ANALOG DEVICES AD9251 Service Manual
14-Bit, 20 MSPS/40 MSPS/65 MSPS/80 MSPS,
O
A
V
FEATURES
1.8 V analog supply operation
1.8 V to 3.3 V output supply
SNR
74.3 dBFS at 9.7 MHz input
71.5 dBFS at 200 MHz input
SFDR
93 dBc at 9.7 MHz input
80 dBc at 200 MHz input
Low power
33 mW per channel at 20 MSPS
73 mW per channel at 80 MSPS
Differential input with 700 MHz bandwidth
On-chip voltage reference and sample-and-hold circuit
2 V p-p differential analog input
DNL = ±0.45 LSB
Serial port control options
Offset binary, gray code, or twos complement data format
Optional clock duty cycle stabilizer
Integer 1-to-8 input clock divider
Data output multiplex option
Built-in selectable digital test pattern generation
Energy-saving power-down modes
Data clock out with programmable clock and data
alignment
APPLICATIONS
Communications
Diversity radio systems
Multimode digital receivers
GSM, EDGE, W-CDMA, LTE, CDMA2000, WiMAX, TD-SCDMA
I/Q demodulation systems
Smart antenna systems
Battery-powered instruments
Hand held scope meters
Portable medical imaging
Ultrasound
Radar/LIDAR
1.8 V Dual Analog-to-Digital Converter
AD9251
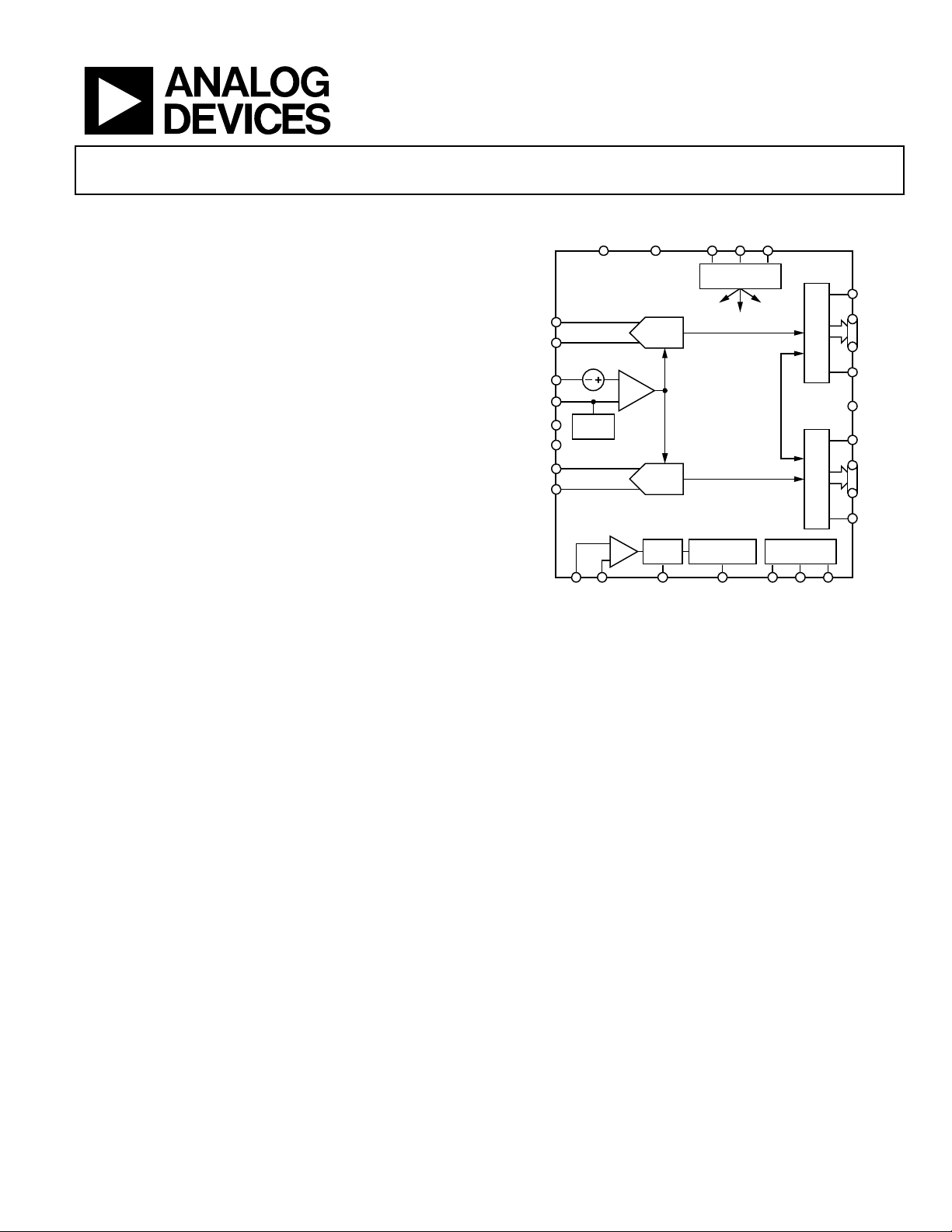
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DCS
SPI
CSB
MUX OPTION
CONTROLS
PDWN DFSCLK+ CLK–
MODE
CMOS
CMOS
OEB
ORA
D13A
D0A
OUTPUT BUFFER
DCOA
DRVDD
ORB
D13B
D0B
OUTPUT BUFFE R
DCOB
SDI
PROGRAMMING DATA
AD9251
DUTY CYCLE
STABILIZER
Figure 1.
VIN+A
VIN–A
VREF
SENSE
VCM
RBIAS
VIN–B
VIN+B
GND
DD SCLK
ADC
REF
SELECT
ADC
DIVIDE
1TO 8
SYNC
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD9251 operates from a single 1.8 V analog power
supply and features a separate digital output driver supply
to accommodate 1.8 V to 3.3 V logic families.
2. The patented sample-and-hold circuit maintains excellent
performance for input frequencies up to 200 MHz and is
designed for low cost, low power, and ease of use.
3. A standard serial port interface supports various product
features and functions, such as data output formatting,
internal clock divider, power-down, DCO/DATA timing
and offset adjustments, and voltage reference modes.
