Analog Devices AD10265 Datasheet
Dual Channel, 12-Bit, 65 MSPS A/D Converter
a
FEATURES
Dual, 65 MSPS Minimum Sample Rate
Channel-Channel Matching, ⴞ0.1% Gain Error
Channel-Channel Isolation, >80 dB
AC-Coupled Signal Conditioning Included
Selectable Bipolar Input Voltage Range
(ⴞ0.5 V, ⴞ1.0 V, ⴞ2.0 V)
Gain Flatness up to Nyquist: < 0.5 dB
80 dB Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
Twos Complement Output Format
+3.3 V or +5 V CMOS-Compatible Output Levels
1.05 W Per Channel
Industrial and Military Grade
APPLICATIONS
Phased Array Receivers
Communications Receivers
FLIR Processing
Secure Communications
GPS Anti-Jamming Receivers
Multichannel, Multimode Receivers
with Analog Input Signal Conditioning
AD10265
65 MSPS performance. The AD10265 uses innovative highdensity circuit design and laser-trimmed thin-film resistor
networks to achieve exceptional matching and performance
while still maintaining excellent isolation, and providing for
significant board area savings.
The AD10265 operates with ±5.0 V for the analog signal
conditioning with a separate +3.3 V supply for the analog-todigital conversion. Each channel is completely independent
allowing operation with independent Encode and Analog inputs. The AD10265 also offers the user a choice of Analog
Input Signal ranges to further minimize additional external
signal conditioning, while still remaining general-purpose.
The AD10265 is packaged in a 68-lead Ceramic Gull Wing
Package, footprint compatible with the earlier generation
AD10242 (12-bit, 40 MSPS). Manufacturing is done on
Analog Devices’ MIL-38534 Qualified Manufacturers Line
(QML) and components are available up to Class-H (–55°C to
+125°C). The AD6640 internal components are manufactured
on Analog Devices’ high speed complementary bipolar process
(XFCB).
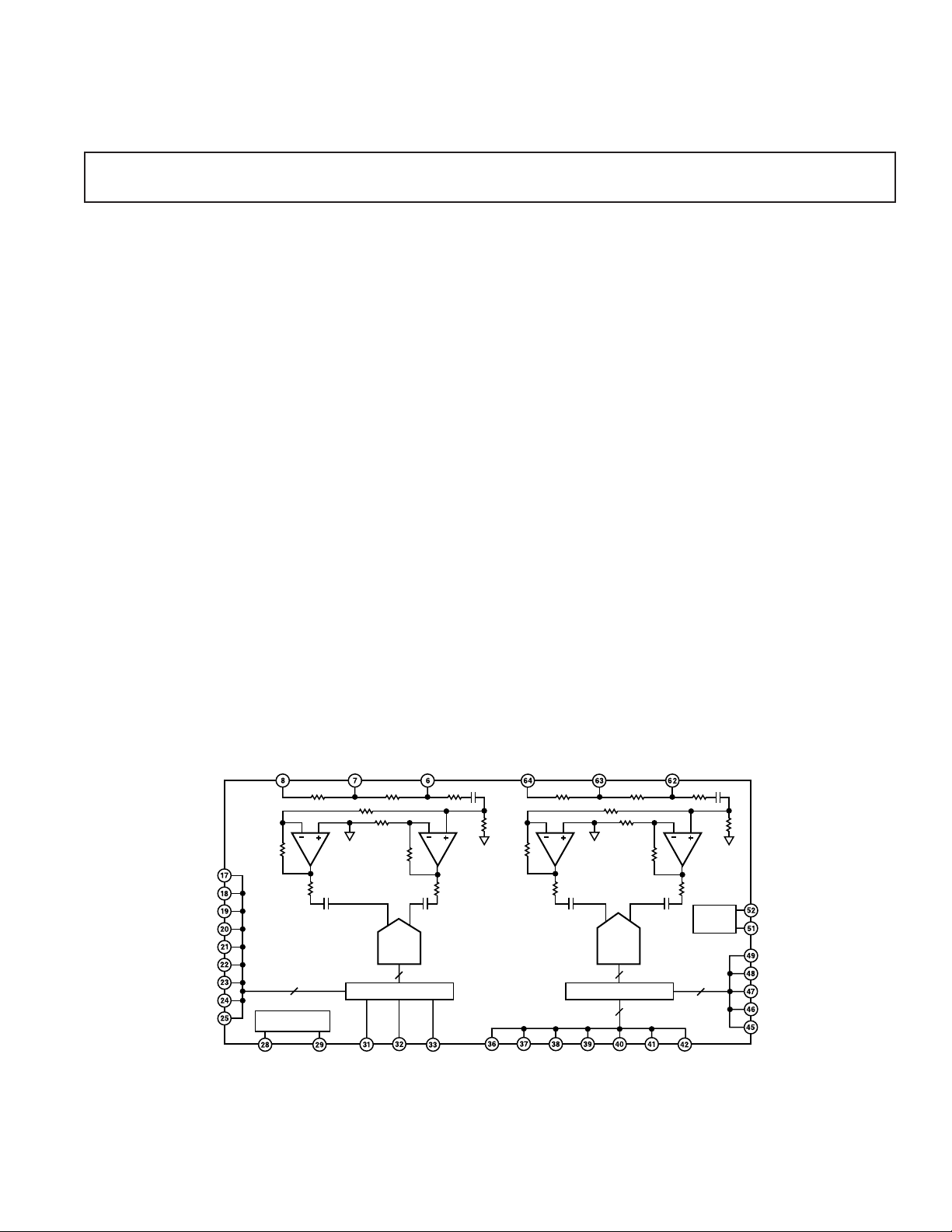
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD10265 is a full channel ADC solution with on-module
signal conditioning for improved dynamic performance and
fully matched channel-to-channel performance. The module
includes two wide dynamic range AD6640 ADCs. Each
