High Performance
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
Low power, zero-IF RF transceiver
Frequency bands
431 MHz to 464 MHz
862 MHz to 870 MHz
902 MHz to 928 MHz
Data rates supported
9.6 kbps to 384 kbps, FSK
2.3 V to 3.6 V power supply
Programmable output power
−16 dBm to +13 dBm in 63 steps
Receiver sensitivity
−104.2 dBm at 38.4 kbps, FSK
−100 dBm at 172.8 kbps, FSK
−95.8 dBm at 384 kbps, FSK
Low power consumption
19 mA in receive mode
28 mA in transmit mode (10 dBm output)
ISM Band Transceiver IC
ADF7025
On-chip VCO and Fractional-N PLL
On-chip, 7-bit ADC and temperature sensor
Digital RSSI
Integrated TRx switch
Leakage current < 1 µA in power-down mode
APPLICATIONS
Wireless audio/video
Remote control/security systems
Wireless metering
Keyless entry
Home automation
R
LNA
R
FIN
R
FINB
RFOUT
BIAS LDO(1:4)
LNA
GAIN
DIVIDERS/
MUXING
LP FILTER
VCO
VCOIN CPOUT
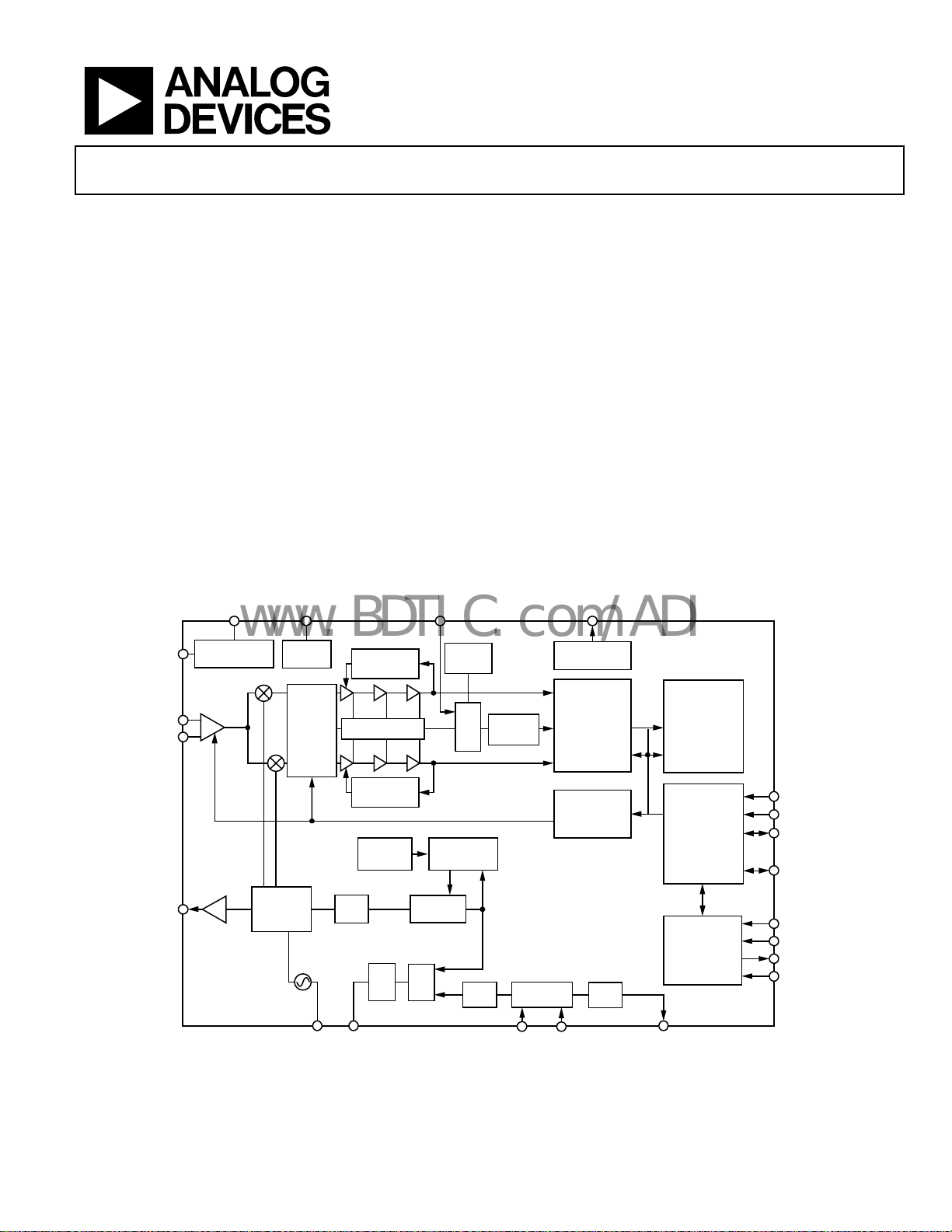
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DCINRSET CREG(1:4)
MODULATOR
N/N+1DIV P
PFD
TEMP
SENSOR
MUX
Σ-∆
DIV R
Figure 1.
7-BIT ADC
RING OSC
OSC1
DEMODUL ATOR
OSC2
OFFSET
CORRECTION
RSSI
OFFSET
CORRECTION
FSK MOD
CONTROL
CP
MUXOUT
TEST MUX
FSK
AGC
CONTROL
CLK
DIV
SYNCHRONIZER
CONTROL
CLKOUT
DATA
Tx/Rx
SERIAL
PORT
CE
DATA CLK
DATA I/O
INT/LOCK
SLE
SDATA
SREAD
SCLK
05542-001
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Automatic Sync Word Recognition ......................................... 22
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
General Description......................................................................... 3
Specifications..................................................................................... 4
Timing Characteristics..................................................................... 7
Timing Diagrams.......................................................................... 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 9
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 9
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 10
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 12
Frequency Synthesizer ................................................................... 15
Reference Input Section............................................................. 15
Choosing Channels for Best System Performance................. 17
Tr an sm it t er ...................................................................................... 18
Applications Section....................................................................... 23
LNA/PA Matching...................................................................... 23
Transmit Protocol and Coding Considerations ..................... 24
Device Programming after Initial Power-Up............................. 24
Interfacing to Microcontroller/DSP ........................................ 24
Serial Interface................................................................................ 27
Readback Format........................................................................ 27
Registers........................................................................................... 28
Register 0—N Register............................................................... 28
Register 1—Oscillator/Filter Register...................................... 29
Register 2—Transmit Modulation Register ............................ 30
Register 3—Receiver Clock Register ....................................... 31
Register 4—Demodulator Setup Register............................... 32
Register 5—Sync Byte Register................................................. 33
Register 6—Correlator/Demodulator Register ...................... 34
RF Output Stage.......................................................................... 18
Modulation Scheme ................................................................... 18
Receiver............................................................................................ 19
RF Front End............................................................................... 19
RSSI/AGC.................................................................................... 20
FSK Demodulators on the ADF7025....................................... 20
FSK Correlator/Demodulator................................................... 20
Linear FSK Demodulator.......................................................... 22
REVISION HISTORY
2/06—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Replaced Figure 40 ................................................................Page 29
1/06—Revision 0: Initial Version
Register 7—Readback Setup Register...................................... 35
Register 8—Power-Down Test Register .................................. 36
Register 9—AGC Register......................................................... 37
Register 10—AGC 2 Register.................................................... 38
Register 12—Test Register......................................................... 39
Register 13—Offset Removal and Signal Gain Register ....... 40
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 41
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 41
Rev. A | Page 2 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADF7025 is a low power, highly integrated FSK transceiver.
It is designed for operation in the license–free ISM bands of
433 MHz, 863 MHz to 870 MHz, and 902 MHz to 928 MHz.
The ADF7025 can be used for applications operating under the
European ETSI EN300-220 or the North American FCC (Part 15)
regulatory standards. The ADF7025 is intended for wideband,
high data rate applications with deviation frequencies from
100 kHz to 750 kHz and data rates from 9.6 kbps to 384 kbps.
A complete transceiver can be built using a small number of
external discrete components, making the ADF7025 very
suitable for price-sensitive and area-sensitive applications.
The transmit section contains a VCO and low noise
ractional-N PLL with output resolution of <1 ppm. The VCO
F
operates at twice the fundamental frequency to reduce spurious
emissions and frequency pulling problems.
The transmitter output power is programmable in 0.3 dB steps
f
rom −16 dBm to +13 dBm. The transceiver RF frequency, channel
spacing, and modulation are programmable using a simple 3-wire
interface. The device operates with a power supply range of 2.3 V
to 3.6 V and can be powered down when not in use.
A zero-IF architecture is used in the receiver, minimizing power
co
nsumption and the external component count, while avoiding
the need for image rejection. The baseband filter (low-pass) has
programmable bandwidths of ±300 kHz, ±450 kHz, and ±600 kHz.
A high-pass pole at ~60 kHz eliminates the problem of dc offsets
that is characteristic of zero-IF architecture.
The ADF7025 supports a wide variety of programmable
fe
atures, including Rx linearity, sensitivity, and filter bandwidth,
allowing the user to trade off receiver sensitivity and selectivity
against current consumption, depending on the application.
An on-chip ADC provides readback of an i
ture sensor, an external analog input, the battery voltage, or the
RSSI signal, which provides savings on an ADC in some
applications. The temperature sensor is accurate to ±10°C over
the full operating temperature range of −40°C to +85°C. This
accuracy can be improved by doing a 1-point calibration at
room temperature and storing the result in memory.
ntegrated tempera-
Rev. A | Page 3 of 44
ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = 2.3 V to 3.6 V, GND = 0 V, TA = T
All measurements are performed using the EVAL-ADF7025DB1 using PN9 data sequence, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
RF CHARACTERISTICS
Frequency Ranges (Direct Output) 862 870 MHz VCO adjust = 0, VCO bias = 10
902 928 VCO adjust = 3, VCO bias = 12
Frequency Ranges (Divide-by-2 Mode) 431 464 MHz See conditions for direct output
Phase Frequency Detector Frequency RF/256 24 MHz
TRANSMISSION PARAMETERS
Data Rate
FSK 9.6 384 kbps
FSK Frequency Deviation 100 311.89 kHz PFD = 10 MHz, direct output
100 748.54 kHz PFD = 24 MHz, direct output
100 374.27 kHz PFD =24MHz, divide-by-2 mode
Deviation Frequency Resolution 221 Hz PFD = 3.625 MHz
Gaussian Filter BT 0.5
Transmit Power1 −20 +13 dBm VDD = 3.0 V, TA = 25°C
Transmit Power Variation vs. Temperature ±1 dB From −40°C to +85°C
Transmit Power Variation vs. V
Transmit Power Flatness ±1 dB From 902 MHz to 928 MHz, 3 V, TA = 25°C
Programmable Step Size
−20 dBm to +13 dBm 0.3125 dB
Spurious Emissions
Integer Boundary −55 dBc 50 kHz loop B/W
Reference −65 dBc
Harmonics
Second Harmonic −27 dBc Unfiltered conductive
Third Harmonic −21 dBc
All Other Harmonics −35 dBc
VCO Frequency Pulling 30 kHz rms DR = 9.6 kbps
Optimum PA Load Impedance 39 + j61 Ω FRF = 915 MHz
48 + j54 Ω FRF = 868 MHz
54 + j94 Ω FRF = 433 MHz
RECEIVER PARAMETERS
FSK Input Sensitivity
Sensitivity at 38.4 kbps −104.2 dBm FDEV = 200 kHz, LPF B/W = ±300kHz
Sensitivity at 172.8 kbps −100 dBm FDEV = 200 kHz, LPF B/W = ±450kHz
Sensitivity at 384 kbps −95.8 dBm FDEV = 450kHz, LPF B/W = ±600kHz
Baseband Filter (Low-Pass) Bandwidths Programmable
±300 kHz
±450 kHz
±600 kHz
LNA and Mixer, Input IP3
Enhanced Linearity Mode +6.8 dBm
Low Current Mode −3.2 dBm
High Sensitivity Mode −35 dBm
Rx Spurious Emissions
−47 dBm >1 GHz at antenna input
DD
3
MIN
to T
, unless otherwise noted. Typical specifications are at VDD = 3 V, TA = 25°C.
MAX
±1 dB From 2.3 V to 3.6 V at 915 MHz, TA = 25°C
At BER = 1E − 3, FRF = 915 MHz,
LNA and P
Pin = −20 dBm, 2 CW interferers
FRF = 915 MHz, f1 = FRF + 3 MHz
F2 = FRF + 6 MHz, maximum gain
−57 dBm <1 GHz at antenna input
A matched separately
2
Rev. A | Page 4 of 44
ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
CHANNEL FILTERING
Adjacent Channel Rejection
27 dB
(Offset = ±1 × LP Filter BW Setting)
Second Adjacent Channel Rejection
40 dB
(Offset = ±2 × LP Filter BW Setting)
Third Adjacent Channel Rejection
43 dB
(Offset = ±3 × LP Filter BW Setting)
Co-Channel Rejection −2 +24 dB
Wideband Interference Rejection 70 dB
BLOCKING
±1 MHz
42
dB
±2 MHz 51 dB
±10 MHz 64 dB
Saturation (Maximum Input Level) 12 dBm FSK mode, BER = 10
LNA Input Impedance
24 − j60
26 − j63
71 − j128
Ω FRF = 915 MHz, RFIN to GND
Ω FRF = 868 MHz
Ω FRF = 433 MHz
RSSI
Range at Input
−100 to
dBm
−36
Linearity ±2 dB
Absolute Accuracy ±3 dB
Response Time 150 µs
PHASE-LOCKED LOOP
VCO Gain 65 MHz/V
83 MHz/V
Phase Noise (In-Band) −89 dBc/Hz
Phase Noise (Out-of-Band) −110 dBc/Hz 1 MHz offset
Residual FM 128 Hz From 200 Hz to 20 kHz, FRF = 868MHz
PLL Settling Time 40 µs
REFERENCE INPUT
Crystal Reference 3.625 24 MHz
External Oscillator 3.625 24 MHz
Load Capacitance 33 pF
Crystal Start-Up Time 1.0 ms Using 33 pF load capacitors
Input Level
CMOS
els
lev
TIMING INFORMATION
Chip Enabled to Regulator Ready 10 µs C
Crystal Oscillator Startup Time 1 ms With 19.2 MHz XTAL
Tx to Rx Turnaround Time
150 µs +
T
(5 ×
)
BIT
Desired signal (38.4 kbps DR, 200 kHz FDEV,
±300 KH
input sensitivity level, CW interferer power
level increased until BER = 10
z LP filter B/W) 6 dB above the
−3
Maximum rejection measured with CW
terferer at center of channel
in
Swept from 100 MHz to 2 GHz,
ed as channel rejection
measur
Desired signal (38.4 kbps DR, 200 kHz FDEV,
±300 KH
input sensitivity level, CW interferer power
level increased until BER = 10
z LP filter B/W) 6 dB above the
−3
−3
902 MHz to 928 MHz band,
O adjust = 3, VCO_BIAS_SETTING = 12
VC
862 MHz to 870 MHz band,
O adjust = 0, VCO_BIAS_SETTING = 10
VC
PA = 0 dB m , V
= 3.0 V, PFD = 10 MHz,
DD
FRF = 868 MHz, VCO_BIAS_SETTING = 10
Measured for a 10 MHz frequency step
hin 5 ppm accuracy,
to wit
PFD = 20 MHz, LBW = 50kHz
= 100 nF
REG
Time to synchronized data,
includes A
GC settling
Rev. A | Page 5 of 44
ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
Input Capacitance, C
INH
INL
INH/IINL
IN
Control Clock Input 50 MHz
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, V
Output Low Voltage, V
CLK
Rise/Fall 5 ns
OUT
CLK
Load 10 pF
OUT
OH
OL
TEMPERATURE RANGE, TA −40 +85 °C
POWER SUPPLIES
Voltage Supply
V
DD
Transmit Current Consumption
−20 dBm 14.6 mA
−10 dBm 15.8 mA
0 dBm 19.3 mA
10 dBm 28 mA
Receive Current Consumption
Low Current Mode 19 mA
High Sensitivity Mode 21 mA
Power-Down Mode
Low Power Sleep Mode
1
Measured as maximum unmodulated power. Output power varies with both supply and temperature.