4. The AD9251 is packaged in a 64-lead RoHS compliant
LFCSP that is pin compatible with the AD9268 16-bit
ADC, the AD9258 14-bit ADC, the AD9231 12-bit ADC,
and the AD9204 10-bit ADC, enabling a simple migration
path between 10-bit and 16-bit converters sampling from
20 MSPS to 125 MSPS.
07938-001
Rev. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD9251
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
General Description ......................................................................... 3
Specifications ..................................................................................... 4
DC Specifications ......................................................................... 4
AC Specifications .......................................................................... 5
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 6
Switching Specifications .............................................................. 7
Timing Specifications .................................................................. 8
Absolute Maximum Ratings .......................................................... 10
Thermal Characteristics ............................................................ 10
ESD Caution ................................................................................ 10
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ........................... 11
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 13
AD9251-80 .................................................................................. 13
AD9251-65 .................................................................................. 15
AD9251-40 .................................................................................. 16
AD9251-20 .................................................................................. 17
Equivalent Circuits ......................................................................... 18
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 20
ADC Architecture ...................................................................... 20
Analog Input Considerations .................................................... 20
Voltage Reference ....................................................................... 23
Clock Input Considerations ...................................................... 24
Channel/Chip Synchronization ................................................ 26
Power Dissipation and Standby Mode .................................... 26
Digital Outputs ........................................................................... 27
Timing ......................................................................................... 27
Built-In Self-Test (BIST) and Output Test .................................. 28
Built-In Self-Test (BIST) ............................................................ 28
Output Test Modes ..................................................................... 28
Serial Port Interface (SPI) .............................................................. 29
Configuration Using the SPI ..................................................... 29
