Page 1

AlliedWareTM OS
How To |
Create a VPN between an Allied Telesis Router
and a Microsoft Windows 2000
1
Client, Without
Using NAT-T
Introduction
This document describes how to provide secure remote access through IP security (IPSec)
Virtual Private Networks (VPN).
This VPN solution is suitable for any business deployment and provides your office with
secure internet access and firewall protection, plus remote encrypted VPN access for staff
who work from home.
You should use the companion Note How To Create A VPN Between An Allied Telesis Router And
A Microsoft Windows 2000 Client, Over NAT-T instead, if:
z the Allied Telesis router is connected to the Internet through a NAT gateway device, such
as an ADSL modem, and/or
z you want to let travelling staff connect to your office from such places as hotel rooms.
This companion How To Note is available from www.alliedtelesis.com/resources/literature/
howto.aspx.
Consider the following typical scenario:
You are the manager of a small business and you have purchased an AR415S for your small
office premises. You have five PCs networked together with a server in your office. You
intend to use your AR4
You also have people who sometimes work from home. You would like these staff members
to have secure (encrypted) remote access through the Internet to the servers in your office,
to allow them to access files, the private Intranet, and business email.
Each staff member has a laptop or PC with Windows 2000 installed.
1. Internet Explorer and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
1
5S as your Internet gateway and for it to provide firewall protection.
C613-16004-00 REV D
www.alliedtelesis.com
Page 2

