example ....................................................7-14
Table 7.4 SYSTAT Status Bits ..............................................................................7-34
Table 8.1 Host Interface Signals .............................................................................8-3
Table 8.2 Address Bits To Be Driven During Asynchronous Host Accesses..........8-8
Table 8.3 SYSCON Control Bits For Host Interface Packing................................8-21
Table 8.4 Data Bus Lines Used For Different Host Packing Modes .....................8-25
Table 8.5 SYSTAT Status Bits ..............................................................................8-29
Table 9.1 Link Port Pins ..........................................................................................9-2
Table 9.2 Link Control Register (LCTL)...................................................................9-6
Table 9.3 Link Common Control Register (LCOM) .................................................9-9
Table 9.4 Link Assignment Register (LAR) ...........................................................9-12
Table 9.5 Link Service Request Register (LSRQ).................................................9-21
Table 10.1 Serial Port Pins .....................................................................................10-2
Table 10.2 SPORT Interrupts ..................................................................................10-4
Table 10.3 SPORT Register Addresses & Initialization ..........................................10-6
Table 10.4 STCTLx Transmit Control Register Bits................................................10-9
Table 10.5 SRCTLx Receive Control Register Bits...............................................10-11
Table 10.6 Transmit Divisor Register Bit Fields....................................................10-13
Table 10.7 Receive Divisor Register Bit Fields.....................................................10-13
Table 10.8 Parameter Registers For Each SPORT DMA Channel.......................10-34
Table 10.9 SPORT DMA Parameter Registers.....................................................10-35
Table 11.1 ADSP-2106x Pin States At RESET.......................................................11-9
Table 11.2 Boot Mode Selection Pins...................................................................11-28
xxiii

Contents
Table 11.3 DMA Channel 6 Parameter Register Initialization
For EPROM Booting ...........................................................................11-30
Table 11.4 Ext. Port DMA Channel 6 Parameter Register Initialization
For Host Booting .................................................................................11-33
Table 11.5 Data Delays & Throughputs................................................................11-46
Table 11.6 Latencies & Throughputs ....................................................................11-47
Table B.1 Fixed-Point ALU Operations ...................................................................B-2
Table B.2 Floating-Point ALU Operations ...............................................................B-3
Table B.3 Multiplier Operations.............................................................................B-45
Table B.4 Multiplier Mod2 Options ........................................................................B-46
Table B.5 Multiplier Mod1 Options ........................................................................B-46
Table B.6 Shifter Operations.................................................................................B-54
Table B.7 Parallel Multiplier/ALU Computations ...................................................B-81
Table C.1 IEEE Single-Precision Floating-Point Data Types ..................................C-2
Table D.1 Test Instructions .....................................................................................D-3
Table E.1 System Registers (Core Registers) ........................................................E-1
Table E.2 IOP Registers (I/.O Processor) ...............................................................E-1
Table E.3 IOP Registers (System Control) .............................................................E-5
Table E.4 IOP Registers (DMA) ..............................................................................E-6
Table E.5 IOP Registers (Link Ports) ......................................................................E-7
Table E.6 IOP Registers (Serial Ports) ...................................................................E-7
Table E.7 IOP Register Addresses, RESET Initialization, & Grouping .................E-11
xxiv
LISTINGS
Listing 9.1 Core-Driven Example............................................................................9-28
Listing 9.2 DMA Transfer Example.........................................................................9-39
Listing 9.3 Link Token Passing Example................................................................9-31
Listing 10.1 Non-Interrupt-Driven SPORT Control (Single-Word Transfers) ..........10-38
Listing 10.2 Interrupt-Driven SPORT Control (Single-Word Transfers)..................10-40
Listing 10.3 SPORT DMA Example........................................................................10-42

Introduction
1.1 OVERVIEW
The ADSP-2106x SHARC—Super Harvard Architecture Computer—is a
high-performance 32-bit digital signal processor for speech, sound, graphics,
and imaging applications. The SHARC builds on the ADSP-21000 Family
DSP core to form a complete system-on-a-chip, adding a dual-ported on-chip
SRAM and integrated I/O peripherals supported by a dedicated I/O bus.
