
FINAL
Publication# 18723 Rev: C Amendment/+1
Issue Date: May 1998
AmC0XXCFLKA
1, 2, 4, or 10 Megabyte 5.0 V-only Flash Memory PC Card
DISTINCTIVE CHARACTERISTICS
■ High performance
— 150 ns maximum access time
■ Single supply operation
— Write and erase voltage, 5.0 V ±5%
— Read voltage, 5.0 V ±5%
■ CMOS low power consumption
— 45 mA maximum active read current (x8 mode)
— 65 mA maximum active erase/write current
(x8 mode)
■ High write endurance
— Minimum 100,000 erase/write cycles
■ PCMCIA/JEIDA 68-pin standard
— Selectable byte- or word-wide configuration
■ Write protect switch
— Prevents accidental data loss
■ Zero data retention power
— Batteries not required for data storage
■ Separate attribute memory
— 512 byte EEPROM
■ Automated write and erase operations increase
system write performance
— 64K byte memory sectors for faster automated
erase speed
— Typically 1.5 seconds per single memory sector
erase
— Random address writes to previously erased
bytes (16 µs typical per byte)
■ Total system integration solution
— Support from independent software and
hardware vendors
■ Low insertion and removal force
— State-of-the-art connector allows for minimum
card insertion and removal effort
■ Sector erase suspend/resume
— Suspend the erase operation to allow a read
operation in another sector within the same
device
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AMD’s 5.0 V-only Flash Memory PC Card provides the
highest system level performance for data and file storage solutions to the portable PC market segment. Manufactured with AMD’s Negative Gate Erase, 5.0 V-only
technology, the AMD 5.0 V-only Flash Memory Car ds
are the most cost-effective and reliable approach to
single-supply Fla sh memory cards. Data files and application programs c an be stored on the “C ” series
cards. This allows OEM manufacturers of portable systems to eliminate the weight, high power consump tion
and reliability issue s as soci ated w ith el ect romec hani cal
disk-based systems. The “C” series cards also allow today’s bulky and heavy battery packs to be reduc ed in
weight and size. Typically only two “AA” alkaline batteries are required for total system operation. AMD’s
Flash Memory PC Cards provide the most effici ent
method to transfer useful work between different hardware platforms. The enabling technology of the “C” series cards enhances the productivity of mobile workers.
Widespread acceptanc e of the “C” ser ies cards is assured due to their compatibility with the 68-pin PCM-
