Page 1
1.2 GHz Clock Distribution IC, 1.6 GHz Inputs,
FEATURES
Two 1.6 GHz, differential clock inputs
5 programmable dividers, 1 to 32, all integers
Phase select for output-to-output coarse delay adjust
3 independent 1.2 GHz LVPECL outputs
Additive output jitter 225 fs rms
2 independent 800 MHz/250 MHz LVDS/CMOS clock outputs
Additive output jitter 275 fs rms
Fine delay adjust on 1 LVDS/CMOS output
Serial control port
Space-saving 48-lead LFCSP
APPLICATIONS
Low jitter, low phase noise clock distribution
Clocking high speed ADCs, DACs, DDSs, DDCs, DUCs, MxFEs
High performance wireless transceivers
High performance instrumentation
Broadband infrastructure
Dividers, Delay Adjust, Five Outputs
AD9512
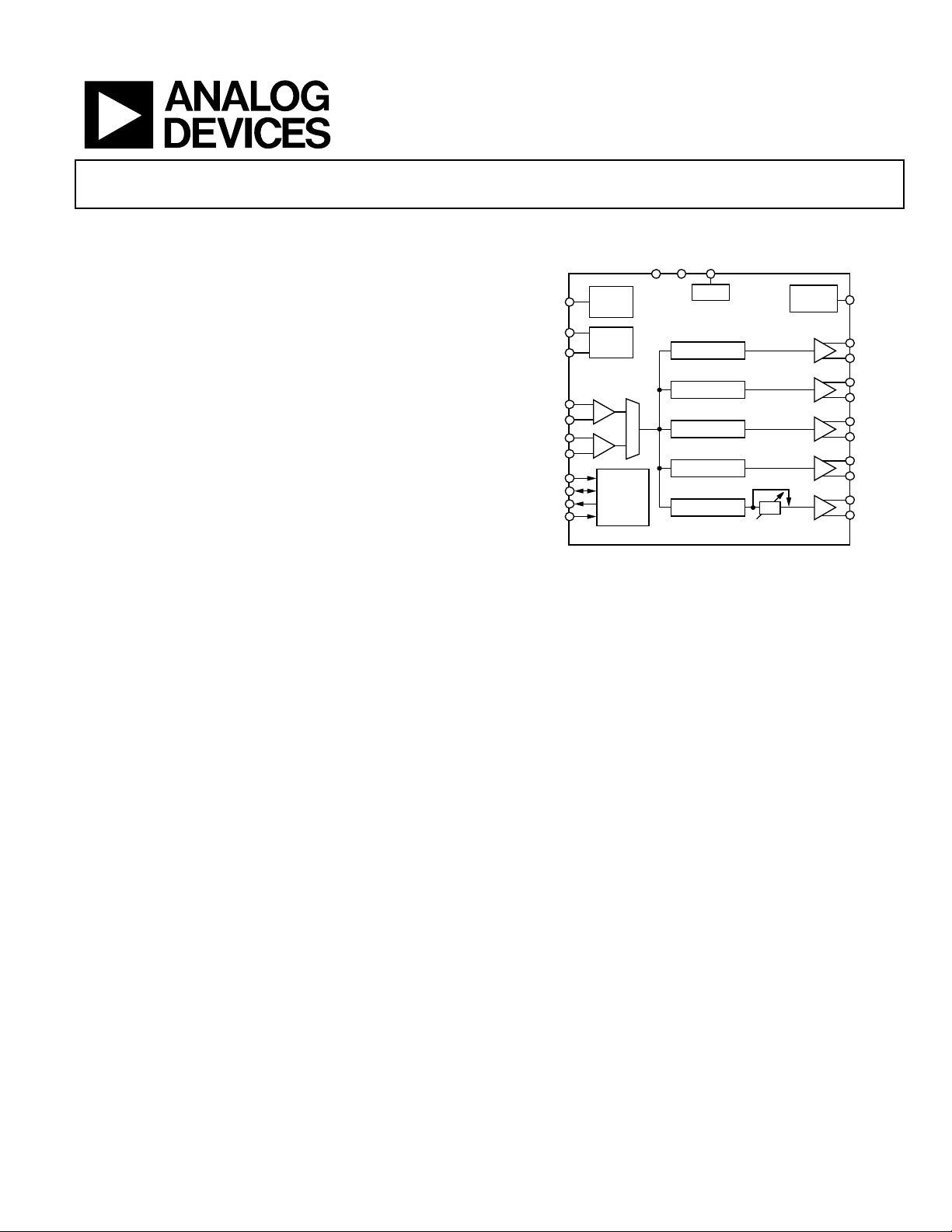
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
GNDVS
RSET
FUNCTION
DSYNC
DSYNCB
CLK1
CLK1B
CLK2
CLK2B
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CSB
SYNCB,
RESETB
PDB
DETECT
SYNC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
VREF
PROGRAMMABLE
DIVIDERS AND
PHASE ADJUST
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
Figure 1.
AD9512
DELAY
ADJUST
Δ
T
SYNC
STATUS
LVPECL
LVPECL
LVPECL
LVDS/CMOS
LVDS/CMOS
SYNC
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0B
OUT1
OUT1B
OUT2
OUT2B
OUT3
OUT3B
OUT4
OUT4B
05287-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9512 provides a multi-output clock distribution in a
design that emphasizes low jitter and low phase noise to
maximize data converter performance. Other applications with
demanding phase noise and jitter requirements can also benefit
from this part.
There are five independent clock outputs. Three outputs are
LVPECL (1.2 GHz), and two are selectable as either LVDS
(800 MHz) or CMOS (250 MHz) levels.
Each output has a programmable divider that may be bypassed
or set to divide by any integer up to 32. The phase of one clock
output relative to another clock output may be varied by means
of a divider phase select function that serves as a coarse timing
adjustment.
One of the LVDS/CMOS outputs features a programmable
delay element with a range of up to 10 ns of delay. This fine
tuning delay block has 5-bit resolution, giving 32 possible delays
from which to choose.
The AD9512 is ideally suited for data converter clocking
applications where maximum converter performance is
achieved by encode signals with subpicosecond jitter.
The AD9512 is available in a 48-lead LFCSP and can be
operated from a single 3.3 V supply. The temperature range is
−40°C to +85°C.
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

AD9512
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 4
Outputs ........................................................................................ 30
Clock Inputs.................................................................................. 4
Clock Outputs............................................................................... 4
Timing Characteristics ................................................................ 5
Clock Output Phase Noise .......................................................... 7
Clock Output Additive Time Jitter........................................... 10
Serial Control Port ..................................................................... 12
FUNCTION Pin ......................................................................... 13
SYNC Status Pin ......................................................................... 13
Power ............................................................................................14
Timing Diagrams............................................................................ 15
Absolute Maximum Ratings.......................................................... 16
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 16
ESD Caution................................................................................ 16
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions........................... 17
Te r mi n ol o g y .................................................................................... 19
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 20
Functional Description .................................................................. 24
Overall.......................................................................................... 24
FUNCTION Pin ......................................................................... 24
RESETB: 58h<6:5> = 00b (Default)..................................... 24
SYNCB: 58h<6:5> = 01b .......................................................24
PDB: 58h<6:5> = 11b............................................................. 24
DSYNC and DSYNCB Pins....................................................... 24
Clock Inputs................................................................................ 24
Dividers........................................................................................ 25
Setting the Divide Ratio ........................................................ 25
Setting the Duty Cycle........................................................... 25
Divider Phase Offset .............................................................. 29
Delay Block.................................................................................. 30
Calculating the Delay............................................................. 30
Power-Down Modes .................................................................. 31
Chip Power-Down or Sleep Mode—PDB........................... 31
Distribution Power-Down .................................................... 31
Individual Clock Output Power-Down............................... 31
Individual Circuit Block Power-Down................................ 31
Reset Modes ................................................................................ 31
Power-On Reset—Start-Up Conditions when
VS is Applied........................................................................... 31
Asynchronous Reset via the FUNCTION Pin ................... 31
Soft Reset via the Serial Port................................................. 31
Single-Chip Synchronization.................................................... 32
SYNCB—Hardware SYNC ................................................... 32
Soft SYNC—Register 58h<2>............................................... 32
Multichip Synchronization ....................................................... 32
Serial Control Port ......................................................................... 33
Serial Control Port Pin Descriptions....................................... 33
General Operation of Serial Control Port............................... 33
Framing a Communication Cycle with CSB ...................... 33
Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus Data................. 33
Wr it e ........................................................................................ 33
Read ......................................................................................... 34
The Instruction Word (16 Bits)................................................ 34
MSB/LSB First Transfers ........................................................... 34
Register Map and Description...................................................... 37
Summary Table........................................................................... 37
Register Map Description ......................................................... 39
Power Supply................................................................................... 43
Power Management ................................................................... 43
Applications..................................................................................... 44
Using the AD9512 Outputs for ADC Clock Applications.... 44
CMOS Clock Distribution ........................................................ 44
Rev. A | Page 2 of 48
Page 3

