REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
AD9832
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1999
CMOS
Complete DDS
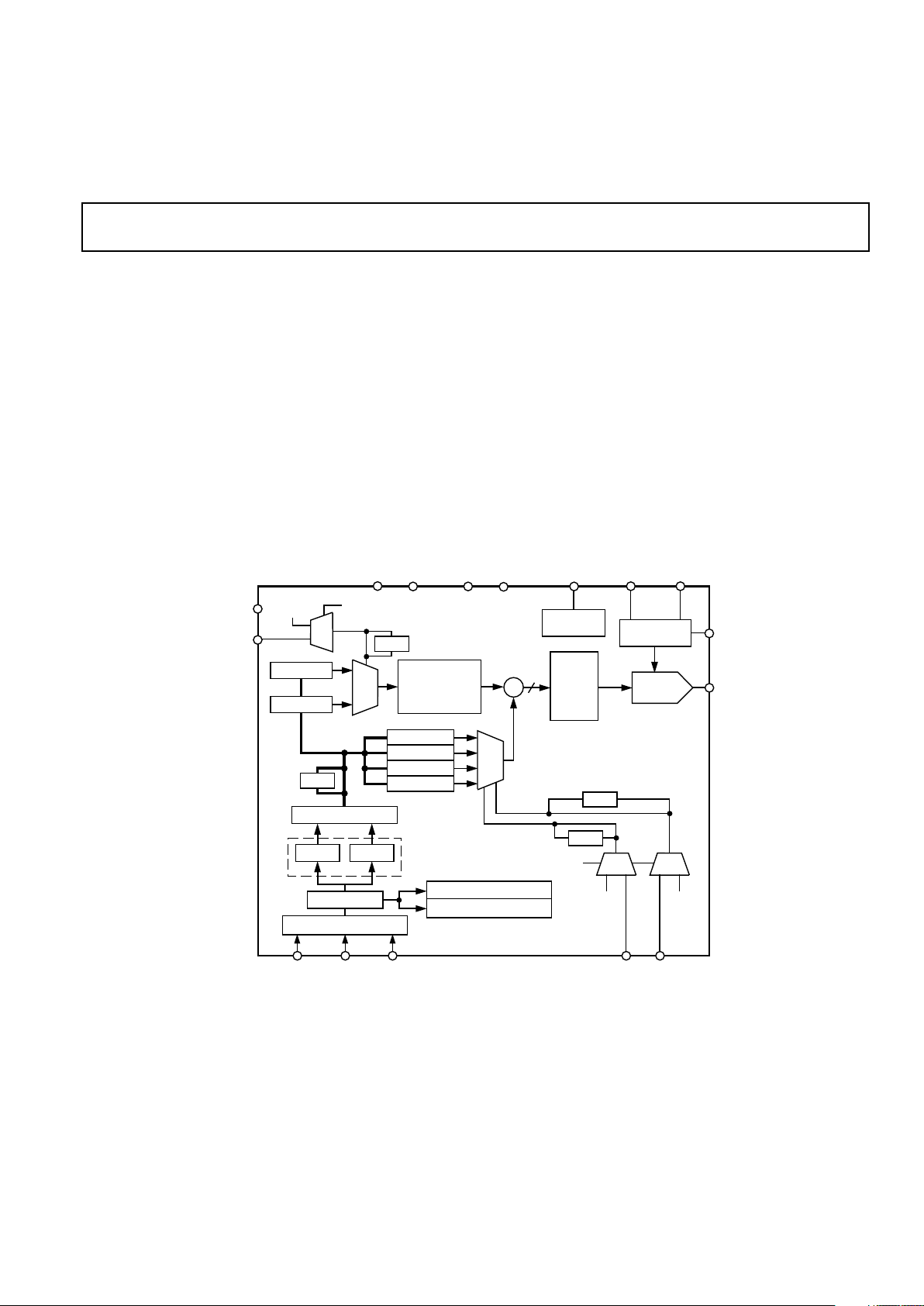
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
IOUT
COMP
REFINFS ADJUST
REFOUT
AGND
AVDDDGND
DVDD
MCLK
PSEL0
PSEL1
12
Σ
AD9832
ON-BOARD
REFERENCE
10-BIT DAC
PHASE0 REG
PHASE1 REG
PHASE2 REG
PHASE3 REG
FULL-SCALE
CONTROL
SIN
ROM
PHASE
ACCUMULATOR
(32 BIT)
MUX
FREQ0 REG
FREQ1 REG
MUX
16-BIT DATA REGISTER
SYNC
FSELECT
FSELECT
BIT
SELSRC
SYNC
8 LSBs8 MSBs
DECODE LOGIC
FSYNC SCLK SDATA
SERIAL REGISTER
CONTROL REGISTER
FSELECT/PSEL REGISTER
DEFER REGISTER
SYNC
SYNC
SELSRC
PSEL0
BIT
PSEL1
BIT
FEATURES
3 V/5 V Power Supply
25 MHz Speed
On-Chip SINE Look-Up Table
On-Chip 10-Bit DAC
Serial Loading
Power-Down Option
45 mW Power Consumption
16-Lead TSSOP
APPLICATIONS
DDS Tuning
Digital Demodulation
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9832 is a numerically controlled oscillator employing
a phase accumulator, a sine look-up table and a 10-bit D/A
converter integrated on a single CMOS chip. Modulation
capabilities are provided for phase modulation and frequency
modulation.
Clock rates up to 25 MHz are supported. Frequency accuracy
can be controlled to one part in 4 billion. Modulation is effected
by loading registers through the serial interface.
A power-down bit allows the user to power down the AD9832
when it is not in use, the power consumption being reduced to
5 mW (5 V) or 3 mW (3 V). The part is available in a 16-lead
TSSOP package.
–2– REV. A
AD9832–SPECIFICATIONS
1