CIA/JEIDA international standard. AMD’s Flash
Memory Cards can be read in either a byte-wide or
word-wide mode wh ich allows for flexible integration
into various system platforms. Compatibility is assured
at the hardware interface and software interchange
specification. The Card Information Str ucture (CIS) or
Metaformat, can be written by the OEM at the memory
card’s attribute memory address space begin ning at
address 00000H by using a for mat util ity. The CIS appears at the beginni ng of the Card’s attribute memor y
space and defines the low-level organization of data on
the PC Card. The “C” series cards contains a separate
512 byte EEPROM memory for the cards’ attribute
memory space. This allows all of the Flash memory to
be used for the common memory space.
Third party software solutions such as Microsoft’s
Flash File System (FFS), M-System’s True FFS, and
SCM’s SCM-FFS, enable AMD’s Flash Memory PC
Card to replicate the function of traditional disk-based
memory systems.
2 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
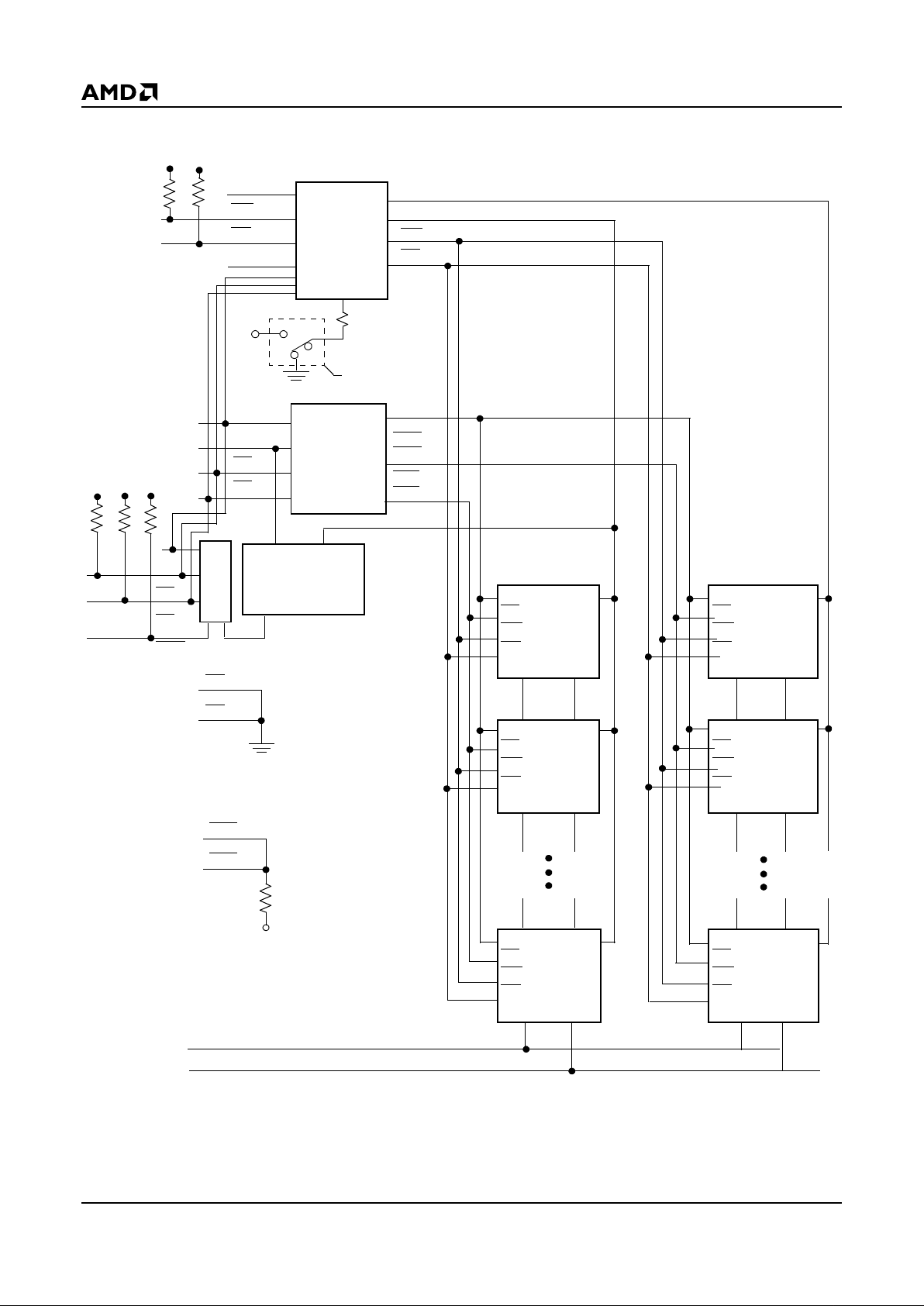
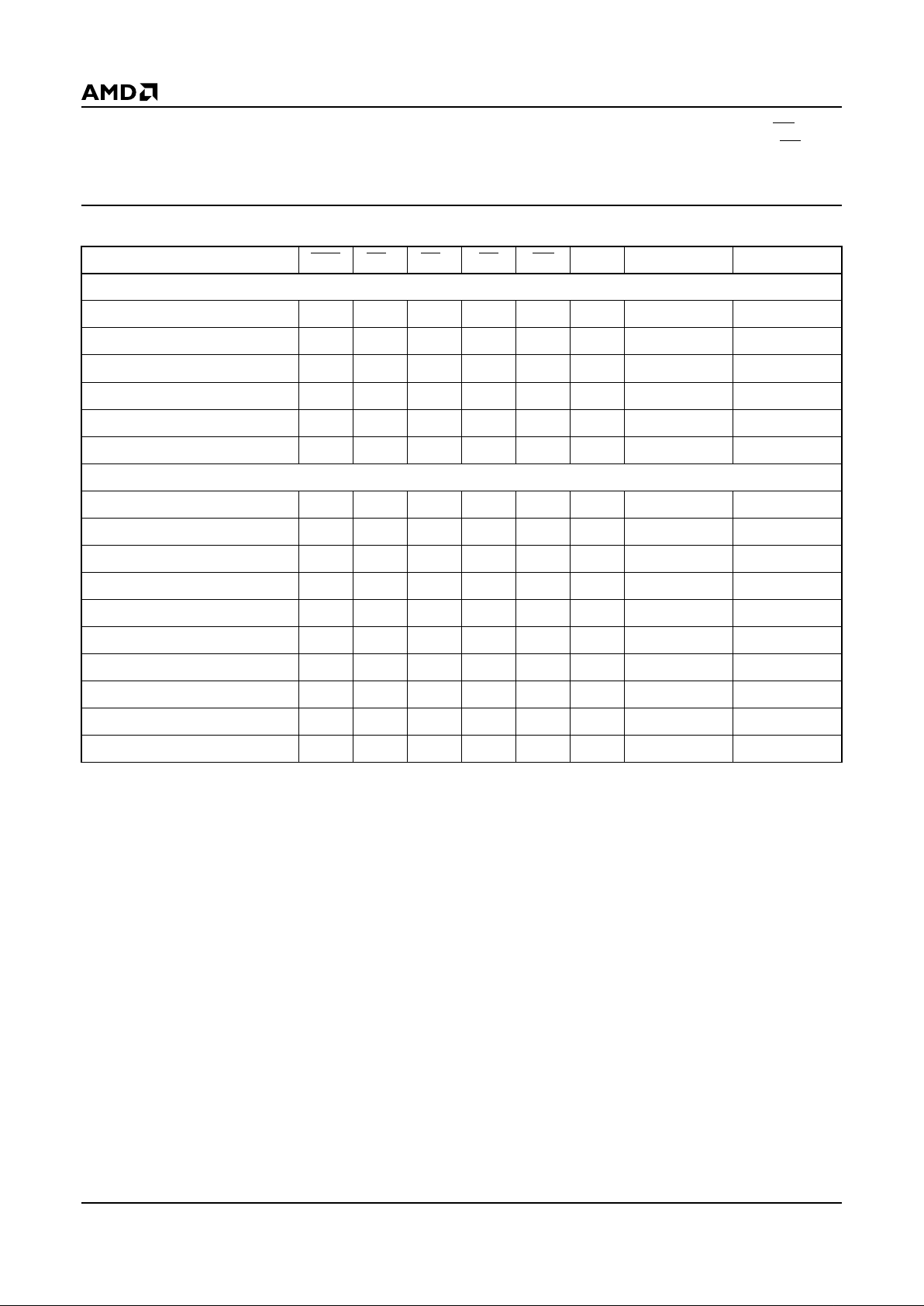
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Notes:
R = 20 K(min)/140 K
Ω
(max)
*1 Mbyte card = S0 + S1, *2 Mbyte card = S0…S3, *4 Mbyte card = S0…S7, *10 Mbyte card = S0…S19
Address
Buffers
and
Decoders
I/O
Transceivers
and
Buffers WP
(Note 1)
A0–A8 D0–D7
Attribute Memory
CE
Write Protect
Switch
V
CC
A0–A18
CEH
0–
CEH
9
CEL
0–
CEL
9
D0–D15
WE
OE
WP
D8–D15
D0–D7
WE
OE
A0
A1–A23*
CE
2
CE
1
A1–A9
A0
CE
2
CE1
REG
CD1
CD
2
Card Detect
BVD1
BVD
2
V
CC
Battery Voltage
Detect
GND
V
CC
10K
V
CC
RR
R
Decoder
V
CC
RR
Am29F040
A0–A18 D0–D7
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S0*
Am29F040
A0–A18 D8–D15
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S1*
A0–A18 D0–D7
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S2*
A0–A18 D8–D15
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S3*
A0–A18 D0–D7
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S18*
A0–A18 D8–D15
CE
WE
OE
VSS V
CC
S19*
18723C-1
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 3
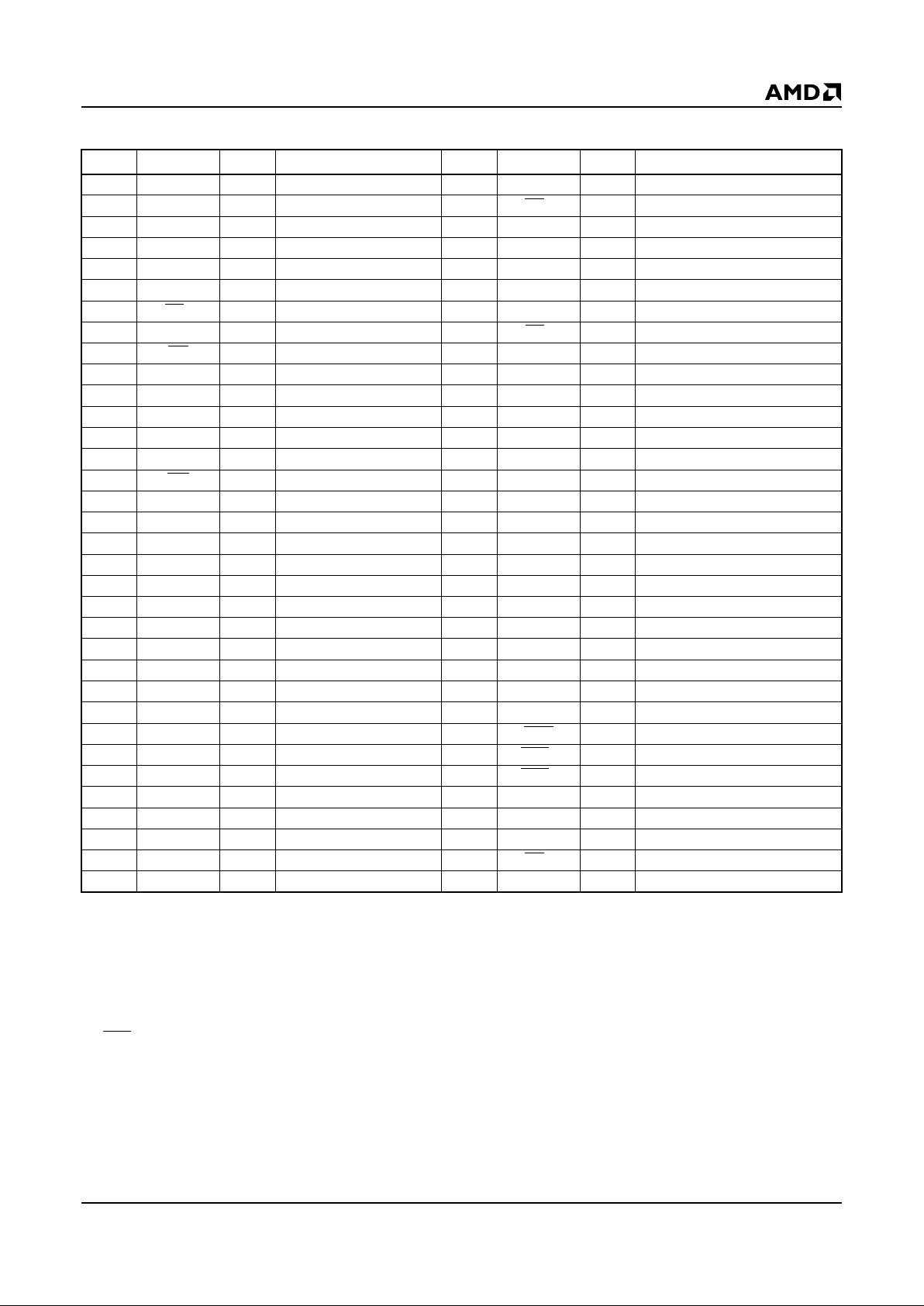
PC CARD PIN ASSIGNMENTS
Notes:
I = Input to card, O = Output from card
I/O = Bidirectional
NC = No connect
In systems which switch V
CC
individually to cards, no signal should be directly connected between cards other than ground.
1. V
PP
not required for Programming or R eading operations.
2. BVD
= Internally pulled-up.
