Low Power, High Output Current,
V
Dual-Port ADSL/ADSL2+ Line Driver
FEATURES
2 differential DSL channels comprised of current feedback,
high output current amplifiers
Integrated feedback and gain resistors
Integrated biasing network
Ideal for use as ADSL/ADSL2+ dual-channel Central Office
(CO) line drivers
Low power consumption
Dual-supply operation from ±6 V to ±12 V
Single-supply operation from 12 V to 24 V
10.8 mA quiescent supply current in full power mode
1.4 mA quiescent supply current in shutdown mode
Less than 700 mW internal power dissipation while driving
20.4 dBm line power, 1:1 transformer
High output voltage and current drive
43.4 V p-p differential output voltage
Low distortion
−66 dBc typical MTPR @ 20.4 dBm, 26 kHz to 2.2 MHz
High speed: 170 V/μs differential slew rate
APPLICATIONS
ADSL/ADSL2+ CO line drivers
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD8396 is comprised of four high output current, low
power consumption operational amplifiers. It is particularly
well suited for the CO driver interface in digital subscriber line
systems, such as ADSL and ADSL2+. The driver can deliver
20.4 dBm to a line while compensating for losses due to hybrid
insertion and back-termination resistors.
The low power consumption, high output current, high output
voltage swing, and robust thermal packaging enable the AD8396 to
be used as the CO line driver in ADSL and other xDSL systems.
The AD8396 is available in a 4 mm × 4 mm 16-lead LFCSP.
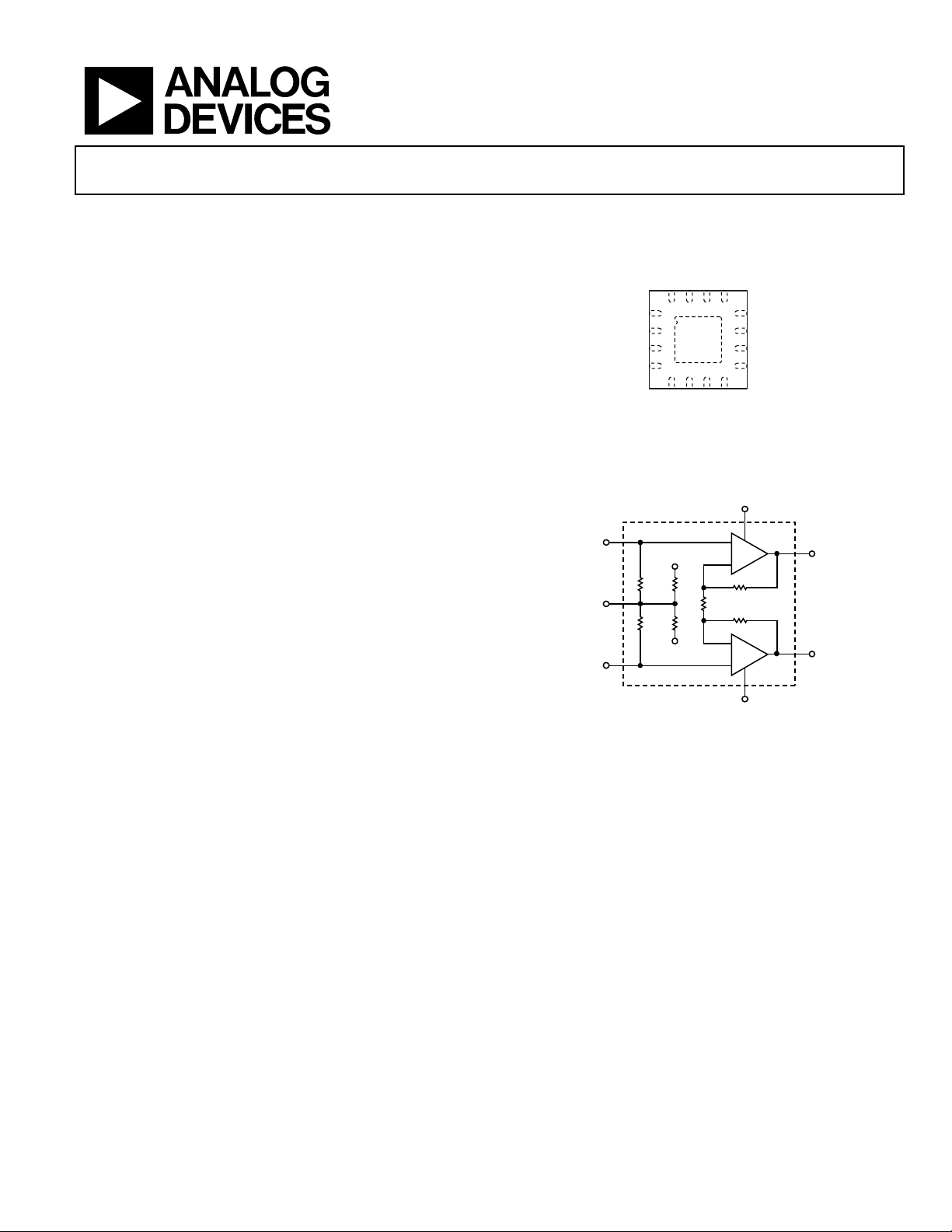
AD8396
PIN CONFIGURATION
VCOM-A
PD_A
VCC
51
41
TOP
VIEW
7
6
B
PD_B
VCOM-
Figure 1.
