Analog Devices AD7933 4 Datasheet
V
4-Channel, 1.5 MSPS, 12-Bit and 10 Bit
FEATURES
Fast throughput rate: 1.5 MSPS
Specified for V
Low power
6 mW max at 1.5 MSPS with 3 V supplies
13.5 mW max at 1.5 MSPS with 5 V supplies
4 analog input channels with a sequencer
Software configurable analog inputs
4-channel single-ended inputs
2-channel fully differential inputs
2-channel pseudo-differential inputs
Accurate on-chip 2.5 V reference
±0.2% max @ 25°C, 25 ppm/°C max (AD7934)
70 dB SINAD at 50 kHz input frequency
No pipeline delays
High speed parallel interface—word/byte modes
Full shutdown mode: 2 µA max
28-lead TSSOP package
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7933/AD7934 are 12-bit and 10-bit, high speed, low
power, successive approximation (SAR) ADCs. The parts
operate from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and feature
throughput rates to 1.5 MSPS. The parts contain a low noise,
wide bandwidth, differential track-and-hold amplifier that
handles input frequencies up to 50 MHz.
of 2.7 V to 5.25 V
DD
Parallel ADCs with a Sequencer
AD7933/AD7934
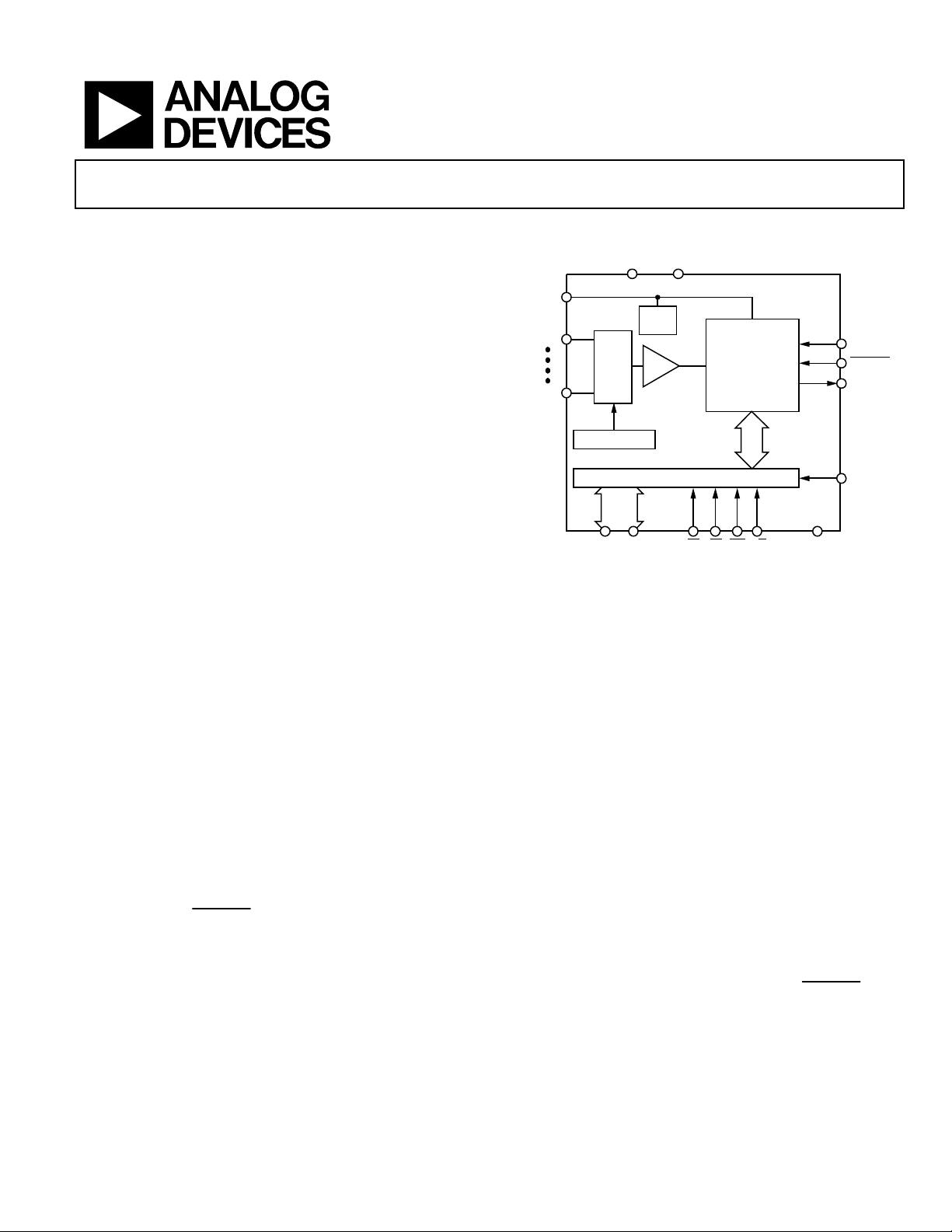
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
V
AGND
DD
V
REFIN/
REFOUT
VIN0
VIN3
SEQUENCER
PARALLEL INTERFACE/CONTROL REGISTER
DB0 DB11
I/P
MUX
2.5V
VREF
T/H
Figure 1.