Which products and releases does it apply to? >
This document describes how to configure the Windows system to use IPSec VPN to connect
1
to your office through the AR4
5S router.
When your staff want to connect to the office they simply use the VPN icon on their desktop to
initiate the IPSec VPN connection.
Which products and releases does it apply to?
The following Allied Telesis routers are most suitable as VPN gateways because they have fast
hardware encryption support and high performance:
z AR4
z AR750S and AR770S
The AR4
1
5S, AR44xS series, and AR450S
1
5S achieves up to 90 Mbps throughput with 3DES or AES encryption.
You can also use older routers as VPN gateways, but they will not have as high performance. The
older routers depend on either the Encryption Mini Accelerator Card (EMAC) or the
Encryption PCI Accelerator Card (EPAC) to perform encryption. They include:
z AR725, AR745, AR720 and AR740 routers
z AR4
z AR300 series routers
1
0 series routers
Finally, you can also use the Rapier 24 and Rapier 24i switches as VPN gateways, but this is
usually not a recommended practice. Doing so means you will lose wire-speed switching of data,
because all traffic needs to be inspected by the firewall and IPSec at CPU processing speed.
Encryption algorithms such as 3DES and AES require a feature licence. This is included on some
models. See your Allied Telesis representative for more information.
1
The configuration is supported on all AlliedWare versions since 2.3.
and was tested using a PC
running Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional, Service Pack 4.
Related How To Notes
Allied Telesis offers How To Notes with a wide range of VPN solutions, from quick and simple
solutions for connecting home and remote offices, to advanced multi-feature setups. Notes also
describe how to create a VPN between an Allied Telesis router and equipment from a number of
other vendors.
For a complete list of VPN How To Notes, see the Overview of VPN Solutions in How To Notes in
the How To Library at www.alliedtelesis.com/resources/literature/howto.aspx.
The collection includes Notes that describe how to interoperate with Windows 2000, XP and
Vista clients.
Page 2 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 3
Security issue >
Office PCs
Office
Windows 2000 Professional
office’s public
IP address
dial-up modem
dial-up modem
cable modem
2 MB pipe
DSL
VPN router
Internet
remote
teleworker
remote
teleworker
remote
teleworker
remote
teleworker
remote
teleworker
network.eps
Security issue
Since this Windows VPN solution is usually used to allow remote access into corporate
networks, a common security concern is “what happens if the remote laptop or PC is stolen or
falls into unauthorised hands?” This is particularly a concern because the VPN connection is
enabled through the standard dial-up networking window that allows username and passwords
to be saved.
A solution to this security concern is to disable the standard behaviour that allows passwords to
be saved. VPN users will then have to enter their password each time they connect.
If you would like to implement this security measure, refer to Microsoft Knowledge Base article
1
72430 by following this link: support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=172430.
This solution works on both Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
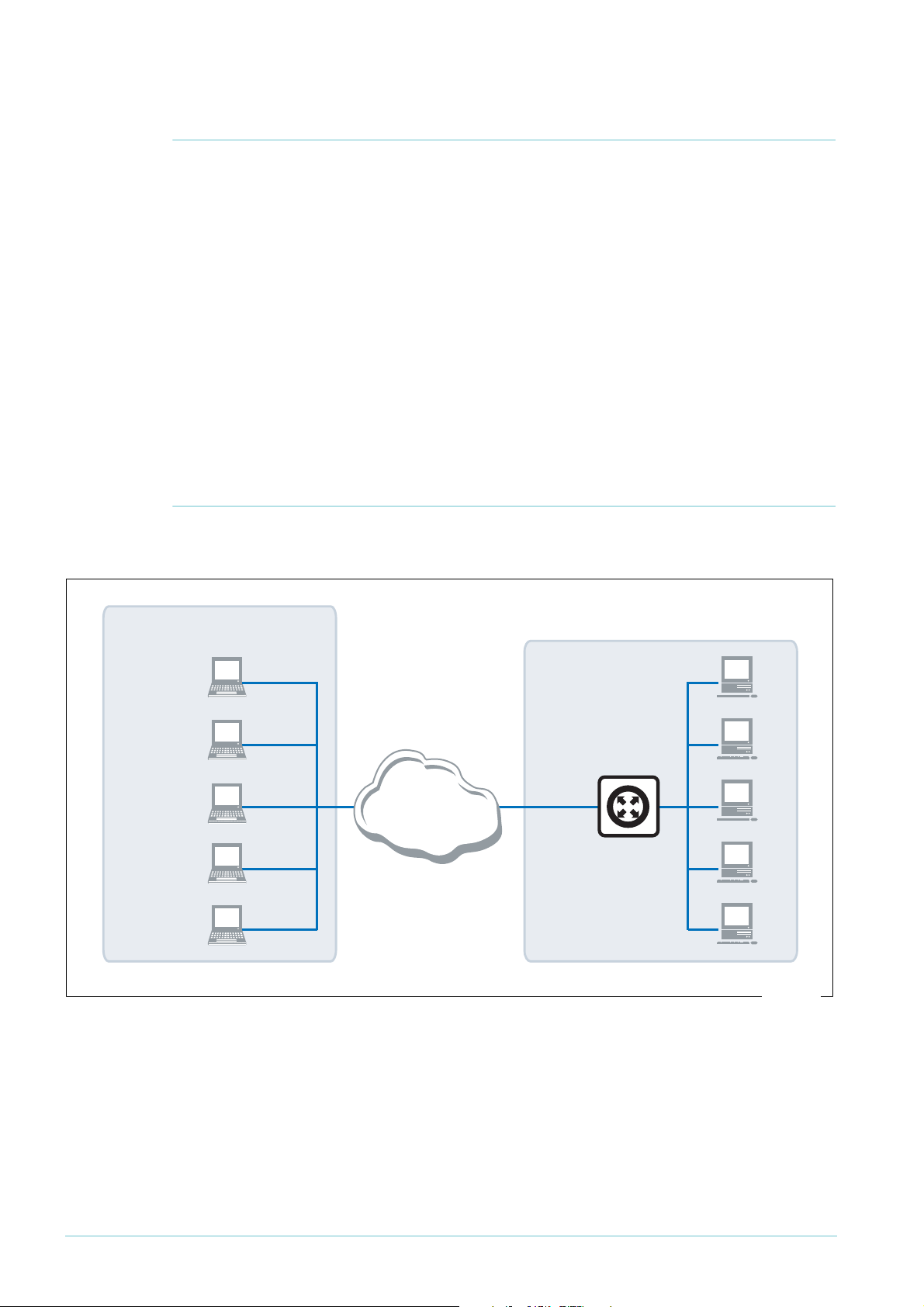
Example network
The following figure shows an example of a network that could use this configuration.
Page 3 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 4