3. Signal must not be connected between cards.
4. Highest address bit for 1 Mbyte card.
5. Highest address bit for 2 Mbyte card.
6. Highest address bit for 4 Mbyte card.
7. Highest address bit for 10 Mbyte card.
Pin# 3 3 Function Pin# Signal I/O Function
1 GND Ground 35 GND Ground
2 D3 I/O Data Bit 3 36 CD1 O Card Detect 1 (Note 3)
3 D4 I/O Data Bit 4 37 D11 I/O Data Bit 11
4 D5 I/O Data Bit 5 38 D12 I/O Data Bit 12
5 D6 I/O Data Bit 6 39 D13 I/O Data Bit 13
6 D7 I/O Data Bit 7 40 D14 I/O Data Bit 14
7CE
1 I Card Enable 1 (Note 3) 41 D15 I/O Data Bit 15
8 A10 I Address Bit 10 42 CE2 I Card Enable 2 (Note 3)
9OE
I Output Enable 43 NC No Connect
10 A11 I Address Bit 11 44 NC No Connect
11 A9 I Address Bit 9 45 NC No Connect
12 A8 I Address Bit 8 46 A17 I Address Bit 17
13 A13 I Address Bit 13 47 A18 I Address Bit 18
14 A14 I Address Bit 14 48 A19 I Address Bit 19 (Note 4)
15 WE
I Write Enable 49 A20 I Address Bit 20 (Note 5)
16 NC No Connect 50 A21 I Address Bit 21 (Note 6)
17 V
CC1
Pow er Supp ly 51 V
CC2
Power Supply
18 NC No Connect (Note 1) 52 NC No Connect (Note 1)
19 A16 I Address Bit 16 53 A22 I Address Bit 22
20 A15 I Address Bit 15 54 A23 I Address Bit 23 (Note 7)
21 A12 I Address Bit 12 55 NC No Connect
22 A7 I Address Bit 7 56 NC No Connect
23 A6 I Address Bit 6 57 NC No Connect
24 A5 I Address Bit 5 58 NC No Connect
25 A4 I Address Bit 4 59 NC No Connect
26 A3 I Address Bit 3 60 NC No Connect
27 A2 I Address Bit 2 61 REG
I Register Select
28 A1 I Address Bit 1 62 BVD2 O Battery V oltage Dete ct 2 (Note 2)
29 A0 I Address Bit 0 63 BVD1 O Battery V oltage Dete ct 1 (Note 2)
30 D0 I/O Data Bit 0 64 D8 I/O Data Bit 8
31 D1 I/O Data Bit 1 65 D9 I/O Data Bit 9
32 D2 I/O Data Bit 2 66 D10 I/O Data Bit 10
33 WP O Write Protect (Note 3) 67 CD
2 O Card Detect 2 (Note 3)
34 GND Ground 68 GND Ground
4 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
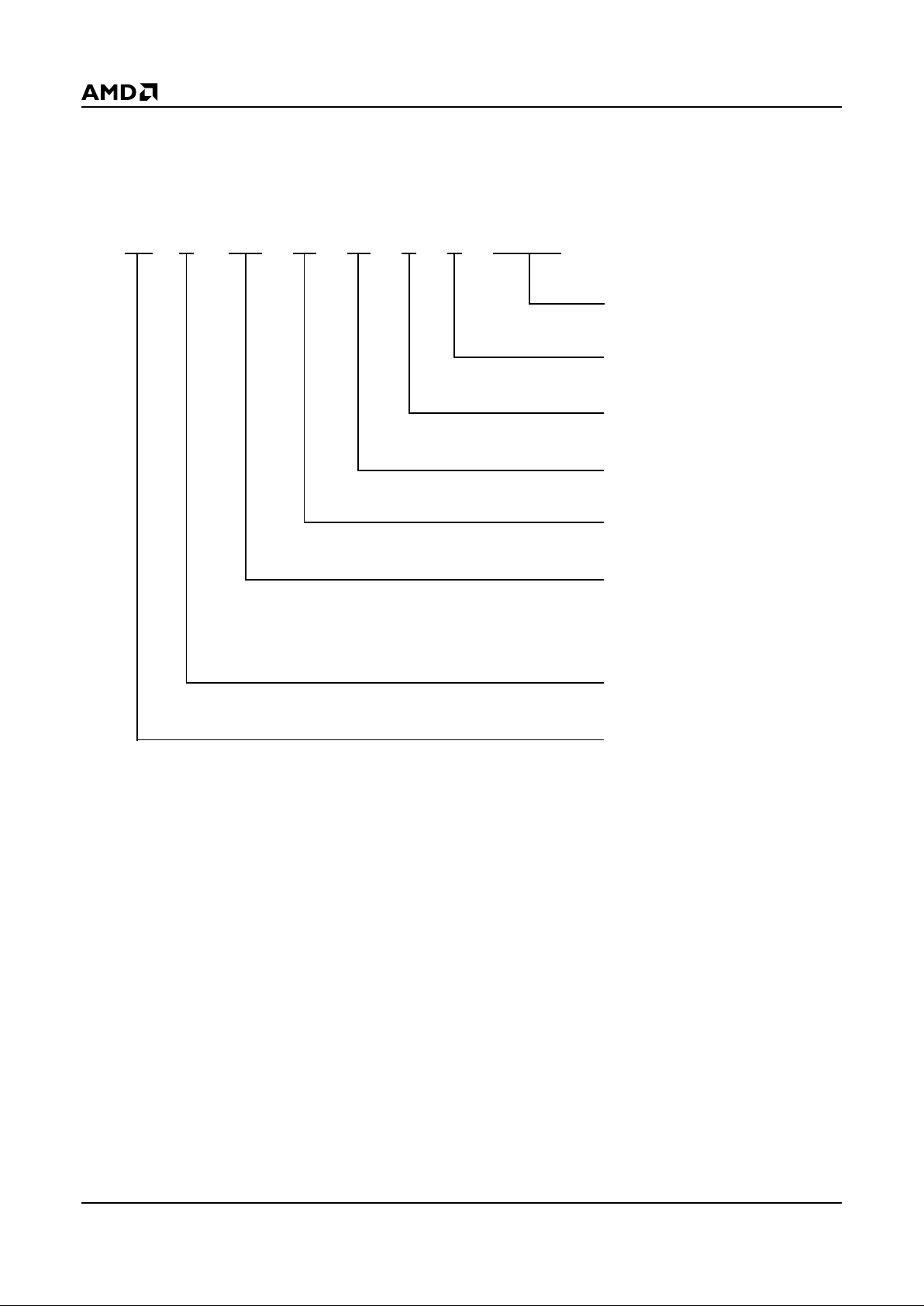
ORDERING INFORMATION
Standard Products
AMD standard produ cts are a vailab le in s ev eral pa ckages a nd operati ng ranges . The orde r number (Valid Combination) is f ormed
by a combination of:
SPEED OPTION
-150 ns
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION:
(x16/x8)
FLASH TECHNOLOGY
PC MEMORY CARD
MEMORY CARD DENSITY
001 = One Megabyte
002 = Two Megabyte
004 = Four Megabyte
010 = Ten Megabyte
AMD
REVISION LEVEL
SERIES
AM C 0XX C FL
K
Axxx
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 5
PIN DESCRIPTION
A0–A23
Address Inputs
These inputs are internally latched during write cycles.
BVD1, BVD2
Battery Voltage Detect
Internally pulled-up.
CD1, CD2
Card Detect
When card detect 1 and 2 = ground the system detects
the card.
CE1, CE2
Card Enable
This input is active low. The memory card is deselected
and power consumption is reduced to standby levels
when CE
is high. CE activates the internal memory
card circuitry that controls the high and low byte control
logic of the card, input buffers segment decoders, and
associated memory devices.
D0–D15
Data Input/Output
Data inputs are internally latched on write cycles. Data
outputs during re ad cycles. Data pins are active high.
When the memory ca rd is deselected or the outputs
are disabled the outputs float to tristate.
GND
Ground
NC
No Connect
Corresponding pin is not co nnec ted i nternally t o th e die .
OE
Output Enable
This input is active low and enables the data buffers
through the card outputs during read cycles.
REG
Attribute Memory Select
This input is active low and enables reading the CIS
from the EEPROM.
V
CC
PC Card Power Supply
For device operation (5.0 V ± 5%).
WE
Write Enable
This input is active low and controls the write function
of the comma nd register to the m emory array. The
target address is latched on the falling edge of the WE
pulse and the appropri ate data is latch ed on the r isin g
edge of the pulse.