These parts use advanced design techniques to achieve very
low power dissipation at high throughput rates. They also
feature flexible power management options. An on-chip control
register allows the user to set up different operating conditions,
including analog input range and configuration, output coding,
power management, and channel sequencing.
AD7933/AD7934
12-/10-BIT
SAR ADC
AND
CONTROL
CS DGNDRD WR W/B
CLKIN
CONVST
BUSY
V
DRIVE
03713-0-001
The AD7933/AD7934 feature four analog input channels with a
channel sequencer to allow a consecutive sequence of channels
to be converted on. These parts can accept either single-ended,
fully differential, or pseudo-differential analog inputs.
The conversion process and data acquisition are controlled
using standard control inputs, which allow for easy interfacing
to microprocessors and DSPs. The input signal is sampled on
the falling edge of
CONVST
, and the conversion is also initiated
at this point.
The AD7933/AD7934 has an accurate on-chip 2.5 V reference
that can be used as the reference source for the analog-to-digital
conversion. Alternatively, this pin can be overdriven to provide
an external reference.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. High throughput with low power consumption.
2. Four analog inputs with a channel sequencer.
3. Accurate on-chip 2.5 V reference.
4. Software configurable analog inputs. Single-ended, pseudo-
differential, or fully differential analog inputs that are
software selectable.
5. Single-supply operation with V
function allows the parallel interface to connect directly to
3 V or 5 V processor systems independent of V
6. No pipeline delay.
7. Accurate control of the sampling instant via a
and once off conversion control.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com
function. The V
DRIVE
DRIVE
.
DD
CONVST
input

AD7933/AD7934
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AD7933—Specifications.................................................................. 3
Analog Input Structure.............................................................. 18
AD7934—Specifications.................................................................. 5
Timing Specifications....................................................................... 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 8
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 8
Pin Configuration And Function Descriptions............................ 9
Te r m in o l o g y .................................................................................... 11
Typical Performance Characteristics........................................... 13
Control Register.......................................................................... 15
Sequencer Operation .................................................................16
Circuit Information........................................................................ 17
Converter Operation.................................................................. 17
ADC Transfer Function............................................................. 17
Typical C o n nect i o n D iagram ................................................... 18
REVISION HISTORY
Analog Inputs.............................................................................. 19
Analog Input Selection.............................................................. 21
Reference Section ....................................................................... 22
Parallel Interface ......................................................................... 23
Power Modes of Operation ....................................................... 26
Power vs. Throughput Rate ....................................................... 27
Microprocessor Interfacing....................................................... 27
Application Hints ........................................................................... 29
Grounding and Layout .............................................................. 29
Evaluating the AD7933/AD7934 Performances .................... 29
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 30
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 30
1/05—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
AD7933—SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = V
= T
T
A
Table 1.