Configuring the router > Perform initial security configuration on the router
Configuring the router
This section contains a script file for running IPSec encapsulating L2TP on a Head Office AR400
series router, configured to support IPSec remote PC clients.
Using this script involves the following steps:
1. "Perform initial security configuration on the router", on this page.
2. Make a copy the script, which starts on page 5. Name it (for example) vpn.cfg.
3. Personalise IP addresses, passwords etc in the script, so that they apply to your network.
Placeholders for these are indicated in the script by text within < >.
4. Load the script onto the router using ZMODEM or TFTP.
5. "Set the router to use the configuration" on page 7.
6. Restart the router or activate the script.
Perform initial security configuration on the router
Before loading the configuration, you need to do the following steps.
1. Define a security officer.
add user=secoff password=<your-password> priv=securityofficer
This command must be in the configuration script as well.
2. Enable system security. Unless you do this, rebooting the router destroys encryption keys.
enable system security
3. Log in as the security officer.
login secoff
4. Generate a random key.
create enco key=1 type=general value=<alphanumeric-string>
Note the value of the string you have entered so that you can load it on the PC clients. This
shared key will be used to encrypt ISAKMP negotiation.
Page 4 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 5
Configuring the router > The configuration script
The configuration script
Note: Comments are indicated in the script below using the # symbol.
Placeholders for IP addresses, passwords, etc are indicated by text within < >
set system name=”IPSec Gateway”
# The command below shows the Security Officer inactive timeout delay.
# The default is 60 seconds. During setup you can instead use 600
# seconds if desired.
set user securedelay=600
# The incoming L2TP calls will be CHAP authenticated.
# They may be authenticated against the router's user database as
# configured below, or against a RADIUS Server if configured.
add user=dialin1 pass=friend1 login=no
add user=dialin2 pass=friend2 login=no
add user=dialin3 pass=friend3 login=no
add user=dialin4 pass=friend4 login=no
add user=secoff pass=<your-password> priv=securityOfficer login=yes
set user=secoff description=”Security Officer Account”
# If RADIUS server support is needed, use a line such as this:
# add radius server=<your-RADIUS-server-address> secret=<secret-key>
# All dynamic incoming L2TP calls will associate with this PPP template
# as indicated below.
create ppp template=1 bap=off ippool="ip" authentication=chap echo=10
lqr=off
# To cater for dynamic creation of incoming L2TP calls enter the
# following commands.
enable l2tp
enable l2tp server=both
add l2tp ip=1.1.1.1-255.255.255.254 ppptemplate=1
# The IP address allows for any valid Internet address.
enable ip
add ip int=vlan1 ip=<office-private-LAN-address>
add ip int=eth0 ip=<office-Internet-address> mask=<appropriate-mask>
# The default route to the Internet.
add ip route=0.0.0.0 mask=0.0.0.0 int=eth0
next=<your-Internet-gateway-or-ISP-next-hop-address>
# The IP pool addresses are the internal address ranges you want to
# allocate to your IPSec remote PC clients
# (e.g. ip=192.168.8.1-192.168.8.254).
create ip pool=ip ip=<pool-range>
Page 5 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 6

Configuring the router > The configuration script
# Firewall
enable fire
create fire poli=main
create fire poli=main dy=dynamic
add fire poli=main dy=dynamic user=ANY
add fire poli=main int=vlan1 type=private
# Dynamic private interfaces are accepted from L2TP, which are from
# IPSec only.
add fire poli=main int=dyn-dynamic type=private
add fire poli=main int=eth0 type=public
# The firewall allows for internally generated access to the Internet
# through the following NAT definition.
add fire poli=main nat=enhanced int=vlan1 gblint=eth0
# This NAT definition allows Internet access for remote VPN users by
# providing address translation.
add fire poli=main nat=enhanced int=dyn-dynamic gblint=eth0
add fire poli=main rule=1 int=eth0 action=allow prot=udp
ip=<office-Internet-address> port=500
gblip=<office-Internet-address> gblpo=500
# Rule 2 becomes the L2TP tunnel allow rule. Additional security is
# provided by only allowing traffic from IPSec tunnels.
add fire poli=main rule=2 int=eth0 action=allow prot=udp
ip=<office-Internet-address> port=1701
gblip=<office-Internet-address> gblpo=1701 encap=ipsec
create ipsec sas=1 key=isakmp prot=esp encalg=3desouter hashalg=sha
mode=transport
create ipsec sas=2 key=isakmp prot=esp encalg=3desouter hashalg=md5
mode=transport
create ipsec sas=3 key=isakmp prot=esp encalg=des hashalg=sha
mode=transport
create ipsec sas=4 key=isakmp prot=esp encalg=des hashalg=md5
mode=transport
# The ORDER of proposals is important. You should propose the strongest
# encryption first.
create ipsec bundle=1 key=isakmp string=”1 or 2 or 3 or 4”
create ipsec policy=isakmp int=eth0 action=permit lport=500 rport=500
# This is a generic IPSec policy that multiple IPSec remote PC clients
# can connect through.
create ipsec policy=to_HQ int=eth0 action=ipsec key=isakmp bundle=1
peer=any isa=keys
set ipsec policy=to_HQ transport=udp rport=1701
# The following policy allows for internally generated Internet access.
create ipsec policy=Internet int=eth0 act=permit
enable ipsec
create isakmp policy=keys peer=any key=1
set isakmp policy=keys sendd=true
enable isakmp
Page 6 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 7