AD6640 has an AD9631/AD9632 ac-coupled amplifier front
end. The AD6640s have on-chip track-and-hold circuitry, and
utilize an innovative multipass architecture, to achieve 12-bit,
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
AINA2 AINA1AINA3
(LSB) D0A
D1A
D2A
D3A
D4A
D5A
D6A
D7A
D8A
9
TIMING
AD9632
AIN
AD6640
OUTPUT BUFFERING
AD9631
AIN
AD10265
12
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Guaranteed sample rate of 65 MSPS.
2. Input amplitude options, user configurable.
3. Input signal conditioning included; both channels matched
for gain.
4. Fully tested/characterized performance for full channel.
5. Footprint compatible family; 68-lead LCCC.
AINB3
AINB2 AINB1
AD9632
AIN
OUTPUT BUFFERING
AIN
AD6640
12
7
AD9631
TIMING
5
ENCODEB
ENCODEB
D11B (MSB)
D10B
D9B
D8B
D7B
ENCODEA
ENCODEA
D9A D10A
D11A
(MSB)
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
D0B
D1B D2B
(LSB)
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1998
D3B D4B D5B
D6B
AD10265–SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics
(AVCC = +5 V; AVEE = –5.0 V; DVCC = +3.3 V; applies to each ADC unless otherwise noted)
Test Mil AD10265AZ
Parameter Temp Level Subgroup Min Typ Max Units
RESOLUTION 12 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Full VI 1, 2, 3 Guaranteed
Offset Error Full IV 2, 3 –10 3.5 +10 mV
Gain Error
1
+25°C I 1 –1.0 ±0.5 +1.0 % FS
Full VI 2, 3 –2.0 ±0.8 +2.0 % FS
Gain Error Channel Match Full V ±0.1 %
Pass Band Ripple to Nyquist Full I 12 0.2 0.5 dB
ANALOG INPUT (A
)
IN
Input Voltage Range
A
1 Full I ±0.5 V
IN
2 Full I ±1.0 V
A
IN
A
3 Full I ±2V
IN
Input Resistance
1 Full IV 12 99 100 101 Ω
A
IN
A
2 Full IV 12 198 200 202 Ω
IN
3 Full IV 12 396 400 404 Ω
A
IN
Input Capacitance
Analog Input Bandwidth High
Analog Input Bandwidth Low
ENCODE INPUT
4, 5
2
3
3
+25°CIV 12 0 4.0 7.0 pF
+25°C V 160 MHz
+25°CV 50 kHz
Logic Compatibility TTL/CMOS
Logic “1” Voltage Full I 1, 2, 3 2.0 5.0 V
Logic “0” Voltage Full I 1, 2, 3 0 0.8 V
Logic “1” Current (V
Logic “0” Current (V
= 5 V) Full I 1, 2, 3 500 650 800 µA
INH
= 0 V) Full I 1, 2, 3 –400 –320 –200 µA
INL
Input Capacitance +25°CV 12 4.5 7.0 pF
SWITCHING PERFORMANCE