WP
Write Protect
This output is active high and disables a ll card write
operations.
MEMORY CARD OPERATIONS
The “C” series Flash Me mor y Ca rd is org anized as an
array of individual devices. Each device is 512K bytes
in size with eight 64K byte sectors. Although the address space is continuous each physical device defines
a logical address segment size.
Byte-wide erase operations could be performed in
four ways:
■ In increments of the segment size
■ In increments of the sectors in individual segments
■ All eight sectors in parallel within individual
segments
■ Selected sectors of the eight sectors in parallel
within individual segments
Multiple segments may be erased concurrently when
additional I
CC
current is supplied to the device. Once a
memory se ctor or mem or y segm ent i s erased any address location may be programmed. Fla sh technology
allows any logical “1” data bit to be programmed to a
logical “0”. The on ly way to reset bits to a l ogica l “1” is
to erase the entire memory sector of 64K bytes or
memory segment of 512K bytes.
Erase operations are the on ly operations tha t work o n
entire memor y se ctors or memo r y seg men ts. All other
operations such as word-wide programming are not affected by the physical memory segments.
The common memory space data contents are altered
in a similar manner as writing to individual Flash memory devices. On-card address and data buffers activate
the appropriate Flash device in the memory array. Each
device internally latches address and data during write
cycles. Refer to Table 1.
Attribute memor y i s a se parat ely ac c esse d c ar d m emory space. The regis ter memor y space is ac tive when
the REG
pin is driven low. The Card Information Structure (CIS) desc ribes the capa bilities and sp ecification
of a card. The CIS is stored in the attribute memory
space beginning at ad dress 00000H. The “C” ser ies
cards contain a separate 512 byte EEPROM memor y
for the Card Information Structure. D0–D7 are active
during attribute memory accesses. D8–D15 s hould b e
ignored. Odd order bytes present invalid data. Refer to
Table 2.
6 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
Word-Wide Operations
The “C” series cards provide the flexibility to operate on
data in a byte-wide or word-wide format. In word-wide
operations the Low-bytes are controlled with CE
1 when
A0 = 0. The High-bytes are controlled with CE
2 with
A0 = don’t care.
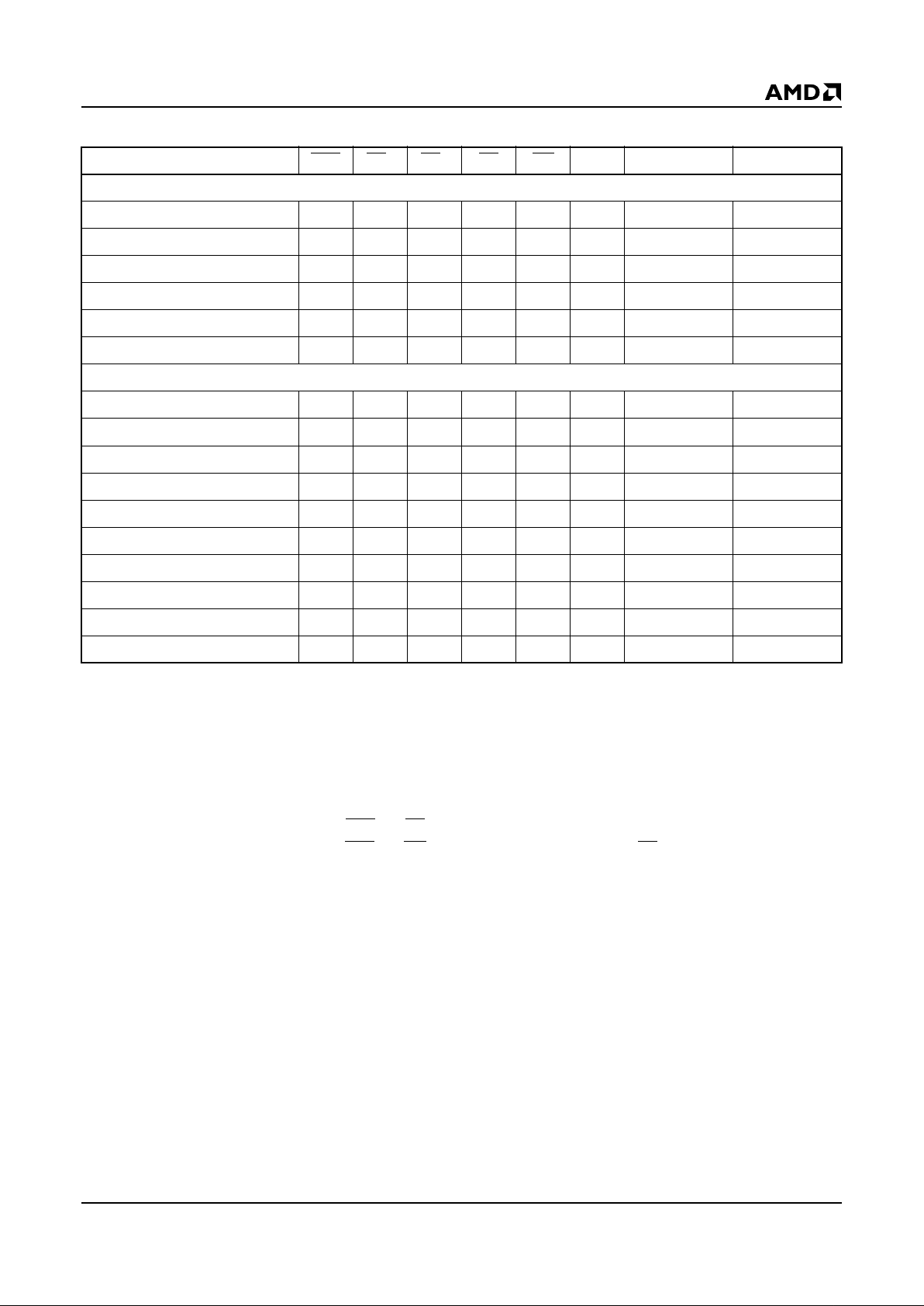
Table 1. Common Memory Bus Operations
Legend:
X = Don’t Care, whe re Don’t Care is either at V
IL
or VIH level. See DC Characteristics for voltage levels of normal TTL or CMOS
input levels.
Notes:
1. V
PP
pins are not connected in th e 5.0 V-Only Flash Memory Card.
2. Manufacturer an d de vice codes ma y be accessed via a com mand registe r write seq uence . (Ref er to A utosel ect Comma nd in
Tables 3 and 4.)
3. Standby current is I
CCS
.
4. Refer to Tables 3 and 4 for valid D
IN
during a byte write operation.
5. Refer to Table 5 for valid D
IN
during a word write operation.
6. Byte access—Even. In this x8 mode, A0 = V
IL
outputs or inputs the “even” byte (low byte) of the x16 word on D0–D7.
7. Byte access—Odd. In this x8 mode, A0 = V
IH
outputs or inputs the “odd” byte (high byte) of the x16 word on D0–D7. This is
accomplished internal to the card by transposing D8–D15 to D0–D7.
8. Odd byte only access. In this x8 mode, A0 = X outputs or inputs the “odd” byte (high byte) of the x16 word on D8–D15.
9. x16 word accesses present both “even” (low) and “odd” (high) bytes. A0 = X.
Pins/Operation REG CE2CE1OEWE A0 D8–D15 D0–D7
READ-ONLY
Read (x8) (Note 6) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
High-Z Data Out-Even
Read (x8) (Note 7) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
High-Z Data Out-Odd
Read (x8) (Note 8) V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
X Data Out-Odd High-Z
Read (x16) (Note 9) V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
X Data Out-Odd Data Out-Even
Output Disable V
IH
XXVIHV
IH
X High-Z High-Z
Standby (Note 3) X V
IH
V
IH
X X X High-Z High-Z
READ/WRITE
Read (x8) (Notes 2, 6) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
High-Z Data Out-Even
Read (x8) (Notes 2, 7) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
High-Z Data Out-Odd
Read (x8) (Notes 2, 8) V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
X Data Out-Odd High-Z
Read (x16) (Notes 2, 9) V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
X Data Out-Odd Data Out-Even
Write (x8) (Notes 4, 6) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
High-Z Data In-Even
Write (x8) (Notes 4, 7) V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
High-Z Data In-Odd
Write (x8) (Notes 4, 8) V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
X Data In-Odd High-Z
Write (x16) (Notes 5, 9) V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
X Data In-Odd Data In-Even
Output Disable V
IH
XXVIHV
IL
X High-Z High-Z
Standby (Note 3) X V
IH
V
IH
X X X High-Z High-Z
Volt-only?