Hardware Interface ..................................................................... 30
Configuration Without the SPI ................................................ 30
SPI Accessible Features .............................................................. 30
Memory Map .................................................................................. 31
Reading the Memory Map Register Table ............................... 31
Open Locations .......................................................................... 31
Default Values ............................................................................. 31
Memory Map Register Table ..................................................... 32
Memory Map Register Descriptions ........................................ 34
Applications Information .............................................................. 35
Design Guidelines ...................................................................... 35
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 36
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 36
REVISION HISTORY
10/09—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Features .......................................................................... 1
Change to Table 1 ............................................................................. 4
Moved Timing Diagrams................................................................. 8
Deleted Table 11; Renumbered Sequentially .............................. 22
Changes to Internal Reference Connection Section .................. 23
Moved Channel/Chip Synchronization Section ......................... 26
Change to Table 15 ......................................................................... 30
Changes to Reading the Memory Map Register
Table Section ................................................................................... 31
Changes to Table 16 ........................................................................ 32
7/09—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 2 of 36

AD9251
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9251 is a monolithic, dual-channel, 1.8 V supply,
14-bit, 20 MSPS/40 MSPS/65 MSPS/80 MSPS analog-to-digital
converter (ADC). It features a high performance sample-andhold circuit and on-chip voltage reference.
The product uses multistage differential pipeline architecture
with output error correction logic to provide 14-bit accuracy at
80 MSPS data rates and to guarantee no missing codes over the
full operating temperature range.
The ADC contains several features designed to maximize
flexibility and minimize system cost, such as programmable
clock and data alignment and programmable digital test pattern
generation. The available digital test patterns include built-in
deterministic and pseudorandom patterns, along with custom
user-defined test patterns entered via the serial port interface (SPI).
A differential clock input controls all internal conversion cycles.
An optional duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) compensates for wide
variations in the clock duty cycle while maintaining excellent
overall ADC performance.
The digital output data is presented in offset binary, gray code,