AD9512
LVPECL Clock D i s t r ib ut i o n ......................................................45
LVDS Clock Distribution...........................................................45
Power and Grounding Considerations and Power Supply
Rejection.......................................................................................45
Outline Dimensions ........................................................................46
Ordering Guide ...........................................................................46
REVISION HISTORY
6/05—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Features..........................................................................1
Changes to General Description .....................................................1
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................4
Changes to Table 3 ............................................................................5
Changes to Table 4 ............................................................................7
Changes to Table 5 and Table 6 .....................................................12
Changes to Table 7 ..........................................................................13
Changes to Figure 12 and Figure 14 to Figure 16 .......................21
Changes to Figure 17 Caption .......................................................22
Changes to Figure 23 ......................................................................23
Changes to Divider Phase Offset Section ....................................29
Changes to Chip Power-Down or Sleep Mode—PDB Section .31
Changes to Distribution Power-Down Section...........................31
Changes to Individual Clock Output Power-Down Section .....31
Changes to Individual Circuit Block Power-Down Section ......31
Changes to Soft Reset via the Serial Port Section .......................31
Changes to SYNCB—Hardware SYNC Section..........................32
Changes to Soft SYNC Register 58h<2> Section ........................32
Changes to Multichip Synchronization Section..........................32
Changes to Serial Control Port Section .......................................33
Changes to Serial Control Port Pin Descriptions Section.........33
Changes to General Operation of Serial
Control Port Section.......................................................................33
Added Framing a Communication Cycle with CSB Section ....33
Added Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus
Data Section.....................................................................................33
Changes to Write Section ............................................................... 33
Changes to Read Section................................................................34
Changes to Instruction Word (16 Bits) Section ..........................34
Changes to MSB/LSB First Transfers Section..............................34
Changes to Figure 32 and Figure 36 .............................................35
Added Figure 38; Renumbered Sequentially...............................36
Changes to Table 17 ........................................................................37
Changes to Table 18 ........................................................................39
Changes to Power Supply Section.................................................43
Changes to Power Management Section......................................43
4/05—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 3 of 48
Page 4
AD9512
SPECIFICATIONS
Typical ( Ty p ) i s g iv e n f o r VS = 3.3 V ± 5%; TA = 25°C, R
values are given over full V
and TA (−40°C to +85°C) variation.
S
CLOCK INPUTS
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLOCK INPUTS (CLK1, CLK2)
Input Frequency 0 1.6 GHz
Input Sensitivity 1502 mV p-p
Input Level 2
Input Common-Mode Voltage, V
Input Common-Mode Range, V
Input Sensitivity, Single-Ended 150 mV p-p CLK2 ac-coupled; CLK2B ac bypassed to RF ground.
Input Resistance 4.0 4.8 5.6 kΩ Self-biased.
Input Capacitance 2 pF
1
CLK1 and CLK2 are electrically identical; each can be used as either differential or single-ended input.
2
With a 50 Ω termination, this is −12.5 dBm.
3
With a 50 Ω termination, this is +10 dBm.
1
CM
CMR
1.5 1.6 1.7 V Self-biased; enables ac coupling.
1.3 1.8 V With 200 mV p-p signal applied; dc-coupled.
= 4.12 kΩ, unless otherwise noted. Minimum (Min) and Maximum (Max)
SET
Jitter performance can be improved with higher slew
rates (greater swing).
3
V p-p
Larger swings turn on the protection diodes and can
degrade jitter performance.
CLOCK OUTPUTS
Table 2.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL CLOCK OUTPUTS Termination = 50 Ω to VS − 2 V
OUT0, OUT1, OUT2; Differential Output level 3Dh (3Eh) (3Fh)<3:2> = 10b
Output Frequency 1200 MHz See Figure 14
Output High Voltage (VOH) VS − 1.22 VS − 0.98 VS − 0.93 V
Output Low Voltage (VOL) VS − 2.10 VS − 1.80 VS − 1.67 V
Output Differential Voltage (VOD) 660 810 965 mV
LVDS CLOCK OUTPUTS Termination = 100 Ω differential; default
OUT3, OUT4; Differential
Output Frequency 800 MHz See Figure 15
Differential Output Voltage (VOD) 250 360 450 mV
Delta V
OD
25 mV
Output Offset Voltage (VOS) 1.125 1.23 1.375 V
Delta V
OS
25 mV
Short-Circuit Current (ISA, ISB) 14 24 mA Output shorted to GND
CMOS CLOCK OUTPUTS
OUT3, OUT4
Output Frequency 250 MHz With 5 pF load each output; see Figure 16
Output Voltage High (VOH) VS − 0.1 V @ 1 mA load
Output Voltage Low (VOL) 0.1 V @ 1 mA load
Output level 40h (41h)<2:1> = 01b
3.5 mA termination current
Single-ended measurements;
B outputs: inverted, termination open
Rev. A | Page 4 of 48
Page 5
AD9512
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Table 3.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL
Termination = 50 Ω to V
Output level 3Dh (3Eh) (3Fh)<3:2> = 10b
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
RP
FP
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
, CLK-TO-LVPECL OUT
PECL
1
130 180 ps 20% to 80%, measured differentially
130 180 ps 80% to 20%, measured differentially
Divide = Bypass 335 490 635 ps
Divide = 2 − 32 375 545 695 ps
Variation with Temperature 0.5 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, LVPECL OUTPUTS
OUT1 to OUT0 on Same Part, t
OUT1 to OUT2 on Same Part, t
OUT0 to OUT2 on Same Part, t
All LVPECL OUT Across Multiple Parts, t
Same LVPECL OUT Across Multiple Parts, t
LVDS
SKP
SKP
SKP
2
2
2
3
SKP_AB
3
SKP_AB
70 100 140 ps
15 45 80 ps
45 65 90 Ps
275 ps
130 ps
Termination = 100 Ω differential
Output level 40h (41h) <2:1> = 01b
3.5 mA termination current
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
RL
FL
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
, CLK-TO-LVDS OUT
LVDS
1
200 350 ps 20% to 80%, measured differentially
210 350 ps 80% to 20%, measured differentially
Delay off on OUT4
OUT3 to OUT4
Divide = Bypass 0.99 1.33 1.59 ns
Divide = 2 − 32 1.04 1.38 1.64 ns
Variation with Temperature 0.9 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, LVDS OUTPUTS Delay off on OUT4
OUT3 to OUT4 on Same Part, t
All LVDS OUTs Across Multiple Parts, t
Same LVDS OUT Across Multiple Parts, t
SKV
2
3
SKV_AB
3
SKV_AB
−85 +270 ps
450 ps
325 ps
CMOS B outputs are inverted; termination = open
Output Rise Time, t
Output Fall Time, t
RC
FC
PROPAGATION DELAY, t
, CLK-TO-CMOS OUT
CMOS
1
681 865 ps 20% to 80%; C
646 992 ps 80% to 20%; C
LOAD
LOAD
Delay off on OUT4
Divide = Bypass 1.02 1.39 1.71 ns
Divide = 2 − 32 1.07 1.44 1.76 ns
Variation with Temperature 1 ps/°C
OUTPUT SKEW, CMOS OUTPUTS Delay off on OUT4
OUT3 to OUT4 on Same Part, t
All CMOS OUT Across Multiple Parts, t
Same CMOS OUT Across Multiple Parts, t
SKC
2
3
SKC_AB
3
SKC_AB
−140 +145 +300
650 ps
500 ps
LVPECL-TO-LVDS OUT Everything the same; different logic type
Output Skew, t
SKP_V
0.74 0.92 1.14 ns LVPECL to LVDS on same part
LVPECL-TO-CMOS OUT Everything the same; different logic type
Output Skew, t
SKP_C
0.88 1.14 1.43 ns LVPECL to CMOS on same part
LVDS-TO-CMOS OUT Everything the same; different logic type
Output Skew, t
SKV_C
158 353 506 ps LVDS to CMOS on same part
= 3 pF
= 3 pF
− 2 V
S
Rev. A | Page 5 of 48
Page 6
AD9512
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DELAY ADJUST OUT4; LVDS and CMOS
Shortest Delay Range
Zero Scale 0.05 0.36 0.68 ns 36h <5:1> 00000b
Full Scale 0.72 1.12 1.51 ns 36h <5:1> 11111b
Linearity, DNL 0.5 LSB
Linearity, INL 0.8 LSB
Longest Delay Range
Zero Scale 0.20 0.57 0.95 ns 36h <5:1> 00000b
Full Scale 9.0 10.2 11.6 ns 36h <5:1> 11111b
Linearity, DNL 0.3 LSB
Linearity, INL 0.6 LSB
Delay Variation with Temperature
Long Delay Range, 10 ns
Zero Scale 0.35 ps/°C
Full Scale −0.14 ps/°C
Short Delay Range, 1 ns
Zero Scale 0.51 ps/°C
Full Scale 0.67 ps/°C
1
The measurements are for CLK1. For CLK2, add approximately 25 ps.
2
This is the difference between any two similar delay paths within a single device operating at the same voltage and temperature.
3
This is the difference between any two similar delay paths across multiple devices operating at the same voltage and temperature.
4
Incremental delay; does not include propagation delay.
5
All delays between the zero scale and full scale can be estimated by linear interpolation.
4
4
5
5
35h <5:1> 11111b
35h <5:1> 00000b
Rev. A | Page 6 of 48
Page 7
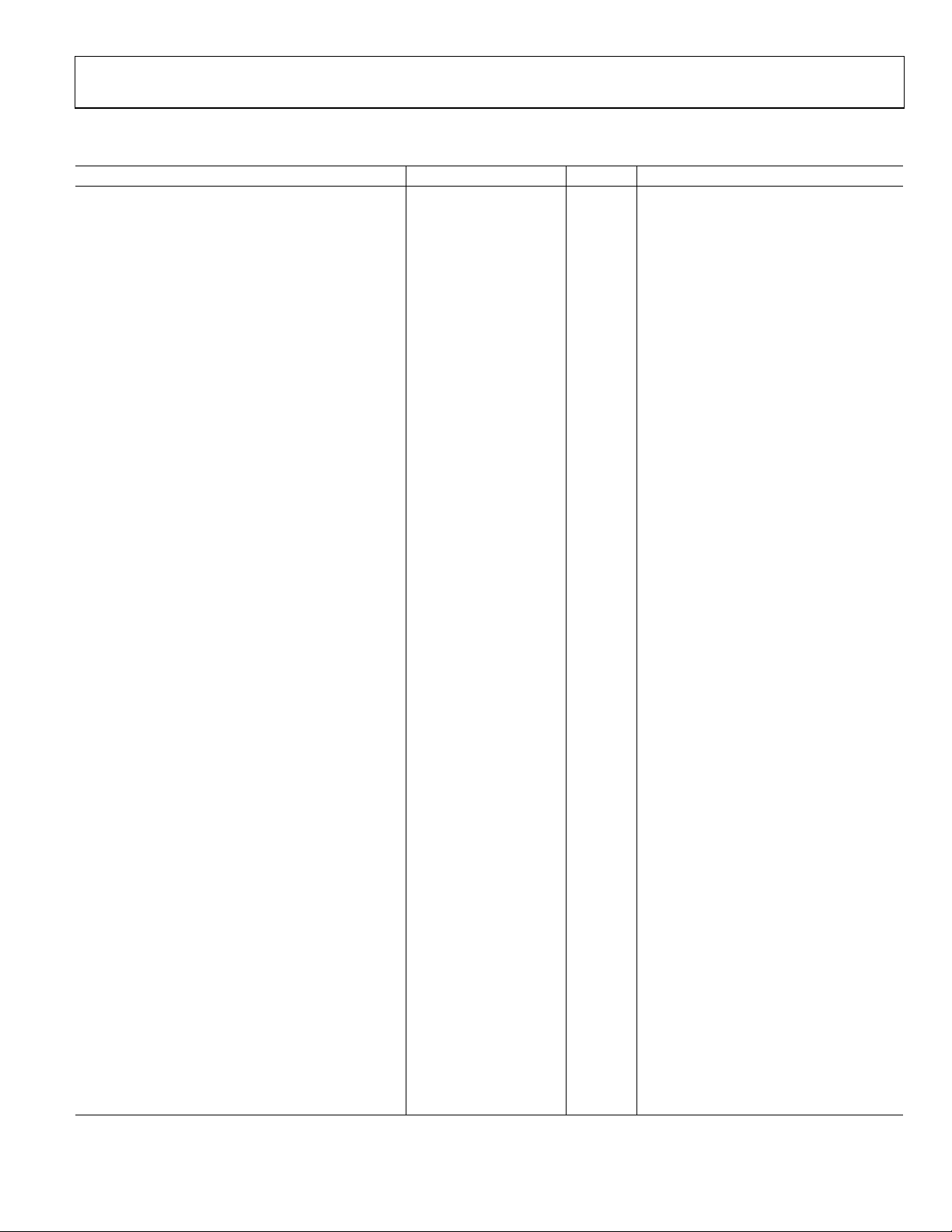
AD9512
CLOCK OUTPUT PHASE NOISE
Table 4.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK1-TO-LVPECL ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz, OUT = 622.08 MHz Input slew rate > 1 V/ns
Divide Ratio = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −125 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −153 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −154 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz, OUT = 155.52 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −128 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −161 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −161 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz, OUT = 38.88 MHz
Divide Ratio = 16
@ 10 Hz Offset −135 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −145 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −165 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −165 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −166 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 491.52 MHz, OUT = 61.44 MHz
Divide Ratio = 8
@ 10 Hz Offset −131 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −142 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −153 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −160 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −165 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −165 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 491.52 MHz, OUT = 245.76 MHz
Divide Ratio = 2
@ 10 Hz Offset −125 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −151 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −157 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 245.76 MHz, OUT = 61.44 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −138 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −144 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −154 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −163 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −164 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −165 dBc/Hz
Rev. A | Page 7 of 48
Page 8
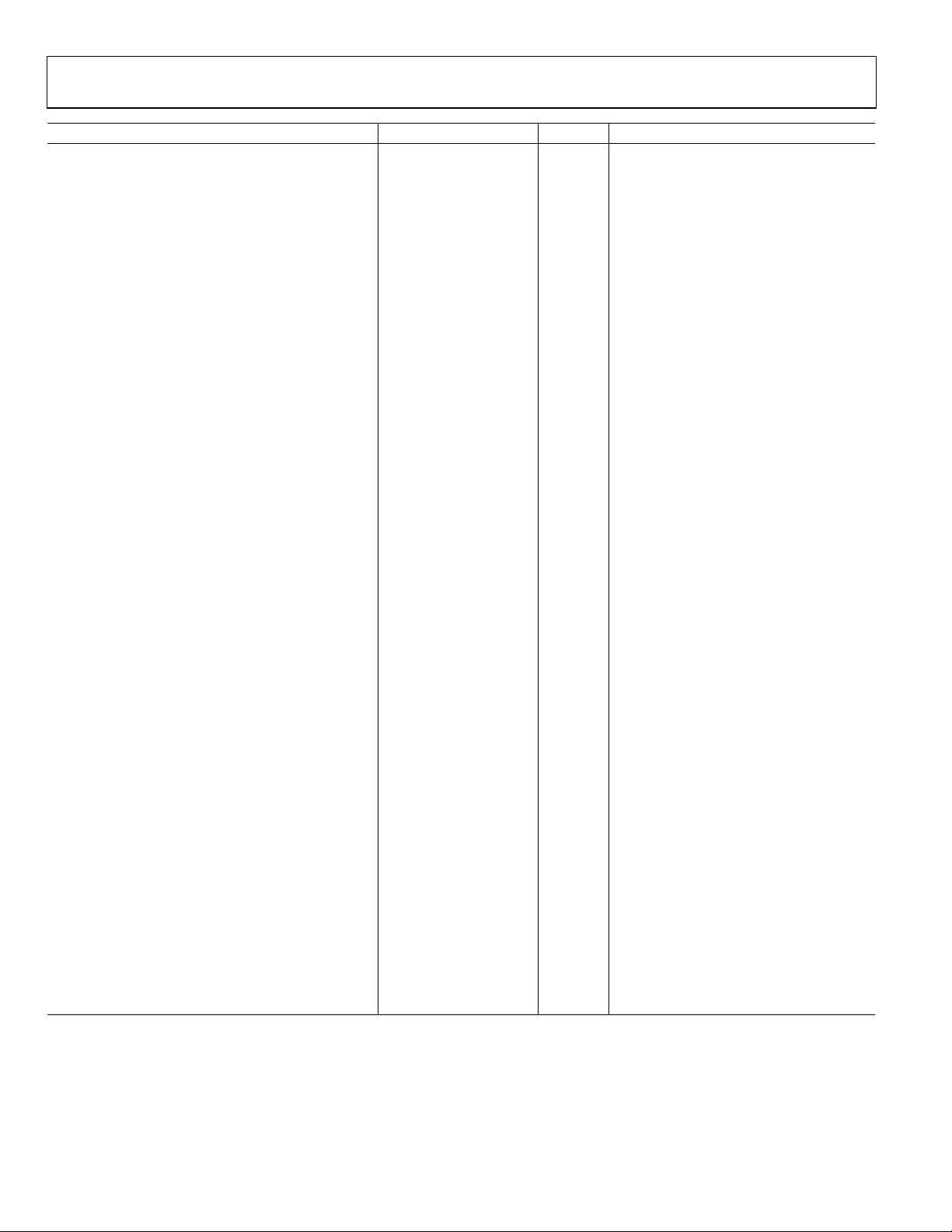
AD9512
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK1-TO-LVDS ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz, OUT = 622.08 MHz
Divide Ratio = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −100 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −110 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −129 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −135 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz, OUT = 155.52 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −112 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −122 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −142 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −152 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 491.52 MHz, OUT = 245.76 MHz