Parameter B Version
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE FIN = 50 kHz sine wave
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion (SINAD)
60 dB min Single-ended mode
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)2 −70 dB max
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise (SFDR)2 −72 dB max
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)2 fa = 30 kHz, fb = 50 kHz
Channel-to-Channel Isolation −75 dB typ FIN = 50 kHz, F
Aperture Delay2 5 ns typ
Aperture Jitter2 72 ps typ
Full Power Bandwidth2 50 MHz typ @ 3 dB
10 MHz typ @ 0.1 dB
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 10 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity2 ±0.5 LSB max
Differential Nonlinearity2 ±0.5 LSB max Guaranteed no missed codes to 10 bits
Single-Ended and Pseudo Differential Input Straight binary output coding
Fully Differential Input Twos complement output coding
ANALOG INPUT
Single-Ended Input Range 0 to V
Pseudo-Differential Input Range: V
Fully Differential Input Range: V
DC Leakage Current
Input Capacitance 45 pF typ When in track
10 pF typ When in hold
REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT
V
REF
DC Leakage Current4 ±1 µA max
V
REFOUT
V
REFOUT
V
REF
130 µV typ 0.1 Hz to 1 MHz bandwidth
= 2.7 V to 5.25 V, internal/external V
DRIVE
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
2
= 2.5 V, unless otherwise noted, F
REF
1
Unit Test Conditions/Comments
= 25.5 MHz, F
CLKIN
SAMPLE
61 dB min Differential mode
= 1.5 MSPS;
Second-Order Terms −86 dB typ
Third-Order Terms −90 dB typ
= 300 kHz
NOISE
Offset Error2 ±2 LSB max
Offset Error Match2 ±0.5 LSB max
Gain Error2 ±1.5 LSB max
Gain Error Match2 ±0.5 LSB max
Positive Gain Error2 ±1.5 LSB max
Positive Gain Error Match2 ±0.5 LSB max
Zero-Code Error2 ±2 LSB max
Zero-Code Error Match2 ±0.5 LSB max
Negative Gain Error2 ±1.5 LSB max
Negative Gain Error Match2 ±0.5 LSB max
or 0 to 2 × V
REF
0 to V
IN+
V
IN−
or 2 × V
REF
−0.3 to +0.7 V typ VDD = 3 V
V RANGE bit = 0, or RANGE bit = 1, respectively
REF
V RANGE bit = 0, or RANGE bit = 1, respectively
REF
−0.3 to +1.8 V typ VDD = 5 V
and V
IN+
V
IN+
4
and V
IN−VCM
IN−VCM
± V
/2 V VCM = common-mode voltage3 = V
REF
± V
REF
V
±1 µA max
= V
V
CM
GND/V
, V
or V
REF
IN+
DD
must remain within
IN−
Input Voltage5 2.5 V ±1% specified performance
Output Voltage 2.5 V ±0.2% max @ 25°C
Temperature Coefficient 40 ppm/°C typ
Noise 10 µV typ 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz bandwidth
REF
/2
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
Parameter B Version
V
Output Impedance 10 Ω typ
REF
V
Input Capacitance 15 pF typ When in track
REF
1
Unit Test Conditions/Comments
25 pF typ When in hold
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
INH
INL
2.4 V min
0.8 V max
Input Current, IIN ±5 µA max Typically 10 nA, VIN = 0 V or V
Input Capacitance, C
4
IN
10 pF max
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, V
OH
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 V max I
2.4 V min I
SOURCE
= 200 µA
SINK
= 200 µA
Floating-State Leakage Current ±3 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance4 10 pF max
Output Coding CODING bit = 0
Straight (Natural) Binary
Twos Complement
CODING bit = 1
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time t2 + 13 t
ns
CLK
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time 125 ns max Full-scale step input
Throughput Rate 1.5 MSPS max
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD 2.7/5.25 V min/max
V
2.7 /5.25 V min/max
DRIVE
6
I
DD
Digital I/PS = 0 V or V
DRIVE
Normal Mode (Static) 0.8 mA typ VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, SCLK on or off
Normal Mode (Operational) 2.7 mA max VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
2.0 mA max VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V
Autostandby Mode 0.3 mA typ F
= 100 kSPS, VDD = 5 V
SAMPLE
160 µA typ (Static)
Full/Autoshutdown Mode (Static) 2 µA max SCLK on or off
Power Dissipation
Normal Mode (Operational) 13.5 mW max VDD = 5 V
6 mW max VDD = 3 V
Autostandby Mode (Static) 800 µW typ VDD = 5 V
480 µW typ VDD = 3 V
Full/Autoshutdown Mode 10/6 µW max VDD = 5 V/3 V
1
Temperature range is as follows: B Versions: −40°C to +85°C.
