Page 1

x310 Series
Fast Ethernet Switches
AT-x310-26FT
AT-x310-26FP
AT-x310-50FT
AT-x310-50FP
Installation Guide for VCStack
613-001964 Rev. A
™
Page 2

Copyright 2014 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis and the Allied Telesis logo are trademarks of Allied Telesis, Incorporated. All other product names, company names,
logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior
written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesis, Inc. be liable for
any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related
to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been advised of, known, or should have known, the
possibility of such damages.
Page 3
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards
Laser Safety EN60825
This product meets the following standards.
U.S. Federal Communications Commission
Radiated Energy
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device pursuant to Part 15
of FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses , and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with this instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Note: Modifications or changes not expressly approved of by the manufacturer or the FCC, can void your right to operate
this equipment.
Industry Canada
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
RFI Emissions: FCC Class A, EN55022 Class A, EN61000-3-2, EN61000-3-3, VCCI Class A,
C-TICK, CE
Warning: In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
EMC (Immunity): EN55024
Electrical Safety: EN60950-1 (TUV), UL 60950-1 (
CULUS
)
3
Page 4
Translated Safety Statements
Important: Safety statements that have the symbol are translated into multiple languages in the
Translated Safety Statements document at www.alliedtelesis.com/support.
4
Page 5

Contents
Preface ..............................................................................................................................................................................11
Document Conventions .......................................................................................................................................................12
Contacting Allied Telesis .....................................................................................................................................................13
Chapter 1: Overview ........................................................................................................................................................ 15
Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................16
x310 Models............................ .....................................................................................................................................16
10/100 Mbps Twisted Pair Ports ..................................................................................................................................16
10/100/1000 Mbps Twisted Pair Ports .........................................................................................................................16
Power Over Ethernet....................................................................................................................................................17
SFP Slots .....................................................................................................................................................................17
S1 and S2 Stacking Slots.............................................................................................................................................17
LEDs.............................................................................................................................................................................18
Installation Options.......................................................................................................................................................18
MAC Address Table ..................................................... .................................... ............................................................18
Management Software and Interfaces .........................................................................................................................18
Management Methods..................................................................................................................................................18
Front and Back Panels........................................................................................................................................................19
Management Panel .............................................................................................................................................................22
10/100Base-TX Twisted Pair Ports......................................................................................................................................23
Speed...........................................................................................................................................................................23
Duplex Mode................................................................................................................................................................23
Wiring Configuration.....................................................................................................................................................23
Maximum Distance.......................................................................................................................................................24
Power Over Ethernet....................................................................................................................................................24
Cable Requirements.....................................................................................................................................................24
10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports...............................................................................................................................25
Speed...........................................................................................................................................................................25
Duplex Mode................................................................................................................................................................25
Wiring Configuration.....................................................................................................................................................25
Maximum Distance...............................................................................................................
Power Over Ethernet....................................................................................................................................................25
Cable Requirements.....................................................................................................................................................25
Port Pinouts........................................... ..................................... ..................................................................................26
Power Over Ethernet...........................................................................................................................................................27
PoE Standards.............................................................................................................................................................27
Powered Device Classes .............................................................................................................................................28
Cable Requirements.....................................................................................................................................................28
Power Budget...............................................................................................................................................................28
Port Prioritization..........................................................................................................................................................29
Wiring Implementation..................................................................................................................................................30
SFP Slots.............................................................................................................................................................................31
Combo 10/100/1000Base-T Ports and SFP Slots ...............................................................................................................32
Stacking Slots......................................................................................................................................................................33
eco-friendly Button...............................................................................................................................................................34
LEDs....................................................................................................................................................................................35
LEDs for the 10/100Mbps Twisted Pair Ports...............................................................................................................35
LEDs for the PoE 10/100Mbps Twisted Pair Ports.......................................................................................................36
LEDs for the 10/100/1000Mbps Twisted Pair Ports......................................................................................................38
........................................25
5
Page 6

Contents
LEDs for the SFP Slots................................................................................................................................................ 40
LEDs for the Stacking Slots......................................................................................................................................... 40
Switch ID LED ............................................................................................................................................................. 41
USB Port........................................... ................................................................... ... ............................................................ 43
Console Port....................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Power Supply...................................................................................................................................................................... 45
Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking ..............................................................................................................................47
Overview............................................................................................................................................................................. 48
Stacking Slots and Transceiver .......................................................................................................................................... 49
Stacking Port Topologies.................................................................................................................................................... 50
Master and Member Switches............................................................................................................................................ 54
Selection of the Master Switch....................................................................................................................................54
ID Numbers ................................................................................................................................................................. 55
Specifying Ports in the Command Line Interface................................................................................................................ 56
Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation ............................................................................................................................57
Reviewing Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................58
Selecting a Site for the Stack.............................................................................................................................................. 62
Planning a Stack............................................. .................................... ................................................................................64
Unpacking the Switch ......................................................................................................................................................... 65
Chapter 4: Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack .......................................................................69
Installing the Switch on a Table .......................................................................................................................................... 70
Installing the Switch in an Equipment Rack........................................................................................................................ 71
Chapter 5: Verifying the Status of VCStack ..................................................................................................................77
Verifying the Status of VCStack..........................................................................................................................................78
Activating the VCStack Feature.......................................................................................................................................... 79
Starting a Local Management Session........................................................................................................................79
Activating VCStack......................................................................................................................................................80
Chapter 6: Cabling the Stacking Ports ..........................................................................................................................83
Cabling Switches with AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceivers......................................................................................................... 84
Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack .................................................................................................................................89
Installing the Power Cord Retaining Clip .......................................................................................
Powering On the Switches Individually...............................................................................................................................91
Powering On the Switches Simultaneously ........................................................................................................................ 94
Verifying the Stack.............................................................................................................................................................. 96
Setting the Priority Numbers........................................................................................................................................97
Monitoring the Initialization Processes................................................................................................................................99
Chapter 8: Cabling the Networking Ports ....................................................................................................................103
Cabling the Twisted Pair Ports.......................................................................................................................................... 104
Installing SFP Transceivers..............................................................................................................................................106
Chapter 9: Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................111
Appendix A: Technical Specifications .........................................................................................................................115
Physical Specifications ..................................................................................................................................................... 115
Environmental Specifications............................................................................................................................................ 116
Power Specifications......................................................................................................................................................... 116
Certifications..................................................................................................................................................................... 117
RJ-45 Twisted Pair Port Pinouts.......................................................................................................................................117
RJ-45 Style Serial Console Port Pinouts.......................................................................................................................... 119
..................................... 90
6
Page 7

Figures
Figure 1: Front Panels of the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-26FP Switches.........................................................................19
Figure 2: Front Panels of the AT-x310-50FT and AT-x310-50FP Switches.........................................................................20
Figure 3: Back Panel of the AT-x310-26FT Switches...........................................................................................................21
Figure 4: Back Panel of the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches...........................................................................21
Figure 5: Back Panel of the AT-x310-50FT Switch...............................................................................................................21
Figure 6: x310 Series Management Panel...........................................................................................................................22
Figure 7: AT-StackXS/1.0 Stacking Transceiver..................................................................................................................33
Figure 8: LEDs for the 10/100Mbps Ports on the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-50FT Switches...........................................35
Figure 9: LEDs for the PoE 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches.............................37
Figure 10: LEDs for the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports...............................................................................................................39
Figure 11: SFP Slot LEDs ....................................................................................................................................................40
Figure 12: Switch ID LED.....................................................................................................................................................41
Figure 13: Switch ID LED.....................................................................................................................................................42
Figure 14: Switch ID LEDs in the Low Power Mode.............................................................................................................42
Figure 15: AT-StackXS/1.0 Stacking Transceiver ................................................................................................................49
Figure 16: Stack of Two Switches in the Linear Topology....................................................................................................50
Figure 17: Stack of Four Switches in the Linear Topology...................................................................................................51
Figure 18: Stack of Two Switches in the Ring Topology ......................................................................................................52
Figure 19: Stack of Four Switches in the Ring Topology......................................................................................................53
Figure 20: PORT Parameter in the Command Line Interface...............................................................................................56
Figure 21: Components of the Switches...............................................................................................................................65
Figure 22: Components of the AT-x310-26FT Switch ..........................................................................................................66
Figure 23: Turning the Switch Upside Down........................................................................................................................71
Figure 24: Removing the Rubber Feet .................................................................................................................................71
Figure 25: Installing Brackets on the AT-x310-26FT Switch......................................................................
Figure 26: Attaching Brackets to the AT-x310-26FP, AT-x310-50FT, or AT-x310-50FP Switch ..........................................73
Figure 27: Attaching Brackets to the AT-x310-26FP, AT-x310-50FT, or AT-x310-50FP Switch (Continued)......................74
Figure 28: Mounting the Switch in an Equipment Rack. .......................................................................................................75
Figure 29: Connecting the Management Cable to the Console Port ...................................................... ..............................79
Figure 30: User Exec Mode Prompt.....................................................................................................................................80
Figure 31: Moving to the Privileged Exec Mode with the ENABLE Command......................... ... ... ......................................80
Figure 32: Moving to the Global Configuration Mode with the CONFIGURE TERMINAL Command ..................................80
Figure 33: Activating VCStack with the STACK ENABLE Command...................................................................................81
Figure 34: Returning to the Privileged Exec Mode with the EXIT Command ....................................................... ................81
Figure 35: Saving the Change with the WRITE Command ..................................................................................................81
Figure 36: Rebooting the Switch with the REBOOT Command ...........................................................................................81
Figure 37: Removing the Dust Plug from the S1 Slot...........................................................................................................84
Figure 38: Removing the Dust Cover from the AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceiver.......................................................................85
Figure 39: Installing the AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceiver in Slot S1..........................................................................................85
Figure 40: Removing the Dust Plug from the S2 Slot...........................................................................................................86
Figure 41: Installing the AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceiver in Slot S2..........................................................................................87
Figure 42: Installing the Retaining Clip.................................................................................................................................90
Figure 43: Plugging in the AC Power Cord...........................................................................................................................92
Figure 44: Lowering the Retaining Clip.................................................................................................................................93
Figure 45: SHOW STACK Command...................................................................................................................................96
Figure 46: Moving to the Global Configuration Mode with the CONFIGURE TERMINAL Command ..................................97
Figure 47: Returning to the Privileged Exec Mode...............................................................................................................98
Figure 48: Saving the Priority Values with the WRITE Command........................................................................................98
Figure 49: Switch Initialization Messages.............................................................................................................................99
...........................72
7
Page 8

Figures
Figure 50: Switch Initialization Messages (Continued) .......................................................................................................100
Figure 51: Switch Initialization Messages (Continued) .......................................................................................................101
Figure 52: Removing the Dust Plug from an SFP Slot........................................................................................................107
Figure 53: Installing an SFP Transceiver............................................................................................................................107
Figure 54: Removing the Dust Cover from an SFP Transceiver.........................................................................................108
Figure 55: Positioning the SFP Handle in the Upright Position...........................................................................................108
Figure 56: Connecting a Fiber Optic Cable to an SFP Transceiver....................................................................................109
Figure 57: RJ-45 Socket Pin Layout (Front View)...............................................................................................................117
8
Page 9