Divide Ratio = 2
@ 10 Hz Offset −108 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −128 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −138 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −145 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −154 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 491.52 MHz, OUT = 122.88 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −129 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −136 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −153 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −156 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 245.76 MHz, OUT = 245.76 MHz
Divide Ratio = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −108 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −128 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −138 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −145 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −148 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
Rev. A | Page 8 of 48
Page 9
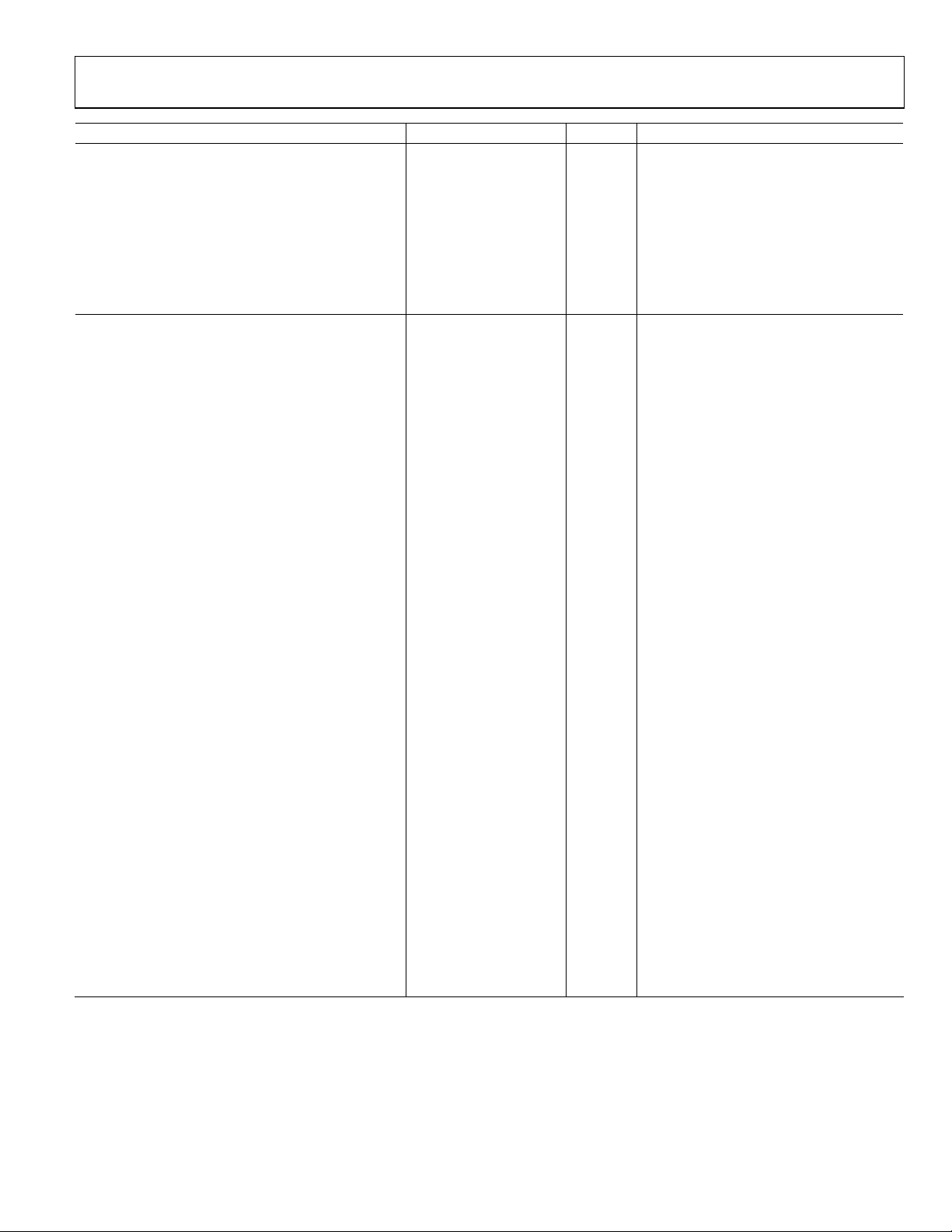
AD9512
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK1 = 245.76 MHz, OUT = 122.88 MHz
Divide Ratio = 2
@ 10 Hz Offset −118 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −127 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −137 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −147 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −154 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −156 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
CLK1-TO-CMOS ADDITIVE PHASE NOISE
CLK1 = 245.76 MHz, OUT = 245.76 MHz
Divide Ratio = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −110 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −121 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −130 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −145 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −149 dBc/Hz
> 10 MHz Offset −156 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 245.76 MHz, OUT = 61.44 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
@ 10 Hz Offset −122 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −143 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −152 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −160 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −162 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 78.6432 MHz, OUT = 78.6432 MHz
Divide Ratio = 1
@ 10 Hz Offset −122 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −132 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −140 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −150 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
@ 1 MHz Offset −158 dBc/Hz
>10 MHz Offset −160 dBc/Hz
CLK1 = 78.6432 MHz, OUT = 39.3216 MHz
Divide Ratio = 2
@ 10 Hz Offset −128 dBc/Hz
@ 100 Hz Offset −136 dBc/Hz
@ 1 kHz Offset −146 dBc/Hz
@ 10 kHz Offset −155 dBc/Hz
@ 100 kHz Offset −161 dBc/Hz
>1 MHz Offset −162 dBc/Hz
Rev. A | Page 9 of 48
Page 10
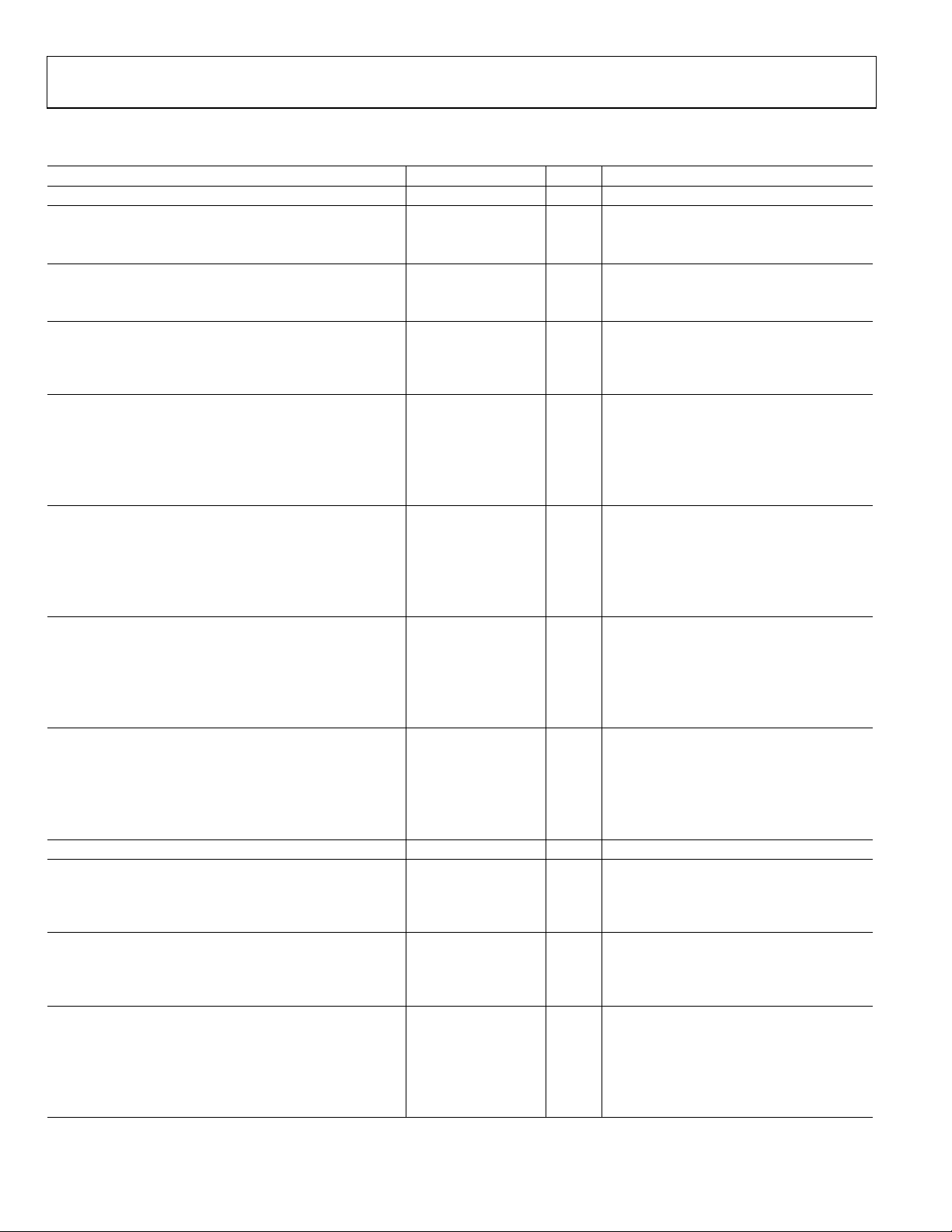
AD9512
CLOCK OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
Table 5.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
LVPECL OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz 40 fs rms BW = 12 kHz − 20 MHz (OC-12)
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 622.08 MHz
Divide Ratio = 1
CLK1 = 622.08 MHz 55 fs rms BW = 12 kHz − 20 MHz (OC-3)
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 155.52 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CLK1 = 400 MHz 215 fs rms
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CLK1 = 400 MHz 215 fs rms
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
Other LVPECL = 100 MHz Interferer(s)
Both LVDS (OUT3, OUT4) = 100 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 222 fs rms
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
Other LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
Both LVDS (OUT3, OUT4) = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 225 fs rms
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
Other LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
Both CMOS (OUT3, OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Outputs Off) Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 225 fs rms
Any LVPECL (OUT0 to OUT2) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
Other LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
Both CMOS (OUT3, OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Outputs On) Interferer(s)
LVDS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK1 = 400 MHz 264 fs rms
LVDS (OUT3) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CLK1 = 400 MHz 319 fs rms
LVDS (OUT4) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CLK1 = 400 MHz 395 fs rms
LVDS (OUT3) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
LVDS (OUT4) = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Rev. A | Page 10 of 48
Page 11
AD9512
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CLK1 = 400 MHz 395 fs rms
LVDS (OUT4) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
LVDS (OUT3) = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 367 fs rms
LVDS (OUT3) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CMOS (OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Outputs Off) Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 367 fs rms
LVDS (OUT4) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CMOS (OUT3) = 50 MHz (B Outputs Off) Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 548 fs rms
LVDS (OUT3) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CMOS (OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Outputs On) Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 548 fs rms
LVDS (OUT4) = 100 MHz
Divide Ratio = 4
CMOS (OUT3) = 50 MHz (B Outputs On) Interferer(s)
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CMOS OUTPUT ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
CLK1 = 400 MHz 275 fs rms
Both CMOS (OUT3, OUT4) = 100 MHz (B Output On)
Divide Ratio = 4
CLK1 = 400 MHz 400 fs rms
CMOS (OUT3) = 100 MHz (B Output On)
Divide Ratio = 4
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
LVDS (OUT4) = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 374 fs rms
CMOS (OUT3) = 100 MHz (B Output On)
Divide Ratio = 4
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CMOS (OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Output Off) Interferer(s)
CLK1 = 400 MHz 555 fs rms
CMOS (OUT3) = 100 MHz (B Output On)
Divide Ratio = 4
All LVPECL = 50 MHz Interferer(s)
CMOS (OUT4) = 50 MHz (B Output On) Interferer(s)
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
F
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Calculated from SNR of ADC method;
= 100 MHz with AIN = 170 MHz
F
C
Rev. A | Page 11 of 48
Page 12
AD9512
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DELAY BLOCK ADDITIVE TIME JITTER
100 MHz Output
Delay FS = 1 ns (1600 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 00000 0.61 ps
Delay FS = 1 ns (1600 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 11111 0.73 ps
Delay FS = 2 ns (800 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 00000 0.71 ps
Delay FS = 2 ns (800 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 11111 1.2 ps
Delay FS = 3 ns (800 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 00000 0.86 ps
Delay FS = 3 ns (800 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 11111 1.8 ps
Delay FS = 4 ns (400 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 00000 1.2 ps
Delay FS = 4 ns (400 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 11111 2.1 ps
Delay FS = 5 ns (200 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 00000 1.3 ps
Delay FS = 5 ns (200 A, 1C) Fine Adj. 11111 2.7 ps
Delay FS = 11 ns (200 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 00000 2.0 ps
Delay FS = 11 ns (200 A, 4C) Fine Adj. 00100 2.8 ps
1
This value is incremental. That is, it is in addition to the jitter of the LVDS or CMOS output without the delay. To estimate the total jitter, the LVDS or CMOS output jitter
should be added to this value using the root sum of the squares (RSS) method.
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
Table 6.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
CSB, SCLK (INPUTS)
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Current 110 µA
Input Logic 0 Current 1 µA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SDIO (WHEN INPUT)
Input Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Input Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Input Logic 1 Current 10 nA
Input Logic 0 Current 10 nA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
SDIO, SDO (OUTPUTS)
Output Logic 1 Voltage 2.7 V
Output Logic 0 Voltage 0.4 V
TIMING
Clock Rate (SCLK, 1/t
Pulse Width High, t
Pulse Width Low, t
SDIO to SCLK Setup, t
SCLK to SDIO Hold, t
SCLK to Valid SDIO and SDO, t
CSB to SCLK Setup and Hold, tS, t
CSB Minimum Pulse Width High, t
) 25 MHz
SCLK
PWH
PWL
DS
DH
1
Incremental additive jitter
1
CSB and SCLK have 30 kΩ
internal pull-down resistors
16 ns
16 ns
2 ns
1 ns
DV
H
PWH
6 ns
2 ns
3 ns
Rev. A | Page 12 of 48
Page 13
AD9512
FUNCTION PIN
Table 7.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Logic 1 Voltage 2.0 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.8 V
Logic 1 Current 110 µA
Logic 0 Current 1 µA
Capacitance 2 pF
RESET TIMING
Pulse Width Low 50 ns
SYNC TIMING
Pulse Width Low 1.5 High speed clock cycles
SYNC STATUS PIN
Table 8.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High (VOH) 2.7 V
Output Voltage Low (VOL) 0.4 V
The FUNCTION pin has a 30 kΩ internal pull-down resistor.
This pin should normally be held high. Do not leave NC.
High speed clock is CLK1 or CLK2, whichever is being used
for distribution.
Rev. A | Page 13 of 48
Page 14
AD9512
POWER
Table 9.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
POWER-UP DEFAULT MODE POWER DISSIPATION 550 600 mW
POWER DISSIPATION 800 mW
850 mW
Full Sleep Power-Down 35 60 mW
Power-Down (PDB) 60 80 mW
POWER DELTA
CLK1, CLK2 Power-Down 10 15 25 mW
Divider, DIV 2 − 32 to Bypass 23 27 33 mW For each divider.
LVPECL Output Power-Down (PD2, PD3) 50 65 75 mW
LVDS Output Power-Down 80 92 110 mW For each output.
CMOS Output Power-Down (Static) 56 70 85 mW For each output. Static (no clock).
CMOS Output Power-Down (Dynamic) 115 150 190 mW
CMOS Output Power-Down (Dynamic) 125 165 210 mW
Delay Block Bypass 20 24 60 mW
Power-up default state; does not include power
dissipated in output load resistors. No clock.
All outputs on. Three LVPECL outputs @ 800 MHz,
two CMOS out @ 62 MHz (5 pF load). Does not include
power dissipated in external resistors.
All outputs on. Three LVPECL outputs @ 800 MHz,
two CMOS out @ 125 MHz (5 pF load). Does not include
power dissipated in external resistors.
Maximum sleep is entered by setting 0Ah<1:0> = 01b
and 58h<4> = 1b. This powers off all band gap
references. Does not include power dissipated in
terminations.
Set FUNCTION pin for PDB operation by setting
58h<6:5> = 11b. Pull PDB low. Does not include
power dissipated in terminations.
For each output. Does not include dissipation
in termination (PD2 only).
For each CMOS output, single-ended. Clocking at
62 MHz with 5 pF load.
For each CMOS output, single-ended. Clocking at
125 MHz with 5 pF load.
Vs. delay block operation at 1 ns fs with maximum
delay; output clocking at 25 MHz.
Rev. A | Page 14 of 48
Page 15
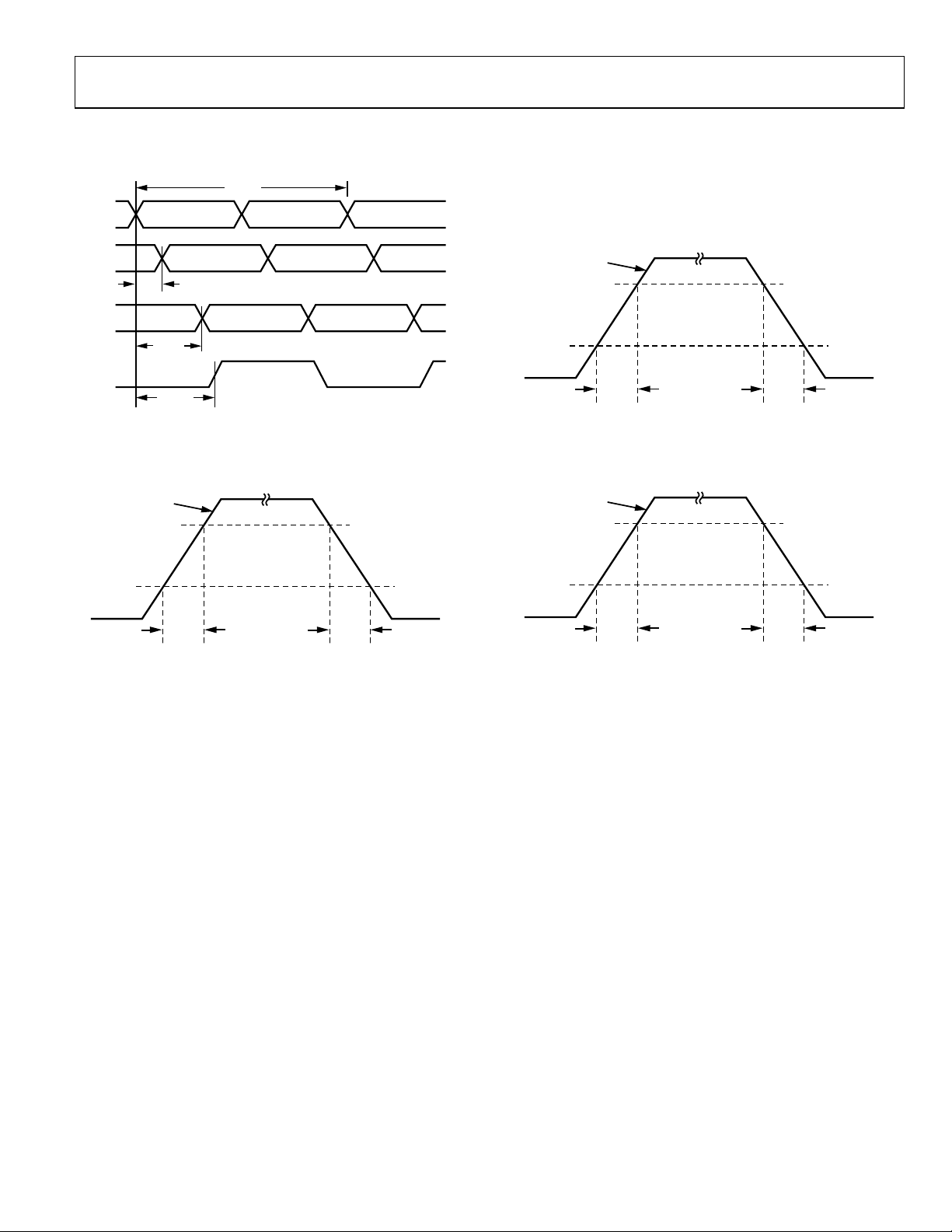
AD9512
C
TIMING DIAGRAMS
LK1
t
CLK1
DIFFERENTIAL
t
PECL
t
LVDS
t
CMOS
Figure 2. CLK1/CLK1B to Clock Output Timing, DIV = 1 Mode
DIFFERENTIAL
80%
LVPECL
20%
t
RP
Figure 3. LVPECL Timing, Differential
80%
LVDS
20%
t
05287-002
RL
t
FL
05287-065
Figure 4. LVDS Timing, Differential
SINGLE-ENDED
80%
CMOS
3pF LOAD
20%
t
FP
05287-064
t
RC
t
FC
05287-066
Figure 5. CMOS Timing, Single-Ended, 3 pF Load
Rev. A | Page 15 of 48
Page 16