(VDD = +3.3 V ⴞ 10%; +5 V ⴞ 10%; AGND = DGND = 0 V; TA = T
MIN
to T
MAX
; REFIN =
REFOUT; R
SET
= 3.9 k⍀; R
LOAD
= 300 ⍀ for IOUT unless otherwise noted)
Parameter AD9832B Units Test Conditions/Comments
SIGNAL DAC SPECIFICATIONS
Resolution 10 Bits
Update Rate (f
MAX
) 25 MSPS nom
I
OUT
Full Scale 4 mA nom
4.5 mA max
Output Compliance 1.35 V max 3 V Power Supply
DC Accuracy
Integral Nonlinearity ±1 LSB typ
Differential Nonlinearity ±0.5 LSB typ
DDS SPECIFICATIONS
2
Dynamic Specifications
Signal to Noise Ratio 50 dB min f
MCLK
= 25 MHz, f
OUT
= 1 MHz
Total Harmonic Distortion –53 dBc max f
MCLK
= 25 MHz, f
OUT
= 1 MHz
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
3
f
MCLK
= 6.25 MHz, f
OUT
= 2.11 MHz
Narrow Band (±50 kHz) –72 dBc min 5 V Power Supply
–70 dBc min 3 V Power Supply
Wide Band (±2 MHz) –50 dBc min
Clock Feedthrough –60 dBc typ
Wake-Up Time
4
1 ms typ
Power-Down Option Yes
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Internal Reference @ +25°C 1.21 Volts typ
T
MIN
to T
MAX
1.21 ± 7% Volts min/max
REFIN Input Impedance 10 MΩ typ
Reference TC 100 ppm/°C typ
REFOUT Output Impedance 300 Ω typ
LOGIC INPUTS
V
INH
, Input High Voltage VDD – 0.9 V min
V
INL
, Input Low Voltage 0.9 V max
I
INH
, Input Current 10 µA
max
CIN, Input Capacitance 10 pF max
POWER SUPPLIES
AVDD 2.97/5.5 V
min/V max
DVDD 2.97/5.5 V
min/V max
I
AA
5mA
max 5 V Power Supply
I
DD
2.5 + 0.4/MHz mA typ 5 V Power Supply
I
AA
+ I
DD
5
15 mA max 3 V Power Supply
24 mA
max 5 V Power Supply
Low Power Sleep Mode 350 µA max
NOTES
1
Operating temperature range is as follows: B Version, –40 °C to +85°C.