Configuring the router > Set the router to use the configuration
Set the router to use the configuration
After loading the configuration onto the switch, set the router to use the script after a reboot. If
you named the script vpn.cfg, enter the command:
set conf=vpn.cfg
If you entered the configuration directly into the command line instead of loading the script, save
the configuration by entering the commands:
create conf=vpn.cfg
set conf=vpn.cfg
Page 7 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 8

Configuring the VPN client > Add a new registry entry
Configuring the VPN client
Configuring the Windows 2000 VPN client involves the following stages:
z "Add a new registry entry", on this page
z "Add the IP Security Policy Management snap-in" on page 9
z "Create an IP Security Policy" on page 11
z "Create an IP Security Rule" on page 13
z "Create an IP Filter" on page 16
z "Configure the connection" on page 23
Add a new registry entry
To ensure compatibility, you need to make a change to the registry. This Windows registry
change allows the Windows client to bypass the default encryption scheme, and allows for user
defined encryption parameters, or no encryption.
1. On your desktop, select Start > Run and enter the following command:
regedit
Then click OK.
This opens the Registry Editor.
2. In the Registry Editor, browse to the following folder:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters
3. Right-click on this folder and select New > DWOR D Value . This creates a new entry.
4. Name the new entry “ProhibitIpSec”.
5. Double-click on the ProhibitIpSec entry. This opens a dialog box with the entry’s settings.
6. In the Value data field, enter
1
. Click OK.
7. Restart Windows 2000 so that the changes take effect.
Page 8 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 9

Configuring the VPN client > Add the IP Security Policy Management snap-in
Add the IP Security Policy Management snap-in
Note: You need to know the public IP address for the router from your Internet Service
Provider (ISP) for this configuration.
This example assumes that you have already set up your internet connection.
1. On your desktop, select Start > Run and enter the following command:
mmc
This opens the Console window, as shown in the following figure.
2. Select Console Root > Add/Remove Snap-In.
This opens the Add/Remove Snap-in window, as shown in the following figure.
Page 9 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 10

Configuring the VPN client > Add the IP Security Policy Management snap-in
3. Click Add.
This opens the Add Standalone Snap-In window.
Scroll down the list of Available Standalone Snap-ins and select IP Security Policy Management, as
shown in the following figure.
4. Click Add.
This opens the Select Computer window, which lets you select the computer or domain that
the snap-in will manage. Select Local computer, as shown in the following figure.
5. Click Finish, then Close, then OK, to return to the Console window.
Page 10 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 11