2
Sensitivity for combined matching network case is typically 2 dB less than separate matching networks.
3
Follow the matching and layout guidelines in the LN section to achieve the relevant FCC/ETSI specifications. A/PA Matching
0.7 × V
V
DD
0.2 × VDDV
±1 µA
10 pF
DVDD − 0.4
V IOH = 500 µA
0.4 V IOL = 500 µA
2.3 3.6 V All VDD pins must be tied together
FRF = 915 MHz, V
= 3.0 V,
DD
PA is matched in to 50 Ω
0.1 1 µA
Rev. A | Page 6 of 44
ADF7025
S
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
VDD = 3 V ± 10%; VGND = 0 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
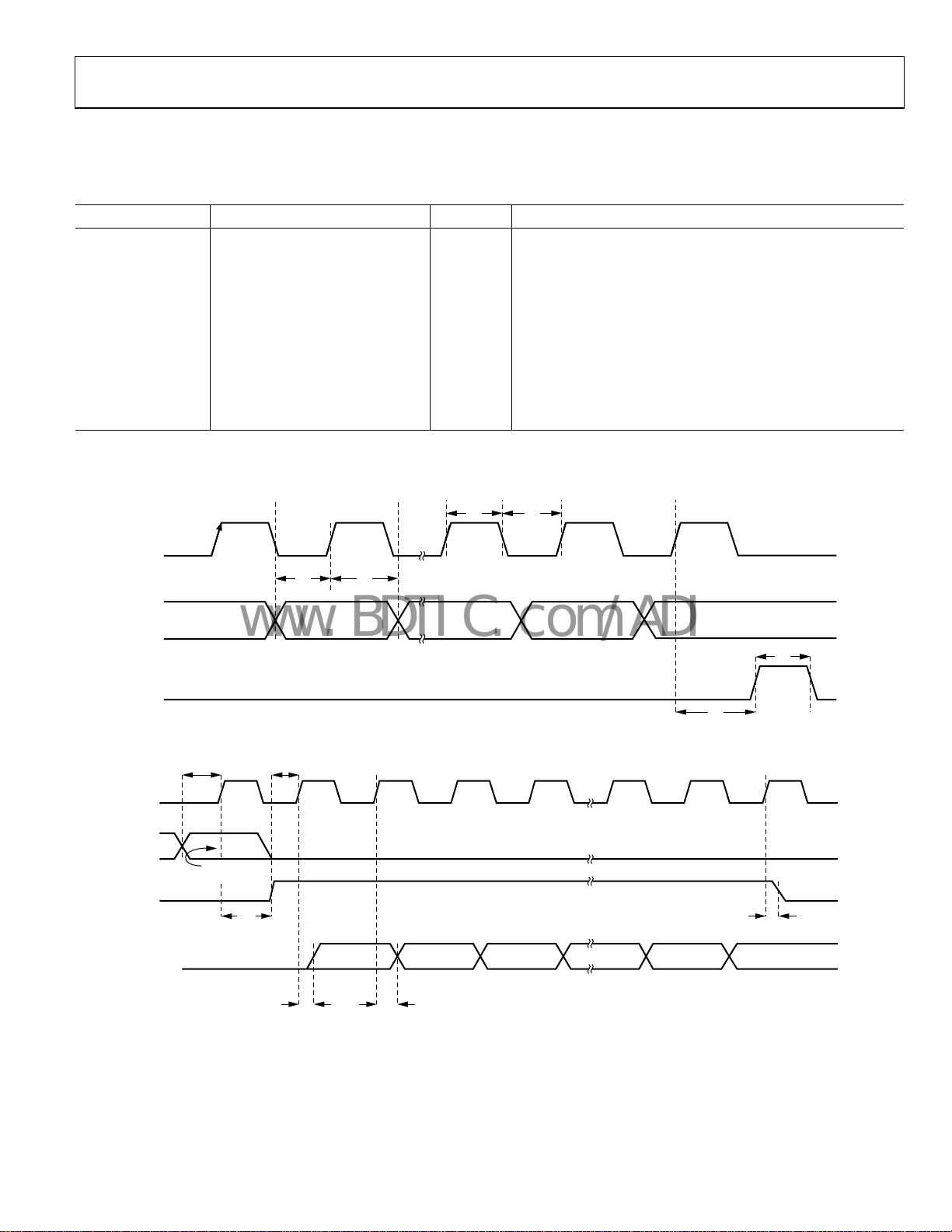
SCLK
1
Limit at T
MIN
to T
MAX
Unit Test Conditions/Comments
<10 ns SDATA to SCLK setup time
<25 ns SCLK to SREAD data valid, readback
<25 ns SREAD hold time after SCLK, readback
<10 ns SCLK to SLE disable time, readback
t
3
t
4
Parameter
t
1
t2 <10 ns SDATA to SCLK hold time
t3 <25 ns SCLK high duration
t4 <25 ns SCLK low duration
t5 <10 ns SCLK to SLE setup time
t6 <20 ns SLE pulse width
t
8
t
9
t
10
1
Guaranteed by design, not production tested.
TIMING DIAGRAMS
DATA
SLE
SCLK
SDATA
SLE
SREAD
t
1
DB31 (MSB) DB30 DB2
t
2
Figure 2. Serial Interface Timing Diagram
t
1
REG7 DB0
(CONTROL BIT C1)
t
2
t
3
X RV16 RV15 RV2 RV1
t
8
t
9
Figure 3. Readback Timing Diagram
DB1
(CONTROL BIT C2)
DB0 (LSB)
(CONTROL BIT C1)
t
5
t
10
t
6
05542-002
05542-003
Rev. A | Page 7 of 44
ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
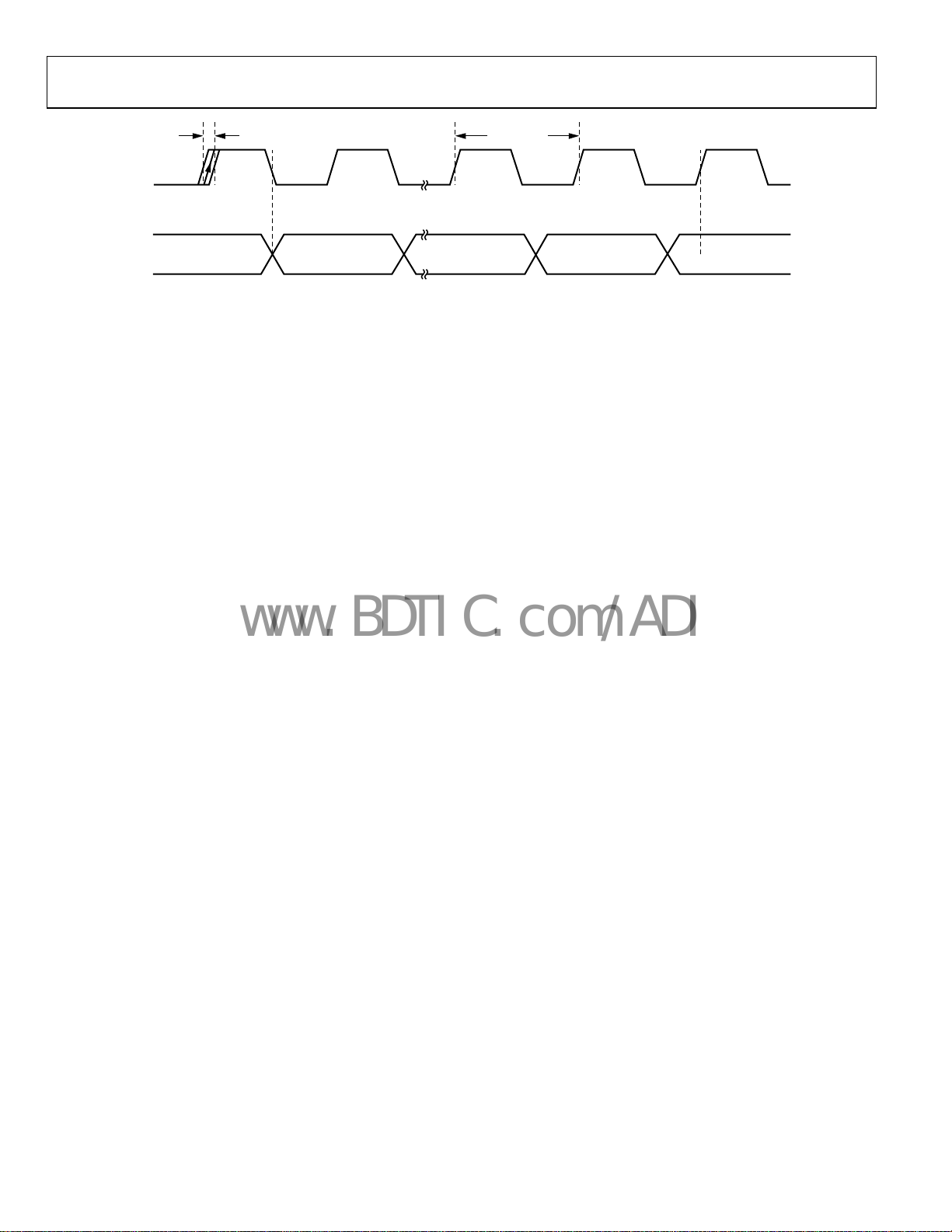
±1 × DATA RATE/32 1/DATA RATE
RxCLK
RxDATA
DATA
Figure 4. RxData/RxCLK Timing Diagram
05542-004
Rev. A | Page 8 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Rating
VDD to GND
Analog I/O Voltage to GND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Digital I/O Voltage to GND −0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (B Version) −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +125°C
Maximum Junction Temperature 125°C
MLF θJA Thermal Impedance
Lead Temperature Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) 235°C
Infrared (15 sec) 240°C
1
GND = CPGND = RFGND = DGND = AGND = 0 V.
1
−0.3 V to +5 V
26°C/W
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
This device is a high performance, RF integrated circuit with an
ESD rating of <2 kV, and it is ESD sensitive. Proper precautions
should be taken for handling and assembly.
Rev. A | Page 9 of 44
ADF7025
K
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
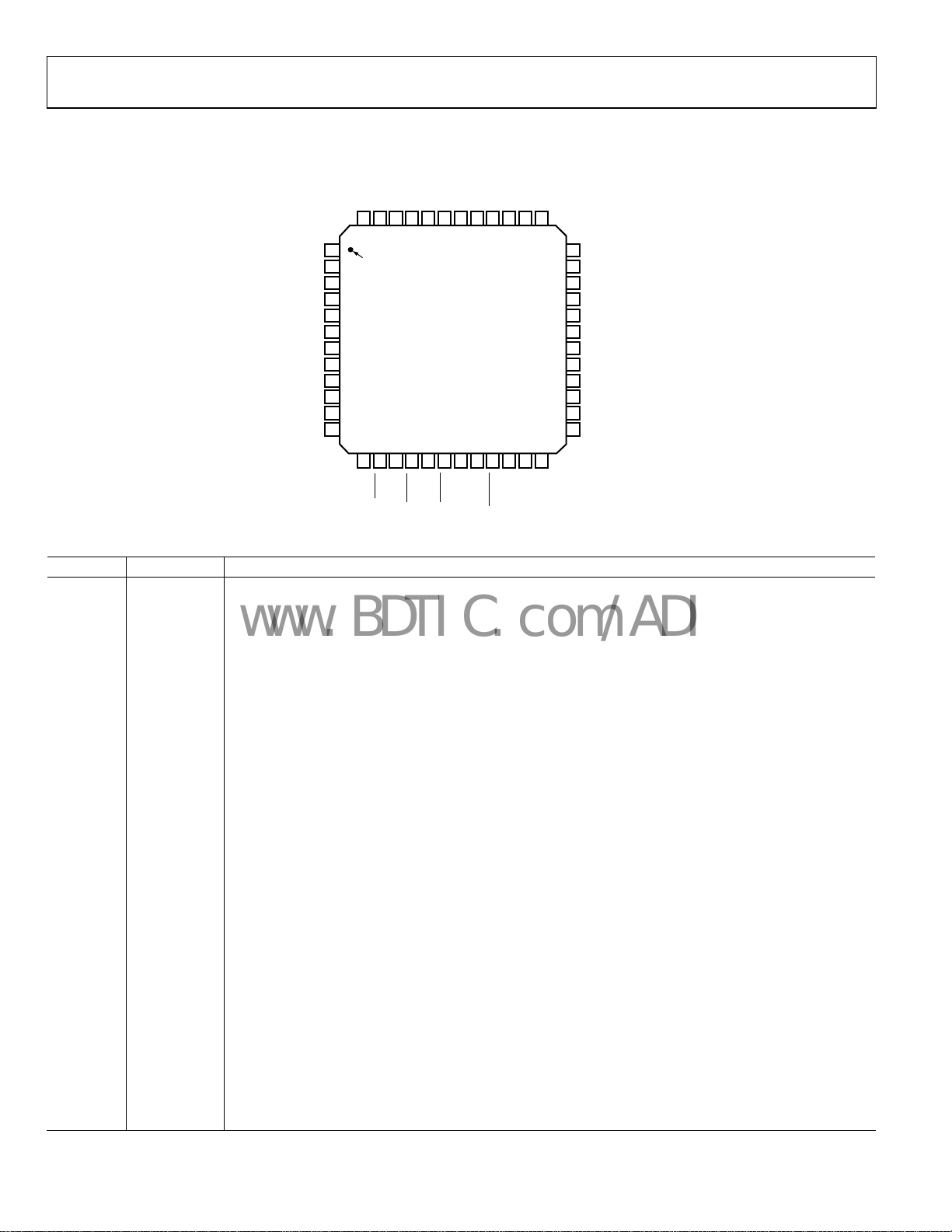
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
D
N
G
1
O
D
D
C
V
C
8
4
O
N
N
C
G
G
V
7
6
5
4
4
4
T
3
U
3
D
N
G
4
4
G
D
O
E
D
P
D
R
V
3
4
D
C
V
V
1
0
2
4
4
4
T
U
O
2
1
X
C
C
U
S
S
M
O
O
8
7
9
3
3
3
VCOIN
VREG1
VDD1
RFOUT
RFGND
RFIN
RFINB
R
LNA
VDD4
RSET
VREG4
GND4
1
PIN 1
INDICATO R
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
3
1
I
_
X
I
M
4
1
I
_
X
I
M
ADF7025
(Not to Sca le)
5
6
1
1
Q
Q
_
_
X
X
I
I
M
M
TOP VIEW
8
9
7
1
1
1
I
I
4
_
_
D
T
T
N
L
L
I
I
G
F
F
0
2
Q
_
T
L
I
F
3
1
2
2
2
2
4
A
Q
_
D
_
T
T
N
S
L
G
I
E
F
CLKOUT
36
DATA CL
35
DATA I/O
34
INT/LOCK
33
VDD2
32
VREG2
31
ADCIN
30
GND2
29
SCLK
28
SREAD
27
SDATA
26
SLE
25
4
2
E
C
5542-006
Figure 5. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 VCOIN
The tuning voltage on this pin determines the output frequency of the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO).