Tables
Table 1: Twisted Pair Cable Requirements for the 10/100Base-TX Ports ...........................................................................24
Table 2: Twisted Pair Cable for the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports ...........................................................................................26
Table 3: IEEE Powered Device Classes ..............................................................................................................................28
Table 4: Combo Port Pairs ..................................................................................................................................................32
Table 5: LEDs on the 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-50FT Switches ......................................36
Table 6: LEDs for the PoE 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches .............................37
Table 7: LEDs on the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports ................................................................................................................. 39
Table 8: SFP Slot LEDs .......................................................................................................................................................40
Table 9: S1 and S2 Slot LEDs .............................................................................................................................................41
Table 10: Product Dimensions ...........................................................................................................................................115
Table 11: Product Weights ................................................................................................................................................115
Table 12: Ventilation Requirements ................................................................................................................................... 115
Table 13: Environmental Specifications .............................................................................................................................116
Table 14: Input Voltages ....................................................................................................................................................116
Table 15: Maximum Power Consumption ..........................................................................................................................116
Table 16: Heat Dissipation ................................................................................................................................................117
Table 17: Product Certifications .........................................................................................................................................117
Table 18: Pin Signals for 10 and 100 Mbps .......................................................................................................................118
Table 19: Pin Signals for 1000 Mbps .................................................................................................................................118
Table 20: RJ-45 Style Serial Console Port Pin Signals .....................................................................................................119
9
Page 10

Tables
10
Page 11

Preface
Note
This guide contains the installation instructions for the x310 Series of
Layer 2+ Fast Ethernet switches. This preface contains the following
sections:
“Document Conventions” on page 12
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 13
This guide explains how to install the switches in a stack with the
Virtual Chassis Stack (VCStack
to install the switches as stand-alone units, refer to the x310 Series
Installation Guide for Stand-alone Switches.
™) feature. For instructions on how
11
Page 12

Preface
Note
Caution
Warning
Document Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Notes provide additional information.
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
12
Page 13

Contacting Allied Telesis
If you need assistance with this product, you may contact Allied Telesis
technical support by going to the Support & Services section of the Allied
Telesis web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. You can find links for
the following services on this page:
24/7 Online Support — Enter our interactive support center to
search for answers to your product questions in our knowledge
database, to check support tickets, to learn about RMAs, and to
contact Allied Telesis technical experts.
USA and EMEA phone support — Select the phone number that
best fits your location and customer type.
Hardware warranty information — Learn about Allied Telesis
warranties and register your product online.
Replacement Services — Submit a Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) request via our interactive support center.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Documentation — View the most recent installation and user
guides, software release notes, white papers, and data sheets for
your products.
Software Downloads — Download the latest software releases for
your managed products.
For sales or corporate information, go to www.alliedtelesis.com/
purchase and select your region.
13
Page 14

Preface
14
Page 15

Chapter 1
Note
Overview
This chapter contains the following sections:
“Features” on page 16
“Front and Back Panels” on page 19
“Management Panel” on page 22
“10/100Base-TX Twisted Pair Ports” on page 23
“10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports” on page 25
“Power Over Ethernet” on page 27
“SFP Slots” on page 31
“Combo 10/100/1000Base-T Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32
“Stacking Slots” on page 33
“eco-friendly Button” on page 34
“LEDs” on page 35
“USB Port” on page 43
“Console Port” on page 44
“Power Supply” on page 45
This guide explains how to install the switches in a stack with the
Virtual Chassis Stack (VCStack
™) feature. For instructions on how
to install the switches as stand-alone units, refer to the x310 Series
Installation Guide for Stand-alone Switches.
15
Page 16

Chapter 1: Overview
Features
x310 Models Here are model names of the x310 Series switches:
The x310 Series Switches and their features are listed in this section:
AT-x310-26FT
AT-x310-26FP
AT-x310-50FT
AT-x310-50FP
10/100 Mbps
Twisted Pair
Ports
10/100/1000
Mbps Twisted
Pair Ports
Here are the basic features of the 10/100 Mbps twisted pair ports:
24 or 48 ports per switch
10Base-T and 100Base-TX compliant
IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation compliant
Auto-MDI/MDIX
100 meters (328 feet) maximum operating distance
IEEE 802.3x flow control in full-duplex mode
IEEE 802.3x backpressure in half-duplex mode
Jumbo frames up to 13KB
RJ-45 connectors
Here are the basic features of the 10/100/1000 Mbps twisted pair ports:
2 ports per switch
10Base-T, 100Base-TX, and 1000Base-T compliant
IEEE 802.3u Auto-Negotiation compliant
Auto-MDI/MDIX
16
100 meters (328 feet) maximum operating distance
IEEE 802.3x flow control in 10/100Base-TX full-duplex mode
IEEE 802.3x backpressure in 10/100Base-TX half-duplex mode
IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T
Jumbo frames up to 13KB
RJ-45 connectors
Page 17

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Note
Note
Note
The 10/100/1000Base-T ports are paired with the SFP slots to form
combo ports. For information, refer to “Combo 10/100/1000Base-T
Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32.
Power Over
Ethernet
Here are the basic features of Power over Ethernet (PoE) on the twisted
pair ports on the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches:
Supported on ports 1 to 24 on the AT-x310-26FP Switch and ports
1 to 48 on the AT-x310-50FP Switch
Supports PoE (15.4 watts maximum) and PoE+ (30 watts
maximum) powered devices
Supports powered device classes 0 to 4
Maximum power budget of 370 watts
Port prioritization
Mode A wiring
SFP Slots Here are the basic features of the two SFP slots on the switches:
Supports 1000Base-SX/LX SFP transceivers
Supports single-port BiDi 1000Base-LX SFP transceivers
Supports 1000Base-ZX SFP transceivers
SFP transceivers must be purchased separately. For a list of
supported transceivers, contact your Allied Telesis distributor or
reseller.
S1 and S2
Stacking Slots
The SFP slots are paired with the 10/100/1000Base-T ports to form
combo port pairs. For information, refer to “Combo 10/100/
1000Base-T Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32.
The S1 and S2 slots are stacking ports for the VCStack feature. You may
use the slots to build a stack of up to four switches. The slots support the
AT-StackXS/1.0 Twisted Pair Transceiver. For further information, refer to
Chapter 2, “Virtual Chassis Stacking” on page 47.
17
Page 18

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
LEDs Here are the port LEDs:
Link/activity and duplex mode LEDs for the twisted pair ports on
non-PoE switches
Link/activity and PoE status LEDs for the twisted pair ports on PoE
switches
Link/activity LEDs for SFP and SFP+ slots
Switch ID number LED
eco-friendly button turns off the LEDs to conserve electricity
Installation
Options
MAC Address
Table
Management
Software and
Interfaces
Here are the installation options for the switches of a stack:
19-inch equipment rack
Desk or tabletop
The switches come with wall anchors and screws. Allied Telesis
does not recommend installing the switches of a stack on a wall.
Instead, they should be installed in an equipment rack or on a table.
Here are the basic features of the MAC address tables of the switches:
Storage capacity of 16,000 dynamic MAC address entries
Storage capacity of 256 static MAC address entries
Automatic learning and aging
Here are the management software and interfaces:
AlliedWare Plus Management Software
Command line interface
18
Management
Methods
Web browser interface
Here are the methods for managing the switches:
Local management through the Console port
Remote Telnet and Secure Shell management
Remote HTTP and HTTPS web browser management
SNMPv1, v2c, and v3
Page 19

Front and Back Panels
10/100Base-TX Ports
10/100/1000Base-T Ports
SFP Slots
Stacking Slots
Management Panel
AT-x310-26FT
10/100Base-TX Ports with PoE
10/100/1000Base-T Ports
SFP Slots
Stacking Slots
Management Panel
AT-x310-26FP
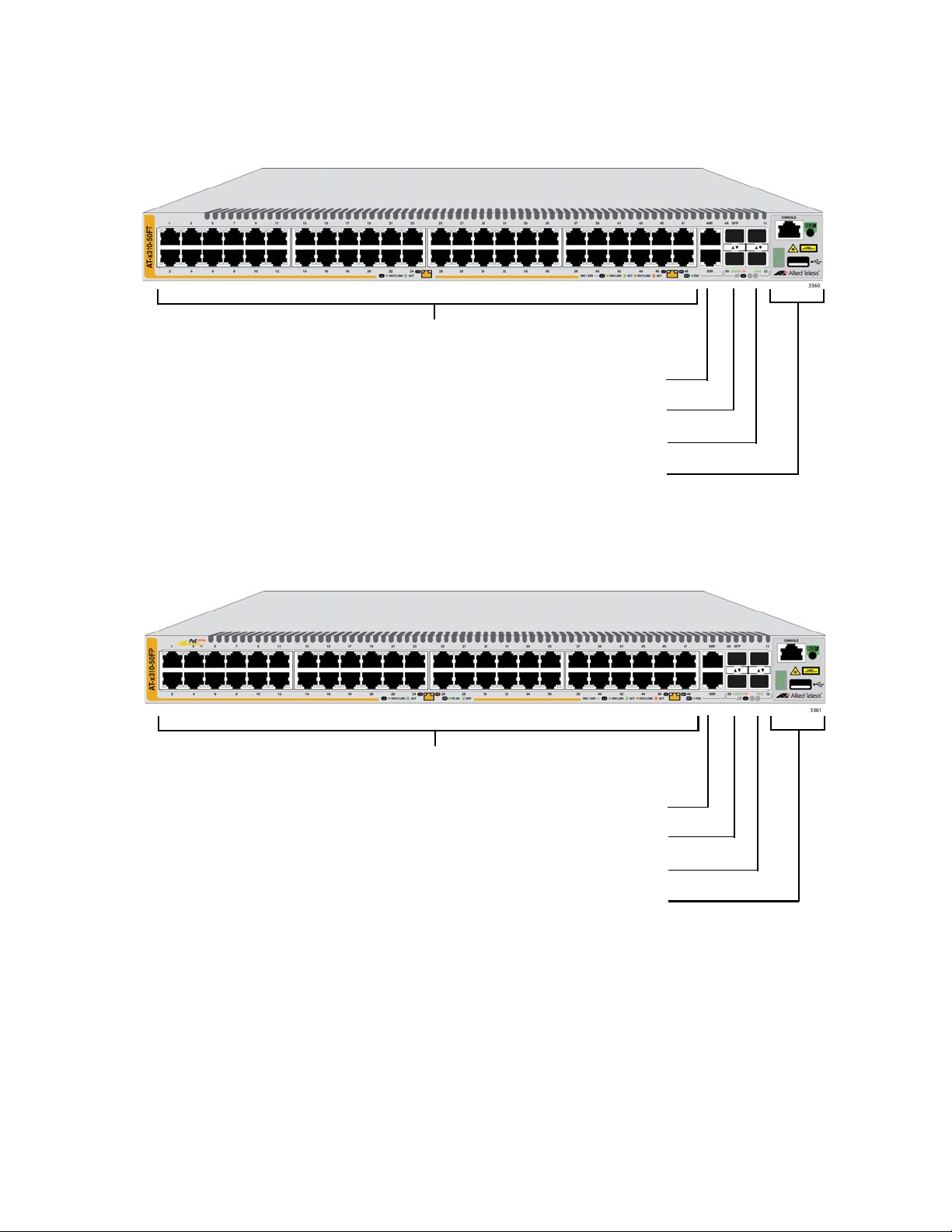
The front panels of the x310 Series switches are shown in Figure 1 here
and Figure 2 on page 20.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 1. Front Panels of the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-26FP Switches
19
Page 20
Chapter 1: Overview
10/100Base-TX Ports
10/100/1000Base-T Ports
SFP Slots
Stacking Slots
Management Panel
10/100Base-TX Ports with PoE
10/100/1000Base-T Ports
SFP Slots
Stacking Slots
Management Panel
AT-x310-50FP
AT-x310-50FT
Figure 2. Front Panels of the AT-x310-50FT and AT-x310-50FP Switches
20
Page 21

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
AC Power
Connector
AC Power Connector
AC Power Connector
The back panel of the AT-x310-26FT Switch is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Back Panel of the AT-x310-26FT Switches
The back panel of the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches is
shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Back Panel of the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches
The back panel of the AT-x310-50FT Switch is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Back Panel of the AT-x310-50FT Switch
21
Page 22

Chapter 1: Overview
eco-friendly
button
USB Port
Switch ID LED
Console Management Port
Management Panel
Figure 6 identifies the components in the management panels on the x310
Series switches.
Figure 6. x310 Series Management Panel
22
Page 23