With its on-chip instruction cache, the processor can execute every
instruction in a single cycle. Four independent buses for dual data,
instructions, and I/O, plus crossbar switch memory connections, comprise
the Super Harvard Architecture of the ADSP-2106x.
The ADSP-2106x SHARC represents a new standard of integration for digital
signal processors, combining a high-performance floating-point DSP core
with integrated, on-chip features including a host processor interface, DMA
controller, serial ports, and link port and shared bus connectivity for glueless
DSP multiprocessing.
1
Figure 1.1 illustrates the Super Harvard Architecture of the ADSP-2106x:
a crossbar bus switch connecting the core numeric processor to an
independent I/O processor, dual-ported memory, and parallel system bus
port. Figure 1.2 shows a detailed block diagram of the processor, illustrating
the following architectural features:
• 32-Bit IEEE Floating-Point Computation Units—Multiplier, ALU, and Shifter
• Data Register File
• Data Address Generators (DAG1, DAG2)
• Program Sequencer with Instruction Cache
• Interval Timer
• Dual-Ported SRAM
• External Port for Interfacing to Off-Chip Memory & Peripherals
• Host Port & Multiprocessor Interface
• DMA Controller
• Serial Ports
• Link Ports
• JTAG Test Access Port
1 – 1
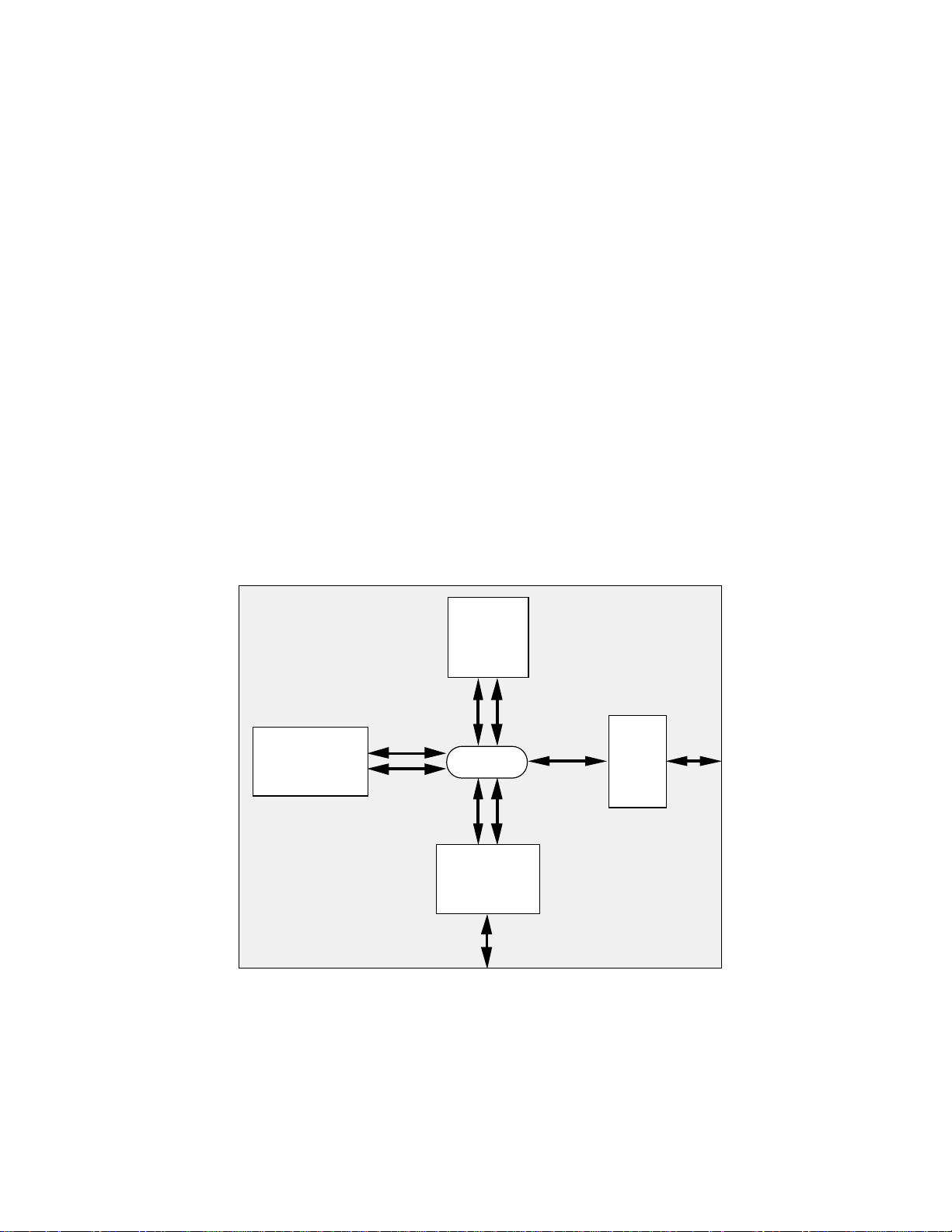
1
Introduction
Figure 1.2 also shows the three on-chip buses of the ADSP-2106x:
the PM bus (program memory), DM bus (data memory), and I/O bus.
