Page 1
SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Hardware Reference
AT-SB4108-00
AT-SB4108-60
AT-SB4108-80
AT-SB4104-00
AT-SB4104-80
Page 2

SwitchBlade Hardware Reference
Document Number C613-03060-00 REV H.
© 2002-2009 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to change specifications and other information in
this document without prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject
to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesis, Inc. be liable for any
incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not
limited to lost profits, arising out of or related to this manual or the information
contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been advised of, known, or should have
known, the possibility of such damages.
All company names, logos, and product designs that are trademarks or registered
trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Hardware Reference 3
Contents
Models Covered by this Reference .................................................................... 5
Why You Should Read this Reference ................................................................ 6
Where to Find More Information ....................................................................... 6
SwitchBlade Overview ....................................................................................... 7
Key Hardware Components ........................................................................ 7
Chassis Models ........................................................................................... 7
Power Supplies ........................................................................................... 9
Switching Performance and Characteristics ............................................... 10
Master Switch Controller and Slave Switch Controller Interactions ............ 10
Hot Swapping ................................................................................................. 10
Hot-swapping a Line Card ........................................................................ 11
Physical and Operating Specifications .............................................................. 15
AT-SB4108 SwitchBlade 8 Card Chassis .................................................... 15
AT-SB4104 SwitchBlade 4 Slot Chassis ...................................................... 17
AT-SB4161 & 2 SwitchBlade Power Supply Units ....................................... 19
AT-SB4152 Fan Tray (For SwitchBlade 8) .................................................... 21
AT-SB4151 Fan Tray (For SwitchBlade 4) .................................................... 21
AT-SB4211 and AT-SB4211 V2, Switch Controller ..................................... 22
AT-SB4215 Bandwidth Expander ............................................................... 23
AT-SB4311 and AT-SB4311 V2 48-Port (RJ-45) Fast Ethernet Line Card ...... 24
AT-SB4352 and AT-SB4352 V2
32-Port (MT-RJ) Fast Ethernet Line Card .............................................. 25
AT-SB4412 and AT-SB4412 V2 24-Port Gigabit (RJ-45) Ethernet Line Card 26
AT-SB4442 V2 24-Port Gigabit (SFP) Ethernet Line Card ............................ 28
AT-SB4441 and AT-SB4441 V2, 8-GBIC Line Card ..................................... 30
AT-SB4541 V2, 1-port 10GBASE-R Gigabit Ethernet Line Card .................. 31
Alarm Relays and Monitoring .......................................................................... 32
Alarm Relays ............................................................................................ 32
Monitoring ............................................................................................... 33
How Many PSUs do You Need? ....................................................................... 33
Online Documentation .................................................................................... 33
Accessing the CD-ROM and Online Documentation .................................. 33
AT-TFTP Server ................................................................................................. 34
Switch Start-up ............................................................................................... 35
To log In ................................................................................................... 35
To access help .......................................................................................... 36
Start-up Procedures .................................................................................. 37
Management Interfaces .................................................................................. 39
RS-232 Terminal Port (ASYN0) .................................................................. 39
RJ-45 Management Port (ETH0) ................................................................ 40
Useful Cables .................................................................................................. 41
RS-232 Terminal and Modem Cables ........................................................ 41
Cables for RJ-45 Ethernet LAN Interfaces .................................................. 43
Test Facility ..................................................................................................... 45
Ethernet LAN Port Tests ............................................................................ 45
Other Interface Tests ................................................................................. 46
Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 47
LEDs and What They Mean ....................................................................... 47
Check these first ...................................................................................... 50
Some common problems and how to solve them ..................................... 50
Content Addressable Memory (CAM) .............................................................. 51
Expansion Options .......................................................................................... 52
Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs) ..................................................... 52
Installing DIMM ........................................................................................ 52
Testing DIMM ........................................................................................... 54
Gigabit Interface Converters (GBICs) ......................................................... 56
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 4

4 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Port, Connector, and Cable Combinations ...................................................... 58
Using Windows Terminal and Hyperterminal ................................................... 59
Restricted Procedures ...................................................................................... 62
Diagnostics ............................................................................................... 62
Contacting Us ................................................................................................. 64
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 5
Hardware Reference 5
Documentation Roadmap
SwitchBlade
Safety and Statutory Information Booklet
Hardware Reference
Software Reference
Chassis & Fan Tray Quick Install Guide
Power Supply Unit Quick Install Guide
Switch Controller Quick Install Guide
Line Card Quick Install Guide
Bandwidth Expander Quick Install Guide
CAM Quick Install Guide
General Customer Support
Visit www.alliedtelesyn.co.nz for
the latest documentation, FAQs,
and support information.