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 7
Table 2. Attribute Memory Bus Operations
Legend:
X = Don’t Care, where Don’t Care is either V
IL
or VIH levels. See DC Characteristics for voltage levels of normal TTL or CMOS
input levels.
Notes:
1. V
PP
pins are not connected in th e 5.0 V-Only Flash Memory Card.
2. In this x8 mode, A0 = V
IL
outputs or inputs the “even” byte (low byte) of the x16 word on D0–D7.
3. Only even-byte dat a is valid during Attribute Memory Read function.
4. During Attribute Memory Read function, REG
and OE must be active for the entire cycle.
5. During Attr ibute Memory Write function, REG
and WE must be activ e for the entire cycle, OE must be inactive for the entire
cycle.
6. Standby current is I
CCS
.
Pins/Operation REG CE2CE1OEWE A0 D8–D15 D0–D7
READ-ONLY
Read (x8) (Notes 2, 4) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
High-Z Data Out-Even
Read (x8) (Notes 3, 4) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
High-Z Not Valid
Read (x8) (Note 3) V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
X Not Valid High-Z
Read (x16) (Notes 3, 4, 5) V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
X Not Valid Data Out-Even
Output Disable V
IL
XXVIHV
IH
X High-Z High-Z
Standby (Note 6) X V
IH
V
IH
X X X High-Z High-Z
READ/WRITE
Read (x8) (Notes 2, 4) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
High-Z Data Out-Even
Read (x8) (Notes 3, 4) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
High-Z Not Valid
Read (x8) (Note 4) V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
X Not Valid High-Z
Read (x16) (Note 4) V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
X Not Valid Data Out-Even
Write (x8) (Notes 2, 5) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
High-Z Data In-Even
Write (x8) (Note 5) V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
High-Z High-Z
Write (x8) (Notes 4, 5) V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
X High-Z High-Z
Write (x16) (Note 5) V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
X High-Z Data In-Even
Output Disable V
IL
XXVIHV
IL
X High-Z High-Z
Standby (Note 6) X V
IH
V
IH
X X X High-Z High-Z
Volt-only?
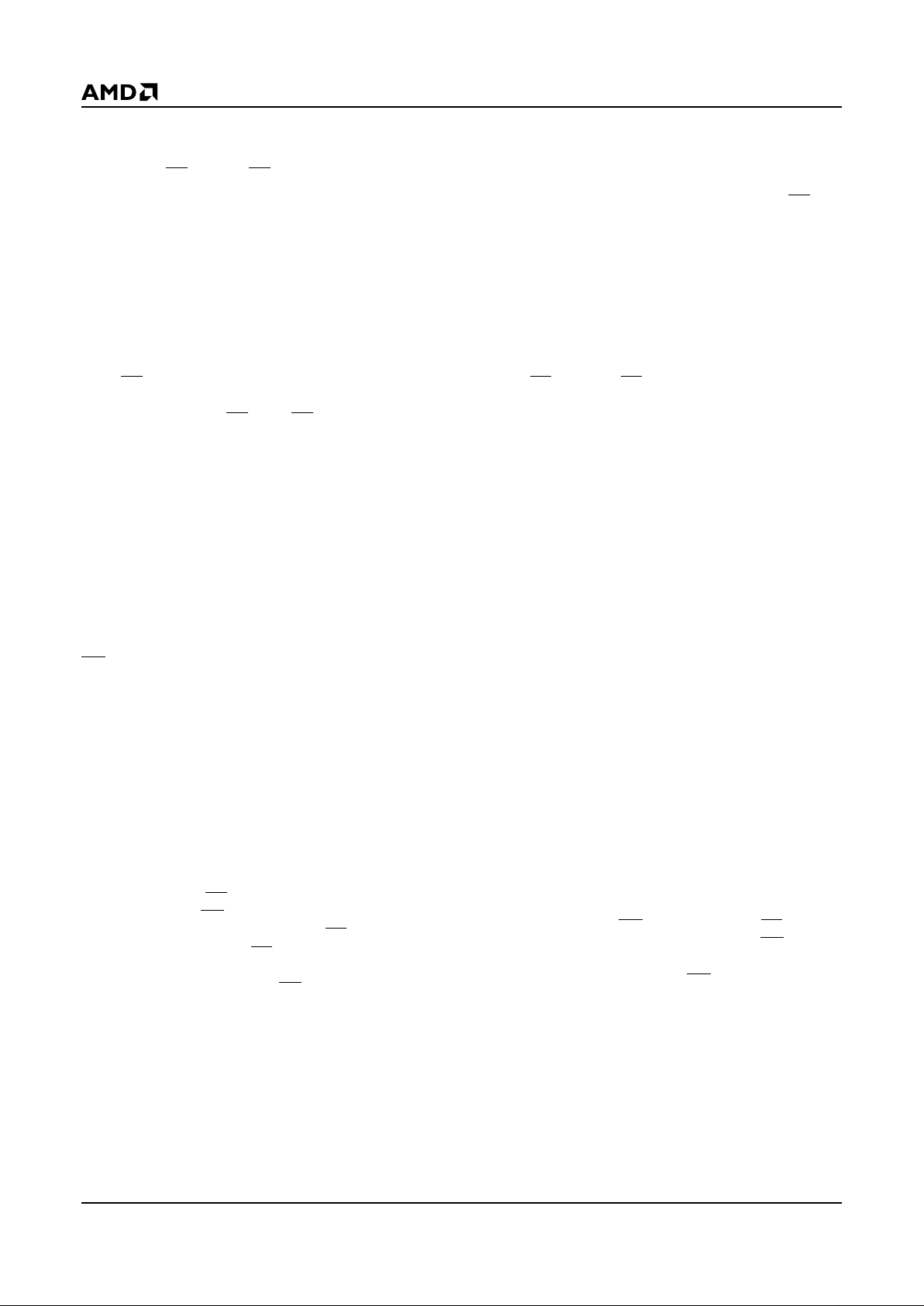
8 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
Byte-Wide Operations
Byte-wide data is available on D0–D7 for read and write
operations (CE
1 = low, CE2 = high). Even and odd
bytes are stored in separate memory segments (i.e.,
S0 and S1) and are accessed when A0 is low and high
respectively. The even byte is the low order byte and
the odd byte is the high order byte of a 16-bit word.
Erase operations in the byte-wide mode must ac count
for da ta multip lexin g on D0–D7 by chan ging the s tate of
A0. Each memory sector or memory segment pair
must be addressed separately for erase operations.
Card Detection
Each CD (output) pin s hould be r ead by the host system to determine i f the memory card is adeq uately
seated in the socket. CD
1 and CD2 are internally tied
to ground. If both bits are not detected, the system
should indicate that the card must be reinserted.
Write Protection
The AMD Flash memor y card has thr ee types of writ e
protection. The PCMCIA /JEIDA socket itself provides
the first type of write protection. Power supply and control pins have specific pin lengths in order to protect the
card with proper power supp ly se quenci ng in th e case
of hot insertion and removal.
A mechanical write protect switch provides a second
type of write protectio n. When this switch is act ivated,
WE
is internall y forced high. The Flash mem ory command register is disabled from acce pting any write
commands.
The third type of write protection is achieved with V
CC1
and V
CC2
below V
LKO
. Each Flash memory device that
comprises a Flash memory segment will reset the command register to the read-only mode when V
CC
is
below V
LKO
. V
LKO
is the voltage below which writ e op-
erations to individual command registers are disabled.
MEMORY CARD BUS OPERATIONS
Read Enable
Two Card En able (CE) pin s are available on the memory card. Both CE
pins must be active low for
word-wide read acces ses. O nly on e CE
is required for
byte-wide accesses. The CE
pins control the sel ectio n
and gates power to t he high and low memo ry segments. The Output Enable (OE
) controls gating ac-
cessed data from the memory segment outputs.
The device will automatically power-up in the read/
reset state. In this case, a command s equence is not
required to read data. Standard microprocessor read
cycles will retrieve array data. This default value ensures that no spurious alteration of the memory content
occurs during the power transition. Refer to the AC
Read Characteristics and Waveforms for the specific
timing parameters.