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Note
10/100Base-TX Twisted Pair Ports
The x310 Series switches have 24 or 48 10/100Base-TX ports, depending
on the model.
Speed The ports can operate at either 10 or 100 Mbps. The speeds may be set
manually using the management software or automatically with AutoNegotiation (IEEE 802.3u), the default setting.
Duplex Mode The twisted pair ports can operate in either half- or full-duplex mode. The
duplex mode determines the manner in which a port transmits data. A port
set to half-duplex can either transmit or receive data at one time, while a
port operating in full-duplex can transmit and receive data at the same
time. The best network performance is achieved with the full-duplex
setting, but not all network equipment is designed to support that duplex
mode.
The duplex modes, like port speeds, may be set manually using the
management software or automatically with Auto-Negotiation (IEEE
802.3u), the default setting.
Wiring
Configuration
The switch allows you to set the speed and duplex mode settings of a port
independently of each other. For example, you might set the speed
manually and the duplex mode with Auto-Negotiation.
A switch port that is connected to a network device that does not
support Auto-Negotiation and has a fixed duplex mode of full-duplex
should not set its duplex mode with Auto-Negotiation. A duplexmode mismatch in which a switch port and a network device operate
at different duplex modes, may occur. The duplex modes of switch
ports that are connected to network devices that do not support
Auto-Negotiation should be set manually through the management
software.
The wiring configuration of a port can be MDI or MDI-X. The wiring
configurations of a switch port and a network device connected with
straight-through twisted pair cabling have to be opposite, such that one
device is using MDI and the other MDI-X. For instance, a switch port has
to be set to MDI-X if it is connected to a network device set to MDI.
You may set the wiring configurations of the ports manually or let the
switch configure them automatically with auto-MDI/MDI-X (IEEE 802.3abcompliant). This feature enables the switch to negotiate with network
devices to establish the proper settings, so that the ports on the devices
are using different wiring configurations.
23
Page 24
Chapter 1: Overview
Maximum
The ports have a maximum operating distance of 100 meters (328 feet).
Distance
Power Over
Ethernet
Cable
The 10/100Base-TX ports on the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP
Switches support Power over Ethernet (PoE). The ports supply DC power
to network devices over the network twisted pair cables. The switches
support PoE (IEEE 802.3af) and PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at). For background
information, refer to “Power Over Ethernet” on page 27.
The cable requirements of the ports are given in Table 1.
Requirements
Table 1. Twisted Pair Cable Requirements for the 10/100Base-TX Ports
Cable Type
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Bcompliant Category 3 shielded
or unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 16 MHz.
10Mbps 100Mbps
Non-
PoE
Yes No No Yes No No
PoE PoE+
Non-
PoE
PoE PoE+
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Acompliant Category 5 shielded
or unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Bcompliant Enhanced Category
5 (Cat 5e) shielded or
unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-Bcompliant Category 6 or 6a
shielded cabling.
Yes Yes No Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
24
Page 25

10/100/1000Base-T Twisted Pair Ports
Note
Note
The switches have two 10/100/1000Base-T ports.
The 10/100/1000Base-T ports are paired with the SFP slots to form
combo ports. For information, refer to “Combo 10/100/1000Base-T
Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32.
Speed The ports can operate at 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps. The speeds may be set
manually using the management software or automatically with AutoNegotiation (IEEE 802.3u), the default setting.
The ports must be set to Auto-Negotiation to function at 1000 Mbps
and are not compatible with devices that are not IEEE 802.3u
compliant.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Duplex Mode The 10/100/1000Base-T ports twisted pair ports support full-duplex mode.
They do not support half-duplex mode.
Wiring
Configuration
Maximum
The wiring configuration of a port operating at 10 or 100 Mbps can be MDI
or MDI-X. The wiring configurations of a switch port and a network device
connected with straight-through twisted pair cabling have to be opposite,
such that one device is using MDI and the other MDI-X. For instance, a
switch port has to be set to MDI-X if it is connected to a network device set
to MDI.
You may set the wiring configurations of the ports manually or let the
switch configure them automatically with auto-MDI/MDI-X (IEEE 802.3abcompliant). This feature enables the switch to automatically negotiate with
network devices to establish their proper settings.
The MDI and MDI-X settings do not apply when ports are operating at
1000 Mbps.
The ports have a maximum operating distance of 100 meters (328 feet).
Distance
Power Over
The 10/100/1000Base-T ports on the switches do not support PoE.
Ethernet
Cable
Requirements
The cable requirements of the ports are given in Table 2 on page 26.
25
Page 26
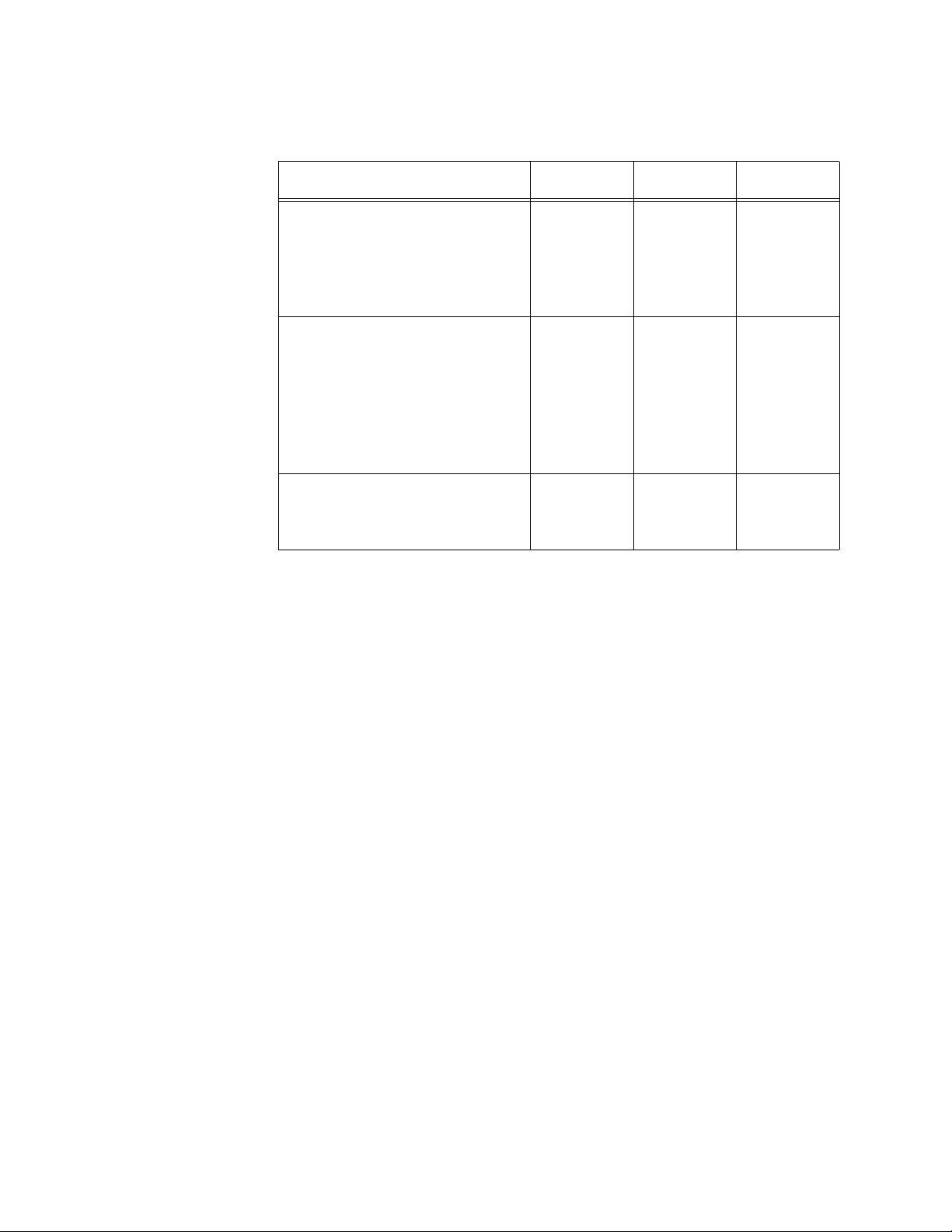
Chapter 1: Overview
Table 2. Twisted Pair Cable for the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports
Cable Type 10Mbps 100Mbps 1000Mbps
Standard TIA/EIA 568-B-
Yes Yes No
compliant Category 3 shielded
or unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 16 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-A-
Yes Yes Yes
compliant Category 5 or TIA/
EIA 568-B-compliant Enhanced
Category 5 (Cat 5e) shielded or
unshielded cabling with 100
ohm impedance and a
frequency of 100 MHz.
Standard TIA/EIA 568-B-
Yes Yes Yes
compliant Category 6 or 6a
shielded cabling.
Port Pinouts Refer to Table 18 on page 118 and Table 19 on page 118 for the port
pinouts of the 10/100/1000Base-T twisted pair ports.
26
Page 27