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Security Policy
Create an IP Security Policy
1. On the Console window, click, then right-click IP Security Policies on Local Machine.
2. Select Create IP Security Policy.
This opens the IP Security Policy Wizard, as shown in the following figure.
Page 11 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 12
Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Security Policy
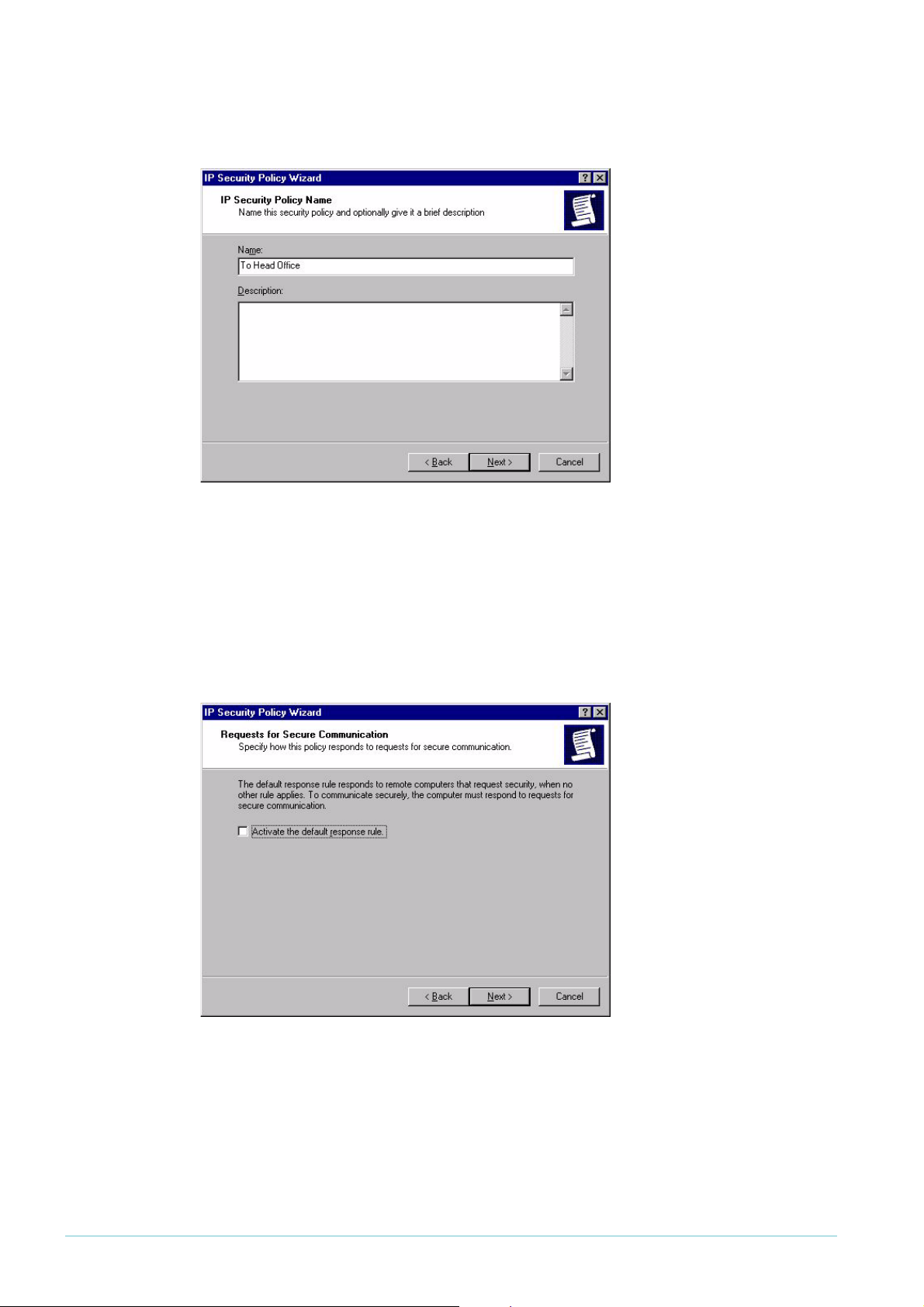
3. Click Next, then enter a name for your security policy (e.g. “To Head Office”), as shown in
the following figure.
4. Click Next.
This opens the Requests for Secure Communication window. Clear the Activate the default
response rule checkbox, as shown in the following figure.
Page 12 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 13