Maximum Conversion Rate
Minimum Conversion Rate
Aperture Delay (t
) +25°C V 400 ps
A
6
6
Full VI 4, 5, 6 65 MSPS
Full V 12 6.5 MSPS
Aperture Delay Matching +25°CV ±2.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter) +25°C V 0.3 ps rms
ENCODE Pulsewidth High +25°C IV 12 6.5 ns
ENCODE Pulsewidth Low +25°C IV 12 6.5 ns
Output Delay (tOD) Full IV 12 7.0 9.0 12.5 ns
7
SNR
Analog Input @ 1.24 MHz +25°CI 4 62 66 dB
Full II 5, 6 60.5 66 dB
@ 17 MHz +25°CI 4 61 65 dB
Full II 5, 6 60 65 dB
@ 32 MHz +25°CI 4 61 63 dB
Full II 5, 6 59.5 62 dB
8
SINAD
Analog Input @ 1.24 MHz +25°CI 4 61 65 dB
Full II 5, 6 60 64 dB
@ 17 MHz +25°CI 4 61 64 dB
Full II 5, 6 59.5 63 dB
@ 32 MHz +25°CI 4 61 62 dB
Full II 5, 6 59 62 dB
–2–
REV. 0
AD10265
Test Mil AD10265AZ
Parameter Temp Level Subgroup Min Typ Max Units
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE
Analog Input @ 1.24 MHz +25°C I 4 75 80 dBFS
@ 17 MHz +25°C I 4 72 80 dBFS
@ 32 MHz +25°C I 4 72 79 dBFS
TWO-TONE IMD REJECTION
f1, f2 @ –7 dBFS Full II 4, 5, 6 72 80 dBc
CHANNEL-TO-CHANNEL ISOLATION
LINEARITY
Differential Nonlinearity
(Encode = 20 MHz) +25°C IV 12 –1.0 ±0.5 1.5 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity
(Encode = 20 MHz) Full V ±1.25 LSB
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Logic Compatibility CMOS
Logic “1” Voltage Full I 1, 2, 3 2.8 DV
Logic “0” Voltage Full I 1, 2, 3 0.2 0.5 V
Output Coding Twos Complement
POWER SUPPLY
AVCC Supply Voltage Full VI +5.0 V
) Current Full V 336 mA
I (AV
CC
AV
Supply Voltage Full VI –5.0 V
EE
) Current Full V 66 mA
I (AV
EE
DV
Supply Voltage Full VI +3.3 V
CC
I (DV
I
) Current Full V 20 mA
CC
(Total) Supply Current Full I 1, 2, 3 422 520 mA
CC
Power Dissipation (Total) Full I 1, 2, 3 2.1 2.4 W
Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) Full IV 7, 8 0.01 0.02 % FSR/% V
NOTES
1
Gain tests are performed on AIN1 over specified input voltage range.
2
Input capacitance specifications show only ceramic package capacitance.
3
Full power bandwidth is the frequency at which the spectral power of the fundamental frequency (as determined by FFT analysis) is reduced by 3 dB.