Output Disable
Data outputs from the card are disabled when OE is at
a logic-high level. Under this condit ion, outputs are i n
the high-impedance state.
Standby Operations
Byte-wide read accesse s only r equir e half of the read /
write output buffer (x16) to be active. In addition, only
one memory segment is active within either the high
order or low orde r bank. Activation o f the appropr iate
half of the output buffer is controlled by the combination
of both CE
pins. The CE pins also control power to the
high and low-order banks of memor y. Outputs of the
memory b ank not select ed are placed i n the high impedance state. The individual memory segment is activated by the address decoders. The othe r memory
segments operate in standby. An active memory segment continues to draw power until completion of a
write or erase operation if the card is deselected in the
process of one of these operations.
Auto Select Operation
A host system or external card reader/writer can determine the on-card manufacturer and device I.D. codes.
Codes are available after writing the 90H co mmand t o
the command register of a memory segment per
T ab les 3 and 4. Reading from address location 00000H
in any segment provides the manufacturer I.D. while
address location 00002H provides the device I.D.
To terminate the Auto Select o peratio n, i t is ne ces s ary
to write the Read/Reset command sequence into the
register.
Write Operations
Write and erase operations are valid on ly when V
CC1
and V
CC2
are above 4.75 V. This activates the state
machine of an addressed memory segment. The command register is a latch which saves address, commands, and data information used by the state
machine and memory array.
When Write Enable (WE
) and appropriate CE(s) are at
a logic-level low, and Output Enable (OE
) is at a
logic-high, the command register is enabled for write
operations. The falling edge of WE
latches address information and the rising edge latches data/command
information.
Write or erase operations are performed by writing appropriate data patterns to the command register of accessed Flash memory sectors or memory segments.
The byte-wide and word-wide commands are defined
in Tables 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 9
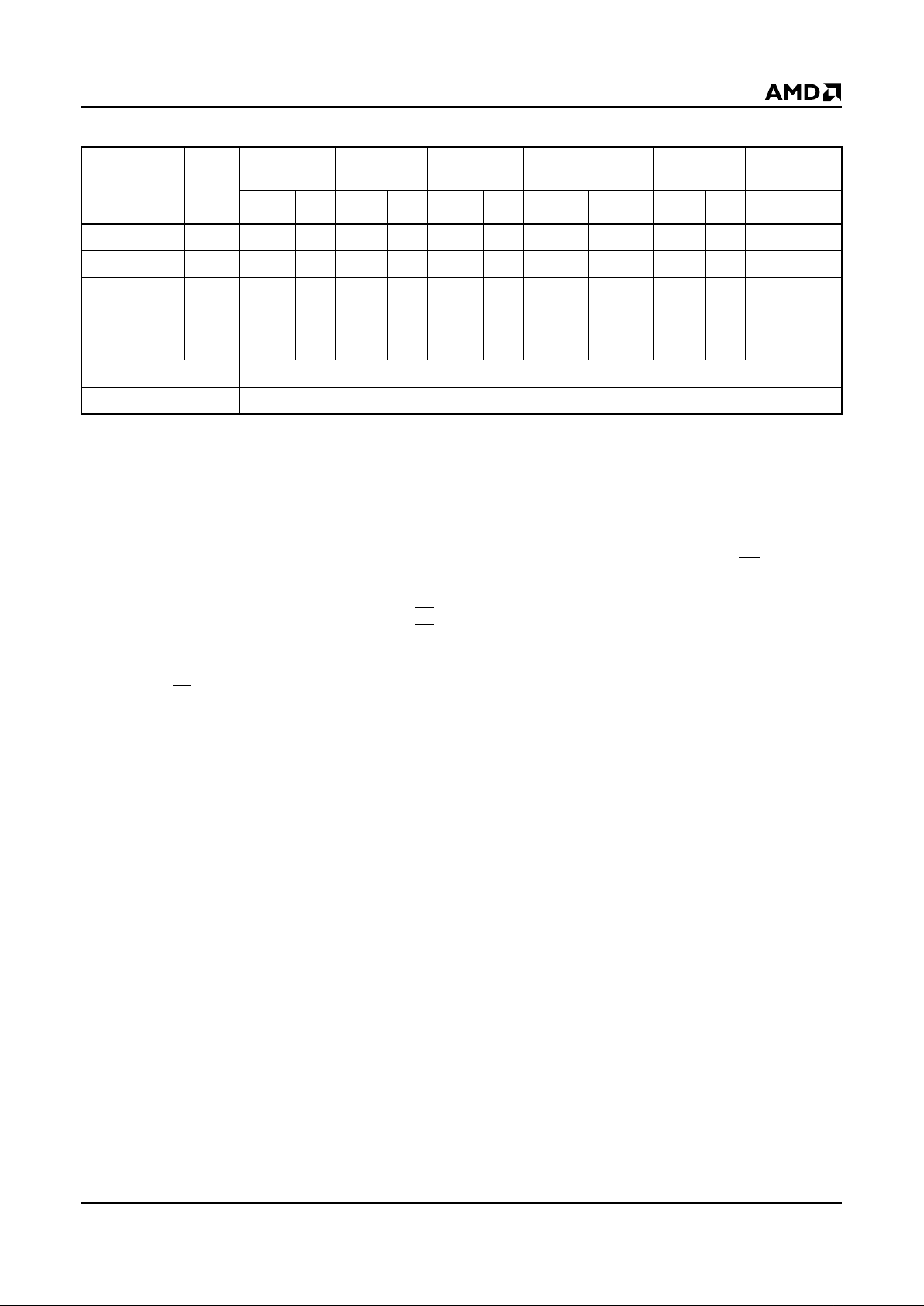
Table 3. Even Byte Command Definitions (Note 5)
* Address fo r Memory Segment 0 (S0) o nly. Address for the higher ev en memo ry segments (S2–S18) = (Addr) + (N/2)* 100 000H
where N = Memory Segment number (0) for 1 Mb yte, N = (0, 2) fo r 2 Mbyte, N = (0, 2, 4, 6) f or 4 Mbyte, N = (0…18) f or 10 Mb yte.
Notes:
1. Address bit A16 = X = Don’t Car e for all ad dress commands e xcept f or Progra m Address (PA), Read Address (RA) and Sector
Address (SA).
2. Bus operations are defined in Table 1.
3. RA = Address of the memory location to be read.
PA = Address of the memory location to be programmed. Addresses are latched on the falling edge of the WE
pulse.
SA = Address of the sector to be erased. The combination of A17, A18, A19 will uniquely select any sector of a segment.
To select the memory segment:1 and 2 Mbyte: Use CE1 and A20
4 Mbyte: Use CE
1 and A20, A21
10 Mbyte: Use CE
1 and A20–A23.
4. RD = Data read from location RA during read operation.
PD = Data to be programmed at location PA. Data is latched on the rising edge of WE pulse .
5. A0 = 0 a nd CE
1 = 0
Embedded
Command
Sequence
Bus
Write
Cycles
Req’ d
First Bus
Write Cycle
Second Bus
Write Cycle
Third Bus
Write Cycle
Fourth Bus
Read/Write Cycle
Fifth Bus
Write Cycle
Sixth Bus
Write Cycle
Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data
Reset/Read 4 AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH F0H RA RD
Autoselect 4 AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH 90H 00H/02H 01H/A4H
Byte Write 4 AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH A0H PA PD
Segment Erase 6 AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH 80H AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH 10H
Sector Erase 6 AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H AAAAH 80H AAAAH AAH 5554H 55H SA 30H
Sector Erase Suspend Erase can be suspended during sector erase with Addr (don’t care), Data (B0H)
Sector Erase Resume Erase can be resumed after suspend with Addr (don’t care), Data (30H)
10 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
Table 4. Odd Byte Command Definitions (Note 5)
*Address for Memory Segment 1 (S1) only. Address for the higher odd memory segments (S3–S19) = (Addr) + ((N–1)/2)*
100000H + 80000H where N = Memory Segment number (1) for 1 Mbyte, N = (1, 3) for 2 Mbyte, N = (1, 3, 5, 7) for 4 Mbyte,
N = (1…19) for 10 Mbyte.
Notes:
1. Address bit A16 = X = Don’t Car e for all ad dress commands e xcept f or Progra m Address (PA), Read Address (RA) and Sector
Address (SA).