2
100% production tested.
3
f
MCLK
= 6.25 MHz, Frequency Word = 5671C71C HEX, f
OUT
= 2.11 MHz.
4
See Figure 11. To reduce the wake-up time at low power supplies and low temperature, the use of an external reference is suggested.
5
Measured with the digital inputs static and equal to 0 V or DVDD.
The AD9832 is tested with a capacitive load of 50 pF. The part can be operated with higher capacitive loads, but the magnitude of the analog output will be attenuated.
For example, a 5 MHz output signal will be attenuated by 3 dB when the load capacitance equals 85 pF.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
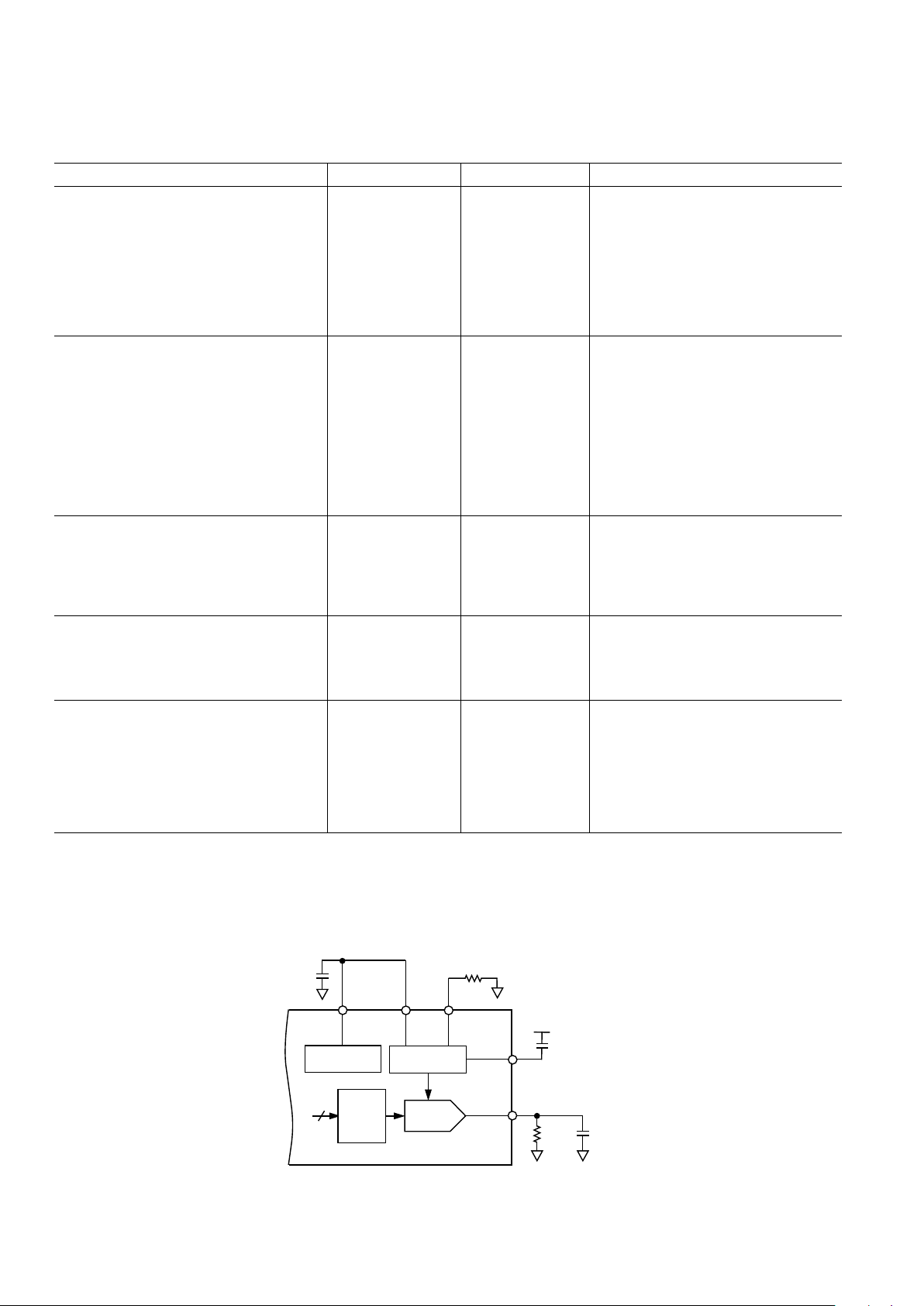
IOUT
COMP
REFIN
FS
ADJUST
REFOUT
12
AD9832
ON-BOARD
REFERENCE
10-BIT DAC
SIN
ROM
FULL-SCALE
CONTROL
300Ω 50pF
R
SET
3.9kΩ
10nF
10nF
AVDD
Figure 1. Test Circuit with Which Specifications Are Tested
–3–
AD9832
REV. A
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