4
ENCODE driven by single-ended source; ENCODE bypassed to ground through 0.01 µF capacitor.
5
ENCODE may also be driven differentially in conjunction with ENCODE; see “Encoding the AD10265” for details.
6
Minimum and maximum conversion rates allow for variation in Encode Duty Cycle of 50% ± 5%.
7
Analog Input signal power at –1 dBFS; signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is the ratio of signal level to total noise (first 5 harmonics removed). Encode = 65 MSPS.
8
Analog Input signal power at –1 dBFS; signal-to-noise and distortion (SINAD) is the ratio of signal level to total noise + harmonics. Encode = 65 MSPS.
9
Analog Input signal equal –1 dBFS; SFDR is ratio of converter full scale to worst spur.
10
Both input tones at –7 dBFS; two tone intermodulation distortion (IMD) rejection is the ratio of either tone to the worst 3rd order intermod product. f1 = 17.0 MHz
± 100 kHz, f 2 = 18.0 MHz ± 100 kHz.
11
Channel-to-channel isolation tested with A channel/50 ohm terminated <AIN2 grounded, and a full-scale signal applied to B channel (AIN1).
All specifications guaranteed within 100 ms of initial power up regardless of sequencing.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
9
Full II 5, 6 75 80 dBFS
Full II 5, 6 72 79 dBFS
Full II 5, 6 72 79 dBFS
10
11
+25°CIV 12 80 dB
– 0.2 V
CC
S
REV. 0
–3–
AD10265
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
1
Parameter Min Max Units
ELECTRICAL
V
Voltage 0 7 V
CC
Voltage –7 0 V
V
EE
Analog Input Voltage V
EE
V
V
CC
Analog Input Current –10 +10 mA
Digital Input Voltage (ENCODE) 0 AV
CC
V
ENCODE, ENCODE Differential Voltage 4 V
Digital Output Current –10 +10 mA
ENVIRONMENTAL
2
Operating Temperature (Case) –55 +125 °C
Maximum Junction Temperature +175 °C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) +300 °C
Storage Temperature Range (Ambient) –65 +150 °C
NOTES
1
Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values to be applied individually, and
beyond which the serviceability of the circuit may be impaired. Functional
operability is not necessarily implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for an extended period of time may affect device reliability.
2
Typical thermal impedances for “Z” package: θJC = 11°C/W; θJA = 30°C/W.
ORDERING GUIDE
Table I. Output Coding
MSB LSB Base 10 Input
0111111111111 2047 +FS
0000000000001 +1
0000000000000 0 0.0 V
1111111111111 –1
1000000000000 2048 –FS
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level
I – 100% Production Tested.
II – 100% production tested at +25°C, and sample tested at
specified temperatures. AC testing done on sample basis.
III – Sample Tested Only.
IV – Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization
testing.
V – Parameter is a typical value only.
VI – All devices are 100% production tested at +25°C; sample
tested at temperature extremes.