The higher the tuning voltage, the higher the output frequency.
2 VREG1
Regulator Voltage for PA Block. A 100 nF in parallel with a 5.1 pF capacitor should be placed between this pin
and ground for regulator stability and noise rejection.
3 VDD1
Voltage Supply for PA Block. Decoupling capacitors of 0.1 µF and 10 pF should be placed as close as possible
to this pin. All VDD pins should be tied together.
4 RFOUT
The modulated signal is available at this pin. Output power levels are from −20 dBm to +13 dBm. The output
should be impedance-matched to the desired load using suitable components. See the Transmitter section.
5 RFGND Ground for Output Stage of Transmitter.
6 RFIN
LNA Input for Receiver Section. Input matching is required between the antenna and the differential LNA
input to ensure maximum power transfer. See the LNA/PA Matching section.
7 RFINB Complementary LNA Input. See the LNA/PA Matching section.
8 R
External bias resistor for LNA. Optimum resistor is 1.1 kΩ with 5% tolerance.
LNA
9 VDD4 Voltage supply for LNA/MIXER Block. This pin should be decoupled to ground with a 10 nF capacitor.
10 RSET External Resistor to Set Charge Pump Current and Some Internal Bias Currents. Use 3.6 kΩ with 5% tolerance.
11 VREG4
Regulator Voltage for LNA/MIXER Block. A 100 nF capacitor should be placed between this pin and GND
for regulator stability and noise rejection.
12 GND4 Ground for LNA/MIXER Block.
13 to 18 MIX/FILT Signal Chain Test Pins. These pins are high impedance under normal conditions and should be left unconnected.
19, 22 GND4 Ground for LNA/MIXER Block.
20, 21, 23 FILT/TEST_A Signal Chain Test Pins. These pins are high impedance under normal conditions and should be left unconnected.
24 CE
Chip Enable. Bringing CE low puts the ADF7025 into complete power-down. Register values are lost
when CE is low, and the part must be reprogrammed once CE is brought high.
25 SLE
Load Enable, CMOS Input. When LE goes high, the data stored in the shift registers is loaded into one
of the four latches. A latch is selected using the control bits.
26 SDATA
Serial Data Input. The serial data is loaded MSB first with the two LSBs as the control bits. This pin is
a high impedance CMOS input.
27 SREAD
Serial Data Output. This pin is used to feed readback data from the ADF7025 to the microcontroller.
The SCLK input is used to clock each readback bit (ADC readback) from the SREAD pin.
28 SCLK
Serial Clock Input. This serial clock is used to clock in the serial data to the registers. The data is latched
into the 24-bit shift register on the CLK rising edge. This pin is a digital CMOS input.
Rev. A | Page 10 of 44
ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
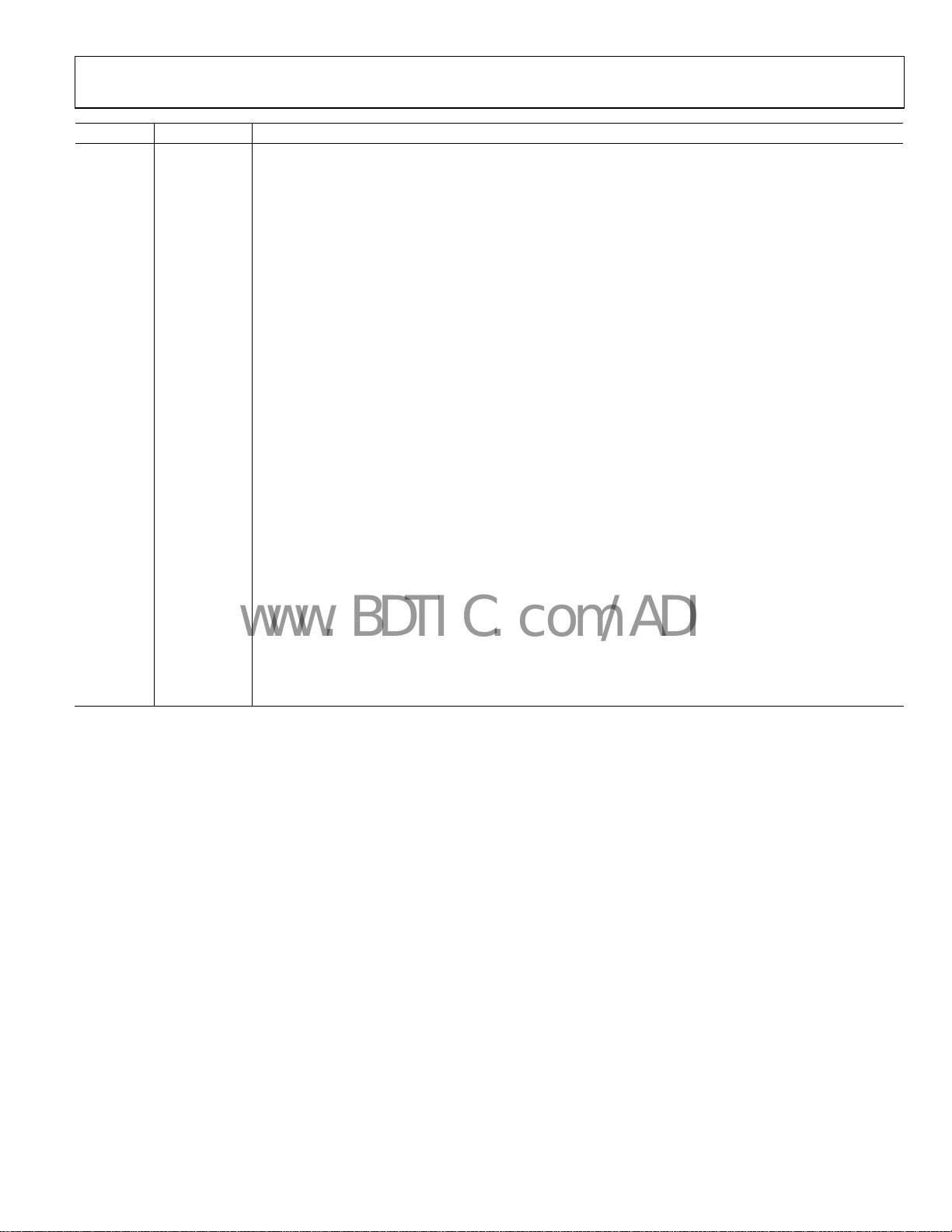
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
29 GND2 Ground for Digital Section.
30 ADCIN
31 VREG2
32 VDD2
33 INT/LOCK
34 DATA I/O Transmit Data Input/Received Data Output. This is a digital pin, and normal CMOS levels apply.
35 DATA CLK
36 CLKOUT
37 MUXOUT
38 OSC2
39 OSC1 The reference crystal should be connected between this pin and OSC2.
40 VDD3
41 VREG3
42 CPOUT
43 VDD Voltage Supply for VCO Tank Circuit. This pin should be decoupled to ground with a 0.01 µF capacitor.
44 to 47 GND Grounds for VCO Block.
48 CVCO A 22 nF capacitor should be placed between this pin and VREG1 to reduce VCO noise.
Analog-to-Digital Converter Input. The internal 7-bit ADC can be ac
Full scale is 0 V to 1.9 V. Readback is made using the SREAD pin.
Regulator Voltage for Digital Block. A 100 nF in paralle
between this pin and ground for regulator stability and noise rejection.
Voltage Supply for Digital Block. A decoupling capacitor of 10 nF should be placed as close as possible
his pin.
to t
Bidirectional Pin. In output mode (interrupt mod
it has found a match for the preamble sequence.
In input mode (lock mode), the microcontroller can be used to lock the demodulator threshold
when a valid
In this mode, a demodulator lock can be asserted with minimum delay.
In receive mode, the pin outputs the synchronized data clock
center of the received data.
A Divided-Down Version of the Crystal Reference with O
to drive several other CMOS inputs, such as a microcontroller clock. The output has a 50:50 mark-space ratio.
This pin provides the lock_detect signal, which is used t
frequency. Other signals include regulator_ready, which is an indicator of the status of the serial interface
regulator.
The reference crystal should be connected between this pin and OSC1. A TCXO reference can be used by
riving this pin with CMOS levels and disabling the crystal oscillator.
d
Voltage Supply for the Charge Pump and PLL Dividers
with a 0.01 µF capacitor.
Regulator Voltage for Charge Pump and PLL Dividers. A 100 nF in parallel with a 5.1 pF capacitor
should be pl
Charge Pump Output. This output generates current pul
The integrated current changes the control voltage on the input to the VCO.
preamble has been detected. Once the threshold is locked, NRZ data can be reliably received.
aced between this pin and ground for regulator stability and noise rejection.
l with a 5.1 pF capacitor should be placed
e), the ADF7025 asserts the INT/LOCK pin when
utput Driver. The digital clock output can be used
o determine if the PLL is locked to the correct
. This pin should be decoupled to ground
ses that are integrated in the loop filter.
cessed through this pin.
. The positive clock edge is matched to the
Rev. A | Page 11 of 44
ADF7025
A
m
G
A
R
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
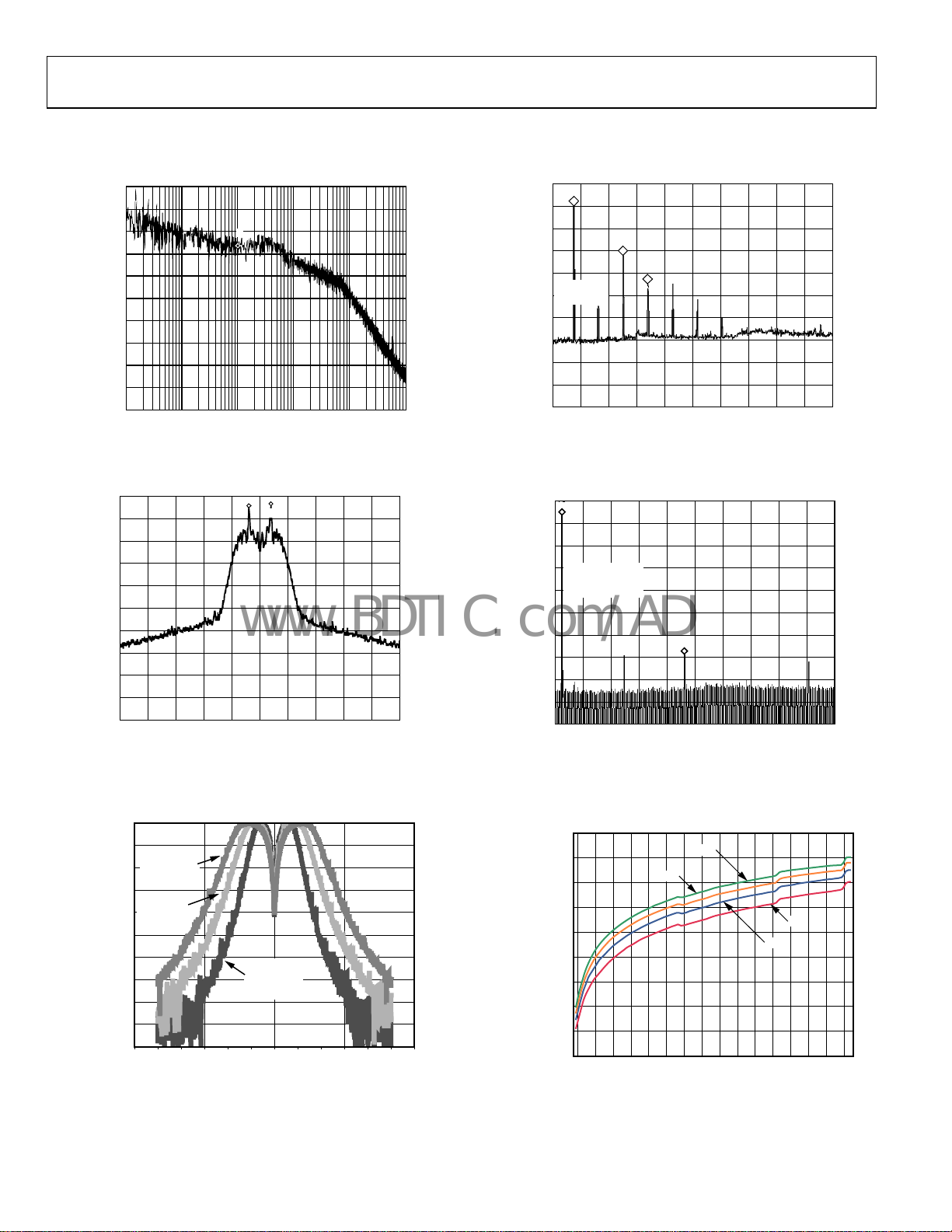
CARRIER POWER 6.11dBm
REF –60dBc/Hz 10.00dB/
ATTEN 2.00d B MKR1 10.00KHz
1
–88.46dBc/Hz
REF 10dB
PEAK
LO
10dB/
1
REF LEVEL
10.00dBm
ATTEN 20dB
3
4
MKR4 3.482GHz
SWEEP 16.52ms (601pts)
100Hz 10Hz
FREQUENCY OFFSET
05542-007
Figure 6. Phase Noise Response at 915 MHz, VDD = 3.0 V, ICP = 0.867 mA
REF 10dBm
NORM LO G 10d B/
CENTER 915.00MHz
#RES BW 10kHz
ATTEN 20dB
1R
1
VBW 10kHz S PAN 5MHz
SWEEP 60. 32ms (601pts)
MKR1 400Hz
0.69dB
05542-008
Figure 7. Output Spectrum in FSK Modulation (915 MHz,
172.8 kbps Data Rate, 200 kHz Frequency Deviation)
0
–5
±600KHz
–10
FILTER B/W
–15
±450KHz
–20
FILTER B/W
–25
TION LEVEL (dB)
–30
–35
ATTENU
–40
–45
–50
–1500 –1200 –600 –300 300 600 1200 1500
–1800 –900 0 900 1800
±300KHz
FILTER B/W
FREQUENCY (KHz)
Figure 8. Baseba nd Filter R esponse
START 100MHz
RES BW 3MHz
VBW 3MHz
STOP 10.000GHz
SWEEP 16.52ms (601pts)
05542-010
Figure 9. Harmonic Response, RFOUT Matched to 50 Ω, No Filter
REF 15dBm ATTEN 30d B
1R
NORM
LOG
10dB/
MARKER ∆
1.834000000GHz
–62.57dB
LgAv
W1S2
S3FC
AA
£(f):
FTun
Swp
START 800MHz
#RES BW 30kHz
1
VBW 30kHz
∆ Mkr1 1.834GHz
–62.57dB
STOP 5.000GHz
SWEEP 5.627s ( 601pts)
05542-011
Figure 10. Harmonic Response, Murata Dielectric Filter
20
11µA
9µA
PA SE T T I NG
5µA
7µA
05542-053
15
10
5
0
–5
OUTPUT POWE
–10
P
–15
–20
–25
05542-009
1 5 9 13172125293337414549535761
Figure 11. PA Output Power vs. Setting
Rev. A | Page 12 of 44
ADF7025
C
d
–
–
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
20
RSSI LEVEL (d B)
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
ACTUAL INPUT LEVEL
RSSI READBACK LEVE L