or twos complement format. A data output clock (DCO) is
provided for each ADC channel to ensure proper latch timing
with receiving logic. Both 1.8 V and 3.3 V CMOS levels are
supported and output data can be multiplexed onto a single
output bus.
The AD9251 is available in a 64-lead RoHS Compliant LFCSP
and is specified over the industrial temperature range (−40°C
to +85°C).
Rev. A | Page 3 of 36
AD9251
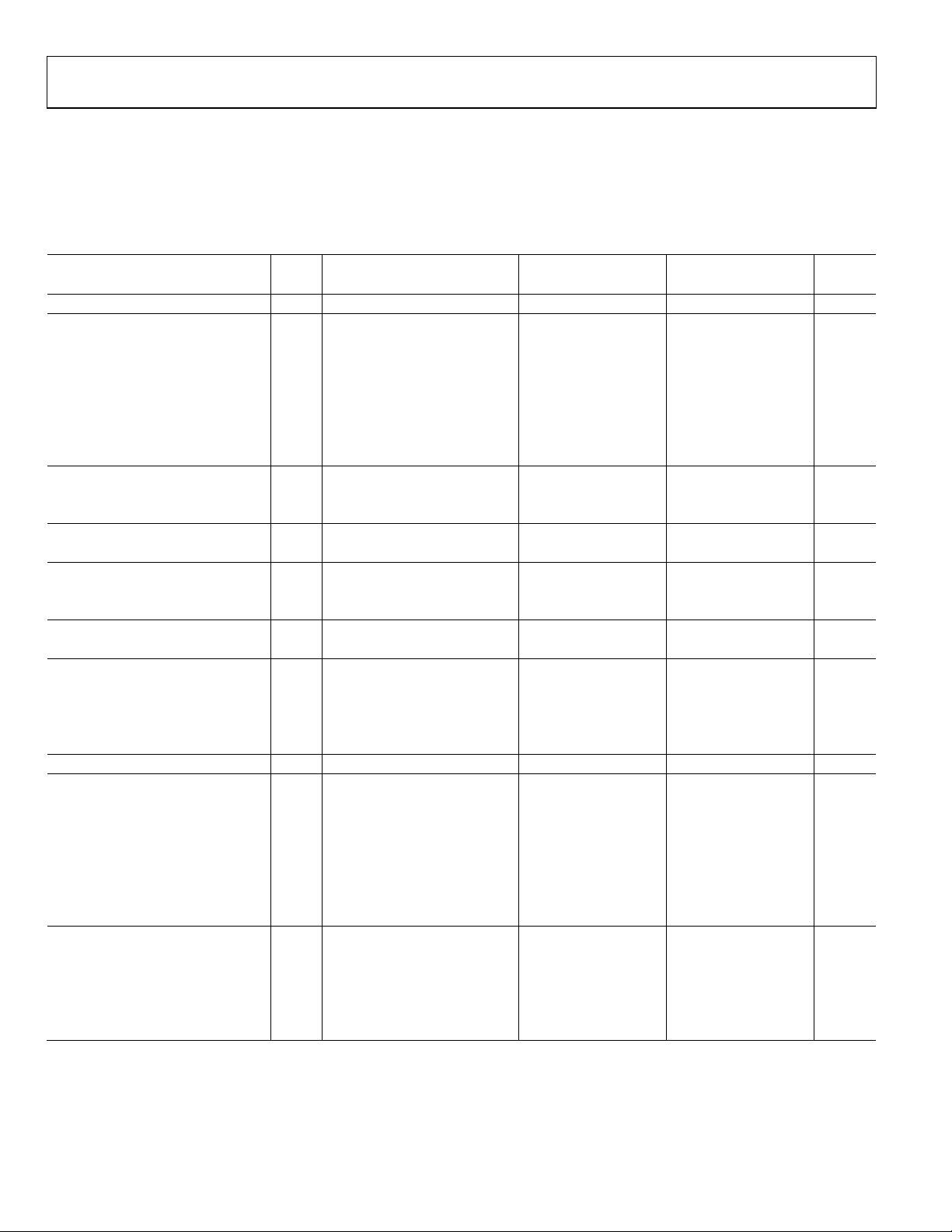
SPECIFICATIONS
DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V; DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference; AIN = −1.0 dBFS,
DCS disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
AD9251-20/AD9251-40 AD9251-65 AD9251-80
Parameter Temp
RESOLUTION Full 14 14 14 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full Guaranteed Guaranteed Guaranteed
Offset Error Full ±0.1 ±0.70 ±0.1 ±0.50 ±0.1 ±0.70 % FSR
Gain Error
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
1
Full −1.5 −1.5 −1.5 % FSR
2
Full ±0.60 ±0.75 ±0.70 LSB
25°C ±0.3 ±0.45 ±0.45 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
2
Full ±1.75 ±1.75 ±2.50 LSB
25°C ±0.6 ±0.6 ±1.0 LSB
MATCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Error 25°C ±0.0 ±0.65 ±0.0 ±0.65 ±0.0 ±0.65 % FSR
Gain Error
1
25°C ±0.2 ±0.2 ±0.2 % FSR
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full ±2 ±2 ±2 ppm/°C
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage (1 V Mode) Full 0.981 0.993 1.005 0.981 0.993 1.005 0.981 0.993 1.005 V
Load Regulation Error at 1.0 mA Full 2 2 2 mV
INPUT-REFERRED NOISE
VREF = 1.0 V 25°C 0.98 0.98 0.98 LSB rms
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span, VREF = 1.0 V Full 2 2 2 V p-p
Input Capacitance
3
Full 6 6 6 pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Full 0.9 0.9 0.9 V
Input Common-Mode Range Full 0.5 1.3 0.5 1.3 0.5 1.3 V
REFERENCE INPUT RESISTANCE Full 7.5 7.5 7.5 kΩ
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltage
AVDD Full 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.7 1.8 1.9 V
DRVDD Full 1.7 3.6 1.7 3.6 1.7 3.6 V
Supply Current
2
IAVDD
Full 36.5/49.5 39.4/52.8 69.0 72.9 80.5 85.5 mA
IDRVDD2 (1.8 V) Full 3.4/5.6 8.4 10.3 mA
IDRVDD2 (3.3 V) Full 6.3/10.6 16.0 19.5 mA
POWER CONSUMPTION
DC Input Full 66/89 125 145 mW
Sine Wave Input2 (DRVDD = 1.8 V) Full 71.8/99 77.0/105.5 139.0 146.5 163.4 173 mW
Sine Wave Input2 (DRVDD = 3.3 V) Full 86.5/124 176.7 209 mW
Standby Power
4
Full 37 37 37 mW
Power-Down Power Full 2.2 2.2 2.2 mW
1
Measured with 1.0 V external reference.
2
Measured with a 10 MHz input frequency at rated sample rate, full-scale sine wave, with approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit.
3
Input capacitance refers to the effective capacitance between one differential input pin and AGND.
4
Standby power is measured with a dc input and the CLK active.
Unit Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Rev. A | Page 4 of 36
AD9251
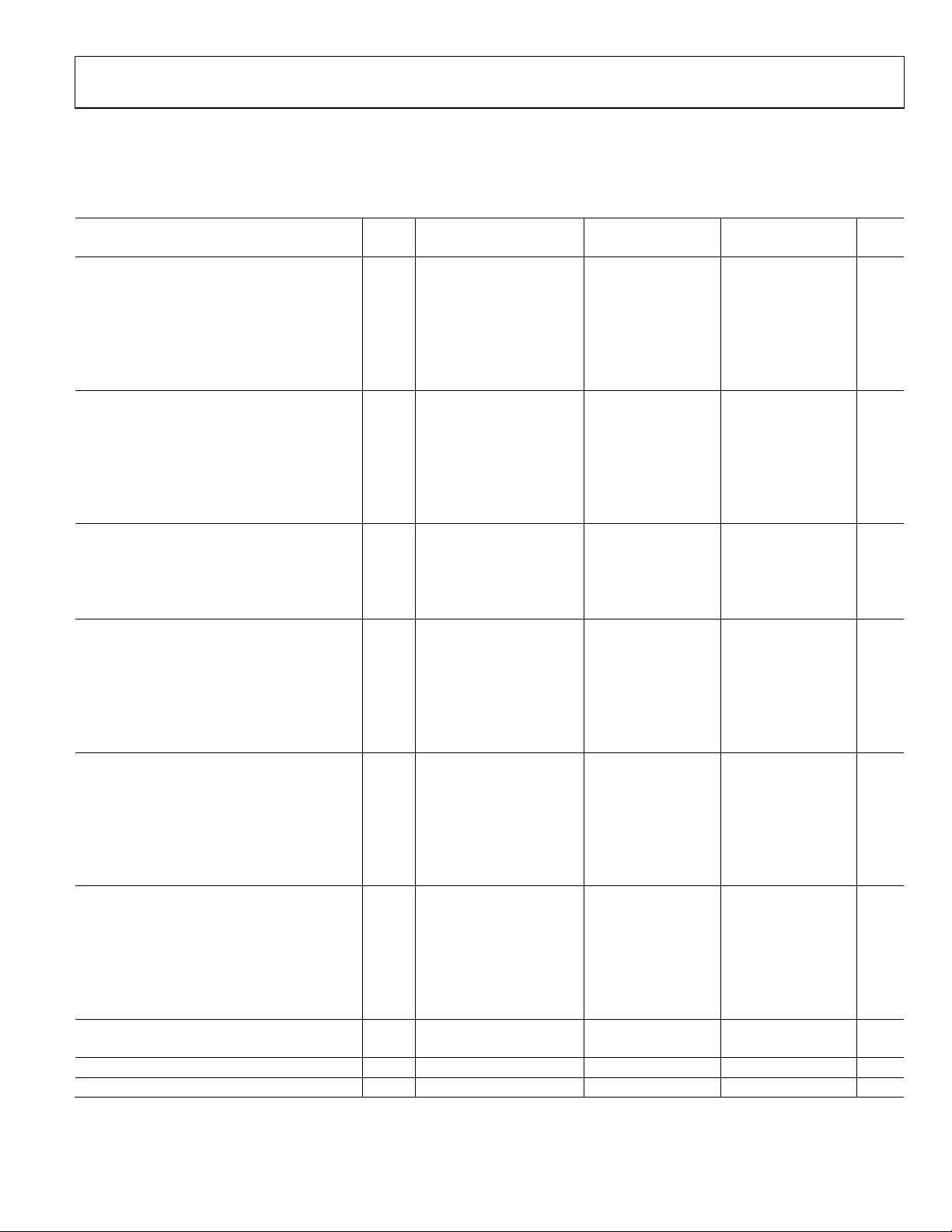
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V; DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference; AIN = −1.0 dBFS,
DCS disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
1
Parameter