2
See section. Terminology
3
For full common-mode range, see Fi and . gure 25 Figure 26
4
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance.
5
This device is operational with an external reference in the range 0.1 V to VDD . See the R for more information. eference Section
6
Measured with a midscale dc analog input.
DRIVE
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
AD7934—SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = V
= T
T
A
Table 2.
Parameter B Version
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE FIN = 50 kHz sine wave
Signal-to-Noise + Distortion (SINAD)
68 dB min Single-ended mode
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)2 71 dB min Differential mode
69 dB min Single-ended mode
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)2 −73 dB max −85 dB typ, differential mode
−70 dB max −80 dB typ, single-ended mode
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise (SFDR)2 −73 dB max −82 dB typ
Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)2 fa = 30 kHz, fb = 50 kHz
Channel-to-Channel Isolation −85 dB typ FIN = 50 kHz, F
Aperture Delay2 5 ns typ
Aperture Jitter2 72 ps typ
Full Power Bandwidth2 50 MHz typ @ 3 dB
10 MHz typ @ 0.1 dB
DC ACCURACY
Resolution 12 Bits
Integral Nonlinearity2 ±1 LSB max Differential mode
±1.5 LSB max Single-ended mode
Differential Nonlinearity 2
Single-Ended and Pseudo-Differential Input Straight binary output coding
Fully Differential Input
ANALOG INPUT
Single-Ended Input Range 0 to V
Pseudo-Differential Input Range: V
Fully Differential Input Range: V
DC Leakage Current
Input Capacitance 45 pF typ When in track
10 pF typ When in hold
= 2.7 V to 5.25 V, internal/external V
DRIVE
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
2
= 2.5 V, unless otherwise noted, F
REF
1
Unit Test Conditions/Comments
= 25.5 MHz, F
CLKIN
SAMPLE
70 dB min Differential mode
= 1.5 MSPS;
Second-Order Terms −86 dB typ
Third-Order Terms −90 dB typ
= 300 kHz
NOISE
Differential Mode ±0.95 LSB max Guaranteed no missed codes to 12 bits
Single-Ended Mode −0.95/+1.5 LSB max Guaranteed no missed codes to 12 bits
Offset Error2 ±6 LSB max
Offset Error Match2 ±1 LSB max
Gain Error2 ±3 LSB max
Gain Error Match2 ±1 LSB max Twos complement output coding
Positive Gain Error2 ±3 LSB max
Positive Gain Error Match2 ±1 LSB max
Zero-Code Error2 ±6 LSB max
Zero-Code Error Match2 ±1 LSB max
Negative Gain Error2 ±3 LSB max
Negative Gain Error Match2 ±1 LSB max
or 0 to 2 × V
REF
0 to V
IN+
V
IN−
or 2 × V
REF
REF
−0.3 to +0.7 V typ VDD = 3 V
V RANGE bit = 0, or RANGE bit = 1, respectively
REF
V RANGE bit = 0, or RANGE bit = 1, respectively
−0.3 to +1.8 V typ VDD = 5 V
and V
IN+
V
and V
4
IN+
IN−
IN−
VCM ± V
VCM ± V
/2 V VCM = common-mode voltage3 = V
REF
REF
±1 µA max
V VCM = V
REF
, V
IN+
or V
must remain within GND/V
IN−
REF
/2
DD
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
Parameter B Version
1
Unit Test Conditions/Comments
REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT
V
Input Voltage5 2.5 V ±1% specified performance
REF
DC Leakage Current ±1 µA max
V
Output Voltage 2.5 V ±0.2% max @ 25°C
REFOUT
V
Temperature Coefficient 25 ppm/°C max 5 ppm/°C typ
REFOUT
V
Noise 10 µV typ 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz bandwidth