Power Over Ethernet
Note
The AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches feature Power over
Ethernet (PoE) on the 10/100Base-TX ports. PoE is used to supply power
to network devices over the same twisted pair cables that carry the
network traffic.
The main advantage of PoE is that it can make it easier to install a
network. The selection of a location for a network device is often limited by
whether there is a power source nearby. This often limits equipment
placement or requires the added time and cost of having additional
electrical sources installed. But with PoE, you can install PoE-compatible
devices wherever they are needed without having to worry about whether
there are power sources nearby.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
PoE is not available on the two 10/10/10000Base-T ports.
A device that provides PoE to other network devices is referred to as
power sourcing equipment (PSE). The AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP
Switches act as PSE units by adding DC power to the network cable, thus
functioning as a central power source for other network devices.
Devices that receive their power from a PSE are called powered devices
(PD). Examples include wireless access points, IP telephones, webcams,
and even other Ethernet switches.
The switch automatically determines whether or not a device connected to
a port is a powered device. Ports that are connected to network nodes that
are not powered devices (that is, devices that receive their power from
another power source) function as regular Ethernet ports, without PoE.
The PoE feature remains activated on the ports but no power is delivered
to the devices.
PoE Standards The AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches support these PoE
standards:
PoE (IEEE 802.3af): This standard provides up to 15.4 watts at the
switch port to support powered devices that require up to 12.95
watts.
PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at): This standard provides up to 30.0 watts at
the switch port to support powered devices that require up to 25.5
watts.
27
Page 28
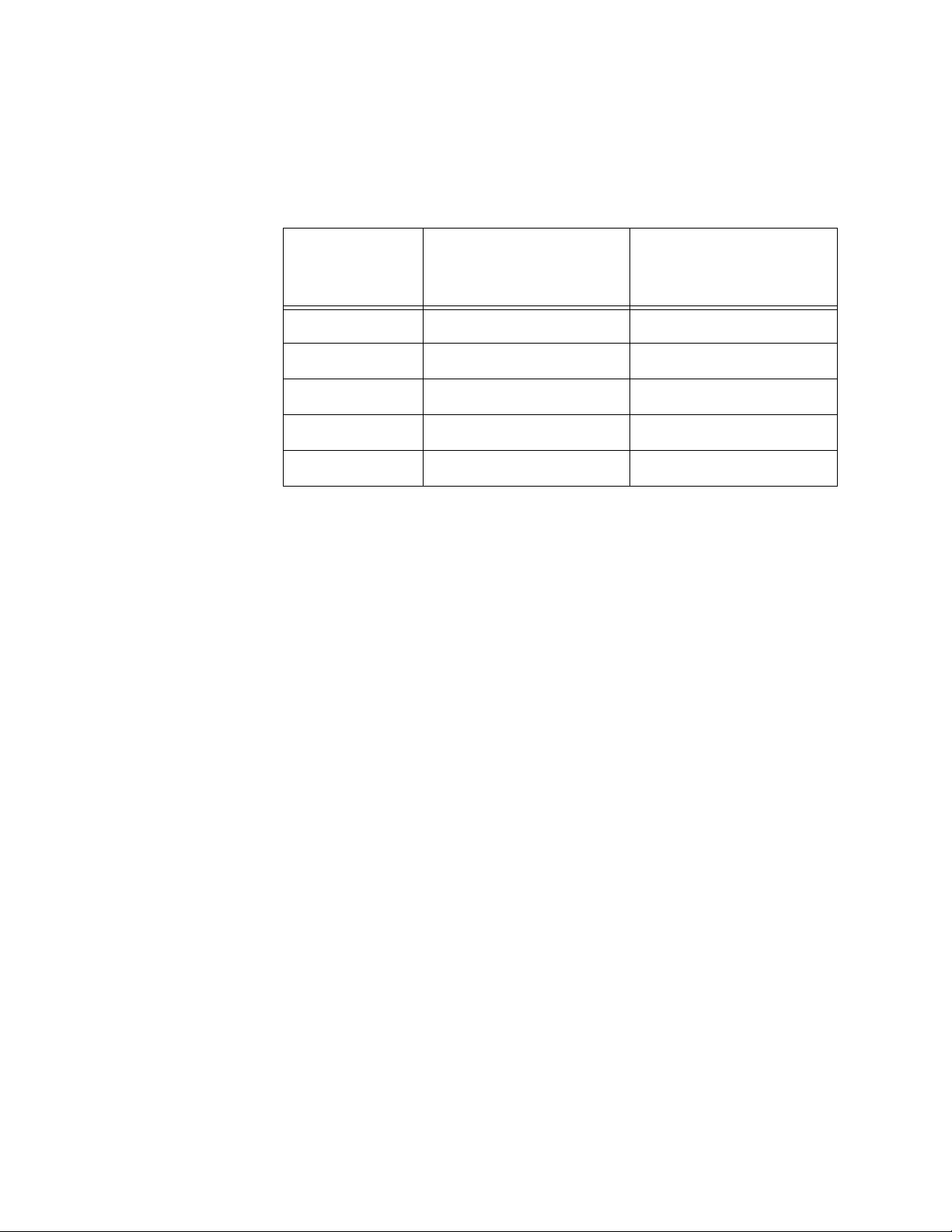
Chapter 1: Overview
Powered Device
Classes
Cable
Requirements
Powered devices are grouped into the five classes listed in Table 3 on
page 28. The classes are based on the amount of power the devices
require. The switches support all five classes.
Table 3. IEEE Powered Device Classes
Maximum Power
Class
0 15.4W 0.44W to 12.95W
1 4.0W 0.44W to 3.84W
2 7.0W 3.84W to 6.49W
3 15.4W 6.49W to 12.95W
4 30.0W 12.95W to 25.5W
The cable requirements for ports operating at 10 or 100Mbps are given in
Table 1 on page 24.
Output from a Switch
Port
PD Power Range
Power Budget The AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches have a power budget of
370 watts. This is the maximum amount of power the switches can provide
at one time to the powered devices.
The power requirements of the PoE devices determine the maximum
number of devices the switch can support at one time. So long as the total
power requirements of the powered devices is less than the power budget
of the switch, the switch can supply power to all the devices. But if the total
power requirements exceed the power budget, the switch denies p ower to
one or more ports using a mechanism referred to as port prioritization.
To determine whether the power requirements of the PoE devices you
plan to connect to the switch exceed its power budget, refer to their
documentation for their power requirements and add the requirements
together. The switch should be able to power all the devices
simultaneously as long as the total is below its power budget. If the total
exceeds the available power budget, you should consider reducing the
number of PoE devices so that all of the devices receive power.
Otherwise, the switch powers a subset of the devices, based on port
prioritization.
The switch can handle different power requirements on different ports.
This enables you to connect different classes of PoE equipment to the
ports on the switch.
28
Page 29

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Port
Prioritization
If the power requirements of the powered devices exceed the switch’s
power budget, the switch denies power to some ports based on a system
called port prioritization. You may use this mechanism to ensure that
powered devices critical to the operations of your network are given
preferential treatment by the switch in the distribution of power should the
demands of the devices exceed the available capacity.
There are three priority levels:
Critical
High
Low
Ports set to the Critical level, the highest priority level, are guaranteed
power before any of the ports assigned to the other two priority levels.
Ports assigned to the other priority levels receive power only if all the
Critical ports are receiving power. Ports that are connected to your most
critical powered devices should be assigned to this level. If there is not
enough power to support all the ports set to the Critical priority level, power
is provided to the ports based on port number, in ascending order.
The High level is the second highest level. Ports set to this level receive
power only if all the ports set to the Critical level are already receiving
power. If there is not enough power to support all of the ports set to the
High priority level, power is provided to the ports based on port numbe r, in
ascending order.
The lowest priority level is Low. This is the default setting. Ports set to this
level only receive power if all of the ports assigned to the other two levels
are already receiving power. As with the other levels, if there is not enough
power to support all of the ports set to the Low priority level, power is
provided to the ports based on port number, in ascending order.
Power allocation is dynamic. Ports supplying power to powered devices
may cease power transmission if the switch’s power budget is at maximum
usage and new powered devices, connected to ports with higher priorities,
become active.
You can use port prioritization on dual power supply PoE switches to
protect your important networking devices from loss of power should one
of the power supplies fail or lose power. If you limit the power requirements
of the critical devices connected to a switch to less than 185 watts, the
PoE power provided by a single power supply, a switch will have sufficient
power to support the critical devices even if it has only one functional
power supply.
29
Page 30

Chapter 1: Overview
Wiring
Implementation
The IEEE 802.3af standard defines two methods for delivering DC power
over twisted pair cable by a PSE, such as a switch, to PDs. These
methods, known as Alternatives A and B, identify which of the wires within
the cables are to carry the DC power from the switches to the PDs.
Twisted pair cabling typically consists of eight wires. With 10Base-T and
100Base-TX devices, the wires connected to pins 1, 2, 3, and 6 on the RJ45 connectors carry the network traffic while the wires connected to pins 4,
5, 7, and 8 are unused. With 1000Base-T devices, all eight wires are used
to carry network data.
It takes four wires to deliver DC power to a PD. With Alternative A, the
power is delivered on pins 1, 2, 3, and 6. These are the same pins in
10Base-T and 100Base-TX devices that carry the network data. With
Alternative B, the power is provided over 4, 5, 7, and 8, which are spare
wires.
The ports on the AT-x310-26FP and AT-x310-50FP Switches deliver the
power using pins 4, 5, 7, and 8, which corresponds to Alternative B in the
IEEE 802.3af standard. Therefore, the switches can support PDs that use
Alternative B to receive power.
PDs that comply with the IEEE 802.3af and 802.3at standards are
required to support both Alternative A and B. However, non-standard PDs
and PDs that were manufactured before the completion of the IEEE
802.3af and 802.3at standards and that support only Alternative A will not
work with the switches.
30
Page 31

SFP Slots
Note
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
The switches have two SFP slots that support the following types of SFP
1000Mbps transceivers:
1000Base-SX/LX SFP transceivers
Single-port BiDi 1000Base-LX SFP transceivers
1000Base-ZX SFP transceivers
You may use the transceivers to connect switches to other network
devices over large distances, build high-speed backbone networks
between network devices, or connect high-speed devices, such as
servers, to your network.
The switches support a variety of short and long distance SFP modules.
For a list of supported SFP modules, contact your Allied Telesis
representative or visit our web site.
The SFP slots and 10/100/1000Base-T ports are paired together to
form combo port pairs. For information, refer to “Combo 10/100/
1000Base-T Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32.
31
Page 32

Chapter 1: Overview
Combo 10/100/1000Base-T Ports and SFP Slots
The two 10/100/1000Base-T ports and SFP slots are paired together to
form combo port pairs. Each pair contains one 10/100/1000Base-T port
and one SFP slot. The combo port pairs for the switches are listed in
Table 4.
Table 4 Combo Port Pairs
Model
10/100/1000
Base-T Port
SFP Slot
AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-26FP 25R 25
26R 26
AT-x310-50FT and AT-x310-50FP 49R 49
50R 50
The rule to follow when using the combo port pairs is to use only one
device in a pair at a time. For example, if you decide to use twisted pair
port 25R on the AT-x310-26FT or AT-x310-26FP Switch, then you cannot
use SFP slot 25. Or, if you choose to use SFP slot 49 on the AT-x31050FT or AT-x310-50FP Switch, then you cannot use the twisted pair port
49R.
The rules for using the combo port pairs are listed here:
You may use either the twisted pair port or SFP slot of a combo
port pair, but not both at the same time.
If you connect both the twisted pair port and SFP slot of a combo
port pair to network devices, the SFP slot takes priority and the
twisted pair port is blocked.
32
The SFP slot becomes active when the SFP transceiver
establishes a link to a network device.
The twisted pair port and SFP slot of a combo port pair share the
same settings, such as VLAN assignments, access control lists,
and spanning tree.
Page 33

Stacking Slots
Note
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
The S1 and S2 slots on the front panel of the switch are used with the
VCStack feature and the stacking transceiver to create a stack of up to
four switches. The switches of a stack act as a single virtual unit. They
synchronize their actions so that switching operations, like spanning tree
protocols, virtual LANs, and static port trunks, span across all the units and
ports. The two main advantages of stacks are:
You can manage multiple units simultaneously, which can simplify
network management.
You have more flexibility with some of the features. For instance, a
static port trunk on a stand-alone switch has to consist of ports
from the same switch. In contrast, a static trunk on a stack may
consist of ports from different switches in the same stack.
The stacking transceiver is shown in Figure 7. It is called the AT-StackXS/
1.0 transceiver. It has two SFP transceiver-style connectors and one
meter of twinax cable.
Figure 7. AT-StackXS/1.0 Stacking Transceiver
The stacking slots only support the stacking transceiver. They
cannot be used as regular networking ports.
33
Page 34

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
eco-friendly Button
The eco-friendly button on the front panel of the switch is used to toggle
the port LEDs on or off. You might turn off the LEDs to conserve electricity
when you are not monitoring the device. You can also toggle the LEDs
with the ECOFRIENDLY LED and NO ECOFRIENDLY LED commands in
the Global Configuration mode of the command line interface. The switch
is said to be operating in a low power mode when the LEDs are turned off.
Operating the switch in the low power mode with the LEDs turned off does
not interfere with the network operations of the device.
The management software on the switch has a command that blinks the
LEDs so that you can quickly and easily identify a specific unit among the
devices in an equipment rack. It is the FINDME command. The command
works on the switch even if you turned off the LEDs with the eco-friendly
button or NO ECOFRIENDLY LED command.
The Switch ID LED is always on, but it displays different information
depending on whether the LEDs are on or off. When the LEDs are on, the
ID LED displays the ID number of the switch. When the switch is operating
in the low power mode with the LEDs off, the ID LED indicates whether the
switch is a stand-alone unit or the master or member switch of a VCStack,
as detailed in Figure 14 on page 42.
Before checking or troubleshooting the network connections to the
ports on the switch, you should always check to be sure that the
LEDs are on by either pressing the eco-friendly button or issuing the
ECOFRIENDLY LED and NO ECOFRIENDLY LED commands in
the Global Configuration mode of the command line interface.
34
Page 35

LEDs
Link/Activity LED
Link/Activity LED
Duplex Mode LED
Duplex Mode LED
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
This section describes the functions of the LEDs.
LEDs for the 10/
100Mbps Twisted
Pair Ports
The 10/100Mbps ports on the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-50FT Switches
have two LEDs that display link, activity and duplex mode information. The
LEDs are shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. LEDs for the 10/100Mbps Ports on the AT-x310-26FT and AT-
x310-50FT Switches
The LEDs are described in Table 5 on page 36.
35
Page 36