2. Bus operations are defined in Table 1.
3. RA = Address of the memory location to be read.
PA = Address of the memory location to be programmed. Addresses are latched on the falling edge of the WE
pulse.
SA = Address of the sector to be erased. The combination of A17, A18, A19 will uniquely select any sector of a segment.
To select the memory segment:1 and 2 Mbyte: Use CE2 and A20
4 Mbyte: Use CE
2 and A20, A21
10 Mbyte: Use CE
2 and A20–A23.
4. RD = Data read from location RA during read operation.
PD = Data to be programmed at location PA. Data is latched on the rising edge of WE
pulse.
5. A0 = 1 a nd CE
1 = 0 or A0 = X and CE2 = 0.
Embedded
Command
Sequence
Bus
Write
Cycles
Req’d
First Bus
Write Cycle
Second Bus
Write Cycle
Third Bus
Write Cycle
Fourth Bus
Read/Write Cycle
Fifth Bus
Write Cycle
Sixth Bus
Write Cycle
Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data
Reset/Read 4 AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH F0H RA RD
Autoselect 4 AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH 90H 00H/02H 01H/A4H
Byte Write 4 AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH A0H PA PD
Segment Erase 6 AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH 80H AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH 10H
Sector Erase 6 AAABH AAH 5555H 55H AAABH 80H AAABH AAH 5555H 55H SA 30H
Sector Erase Suspend Erase can be suspended during sector erase with Addr (don’t care), Data (B0H)
Sector Erase Resume Erase can be resumed after suspend with Addr (don’t care), Data (30H)
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 11
Table 5. Word Command Definitions (Note 7)
Notes:
1. Address bit A16 = X = Don’t Care for all address commands except for Program Address (PA) and Sector Address (SA).
2. Bus operations are defined in Table 1.
3. RA = Address of the memory location to be read.
PA = Address of the memory location to be programmed. Addresses are latched on the falling edge of the WE
pulse.
SA = Address of the sector to be erased. The combination of A17, A18, A19 will uniquely select any sector of a segment.
To select the memory segment:1 and 2 Mbyte: Use CE
1, CE2, A20
4 Mbyte: Use CE
1, CE2, A20, A21
0 Mbyte: Use CE
1, CE2, A20–A23.
4. RW = Data read from locat ion RA during read operation. (Word Mode).
PW = Data to be programmed at location PA. Data is latched on the rising edge of WE
. (Word Mode).
5. Address for Memory Segment Pair 0 (S0 and S1) only. Address for the higher Memory Segment Pairs (S2, S3 = Pair 1, S4,
S5 = Pair 2, S6, S7 = Pair 3…) is equal to (Addr) + M* (80000H) where M = Memory Segment Pair number.
6. Word = 2 bytes = odd byte and even byte.
7. CE1 = 0 and CE2 = 0.
Table 6. Memory Sector Address Table
for Memory Segment S0
FLASH MEMORY WRITE/ERASE
OPERATIONS
Details of AMD’s Embedded Write and
Erase Operations
Embedded Erase™ Algorithm
The automatic me mory sector or memory segmen t
erase does not require the device to be entirely preprogramming prior to executing the Embedded Erase
command. Upon executing the Embedded Erase command sequence, the addressed memory sector or
memory segment will automatically write and verify the
entire memory segment or memory sector for an all
“zero” data pattern. The system is not requ ired to provide any controls or timing during these operations.
When the memory sector or memory segment is automatically verified to contain an all “zero” pattern, a
self-timed chip erase-and-verify begins. The erase and
verify operations are complete when the data on D7 of
the memory sector or memory segment is “1” (see
“Write Operation Sta tus” section) at which time the
Embedded
Command
Sequence
Bus
Write
Cycles
Req’d
First Bus
Write Cycle
Second Bus
Write Cycle
Third Bus
Write Cycle
Fourth Bus
Read/Write Cycle
Fifth Bus
Write Cycle
Sixth Bus
Write Cycle
Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data Addr* Data
Reset/Read 4 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH F0F0 RA RW
Autoselect 4 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH 9090 00H/02H
0101/
A4A4
Byte Write 4 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH A0A0 PA PW
Segment Erase 6 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH 8080 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH 1010
Sector Erase 6 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 AAAAH 8080 AAAAH AAAA 5554H 5555 SA 3030
Sector Erase Suspend Erase can be suspended during sector erase with Addr (don’t care), Data (B0H)
Sector Erase Resume Erase can be resumed after suspend with Addr (don’t care), Data (30H)
Sector A19 A18 A17 Address Range
0 0 0 0 00000h-0FFFFh
1 0 0 1 10000h-1FFFFh
2 0 1 0 20000h-2FFFFh
3 0 1 1 30000h-3FFFFh
4 1 0 0 40000h-4FFFFh
5 1 0 1 50000h-5FFFFh
6 1 1 0 60000h-6FFFFh
7 1 1 1 70000h-7FFFFh
Note: A0 is not mapped internally.
12 AmC0XXCFLKA 5/4/98
device returns to the Read mode (D15 on the odd
byte). The system is not required to provide any control
or timing during these operations. A Reset command
after the device has begun execution will stop the device but the data in the operated segment will be undefined. In that case, restart the erase on that sector and
allow it to complete.
When using the Embedded Erase algorithm, the erase
automatically terminates when adequ ate erase margin
has been achieved for the memory array (no erase verify command i s requir ed). The m argin voltag es are internally ge nerated in the same man ner as when the
standard erase verify command is used.
The Embedded Erase command sequence is a command only operation that stages the memory sector or
memory segment for automatic electrical erasure of all
bytes in the array. Th e automatic erase beg ins on the
rising edge of the WE
and terminates when the data on
D7 of the memory sector or memory segment is “1”
(see “Write Operation Stat us” section) at which time
the device returns to the Read mode. Plea se note tha t
for the memory segment or memory sector erase operation, Data
Polling may be performed at any address in
that segment or sector.
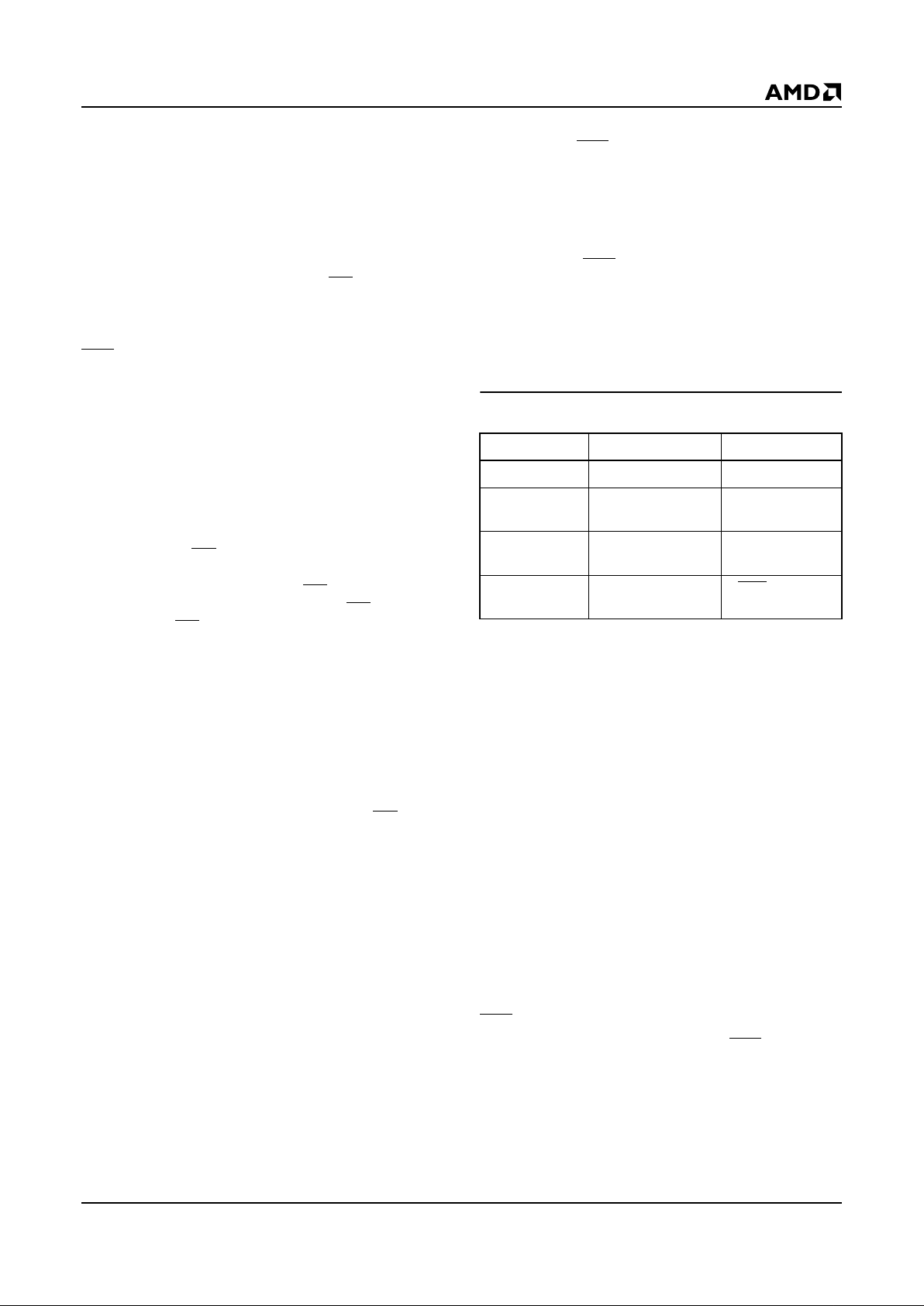
Figure 1 and Table 7 illustrate the Embedded Erase Al-
gorithm, a typical co mm an d strin g an d b u s op er a ti on s .