REF
130 µV typ 0.1 Hz to 1 MHz bandwidth
V
Output Impedance 10 Ω typ
REF
V
Input Capacitance 15 pF typ When in track-and-hold
REF
25 pF typ When in track-and-hold
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
INH
INL
2.4 V min
0.8 V max
Input Current, IIN ±5 µA max Typically 10 nA, VIN = 0 V or V
Input Capacitance, C
4
IN
10 pF max
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, V
OH
Output Low Voltage, VOL 0.4 V max I
2.4 V min I
= 200 µA
SOURCE
= 200 µA
SINK
Floating-State Leakage Current ±3 µA max
Floating-State Output Capacitance4 10 pF max
Output Coding CODING bit = 0
Straight (Natural) Binary
Twos Complement
CODING bit = 1
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time t2 + 13 t
ns
CLK
Track-and-Hold Acquisition Time 125 ns max Full-scale step input
Throughput Rate 1.5 MSPS max
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VDD 2.7/5.25 V min/max
V
2.7/5.25 V min/max
DRIVE
6
I
DD
Digital I/PS = 0 V or V
DRIVE
Normal Mode (Static) 0.8 mA typ VDD = 2.7 V to 5.25 V, SCLK on or off
Normal Mode (Operational) 2.7 mA max VDD = 4.75 V to 5.25 V
2.0 mA max VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V
Autostandby Mode 0.3 mA typ F
= 100 kSPS, VDD = 5 V
SAMPLE
160 µA typ (Static)
Full/Autoshutdown Mode (Static) 2 µA max SCLK on or off
Power Dissipation
Normal Mode (Operational) 13.5 mW max VDD = 5 V
6 mW max VDD = 3 V
Autostandby Mode (Static) 800 µW typ VDD = 5 V
480 µW typ VDD = 3 V
Full/Autoshutdown Mode 10/6 µW max VDD = 5 V/3 V
1
Temperature ranges is as follows: B Versions: −40°C to +85°C.
2
See the section. Terminology
3
For full common-mode range, see Fi and . gure 25 Figure 26
4
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance.
5
This device is operational with an external reference in the range 0.1 V to VDD. See the Reference Section for more information.
6
Measured with a midscale dc analog input.
DRIVE
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
VDD = V
= T
T
A
Table 3.
Limit at T
Parameter AD7933 AD7934 Unit Description
f
CLKIN
25.5 25.5 MHz max
t
QUIET
t
1
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
5
t
6
t
7
t
8
t
9
t
10
t
11
t
12
2
t
13
3
t
14
50 50 ns max
t
15
t
16
t
17
t
18
t
19
t
20
t
21
t
22
1
Sample tested during initial release to ensure compliance. All input signals are specified with tr = tf = 5 ns (10% to 90% of VDD) and timed from a voltage level of 1.6 V.
All timing specifications given above are with a 25 pF load capacitance (see , , and ).
2
The time required for the output to cross 0.4 V or 2.4 V.
3
t14 is derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change 0.5 V. The measured number is then extrapolated back to remove the effects of charging or
discharging the 25 pF capacitor. This means that the time, t
bus loading.
= 2.7 V to 5.25 V, internal/external V
DRIVE
to T
MIN
, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
, T
MIN
50 50 kHz min
30 30 ns min
10 10 ns min
15 15 ns min
50 50 ns min CLKIN Falling Edge to BUSY Rising Edge.
0 0 ns min
0 0 ns min
10 10 ns min
10 10 ns min
10 10 ns min
10 10 ns min New Data Valid before Falling Edge of BUSY.
0 0 ns min
0 0 ns min
30 30 ns min
30 30 ns max
3 3 ns min
0 0 ns min
0 0 ns min
10 10 ns min Minimum Time between Reads/Writes.