AD9512
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 10.
With
Respect
Parameter or Pin
VS GND −0.3 +3.6 V
DSYNC/DSYNCB GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
RSET GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
CLK1, CLK1B, CLK2, CLK2B GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
CLK1 CLK1B −1.2 +1.2 V
CLK2 CLK2B −1.2 +1.2 V
SCLK, SDIO, SDO, CSB GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
OUT0, OUT1,
OUT2, OUT3, OUT4
FUNCTION GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
SYNC STATUS GND −0.3 VS + 0.3 V
Junction Temperature 150 °C
Storage Temperature −65 +150 °C
Lead Temperature (10 sec) 300 °C
to
GND −0.3 V
Min Max Unit
+ 0.3 V
S
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to
absolute maximum ratings for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
Thermal Resistance
48-Lead LFCSP
θ
= 28.5°C/W
JA
1
Thermal impedance measurements were taken on a 4-layer board in still air,
in accordance with EIA/JESD51-7.
1
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. A | Page 16 of 48
Page 17

AD9512
B
T
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
VS
OUT0
OUT0
GND
OUT2B
VSVSGND
24
VS
VS
GND
OUT2
37 GND
36
VS
35
OUT3
34
OUT3B
33
VS
32
VS
31
OUT4
30
OUT4B
29
VS
28
VS
27
OUT1
26
OUT1B
25
VS
05287-003
DSYNC
DSYNCB
CLK2B
CLK1B
FUNCTION
DNC = DO NO CONNEC
VS
VS
DNC
VS
CLK2
VS
CLK1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
VSVSGND
RSETVSGND
4847464544434241403938
PIN 1
INDICATOR
AD9512
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
1314151617181920212223
CSB
SDO
SDIO
SCLK
STATUS
Figure 6. 48-Lead LFCSP Pin Configuration
Note that the exposed paddle on this package is an electrical connection as well as a thermal enhancement. For the device to
function properly, the paddle must be attached to ground, GND.
Rev. A | Page 17 of 48
Page 18

AD9512
Table 11. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 DSYNC Detect Sync. Used for multichip synchronization.
2 DSYNCB Detect Sync Complement. Used for multichip synchronization.
3, 4, 6, 9, 18,
22, 23, 25, 28,
29, 32, 33, 36,
39, 40, 44, 47, 48
5 DNC Do Not Connect.
7 CLK2 Clock Input.
8 CLK2B Complementary Clock Input. Used in conjunction with CLK2.
10 CLK1 Clock Input.
11 CLK1B Complementary Clock Input. Used in conjunction with CLK1.
12 FUNCTION Multipurpose Input. Can be programmed as a reset (RESETB), sync (SYNCB), or power-down (PDB) pin.
13 STATUS Output Used to Monitor the Status of Multichip Synchronization.
14 SCLK Serial Data Clock.
15 SDIO Serial Data I/O.
16 SDO Serial Data Output.
17 CSB Serial Port Chip Select.
19, 24, 37,
38, 43, 46
20 OUT2B Complementary LVPECL Output.
21 OUT2 LVPECL Output.
26 OUT1B Complementary LVPECL Output.
27 OUT1 LVPECL Output.
30 OUT4B Complementary LVDS/Inverted CMOS Output. OUT4 includes a delay block.
31 OUT4 LVDS/CMOS Output. OUT4 includes a delay block.
34 OUT3B Complementary LVDS/Inverted CMOS Output.
35 OUT3 LVDS/CMOS Output.
41 OUT0B Complementary LVPECL Output.
42 OUT0 LVPECL Output.
45 RSET Current Set Resistor to Ground. Nominal value = 4.12 kΩ.
VS Power Supply (3.3 V).
GND Ground.
Note that the exposed paddle on this package is an electrical connection as well as a thermal enhancement. For the device to
function properly, the paddle must be attached to ground, GND.
Rev. A | Page 18 of 48
Page 19

AD9512
TERMINOLOGY
Phase Jitter and Phase Noise
An ideal sine wave can be thought of as having a continuous
and even progression of phase with time from 0 degrees to
360 degrees for each cycle. Actual signals, however, display a
certain amount of variation from ideal phase progression over
time. This phenomenon is called phase jitter. Although many
causes can contribute to phase jitter, one major cause is random
noise, which is characterized statistically as being Gaussian
(normal) in distribution.
This phase jitter leads to a spreading out of the energy of the
sine wave in the frequency domain, producing a continuous
power spectrum. This power spectrum is usually reported as a
series of values whose units are dBc/Hz at a given offset in
frequency from the sine wave (carrier). The value is a ratio
(expressed in dB) of the power contained within a 1 Hz
bandwidth with respect to the power at the carrier frequency.
For each measurement, the offset from the carrier frequency is
also given.
It is meaningful to integrate the total power contained within
some interval of offset frequencies (for example, 10 kHz to
10 MHz). This is called the integrated phase noise over that
frequency offset interval and can be readily related to the time
jitter due to the phase noise within that offset frequency
interval.
Phase noise has a detrimental effect on the performance of
ADCs, DACs, and RF mixers. It lowers the achievable dynamic
range of the converters and mixers, although they are affected
in somewhat different ways.
Time Jitter
Phase noise is a frequency domain phenomenon. In the time
domain, the same effect is exhibited as time jitter. When
observing a sine wave, the time of successive zero crossings is
seen to vary. In a square wave, the time jitter is seen as a
displacement of the edges from their ideal (regular) times of
occurrence. In both cases, the variations in timing from the
ideal are the time jitter. Since these variations are random in
nature, the time jitter is specified in units of seconds root mean
square (rms) or 1 sigma of the Gaussian distribution.
Time jitter that occurs on a sampling clock for a DAC or an
ADC decreases the SNR and dynamic range of the converter.
A sampling clock with the lowest possible jitter provides the
highest performance from a given converter.
Additive Phase Noise
It is the amount of phase noise that is attributable to the device
or subsystem being measured. The phase noise of any external
oscillators or clock sources has been subtracted. This makes it
possible to predict the degree to which the device impacts the
total system phase noise when used in conjunction with the
various oscillators and clock sources, each of which contribute
their own phase noise to the total. In many cases, the phase
noise of one element dominates the system phase noise.
Additive Time Jitter
It is the amount of time jitter that is attributable to the device
or subsystem being measured. The time jitter of any external
oscillators or clock sources has been subtracted. This makes it
possible to predict the degree to which the device will impact
the total system time jitter when used in conjunction with the
various oscillators and clock sources, each of which contribute
their own time jitter to the total. In many cases, the time jitter of
the external oscillators and clock sources dominates the system
time jitter.
Rev. A | Page 19 of 48
Page 20

AD9512
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
0.6
DEFAULT – 3 LVPECL + 2 LVDS (DIV ON)
0.7
0.5
POWER (W)
3 LVPECL + 2 LVDS (DIV BYPASSED)
0.4
3 LVPECL (DIV ON) 2 LVDS (DIV ON)
0.3
0 800400
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 7. Power vs. Frequency—LVPECL, LVDS
3GHz
CLK1 (EVAL BOARD)
5MHz
05287-080
0.6
POWER (W)
0.5
0.4
0 12010080604020
3GHz
3 LVPECL + 2 CMOS (DIV ON)
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 9. Power vs. Frequency—LVPECL, CMOS
CLK2 (EVAL BOARD)
5MHz
05287-081
Figure 8. CLK1 Smith Chart (Evaluation Board)
05287-043
Figure 10. CLK2 Smith Chart (Evaluation Board)
05287-044
Rev. A | Page 20 of 48
Page 21

AD9512
1.8
1.7
1.6
1.5
1.4
DIFFERENTIAL SWING (V p-p)
1.3
VERT 500mV/DIV HORIZ 500ps/DI V
Figure 11. LVPECL Differential Output @ 800 MHz
VERT 100mV/DIV HORIZ 500ps/ DIV
Figure 12. LVDS Differential Output @ 800 MHz
05287-053
1.2
100 16001100600
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
05287-056
Figure 14. LVPECL Differential Output Swing vs. Frequency
750
700
650
600
550
DIFFERENTIAL SWING (mV p-p)
05287-054
500
100 900700500300
OUTPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
05287-050
Figure 15. LVDS Differential Output Swing vs. Frequency
3.5
2pF
3.0
VERT 500mV/DIV HORIZ 1n s/ DIV
Figure 13. CMOS Single-Ended Output @ 250 MHz with 10 pF Load
)
OUTPUT (V
05287-055
Rev. A | Page 21 of 48
2.5
PK
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0
0 600500400300200100
OUTPUT F REQUENCY (MHz)
10pF
20pF
Figure 16. CMOS Single-Ended Output Swing vs. Frequency and Load
05287-047
Page 22

AD9512
–
–
–
–
–
110
110
–120
–130
–140
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
Figure 17. Additive Phase Noise—LVPECL DIV1, 245.76 MHz
Distribution Section Only
80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–140
–120
–130
–140
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
05287-051
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
05287-052
Figure 20. Additive Phase Noise—LVPECL DIV1, 622.08 MHz
80
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–140
–150
–160
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
Figure 18. Additive Phase Noise—LVDS DIV1, 245.76 MHz
100
–110
–120
–130
–140
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
Figure 19. Additive Phase Noise—CMOS DIV1, 245.76 MHz
–150
–160
05287-048
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
05287-049
Figure 21. Additive Phase Noise—LVDS DIV2, 122.88 MHz
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
L(f) (dBc/Hz)
–150
–160
05287-045
–170
10 10M1M100k10k1k100
OFFSET (Hz)
05287-046
Figure 22. Additive Phase Noise—CMOS DIV4, 61.44 MHz
Rev. A | Page 22 of 48
Page 23

AD9512
V
RSET
GND
S
FUNCTION
DSYNC
DSYNCB
CLK1
CLK1B
CLK2
CLK2B
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
CSB
SYNCB,
RESETB
PDB
DETECT
SYNC
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
VREF
PROGRAMMABLE
DIVIDERS AND
PHASE ADJUST
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
/1, /2, /3... /31, /32
AD9512
Δ
DELAY
ADJUST
T
SYNC
STATUS
LVPECL
LVPECL
LVPECL
LVDS/CMOS
LVDS/CMOS
SYNC
STATUS
OUT0
OUT0B
OUT1
OUT1B
OUT2
OUT2B
OUT3
OUT3B
OUT4
OUT4B
05287-090
Figure 23. Functional Block Diagram Showing Maximum Frequencies
Rev. A | Page 23 of 48
Page 24