(VDD = +3.3 V ⴞ 10%; +5 V ⴞ 10%; AGND = DGND = 0 V, unless otherwise noted)
Limit at
T
MIN
to T
MAX
Parameter (B Version) Units Test Conditions/Comments
t
1
40 ns min MCLK Period
t
2
16 ns min MCLK High Duration
t
3
16 ns min MCLK Low Duration
t
4
50 ns min SCLK Period
t
5
20 ns min SCLK High Duration
t
6
20 ns min SCLK Low Duration
t
7
15 ns min FSYNC to SCLK Falling Edge Setup Time
t
8
20 ns min FSYNC to SCLK Hold Time
SCLK – 5 ns max
t
9
15 ns min Data Setup Time
t
10
5 ns min Data Hold Time
t
11
8 ns min FSELECT, PSEL0, PSEL1 Setup Time Before MCLK Rising Edge
t
11A
* 8 ns min FSELECT, PSEL0, PSEL1 Setup Time After MCLK Rising Edge
*See Pin Function Descriptions.
Guaranteed by design but not production tested.
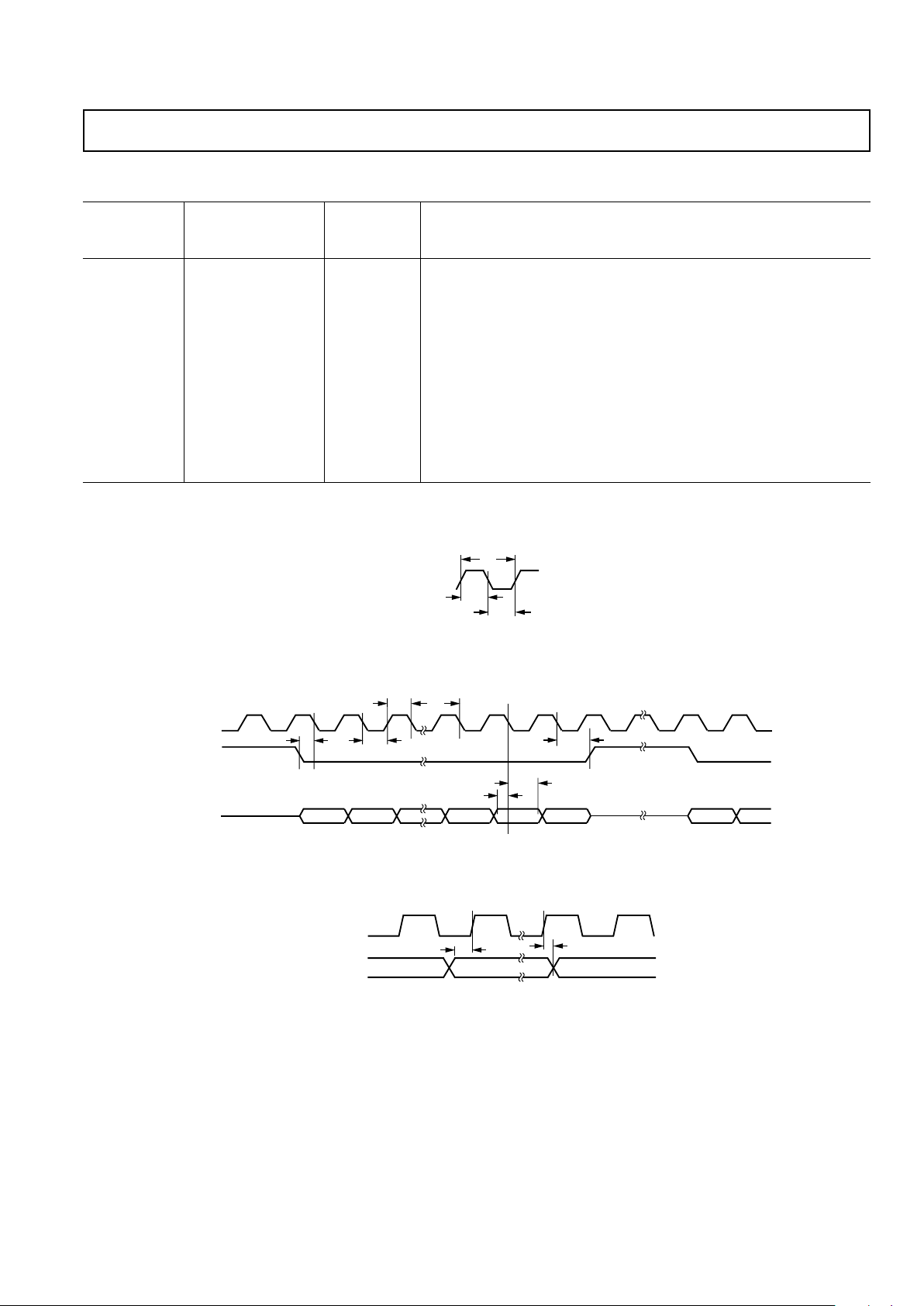
MCLK
t
2
t
1
t
3
Figure 2. Master Clock
SCLK
FSYNC
SDATA
t
5
t
4
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
10
t
9
D15 D14 D2 D1 D0 D15 D14
Figure 3. Serial Timing
t
11A
t
11
VALID DATA VALID DATA VALID DATA
MCLK
FSELECT
PSEL0, PSEL1
Figure 4. Control Timing
AD9832
–4– REV. A
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(T
A
= +25°C unless otherwise noted)
AVDD to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
DVDD to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +7 V
AVDD to DVDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
AGND to DGND. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.3 V to +0.3 V
Digital I/O Voltage to DGND . . . . –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V
Analog I/O Voltage to AGND . . . . . –0.3 V to AVDD + 0.3 V
Operating Temperature Range
Industrial (B Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +150°C
TSSOP θ
JA
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +220°C
ESD Rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . > 4500 V
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option*
AD9832BRU –40°C to +85°C 16-Lead TSSOP RU-16
*RU = Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP).