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
Table 5. LEDs on the 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FT and
AT-x310-50FT Switches
LED State Description
Solid Green A port has established a 100 Mbps link to a
network device.
LEDs for the PoE
10/100Mbps
Twisted Pair
Ports
Flashing
Link/
Activity
LED
Duplex
Mode
LED
The PoE 10/100Mbps twisted pair ports on the AT-x310-26FP and ATx310-50FP Switches have two LEDs that display link, activity and PoE
information. The LEDs are shown in Figure 9 on page 37.
Green
Solid Amber A port has established a 10 Mbps link to a
Flashing
Amber
Off A port has not established a link with
Solid Green A port is operating in full duplex mode.
Solid Amber A port is operating in half-duplex mode.
Flashing
Amber
A port is transmitting or receiving data at
100 Mbps.
network device.
A port is transmitting or receiving data at 10
Mbps.
another network device or the LEDs are
turned off. To turn on the LEDs, use the
eco-friendly button.
Collisions are occurring on a port.
The duplex mode information for the ports on the AT-x310-26FP and
AT-x310-50FP Switches is available from the management
software.
36
Page 37

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Link/Activity LED
Link/Activity LED
PoE LED
PoE LED
Figure 9. LEDs for the PoE 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FP
and AT-x310-50FP Switches
The LEDs are described in Table 6.
Table 6. LEDs for the PoE 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FP
and AT-x310-50FP Switches
LED State Description
Solid Green A port has established a 100 Mbps link to a
network device.
Link/
Activity
LED
Flashing
Green
Solid Amber A port has established a 10 Mbps link to a
Flashing
Amber
A port is transmitting or receiving data at
100 Mbps.
network device.
A port is transmitting or receiving data at 10
Mbps.
Off A port has not established a link with
another network device or the LEDs are
turned off. To turn on the LEDs, use the
eco-friendly button.
37
Page 38

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
Note
Table 6. LEDs for the PoE 10/100Base-TX Ports on the AT-x310-26FP
and AT-x310-50FP Switches (Continued)
LED State Description
PoE Green The switch is detecting a powered device
(PD) on the port and is delivering power to
it.
Solid Amber The switch has shutdown PoE+ on the port
because of a fault condition.
LEDs for the 10/
100/1000Mbps
Twisted Pair
Ports
Flashing
Amber
The switch is detecting a PD on the port but
is not delivering power to it because the
maximum power budget has been reached.
Off This LED state can result from the following
conditions:
The port is not connected to a PD.
The PD is powered off.
The port is disabled in the
management software.
PoE is disabled on the port.
The LEDs on the Ethernet line cards
are turned off. To turn on the LEDs,
use the eco-friendly button.
Ports 25R and 26R on the AT-x310-26FT and AT-x310-26FP Switches
and ports 49R and 50R on the AT-x310-50FT and AT-x310-50FP
Switches are 10/100/1000Base-T ports. The ports have two LEDs that
display link, activity and duplex mode information. The LEDs are shown in
Figure 10 on page 39.
The 10/100/1000Base-T ports are paired with the SFP slots to form
combo ports. For information, refer to “Combo 10/100/1000Base-T
Ports and SFP Slots” on page 32.
The ports support full-duplex mode, but not half-duplex mode.
38
Page 39

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Link/Activity LED
Link/Activity LED
Duplex Mode LED
Duplex Mode LED
Figure 10. LEDs for the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports
The LEDs are described in Table 7.
Table 7. LEDs on the 10/100/1000Base-T Ports
LED State Description
Solid Green A port has established a 1000 Mbps link to
a network device.
Link/
Activity
LED
Flashing
Green
Solid Amber A port has established a 10 or 100 Mbps
Flashing
Amber
A port is transmitting or receiving data at
1000 Mbps.
link to a network device.
A port is transmitting or receiving data at 10
or 100 Mbps.
Off A port has not established a link with
another network device or the LEDs are
turned off. To turn on the LEDs, use the
Duplex
Mode
Solid Green A port is operating in full duplex mode. (The
eco-friendly button.
ports do not support half-duplex mode.)
LED
Off A port has not established a link with
another network device or the LEDs are
turned off. To turn on the LEDs, use the
eco-friendly button.
39
Page 40

Chapter 1: Overview
SFP Slot
LEDs
LEDs for the SFP
Slots
The LEDs for the SFP slots are located between the slots, as shown in
Figure 11. Each SFP slot has one LED. The left-hand LED is for the top
slot and the right-hand LED is for the bottom slot.
Figure 11. SFP Slot LEDs
The LEDs are described in Table 8.
Table 8. SFP Slot LEDs
LEDs for the
Stacking Slots
LED State Description
Link/Activity Off The slot is empty, the SFP transceiver
has not established a link to a network
device, or the LEDs are turned off. To turn
on the LEDs, use the eco-friendly button.
Solid green The SFP transceiver has established a
100 or 1000 Mbps link to a network
device.
Flashing
green
Slots S1 and S2 are stacking slots for the VCStack feature. You can use
the slots to build a virtual switch of up to four switches. For background
information, refer to Chapter 2, “Virtual Chassis Stacking” on page 47.
Table 9 on page 41 defines the LED states when the slots contain
stacking transceivers.
The SFP transceiver is receiving or
transmitting packets to a network device.
40
Page 41

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Switch ID LED
Table 9. S1 and S2 Slot LEDs
LED State Description
Link/Activity Off The slot is empty, the stacking transceiver
has not established a link to a network
device, or the LEDs are turned off. To turn
on the LEDs, use the eco-friendly button.
Solid green The stacking transceiver has established
a link to another switch in the stack.
Flashing
green
The stacking transceiver is receiving or
transmitting packets.
Switch ID LED The Switch ID LED, shown in Figure 12, displays the ID number of the
switch. A stand-alone switch has the ID number 0. Switches in a VCStack
have the numbers 1 to 4.
Figure 12. Switch ID LED
The states of the LED when the switch is not operating in the low power
mode are shown in Figure 13 on page 42.
41
Page 42

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
The switch is booting up.
The switch has encountered a fault condition.
The switch is operating as a stand-alone unit, with the ID
number 0.
The switch has an ID number of 1 to 4 as part of a VCStack.
The dot in the lower right corner flashes when the switch
accesses USB memory.
The switch is the master switch of a VCStack.
The switch is operating as a stand-alone unit.
The switch is a member switch of a VCStack.
Figure 13. Switch ID LED
The switch displays the letter “F” for fault on the ID LED if it encounters
one of the following problems:
A cooling fan has failed.
The internal temperature of the switch has exceeded the normal
operating range and the switch may shut down.
You can use the SHOW SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT command in the
command line interface to identify the source of the problem.
The states of the LED when the switch is operating in the low power mode
are shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14. Switch ID LEDs in the Low Power Mode
42
Page 43

USB Port
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
The management panel has a USB port. You may use the port to store
configuration files on flash drives and to restore configuration files to
switches whose settings have been lost or corrupted, or to quickly
configure replacement units. You may also use the port and flash drives to
update the management firmware on the switches.
The port is USB2.0 compatible.
43
Page 44

Chapter 1: Overview
Note
Console Port
The Console port is used to conduct management sessions with the
switch to configure its features and parameter settings. This type of
management uses serial RS-232 and is commonly referred to as local or
out-of-band management because it is not conducted over your network.
To perform local management, you must be at the location of the switch
and must use the management cable included with the switch.
To establish a local management session with the switch, connect a
terminal or a personal computer with a terminal emulation program to the
Console port, which has an RJ-45 style (8P8C) connector, using the
provided management cable. The cable has RJ-45 RJ-style (8P8C) and
DB-9 (D-sub 9-pin) connectors.
The Console port is set to the following specifications:
Default baud rate: 9600 bps (Range is 9600 to 115200 bps)
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
These settings are for a DEC VT100 or ANSI terminal, or an
equivalent terminal emulation program.
44
Page 45

Power Supply
Warning
Note
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
The x310 Series switches come with one AC power supply. The back
panels have one AC connector. The power supply is not field-replaceable,
Refer to “Technical Specifications” on page 115 for the input voltage
range.
Power cord is used as a disconnection device. To de-energize
equipment, disconnect the power cord. E3
The switches are powered on or off by connecting or disconnecting
the power cords.
45
Page 46

Chapter 1: Overview
46
Page 47

Chapter 2
Note
Virtual Chassis Stacking
The sections in this chapter are:
“Overview” on page 48
“Stacking Slots and Transceiver” on page 49
“Stacking Port Topologies” on page 50
“Master and Member Switches” on page 54
“Specifying Ports in the Command Line Interface” on page 56
For more information on the VCStack feature, refer to the Stacking
Introduction and Stacking Commands chapters in the Software
Reference for x310 Series Switches, AlliedWare Plus Operating
System from www.alliedtelesis.com.
47
Page 48

Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking
Overview
The Virtual Chassis Stack (VCStack) feature allows you to connect up four
x310 Series switches to form a virtual switch so that the devices function
as a single networking unit. The benefits of the VCStack feature are:
Simplifies management - You can manage the devices of the stack
as a single unit, rather than individually. Your local and remote
management sessions automatically give you management
access to all the devices.
Reduces IP addresses - A stack requires only one IP address for
remote management access, thereby reducing the number of IP
addresses you have to assign to network devices, The one
address gives you management access to all the units.
Adds feature flexibility and resiliency - A stack gives you more
flexibility in the available configurations of features. For instance,
you can create port aggregators of ports from different switches in
the stack, rather than from only one switch. If you distribute the
ports of an aggregator across two or more switches in a stack, you
increase its resiliency because the aggregator will continue to
function, though at a reduced bandwidth, if one of the switches
stops functioning.
Reduces protocol requirements - Creating a stack might eliminate
your need to configure some protocols, such as the Virtual Router
Redundancy Protocol and Spanning Tree Protocol.
48
Page 49

Stacking Slots and Transceiver
Note
The x310 Series Switches come with two stacking slots. The slots are
labeled “S1” and “S2”. The slots may only be used with the VCStack
feature and only with stacking transceivers. The slots do not support
standard SFP transceivers.
The stacking transceiver is shown in Figure 15. It is called the ATStackXS/1.0 transceiver. It has two SFP transceiver-style connectors and
one meter of twinax cable.
Figure 15. AT-StackXS/1.0 Stacking Transceiver
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Stacking transceivers must be purchased separately.
49
Page 50

Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking
Caution
Stacking Port Topologies
The switches of a stack are connected with the S1 and S2 ports and ATStackXS/1.0 transceivers, shown in Figure 15 on page 49.
There are two wiring configurations. The first topology is called the linear
topology. In this topology the switches are connected with a single
pathway. The connections must crossover to different stacking slots on
the switches. Slot S1 on one switch must be connected to slot S2 on the
next switch.
Figure 16 is an example of a stack of two switches in the linear topology.
The AT-StackXS/1.0 stacking transceiver connects the S1 slot on the top
switch to the S2 slot on the bottom switch.
50
Figure 16. Stack of Two Switches in the Linear Topology
The stack will not function if the connections to the S1 and S2 slots
do not crossover on the switches. The switches will not form a stack
and instead operate as stand-alone devices.
The stack in Figure 17 on page 51 has four switches in the linear topo logy.
Page 51

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 17. Stack of Four Switches in the Linear Topology
The second topology is called the ring topology. It is similar to the linear
topology, except that the unused stacking slots on the end switches of the
stack are connected to form a physical loop. This topology is more resilient
than the linear topology because there are two pathways through the
stack. If one pathway fails, the switches can maintain communications
through the alternate pathway. The example in Figure 18 on page 52
shows a ring topology of two switches.
51
Page 52

Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking
Figure 18. Stack of Two Switches in the Ring Topology
Figure 19 on page 53 is an example of a stack of four switches in the ring
topology.
52
Page 53