AD9512
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
OVERALL
Figure 23 shows a block diagram of the AD9512. The AD9512
accepts inputs on either of two clock inputs (CLK1 or CLK2).
This clock can be divided by any integer value from 1 to 32.
The duty cycle and relative phase of the outputs can be selected.
There are three LVPECL outputs (OUT0, OUT1, OUT2) and
two outputs that can be either LVDS or CMOS level outputs
(OUT3, OUT4). OUT4 can also make use of a variable
delay block.
The AD9512 provides clock distribution function only; there is
no clock clean-up. The jitter of the input clock signal is passed
along directly to the distribution section and can dominate at
the clock outputs.
Figure 24 for the equivalent circuit of CLK1 and CLK2.
See
CLOCK INPUT
V
S
CLK
CLKB
2.5kΩ 2.5kΩ
5kΩ
5kΩ
Figure 24. CLK1, CLK2 Equivalent Input Circuit
FUNCTION PIN
The FUNCTION pin (Pin 12) has three functions that are
selected by the value in Register 58h<6:5>. There is an internal
30 kΩ pull-down resistor on this pin.
RESETB: 58h<6:5> = 00b (Default)
In its default mode, the FUNCTION pin acts as RESETB, which
generates an asynchronous reset or hard reset when pulled low.
The resulting reset writes the default values into the serial
control port buffer registers as well as loading them into the
chip control registers. The AD9512 immediately resumes
operation according to the default values. When the pin is taken
high again, an asynchronous sync is issued (see the
58h<6:5> = 01b
section).
STAGE
05287-016
SYNCB:
SYNCB: 58h<6:5> = 01b
The FUNCTION pin can be used to cause a synchronization
or alignment of phase among the various clock outputs.
The synchronization applies only to clock outputs that:
• are not powered down
• the divider is not masked (no sync = 0)
• are not bypassed (bypass = 0)
SYNCB is level and rising edge sensitive. When SYNCB is low,
the set of affected outputs are held in a predetermined state,
defined by each divider’s start high bit. On a rising edge, the
dividers begin after a predefined number of fast clock cycles
(fast clock is the selected clock input, CLK1 or CLK2) as
determined by the values in the divider’s phase offset bits.
The SYNCB application of the FUNCTION pin is always active,
regardless of whether the pin is also assigned to perform reset
or power-down. When the SYNCB function is selected, the
FUNCTION pin does not act as either RESETB or PDB.
PDB: 58h<6:5> = 11b
The FUNCTION pin can also be programmed to work as an
asynchronous full power-down, PDB. Even in this full powerdown mode, there is still some residual V
current because
S
some on-chip references continue to operate. In PDB mode, the
FUNCTION pin is active low. The chip remains in a powerdown state until PDB is returned to logic high. The chip returns
to the settings programmed prior to the power-down.
Chip Power-Down or Sleep Mode—PDB section for more
See the
details on what occurs during a PDB initiated power-down.
DSYNC AND DSYNCB PINS
The DSYNC and DSYNCB pins (Pin 1 and Pin 2) are used
when the AD9512 is used in a multichip synchronized
configuration (see the
Multichip Synchronization section).
CLOCK INPUTS
Two clock inputs (CLK1, CLK2) are available for use on the
AD9512. CLK1 and CLK2 can accept inputs up to 1600 MHz.
Figure 24 for the CLK1 and CLK2 equivalent input circuit.
See
The clock inputs are fully differential and self-biased. The signal
should be ac-coupled using capacitors. If a single-ended input
must be used, this can be accommodated by ac coupling to one
side of the differential input only. The other side of the input
should be bypassed to a quiet ac ground by a capacitor.
The unselected clock input (either CLK1 or CLK2) should be
powered down to eliminate any possibility of unwanted
crosstalk between the selected clock input and the unselected
clock input.
Rev. A | Page 24 of 48
Page 25

AD9512
DIVIDERS
Each of the five clock outputs of the AD9512 has its own
divider. The divider can be bypassed to get an output at the
same frequency as the input (1×). When a divider is bypassed, it
is powered down to save power.
All integer divide ratios from 1 to 32 may be selected. A divide
ratio of 1 is selected by bypassing the divider.
Example 2:
Set Divide Ratio = 8
high_cycles = 3
low_cycles = 3
Divide Ratio = (3 + 1) + (3 + 1) = 8
Each divider can be configured for divide ratio, phase, and duty
cycle. The phase and duty cycle values that can be selected
depend on the divide ratio that is chosen.
Setting the Divide Ratio
The divide ratio is determined by the values written via the SCP
to the registers that control each individual output, OUT0 to
OUT4. These are the even numbered registers beginning at 4Ah
and going through 52h. Each of these registers is divided into
bits that control the number of clock cycles the divider output
stays high (high_cycles <3:0>) and the number of clock cycles
the divider output stays low (low_cycles <7:4>). Each value is 4
bits and has the range of 0 to 15.
The divide ratio is set by
Divide Ratio = (high_cycles + 1) + (low_cycles + 1)
Example 1:
Set the Divide Ratio = 2
high_cycles = 0
low_cycles = 0
Divide Ratio = (0 + 1) + (0 + 1) = 2
Note that a Divide Ratio of 8 may also be obtained by setting:
high_cycles = 2
low_cycles = 4
Divide Ratio = (2 + 1) + (4 + 1) = 8
Although the second set of settings produces the same divide
ratio, the resulting duty cycle is not the same.
Setting the Duty Cycle
The duty cycle and the divide ratio are related. Different divide
ratios have different duty cycle options. For example, if Divide
Ratio = 2, the only duty cycle possible is 50%. If the Divide
Ratio = 4, the duty cycle can be 25%, 50%, or 75%.
The duty cycle is set by
Duty Cycle = (high_cycles + 1)/[(high_cycles + 1) + (low_cycles + 1)]
Tabl e 12 for the values of the available duty cycles for each
See
divide ratio.
Table 12. Duty Cycle and Divide Ratio
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
2 50 0 0
3 67 0 1
3 33 1 0
4 50 1 1
4 75 0 2
4 25 2 0
5 60 1 2
5 40 2 1
5 80 0 3
5 20 3 0
6 50 2 2
6 67 1 3
6 33 3 1
6 83 0 4
6 17 4 0
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Rev. A | Page 25 of 48
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
7 57 2 3
7 43 3 2
7 71 1 4
7 29 4 1
7 86 0 5
7 14 5 0
8 50 3 3
8 63 2 4
8 38 4 2
8 75 1 5
8 25 5 1
8 88 0 6
8 13 6 0
9 56 3 4
9 44 4 3
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Page 26

AD9512
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
9 67 2 5
9 33 5 2
9 78 1 6
9 22 6 1
9 89 0 7
9 11 7 0
10 50 4 4
10 60 3 5
10 40 5 3
10 70 2 6
10 30 6 2
10 80 1 7
10 20 7 1
10 90 0 8
10 10 8 0
11 55 4 5
11 45 5 4
11 64 3 6
11 36 6 3
11 73 2 7
11 27 7 2
11 82 1 8
11 18 8 1
11 91 0 9
11 9 9 0
12 50 5 5
12 58 4 6
12 42 6 4
12 67 3 7
12 33 7 3
12 75 2 8
12 25 8 2
12 83 1 9
12 17 9 1
12 92 0 A
12 8 A 0
13 54 5 6
13 46 6 5
13 62 4 7
13 38 7 4
13 69 3 8
13 31 8 3
13 77 2 9
13 23 9 2
13 85 1 A
13 15 A 1
13 92 0 B
13 8 B 0
14 50 6 6
14 57 5 7
14 43 7 5
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
14 64 4 8
14 36 8 4
14 71 3 9
14 29 9 3
14 79 2 A
14 21 A 2
14 86 1 B
14 14 B 1
14 93 0 C
14 7 C 0
15 53 6 7
15 47 7 6
15 60 5 8
15 40 8 5
15 67 4 9
15 33 9 4
15 73 3 A
15 27 A 3
15 80 2 B
15 20 B 2
15 87 1 C
15 13 C 1
15 93 0 D
15 7 D 0
16 50 7 7
16 56 6 8
16 44 8 6
16 63 5 9
16 38 9 5
16 69 4 A
16 31 A 4
16 75 3 B
16 25 B 3
16 81 2 C
16 19 C 2
16 88 1 D
16 13 D 1
16 94 0 E
16 6 E 0
17 53 7 8
17 47 8 7
17 59 6 9
17 41 9 6
17 65 5 A
17 35 A 5
17 71 4 B
17 29 B 4
17 76 3 C
17 24 C 3
17 82 2 D
17 18 D 2
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Rev. A | Page 26 of 48
Page 27

AD9512
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
17 88 1 E
17 12 E 1
17 94 0 F
17 6 F 0
18 50 8 8
18 56 7 9
18 44 9 7
18 61 6 A
18 39 A 6
18 67 5 B
18 33 B 5
18 72 4 C
18 28 C 4
18 78 3 D
18 22 D 3
18 83 2 E
18 17 E 2
18 89 1 F
18 11 F 1
19 53 8 9
19 47 9 8
19 58 7 A
19 42 A 7
19 63 6 B
19 37 B 6
19 68 5 C
19 32 C 5
19 74 4 D
19 26 D 4
19 79 3 E
19 21 E 3
19 84 2 F
19 16 F 2
20 50 9 9
20 55 8 A
20 45 A 8
20 60 7 B
20 40 B 7
20 65 6 C
20 35 C 6
20 70 5 D
20 30 D 5
20 75 4 E
20 25 E 4
20 80 3 F
20 20 F 3
21 52 9 A
21 48 A 9
21 57 8 B
21 43 B 8
21 62 7 C
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
21 38 C 7
21 67 6 D
21 33 D 6
21 71 5 E
21 29 E 5
21 76 4 F
21 24 F 4
22 50 A A
22 55 9 B
22 45 B 9
22 59 8 C
22 41 C 8
22 64 7 D
22 36 D 7
22 68 6 E
22 32 E 6
22 73 5 F
22 27 F 5
23 52 A B
23 48 B A
23 57 9 C
23 43 C 9
23 61 8 D
23 39 D 8
23 65 7 E
23 35 E 7
23 70 6 F
23 30 F 6
24 50 B B
24 54 A C
24 46 C A
24 58 9 D
24 42 D 9
24 63 8 E
24 38 E 8
24 67 7 F
24 33 F 7
25 52 B C
25 48 C B
25 56 A D
25 44 D A
25 60 9 E
25 40 E 9
25 64 8 F
25 36 F 8
26 50 C C
26 54 B D
26 46 D B
26 58 A E
26 42 E A
26 62 9 F
4Ah to 52h
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Rev. A | Page 27 of 48
Page 28

AD9512
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
26 38 F 9
27 52 C D
27 48 D C
27 56 B E
27 44 E B
27 59 A F
27 41 F A
28 50 D D
28 54 C E
28 46 E C
28 57 B F
28 43 F B
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
4Ah to 52h
Divide Ratio Duty Cycle (%)
29 52 D E
29 48 E D
29 55 C F
29 45 F C
30 50 E E
30 53 D F
30 47 F D
31 52 E F
31 48 F E
32 50 F F
LO<7:4> HI<3:0>
Rev. A | Page 28 of 48
Page 29

AD9512
Divider Phase Offset
The phase of each output may be selected, depending on the
divide ratio chosen. This is selected by writing the appropriate
values to the registers, which set the phase and start high/low
bit for each output. These are the odd numbered registers from
4Bh to 53h. Each divider has a 4-bit phase offset <3:0> and a
start high or low bit <4>.
Following a sync pulse, the phase offset word determines how
many fast clock (CLK1 or CLK2) cycles to wait before initiating
a clock output edge. The Start H/L bit determines if the divider
output starts low or high. By giving each divider a different
phase offset, output-to-output delays can be set in increments of
the fast clock period, t
CLK
.
Figure 25 shows three dividers, each set for DIV = 4, 50% duty
cycle. By incrementing the phase offset from 0 to 2, each output
is offset from the initial edge by a multiple of t
123456789101112131415
0
CLOCK INPUT
CLK
DIVIDER OUTPUTS
DIV = 4, DUTY = 50%
START = 0,
PHASE = 0
START = 0,
PHASE = 1
START = 0,
PHASE = 2
Figure 25. Phase Offset—All Dividers Set for DIV = 4, Phase Set from 0 to 2
t
CLK
t
CLK
2 ×
t
CLK
CLK
.
For example:
CLK1 = 491.52 MHz
t
= 1/491.52 = 2.0345 ns
CLK1
For DIV = 4
Phase Offset 0 = 0 ns
Phase Offset 1 = 2.0345 ns
Phase Offset 2 = 4.069 ns
The three outputs may also be described as:
OUT1 = 0°
OUT2 = 90°
OUT3 = 180°
Setting the phase offset to Phase = 4 results in the same relative
phase as the first channel, Phase = 0° or 360°.
05287-091
In general, by combining the 4-bit phase offset and the Start
H/L bit, there are 32 possible phase offset states (see Tab le 1 3 ).
Table 13. Phase Offset—Start H/L Bit
Phase Offset
(Fast Clock
Rising Edges)
Phase Offset <3:0> Start H/L <4>
4Bh to 53h
0 0 0
1 1 0
2 2 0
3 3 0
4 4 0
5 5 0
6 6 0
7 7 0
8 8 0
9 9 0
10 10 0
11 11 0
12 12 0
13 13 0
14 14 0
15 15 0
16 0 1
17 1 1
18 2 1
19 3 1
20 4 1
21 5 1
22 6 1
23 7 1
24 8 1
25 9 1
26 10 1
27 11 1
28 12 1
29 13 1
30 14 1
31 15 1
The resolution of the phase offset is set by the fast clock period
) at CLK1 or CLK2. As a result, every divide ratio does not
(t
CLK
have 32 unique phase offsets available. For any divide ratio, the
number of unique phase offsets is numerically equal to the
divide ratio (see Tab l e
13 ):
DIV = 4
Unique Phase Offsets Are Phase = 0, 1, 2, 3
DIV= 7
Unique Phase Offsets Are Phase = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Rev. A | Page 29 of 48
Page 30