M
odel Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD10265AZ –25°C to +85°C (Case) 68-Lead Leaded Ceramic Chip Carrier Z-68A
AD10265/PCB +25°C Evaluation Board with AD10265AZ
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD10265 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–4–
REV. 0
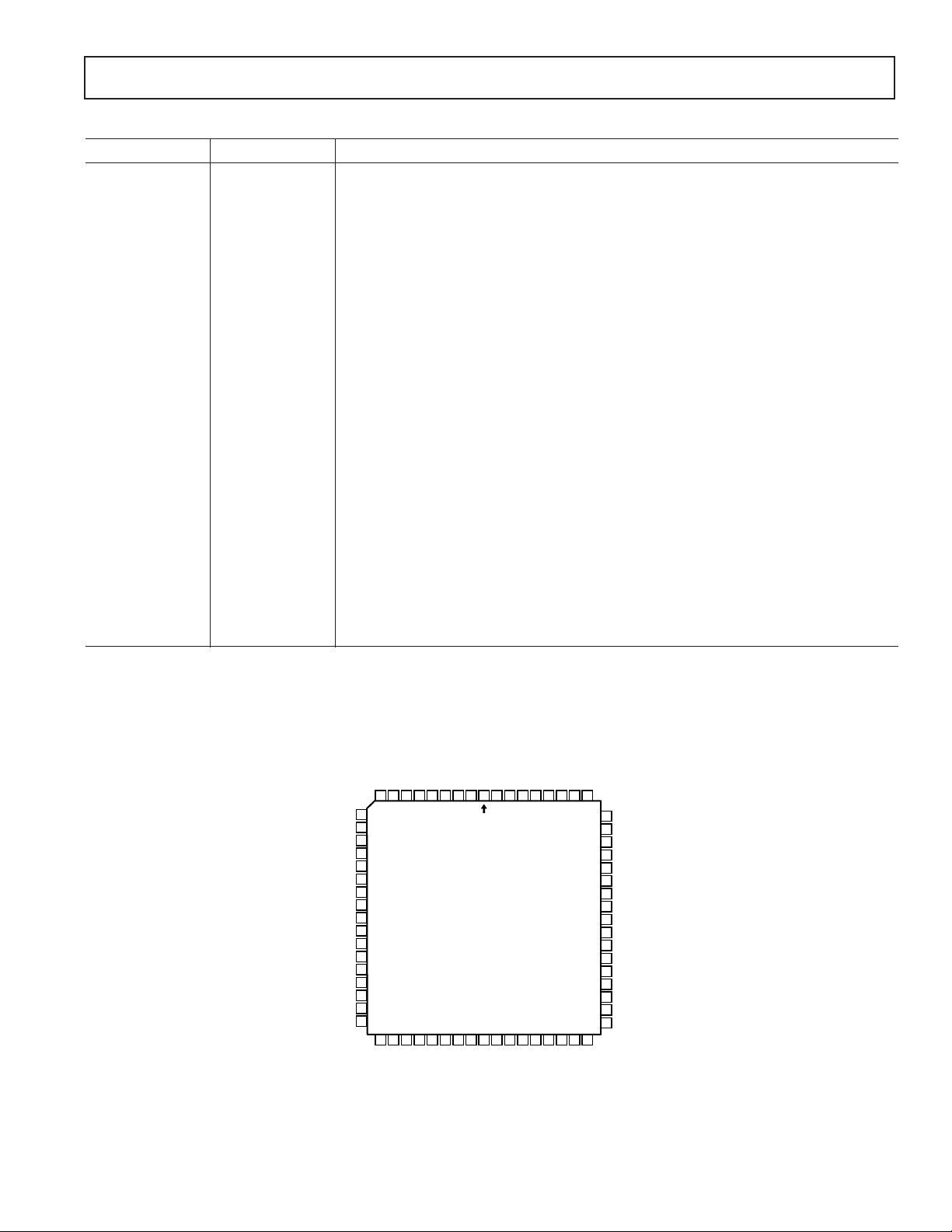
AD10265
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin No. Name Function
1 SHIELD Internal Ground Shield between channels.
2, 5, 9–11, 26, 27 GNDA A Channel Ground. A and B grounds should be connected as close to the device as possible.
3, 4, 12, 15, 16, NC No Connect. Pins 15 and 17 are internal test pins: it is recommended to connect them to
34, 35, 55–57 GND
6A
7A
8A
13 AV
14 AV
17–25, 31–33 D0A–D11A Digital Outputs for ADC A. D0 (LSB).
28 ENCODEA ENCODE is complement of ENCODE.
29 ENCODEA Data conversion initiated on rising edge of ENCODE input.
30 DV
36–42, 45–49 D0B–D11B Digital Outputs for ADC B. D0 (LSB).
43, 44, 53, 54, GNDB B Channel Ground. A and B grounds should be connected as close to the device
58–61, 65, 68 as possible.
50 DV
51 ENCODEB Data conversion initiated on rising edge of ENCODE input.
52 ENCODEB ENCODE is complement of ENCODE.
62 A
63 A
64 A
66 AV
67 AV
A1 Analog Input for A side ADC (nominally ±0.5 V).