Printed Acrobat PDF
Website
Models Covered by this Reference
This Hardware Reference includes information on the following SwitchBlade
components:
■ AT-SB4108-00 SwitchBlade 8 Triple AC Feed Chassis
■ AT-SB4108-60 SwitchBlade 8 Dual AC Feed Chassis
■ AT-SB4108-80 SwitchBlade 8 Dual DC Feed Chassis
■ AT-SB4104-00 SwitchBlade 4 AC Chassis
■ AT-SB4104-80 SwitchBlade 4 DC Chassis
■ AT-SB4161 SwitchBlade AC Power Supply Unit
■ AT-SB4161-80 SwitchBlade DC Power Supply Unit
■ AT-SB4162-V2 SwitchBlade AC Power Supply Unit
■ AT-SB4162-80 SwitchBlade DC Power Supply Unit
■ AT-SB4152 SwitchBlade 8 Fan Tray
C613-03060-00 REV H
■ AT-SB4151 SwitchBlade 4 Fan Tray
■ AT-SB4211 Switch Controller
■ AT-SB4215 Bandwidth Expander
■ AT-SB4311 48-port 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX (RJ-45) Line Card
■ AT-SB4352 32-port 100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) Line Card
■ AT-SB4412 24-port Gigabit (RJ-45) Line Card
■ AT-SB4442 24-port 1000Base-X (SFP) Line Card
■ AT-SB4441 8-port 1000BASE-X (GBIC) Line Card
■ AT-SB4541 1-port 10GBASE-LE (XFP) Line Card
Page 6

6 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
The latest SwitchBlade Hardware Reference can be found at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
Why You Should Read this Reference
This reference provides hardware related information for the SwitchBlade,
including information on the chassis, switch controllers, line cards, power
supplies, and fan tray.
The reference has two primary aims:
1. To familiarise you with the SwitchBlade’s hardware features.
2. To assist you with setting up and maintaining your SwitchBlade’s
hardware.
Step by step instructions for installing specific SwitchBlade components (such
as switch controllers and line cards) can be found in the Quick Install Guide for
each component.
Keep this reference (or its CD-ROM) in a safe place, you will need it if you purchase
switch expansion options, such as line cards, in the future.
This reference does not cover software configuration or software installation procedures.
For information on software, refer to the SwitchBlade Software Reference.
Where to Find More Information
The Documentation and Tools CD-ROM bundled with each switch controller
and chassis contains the complete document set for the switch and its
expansion options, as well as tools for managing the switch. This includes the
following:
■ SwitchBlade Safety Booklet - Provides safety and statutory information.
■ SwitchBlade Software Reference - Provides detailed information on
configuring the switch and its software.
■ SwitchBlade Chassis and Fan Tray Quick Install Guide - Outlines the procedure
for installing chassis and fan trays.
■ SwitchBlade Switch Controller Quick Install Guide - Outlines the procedure for
installing switch controllers.
■ SwitchBlade Line Card Quick Install Guide - Outlines the procedure for
installing line cards.
■ SwitchBlade Power Supply Unit Quick Install Guide - Outlines the procedure
for installing AC and DC PSUs.
■ SwitchBlade Bandwidth Expander Quick Install Guide - Outlines the procedure
for installing bandwidth expanders.
■ AT-TFTP Server for Windows - Provides a facility for downloading software
versions.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 7

Hardware Reference 7
■ Adobe Acrobat Reader - Provides a facility for viewing online documentation
in PDF format.