0 0 ns min
10 10 ns min
40 40 ns max CLKIN Falling Edge to BUSY Falling Edge.
15.7 15.7 ns min CLKIN Low Pulse Width
7.8 7.8 ns min CLKIN High Pulse Width.
1
MAX
= 2.5 V, unless otherwise noted, F
REF
= 25.5 MHz, F
CLKIN
= 1.5 MSPS;
SAMPLE
Minimum time between end of read and start of next conversion, i.e., time from
when the data bus goes into three-state until the next falling edge of
CONVST.
CONVST Pulse Width.
CONVST Falling Edge to CLKIN Falling Edge Setup Time.
CS to WR Setup Time.
CS to WR Hold Time.
WR Pulse Width.
Data Setup Time before
Data Hold after
WR.
WR.
CS to RD Setup Time.
CS to RD Hold Time.
RD Pulse Width.
Data Access Time after
Bus Relinquish Time after
Bus Relinquish Time after
HBEN to
HBEN to
HBEN to
HBEN to
, quoted in the timing characteristics is the true bus relinquish time of the part and is independent of the
14
RD Setup Time.
RD Hold Time.
WR Setup Time.
WR Hold Time.
Figure 35 Figure 36 Figure 37, Figure 38
RD.
RD.
RD.
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
T
= 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
A
Table 4.
Parameter Rating
VDD to AGND/DGND −0.3 V to +7 V
V
to AGND/DGND −0.3 V to VDD +0.3 V
DRIVE
Analog Input Voltage to AGND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND −0.3 V to +7 V
V
to V
DRIVE
DD
Digital Output Voltage to AGND −0.3 V to V
V
to AGND −0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
REFIN
−0.3 V to VDD + 0.3 V
+ 0.3 V
DRIVE
AGND to DGND −0.3 V to +0.3 V
Input Current to Any Pin Except Supplies
1
±10 mA
Operating Temperature Range
Commercial (B Version) −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature 150°C
θJA Thermal Impedance 97.9°C/W (TSSOP)
θJC Thermal Impedance 14°C/W (TSSOP)
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Reflow Temperature (10 sec to 30 sec) 255°C
ESD 1.5 kV
1
Transient currents of up to 100 mA do not cause SCR latch-up.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those listed in the operational sections
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate
on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 32
AD7933/AD7934
T
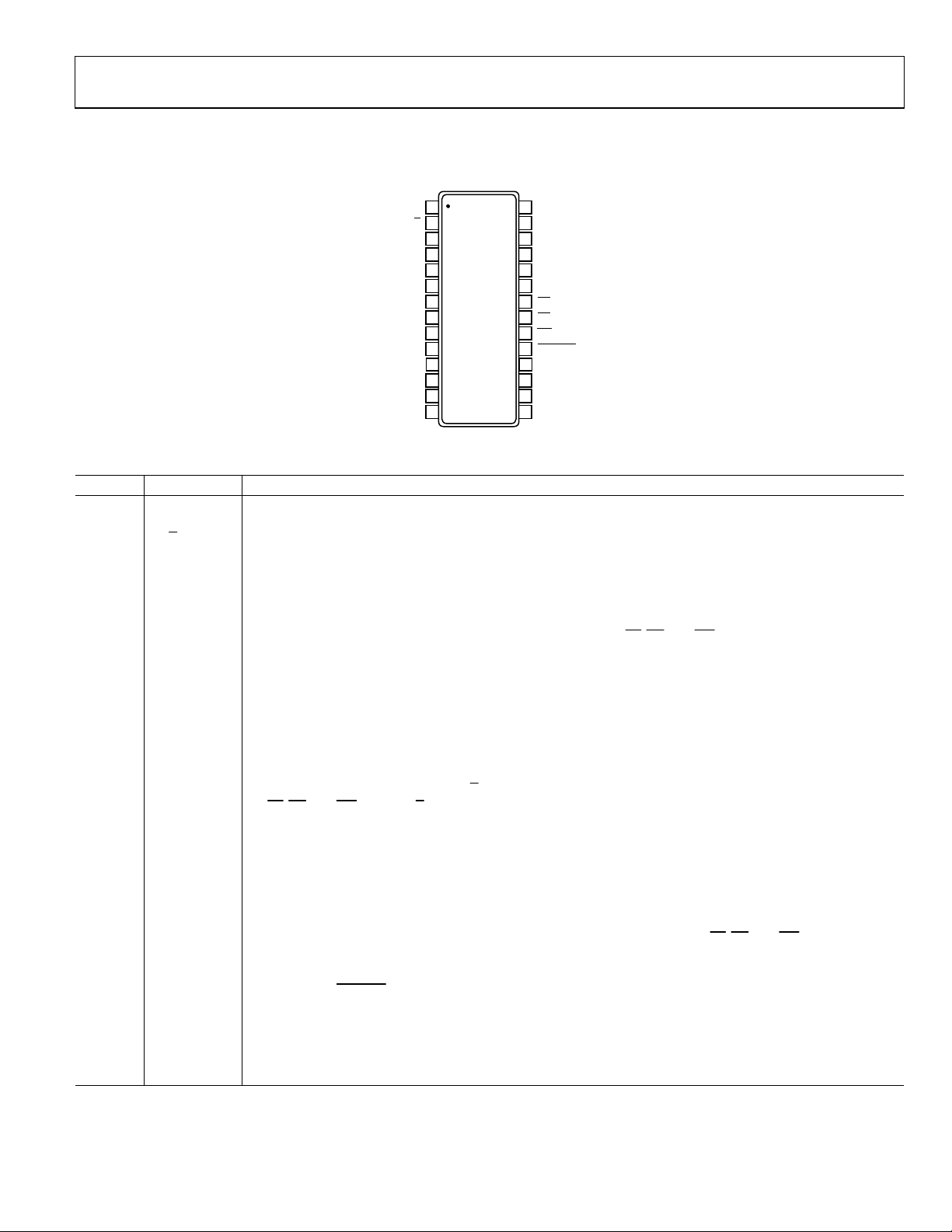
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Table 5. Pin Function Description