VOPA
31
8
VEE
CC
AV = 13
VEE
12
VONA
11
DGND
10
VOPB
9
VONB
07022-001
VOPA
VONA
07022-002
61
1
INPA
2
INNA
DGND
INPB
AD8396
3
4
5
INNB
INPA
VCOM-A
INNA
Figure 2. Channel A Internal Schematics
VCC
4k
4k
VEE
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007–2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD8396
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Pin Configuration ............................................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Specifications ..................................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 4
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 4
Maximum Power Dissipation ..................................................... 4
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 4
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 5
REVISION HISTORY
8/09—Revision C: Initial Version
Typical Performance Characteristics ..............................................6
Theory of Operation .........................................................................8
Applications Information .................................................................9
Supplies, Grounding, and Layout ................................................9
Power Management ......................................................................9
Typical ADSL/ADSL2+ Application ...........................................9
Multitone Power Ratio (MTPR) ..................................................9
Lightning and AC Power Fault ................................................. 10
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 11
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 11
Rev. C | Page 2 of 12
AD8396
SPECIFICATIONS
(VCC − VEE) = 24 V, RL = 100 Ω, G
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Test Conditions/Comments
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
−3 dB Small-Signal Bandwidth 8 MHz V
−3 dB Large-Signal Bandwidth 8 MHz V
Slew Rate 170 V/μs V
Differential Gain 12.8 13 13.2 V/V
NOISE/DISTORTION PERFORMANCE
Second Harmonic Distortion −90 dBc fC = 2 MHz, V
Third Harmonic Distortion −62 dBc fC = 2 MHz, V
Multitone Input Power Ratio (MTPR) −66 dBc
Differential Output Noise 140 nV/√Hz f = 10 kHz
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
RTO Offset Voltage −15 −0.7 +15 mV Single-ended
−15 +0.3 +15 mV Differential
RTO Offset Voltage @ PD = (1) −30 +0.1 +30 mV Differential
Input Bias Current −5 −1.5 +5 μA
Input Resistance 8 kΩ Differential
Input Capacitance 1 pF Differential
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Output Voltage Swing 42.6 43.4 44 V p-p ΔV
Single-Ended Output Voltage Swing 21.3 21.7 22 V p-p ΔV
Output Leakage Current −100 +100 μA PD = (1)
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range, Dual Supply ±6 ±12 V
Operating Range, Single Supply 12 24 V
Total Quiescent Current
PD = (0) 9.0 10.8 13.0 mA
PD = (1) Shutdown State 0 1.4 3.0 mA
Common-Mode Voltage −10 +0.2 +10 mV VCM
PD = (0) Threshold 0.8 V (0) = 0 V
PD = (1) Threshold 1.6 V (1) = 5 V
PD = (0) Input Current −100 −47 +100 μA (0) = 0 V
PD = (1) Input Current −100 +1 +100 μA (1) = 5 V
+Power Supply Rejection Ratio −80 −60 dB ΔV
−Power Supply Rejection Ratio −80 −60 dB ΔV
= 13 (fixed), PD = (0), T = 25°C, typical DSL application circuit, unless otherwise noted.
DIFF
= 0.1 V p-p, differential
OUT
= 2 V p-p, differential
OUT
= 4 V p-p, differential
OUT
= 2 V p-p, differential
OUT
= 2 V p-p, differential
OUT
26 kHz to 2.2 MHz, Z
= 100 Ω, differential
LINE
load
, RL = 100 Ω
OUT
, RL = 50 Ω
OUT
/ΔVCC, ΔVCC = ±1 V, differential
OS, DM (RTI)
/ΔVEE, ΔVEE = ±1 V, differential
OS, DM (RTI)
Rev. C | Page 3 of 12
AD8396
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage, VCC − VEE 26.4 V
Power Dissipation See Figure 3
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) 300°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
θJA is specified in still air with exposed pad soldered to 4-layer
JEDEC test board. θ
is specified at the exposed pad.
JC
Table 3.
Package Type θJA θ
Unit
JC
16-Lead LFCSP 56 9.1 °C/W
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum safe power dissipation for the AD8396 is limited
by its junction temperature on the die.
The maximum safe junction temperature of plastic encapsulated
devices, as determined by the glass transition temperature of the
plastic, is 150°C. Exceeding this limit can temporarily cause a shift
in the parametric performance due to a change in the stresses
exerted on the die by the package. Exceeding this limit for an
extended period can result in device failure.