The documents listed here can also be downloaded from the SwitchBlade
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
SwitchBlade Overview
This section provides an introduction to the SwitchBlade’s hardware and
operational characteristics.
Key Hardware Components
SwitchBlade switches are based on a modular design. Several key components
(or modules) are required before the switch will function, these are listed
below:
• Chassis - Contains and interconnects switch components.
• Power Supply Units (PSU) - Provides a number of low voltage DC
supplies for the switches’ internal circuitry. Users may specify either
AC or DC power supplies. For some switch configurations two PSUs
may be necessary, plus an additional PSU where N+1 redundancy is
required.
• Fan tray - Provides cooling fans for the switch and line cards.
• Line cards - Provides layer 2/3 switching and the physical interfaces for
connecting the cables/fibre. Additional line cards may be added to
provide more ports and more port types than can be supplied by a
single card.
• Switch controller - Provides advanced switching operations and
configuration ports for the switch. An additional switch controller may
be added to increase speed and provide switch processing redundancy.
The SwitchBlade’s modular design delivers both reliability and scalability.
Dual switch controllers and multiple power supply units provide the
redundancy needed to ensure continuous network service. Line cards
incorporating Ethernet, fast Ethernet, and gigabit Ethernet (with both copper
and fibre interface options) are supported to meet the needs of rapidly
evolving networks.
Chassis Models
C613-03060-00 REV H
SwitchBlade chassis are available in two fundamental types: an eight slot
chassis (AT-SB4108), and a four slot chassis (AT-SB4104).
The eight slot chassis (AT-SB4108) provides space for the following units:
• two switch controller cards
• eight line cards
• three PSUs
• one AT-SB4151 fan tray
• one cable manager with four loops
Page 8

8 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
The four slot chassis (AT-SB4104) provides space for the following units:
• two switch controller cards (or one switch controller and one
bandwidth expander)
•four line cards
•two PSUs
• one AT-SB4151 fan tray
Both chassis types are available in either AC or DC power supply.
The eight slot AC chassis models can be supplied with either dual or triple
power feeds. These models are listed below:
• AT-SB108-00 triple AC feed
• AT-SB108-60 dual AC feed
All the four slot and DC chassis models are supplied with dual power feeds.
All SwitchBlade controller cards and line cards are compatible with both the
four and eight slot chassis types. For example, an AT-SB4211 switch controller
can be used in both the eight slot chassis and the four slot chassis.
Eight Slot Triple Feed
Models
Eight Slot Dual Feed
Models
The bandwidth expander (AT-SB4215) can be used only in switch controller
bay B of the four slot chassis.
Fan trays can be used only in their own particular chassis type. The AT-SB4151
fan tray can only be used in the four slot chassis, while the AT-SB4152 fan tray
can only be used in the eight slot chassis.
Power Feed Options
The eight slot AC chassis is available with either triple AC power feeds or dual
AC power feeds. The eight slot DC chassis is only available with dual DC
power feeds.
In these models each power feed connects only to its own associated power
supply. Therefore, if power to a particular feed is lost, then the PSU associated
with that feed will cease to operate. If the chassis contains three PSUs then
power will continue be drawn from the remaining two PSUs. However, with
only two PSUs installed, a disconnected power feed will result in power only
being supplied from the single remaining PSU, which, depending on
configuration, may - or may not - be sufficient to meet the chassis’ full power
requirements.