Temp
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (SNR)
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C 74.7 74.5 74.3 dBFS
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C 74.4 74.3 74.1 dBFS
Full 73.6 73.6 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 73.7 73.7 73.6 dBFS
Full 72.5 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 71.5 71.5 71.5 dBFS
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE-AND-DISTORTION (SINAD)
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C 74.6 74.4 74.1 dBFS
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C 74.3 74.2 74.0 dBFS
Full 73.4 73.4 dBFS
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 73.6 73.6 73.5 dBFS
Full 72.4 dBFS
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 70.0 70.0 70.0 dBFS
EFFECTIVE NUMBER OF BITS (ENOB)
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C 12.0 12.0 12.0 Bits
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C 12.0 12.0 12.0 Bits
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 11.9 11.9 11.9 Bits
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 11.3 11.3 11.3 Bits
WORST SECOND OR THIRD HARMONIC
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C −95 −95 −93 dBc
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C −95 −95 −93 dBc
Full −81 −81 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C −94 −94 −92 dBc
Full −81 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C −80 −80 −80 dBc
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C 95 95 93 dBc
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C 94 94 93 dBc
Full 81 81 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C 93 93 92 dBc
Full 81 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C 80 80 80 dBc
WORST OTHER (HARMONIC OR SPUR)
fIN = 9.7 MHz 25°C −98 −98 −97 dBc
fIN = 30.5 MHz 25°C −98 −98 −97 dBc
Full −90 −90 dBc
fIN = 70 MHz 25°C −98 −98 −96 dBc
Full −89 dBc
fIN = 200 MHz 25°C −95 −95 −95 dBc
TWO-TONE SFDR
fIN = 30.5 MHz (−7 dBFS), 32.5 MHz (−7 dBFS) 25°C 90 90 90 dBc
CROSSTALK
2
Full −110 −110 −110 dBc
ANALOG INPUT BANDWIDTH 25°C 700 700 700 MHz
1
See the AN-835 Application Note, Understanding High Speed ADC Testing and Evaluation, for a complete set of definitions.
2
Crosstalk is measured at 100 MHz with −1.0 dBFS on one channel and no input on the alternate channel.
AD9251-20/AD9251-40 AD9251-65 AD9251-80
Unit Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Rev. A | Page 5 of 36
AD9251
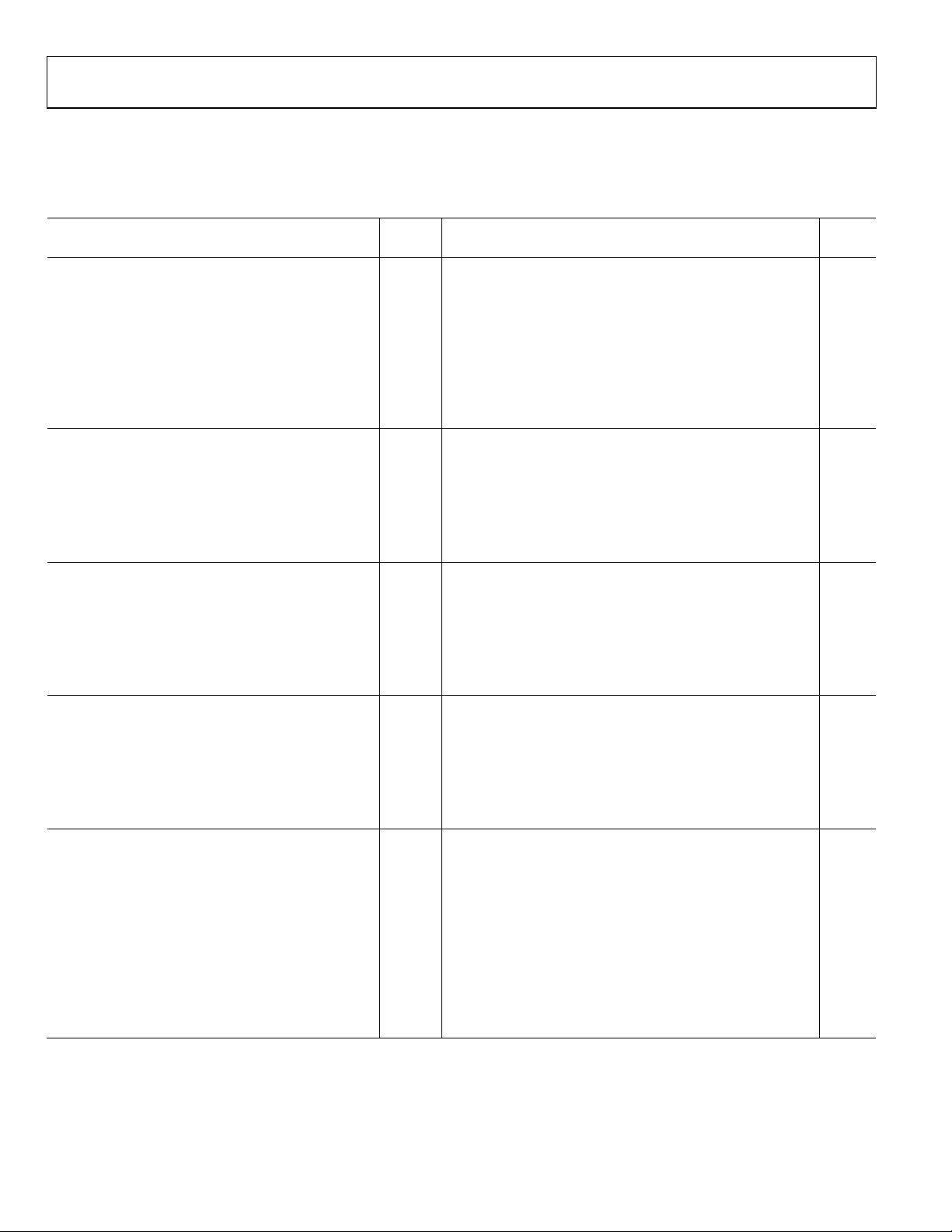
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V; DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference; AIN = −1.0 dBFS,
DCS disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
AD9251-20/AD9251-40/AD9251-65/AD9251-80
Parameter Temp
DIFFERENTIAL CLOCK INPUTS (CLK+, CLK−)
Logic Compliance CMOS/LVDS/LVPECL
Internal Common-Mode Bias Full 0.9 V
Differential Input Voltage Full 0.2 3.6 V p-p
Input Voltage Range Full GND − 0.3 AVDD + 0.2 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 8 10 12 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 4 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (SCLK/DFS, SYNC, PDWN)
1
