Page 1
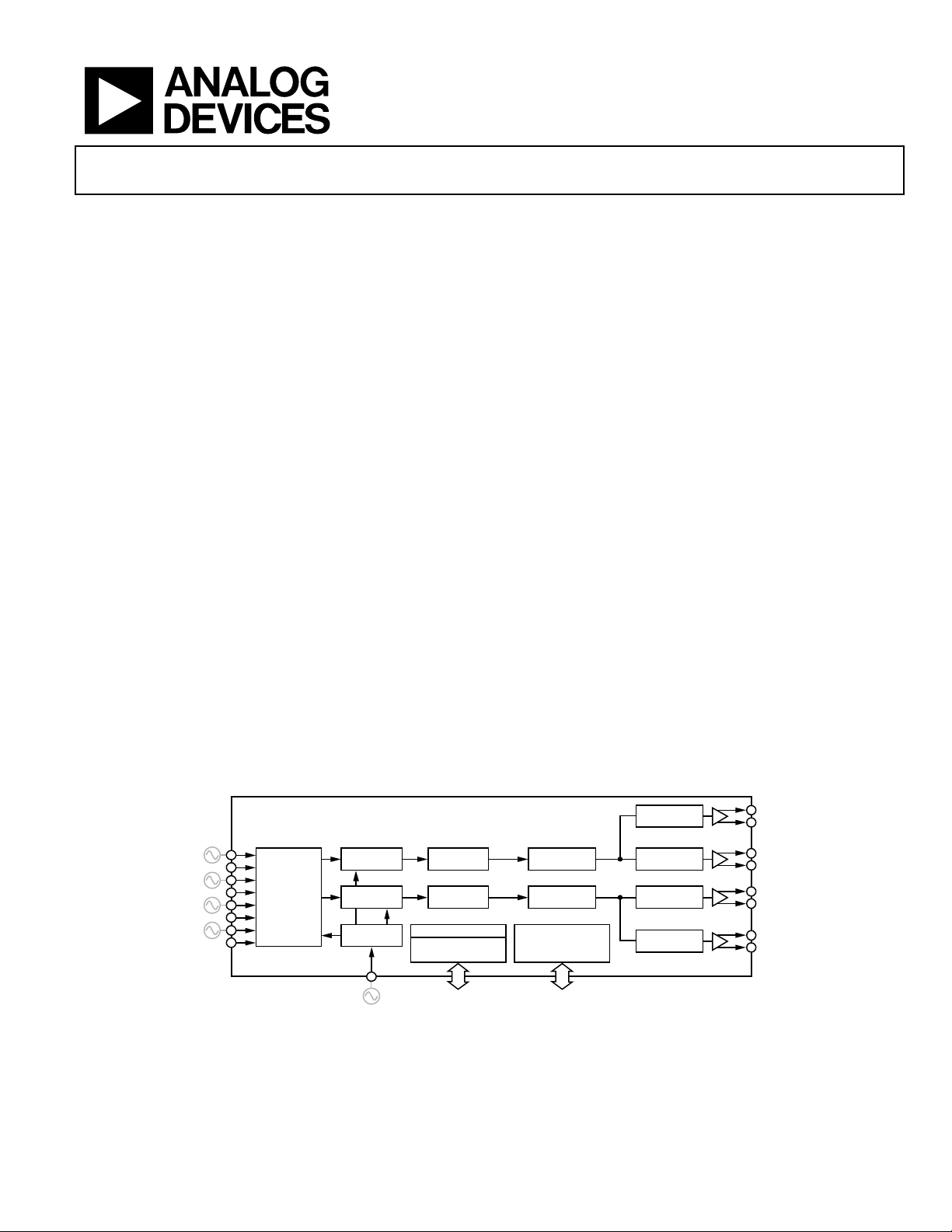
Line Card Adaptive Clock Translator
AD9559
Rev. 0
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the prop erty of their respective owners.
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
REFERENCE
INPUT
MONITOR
AND MUX
STABLE
SOURCE
DIGITAL
PLL 0
DIGITAL
PLL 1
CLOCK
MULTIPLIER
ANALOG
PLL 0
ANALOG
PLL 1
÷3 TO ÷11
HF DIVIDER 0
÷3 TO ÷11
HF DIVIDER 1
EEPROM
SERIAL INTERFACE
(SPI OR I
2
C)
STATUS AND
CONTROL PINS
CHANNEL 0B
DIVIDER
CHANNEL 0A
DIVIDER
CHANNEL 1A
DIVIDER
CHANNEL 1B
DIVIDER
AD9559
10644-001
Data Sheet
FEATURES
Supports GR-1244 Stratum 3 stability in holdover mode
Supports smooth reference switchover with virtually
no disturbance on output phase
Supports Telcordia GR-253 jitter generation, transfer, and
tolerance for SONET/SDH up to OC-192 systems
Supports ITU-T G.8262 synchronous Ethernet slave clocks
Supports ITU-T G.823, G.824, G.825, and G.8261
Auto/manual holdover and reference switchover
Adaptive clocking allows dynamic adjustment of feedback
dividers for use in OTN mapping/demapping applications
Dual digital PLL architecture with four reference inputs
(single-ended or differential)
4x2 crosspoint allows any reference input to drive either PLL
Input reference frequencies from 2 kHz to 1250 MHz
Reference validation and frequency monitoring (2 ppm)
Programmable input reference switchover priority
20-bit programmable input reference divider
4 pairs of clock output pins with each pair configurable as a
single differential LVDS/HSTL output or as 2 single-ended
CMOS outputs
Output frequencies: 262 kHz to 1250 MHz
Programmable 17-bit integer and 24-bit fractional
feedback divider in digital PLL
Programmable digital loop filter covering loop bandwidths
from 0.1 Hz to 2 kHz
Low noise system clock multiplier
Optional crystal resonator for system clock input
On-chip EEPROM to store multiple power-up profiles
Dual PLL, Quad Input, Multiservice
Pin program function for easy frequency translation
configuration
Software controlled power-down
72-lead (10 mm × 10 mm) LFCSP package
APPLICATIONS
Network synchronization, including synchronous Ethernet
and SDH to OTN mapping/demapping
Cleanup of reference clock jitter
SONET/SDH clocks up to OC-192, including FEC
Stratum 3 holdover, jitter cleanup, and phase transient
control
Wireless base station controllers
Cable infrastructure
Data communications
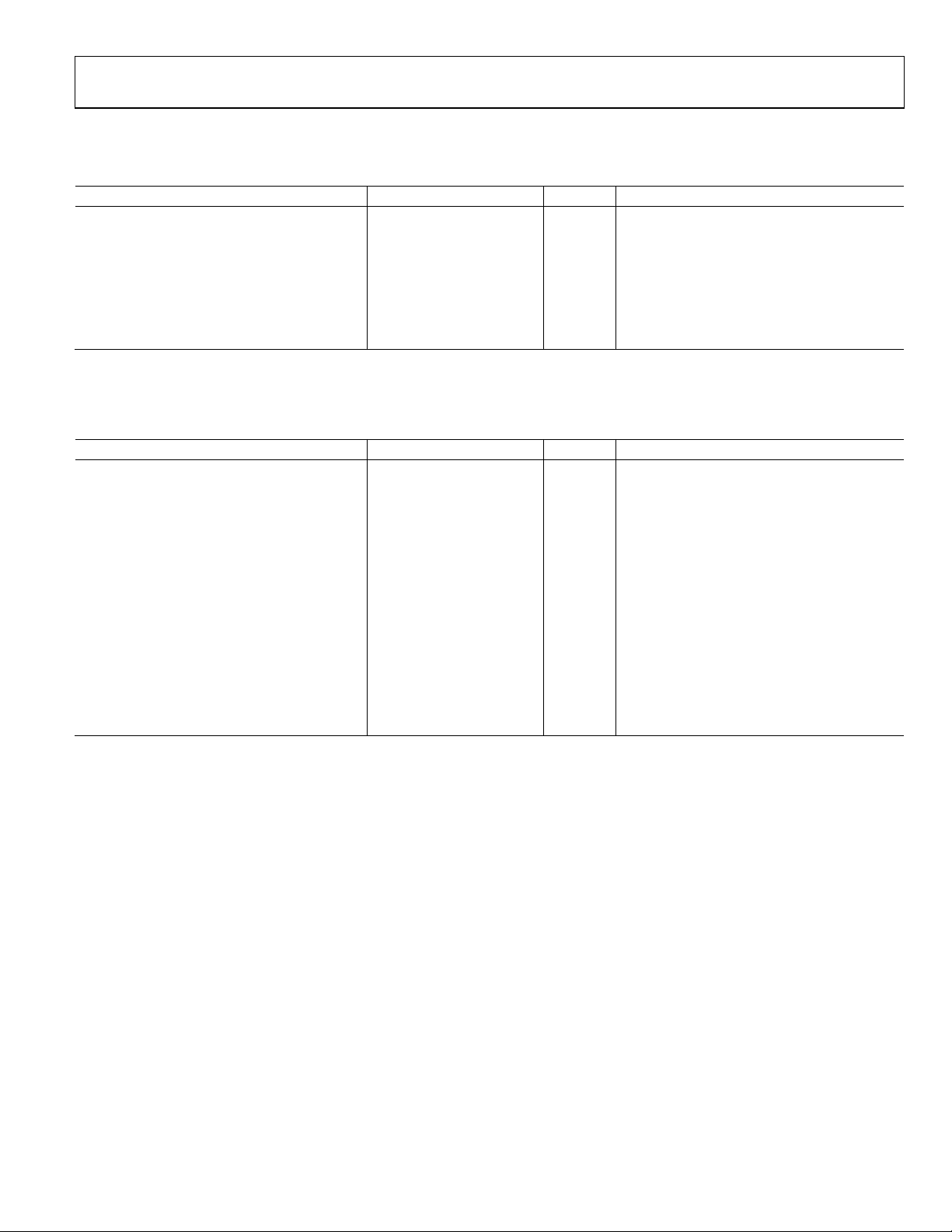
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9559 is a low loop bandwidth clock multiplier that
provides jitter cleanup and synchronization for many systems,
including synchronous optical networks (SONET/SDH). The
AD9559 generates an output clock synchronized to up to four
external input references. The digital PLL allows for reduction
of input time jitter or phase noise associated with the external
references. The digitally controlled loop and holdover circuitry
of the AD9559 continuously generates a low jitter output clock
even when all reference inputs have failed.
The AD9559 operates over an industrial temperature range of
−40°C to +85°C. If a single DPLL version of this part is needed,
refer to the
AD9557.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subj ect to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Page 2

AD9559 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 3
Specifications ..................................................................................... 4
Supply Voltage ............................................................................... 4
Supply Current .............................................................................. 4
Power Dissipation ......................................................................... 5
System Clock Inputs (XOA, XOB) ............................................. 5
Reference Inputs ........................................................................... 6
Reference Monitors ...................................................................... 7
Reference Switchover Specifications .......................................... 7
Distribution Clock Outputs ........................................................ 8
Time Duration of Digital Functions ........................................ 10
Digital PLL (DPLL_0 and DPLL_1) ........................................ 10
Analog PLL (APLL_0 and APLL_1) ........................................ 10
Digital PLL Lock Detection ...................................................... 10
Holdover Specifications ............................................................. 10
Serial Port Specifications—SPI Mode ...................................... 11
Serial Port Specifications—I2C Mode ...................................... 12
Logic Inputs (
Logic Outputs (M5 to M0) ........................................................ 12
Jitter Generation ......................................................................... 13
Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................... 16
ESD Caution ................................................................................ 16
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ........................... 17
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 20
Input/Output Termination Recommendations .......................... 26
Getting Started ................................................................................ 27
Chip Power Monitor and Startup ............................................. 27
Multifunction Pins at Reset/Power-Up ................................... 27
Device Register Programming Using a Register Setup File .. 27
Register Programming Overview ............................................. 28
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 31
Overview ...................................................................................... 31
Reference Input Physical Connections .................................... 32
Reference Monitors .................................................................... 32
Reference Input Block ................................................................ 32
Reference Switchover ................................................................. 33
RESET
, M5 to M0) ............................................. 12
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 120
Digital PLL (DPLL) Core .......................................................... 34
Loop Control State Machine ..................................................... 36
System Clock (SYSCLK) ................................................................ 37
SYSCLK Inputs ........................................................................... 37
SYSCLK Multiplier ..................................................................... 37
Output PLL (APLL) ....................................................................... 39
APLL Configuration .................................................................. 39
APLL Calibration ....................................................................... 39
Clock Distribution .......................................................................... 40
Clock Dividers ............................................................................ 40
Output Enable ............................................................................. 40
Output Mode and Power-Down ............................................... 40
Clock Distribution Synchronization ........................................ 41
Status and Control .......................................................................... 42
Multifunction Pins (M0 to M5) ............................................... 42
IRQ Function .............................................................................. 42
Watchd o g Tim e r ......................................................................... 43
EEPROM ..................................................................................... 43
Serial Control Port ......................................................................... 49
SPI/I²C Port Selection ................................................................ 49
SPI Serial Port Operation .......................................................... 49
I²C Serial Port Operation .......................................................... 53
Programming the I/O Registers ................................................... 56
Buffered/Active Registers .......................................................... 56
Write Detect Registers ............................................................... 56
Autoclear Registers ..................................................................... 56
Register Access Restrictions ...................................................... 56
Thermal Performance .................................................................... 57
Power Supply Partitions ................................................................. 58
3.3 V Supplies .............................................................................. 58
1.8 V Supplies .............................................................................. 58
Bypass Capacitors for Pin 21 and Pin 33 ................................. 58
Register Map ................................................................................... 59
Register Map Bit Descriptions ...................................................... 72
Serial Control Port Configuration (Register 0x0000 to
Register 0x0005) ......................................................................... 72
Clock Part Family ID (Register 0x000C and
Register 0x000D) ........................................................................ 72
User Scratchpad (Register 0x000E and Register 0x000F) ..... 73
General Configuration (Register 0x0100 to
Register 0x0109) ......................................................................... 73
Page 3

Data Sheet AD9559
IRQ Mask (Register 0x010A to Register 0x112) ..................... 74
System Clock (Register 0x0200 to Register 0x0207) .............. 76
Reference Input A (Register 0x0300 to Register 0x031A) ..... 77
Reference Input B (Register 0x0320 to Register 0x033A) ...... 78
Reference Input C (Register 0x0340 to Register 0x035A) ..... 79
Reference Input D (Register 0x0360 to Register 0x037A) ..... 81
DPLL_0 Controls (Register 0x0400 to Register 0x0415) ....... 82
APLL_0 Configuration (Register 0x0420 to
Register 0x0423) .......................................................................... 84
PLL_0 Output Sync and Clock Distribution
(Register 0x0424 to Register 0x042E) ....................................... 85
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input A (REFA)
(Register 0x0440 to Register 0x044C) ...................................... 87
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input B (REFB)
(Register 0x044D to Register 0x0459) ...................................... 88
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input C (REFC)
(Register 0x045A to Register 0x0466) ...................................... 89
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input D (REFD)
(Register 0x0467 to Register 0x0473) ....................................... 90
DPLL_1 Controls (Register 0x0500 to Register 0x0515) ....... 91
APLL_1 Configuration (Register 0x0520 to
Register 0x0523) .......................................................................... 93
PLL_1 Output Sync and Clock Distribution
(Register 0x0524 to Register 0x052E) ....................................... 94
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input C (REFC)
(Register 0x0540 to Register 0x054C) ...................................... 96
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input D (REFD)
(Register 0x054D to Register 0x0559) ...................................... 97
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input A (REFA)
(Register 0x055A to Register 0x0566) ...................................... 98
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input B (REFB)
(Register 0x0567 to Register 0x0573) ....................................... 99
Digital Loop Filter Coefficients (Register 0x0800 to
Register 0x0817) ........................................................................ 100
Common Operational Controls (Register 0x0A00 to
Register 0x0A0E) ...................................................................... 101
PLL_0 Operational Controls (Register 0x0A20 to
Register 0x0A24) ....................................................................... 104
PLL_1 Operational Controls (Register 0x0A40 to
Register 0x0A44) ....................................................................... 106
Status ReadBack (Register 0x0D00 to Register 0x0D05) ..... 107
IRQ Monitor (Register 0x0D08 to Register 0x0D10) .......... 108
PLL_0 Read-Only Status (Register 0x0D20 to
Register 0x0D2A) ...................................................................... 110
PLL_1 Read-Only Status (Register 0x0D40 to
Register 0x0D4A) ...................................................................... 112
EEPROM Control (Register 0x0E00 to Register 0x0E03) ... 113
EEPROM Storage Sequence (Register 0x0E10 to
Register 0x0E3C) ....................................................................... 113
Outline Dimensions ...................................................................... 120
Ordering Guide ......................................................................... 120
REVISION HISTORY
7/12—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 120
Page 4
AD9559 Data Sheet
VDD
1.71
1.80
1.89 V
SPECIFICATIONS
Minimum (min) and maximum (max) values apply for the full range of supply voltage and operating temperature variations. Typical (typ)
values apply for VDD3 = 3.3 V; VDD = 1.8 V; T
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SUPPLY VOLTAGE
VDD3 3.135 3.30 3.465 V
SUPPLY CURRENT
The test conditions for the maximum (max) supply current are at the maximum supply voltage found in Tab l e 1.
The test conditions for the typical (typ) supply current are at the typical supply voltage found in Tabl e 1.
The test conditions for the minimum (min) supply current are at the minimum supply voltage found in Table 1.
Table 2.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SUPPLY CURRENT FOR TYPICAL CONFIGURATION
I
34 42 50 mA
VDD3
I
253 316 380 mA
VDD
SUPPLY CURRENT FOR ALL BLOCKS RUNNING
CONFIGURATION
I
75 94 113 mA
VDD3
I
256 320 384 mA
VDD
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
A
Typical values are for the Typical Configuration
parameter listed in Table 3
Maximum values are for the All Blocks Running
parameter listed in Table 3
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 120
Page 5
Data Sheet AD9559
POWER DISSIPATION
All Blocks Running
0.71
0.89
1.1
W
SYSTEM CLOCK REFERENCE INPUT PATH
POWER DISSIPATION
Table 3.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Typical Configuration 0.57 0.71 0.85 W
Full Power-Down 75 110 mW
Incremental Power Dissipation
Complete DPLL/APLL On/Off 171 214 257 mW
Input Reference On/Off
Differential Without Divide-by-2 19 25 31 mW Additional current draw is in the VDD3 domain only
Differential With Divide-by-2 25 32 39 mW Additional current draw is in the VDD3 domain only
Single-Ended (Without Divide-by-2) 5 6.6 8 mW Additional current draw is in the VDD3 domain only
Output Distribution Driver On/Off
LVDS (at 750 MHz) 12 17 22 mW Additional current draw is in the VDD domain only
HSTL (at 750 MHz) 14 21 28 mW Additional current draw is in the VDD domain only
1.8 V CMOS (at 250 MHz) 14 21 28 mW A single 1.8 V CMOS output with an 80 pF load
3.3 V CMOS (at 250 MHz) 18 27 36 mW A single 3.3 V CMOS output with an 80 pF load
System clock: 49.152 MHz crystal; two DPLLs active;
two 19.44 MHz input references in differential mode;
two HSTL drivers at 644.53125 MHz; two 3.3 V CMOS
drivers at 161.1328125 MHz and 80 pF capacitive load
on CMOS output
System clock: 49.152 MHz crystal; two DPLLs active,
all input references in differential mode; two HSTL
drivers at 750 MHz; four 3.3 V CMOS drivers at 250 MHz
and 80 pF capacitive load on CMOS outputs
Typical configuration with no external pull-up or pulldown resistors; about 2/3 of this power is on VDD3
Typical configuration; table values show the change in
power due to the indicated operation
This power delta is computed relative to the typical
configuration; the blocks powered down include one
reference input, one DPLL, one APLL, one P divider, two
channel dividers, one HSTL driver, and one CMOS driver;
roughly 2/3 of the power savings is on the 1.8 V supply
SYSTEM CLOCK INPUTS (XOA, XOB)
Table 4.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SYSTEM CLOCK MULTIPLIER
PLL Output Frequency Range 750 805 MHz
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) Rate 150 MHz
Frequency Multiplication Range 4 255 Assumes valid system clock and PFD rates
Input Frequency Range 10 400 MHz
Minimum Input Slew Rate 50 V/μs
Common-Mode Voltage 1.05 1.16 1.27 V Internally generated
Differential Input Voltage Sensitivity 250 mV p-p
System Clock Input Doubler Duty Cycle
System Clock input = 50 MHz 45 50 55 %
System Clock input = 20 MHz 46 50 54 %
System Clock input = 16 MHz to 20 MHz 47 50 53 %
Input Capacitance 3 pF Single-ended, each pin
Input Resistance 4.1 kΩ
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 120
VCO range may place limitations on nonstandard system
clock input frequencies
Minimum limit imposed for jitter performance; jitter
performance affected if sine wave input ≤ 20 MHz
Minimum voltage across pins required to ensure switching
between logic states; the instantaneous voltage on either
pin must not exceed supply rails; single-ended input can
be accommodated by ac grounding complementary input;
1 V p-p recommended for optimal jitter performance
Amount of duty cycle variation that can be tolerated on
the system clock input to use the doubler
Page 6
AD9559 Data Sheet
Sinusoidal Input
10 750
MHz
fIN = 800 MHz to 1050 MHz
320
mV
LVPECL
390
ps
Input Voltage High (VIH)
1.8 V to 2.5 V Threshold Setting
0.5 V
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CRYSTAL RESONATOR PAT H
Crystal Resonator Frequency Range 10 50 MHz Fundamental mode, AT cut crystal
Maximum Crystal Motional Resistance 100 Ω
REFERENCE INPUTS
Table 5.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DIFFERENTIAL OPERATION
Frequency Range
LVPECL Input 0.002 1250 MHz
LVDS Input 0.002 750 MHz
Minimum Input Slew Rate 40 V/μs Minimum limit imposed for jitter performance
Common-Mode Input Voltage
AC-Coupled 1.9 2 2.1 V Internally generated
DC-Coupled 1.0 2.4 V
Differential Input Voltage Sensitivity mV
fIN < 800 MHz 240 mV
The reference input divide-by-2 block must be engaged
> 705 MHz
for f
IN
Minimum differential voltage across pins required to
ensure switching between logic levels; instantaneous
voltage on either pin must not exceed the supply rails
fIN = 1050 MHz to 1250 MHz 400 mV
Differential Input Voltage Hysteresis 55 100 mV
Input Resistance 21 kΩ
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Minimum Pulse Width High
LVDS 640 ps
Minimum Pulse Width Low
LVPECL 390 ps
LVDS 640 ps
SINGLE-ENDED OPERATION
Frequency Range (CMOS) 0.002 300 MHz
Minimum Input Slew Rate 40 V/μs Minimum limit imposed for jitter performance
1.2 V to 1.5 V Threshold Setting 1.0 V
1.8 V to 2.5 V Threshold Setting 1.4 V
3.0 V to 3.3 V Threshold Setting 2.0 V
Input Voltage Low (VIL)
1.2 V to 1.5 V Threshold Setting 0.35 V
3.0 V to 3.3 V Threshold Setting 1.0 V
Input Resistance 47 kΩ
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Minimum Pulse Width High 1.5 ns
Minimum Pulse Width Low 1.5 ns
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 120
Page 7
Data Sheet AD9559
REFERENCE MONITORS
REFERENCE MONITORS
Table 6.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Reference Monitor
Loss of Reference Detection Time 1.15
DPLL PFD
Nominal phase detector period = R/f
period
Frequency Out-of Range Limits 2 105
Δf/f
REF
(ppm)
Programmable (lower bound subject to quality
of the system clock (SYSCLK)); SYSCLK accuracy
must be less than the lower bound
Validation Timer 0.001 65.535 sec Programmable in 1 ms increments
1
f
is the frequency of the active reference; R is the frequency division factor determined by the R divider.
REF
REFERENCE SWITCHOVER SPECIFICATIONS
Table 7.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
REFERENCE SWITCHOVER SPECIFICATIONS
Maximum Output Phase Perturbation
(Phase Build-Out Switchover)
50 Hz DPLL Loop Bandwidth
Peak ±55 ±100 ps
Steady State ±55 ±100 ps
Time Required to Switch to a New Reference
Phase Build-Out Switchover 10
DPLL PFD
period
Assumes a jitter-free reference; satisfies
Telcordia GR-1244-CORE requirements;
base loop filter selection bit set to 1b for
all active references
Tes t conditions: 19.44 MHz to 174.70308 MHz;
DPLL BW = 50 Hz; 49.152 MHz signal generator
used for system clock source
Calculated using the nominal phase detector
period (NPDP = R/f
); the total time required
REF
is the time plus the reference validation time,
plus the time required to lock to the new
reference
REF
1
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 120
Page 8
AD9559 Data Sheet
HSTL MODE
Up to f
= 700 MHz
44
48
53 %
0.262
1250
MHz
Up to f
= 800 MHz
42.5
48
53.5 %
1.8 V Supply
0.302
250
MHz
10 pF load
DISTRIBUTION CLOCK OUTPUTS
Table 8.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Output Frequency
OUT0A, OUT0A and OUT0B, OUT0B
OUT1A, OUT1A and OUT1B, OUT1B
Rise/Fall Time (20% to 80%)1 140 250 ps 100 Ω termination across the output pair
Duty Cycle
OUT
Up to f
Up to f
Differential Output Voltage Swing
= 750 MHz 43 48 54 %
OUT
= 1250 MHz 43 %
OUT
Common-Mode Output Voltage 750 850 1000 mV Output driver static
Reference Input-to-Output Delay Variation
over Temperature
Static Phase Offset Variation from Active
Reference to Output over Voltage
Extremes
LVDS MODE
Output Frequency
OUT0A, OUT0A and OUT0B, OUT0B
OUT1A, OUT1A and OUT1B, OUT1B
Rise/Fall Time (20% to 80%)1 185 280 ps 100 Ω termination across the output pair
Duty Cycle
Up to f
Up to f
Differential Output Voltage Swing
= 750 MHz 43 48 53 %
OUT
OUT
= 1250 MHz 43 %
OUT
Balanced, VOD 247 454 mV
Unbalanced, ΔVOD 50 mV
Offset Voltage
Common Mode, VOS 1.125 1.25 1.375 V Output driver static
Common-Mode Difference, ΔVOS 50 mV
Short-Circuit Output Current 10 24 mA Output driver static
CMOS MODE
Output Frequency
0.262 1250 MHz
0.302 1250 MHz
700 925 1200 mV
3.2 ps/°C
0.875 ps/mV
0.302 1250 MHz
Magnitude of voltage across pins; output
driver static
HSTL mode; DPLL locked to same input
reference at all times; stable system clock
source (non-XTAL)
Valid for HSTL, LVDS, and 1.8 V CMOS output
driver modes
Voltage swing between output pins; output
driver static
Absolute difference between voltage swing of
normal pin and inverted pin; output driver static
Voltage difference between pins; output driver
static
OUT0A, OUT0A and OUT0B, OUT0B
OUT1A, OUT1A and OUT1B, OUT1B
0.262 250 MHz 10 pF load
0.302 250 MHz 10 pF load
3.3 V Supply (OUT0A and OUT1A)
Strong Drive Strength Setting
OUT0A, OUT0A
0.262 250 MHz 10 pF load
OUT1A, OUT1A
Weak Drive Strength Setting
OUT0A, OUT0A
OUT1A, OUT1A
0.262 25 MHz 10 pF load
0.302 25 MHz 10 pF load
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 120
Page 9
Data Sheet AD9559
Duty Cycle
VDD3 = 3.3 V, IOH = 1 mA
VDD3 − 0.1
V
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Rise/Fall Time (20% to 80%)1
1.8 V Mode 1.5 3 ns 10 pF load
3.3 V Strong Mode 0.4 0.6 ns 10 pF load
3.3 V Weak Mode 8 ns 10 pF load
1.8 V Mode 50 % 10 pF load
3.3 V Strong Mode 47 51 56 % 10 pF load
3.3 V Weak Mode 51 % 10 pF load
Output Voltage High (VOH) Output driver static; strong drive strength
VDD3 = 3.3 V, IOH = 10 mA VDD3 − 0.3 V
VDD3 = 1.8 V, IOH = 1 mA VDD − 0.2 V
Output Voltage Low (VOL) Output driver static; strong drive strength
VDD3 = 3.3 V, IOL = 10 mA 0.3 V
VDD3 = 3.3 V, IOL = 1 mA 0.1 V
VDD3 = 1.8 V, IOL = 1 mA 0.1 V
OUTPUT TIMING SKEW 10 pF load
Between OUT0A, OUT0A and OUT0B, OUT0B
or OUT1A, OUT1A and OUT1B, OUT1B
Additional Delay on One Driver by
Changing Its Logic Type
HSTL to LVDS 0 +15 +35 ps
HSTL to 1.8 V CMOS −5 0 +5 ps
OUT0B, OUT0B HSTL to OUT0B, OUT0B
3.3 V CMOS, Strong Mode
OUT1B, OUT1B HSTL to OUT1B, OUT1B
3.3 V CMOS, Strong Mode
1
The listed values are for the slower edge (rising or falling).
116 265 ps
HSTL mode on both drivers; rising edge only;
any divide value
Positive value indicates that the LVDS edge is
delayed relative to HSTL
Positive value indicates that the CMOS edge is
delayed relative to HSTL
−765 −280 +250 ns The CMOS edge is delayed relative to HSTL
−765 −280 +250 ns The CMOS edge is delayed relative to HSTL
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 120
Page 10
AD9559 Data Sheet
Closed Loop Peaking
<0.1
dB
Programmable design parameter; part can be programmed
TIME DURATION OF DIGITAL FUNCTIONS
Table 9.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
TIME DURATION OF DIGITAL FUNCTIONS
EEPROM-to-Register Download Time 16 25 ms Uses default EEPROM storage sequence (see Register 0x0E10
Register-to-EEPROM Upload Time 180 ms Uses default EEPROM storage sequence (see Register 0x0E10
Power-Down Exit Time
1
ms Time from power-down exit to system clock lock detect; system
DIGITAL PLL (DPLL_0 AND DPLL_1)
Table 10.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DIGITAL PLL
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) Input
Frequency Range
Loop Bandwidth 0.1 2000 Hz Programmable design parameter;
Phase Margin 45 89 Degrees Programmable design parameter
2 100 kHz
to Register 0x0E4F)
to Register 0x0E4F
clock stability timer setting should be added to calculate the
time needed for system clock stable
note that (f
for <0.1 dB peaking in accordance with Telcordia GR-253-CORE
jitter transfer
/loop BW) ≥ 20
PFD
ANALOG PLL (APLL_0 AND APLL_1)
Table 11.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
ANALOG PLL0
VCO Frequency Range 2940 3543 MHz
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) Input
Frequency Range
Loop Bandwidth 240 kHz Programmable design parameter
Phase Margin 68 Degrees Programmable design parameter
ANALOG PLL1
VCO Frequency Range 3405 4260 MHz
Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) Input
Frequency Range
Loop Bandwidth 240 kHz Programmable design parameter
Phase Margin 68 Degrees Programmable design parameter
180 195 MHz
180 195 MHz
DIGITAL PLL LOCK DETECTION
Table 12.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
PHASE LOCK DETECTOR
Threshold Programming Range 10 224 − 1 ps Reference-to-feedback phase difference
Threshold Resolution 1 ps
FREQUENCY LOCK DETECTOR
Threshold Programming Range 10 224 − 1 ps Reference-to-feedback period difference
Threshold Resolution 1 ps
HOLDOVER SPECIFICATIONS
Table 13.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
HOLDOVER SPECIFICATIONS
Initial Frequency Accuracy <0.01 ppm Excludes frequency drift of SYSCLK source; excludes frequency
drift of input reference prior to entering holdover; compliant
with GR-1244 Stratum 3
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 120
Page 11
Data Sheet AD9559
M5/EE CS
M5/ACS
is a dual function pin; the values in
Input Logic 0 Voltage
0.8 V
Input Logic 0 Current
1
µA
As an Input
Output Logic 1 Voltage
VDD3 − 0.6
V
1 mA load current
SCLK
SERIAL PORT SPECIFICATIONS—SPI MODE
Table 14.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
Input Logic 1 Voltage
2.2 V
Input Logic 1 Current 20 µA
Input Logic 0 Current
Input Capacitance
SCLK
Input Logic 1 Voltage
Input Logic 0 Voltage
Input Logic 1 Current
50 µA
2 pF
Internal 10 kΩ pull-down resistor
2.2 V
0.8 V
200 µA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SDIO
E
A
this table apply when this pin is used as a
serial port pin, that is, ACS
EE
A
; see Table 16 for
the specifications when this pin is used as
a multifunction pin (M5)
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.2 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage
Input Logic 1 Current
Input Logic 0 Current
Input Capacitance
As an Output
Output Logic 1 Voltage
Output Logic 0 Voltage
M4/SDO
0.8 V
1 µA
1 µA
2 pF
VDD3 − 0.6 V 1 mA load current
0.4 V 1 mA load current
M4/SDO is a dual function pin; the values in
this table apply when this pin is used as
a serial port pin, that is SDO; see Table 16
for the specifications when this pin is used
as a multifunction pin (M4)
Output Logic 0 Voltage 0.4 V 1 mA load current
TIMING
Clock Rate, 1/t
Pulse Width High, t
Pulse Width Low, t
SDIO to SCLK Setup, t
SCLK to SDIO Hold, t
40 MHz
CLK
HIGH
LOW
DS
DH
SCLK to Valid SDIO and SDO, t
EE
AA
AACS
to SCLK Setup (tS)
EE
AA
AACS
to SCLK Hold (tC)
EE
AA
AACS
Minimum Pulse Width High
10 ns
13 ns
3 ns
6 ns
See Figure 47 and Figure 50
10 ns
DV
10 ns
0 ns
6 ns
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 120
Page 12
AD9559 Data Sheet
Input Logic 1 Voltage
0.7 × VDD3
V
SERIAL PORT SPECIFICATIONS—I2C MODE
Table 15.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
SDA, SCL (AS INPUTS)
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.3 × VDD3 V
Input Current
Hysteresis of Schmitt Trigger Inputs
Pulse Width of Spikes That Must Be Suppressed
by the Input Filter, t
SP
SDA (AS OUTPUT)
Output Logic 0 Voltage
Output Fall Time from V
IHmin
to V
20 + 0.1 C
ILmax
TIMING
SCL Clock Rate
Bus-Free Time Between a Stop and Start
Condition, t
Repeated Start Condition Setup Time, t
BUF
SU; STA
Repeated Hold Time Start Condition, t
Stop Condition Setup Time, t
Low Period of the SCL Clock, t
High Period of the SCL Clock, t
SCL/SDA Rise Time, t
SCL/SDA Fall Time, t
Data Setup Time, t
Data Hold Time, t
R
20 + 0.1 C
F
100 ns
SU; DAT
100 ns
HD; DAT
Capacitive Load for Each Bus Line, C
1
Cb is the capacitance (pF) of a single bus line.
SU; STO
LOW
HIGH
1
b
−10 +10 µA For VIN = 10% to 90% of VDD3
0.015 × VDD3
50 ns
0.4 V IO = 3 mA
1
2F
250 ns 10 pF ≤ Cb ≤ 400 pF
b
400 kHz
1.3 µs
0.6 µs
0.6 µs After this period, the first clock pulse is
HD ; STA
generated
0.6 µs
1.3 µs
0.6 µs
20 + 0.1 C
1
300 ns
b
1
300 ns
b
400 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (RESET, M5 TO M0)
Table 16.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
E
RESET
A
A
PINA
Input High Voltage (V
Input Low Voltage (V
Input Current (I
Input Capacitance (C
) 2.1 V
IH
) 0.8 V
IL
, I
) ±85 ±125 µA
INH
INL
) 3 pF
IN
LOGIC INPUTS (M5 to M0)
Input High Voltage (VIH) 2.5 V
Input Low Voltage (V
Input Current (I
Input Capacitance (C
) 0.6 V
IL
, I
) ±1 ±5 µA
INH
INL
) 3 pF
IN
The M4 and M5 pins are dual function pins; the
values in this table apply when M4/SDO and
E
CS
A
A
are used as M pins; see Table 14 in the
M5/
Serial Port Specifications—SPI Mode
for the specifications when these pins are used
as serial port pins (SDO,
CS
A
E
A
)
LOGIC OUTPUTS (M5 TO M0)
Table 17.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LOGIC OUTPUTS (M5 to M0)
Output High Voltage (V
Output Low Voltage (V
) VDD3 − 0.4 V IOH = 1 mA
OH
) 0.4 V IOL = 1 mA
OL
section
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 120
Page 13
Data Sheet AD9559
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Test Conditions/Comments
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
310 fs rms
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
308 fs rms
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
335 fs rms
JITTER GENERATION
Jitter Generation (Random Jitter)—49.152 MHz Crystal for System Clock Input
Table 18.
JITTER GENERATION System clock doubler enabled.
High phase margin mode enabled.
Both PLLs are running with same output frequency.
In cases where the two PLLs have different jitter, the
higher jitter is listed. When two driver types are listed,
both were tested at those conditions; the driver type
with higher jitter is quoted, although there is usually not
a significant jitter difference between driver types.
= 19.44 MHz; f
f
REF
= 622.08 MHz; f
OUT
= 50 Hz;
LOOP
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
307 fs rms
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz 313 fs rms
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 16 MHz to 320 MHz
= 19.44 MHz; f
f
REF
= 644.53 MHz; f
OUT
= 50 Hz;
LOOP
292 fs rms
149 fs rms
HSTL Driver,
LVDS Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
313 fs rms
306 fs rms
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz 286 fs rms
Bandwidth: 16 MHz to 320 MHz
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
= 693.48 MHz; f
OUT
= 50 Hz;
LOOP
154 fs rms
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 16 MHz to 320 MHz
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
= 174.703 MHz; f
OUT
LOOP
= 1 kHz;
335 fs rms
328 fs rms
328 fs rms
298 fs rms
150 fs rms
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
396 fs rms
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz 369 fs rms
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 4 MHz to 80 MHz
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
LVDS Driver,
3.3 V CMOS Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 4 MHz to 80 MHz
f
= 25 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 4 MHz to 80 MHz
= 174.703 MHz; f
OUT
= 161.1328 MHz; f
OUT
LOOP
= 100 Hz;
LOOP
= 100 Hz;
347 fs rms
230 fs rms
337 fs rms
330 fs rms
354 fs rms
339 fs rms
220 fs rms
318 fs rms
310 fs rms
384 fs rms
361 fs rms
267 fs rms
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 120
Page 14
AD9559 Data Sheet
Bandwidth: 100 kHz to 10 MHz
256 fs rms
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
373
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
396
fs rms
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
= 2 kHz; f
f
REF
HSTL Driver,
3.3 V CMOS Driver
Bandwidth: 10Hz to 30 MHz
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 10 kHz to 400 kHz
f
= 25 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 100 Hz to 500 MHz (Broadband)
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Jitter Generation (Random Jitter)—19.2 MHz TCXO for System Clock Input
Table 19.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
JITTER GENERATION
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz 348
Bandwidth: 16 MHz to 320 MHz
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 16 MHz to 320 MHz
f
= 19.44 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 50 kHz to 80 MHz
Bandwidth: 4 MHz to 80 MHz
f
= 25 MHz; f
REF
HSTL Driver
Bandwidth: 5 kHz to 20 MHz 384
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 20 kHz to 80 MHz
= 70.656 MHz; f
OUT
= 1 GHz; f
OUT
= 644.53 MHz; f
OUT
= 693.48 MHz; f
OUT
= 312.5 MHz; f
OUT
= 161.1328 MHz; f
OUT
LOOP
= 500 Hz;
LOOP
= 100 Hz;
= 10 Hz;
LOOP
= 10 Hz;
LOOP
= 10 Hz;
LOOP
= 10 Hz;
LOOP
6.5 ps rms
343 fs rms
335 fs rms
243 fs rms
881 fs rms
331 fs rms
330 fs rms
380
373
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
148
fs rms
390
383
382
350
144
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
398
392
400
379
172
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
378
416
fs rms
fs rms
System clock doubler enabled.
High phase margin mode enabled.
Both PLLs are running with same output frequency.
In cases where the two PLLs have different jitter, the
higher jitter is listed. Where two driver types are listed,
both were tested at those conditions; the driver type
with higher jitter is quoted, although there is usually
not a significant jitter difference between driver types.
Bandwidth: 4 MHz to 80 MHz 223
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 120
fs rms
Page 15
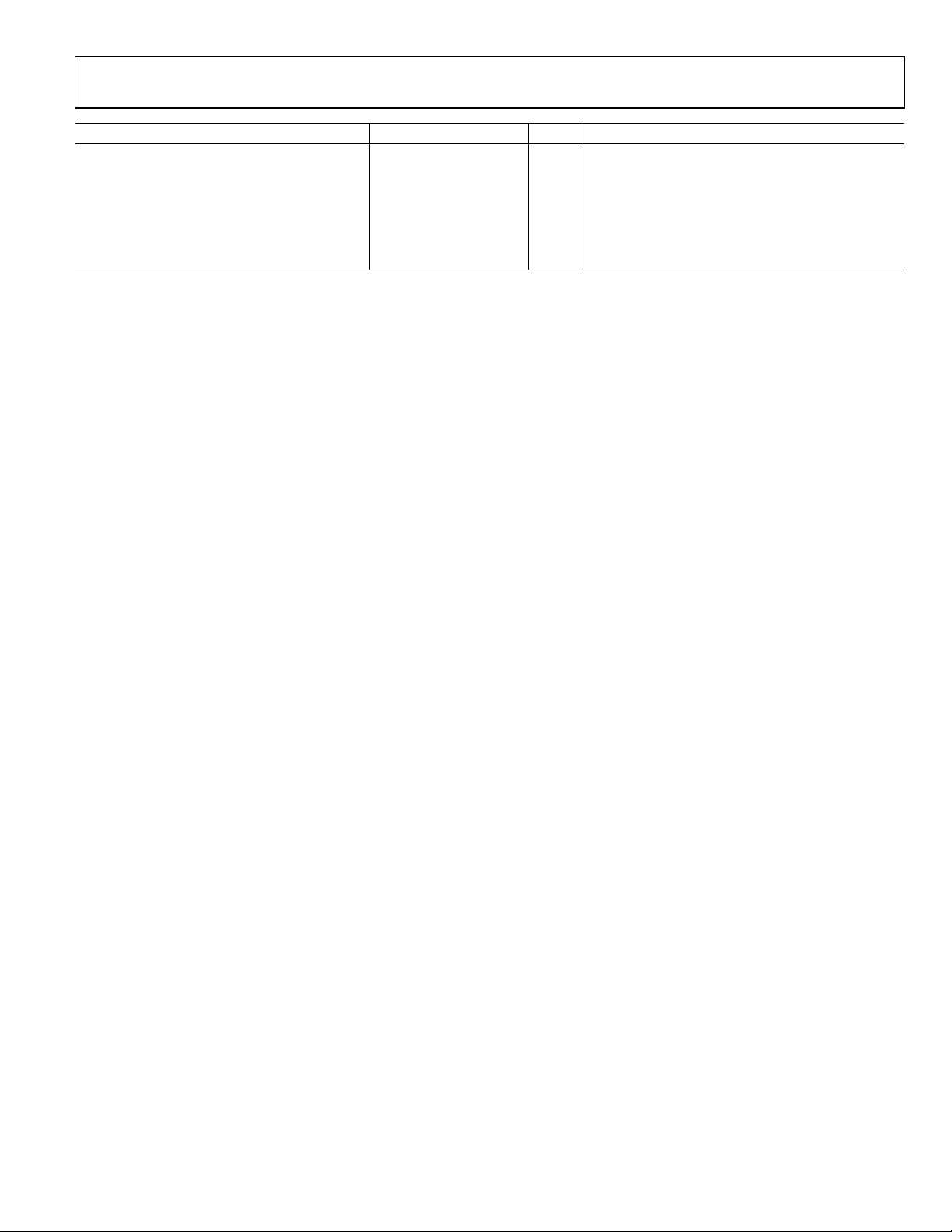
Data Sheet AD9559
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
f
= 2 kHz; f
REF
= 70.656 MHz; f
OUT
HSTL Driver,
3.3 V CMOS Driver
Bandwidth: 10 Hz to 30 MHz
Bandwidth: 12 kHz to 20 MHz
Bandwidth: 10 kHz to 400 kHz
Bandwidth: 100 kHz to 10 MHz
= 10 Hz;
LOOP
3.19
418
339
348
ps rms
fs rms
fs rms
fs rms
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 120
Page 16