As described ear lier, once the memor y sector in a device or memory se gment completes the Embedded
Erase operation it returns to the Read mode and addresses are no longer latched. Therefore, the device
requires that a valid address input to the device is supplied by the system at this particular instant of time.
Otherwise, the system will never read a “1” on D7. A
system designer has two choices to implement the Embedded Erase algorithm:
1. The system (CPU) keeps the sector address (within
any of the sectors being erased) valid during the entire Embedded Erase operation, or
2. Once the system executes the Embedded Erase
command sequence, the CPU takes away the address from the device and becomes free to do other
tasks. In this case, the CPU is required to keep track
of the valid sector address by loading it into a temporary register. When the CPU comes back for performing Data
Polling, it should reassert the sam e
address.
Since the Embedded Erase operation takes a significant amount of time (1.5–30 s), option 2 makes more
sense. However, the choice of these two options has
been left to the system designer.
Sector Erase
Sector erase is a six bus cycle operation. There are two
“unlock” write cycles. These are followed by writing the
“set-up” command. Two more “unlock” write cycles are
then followed by the sector erase command. The sector
address (any address locati on within the desired sector) is latched on the falling edge of WE
, while the com-
mand (data) is latched on the rising edge of WE
. A
time-out of 100 µs from the rising edge of the last sector erase command will initiate the sector erase
command(s).
Multiple sectors may be erased concurrently by writing
the six bus cycle operat ions as descr ibed ab ove. This
sequence is followed with wr ites of the sect or erase
command 30H to addresses in other sectors desired to
be concurrently erased. A time-out of 100 µs from the
rising edge of the WE
pulse for the last sector erase
command will initiate the sector erase. If another sector
erase command is written within the 100 µs time-out
window the timer is reset. Any command other than
sector erase within the time-out window will reset the
device to the read mode, ignoring the previous command string (refer to “Wri te Operation Status” sectio n
for Sector Erase Timer operation). Loa ding the sector
erase buffer may be done in any sequence and with
anysector number.
Sector erase does not requi re the user to program the
device prior to erase. The device automatically programs all memory locations in the sector(s) to be
erased prior to electrical erase. When erasing a sector
Table 7. Embedded Erase Algorithm
Bus Operation Command Comments
Standby Wait for VCC ramp
Write
Embedded Erase
command sequence
6 bus cycle
operation
Read
Data
Polling to
verify erasure
18723C-2
Figure 1. Embedded Erase Algorithm
Write Embedded Erase
Command Sequence
(Table 3 and 4)
Data Poll from Device
(Figure 3)
Start
Erasure Complete
5/4/98 AmC0XXCFLKA 13
or sectors the remaining unselected sectors are not affected. The system is not required to provide any controls or timings during these operations. A Reset
command after the device has begun execution will
stop the device but the data i n the operated segm ent
will be undefined. In that case, restart the erase on that
sector and allow it to complete.
The automatic sector erase begins after the 100 µs
time out from th e rising ed ge of the WE
pulse for the
last sector erase command pulse and terminates when
the data on D7 is “1” (see “Write Operation Status” section) at which time the d evice returns to read m ode.
Data
Polling must be performed at an address within
any of the sectors being erased.
Figure 1 illustrates th e Embedded Erase Algori thm
using typical command strings and bus operations.
Embedded Program™ Algorithm
The Embedded Program Setup is a four bus cycle o peration that stages the addres sed memory sec tor or
memory segment for automatic programming.
Once the Embedded P rogram Setup operation i s performed, the next WE
pulse causes a transition to an active programming operation. Addresses are internally
latched on the falling edge of the WE
pulse. Data is in-
ternally latched on the rising edge of the WE
pulse. T he
rising edge of WE
also begins the programming operation. The system is not required to provide further control or timing. The device will automati cally provide an
adequate inter nally generated wr ite pulse and verify
margin. The automatic programming operation is completed when the data o n D7 of the a ddres s ed mem ory
sector or memory segment is equivalent to data written
to this bit (see Write Operation Status section) at which
time the device returns to the Read mode (no write verify command is required).
Addresses are latched on the falling edge of WE
during
the Embedded Program command execution and
hence the system is not required to keep the addresses
stable during the entire Programm ing operation. However, once the device completes the Embedded Program operation, it returns to the Read mode and
addresses are no longer latched. Therefore, the device
requires that a valid address input to the device is supplied by the system at this particular i nstant of time.
Otherwise, the system will never read a valid data on
D7. A system designer has two choices to imple ment
the Embedded Programming algorithm:
1. The system (CPU) keeps the address valid dur ing
the entire Embedded Programming operation, or
2. Once the system executes the Embedded Program-
ming command sequence, the CPU takes away the
address from the device and becomes free to do
other tasks. In this case, the CPU is required to
keep track of the valid address by loading i t into a
temporary regis ter. When the CPU comes back for
performing Data
Polling, it should reassert the same
address.
However , since the Embedded Programming operation
takes only 16 µs typically, it may be easier for the CPU
to keep the address stable during the entire Embedded
Programming operation instead of reasserting the valid
address during Data
Poll ing. An yw a y, this has been left
to the system desi gner’s choice to go for eith er operation. Any commands written to the segment during this
period will be ignored.
Figure 2 and Table 8 illustrate the Embedded Program
Algorithm, a typical comm and string, an d bus o perat ion.
Reset Command
The Reset command initiali zes the sector or segment
to the read mode. Please refer to Tables 3 and 4, “Byte
Command Definitions,” and Table 5, “Word Command
Definitions” for the Reset com mand operation. The
sector or segment r emains enabled for reads unti l the
command register contents are altered. There is a 6 µs
Write Recovery Time before Read for the first read
after a write.
The Reset command will safely reset the segment
memory to th e Read mode. Memor y content s are not
altered. Following any other command, write the Reset
command once to the segment. This will safely abor t
any operation and reset the device to the Read mode.
The Reset is needed to terminate the auto select operation. It can b e used to ter minate an E rase or Sect or
Erase operation, but the data in the s ec tor or seg men t
being erased would then be undefined.
Write Operation Status
Data Polling—D7 (D15 on Odd Byte)
The Flash Memory PC Card features Data
Polling as a
method to indicate to the host system that the Embedded algorithms are either in progress or completed.
While the Embedded Programming algori thm is in operation, an attempt to read th e device will prod uce th e
complement of expected valid data on D7 of the addressed memory sector or memor y segment. Upon
Table 8. Embedded Program Algorithm
Bus Operation Command Comments
Standby Wait for VCC ramp
Write
Embedded Progr am
command sequence
3 bus cycle
operation
Write
Program
Address/Data
1 bus cycle
operation
Read
Data
Polling to
verify program
 Loading...
Loading...