The PM bus is used to access either instructions or data. During a
single cycle the processor can access two data operands, one over the
PM bus and one over the DM bus, an instruction (from the cache), and
perform a DMA transfer.
The ADSP-2106x’s external port provides the processor’s interface to
external memory, memory-mapped I/O, a host processor, and
additional multiprocessing ADSP-2106xs. The external port performs
internal and external bus arbitration as well as supplying control
signals to shared, global memory and I/O devices.
Figure 1.3 illustrates a typical single-processor system. A
multiprocessor system is shown in Chapter 7, Multiprocessing.
Dual-Ported,
Multi-Access
Memory
1 – 2
Numeric Processor
Figure 1.1 Super Harvard Architecture
Crossbar Bus
Interconnect
I/O Processor
&
DMA Controller
Parallel
System
Bus
Port
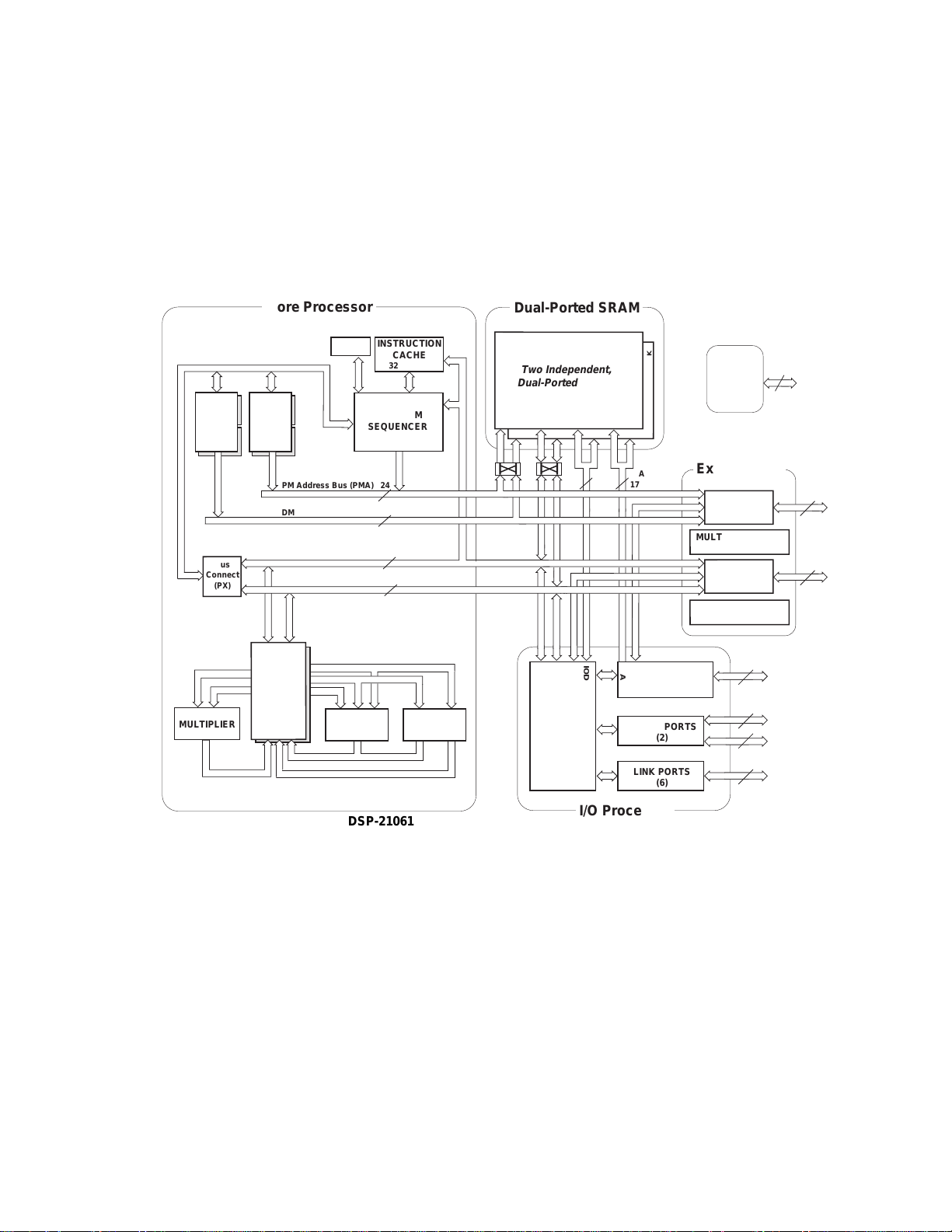
1Introduction
A
A
A
A
DAG1
8 x 4 x 32
Bus
Connect
(PX)
MULTIPLIER
Core Processor
DAG2
8 x 4 x 24
PM Address Bus (PMA) 24