AD9559 Data Sheet
3.3 V Supply Voltage ( VDD3)
3.6 V
Junction Temperature
150°C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 20.
Parameter Rating
1.8 V Supply Voltage ( VDD)
Maximum Digital Input Voltage −0.5 V to VDD3 + 0.5 V
Storage Temperature Range
Operating Temperature Range
Lead Temperature
(Soldering 10 sec)
2 V
−65°C to +150°C
−40°C to +85°C
300°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 120
Page 17
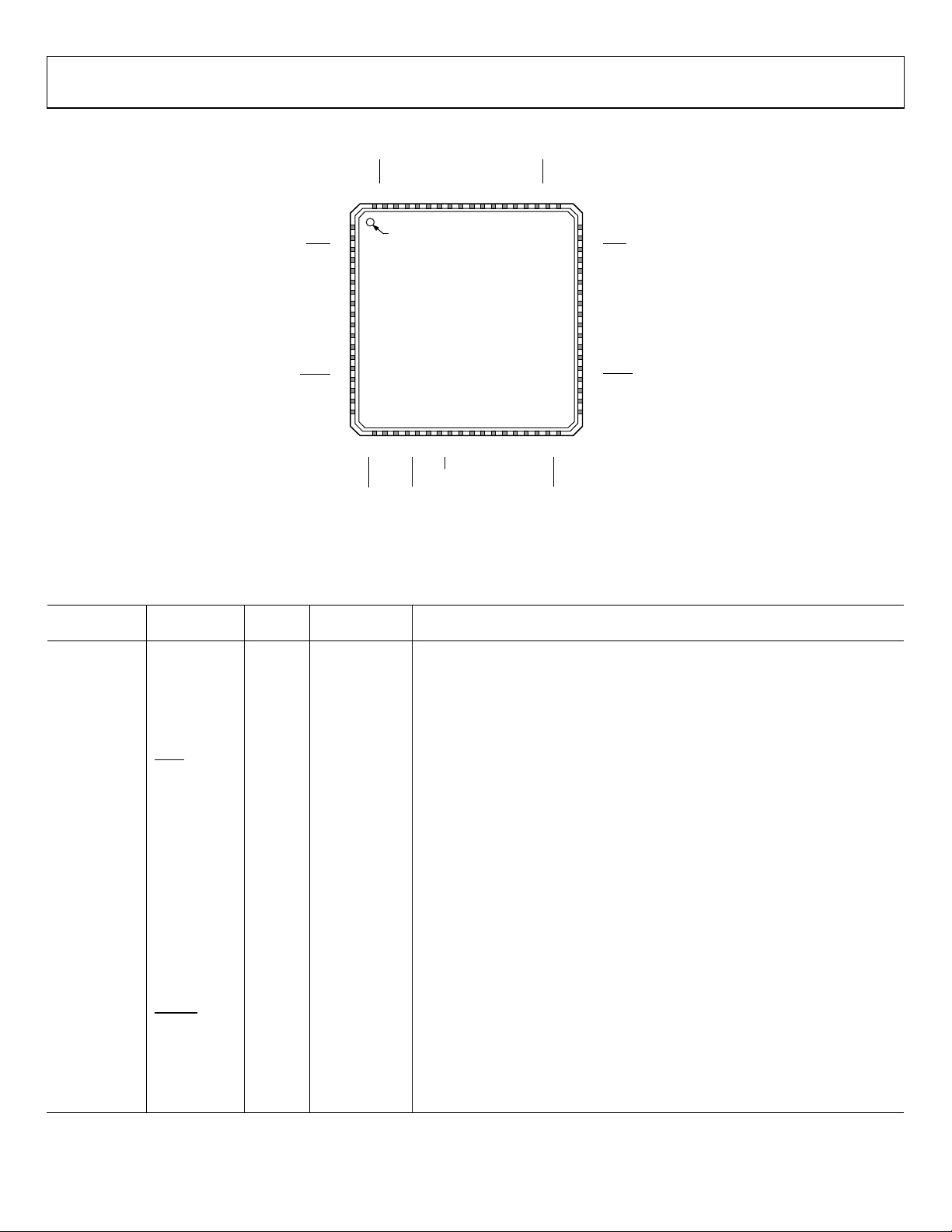
Data Sheet AD9559
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VDD3
REFA
REFA
VDD
VDD
GND
VDD
VDD
VDD
LDO_0
LF_0
VDD3
VDD
VDD
OUT0A
OUT0A
17VDD
18VDD3
192021222324252627282930313233
34
OUT0B
OUT0B
VDD
GND
RESET
SCLK/SCL
SDIO/SDA
M5/CS
M4/SDO
VDD3
M3M2M1
M0
GND
VDD
35OUT1B
36OUT1B
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
VDD3
REFC
REFC
VDD
VDD
GND
VDD
VDD
VDD
LDO_1
LF_1
VDD3
VDD
VDD
OUT1A
OUT1A
VDD
VDD3
7271706968676665646362616059585756
55
VDD3
REFB
REFB
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
XOA
XOB
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
REFD
REFD
VDD3
PIN 1
INDICATOR
AD9559
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
NOTES
1. THE EXPO S E D P AD IS THE GRO UND CONNECTION ON THE CHIP.
IT MUST BE SOLDERED TO THE ANALOG GROUND OF THE PCB
TO ENSURE PROPER FUNCTI ONALITY AND HE AT DISSIPATION,
NOISE, AND M E CHANICAL STRENG TH BENEFIT S .
10644-002
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Table 21. Pin Function Descriptions
Input/
Pin No. Mnemonic
1, 12, 18, 28,
VDD3 I Power
Output
37, 43, 54, 55,
72
2 REFA I
3
4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 13,
E
AREFA
VDD I Power
I
14, 17, 21, 34,
38, 41, 42, 46,
47, 48, 50, 51,
O
58, 59, 60, 61,
62, 65, 66, 67,
68, 69
6, 22, 33, 49 GND O Ground Connect these pins (along with the exposed die pad) to ground.
10
11
15
16
LDO_0 I LDO bypass
LF_0 I/O
AOUT0A
E
OUT0A O
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
Pi n Typ e Description
Differential
input
Differential
input
Loop filter for
APLL_0
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS
3.3 V Power Supply. See the Power Supply Partitions section for information
about the recommended grouping of the power supply pins.
Reference A Input. This internally biased input is typically ac-coupled; when
configured in this manner, it can accept any differential signal with single-ended
swing up to 3.3 V. If dc-coupled, input can be LVPECL, LVDS, or single-ended
CMOS.
Complementary Reference A Input. Complementary signal to the input provided
on Pin 2.
1.8 V Power Supply. See the Power Supply Partitions section for information
about the recommended grouping of the power supply pins.
Note that, for Pin 34 and Pin 21, it is recommended that a Size 0201, 0.1 µF bypass
capacitor be placed between Pin 33 and Pin 34, as well as between Pin 21 and Pin 22,
as close as possible to the AD9559.
Output PLL0 Loop Filter Voltage Regulator. Connect a 0.47 μF capacitor from this
pin to ground. This pin is also the ac ground reference for the integrated output
PLL external loop filter.
Loop Filter Node for the Output PLL0. Connect an external 6.8 nF capacitor from
this pin to Pin 10 (LDO_0).
PLL0 Complementary Output 0A. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or
single-ended 1.8 V CMOS.
PLL0 Output 0A. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or single-ended
1.8 V CMOS. LVPECL levels can be achieved by ac-coupling and using the
Thevenin-equivalent termination as described in the Input/Output Termination
Recommendations section.
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 120
Page 18
AD9559 Data Sheet
Input/
Pin No. Mnemonic
19
20
23
24
25
26
27
29, 30, 31, 32
E
AOUT0B
OUT0B O
E
ARESET
SCLK/SCL I 3.3 V CMOS
SDIO/SDA I/O 3.3 V CMOS
M5/ACSE
M4/SDO I/O 3.3 V CMOS Configurable I/O Pin (M4). Used for status and control of the AD9559.
M3, M2, M1,
M0
35
36
39
40
44
45
52
53
56
57
OUT1B O
E
AOUT1B
OUT1A O
E
AOUT1A
LF_1 I/O
LDO_1 I LDO bypass
E
AREFC
REFC I
E
AREFD
REFD I
Output Pi n Typ e Description
O
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS,
PLL0 Complementary Output 0B. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS,
or single-ended 1.8 V or 3.3 V CMOS.
3.3 V CMOS
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS,
3.3 V CMOS
PLL0 Output 0B. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or single-ended 1.8 V
or 3.3 V CMOS. LVPECL levels can be achieved by ac-coupling and using the
Thevenin-equivalent termination as described in the Input/Output Termination
Recommendations section.
I
3.3 V CMOS
Logic
Chip Reset. When this active low pin is asserted, the chip goes into reset. This pin
has an internal 50 kΩ pull-up resistor.
Serial Programming Clock in SPI Mode (SCLK). Data clock for serial programming.
Serial Clock Pin in I
2
C Mode (SCL).
Serial Data Input/Output (SDIO). When the device is in 4-wire SPI mode, data is
written via this pin. In 3-wire SPI mode, data reads and writes both occur on this
pin. There is no internal pull-up/pull-down resistor on this pin.
Serial Data Pin in I2C Mode (SDA).
I/O 3.3 V CMOS Configurable I/O Pin (M5). Used for status and control of the AD9559.
Chip Select in SPI Mode (ACS
E
A
). Active low input. When programming a device in
SPI, this pin must be held low. In systems where more than one AD9559 is present,
this pin enables individual programming of each AD9559. This pin has an internal
10 kΩ pull-up resistor.
Serial Data Output (SDO). In 4-wire SPI mode, this pin is used for reading serial data.
I/O 3.3 V CMOS
Configurable I/O Pins. These pins are used for status and control of the AD9559.
These pins are also used at power-up and reset to control the serial port configuration
and EEPROM loading. See Table 23 and Table 25 for more information. These pins
do NOT have internal pull-down resistors.
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS,
3.3 V CMOS
PLL1 Output 1B. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or single-ended 1.8 V
or 3.3 V CMOS. LVPECL levels can be achieved by ac-coupling and using the
Thevenin-equivalent termination as described in the Input/Output Termination
Recommendations section.
O
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS,
PLL1 Complementary Output 1B. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS,
or single-ended 1.8 V or 3.3 V CMOS.
3.3 V CMOS
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS
PLL1 Output 1A. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or single-ended
1.8 V CMOS. LVPECL levels can be achieved by ac-coupling and using the
Thevenin-equivalent termination as described in the Input/Output Termination
Recommendations section.
O
HSTL, LVDS,
1.8 V CMOS
Loop filter for
APLL_1
PLL1 Complementary Output 1A. This output can be configured as HSTL, LVDS, or
single-ended 1.8 V CMOS.
Loop Filter Node for the Output PLL1. Connect an external 6.8 nF capacitor from
this pin to Pin 45 (LDO_1).
Output PLL1 Loop Filter Voltage Regulator. Connect a 0.47 μF capacitor from this
pin to ground. This pin is also the ac ground reference for the integrated output
PLL external loop filter.
I
Differential
input
Differential
input
Complementary Reference C Input. Complementary signal to the input provided
on Pin 53.
Reference C Input. This internally biased input is typically ac-coupled; when
configured in that manner, it can accept any differential signal with single-ended
swing up to 3.3 V. If dc-coupled, input can be LVPECL, LVDS, or single-ended
CMOS.
I
Differential
input
Differential
input
Complementary Reference D Input. Complementary signal to the input provided
on Pin 57.
Reference D Input. This internally biased input is typically ac-coupled; when
configured in this manner, it can accept any differential signal with single-ended
swing up to 3.3 V. If dc-coupled, input can be LVPECL, LVDS, or single-ended CMOS.
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 120
Page 19
Data Sheet AD9559
70
REFB
I
Differential
Reference B Input. This internally biased input is typically ac-coupled; when
Input/
Pin No. Mnemonic
63
64
XOB I
XOA I
Output Pi n Typ e Description
Differential
input
Complementary System Clock Input. Complementary signal to XOA. XOB contains
internal dc biasing and should be ac-coupled with a 0.1 μF capacitor except when
using a crystal. When a crystal is used, connect the crystal across XOA and XOB.
Differential
input
System Clock Input. XOA contains internal dc biasing and should be ac-coupled
with a 0.01 μF capacitor except when using a crystal. When a crystal is used,
connect the crystal across XOA and XOB. Single-ended 1.8 V CMOS is also an option,
but a spur may be introduced if the duty cycle is not 50%. When using XOA as
a single-ended input, connect a 0.1 μF capacitor from XOB to ground.
71
EP
input
AREFB
E
I
Differential
input
GND O Exposed pad
configured in this manner, it can accept any differential signal with single-ended
swing up to 3.3 V. If dc-coupled, input can be LVPECL, LVDS, or single-ended CMOS.
Complementary Reference B Input. Complementary signal to the input provided
on Pin 70.
The exposed pad is the ground connection on the chip. It must be soldered to the
analog ground of the PCB to ensure proper functionality and heat dissipation,
noise, and mechanical strength benefits.
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 120
Page 20
AD9559 Data Sheet
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OF F SET (Hz)
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 331fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –75
100Hz –92
1kHz –116
10kHz –126
100kHz –130
1MHz –143
10MHz –152
FLOOR –158
10644-300
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OF F SET (Hz)
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 310fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –71
100Hz –82
1kHz –105
10kHz –114
100kHz –117
1MHz –133
10MHz –142
FLOOR –153
10644-003
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OF F SET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 306fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
10Hz –70
100Hz –86
1kHz –105
10kHz –114
100kHz –117
1MHz –134
10M
Hz –141
FLOOR –153
10644-004
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OF F SET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 328fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –70
100Hz –85
1kHz –105
10kHz –112
100kHz –115
1MHz –133
10MHz –142
10644-005
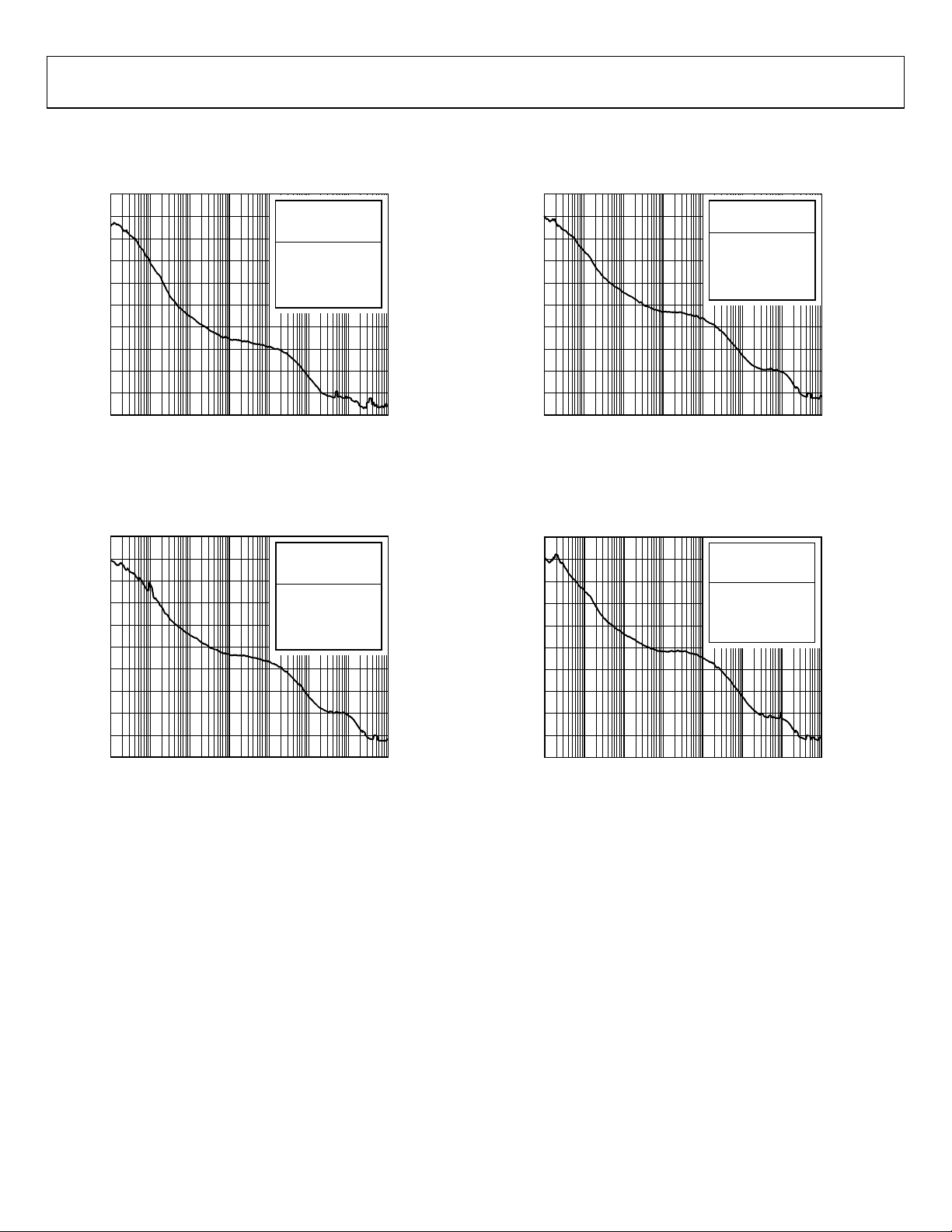
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
fR = input reference clock frequency; f
= output clock frequency; f
OUT
= SYSCLK input frequency; VDD3 and VDD at nominal supply voltage.
SYS
Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 50 Hz, f
= 156.25 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Figure 3. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 50 Hz, f
= 622.08 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Figure 4. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 50 Hz, f
= 644.53125 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Figure 5. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 50 Hz, f
= 693.482991 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 120
Page 21
Data Sheet AD9559
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 335fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –82
100Hz –90
1kHz –96
10kHz –119
100kHz –128
1MHz –143
10MHz –152
FLOOR –158
10644-006
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 309fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –84
100Hz –93
1kHz –116
10kHz –125
100kHz –130
1MHz –144
10MHz –152
FLOOR –158
10644-007
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 321fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –61
100Hz –69
1kHz –108
10kHz –127
100kHz –132
1MHz –146
10MHz –153
10644-008
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 331fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –70
100Hz –75
1kHz –86
10kHz –108
100kHz –112
1MHz –129
10MHz –142
FLOOR –152
10644-009
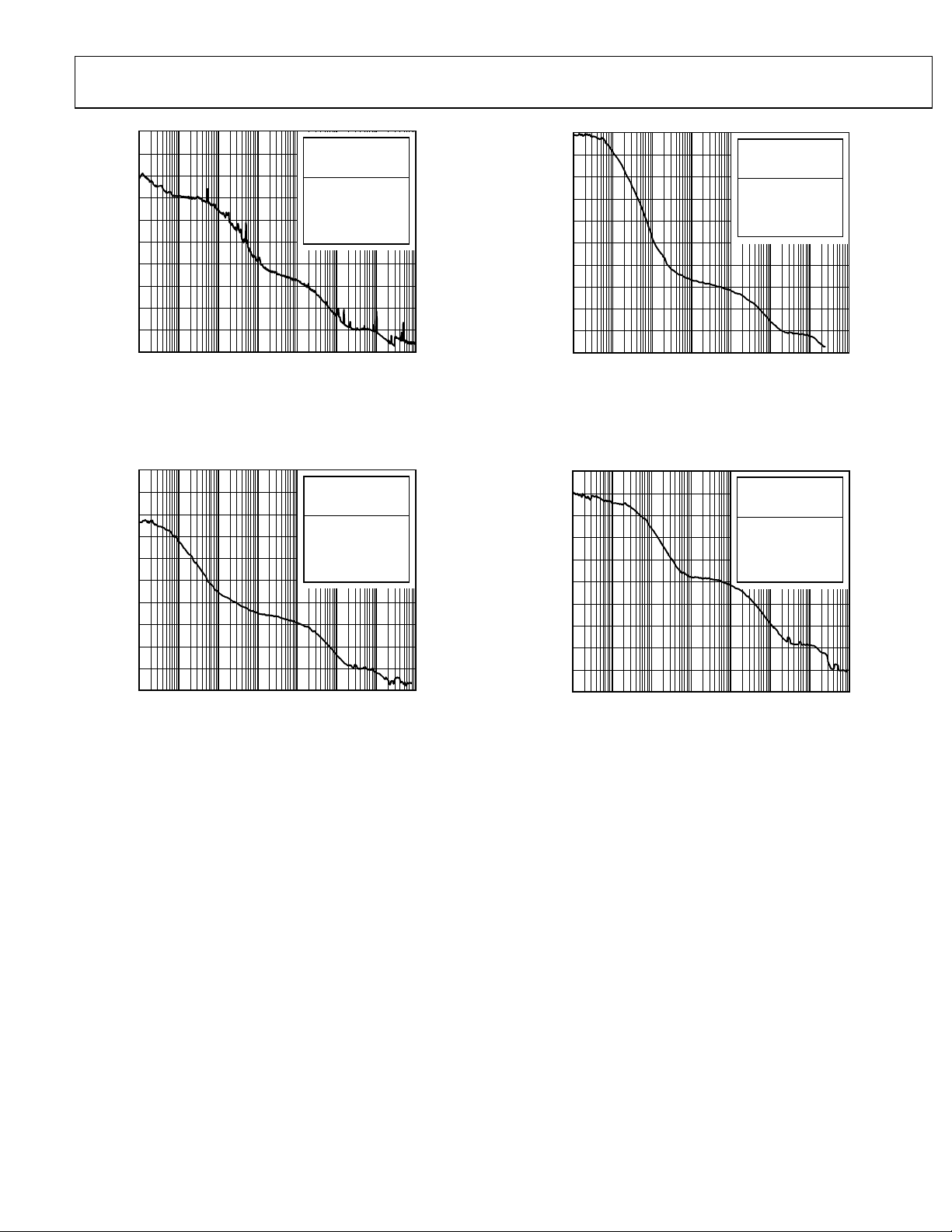
Figure 6. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 1 kHz, f
= 174.703 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Figure 8. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 2 kHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 100 Hz, f
= 125 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Figure 7. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = 3.3.V CMOS),
f
= 19.44 MHz, f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 100 Hz, f
= 161.1328125 MHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Rev. 0 | Page 21 of 120
Figure 9. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
f
= 25 MHz, f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 500 Hz, f
= 1 GHz,
OUT
= 49.152 MHz Crystal
SYS
Page 22
AD9559 Data Sheet
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 383fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc /Hz):
10Hz –60
100Hz –85
1kHz –104
10kHz –112
100kHz –114
1MHz –132
10MHz –141
FLOOR –153
10644-011
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
10644-012
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 392fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc /Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –66
100Hz –91
1kHz –110
10kHz –119
100kHz –121
1MHz –136
10MHz –146
FLOOR –156
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
10644-013
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 378fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc /Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –74
100Hz –97
1kHz –116
10kHz –125
100kHz –127
1MHz –143
10MHz –153
FLOOR –158
–160
–150
–140
–130
–120
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
10644-014
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 418fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc/Hz):
OFFSET LEVEL
10Hz –71
100Hz –96
1kHz –122
10kHz –132
100kHz –134
1MHz –149
10MHz –157
FLOOR –161
INTEGRATED RMS JITTER
–70
–80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–160
1k10 100 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
FREQUENCY OF F SET (Hz)
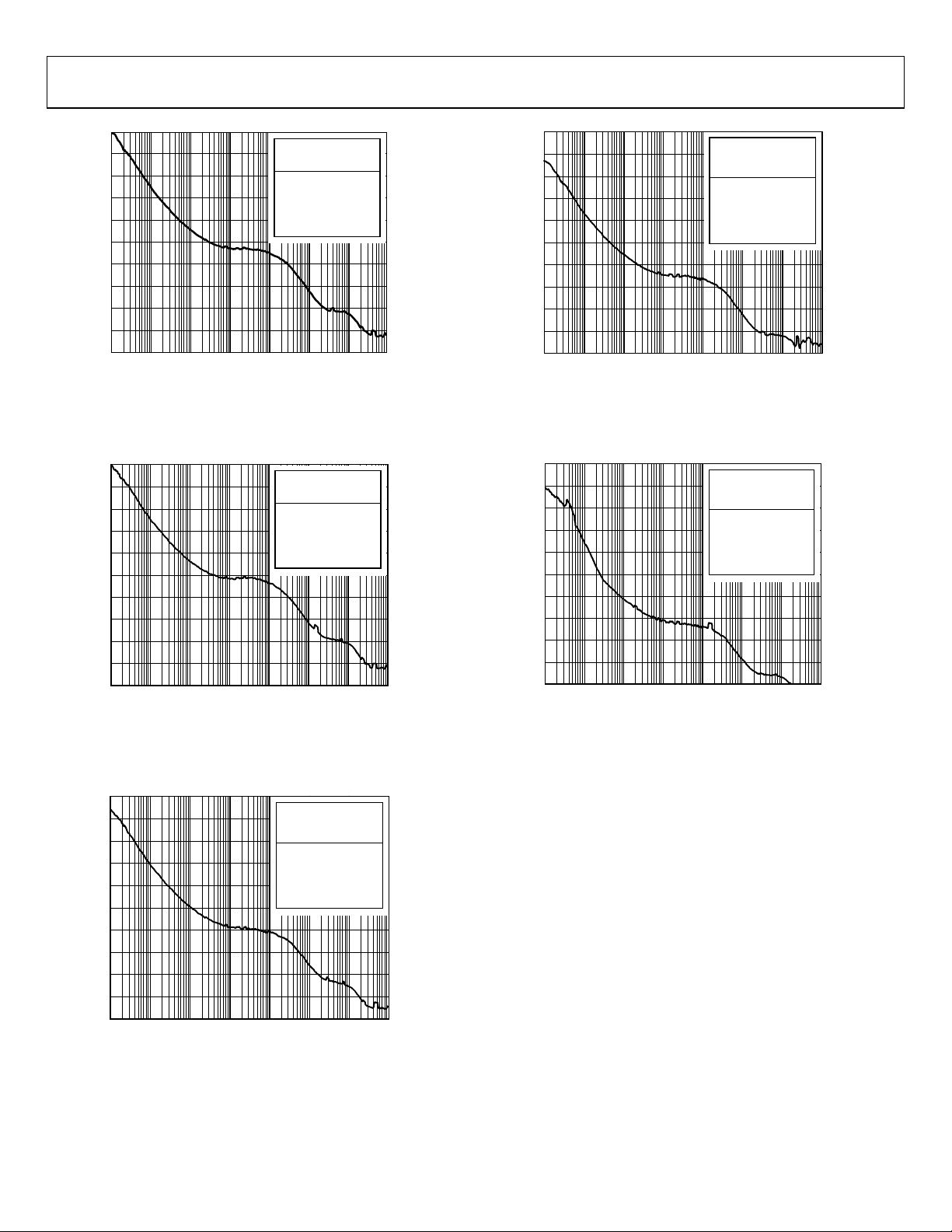
Figure 10. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 10 Hz, f
(12kHz TO 20MHz): 373fs
PHASE NOISE ( d Bc /Hz):
10Hz –60
100Hz –85
1kHz –104
10kHz –113
100kHz –114
1MHz –132
10MHz –142
FLOOR –153
= 644.53 MHz,
OUT
= 19.2 MHz TCXO
SYS
10644-010
Figure 13. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = 3.3 V CMOS),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 10 Hz, f
=161.1328125 MHz,
OUT
= 19.2 MHz TCXO
SYS
Figure 11. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
= 19.44 MHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 10 Hz, f
Figure 12. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = HSTL),
f
= 19.44 MHz, f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 0.1 Hz, f
= 693.482991 MHz,
OUT
= 19.2 MHz TCXO
SYS
= 312.5 MHz,
OUT
= 19.2 MHz TCXO
SYS
Rev. 0 | Page 22 of 120
Figure 14. Absolute Phase Noise (Output Driver = 1.8V CMOS),
= 2 kHz, f
f
R
DPLL Loop BW = 10 Hz, f
= 70.656 MHz,
OUT
= 19.2 MHz TCXO
SYS
Page 23
Data Sheet AD9559
DIFFERENTIAL PEAK-TO-PEAK AMPLITUDE (mV)
0 100 200 300 400 600 800 1000 1200500 700 900 1100
FREQUENCY (MHz)
1.50
1.55
1.60
1.65
1.70
1.75
1.80
1.85
1.90
1.
95
2.00
10644-116
0
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
DIFFERENTIAL PEAK-TO-PEAK AMPLITUDE (mV)
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800
FREQUENCY (MHz)
LVDS (DEFAULT)
LVDS (BOOST)
10644-117
3.5
3.0
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
0 30025020015010050
PEAK-TO-PEAK AMPLITUDE (V)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
1.8 V MODE
3.3V STRONG MODE
10644-118
3.5
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
0 10080604020
PEAK-TO-PEAK AMPLITUDE (V)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
3.3V WEAK MO DE
10644-119
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0 140012001000800600400200
POWER (mW)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10644-120
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 900800
POWER (mW)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10644-121
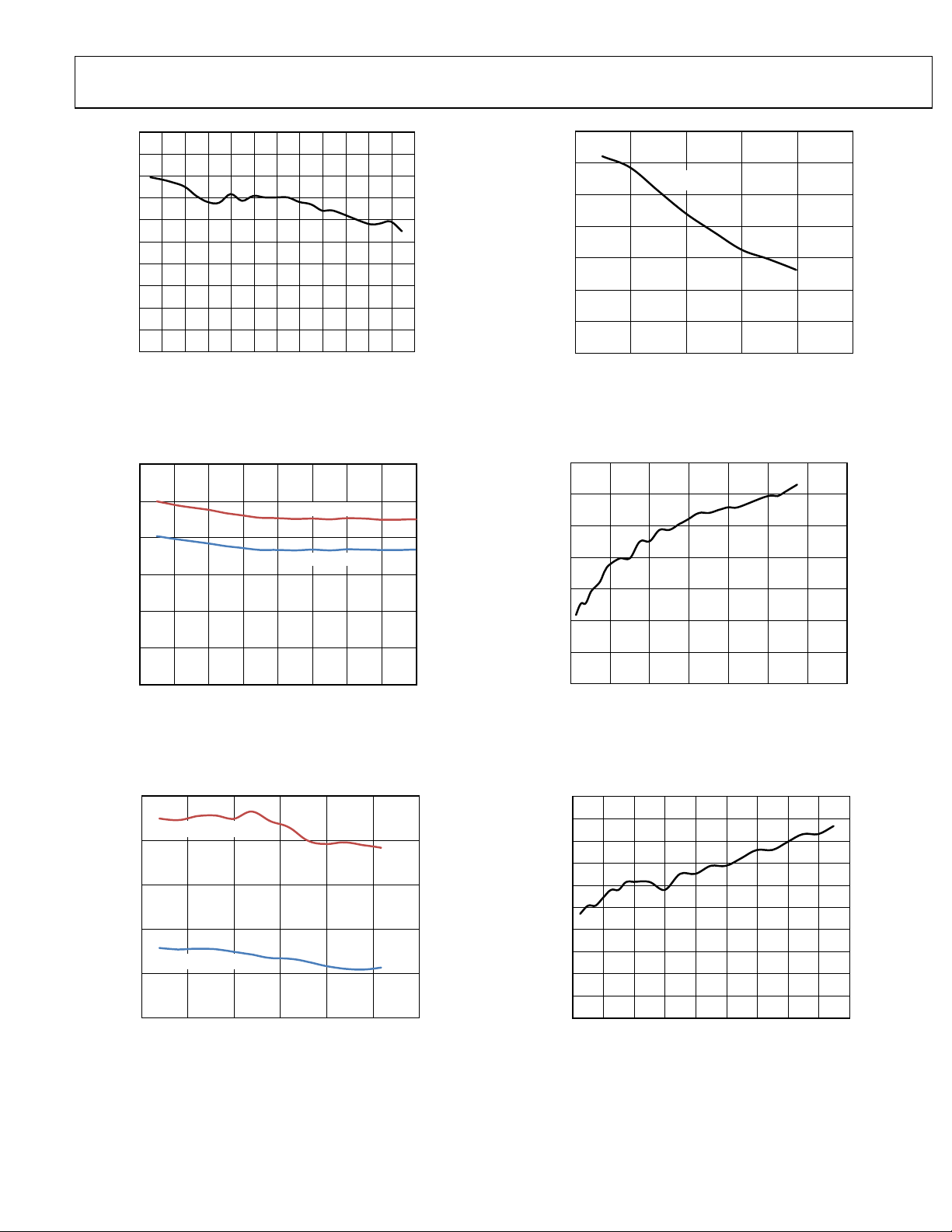
Figure 15. Amplitude vs. Toggle Rate,
HSTL Mode (LVPECL-Compatible Mode)
Figure 16. Amplitude vs. Toggle Rate, LVDS
Figure 18. Amplitude vs. Toggle Rate with 10 pF Load,
3.3 V (Weak Mode) CMOS
Figure 19. Power Consumption vs. Frequency,
HSTL Mode on Output Driver Power Supply Only
(Pin 17, Pin 21, Pin 34, and Pin 38)
Figure 17. Amplitude vs. Toggle Rate with 10 pF Load,
3.3 V (Strong Mode) and 1.8 V CMOS
Figure 20. Power Consumption vs. Frequency,
LVDS Mode on Output Driver Power Supply Only
(Pin 17, Pin 21, Pin 34, and Pin 38)
Rev. 0 | Page 23 of 120
Page 24
AD9559 Data Sheet
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
80
70
0 20018016014012010080604020
POWER (mW)
FREQUENCY (MHz)
10644-122
1.8V CMOS
3.3V CMOS W E AK
3.3V CMOS STRONG
–1.0
–0.8
–0.6
–0.4
–0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
–1 0 1 2 3 4 5
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLITUDE (V)
TIME (ns)
10644-123
–0.4
–0.3
–0.2
–0.1
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
–1 0 1 2 3 4
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLITUDE (V)
TIME (ns)
10644-124
–0.2
0.2
0.6
1.0
1.4
1.8
2.2
2.6
3.0
3.4
–1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
AMPLITUDE (V)
TIME (ns)
10pF LOAD
2pF LOAD
10644-126
–1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
AMPLITUDE (V)
TIME (ns)
–0.1
0.1
0.3
0.5
0.7
0.9
1.1
1.3
1.5
1.7
1.9
10pF LOAD
2pF LOAD
10644-127
0
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
–5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95
AMPLITUDE (V)
TIME (ns)
10pF LOAD
2pF LOAD
10644-128
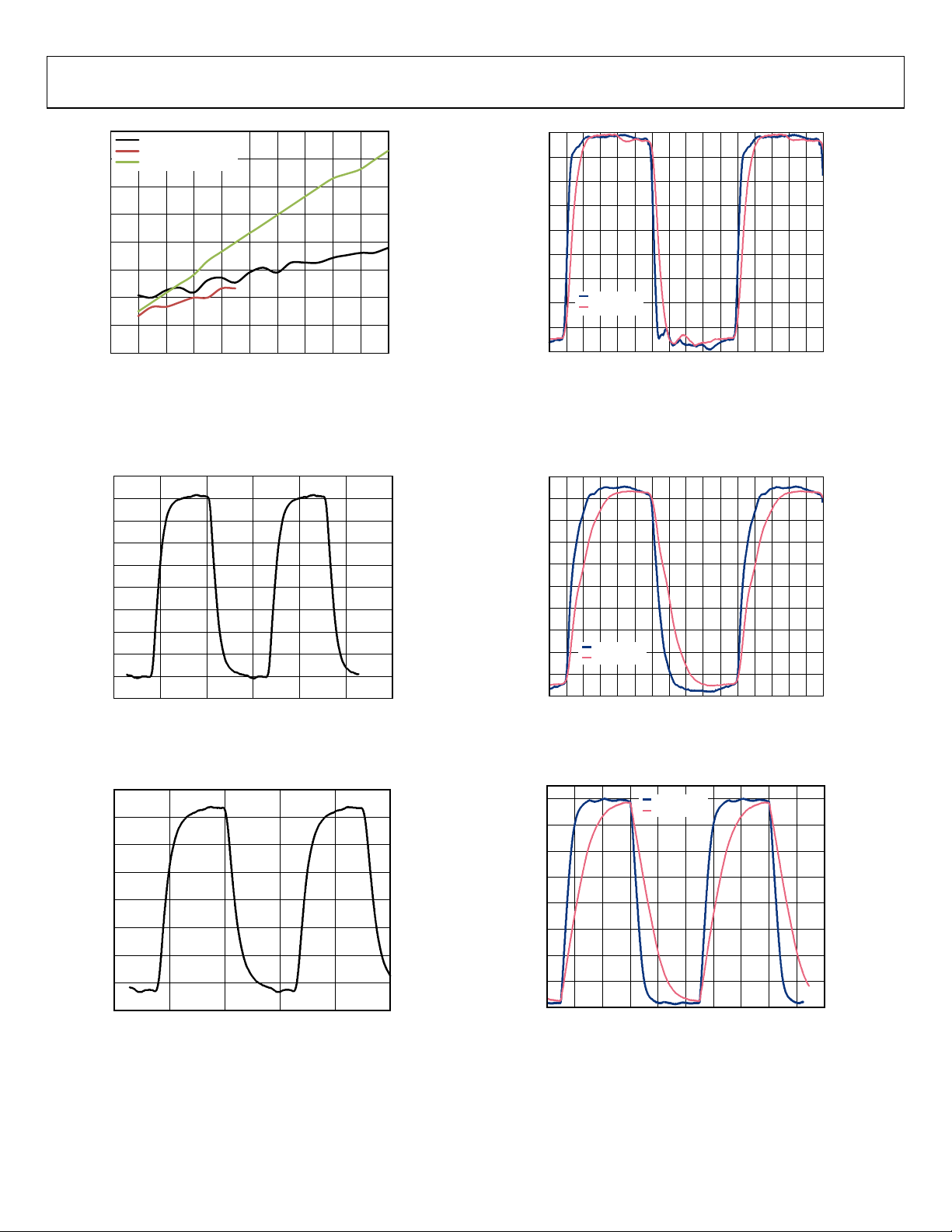
Figure 21. Power Consumption vs. Frequency for Two CMOS Drivers;
Power Is Measured on Output Driver Power Supply Only
(Pin 17, Pin 21, Pin 34, and Pin 38 for 1.8 V CMOS Mode or
on Pin 18 and Pin 37 for 3.3 V CMOS Mode); C
LOAD
= 80 pF
Figure 22. Output Waveform, HSTL (400 MHz)
Figure 24. Output Waveform,
3.3 V CMOS (100 MHz, Strong Mode)
Figure 25. Output Waveform, 1.8 V CMOS (100 MHz)
Figure 23. Output Waveform, LVDS (400 MHz)
Figure 26. Output Waveform, 3.3 V CMOS (20 MHz, Weak Mode)
Rev. 0 | Page 24 of 120
Page 25
Data Sheet AD9559
–30
–27
–24
–21
–18
–15
–12
–9
–6
–3
0
3
10 100 1k 10k 100k
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
LOOP GAIN (dB)
10644-129
LOOP BW = 100Hz;
HIGH PHASE M ARGIN;
PEAKING: 0.06dB; –3dB: 69Hz
LOOP BW = 2kHz;
HIGH PHASE M ARGIN;
PEAKING: 0.097dB; –3dB: 1.23kHz
LOOP BW = 5kHz;
HIGH PHASE M ARGIN;
PEAKING: 0.14dB; –3dB: 4.27kHz
–30
–27
–24
–21
–18
–15
–12
–9
–6
–3
0
3
10 100 1k
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
LOOP GAIN (dB)
10k 100k
10644-230
LOOP BW = 100Hz;
NORMAL PHASE M ARGIN;
PEAKING: 0.09dB; –3dB: 117Hz
LOOP BW = 2kHz;
NORMAL PHASE M ARGIN;
PEAKING: 1.6dB; –3dB: 2.69kHz
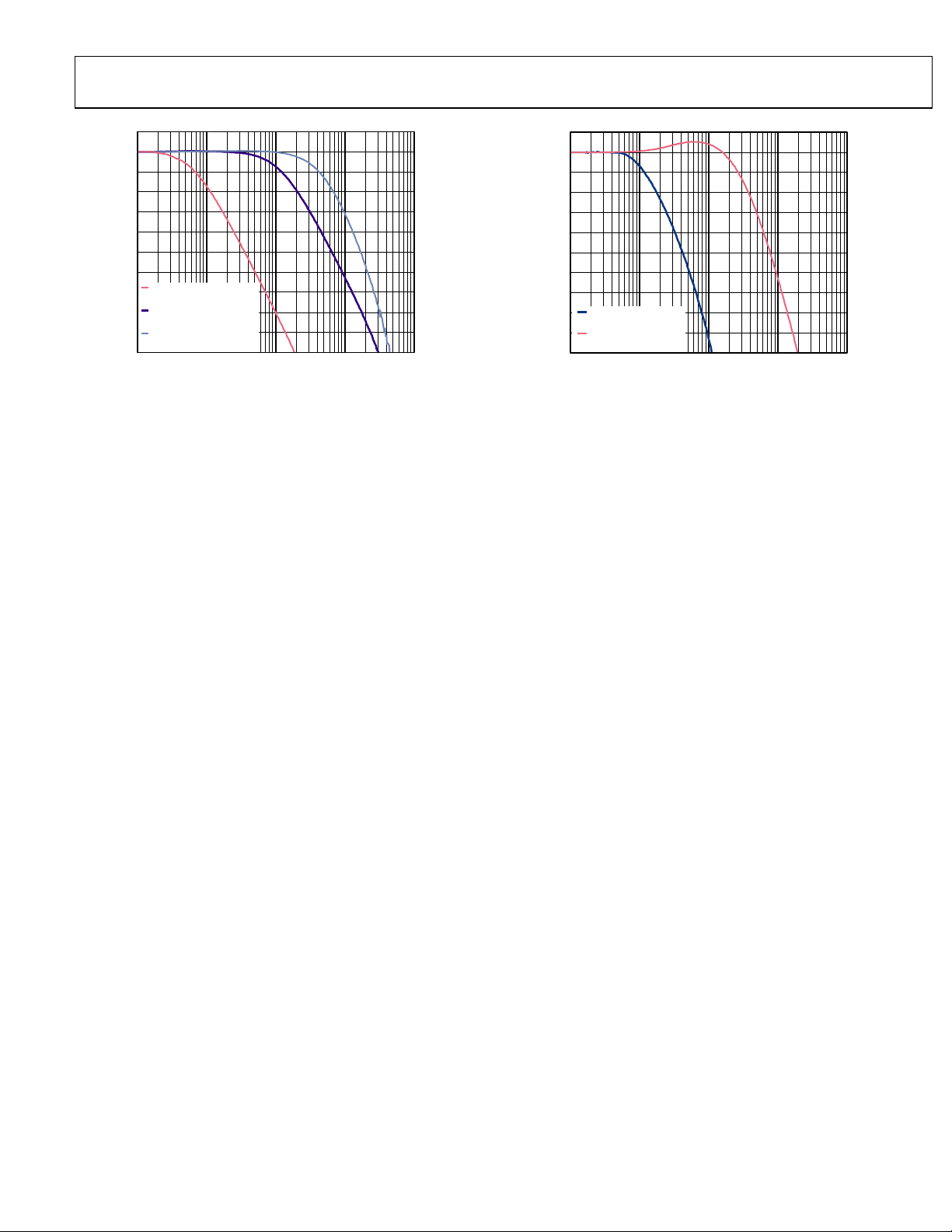
Figure 27. Closed-Loop Transfer Function for 100 Hz, 2 kHz, and 5 kHz Loop
Bandwidth Settings; High Phase Margin Loop Filter Setting
(This figure is compliant with Telcordia GR-253
jitter transfer test for loop bandwidths < 2 kHz.)
Note that bandwidth is defined as the point where t he open loop gain = 0 dB.
Figure 28. Closed-Loop Transfer Function for 100 Hz and 2 kHz Loop
Bandwidth Settings; Normal Phase Margin Loop Filter Setting
Note that bandwidth is defined as the point where t he open loop gain = 0 dB.
Rev. 0 | Page 25 of 120
Page 26
AD9559 Data Sheet
AD9559
HSTL OR
LVDS
DOWNSTREAM
DEVICE
WITH HIGH
IMPEDANCE
INPUT AND
INTERNAL
DC BIAS
0.1µF
0.1µF
100Ω
10644-130
Z0 = 50Ω
Z
0
= 50Ω
SINGLE-ENDED
(NOT COUPLED)
AD9559
HSTL OR
LVDS
Z
0
= 50Ω
Z
0
= 50Ω
SINGLE-ENDED
(NOT COUPLED)
LVDS OR 1.8V HS TL
HIGH IMPE DANCE
DIFFERENTIAL
RECEIVER
100Ω
10644-131
SINGLE-ENDED
(NOT COUPLED)
VS = 3.3V
3.3V
LVPECL
82Ω82Ω
127Ω127Ω
0.1µF
0.1µF
AD9559
1.8V
HSTL
Z0 = 50Ω
Z
0
= 50Ω
10644-132
XOA
XOB
AD9559
10MHz TO 50MHz FUNDAMENTAL
AT-CUT CRYST AL WITH
10pF LOAD CAP ACITANCE
10pF
10pF
10644-133
XOA
300Ω
150Ω
0.1µF
XOB
AD9559
3.3V
CMOS
TCXO
0.1µF
10644-134
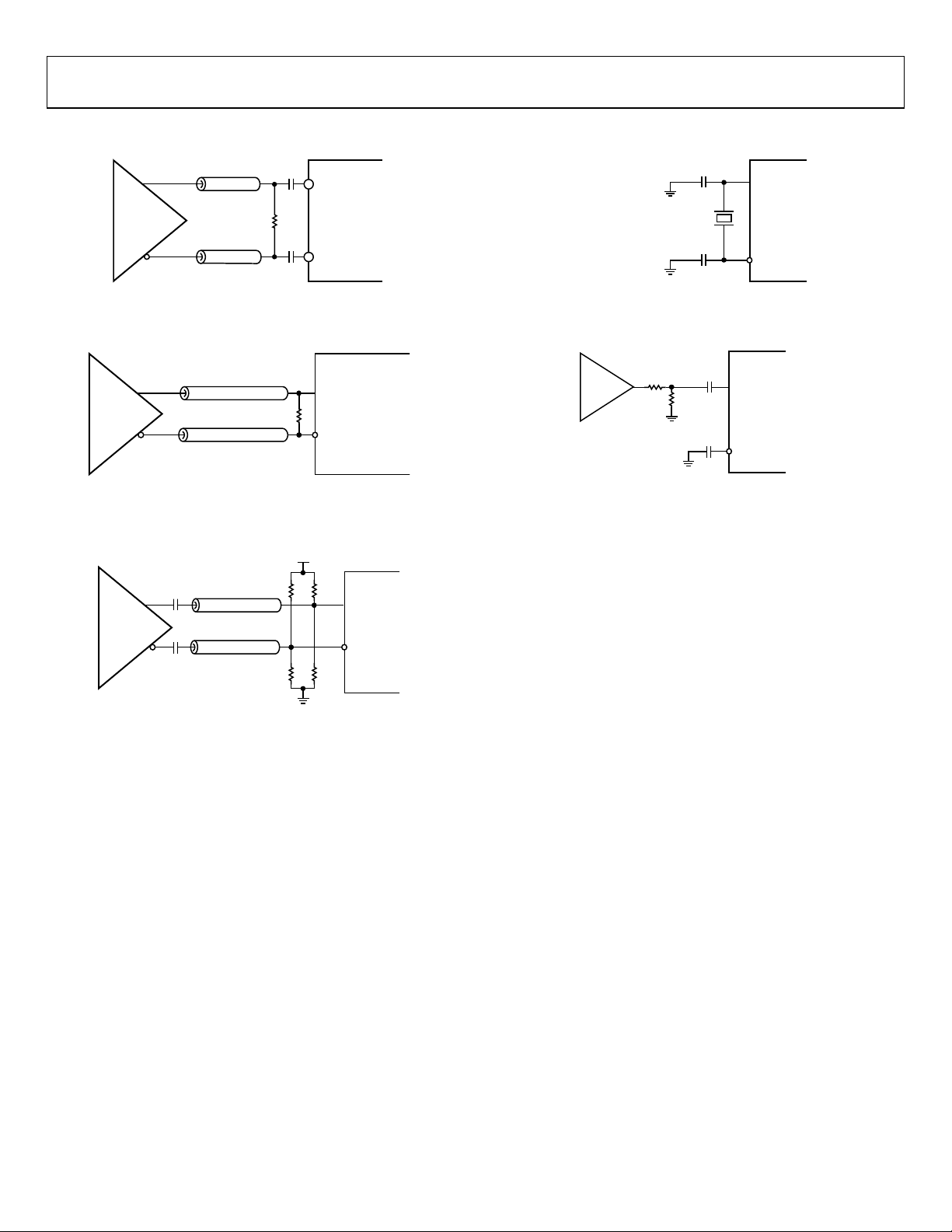
INPUT/OUTPUT TERMINATION RECOMMENDATIONS
Figure 29. AC-Coupled LVDS or HSTL Output Driver
(100 Ω resistor can be placed on either side of decoupling capacitors
and should be as close to the destination receiver as possible.)
Figure 30. DC-Coupled LVDS or HSTL Output Driver
Figure 31. Interfacing the HSTL Driver to a 3.3 V LVPECL Input
(This method incorporates impedance matching and dc-biasing for bipolar
LVPECL receivers. If the receiver is self-biased, the termination scheme shown in
Figure 29 is recommended.)
(The recommended C
Figure 32. System Clock Input (XOA/XOB) in Crystal Mode
shown here should equal the C
When Using a TCXO/OCXO with 3.3 V CMOS Output
= 10 pF is shown. The values of 10 pF shunt capacitors
LOAD
of the crystal.)
LOAD
Figure 33. System Clock Input (XOA, XOB)
Rev. 0 | Page 26 of 120
Page 27
Data Sheet AD9559
GETTING STARTED
CHIP POWER MONITOR AND STARTUP
The AD9559 monitors the voltage on the power supplies at
power-up. When VDD3 is greater than 2.35 V ± 0.1 V and
VDD is greater than 1.4 V ± 0.05 V, the device generates a
20 ms reset pulse. The power-up reset pulse is internal and
independent of the
E
RESET
A
A
pin. This internal power-up reset
sequence eliminates the need for the user to provide external
power supply sequencing. Within 45 ns after the internal reset
pulse, the M5 to M0 multifunction pins behave as high
impedance digital inputs and continue to do so until
programmed otherwise.
During a device reset (either via the power-up reset pulse or
the
E
RESET
A
A
pin), the M3 to M0 multifunction pins behave as
high impedance inputs; and at the point where the reset
condition is cleared, level-sensitive latches capture the logic
pattern that is present on the multifunction pins.
MULTIFUNCTION PINS AT RESET/POWER-UP
At start-up, the M0 and M1 pins allow the user to either bypass
EEPROM loading or load one of three EEPROM profiles. See
Table 23 for information on setting the M0 and M1 pins.
Pin M3 selects SPI or I²C mode: SPI mode is set by pulling M3
low at startup. If M3 is high, I²C mode is set, and the M4 and
M5 pins determine the I²C address. See Ta ble 25 for information
on SPI/I²C configuration.
If 4-wire SPI mode is selected, by setting Bit 7 of Register 0x0000,
the M4/SDO pin functions as SDO and is not available for other
functions as an M pin. However, in I²C mode and in 3-wire SPI
mode, M4 is available as the fifth M pin.
A sixth M pin, M5, is available if the serial port is in I²C mode
or 2-wire SPI mode. In 2-wire SPI mode, there is no
available, and it is assumed that the
AD9559 is the only device
on the SPI bus.
CS
A
E
A
pin
DEVICE REGISTER PROGRAMMING USING A REGISTER SETUP FILE
The evaluation software contains a programming wizard and
a convenient graphical user interface that assists the user in
determining the optimal configuration for the DPLLs, APLLs,
and SYSCLK based on the desired input and output frequencies.
It generates a register setup file with a .STP extension that is
easily readable using a text editor.
The user can configure PLL_0 and PLL_1 independently. To do
so, the user should program the common registers (such as the
system clock and reference inputs) first. Next, the registers that
are unique to PLL_0 or PLL_1 can be configured independently.
After using the evaluation software to create the setup file, use
the following sequence to program the AD9559:
1. Set user free run mode.
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22 = 0x01.
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42 = 0x01.
2. Update all registers (also referred to as IO_UPDATE).
Register 0x0005 = 0x01.
3. Write the register values in the STP file from Address 0x0000
to Address 0x0207.
4. IO_UPDATE. Register 0x0005 = 0x01.
5. Ve r if y that SYSCLK is stable. Register 0x0D01[1] = 1.
The user must issue an IO_UPDATE each time before
polling Register 0x0D01.
6. For the outputs to toggle prior to DPLL phase or frequency
lock, set the following:
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20 = 0x40 (soft sync).
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40 = 0x40 (soft sync).
7. Write the rest of the registers in the STP file starting at
Address 0x0300.
8. Calibrate APLL on next IO_UPDATE.
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20 = 0x20.
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40 = 0x20.
9. IO_UPDATE. Register 0x0005 = 0x01.
10. Clear user free run mode.
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22[0] = 0b.
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42[0] = 0b.
11. IO_UPDATE. Register 0x0005 = 0x01.
Rev. 0 | Page 27 of 120
Page 28