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 DRVDD + 0.3 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full −50 −75 μA
Low Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Input Resistance Full 30 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (CSB)
2
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 DRVDD + 0.3 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 40 135 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 2 pF
LOGIC INPUTS (SDIO/DCS)
2
High Level Input Voltage Full 1.2 DRVDD + 0.3 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full 0 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full −10 +10 μA
Low Level Input Current Full 40 130 μA
Input Resistance Full 26 kΩ
Input Capacitance Full 5 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
DRVDD = 3.3 V
High Level Output Voltage, IOH = 50 μA Full 3.29 V
High Level Output Voltage, IOH = 0.5 mA Full 3.25 V
Low Level Output Voltage, IOL = 1.6 mA Full 0.2 V
Low Level Output Voltage, IOL = 50 μA Full 0.05 V
DRVDD = 1.8 V
High Level Output Voltage, IOH = 50 μA Full 1.79 V
High Level Output Voltage, IOH = 0.5 mA Full 1.75 V
Low Level Output Voltage, IOL = 1.6 mA Full 0.2 V
Low Level Output Voltage, IOL = 50 μA Full 0.05 V
1
Internal 30 kΩ pull-down.
2
Internal 30 kΩ pull-up.
Unit Min Typ Max
Rev. A | Page 6 of 36
AD9251
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 1.8 V; DRVDD = 1.8 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference; AIN = −1.0 dBFS,
DCS disabled, unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
AD9251-20/AD9251-40 AD9251-65 AD9251-80
Parameter Temp
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Input Clock Rate Full 625 625 625 MHz
Conversion Rate
CLK Period—Divide-by-1 Mode (t
1
Full 3 20/40 3 65 3 80 MSPS
) Full
CLK
50/25
15.38 12.5 ns
CLK Pulse Width High (tCH) 25.0/12.5 7.69 6.25 ns
Aperture Delay (tA) Full 1.0 1.0 1.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter, tJ) Full 0.1 0.1 0.1 ps rms
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
Data Propagation Delay (tPD) Full
DCO Propagation Delay (t
DCO to Data Skew (t
SKEW
) Full 3
DCO
) Full 0.1
3
3
3
0.1
3 ns
3 ns
0.1 ns
Pipeline Delay (Latency) Full 9 9 9 Cycles
Wake-Up Time
2
Full 350 350 350 μs
Standby Full 600/400 300 260 ns
OUT-OF-RANGE RECOVERY TIME Full 2 2 2 Cycles
1
Conversion rate is the clock rate after the CLK divider.
2
Wake-up time is dependent on the value of the decoupling capacitors.
Unit Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Rev. A | Page 7 of 36
AD9251
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 5.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
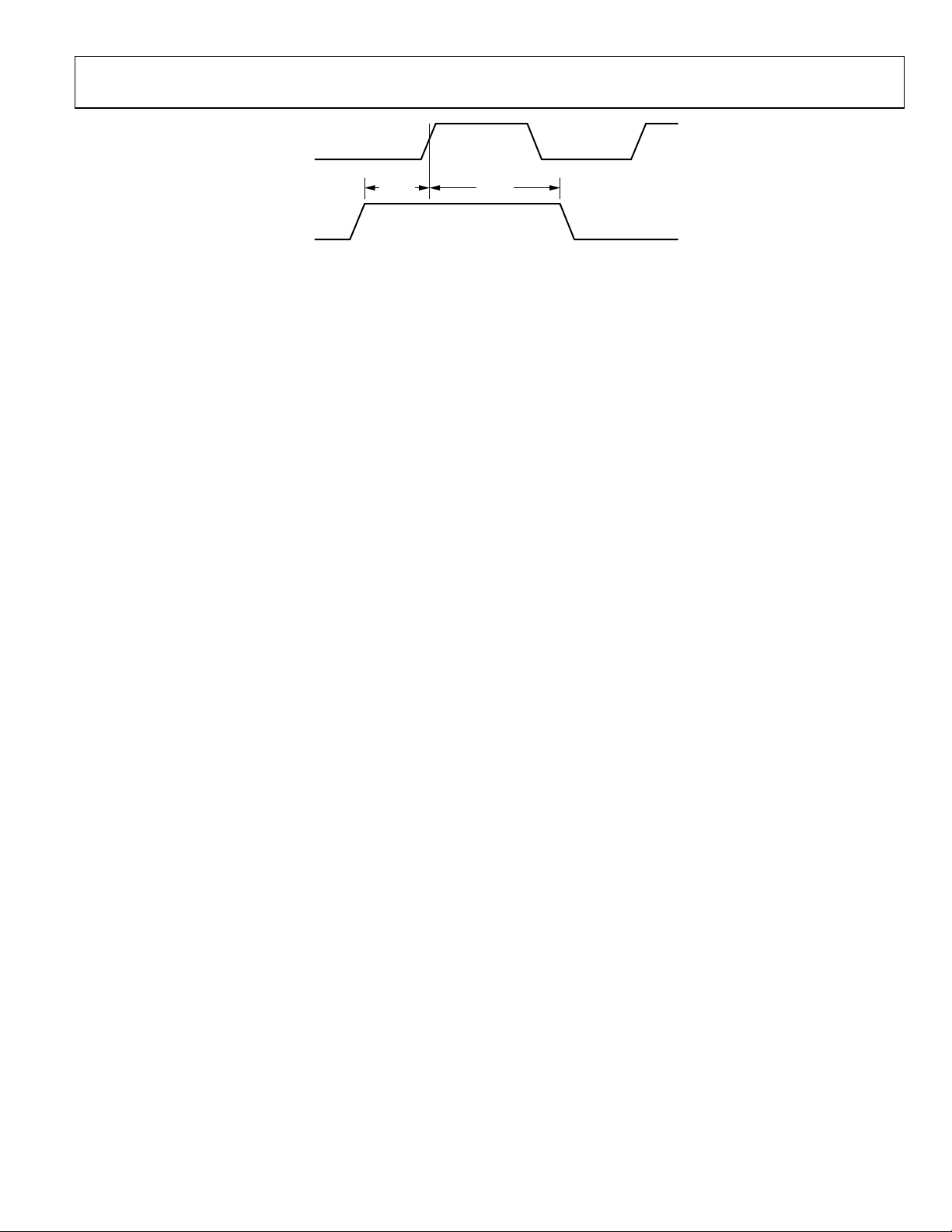
SYNC TIMING REQUIREMENTS
t
SYNC to rising edge of CLK setup time 0.24 ns
SSYNC
t
SYNC to rising edge of CLK hold time 0.40 ns
HSYNC
SPI TIMING REQUIREMENTS
tDS Setup time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
tDH Hold time between the data and the rising edge of SCLK 2 ns
t
Period of the SCLK 40 ns
CLK
tS Setup time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
tH Hold time between CSB and SCLK 2 ns
t
SCLK pulse width high 10 ns
HIGH
t
SCLK pulse width low 10 ns
LOW
t
EN_SDIO