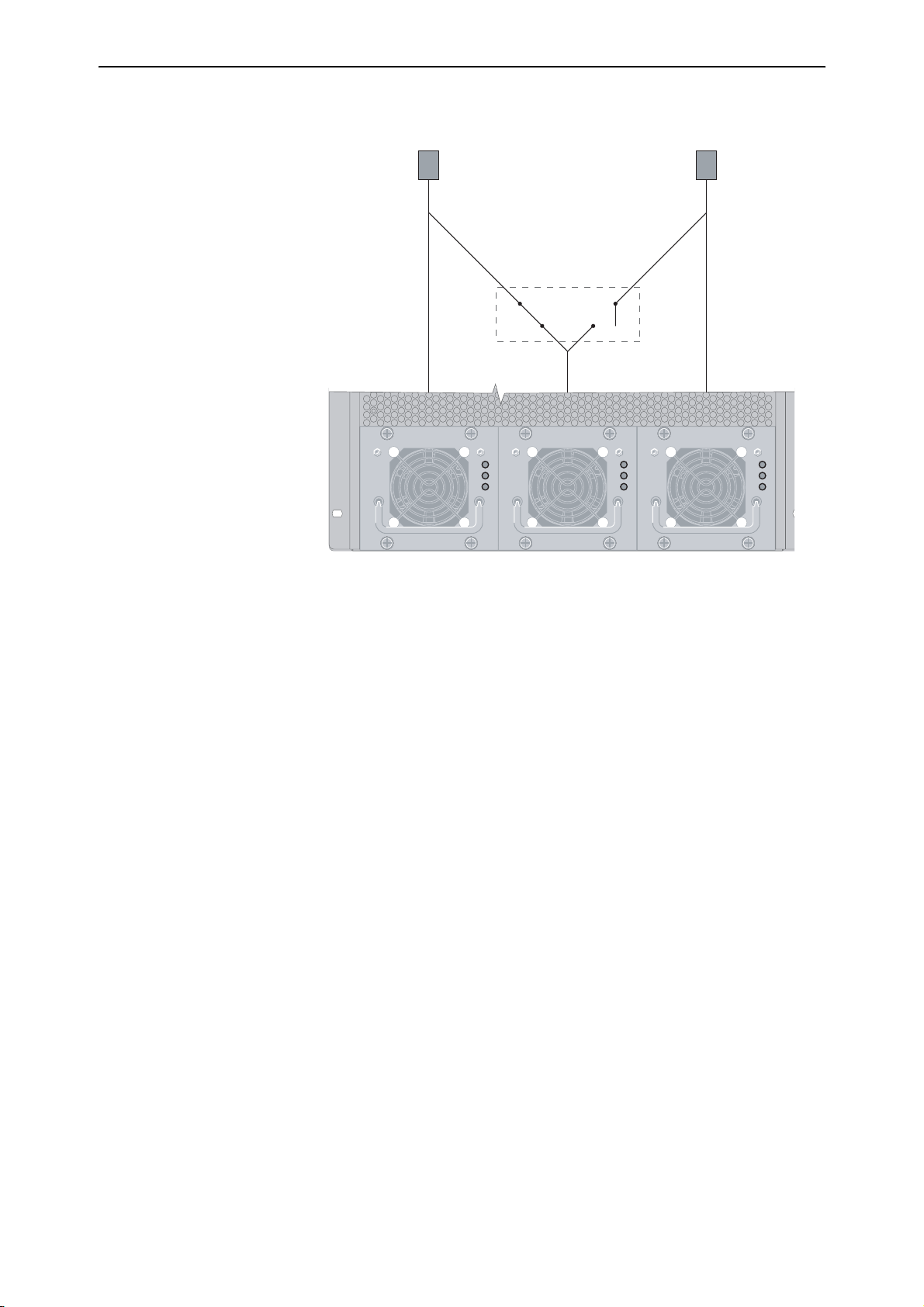
In these models, two feeds supply power to the chassis, which can contain up
to three PSUs. To provide power feed redundancy, a relay is used to enable
each of the two feeds to supply power to both its own PSU, plus the PSU
located in the centre bay, as shown.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 9
Hardware Reference 9
Power Feed 1
Power Feed 2
Relay
AT-SB4162 AC POWER SUPPLY
AT-SB4162 AC POWER SUPPLY
DC
DC
GOOD
GOOD
FAN
FAN
GOOD
GOOD
POWER
POWER
PRESENT
PRESENT
AT-SB4162 AC POWER SUPPLY
AT-SB4162 AC POWER SUPPLY
DC
DC
GOOD
GOOD
FAN
FAN
GOOD
GOOD
POWER
POWER
PRESENT
PRESENT
PSU 1 PSU 2 PSU 3
AT-SB4162 AC POWER SUPPLY
DC
GOOD
FAN
GOOD
POWER
PRESENT
Dual Power Feed Connections
In the default mode, power feed1 supplies power to PSU 1 and PSU 2, and
power feed 2 supplies power only to PSU 3. Power feed redundancy is
provided as follows:
■ If power is disconnected from power feed 2, then PSU 1 and PSU 2 will
continue to supply power from power feed 1.