AD9559 Data Sheet
REGISTER PROGRAMMING OVERVIEW
This section provides a programming overview of the register
blocks in the AD9559, describing what they do and why they
are important. This is supplemental information only, needed
only if the user wishes to load the registers without using the
STP file.
The AD9559 evaluation software contains a wizard that determines
the register settings based on the user’s input and output
frequencies. It is strongly recommended that the evaluation
software be used to determine these settings.
Multifunction Pins (Optional)
This step is required only if the user intends to use any of the
multifunction pins for status or control. The multifunction pin
parameters are at Register 0x0100 to Register 0x0107.
Table 196 has a list of M pin output functions, and Tab l e 197 has
a list of M pin input functions.
IRQ Functions (Optional)
This step is required only if the user intends to use the IRQ feature.
The IRQ functions are divided into three groups: common,
PLL_0, and PLL_1.
The user must first choose the events that trigger an IRQ and
then set them in Register 0x010A to Register 0x0112. Next,
an M pin must be assigned to the IRQ function. The user can
choose to dedicate one M pin to each of the three IRQ groups,
or one M pin can be assigned for all IRQs.
The IRQ monitor registers are located at Register 0x0D08 to
Register 0x0D10. If the desired bits in the IRQ mask registers at
Register 0x010A to Register 0x0112 are set high, the appropriate
IRQ monitor bit at Register 0x0D08 to Register 0x0D10 is set
high when the indicated event occurs.
Individual IRQ events are cleared by using the IRQ clearing
registers at Register 0x0A05 to Register 0x0A0E or by setting
the clear all IRQs bit (Register 0x0A05[0]) to 1b.
The default values of the IRQ mask registers are such that
interrupts are not generated. The default IRQ pin mode is opendrain NMOS.
Watchdog Timer (Optional)
This step is required only if the user intends to use the watchdog
timer. The watchdog timer control is at Register 0x0108 and
Register 0x0109. The watchdog timer is disabled by default.
The watchdog timer is useful for generating an IRQ after a fixed
amount of time. The timer is reset by setting the clear watchdog
timer bit in Register 0x0A05[7] to 1.
The user can also program an M pin for the watchdog timer
output. In this mode, the M pin generates a 40 ns pulse every
time the watchdog timer expires.
System Clock Configuration
The system clock multiplier (SYSCLK) parameters are at
Register 0x0200 to Register 0x0207. For optimal performance,
use the following steps:
1. Set the system clock PLL input type and divider values.
2. Set the system clock period.
It is essential to program the system clock period because
many of the AD9559 subsystems rely on this value.
3. Set the system clock stability timer.
It is highly recommended that the system clock stability
timer be programmed. This is especially important when
using the system clock multiplier and also applies when
using an external system clock source, especially if the
external source is not expected to be completely stable
when power is applied to the AD9559. The system clock
stability timer specifies the amount of time that the system
clock PLL must be locked before the part declares that the
system clock is stable. The default value is 50 ms.
4. Update all registers (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Important Note
The system clock must be stable for the digital PLL blocks to
function correctly and read back the registers updated on the
system clock domain. These registers include the status registers,
as well as the free running tuning word. Therefore, when debugging the
stable by checking Bit 1 in Register 0x0D01.
AD9559, the user mus
t first ensure that the system clock is
Reference Inputs
The reference input parameters and reference dividers are common
to both PLLs; there is only one reference divider (R divider) for
each reference input. The register address for each reference input
is as follows:
• REFA: Register 0x0300 to Register 0x031A
• REFB: Register 0x0320 to Register 0x033A
• REFC: Register 0x0340 to Register 0x035A
• REFD: Register 0x0360 to Register 0x037A
These registers include the following settings:
• Reference logic family
• Reference divider (R divider value)
• Reference input period and tolerance
• Reference validation timer
• Phase and frequency lock detector settings
Rev. 0 | Page 28 of 120
Page 29

Data Sheet AD9559
Other reference input settings can be found at the following
register addresses:
Note that the APLL calibration and synchronization bits can be
found in the following registers:
Reference input enable information is found in the DPLL
Feedback Dividers section.
Reference power-down is found in Register 0x0A01.
Reference priority settings are found in the DPLL profiles.
DPLL_0: Registers 0x0440 through 0x0473
DPLL_1: Registers 0x0540 through 0x0573
Reference switching mode settings are found in
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42
DPLL Controls and Settings
The DPLL control parameters are separate for DPLL_0 and
DPLL_1. They reside in the following locations:
DPLL_0: Register 0x0400 to Register 0x0415
DPLL_1: Register 0x0500 to Register 0x0515
These registers include the following settings:
30-bit free running frequency
DPLL pull-in range limits
DPLL closed-loop phase offset
Tuning word history control (for holdover operation)
Phase slew control (for controlling the phase slew rate
during a closed-loop phase adjustment)
With the exception of the free running tuning word, the default
values of these registers are fine for normal operation. The free
running frequency of the DPLL determines the frequency that
appears at the APLL input when user free run mode is selected.
The correct free running frequency is required for the APLL to
calibrate and lock correctly.
Note that the user free run bits, which enable user free run mode,
can be found in the following registers:
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22 = 0x01
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42 = 0x01
Output PLLs (APLLs) and Output Drivers
The registers controlling the APLLs and output drivers reside at
the following locations:
APLL_0: Register 0x0420 to Register 0x042E
APLL_1: Register 0x0520 to Register 0x052E
The following functions are controlled in these registers:
APLL settings (feedback divider, charge pump current)
Output synchronization mode
Output divider values
Output enable/disable (disabled by default)
Output logic type
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40
DPLL Feedback Dividers
Each digital PLL has separate feedback divider settings for each
reference input. This allows the user to have each digital PLL
perform a different frequency translation. However, there is
only one reference divider (R divider) for each reference input.
The feedback divider register settings reside in the following
locations:
DPLL_0, REFA: Register 0x0440 to Register 0x044C
DPLL_0, REFB: Register 0x044D to Register 0x0459
DPLL_0, REFC: Register 0x045A to Register 0x0466
DPLL_0, REFD: Register 0x0467 to Register 0x0473
DPLL_1, REFC: Register 0x0540 to Register 0x054C
DPLL_1, REFD: Register 0x054D to Register 0x0559
DPLL_1, REFA: Register 0x055A to Register 0x0566
DPLL_1, REFB: Register 0x0567 to Register 0x0573
These registers include the following settings:
Reference priority
Reference input enable (separate for each DPLL)
DPLL loop bandwidth
DPLL loop filter
DPLL feedback divider (integer portion)
DPLL feedback divider (fractional portion)
Common Operational Controls
The common operational controls reside at Register 0x0A00 to
Register 0x0A0E and include the following:
Simultaneous calibration and synchronization of both PLLs
Global power-down
Reference power-down
Reference validation override
IRQ clearing (for all IRQs)
PLL_0 and PLL_1 Operational Controls
The PLL_0 and PLL_1 operational controls are located at
Register 0x0A20 to Register 0x0A44 and include the following:
APLL calibration and synchronization
Output driver enable and power-down
DPLL reference input switching modes
DPLL phase offset control
Rev. 0 | Page 29 of 120
Page 30

AD9559 Data Sheet
APLL VCO Calibration
VCO calibration ensures that, at the time of calibration, the dc
control voltage of the APLL VCO is centered in the middle of its
operating range. The user can calibrate VCO_0 independently of
VCO_1, and vice versa. It is important to remember the following
conditions when calibrating the APLL VCO:
• The system clock must be stable.
• The APLL VCO must have the correct frequency from the
30-bit DCO (digitally controlled oscillator) during
calibration. The free running tuning word is found in
DPLL_0: Registers 0x0400 to 0x0403
DPLL_1: Registers 0x0500 to 0x0503
• The APLL VCO must be recalibrated any time the APLL
frequency changes.
• APLL VCO calibration occurs on the low-to-high
transition of the APLL VCO calibration bit.
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20[1]
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40[1]
• The VCO calibration bit is not an autoclearing bit.
Therefore, this bit must be cleared (and an IO_UPDATE
issued) before the APLL is recalibrated.
• The best way to monitor successful APLL calibration is
by monitoring the APLL locked bit, in the following registers:
APLL_0: Register 0x0D20[3]
APLL_1: Register 0x0D40[3]
Generate the Output Clock
If Register 0x0425 (for PLL_0) and/or Register 0x0525 (for PLL_1)
is programmed for automatic clock distribution synchronization
via the DPLL phase or frequency lock, the synthesized output
signal appears at the clock distribution outputs. Otherwise, set
and then clear the soft sync bit (Bit 2 in Register 0x0A20 for
APLL_0 and Register 0x0A40 for APPL_1) or use a multifunction
pin input (if programmed accordingly) to generate a clock
distribution sync pulse, which causes the synthesized output
signal to appear at the clock distribution outputs.
Generate the Reference Acquisition
After the registers are programmed, clear the user free run bit
(Bit 0 in Register 0x0A22 for DPLL_0 and Register 0x0A42 for
DPPL_1) and issue an IO_UPDATE using Register 0x0005[0] to
invoke all of the register settings programmed up to this point.
The DPLLs lock to the first available reference that has the
highest priority.
Rev. 0 | Page 30 of 120
Page 31

Data Sheet AD9559
XOA
XOB
REFA
REFA
A
REFB
REFB
B
REFC
REFC
C
REFD
REFD
D
÷2
÷2, ÷4, ÷8
×2
÷R
A
÷2
÷R
B
÷2
÷R
C
÷2
÷R
D
REFERENCE
MONITORS
AND
CROSSPOINT
MUX
SYSCLK
MULTIPLIER
REF
OR
XTAL
SYSTEM
CLOCK
DPFD
LOOP
FILTER
TW
CLAMP
NCO_0
FRAC0 ÷ MOD0
÷N0 ÷M0
÷P0 (÷3 TO ÷11)
PFD/CP
LF
FREE RUN
TUNING WORD
VCO_0
2940MHz TO 3543MHz
÷Q0_A
OUT0A
OUT0A
÷Q0_B
OUT0B
OUT0B
262kHz TO
1.25GHz
÷Q1_A
DPFD
LOOP
FILTER
TW
CLAMP
NCO_1
FRAC1 ÷ MOD1
÷N1
÷M1
÷P1 (÷3 TO ÷11)
PFD/CP
LF
FREE RUN
TUNING WORD
VCO_1
3405MHz TO 4260MHz
÷Q1_B
OUT1A
OUT1A
OUT1B
OUT1B
302kHz TO
1.25GHz
RESET
SCLK/SCL
SDIO/SDA
M5/CS
M4/SDO
M3
M2
M1
M0
CONTROL INTERFACE/LOGIC
AND EEPROM
INPUT REFE RE NCE FREQUENCY RANGE :
2kHz TO 1.25G Hz
10644-035
THEORY OF OPERATION
OVERVIEW
The AD9559 provides clocking outputs that are directly related
in phase and frequency to the selected (active) reference but
with jitter characteristics governed by the system clock, the
digitally controlled oscillator (DCO), and the analog output
PLL (APLL). The AD9559 can be thought of as two copies of
the AD9557 inside one package, with a 4:2 crosspoint controlling
the reference inputs. The AD9559 supports up to four reference
inputs and input frequencies ranging from 2 kHz to 1250 MHz.
The cores of this product are two digital phase-locked loops
(DPLLs). Each DPLL has a programmable digital loop filter that
greatly reduces jitter transferred from the active reference to the
output, and these two DPLLs operate completely independently
of each other. The AD9559 supports both manual and automatic
holdover. While in holdover, the AD9559 continues to provide
an output as long as the system clock is present. The holdover
output frequency is a time average of the output frequency history
just prior to the transition to the holdover condition. The device
offers manual and automatic reference switchover capability if
the active reference is degraded or fails completely. The AD9559
also has adaptive clocking capability that allows the user to
dynamically change the DPLL divide ratios while the DPLLs
are locked.
The AD9559 includes a system clock multiplier, two DPLLs,
and two APLLs. The input signal goes first to the DPLL, which
performs the jitter cleaning and most of the frequency translation.
Each DPLL features a 30-bit digitally controlled oscillator (DCO)
output that generates a signal in the range of 175 MHz to 200 MHz.
Figure 34. Detailed Block Diagram
The DCO output goes to the APLL, which multiplies the signal
up to a range of 2.9 GHz to 4.2 GHz. That signal is then sent to
the clock distribution section, which has a divide-by-3 to
divide-by-11 P divider cascaded with 10-bit integer channel
dividers (divide-by-1 to divide-by-1024).
The XOA and XOB inputs provide the input for the system clock.
These bits accept a reference clock in the 10 MHz to 600 MHz
range or a 10 MHz to 50 MHz crystal connected directly across
the XOA and XOB inputs. The system clock provides the clocks
to the frequency monitors, the DPLLs, and internal switching logic.
Each APLL on the AD9559 has two differential output drivers.
Each of the four output drivers has a dedicated 10-bit programmable post divider. Each differential driver is programmable as
either a single differential or dual single-ended CMOS output.
The clock distribution section operates at up to 1250 MHz.
In differential mode, the output drivers run on a 1.8 V power
supply to offer very high performance with minimal power
consumption. There are two differential modes: LVDS and 1.8 V
HSTL. In 1.8 V HSTL mode, the voltage swing is compatible
with LVPECL. If LVPECL signal levels are required, the designer
can ac-couple the
termination at the destination to drive LVPECL inputs.
In single-ended mode, each differential output driver can operate
as two single-ended CMOS outputs. OUT0A,
OUT1A,
OUT0B,
V CMOS operation.
Rev. 0 | Page 31 of 120
OUT1A
OUT0B
AD9559 output and use Thev
support only 1.8 V CMOS operation.
and OUT1B,
OUT1B
support either 1.8 V or 3.3
enin-equivalent
OUT0A
and
Page 32