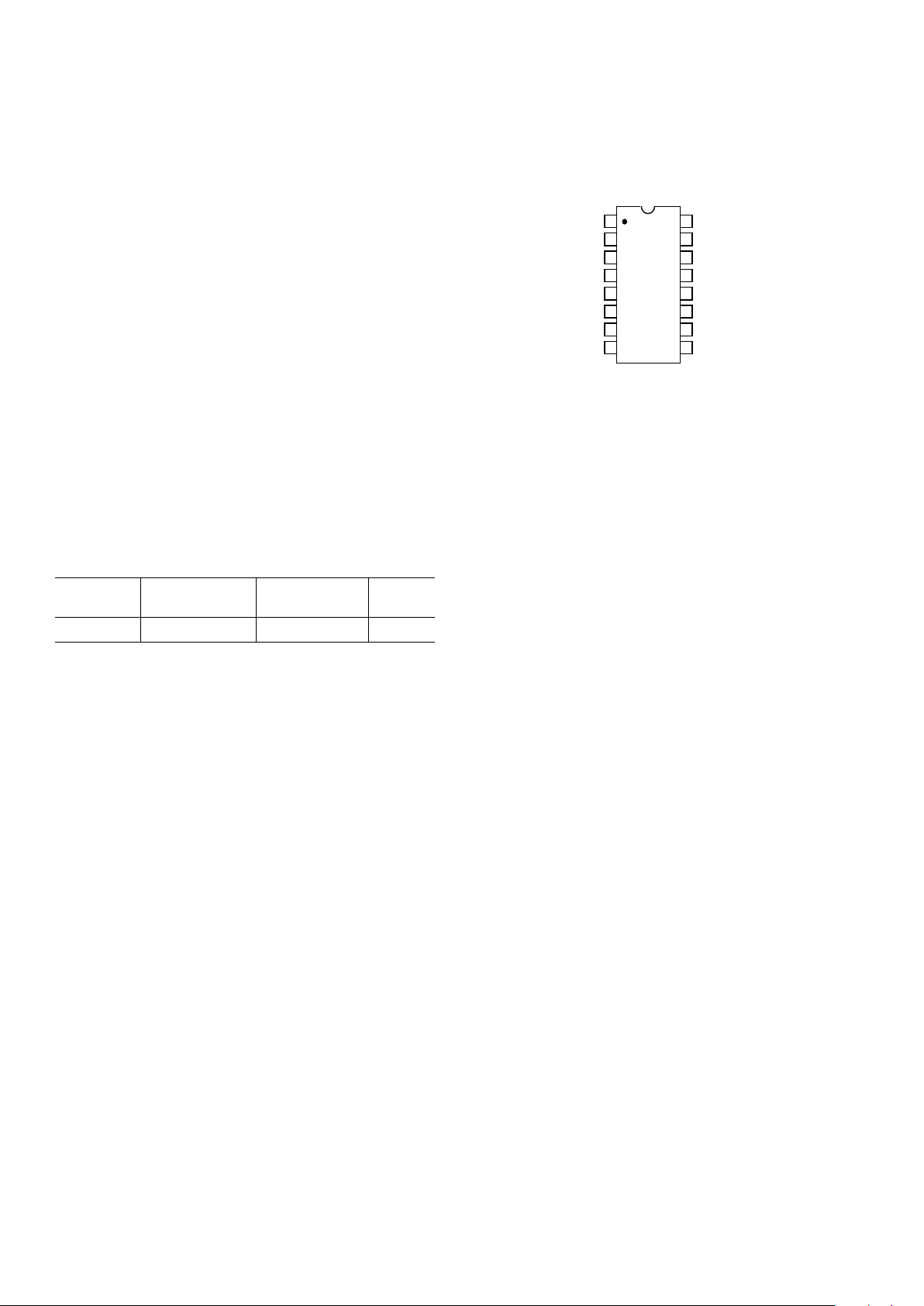
PIN CONFIGURATION
14
13
12
11
16
15
10
9
8
1
2
3
4
7
6
5
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
AD9832
FS ADJUST
AGND
IOUT
AVDD
COMP
REFIN
REFOUT
DVDD
FSELECT
PSEL1
PSEL0DGND
MCLK
SCLK
SDATA
FSYNC

–5–
AD9832
REV. A
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin # Mnemonic Function
ANALOG SIGNAL AND REFERENCE
1 FS ADJUST Full-Scale Adjust Control. A resistor (R
SET
) is connected between this pin and AGND. This determines
the magnitude of the full-scale DAC current. The relationship between R
SET
and the full-scale current is
as follows:
IOUT
FULL-SCALE
= 12.5 × V
REFIN/RSET
V
REFIN
= 1.21 V nominal, R
SET
= 3.9 kΩ typical
2 REFIN Voltage Reference Input. The AD9832 can be used with either the onboard reference, which is available
from pin REFOUT, or an external reference. The reference to be used is connected to the REFIN pin.