■ If power is disconnected from feed 1, then the relay will switch to
disconnect PSU 2 from power feed 1 and reconnect it to power feed 2. DC
power will then be provided via PSU 2 and PSU 3.
Power Supplies
The SwitchBlade chassis and power supplies offer a number of options such as
hot swapping that provide varying degrees of resiliency and recovery.
See “Power Feed Options” on page 8, “AT-SB4161 & 2 SwitchBlade Power
Supply Units” on page 19, and “How Many PSUs do You Need?” on page 33.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 10

10 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Switching Performance and Characteristics
The SwitchBlade architecture is based on a non-blocking wire-speed Layer 2
and 3 switching fabric. Layer 3 switching is performed by line cards as well as
switch controllers. As with other Allied Telesis Layer 3 switches, the
SwitchBlade includes full multiprotocol routing capabilities.
Layer 3 switching performance is determined by the number of switch
controllers and line cards that are installed. If two switch controllers are
installed, each line card operates at maximum bandwidth. This provides
switching capacity of 192 Gbps for the 4 slot chassis, and 384 Gbps for the 8 slot
chassis. The 4 slot chassis can also achieve maximum bandwidth when one
switch controller and a bandwidth expander (AT-SB4215) are installed.
Master Switch Controller and Slave Switch Controller Interactions
The first switch controller to be installed in a chassis should be located in
switch controller bay A. This controller acts as the master switch controller,
performing all table updates and packet exception processing. Its “Master”
LED lights to confirm that it is the master switch controller.
When a second switch controller is installed, it is automatically designated
slave status. In this case the master still performs all table updates and packet
exception processing, but the switching load is shared between the two
controllers, while the slave maintains copies of the master’s routing tables.
Installing two switch controllers enables processing redundancy. If a switch
controller fails, or is removed, then the other controller assumes master status
and continues all processing operations. If the only operational controller is in
Bay B, then this will retain master status until an operational controller is
inserted in Bay A and a system reset or restart occurs.
Hot Swapping
Hot swapping is the replacement of a component (such as a line card) while the
switch is powered up. The following SwitchBlade components can be hot
swapped:
• Power supply units (PSUs). The switch will continue to operate as long
as sufficient functional PSUs remain in place to meet the switch’s power
demand. “How Many PSUs do You Need?” on page 33 provides more
information on switch configurations and their power demands.
Note that only certain power supplies are fully hot swapable and that
this ability relates to the PSU being inserted, not the one being removed.
The following PSUs are fully hot swapable: AT-SB4162-V2 AC PSU, and
AT-SB4162-80 DC PSU.
• Fan trays. Although the switch can operate for short periods without a
fan tray, such as while exchanging fan trays, it should not left running
for longer periods without a fan tray operating.
• Switch controllers. The switch will continue to operate as long as at least
one functional switch controller (master or slave) remains in place,
although a brief pause in switching and routing may occur. Packets
passing through the switch during a switch-controller hot swap will be
lost.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 11

Hardware Reference 11
• Line cards. Equivalent cards can be exchanged without having to
reconfigure the switch. For example, if an AT-SB-4311 line card is
removed and replaced with a new AT-SB-4311 (in the same bay), the
new card will use the original card’s configuration (as long as the switch
is not restarted before the new card is installed).
The next section describes the configuration effects of hot-swapping a
line card.
Hot-swapping a Line Card
Line cards can be hot swapped without requiring without requiring any
notification to the switch. The SwitchBlade detects that a card is being removed
and sets itself to a safe state. Insertion of any card into the SwitchBlade is
detected and initialised automatically.
Hot-swapping line cards has the following scenarios:
■ A bay was previously empty and a card is being hot swapped in.