AD9559 Data Sheet
1+=R
f
f
R
TDC
REFERENCE INPUT PHYSICAL CONNECTIONS
Four pairs of pins (REFA,
access to the reference clock receivers. To accommodate input
signals with slow rising and falling edges, both the differential
and single-ended input receivers employ hysteresis. Hysteresis
also ensures that a disconnected or floating input does not
cause the receiver to oscillate.
When configured for differential operation, the input receivers
accommodate either ac- or dc-coupled input signals. The input
receivers are capable of accepting dc-coupled LVDS and 2.5 V
and 3.3 V LVPECL signals. The receiver is internally dc biased
to handle ac-coupled operation, but there is no internal 50 Ω or
100 Ω termination.
When configured for single-ended operation, the input
receivers exhibit a pull-down load of 47 kΩ (typical). Three
user-programmable threshold voltage ranges are available for
each single-ended receiver. See Register 0x0300 to Register
0x037A for the settings for the reference inputs.
REFA
through REFD,
REFD
) provide
REFERENCE MONITORS
The accuracy of the input reference monitors depends on
a known and accurate system clock period. Therefore, the
functioning of the reference monitors is not operable until the
system clock is stable.
Reference Period Monitor
Each reference input has a dedicated monitor that repeatedly
measures the reference period. The AD9559 uses the reference
period measurements to determine the validity of the reference
based on a set of user-provided parameters in the reference input
area of the register map. See Register 0x0304 through Register
0x030E for the settings for Reference A. There are corresponding
registers for Reference B, C, and D.
The monitor works by comparing the measured period of
a particular reference input with the parameters stored in the
profile register assigned to that same reference input. The
parameters include the reference period, an inner tolerance, and
an outer tolerance. A 40-bit number defines the reference period
in units of femtoseconds (fs). The 40-bit range allows for a
reference period entry of up to 1.1 ms. A 20-bit number defines
the inner and outer tolerances. The value stored in the register
is the reciprocal of the tolerance specification. For example,
a tolerance specification of 50 ppm yields a register value of
1/(50 ppm) = 1/0.000050 = 20,000 (0x04E20).
The use of two tolerance values provides hysteresis for the monitor
decision logic. The inner tolerance applies to a previously faulted
reference and specifies the largest period tolerance that a previously
faulted reference can exhibit before it qualifies as unfaulted. The
outer tolerance applies to an already unfaulted reference. It specifies
the largest period tolerance that an unfaulted reference can
exhibit before being faulted.
To produce decision hysteresis, the inner tolerance must be less
than the outer tolerance. That is, a faulted reference must meet
tighter requirements to become unfaulted than an unfaulted
reference must meet to become faulted.
Reference Validation Timer
Each reference input has a dedicated validation timer. The
validation timer establishes the amount of time that a previously
faulted reference must remain unfaulted before the AD9559
declares that it is valid. The timeout period of the validation
timer is programmable via a 16-bit register (Address 0x030F
and Address 0x0310 for Reference A). The 16-bit number stored
in the validation register represents units of milliseconds (ms),
which yields a maximum timeout period of 65,535 ms.
It is possible to disable the validation timer by programming the
validation timer to 0. With the validation timer disabled, the user
must validate a reference manually via the manual reference
validation override controls register (Address 0x0A02).
Reference Validation Override Control
The user can also override the reference validation logic, and
can either force an invalid reference to be treated as valid, or
force a valid reference to be treated as an invalid reference.
These controls are in Register 0x0A02 to Register 0x0A03.
REFERENCE INPUT BLOCK
Unlike the AD9557, the AD9559 separates the DPLL reference
dividers from the feedback dividers.
The reference input block includes the input receiver, the reference
divider (R divider), and the reference input frequency monitor
for each reference input. The reference input settings are grouped
together in Register 0x0300 to Register 0x037A.
These registers include the following settings:
• Reference logic type (such as differential, single-ended)
• Reference divider (20-bit R divider value)
• Reference input period and tolerance
• Reference validation timer
• Phase and frequency lock detector settings
The reference prescaler reduces the frequency of this signal by
an integer factor, R + 1, where R is the 20-bit value stored in the
appropriate profile register and 0 ≤ R ≤ 1,048,575. Therefore, the
frequency at the output of the R divider (or the input to the
time-to-digital converter, TDC) is as follows:
After the R divider, the signal passes to a 4:2 crosspoint that
allows any reference input signal to go to either DPLL.
Each DPLL on the AD9559 has an independent set of feedback
dividers for each reference input, and a description of these
settings can be found in the Digital PLL (DPLL) Core section.
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 120
Page 33

Data Sheet AD9559
The AD9559 evaluation software includes a frequency planning
wizard that configures the profile parameters, based on the
input and output frequencies.
REFERENCE SWITCHOVER
An attractive feature of the AD9559 is its versatile reference
switchover capability. The flexibility of the reference switchover
functionality resides in a sophisticated prioritization algorithm
that is coupled with register-based controls. This scheme provides
the user with maximum control over the state machine that
handles reference switchover.
The main reference switchover control resides in the user mode
registers in the PLL_0/PLL_1 operational controls registers. The
reference switching mode bits (Bits[4:2] in Register 0x0A22 for
DPLL_0 and Register 0x0A42 for DPLL_1) allow the user to
select one of the five operating modes of the reference
switchover state machine, as follows:
• Automatic revertive mode
• Automatic nonrevertive mode
• Manual with automatic fallback mode
• Manual with automatic holdover mode
• Full manual mode without holdover
In the automatic modes, a fully automatic priority-based algorithm
selects the active reference. When programmed for an automatic
mode, the device chooses the highest priority valid reference.
When two or more references have the same priority, REFA has
preference over REFB, and so on in alphabetical order. However,
the reference position is used only as a tiebreaker and does not
initiate a reference switch.
The following list gives an overview of the five operating modes:
• Automatic revertive mode. The device selects the highest
priority valid reference and switches to a higher priority
reference if it becomes available, even if the reference in use
is still valid. In this mode, the user reference is ignored.
• Automatic nonrevertive mode. The device stays with the
currently selected reference as long as it is valid, even if
a higher priority reference becomes available. The user
reference is ignored in this mode.
• Manual with automatic fallback mode. The device uses the
user reference for as long as it is valid. If it becomes invalid,
the reference input with the highest priority is chosen in
accordance with the priority-based algorithm.
• Manual with automatic holdover mode. The user reference
is the active reference until it becomes invalid. At that
point, the device automatically goes into holdover.
• Full manual mode without holdover. The user reference is
the active reference, regardless of whether or not it is valid.
The user also has the option to force the device directly into
holdover or free run operation via the user holdover and user
free run bits. In free run mode, the free run frequency tuning
word register defines the free run output frequency. In holdover
mode, the output frequency depends on the holdover control
settings (see the Holdover section).
Phase Build-Out Reference Switching
The AD9559 supports phase build-out reference switching,
which is the term given to a reference switchover that
completely masks any phase difference between the previous
reference and the new reference. That is, there is virtually no
phase change detectable at the output when a phase build-out
switchover occurs.
Rev. 0 | Page 33 of 120
Page 34
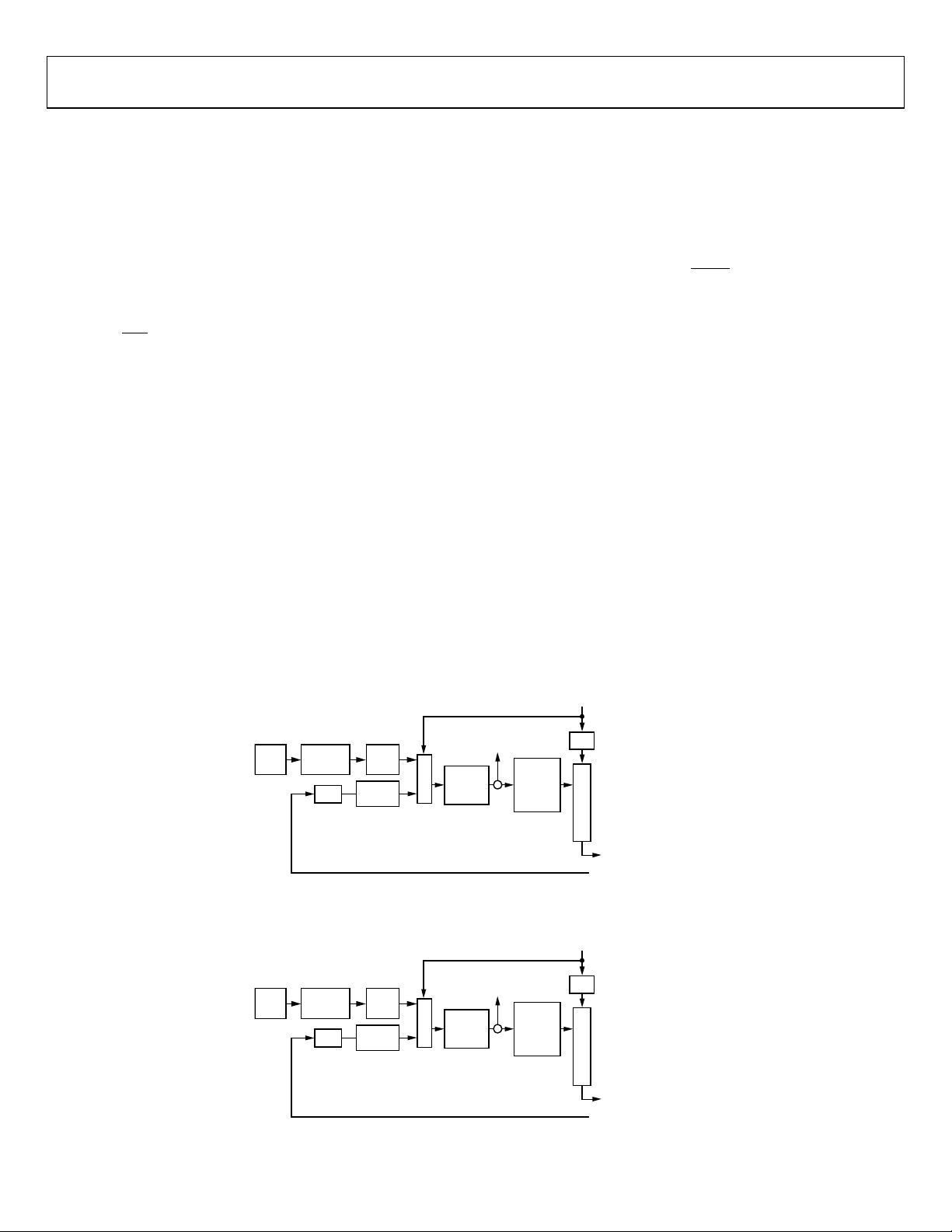
AD9559 Data Sheet
1+=R
f
f
R
TDC
++×=
MOD
FRAC
Nff
TDCDPLLOUT
)1(
_
DIGITAL
LOOP
FILTER
÷N0
24-BIT/24-BIT
RESOLUTION
FRAC0/
MOD0
17-BIT
INTEGER
TUNING
WORD
CLAMP
AND
HISTORY
×2
FREE RUN
TW
+
30-BIT NCO
DPFD
SYSTEM
CLOCK
FROM APLL_0
TO APLL_0
10644-137
R DIVIDER
(20-BIT)
REF
INPUT
MUX
REF
INPUT
DIGITAL
LOOP
FILTER
÷N1
24-BIT/24-BIT
RESOLUTION
FRAC1/
MOD1
17-BIT
INTEGER
TUNING
WORD
CLAMP
AND
HISTORY
×2
FREE RUN
TW
+
30-BIT NCO
DPFD
SYSTEM
CLOCK
FROM APLL_1
TO APLL_1
10644-136
R DIVIDER
(20-BIT)
REF
INPUT
MUX
REF
INPUT
DIGITAL PLL (DPLL) CORE
DPLL Overview
Diagrams of the DPLL cores of the AD9559 (DPLL_0 and
DPLL_1) are shown in Figure 35 and Figure 36, respectively.
The blocks shown in these diagrams are purely digital.
The start of the DPLL signal chain is the reference signal, f
which has been divided by the R divider and then routed through
the crosspoint switch to the DPLL. The frequency of this signal,
f
, is:
TDC
This is the frequency used by the time-to-digital converter,
TDC, inside the DPLL.
A TDC samples the output of the R divider. The TDC/PFD
produces a time series of digital words and delivers them to the
digital loop filter. The digital loop filter offers the following:
• The determination of the filter response by numeric
coefficients rather than by discrete component values
• The absence of analog components (R/L/C), which
eliminates tolerance variations due to aging
• The absence of thermal noise associated with analog
components
• The absence of control node leakage current associated
with analog components (a source of reference feedthrough spurs in the output spectrum of a traditional APLL)
The digital loop filter produces a time series of digital words at
its output and delivers them to the frequency tuning input of a
,
R
sigma-delta (Σ-Δ) modulator. The digital words from the loop
filter steer the SDM frequency toward frequency and phase lock
with the input signal (f
TDC
).
Each DPLL includes a feedback divider that causes the digital
loop to operate at an integer-plus-fractional multiple. The
output of the DPLL is
where N is the 17-bit value stored in the appropriate profile
registers (Register 0x0440 to Register 0x044C for DPLL_0
REFA). FRAC and MOD are the 24-bit numerators and
denominators of the fractional feedback divider block. The
fractional portion of the feedback divider can be bypassed by
setting FRAC to 0. MOD can be set to 0, but never change MOD
from 0 to nonzero without first entering free run mode.
Note that there are two DPLLs. In the Register Map and Register
Map Bit Descriptions sections, N0, FRAC0, and MOD0 are used
for DPLL_0; N1, FRAC1, and MOD1 are used for DPLL_1.
For optimal performance, the DPLL output frequency is typically
175 MHz to 200 MHz.
TDC/PFD
The phase frequency detector (PFD) is an all-digital block. It
compares the digital output from the TDC (which relates to the
active reference edge) with the digital word from the feedback
block. It uses a digital code pump and digital integrator (rather
than a conventional charge pump and capacitor) to generate the
error signal that steers the SDM frequency toward phase lock.
Figure 35. DPLL_0 Core
Figure 36. DPLL_1 Core
Rev. 0 | Page 34 of 120
Page 35

C
3
C
2
C
1
R
2
R
3
10644-015
2
2
0
2048
–2048
1024
–1024
LOCK LEVEL
UNLOCK LEVE L
LOCKED UNLOCKED
PREVIOUS
STATE
FILL
RATE
DRAIN
RATE
10644-017
Data Sheet AD9559
Programmable Digital Loop Filter
The AD9559 loop filter is a third-order digital IIR filter that is
analogous to the third order analog filter shown in Figure 37.
Figure 37. Third Order Analog Loop Filter
The AD9559 has default loop filter coefficients for two DPLL
settings: nominal (70°) phase margin, and high (88.5°) phase
margin. The high phase margin setting is intended for applications
that require <0.1 dB of closed-loop peaking. While these settings
do not normally need to be changed, the user can contact Analog
Devices, Inc. for a tool to calculate new coefficients to tailor the
loop filter to specific requirements.
The AD9559 loop filter block features a simplified architecture
in which the user enters the desired loop characteristics (such
as loop bandwidth) directly into the DPLL registers. This
architecture makes the calculation of individual coefficients
unnecessary in most cases, while still offering complete
flexibility.
To change a digital loop filter coefficient on a profile that is currently in use, the user must momentarily break the loop for the
new setting to take effect. The user can do this by selecting free
run or holdover mode, or by invalidating (and then revalidating)
the reference input.
DPLL Digitally Controlled Oscillator Free Run Frequency
The AD9559 uses a Σ-Δ modulator as a digitally controlled
oscillator (DCO). The DCO free run frequency can be calculated
from the following equation:
ff
×=
_
SYSfreerundco
FTW
8
+
0
30
where FTW0 is the value in Register 0x0400 to Register 0x0403
for DPLL_0 (or Register 0x0500 to Register 0x0503 for DPLL_1),
is the system clock frequency. See the System Clock
and f
SYS
section for information on calculating the system clock frequency.
Adaptive Clocking
The AD9559 can support adaptive clocking applications such as
asynchronous mapping and demapping. For these applications,
the output frequency can be dynamically adjusted by up to
±100 ppm from the nominal output frequency without manually
breaking the DPLL loop and reprogramming the part.
The following registers are used in this function:
• Register 0x0444 to Register 0x0446 (DPLL N0 divider)
• Register 0x0447 to Register 0x0449 (DPLL FRAC0 divider)
• Register 0x044A to Register 0x044C (DPLL MOD0 divider)
Note that the register values shown are for REFA/DPLL_0.
There are corresponding registers for all reference input and
DPLL combinations.
Rev. 0 | Page 35 of 120
Writing to these registers requires an IO_UPDATE by writing
0x01 to Register 0x0005 before the new values take effect.
To make small adjustments to the output frequency, the user
can vary the FRAC (FRAC0 or FRAC1) and issue an IO_UPDATE.
The advantage to using only FRAC to adjust the output frequency
is that the DPLL does not briefly enter holdover. Therefore,
the FRAC bit can be updated as quickly as the phase detector
frequency of the DPLL.
Writing to the N (N0 or N1) and MOD (M0 or M1) dividers allows
for larger changes to the output frequency. When the AD9559
detects a change in the N or MOD value, it automatically enters
and exits holdover for a brief instant without any disturbance in
the output fre quency. This limits how quickly the output frequency
can be adapted.
It is important to note that the amount of frequency adjustment
is limited to ±100 ppm before the output PLL (APLL) needs a
recalibration. Variations larger than ±100 ppm are possible, but
such variations may compromise the ability of the AD9559 to
maintain lock over temperature extremes.
It is also important to remember that the rate of change in
output frequency depends on the DPLL loop bandwidth.
DPLL Phase Lock Detector
The DPLL contains an all-digital phase lock detector. The user
controls the threshold sensitivity and hysteresis of the phase
detector via the profile registers.
The phase lock detector behaves in a manner analogous to water in
a tub (see Figure 38). The total capacity of the tub is 4096 units,
with −2048 denoting empty, 0 denoting the 50% point, and +2048
denoting full. The tub also has a safeguard to prevent overflow.
Furthermore, the tub has a low water mark at −1024 and a high
water mark at +1024. To change the water level, the user adds
water with a fill bucket or removes water with a drain bucket.
The user specifies the size of the fill and drain buckets via the
8-bit fill rate and drain rate values in the profile registers.
Figure 38. Lock Detector Diagram
The water level in the tub is what the lock detector uses to
determine the lock and unlock conditions. When the water level
is below the low water mark (−1024), the detector indicates an
unlock condition. Conversely, when the water level is above the
high water mark (+1024), the detector indicates a lock condition.
When the water level is between the marks, the detector holds
its last condition. This concept appears graphically in Figure 38,
with an overlay of an example of the instantaneous water level
(vertical) vs. time (horizontal) and the resulting lock/unlock states.
Page 36

AD9559 Data Sheet
During any given PFD phase error sample, the detector either adds
water with the fill bucket or removes water with the drain bucket
(one or the other but not both). The decision of whether to add
or remove water depends on the threshold level specified by the
user. The phase lock threshold value is a 24-bit number stored in
the profile registers and is expressed in picoseconds. Thus, the
phase lock threshold extends from 0 ns to ±65.535 ns and represents the magnitude of the phase error at the output of the PFD.
The phase lock detector compares each phase error sample at the
output of the PFD to the programmed phase threshold value. If
the absolute value of the phase error sample is less than or equal
to the programmed phase threshold value, the detector control
logic dumps one fill bucket into the tub. Otherwise, it removes
one drain bucket from the tub. Note that it is the magnitude,
relative to the phase threshold value, that determines whether
to fill or drain, and not the polarity of the phase error sample.
If more filling is taking place than draining, the water level in
the tub eventually rises above the high water mark (+1024), which
causes the phase lock detector to indicate lock. If more draining is
taking place than filling, the water level in the tub eventually
falls below the low water mark (−1024), which causes the phase
lock detector to indicate unlock. The ability to specify the threshold
level, fill rate, and drain rate enables the user to tailor the operation
of the phase lock detector to the statistics of the timing jitter
associated with the input reference signal.
Note that whenever the AD9559 enters the free run or holdover
mode, the DPLL phase lock detector indicates an unlocked
state. However, when the AD9559 performs a reference switch,
the state of the lock detector prior to the switch is preserved
during the transition period.
DPLL Frequency Lock Detector
The operation of the frequency lock detector is identical to that
of the phase lock detector. The only difference is that the fill or
drain decision is based on the period deviation between the
reference and feedback signals of the DPLL instead of the phase
error at the output of the PFD.
The frequency lock detector uses a 24-bit frequency threshold
register specified in units of picoseconds. Thus, the frequency
threshold value extends from 0 μs to ±16.777215 μs. It represents
the magnitude of the difference in period between the reference
and feedback signals at the input to the DPLL. For example,
if the divided down reference signal is 80 kHz and the feedback
signal is 79.32 kHz, the period difference is approximately
75.36 ns (|1/80,000 − 1/79,320| ≈ 107.16 ns).
Frequency Clamp
The AD9559 digital PLL features a digital tuning word clamp
that ensures that the digital PLL output frequency stays within a
defined range. This feature is very useful to eliminate
undesirable behavior in cases where the reference input clocks
may be unpredictable. The tuning word clamp is also useful to
guarantee that the APLL never loses lock by ensuring that the
APLL VCO frequency stays within its tuning range.
Frequency Tuning Word History
The AD9559 has the ability to track the history of the tuning
word samples generated by the DPLL digital loop filter output.
It does so by periodically computing the average tuning word
value over a user-specified interval. This average tuning word is
used during holdover mode to maintain the average frequency
when no input references are present.
LOOP CONTROL STATE MACHINE
Switchover
Switchover occurs when the loop controller switches directly
from one input reference to another. The AD9559 handles a
reference switchover by briefly entering holdover mode, loading
the new DPLL parameters, and then immediately recovering.
During the switchover event, however, the AD9559 preserves
the status of the lock detectors to avoid phantom unlock
indications.
Holdover
The holdover state of the DPLL is typically used when none of
the input references are present, although the user can also
manually engage holdover mode. In holdover mode, the output
frequency remains constant. The accuracy of the AD9559 in
holdover mode is dependent on the device programming and
availability of tuning word history.
Recovery from Holdover
When in holdover and a valid reference becomes available, the
device exits holdover operation. The loop state machine restores
the DPLL to closed-loop operation, locks to the selected reference,
and sequences the recovery of all the loop parameters based on
the profile settings for the active reference.
Note that, if the user holdover bit is set, the device does not
automatically exit holdover when a valid reference is available.
However, automatic recovery can occur after clearing the user
holdover bit.
Rev. 0 | Page 36 of 120
Page 37

Data Sheet AD9559
Jdivsysclk
Kdivsysclk
ff
OSCSYS
_
_
×=
SYSTEM CLOCK (SYSCLK)
SYSCLK INPUTS
Functional Description
The SYSCLK circuit provides a low jitter, stable, high frequency
clock for use by the rest of the chip. The XOA and XOB pins
connect to the internal SYSCLK multiplier. The SYSCLK multiplier
can synthesize the system clock by connecting a crystal resonator
across the XOA and XOB input pins or by connecting a low
frequency clock source. The optimal signal for the system clock
input is either a crystal in the 50 MHz range or an ac-coupled
square wave with a 1 V p-p amplitude.
SYSCLK Period
For the AD9559 to accurately measure the frequency of incoming
reference signals, the user must enter the system clock period into
the nominal system clock period registers (Register 0x0202 to
Register 0x0204). The SYSCLK period is entered in units of
femtoseconds (fs).
Choosing the SYSCLK Source
There are two internal paths for the SYSCLK input signal: low
frequency non-XTAL) (LF) and crystal resonator (XTAL).
Using a TCXO for the system clock is a common use for the
LF path. Applications requiring DPLL loop bandwidths of less
than 50 Hz or high stability in holdover require a TCXO or OCXO.
As an alternative to the 49.152 MHz crystal for these applications,
the AD9559 reference design uses a 19.2 MHz TCXO, which
offers excellent holdover stability and a good combination of
low jitter and low spurious content.
The 1.8 V differential receiver connected to the XOA and XOB pins
is self-biased to a dc level of ~1 V, and ac coupling is strongly
recommended to maintain a 50% input duty cycle. When a 3.3 V
CMOS oscillator is in use, it is important to use a voltage divider
to reduce the input high voltage to a maximum of 1.8 V. See
Figure 33 for details on connecting a 3.3 V CMOS TCXO to the
system clock input.
The non-XTAL) input path permits the user to provide an
LVPECL, LVDS, 1.8 V CMOS, or sinusoidal low frequency clock
for multiplication by the integrated SYSCLK PLL. The LF path
handles input frequencies from 10 MHz up to 100 MHz.
However, when using a sinusoidal input signal, it is best to use
a frequency of ≥20 MHz. Otherwise, the resulting low slew rate
can lead to poor noise performance. Note that there is an
optional 2× frequency multiplier to double the rate at the input
to the SYSCLK PLL and potentially reduce the PLL in-band noise.
However, to avoid exceeding the maximum PFD rate of 150 MHz,
the 2× frequency multiplier is only for input frequencies that are
below 75 MHz.
The non-XTAL) path also includes an input divider (M) that is
programmable for divide-by-1, -2, -4, or -8. The purpose of
the divider is to limit the frequency at the input to the PLLs
to less than 150 MHz (the maximum PFD rate).
The XTAL path enables the connection of a crystal resonator
(typically 10 MHz to 50 MHz) across the XOA and XOB pins.
An internal amplifier provides the negative resistance required
to induce oscillation. The internal amplifier expects an AT cut,
fundamental mode crystal with a maximum motional resistance
of 100 Ω. The following crystals, listed in alphabetical order, may
meet these criteria. Analog Devices does not guarantee their
operation with the AD9559, nor does Analog Devices endorse one
crystal supplier over another. The AD9559 reference design uses
a 49.152 MHz crystal, which is high performance, low spurious
content, and readily available.
• AVX/Kyocera CX3225SB
• ECS ECX-32
• Epson/Toyocom TSX-3225
• Fox FX3225BS
• NDK NX3225SA
• Siward SX-3225
• Suntsu SCM10B48-49.152 MHz
SYSCLK MULTIPLIER
The SYSCLK PLL multiplier is an integer-N design with an
integrated VCO. It provides a means to convert a low frequency
clock input to the desired system clock frequency, f
to 805 MHz). The SYSCLK PLL multiplier accepts input signals
of between 10 MHz and 400 MHz, but frequencies that are in
excess of 150 MHz require the J1 divider of the system clock to
ensure compliance with the maximum PFD rate (150 MHz). The
PLL contains a feedback divider (K) that is programmable for
divide values between 4 and 255.
where:
f
is the frequency at the XOA and XOB pins.
OSC
sysclk_Kdiv is the value stored in Register 0x0200.
sysclk_Jdiv is the system clock J1 divider that is determined by the
setting of Register 0x0201[2:1].
If the system clock doubler is used, the value of sysclk_Kdiv
should be half of its original value.
The system clock multiplier features a simple lock detector that
compares the time difference between the reference and feedback
edges. The most common cause of the SYSCLK multiplier not
locking is a non-50% duty cycle at the SYSCLK input while the
system clock doubler is enabled.
(750 MHz
SYS
Rev. 0 | Page 37 of 120
Page 38

AD9559 Data Sheet
System Clock Stability Timer
Because the reference monitors depend on the system clock
being at a known frequency, it is important that the system clock
be stable before activating the monitors. At initial power-up,
the system clock status is not known; therefore, it is reported as
being unstable. After the part has been programmed, the system
clock PLL eventually locks.
When a stable operating condition is detected, a timer is run
for the duration that is stored in the system clock stability
period registers. If, at any time during this waiting period, the
condition is violated, the timer is reset and halted until a stable
condition is reestablished. After the specified period elapses,
the AD9559 reports the system clock as stable.
Note that, any time the system clock stability timer is changed in
Register 0x0205 through Register 0x0207, it is reset automatically.
The system clock stability timer starts counting when the next
IO_UDATE is issued.
Rev. 0 | Page 38 of 120
Page 39

Data Sheet AD9559
10644-138
LF_0 CAP
LF_0 PIN
VCO_0
3405MHz TO 4260MHz
PFD
FROM DPLL_0
TO P0
DIVIDER
LF
CP
INTEGER DIVIDER
OUTPUT PLL DIVIDER (APLL_0)
÷N0
11
LDO_0 PIN
10
10644-140
VCO_1
3405MHz TO 4260MHz
PFD
FROM DPLL_1
TO P1
DIVIDER
LF
CP
INTEGER DIVIDER
OUTPUT PLL DIVIDER (APLL_1)
÷N1
LF_1 CAP
LF_1 PIN
44
LDO_1 PIN
45
OUTPUT PLL (APLL)
There are two output PLLs (APLLs) on the AD9559. They
provide the frequency upconversion from the digital PLL
(DPLL) outputs. The frequency range is 2940 MHz to 3543 MHz
for the APLL_0 and 3405 MHz to 4260 MHz for the APLL_1,
while also providing noise filter on the DPLL output. The APLL
reference input is the output of the DPLL. The feedback divider is
an integer divider. The loop filter is partially integrated with the
one external 6.8 nF capacitor that connects to an internal LDO.
The nominal loop bandwidth for both of the APLLs is 240 kHz.
The APLL_0 and APLL_1 block diagrams are shown in Figure 39
and Figure 40, respectively.
Figure 39. APLL_0 Block Diagram
Figure 40. APLL_1 Block Diagram
APLL CONFIGURATION
The frequency wizard that is included in the evaluation software
configures the APLL, and the user should not need to make
changes to the APLL settings. However, there may be special cases
where the user may wish to adjust the APLL loop bandwidth to
meet a specific phase noise requirement. The easiest way to change
the APLL loop bandwidth is to adjust the APLL charge pump
current in Register 0x0420 (APLL_0) or Register 0x0520 (APLL_1).
There is sufficient stability (68° of phase margin) in the APLL
default settings to permit a broad range of adjustment without
causing the APLL to be unstable. The user should contact
Analog Devices directly if more information is needed.
APLL CALIBRATION
Calibration of the APLLs must be performed at startup and
whenever the nominal input frequency to the APLL changes
by more than ±100 ppm, although the APLL maintains lock
over voltage and temperature extremes without recalibration.
Calibration centers the dc operating voltage at the input to the
APLL VCO.
APLL calibration at startup is normally performed during initial
register loading by following the instructions in the Device
Register Programming Using a Register Setup File section of
this datasheet.
To recalibrate the APLL VCO after the chip has been running,
first input the new settings (if any). Ensure that the system clock
is still locked and stable, and that the DPLL is in free run mode
with the free run tuning word set to the same output frequency
that is used when the DPLL is locked. The user can calibrate
APLL_0 without disturbing APLL_1 and vice versa.
Use the following steps to recalibrate the APLL VCO.
Important: An IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01)
is needed after each of these steps.
1. Ensure that the system clock is locked and stable.
(Register 0x0D01[1] = 1b).
2. Ensure that the DPLL free run tuning word is set.
DPLL_0: Register 0x0400 to Register 0x0403
DPLL_1: Register 0x0500 to Register 0x0503
3. Set free run mode for the appropriate DPLL.
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22[0] = 1b
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42[0] = 1b
4. Clear APLL calibration bit.
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20 = 0x00
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40 = 0x00
5. Set APLL calibration bit.
APLL_0: Register 0x0A20 = 0x02
APLL_1: Register 0x0A40 = 0x02
6. Poll the APLL lock status.
APLL_0: Register 0x0D20[3] = 1b indicates lock.
APLL_1: Register 0x0D40[3] = 1b indicates lock.
7. Clear the DPLL mode for the appropriate DPLL.
DPLL_0: Register 0x0A22[0] = 0b
DPLL_1: Register 0x0A42[0] = 0b
Rev. 0 | Page 39 of 120
Page 40

AD9559 Data Sheet
10644-139
FROM VCO_0
(2940MHz TO 3543MHz )
CHIP RESET
SYNC
10-BIT INTEGER
262kHz TO 1.25G Hz
CHANNEL
SYNC
BLOCK
MAX
1.25GHz
MAX
1.25GHz
CHANNEL SYNC
(TO Q0_A AND Q0_
B)
OUT0A
OUT0A
OUT0B
OUT0B
P0
DIVIDER
10-BIT INTEGER
÷Q0_A
÷Q0_B
FROM VCO_1
(3405MHz TO 4260MHz )
CHIP RESET
SYNC
10-BIT INTEGER
302kHz TO 1.25G Hz
10-BIT INTEGER
CHANNEL
SYNC
BLOCK
MAX
1.25GHz
MAX
1.25GHz
CHANNEL SYNC
(TO Q1_A AND Q1_B)
OUT1A
OUT1A
OUT1B
OUT1B
10644-141
÷Q1_A
÷Q1_B
CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
Figure 41. Clock Distribution Block Diagram from VCO_0
The AD9559 has two identical clock distribution sections: one
for PLL_0 from VCO_0 and the other for PLL_1. See Figure 41
for a diagram of the clock distribution block for PLL_0 and
Figure 42 for the PLL_1 block.
CLOCK DIVIDERS
P0 and P1 Dividers
The first block in each clock distribution section is the P divider.
The P divider divides the VCO output frequency down to a
maximum frequency of ≤1.25 GHz and has special circuitry to
maintain a 50% duty cycle for any divide ratio.
The following register addresses contain the P divider settings:
• PLL_0, P0 divider: Register 0x0424[3:0]
• PLL_1, P1 divider: Register 0x0524[3:0]
Channel Dividers
The channel divider blocks, Q0_A, Q0_B, Q1_B, and Q1_A,
are 10-bit integer dividers with a divide range of 1 to 1024.
The channel divider block contains duty cycle correction that
guarantees 50% duty cycle for both even and odd divide ratios.
The maximum input frequency to the channel dividers is
1.25 GHz.
The channel dividers are at the following register addresses:
• Q0_A divider: Register 0x0428 to Register 0x042A
• Q0_B divider: Register 0x042C to Register 0x042E
• Q1_A divider: Register 0x0528 to Register 0x052A
• Q1_B divider: Register 0x052C to Register 0x052E
Figure 42. Clock Distribution Block Diagram from VCO_1
OUTPUT ENABLE
Each of the output channels offers independent control of enable/
disable functionality via the distribution enable register. The
distribution outputs use synchronization logic to control
enable/disable activity to avoid the production of runt pulses
and to ensure that outputs with the same divide ratios become
active/inactive in unison.
OUTPUT MODE AND POWER-DOWN
The output drivers can be individually powered down. The
output mode control (including power-down) can be found
at the following register addresses:
• OUT0A: Register 0x0427[6:4]
• OUT0B: Register 0x042B[7:4]
• OUT1A: Register 0x0527[6:4]
• OUT1B: Register 0x052B[7:4]
The operating mode control includes
• Logic type and pin function
• Output drive strength
• Output polarity
• Divide ratio
• Phase of each output channel
OUT0B and OUT1B provide the 3.3 V CMOS, 1.8 V CMOS,
LVDS, and HSTL modes.
OUT0A and OUT1A provide the 1.8 V CMOS, LVDS, and
Rev. 0 | Page 40 of 120
HSTL modes.
Page 41

Data Sheet AD9559
The 3.3 V CMOS drivers feature a CMOS drive strength that
allows the user to choose between a strong, high performance
CMOS driver or a lower power setting with less EMI and
crosstalk. The best setting is application dependent.
• All outputs have an LVDS boost mode that provides
increased output amplitude in applications that require it.
• For applications where LVPECL levels are required, the
user should choose the HSTL mode and then ac-couple
the output signal. See the Input/Output Termination
Recommendations section for recommended termination
schemes.
CLOCK DISTRIBUTION SYNCHRONIZATION
Divider Synchronization
The dividers in the channels can be synchronized with each other.
At power-up, they are held static until a sync signal is initiated
through serial port, EEPROM event, DPLL locked sync, or
a reference edge-initiated sync. This provides time for programming the dividers and for the DPLL to lock before the outputs are
enabled. A user-initiated sync signal can also be supplied to the
dividers at any time (as a manual synchronization) using an M pin.
A channel can be programmed to ignore the sync function.
When programmed to ignore the sync, the channel sync block
issues a sync pulse immediately, and the channel ignores all
other sync signals.
The digital logic triggers a sync event from one of the following
sources:
• Register programming through serial port
• EEPROM programming
• A multifunction pin configured for the SYNC signal
• Other automatic conditions determined by the DPLL
configuration: DPLL lock or feedback divider pulse
Rev. 0 | Page 41 of 120
Page 42

AD9559 Data Sheet
STATUS AND CONTROL
MULTIFUNCTION PINS (M0 TO M5)
The AD9559 has six digital CMOS I/O pins (M0 to M5) that are
configurable for a variety of uses. To use these functions, the user
must set them by writing to Register 0x0100 and Register 0x0101.
The function of these pins is programmable via the register map.
Each pin can control or monitor an assortment of internal
functions based on Register 0x0102 to Register 0x0107.
The M pins feature a special write detection logic that prevents
them from behaving unpredictably when their function changes.
When the when the user writes to these registers, the existing M
pin function stops. The new M pin function takes effect on the
next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
The M4 and M5 pins are multiplexed with serial port functions.
For the M4/SDO pin to function as M4, the AD9559 must not be
in 4-wire SPI mode. For the M5/
IC or 2-wire SPI mode must be in use.
The M pins operate in one of four modes: active high CMOS,
active low CMOS, open-drain PMOS, and open-drain NMOS.
00—Active high CMOS: The M pin is Logic 0 when deasserted and
Logic 1 when asserted. This is the default operating mode.
01—Active low CMOS: The M pin is Logic 1 when deasserted
and Logic 0 when asserted.
10—Open-drain PMOS: The M pin is high impedance when
deasserted and active high when asserted; it requires an
external pull-down resistor.
11—Open-drain NMOS: The M pin is high impedance when
deasserted and active low when asserted; it requires an
external pull-up resistor.
To monitor an internal function with a multifunction pin, write a
Logic 1 to the most significant bit of the register associated with
the desired multifunction pin. The value of the seven least
significant bits of the register defines the control function, as
shown in Table 196.
To control an internal function with a multifunction pin, write a
Logic 0 to the most significant bit of the register associated with
the desired multifunction pin. The monitored function depends
on the value of the seven least significant bits of the register, as
shown in Table 197.
If more than one multifunction pin operates on the same control
signal, internal priority logic ensures that only one multifunction
pin serves as the signal source. The selected pin is the one with
the lowest numeric suffix. For example, if both M0 and M3
operate on the same control signal, M0 is used as the signal
source and the redundant pins are ignored.
CS
pin to function as M5, either
At power-up, the multifunction pins can force the device into
certain configurations as defined in the Multifunction Pins at
Reset/Power-Up section. This behavior is valid only during
power-up or following a reset, after which the pins can be
reconfigured via the serial programming port or via the EEPROM.
IRQ FUNCTION
The AD9559 IRQ function can be assigned to any M pin. There
are three IRQ categories: PLL0, PLL1, and common. This means
an M pin can be set to respond only to IRQs that relate to PLL0,
PLL1, or to common functions. An M pin can also be set to
respond to all IRQs.
The AD9559 asserts the IRQ pin when any bit in the IRQ monitor
register (Address 0x0D08 to Address 0x0D10) is a Logic 1. Each
bit in this register is associated with an internal function that is
capable of producing an interrupt. Furthermore, each bit of the
IRQ monitor register is the result of a logical AND of the associated
internal interrupt signal and the corresponding bit in the IRQ
mask register (Address 0x010A to Address 0x0112). That is, the
bits in the IRQ mask register have a one-to-one correspondence
with the bits in the IRQ monitor register. When an internal
function produces an interrupt signal and the associated IRQ mask
bit is set, the corresponding bit in the IRQ monitor register is set.
Be aware that clearing a bit in the IRQ mask register removes only
the mask associated with the internal interrupt signal. It does not
clear the corresponding bit in the IRQ monitor register.
The IRQ function is edge-triggered. This means that if the
condition that generated an IRQ (for example, loss of DPLL_0
lock) still exists after an IRQ is cleared, the IRQ does not reactivate
until DPLL_0 lock is restored and lost again. However, if the IRQs
are enabled when DPLL_0 is not locked, an IRQ is generated.
The IRQ function of an M pin is the result of a logical OR of all
the IRQ monitor register bits. The AD9559 asserts an IRQ as long
as any of the IRQ monitor register bits is a Logic 1. Note that it
is possible to have multiple bits set in the IRQ monitor register.
Therefore, when the AD9559 asserts an IRQ, it may indicate an
interrupt from several different internal functions. The IRQ
monitor register provides a way to interrogate the AD9559 to
determine which internal function(s) produced the interrupt.
Typically, when the AD9559 asserts an IRQ, the user interrogates
the IRQ monitor register to identify the source of the interrupt
request. After servicing an indicated interrupt, the user should
clear the associated IRQ monitor register bit via the IRQ clearing
register (Address 0x0A05 to Address 0x0A0E). The bits in the
IRQ clearing register have a one-to-one correspondence with
the bits in the IRQ monitor register.
Note that the IRQ clearing registers are autoclearing. The M pin
associated with an IRQ remains asserted until the user clears all of
the bits in the IRQ monitor register that indicate an interrupt.
Rev. 0 | Page 42 of 120
Page 43