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 VDD
Power Supply Input. The V
decoupled to AGND with a 0.1 µF capacitor and a 10 µF tantalum capacitor.
2
B Word/Byte Input. When this input is logic high, word transfer mode is enabled, and data is transferred to and
W/
from the AD7933/AD7934 in 12-/10-bit words on Pins DB0/DB2 to DB11. When this pin is logic low, byte
transfer mode is enabled. Data and the channel ID are transferred on Pins DB0 to DB7, and Pin DB8/HBEN
assumes its HBEN functionality. Unused data lines when operating in byte transfer mode should be tied off to
DGND.
3 to 10 DB0 to DB7
Data Bits 0 to 7. Three-state parallel digital I/O pins that provide the conversion result and also allow the
control register to be programmed. These pins are controlled by
levels for these pins are determined by the V
DB1) are always 0 and the LSB of the conversion result is available on DB2.
11 V
DRIVE
Logic Power Supply Input. The voltage supplied at this pin determines at what voltage the parallel interface of
the AD7933/AD7934 operates. This pin should be decoupled to DGND. The voltage at this pin may be different
12 DGND
to that at V
Digital Ground. This is the ground reference point for all digital circuitry on the AD7933/AD7934. This pin
DD
should connect to the DGND plane of a system. The DGND and AGND voltages should ideally be at the same
potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart, even on a transient basis.
13 DB8/HBEN
Data Bit 8/High Byte Enable. When W/
CS, RD, and WR. When W/B is low, this pin acts as the high byte enable pin. When HBEN is low, the low byte
by
of data written to or read from the AD7933/AD7934 is on DB0 to DB7. When HBEN is high, the top four bits of
the data being written to or read from the AD7933/AD7934 are on DB0 to DB3. When reading from the device,
DB4 of the high byte is always 0 and DB5 and DB6 will contain the ID of the channel to which the conversion
result corresponds (see Channel Address Bits in Table 9). When writing to the device, DB4 to DB7 of the high
byte must be all 0s. Note that when reading from the AD7933, the two LSBs in the low byte are 0s and the
remaining 6 bits, conversion data.