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 19. Stack of Four Switches in the Ring Topology
The topologies are the same in terms of network speed and performance.
However, the ring topology is the recommended wiring configuration
because of the secondary path through the stacking ports. The two
pathways protect the switches of the stack against the loss of
communications due to a failure of a stacking port, cable, or switch.
53
Page 54

Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking
Master and Member Switches
The stack has one master switch. The functions of the master switch
include:
Coordinating and monitoring stack operations.
Verifying that the switches are using the same version of
management software. It automatically downloads its management
software over the stacking cables to switches with different
software versions.
Verifying that the switches have different ID numbers. It
automatically assigns new ID numbers to resolve situations where
two or more switches have the same ID number.
Verifying that the stacking transceivers that connect the switches
together are cabled correctly.
The other switches are called member switches. There can be up to three
member switches in addition to the master switch. A member switch can
automatically transition to the master role if the current master switch is
removed from the stack or powered off. This ensures continued operations
of the stack even if the master switch stops operating.
Selection of the
Master Switch
The devices compare the following numbers to choose the master switch
when the stack is reset or powered on:
Stack priority numbers
MAC addresses
The stack priority number is an adjustable value of 0 to 255, where the
lower the number, the higher the priority. The switch with the lowest
priority number (highest priority) becomes the master switch of a stack.
The default priority value is 128.
If the switches have the same priority values, the selection of the master
switch is based on their MAC addresses. As with the priority value, the
lower the MAC address, the higher the priority. The switch with the lowest
MAC address becomes the master switch.
If you power on the stack for the first time without adjusting the priority
values, the master switch is selected based on the MAC addresses if the
units are powered on simultaneously. If you power on the switches one at
a time, the master switch is the first switch to be powered on. This is
explained in Chapter 7, “Powering On the Stack” on page 89.
After the stack is established and operating, you may, if you choose,
change the priority settings on the individual units and so control which
switch will be the master switch after subsequent power cycles and resets.
54
Page 55

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Caution
ID Numbers Each switch must be assigned an ID number. The range is 1 to 4 and the
default is 1. The ID numbers are displayed on the ID LEDs on the front
panels of the units. You may assign the numbers yourself or you can let
the master switch assign the numbers automatically., as explained in
Chapter 7, “Powering On the Stack” on page 89.
You use the ID numbers to identify the individual ports and switches when
you configure the devices with the commands in the management
software. For further information, refer to “Specifying Ports in the
Command Line Interface” on page 56.
The ID numbers are also used to identify the parameter settings that are
stored in the configuration file. When the stack is reset or power cycled,
the ID numbers identify the devices to which the parameter settings
belong.
You should not change the ID numbers of the switches after you
have started to configure the parameter settings. Otherwise, the
parameter settings might be applied to the wrong devices when you
reset or power cycle the stack.
The switches do not use the ID numbers to select the master switch. The
selection of the master switch is typically based on the priority numbers
and MAC addresses, as previously explained.
55
Page 56

Chapter 2: Virtual Chassis Stacking
port1.0
.n
Module ID
Port Number
Stack ID
Specifying Ports in the Command Line Interface
The command line interface in the management software on the switch
has a parameter that you use to specify the individual ports. The
parameter is the PORT parameter and Figure 20 shows its format.
Figure 20. PORT Parameter in the Command Line Interface
The first number is the switch’s ID number. The ID numbers of switches in
a stack are displayed on their ID LEDs. You can also view the ID numbers
with the SHOW STACK command in the command line interface.
The module ID value is used with multi-module products. This value does
not apply to the x310 Series switches and should always be 0.
The third value is a port number on the switch. You may specify only one
port number in a PORT parameter, but you may specify more than one
PORT parameter in many of the commands where the parameter is
supported.
Here is an example of the PORT parameter. It uses the INTERFACE
command to enter the Port Interface mode for ports 15 and 17 on the
switch with ID 2:
awplus> enable
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# interface port2.0.15,port2.0.17
For instructions on the command line interface and the PORT parameter,
refer to the Software Reference for x310 Series Switches, AlliedWare Plus
Operating System.
56
Page 57

Chapter 3
Beginning the Installation
The chapter contains the following sections:
“Reviewing Safety Precautions” on page 58
“Selecting a Site for the Stack” on page 62
“Planning a Stack” on page 64
“Unpacking the Switch” on page 65
57
Page 58

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
Note
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Reviewing Safety Precautions
Please review the following safety precautions before beginning the
installation procedure.
Safety statements that have the symbol are translated into
multiple languages in the T ranslated Safety S t atements document at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support.
Class 1 Laser product. L1
Do not stare into the laser beam. L2
Do not look directly at the fiber optic cable ends or inspect the cable
ends with an optical lens. L6
To prevent electric shock, do not remove the cover. No userserviceable parts inside. This unit contains hazardous voltages and
should only be opened by a trained and qualified technician. To
avoid the possibility of electric shock, disconnect electric power to
the product before connecting or disconnecting the LAN cables.
E1
Do not work on equipment or cables during periods of lightning
activity. E2
Power cord is used as a disconnection device. To de-energize
equipment, disconnect the power cord. E3
58
Page 59

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Warning
Note
Caution
Warning
Note
Warning
Caution
Class I Equipment. This equipment must be earthed. The power
plug must be connected to a properly wired earth ground socket
outlet. An improperly wired socket outlet could place hazardous
voltages on accessible metal parts. E4
Pluggable Equipment. The socket outlet shall be installed near the
equipment and shall be easily accessible. E5
Air vents must not be blocked and must have free access to the
room ambient air for cooling. E6
Operating Temperatures. All the switches are designed for a
maximum ambient temperature of 45° degrees C.
All Countries: Install product in accordance with local and National
Electrical Codes. E8
Only trained and qualified personnel are allowed to install or replace
this equipment. E14
Circuit Overloading: Consideration should be given to the
connection of the equipment to the supply circuit and the effect that
overloading of circuits might have on overcurrent protection and
supply wiring. Appropriate consideration of equipment nameplate
ratings should be used when addressing this concern. E21
59
Page 60

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
Caution
Warning
Note
Warning
Note
Caution
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Replace
only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
Attention: Le remplacement de la batterie par une batterie de type
incorrect peut provoquer un danger d’explosion. La remplacer
uniquement par une batterie du même type ou de type équivalent
recommandée par le constructeur. Les batteries doivent être
éliminées conformément aux instructions du constructeur. E22
Mounting of the equipment in the rack should be such that a
hazardous condition is not created due to uneven mechanical
loading. E25
Use dedicated power circuits or power conditioners to supply
reliable electrical power to the device. E27
This unit might have more than one power cord. To reduce the risk
of electric shock, disconnect all power cords before servicing the
unit. E30
If installed in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating
ambient temperature of the rack environment may be greater than
the room ambient temperature. Therefore, consideration should be
given to installing the equipment in an environment compatible with
the manufacturer’s maximum rated ambient temperature (Tmra).
E35
Installation of the equipment in a rack should be such that the
amount of air flow required for safe operation of the equipment is not
compromised. E36
60
Page 61

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Warning
Warning
Caution
Warning
Reliable earthing of rack-mounted equipment should be maintained.
Particular attention should be given to supply connections other than
direct connections to the branch circuits (e.g., use of power strips).
E37
To reduce the risk of electric shock, the PoE ports on this product
must not connect to cabling that is routed outside the building where
this device is located. E40
The unit does not contain serviceable components. Please return
damaged units for servicing. E42
When you remove an SFP module from this product, the case
temperature of the SFP may exceed 40° C (158° F). Exercise
caution when handling with unprotected hands. E43
61
Page 62

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
Note
Selecting a Site for the Stack
Here are the site guidelines for the stack:
The switches of the stack should be installed on a table or in an
equipment rack. They should not be installed on a wall.
The power outlets should be located near the switches and be
easily accessible.
The site should allow for easy access to the ports on the front of
the switches, so that you can easily connect and disconnect
cables, and view the port LEDs.
The site should allow for adequate air flow around the units and
through the cooling vents on the front and rear panels. (The
ventilation direction in a unit with a cooling fan is from front to back,
with the fan on the back panel drawing the air out of the unit.)
If you are installing the switches of the stack in an equipment rack,
you should verify that the rack is safely secured so that it will not tip
over. You should install devices starting at the bottom of the rack,
with the heavier devices near the bottom.
If you are installing the stack on a table or desk, you should verify
that the table or desk is level and secure.
If you are installing the stack on a table or desk, you should place
the units side-by-side. Do not stack them on top of each other
because that could pose a safety hazard.
The site should not expose the switches to moisture or water.
The site should be a dust-free environment.
The site should include dedicated power circuits or power
conditioners to supply reliable electrical power to the network
devices.
The site should not expose the twisted pair cabling to sources of
electrical noise, such as radio transmitters, broadband amplifiers,
power lines, electric motors, and fluorescent fixtures.
Switch ports are suitable for intra-building connections, or where
non-exposed cabling is required.
Do not place objects on top of the switches.
Do not install the switches in a wiring or utility box because they
will overheat and fail from inadequate airflow.
62
Page 63

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Warning
Switches should not be stacked on top of one another on a table or
desktop because that could present a personal safety hazard if you
need to move or replace switches.
63
Page 64

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
Planning a Stack
Here are the guidelines to planning a stack:
A stack can have up to four x310 Series switches.
A stack can have different models of x310 Series switches.
Any x310 Series switch model can be the master switch of a stack.
Switches connected with AT-StackXS/1.0 stacking cables should
be installed in a standard 19-inch equipment rack and not more
than one meter apart, the length of the stacking cable. The end
switches cannot be more than one meter apart if you want to
create the ring topology, shown in Figure 18 on page 52 and
Figure 19 on page 53.
The wiring topology of the stack may be either linear or ring. Both
topologies offer the same in terms of speed, but the ring topology
adds wiring redundancy.
The x310 Series stack may not contain other stacking switches,
such as x600 and x610 Series switches.
The x310 Series switches do not need any additional software for
stacking. However, they do need stacking transceivers.
All the switches must have the same licenses of optional features.
If you install an optional feature on one switch, you must install it
on all switches before assembling the stack.
64
Page 65

Unpacking the Switch
Two wall or equipment rack mounting brackets
One 2 m (6.6 ft) local management cable with
RJ-45 (8P8C) and DB-9 (D-sub 9-pin)
connectors.
Eight bracket screws
One regional AC power cord
Two anchors for concrete walls:
Length: 29.6 mm (1 1/8 in.)
Diameter: 6.0 mm (0.25 in)
Two screws for wood or concrete walls:
Length: 31 mm (1 1/4 in.)
Width: 4.3 mm (1/8 in.)
Power cord retaining clip
All switches, except the AT-x310-26FT Switch, come with the components
listed in Figure 21. If any item is missing or damaged, contact your Allied
Telesis sales representative for assistance.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 21. Components of the Switches
The AT-x310-26FT Switch comes with the components shown in Figure
22 on page 66.
65
Page 66

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
One wall or equipment rack mounting bracket
One 2 m (6.6 ft) local management cable
with RJ-45 (8P8C) and DB-9 (D-sub 9-pin)
connectors.
Eight bracket screws
One regional AC power cord
Two anchors for concrete walls:
Length: 29.6 mm (1 1/8 in.)
Diameter: 6.0 mm (0.25 in)
Two screws for wood or concrete walls:
Length: 31 mm (1 1/4 in.)
Width: 4.3 mm (1/8 in.)
Power cord retaining clip
One long wall or equipment rack mounting
bracket
66
Figure 22. Components of the AT-x310-26FT Switch
Page 67

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Note
You should retain the original packaging material in the event you
need to return the unit to Allied Telesis.
67
Page 68

Chapter 3: Beginning the Installation
68
Page 69

Chapter 4
Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack
The procedures in this chapter are:
“Installing the Switch on a Table” on page 70
“Installing the Switch in an Equipment Rack” on page 71
69
Page 70