Data Sheet AD9559
A
All IRQ monitor register bits can be cleared by setting the clear all
IRQs bit in the IRQ register (Register 0x0A05). Note that the bits
in Register 0x0A05 are autoclearing. Setting Bit 0 results in the
deassertion of all IRQs. Alternatively, the user can program any of
the multifunction pins to clear all IRQs, which allows the user to
clear all IRQs by means of a hardware pin rather than by a serial
I/O port operation.
WATCHDOG TIMER
The watchdog timer is a general-purpose programmable timer.
To set the timeout period, the user writes to the 16-bit watchdog
timer register (Address 0x0108 to Address 0x0109). A value of
0x0000 in this register disables the timer. A nonzero value sets
the timeout period in milliseconds, giving the watchdog timer
a range of 1 ms to 65.535 sec. The relative accuracy of the timer
is approximately 0.1% with an uncertainty of 0.5 ms.
If enabled, the timer runs continuously and generates a timeout
event when the timeout period expires. The user has access
to the watchdog timer status via the IRQ mechanism and the
multifunction pins (M0 to M3). The M4 and M5 multifunction
pins are available if they are not used for the serial port. In the
case of the multifunction pins, the timeout event of the watchdog
timer is a pulse that lasts 32 system clock periods.
There are two ways to reset the watchdog timer (thereby preventing
it from causing a timeout event). The first method is to write a
Logic 1 to the autoclearing clear watchdog timer bit in the clear
IRQ groups register (Register 0x0A05, Bit 7). Alternatively, the
user can program any of the multifunction pins to reset the
watchdog timer. This allows the user to reset the timer by means
of a hardware pin rather than by a serial I/O port operation.
EEPROM
EEPROM Overview
The AD9559 contains an integrated 2048-byte, electrically
erasable, programmable read-only memory (EEPROM). The
AD9559 can be configured to perform a download at power-up
via the multifunction pins (M1 and M0), but uploads and
downloads can also be performed on demand via the EEPROM
control registers (Address 0x0E00 to Address 0x0E03).
The EEPROM provides the ability to upload and download
configuration settings to and from the register map. Figure 43
shows a functional diagram of the EEPROM.
Register 0x0E10 to Register 0x0E4F represent a 64-byte EEPROM
storage sequence area (referred to as the scratchpad in this
section) that enables the user to store a sequence of instructions
for transferring data to the EEPROM from the device settings
portion of the register map. Note that the default values for these
registers provide a sample sequence for saving/retrieving all of the
AD9559 EEPROM-accessible registers. Figure 43 shows the
connectivity between the EEPROM and the controller that
manages data transfer between the EEPROM and the register map.
The controller oversees the process of transferring EEPROM data
to and from the register map. There are two modes of operation
handled by the controller: saving data to the EEPROM (upload
mode) or retrieving data from the EEPROM (download mode).
In either case, the controller relies on a specific instruction set.
DAT
M1
M0
DEVICE
SETTINGS
ADDRESS
POINTER
EEPROM
CONTROLLER
DATA
DATA
EEPROM
ADDRESS
POINTER
SCRATCH PAD
ADDRESS
POINTER
EEPROM
(0x000
TO 0x7FF)
DEVICE
SETTINGS
REGISTER MAP
Figure 43. EEPROM Functional Diagram
SCRATCH PAD
(0x0E10 TO 0x0E4F)
0x0E01[3:0]
CONDITION
SERIAL
INPUT/OUTPUT
PORT
10644-024
Rev. 0 | Page 43 of 120
Page 44

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x00 to 0x7F
Data
3
A data instruction tells the controller to transfer data to or from the device settings part
0x90
1
0xA2
Distribution sync
1
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
0xFE
Pause
1
0xFF
End of data
1
When the controller encounters this instruction in the scratchpad while uploading to the
EEPROM Instructions
Table 22 lists the EEPROM controller instruction set. The
controller recognizes all instruction types whether it is in
upload or download mode, except for the pause instruction,
which is only recognizes in upload mode.
The IO_UPDATE, calibrate, distribution sync, and end instructtions are, for the most part, self-explanatory. The others, however,
warrant further detail, as described in the following paragraphs.
Table 22. EEPROM Controller Instruction Set
Instruction
Value (Hex) Instruction Type
0x80 IO_UPDATE 1
Calibrate both
APLLs
0x91 Calibrate APLL_0 1
0x92 Calibrate APLL_1 1
0x98
0x99
0x9A
0xA0
0xA1
Set User Free run
Mode (both PLLs)
Set User Free run
Mode (DPLL_0)
Set User Free run
Mode (DPLL_1)
Distribution sync
(all outputs)
Distribution sync
(PLL0 outputs)
Bytes
Needed Description
of the register map. A data instruction requires two additional bytes that, together,
indicate a starting address in the register map. Encoded in the data instruction is the
number of bytes to transfer, which is one more than the instruction value.
The controller issues a soft IO_UPDATE (which is analogous to the user writing
Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
The controller initiates an APLL calibration sequence to both APLL_0 and APLL_1 while
downloading from the EEPROM. APLL calibration is gated by the system clock being stable.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it initiates an APLL_0 calibration sequence. APLL calibration is gated by the system clock
being stable.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it initiates an APLL_1 calibration sequence. APLL calibration is gated by the system clock
being stable.
1
1
1
1
1
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it forces both of the DPLLs into user free run mode.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it forces both of the DPLLs into user free run mode.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it forces both of the DPLLs into user free run mode.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it issues a sync pulse to the PLL0 and PLL1 channel dividers.
Note that the APLL_0 must be locked before the sync pulse reaches the PLL_0 channel
dividers, and APLL_1 must be locked before the sync pulse reaches the PLL_1 channel
dividers, unless overridden.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM, it
issues a sync pulse to the PLL_0 channel dividers.
Note that, unless overridden, this sync pulse is gated by the APLL_0 lock detect signal.
Data instructions are those that have a value from 0x00 to 0x7F.
A data instruction tells the controller to transfer data between
the EEPROM and the register map. The controller needs the
following two parameters to carry out the data transfer:
• The number of bytes to transfer
• The register map target address
(PLL1 outputs)
0xB0 Clear condition 1 0xB0 is the null condition instruction (see the EEPROM Conditional Processing section).
0xB1 to 0xBF Condition 1
it issues a sync pulse to the PLL1 channel dividers.
Note that, unless overridden, this sync pulse is gated by the APLL_1 lock detect signal.
0xB1 to 0xBF are condition instructions and correspond to Condition 1 through
Condition 15, respectively (see the EEPROM Conditional Processing section).
When the controller encounters this instruction in the scratchpad while uploading to the
EEPROM, it resets the scratchpad address pointer and holds the EEPROM address pointer
at its last value. This allows storage of more than one instruction sequence in the
EEPROM. Note that the controller does not copy this instruction to the EEPROM during
upload.
EEPROM, it resets both the scratchpad address pointer and the EEPROM address pointer
and then enters an idle state.
When the controller encounters this instruction while downloading from the EEPROM,
it resets the EEPROM address pointer and then enters an idle state.
Rev. 0 | Page 44 of 120
Page 45

Data Sheet AD9559
The controller decodes the number of bytes to transfer directly
from the data instruction itself by adding 1 to the value of the
instruction. For example, Data Instruction 0x1A has a decimal
value of 26; therefore, the controller knows to transfer 27 bytes
(one more than the value of the instruction). When the controller
encounters a data instruction, it knows to read the next two bytes
in the scratchpad because these contain the register map target
address.
Note that, in the EEPROM scratchpad, the two registers that
comprise the address portion of a data instruction have the
MSB of the address in the D7 position of the lower register
address. The bit weight increases left to right, from the lower
register address to the higher register address. Furthermore, the
starting address always indicates the lowest numbered register
map address in the range of bytes to transfer. That is, the controller
always starts at the register map target address and counts upward,
regardless of whether the serial I/O port is operating in I
LSB-first, or SPI MSB-first mode.
As part of the data transfer process during an EEPROM upload,
the controller calculates a 1-byte checksum and stores it as the
final byte of the data transfer. As part of the data transfer process
during an EEPROM download, however, the controller again
calculates a 1-byte checksum value but compares the newly
calculated checksum with the one that was stored during the
upload process. If an upload/download checksum pair does not
match, the controller sets the EEPROM fault status bit. If the
upload/download checksums match for all data instructions
encountered during a download sequence, the controller sets
the EEPROM complete status bit.
Condition instructions are those that have a value from 0xB0
to 0xBF. The 0xB1 to 0xBF condition instructions represent
Condition 1 to Condition 15, respectively. The 0xB0 condition
instruction is special because it represents the null condition
(see the EEPROM Conditional Processing section).
A pause instruction, like an end instruction, is stored at the end
of a sequence of instructions in the scratchpad. When the controller encounters a pause instruction during an upload sequence,
it keeps the EEPROM address pointer at its last value. Then the
user can store a new instruction sequence in the scratchpad and
upload the new sequence to the EEPROM. The new sequence
is stored in the EEPROM address locations immediately following
the previously saved sequence. This process is repeatable until
an upload sequence contains an end instruction. The pause
instruction is also useful when used in conjunction with condition
processing. It allows the EEPROM to contain multiple occurrences
of the same registers, with each occurrence linked to a set of
conditions (see the EEPROM Conditional Processing section).
2
C, SPI
EEPROM Upload
To upload data to the EEPROM, the user must first ensure that
the write enable bit (Register 0x0E00, Bit 0) is set. Then, on setting
the autoclearing save to EEPROM bit (Register 0x0E02, Bit 0),
the controller initiates the EEPROM data storage process.
Uploading EEPROM data requires the user to first write an
instruction sequence into the scratchpad registers. During the
upload process, the controller reads the scratchpad data byteby-byte, starting at Register 0x0E10 and incrementing the
scratchpad address pointer, as it goes, until it reaches a pause
or end instruction.
As the controller reads the scratchpad data, it transfers the
data from the scratchpad to the EEPROM (byte-by-byte) and
increments the EEPROM address pointer accordingly, unless
it encounters a data instruction. A data instruction tells the
controller to transfer data from the device settings portion of
the register map to the EEPROM. The number of bytes to transfer
is encoded within the data instruction, and the starting address
for the transfer appears in the next two bytes in the scratchpad.
When the controller encounters a data instruction, it stores the
instruction in the EEPROM, increments the EEPROM address
pointer, decodes the number of bytes to be transferred, and
increments the scratchpad address pointer. Then it retrieves
the next two bytes from the scratchpad (the target address)
and increments the scratchpad address pointer by 2. Next, the
controller transfers the specified number of bytes from the register
map (beginning at the target address) to the EEPROM.
When it completes the data transfer, the controller stores
an extra byte in the EEPROM to serve as a checksum for the
transferred block of data. To account for the checksum byte,
the controller increments the EEPROM address pointer by one
more than the number of bytes transferred. Note that, when the
controller transfers data associated with an active register, it actually
transfers the buffered contents of the register (refer to the
Buffered/Active Registers section for details on the difference
between buffered and active registers). This allows for the transfer
of nonzero autoclearing register contents.
Note that conditional processing (see the EEPROM Conditional
Processing section) does not occur during an upload sequence.
Manual EEPROM Download
An EEPROM download results in data transfer from the
EEPROM to the device register map. To download data, the
user sets the autoclearing load from EEPROM bit (Register
0x0E03, Bit 1). This commands the controller to initiate the
EEPROM download process. During download, the controller
reads the EEPROM data byte by byte, incrementing the EEPROM
address pointer as it goes, until it reaches an end instruction.
As the controller reads the EEPROM data, it executes the stored
instructions, which includes transferring stored data to the device
settings portion of the register map whenever it encounters a data
instruction.
Note that conditional processing (see the EEPROM Conditional
Processing section) is applicable only when downloading.
Rev. 0 | Page 45 of 120
Page 46

AD9559 Data Sheet
0 0 0
No
EEPROM
EEPROM CONTROLLER
UPLOAD
PROCEDURE
CONDITION
HANDLER
DOWNLOAD
PROCEDURE
CONDITION
TAG BOARD
1
6
54
32
1110
98
7
15141312
IF 0xB1 ≤ INSTRUCTION ≤ 0xCF,
THEN TAG DECODED CONDITION
SCRATCH
PAD
M1 M0
IF INST RUCTION = 0xB0,
THEN CLEAR ALL TAGS
FncInit, BITS[1:0]
REGISTER
0x0E01, BITS[ 3: 0]
STORE CONDITION
INSTRUCTI ONS AS
THEY ARE READ FROM
THE SCRATCH PAD.
WATCH FOR
OCCURRENCE OF
CONDITION
INSTRUCTIONS
DURING
DOWNLOAD.
IF {NO TAGS} OR {CONDITION = 0}
EXECUTE INS TRUCTIONS
ELSE
IF {CONDITION IS TAGGED}
EXECUTE INS TRUCTIONS
ELSE
SKIP INST RUCTIONS
ENDIF
ENDIF
4
4 2
IF {0x0E01, BITS[3:0] ≠ 0}
CONDITION = 0x0E01, BIT S [ 3: 0]
ELSE
CONDITION = FncInit, BITS[1:0]
ENDIF
EXAMPLE
CONDITION 3 AND
CONDITION 13
ARE TAGGED
EXECUTE/SKIP
INSTRUCTION(S)
CONDITION
10644-025
Automatic EEPROM Download
Following a power-up, an assertion of the
RESET
pin, or a soft
reset (Register 0x0000, Bit 5 = 1), if either the M1 pin or M0 pin
is high (see Ta b l e 23), the instruction sequence stored in the
EEPROM executes automatically with one of three conditions. If
M1 and M0 are low, the EEPROM is bypassed and the factory
defaults are used. In this way, a previously stored set of register
values downloads automatically on power-up or with a hard or
soft reset. See the EEPROM Conditional Processing section for
details regarding conditional processing and the way it modifies
the download process.
Table 23. EEPROM Download M Pin Setup
M1 M0 ID EEPROM Download
0 1 1 Yes, EEPROM Condition 1
1 0 2 Yes, EEPROM Condition 2
1 1 3 Yes, EEPROM Condition 3
EEPROM Conditional Processing
The condition instructions allow conditional execution of
EEPROM instructions during a download sequence. During
an upload sequence, however, they are stored as is and have
no effect on the upload process.
Note that, during EEPROM downloads, the condition instructions
themselves and the end instruction always execute unconditionally.
Conditional processing makes use of two elements: the condition
(from Condition 1 to Condition 15) and the condition tag board.
The relationships among the condition, the condition tag board,
and the EEPROM controller appear schematically in Figure 44.
Figure 44. EEPROM Conditional Processing
Rev. 0 | Page 46 of 120
Page 47

Data Sheet AD9559
0x80
The condition is a 4-bit value with 16 possibilities. Condition = 0
is the null condition. When the null condition is in effect, the
EEPROM controller executes all instructions unconditionally.
The remaining 15 possibilities, condition = 1 through condition =
15, modify the EEPROM controller’s handling of a download
sequence. The condition originates from one of two sources
(see Figure 44), as follows:
• FncInit, Bits[1:0], which is the state of the M1 and M0
multifunction pins at power-up (see Tabl e 23)
(Note that only Condition 1 through Condition 3 are
accessible via the M pins.)
• Register 0x0E01, Bits[3:0]
If Register 0x0E01, Bits[3:0] ≠ 0, then the condition is the value
stored in Register 0x0E01, Bits[3:0]; otherwise, the condition is
FncInit, Bits[1:0]. Note that a nonzero condition present in
Register 0x0E01, Bits[3:0], takes precedence over FncInit,
Bits[1:0].
The condition tag board is a table that is maintained by the
EEPROM controller. When the controller encounters a condition
instruction, it decodes the 0xB1 through 0xBF instructions as
condition = 1 through condition = 15, respectively, and tags that
particular condition in the condition tag board. However, the 0xB0
condition instruction decodes as the null condition, for which the
controller clears the condition tag board, and subsequent download
instructions execute unconditionally (until the controller
encounters a new condition instruction).
During download, the EEPROM controller executes or skips
instructions depending on the value of the condition and the
contents of the condition tag board. Note, however, that
condition instructions and the end instruction always execute
unconditionally during download. If condition = 0, then all
instructions during download execute unconditionally. If
condition ≠ 0 and there are any tagged conditions in the
condition tag board, then the controller executes instructions
only if the condition is tagged. If the condition is not tagged,
then the controller skips instructions until it encounters a
condition instruction that decodes as a tagged condition. Note
that the condition tag board allows for multiple conditions to be
tagged at any given moment. This conditional processing
mechanism enables the user to have one download instruction
sequence with many possible outcomes depending on the value
of the condition and the order in which the controller
encounters condition instructions.
Table 24 lists a sample EEPROM download instruction sequence.
It illustrates the use of condition instructions and how they alter
the download sequence. The table begins with the assumption
that no conditions are in effect. That is, the most recently executed
condition instruction is 0xB0 or no conditional instructions
have been processed.
Table 24. EEPROM Conditional Processing Example
Instruction Action
0x08,
0x01,
0x00
0xB1 Tag Condition 1
0x19,
0x04,
0x00
0xB2 Tag Condition 2
0xB3 Tag Condition 3
0x07,
0x05,
0x00
0x0A
0xB0 Clear the tag condition tag board
0x0A
Transfer the system clock register contents
regardless of the current condition.
Transfer the clock distribution register contents
only if tag condition = 1
Transfer the reference input register contents only
if tag condition = 1, 2, or 3
Calibrate the system clock only if tag condition =
1, 2, or 3
Execute an IO_UPDATE, regardless of the value of
the tag condition
Calibrate the system clock regardless of the value
of the tag condition
Storing Multiple Device Setups in EEPROM
Conditional processing makes it possible to create a number of
different device setups, store them in EEPROM, and download
a specific setup on demand. To do so, first program the device
control registers for a specific setup. Then, store an upload
sequence in the EEPROM scratchpad with the following general
form:
1. Condition instruction (0xB1 to 0xBF) to identify the setup
with a specific condition (1 to 15)
2. Data instructions (to save the register contents) along with
any required calibrate and/or IO_UPDATE instructions
3. Pause instruction (0xFE)
With the upload sequence written to the scratchpad, set the
write enable bit (Register 0x0E00, Bit 0) and perform an
EEPROM upload (Register 0x0E02, Bit 0).
Reprogram the device control registers for the next desired
setup. Then store a new upload sequence in the EEPROM
scratchpad with the following general form:
1. Condition instruction (0xB0)
2. The next desired condition instruction (0xB1 to 0xBF, b ut
different from the one used during the previous upload to
identify a new setup)
3. Data instructions (to save the register contents) along with
any required calibrate and/or IO_UPDATE instructions
4. Pause instruction (0xFE)
With the upload sequence written to the scratchpad, perform an
EEPROM upload (Register 0x0E02, Bit 0).
Rev. 0 | Page 47 of 120
Page 48

AD9559 Data Sheet
Repeat the process of programming the device control registers
for a new setup, storing a new upload sequence in the EEPROM
scratchpad (Step 1 through Step 4), and executing an EEPROM
upload (Register 0x0E02, Bit 0) until all of the desired setups
have been uploaded to the EEPROM.
Note that, on the final upload sequence stored in the scratchpad,
the pause instruction (0xFE) must be replaced with an end
instruction (0xFF).
To download a specific setup on demand, first store the
condition associated with the desired setup in Register 0x0E01,
Bits[3:0]. Then perform an EEPROM download (Register
0x0E03, Bit 1). Alternatively, to download a specific setup at
power-up, apply the required logic levels necessary to encode
the desired condition on the M1 to M0 multifunction pins.
(Note that only Condition 1 through Condition 3 are accessible
via the M pins.) Then power up the device; an automatic EEPROM
download occurs. The condition (as established by the M1 and
M0 multifunction pins) guides the download sequence and
results in a specific setup.
Keep in mind that the number of setups that can be stored
in the EEPROM is limited. The EEPROM can hold a total of
2048 bytes. Each nondata instruction requires one byte of
storage. Each data instruction, however, requires N + 4 bytes of
storage, where N is the number of transferred register bytes and
the other four bytes include the data instruction itself (one byte),
the target address (two bytes), and the checksum calculated by
the EEPROM controller during the upload sequence (one byte).
Rev. 0 | Page 48 of 120
Page 49

Data Sheet AD9559
1 0 3
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
The AD9559 serial control port is a flexible, synchronous serial
communications port that provides a convenient interface to
many industry-standard microcontrollers and microprocessors.
The AD9559 serial control port is compatible with most
synchronous transfer formats, including I²C, Motorola SPI, and
Intel SSR protocols. The serial control port allows read/write
access to the AD9559 register map.
In SPI mode, single or multiple byte transfers are supported.
The SPI port configuration is programmable via Register
0x0000. This register is integrated into the SPI control logic
rather than in the register map and is distinct from the I
2
C
Register 0x0000. It is also inaccessible to the EEPROM
controller.
2
Although the AD9559 supports both the SPI and I
C serial port
protocols, only one is active following power-up (as determined
by the M3, M4/SDO, and M5/
CS
multifunction pins during the
start-up sequence). That is, the only way to change the serial port
protocol is to reset the device (or cycle the device power supply).
SPI/I²C PORT SELECTION
Because the AD9559 supports both SPI and I²C protocols, the
active serial port protocol depends on the logic state of M3,
M4/SDO, and the M5/
CS
pins. See Table 25 for the I2C address
assignments. Note that there are no internal pull-up or pulldown resistors on these pins.
Table 25. SPI/I²C Serial Port Setup
M3 M4/SDO
CS
SPI/I²C Address
M5/
Low Don’t care Don’t care SPI
High Low Low I²C, 1101000
High Low High I²C, 1101001
High High Low I²C, 1101010
High High High I²C, 1101011
SPI SERIAL PORT OPERATION
Pin Descriptions
The SCLK (serial clock) pin serves as the serial shift clock. This
pin is an input. SCLK synchronizes serial control port read and
write operations. The rising edge SCLK registers write data bits,
and the falling edge registers read data bits. The SCLK pin
supports a maximum clock rate of 40 MHz.
The SDIO (serial data input/output) pin is a dual-purpose pin
and acts either as an input only (unidirectional mode) or as
both an input and an output (bidirectional mode). The AD9559
default SPI mode is bidirectional.
The SDO (serial data output) pin is useful only in unidirectional
I/O mode. It serves as the data output pin for read operations.
EE
CS
A
The
(chip select) pin is an active low control that gates read
and write operations. This pin is internally connected to a 30 kΩ
pull-up resistor. When
EE
CS
AA
AA
is high, the SDO and SDIO pins go
into a high impedance state.
SPI Mode Operation
The SPI port supports both 3-wire (bidirectional) and 4-wire
(unidirectional) hardware configurations and both MSB-first
and LSB-first data formats. Both the hardware configuration
and data format features are programmable. By default, the
AD9559 uses the bidirectional MSB-first mode. The reason that
bidirectional is the default mode is so that the user can still
write to the device, if it is wired for unidirectional operation, to
switch to unidirectional mode.
EE
CS
Assertion (active low) of the AA
operation to the
bytes or fewer (excluding the instruction word), the device
supports the
AD9559 SPI port. For data transfers of three
EE
CS
AA
AA
stalled high mode. In this mode, the AA
be temporarily deasserted on any byte boundary, allowing time
for the system controller to process the next byte.
AA
pin initiates a write or read
EE
CS
AA
pin can
EE
CS
AA
AA
can be
deasserted only on byte boundaries, however. This applies to
both the instruction and data portions of the transfer.
During stall high periods, the serial control port state machine
enters a wait state until all data is sent. If the system controller
decides to abort a transfer midstream, the state machine must be
reset by either completing the transfer or by asserting the
pin for at least one complete SCLK cycle (but less than eight
SCLK cycles). Deasserting the
EE
CS
AA
AA
pin on a nonbyte boundary
CS
AA
EE
AA
terminates the serial transfer and flushes the buffer.
In the streaming mode (see Tab l e 26), any number of data bytes
can be transferred in a continuous stream. The register address
is automatically incremented or decremented.
EE
CS
AA
AA
must be
deasserted at the end of the last byte transferred, thereby ending
the stream mode.
Table 26. Byte Transfer Count
W1 W0 Bytes to Transfer
0
0
0 1
1 2
1 1 Streaming mode
Rev. 0 | Page 49 of 120
Page 50

AD9559 Data Sheet
Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus Data
The AD9559 supports the long instruction mode only. The SPI
protocol consists of a two-part communication cycle. The first
part is a 16-bit instruction word that is coincident with the first
16 SCLK rising edges and a payload. The instruction word
provides the AD9559
regarding the payload. The instruction word includes the R/
serial control port with information
AA
W
EE
AA
bit that indicates the direction of the payload transfer (that is, a
read or write operation). The instruction word also indicates
the number of bytes in the payload and the starting register
address of the first payload byte.
Write
If the instruction word indicates a write operation, the payload
is written into the serial control port buffer of the AD9559. Data
bits are registered on the rising edge of SCLK. The length of the
transfer (1, 2, or 3 bytes or streaming mode) depends on the W0
and W1 bits (see Table 26
streaming,
EE
CS
AA
AA
can be deasserted after each sequence of eight bits
to stall the bus (except after the last byte, where it ends the cycle).
When the bus is stalled, the serial transfer resumes when
asserted. Deasserting the
) in the instruction byte. When not
CS
EE
CS
AA
AA
pin on a nonbyte boundary resets the
AA
EE
AA
is
serial control port. Reserved or blank registers are not skipped
over automatically during a write sequence. Therefore, the user
must know what bit pattern to write to the reserved registers to
preserve proper operation of the part. Generally, it does not matter
what data is written to blank registers, but it is customary to use 0s.
Most of the serial port registers are buffered (see the
Buffered/Active Registers section for details on the difference
between buffered and active registers). Therefore, data written
into buffered registers does not take effect immediately. An
additional operation is needed to transfer buffered serial control
port contents to the registers that actually control the device.
This is accomplished with an IO_UPDATE operation, which is
performed in one of two ways. One method is to write a Logic 1
to Register 0x0005, Bit 0 (this bit is an autoclearing bit). The
other method is to use an external signal via an appropriately
programmed multifunction pin. The user can change as many
register bits as desired before executing an IO_UPDATE. The
IO_UPDATE operation transfers the buffer register contents to
their active register counterparts.
Read
If the instruction word indicates a read operation, the next N ×
8 SCLK cycles clock out the data from the address specified in
the instruction word. N is the number of data bytes read and
depends on the W0 and W1 bits of the instruction word. The
readback data is valid on the falling edge of SCLK. Blank registers
are not skipped over during readback.
A readback operation takes data from either the serial control
port buffer registers or the active registers, as determined by
Register 0x0004, Bit 0.
SPI Instruction Word (16 Bits)
EE
W
The MSB of the 16-bit instruction word is R/AA
AA
, which indicates
whether the instruction is a read or a write. The next two bits,
W1 and W0, indicate the number of bytes in the transfer (see
Table 26). The final 13 bits are the register address (A12 to A0),
which indicates the starting register address of the read/write
operation (see Tab l e 28).
SPI MSB-/LSB-First Transfers
The AD9559 instruction word and payload can be MSB first or
LSB first. The default for the AD9559 is MSB first. The LSB-first
mode can be set by writing a 1 to Register 0x0000, Bit 6.
Immediately after the LSB-first bit is set, subsequent serial
control port operations are LSB first.
When MSB-first mode is active, the instruction and data bytes
must be written from MSB to LSB. Multibyte data transfers in
MSB-first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the most significant payload byte. Subsequent
data bytes must follow in order from high address to low
address. In MSB-first mode, the serial control port internal
address generator decrements for each data byte of the multibyte transfer cycle.
When Register 0x0000, Bit 6 = 1 (LSB first), the instruction and
data bytes must be written from LSB to MSB. Multibyte data
transfers in LSB-first format start with an instruction byte that
includes the register address of the least significant payload byte
followed by multiple data bytes. The serial control port internal
byte address generator increments for each byte of the multibyte
transfer cycle.
For multibyte MSB-first (default) I/O operations, the serial control
port register address decrements from the specified starting address
toward Address 0x0000. For multibyte LSB-first I/O operations,
the serial control port register address increments from the starting
address toward Address 0x1FFF. Reserved addresses are not
skipped during multibyte I/O operations; therefore, the user
should write the default value to a reserved register and 0s to
unmapped registers. Note that it is more efficient to issue a new
write command than to write the default value to more than
two consecutive reserved (or unmapped) registers.
Table 27. Streaming Mode (No Addresses Are Skipped)
Write Mode Address Direction Stop Sequence
LSB First
MSB First
Increment 0x0000…0x1FFF
Decrement 0x1FFF…0x0000
Rev. 0 | Page 50 of 120
Page 51

Data Sheet AD9559
MSB
LSB
CS
SCLK
DON'T CARE
SDIO A12W0W1R/W A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
D7
D6 D5
D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGISTE R ( N) DATA REGISTER (N – 1) DATA
10644-029
CS
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
REGISTE R ( N) DATA
16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGI S TER (N – 1) DATA
REGISTE R ( N – 2) DATA REGISTE R ( N – 3) DATA
A12W0W1R/W
A11
A10 A9 A8 A7
A6
A5 A4
A3 A2 A1 A0
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DON'T
CARE
D7
D6 D5
D4 D3
D2 D1
D0 D7 D6
D5
D4 D3
D2
D1
D0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
D7
D6 D5 D4 D3
D2 D1 D0
10644-030
t
S
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
W1 W0 A12 A11
A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
R/W
t
DS
t
DH
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
CLK
t
C
CS
SCLK
SDIO
10644-031
DATA BIT N – 1DATA BIT N
CS
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
t
DV
10644-032
CS
SCLK
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGIS TER (N) DATA REGISTER (N + 1) DATA
SDIO
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
A0 A1 A2
A3 A4
A5 A6
A7 A8 A9
A10 A11
A12
D1D0R/WW1W0 D2
D3 D4
D5 D6 D7
D0
D1 D2 D3
D4 D5
D6 D7
10644-033
Table 28. Serial Control Port, 16-Bit Instruction Word, MSB First
I15 I14 I13 I12 I11 I10 I9 I8 I7 I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0
R/AAWEE
W1 W0 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Figure 45. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, Two Bytes of Data
Figure 46. Serial Control Port Read—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, Four Bytes of Data
Figure 47. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, Timing Measurements
Figure 48. Timing Diagram for Serial Control Port Register Read
Figure 49. Serial Control Port Write—LSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, Two Bytes of Data
Rev. 0 | Page 51 of 120
Page 52

AD9559 Data Sheet
CS
SCLK
SDIO
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
CLK
t
S
t
DS
t
DH
t
C
BIT N BIT N + 1
10644-034
Figure 50. Serial Control Port Timing—Write
Table 29. Serial Control Port Timing
Parameter Description
tDS Setup time between data and the rising edge of SCLK
t
Hold time between data and the rising edge of SCLK
DH
t
Period of the clock
CLK
t
S
tC
t
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic high state
HIGH
t
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic low state
LOW
t
SCLK to valid SDIO and SDO (see Figure 48)
DV
Setup time between the AACS
Setup time between the SCLK rising edge and AACS
EE
AA
falling edge and the SCLK rising edge (start of the communication cycle)
EE
AA
rising edge (end of the communication cycle)
Rev. 0 | Page 52 of 120
Page 53

Data Sheet AD9559
R
Read
DATA LINE
STABLE;
DATA VALID
CHANGE
OF DATA
ALLOWED
SDA
SCL
10644-049
I²C SERIAL PORT OPERATION
The I2C interface has the advantage of requiring only two control
pins and is a de facto standard throughout the I
its disadvantage is programming speed, which is 400 kbps maximum.
The AD9559 I²C port design is based on the I²C fast mode standard;
it supports both the 100 kHz standard mode and 400 kHz fast mode.
Fast mode imposes a glitch tolerance requirement on the control
signals. That is, the input receivers ignore pulses of less than 50 ns
duration.
The AD9559 I²C port consists of a serial data line (SDA) and a
serial clock line (SCL). In an I²C bus system, the AD9559 is
connected to the serial bus (data bus SDA and clock bus SCL)
as a slave device; that is, no clock is generated by the AD9559.
The AD9559 uses direct 16-bit memory addressing instead of
traditional 8-bit memory addressing.
The AD9559 allows up to seven unique slave devices to occupy
2
the I
C bus. These are accessed via a 7-bit slave address
transmitted as part of an I
2
C packet. Only the device with a
matching slave address responds to subsequent I
Table 25 lists the supported device slave addresses.
I2C Bus Characteristics
A summary of the various I2C abbreviations appears in Tabl e 30.
Table 30. I
2
C Bus Abbreviation Definitions
Abbreviation Definition
S
Sr
P
A
AA
AAW
EE
E
Start
Repeated start
Stop
Acknowledge
Nonacknowledge
Write
The transfer of data is shown in Figure 51. One clock pulse is
generated for each data bit transferred. The data on the SDA line
must be stable during the high period of the clock. The high or
low state of the data line can change only when the clock signal on
the SCL line is low.
Figure 51. Valid Bit Transfer
2
C i ndustry. However,
2
C commands.
Start/stop functionality is shown in Figure 52. The start condition
is characterized by a high-to-low transition on the SDA line while
SCL is high. The start condition is always generated by the master
to initialize a data transfer. The stop condition is characterized by
a low-to-high transition on the SDA line while SCL is high. The
stop condition is always generated by the master to terminate
a data transfer. Every byte on the SDA line must be eight bits long.
Each byte must be followed by an acknowledge bit; bytes are sent
MSB first.
The acknowledge bit (A) is the ninth bit attached to any 8-bit data
byte. An acknowledge bit is always generated by the receiving device
(receiver) to inform the transmitter that the byte has been received.
It is done by pulling the SDA line low during the ninth clock pulse
after each 8-bit data byte.
E
A
The nonacknowledge bit (A
A
) is the ninth bit attached to any 8-bit
data byte. A nonacknowledge bit is always generated by the
receiving device (receiver) to inform the transmitter that the byte
has not been received. It is done by leaving the SDA line high
during the ninth clock pulse after each 8-bit data byte.
Data Transfer Process
The master initiates data transfer by asserting a start condition.
This indicates that a data stream follows. All I²C slave devices
connected to the serial bus respond to the start condition.
The master then sends an 8-bit address byte over the SDA line,
consisting of a 7-bit slave address (MSB first) plus an R/
W
A
E
A
bit.
This bit determines the direction of the data transfer, that is,
whether data is written to or read from the slave device (0 = write,
1 = read).
The peripheral whose address corresponds to the transmitted address
responds by sending an acknowledge bit. All other devices on the
bus remain idle while the selected device waits for data to be read
from or written to it. If the R/
writes to the slave device (receiver). If the R/
E
W
A
A
Abit is 0, the master (transmitter)
E
W
AA
AA
bit is 1, the master
(receiver) reads from the slave device (transmitter).
The format for these commands is described in the Data Transfer
Format section.
Data is then sent over the serial bus in the format of nine clock
pulses, one data byte (eight bits) from either master (write mode)
or slave (read mode) followed by an acknowledge bit from the
receiving device. The number of bytes that can be transmitted per
transfer is unrestricted. In write mode, the first two data bytes
immediately after the slave address byte are the internal memory
(control registers) address bytes, with the high address byte first.
This addressing scheme gives a memory address of up to 2
16
− 1 =
65,535. The data bytes after these two memory address bytes are
register data written to or read from the control registers. In read
mode, the data bytes after the slave address byte are register data
written to or read from the control registers.
Rev. 0 | Page 53 of 120
Page 54