DM Address Bus (DMA) 32
PM Data Bus (PMD)
DM Data Bus (DMD)
DATA
REGISTER
FILE
16 x 40-Bit
TIMER
BARREL
SHIFTER
INSTRUCTION
CACHE
32 x 48-Bit
PROGRAM
SEQUENCER
48
32/40
ALU
Dual-Ported SRAM
Two Independent,
Dual-Ported Blocks
PROCESSOR PORT I/O PORT
ADDR
DATA
DATA
IOD
48
PMD
DMD
EPD
IOD
AA
IOP
AA
REGISTERS
Control,
AA
Status, &
Data Buffers
AA
BLOCK 0
BLOCK 1
ADDR
IOA
17
EPA
IOA
CONTROLLER
SERIAL PORTS
(2)
LINK PORTS
*
(6)
Emulation
External Port
PMA
EPA
DMA
MULTIPROCESSOR
INTERFACE
PMD
EPD
DMD
HOST INTERFACE
DMA
JTAG
Test &
Addr
Bus
Mux
Data
Bus
Mux
7
32
48
4
6
6
36
* not available on the ADSP-21061
I/O Processor
Figure 1.2 ADSP-2106x SHARC Block Diagram
This user’s manual contains architectural information and an
instruction set description required for the design and programming of
ADSP-2106x-based systems. In addition to this manual, hardware
designers should refer to the ADSP-21060/62 Data Sheet and the
ADSP-21061 Data Sheet for timing, electrical, and package
specifications.