IN
A2 Analog Input for A side ADC (nominally ±1.0 V).
IN
A3 Analog Input for A side ADC (nominally ±2.0 V).
IN
EE
CC
CC
CC
B1 Analog Input for B side ADC (nominally ±0.5 V).
IN
B2 Analog Input for B side ADC (nominally ±1.0 V).
IN
B3 Analog Input for B side ADC (nominally ±2.0 V).
IN
CC
EE
Analog Negative Supply Voltage (nominally –5.0 V). For A side ADC.
Analog Positive Supply Voltage (nominally +5.0 V). For A side ADC.
Digital positive supply voltage (nominally +3.3 V) for A side ADC.
Digital Positive Supply Voltage (nominally +3.3 V) for B side ADC.
Analog Positive Supply Voltage (nominally +5.0 V). For B side ADC.
Analog Negative Supply Voltage (nominally –5.0 V). For B side ADC.
68-Lead Leaded Ceramic Chip Carrier
10
GNDA
11
GNDA
12
NC
13
AV
EE
14
AV
CC
15
NC
16
NC
(LSB) D0A
17
18
D1A
19
D2A
20
D3A
21
D4A
22
D5A
23
D6A
24
D7A
25
D8A
26
GNDA
NC = NO CONNECT
PIN CONFIGURATION
A2
A3
A1
IN
IN
IN
A
A
GNDA
A
9618 7 6 5 68 67 66 65 64 63 624321
GNDA
NC
NC
GNDA
PIN 1
SHIELD
GNDB
AD10265
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
27 4328 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
GNDA
ENCODEA
CC
DV
ENCODEA
D9A
D10A
NC
NC
(LSB) D0B
(MSB) D11A
EE
AV
D1B
CC
AV
D2B
B3
IN
A
GNDB
D3B
D4B
B2
IN
A
D5B
B1
IN
A
D6B
GNDB
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
GNDB
GNDB
GNDB
GNDB
NC
NC
NC
GNDB
GNDB
ENCODEB
ENCODEB
DV
CC
D11B (MSB)
D10B
D9B
D8B
D7B
GNDB
REV. 0
–5–

AD10265
DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONS
Analog Bandwidth
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the
fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is
reduced by 3 dB.
Aperture Delay
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of the
ENCODE command and the instant at which the analog input
is sampled.
Aperture Uncertainty (Jitter)
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
Differential Nonlinearity
The deviation of any code from an ideal 1 LSB step.
Encode Pulse Width/Duty Cycle
Pulse width high is the minimum amount of time that the
ENCODE pulse should be left in logic “1” state to achieve rated
performance; pulse width low is the minimum time ENCODE
pulse should be left in low state. At a given clock rate, these
Encode
specs define an acceptable
Harmonic Distortion
duty cycle.
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
worst harmonic component.
Integral Nonlinearity
The deviation of the transfer function from a reference line
measured in fractions of 1 LSB using a “best straight line” determined by a least square curve fit.
Minimum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal
frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the guaranteed
limit.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The encode rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Output Propagation Delay
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of ENCODE
command and the time when all output data bits are within
valid logic levels.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
The ratio of a change in input offset voltage to a change in
power supply voltage.
Signal-to-Noise-and-Distortion (SINAD)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, including harmonics but excluding dc.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (without Harmonics)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 1 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components, excluding the first five harmonics and dc.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude to the rms value of the
peak spurious spectral component. The peak spurious component may or may not be a harmonic. May be reported in dBc
(i.e., degrades as signal levels is lowered) or in dBFS (always
related back to converter full scale).
Two-Tone Intermodulation Distortion Rejection
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the worst third order intermodulation product; reported in
dBc.
Two-Tone SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component may or may not be an IMD product. May be reported
in dBc (i.e., degrades as signal levels is lowered) or in dBFS
(always related back to converter full scale).
–6–
REV. 0
 Loading...
Loading...