Chapter 4: Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack
Note
Warning
Installing the Switch on a Table
This section contains the procedure for installing the switch on a table or
desk.
The rubber feet on the bottom of the chassis should be left on for
table installation.
Do not stack switches on top of one another on a table or desktop
because that could result in a safety hazard. The switches could be
damaged or you might be injured if they tip over.
To install the chassis on a table, perform the following procedure:
1. Review “Selecting a Site for the Stack” on page 62 to verify the
suitable of the site for the switch.
2. Check to be sure that the table is strong enough to support the weight
of the switch.
3. Lift the switch onto the table.
4. Go to Chapter 8, “Cabling the Networking Ports” on page 103 to
connect the network cables.
70
Page 71

Installing the Switch in an Equipment Rack
Caution
This procedure requires the following items:
Eight bracket screws (included with the switch)
Two equipment rack brackets (included with the switch)
Flat-head screwdriver (not provided)
Cross-head screwdriver (not provided)
Four standard equipment rack screws (not provided)
Installation guidelines may be found in “Selecting a Site for the Stack” on
page 62. Here is the procedure for installing the switch in a 19-inch
equipment rack.
The chassis may be heavy and awkward to lift. Allied Telesis
recommends that you get assistance when mounting the chassis in
an equipment rack. E28
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
1. Place the unit upside down on a level, secure surface. Refer to
Figure 23.
Figure 23. Turning the Switch Upside Down
2. Using a flat-head screwdriver, pry the rubber feet from the bottom of
the switch. Refer to Figure 24.
Figure 24. Removing the Rubber Feet
71
Page 72

Chapter 4: Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack
3. Turn the switch over.
4. Attach the two rack mount brackets to the sides of the switch with the
eight bracket screws that come with the unit.
The AT-x310-26FT Switch comes with one short bracket and one long
bracket. Allied Telesis recommends installing the short bracket on the
right side and the long bracket on the left side, as yo u fa ce the front of
the unit, so that the stacking ports on the unit align with the same ports
on other x310 Series switches in the equipment rack. The possible
positions of the brackets are shown in Figure 25.
72
Figure 25. Installing Brackets on the AT-x310-26FT Switch
The bracket positions for the AT-x310-26FP, AT-x310-50FT, and ATx310-50FP Switches are shown in Figure 26 on page 73 and Figure 27
on page 74.
Page 73

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 26. Attaching Brackets to the AT-x310-26FP, AT-x310-50FT, or AT-
x310-50FP Switch
73
Page 74

Chapter 4: Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack
74
Figure 27. Attaching Brackets to the AT-x310-26FP, AT-x310-50FT, or
AT-x310-50FP Switch (Continued)
Page 75

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
5. While another person holds the switch in the equipment rack, secure it
with standard equipment rack screws (not provided), as shown in
Figure 28.
Figure 28. Mounting the Switch in an Equipment Rack
6. Go to Chapter 8, “Cabling the Networking Ports” on page 103, to
connect the network cables to the ports on the switch.
75
Page 76

Chapter 4: Installing the Switch on a Table or in an Equipment Rack
76
Page 77

Chapter 5
Verifying the Status of VCStack
The procedures in this chapter are:
“Verifying the Status of VCStack” on page 78
“Activating the VCStack Feature” on page 79
77
Page 78

Chapter 5: Verifying the Status of VCStack
Verifying the Status of VCStack
Before you install the stacking transceivers to build the stack, you should
first test the switches to determine whether the VCStack feature is
enabled or disabled, and enable it on any units where it is disabled. On
new switches, the feature should be activated because that is the default
setting. But on switches that were previously used as stand-alone units,
the feature is probably disabled and needs to be enabled.
Testing the status of VCStack is simple. You power on a switch and watch
the ID LED. If it displays a number from 1 to 4, VCStack is already
enabled. If the LED displays the number 0, the feature is disabled and
needs to be enabled.
To test the status of VCStack, perform the following procedure:
1. Power on one of the switches.
Connect a power cord to one of the power connectors on the back
panel and to an AC power source.
2. Wait one minute for the switch to initialize its management software.
3. View the ID LED and do one of the following:
If the ID LED is displaying a number from 1 to 4 (the default is 1),
VCStack is already enabled on the switch. Power off the unit by
disconnecting the power cord and test the remaining switches in
the same manner. After testing all the switches, be sure the
switches are powered off and go to Chapter 6, “Cabling the
Stacking Ports” on page 83.
If the ID LED is displaying “0,” the VCStack feature is disabled on
the switch. You must enable it by performing the procedure in
“Activating the VCStack Feature” on page 79.
78
Page 79

Activating the VCStack Feature
Perform the following two procedures to activate the VCStack feature on
switches that displayed the number “0” on their ID LEDs in the previous
procedure. The tasks assume that you are continuing directly from the
previous procedure and that the switch is powered on. The first procedure
explains how to establish a local management session on the switch and
the second procedure explains how to active the VCStack feature.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Starting a Local
Management
Session
To start a local management session on the switch, perform the following
procedure:
1. Connect the RJ-45 connector on the management cable to the
Console port on the front panel of the switch, as shown in Figure 29.
Figure 29. Connecting the Management Cable to the Console Port
2. Connect the other end of the cable to an RS-232 port on a terminal or
PC with a terminal emulator program.
3. Configure the terminal or terminal emulator program as follows:
Baud rate: 9600 bps (The baud rate of the Console Port is
adjustable from 1200 to 115200 bps. The default is 9600 bps.)
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
79
Page 80

Chapter 5: Verifying the Status of VCStack
Note
awplus>
awplus> enable
awplus#
awplus# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
awplus(config)#
4. Press Enter.
5. If this is the initial management session of the switch, enter “manager”
The port settings are for a DEC VT100 or ANSI terminal, or an
equivalent terminal emulator program.
You are prompted for a user name and password.
as the user name and “friend” as the password. The user name and
password are case sensitive.
The local management session starts when the User Exec mode
prompt, shown in Figure 30. is displayed.
Figure 30. User Exec Mode Prompt
Activating
VCStack
The User Exec mode is the first level in the command mode interface.
For complete information on the modes and commands, refer to the
Software Reference for x310 Series Switches, AlliedWare Plus
Operating System from www.alliedtelesis.com.
To activate the VCStack feature from the local management session,
perform the following procedure:
1. Enter the ENABLE command to move from the User Exec mode to the
Privileged Exec mode, as shown in Figure 31.
Figure 31. Moving to the Privileged Exec Mode with the ENABLE
Command
2. Enter the CONFIGURE TERMINAL command to move to the Global
Configuration mode, as shown in Figure 32.
Figure 32. Moving to the Global Configuration Mode with the CONFIGURE
TERMINAL Command
80
Page 81

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Note
awplus(config)# stack enable
% The device needs to be restarted for this change to take effect.
awplus(config)#
awplus(config)# exit
awplus#
awplus# write
Building configuration ...
[OK]
awplus#
awplus# reboot
reboot system? (y/n):
awplus#
3. Enter the STACK ENABLE command to activate VCStack on the
switch, as shown in Figure 33:
Figure 33. Activating VCStack with the STACK ENABLE Command
4. Enter the EXIT command to return to the Privileged Exec mode, as
shown in Figure 34.
Figure 34. Returning to the Privileged Exec Mode with the EXIT Command
5. Enter the WRITE command to save your change, as shown in
Figure 35.
Figure 35. Saving the Change with the WRITE Command
If this is the initial management session of the switch, the WRITE
command automatically creates in flash memory a new configuration
file called DEFAULT.CFG in which it stores your configuration
change. You may change the name of the file or designate a
different file after you create the stack.
6. Restart the switch with the REBOOT command, as shown in
Figure 36.
Figure 36. Rebooting the Switch with the REBOOT Command
7. Type “Y” for yes.
8. Wait one minute for the switch to initialize its management software.
81
Page 82

Chapter 5: Verifying the Status of VCStack
9. Check the ID LED and do one of the following:
If the ID LED is displaying the number 1, 2, 3, or 4, VCStack is now
enabled on the switch. Power off the switch by disconnecting the
power cord and repeat the procedures in this chapter on the next
switch. If there are no further switches to test, go to Chapter 6,
“Cabling the Stacking Ports” on page 83.
If the ID LED is still displaying “0,” repeat this procedure. If the
procedure was not successful, it might be because you did not
issue the WRITE command in step 5 to save your change.
82
Page 83

Chapter 6
Cabling the Stacking Ports
This chapter contains the procedure for cabling the S1 and S2 stacking
slots on the switches with AT-StackXS/1.0 stacking transceivers:
83
Page 84

Chapter 6: Cabling the Stacking Ports
Warning
Cabling Switches with AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceivers
To cable the switches of the stack with AT-StackXS/1.0 transceivers,
perform the following procedure:
A transceiver can be damaged by static electricity. Be sure to
observe all standard electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions,
such as wearing an antistatic wrist strap, to avoid damaging the
device.
1. Remove the dust plug from the S1 slot on the top switch of the stack,
as shown in Figure 37.
84
Figure 37. Removing the Dust Plug from the S1 Slot
2. Remove the transceiver from its shipping container and store the
packaging material in a safe location.
3. Remove the dust cap from one end of the transceiver, as shown in
Figure 38 on page 85.
Page 85

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Release tab
Figure 38. Removing the Dust Cover from the AT-StackXS/1.0
Transceiver
4. Position the transceiver with the release tab on top and slide the
transceiver into the slot, as shown in Figure 39.
Figure 39. Installing the AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceiver in Slot S1
85
Page 86

Chapter 6: Cabling the Stacking Ports
Note
5. Remove the dust cover from the S2 slot in the next switch in the stack
as shown in Figure 40.
The cable must crossover to different slots on the switches. The
stack will not work if you connect two S1 or S2 slots together.
Figure 40. Removing the Dust Plug from the S2 Slot
6. Remove the dust cover from the connector on the other end of the
transceiver.
7. Position the transceiver with the release tab on the bottom and slide it
into the slot until it clicks into place, as shown in Figure 41 on page 87.
86
Page 87

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 41. Installing the AT-StackXS/1.0 Transceiver in Slot S2
8. Repeat this procedure to connect additional switches to the stack with
AT-StackXS/1.0 transceivers.
9. To create the redundant path with the ring topology shown in Figure 18
on page 52 and Figure 19 on page 53, connect a stacking cable to the
empty stacking slots on the top and bottom switches.
10. After connecting the stacking cables to all the switches, go to Chapter
7, “Powering On the Stack” on page 89.
87
Page 88

Chapter 6: Cabling the Stacking Ports
88
Page 89

Chapter 7
Caution
Powering On the Stack
This chapter contains the following procedures:
“Installing the Power Cord Retaining Clip” on page 90
“Powering On the Switches Individually” on page 91
“Powering On the Switches Simultaneously” on page 94
“Verifying the Stack” on page 96
“Monitoring the Initialization Processes” on page 99
Perform “Powering On the Switches Individually” on page 91 if you want to
control the assignment of the ID numbers to the switches of the stack. The
numbers are assigned in the order in which you power on the units.
Otherwise, perform “Powering On the Switches Simultaneously” on
page 94 to have the switches assign the numbers automatically. After the
ID numbers are assigned, you may change them with the STACK
RENUMBER command, described in the Software Reference for x310
Series Switches, AlliedWare Plus Operating System.
You should not change the ID numbers of the switches after you
begin to configure the parameter settings. Otherwise, the stack
might assign configuration settings to the wrong units.
89
Page 90

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
Installing the Power Cord Retaining Clip
The power cord retaining clip that comes with the switch protects the
power cord from being accidentally unplugged from the unit.
To install the power cord retaining clip, position it the “u” part facing down,
press in the sides, and insert the ends of the clip into the holes in the
retaining bracket on the AC connector on the switch. Refer to Figure 42.
90
Figure 42. Installing the Retaining Clip
Go to either “Powering On the Switches Individually” on page 91 o
“Powering On the Switches Simultaneously” on page 94.
Page 91