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Security Rule
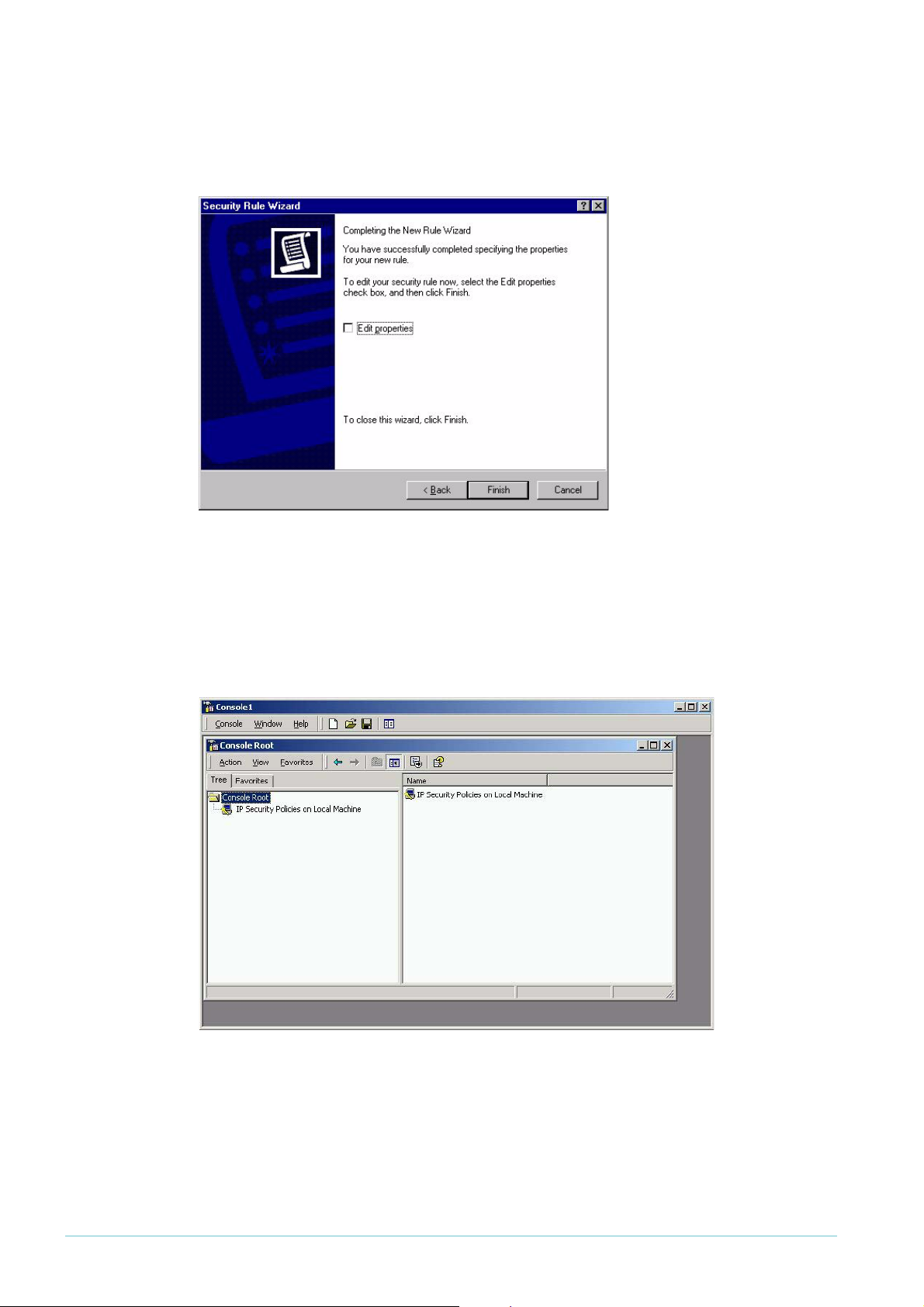
5. Click Next. You have now completed the IP Security Policy Wizard, as shown in the following
figure.
6. Leave the Edit properties checkbox checked. Click Finish.
Create an IP Security Rule
1. Clicking Finish in the previous step opens the IP Security Policy Properties window, as shown in
the following figure.
Page 13 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 14

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Security Rule
2. Click Add. This opens the Security Rule Wizard, as shown in the following figure.
3. Click Next.
The next window lets you specify the tunnel endpoint for the IP Security rule, if required.
A tunnel endpoint is not required for this example. Therefore, make sure This rule does
not specify a tunnel is selected, as shown in the following figure.
Page 14 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 15

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Security Rule
4. Click Next.
The next window lets you specify the network type the IP Security rule applies to. Make sure
the All network connections option is selected, as shown in the following figure.
5. Click Next.
The next window lets you specify the authentication method for the IP Security rule. Select
the Use this string to protect the key exchange (preshared key) option, as shown in the following
figure.
In the text box underneath the option, enter a preshared key that is known to both the
router and the client.
The pre-shared key needs to be the same ISAKMP pre-shared key as is defined on the router
("Generate a random key." on page 4).
Page 15 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 16

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
Create an IP Filter
1. Click Next.
The next window, shown in the following figure, lets you specify the IP filter for the type of
IP traffic the IP Security rule applies to.
2. Click Add to start creating a new filter.
This opens the IP Filter List Name window. Enter a name (e.g. “L2TP Tunnel Filter”), as shown
in the following figure.
Page 16 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 17

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
3. Click Add. This starts the IP Filter Wizard, as shown in the following figure.
4. Click Next.
This opens the IP Traffic Source window. Select My IP Address from the Source address drop-
down box, as shown in the following figure.
Page 17 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 18