AD9559 Data Sheet
SDA
START CONDITION STOP CONDITION
SCL
S
P
10644-036
1 2
8 9
1 2
3 TO 73 TO 7 8 9
10
SDA
SCL
S
MSB
ACK FROM
SLAVE RECEIVER
ACK FROM
SLAVE RECEIVER
P
10644-037
1 2
8 9
1 2
3 TO 73 TO 7 8 9 10
ACK FROM
SLAVE RECEIVER
ACK FROM
SLAVE RECEIVER
SDA
SCL
S
MSB
P
10644-038
1 2
8 9
1 2
3 TO 73 TO 7 8 9 10
ACK FROM
MASTER RECEIVER
NONACK FROM
MASTER RECEIVER
SDA
SCL
S
P
10644-039
When all the data bytes are read or written, stop conditions are
established. In write mode, the master (transmitter) asserts a
stop condition to end data transfer during the 10
th
clock pulse
following the acknowledge bit for the last data byte from the slave
device (receiver). In read mode, the master device (receiver)
receives the last data byte from the slave device (transmitter) but
does not pull SDA low during the ninth clock pulse. This is known
as a nonacknowledge bit. By receiving the nonacknowledge bit,
the slave device knows that the data transfer is finished and enters
idle mode. The master then takes the data line low during the low
period before the 10
th
clock pulse, and high during the 10th clock
pulse to assert a stop condition.
A start condition can be used in place of a stop condition.
Furthermore, a start or stop condition can occur at any time, and
partially transferred bytes are discarded.
Figure 52. Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 53. Acknowledge Bit
Figure 54. Data Transfer Process (Master Write Mode, 2-Byte Transfer)
Figure 55. Data Transfer Process (Master Read Mode, 2-Byte Transfer)
Rev. 0 | Page 54 of 120
Page 55

Data Sheet AD9559
S Sr SP
SDA
SCL
t
SP
t
HD; STA
t
SU; STA
t
SU; DAT
t
HD; DAT
t
HD; STA
t
SU; STO
t
BUF
t
R
t
F
t
R
t
F
t
HIGH
t
LOW
10644-040
t
Data hold time
Data Transfer Format
Write byte format—the write byte protocol is used to write a register address to the RAM starting from the specified RAM address.
S
Slave
address
Send byte format—the send byte protocol is used to set up the register address for subsequent reads.
S
Slave
address
Receive byte format—the receive byte protocol is used to read the data byte(s) from RAM starting from the current address.
S
Slave
address
Read byte format—the combined format of the send byte and the receive byte.
S
Slave
address
I²C Serial Port Timing
E
A
AW
RAM address
high byte
E
A
AAW
RAM address
high byte
A
RAM address
low byte
A
RAM address
low byte
A RAM Data 0 A
A P
R A RAM Data 0 A RAM Data 1 A RAM Data 2
E
A
AAW
RAM address
high byte
A
RAM address
low byte
A Sr
Slave
address
E
AAA
R A
RAM
Data 1
P
RAM
Data 0
A
RAM
A P
Data 2
E
A
RAM
Data 1
A
RAM
Data 2
P
AAA
Table 31. I²C Timing Definitions
Parameter Description
f
Serial clock
SCL
t
Bus free time between stop and start conditions
BUF
t
Repeated hold time start condition
HD; STA
t
Repeated start condition setup time
SU ; STA
t
Stop condition setup time
SU; STO
HD; DAT
t
Date setup time
SU ; DAT
t
SCL clock low period
LOW
t
SCL clock high period
HIGH
t
Minimum/maximum receive SCL and SDA rise time
R
t
Minimum/maximum receive SCL and SDA fall time
F
t
Pulse width of voltage spikes that must be suppressed by the input filter
SP
Figure 56. I²C Serial Port Timing
Rev. 0 | Page 55 of 120
Page 56

AD9559 Data Sheet
W1
The lock detector declares unlock immediately
W5
PROGRAMMING THE I/O REGISTERS
The register map (see Table 34) spans an address range from
0x0000 through 0x0E4F. Each address provides access to one
byte (eight bits) of data. Each individual register is identified by
its four-digit hexadecimal address (for example, Register 0x0A23).
In some cases, a group of addresses collectively defines a register.
In general, when a group of registers defines a control parameter,
the LSB of the value resides in the D0 position of the register
with the lowest address. The bit weight increases right to left,
from the lowest register address to the highest register address.
Note that the EEPROM storage sequence registers (Address 0x0E10
to Address 0x0E4F) are an exception to this convention (see the
EEPROM Instructions section).
BUFFERED/ACTIVE REGISTERS
There are two copies of most registers: buffered and active. The
value in the active registers is the one that is in use. The buffered
registers are the ones that take effect the next time the user writes
0x01 to Register 0x0005 (IO_UPDATE). Buffering the registers
allows the user to update a group of registers (like the APLL
settings) simultaneously, avoiding the potential of unpredictable
behavior in the part. Registers with an L in the option column of
the register map (see Tab l e 34) are live, meaning that they take
effect the moment the serial port transfers that data byte.
WRITE DETECT REGISTERS
A W in the option column of the register map (see Table 34)
identifies a register with write detection. These registers contain
additional logic to avoid glitches or unwanted operation. Write
detection can be disabled by setting Register 0x0004, Bit 3 to 1b.
Table 32. Register Write Detection Description
Option Register Operation
W0
W2
W6
W7
The input reference is immediately faulted when
these registers are written to, and the input
reference validation timer restarts when the next
IO_UPDAT E occurs (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
when these registers are written to, and the lock
detection restarts when the next IO_UPDATE occurs.
After these registers are written to, the DPLL
automatically enters holdover for one PFD cycle
(and then exits) when an IO_UPDATE is issued.
The watchdog timer resets automatically when
these registers are changed, and then resumes
counting on the next IO_UPDATE.
The system clock stability timer is automatically
reset when these registers are changed, and
then resumes counting on the next IO_UPDATE.
If these registers are written to while they are
assigned to an existing function, the existing function
stops immediately. The new function starts when
the next IO_UPDATE occurs.
AUTOCLEAR REGISTERS
An A in the option column of the register map (see Tabl e 34)
identifies an autoclearing register. Typically, the active value for
an auto-clearing register takes effect following an IO_UPDATE.
The bit is cleared by the internal device logic upon completion
of the prescribed action.
REGISTER ACCESS RESTRICTIONS
Read and write access to the register map may be restricted,
depending on the register in question, the source and direction
of access, and the current state of the device. Each register can
be classified into one or more access types. When more than
one type applies, the most restrictive condition is the one that
applies.
When access is denied to a register, all attempts to read the register
return a 0 byte, and all attempts to write to the register are ignored.
Access to nonexistent registers is handled in the same way as for
a denied register.
Regular Access
Registers with regular access do not fall into any other category.
Both read and write access to registers of this type can be from
either the serial ports or EEPROM controller. However, only
one of these sources can have access to a register at any given
time (access is mutually exclusive). When the EEPROM controller
is active, either in load or store mode, it has exclusive access to
these registers.
Read-Only Access
An R in the option column of the register map (see Ta b le 34)
identifies read-only registers. Access is available at all times,
including when the EEPROM controller is active. Note that
read-only registers (R) are inaccessible to the EEPROM as well.
Exclusion from EEPROM Access
An E in the option column of the register map (see Ta ble 34)
identifies a register with contents that are inaccessible to the
EEPROM. That is, the contents of this type of register cannot be
transferred directly to the EEPROM or vice versa. Note that
read-only registers (R) are inaccessible to the EEPROM as well.
Rev. 0 | Page 56 of 120
Page 57

Data Sheet AD9559
ΨJT
Junction-to-top-of-package characterization parameter, 2.5 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air)
0.2
°C/W
THERMAL PERFORMANCE
Table 33. Thermal Parameters for the 72-Lead LFCSP Package
Symbol Thermal Characteristic Using a JEDEC 51-7 Plus JEDEC 51-5 2S2P Test Board1 Value2 Unit
θJA Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, 0.0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) 20.0 °C/W
θ
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, 1.0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air) 18.0 °C/W
JMA
θ
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, 2.5 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air) 16.0 °C/W
JMA
θ
Junction-to-board thermal resistance, 0.0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air) 10.7 °C/W
JB
θ
Junction-to-case thermal resistance (die-to-heat sink) per MIL-Std 883, Method 1012.1 1.1 °C/W
JC
Ψ
Junction-to-top-of-package characterization parameter, 0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) 0.1 °C/W
JT
Ψ
Junction-to-top-of-package characterization parameter, 1.0 m/sec airflow per JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air) 0.1 °C/W
JT
1
The exposed pad on the bottom of the package must be soldered to analog ground to achieve the specified thermal performance.
2
Results are from simulations. The PCB is a JEDEC multilayer type. Thermal performance for actual applications requires careful inspection of the conditions in the
application to determine if they are similar to those assumed in these calculations.
The AD9559 is specified for a case temperature (T
ensure that T
is not exceeded, an airflow source can be used.
CASE
Use the following equation to determine the junction temperature on the application PCB:
T
= T
J
+ (ΨJT × PD)
CASE
where:
T
is the junction temperature (°C).
J
is the case temperature (°C) measured by the customer at
T
CASE
the top center of the package.
Ψ
is the value as indicated in Ta b le 33.
JT
PD is the power dissipation (see the Tab l e 3).
CASE
). To
Valu e s o f θ
design considerations. θ
imation of T
where T
Valu e s o f θ
are provided for package comparison and PCB
JA
can be used for a first-order approx-
JA
by the equation
J
= TA + (θJA × PD)
T
J
is the ambient temperature (°C).
A
are provided for package comparison and PCB
JC
design considerations when an external heat sink is required.
Valu e s o f θ
are provided for package comparison and PCB
JB
design considerations.
Rev. 0 | Page 57 of 120
Page 58

AD9559 Data Sheet
POWER SUPPLY PARTITIONS
The AD9559 power supplies are in two groups: VDD3 and VDD. All
power and ground pins should be connected, even if certain blocks
of the chip are powered down.
Ferrite beads with low (< 0.7 Ω) dc resistance and approximately 600 Ω
impedance at 100 MHz are suitable for this application.
3.3 V SUPPLIES
All of the 3.3 V supplies can be supplied from one 3.3V power supply.
Pin 28 is a serial port power supply and does not require a ferrite
bead from the 3.3 V source.
Pin 1, Pin 12, Pin 18, and Pin 72 belong to PLL_0. It is advisable, but
not mandatory, to have a place for a ferrite bead to isolate them from
the 3.3 V source. The need for a ferrite bead depends on how quiet the
3.3 V source is. This group of pins never consumes more than 90 mA.
Pin 37, Pin 43, Pin 54, and Pin 55 belong to PLL_1, and the same
recommendation given for the PLL_0 3.3 V pins applies here as well.
1.8 V SUPPLIES
All of the 1.8 V supplies can be connected to one common
1.8 V source.
Six ferrite beads should be used in the following locations:
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 13
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 14
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 17
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 38
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 41
• Between the 1.8 V source and Pin 42
The remaining VDD pins can be connected directly to the
1.8 V source.
BYPASS CAPACITORS FOR PIN 21 AND PIN 33
The performance of the AD9559 is enhanced by the use of a
Size 0201, 0.1 µF capacitor between Pin 21 and Pin 22, as well as
between Pin 33 and Pin 34, placed as close to the AD9559 as
possible and without the use of vias.
Rev. 0 | Page 58 of 120
Page 59

Data Sheet AD9559
REGISTER MAP
Register addresses that are not listed in Tab l e 34 are not used, and writing to those registers has no effect. The user should write the
default value to sections of registers marked reserved. R = read only. A = autoclear. E = excluded from EEPROM loading. W1, W2, W5,
W6, and W7 = write detection (see Tabl e 32 for more information). L = live (IO_UPDATE not required for register to take effect or for
a read-only register to be updated.)
Table 34.
Reg
Addr
(Hex) Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Serial Control Port and Part Identification
0x0000 L, E SPI control SDO enable
LSB first/
Soft reset Reserved 0x00
increment
address
0x0000 L I²C control Reserved Soft reset Reserved 0x00
0x0004
Readback
control
Reserved
Reset sans
reg map
Disable
auto actions
Reserved 2-wire SPI
Read
buffer
register
0x0005 A, L IO_UPDATE Reserved
IO_
UPDATE
0x000A R, L Reserved 0x12
0x000B R, L Reserved 0x0F
0x000C R, L
0x000D R, L Clock part family ID, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x000E L
0x000F L User scratchpad, Bits[15:8] 0x00
Part family
ID
User
scratchpad
Clock part family ID, Bits[7:0] 0x02
User scratchpad, Bits[7:0] 0x00
General Configuration
0x0100
0x0101 Reserved M5 driver mode, Bits[1:0] M4 driver mode, Bits[1:0] 0x00
M pin
drivers
0x0102 W7 M0FUNC
0x0103 W7 M1FUNC
0x0104 W7 M2FUNC
0x0105 W7 M3FUNC
0x0106 W7 M4FUNC
0x0107 W7 M5FUNC
0x0108 W5
0x0109 W5 Watchdog timer (ms), Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x010A
Watchdog
timer
IRQ mask
common
0x010B Reserved
0x010C Reserved
0x010D
IRQ mask
DPLL_0
0x010E Switching Free run Holdover
0x010F Reserved
0x0110
IRQ mask
DPLL_1
0x0111 Switching Free run Holdover
0x0112 Reserved
M3 driver mode, Bits[1:0] M2 driver mode, Bits[1:0] M1 driver mode, Bits[1:0] M0 driver mode, Bits[1:0] 0x00
M0
output/ A
M1
output/ A
M2
output/ A
M3
output/ A
M4
output/ A
M5
output/ A
input
input
input
input
input
input
EE
EE
EE
EE
EE
EE
M0 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
M1 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
M2 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
M3 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
M4 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
M5 function, Bits[6:0] 0x00
Watchdog timer (ms), Bits[7:0] 0x00
Reserved
Frequency
unclamped
Frequency
unclamped
SYSCLK
unlocked
REFB
validated
REFD
validated
Frequency
clamped
Frequency
clamped
SYSCLK
stable
REFB fault
cleared
REFD fault
cleared
Phase slew
unlimited
Phase slew
unlimited
SYSCLK
locked
Watchdog
timer
REFB fault Reserved
REFD fault Reserved
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Sync clock
distribution
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Sync clock
distribution
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_0
unlocked
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_1
unlocked
Reserved
REFA
validated
REFC
validated
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_0
locked
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_1
locked
EEPROM
fault
REFA fault
cleared
REFC fault
cleared
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_0 cal
complete
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_1 cal
complete
EEPROM
complete
REFA fault 0x00
REFC fault 0x00
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_0
cal started
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_1
cal started
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 59 of 120
Page 60

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0311
W1
Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[7:0]
0xBC
0x0314
W1
Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0]
0x0A
0x0315
W1
Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0]
0x0A
0x0316
W1
Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0]
0xBC
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
System Clock
0x0200
0x0201 Reserved
0x0202
0x0203 Nominal system clock period (fs), Bits[15:8] (1 ns at 1 ppm accuracy) 0x67
0x0204 Reserved Nominal system clock period, Bits[20:16] 0x13
0x0205 W6
0x0206 W6 System clock stability period (ms), Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0207 W6 Reserved System clock stability period (ms), Bits[19:16] 0x00
Reference Input A
0x0300
0x0301
0x0302 R divider, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0303 Reserved R divider, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x0304 W0
0x0305 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[15:8] 0xEA
0x0306 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[23:16] 0x10
0x0307 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[31:24] 0x03
0x0308 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[39:32] 0x00
0x0309 W0
0x030A W0 Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x030B W0 Reserved Inner tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x030C W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 10%) 0x0A
0x030D W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x030E W0 Reserved Outer tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x030F W0
0x0310 W0 Validation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x00
0x0312 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0313 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits [23:16] 0x00
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SYSCLK PLL
feedback
divider and
config
SYSCLK
period
SYSCLK
stability
REFA
logic type
REFA
R divider
(20 bits)
REFA
period
(up to
1.1 ms)
REFA
frequency
tolerance
REFA
validation
REFA
phase lock
detector
Nominal system clock period (fs), Bits[7:0] (1 ns at 1 ppm accuracy) 0x0E
Reserved
Nominal period (fs), Bits[7:0] (default: 51.44 ns =1/(19.44 MHz) for default system clock setting) 0xC9
Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 5%) 0x14
System clock K divider, Bits[7:0] 0x08
SYSCLK
XTAL enable
System clock stability period (ms), Bits[7:0] 0x32
Enable REFA
divide-by-2
R divider, Bits[7:0] 0xCF
Validation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x0A
SYSCLK J1 divider, Bits[1:0]
Reserved REFA logic type, Bits[1:0] 0x00
SYSCLK
doubler
enable
(J0 divider)
Def
(Hex)
0x09
REFA
0x0317 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0318 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0319 W1 Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x031A W1 Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
Reference Input B
0x0320
0x0321
0x0322 R divider, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0323 Reserved R divider, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x0324 W0
0x0325 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[15:8] 0xEA
0x0326 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[23:16] 0x10
0x0327 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[31:24] 0x03
0x0328 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[39:32] 0x00
0x0329 W0
0x032A W0 Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x032B W0 Reserved Inner tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x032C W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 10%) 0x0A
0x032D W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x032E W0 Reserved Outer tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
frequency
lock
detector
REFB
logic type
REFB
R divider
(20 bits)
REFB
reference
period
(up to
1.1 ms)
REFB
frequency
tolerance
Reserved
Nominal period (fs), Bits[7:0] (default: 51.44 ns =1/(19.44 MHz) for default system clock setting) 0xC9
Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 5%) 0x14
R divider, Bits[7:0] 0xCF
Rev. 0 | Page 60 of 120
Enable REFB
divide-by-2
Reserved REFB logic type, Bits[1:0] 0x00
Page 61
Data Sheet AD9559
0x0345
W0
Nominal period (fs), Bits[15:8]
0xEA
0x0346
W0
Nominal period (fs), Bits[23:16]
0x10
0x036C
W0
Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 10%)
0x0A
0x036D
W0
Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm)
0x00
0x036E
W0
Reserved
Outer tolerance, Bits[19:16]
0x00
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x032F W0
0x0330 W0 Validation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x00
0x0331 W1
0x0332 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0333 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits [23:16] 0x00
0x0334 W1 Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0335 W1 Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0336 W1
0x0337 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0338 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0339 W1 Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x033A W1 Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
Reference Input C
0x0340
0x0341
0x0342 R divider, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0343 Reserved R divider, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x0344 W0
0x0347 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[31:24] 0x03
0x0348 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[39:32] 0x00
0x0349 W0
0x034A W0 Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x034B W0 Reserved Inner tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x034C W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 10%) 0x0A
0x034D W0 Outer tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for lock to unlock; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x034E W0 Reserved Outer tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x034F W0
0x0350 W0 Validation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x00
0x0351 W1
0x0352 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0353 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits [23:16] 0x00
0x0354 W1 Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0355 W1 Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0356 W1
0x0357 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0358 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0359 W1 Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x035A W1 Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
Reference Input D
0x0360
0x0361
0x0362 R divider, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0363 Reserved R divider, Bits[19:16] 0x00
0x0364 W0
0x0365 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[15:8] 0xEA
0x0366 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[23:16] 0x10
0x0367 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[31:24] 0x03
0x0368 W0 Nominal period (fs), Bits[39:32] 0x00
0x0369 W0
0x036A W0 Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[15:8] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) 0x00
0x036B W0 Reserved Inner tolerance, Bits[19:16] 0x00
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
REFB
validation
REFB
phase lock
detector
REFB
frequency
lock
detector
REFC
logic type
REFC
R divider
(20 bits)
REFC
period
(up to
1.1 ms)
REFC
frequency
tolerance
REFC
validation
REFC
phase lock
detector
REFC
frequency
lock
detector
REFD
logic type
REFD
R divider
(20 bits)
REFD
period
(up to
1.1 ms)
REFD
frequency
tolerance
Reserved
Nominal period (fs), Bits[7:0] (default: 51.44 ns =1/(19.44 MHz) for default system clock setting) 0xC9
Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 5%) 0x14
Reserved
Nominal period (fs), Bits[7:0] (default: 51.44 ns =1/(19.44 MHz) for default system clock setting) 0xC9
Inner tolerance (1 ÷ ppm), Bits[7:0] (for unlock to lock condition; max: 10%, min: 2 ppm) (default: 5%) 0x14
Validation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x0A
Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[7:0] 0xBC
Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] 0xBC
Enable REFC
divide-by-2
R divider, Bits[7:0] 0xCF
Validation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x0A
Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[7:0] 0xBC
Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] 0xBC
Enable REFD
divide-by-2
R divider, Bits[7:0] 0xCF
Reserved REFC logic type, Bits[1:0] 0x00
Reserved REFD logic type, Bits[1:0] 0x00
Def
(Hex)
Rev. 0 | Page 61 of 120
Page 62

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0405
Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[7:0]
0x51
0x0406
Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[15:8]
0xB8
0x0407
Reserved
Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[19:16]
0x02
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x036F W0
0x0370 W0 Validation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x00
0x0371 W1
0x0372 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0373 W1 Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits [23:16] 0x00
0x0374 W1 Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0375 W1 Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x0376 W1
0x0377 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] 0x02
0x0378 W1 Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0379 W1 Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
0x037A W1 Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] 0x0A
DPLL_0 General Settings
0x0400
0x0401 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[15:8] 0x15
0x0402 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[23:16] 0x64
0x0403 Reserved 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[29:24] 0x1B
0x0404
0x0408 Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[7:0] 0x3E
0x0409 Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[15:8] 0x0A
0x040A Reserved Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[19:16] 0x0B
0x040B
0x040C History accumulation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65 sec) 0x00
0x040D
0x040E
0x040F Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0410 Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0411 Reserved Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[29:24] 0x00
0x0412 Incremental phase offset step size (ps/step), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 ns/step) 0x00
0x0413 Incremental phase offset step size (ps/step), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 ns/step) 0x00
0x0414
0x0415 Phase slew rate Limit (µs/sec), Bits[15:8] (315 µs/sec up to 65.536 ms/sec) 0x00
Output PLL_0 (APLL_0) and Channel 0 Output Drivers
0x0420
0x0421
0x0422
0x0423 Reserved
0x0424 P0 divider Reserved P0 divider divide ratio, Bits[3:0] 0x04
0x0425 OUT0 sync Reserved
0x0426 Reserved
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
REFD
validation
REFD
phase lock
detector
REFD
frequency
lock
detector
DPLL_0
free run
frequency
TW
DCO_0
control
DPLL_0
frequency
clamp
DPLL_0
holdover
history
DPLL_0
history
mode
DPLL_0
closed loop
phase
offset
(±0.5 ms)
DPLL_0
phase
slew limit
APLL_0
charge
pump
APLL_0
M0 divider
APLL_0
loop filter
control
Reserved Digital oscillator SDM integer part, Bits[3:0] 0x08
Reserved
Phase slew rate limit (µs/sec), Bits[7:0] (315 µs/sec up to 65.536 ms/sec) 0x00
Validation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 sec) 0x0A
Phase lock threshold (ps), Bits[7:0] 0xBC
Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] 0xBC
30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[7:0] 0x12
History accumulation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65 sec) 0x0A
Single
sample
fallback
Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[7:0] 0x00
Output PLL0 (APLL_0) charge pump current, Bits[7:0] 0x81
Output PLL0 (APLL_0) feedback (M0) divider, Bits[7:0] 0x14
APLL_0 loop filter control, Bits[7:0] 0x07
Persistent
history
Sync source
selection
APLL_0
locked
controlled
sync disable
Incremental average 0x00
Bypass
internal
Rzero
Auto sync mode 0x00
Mask
OUT0B
sync
Mask
OUT0A
sync
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 62 of 120
Page 63

Data Sheet AD9559
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x0427 OUT0A Reserved OUT0A format, Bits[2:0] OUT0A polarity, Bits[1:0]
0x0428 Q0_A divider, Bits[7:0] 0x00
0x0429 Reserved Q0_A divider, Bits[9:8] 0x00
0x042A Reserved Q0_A divider phase, Bits[5:0] 0x00
0x042B OUT0B
0x042C Q0_B divider, Bits[7:0] 0x03
0x042D Reserved Q0_B divider, Bits[9:8] 0x00
0x042E Reserved Q0_B divider phase, Bits[5:0] 0x00
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input A
0x0440
0x0441 W2
0x0442 W2 Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x0443 W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x0444 W2
0x0445 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0446 W2 Reserved
0x0447
0x0448 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0449 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x044A W2
0x044B W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x044C W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input B
0x044D
0x044E W2
0x044F W2 Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x0450 W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x0451 W2
0x0452 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0453 W2 Reserved
0x0454
0x0455 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0456 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0457 W2
0x0458 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0459 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reserved 0x10
Reserved 0x10
Enable
REFA
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider,
Integer
Part N0,
Bit 16
Enable
REFB
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider,
Integer
Part N0,
Bit 16
Reference
priority
DPLL_0
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_0
N0 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Reference
priority
DPLL_0
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_0
N0 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Enable 3.3 V
CMOS driver
OUT0A
LVDS boost
OUT0B format[2:0] OUT0B polarity, Bits[1:0]
Reserved REFA priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[7:0] 0x05
Reserved REFB priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[7:0] 0x05
OUT0B
LVDS boost
Def
(Hex)
0x01
0x00
0x01
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 63 of 120
Page 64

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0468
W2
Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz)
0xF4
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input C
0x045A
0x045B W2
0x045C W2 Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x045D W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x045E W2
0x045F W2 Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0460 W2 Reserved
0x0461
0x0462 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0463 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0464 W2
0x0465 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0466 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
DPLL_0 Settings for Reference Input D
0x0467
0x0469 W2 Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x046A W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x046B W2
0x046C W2 Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x046D W2 Reserved
0x046E
0x046F Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0470 Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0471 W2
0x0472 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0473 W2 Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[23:16] 0x00
DPLL_1 General Settings
0x0500
0x0501 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[15:8] 0x15
0x0502 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[23:16] 0x64
0x0503 Reserved 30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[29:24] 0x1B
0x0504
0x0505
0x0506 Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[15:8] 0xB8
0x0507 Reserved Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[19:16] 0x02
0x0508 Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[7:0] 0x3E
0x0509 Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[15:8] 0x0A
0x050A Reserved Upper limit of pull-in range, Bits[19:16] 0x0B
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reference
priority
DPLL_0
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_0
N0 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Reference
priority
DPLL_0
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_0
N0 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_0
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
DPLL_1
free run
frequency
TW
DCO_1
control
DPLL_1
frequency
clamp
Reserved REFC priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_0 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[7:0] 0x05
Reserved REFD priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider—Integer Part N0, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL fractional feedback divider—FRAC0, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL feedback divider modulus—MOD0, Bits[7:0] 0x05
30-bit free running frequency tuning word, Bits[7:0] 0x12
Reserved Digital oscillator SDM integer part, Bits[3:0] 0x08
Lower limit of pull-in range, Bits[7:0] 0x51
Rev. 0 | Page 64 of 120
Enable
REFC
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N0,
Bit 16
Enable
REFD
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N0,
Bit 16
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Page 65

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0522
APLL_1 loop filter control, Bits[7:0]
0x07
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x050B
0x050C History accumulation timer (ms), Bits[15:8] (up to 65 sec] 0x00
0x050D
0x050E
0x050F Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0510 Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0511 Reserved Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[29:24] 0x00
0x0512 Incremental phase offset step size (ps/step), Bits[7:0] (up to 65.5 ns/step) 0x00
0x0513 Incremental phase offset step size (ps/step), Bits[15:8] (up to 65.5 ns/step) 0x00
0x0514
0x0515 Phase slew rate Limit (µs/sec), Bits[15:8] (315 µs/sec up to 65.536 ms/sec) 0x00
Output PLL_1 (APLL_1) and Channel 1 Output Drivers
0x0520
0x0521
0x0523 Reserved
0x0524 P1 divider Reserved P1 divider divide ratio, Bits[3:0] 0x04
0x0525 OUT1 sync Reserved
0x0526 Reserved
0x0527 OUT1A Reserved OUT1A format, Bits[2:0] OUT1A polarity, Bits[1:0]
0x0528 Q1_A divider, Bits[7:0] 0x00
0x0529 Reserved Q1_A divider, Bits[9:8] 0x00
0x052A Reserved Q1_A divider phase, Bits[5:0] 0x00
0x052B OUT1B
0x052C Q1_B divider, Bits[7:0] 0x03
0x052D Reserved Q1_B divider, Bits[9:8] 0x00
0x052E Reserved Q1_B divider phase, Bits[5:0] 0x00
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input C
0x0540
0x0541 W2
0x0542 W2 Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x0543 W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x0544 W2
0x0545 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0546 W2 Reserved
0x0547
0x0548 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0549 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DPLL_1
holdover
history
DPLL_1
history
mode
DPLL_1
closed loop
phase
offset
[±0.5 ms]
DPLL_1
phase
slew limit
APLL _1
charge
pump
APLL_1
M1 divider
APLL_1
loop filter
control
Reference
priority
DPLL_1
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_1
N1 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
Reserved
Enable 3.3 V
CMOS driver
History accumulation timer (ms), Bits[7:0] (up to 65 sec) 0x0A
Single
sample
fallback
Fixed phase offset (signed; ps), Bits[7:0] 0x00
Phase slew rate limit (µs/sec), Bits[7:0] (315 µs/sec up to 65.536 ms/sec) 0x00
Output PLL1 (APLL_1) charge pump current, Bits[7:0] 0x81
Output PLL0 (APLL_1) feedback (M1) divider, Bits[7:0] 0x14
OUT1B format, Bits[2:0] OUT1B polarity, Bits[1:0]
Reserved REFC priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Persistent
history
Sync source
selection
APLL_1
locked
controlled
sync disable
Incremental average 0x00
Bypass
internal
Rzero
Auto sync mode 0x00
Mask
OUT1B
sync
OUT1A
LVDS boost
OUT1B
LVDS boost
Mask
OUT1A
sync
Reserved 0x10
Reserved 0x10
Enable
REFC
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N1,
Bit 16
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x01
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 65 of 120
Page 66

AD9559 Data Sheet
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x054A W2
0x054B W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x054C W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input D
0x054D
0x054E W2
0x054F W2 Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x0550 W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x0551 W2
0x0552 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0553 W2 Reserved
0x0554
0x0555 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0556 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0557 W2
0x0558 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0559 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input A
0x055A
0x055B W2
0x055C W2 Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x055D W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x055E W2
0x055F W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x0560 W2 Reserved
0x0561
0x0562 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0563 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0564 W2
0x0565 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0566 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Reference
priority
DPLL_1
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_1
N1 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Reference
priority
DPLL_1
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_1
N1 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[7:0] 0x05
Reserved REFD priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[7:0] 0x05
Reserved REFA priority, Bits[1:0]
Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[7:0] 0x05
Enable
REFD
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N1,
Bit 16
Enable
REFA
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N1,
Bit 16
Def
(Hex)
0x01
0x00
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 66 of 120
Page 67

Data Sheet AD9559
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
DPLL_1 Settings for Reference Input B
0x0567
0x0568 W2
0x0569 W2 Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[15:8] 0x01
0x056A W2 Reserved Base filter Reserved 0x00
0x056B W2
0x056C W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[15:8] 0x07
0x056D W2 Reserved
0x056E
0x056F Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0570 Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
0x0571 W2
0x0572 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[15:8] 0x00
0x0573 W2 Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[23:16] 0x00
Loop Filters
0x0800 L
0x0801 L NPM Alpha-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0x8C
0x0802 L Reserved NPM Alpha-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x49
0x0803 L NPM Beta-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0x55
0x0804 L NPM Beta-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xC9
0x0805 L Reserved NPM Beta-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x7B
0x0806 L NPM Gamma-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0x9C
0x0807 L NPM Gamma-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xFA
0x0808 L Reserved NPM Gamma-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x55
0x0809 L NPM Delta-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0xEA
0x080A L NPM Delta-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xE2
0x080B L Reserved NPM Delta-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x57
0x080C L
0x080D L HPM Alpha-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xAD
0x080E L Reserved HPM Alpha-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x4C
0x080F L HPM Beta-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0xF5
0x0810 L HPM Beta-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xCB
0x0811 L Reserved HPM Beta-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x73
0x0812 L HPM Gamma-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0x24
0x0813 L HPM Gamma-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0xD8
0x0814 L Reserved HPM Gamma-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x59
0x0815 L HPM Delta-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0xD2
0x0816 L HPM Delta-0 linear, Bits[15:8] 0x8D
0x0817 L Reserved HPM Delta-1 exponent, Bits[6:0] 0x5A
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reference
priority
DPLL_1
loop BW
(16 bits)
DPLL_1
N1 divider
(17 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
(24 bits)
DPLL_1
fractional
feedback
divider
modulus
(24 bits)
Base
loop filter
coefficient
set
(normal
phase
margin
of 70°)
Base loop
filter
coefficient
set (high
phase
margin)
Reserved REFB priority [1:0]
Digital PLL_1 loop BW scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x01F4 = 50 Hz) 0xF4
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider—Integer Part N1, Bits[7:0] 0xCB
Digital PLL_1 fractional feedback divider—FRAC1, Bits[7:0] 0x04
Digital PLL_1 feedback divider modulus—MOD1, Bits[7:0] 0x05
NPM Alpha-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0x24
HPM Alpha-0 linear, Bits[7:0] 0x8C
Enable
REFB
Digital
PLL
feedback
divider—
Integer
Part N1,
Bit 16
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 67 of 120
Page 68

AD9559 Data Sheet
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
Common Operational Controls
0x0A00 L Global Reserved Soft sync all Calibrate all
0x0A01
0x0A02 A Reserved
0x0A03 Reserved REFD fault REFC fault REFB fault REFA fault 0x00
0x0A04 Reserved
0x0A05 A
0x0A06 A
0x0A07 A Reserved
0x0A08 A Reserved
0x0A09 A
0x0A0A A
0x0A0B A Reserved
0x0A0C A
0x0A0D A
0x0A0E A Reserved
PLL_0 Operational Controls
0x0A20
0x0A21
0x0A22
0x0A23 A
0x0A24 A
PLL_1 Operational Controls
0x0A40
0x0A41
0x0A42
0x0A43 A
0x0A44 A
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Powerdown all
Reference
inputs
Clear IRQ
groups
Clear
common
IRQ
Clear
DPLL_0 IRQ
Clear
DPLL_1 IRQ
PLL_0
sync cal
PLL_0
output
PLL_0
user mode
PLL_0
reset
PLL_0
phase
PLL_1
sync cal
PLL_1
output
PLL_1
user mode
PLL_1
reset
PLL_1
phase
Clear
watchdog
timer
Reserved
Frequency
unclamped
DPLL_0
switching
Frequency
unclamped
DPLL_1
switching
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
SYSCLK
unlocked
REFB
validated
REFD
validated
Frequency
clamped
DPLL_0 free
run
Frequency
clamped
DPLL_1
free run
manual reference, Bits[1:0]
manual reference, Bits[1:0]
SYSCLK
stable
REFB fault
cleared
REFD fault
cleared
Phase slew
unlimited
DPLL_0
holdover
Phase slew
unlimited
DPLL_1
holdover
Reserved
Reserved
DPLL_0
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
DPLL_1
Reserved
Reserved
Rev. 0 | Page 68 of 120
REFD powerdown
REFD
timeout
REFD
monitor
bypass
Clear
DPLL_1
IRQs
SYSCLK
locked
REFB fault Reserved
REFD fault Reserved
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Clock dist
sync’d
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Clock dist
sync’d
Watchdog
timer
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_0
unlocked
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_1
unlocked
OUT0B
disable
DPLL_0
switching mode, Bits[2:0]
OUT1B
disable
DPLL_1
switching mode, Bits[2:0]
REFC powerdown
REFC
timeout
REFC
monitor
bypass
Clear
DPLL_0
IRQs
Reserved
REFA
validated
REFC
validated
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_0
locked
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_1
locked
APLL_0 soft
sync
OUT0A
disable
Reset
DPLL_0
loop filter
DPLL_0
reset phase
offset
APLL_1 soft
sync
OUT1A
disable
Reset
DPLL_1
loop filter
DPLL_1
reset phase
offset
REFB powerdown
REFB
timeout
REFB
monitor
bypass
Clear
common
IRQs
EEPROM
fault
REFA fault
cleared
REFC fault
cleared
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_0
cal ended
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_1
cal ended
APLL_0
calibrate
(no self clear)
OUT0B
powerdown
DPLL_0 user
holdover
Reset
DPLL_0
TW history
DPLL_0
decrement
phase offset
APLL_1
calibrate
(no self clear)
OUT1B
powerdown
DPLL_1 user
holdover
Reset
DPLL_1 TW
history
DPLL_1
decrement
phase offset
REFA
powerdown
REFA
timeout
REFA
monitor
bypass
Clear
all IRQs
EEPROM
complete
REFA fault 0x00
REFC fault 0x00
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_0
cal started
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_1
cal started
PLL_0
powerdown
OUT0A
powerdown
DPLL_0
user free
run
Reset
DPLL_0
auto sync
DPLL_0
increment
phase
offset
PLL_1
powerdown
OUT1A
powerdown
DPLL_1
user free
run
Reset
DPLL_1
auto sync
DPLL_1
increment
phase
offset
Def
(Hex)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Page 69