t
DIS_SDIO
Timing Diagrams
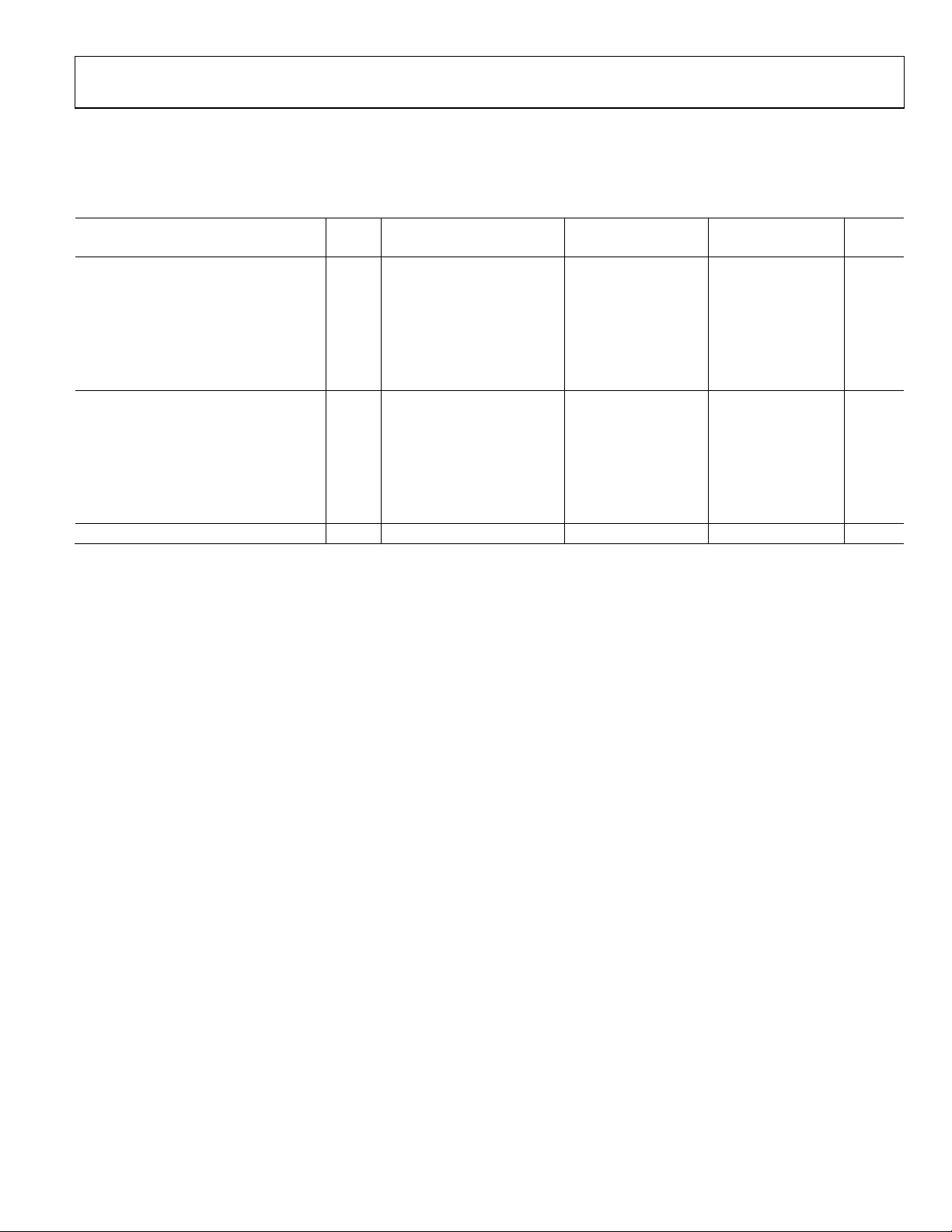
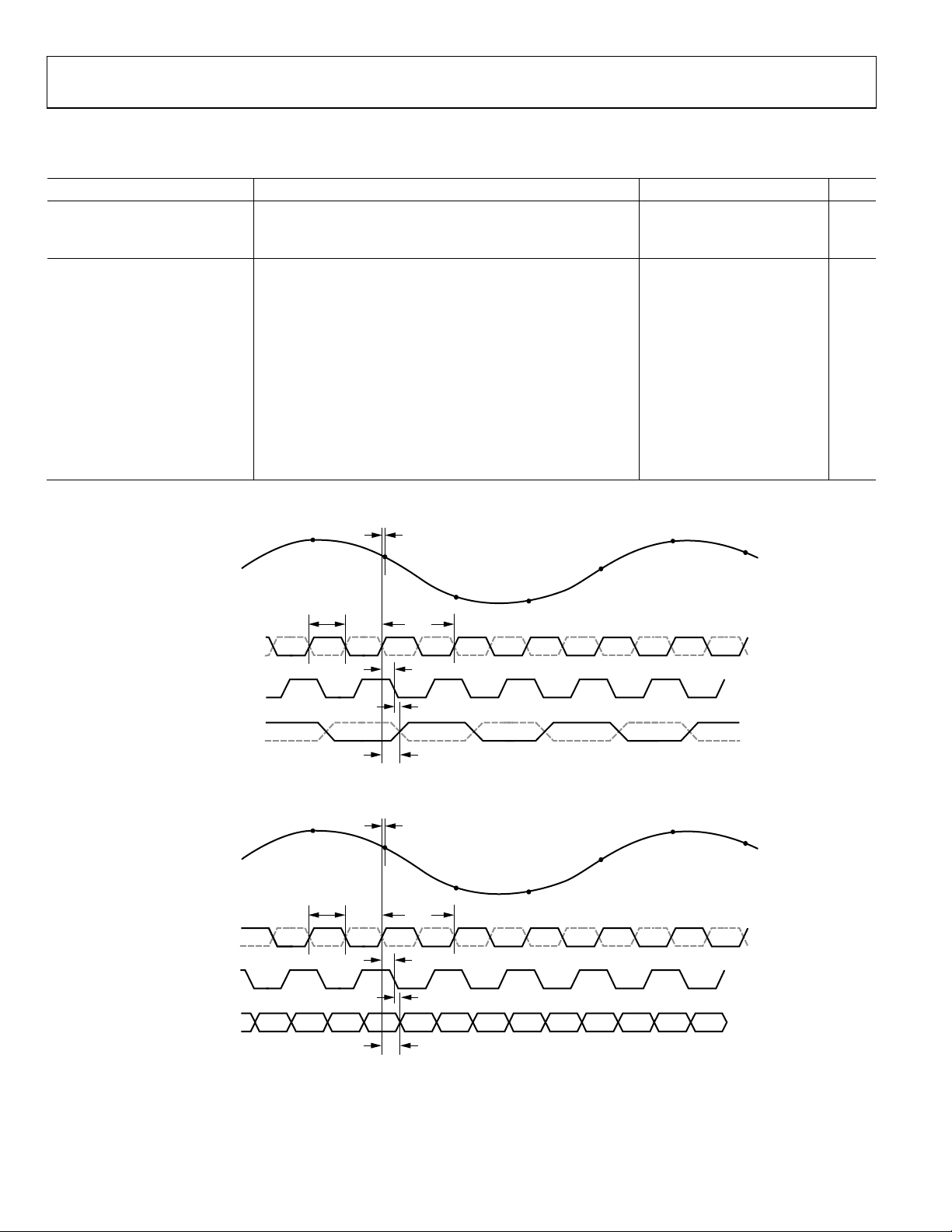
CH A/CH B DATA
CH A/CH B DATA
VIN
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA/DCOB
VIN
CLK+
CLK–
DCOA/DCOB
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an input to an
output relative to the SCLK falling edge
Time required for the SDIO pin to switch from an output to an
input relative to the SCLK rising edge
N – 1
N – 1
t
CH
t
CH
Figure 3. CMOS Interleaved Output Timing
t
A
N
N + 1
t
CLK
t
DCO
t
SKEW
N – 9
t
PD
N + 2
N – 8N – 7N – 6N – 5
Figure 2. CMOS Output Data Timing
t
A
N
N + 1
t
CLK
t
DCO
t
SKEW
CH A
CH B
N – 9
N – 9
t
PD
CH A
N – 8
N + 2
CH B
N – 8
CH A
N – 7
N + 3
N + 3
CH B
N – 7
10 ns
10 ns
CH A
N – 6
N + 4
N + 4
CH B
N – 6
CH A
N – 5
N + 5
N + 5
07938-002
07938-003
Rev. A | Page 8 of 36
AD9251
CLK+
t
HSYNC
7938-004
SYNC
t
SSYNC
Figure 4. SYNC Input Timing Requirements
Rev. A | Page 9 of 36
AD9251
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
AVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +2.0 V
DRVDD to AGND −0.3 V to +3.9 V
VIN+A, VIN+B, VIN−A, VIN−B to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CLK+, CLK− to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
SYNC to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
VREF to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
SENSE to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
VCM to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
RBIAS to AGND −0.3 V to AVDD + 0.2 V
CSB to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SCLK/DFS to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
SDIO/DCS to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
OEB to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
PDWN to AGND −0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
D0A/D0B through D13A/D13B to AGND
DCOA/DCOB to AGND
Operating Temperature Range (Ambient) −40°C to +85°C
Maximum Junction Temperature
Under Bias
Storage Temperature Range (Ambient) −65°C to +150°C
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
−0.3 V to DRVDD + 0.3 V
150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
The exposed paddle is the only ground connection for the chip.
The exposed paddle must be soldered to the AGND plane of the
user’s circuit board. Soldering the exposed paddle to the user’s
board also increases the reliability of the solder joints and
maximizes the thermal capability of the package.
Typical θ
is specified for a 4-layer PCB with a solid ground
JA
plane. As shown in Ta b l e 7 , airflow improves heat dissipation,
which reduces θ
. In addition, metal in direct contact with the
JA
package leads from metal traces, through holes, ground, and
power planes, reduces the θ
.
JA
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
Airflow
Packa ge Type
Veloc ity
(m/sec) θ
1, 2
JA
1, 3
θ
JC
1, 4
θ
Unit
JB
64-Lead LFCSP 0 23 2.0 °C/W
(CP-64-4) 1.0 20 12 °C/W
2.5 18 °C/W
1
Per JEDEC 51-7, plus JEDEC 25-5 2S2P test board.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-2 (still air) or JEDEC JESD51-6 (moving air).
3
Per MIL-Std 883, Method 1012.1.
4
Per JEDEC JESD51-8 (still air).