The line card powers up with no configuration, adding all of its ports to the
default VLAN.
■ A bay was previously occupied and a different card type is being hot
swapped in.
The line card powers up and is configured exactly as if the bay were
previously empty. Previous interfaces marked as swapped out for this bay
are replaced with new card interfaces.
■ A bay was previously occupied and the same card type is being hot
swapped in.
The previous VLAN configuration for the card is restored to its previous
condition and previous trunking settings are restored. Interfaces registered
against this card are marked up or down as appropriate. Switch table
entries are restored except for entries that are timed to allow natural expiry
(for example, MAC and IP multicast).
■ A line card is being removed from a bay.
Interfaces registered against this card are marked as swapped out. All
other modules treat these interfaces as being present but no longer active.
Before hot-swapping a line card out of the switch, we recommend that you
save the current configuration by using the command:
create config
Reconfiguring During Hot swap
After a line card has been hot swapped out, the switch can be reconfigured
before the removed line card is returned. The new configuration can be saved
by using the command:
C613-03060-00 REV H
create config
References to the missing ports are retained in the switch’s memory. The
configuration appears the same as if the line card had not been removed. To
display it, use the command:
show config dynamic
When the line card is hot swapped in again, whether its original configuration
is restored depends on the following factors:
Page 12
12 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
■ Whether a power cycle occurred between the create config command and
the line card being replaced, and
■ If a power cycle did occur, whether another create config command has
been entered.
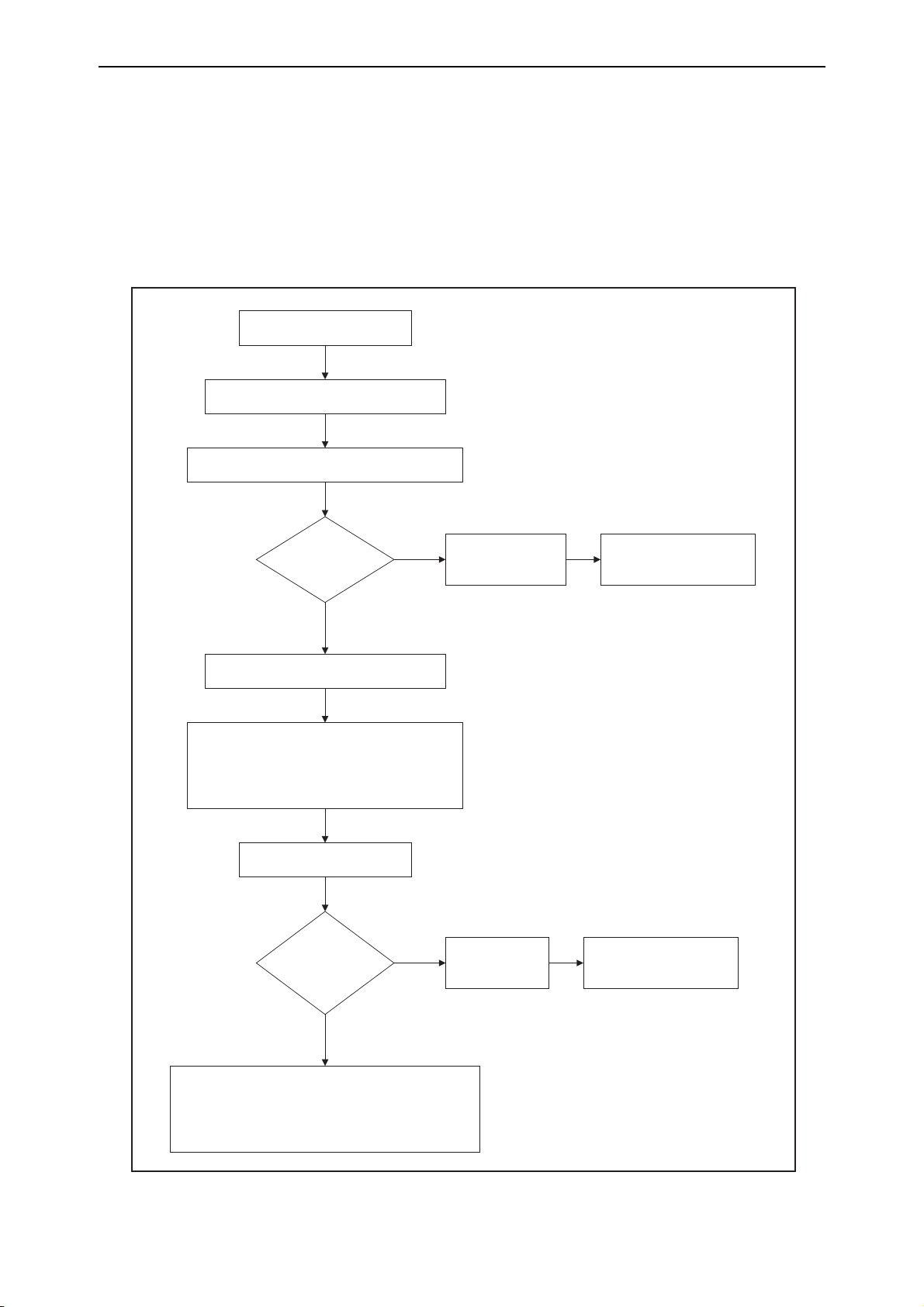
The process flow is shown in Figure 1-1 on page 12.
Figure 1-1: The process flow involved in hot swapping a line card out, changing the switch’s configuration, and then hot
swapping the line card back in
Line card is hotswapped out
The switch is reconfigured.
CREATE CONFIG command is execut ed.
Configuration of swapped-out card is retained,
including references t o miss ing ports .
Power cycle
occ urs?
Yes
Commands referring to missi ng port s fail on
start-up
Switch "remembers" commands with failed ports.
When the dynamic configuration is dis played with
SHOW CONFIG DYNA MIC, missing c ommands
show under "Swapped out" headings.
Card is hotswapped back in.
CREATE CONFIG
exec uted?