RF I/P (dB)
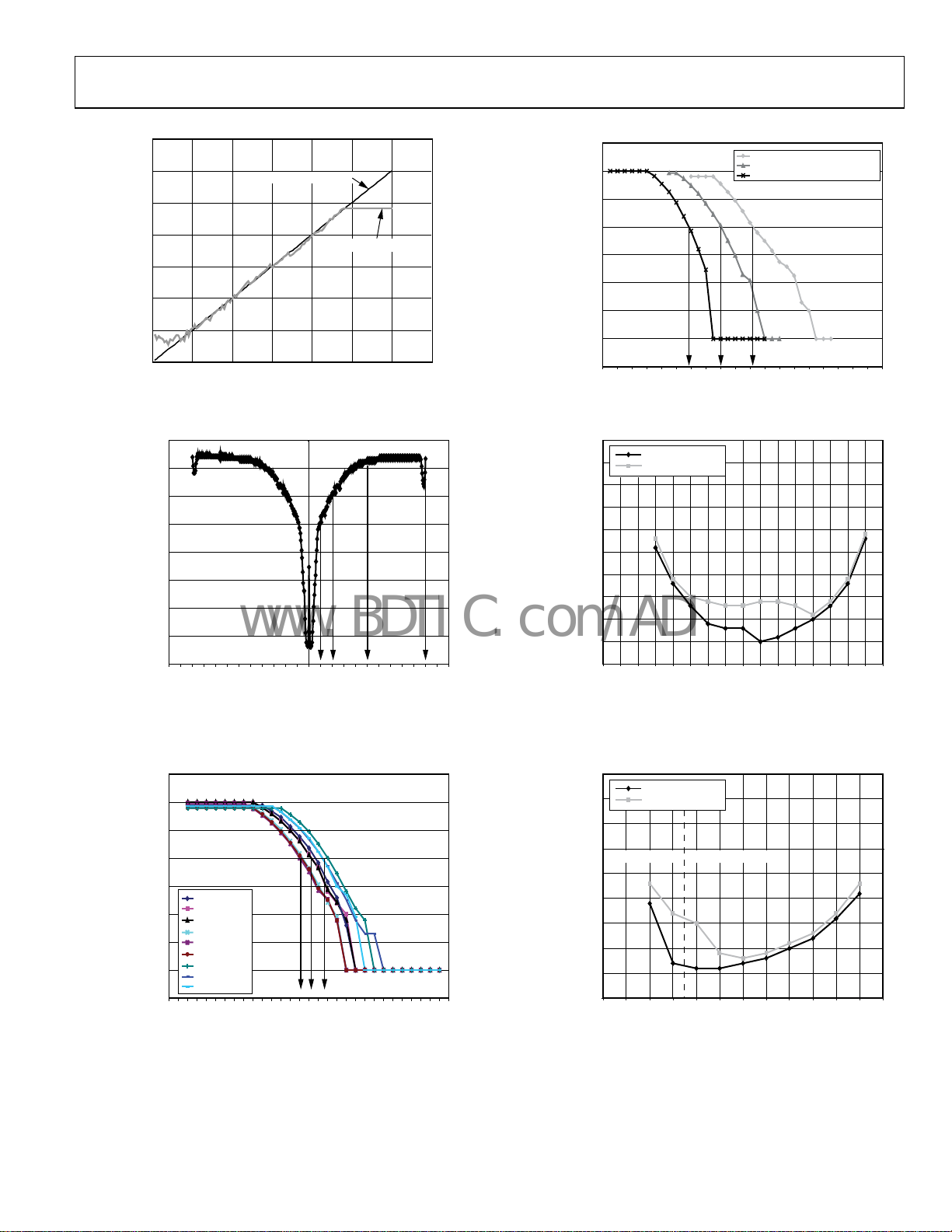
Figure 12. Digital RSSI Readback
70
60
50
40
TION (dB)
30
20
10
LEVEL OF REJE
0
–
10
–12 –6 0 6 12
OFFSET OF INTERFERER FROM WANTED SIGNAL (MHz)
Figure 13. Wideband Interference Rejection;
Wanted Signal (901 MHz, 38.4 kbps Data Rate, 200 kHz Frequency
Deviation) at 6 dB Above Sensitivity Point; Interferer = CW Jammer
20–120 –100 –80 –60 –40 –20 0
05542-014
05542-013
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
LOG (BER)
–5
–6
–7
–8
–116 –108 –100 –90 –78
RF I/P LEVEL (dBm)
DATA RATE = 384k, FDEV = 450k
DATA RATE = 172k, FDEV = 200k
DATA RATE = 38.4k, FDEV = 200k
Figure 15. BER vs. Data Rate (Combined Matching Network)
50
= CORRELATOR
= LINEAR
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800
DEVIATION F REQUENCY (kHz )
Bm)
SENSITIVITY POINT (
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
–95
–100
Figure 16. Sensitivity vs. Mod Index (Data Rate = 384 kbps, Baseband
Filter Bandwidth = ±600 kHz), for Both Demodulator Types
05542-016
05542-017
0
–1
–2
–3
–4
BER
2.3V, +25°C
3V, +25°C
–5
3.6V, +25°C
2.3V, –40°C
–6
3V, –40°C
3.6V, –40°C
2.3V, +85°C
–7
3V, +85°C
3.6V, +85°C
–8
–115 –110 –105 –100 –95 –90 –85
Figure 14. Sensitivity vs. V
RF I/P LEVEL (dBm)
and Temperature
DD
05542-015
(172.8 kbps Data Rate, 200 kHz Frequency Deviation,
Baseband Bandwidth ±600 kHz)
Rev. A | Page 13 of 44
60
= CORRELAT OR
–65
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
SENSITIVITY POI NT (dBm)
–95
–100
–105
= CORRELAT OR
=LINEAR
=LINEAR
BB BW = ±450kHz BB BW = ±600kHz
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600
DEVIATION FREQUENCY (kHz)
05542-018
Figure 17. Sensitivity vs. Mod Index (Data Rate = 172.8 kbps),
for Both Demodulator Types
ADF7025
–
d
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
60
–65
–70
–75
Bm)
–80
–85
–90
–95
SENSITIVITY POINT (
–100
–105
–110
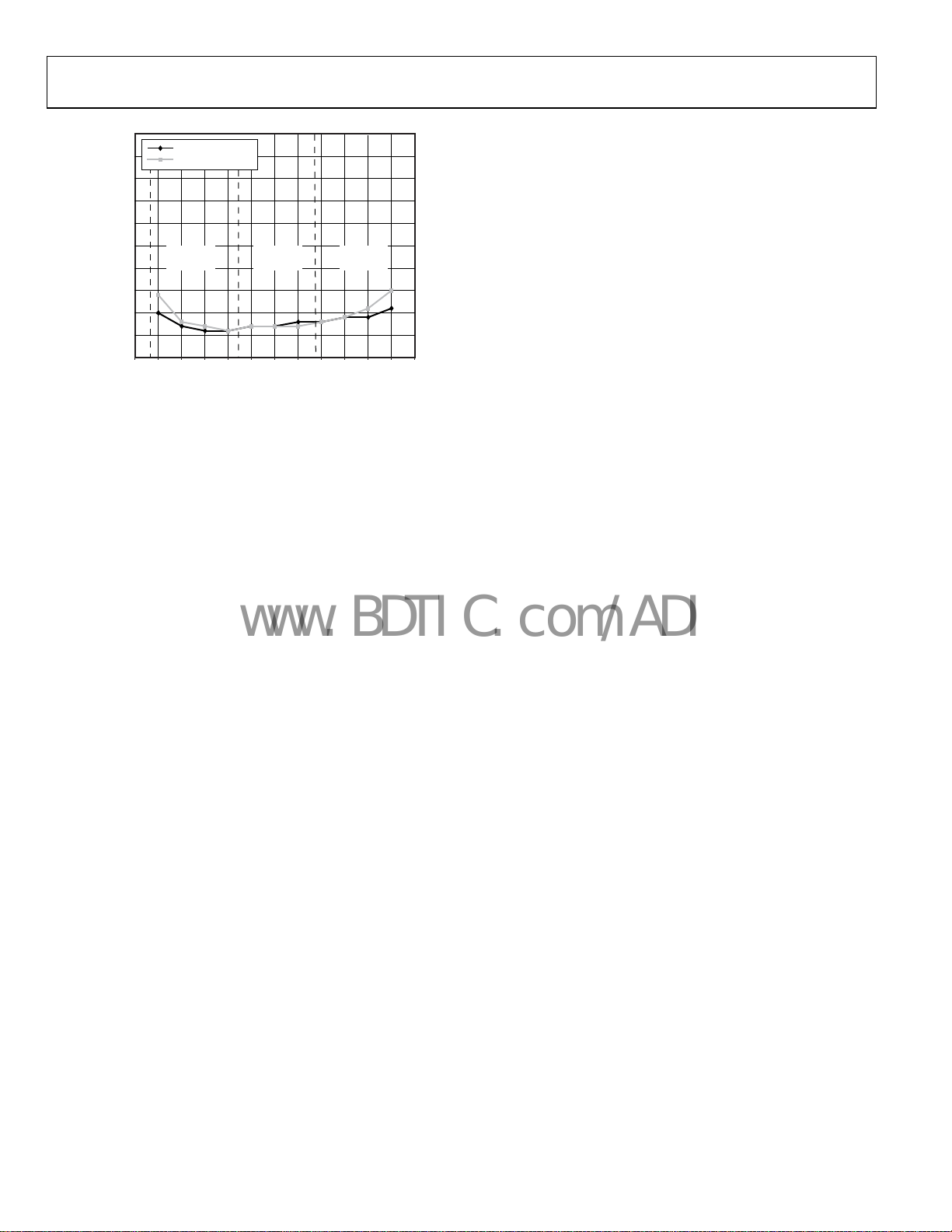
Figure 18. Sensitivity vs. Mod Index (Data Rate = 38.4 kbps),
= CORRELATOR
=LINEAR
BB BW =
±300kHz
0 5 0 100 15 0 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600
DEVIATION F REQUENCY (kHz )
BB BW =
±450kHz
BB BW =
±600kHz
for both Demodulator Types
05542-052
Rev. A | Page 14 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER
REFERENCE INPUT SECTION
The on-board crystal oscillator circuitry (see Figure 19) can use
an inexpensive quartz crystal as the PLL reference. The oscillator
circuit is enabled by setting R1_DB12 high. It is enabled by
default on power-up and is disabled by bringing CE low. Errors
in the crystal can be corrected by adjusting the Fractional-N
value (see the N Counter section). A single-ended reference
(TCXO, CXO) can also be used. The CMOS levels should be
applied to OSC2 with R1_DB12 set low.
R Counter
The 3-bit R counter divides the reference input frequency by an
integer from 1 to 7. The divided-down signal is presented as the
reference clock to the phase frequency detector (PFD). The divide
ratio is set in Register 1. Maximizing the PFD frequency reduces
the N value. This reduces the noise multiplied at a rate of 20 log(N)
to the output, as well as reducing occurrences of spurious
components. The R register defaults to R = 1 on power-up.
PFD [Hz] = XTAL/R
MUXOUT and Lock Detect
OSC1
Figure 19. Oscillator Circuit on the ADF7025
OSC2
CP1CP2
05542-019
Two parallel resonant capacitors are required for oscillation at
the correct frequency; their values are dependent on the crystal
specification. They should be chosen so that the series value of
capacitance added to the PCB track capacitance adds up to the
load capacitance of the crystal, usually 20 pF. Track capacitance
values vary from 2 pF to 5 pF, depending on board layout.
Where possible, choose capacitors that have a very low
temperature coefficient to ensure stable frequency operation
over all conditions.
CLKOUT Divider and Buffer
The CLKOUT circuit takes the reference clock signal from the
oscillator section, shown in Figure 19, and supplies a divideddown 50:50 mark-space signal to the CLKOUT pin. An even
divide from 2 to 30 is available. This divide number is set in
R1_DB [8:11]. On power-up, the CLKOUT defaults to
divide-by-8.
DV
DD
CLKOUT
ENABLE BIT
DIVIDER
1TO 15
Figure 20. CLKOUT Stage
÷2
CLKOUTOSC1
05542-020
To disable CLKOUT, set the divide number to 0. The output
buffer can drive up to a 20 pF load with a 10% rise time at
4.8 MHz. Faster edges can result in some spurious feedthrough
to the output. A small series resistor (50 Ω) can be used to slow
the clock edges to reduce these spurs at F
CLK
.
The MUXOUT pin allows the user to access various digital
points in the ADF7025. The state of MUXOUT is controlled by
Bits R0_DB [29:31].
Regulator Ready
Regulator ready is the default setting on MUXOUT after the
transceiver has been powered up. The power-up time of the
regulator is typically 50 µs. Because the serial interface is powered
from the regulator, the regulator must be at its nominal voltage
before the ADF7025 can be programmed. The status of the
regulator can be monitored at MUXOUT. When the
regulator_ready signal on MUXOUT is high, programming of
the ADF7025 can begin.
DV
DD
REGULATOR READY
DIGITAL LOCK DETECT
ANALOG LO CK DETECT
R COUNTER OUTP UT
N COUNTER OUTP UT
PLL TEST MODES
Σ-∆ TEST MODES
MUX CONTROL
Figure 21. MUXOUT Circuit
MUXOUT
DGND
Digital Lock Detect
Digital lock detect is active high. The lock detect circuit is
located at the PFD. When the phase error on five consecutive
cycles is less than 15 ns, lock detect is set high. Lock detect
remains high until a 25 ns phase error is detected at the PFD.
Because no external components are needed for digital lock
detect, it is more widely used than analog lock detect.
5542-021
Rev. A | Page 15 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Analog Lock Detect
This N-channel open-drain lock detect should be operated with
an external pull-up resistor of 10 kΩ nominal. When a lock has
been detected, this output is high with narrow low-going pulses.
The fractional divide value gives very fine resolution at the
output, where the output frequency of the PLL is calculated as
F
OUT
XTAL
R
(
NInteger
+×=
NFractional
)
15
2
Voltage Regulators
The ADF7025 contains four regulators to supply stable voltages
to the part. The nominal regulator voltage is 2.3 V. Each regulator
should have a 100 nF capacitor connected between VREG and
GND. When CE is high, the regulators and other associated
circuitry are powered on, drawing a total supply current of 2 mA.
Bringing the chip-enable pin low disables the regulators,
reduces the supply current to less than 1 µA, and erases all
values held in the registers. The serial interface operates from
a regulator supply; therefore, to write to the part, the user must
have CE high and the regulator voltage must be stabilized.
Regulator status (VREG4) can be monitored using the regulator
ready signal from MUXOUT.
Loop Filter
The loop filter integrates the current pulses from the charge
pump to form a voltage that tunes the output of the VCO to the
desired frequency. It also attenuates spurious levels generated by
the PLL. A typical loop filter design is shown in Figure 22.