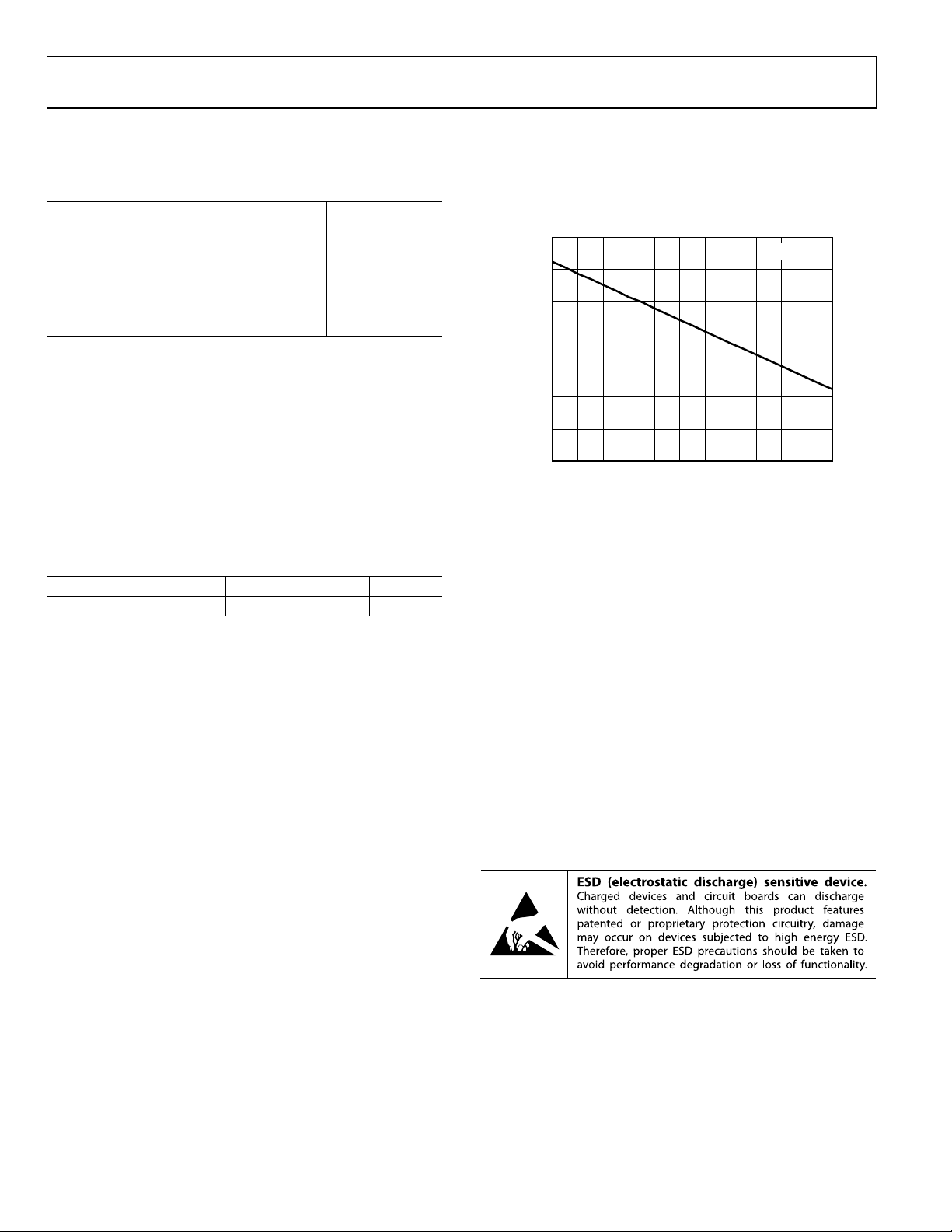
Figure 3 shows the maximum power dissipation in the package
vs. the ambient temperature for the 16-lead LFCSP on a JEDEC
standard 4-layer board. θ
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
MAXIMUM POW ER DISSIPAT ION (W)
0.5
0
–25 85
–15–5 5 15253545556575
Figure 3. Maximum Power Dissipation vs.
Ambient Temperature for a 4-Layer Board
values are approximations.
JA
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
TJ = 150°C
07022-003
The power dissipated in the package (PD) is the sum of the
quiescent power dissipation and the power dissipated in the
package due to the load drive for all outputs. The quiescent
power is the voltage between the supply pins (V
quiescent current (I
to midsupply, the total drive power is V
). Assuming that the load RL is referenced
S
/2 × I
S
is dissipated in the package and part in the load (V
RMS output voltages should be considered. If R
V
, as in single-supply operation, the total power is VS × I
EE
In single supply with R
to VEE, worst case is V
L
Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing θ
) times the
S
, part of which
OUT
× I
OUT
OUT
is referenced to
L
= VS/2.
OUT
JA
OUT
. In
).
.
addition, more copper in direct contact with the package leads
from PCB traces, through-holes, ground, and power planes
reduces θ
.
JA
ESD CAUTION
Rev. C | Page 4 of 12
 Loading...
Loading...