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0D0C
R
N/A
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
Read-Only Status Common Blocks (These registers are accessible during EEPROM transactions.
To show the latest status, Register 0x0D02 to Register 0x0D05 require an IO_UPDATE before being read.)
0x0D00 R, L EEPROM Reserved
0x0D01 R, L
0x0D02 R, L
0x0D03 R, L Reserved
0x0D04 R, L Reserved
0x0D05 R, L Reserved
0x0D06 R, L Reserved N/A
0x0D07 R, L Reserved N/A
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SYSCLK
and PLL
status
Reference
status
Reserved
Reserved
DPLL_1
REFA active
DPLL_1
REFB active
DPLL_1
REFC active
DPLL_1
REFD active
DPLL_0
REFA active
DPLL_0
REFB active
DPLL_0
REFC active
DPLL_0
REFD active
EEPROM
fault
detected
PLL_1
all locked
REFA valid REFA fault REFA fast REFA slow N/A
REFB valid REFB fault REFB fast REFB slow N/A
REFC valid REFC fault REFC fast REFC slow N/A
REFD valid REFD fault REFD fast REFD slow N/A
PLL_0
all locked
EEPROM
load in
progress
SYSCLK
stable
EEPROM
save in
progress
SYSCLK
lock
detect
Def
(Hex)
N/A
N/A
IRQ Monitor
0x0D08 R
0x0D09 R Reserved
0x0D0A R Reserved
0x0D0B R
0x0D0D R Reserved
0x0D0E R
0x0D0F R
0x0D10 R Reserved
PLL_0 Read-Only Status (To show the latest status, these registers require an IO_UPDATE before being read.)
0x0D20 R, L
0x0D21 R
0x0D22 R, L Reserved
0x0D23 R
0x0D24 R DPLL_0 tuning word readback, Bits[15:8] N/A
0x0D25 R DPLL_0 tuning word readback, Bits[23:16] N/A
0x0D26 R Reserved DPLL_0 tuning word readback, Bits[29:24] N/A
0x0D27 R
0x0D28 R Reserved DPLL_0 phase lock detect bucket level, Bits[11:8] N/A
0x0D29 R
0x0D2A R Reserved DPLL_0 frequency lock detect bucket level, Bits[11:8] N/A
IRQ,
common
IRQ,
DPLL_0
IRQ,
DPLL_1
PLL_0
lock status
DPLL_0
loop state
DPLL_0
holdover
history
DPLL_0
phase lock
detect
bucket
DPLL_0
frequency
lock detect
bucket
Reserved
Frequency
unclamped
DPLL_0
switching
Frequency
unclamped
DPLL_1
switching
SYSCLK
unlocked
REFB
validated
REFD
validated
Frequency
clamped
DPLL_0 free
run
Frequency
clamped
DPLL_1 free
run
Reserved
Reserved DPLL_0 active ref, Bits[1:0]
SYSCLK
stable
REFB fault
cleared
REFD fault
cleared
Phase slew
unlimited
DPLL_0
holdover
Phase slew
unlimited
DPLL_1
holdover
DPLL_0 phase lock detect bucket level, Bits[7:0] N/A
DPLL_0 frequency lock detect bucket level, Bits[7:0] N/A
SYSCLK
locked
REFB fault Reserved
REFD fault Reserved
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Clock dist
sync’d
Phase slew
limited
History
updated
Clock dist
sync’d
APLL_0 cal
in progress
DPLL_0 tuning word readback, Bits[7:0] N/A
Watchdog
timer
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_0
unlocked
Frequency
unlocked
REFD
activated
APLL_1
unlocked
APLL_0
locked
Reserved
REFA
validated
REFC
validated
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_0
locked
Frequency
locked
REFC
activated
APLL_1
locked
DPLL_0 freq
lock
DPLL_0
switching
DPLL_0
phase slew
limited
EEPROM
fault
REFA fault
cleared
REFC fault
cleared
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_0
cal ended
Phase
unlocked
REFB
activated
APLL_1
cal ended
DPLL_0
phase Lock
DPLL_0
holdover
DPLL_0
frequency
clamped
EEPROM
complete
REFA fault N/A
REFC fault N/A
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_0
cal started
Phase
locked
REFA
activated
APLL_1
cal started
PLL_0
all locked
DPLL_0
free run
DPLL_0
history
available
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Rev. 0 | Page 69 of 120
Page 70

AD9559 Data Sheet
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
PLL_1 Read-Only Status (To show the latest status, these registers require an IO_UPDATE before being read.)
0x0D40 R, L
0x0D41 R
0x0D42 R, L Reserved
0x0D43 R
0x0D44 R DPLL_1 tuning word readback, Bits[15:8] N/A
0x0D45 R DPLL_1 tuning word readback, Bits[23:16] N/A
0x0D46 R Reserved DPLL_1 tuning word readback, Bits[29:24] N/A
0x0D47 R
0x0D48 R Reserved DPLL_1 phase lock detect bucket level, Bits[11:8] N/A
0x0D49 R
0x0D4A R Reserved DPLL_1 frequency lock detect bucket level, Bits[11:8] N/A
Nonvolatile Memory (EEPROM) Control
0x0E00 E
0x0E01 E Condition Reserved Conditional value, Bits[3:0] 0x00
0x0E02 A, E Save Reserved
0x0E03 A, E Load Reserved
EEPROM Storage Sequence
0x0E10
0x0E11
0x0E12 Starting Address 0x000E 0x00
0x0E13 0x0E
0x0E14
0x0E15 Starting Address 0x0100 0x01
0x0E16 0x00
0x0E17
0x0E18 Starting Address 0x0200 0x02
0x0E19 0x00
0x0E1A IO_UPDATE Command: IO_UPDATE 0x80
0x0E1B REFA Size of transfer: 27 bytes 0x1A
0x0E1C Starting Address 0x0300 0x03
0x0E1D 0x00
0x0E1E REFB Size of transfer: 27 bytes 0x1A
0x0E1F Starting Address 0x0320 0x03
0x0E20 0x20
0x0E21 REFC Size of transfer: 27 bytes 0x1A
0x0E22 Starting Address 0x0340 0x03
0x0E23 0x40
0x0E24 REFD Size of transfer: 27 bytes 0x1A
0x0E25 Starting Address 0x0360 0x03
0x0E26 0x60
0x0E27
0x0E28 Starting Address 0x0400 0x04
0x0E29 0x00
0x0E2A
0x0E2B Starting Address 0x0420 0x04
0x0E2C 0x20
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PLL_1
lock status
DPLL_1
loop state
DPLL_1
holdover
history
DPLL_1
phase lock
detect
bucket
DPLL_1
frequency
lock detect
bucket
Write
protect
User free
run
User
scratchpad
M pins and
IRQ masks
System
clock
DPLL_0
general
settings
APLL_0
config and
output
drivers
Reserved
Reserved DPLL_1 active ref, Bits[1:0]
DPLL_1 phase lock detect bucket level, Bits[7:0] N/A
DPLL_1 frequency lock detect bucket level, Bits[7:0] N/A
APLL_1 cal
in progress
DPLL_1 tuning word readback, Bits[7:0] N/A
Reserved
Command: Set user free run mode 0x98
Size of transfer: two bytes 0x01
Size of transfer: 19 bytes 0x12
Size of transfer: eight bytes 0x07
Size of transfer: 22 bytes 0x15
Size of transfer: 15 bytes 0x0E
APLL_1
locked
DPLL_1 freq
lock
DPLL_1
switching
DPLL_1
phase slew
limited
DPLL_1
phase lock
DPLL_1
holdover
DPLL_1
frequency
clamped
PLL_1
all locked
DPLL_1
free run
DPLL_1
history
available
Write
enable
Save to
EEPROM
Load from
EEPROM
Def
(Hex)
N/A
N/A
N/A
0x00
0x00
0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 70 of 120
Page 71

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0E37
Starting Address 0x0540
0x05
0x0E38
0x40
0x0E39
Loop filter
Size of transfer: 24 bytes
0x17
0x0E3B
0x00
0x0E3C
Size of transfer: 15 bytes
0x0E
Reg
Addr
(Hex)
0x0E2D
0x0E2E Starting Address 0x0440 0x04
0x0E2F 0x40
0x0E30
0x0E31 Starting Address 0x0500 0x05
0x0E32 0x00
0x0E33
0x0E34 Starting Address 0x0520 0x05
0x0E35 0x20
0x0E36
0x0E3A Starting Address 0x0800 0x08
0x0E3D Starting Address 0x0A00 0x0A
0x0E3E 0x00
0x0E3F
0x0E40 Starting Address 0x0A20 0x0A
0x0E41 0x20
0x0E42
0x0E43 Starting Address 0x0A40 0x0A
0x0E44 0x40
0x0E45 IO_UPDATE Command: IO_UPDATE 0x80
0x0E46
0x0E47
0x0E48 End of data Command: end of data 0xFF
0x0E49
to
0x0E4F
Opt Name D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
DPLL_0
dividers
and BW
DPLL_1
general
settings
APLL_1
config and
output
drivers
DPLL_1
dividers
and BW
Common
operational
controls
PLL_0
operational
controls
PLL_1
operational
controls
Calibrate
APLLs
Sync
outputs
Unused Unused (available for additional data transfers and/or commands) 0x00
Size of transfer: 52 bytes 0x33
Size of transfer: 22 bytes 0x15
Size of transfer: 15 bytes 0x0E
Size of transfer: 52 bytes 0x33
Size of transfer: five bytes 0x04
Size of transfer: five bytes 0x04
Command: calibrate output PLLs 0x90
Command: distribution sync 0xA0
Def
(Hex)
Rev. 0 | Page 71 of 120
Page 72

AD9559 Data Sheet
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
0x000C
[7:0]
Clock part family ID, Bits[7:0]
REGISTER MAP BIT DESCRIPTIONS
SERIAL CONTROL PORT CONFIGURATION (REGISTER 0x0000 TO REGISTER 0x0005)
Table 35. Serial Configuration (Note that the contents of Register 0x0000 are not stored to the EEPROM.)
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0000
Table 36. Readback Control
0x0004 [7:5] Reserved Default: 0x00.
7 SDO enable Enables SPI port SDO pin.
1 = 4-wire (SDO pin enabled).
0 (default) = 3-wire.
6 LSB first/increment address Bit order for SPI port.
1 = least significant bit and byte first.
Register addresses are automatically incremented in multibyte transfers.
0 (default) = most significant bit and byte first.
Register addresses are automatically decremented in multibyte transfers.
5 Soft reset
Device reset (invokes an EEPROM download if EEPROM or pin program is enabled.)
See the EEPROM and Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions sections for details.
[4:0] Reserved Default: 0x00.
4 Reset sans reg map Resets the part while maintaining the current register settings.
1 = resets the device.
0 (default) = no action.
Disable auto actions Disables the automatic updating of DPLL parameters.
3
1 = disables the automatic register write detection functions described in Table 32.
0 (default) = the live registers in the DPLL profile registers update immediately.
Reserved Default: 0x00.
2
1
2-wire SPI
Enables 2-wire SPI mode, in which the ACS
E
A
pin state is ignored. Note that the ACS
high function is not available in this mode and that the correct number of clock edges
must be present on the SCLK pin during a transfer.
1 = ignores the state of the ACS
control/status of the
AD9559.
E
A
pin, making the M5/ACS
E
A
pin available as an M pin for
0 (default) = normal SPI operation.
0
Read buffer register
For buffered registers, serial port readback reads from actual (active) registers instead of
the buffer.
1 = reads buffered values that take effect on next assertion of IO_UPDATE.
0 (default) = reads values currently applied to the device’s internal logic.
E
A
stalled
Table 37. Soft IO_UPDATE
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0005 [7:1] Reserved Reserved.
0
CLOCK PART FAMILY ID (REGISTER 0x000C AND REGISTER 0x000D)
Table 38. Clock Part Family ID
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x000D
[7:0] Clock part family ID, Bits[15:8] Default: 0x00 for the AD9559.
IO_UPDATE
Writing a 1 to this bit transfers the data in the serial I/O buffer registers to the device’s
internal control registers. This is an autoclearing bit.
The values in this read-only register and Register 0x000D uniquely identify the AD9559.
This is useful in cases where the user’s software must determine which device is located
at a given I²C address.
Default: 0x02 for the AD9559.
Rev. 0 | Page 72 of 120
Page 73

Data Sheet AD9559
0x000E
[7:0]
User scratchpad, Bits[7:0]
User programmable EEPROM ID registers. These registers enable users to write a unique
0x0106
7
M4 output/AinputE
Input/output control for M3 pin (same as for the M0 pin).
0x0108
[7:0]
USER SCRATCHPAD (REGISTER 0x000E AND REGISTER 0x000F)
Table 39. User Scratchpad
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x000F [7:0] User scratchpad, Bits[15:8]
code of their choosing to keep track of revisions to the EEPROM register loading. It has no
effect on part operation.
Default = 0x0000.
GENERAL CONFIGURATION (REGISTER 0x0100 TO REGISTER 0x0109)
Multifunction Pin Control (M0 to M5) and Watchdog Timer
Table 40. Multifunction Pins (M0 to M5) Control
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0100 [7:6] M3 driver mode, Bits[1:0] 00 (default) = active high CMOS.
01 = active low CMOS.
10 = open-drain PMOS (requires an external pull-down resistor).
11 = open-drain NMOS (requires an external pull-up resistor).
M2 driver mode, Bits[1:0] The settings of these bits are identical to Register 0x0100[7:6].
[5:4]
M1 driver mode, Bits[1:0] The settings of these bits are identical to Register 0x0100[7:6].
[3:2]
M0 driver mode, Bits[1:0] The settings of these bits are identical to Register 0x0100[7:6].
[1:0]
0x0101
0x0102
0x0103
0x0104
0x0105
[7:4] Reserved Reserved.
[3:2]
M5 driver mode, Bits[1:0]
M4 driver mode, Bits[1:0]
[1:0]
7
M0 output/AinputE
M0 function
[6:0]
7
M1 output/AinputE
[6:0]
M1 function
7
M2 output/AinputE
M2 function
[6:0]
7
M3 output/AinputE
[6:0] M3 function
The settings of these bits are identical to Register 0x0100[7:6]. Note that, for this pin to be
an M pin, either I²C or 2-wire SPI mode must be enabled.
The settings of these bits are identical to Register 0x0100[7:6].
Note that, for this pin to be an M pin, 4-wire SPI mode must be disabled.
Input/output control for M0 pin.
0 (default) = input (control pin)
1 = output (status pin)
These bits control the function of the M0 pin. See Table 196 and Table 197 for details
about the input and output functions that are available.
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
Input/output control for M1 pin (same as for the M0 pin).
These bits control the function of the M1 pin and are the same as Register 0x0102[6:0].
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
Input/output control for M2 pin (same as for the M0 pin).
These bits control the function of the M2 pin and are the same as Register 0x0102[6:0].
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
Input/output control for M3 pin (same as for the M0 pin).
These bits control the function of the M3 pin and are the same as Register 0x0102[6:0].
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
[6:0] M4 function
0x0107 7
0x0109
M5 output/AinputE
[6:0] M5 function
Watchdog timer
(in units of ms)
[7:0]
These bits control the function of the M4 pin and are the same as Register 0x0102[6:0].
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
Input/output control for M3 pin (same as for the M0 pin).
These bits control the function of the M5 pin and are the same as Register 0x0102[6:0].
Default: 0x00 = high impedance control pin, no function assigned.
Watchdog timer, Bits[7:0]. The watchdog timer stops when this register is written, and
restarts on the next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Default: 0x00 (0x0000 = disabled).
Watchdog timer, Bits[15:8]. The watchdog timer stops when this register is written, and
restarts on the next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Default: 0x00.
Rev. 0 | Page 73 of 120
Page 74
AD9559 Data Sheet
6
SYSCLK unlocked
Enables IRQ for indicating a SYSCLK PLL state transition from locked to unlocked.
IRQ MASK (REGISTER 0x010A TO REGISTER 0x112)
The IRQ mask register bits form a one-to-one correspondence with the bits of the IRQ monitor register (0x0D08 to 0x0D10). When set to
Logic 1, the IRQ mask bits enable the corresponding IRQ monitor bits to indicate an IRQ event. The default for all IRQ mask bits is Logic 0,
which prevents the IRQ monitor from detecting any internal interrupts.
Table 41. IRQ Mask for SYSCLK, Watchdog Timer, and EEPROM
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x010A
7 Reserved Reserved.
5 SYSCLK stable
SYSCLK locked Enables IRQ for indicating a SYSCLK PLL state transition from unlocked to locked.
4
3
Watchdog timer Enables IRQ for indicating expiration of the watchdog timer.
Reserved Reserved.
2
EEPROM fault Enables IRQ for indicating a fault during an EEPROM load or save operation.
1
0
EEPROM complete Enables IRQ for indicating successful completion of an EEPROM load or save operation.
Enables IRQ for indicating that SYSCLK stability time has expired and that the SYSCLK PLL is
considered to be stable.
Table 42. IRQ Mask for Reference Inputs
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x010B
0x010C
7 Reserved Reserved.
REFB validated Enables IRQ for indicating that REFB has been validated.
6
REFB fault cleared Enables IRQ for indicating that REFB has been cleared of a previous fault.
5
4
REFB fault Enables IRQ for indicating that REFB has been faulted.
Reserved Reserved.
3
REFA validated Enables IRQ for indicating that REFA has been validated.
2
1
REFA fault cleared Enables IRQ for indicating that REFA has been cleared of a previous fault.
REFA fault Enables IRQ for indicating that REFA has been faulted.
0
7 Reserved Reserved.
REFD validated Enables IRQ for indicating that REFD has been validated.
6
5
REFD fault cleared Enables IRQ for indicating that REFD has been cleared of a previous fault.
REFD fault Enables IRQ for indicating that REFD has been faulted.
4
Reserved Reserved.
3
2
REFC validated Enables IRQ for indicating that REFC has been validated.
REFC fault cleared Enables IRQ for indicating that REFC has been cleared of a previous fault.
1
REFC fault Enables IRQ for indicating that REFC has been faulted.
0
Rev. 0 | Page 74 of 120
Page 75

Data Sheet AD9559
6
Frequency clamped
Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has entered a frequency clamped state
1
APLL_0 cal complete
Enables IRQ for APLL_0 calibration complete
3
APLL_1 unlocked
Enables IRQ for APLL_1 unlocked
0
APLL_1 cal started
Enables IRQ for APLL_1 calibration started
Table 43. IRQ Mask for the Digital PLL0 (DPLL_0)
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x010D 7 Frequency unclamped Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has exited a frequency clamped state
5 Phase slew unlimited Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has exited a phase slew limited state
Phase slew limited Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has entered a phase slew limited state
4
3
Frequency unlocked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has lost frequency lock
Frequency locked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has acquired frequency lock
2
Phase unlocked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has lost phase lock
1
0
Phase locked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has acquired phase lock
0x010E
0x010F
7 Switching Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 is switching to a new reference
Free run Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has entered free run mode
6
5
Holdover Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has entered holdover mode
History updated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has updated its tuning word history
4
REFD activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has activated REFD
3
REFC activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has activated REFC
2
1
REFB activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has activated REFB
REFA activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_0 has activated REFA
0
[7:5] Reserved Reserved
4
Sync clock distribution Enables IRQ for indicating a distribution sync event
APLL_0 unlocked Enables IRQ for APLL_0 unlocked
3
APLL_0 locked Enables IRQ for APLL_0 locked
2
0 APLL_0 cal started Enables IRQ for APLL_0 calibration started
Table 44. IRQ Mask for the Digital PLL1 (DPLL_1)
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0110
0x0111
0x0112
7 Frequency unclamped Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has exited a frequency clamped state
Frequency clamped Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has entered a frequency clamped state
6
5
Phase slew unlimited Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has exited a phase slew limited state
Phase slew limited Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has entered a phase slew limited state
4
Frequency unlocked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has lost frequency lock
3
Frequency locked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has acquired frequency lock
2
1
Phase unlocked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has lost phase lock
Phase locked Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has acquired phase lock
0
7 Switching Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 is switching to a new reference
6
Free run Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has entered free run mode
Holdover Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has entered holdover mode
5
History updated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has updated its tuning word history
4
3
REFD activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has activated REFD
REFC activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has activated REFC
2
REFB activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has activated REFB
1
0
REFA activated Enables IRQ to indicate that DPLL_1 has activated REFA
[7:5] Reserved Reserved
Sync clock distribution Enables IRQ for indicating a distribution sync event
4
2 APLL_1 locked Enables IRQ for APLL_1 locked
APLL_1 cal complete Enables IRQ for APLL_1 calibration complete
1
Rev. 0 | Page 75 of 120
Page 76

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0200
[7:0]
System clock K divider
System clock PLL feedback divider value = 4 ≤ K ≤ 255 (default: 0x08).
0x0202
[7:0]
Nominal system clock period (fs)
System clock period, Bits[7:0]. This is the period of the system clock.
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
[3:0]
System clock stability period
SYSTEM CLOCK (REGISTER 0x0200 TO REGISTER 0x0207)
Table 45. System Clock PLL Feedback Divider (K Divider) and Configuration
Address Bits Bit Name Description
Table 46. SYSCLK Configuration
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0201
Table 47. Nominal System Clock Period
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[7:4] Reserved Reserved.
SYSCLK XTAL enable Enables the crystal maintaining amplifier for the system clock input.
4
1 (default) = crystal mode (crystal maintaining amplifier enabled).
0 = external crystal oscillator or other system clock source.
SYSCLK J1 divider System clock input divider.
[2:1]
00 (default) = 1.
01 = 2.
10 = 4.
11 = 8.
0
SYSCLK doubler enable
(J0 divider)
Enables the clock doubler on system clock input to reduce noise. Setting this bit
may prevent the SYSCLK PLL from locking if the input duty cycle is not close
enough to 50%. See Table 4 for the limits on duty cycle.
0 = disable.
1 (default) = enable.
0x0203
0x0204
[7:0]
[7:5] Reserved Default: 0x13.
Nominal system clock period (fs)
[4:0]
Table 48. System Clock Stability Period
0x0205 [7:0] System clock stability period (ms)
0x0206
0x0207
[7:0]
[7:5] Reserved Default: 0x0.
Default: 0x0E. [The default of 0x13670E = 1.271566 ns = 16 × (1/49.152 MHz).]
System clock period, Bits[15:8].
Default: 0x67.
System clock period, Bits[20:16].
Default: 0x13.
System clock period, Bits[7:0]. The system clock stability period is the amount of
time that the system clock PLL must be locked before it is declared stable. The system
clock stability timer is reset automatically if the user writes to this register. The
system clock stability timer restarts on the next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Default: 0x32 (0x000032 = 50 ms).
System clock period, Bits[15:8]. The system clock stability timer is reset
automatically if the user writes to this register. The system clock stability timer
restarts on the next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Default: 0x00.
System clock period, Bits[19:16]. The system clock stability timer is reset
automatically if the user writes to this register. The system clock stability timer
restarts on the next IO_UPDATE (Register 0x0005 = 0x01).
Default: 0x0.
Rev. 0 | Page 76 of 120
Page 77

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0300
[7:4]
Reserved
Default: 0x0
REFERENCE INPUT A (REGISTER 0x0300 TO REGISTER 0x031A)
Table 49. REFA Logic Type
Address Bits Bit Name Description
3 Enable REFA divide-by-2 Enables the reference input divide-by-2 for REFA
0 = bypasses the divide-by-2 (default)
1 = enables the divide-by-2
Reserved Default: 0b
2
REFA logic type Selects logic family for REFA input receiver; only the REFA pin is used in CMOS mode
[1:0]
00 (default) = differential
01 = 1.2 V to 1.5 V CMOS
10 = 1.8 V to 2.5 V CMOS
11 = 3.0 V to 3.3 V CMOS
Table 50. REFA 20-Bit DPLL R Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0301 [7:0] R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCF)
0x0302
0x0303
Table 51. Nominal Period of REFA Input Clock
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0304 [7:0]
0x0305
0x0306
0x0307
0x0308
[7:0] DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[19:16] (default: 0x0)
[3:0]
REFA nominal
reference period (fs)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[15:8] (default: 0xEA)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x10)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[31:24] (default: 0x03)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[39:32] (default: 0x00)
Nominal reference period, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xC9)
Default for Register 0x0304 to Register 0x0308: 0x000310EAC9 = 51.44 ns (1/19.44 MHz).
Table 52. REFA Frequency Tolerance
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0309
0x030A
0x030B
0x030C
0x030D
0x030E
[7:0] Inner tolerance Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x14).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
[3:0]
Inner tolerance
[7:0] Outer tolerance Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
Outer tolerance
[3:0]
Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x0309 to Register 0x30B: 0x000014 = 20 (5% or 50,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm.
The allowable range for the inner tolerance is 0x00A (10%) to 0x8FF (2 ppm).
Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x030C to Register 0x30E = 0x00000A = 10 (10% or 100,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm. The outer tolerance must be greater than
the inner tolerance so that there is hysteresis.
Rev. 0 | Page 77 of 120
Page 78

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0319
[7:0]
Frequency lock fill rate
Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
0x0323
[7:4]
Reserved
Default: 0x0
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
Table 53. REFA Validation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x030F
0x0310
Table 54. REFA Lock Detectors
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0311
0x0312
0x0313
0x0314
0x0315
0x0316
0x0317
0x0318
0x031A [7:0] Frequency lock drain rate Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
REFERENCE INPUT B (REGISTER 0x0320 TO REGISTER 0x033A)
Table 55. REFB Logic Type
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0320
[7:0] Validation timer (ms)
[7:0] Validation timer, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:0] Phase lock threshold Phase lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Phase lock fill rate Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Phase lock drain rate Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
Enable REFB divide-by-2 Enables the reference input divide-by-2 for REFB
3
Reserved Default: 0b
2
REFB logic type Selects logic family for REFB input receiver; only the REFB pin is used in CMOS mode
[1:0]
Validation timer, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
This is the amount of time a reference input must be valid before it is declared valid by the
reference input monitor (default: 10 ms).
0 = bypasses the divide-by-2 (default)
1 = enables the divide-by-2
00 (default) = differential
01 = 1.2 V to 1.5 V CMOS
10 = 1.8 V to 2.5 V CMOS
11 = 3.0 V to 3.3 V CMOS
Table 56. REFB 20-Bit DPLL R Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0321 [7:0] R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCF)
0x0322
[7:0] DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[3:0] R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[19:16] (default: 0x0)
Table 57. Nominal Period of REFB Input Clock
0x0324 [7:0]
0x0325
0x0326
0x0327
0x0328
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[15:8] (default: 0xEA).
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x10).
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[31:24] (default: 0x03).
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[39:32] (default: 0x00).
REFB nominal
reference period (fs)
Nominal reference period, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xC9).
Default for Register 0x0324 to Register 0x0328: 0x000310EAC9 = 51.44 ns (1/19.44 MHz).
Rev. 0 | Page 78 of 120
Page 79
Data Sheet AD9559
0x032A
[7:0]
Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
Table 58. REFB Frequency Tolerance
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0329
0x032B [7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
0x032C
0x032D
0x032E
Table 59. REFB Validation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x032F
0x0330
[7:0] Inner tolerance Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x14)
Inner tolerance
[3:0]
[7:0] Outer tolerance Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
[3:0]
Outer tolerance
[7:0] Validation timer (ms)
[7:0] Validation timer, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x0329 to Register 0x032B: 0x000014 = 20 (5% or 50,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm.
The allowable range for the inner tolerance is 0x00A (10%) to 0x8FF (2 ppm).
Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x032C to Register 0x032E: 0x00000A = 10 (10% or 100,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm. The outer tolerance must be greater
than the inner tolerance so that there is hysteresis.
Validation timer, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
This is the amount of time a reference input must be valid before it is declared valid by the
reference input monitor (default: 10 ms).
Table 60. REFB Lock Detectors
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0331
0x0332
0x0333
0x0334
0x0335
0x0336
0x0337
0x0338
0x0339
0x033A
[7:0] Phase lock threshold Phase lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Phase lock fill rate Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Phase lock drain rate Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A=10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Frequency lock fill rate Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock drain rate Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
REFERENCE INPUT C (REGISTER 0x0340 TO REGISTER 0x035A)
Table 61. REFC Logic Type
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0340
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
Enable REFC divide-by-2 Enables the reference input divide-by-2 for REFC
3
0 = bypasses the divide-by-2 (default)
1 = enables the divide-by-2
Reserved Default: 0b
2
REFC logic type Selects logic family for REFC input receiver; only the REFC pin is used in CMOS mode
[1:0]
00 (default) = differential
01 = 1.2 V to 1.5 V CMOS
10 = 1.8 V to 2.5 V CMOS
11 = 3.0 V to 3.3 V CMOS
Rev. 0 | Page 79 of 120
Page 80
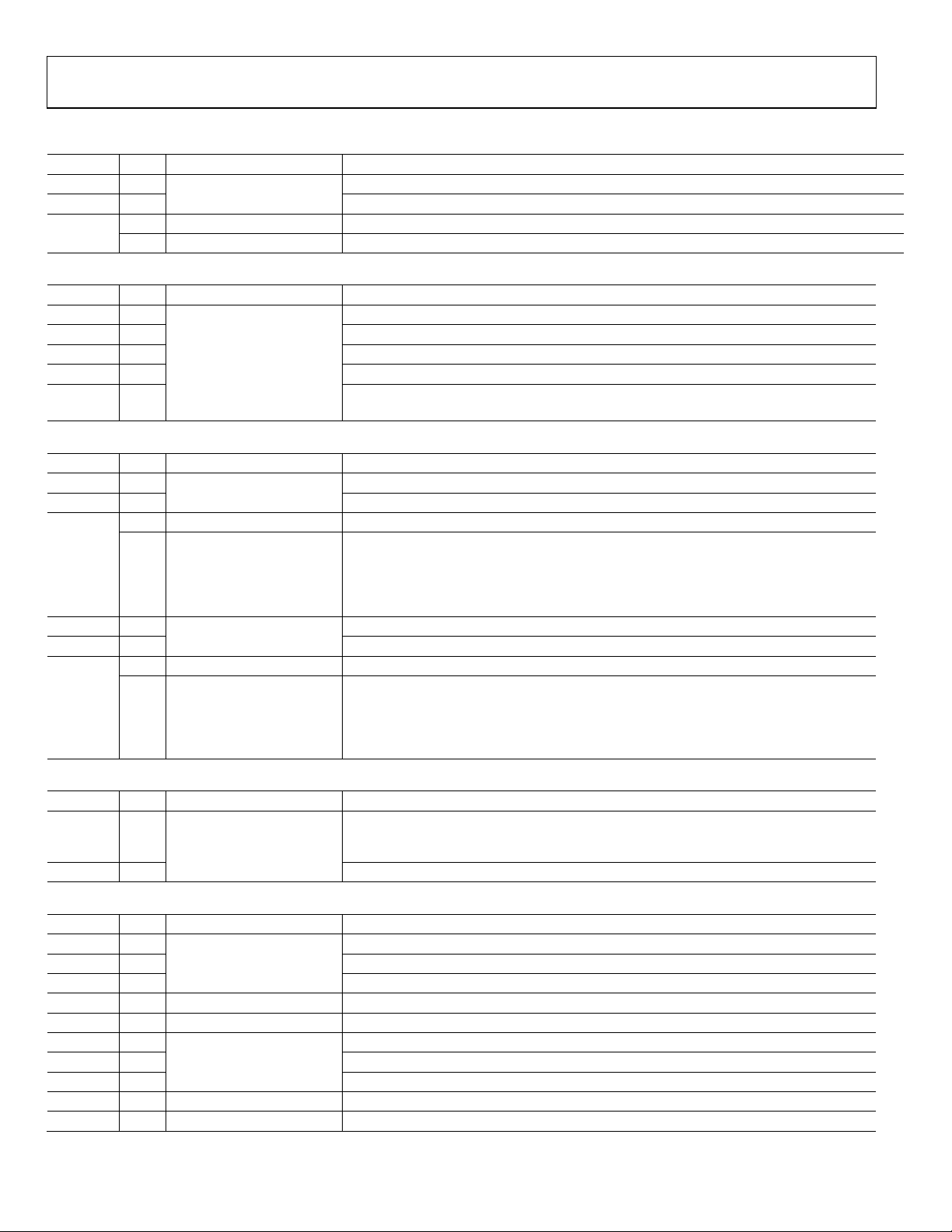
AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0342
[7:0]
DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x034C
[7:0]
Outer tolerance
Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits [7:0] (default: 0x0A).
[3:0]
Outer tolerance
0x0351
[7:0]
Phase lock threshold
Phase lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
Table 62. REFC 20-bit DPLL R Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0341 [7:0] R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCF)
0x0343 [7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
[3:0]
Table 63. Nominal Period of REFC Input Clock
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0344
0x0345
0x0346
0x0347
0x0348
[7:0]
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[15:8] (default: 0xEA)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x10)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[31:24] (default: 0x03)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[39:32] (default: 0x00)
Table 64. REFC Frequency Tolerance
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0349
0x034A
0x034B
[7:0] Inner tolerance Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x14).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
[3:0]
R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[19:16] (default: 0x0)
REFC nominal
reference period (fs)
Inner tolerance
Nominal reference period, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xC9)
Default for Register 0x0344 to Register 0x0348: 0x000310EAC9 = 51.44 ns (1/19.44 MHz)
Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x0349 to Register 0x034B: 0x000014 = 20 (5% or 50,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm.
The allowable range for the inner tolerance is 0x00A (10%) to 0x8FF (2 ppm).
0x034D [7:0] Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
0x034E
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x034C to Register 0x034E: 0x00000A = 10 (10% or 100,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm. The outer tolerance must be greater
than the inner tolerance so that there is hysteresis.
Table 65. REFC Validation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x034F
0x0350
[7:0] Validation timer (ms)
[7:0] Validation timer, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
Validation timer, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
This is the amount of time a reference input must be valid before it is declared valid by
the reference input monitor (default: 10 ms).
Table 66. REFC Lock Detectors
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0352 [7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
0x0353
0x0354
0x0355
0x0356
0x0357
0x0358
0x0359
0x035A
[7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Phase lock fill rate Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Phase lock drain rate Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Frequency lock fill rate Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock drain rate Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
Rev. 0 | Page 80 of 120
Page 81

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0360
[7:4]
Reserved
Default: 0x0
REFERENCE INPUT D (REGISTER 0x0360 TO REGISTER 0x037A)
Table 67. REFD Logic Type
Address Bits Bit Name Description
3 Enable REFD divide-by-2 Enables the reference input divide-by-2 for REFD
0 = bypasses the divide-by-2 (default)
1 = enables the divide-by-2
Reserved Default: 0b
2
REFD logic type Selects logic family for REFD input receiver; only the REFD pin is used in CMOS mode
[1:0]
00 (default) = differential
01 = 1.2 V to 1.5 V CMOS
10 = 1.8 V to 2.5 V CMOS
11 = 3.0 V to 3.3 V CMOS
Table 68. REFD 20-Bit DPLL R Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0361 [7:0] R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCF)
0x0362
0x0363
Table 69. Nominal Period of REFD Input Clock
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0364 [7:0]
0x0365
0x0366
0x0367
0x0368
[7:0] DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
R divider DPLL integer reference divider (minus 1), Bits[19:16] (default: 0x0)
[3:0]
REFD nominal
reference period (fs)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[15:8] (default: 0xEA)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x10)
[7:0] Nominal reference period, Bits[31:24] (default: 0x03)
[7:0] Nominal reference period Bits[39:32] (default: 0x00)
Nominal reference period, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xC9)
Default for Register 0x0364 to Register 0x0368: 0x000310EAC9 = 51.44 ns (1/19.44 MHz)
Table 70. REFD Frequency Tolerance
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0369
0x036A
0x036B
0x036C
0x036D
0x036E
[7:0] Inner tolerance Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x14).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
[3:0]
[7:0] Outer tolerance Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits [7:0] (default: 0x0A).
[7:0] Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0.
[3:0]
Inner tolerance
Outer tolerance
Input reference frequency monitor inner tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x0369 to Register 0x036B: 0x000014 = 20 (5% or 50,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires an outer tolerance of ±48 ppm.
The allowable range for the inner tolerance is 0x00A (10%) to 0x8FF (2 ppm).
Input reference frequency monitor outer tolerance, Bits[19:16].
Default for Register 0x036C to Register 0x036E: 0x00000A = 10 (10% or 100,000 ppm).
The Stratum 3 clock requires an inner tolerance of ±9.2 ppm and outer tolerance of ±12 ppm;
an SMC clock requires outer tolerance of ±48 ppm. The outer tolerance must be greater
than the inner tolerance so that there is hysteresis.
Table 71. REFD Validation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x036F
0x0370
[7:0] Validation timer (ms)
[7:0] Validation timer, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
Validation timer, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A).
This is the amount of time a reference input must be valid before it is declared valid by
the reference input monitor (default: 10 ms).
Rev. 0 | Page 81 of 120
Page 82

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0372
[7:0]
Phase lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
0x0375
[7:0]
Phase lock drain rate
Phase lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A=10 code/PFD cycle)
Table 72. REFD Lock Detectors
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0371
0x0373 [7:0] Phase lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
0x0374
0x0376 [7:0] Frequency lock threshold Frequency lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
0x0377
0x0378
0x0379
0x037A
DPLL_0 CONTROLS (REGISTER 0x0400 TO REGISTER 0x0415)
Table 73. DPLL_0 Free Run Frequency Tuning Word
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0400
0x0401
0x0402
0x0403
[7:0] Phase lock threshold Phase lock threshold, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xBC); default of 0x02BC = 700 ps
[7:0] Phase lock fill rate Phase lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x02)
[7:0] Frequency lock threshold, Bits[23:16] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] Frequency lock fill rate Frequency lock fill rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0] Frequency lock drain rate Frequency lock drain rate, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x0A = 10 code/PFD cycle)
[7:0]
[7:0] Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[15:8]; default: 0x15
[7:0] Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[23:16]; default: 0x64
[7:6] Reserved Default: 00b
[5:0]
30-bit free running
frequency tuning word
30-bit free running
frequency tuning word
Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[7:0]; default: 0x12
Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[29:24]; default: 0x1B
Table 74. DPLL_0 Digital Oscillator Control
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0404
[7:5] Reserved Default: 0x0
[4:0]
Digital oscillator
SDM integer part
0000 to 0011 = invalid
0100 = divide-by-4
0101 = invalid
0110 = divide-by-6
0111 = divide-by-7
1000 = divide-by-8 (default)
1001 = divide-by-9
1010 = divide-by-10
1011 = divide-by-11
1100 = divide-by-12
1101 = divide-by-13
1110 = divide-by-14
1111 = divide-by-15
Table 75. DPLL_0 Frequency Clamp
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0405
0x0406
0x0407
0x0408
0x0409
0x040A
[7:0]
[7:0]
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
[3:0] Lower limit of pull-in range
[7:0]
[7:0]
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
[3:0] Upper limit of pull-in range
Lower limit of pull-in range
(expressed as a 20-bit
frequency tuning word)
Upper limit of pull-in range
(expressed as a 20-bit
frequency tuning word)
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x51
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[15:8]
Default: 0xB8
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[19:16]
Default: 0x2
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x3E
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[15:8]
Default: 0x0A
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[19:16]
Default: 0xB
Rev. 0 | Page 82 of 120
Page 83