CHARGE
PUMP OUT
Figure 22. Typical Loop Filter Configuration
VCO
05542-022
REFERENCE IN
4R
PFD/
CHARGE
PUMP
THIRD-ORDER
Σ-∆ MODULATOR
Figure 23. Fractional-N PLL
VCO
4N
INTEGER-NFRACTIONAL-N
05542-023
The combination of the Integer-N (maximum = 255) and the
Fractional-N (maximum = 16383/16384) gives a maximum N
divider of 255 + 1. Therefore, the minimum usable PFD is
PDF
[Hz] = Maximum Required Output Frequency/(255 + 1)
MIN
For example, when operating in the European 868 MHz to
870 MHz band, PFD
equals 3.4 MHz.
MIN
Voltage Controlled Oscillator
To minimize spurious emissions, the on-chip VCO operates
from 1732 MHz to 1856 MHz. The VCO signal is then divided
by 2 to give the required frequency for the transmitter and the
required LO frequency for the receiver.
In general, a loop filter bandwidth (LBW) of between the data
rate and twice the data rate is recommended. Widening the
LBW excessively reduces the time spent jumping between
frequencies, but it can cause insufficient spurious attenuation.
Narrow-loop bandwidths can result in the loop taking long
periods of time to attain lock. For the ADF7025 in receive mode,
the loop filter bandwidth affects the close-in blocking performance. The narrower the bandwidth of the loop filter, the greater
the close-in interference resilience of the receiver.
Careful design of the loop filter is critical to obtaining accurate
FSK modulation. The free design tool ADIsimPLL can be used
to design loop filters for the ADF7025.
N Counter
The feedback divider in the ADF7025 PLL consists of an 8-bit
integer counter and a 14-bit Σ-∆ Fractional-N divider. The
integer counter is the standard pulse-swallow type common in
PLLs. This sets the minimum integer divide value to 31.
Rev. A | Page 16 of 44
The VCO should be re-centered, depending on the required
frequency of operation, by programming the VCO adjust bits
R1_DB [20:21].
For operation in the 862 MHz to 870 MHz band, it is recommended to use a VCO bias of at least Setting 10 and to set the
VCO adjust bit to Setting 0. For operation in the 902 MHz to
928 MHz band, it is recommended to use a VCO bias of at least
Setting 12 and to set the VCO adjust bit to Setting 3. This is to
ensure correct operation under all conditions.
The VCO is enabled as part of the PLL by the PLL-enable bit,
R0_DB28.
An additional frequency divide-by-2 is included to allow
operation in the lower 431 MHz to 464 MHz bands. To enable
operation in these bands, R1_DB13 should be set to 1. The
VCO needs an external 22 nF between the VCO and the
regulator to reduce internal noise.

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VCO Bias Current
VCO bias current can be adjusted using Bit R1_DB19 to
Bit R1_DB16. To ensure VCO oscillation under all conditions,
the minimum bias current setting is Setting 12 (0xC).
431 MHz to 464 MHz Operation
For operation in the 431 MHz to 464 MHz band, the frequency
divide-by-2 has to be enabled. It is enabled by R1_DB13. Because
this divide is external to the synthesizer loop, the feedback
divider number (N + F) should be programmed to a value twice
the desired RF output frequency.
VCO BIAS
R1_DB (16:19)
LOOP FILTER
CVCO PIN
VCO
220µF
÷2
VCO SELECT BIT
Figure 24. Voltage Controlled Oscillator
÷2
MUX
TO PA AND
N DIVIDER
05542-024
CHOOSING CHANNELS FOR BEST SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
The Fractional-N PLL allows the selection of any channel
within 862 MHz to 928 MHz (and 431 MHz to 464 MHz using
divide-by-2) to a resolution of <300 Hz. This also facilitates
frequency-hopping systems.
Careful selection of the RF transmit channels must be made to
achieve best spurious performance. The architecture of
Fractional-N results in some level of the nearest integer channel
moving through the loop to the RF output. These beat-note
spurs are not attenuated by the loop, if the desired RF channel
and the nearest integer channel are separated by a frequency of
less than the LBW.
The occurrence of beat-note spurs is rare, because the integer
frequencies are at multiples of the reference, which is typically
>10 MHz.
Beat-note spurs can be significantly reduced in amplitude by
avoiding very small or very large values in the fractional
register, using the frequency doubler. By having a channel
1 MHz away from an integer frequency, a 100 kHz loop filter
can reduce the level to less than −45 dBc.
Rev. A | Page 17 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TRANSMITTER
RF OUTPUT STAGE
The PA of the ADF7025 is based on a single-ended, controlled
current, open-drain amplifier that has been designed to deliver
up to 13 dBm into a 50 Ω load at a maximum frequency of
928 MHz.
The PA output current and, consequently, the output power are
programmable over a wide range. The PA configuration is
shown in Figure 25. The output power is independent of the
state of the DATA I/O pin. The output power is set using Bits
R2_DB [9:14].
R2_DB(30:31)
2
MODULATION SCHEME
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
Frequency shift keying is implemented by setting the N value for
the center frequency and then toggling this with the TxData
line. The deviation from the center frequency is set using
Bits R2_DB [15:23]. The deviation from the center frequency in
Hz is
FSK
DEVIATION
[Hz]
×
=
where Modulation Number is a number from 1 to 511
(R2_DB(15:23)).
NumberModulationPFD
14
2
IDAC
RFOUT
+
RFGND
FROM VCO
Figure 25. PA Configuration
6
R2_DB(9:14)
R2_DB4
R2_DB5
DIGITAL
LOCK DETECT
The PA is equipped with overvoltage protection, which makes it
robust in severe mismatch conditions. Depending on the
application, one can design a matching network for the PA to
exhibit optimum efficiency at the desired radiated output power
level for a wide range of different antennas, such as loop or
monopole antennas. See the LNA/PA Matching section for
details.
PA Bias Currents
Control Bits R2_DB [30:31] facilitate an adjustment of the PA
bias current to further extend the output power control range, if
necessary. If this feature is not required, the default value of
7 µA is recommended. The output stage is powered down by
resetting Bit R2_DB4.
Select FSK using Bits R2_DB [6:8].
4R
05542-025
FSK DEVIATION
FREQUENCY
–F
DEV
+F
DEV
TxDATA
PFD/
CHARGE
PUMP
THIRD-ORDER
Σ-∆ MODULATOR
Figure 26. FSK Implementation
INTEGER-NFRACTIONAL-N
VCO
÷N
PA STA G E
05542-026
Modulation Index
The choice of deviation frequency for a given data rate is critical
to get optimum sensitivity performance from the ADF7025.
The modulation index (MI) of an FSK modulated signal is
defined as
MI×=
DeviationFrequency
RateData
[bps]
[Hz]2
It is recommended to use a MI > 1 for the ADF7025. The
variation of receiver sensitivity with modulation index, for
various data rates, can be observed in Figure 16, Figure 17,
and Figure 18.
Rev. A | Page 18 of 44

ADF7025
T
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
RECEIVER
RF FRONT END
The ADF7025 is based on a fully integrated, zero-IF receiver
architecture. The zero-IF architecture minimizes power
consumption and the external component count while avoiding
the need for image rejection.
Figure 27 shows the structure of the receiver front end. The
numerous programming options allow users to trade off
sensitivity, linearity, and current consumption against each
other in the way best suitable for their applications. To achieve a
high level of resilience against spurious reception, the LNA
features a differential input. Switch SW2 shorts the LNA input
when transmit mode is selected (R0_DB27 = 0). This feature
facilitates the design of a combined LNA/PA matching network,
avoiding the need for an external Rx/Tx switch. See the
LNA/PA Matching section for details on the design of the
matching network.
I (TO FILTER)
LO
Q (TO FILTER)
MIXER LINEARITY
[R6_DB18]
[R0_DB27]
LNA CURRENT
[R6_DB(16:17) ]
[R9_DB(20:21) ]
RFIN
RFINB
LNA MODE
[R6_DB15]
LNA GAIN
[R8_DB6]
SW2 LNA
Figure 27. ADF7025 RF Front End
x/Rx SELECT
LNA/MIXER ENABLE
The LNA is followed by a quadrature downconversion mixer,
which converts the RF signal direct to baseband. The output
frequency of the synthesizer must be programmed to the value
equal to the center frequency of the received channel.
05542-027
Based on the specific sensitivity and linearity requirements of
the application, it is recommended to adjust control bits
LNA_mode (R6_DB15) and mixer_linearity (R6_DB18).
The gain of the LNA is configured by the LNA_gain field,
R9_DB [20:21] and can be set by either the user or the
automatic gain control (AGC) logic.
Filter Settings/Calibration
Out-of-band interference is rejected by means of a fifth-order,
low-pass filter (LPF). The bandwidth of the filter can be
programmed to be ±300 kHz, ±450 kHz, or ±600 kHz by means
of Control Bits R1_DB [22:23] and should be chosen as a
compromise between interference rejection and attenuation of
the desired signal. A high-pass filter is also included as part of
the low-pass filter to prevent against dc offset problems. The
bandwidth of this filter is ~60 kHz. To avoid significant loss of
FSK modulated signal in the filter, the frequency deviation
needs to be significantly larger than this pole (refer to the
Modulation Index section). The minimum allowable frequency
deviation is 100 kHz.
To compensate for manufacturing tolerances, the LPF should
be calibrated once after power-up. The LPF calibration logic
requires that the LPF divider in Bits R6_DB [20:28] be set
depending on the crystal frequency. Once initiated by setting
Bit R6_DB19, the calibration is performed automatically
without any user intervention. The calibration time is 200 µs,
during which the ADF7025 should not be accessed. It is
important not to initiate the calibration cycle before the crystal
oscillator has fully settled. If the AGC loop is disabled, the gain
of LPF can be set to three levels using the filter_gain field,
R9_DB [20:21]. The filter gain is adjusted automatically, if the
AGC loop is enabled.
The LNA has two basic operating modes: high gain/low noise
mode and low gain/low power mode. To switch between the
two modes, use the LNA_mode bit, R6_DB15. The mixer is also
configurable between a low current and an enhanced linearity
mode using the mixer_linearity bit, R6_DB18.
Rev. A | Page 19 of 44

ADF7025
Y
L
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
RSSI/AGC
The RSSI is implemented as a successive compression log amp
following the baseband channel filtering. The log amp achieves
±3 dB log linearity. It also doubles as a limiter to convert the
signal-to-digital levels for the FSK demodulator. Offset
correction is achieved using a switched capacitor integrator in
feedback around the log amp. This uses the BB offset clock
divide. The RSSI level is converted for user readback and
digitally controlled AGC by an 80-level (7-bit) flash ADC. This
level can be converted to input power in dBm.
OFFSET
CORRECTION
FSK
×
XTAL
DEMOD
ADC
RSSI
DEMOD
___
05542-028
DIVIDECLKSEQDELAYAGC
1
IFWR IFWR IFWR IFWR
R
Figure 28. RSSI Block Diagram
LATCHAAA
CLK
Offset Correction Clock
In Register 3, the user should set the BB offset clock divide bits
R3_DB [4:5] to give an offset clock between 1 MHz and 2 MHz,
where BBOS _CLK [Hz] = XTAL/(BBOS_CLK_DIVIDE).
BBOS_CLK_DIVIDE can be set to 4, 8, or 16.
AGC Information
In Register 9, the user should select automatic gain control by
selecting Auto In R9_DB18 and Auto In R9_DB19. The user
should then program AGC Low Threshold R9_DB [4:10] and
AGC High Threshold R9_DB [11:17]. The default values for the
low and high thresholds are 30 and 70, respectively; however,
these are not the optimum settings for all operating conditions.
The recommended values for the low and high thresholds are
15 and 79, respectively. In the AGC 2 register (Register 10), the
user should program the AGC delay to be long enough to allow
the loop to settle. The default/recommended value is 10.
TimeWaitAGC
__
=
AGC Settling = AGC_Wait_Time × Number of Gain Changes
Thus, in the worst case, if the AGC loop has to go through all five
gain changes, AGC delay = 10, and SEQ_CLK = 200 kHz, then
AGC settling = 10 × 5 µs × 5 = 250 μs. Minimum AGC_Wait_Time
must be at least 25 µs.
RSSI Formula (Converting to dBm)
Input_Power [dBm] = −98 dBm + (Readback_Code +
Gain_Mode_Correction ) × 0.5
where:
Readback_Code is given by Bit RV7 to Bit RV1 in the readback
register (see the Readback Format section).
Gain_Mode_Correction is given by the values in Table 5.
LNA gain and filter gain (LG2/LG1, FG2/FG1) are also
obtained from the readback register.
Table 5. Gain Mode Correction
LNA Gain
(LG2, LG1)
Filter Gain
(FG2, FG1) Gain Mode Correction
H (11) H (10) 0
M (10) H (10) 17
M (10) M (01) 53
M (10) L (00) 65
L (01) L (00) 90
EL (00) L (00) 113
These numbers are for an unmodulated tone. For a modulated
signal, the RSSI readback may have to be adjusted to get the
required accuracy. An additional factor should also be
introduced to account for losses in the front-end matching
network/antenna.
FSK DEMODULATORS ON THE ADF7025
The two FSK demodulators on the ADF7025 are
• FSK correlator/demodulator
• Linear demodulator
Select these using the Demod Select Bits R4_DB [4:5].
FSK CORRELATOR/DEMODULATOR
The quadrature outputs of the IF filter are first limited and then
fed to a pair of digital frequency correlators that perform bandpass filtering of the binary FSK frequencies at (IF + F
(IF − F
DEV). Data is recovered by comparing the output levels
from each of the two correlators. The performance of this
frequency discriminator approximates that of a matched filter
detector, which is known to provide optimum detection in the
presence of AWGN.
CORRE
I
LIMITERS
Q
TOR
0
– F
DB(4:13)
Figure 29. FSK Correlator/Demodulator Block Diagram
DEV
DB(14)
+ F
DEV
SLICERFREQUENC
+
POST
–
DEMOD FILTER
0
DATA
DB(8:15)
DEV) and
Rx DATA
Rx CLK
SYNCHRONIZER
5542-029
Rev. A | Page 20 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Postdemodulator Filter
A second-order, digital low-pass filter removes excess noise
from the demodulated bit stream at the output of the
discriminator. The bandwidth of this postdemodulator filter is
programmable and must be optimized for the user’s data rate. If
the bandwidth is set too narrow, performance is degraded due
to intersymbol interference (ISI). If the bandwidth is set too
wide, excess noise degrades the receiver’s performance.
Typically, the 3 dB bandwidth of this filter is set at approximately
0.75 times the user’s data rate, using Bits R4_DB [6:15].
Bit Slicer
The received data is recovered by the threshold detecting the
output of the postdemodulator low-pass filter. In the correlator/
demodulator, the binary output signal levels of the frequency
discriminator are always centered on 0. Therefore, the slicer
threshold level can be fixed at 0, and the demodulator
performance is independent of the run-length constraints of the
transmit data bit stream. This results in robust data recovery,
which does not suffer from the classic baseline wander
problems that exist in more traditional FSK demodulators.
Data Synchronizer
An oversampled digital PLL is used to resynchronize the received
bit stream to a local clock. The oversampled clock rate of the
PLL (CDR_CLK) must be set at 32 times the data rate. See the
Register 3—Receiver Clock Register section for a definition of
how to program. The clock recovery PLL can accommodate
frequency errors of up to ±2%.