ESD CAUTION
Rev. A | Page 10 of 36
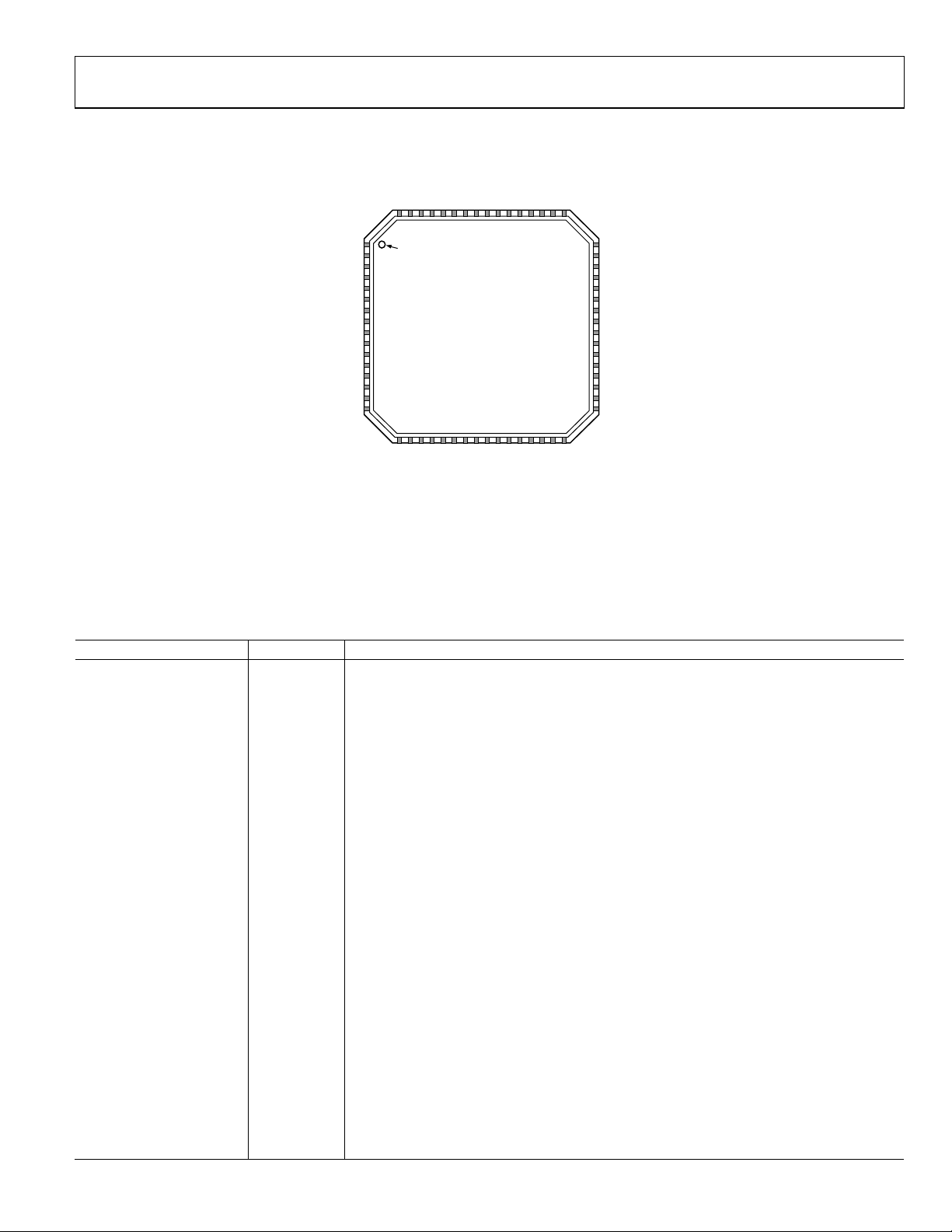
AD9251
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
AVDD
AVDD
VIN+B
VIN–B
AVDD
AVDD
RBIAS
VCM
SENSE
VREF
AVDD
AVDD
VIN–A
VIN+A
AVDD
646362616059585756555453525150
AVDD
49
CLK+
CLK–
SYNC
NC
NC
(LSB) D0B
D1B
D2B
D3B
DRVDD
10
D4B
11
D5B
12
D6B
13
D7B
14
D8B
15
D9B
16
NOTES
1. NC = NO CONNECT
2. THE EXPOSED PADDLE MUS T BE SOLDER ED TO THE PCB GROUND
TO ENSURE PRO P ER HEAT DISSI P ATION, NOISE, AND MECHANICAL
STRENGTH BENEFITS.
PIN 1
1
INDICATOR
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
171819202122232425262728293031
D10B
D11B
D12B
DRVDD
(MSB) D13B
AD9251
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
NC
ORB
DCOA
DCOB
NC
D1A
D2A
D3A
DRVDD
(LSB) D0A
48
PDWN
47
OEB
46
CSB
45
SCLK/DFS
44
SDIO/DCS
43
ORA
42
D13A (MSB)
41
D12A
40
D11A
39
D10A
38
D9A
37
DRVDD
36
D8A
35
D7A
34
D6A
33
D5A
32
D4A
07938-005
Figure 5. Pin Configuration
Table 8. Pin Function Description
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
0 GND Exposed paddle is the only ground connection for the chip. Must be connected to PCB AGND.
1, 2 CLK+, CLK− Differential Encode Clock. PECL, LVDS, or 1.8 V CMOS inputs.
3 SYNC Digital Input. SYNC input to clock divider. 30 kΩ internal pull-down.
4, 5, 25, 26 NC Do Not Connect.
6 to 9, 11 to 18, 20, 21 D0B to D13B Channel B Digital Outputs. D13B = MSB.
10, 19, 28, 37 DRVDD Digital Output Driver Supply (1.8 V to 3.3 V).
22 ORB Channel B Out-of-Range Digital Output.
23 DCOB Channel B Data Clock Digital Output.
24 DCOA Channel A Data Clock Digital Output.
27, 29 to 36, 38 to 42 D0A to D13A Channel A Digital Outputs. D13A = MSB.
43 ORA Channel A Out-of-Range Digital Output.
44 SDIO/DCS
SPI Data Input/Output (SDIO). Bidirectional SPI Data I/O in SPI mode. 30 kΩ internal pulldown in SPI mode.
Duty Cycle Stabilizer (DCS). Static enable input for duty cycle stabilizer in non-SPI mode.
30 kΩ internal pull-up in non-SPI (DCS) mode.
45 SCLK/DFS
SPI Clock (SCLK) Input in SPI mode. 30 kΩ internal pull-down.
Data Format Select (DFS). Static control of data output format in non-SPI mode. 30 kΩ internal
pull-down.
DFS high = twos complement output.
DFS low = offset binary output.
46 CSB SPI Chip Select. Active low enable; 30 kΩ internal pull-up.
47 OEB
Digital Input. Enable Channel A and Channel B digital outputs if low, tristate outputs if high.
30 kΩ internal pull-down.
48 PDWN
Digital Input. 30 kΩ internal pull-down.
PDWN high = power-down device.
PDWN low = run device, normal operation.
49, 50, 53, 54, 59, 60, 63, 64 AVDD 1.8 V Analog Supply Pins.
51, 52 VIN+A, VIN−A Channel A Analog Inputs.
Rev. A | Page 11 of 36
 Loading...
Loading...