AD9512
DIV = 18
Unique Phase Offsets Are Phase = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10,
11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17
Phase offsets may be related to degrees by calculating the phase
step for a particular divide ratio:
Phase Step = 360°/(Divide Ratio) = 360°/DIV
Using some of the same examples,
DIV = 4
Phase Step = 360°/4 = 90°
Unique Phase Offsets in Degrees Are Phase = 0°, 90°,
180°, 270°
DIV = 7
Phase Step = 360°/7 = 51.43°
This path adds some jitter greater than that specified for the
nondelay outputs. This means that the delay function should be
used primarily for clocking digital chips, such as FPGA, ASIC,
DUC, and DDC, rather than for data converters. The jitter is
higher for long full scales (~10 ns). This is because the delay
block uses a ramp and trip points to create the variable delay. A
longer ramp means more noise might be introduced.
Calculating the Delay
The following values and equations are used to calculate the
delay of the delay block.
Value of Ramp Current Control Bits (Register 35h or Register 39h
<2:0>) = Iramp_bits
(µA) = 200 × (Iramp_bits + 1)
I
RAMP
No. of Caps = No. of 0s + 1 in Ramp Control Capacitor
(Register 35h or Register 39h <5:3>), that is, 101 = 1 + 1 = 2;
110 = 2; 100 = 2 + 1 = 3; 001 = 2 + 1 = 3; 111 = 0 + 1 = 1)
Unique Phase Offsets in Degrees Are Phase = 0°, 51.43°,
102.86°, 154.29°, 205.71°, 257.15°, 308.57°
DELAY BLOCK
OUT4 (LVDS/CMOS) includes an analog delay element that
can be programmed (Register 34h to Register 36h) to give
variable time delays (T) in the clock signal passing through
that output.
CLOCK INPUT
OUT4 ONLY
÷N
∅SELECT
ΔT
FINE DELAYADJUST
(32 STEPS)
FULL-SCALE: 1ns TO 10ns
Figure 26. Analog Delay (OUT4)
The amount of delay that can be used is determined by the
frequency of the clock being delayed. The amount of delay can
approach one-half cycle of the clock period. For example, for a
10 MHz clock, the delay can extend to the full 10 ns maximum
of which the delay element is capable. However, for a 100 MHz
clock (with 50% duty cycle), the maximum delay is less than
5 ns (or half of the period).
OUT4 allows a full-scale delay in the range 1 ns to 10 ns. The
full-scale delay is selected by choosing a combination of ramp
current and the number of capacitors by writing the appropriate
values into Register 35h. There are 32 fine delay settings for
each full scale, set by Register 36h.
MUX
LVDS
CMOS
OUTPUT
DRIVER
Delay_Range (ns) = 200 × [(No. of Caps + 3)/(I
⎛
4
−
()
()
IOffset
RAMP
⎜
1016000.34ns
+×−+=
⎜
⎝
)] × 1.3286
RAMP
CapsofNo.
I
RAMP
⎞
1
−
⎟
6
×
⎟
⎠
Delay_Full_Scale (ns) = Delay_Range + Offset
Fine_Adj = Value of Delay Fine Adjust (Register 36h or
Register 3Ah <5:1>), that is, 11111 = 31
Delay (ns) = Offset + Delay_Range × Fine_adj × (1/31)
OUTPUTS
The AD9512 offers three different output level choices:
LVPECL, LVDS, and CMOS . O U T 0 to O U T 2 are LV P E C L o n l y.
OUT3 and OUT4 can be selected as either LVDS or CMOS.
Each output can be enabled or turned off as needed to save
05287-092
power.
The simplified equivalent circuit of the LVPECL outputs is
shown in Figure 27.
3.3V
OUT
OUTB
GND
Figure 27. LVPECL Output Simplified Equivalent Circuit
05287-037
Rev. A | Page 30 of 48
Page 31

AD9512
3
A
3
A
.5m
the LVPECL power-down mode is set to <11b>, the LVPECL
output is not protected from reverse bias and can be damaged
under certain termination conditions.
OUT
OUTB
.5m
05287-038
Figure 28. LVDS Output Simplified Equivalent Circuit
POWER-DOWN MODES
Chip Power-Down or Sleep Mode—PDB
The PDB chip power-down turns off most of the functions and
currents in the AD9512. When the PDB mode is enabled, a chip
power-down is activated by taking the FUNCTION pin to a
logic low level. The chip remains in this power-down state until
PDB is brought back to logic high. When woken up, the
AD9512 returns to the settings programmed into its registers
prior to the power-down, unless the registers are changed by
new programming while the PDB mode is active.
The PDB power-down mode shuts down the currents on the
chip, except the bias current necessary to maintain the LVPECL
outputs in a safe shutdown mode. This is needed to protect the
LVPECL output circuitry from damage that could be caused by
certain termination and load configurations when tri-stated.
Because this is not a complete power-down, it can be called
sleep mode.
When the AD9512 is in a PDB power-down or sleep mode, the
chip is in the following state:
• All clocks and sync circuits are off.
• All dividers are off.
• All LVDS/CMOS outputs are off.
• All LVPECL outputs are in safe off mode.
• The serial control port is active, and the chip responds to
commands.
If the AD9512 clock outputs must be synchronized to each
other, a SYNC (see the Single-Chip Synchronization section) is
required when exiting power-down mode.
Distribution Power-Down
The distribution section can be powered down by writing 1 to
Register 58h<3>. This turns off the bias to the distribution
section. If the LVPECL power-down mode is normal operation
<00>, it is possible for a low impedance load on that LVPECL
output to draw significant current during this power-down. If
Individual Clock Output Power-Down
Any of the five clock distribution outputs may be powered
down individually by writing to the appropriate registers via the
SCP. The register map details the individual power-down
settings for each output. The LVDS/CMOS outputs may be
powered down, regardless of their output load configuration.
The LVPECL outputs have multiple power-down modes
(see Register 3Dh, Register 3Eh, and Register 3Fh in Tab le 18 ).
These give some flexibility in dealing with various output
termination conditions. When the mode is set to <10b>, the
LVPECL output is protected from reverse bias to 2 V
+ 1 V. If
BE
the mode is set to <11b>, the LVPECL output is not protected
from reverse bias and can be damaged under certain
termination conditions. This setting also affects the operation
when the distribution block is powered down with Register
58h<3> = 1b (see the Distribution Power-Down section).
Individual Circuit Block Power-Down
Several of the AD9512 circuit blocks (such as CLK1 and CLK2)
can be powered down individually. This gives flexibility in
configuring the part for power savings when all chip
functionality is not needed.
RESET MODES
The AD9512 has several ways to force the chip into a reset
condition.
Power-On Reset—Start-Up Conditions when VS is Applied
A power-on reset (POR) is issued when the VS power supply is
turned on. This initializes the chip to the power-on conditions
that are determined by the default register settings. These are
indicated in the default value column of Tabl e 17 .
Asynchronous Reset via the FUNCTION Pin
As mentioned in the FUNCTION Pin section, a hard reset,
RESETB: 58h<6:5> = 00b (Default), restores the chip to the
default settings.
Soft Reset via the Serial Port
The serial control port allows a soft reset by writing to
Register 00h<5> = 1b. When this bit is set, the chip executes a
soft reset. This restores the default values to the internal
registers, except for Register 00h itself.
This bit is not self-clearing. The bit must be written to
00h<5> = 0b for the operation of the part to continue.
Rev. A | Page 31 of 48
Page 32

AD9512
SINGLE-CHIP SYNCHRONIZATION
SYNCB—Hardware SYNC
The AD9512 clocks can be synchronized to each other at any
time. The outputs of the clocks are forced into a known state
with respect to each other and then allowed to continue
clocking from that state in synchronicity. Before a
synchronization is done, the FUNCTION Pin must be set as the
input (58h<6:5> = 01b). Synchronization is done by forcing the
FUNCTION pin low, creating a SYNCB signal and then
releasing it.
See the SYNCB: 58h<6:5> = 01b section for a more detailed
description of what happens when the SYNCB: 58h<6:5> = 01b
signal is issued.
Soft SYNC—Register 58h<2>
A soft SYNC can be issued by means of a bit in
Register 58h<2>. This soft SYNC works the same as the
SYNCB, except that the polarity is reversed. A 1 written to this
bit forces the clock outputs into a known state with respect to
each other. When a 0 is subsequently written to this bit, the
clock outputs continue clocking from that state in
synchronicity.
slave must provide this same frequency back to the DSYNCB
input of the slave.
Multichip synchronization is enabled by writing to
Register 58h<0> = 1b on the slave AD9512. When this bit
is set, the STATUS pin becomes the output for the SYNC
signal. A low signal indicates an in-sync condition, and
a high indicates an out-of-sync condition.
Register 58h<1> selects the number of fast clock cycles that are
the maximum separation of the slow clock edges that are
considered synchronized. When 58h<1> = 0b (default), the
slow clock edges must be coincident within 1 to 1.5 high speed
clock cycles. If the coincidence of the slow clock edges is closer
than this amount, the SYNC flag stays low. If the coincidence of
the slow clock edges is greater than this amount, the SYNC flag
is set high. When Register 58h<1> = 1b, the amount of
coincidence required is 0.5 fast clock cycles to 1 fast clock
cycles.
Whenever the SYNC flag is set (high), indicating an out-of-sync
condition, a SYNCB signal applied simultaneously at the
FUNCTION pins of both AD9512s brings the slow clocks into
synchronization.
MULTICHIP SYNCHRONIZATION
The AD9512 provides a means of synchronizing two or more
AD9512s. This is not an active synchronization; it requires user
monitoring and action. The arrangement of two AD9512s to be
synchronized is shown in Figure 29.
Synchronization of two or more AD9512s requires a fast clock
and a slow clock. The fast clock can be up to 1 GHz and can be
the clock driving the master AD9512 CLK1 input or one of the
outputs of the master. The fast clock acts as the input to the
distribution section of the slave AD9512 and is connected to its
CLK1 input.
The slow clock is the clock that is synchronized across the two
chips. This clock must be no faster than one-fourth of the fast
clock, and no greater than 250 MHz. The slow clock is taken
from one of the outputs of the master AD9512 and acts as a
DSYNC input to the slave AD9512. One of the outputs of the
SYNCB
AD9512
MASTER
FUNCTION
(SYNCB)
DSYNC DSYNCB
AD9512
SLAVE
FAST CLOCK
<1GHz
CLK1
(SYNCB)
Figure 29. Multichip Synchronization
DETECT
FAST CLOCK
<1GHz
SLOW CLOCK
<250MHz
CLOCK
<250MHz
SYNC
SLOW
OUTN
OUTM
F
SYNC
OUTY
SYNCSTATUSFUNCTION
F
SYNC
05287-093
Rev. A | Page 32 of 48
Page 33

AD9512
SERIAL CONTROL PORT
The AD9512 serial control port is a flexible, synchronous, serial
communications port that allows an easy interface with many
industry-standard microcontrollers and microprocessors. The
AD9512 serial control port is compatible with most
synchronous transfer formats, including both the Motorola SPI®
and Intel® SSR protocols. The serial control port allows
read/write access to all registers that configure the AD9512.
Single or multiple byte transfers are supported, as well as MSB
first or LSB first transfer formats. The AD9512 serial control
port can be configured for a single bidirectional I/O pin (SDIO
only) or for two unidirectional I/O pins (SDIO/SDO).
SERIAL CONTROL PORT PIN DESCRIPTIONS
SCLK (serial clock) is the serial shift clock. This pin is an input.
SCLK is used to synchronize serial control port reads and
writes. Write data bits are registered on the rising edge of this
clock, and read data bits are registered on the falling edge. This
pin is internally pulled down by a 30 kΩ resistor to ground.
SDIO (serial data input/output) is a dual-purpose pin and acts
as either an input only or as both an input/output. The AD9512
defaults to two unidirectional pins for I/O, with SDIO used as
an input and SDO as an output. Alternatively, SDIO can be used
as a bidirectional I/O pin by writing to the SDO enable register
at 00h<7> = 1b.
SDO (serial data out) is used only in the unidirectional I/O
mode (00h<7> = 0b, default) as a separate output pin for
reading back data. The AD9512 defaults to this I/O mode.
Bidirectional I/O mode (using SDIO as both input and output)
may be enabled by writing to the SDO enable register at
00h<7> = 1b.
CSB (chip select bar) is an active low control that gates the read
and write cycles. When CSB is high, SDO and SDIO are in a
high impedance state. This pin is internally pulled down by a
30 kΩ resistor to ground. It should not be left NC or tied low.
See the Framing a Communication Cycle with CSB section on
the use of the CSB in a communication cycle.
SCLK (PIN 14)
SDIO (PIN 15)
SDO (PIN 16)
CSB (PIN 17)
Figure 30. Serial Control Port
AD9512
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
05287-094
GENERAL OPERATION OF SERIAL CONTROL PORT
Framing a Communication Cycle with CSB
Each communication cycle (a write or a read operation) is gated
by the CSB line. CSB must be brought low to initiate a
communication cycle. CSB must be brought high at the
completion of a communication cycle (see Figure 38). If CSB is
not brought high at the end of each write or read cycle (on a
byte boundary), the last byte is not loaded into the register
buffer.
CSB stall high is supported in modes where three or fewer bytes
of data (plus instruction data) are transferred (W1:W0 must be
set to 00, 01, or 10, see Tabl e
14 ). In these modes, CSB can
temporarily return high on any byte boundary, allowing time
for the system controller to process the next byte. CSB can go
high on byte boundaries only and can go high during either
part (instruction or data) of the transfer. During this period, the
serial control port state machine enters a wait state until all data
has been sent. If the system controller decides to abort the
transfer before all of the data is sent, the state machine must be
reset by either completing the remaining transfer or by
returning the CSB low for at least one complete SCLK cycle (but
less than eight SCLK cycles). Raising the CSB on a nonbyte
boundary terminates the serial transfer and flushes the buffer.
In the streaming mode (W1:W0 = 11b), any number of data
bytes can be transferred in a continuous stream. The register
address is automatically incremented or decremented (see the
MSB/LSB First Transfers section).
CSB must be raised at the
end of the last byte to be transferred, thereby ending the stream
mode.
Communication Cycle—Instruction Plus Data
There are two parts to a communication cycle with the AD9512.
The first writes a 16-bit instruction word into the AD9512,
coincident with the first 16 SCLK rising edges. The instruction
word provides the AD9512 serial control port with information
regarding the data transfer, which is the second part of the
communication cycle. The instruction word defines whether
the upcoming data transfer is a read or a write, the number of
bytes in the data transfer, and the starting register address for
the first byte of the data transfer.
Write
If the instruction word is for a write operation (I15 = 0b), the
second part is the transfer of data into the serial control port
buffer of the AD9512. The length of the transfer (1, 2, 3 bytes,
or streaming mode) is indicated by two bits (W1:W0) in the
instruction byte. CSB can be raised after each sequence of eight
bits to stall the bus (except after the last byte, where it ends the
cycle). When the bus is stalled, the serial transfer resumes when
CSB is lowered. Stalling on nonbyte boundaries resets the serial
control port.
Since data is written into a serial control port buffer area, not
directly into the AD9512’s actual control registers, an additional
operation is needed to transfer the serial control port buffer
contents to the actual control registers of the AD9512, thereby
causing them to take effect. This update command consists of
Rev. A | Page 33 of 48
Page 34