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
5. Click Next.
This opens the IP Traffic Destination window. Select A specific IP Address from the Destination
address drop-down box, as shown in the following figure. Enter the destination IP address of
your Allied Telesyn router. This must be a valid Internet address.
6. Click Next.
This opens the IP Protocol Type window. Select UDP from the drop-down box, as shown in the
following figure.
Page 18 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 19
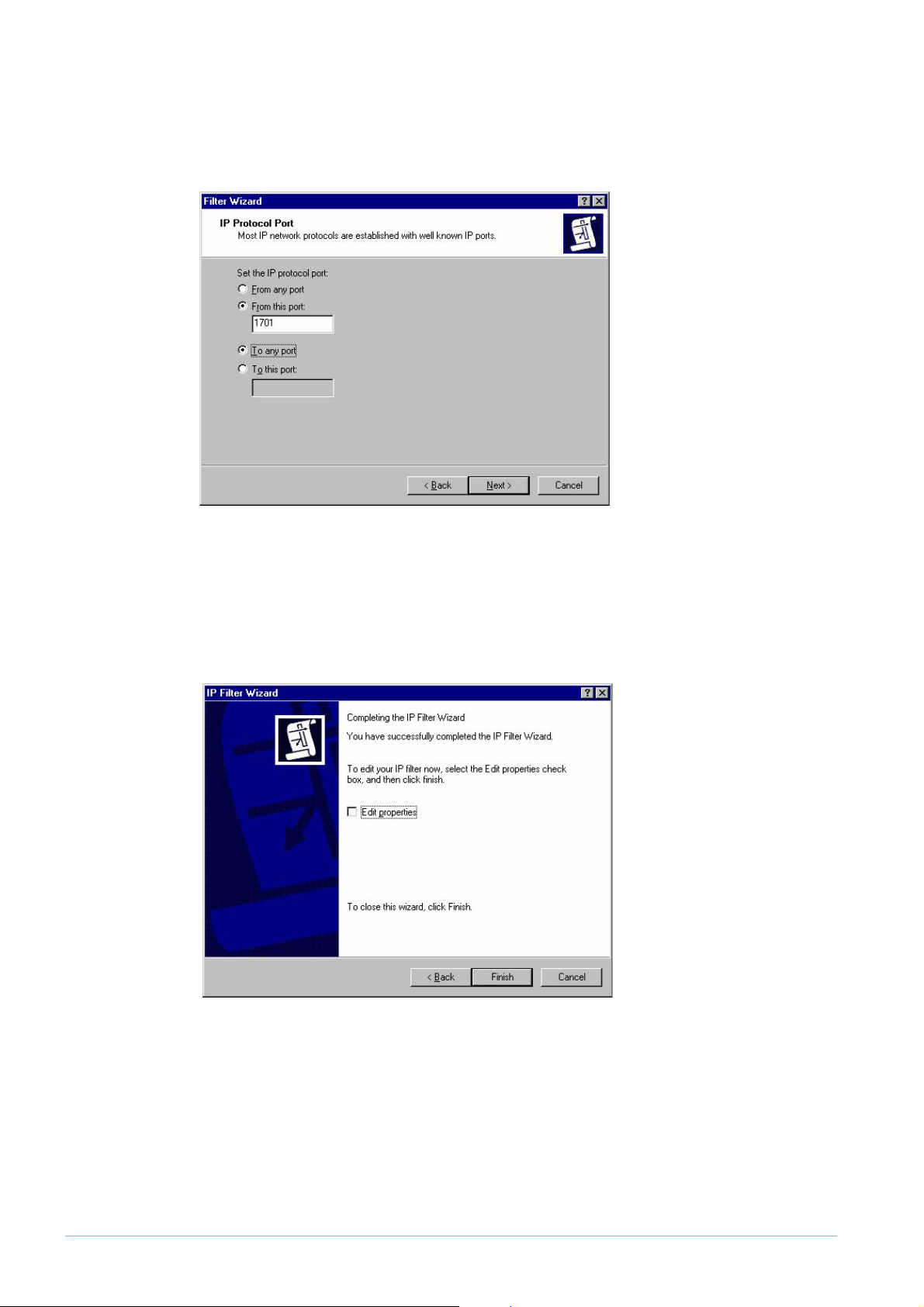
7. Click Next.
Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
This opens the IP Protocol Port window. Select From this port and enter
following figure.
1701
, as shown in the
8. Click Next.
This completes the IP Filter wizard. Leave the Edit properties box unchecked, as shown in the
following figure.
Page 19 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 20

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
9. Click Finish, then on the IP Filter List window, click Close.
This returns you to the Security Rule Wizard IP Filter List window. The filter list now includes
your new L2TP Tunnel Filter filter, as shown in the following figure.
10. Select L2TP Tunnel Filter and click Next.
This opens the Filter Action window. Select Require Security, as shown in the following figure.
This option forces the VPN client to use strong security. Microsoft Windows will not accept
any incoming calls by default. All outgoing calls to your Allied Telesis router will be required
to use IPSec encryption (assuming you use the router configuration from "The configuration
script" on page 5).
Page 20 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 21
Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
11. Click Next.
This completes the Rule wizard. Leave the Edit properties box unchecked, as shown in the
following figure.
12. Click Finish, then on the To Head Office Properties window, click Close.
This returns you to the Console Root window, as shown in the following figure.
Click IP Security Policies on Local Machine.
Page 21 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 22