1 – 3
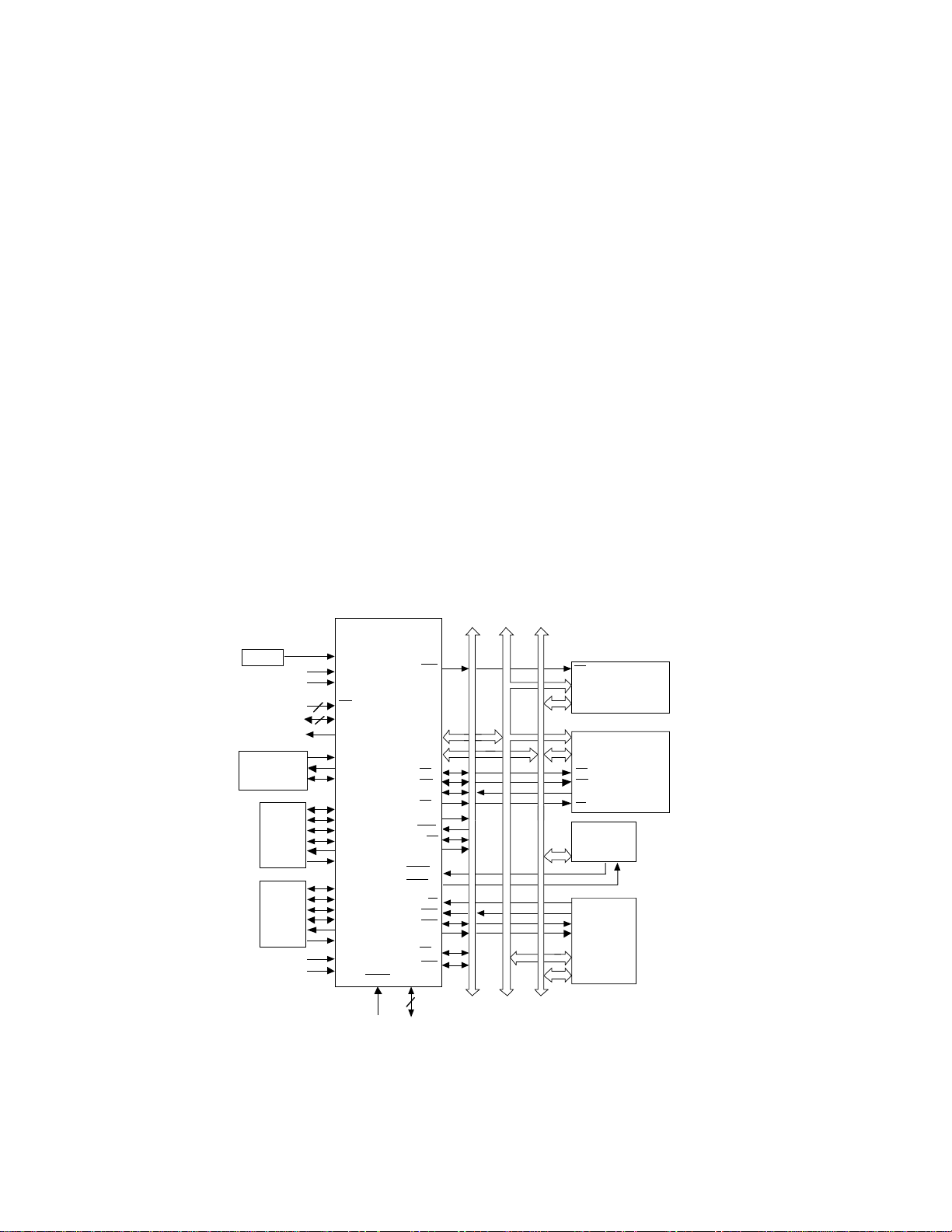
1
Introduction
This manual covers three ADSP-2106x processors: the ADSP-21060,
ADSP-21062, and ADSP-21061. The ADSP-21060 contains 4 megabits of onchip SRAM, the ADSP-21062 contains 2 megabits, and the ADSP-21061
contains 1 megabit. The Memory chapter of this manual describes the
differences in memory architecture and programming considerations of the
three processors. All three processors are code- and function-compatible
with the ADSP-21020 processor. With the exception of memory size, the
ADSP-21060 and ADSP-21062 are identical in all other aspects as well.
Besides memory size, there are four differences between these two
processors and the ADSP-21061:
• No link ports on the ADSP-21061
• 6 DMA channels — 4 for serial port and 2 for external port (instead of 4)
• Additional features and changes in DMA for the serial port
• New idle 16 instruction for a further reduced power mode
These differences are described in detail in the DMA, Serial Port, and
Program Sequencer chapters.