AD9512
SCLK
writing to Register 5Ah<0> = 1b. This update bit is self-clearing
(it is not required to write 0 to it to clear it). Since any number
of bytes of data can be changed before issuing an update
command, the update simultaneously enables all register
changes since any previous update.
Phase offsets or divider synchronization will not become
effective until a SYNC is issued (see the Single-Chip
Synchronization
Read
If the instruction word is for a read operation (I15 = 1b), the
next N × 8 SCLK cycles clock out the data from the address
specified in the instruction word, where N is 1 to 4 as
determined by W1:W0. The readback data is valid on the falling
edge of SCLK.
The default mode of the AD9512 serial control port is
unidirectional mode; therefore, the requested data appears on
the SDO pin. It is possible to set the AD9512 to bidirectional
mode by writing the SDO enable register at 00h<7> = 1b. In
bidirectional mode, the readback data appears on the SDIO pin.
A readback request reads the data that is in the serial control
port buffer area, not the active data in the AD9512’s actual
control registers.
secti
on).
For a write, the instruction word is followed by the number of
bytes of data indicated by Bits W1:W0, which is interpreted
according to Tab le
14 .
Table 14. Byte Transfer Count
W1 W0 Bytes to Transfer
0 0 1
0 1 2
1 0 3
1 1 4
A12:A0: These 13 bits select the address within the register map
that is written to or read from during the data transfer portion
of the communications cycle. The AD9512 does not use all of
the 13-bit address space. Only Bits A6:A0 are needed to cover
the range of the 5Ah registers used by the AD9512. Bits A12:A7
must always be 0b. For multibyte transfers, this address is the
starting byte address. In MSB first mode, subsequent bytes
increment the address.
MSB/LSB FIRST TRANSFERS
The AD9512 instruction word and byte data may be MSB first
or LSB first. The default for the AD9512 is MSB first. The LSB
first mode may be set by writing 1b to Register 00h<6>. This
takes effect immediately (because it only affects the operation of
the serial control port) and does not require that an update be
executed. Immediately after the LSB first bit is set, all serial
control port operations are changed to LSB first order.
SDIO
SDO
CSB
SERIAL
CONTROL
PORT
Figure 31. Relationship Between Serial Control Port Register Buffers and
Control Registers of the AD9512
UPDATE
REGISTERS
5Ah <0>
REGISTER BUFFERS
CONTROL REGISTERS
AD9512
CORE
05287-095
The AD9512 uses Address 00h to Address 5Ah. Although the
AD9512 serial control port allows both 8-bit and 16-bit
instructions, the 8-bit instruction mode provides access to five
address bits (A4 to A0) only, which restricts its use to the
address space 00h to 01F. The AD9512 defaults to 16-bit
instruction mode on power-up. The 8-bit instruction mode
(although defined for this serial control port) is not useful for
the AD9512; therefore, it is not discussed further in this data
sheet.
THE INSTRUCTION WORD (16 BITS)
The MSB of the instruction word is R/W, which indicates
whether the instruction is a read or a write. The next two bits,
W1:W0, indicate the length of the transfer in bytes. The final 13
bits are the addresses (A12:A0) at which to begin the read or
write operation.
When MSB first mode is active, the instruction and data bytes
must be written from MSB to LSB. Multibyte data transfers in
MSB first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the most significant data byte. Subsequent
data bytes must follow in order from high address to low
address. In MSB first mode, the serial control port internal
address generator decrements for each data byte of the
multibyte transfer cycle.
When LSB_First = 1b (LSB first), the instruction and data bytes
must be written from LSB to MSB. Multibyte data transfers in
LSB first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the least significant data byte followed by
multiple data bytes. The serial control port internal byte address
generator increments for each byte of the multibyte transfer
cycle.
The AD9512 serial control port register address decrements
from the register address just written toward 0000h for
multibyte I/O operations if the MSB first mode is active
(default). If the LSB first mode is active, the serial control port
register address increments from the address just written
toward 1FFFh for multibyte I/O operations.
Unused addresses are not skipped during multibyte I/O
operations; therefore, it is important to avoid multibyte I/O
operations that would include these addresses.
Rev. A | Page 34 of 48
Page 35

AD9512
K
Table 15. Serial Control Port, 16-Bit Instruction Word, MSB First
MSB
I15 I14 I13 I12 I11 I10 I9 I8 I7 I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0
R/
CSB
SCLK
W1 W0 A12 = 0 A11 = 0 A10 = 0 A9 = 0 A8 = 0 A7 = 0 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
W
DON’T C AR E
LSB
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
SDIO A12W0W1R/W A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGISTER (N) DATA REGI ST E R (N – 1) DATA
Figure 32. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, 2 Bytes of Data
CSB
SCLK
DON'T CARE
SDIO
SDO
DON'T CARE
A12W0W1R/W A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
REGISTER (N) DATA16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGISTER (N – 1) DATA REGISTER (N – 2) DATA REGISTER (N – 3) DATA
Figure 33. Serial Control Port Read—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, 4 Bytes of Data
t
CSB
SCLK
SDIO
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
DS
t
S
R/W
t
DH
W1W0A12A11A10A9A8A7A6A5D4D3D2D1D0
t
HI
t
CLK
t
LO
t
H
Figure 34. Serial Control Port Write—MSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, Timing Measurements
CSB
DON'T CARE
DON'T CA RE
DON'T
CARE
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
5287-019
05287-020
05287-021
SCL
t
DV
SDIO
SDO
DATA BIT N – 1DATA BIT N
05287-022
Figure 35. Timing Diagram for Serial Control Port Register Read
CSB
DON’T C AR E
SCLK
SDIO
DON'T CARE
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 D1D0R/WW1W0 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7
16-BIT INSTRUCTION HEADER REGISTER (N) DATA REGIST E R (N + 1) DATA
DON'T CARE
DON'T CARE
5287-023
Figure 36. Serial Control Port Write—LSB First, 16-Bit Instruction, 2 Bytes Data
Rev. A | Page 35 of 48
Page 36

AD9512
A
t
S
CSB
t
CLK
t
HI
t
SCLK
SDIO
DS
t
DH
BI N BI N + 1
Figure 37. Serial Control Port Timing—Write
Table 16. Serial Control Port Timing
Parameter Description
t
DS
t
DH
t
CLK
t
S
t
H
t
HI
t
LO
Setup time between data and rising edge of SCLK
Hold time between data and rising edge of SCLK
Period of the clock
Setup time between CSB and SCLK
Hold time between CSB and SCLK
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic high state
Minimum period that SCLK should be in a logic low state
CSB
16 INSTRUCTI ON BITS + 8 DATA BITS 16 INSTRUCT ION BITS + 8 DATA BITS
SCLK
t
LO
CSB TOGGLE INDIC
CYCLE COMPLET E
t
TES
PWH
t
H
05287-040
SDIO
TIMING DIAGRAM FOR TWO SUCCESSIVE COMMUNICATION CYCLES. NO TE THAT CSB MUST
BE TOG G LED HIGH AND THEN LOW AT THE COMP L ET I ON OF A COMMUNICATIO N CYCLE.
COMMUNICATIO N CY CLE 1 COMMUNICATION CYCLE 2
05287-067
Figure 38. Use of CSB to Define Communication Cycles
Rev. A | Page 36 of 48
Page 37

AD9512
REGISTER MAP AND DESCRIPTION
SUMMARY TABLE
Table 17. AD9512 Register Map
Def.
Addr
(Hex)
00
01 to
33
34 Delay Bypass 4 Not Used Bypass 01
35
36
37, 38,
39, 3A,
3B, 3C
3D LVPECL OUT0 Not Used
3E LVPECL OUT1 Not Used
3F LVPECL OUT2 Not Used
40
41
42, 43,
44
45
46, 47,
48, 49
4A Divider 0 Low Cycles <7:4> High Cycles <3:0> 00 Divide by 2
4B Divider 0 Bypass
4C Divider 1 Low Cycles <7:4> High Cycles <3:0> 11 Divide by 4
4D Divider 1 Bypass
4E Divider 2 Low Cycles <7:4> High Cycles <3:0> 33 Divide by 8
Parameter Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
Serial
Control Port
Configuration
Not Used
FINE DELAY
ADJUST
Delay
Full-Scale 4
Delay Fine
Adjust 4
Not Used
OUTPUTS
LVDS_CMOS
OUT 3
LVDS_CMOS
OUT 4
Not Used
CLK1 AND
CLK2
Clocks Select,
Power-Down
(PD) Options
Not Used
DIVIDERS
SDO Inactive
(Bidirectional
Mode)
Not Used Ramp Capacitor <5:3> Ramp Current <2:0> 00
Not Used 5-Bit Fine Delay <5:1> Not Used 00
Not Used
LSB
First
Not Used
Not Used
No
Sync
No
Sync
Soft
Reset
CLKs
in
PD
Force Start H/L Phase Offset <3:0> 00 Phase = 0
Force Start H/L Phase Offset <3:0> 00 Phase = 0
Long
Instruction
CMOS
Inverted
Driver On
CMOS
Inverted
Driver On
Not Used
Output Level
<3:2>
Output Level
<3:2>
Output Level
<3:2>
Logic
Select
Logic
Select
Not
Used
Not Used 10
Output Level
<2:1>
Output Level
<2:1>
CLK2
PD
CLK1
Bit 0
(LSB)
Power-Down
<1:0>
Power-Down
<1:0>
Power-Down
<1:0>
Output
Power
Output
Power
Select
PD
CLK IN
Value
(Hex)
08 ON
08 ON
08 ON
02 LVDS, ON
02 LVDS, ON
01
Notes
Fine
Delays
Bypassed
Bypass
Delay
Max. Delay
Full-Scale
Min. Delay
Value
Input
Receivers
All Clocks
ON, Select
CLK1
Rev. A | Page 37 of 48
Page 38

AD9512
Def.
Addr
(Hex) Parameter Bit 7 (MSB) Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1
4F Divider 2 Bypass
Sync
50 Divider 3 Low Cycles <7:4> High Cycles <3:0> 00 Divide by 2
51 Divider 3 Bypass
Sync
52 Divider 4 Low Cycles <7:4> High Cycles <3:0> 11 Divide by 4
53 Divider 4 Bypass
Sync
54, 55,
56, 57
58
59 Not Used
5A
Not Used
FUNCTION
FUNCTION
Pin and Sync
Update
Registers
END
Not
Used
Set FUNCTION
Force Start H/L Phase Offset <3:0> 00 Phase = 0
No
Force Start H/L Phase Offset <3:0> 00 Phase = 0
No
Force Start H/L Phase Offset <3:0> 00 Phase = 0
No
PD Sync
Pin
Not Used
PD All
Ref
Sync
Reg
Sync
Select
Bit 0
(LSB)
Sync
Enable
Update
Registers
Value
(Hex)
00
00
Notes
FUNCTION
Pin =
RESETB
SelfClearing
Bit
Rev. A | Page 38 of 48
Page 39

AD9512
REGISTER MAP DESCRIPTION
Tabl e 18 lists the AD9512 control registers by hexadecimal address. A specific bit or range of bits within a register is indicated by angle
brackets. For example, <3> refers to Bit 3, while <5:2> refers to the range of bits from Bit 5 through Bit 2.
functionality of the control registers on a bit-by-bit basis. For a more concise (but less descriptive) table, see
Table 18. AD9512 Register Descriptions
Reg.
Addr.
(Hex)
00 <3:0> Not Used.
00 <4> Long Instruction
00 <5> Soft Reset
00 <6> LSB First
00 <7>
Not Used
01 to 33 <7:0> Not Used.
Fine Delay Adjust
34 <0>
34 <7:1> Not Used.
35 <2:0>
0 0 0 200
0 0 1 400
0 1 0 600
0 1 1 800
1 0 0 1000
1 0 1 1200
1 1 0 1400
1 1 1 1600
35 <5:3>
0 0 0 4 (Default)
0 0 1 3
0 1 0 3
0 1 1 2
1 0 0 3
1 0 1 2
1 1 0 2
1 1 1 1
Bit(s) Name Description
Serial Control Port
Configuration
SDO Inactive
(Bidirectional
Mode)
Delay Control
OUT4
Ramp Current
OUT4
Ramp Capacitor
OUT4
Any changes to this register takes effect immediately. Register 5Ah<0> Update Registers
does not have to be written.
When this bit is set (1), the instruction phase is 16 bits. When clear (0), the instruction phase
is 8 bits. The default, and only, mode for this part is long instruction (Default = 1b).
When this bit is set (1), the chip executes a soft reset, restoring default values to the internal
registers, except for this register, 00h. This bit is not self-clearing. A clear (0) has to be written
to it in order to clear it.
When this bit is set (1), the input and output data is oriented as LSB first. Additionally, register
addressing increments. If this bit is clear (0), data is oriented as MSB first and register
addressing decrements. (Default = 0b, MSB first.)
When set (1), the SDO pin is tri-state and all read data goes to the SDIO pin. When clear (0),
the SDO is active (unidirectional mode). (Default = 0b).
Delay Block Control Bit.
Bypasses Delay Block and Powers It Down (Default = 1b).
The slowest ramp (200 µs) sets the longest full scale of approximately 10 ns.
<2> <1> <0> Ramp Current (μs)
Selects the Number of Capacitors in Ramp Generation Circuit.
More Capacitors => Slower Ramp.
<5> <4> <3> Number of Capacitors
Tabl e 1 8 describes the
Tabl e 17 .
35 <7:6> Not Used.
36 <0> Not Used.
Rev. A | Page 39 of 48
Page 40

AD9512
Reg.
Addr.
(Hex)
36 <5:1>
36 <7:6> Not Used.
37 (38)
(39)
(3A) (3B)
(3C)
OUTPUTS
3D (3E)
(3F)
ON 0 0 Normal Operation. ON
PD1 0 1 Test Only—Do Not Use. OFF
PD2 1 0
Bit(s) Name Description
Delay Fine Adjust
OUT4
<7:0> Not Used.
<1:0>
Power-Down LVPECL
OUT0
(OUT1)
(OUT2)
Sets Delay Within Full Scale of the Ramp; There Are 32 Steps.
00000b => Zero Delay (Default).
11111b => Maximum Delay.
Mode <1> <0> Description Output
Safe Power-Down.
Partial Power-Down; Use If Output Has
Load Resistors.
OFF
PD3 1 1
3D (3E)
(3F)
0 0 490
0 1 330
1 0 805 (Default)
1 1 650
3D (3E)
(3F)
40 (41) <0>
0 0 1.75 100
0 1 3.5 (Default) 100
1 0 5.25 50
1 1 7 50
40 (41) <3>
40 (41) <4>
40 (41) <7:5> Not Used.
<3:2>
<7:4> Not Used.
Output Level LVPECL
OUT0
(OUT1)
(OUT2)
Power-Down
LVDS/CMOS
OUT3
(OUT4)
Output Current Level
LVDS
OUT3
(OUT4)
LVDS/CMOS Select
OUT3
(OUT4)
Inverted CMOS Driver
OUT3
(OUT4)
Output Single-Ended Voltage Levels for LVPECL Outputs.
<3> <2> Output Voltage (mV)
Power-Down Bit for Both Output and LVDS Driver.
0 = LVDS/CMOS on (Default).
1 = LVDS/CMOS Power-Down.
40 (41) <2:1>
<2> <1> Current (mA) Termination (Ω)
0 = LVDS (Default).
1 = CMOS.
Affects Output Only when in CMOS Mode.
0 = Disable Inverted CMOS Driver (Default).
1 = Enable Inverted CMOS Driver.
Total Power-Down.
Use Only If Output Has No Load Resistors.
OFF
Rev. A | Page 40 of 48
Page 41