The AD9832 accepts a reference of 1.21 V nominal.
3 REFOUT Voltage Reference Output. The AD9832 has an onboard reference of value 1.21 V nominal. The refer-
ence is made available on the REFOUT pin. This reference is used as the reference to the DAC by connecting REFOUT to REFIN. REFOUT should be decoupled with a 10 nF capacitor to AGND.
14 IOUT Current Output. This is a high impedance current source. A load resistor should be connected between
IOUT and AGND.
16 COMP Compensation pin. This is a compensation pin for the internal reference amplifier. A 10 nF decoupling
ceramic capacitor should be connected between COMP and AVDD.
POWER SUPPLY
4 DVDD Positive Power Supply for the Digital Section. A 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor should be connected be-
tween DVDD and DGND. DVDD can have a value of +5 V ± 10% or +3.3 V ± 10%.
5 DGND Digital Ground.
13 AGND Analog Ground.
15 AVDD Positive Power Supply for the Analog Section. A 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor should be connected be-
tween AVDD and AGND. AVDD can have a value of +5 V ± 10% or +3.3 V ± 10%.
DIGITAL INTERFACE AND CONTROL
6 MCLK Digital Clock Input. DDS output frequencies are expressed as a binary fraction of the frequency of MCLK.
The output frequency accuracy and phase noise are determined by this clock.
7 SCLK Serial Clock, Logic Input. Data is clocked into the AD9832 on each falling SCLK edge.
8 SDATA Serial Data In, Logic Input. The 16-bit serial data word is applied to this input.
9 FSYNC Data Synchronization Signal, Logic Input. When this input is taken low, the internal logic is informed
that a new word is being loaded into the device.
10 FSELECT Frequency Select Input. FSELECT controls which frequency register, FREQ0 or FREQ1, is used in the
phase accumulator. The frequency register to be used can be selected using the pin FSELECT or the bit
FSELECT. FSELECT is sampled on the rising MCLK edge. FSELECT needs to be in steady state
when an MCLK rising edge occurs. If FSELECT changes value when a rising edge occurs, there is an
uncertainty of one MCLK cycle as to when control is transferred to the other frequency register. To avoid
any uncertainty, a change on FSELECT should not coincide with an MCLK rising edge. When the bit is
being used to select the frequency register, the pin FSELECT should be tied to DGND.
11, 12 PSEL0, PSEL1 Phase Select Input. The AD9832 has four phase registers. These registers can be used to alter the value
being input to the SIN ROM. The contents of the phase register are added to the phase accumulator out-
put, the inputs PSEL0 and PSEL1 selecting the phase register to be used. Alternatively, the phase register
to be used can be selected using the bits PSEL0 and PSEL1. Like the FSELECT input, PSEL0 and PSEL1
are sampled on the rising MCLK edge. Therefore, these inputs need to be in steady state when an MCLK
rising edge occurs or there is an uncertainty of one MCLK cycle as to when control is transferred to the
selected phase register. When the phase registers are being controlled by the bits PSEL0 and PSEL1, the
pins should be tied to DGND.
 Loading...
Loading...