Configuring the VPN client > Create an IP Filter
13. Click and then right-click on To Head Office, and select Assign. The policy is now assigned or
enabled on your PC host, indicated by Yes in the Policy Assigned column, as shown in the
following figure.
14. Select Exit from the Console menu, to close and save the console window to your local hard
1
drive. This uses the default name of Console
, as shown in the following figure.
Page 22 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 23

Configuring the VPN client > Configure the connection
Configure the connection
1. On your desktop, click Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network and Dial-Up Connection folder.
This opens the window shown in the following figure. Double-click the Make New Connection
icon.
3. This opens the New Connection Wizard. Click Next.
4. Select Connect to a private network through the internet, as shown in the following figure.
Page 23 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 24

Configuring the VPN client > Configure the connection
5. Click Next.
The next window lets you assign an associated dialled call or select Do not dial the initial
connection. Selecting Do not dial the initial connection is appropriate if you will have LAN access
available before initiating the VPN call (for example, if you have a cable modem).
6. Click Next.
Enter the name or IP address of the office router. This will be its Public Internet address,
which the ISP will have allocated you.
Page 24 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 25

Configuring the VPN client > Configure the connection
7. Click Next.
This opens the Connection Availability window. Select Only for myself, as shown in the following
figure.
8. Click Next.
Enter the name for your connection (e.g. Virtual Private Connection to Head Office), as
shown in the following figure. If you want to, check the Add a shortcut to this connection to my
desktop check box.
Page 25 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 26

Configuring the VPN client > Configure the connection
9. Click Finish.
This opens the Connection Window. Enter your user name and password as shown in the
following figure. These are the user name and password that are (or will be) configured on
the router’s user database or RADIUS server.
10. Click Properties.
This opens the Virtual Private Connection to Head Office window. Click the Networking Tab.
Select Layer-2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) in the drop-down box, as shown in the following figure.
Page 26 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 27

Configuring the VPN client > Configure the connection
11. Click OK.
This completes the configuration of the L2TP client. To connect to the office, click Connect.
Note that the connection will fail if the router has not yet been configured.
If the connection succeeds, the following dialog box displays. Click OK.
Page 27 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 28

Testing the tunnel > Checking the connection from the Windows client
Testing the tunnel
The simplest way to tell if traffic is passing through the tunnel is to perform a traceroute from
the Windows 2000 client to a PC in the router’s LAN. To do this, use the following command at
the command prompt on the Windows 2000 client:
tracert <ip-address>
If traffic goes through the tunnel, the traceroute may display IP addresses from one or both
peers’ private networks and public interfaces. If it shows other public IP addresses, then traffic is
not passing through the tunnel.
Checking the connection from the Windows client
To check your connection details, right-click on your connection icon (e.g. Virtual Private
Connection to Head Office) in the Network Connections folder, or on your desktop.
Click Status. Then click the Details tab to check your connection information, as shown in the
following figure.
Troubleshooting
If your tunnel is not working, see the How To Note How To Troubleshoot A Virtual Private Network
(VPN).
This How To Note has detailed information about testing and troubleshooting VPNs on the
router.
Page 28 | AlliedWare™ OS How To Note: VPNs with Windows 2000 clients, without NAT-T
Page 29

USA Headquar ters | 19800 Nor th Cr eek Parkwa y | Suite 200 | Bothell | WA 98011 | USA | T: +1 800 424 4284 | F: +1 425 481 3895
Eur opean Headquar ters | Via Motta 24 | 6830 Chiasso | Switzerland | T: +41 91 69769.00 | F: +41 91 69769.11
Asia-Pacific Headquar ters | 11 T ai Seng Link | Singapor e | 534182 | T: +65 6383 3832 | F: +65 6383 3830
www .alliedtelesis.com
© 2007 Allied Tel esis,
Inc. All rights reser ved.Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
All company names, logos,and product designs that are trademar ks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis is a trademark or registered trademark of Allied Telesis, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Closing the connection
To close your connection, right-click on your connection icon (e.g. Virtual Private
Connection to Head Office) and click Disconnect. The following figure shows this.
.
C613-16004-00 REV D
 Loading...
Loading...