AD9512
Reg.
Addr.
(Hex)
CLK1 AND CLK2
45 <0> Clock Select
45 <1> CLK1 Power-Down 1 = CLK1 Input Is Powered Down (Default = 0b).
45 <2> CLK2 Power-Down 1 = CLK2 Input Is Powered Down (Default = 0b).
45 <4:3> Not Used.
Bit(s) Name Description
0: CLK2 Drives Distribution Section.
1: CLK1 Drives Distribution Section (Default).
45 <5>
45 <7:6> Not Used.
46 (47)
(48) (49)
DIVIDERS
<3:0> Divider High Number of Clock Cycles Divider Output Stays High.
4A OUT0
(4C) (OUT1)
(4E) (OUT2)
(50) (OUT3)
(52) (OUT4)
<7:4> Divider Low Number of Clock Cycles Divider Output Stays Low.
4A OUT0
(4C) (OUT1)
(4E) (OUT2)
(50) (OUT3)
(52) (OUT4)
<3:0> Phase Offset Phase Offset (Default = 0000b).
4B OUT0
(4D) (OUT1)
(4F) (OUT2)
(51) (OUT3)
(53) (OUT4)
<4> Start Selects Start High or Start Low.
4B OUT0 (Default = 0b).
(4D) (OUT1)
(4F) (OUT2)
(51) (OUT3)
(53) (OUT4)
4B OUT0
(4D) (OUT1)
(4F) (OUT2)
(51) (OUT3)
(53) (OUT4)
<6> Nosync Ignore Chip-Level Sync Signal (Default = 0b).
4B OUT0
(4D) (OUT1)
(4F) (OUT2)
(51) (OUT3)
(53) (OUT4)
<7:0> Not Used.
<5> Force
All Clock Inputs PowerDown
1 = Power-Down CLK1 and CLK2 Inputs and Associated Bias and Internal Clock Tree;
(Default = 0b).
Forces Individual Outputs to the State Specified in Start (Above).
This Function Requires That Nosync (Below) Also Be Set (Default = 0b).
Rev. A | Page 41 of 48
Page 42

AD9512
Reg.
Addr.
(Hex)
<7> Bypass Divider Bypass and Power-Down Divider Logic; Route Clock Directly to Output (Default = 0b).
4B OUT0
(4D) (OUT1)
(4F) (OUT2)
(51) (OUT3)
(53) (OUT4)
54 (55)
(56) (57)
FUNCTION
58 <0> SYNC Detect Enable 1 = Enable SYNC Detect (Default = 0b).
58 <1> SYNC Select
58 <2> Soft SYNC
58 <3> Dist Ref Power-Down 1 = Power-Down the References for the Distribution Section (Default = 0b).
58 <4> SYNC Power-Down 1 = Power-Down the SYNC (Default = 0b).
58 <6:5> FUNCTION Pin Select
58 <7> Not Used.
59 <7:0> Not Used.
5A <0> Update Registers
5A <7:1> Not Used.
END
Bit(s) Name Description
<7:0> Not Used.
1 = Raise Flag if Slow Clocks Are Out-of-Sync by 0.5 to 1 High Speed Clock Cycles.
0 (Default) = Raise Flag if Slow Clocks Are Out-of-Sync by 1 to 1.5 High Speed Clock Cycles.
Soft SYNC bit works the same as the FUNCTION pin when in SYNCB mode, except that this bit’s
polarity is reversed. That is, a high level forces selected outputs into a known state, and a high >
low transition triggers a sync (Default = 0b).
<6> <5> Function
0 0 RESETB (Default)
0 1 SYNCB
1 0 Test Only; Do Not Use
1 1 PDB
1 written to this bit updates all registers and transfers all serial control port register buffer
contents to the control registers on the next rising SCLK edge. This is a self-clearing bit. 0 does
not have to be written to clear it.
Rev. A | Page 42 of 48
Page 43

AD9512
POWER SUPPLY
The AD9512 requires a 3.3 V ± 5% power supply for VS.
The tables in the
Specifications section give the performance
expected from the AD9512 with the power supply voltage
within this range. The absolute maximum range of −0.3 V to
+3.6 V, with respect to GND, must never be exceeded on
the VS pin.
Good engineering practice should be followed in the layout of
power supply traces and ground plane of the PCB. The power
supply should be bypassed on the PCB with adequate
capacitance (>10 F). The AD9512 should be bypassed with
adequate capacitors (0.1 F) at all power pins, as close as
possible to the part. The layout of the AD9512 evaluation board
(AD9512/PCB) is a good example.
The AD9512 is a complex part that is programmed for its
desired operating configuration by on-chip registers. These
registers are not maintained over a shutdown of external power.
This means that the registers can lose their programmed values
if V
is lost long enough for the internal voltages to collapse.
S
Careful bypassing should protect the part from memory loss
under normal conditions. Nonetheless, it is important that the
V
power supply not become intermittent, or the AD9512 risks
S
losing its programming.
The internal bias currents of the AD9512 are set by the R
SET
resistors. This resistor should be as close as possible to the value
given as conditions in the
(R
= 4.12 kΩ). This is a standard 1% resistor value and should
SET
Specifications section
be readily obtainable. The bias currents set by this resistor
determine the logic levels and operating conditions of the
internal blocks of the AD9512. The performance figures given
in the
Specifications section assume that this specific resistor
value is used.
POWER MANAGEMENT
The power usage of the AD9512 can be managed to use only the
power required for the functions that are being used. Unused
features and circuitry can be powered down to save power. The
following circuit blocks can be powered down, or are powered
down when not selected (see the
section):
• Any of the dividers are powered down when bypassed—
equivalent to divide-by-one.
• The adjustable delay block on OUT4 is powered down
when not selected.
• Any output can be powered down. However, LVPECL
outputs have both a safe and an off condition. When the
LVPECL output is terminated, only the safe shutdown
should be used to protect the LVPECL output devices. This
still consumes some power.
• The entire distribution section can be powered down when
not needed.
Powering down a functional block does not cause the
programming information for that block (in the registers) to be
lost. This means that blocks can be powered on and off without
otherwise having to reprogram the AD9512. However,
synchronization is lost. A SYNC must be issued to
resynchronize (see the
Single-Chip Synchronization section).
Register Map and Description
The exposed metal paddle on the AD9512 package is an
electrical connection, as well as a thermal enhancement. For
the device to function properly, the paddle must be properly
attached to ground (GND). The PCB acts as a heat sink for the
AD9512; therefore, this GND connection should provide a
good thermal path to a larger dissipation area, such as a ground
plane on the PCB. See the layout of the AD9512 evaluation
board (AD9512/PCB or AD9512-VCO/PCB) for a good
example.
Rev. A | Page 43 of 48
Page 44

AD9512
APPLICATIONS
USING THE AD9512 OUTPUTS FOR ADC CLOCK APPLICATIONS
Any high speed analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is extremely
sensitive to the quality of the sampling clock provided by the
user. An ADC can be thought of as a sampling mixer; any noise,
distortion, or timing jitter on the clock is combined with the
desired signal at the A/D output. Clock integrity requirements
scale with the analog input frequency and resolution, with
higher analog input frequency applications at ≥14-bit resolution
being the most stringent. The theoretical SNR of an ADC is
limited by the ADC resolution and the jitter on the sampling
clock. Considering an ideal ADC of infinite resolution where
the step size and quantization error can be ignored, the available
SNR can be expressed approximately by
⎤
⎡
1
SNR
×=
log20
⎢
⎢
⎣
where f is the highest analog frequency being digitized, and t
the rms jitter on the sampling clock.
required sampling clock jitter as a function of the analog
frequency and effective number of bits (ENOB).
120
tj = 0.1ps
100
80
SNR (dB)
60
40
20
1 3 10 30 100
FULL-SCALE SINE WAVE ANALOG INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 39. ENOB and SNR vs. Analog Input Frequency
See Application Notes AN-756 and AN-501 on the ADI website
at
www.analog.com.
Many high performance ADCs feature differential clock inputs
to simplify the task of providing the required low jitter clock on
a noisy PCB. (Distributing a single-ended clock on a noisy PCB
can result in coupled noise on the sample clock. Differential
distribution has inherent common-mode rejection, which can
provide superior clock performance in a noisy environment.)
The AD9512 features both LVPECL and LVDS outputs that
provide differential clock outputs, which enable clock solutions
that maximize converter SNR performance. The input
requirements of the ADC (differential or single-ended, logic
2π
⎥
ft
⎥
j
⎦
tj = 50fs
tj = 1ns
tj = 1ps
tj = 10ps
tj = 100ps
Figure 39 shows the
SNR = 20log
1
10
2πft
j
is
j
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
ENOB
05287-024
level, termination) should be considered when selecting the best
clocking/converter solution.
CMOS CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
The AD9512 provides two clock outputs (OUT3 and OUT4),
which are selectable as either CMOS or LVDS levels. When
selected as CMOS, these outputs provide for driving devices
requiring CMOS level logic at their clock inputs.
Whenever single-ended CMOS clocking is used, some of the
following general guidelines should be followed.
Point-to-point nets should be designed such that a driver has
one receiver only on the net, if possible. This allows for simple
termination schemes and minimizes ringing due to possible
mismatched impedances on the net. Series termination at the
source is generally required to provide transmission line
matching and/or to reduce current transients at the driver. The
value of the resistor is dependent on the board design and
timing requirements (typically 10 Ω to 100 Ω is used). CMOS
outputs are limited in terms of the capacitive load or trace
length that they can drive. Typically, trace lengths less than
3 inches are recommended to preserve signal rise/fall times and
preserve signal integrity.
60.4Ω
1.0 INCH
CMOS
Figure 40. Series Termination of CMOS Output
Termination at the far end of the PCB trace is a second option.
The CMOS outputs of the AD9512 do not supply enough
current to provide a full voltage swing with a low impedance
resistive, far-end termination, as shown in
end termination network should match the PCB trace
impedance and provide the desired switching point. The
reduced signal swing can still meet receiver input requirements
in some applications. This can be useful when driving long
trace lengths on less critical nets.
CMOS
10Ω
OUT3, OUT4
SELECTED AS CMOS
Figure 41. CMOS Output with Far-End Termination
10Ω
50Ω
MICROSTRIP
50pF
V
PULLUP
GND
05287-096
Figure 41. The far-
= 3.3V
100Ω
100Ω
3pF
05287-097
Rev. A | Page 44 of 48
Page 45

AD9512
Because of the limitations of single-ended CMOS clocking,
consider using differential outputs when driving high speed
signals over long traces. The AD9512 offers both LVPECL and
LVDS outputs, which are better suited for driving long traces
where the inherent noise immunity of differential signaling
provides superior performance for clocking converters.
LVPECL CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
The low voltage, positive emitter-coupled, logic (LVPECL)
outputs of the AD9512 provide the lowest jitter clock signals
available from the AD9512. The LVPECL outputs (because they
are open emitter) require a dc termination to bias the output
transistors. A simplified equivalent circuit in
the LVPECL output stage.
In most applications, a standard LVPECL far-end termination is
recommended, as shown in
Figure 42. The resistor network is
designed to match the transmission line impedance (50 Ω) and
the desired switching threshold (1.3 V).
3.3V
50Ω
Figure 27 shows
3.3V
127Ω127Ω
3.3V
LVDS CLOCK DISTRIBUTION
Low voltage differential signaling (LVDS) is a second
differential output option for the AD9512. LVDS uses a current
mode output stage with several user-selectable current levels.
The normal value (default) for this current is 3.5 mA, which
yields 350 mV output swing across a 100 Ω resistor. The LVDS
outputs meet or exceed all ANSI/TIA/EIA—644 specifications.
A recommended termination circuit for the LVDS outputs is
shown in
See Application Note AN-586 on the ADI website at
www.analog.com for more information on LVDS.
Figure 44.
3.3V
LVDS
DIFFERENTIAL (COUPLED)
Figure 44. LVDS Output Termination
100Ω
100Ω
3.3V
LVDS
05287-032
LVPECL
3.3V
LVPECL
200Ω 200Ω
SINGLE-ENDED
(NOT COUPLED)
50Ω
V
= VCC– 1.3V
T
Figure 42. LVPECL Far-End Termination
0.1nF
DIFFERENTIAL
0.1nF
Figure 43. LVPECL with Parallel Transmission Line
(COUPLED)
100Ω
LVPECL
POWER AND GROUNDING CONSIDERATIONS AND POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
Many applications seek high speed and performance under less
83Ω83Ω
than ideal operating conditions. In these application circuits,
the implementation and construction of the PCB is as
05287-030
important as the circuit design. Proper RF techniques must be
used for device selection, placement, and routing, as well as for
power supply bypassing and grounding to ensure optimum
3.3V
LVPECL
05287-031
performance.
Rev. A | Page 45 of 48
Page 46

AD9512
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
1.00
0.85
0.80
12° MAX
SEATING
PLANE
7.00
BSC SQ
PIN 1
INDICATOR
VIEW
0.60 MAX
37
36
TOP
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.50 BSC
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VKKD-2
6.75
BSC SQ
0.20REF
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
25
24
COPLANARITY
0.08
Figure 45. 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
7 mm × 7 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-48-1)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
0.60 MAX
EXPOSED
PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
5.50
REF
0.30
0.23
0.18
PIN 1
48
1
12
13
INDICATOR
5.25
5.10 SQ
4.95
0.25 MIN
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9512BCPZ
AD9512BCPZ-REEL7
AD9512/PCB Evaluation Board Without VCO, VCXO, or Loop Filter
1
Z = Pb-free part.
1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-48-1
1
−40°C to +85°C 48-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package (LFCSP_VQ) CP-48-1
Rev. A | Page 46 of 48
Page 47

AD9512
NOTES
Rev. A | Page 47 of 48
Page 48

AD9512
NOTES
© 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D05287–0–6/05(A)
Rev. A | Page 48 of 48
 Loading...
Loading...