14 to 16 DB9 to DB11
Data Bits 9 to 11. Three-state parallel digital I/O pins that provide the conversion result and also allow the
control register to be programmed in word mode. These pins are controlled by
high/low voltage levels for these pins are determined by the V
17 BUSY
Busy Output. Logic output indicating the status of the conversion. The BUSY output goes high following the
falling edge of
the result is available in the output register, the BUSY output goes low. The track-and-hold returns to track
mode just prior to the falling edge of BUSY, on the 13
18 CLKIN
Master Clock Input. The clock source for the conversion process is applied to this pin. Conversion time for the
AD7933/AD7934 takes 13 clock cycles + t
conversion time and achievable throughput rate. The CLKIN signal may be a continuous or burst clock.
1
V
DD
2
W/B
3
DB0
4
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
V
DRIVE
DGND
DB8/HBEN DB11
DB9
5
6
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
AD7933/
AD7934
TOP VIEW
28
V
IN
27
VIN2
26
V
IN
25
V
IN
24
V
REFIN/VREFOU
23
AGND
22
CS
21
RD
20
WR
19
CONVST
18
CLKIN
17
BUSY
16
15
DB10
3
1
0
03713-0-006
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
range for the AD7933/AD7934 is from 2.7 V to 5.25 V. The supply should be
DD
CS, RD, and WR. The logic high/low voltage
input. When reading from the AD7933, the two LSBs (DB0 and
DRIVE
but should never exceed VDD by more than 0.3 V.
B is high, this pin acts as Data Bit 8, a three-state I/O pin that is controlled
CS, RD, and WR. The logic
input.
DRIVE
CONVST and stays high for the duration of the conversion. Once the conversion is complete and
th
rising edge of SCLK, see Figure 34.
. The frequency of the master clock input therefore determines the
2
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 32

AD7933/AD7934
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
19
20
21
22
23 AGND
24 V
25 to 28 VIN0 to VIN3
CONVST Conversion Start Input. A falling edge on CONVST is used to initiate a conversion. The track-and-hold goes from
track to hold mode on the falling edge of
Following power-down, when operating in the autoshutdown or autostandby mode, a rising edge on
is used to power up the device.
WR Write Input. Active low logic input used in conjunction with CS to write data to the control register.
RD Read Input. Active low logic input used in conjunction with CS to access the conversion result. The conversion
result is placed on the data bus following the falling edge of
CS Chip Select. Active low logic input used in conjunction with RD and WR to read conversion data or write data to
the control register.
Analog Ground. This is the ground reference point for all analog circuitry on the AD7933/AD7934. All analog
input signals and any external reference signal should be referred to this AGND voltage. The AGND and DGND
voltages should ideally be at the same potential and must not be more than 0.3 V apart, even on a transient
basis.
REFIN/VREFOUT
Reference Input/Output. This pin is connected to the internal reference and is the reference source for the ADC.
The nominal internal reference voltage is 2.5 V, and this appears at this pin. This pin can be overdriven by an
external reference. The input voltage range for the external reference is 0.1 V to V
taken to ensure that the analog input range does not exceed V
Analog Input 0 to Analog Input 3. Four analog input channels that are multiplexed into the on-chip track-and-
hold. The analog inputs can be programmed to be four single ended inputs, two fully differential pairs or two
pseudo-differential pairs by setting the MODE bits in the control register appropriately (see Table 9). The
analog input channel to be converted can either be selected by writing to the address bits (ADD1 and ADD0) in
the control register prior to the conversion, or the on-chip sequencer can be used. The input range for all input
channels can either be 0 V to V
depending on the states of the RANGE and CODING bits in the control register. Any unused input channels
should be connected to AGND to avoid noise pickup.
or 0 V to 2 × V
REF
CONVST, and the conversion process is initiated at this point.
RD read while CS is low.
; however, care must be
+ 0.3 V. See the Reference Section.
DD
and the coding can be binary or twos complement,
REF
DD
CONVST
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 32
 Loading...
Loading...