FSK Correlator Register Settings
To enable the FSK correlator/demodulator, Bits R4_DB [5:4]
should be set to 01. To achieve best performance, the bandwidth
of the FSK correlator must be optimized for the specific deviation
frequency that is used by the FSK transmitter.
The discriminator BW is controlled in Register 6 by
R6_DB [4:13] and is defined as
Discriminator_BW = DEMOD_CLK/(4 × F
DEV
)
where:
DEMOD_CLK is as defined in the Register 3—Receiver Clock
Register section.
F
is the deviation from the carrier frequency in FSK
DEV
modulation.
Postdemodulator Bandwidth Register Settings
The 3 dB bandwidth of the postdemodulator filter is controlled
by Bits R4_ DB [6:15] and is given by
where F
Setting_BW_Demod_Post
is the target 3 dB bandwidth in Hz of the post-
CUTOFF
10
=
F
××
π
22
CUTOFF
CLK_DEMOD
demodulator filter. This should typically be set to 0.75 times
the data rate (DR).
Some sample settings for the FSK correlator/demodulator are
DEMOD_CLK = 11.0592 MHz
DR = 200 kbps
F
= 300 kHz
DEV
Therefore,
= 0.75 × 200 × 103 Hz
F
CUTOFF
Post_Demod_BW = 2
11
× π × 150 × 103 Hz/(11.0592 MHz)
Post_Demod_BW = Round (87.266) = 87
and
3
Discriminator_BW = (11.0592 MHz )/(4 × 300 × 10
) =
9.21 = 9 (rounded to the nearest integer)
Table 6. Register Settings
Setting Name Register Address Value
Post_Demod_BW R4_DB [6:15] 0x09
Discriminator BW R6_DB [4:13] 0x58
Rev. A | Page 21 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
LINEAR FSK DEMODULATOR
A block diagram of the linear FSK demodulator is shown in
Figure 30.
ENVELOPE
××
DETECTOR
F
CUTOFF
CLKDEMOD
_
SLICER
+
Rx DATA
–
MUX 1
FREQ
7
FILTER
AVERAGING
DB(6:15)
ADC RSSI OUTP UT
LEVEL
I
LIMITER
Q
LINEAR DISCRIM INATOR
Figure 30. Block Diagram of Linear FSK Demodulator
0Hz
This method of frequency demodulation is useful when very
short preamble length is required.
A digital frequency discriminator provides an output signal that
is linearly proportional to the frequency of the limiter outputs.
The discriminator output is then filtered and averaged using a
combined averaging filter and envelope detector. The demodulated FSK data is recovered by threshold-detecting the output of
the averaging filter, as shown in Figure 30. In this mode, the
slicer output shown in Figure 30 is routed to the data synchronizer PLL for clock synchronization. To enable the linear FSK
demodulator, Bits R4_DB [4:5] are set to [00].
The 3 dB bandwidth of the postdemodulation filter is set in the
same way as the FSK correlator/demodulator, which is set in
R4_DB(6:15) and is defined as
10
22
SettingBWDemodPost
___
=
π
05542-030
AUTOMATIC SYNC WORD RECOGNITION
The ADF7025 also supports automatic detection of the sync or
ID fields. To activate this mode, the sync (or ID) word must be
preprogrammed into the ADF7025. In receive mode, this
preprogrammed word is compared to the received bit stream
and, when a valid match is identified, the external pin
INT/LOCK is asserted by the ADF7025.
This feature can be used to alert the microprocessor that a valid
channel has been detected. It relaxes the computational requirements of the microprocessor and reduces the overall power
consumption. The INT/LOCK is automatically de-asserted
again after nine data clock cycles.
The automatic sync/ID word detection feature is enabled by
selecting Demod Mode 2 or Demod Mode 3 in the demodulator
setup register. Do this by setting R4_DB [25:23] = [010] or
R4_DB [25:23] = [011]. Bits R5_DB [4:5] are used to set the
length of the sync/ID word, which can be either 12 bits, 16 bits,
20 bits, or 24 bits long. The transmitter must transmit the MSB
of the sync byte first and the LSB last to ensure proper
alignment in the receiver sync byte detection hardware.
For systems using FEC, an error tolerance parameter can also
be programmed that accepts a valid match when up to three bits
of the word are incorrect. The error tolerance value is assigned
in R5_DB [6:7].
where:
is the target 3 dB bandwidth in Hz of the
F
CUTOFF
postdemodulator filter.
DEMOD_CLK is as defined in the Register 3—Receiver Clock
Register section.
Rev. A | Page 22 of 44

ADF7025
V
V
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
APPLICATIONS SECTION
LNA/PA MATCHING
The ADF7025 exhibits optimum performance in terms of
sensitivity, transmit power, and current consumption only if its
RF input and output ports are properly matched to the antenna
impedance. For cost-sensitive applications, the ADF7025 is
equipped with an internal Rx/Tx switch, which facilitates the
use of a simple combined passive PA/LNA matching network.
Alternatively, an external Rx/Tx switch, such as the Analog
Devices ADG919, can be used, which yields a slightly improved
receiver sensitivity and lower transmitter power consumption.
External Rx/Tx Switch
Figure 31 shows a configuration using an external Rx/Tx switch.
This configuration allows an independent optimization of the
matching and filter network in the transmit and receive path,
and is, therefore, more flexible and less difficult to design than
the configuration using the internal Rx/Tx switch. The PA is
biased through Inductor L1, while C1 blocks dc current. Both
elements, L1 and C1, also form the matching network, which
transforms the source impedance into the optimum PA load
impedance, Z
ANTENNA
Rx/Tx – SEL ECT
Z
_PA depends on various factors such as the required output
OPT
power, the frequency range, the supply voltage range, and the
temperature range. Selecting an appropriate Z
minimize the Tx current consumption in the application. This
data sheet contains a number of Z
tive conditions. Under certain conditions, however, it is
recommended to obtain a suitable Z
load-pull measurement.
Due to the differential LNA input, the LNA matching network
must be designed to provide both a single-ended to differential
conversion and a complex conjugate impedance match. The
network with the lowest component count that can satisfy these
requirements is the configuration shown in Figure 31, which
consists of two capacitors and one inductor.
_PA.
OPT
BAT
OPTIONAL
LPF
OPTIONAL
BPF
(SAW)
ADG919
Figure 31. ADF7025 with External Rx/Tx Switch
L1
Z
Z
C
A
L
ZIN_RFIN
C
B
_PA values for representa-
OPT
OPT
PA_ OUT
_PA
OPT
_RFIN
IN
RFIN
A
RFINB
ADF7025
OPT
_PA value by means of a
PA
LNA
_PA helps to
05542-031
A first-order implementation of the matching network can be
obtained by understanding the arrangement as two L-type
matching networks in a back-to-back configuration. Due to the
asymmetry of the network with respect to ground, a compromise between the input reflection coefficient and the maximum
differential signal swing at the LNA input must be established.
The use of appropriate CAD software is strongly recommended
for this optimization.
Depending on the antenna configuration, the user might need a
harmonic filter at the PA output to satisfy the spurious emission
requirement of the applicable government regulations. The
harmonic filter can be implemented in various ways, such as a
discrete LC filter or T-stage filter. Dielectric low-pass filter
components such as the LFL18924MTC1A052 (for operation in
the 915 MHz band), or LFL18869MTC2A160 (for operation in
the 868 MHz band), both by Murata Mfg. Co., Ltd., represent an
attractive alternative to discrete designs. The immunity of the
ADF7025 to strong out-of-band interference can be improved
by adding a band-pass filter in the Rx path.
Internal Rx/Tx Switch
Figure 32 shows the ADF7025 in a configuration where the
internal Rx/Tx switch is used with a combined LNA/PA
matching network. This is the configuration used in the
ADF7025DB1 Evaluation Board. For most applications, the
slight performance degradation of 1 dB to 2 dB caused by the
internal Rx/Tx switch is acceptable, allowing the user to take
advantage of the cost-saving potential of this solution. The
design of the combined matching network must compensate for
the reactance presented by the networks in the Tx and the Rx
paths, taking the state of the Rx/Tx switch into consideration.
BAT
L1
NTENNA
C1
OPTIONAL
BPF OR LPF
Figure 32. ADF7025 with Internal Rx/Tx Switch
Z
Z
C
A
L
A
ZIN_RFIN
C
B
OPT
IN
_PA
_RFIN
PA_ OUT
RFIN
RFINB
ADF7025
PA
LNA
05542-032
Rev. A | Page 23 of 44

ADF7025
A
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
The procedure typically requires several iterations until an
acceptable compromise is reached. The successful implementation
of a combined LNA/PA matching network for the ADF7025 is
critically dependent on the availability of an accurate electrical
model for the PC board. In this context, the use of a suitable CAD
package is strongly recommended. To avoid this effort, however, a
small form-factor reference design for the ADF7025 is provided,
including matching and harmonic filter components. The design
is on a 2-layer PCB to minimize cost. Gerber files are available
on the www.analog.com website.
TRANSMIT PROTOCOL AND CODING CONSIDERATIONS
PREAMBLE
A dc-free preamble pattern is recommended for FSK
demodulation. The recommended preamble pattern is a dc-free
pattern such as a 10101010… pattern. Preamble patterns with
longer run-length constraints such as 11001100…. can also be
used. However, this results in a longer synchronization time of
the received bit stream in the receiver.
Manchester coding can be used for the entire transmit protocol.
However, the remaining fields that follow the preamble header
do not have to use dc-free coding. For these fields, the ADF7025
can accommodate coding schemes with a run-length of up to
six bits without any performance degradation.
SYNC
WORDIDFIELD
Figure 33. Typical Format of a Transmit Protocol
DATA FIELD CRC
05542-033
Table 7. Minimum Register Writes Required for Tx/Rx Setup
Mode Registers
Tx 0 1 2
Rx (FSK) 0 1 2 4 6 9
1
Tx to Rx and Rx to Tx 0
1
Register 9 should be programmed in receive mode in order to set the
recommended AGC threshold settings (low = 15, high = 79).
Figure 36 and Figure 37 show the recommended programming
sequence and associated timing for power-up from standby
mode.
INTERFACING TO MICROCONTROLLER/DSP
Low level device drivers are available for interfacing to the
ADF7025, the ADI ADuC84x microcontroller parts, or the
Blackfin® BF53x DSPs using the hardware connections shown in
Figure 34 and Figure 35.
ADuC84x
MISO
MOSI
SCLOCK
SS
P3.7
P3.2/INT0
P2.4
P2.5
GPIO
P2.6
P2.7
Figure 34. ADuC84X to ADF7025 Connection D iagram
DF7025
TxRxDATA
RxCLK
CE
INT/LOCK
SREAD
SLE
SDATA
SCLK
5542-034
If longer run-length coding must be supported, the ADF7025
has several other features that can be activated. These involve a
range of programmable options that allow the envelope detector
output to be frozen after preamble acquisition.
DEVICE PROGRAMMING AFTER INITIAL POWER-UP
Table 7 lists the minimum number of writes needed to set up
the ADF7025 in either Tx or Rx mode after CE is brought high.
Additional registers can also be written to tailor the part to a
particular application, such as setting up sync byte detection.
When going from Tx to Rx or vice versa, the user needs to write
only to the N register to alter the LO by 200 kHz and to toggle
the Tx/Rx bit.
ADSP-BF533
SCK SCLK
MOSI
MISO
PF5
RSCLK1
DT1PRI
DR1PRI
RFS1
PF6
VCC
GND
Figure 35. BF533 to ADF7025 Connection Diagram
ADF7025
SDATA
SREAD
SLE
TxRxCLK
TxRxDATA
INT/LOCK
CE
VCC
GND
5542-035
Rev. A | Page 24 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
19mA TO
22mA
14mA
3.65mA
2.0mA
I
5
2
0
7
F
D
A
D
D
REG.
READY
T
XTAL
T
0
AGC/
WR0
WR1
T
1
T
2
VCO
3
T
WR3
WR4
T
4
T
5
RSSI
WR6
T
6
7
CDR
T
T
8
9
RxDATA
T
11
TIME
Figure 36. Rx Programming Sequence and Timing Diagram
Table 8. Power-Up Sequence Description
Parameter Value Description/Notes
T
0
2 ms
XTAL starts power-up after CE is brought high. This typically depends on the XTAL
type and the load capacitance specified.
T
1
T2, T3, T5,
, T
T
6
7
T
4
10 µs Time for regulator to power up. The serial interface can be written to after this time. MUXOUT
32 × 1/SPI_CLK Time to write to a single register. Maximum SPI_CLK is 25 MHz.
1 ms
The VCO can power-up in parallel with the XTAL. This depends on the CVCO
capacitance value used. A value of 22 nF is recommended as a trade-off
between phase noise performance and power-up time.
T
8
150 µs
This depends on the number of gain changes the AGC loop needs to cycle through
and AGC settings programmed. This is described in more detail in the AGC Information
section.
T
9
5 × bit_period
This is the time for the clock and data recovery circuit to settle. This typically requires
5-bit transitions to acquire sync and is usually covered by the preamble.
T
11
Packet length Number of bits in payload by the bit period.
T
ON
T
OFF
5542-036
Signal to
Monitor
CLKOUT
CVCO pin
Analog RSSI
on TEST_A pin
Rev. A | Page 25 of 44

ADF7025
D
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
D
I
5
2
0
7
F
D
A
15mA TO
30mA
14mA
3.65mA
2.0mA
REG.
READY
T
1
WR0
T
WR1
2
XTAL + VCO
T
3
T
4
WR2
T
5
T
ON
TxDATA
T
12
T
OFF
TIME
05542-037
Figure 37. Tx Programming Sequence and Timing Diagram
Rev. A | Page 26 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SERIAL INTERFACE
The serial interface allows the user to program the eleven 32-bit
registers using a 3-wire interface (SCLK, SDATA, and SLE). It
consists of a level shifter, a 32-bit shift register, and 11 latches.
Signals should be CMOS-compatible. The serial interface is
powered by the regulator, and, therefore, is inactive when CE
is low.
Battery Voltage ADCIN/Temperature Sensor Readback
The battery voltage is measured at Pin VDD4. The readback
information is contained in Bit RV1 to Bit RV7. This also
applies for the readback of the voltage at the ADCIN pin and
the temperature sensor. From the readback information, the
battery or ADCIN voltage can be determined using
Data is clocked into the register, MSB first, on the rising edge of
each clock (SCLK). Data is transferred to one of 11 latches on
the rising edge of SLE. The destination latch is determined by
the value of the four control bits (C4 to C1). These are the
bottom four LSBs, DB3 to DB0, as shown in the timing diagram
in Figure 2. Data can also be read back on the SREAD pin.
READBACK FORMAT
The readback operation is initiated by writing a valid control
word to the readback register and setting the readback-enable
bit (R7_DB8 = 1). The readback can begin after the control
word has been latched with the SLE signal. SLE must be kept
high while the data is being read out. Each active edge at the
SCLK pin clocks the readback word out successively at the
SREAD pin, as shown in Figure 38, starting with the MSB first.
The data appearing at the first clock cycle following the latch
operation must be ignored.
RSSI Readback
The RSSI readback operation yields valid results in Rx mode.
The format of the readback word is shown in Figure 38. It
comprises the RSSI level information (Bit RV1 to Bit RV7), the
current filter gain (FG1 and FG2), and the current LNA gain
(LG1 and LG2) setting. The filter and LNA gain are coded in
accordance with the definitions in Register 9—AGC Register.