Powering On the Switches Individually
This procedure explains how you can control the assignment of the ID
numbers of the switches by powering on the units one at a time during the
initial power-on sequence. The first switch is assigned ID number 1, the
next unit is assigned ID number 2, and so on. This procedure is useful
when the switches are installed in the same equipment rack and you want
to number them in sequence, such as from top to bottom, to make them
easy to identify. After the ID number are assigned, the switches retain their
assignments even when you power off or reset the stack.
During the initial power on sequence, the first switch to be powered on
becomes the master switch of the stack. However, if you do not change
the priority values of the units, the next time you reset or power cycle the
stack the units use their MAC addresses to select the master switch. This
might result in a different switch being assigned that role. However, this
does not affect their ID number assignments, the configuration of the
switches, or the manner in which you manage the stack.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
This procedure assumes the following:
This is the initial power-on sequence of the stack.
You verified that VCStack is enabled on the switches, as explained
in Chapter 5, “Verifying the Status of VCStack” on page 77.
You connected the switches with stacking transceivers, as
explained in Chapter 6, “Cabling the Stacking Ports” on page 83.
The ID numbers are set to the default 1.
.All the switches are powered off.
If you want to monitor the power on sequence, you may connect a terminal
or PC with a terminal emulator program to the Console port on the switch
you intend to power on first. The messages are found in “Monitoring the
Initialization Processes” on page 99.
Before powering on the switch, refer to “Power Specifications” on
page 116 for the power specifications.To install the power cord retaining
clip and power on the switch, perform the following procedure:
To power on the switches, perform the following procedure:
1. Power on the switch you want to be assigned ID number 1 by
connecting its power cord to the AC connector on the back panel and
to an appropriate power source. Refer to Figure 43 on page 92. Refer
to “Power Specifications” on page 116 for the power specifications of
the switches.
91
Page 92

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
Warning
Note
Figure 43. Plugging in the AC Power Cord
Power cord is used as a disconnection device. To de-energize
equipment, disconnect the power cord. E3
Pluggable Equipment. The socket outlet shall be installed near the
equipment and shall be easily accessible. E5
2. Wait one minute for the switch to initialize its management software.
The switch should be displaying the number 1 on its ID LED.
3. Power on the switch to be assigned ID number 2.
4. Wait two minutes for the new switch to join the stack as a member.
As the new switch boots up, the first switch, which has the ID number 1
and at this point is the master switch of the stack, notifies the new
switch that its current ID number is already being used and that it
should change its number to the next available number, which is 2.
The new switch responses by automatically changing its ID number to
2 and reboots. So the new switch is actually booting up twice, once
with the ID number 1 and again with its new ID number 2, which is why
it takes two minutes before the device becomes a full member of the
stack.
5. If there is a third switch, power it on and wait another two minutes for it
to join the stack as a member with the ID number 3.
92
Page 93

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
6. If there is a fourth switch, power it on and wait two minutes for it to join
the stack as a member with the ID number 4.
At this point, the stack is operational.
The ID numbers are automatically stored in special files in the flash
memories of the switches and are retained by the devices even if you
reset or power cycle the stack.
7. Secure the power cords to the switches by lowering the retaining clips.
Refer to Figure 44.
Figure 44. Lowering the Retaining Clip
8. To continue with the installation, go to “Verifying the Stack” on
page 96.
93
Page 94

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
Warning
Powering On the Switches Simultaneously
If you want the switches of the stack to use their MAC addresses to
automatically assign the ID numbers during the initial power on sequence,
all you have to do is power them on simultaneously, rather than one at a
time as in the previous procedure. Here are the steps the switches
perform:
They initialize their management software and compare their MAC
addresses.
The switch with the lowest address is designated as the master
switch of the stack.
The master switch assigns itself the ID number 1.
The master switch assigns ID numbers to the other switches.
The other switches reset and initialize their management software
again, with their new ID numbers.
This procedure assumes the following:
This is the initial power on sequence of the stack.
You verified that VCStack is enabled on the switches, as explained
in Chapter 5, “Verifying the Status of VCStack” on page 77.
You connected the switches with stacking transceivers, as
explained in Chapter 6, “Cabling the Stacking Ports” on page 83.
.All the switches are powered off.
If you want to monitor the power on sequence, you may connect a terminal
or PC with a terminal emulator program to the Console port on any of the
switches. The messages are found in “Monitoring the Initialization
Processes” on page 99.
To have the switches automatically assign the ID numbers, perform the
following procedure:
1. Power on all the switches in the stack at the same time.
Connect the power cords to the connectors on the back panels and to
the appropriate power sources, as shown in Figure 43 on page 92.
Refer to “Power Specifications” on page 116 for the power
specifications of the switches.
94
Power cord is used as a disconnection device. To de-energize
equipment, disconnect the power cord. E3
Page 95

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Note
Pluggable Equipment. The socket outlet shall be installed near the
equipment and shall be easily accessible. E5
2. Wait two or three minutes for the switches to select a master switch
and to assign the ID numbers.
At this point, the stack is operational. The ID numbers are
automatically stored in special files in the flash memories of the
switches and are retained by the devices even if you reset or power
cycle the stack.
3. To continue with the installation, go to “Verifying the Stack” on
page 96.
95
Page 96

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
awplus> show stack
Virtual Chassis Stacking summary inf or ma tio n
ID Pending ID MAC address Priority Status Role
1 - eccd:6dc1:ed30 128 Ready Active Master
2 - eccd:6dc1:65ab 128 Ready Backup Member
3 - eccd:6dc1:d4a7 128 Ready Backup Member
4 - eccd:6dc1:c431 128 Ready Backup Member
Operational Status Normal operations
Stack MAC address eccd:6dc1:ed30
awplus(config)#
Verifying the Stack
To verify stack operations, perform the following procedure:
1. Establish a local management session on any switch in the stack. For
instructions, refer to “Starting a Local Management Session” on
page 79.
2. From the User Exec mode, enter the SHOW STACK command:
awplus> show stack
The command lists the switches in the stack. An example is show in
Figure 45.
Figure 45. SHOW STACK Command
Here are a couple items to consider:
The command should list all the switches in the stack. If the list is
incomplete, refer to Chapter 9, “Troubleshooting” on page 111.
The Operational Status field displays “Normal operations” when
the switches are connected in the ring topology and “Not all stack
ports are up” when the switches are connected in the linear
topology.
The priority values will be 128, the default value, if you did not
change them.
Given that there is no relationship between the ID numbers and the
selection of the master switch, the active master in the SHOW
STACK command might not have the ID number 1.
3. Do one of the following:
96
If you want to change the priority values of the switches, go to
“Setting the Priority Numbers” on page 97. The procedure is
optional.
Page 97

x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
awplus# configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
awplus(config)#
Otherwise, go to Chapter 8, “Cabling the Networking Ports” on
page 103, to continue with the installation.
Setting the
Priority Numbers
This procedure is optional. It explains how to configure the priority settings
of the switches. Changing the priority settings protects the stack
configuration should you ever power on the stack with a new member
switch that has a lower MAC address than an existing master or member
switch.
This procedure assumes you are continuing directly on from the previous
procedure.
To set the priority values of the switches, perform the following procedure:
1. Use the CONFIGURE TERMINAL command to move from the
Privileged Exec mode to the Global Configuration mode, as shown in
Figure 46.
Figure 46. Moving to the Global Configuration Mode with the CONFIGURE
TERMINAL Command
2. Use the STACK PRIORITY command to set the priority numbers. The
command has this format:
stack
ID_number
priority
priority
The ID_NUMBER parameter is the ID number of the switch whose
priority value you are setting. The range is 1 to 4. The PRIORITY
parameter is the new priority value for the switch. The range is 0 to
255. The default is 128.
Here are a couple examples. To assign the priority value 1 to the
switch with the ID number 1, you enter this command:
awplus(config)# stack 1 priority 1
To set the priority value to 2 on the switch with the ID number 2, you
enter:
awplus(config)# stack 2 priority 2
3. After setting the priority values, enter the EXIT command to return to
the Privileged Exec mode, as shown in Figure 47 on page 98.
97
Page 98

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
awplus(config)# exit
awplus#
awplus# write
Building configuration ...
[OK]
awplus#
Figure 47. Returning to the Privileged Exec Mode
4. Enter the WRITE command to save your change in the configuration
file. The switch displays the confirmation prompt in Figure 48.
Figure 48. Saving the Priority Values with the WRITE Command
5. To end the management session, enter the EXIT command.
6. Go to Chapter 8, “Cabling the Networking Ports” on page 103, to
continue with the installation.
98
Page 99

Monitoring the Initialization Processes
Bootloader 3.0.2 loaded
Press <Ctrl+B> for the Boot Menu
Reading filesystem...
Loading flash:x310-1706_x950-latest.rel...
Verifying release... OK
Booting...
Starting base/first... [ OK ]
Mounting virtual filesystems... [ OK ]
______________ ____
/\ \ / /______\
/ \ \_ __/ /| ______ |
/ \ | | / | ______ |
/ \ \ / / \ ____ /
/______/\____\ \/ /____________/
Allied Telesis Inc.
AlliedWare Plus (TM) v0.0.0
Current release filename: x310-1706_x950-latest.rel
Original release filename: x310-1 706 _x 95 0- 201 40 20 6- 1.rel
Built: Thu Feb 6 01:14:24 NZdT 2014
hwclock:settimeofday: Invalid arg ume nt
Mounting static filesystems... [ OK ]
Checking flash filesystem... [ OK ]
Mounting flash filesystem... [ OK ]
Checking for last gasp debug output... [ OK ]
Checking NVS filesystem... [ OK ]
Mounting NVS filesystem... [ OK ]
Starting base/dbus... [ OK ]
Starting base/syslog... [ OK ]
Starting base/loopback... [ OK ]
You may monitor the initialization sequence of the stack by connecting a
terminal or computer that has a terminal emulator program to the Console
port on any switch in the stack. You will see the messages in Figure 49
here to Figure 51 on page 101.
x310 Series Installation Guide for VCStack
Figure 49. Switch Initialization Messages
99
Page 100

Chapter 7: Powering On the Stack
Starting base/poe_done... [ OK ]
Starting base/sysctl... [ OK ]
Received event poefw.done
Starting base/portmapper... [ OK ]
Received event syslog.done
Starting base/reboot-stability... [ OK ]
Checking system reboot stability... [ OK ]
Starting base/cron... [ OK ]
Starting base/appmond... [ OK ]
Starting hardware/openhpi... [ OK ]
Starting hardware/timeout... [ OK ]
Starting base/inet... [ OK ]
Starting base/modules... [ OK ]
Received event modules.done
Received event board.inserted
Received event hardware.done
Starting network/startup... [ OK ]
Starting base/external-media... [ OK ]
Starting network/stackd... [ OK ]
Starting network/election.timeout... [ OK ]
Received event network.enabled
Initializing HA processes:
hostd, auth, cntrd, epsr, hsl, imipro xyd , ms tp
nsm, rmon, sflowd, udldd, atmfd, imi, irdp d
lacp, lldp, loopprot
Received event network.initialized
00:00:58 awplus-1 HPI: HOTSWAP Pluggable 1.0.27 hotswapped in: 2127931-2
00:00:58 awplus-1 HSL[829]: ERROR: Port 1.0.27 - Only AT-StackXS and AT-
StackOP supported in this port. Please remove.
VCS[904]: No neighboring members found, unit may be in a stand alone
configuration
Received event vcs.elected-master
00:00:58 awplus-1 VCS[904]: Startup speed can be improved by adding 'no stack
1 to configuration
00:00:58 awplus-1 VCS[904]: Member 1 (eccd.6dc1.19ff) has become the Active
Master
Figure 50. Switch Initialization Messages (Continued)
100
 Loading...
Loading...