Data Sheet AD9559
0x040D
[7:5]
Reserved
Reserved.
3
Persistent history
Controls holdover history initialization. When switching to a new reference:
[2:0]
Incremental average
History mode value from 0 to 7 (default: 0).
0x0413
[7:0]
Incremental phase offset step size, Bits[15:8]. Default: 0x00.
Table 76. DPLL_0 History Accumulation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x040B
0x040C
Table 77. DPLL_0 History Mode
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[7:0]
History accumulation timer
(expressed in units of ms)
[7:0]
History accumulation timer, Bits[7:0].
Default: 0x0A. For Register 0x040B and Register 0x040C, 0x000A = 10 ms.
Maximum: 65 sec. This register controls the amount of tuning word averaging used to
determine the tuning word used in holdover. Never program a timer value of 0.
Default value: 0x000A = 10 (10 ms).
History accumulation timer, Bits[15:8].
Default: 0x00.
4 Single sample fallback
Controls holdover history. If tuning word history is not available for the reference that was
active just prior to holdover, then:
0 (default) = uses the free running frequency tuning word register value.
1 = uses the last tuning word from the DPLL.
0 (default) = clears the tuning word history.
1 = retains the previous tuning word history.
When set to nonzero, causes the first history accumulation to update prior to the first
complete averaging period. After the first full interval, updates occur only at the full period.
0 (default) = update only after the full interval has elapsed.
1 = update at 1/2 the full interval.
2 = update at 1/4 and 1/2 of the full interval.
3 = update at 1/8, 1/4, and 1/2 of the full interval.
…
7 = update at 1/256, 1/128, 1/64, 1/32, 1/16, 1/8, 1/4, and 1/2 of the full interval.
Table 78. DPLL_0 Fixed Closed Loop Phase Offset
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x040E [7:0]
0x040F
Fixed phase offset
(signed; ps)
[7:0]
Fixed phase offset, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x00
Fixed phase offset, Bits[15:8]
Default 0x00
0x0410
[7:0]
Fixed phase offset, Bits[23:16]
Default: 0x00
0x0411
[7:6] Reserved Reserved; default: 0x0
[5:0]
Fixed phase offset
(signed; ps)
Fixed phase offset, Bits[29:24]
Default: 0x00
Table 79. DPLL_0 Incremental Closed-Loop Phase Offset Step Size1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[7:0]
Incremental phase offset
step size (ps)
Incremental phase offset step size, Bits[7:0]. Default: 0x00.
This register controls the static phase offset of the DPLL while it is locked.
This register controls the static phase offset of the DPLL while it is locked.
0x0412
1
Note that the default incremental closed loop phase lock offset step size value is 0x0000 = 0 (0 ns).
Table 80. DPLL_0 Phase Slew Rate Limit
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0414 [7:0]
Phase slew rate limit
(µs/sec)
Phase slew rate limit, Bits[7:0].
Default: 0x00.
This register controls the maximum allowable phase slewing during phase adjustment.
0x0415
[7:0]
(The phase adjustment controls are in Register 0x040E to Register 0x0411.)
Default phase slew rate limit: 0, or disabled. Minimum useful value is 310 µs/sec.
Phase slew rate limit, Bits[15:8].
Default = 0x00
Rev. 0 | Page 83 of 120
Page 84

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0420
[7:0]
APLL_0 charge pump
LSB: 3.5 µA
0x0421
[7:0]
Division: 14 to 255
1000
1 0 1
[2:0]
Pole 1, Cp1
0x0423
[7:1]
Reserved
Default: 0x00.
APLL_0 CONFIGURATION (REGISTER 0x0420 TO REGISTER 0x0423)
Table 81. Output PLL_0 (APLL_0) Setting1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
current
00000001 = 1 × LSB; 00000010 = 2 × LSB; 11111111 = 255 × LSB
Default: 0x81 = 451 µA CP current
APLL_0 M0 (feedback)
divider
Default: 0x14 = divide-by-20
0x0422 [7:6] APLL_0 loop filter control Pole 2 resistor, Rp2; default: 0x07
Rp2 (Ω)
Bit 7 Bit 6
500 (default) 0 0
[5:3]
333
250
200
Zero resistor, Rzero
Rzero (Ω)
1500 (default)
1250
1000
930
1250
0 1
1 0
1 1
Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
750 1 1 0
680
1 1 1
Cp1 (pF) Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0
20
80
100
20
40
100
120 (default)
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
1
Note that the default APLL loop BW is 240 kHz.
0 Bypass internal Rzero 0 (default) = use the internal Rzero resistor
1 = bypass the internal Rzero resistor (makes Rzero = 0 and requires the use of a series
external zero resistor in addition to the capacitor to ground on the LF_0 pin)
Rev. 0 | Page 84 of 120
Page 85

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0424
[7:4]
Reserved
Default: 0x0
[1:0]
Automatic sync mode
Auto sync mode.
2
0
Mask OUT0A sync
Masks the synchronous reset to the OUT0A divider.
PLL_0 OUTPUT SYNC AND CLOCK DISTRIBUTION (REGISTER 0x0424 TO REGISTER 0x042E)
Table 82. APLL_0 P0 Divider Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[3:0] P0 divider divide ratio 0000/0001 = 3
0010 = 4
0011 = 5
0100 = 6 (default)
0101 = 7
0110 = 8
0111 = 9
1000 = 10
1001 = 11
Table 83. Distribution Output Synchronization Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0425 [7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b
2
Sync source selection Selects the sync source for the clock distribution output channels.
0 (default) = direct.
1 = active reference.
00 = (default) disabled.
01 = sync on DPLL frequency lock.
10 = sync on DPLL phase lock.
11 = reserved.
0x0426
[7:3] Reserved Reserved.
APLL_0 locked controlled
sync disable
Mask OUT0B sync Masks the synchronous reset to the OUT0B divider.
1
0 (default) = the clock distribution SYNC function is not enabled until the APLL has
been calibrated and is locked. After APLL calibration and lock, the output clock
distribution sync is armed, and the SYNC function for the clock outputs is under the
control of Register 0x0425.
1 = overrides the lock detector state of the APLL; allows Register 0x0425 to control the
output SYNC function regardless of the APLL lock status.
0 (default) = unmasked.
1 = masked. Setting this bit asynchronously releases the OUT0B divider from static sync
state, thus allowing the OUT0B divider to toggle. OUT0B ignores all sync events while
this bit is set. Setting this bit does not enable the output drivers connected to this channel.
0 (default) = unmasked.
1 = masked. Setting this bit asynchronously releases the OUT0A divider from static sync
state, thus allowing the OUT0A divider to toggle. OUT0A ignores all sync events while
this bit is set. Setting this bit does not enable the output drivers connected to this channel.
Rev. 0 | Page 85 of 120
Page 86

AD9559 Data Sheet
Table 84. Distribution OUT0A Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0427 7 Reserved Default: 0b
[6:4] OUT0A format
[3:2] OUT0A polarity
1 OUT0A LVDS boost
0 Reserved Default: 0b.
Table 85. Q0_A Divider Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0428 [7:0] Q0_A divider
0x0429 [7:2] Reserved Reserved.
[1:0] Q0_A divider 10-bit channel divider, Bits[9:8] (MSB), Bits[1:0].
0x042A [7:6] Reserved Reserved.
[5:0] Q0_A divider phase
Selects the operating mode of OUT0A.
000 = power-down, tristate.
001 (default) = HSTL.
010 = LVDS.
011 = reserved.
100 = CMOS, both outputs active.
101 = CMOS, P output active, N output power-down.
110 = CMOS, N output active, P output power-down.
111 = reserved.
Controls the OUT0A polarity.
00 (default) = positive, negative.
01 = positive, positive.
10 = negative, positive.
11 = negative, negative.
Controls the output drive capability of OUT0A.
0 (default) = LVDS: 3.5 mA drive strength.
1 = LVDS: 4.5 mA drive strength (LVDS boost mode).
10-bit channel divider, Bits[7:0] (LSB).
Division equals channel divider, Bits[9:0] + 1.
([9:0] = 0 is divide-by-1, [9:0] = 1 is divide-by-2…[9:0] = 1023 is divide-by-1024)
Divider initial phase after sync relative to the divider input clock (from the P0 divider output).
LSB is ½ of a period of the divider input clock.
Phase = 0 is no phase offset.
Phase = 1 is ½ a period offset.
Table 86. Distribution OUT0B Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x042B 7 Enable 3.3 V CMOS driver
[6:4] OUT0B format
[3:2] OUT0B polarity
1 OUT0B LVDS boost
0 Reserved Default: 0b.
0 (default) = disables 3.3 V CMOS driver. OUT0B logic is controlled by Register 0x042B[6:4].
1 = enables 3.3 V CMOS driver as operating mode of OUT0B.
This bit should be enabled only if Bits[6:4] are in CMOS mode.
Select the operating mode of OUT0B.
000 = power-down, tristate.
001 = HSTL.
010 = LVDS.
011 = reserved.
100 = CMOS, both outputs active.
101 = CMOS, P output active, N output power-down.
110 = CMOS, N output active, P output power-down.
111 = reserved.
Configure the OUT0B polarity in CMOS mode. These bits are active in CMOS mode only.
00 (default) = positive, negative.
01 = positive, positive.
10 = negative, positive.
11 = negative, negative.
Controls the output drive capability of OUT0B.
0 (default) = LVDS: 3.5 mA drive strength.
1 = LVDS: 4.5 mA drive strength (LVDS boost mode).
Rev. 0 | Page 86 of 120
Page 87

Data Sheet AD9559
Table 87. Q0B_B Divider Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x042C [7:0] Q0_B divider 10-bit channel divider, Bits[7:0] (LSB).
Division equals channel divider, Bits[9:0] + 1.
([9:0] = 0 is divide-by-1, [9:0] = 1 is divide-by-2…[9:0] = 1023 is divide-by-1024).
0x042D [7:2] Reserved Default: 000000b.
[1:0] Q0_B divider 10-bit channel divider, Bits[9:8] (MSB), Bits[1:0].
0x042E [7:6] Reserved Default: 00b.
[5:0] Q0_B divider phase
DPLL_0 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT A (REFA) (REGISTER 0x0440 TO REGISTER 0x044C)
Table 88. DPLL_0 REFA Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0440 [7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b
[2:1] REFA priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFA relative to the other input references.
0 Enable REFA This bit enables DPLL_0 to lock to REFA.
Divider initial phase after sync relative to the divider input clock (from the P0 divider output).
LSB is ½ of a period of the divider input clock.
Phase = 0 is no phase offset.
Phase = 1 is ½ a period offset.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
0 = REFA is not enabled for use by DPLL_0.
1 (default) = REFA is enabled for use by DPLL_0.
Table 89. DPLL_0 REFA Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0441 [7:0]
0x0442 [7:0] Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
0x0443 [7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
DPLL loop BW scaling
factor (unit of 0.1 Hz)
1
Base loop filter
selection
0 Reserved Default: 0b.
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
The default for Register 0x0441 and Register 0x0442 = 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency divided
by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal is used for
the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BW ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this bit is
also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 90. DPLL_0 REFA Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0444 [7:0] Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB)
0x0445 [7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07)
0x0446 [7:1] Reserved Default: 0x00
0 Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b)
Default for Register 0x0444 to Register 0x0446: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996)
Table 91. DPLL_0 REFA Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0447 [7:0]
0x0448 [7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x0449 [7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
Digital PLL fractional
feedback divider
FRAC0
—
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
Rev. 0 | Page 87 of 120
Page 88
AD9559 Data Sheet
0x044B
[7:0]
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x044E
[7:0]
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
0
Reserved
Default: 0b.
0x0457
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
Table 92. DPLL_0 REFA Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x044A
0x044C [7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
DPLL_0 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT B (REFB) (REGISTER 0x044D TO REGISTER 0x0459)
Table 93. DPLL_0 REFB Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x044D
Table 94. DPLL_0 REFB Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x044F [7:0] Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
0x0450 [7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
modulus
[7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b.
REFB priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFB relative to the other input references.
[2:1]
Enable REFB This bit enables DPLL_0 to lock to REFB.
0
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
—MOD0
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
0 = REFB is not enabled for use by DPLL_0.
1 (default) = REFB is enabled for use by DPLL_0.
The default for Register 0x044E and Register 0x044F = 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency
divided by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal
is used for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BWs ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this
bit is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 95. DPLL_0 REFB Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0451 [7:0] Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB)
0x0452
0x0453
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07)
[7:1] Reserved Default: 0x00
0
Table 96. DPLL_0 REFB Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider—FRAC0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0454 [7:0]
0x0455
0x0456
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
Table 97. DPLL_0 REFB Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider—MOD0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0458 [7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x0459
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 17 (default: 0b)
Default for Register 0x0451 to Register 0x453: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996)
Digital PLL fractional
feedback divider—FRAC0
modulus—MOD0
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
Rev. 0 | Page 88 of 120
Page 89

Data Sheet AD9559
0x045A
[7:3]
Reserved
Default: 00000b.
0x0460
[7:1]
Reserved
Default: 0x00.
0x0461
[7:0]
Digital PLL fractional
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04).
DPLL_0 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT C (REFC) (REGISTER 0x045A TO REGISTER 0x0466)
Table 98. DPLL_0 REFC Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[2:1] REFC priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFC relative to the other input references.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
Enable REFC This bit enables DPLL_0 to lock to REFC.
0
0 (default) = REFC is not enabled for use by DPLL_0.
1 = REFC is enabled for use by DPLL_0.
Table 99. DPLL_0 REFC Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x045B
0x045C
0x045D
[7:0]
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
[7:0]
[7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
0
Reserved Default: 0b.
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
The default for Register 0x045B and Register 0x045C: 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency
divided by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal
is used for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BW ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this
bit is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 100. DPLL_0 REFC Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x045E
0x045F
[7:0] Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB).
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07).
0 Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b).
The default for Register 0x045E to Register 0x460: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996).
Table 101. DPLL_0 REFC Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0462 [7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
0x0463
feedback divider—FRAC0
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00).
Table 102. DPLL_0 REFC Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0464
0x0465
0x0466
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
modulus—MOD0
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00).
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00).
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05).
Rev. 0 | Page 89 of 120
Page 90

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0467
[7:3]
Reserved
Default: 00000b.
0x046D
[7:1]
Reserved
Default: 0x00.
0x046E
[7:0]
Digital PLL fractional
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
DPLL_0 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT D (REFD) (REGISTER 0x0467 TO REGISTER 0x0473)
Table 103. DPLL_0 REFD Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[2:1] REFD priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFD relative to the other input references.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
Enable REFD This bit enables DPLL_0 to lock to REFD.
0
0 (default) = REFD is not enabled for use by DPLL_0.
1 = REFD is enabled for use by DPLL_0.
Table 104. DPLL_0 REFD Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0468
0x0469
0x046A
[7:0]
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
[7:0]
[7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
0
Reserved Default: 0b.
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
The default for Register 0x0468 and Register 0x0469 = 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency
divided by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal
is used for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BWs ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this
bit is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 105. DPLL_0 REFD Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x046B
0x046C
[7:0] Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB).
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07).
0 Integer Part N0 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 17 (default: 0b).
The default for Register 0x046B to Register 0x46D: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996).
Table 106. DPLL_0 REFD Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x046F [7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x0470
feedback divider—FRAC0
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
Table 107. DPLL_0 REFD Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD0
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0471
0x0472
0x0473
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
modulus—MOD0
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
Rev. 0 | Page 90 of 120
Page 91

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0500
[7:0]
30-bit free running frequency tuning word
Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x12)
0x0503
[7:6]
Reserved
Default: 00b
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
0x0508
[7:0]
[3:0]
Upper limit of pull-in range
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[19:16]
DPLL_1 CONTROLS (REGISTER 0x0500 TO REGISTER 0x0515)
Table 108. DPLL_1 Free Run Frequency Tuning Word
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0501 [7:0]
0x0502
[5:0] 30-bit free running frequency word Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[29:24] (default: 0x1B)
[7:0]
Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x15)
Free running frequency tuning word, Bits[23:9] (default: 0x64)
Table 109. DPLL_1 Digital Oscillator Control
0x0504 [7:5] Reserved Default: 0x0
Digital oscillator SDM integer part 0000 to 0011 = invalid
[4:0]
0100 = divide-by-4
0101 = invalid
0110 = divide-by-6
0111 = divide-by-7
1000 = divide-by-8 (default)
1001 = divide-by-9
1010 = divide-by-10
1011 = divide-by-11
1100 = divide-by-12
1101 = divide-by-13
1110 = divide-by-14
1111 = divide-by-15
Table 110. DPLL_1 Frequency Clamp
0x0505 [7:0]
0x0506
0x0507
0x0509
0x050A
Lower limit of pull-in range
(expressed as a 20-bit frequency
tuning word)
[7:0]
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
[3:0] Lower limit of pull-in range
Upper limit of pull-in range
(expressed as a 20-bit frequency
tuning word)
[7:0]
[7:4] Reserved Default: 0x0
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x51
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[15:8]
Default: 0xB8
Lower limit pull-in range, Bits[19:16]
Default: 0x2
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x3E
Upper limit pull-in range, Bits[15:8]
Default: 0x0A
Table 111. DPLL_1 History Accumulation Timer
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x050B
0x050C
[7:0]
History accumulation timer
(expressed in units of ms)
[7:0]
Default: 0xB
History accumulation timer, Bits[7:0].
Default: 0x0A.
For Register 0x050B and Register 0x050C, 0x000A = 10 ms. Maximum: 65 sec.
This register controls the amount of tuning word averaging used to
determine the tuning word used in holdover. Never program a timer value of 0.
Default value: 0x000A = 10 (10 ms).
History accumulation timer, Bits[15:8].
Default: 0x00.
Rev. 0 | Page 91 of 120
Page 92

AD9559 Data Sheet
4
Single sample fallback
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
Table 112. DPLL_1 History Mode
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x050D [7:5] Reserved Reserved.
Controls holdover history. If tuning word history is not available for the reference that was
active just prior to holdover, then:
0 (default) = use the free running frequency tuning word register value.
1 = use the last tuning word from the DPLL.
Persistent history Controls holdover history initialization. When switching to a new reference:
3
0 (default) = clear the tuning word history.
1 = retain the previous tuning word history.
Incremental average History mode value from 0 to 7 (default = 0)
[2:0]
When set to nonzero, causes the first history accumulation to update prior to the first
complete averaging period. After the first full interval, updates occur only at the full period.
0 (default) = update only after the full interval has elapsed.
1 = update at 1/2 the full interval.
2 = update at 1/4 and 1/2 of the full interval.
3 = update at 1/8, 1/4, and 1/2 of the full interval.
…
7 = update at 1/256, 1/128, 1/64, 1/32, 1/16, 1/8, 1/4, and 1/2 of the full interval.
Table 113. DPLL_1 Fixed Closed Loop Phase Offset
0x050E [7:0]
0x050F
Fixed phase offset
(signed; ps)
[7:0]
Fixed phase offset, Bits[7:0]
Default: 0x00
Fixed phase offset, Bits[15:8]
Default 0x00
0x0510
[7:0]
Fixed phase offset, Bits[23:16]
Default: 0x00
0x0511
[7:6] Reserved Reserved; default: 0x0
[5:0]
Fixed phase offset
(signed; ps)
Fixed phase offset, Bits[29:24]
Default: 0x00
Table 114. DPLL_1 Incremental Closed-Loop Phase Offset Step Size1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0512
[7:0]
Incremental phase
offset step size (ps)
Incremental phase offset step size, Bits[7:0].
Default: 0x00.
This register controls the static phase offset of the DPLL while it is locked.
0x0513
[7:0]
Incremental phase offset step size, Bits[15:8].
Default: 0x00.
1
Note that the default incremental closed loop phase lock offset step size value is 0x0000 = 0 (0 ns).
This register controls the static phase offset of the DPLL while it is locked.
Table 115. DPLL_1 Phase Slew Rate Limit
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0514 [7:0]
Phase slew rate limit
(µs/sec)
Phase slew rate limit, Bits[7:0].
Default: 0x00.
This register controls the maximum allowable phase slewing during phase adjustment
(The phase adjustment controls are in Register 0x050E to Register 0x0511.)
Default phase slew rate limit: 0, or disabled. Minimum useful value is 310 µs/sec.
0x0515
[7:0]
Phase slew rate limit, Bits[15:8].
Default = 0x00.
Rev. 0 | Page 92 of 120
Page 93
Data Sheet AD9559
0x0520
[7:0]
APLL_1 charge pump
LSB = 3.5 µA
0x0521
[7:0]
Division: 14 to 255
1000
1 0 1
[2:0]
0x0523
[7:1]
Reserved
Default: 0x00
APLL_1 CONFIGURATION (REGISTER 0x0520 TO REGISTER 0x0523)
Table 116. Output PLL_1 (APLL_1) Setting1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
current
00000001 = 1 × LSB; 00000010 = 2 × LSB; 11111111 = 255 × LSB
Default: 0x81 = 451 µA CP current
APLL_1 M1 (feedback)
divider
Default: 0x14 = divide-by-20
0x0522 [7:6] APLL_1 loop filter control Pole 2 resistor, Rp2; default: 0x07
Rp2 (Ω)
Bit 7 Bit 6
500 (default) 0 0
333
250
200
[5:3]
Zero resistor, Rzero.
Rzero (Ω)
1500 (default)
1250
1000
930
1250
0 1
1 0
1 1
Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
750 1 1 0
680
1 1 1
Pole 1, Cp1
Cp1 (pF)
0
20
80
100
20
40
100
120 (default)
Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
1
Note that the default APLL loop BW is 240 kHz.
0 Bypass internal Rzero 0 (default) = uses the internal Rzero resistor
1 = bypasses the internal Rzero resistor (makes Rzero = 0 and requires the use of a series
external zero resistor in addition to the capacitor to ground on the LF_1 pin)
Rev. 0 | Page 93 of 120
Page 94

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0524
[7:4]
Reserved
Default: 0x0
[1:0]
Automatic sync mode
Automatic sync mode.
2
PLL_1 OUTPUT SYNC AND CLOCK DISTRIBUTION (REGISTER 0x0524 TO REGISTER 0x052E)
Table 117. APLL_1 P1 Divider Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[3:0] P1 divider divide ratio 0000/0001 = 3
0010 = 4
0011 = 5
0100 = 6 (default)
0101 = 7
0110 = 8
0111 = 9
1000 = 10
1001 = 11
Table 118. Distribution Output Synchronization Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0525 [7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b.
2
Sync source selection Selects the sync source for the clock distribution output channels.
0 (default) = direct.
1 = active reference.
00 (default) = disabled.
01 = sync on DPLL frequency lock.
10 = sync on DPLL phase lock.
11 = reserved.
0x0526
[7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b.
APLL_1 locked
controlled sync disable
Mask OUT1B sync Masks the synchronous reset to the OUT1B divider.
1
0
Mask OUT1A sync Masks the synchronous reset to the OUT1A divider.
0 (default) = the clock distribution SYNC function is not enabled until APLL_1 has been
calibrated and is locked. After APLL calibration and lock, the output clock distribution sync is
armed, and the SYNC function for the clock outputs is under the control of Register 0x0525.
1 = overrides the lock detector state of the APLL; allows Register 0x0525 to control the output
SYNC function regardless of the APLL lock status.
0 (default) = unmasked.
1 = masked. Setting this bit asynchronously releases the OUT1B divider from the static SYNC
state, thus allowing the OUT1B divider to toggle. OUT1B ignores all SYNC events while this bit
is set. Setting this bit does not enable the output drivers connected to this channel.
0 (default) = unmasked.
1 = masked. Setting this bit asynchronously releases the OUT1A divider from the static SYNC
state, thus allowing the OUT1A divider to toggle. OUT1A ignores all SYNC events while this bit
is set. Setting this bit does not enable the output drivers connected to this channel.
Rev. 0 | Page 94 of 120
Page 95

Data Sheet AD9559
Table 119. Distribution OUT1A Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0527 7 Reserved Default: 0b.
[6:4] OUT1A format
[3:2] OUT1A polarity
1 OUT1A LVDS boost
0 Reserved Default: 0b.
Table 120. Q1_A Divider Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0528 [7:0] Q1_A divider
0x0529 [7:2] Reserved Reserved.
[1:0] Q1_A divider 10-bit channel divider, Bits[9:8] (MSB), Bits[1:0].
0x052A [7:6] Reserved Reserved.
[5:0] Q1_A divider phase
Select the operating mode of OUT1A.
000 = power-down, tristate.
001 (default) = HSTL.
010 = LVDS.
011 = reserved.
100 = CMOS, both outputs active.
101 = CMOS, P output active, N output power-down.
110 = CMOS, N output active, P output power-down.
111 = reserved.
Control the OUT1A polarity.
00 (default) = positive, negative.
01 = positive, positive.
10 = negative, positive.
11 = negative, negative.
Controls the output drive capability of OUT1A.
0 (default) = LVDS: 3.5 mA drive strength.
1 = LVDS: 4.5 mA drive strength (LVDS boost mode).
10-bit channel divider, Bits[7:0] (LSB).
Division equals channel divider, Bits[9:0] + 1.
([9:0] = 0 is divide-by-1, [9:0] = 1 is divide-by-2…[9:0] = 1023 is divide-by-1024).
Divider initial phase after sync relative to the divider input clock (from the P1 divider output).
LSB is ½ of a period of the divider input clock.
Phase = 0 is no phase offset.
Phase = 1 is ½ a period offset.
Table 121. Distribution OUT1B Settings
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x052B 7 Enable 3.3 V CMOS driver
[6:4] OUT1B format
[3:2] OUT1B polarity
1 OUT1B LVDS boost
0 Reserved Default: 0b.
0 (default) = disables 3.3 V CMOS driver, and OUT1B logic is controlled by 0x052B[6:4].
1 = enables 3.3 V CMOS driver as operating mode of OUT1.
This bit should be enabled only if Bits[6:4] are in CMOS mode.
Select the operating mode of OUT1B.
000 = power-down, tristate.
001 = HSTL.
010 = LVDS.
011 = reserved.
100 = CMOS, both outputs active.
101 = CMOS, P output active, N output power-down.
110 = CMOS, N output active, P output power-down.
111 = reserved.
Configure the OUT1B polarity in CMOS mode. These bits are active in CMOS mode only.
00 (default) = positive, negative.
01 = positive, positive.
10 = negative, positive.
11 = negative, negative.
Controls the output drive capability of OUT1B.
0 (default) = LVDS: 3.5 mA drive strength.
1 = LVDS: 4.5 mA drive strength (LVDS boost mode).
Rev. 0 | Page 95 of 120
Page 96

AD9559 Data Sheet
[1:0]
Q1_B divider
10-bit channel divider, Bits[9:8] (MSB), Bits[1:0].
1
Base loop filter selection
0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
0x0545
[7:0]
DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07).
Table 122. OUT1B Divider Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x052C
0x052D
0x052E [7:6] Reserved Default: 00b.
DPLL_1 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT C (REFC) (REGISTER 0x0540 TO REGISTER 0x054C)
Table 123. DPLL_1 REFC Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0540 [7:3] Reserved Reserved.
[7:0] Q1_B divider 10-bit channel divider, Bits[7:0] (LSB).
Division equals channel divider, Bits[9:0] + 1.
([9:0] = 0 is divide-by-1, [9:0] = 1 is divide-by-2…[9:0] = 1023 is divide-by-1024).
[7:2] Reserved Default: 000000b.
Q1_B divider phase
[5:0]
[2:1]
REFC priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFD relative to the other input references.
Enable REFC This bit enables DPLL_1 to lock to REFC.
0
Divider initial phase after sync relative to the divider input clock (from the P1 divider output).
LSB is ½ of a period of the divider input clock.
Phase = 0 is no phase offset.
Phase = 1 is ½ a period offset.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
0 = REFC is not enabled for use by DPLL_1.
1 (default) = REFC is enabled for use by DPLL_1.
Table 124. DPLL_1 REFC Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0541
0x0542
0x0543
[7:0]
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
[7:0] Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
[7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
Reserved Default: 0b.
0
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
Default for Register 0x0541 and Register 0x0542: 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency divided
by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal is used
for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BW ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this bit
is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 125. DPLL_1 REFC Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0544
0x0546 [7:1] Reserved Default: 0x00.
[7:0] Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB).
0
Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b).
Default for Register 0x0544 to Register 0x0546: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996).
Table 126. DPLL_1 REFC Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0547
0x0548
0x0549
[7:0]
Digital PLL fractional
feedback divider—FRAC1
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
Rev. 0 | Page 96 of 120
Page 97

Data Sheet AD9559
0x054B
[7:0]
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x054E
[7:0]
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
0
Reserved
Default: 0b.
0x0557
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
Table 127. DPLL_1 REFC Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider Mod1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x054A
0x054C [7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
DPLL_1 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT D (REFD) (REGISTER 0x054D TO REGISTER 0x0559)
Table 128. DPLL_1 REFD Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x054D
Table 129. DPLL_1 REFD Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x054F [7:0] Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
0x0550 [7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback
divider modulus—MOD1
[7:3] Reserved Default: 00000b.
REFD priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFD relative to the other input references.
[2:1]
Enable REFD This bit enables DPLL_1 to lock to REFD.
0
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1
10 = 2
11 = 3
0 = REFD is not enabled for use by DPLL_1
1 (default) = REFD is enabled for use by DPLL_1
The default for Register 0x054E and Register 0x054F = 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency
divided by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal
is used for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BW ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this
bit is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 130. DPLL_1 REFD Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0551 [7:0] Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB).
0x0552
0x0553
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07).
[7:1] Reserved Default: 0x00.
0
Table 131. DPLL_1 REFD Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0554 [7:0]
0x0555
0x0556
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
Table 132. DPLL_1 REFD Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0558 [7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x0559
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b).
The default for Register 0x0551 to Register 0x0553: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996).
Digital PLL fractional
feedback divider—FRAC1
modulus—MOD1
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
Rev. 0 | Page 97 of 120
Page 98

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x055A
[7:3]
Reserved
Default: 00000b.
0x0560
[7:1]
Reserved
Default: 0x00.
0x0561
[7:0]
Digital PLL fractional
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
DPLL_1 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT A (REFA) (REGISTER 0x055A TO REGISTER 0x0566)
Table 133. DPLL_1 REFA Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[2:1] REFA priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFA relative to the other input references.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
Enable REFA This bit enables DPLL_1 to lock to REFA.
0
0 (default) = RE FA is not enabled for use by DPLL_1.
1 = REFA is enabled for use by DPLL_1.
Table 134. DPLL_1 REFA Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x055B
0x055C
0x055D
[7:0]
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
[7:0]
[7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
0
Reserved Default: 0b.
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
The default for Register 0x055B and Register 0x0555C = 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW).
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency divided
by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal is used
for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for details.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BW ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this bit
is also recommended for loop BW > 2 kHz.)
Table 135. DPLL_1 REFA Integer Part of Feedback Divider
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x055E
0x055F
[7:0] Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB).
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07).
0 Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b).
The default for Register 0x055E to Register 0x0560: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996).
Table 136. DPLL_1 REFA Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0562 [7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
0x0563
feedback divider—FRAC1
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
Table 137. DPLL_1 REFA Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0564
0x0565
0x0566
[7:0]
Digital PLL feedback divider
modulus—MOD1
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
Rev. 0 | Page 98 of 120
Page 99

Data Sheet AD9559
0x0567
[7:3]
Reserved
Default: 00000b.
Address
Bits
Bit Name
Description
0x0573
[7:0]
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:17] (default: 0x00)
DPLL_1 SETTINGS FOR REFERENCE INPUT B (REFB) (REGISTER 0x0567 TO REGISTER 0x0573)
Table 138. DPLL_1 REFB Priority Setting
Address Bits Bit Name Description
[2:1] REFB priority These bits set the priority level (0 to 3) of REFA relative to the other input references.
00 (default) = 0 (highest).
01 = 1.
10 = 2.
11 = 3.
Enable REFB This bit enables DPLL_1 to lock to REFB.
0
0 (default) = REFB is not enabled for use by DPLL_1.
1 = REFB is enabled for use by DPLL_1.
Table 139. DPLL_1 REFB Loop BW Scaling Factor
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0568
0x0569
0x056A [7:2] Reserved Default: 0x00.
[7:0]
DPLL loop BW scaling factor
(unit of 0.1 Hz)
[7:0]
Base loop filter selection 0 = base loop filter with normal (70°) phase margin (default).
1
Reserved Default: 0b.
0
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[7:0] (default: 0xF4).
Digital PLL loop bandwidth scaling factor, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x01).
Default for Register 0x0568 to Register 0x056A: 0x01F4 = 500 (50 Hz loop BW.
The loop bandwidth should always be less than the DPLL phase detector frequency
divided by 20. The DPLL may not lock reliably if the DPLL loop BW is <50 Hz and a crystal
oscillator is used for the system clock. See the Choosing the SYSCLK Source section for
more information.
1 = base loop filter with high phase margin.
(≤0.1 dB peaking in the closed-loop transfer function for loop BWs ≤ 2 kHz. Setting this
bit is also recommended for loop BW > 2kHz.)
Table 140. DPLL_1 REFB Integer Part of Feedback Divider
0x056B [7:0] Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider (minus 1), Bits[7:0] (default: 0xCB)
0x056C
0x056D
[7:0] DPLL integer feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x07)
[7:1] Reserved Default: 0x00
0
Integer Part N1 DPLL integer feedback divider, Bit 16 (default: 0b)
Default for Register 0x056B to Register 0x056D: 0x007CB (which equals N1 = 1996)
Table 141. DPLL_1 REFB Fractional Part of Fractional Feedback Divider FRAC1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x056E
0x056F
0x0570
[7:0]
Digital PLL fractional
feedback divider—FRAC1
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
[7:0] The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[23:18] (default: 0x00)
The numerator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x04)
Table 142. DPLL_1 REFB Modulus of Fractional Feedback Divider MOD1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0571 [7:0]
0x0572
[7:0] The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[15:8] (default: 0x00)
Digital PLL feedback divider
modulus—MOD1
The denominator of the fractional-N feedback divider, Bits[7:0] (default: 0x05)
Rev. 0 | Page 99 of 120
Page 100

AD9559 Data Sheet
0x0800
[7:0]
NPM Alpha-0 linear
Alpha-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0x24
[6:0]
NPM Alpha-1 exponent
Alpha-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x49
0x0807
[7:0] Gamma-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xFA
[6:0]
HPM Beta-1 exponent
Beta-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x73
0x0814
7
Reserved
Default: 0b
0x0816
[7:0]
Delta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0x8D
DIGITAL LOOP FILTER COEFFICIENTS (REGISTER 0x0800 TO REGISTER 0x0817)
Table 143. Base Digital Loop Filter with Normal Phase Margin (PM = 70°, BW = 0.1 Hz, Third Pole Frequency = 1 Hz, N1 = 1)1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x0801 [7:0] Alpha-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0x8C
0x0802
0x0803 [7:0] NPM Beta-0 linear Beta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0x55
0x0804
0x0805
0x0806
0x0808 7 Reserved Default: 0b
0x0809
0x080A
0x080B
1
Note that the digital loop filter base coefficients (α, β, γ, and δ) have the general form: x(2y), where x is the linear component and y is the exponential component of the
coefficient. The value of the linear component (x) constitutes a fraction, where 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The exponential component (y) is a signed integer. These are live registers;
therefore, an IO_UPDATE is not needed. However, the updated coefficients do not take effect while the loop is locked.
7 Reserved Default: 0b
[7:0] Beta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xC9
7 Reserved Default: 0b
[6:0] NPM Beta-1 exponent Beta-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x7B
[7:0] NPM Gamma-0 linear Gamma-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0x9C
[6:0] NPM Gamma -1 exponent Gamma-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x55
[7:0] NPM Delta-0 linear Delta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0xEA
[7:0] Delta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xE2
7 Reserved Default: 0b
[6:0] NPM Delta-1 exponent Delta-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x57
Table 144. Base Digital Loop Filter with High Phase Margin (PM = 88.5°, BW = 0.1 Hz, Third Pole Frequency = 20 Hz, N1 = 1)1
Address Bits Bit Name Description
0x080C
0x080D
0x080E
0x080F
0x0810
0x0811
[7:0] HPM Alpha-0 linear Alpha-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default = 0x8C
[7:0] Alpha-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xAD
7 Reserved Default: 0b
[6:0]
HPM Alpha-1 exponent Alpha-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x4C
[7:0] HPM Beta-0 linear Beta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0xF5
[7:0] Beta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xCB
7 Reserved Default: 0b
0x0812 [7:0] HPM Gamma-0 linear Gamma-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0x24
0x0813
[7:0] Gamma-0 coefficient linear, Bits[15:8]; default: 0xD8
[6:0] HPM Gamma-1 exponent Gamma-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x59
0x0815
[7:0] HPM Delta-0 linear Delta-0 coefficient linear, Bits[7:0]; default: 0xD2
0x0817 7 Reserved Default: 0b
1
Note that the base digital loop filter coefficients (α, β, γ, and δ) have the general form: x(2y), where x is the linear component and y is the exponential component of
the coefficient. The value of the linear component (x) constitutes a fraction, where 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The exponential component (y) is a signed integer. These are live registers;
therefore, an IO_UPDATE is not needed. However, the updated coefficients do not take effect while the loop is locked.
[6:0] HPM Delta-1 exponent Delta-1 coefficient exponent, Bits[6:0]; default: 0x5A
Rev. 0 | Page 100 of 120
 Loading...
Loading...