The input power can be calculated from the RSSI readback
value, as outlined in the RSSI/AGC section.
V
= (Battery_Voltage_Readback)/21.1
BATTERY
V
= (ADCIN_Voltage_Readback)/42.1
ADCIN
Silicon Revision Readback
The silicon revision readback word is valid without setting any
other registers, especially directly after power-up. The silicon
revision word is coded with four quartets in BCD format. The
product code (PC) is coded with two quartets extending from
Bit RV9 to Bit RV16. The revision code (RV) is coded with one
quartet extending from Bit RV1 to Bit RV8. The product code
should read back as PC = 0x25. The current revision code
should read as RC = 0x08.
Filter Calibration Readback
The filter calibration readback word is contained in Bit RV1 to
Bit RV8 and is for diagnostic purposes only. Using the automatic
filter calibration function, accessible through Register 6, is
recommended. Before filter calibration is initiated, Decimal 32
should be read back.
READBACK MODE
DB14
RSSI READBACK
BATTERY VOLTAGE/ADCIN/
TEMP. SENSOR READBACK
SILICON RE VISION
FILTER CAL READBACK
DB15
X
X
RV16
0
X
X
RV15
0
DB13
X
X
RV14
0
DB12
X
X
RV13
0
DB11
X
X
RV12
0
DB10
LG2
X
RV11
0
Figure 38. Readback Value Table
Rev. A | Page 27 of 44
READBACK VALUE
DB9
DB8
LG1
FG2
X
X
RV10
RV9
0
0
DB7
FG1
RV8
RV8
DB6
DB5
DB4
DB3
DB2
DB1
DB0
RV7
RV6
RV5
RV4
RV3
RV2
RV1
X
RV7
RV6
RV5
RV4
RV3
RV2
RV1
RV7
RV6
RV5
RV4
RV3
RV2
RV1
RV7
RV6
RV5
RV4
RV3
RV2
RV1
05542-038

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTERS
REGISTER 0—N REGISTER
MUXOUT
DB31
M3
M3 M2 M1 MUXOUT
0 REGULATOR READY (DEFAULT)
0
0 N DIVIDER OUTPUT
0 DIGITAL LOCK DETECT
1 ANALOG LOCK DET ECT
1 THREE-STATE
1PLL TEST MODES
1
PLL
Tx/Rx
ENABLE
DB27
DB28
DB29
DB30
M1
M2
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
TR1
PLE1
TR1
0 TRANSMIT
1
PLE1 PLL ENABLE
0 PLL OFF
1 PLL ON
0
R
1
0
1
0
1
0
1 Σ-∆ TEST MODES
TRANSMIT/
RECEIVE
RECEIVE
D
I
V
I
DB21
DB22
DB23
DB24
DB26
DB25
N5
N8
N7
D
E
R
U
T
O
P
N8 N7 N6 N5 N4 N3 N2 N1
031
032
.
.
.
1253
1254
1
N4
N6
U
T
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
N3
1
0
0
1
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
1
1
DB16
DB15
DB20
N2
1
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
DB17
DB19
DB18
N1
M15
1
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
M13
M14
1
0
.
.
.
0
1
1
M12
1
0
.
.
.
1
0
1255
Figure 39. Register 0—N Register
15-BIT FRACTI ONAL-N8-BIT INTEGER-N
DB14
DB13
DB12
M9
M11
M10
M15
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
N COUNTER
DIVIDE RATIO
.
.
.
DB11
M8
M14
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
DB10
M7
M13
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
DB9
M6
DB8
M5
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
DB7
M4
M3
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
DB6
M3
M2
0
0
1
.
.
.
0
0
1
1
DB5
M2
DB4
M1
M1
0
1
0
.
.
.
0
1
0
1
ADDRESS
BITS
DB2
DB3
C3 (0)
C4 (0)
FRACTIONAL
DIVIDE RATIO
0
1
2
.
.
.
32764
32765
32766
32767
DB1
C2 (0)
DB0
C1 (0)
05542-039
Register 0—N Register Comments
• The Tx/Rx bit (R0_DB27) configures the part in Tx or Rx mode and also controls the state of the internal Tx/Rx switch.
XTAL
F
•
OUT
(
R
NInteger
+×=
NFractional
)
15
2
• If operating in 433 MHz band with the VCO band bit set, the desired frequency, F
operating frequency, due to removal of the divide-by-2 stage in feedback path.
Rev. A | Page 28 of 44
, should be programmed to be twice the desired
OUT

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 1—OSCILLATOR/FILTER REGISTER
VA2 VA1
0 850–920
0 860–930
1 870–940
1
IR2 IR1
0 600kHz
0 900kHz
1 1200kHz
1
FILTER
BANDWIDTH
0
1
0
1NOT USED
DB16
VB1
DB15
DD2
I
CP
3.6kΩ
CP
(MA)
CURRENT
DB14
DD1
XOSC
ENABLE
VCO BAND
DB13
DB12
X1
V1
X1 XTAL OSC
0OFF
1ON
VCO BAND
V1
(MHz)
0 862–956
1 431–478
VCO
IF FILTER BW
DB21
DB22
DB23
IR2
IR1
VA2
FREQUENCY
OF OPERATION
0
1
0
1 88 0–950
VB4 VB3 VB2 VB1
0
00.25mA
0
00.5mA
.
.
14mA
1
VCO BIAS
ADJUST
DB20
DB19
VA1
VB4
0
1
1
0
.
.
1
1
CP2
000.3
010.9
101.5
112.1
DB18
VB3
VCO BIAS
CURRENT
DB17
VB2
CP1
RSET
Figure 40. Register 1—Oscillator/Filter Register
CLOCKOUT
DIVIDE
DB9
DB11
DB10
CL2
CL3
CL4
CL4 CL3 CL2 CL1
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
R COUNTER
XTAL
DOUBLER
DB8
DB7
DB6
D1
R3
CL1
R3 R2 R1
0
0
1
0
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
XTAL
D1
DOUBLER
0DISABLE
ENABLED
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
DB5
R2
0
1
0
.
.
.
1
ADDRESS
DB4
DB3
R1
C4 (0)
RF R COUNTER
DIVIDE RATIO
1
1
0
2
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
7
CLK
OUT
DIVIDE RATIO
OFF
2
4
.
.
.
30
BITS
DB2
C3 (0)
DB1
DB0
C2 (0)
C1 (1)
05542-040
Register 1—Oscillator/Filter Register Comments
• The VCO Adjust Bits R1_DB[20:21] should be set to 0 for operation in the 862 MHz to 870 MHz band and set to 3 for operation in the
902 MHz to 928 MHz band.
• VCO bias setting should be 0xA for operation in the 862 MHz to 870 MHz band and 0xC for operation in the 902 MHz to 928 MHz
band. All VCO gain numbers are specified for these settings.
Rev. A | Page 29 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 2—TRANSMIT MODULATION REGISTER
PA BIAS
DB31
PA2
PA2
0
0
1
1
INDEX
TxDATA
INVERT
DB28
DB29
DB30
IC2
DI1
PA1
IC2XIC1XMC3XMC2XMC1
DI1
0
TxDATA
1
TxDATA
PA BIAS
PA1
5µA
0
7µA
1
9µA
0
11µA
1
COUNTER
DB27
IC1
GFSK MOD
CONTROL
DB26
DB25
MC3
MC2
ADDRESS
PA
BITS
ENABLE
DB4
PE1
POWER AMPLIFIER
OFF
ON
MUTE PA UNTIL
LOCK DETECT HIGH
OFF
ON
DB3
C4 (0)
DB2
C3 (0)
DB1
C2 (1)
DB0
C1 (0)
05542-041
DB10
P2
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
MODULATION
SCHEME
DB9
DB8
S3
P1
S3
S1
S2
0
0
0
X
X
X
P2
.
X
.
0
.
0
.
1
.
.
.
.
.
1
.
MUTE PA
UNTIL LOCK
DB7
DB6
DB5
S2
S1
MP1
PE1
0
1
MP1
0
1
MODULATION SCHEME
FSK
INVALID
P1
X
PA OFF
0
–16.0dBm
1
–16 + 0.45dBm
0
–16 + 0.90dBm
.
.
.
.
1
13dBm
MODULATION PARAMETER POWE R AMPLIFIER
DB16
DB15
DB19
D5
D2
0
0
1
1
.
1
DB18
D4
D1
0
1
0
1
.
1
DB17
D3
F DEVIATION
PLL MODE
1 × F
2 × F
3 × F
.
511 × F
DB20
DB21
DB22
DB23
DB24
D9
D8
D6
MC1
X
D7
FOR FSK MO DE,
....
D9
0
0
0
0
.
1
D3
....
0
....
0
....
0
....
0
....
.
....
1
DB14
P6
D1
D2
STEP
STEP
STEP
STEP
DB11
DB13
DB12
P3
P4
P5
POWER AMPLIFIER OUTPUT LEVEL
P6
0
0
0
0
.
.
1
Figure 41. Register 2—Transmit Modulation Register
Register 2—Transmit Modulation Register Comments
• F
= PFD/1214.
STEP
• When operating in the 431 MHz to 464 MHz band, F
= PFD/1215.
STEP
• PA bias d e f au lt = 9 µA .
Rev. A | Page 30 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 3—RECEIVER CLOCK REGISTER
SEQUENCER CLO CK DIVIDE CDR CLOCK DIVIDE
DB16
DB15
DB23
SK8
SK8
0
0
.
1
1
DB20
DB21
DB22
SK7
SK5
SK6
...
SK7
0
0
.
1
1
SK3
...
0
...
0
...
.
...
1
...
1
DB17
DB19
DB18
SK3
SK4
SK2
SK1
SK2
1
0
0
1
.
.
0
1
1
1
FS8
0
0
.
1
1
DB14
FS8
FS7
SK1
SEQ_CLK_DIVIDE
1
2
.
254
255
...
FS7
...
0
...
0
...
.
...
1
...
1
DB13
DB12
FS5
FS6
FS3
0
0
.
1
1
DB11
FS4
FS2
0
1
.
1
1
DB9
DB10
FS2
FS3
FS1
1
0
.
0
1
DEMOD
CLOCK DIVIDE
DB8
DB7
DB6
FS1
OK2
OK1
BK2
0
0
1
OK1
OK2
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
CDR_CLK_DIVIDE
1
2
.
254
255
BB OFFSET
DB5
BK2
BK1
0
1
x
DEMOD_CLK_DIVIDE
4
1
2
3
ADDRESS
BITS
CLOCK DIVIDE
DB4
DB3
BK1
C4(0)
BBOS_CLK_DIVI DE
4
8
16
Figure 42. Register 3—Receiver Clock Register
Register 3—Receiver Clock Register Comments
• Baseband offset clock frequency (BBOS_CLK) must be greater than 1 MHz and less than 2 MHz, where:
CLKBBOS___ =
XTAL
DIVIDECLKBBOS
DB1
DB0
DB2
C2(1)
C1(1)
C3(0)
05542-042
• The demodulator clock (DEMOD_CLK) must be < 12 MHz, where:
CLKDEMOD___ =
XTAL
DIVIDECLKDEMOD
• Data/clock recovery frequency (CDR_CLK) should be within 2% of (32 × data rate), where:
CLKCDR
_ =
_
DIVIDECLKCDR
__
CLKDEMOD
Note that this can affect the choice of XTAL, depending on the desired data rate.
• The sequencer clock (SEQ_CLK) supplies the clock to the digital receive block. It should be close to 100 kHz.
CLKSEQ___ =
XTAL
DIVIDECLKSEQ
Rev. A | Page 31 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 4—DEMODULATOR SETUP REGISTER
ADDRESS
DEMOD
DB31
DB30
DB29
DB28
DB27
DB26
DEMOD LOCK/
DB25
LM2
DEMODULATOR LOCK SET TING PO STDEMODULATOR BW
SYNC WORD MATCH
DB16
DB15
DB24
LM1
DB23
DL8
DB22
DL7
DB21
DL6
DB20
DL5
DB19
DL4
DB18
DL3
DB17
DL2
DB14
DB13
DB12
DL1
DW10
DW7
DW8
DW9
DB9
DB8
DB11
DB10
DW5
DW6
DB7
DW3
DW4
DW2
DB6
DW1
DB5
DS2
SELECT
DB4
DS1
DB3
C4(0)
BITS
DB2
C3(1)
DB1
C2(0)
DB0
C1(0)
DEMODUL ATOR
DS1
TYPE
0
LINEAR DEMODUL ATOR
1
CORRELATOR/DEMODULATOR
0
INVALID
1
INVALID
05542-043
DEMOD MODE
0
1
2
3
4
5
LM2
0
0
0
0
1
1
LM1
0
0
1
1
0
1
DEMOD LOCK/ SYNC WORD MATCH
DL8
SERIAL PORT CONTROL – FREE RUNNING
0
SERIAL PORT CONTROL – LOCK THRESHOLD
1
SYNC WORD DET ECT – FREE RUNNI NG
0
SYNC WORD DET ECT – LOCK T HRESHOLD
1
INTERRUPT/ LOCK PIN L OCKS THRESHOLD
X
DEMOD LOCKED AFTER DL8–DL1 BIT S
DL8
MODE5 ONLY
DL7
DL8
0
0
0
.
1
1
0
0
0
.
1
1
DL3
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
DL2
DL1
0
0
0
0
.
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
.
.
1
0
1
1
INT/LO CK PIN
–
–
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
INPUT
–
LOCK_THRESHOLD_TIM EOUT
0
1
2
.
254
255
DS2
0
0
1
1
Figure 43. Register 4—Demodulator Setup Register
Register 4—Demodulator Setup Register Comments
• Demodulator Mode 1, Demodulator Mode 3, Demodulator Mode 4, and Demodulator Mode 5 are modes that can be activated to allow
the ADF7025 to demodulate data-encoding schemes that have run-length constraints greater than 7.
11
Fπ2
××
• Post_Demod_BW =
DEMOD_CLK
CUTOFF
, where the cutoff frequency (F
) of the postdemodulator filter should typically be 0.75 times
CUTOFF
the data rate.
• For Mode 5, the Timeout Delay to Lock Threshold = (LOCK_THRESHOLD_SETTING)/SEQ_CLK, where SEQ_CLK is defined in the
Register 3—Receiver Clock Register section.
Rev. A | Page 32 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 5—SYNC BYTE REGISTER
LENGTH
PL1
0
1
0
1
DB4
PL1
CONTRO L
BITS
DB2
DB3
C3(1)
C4(0)
SYNC BYTE
LENGTH
12 BITS
16 BITS
20 BITS
24 BITS
DB1
DB0
C2(0)
C1(1)
05542-044
DB31
DB30
DB29
DB28
DB27
DB26
DB25
SYNC BYTE SEQ UENCE
DB22
DB23
DB24
DB21
DB20
DB19
DB18
DB17
DB16
DB15
DB14
DB13
DB12
MATCHING
SYNC BYTE
TOLERANCE
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
MT2
MT1
0
1
0
1
MT1
DB5
PL2
PL2
0
0
1
1
MATCHING
TOLERANCE
0 ERRORS
1 ERROR
2 ERRORS
3 ERRORS
DB11
DB10
MT2
0
0
1
1
Figure 44. Register 5—Sync Byte Register
Register 5—Sync Byte Register Comments
• Sync byte detect is enabled by programming Bits R4_DB [25:23] to 010 or 011.