ADSP-2106x
1x CLOCK
LINK DEVICES
(6 Maximum)
(OPTIONAL)
SERIAL
DEVICE
(OPTIONAL)
SERIAL
DEVICE
(OPTIONAL)
CLKIN
EBOOT
LBOOT
3
IRQ
2-0
4
FLAG
3-0
TIMEXP
LxCLK
LxACK
LxDAT
3-0
TCLK0
RCLK0
TFS0
RFS0
DT0
DR0
TCLK1
RCLK1
TFS1
RFS1
DT1
DR1
RPBA
ID
2-0
RESET
ADDR
DATA
RD
WR
ACK
MS
PAGE
SBTS
ADRCLK
DMAR
DMAG
REDY
BR
JTAG
7
BMS
31-0
47-0
SW
1-2
1-2
CS
HBR
HBG
CPA
CS
BOOT
ADDR
EPROM
(OPTIONAL)
DATA
DATA
ADDR
DATA
MEMORY &
PERIPHERALS
OE
(OPTIONAL)
WE
ACK
CS
DMA DEVICE
(OPTIONAL)
DATA
HOST
PROCESSOR
INTERFACE
(OPTIONAL)
ADDR
DATA
ADDRESS
CONTROL
3-0
1-6
1 – 4
Figure 1.3 ADSP-2106x System

1.2 ADSP-21000 FAMILY FEATURES & BENEFITS
The ADSP-2106x SHARC processors belong to the ADSP-21000 Family of
floating-point digital signal processors (DSPs). The ADSP-21000
Family architecture further addresses the five central requirements for
DSPs established in the ADSP-2100 Family of 16-bit fixed-point DSPs:
• Fast, flexible arithmetic computation units
• Unconstrained data flow to and from the computation units
• Extended precision and dynamic range in the computation units
• Dual address generators
• Efficient program sequencing
Fast, Flexible Arithmetic. The ADSP-21000 Family processors execute
all instructions in a single cycle. They provide both fast cycle times and
a complete set of arithmetic operations including Seed 1/X, Seed 1/√
Min, Max, Clip, Shift, and Rotate, in addition to the traditional
multiplication, addition, subtraction, and combined multiplication/
addition. The processors are IEEE floating-point compatible and allow
either interrupt on arithmetic exception or latched status exception
handling.
Unconstrained Data Flow. The ADSP-2106x has an enhanced Harvard
architecture combined with a 10-port data register file. In every cycle:
X
,
1Introduction
• Two operands can be read or written to or from the register file,
• Two operands can be supplied to the ALU,
• Two operands can be supplied to the multiplier, and
• Two results can be received from the ALU and multiplier.
The processor’s 48-bit orthogonal instruction word supports fully
parallel data transfer and arithmetic operations in the same instruction.
40-Bit Extended Precision. The ADSP-21000 Family processors handle
32-bit IEEE floating-point format, 32-bit integer and fractional formats
(twos-complement and unsigned), and extended-precision 40-bit IEEE
floating-point format. The processors carry extended precision
throughout their computation units, limiting intermediate data
truncation errors. When working with data on-chip, the
extended-precision 32-bit mantissa can be transferred to and from all
computation units. The 40-bit data bus may be extended off-chip if
desired. The fixed-point formats have an 80-bit accumulator for true
32-bit fixed-point computations.
1 – 5

1
Introduction
Dual Address Generators. The ADSP-21000 Family processors have
two data address generators (DAGs) that provide immediate or
indirect (pre- and post-modify) addressing. Modulus and bit-reverse
operations are supported with no constraints on data buffer placement.
Efficient Program Sequencing. In addition to zero-overhead loops, the
ADSP-21000 Family processors support single-cycle setup and exit for
loops. Loops are both nestable (six levels in hardware) and
interruptable. The processors support both delayed and non-delayed
branches.
1.2.1 System-Level Enhancements
The ADSP-21000 Family processors include several enhancements that
simplify system development. The enhancements occur in three key
areas:
• Architectural features supporting high-level languages and operating
systems
• IEEE 1149.1 JTAG serial scan path and on-chip emulation features
• Support of IEEE floating-point formats
High Level Languages. The ADSP-21000 Family architecture has
several features that directly support high-level language compilers
and operating systems:
1 – 6
• General purpose data and address register files
• 32-bit native data types
• Large address space
• Pre- and post-modify addressing
• Unconstrained circular data buffer placement
• On-chip program, loop, and interrupt stacks
Additionally, the ADSP-21000 Family architecture is designed
specifically to support ANSI-standard Numerical C extensions—the
first compiled language to support vector data types and operators for
numeric and signal processing.
Serial Scan and Emulation Features. The ADSP-21000 Family
processors support the IEEE standard P1149.1 Joint Test Action Group
(JTAG) standard for system test. This standard defines a method for
serially scanning the I/O status of each component in a system. The
JTAG serial port is also used by the ADSP-2106x EZ-ICE to gain access
to the processor’s on-chip emulation features.
 Loading...
Loading...