• This register allows a 24-bit sync byte sequence to be stored internally. If the sync byte detect mode is selected, then the INT/LOCK pin
goes high when the sync byte has been detected in Rx mode. Once the sync word detect signal has gone high, it goes low again after
nine data bits.
• The transmitter must transmit the MSB of the sync byte first and the LSB last to ensure proper alignment in the receiver sync byte
detection hardware.
• Choose a sync byte pattern that has good autocorrelation properties.
Rev. A | Page 33 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 6—CORRELATOR/DEMODULATOR REGISTER
RESET
DB31
CDR
RESET
Rx
DB30
DEMOD
RESET
RI1
0
1
RxDATA
FC9
0
0
.
.
.
.
1
INVERT
DB29
RI1
DB28
FC9
RxDATA
INVERT
RxDATA
RxDATA
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
DB4
TD1
ADDRESS
BITS
DB3
C4(0)
DB2
C3(1)
DB1
C2(1)
DB0
C1(0)
05542-045
LNA
CAL
MIXER
IF FILTER
LINEARITY
DB19
CA1
DB17
DB18
LI2
ML1
800µA (DEFAULT)
DB20
DB21
DB22
DB23
DB24
DB26
DB27
DB25
FC4
FC7
FC8
FC6
ML1
0
1
FC4
FC5
FC6
0
0
.
.
.
.
1
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
FC3
FC5
CA1
FILTER CAL
0
NO CAL
1
CALIBRATE
MIXER LINEARITY
DEFAULT
HIGH
FC2
FC3
0
0
1
0
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
FC1
FC2
LI20LI10LNA BIAS
FILTER CLOCK
FC1
DIVIDE RATIO
1
1
0
2
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
511
DOT
CURRENT
DB16
LI1
PRODUCT
LNA MODE
DB15
DB14
DB13
LG1
DP1
TD10
DP1
0
1
LG1
0
1
DISCRIMINATOR BWIF FILTER DIVIDER
DB9
DB11
DB12
DB10
TD6
TD7
TD8
TD9
DOT PRODUCT
CROSS PRODUCT
INVALID
LNA MODE
DEFAULT
REDUCED GAIN
DB8
TD5
DB7
TD4
DB6
TD3
DB5
TD2
Figure 45. Register 6—Correlator/Demodulator Register
Register 6—Correlator/Demodulator Register Comments
• See the FSK Correlator/Demodulator section for an example of how to determine register settings.
• Nonadherence to correlator programming guidelines results in poor sensitivity.
• The filter clock is used to calibrate the LP filter. The filter clock divide ratio should be adjusted so that the frequency is 50 kHz.
The formula is XTAL/FILTER_CLOCK_DIVIDE.
• The filter should be calibrated only when the crystal oscillator is settled. The filter calibration is initiated every time Bit R6_DB19
is set high.
• Discriminator_BW = DEMOD_CLK/(4 × DEVIATION_Frequency). See the FSK Correlator/Demodulator section.
Maximum value = 600.
• When LNA Mode = 1 (reduced gain mode), the Rx is prevented from selecting the highest LNA gain setting. This can be used when
linearity is a concern. See the Readback Format section for details of the different Rx modes.
Rev. A | Page 34 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 7—READBACK SETUP REGISTER
RB3
0
1
READBACK
DISABLED
ENABLED
DB8
RB3
RB2
0
0
1
1
READBACK
SELECT
DB7
RB1
0
1
0
1
ADC
MODE
DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2
AD1AD2RB1RB2
READBACK MODE
INVALID
ADC OUTPUT
FILTER CAL
SILICON RE V
AD2
0
0
1
1
CONTROL
BITS
C3(1)C4(0)
ADC MODE
AD1
MEASURE RSSI
0
BATTERY VOLTAGE
1
TEMP SENSOR
0
TO EXTERNAL PIN
1
DB1 DB0
C2(1) C1(1)
05542-046
Figure 46. Register 7—Readback Setup Register
Register 7—Readback Setup Register Comments
• Readback of the measured RSSI value is valid only in Rx mode. Readback of the battery voltage, the temperature sensor, and the voltage
at the external pin is not available in Rx mode if AGC is enabled.
• Readback of the ADC value is valid in Tx mode only if the log amp/RSSI has not been disabled through the Power-Down Bit R8_DB10.
The log amp/RSSI section is active by default upon enabling Tx mode.
• See the Readback Format section for more information.
Rev. A | Page 35 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 8—POWER-DOWN TEST REGISTER
CONTROL
C3(0)C4(1)
PLE1
(FROM REG 0)
0
0
0
0
1
BITS
DB1 DB0
C2(0) C1(0)
PD2
0
0
1
1
X
PD1
0
1
0
1
X
LOOP
CONDIT ION
VCO/PLL OFF
PLL ON
VCO ON
PLL/VCO ON
PLL/VCO ON
5542-047
PA ENABLE
DB15 DB14 DB13 DB12 DB11
PD7
PA (R x M O DE )
PD7
PA OF F
0
PA ON
1
Tx/Rx SWITCH
SW1
DEFAULT (ON)
0
OFF
1
RSSI MODE
LR1
LR2
RSSI OFF
0
X
X
RSSI ON
1
Rx MODE
INTERNAL Tx/ Rx
DEMOD ENABLE
PD6
DEMOD OFF
0
DEMOD ON
1
SWITCH ENABLE
LOG AMP/
RSSI
LR2SW1
DB10 DB9
LR1 PD6
DEMOD
PD5
0
1
ENABLE
ADC
FILTER
ENABLE
DB7
DB8
PD5
ADC ENABLE
ADC OFF
ADC ON
VCO
SYNTH
ENABLE
ENABLE
ENABLE
ENABLE
LNA/MIXER
DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2
PD1PD2PD3PD4
LNA/MIXER E NABLE
PD3
LNA/MIXER O FF
0
LNA/MIXER O N
1
FILTER ENABLE
PD4
FILTER OFF
0
FILTER ON
1
Figure 47. Register 8—Power-Down Test Register
Register 8—Power-Down Test Register Comments
• For a combined LNA/PA matching network, Bit R8_DB12 should always be set to 0. This is the power-up default condition.
• It is not necessary to write to this register under normal operating conditions.
Rev. A | Page 36 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 9—AGC REGISTER
DB31
DB30
DB29
DB28
FI1
0
1
DB27
FG2
0
0
1
1
DIGITAL
TEST IQ
FILTER CURRENT
LOW
HIGH
DB26
FG1
0
1
0
1
FILTER
CURRENT
DB24
DB25
FI1
FILTER GAIN
8
24
72
INVALID
FILTER
GAIN
DB23
FG2
LG2
0
0
1
1
DB22
FG1
LNA
GAIN
DB21
LG2
LG1
0
1
0
1
AGC HIGH THRESHOLD
AGC
GAIN
SEARCH
CONTROL
DB16
DB15
DB20
DB19
LG1
GC1
GS1
0
1
GC1
0
1
LNA GAIN
<1
3
10
30
DB17
DB18
GS1
GH7
AGC SEARCH
AUTO AGC
HOLD SETTING
GAIN CONTROL
AUTO
USER
DB14
GH5
GH6
GH4
GH7
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
Figure 48. Register 9—AGC Register
DB13
GH3
GH6
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
0
0
0
GL7
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
DB12
GH2
GH5
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
0
0
1
AGC LOW T HRESHOLD
DB9
DB11
DB10
GL6
GL7
GH1
GL5
GL6
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
1
1
GH4
GH3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
1
1
1
0
0
GL4
0
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
1
1
GH2
0
1
1
0
.
.
.
1
1
0
DB8
GL5
GL3
0
0
0
1
.
.
.
1
1
1
DB7
GL4
GH1
1
0
1
0
.
.
.
0
1
0
DB6
GL3
GL2
GL1
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
.
.
.
.
.
.
0
1
1
0
1
1
RSSI LEVEL
CODE
1
2
3
4
.
.
.
78
79
80
DB5
GL2
ADDRESS
BITS
DB4
DB3
GL1
C4(1)
AGC LOW
THRESHOLD
1
2
3
4
.
.
.
61
62
63
DB1
DB0
DB2
C2(0)
C1(1)
C3(0)
05542-048
Register 9—AGC Register Comments
• The recommended AGC threshold settings are AGC_LOW_THRESHOLD = 15, AGC_HIGH_THRESHOLD = 79.
The default settings (that is, if this register is not programmed) are AGC_LOW_THRESHOLD = 30,
default AGC_HIGH_THRESHOLD = 70. See the RSSI/AGC section for details.
• AGC high and low settings must be more than 30 apart to ensure correct operation.
• LNA gain of 30 is available only if LNA mode, R6_DB15, is set to 0.
Rev. A | Page 37 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 10—AGC 2 REGISTER
DB31
I/Q
SELECT
DB28
DB29
DB30
SIQ2
SIQ2
SELECT IQ
0
PHASE TO I CHANNE L
1
PHASE TO Q CHANNE L
I/Q PHASE
ADJUST
DB26
DB27
PH3
PH4
DB25
PH2
DB24
PH1
I/Q
SELECT
RESERVED
DB22
DB23
R1
SIQ1
SIQ2
SELECT IQ
0
GAIN TO I CHANNEL
1
GAIN TO Q CHANNEL
UP/DOW N
DB21
UD1
DB20
GC5
DB19
GC4
DB18
GC3
DB17
GC2
DB16
GC1
Figure 49. Register 10—AGC 2 Register
Register 10—AGC 2 Register Comments
• Register 10 is not used under normal operating conditions.
• If adjusting AGC Delay or Leak Factor, clear Bit DB31 to Bit DB16.
AGC DELAYI/Q GAINADJUST L EAK FACTOR
DB13
DH2
DB12
DH1
DB11
DB10
GL6
GL7
DEFAULT = 0xA
DB15
DB14
DH4
DH3
DEFAULT = 0xA DE FAULT = 0x2
DB9
GL5
DB8
GL4
PEAK RESPONSE
DB7
DB6
PR4
PR3
ADDRESS
BITS
DB5
DB4
PR1
PR2
DB1
DB0
DB2
DB3
C2(1)
C1(0)
C3(0)
C4(1)
05542-049
Rev. A | Page 38 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 12—TEST REGISTER
P
0
1
PRESCALER
DB31
PRE
ANALOG TES T
MUX
DB28
DB29
DB30
PRESCALER
4/5 (DEFAULT)
8/9
DB27
FORCE
CS1
0
1
LD HIGH
DB26
OSC TEST
DB25
QT1
CAL SOURCE
INTERNAL
SERIAL IF BW CAL
IMAGE FILTER ADJUST
SOURCE
DB22
DB23
DB24
SF6
SF5
CS1
DEFAULT = 32. INCREASE
NUMBER TO INCREASE BW
IF USER CAL ON
DB21
SF4
DB20
SF3
DB19
SF2
DB18
SF1
Figure 50. Register 12—Test Register
Using the Test DAC on the ADF7025 to Implement
Analog FM DEMOD and Measuring SNR
The test DAC allows the output of the postdemodulator filter
for both the linear and correlator/demodulators to be viewed
externally. It takes the 16-bit filter output and converts it to a
high frequency, single-bit output using a second-order error
feedback Σ-Δ converter. The output can be viewed on the
XCLK
pin. This signal, when IF-filtered appropriately, can
OUT
then be used to
• Monitor the signals at the FSK postdemodulator filter
output. This allows the demodulator output SNR to be
measured. Eye diagrams can also be constructed of the
received bit stream to measure the received signal quality.
DIGITAL
TEST MODES
DB16
DB15
DB17
DB14
COUNTER
CR1
0
1
DB13
Σ-∆
TEST MODES
RESET
DB11
DB12
T8
T9
COUNTER RESET
DEFAULT
RESET
DB10
T7
PLL TEST MODES
DB9
DB8
T5
T6
DB7
T4
DB6
T3
DB5
T2
DB4
T1
ADDRESS
BITS
DB2
DB3
C3(1)
C4(1)
DB1
C2(0)
DB0
C1(0)
5542-050
Programming the test register, Register 12, enables the test
DAC. Both the linear and correlator/demodulator outputs
can be multiplexed into the DAC.
Register 13 allows a fixed offset term to be removed from the
signal in the case where there is an error in the received signal
frequency. If there is a frequency error in the signal, the user
should program half this value into the offset removal field.
It also has a signal gain term to allow usage of the maximum
dynamic range of the DAC.
Setting Up the Test DAC
• Digital test modes = 7: enables the test DAC, with no
offset removal (0x0001C00C).
• Provide analog FM demodulation.
While the correlators and filters are clocked by DEMOD_CLK,
CDR_CLK clocks the test DAC. Note that, although the test
DAC functions in a regular user mode, the best performance is
achieved when the CDR_CLK is increased up to or above the
frequency of DEMOD_CLK. The CDR block does not function
when this condition exists.
Rev. A | Page 39 of 44
• Digital test modes = 10: enables the test DAC, with
offset removal.
The output of the active demodulator drives the DAC; that is, if
the FSK correlator/demodulator is selected, the correlator filter
output drives the DAC.

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
REGISTER 13—OFFSET REMOVAL AND SIGNAL GAIN REGISTER
DB4
CONTROL
BITS
DB2
DB3
C3(1)
C4(1)
DB1
C2(0)
TEST DAC GAI N TEST DAC OF FSET REMOVAL
DB20
DB21
DB22
DB23
DB24
DB26
DB27
DB31
DB30
DB29
DB28
DB25
PE4
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
DB19
PE3
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
DB18
PE2
0
0
1
.
.
.
1
PULSE
EXTENSION
DB16
DB15
DB17
PE4
PE1
PULSE EXTENSION
0
NORMAL PULSE W IDTH
1
2× PULSE W IDTH
0
3× PULSE W IDTH
.
.
.
.
.
.
1
16× PULSE WIDTH
DB14
PE3
DB13
PE2
DB12
PE1
KPKI
DB9
DB8
DB7
DB6
DB11
DB10
DB5
Figure 51. Register 13—Offset Removal and Signal Gain Register
Register 13—Offset Removal and Signal Gain Register Comments
Because the linear demodulator output is proportional to frequency, it usually consists of an offset combined with a relatively
low signal. The offset can be removed, up to a maximum of 1.0, and gained to use the full dynamic range of the DAC, as follows:
DAC_Input = (2^ Test_DAC_Gain) × (Signal − Test_DAC_Offset_Removal/4096).
DB0
C1(1)
05542-051
Rev. A | Page 40 of 44

ADF7025
R
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
0.30
0.23
0.18
PIN 1
48
INDICATO
1
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
7.00
0.60 MAX
37
36
0.60 MAX
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
TOP
VIEW
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
6.75
BSC SQ
0.20 REF
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
COPLANARITY
0.08
25
24
EXPOSED
PA D
(BOTTOM VIEW)
5.50
REF
13
4.25
4.10 SQ
3.95
12
0.25 MIN
Figure 52. 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
7 mm × 7 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-48-3)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
ADF7025BCPZ
ADF7025BCPZ-RL1 −40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-48-3
ADF7025BCPZ-RL71 −40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-48-3
EVAL-ADF70XXMB Control Mother Board
EVAL-ADF70XXMB2 Evaluation Platform
EVAL-ADF7025DB1 902–928 MHz Daughter Board
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ] CP-48-3
Rev. A | Page 41 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 42 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 43 of 44

ADF7025
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
NOTES
©2006 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05542-0-2/06(A)
Rev. A | Page 44 of 44
 Loading...
Loading...