No
No
Card is hotswapped
back in.
Switch restarted.
Card's configuration is
restored to what it was
before it was removed.
Card's configuration is
restored to what it was
before it was removed.
Yes
Card's original configuration is lost.
Warning: under these c ircumstances, do not enter
CREATE CONFIG without first res tarting the swi tch,
unless you want t o delete t he original c onfiguration of the
previously-hotswapped card.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 13
Hardware Reference 13
The most desirable situation is to avoid a power cycle before replacing the line
card. However, if a power cycle does occur, the line card’s original
configuration is saved by the switch and can be displayed by using the
command:
show config dynamic
Look for “Swapped out” headings in the Switch (post-VLAN and pre-VLAN),
STP, VLAN, QOS, and GARP sections. To restore the line card’s original
configuration, hot swap the line card back in and restart the switch by using
one of the commands:
restart switch
restart reboot
Do not enter the create config command before performing this restart unless
you want to delete the original configuration of the line card that you hot
swapped back in.
When a configuration file is manually edited, port ranges can only be entered
as a single term when the range does not span across line cards. For example, a
correct entry in a configuration file is:
add vlan=2 port=1.1-1.8,5.1-5.7
An incorrect entry is:
add vlan=2 port=1.1-5.7
If a range that spans several line cards is specified as a single term, the switch is
unable to determine at start-up whether any line cards within the range have
been removed.
This limitation does not apply when a range of ports is entered into a
command on the command line interface because the switch correctly splits the
range when performing a create config command.
Examples
The following examples describe possible scenarios where slots 1 and 2 are
occupied by 8-port line cards and Line Card 1 is hot swapped out.
1. Line Card 1 is removed after being configured via a boot configuration. A
line card of the same type is replaced in the slot.
The second line card is reconfigured to behave exactly as the original line
card. All switch table entries are restored except for entries timed to allow
natural expiry (for example, MAC and IP multicast). Changes to hardware
such as RDRAM or silicon version are used to the greatest extent possible
(for example, performance may change but functionality remains the same).
C613-03060-00 REV H
2. Line Card 1 is removed after being configured via a boot configuration. A
line card of a different type is replaced in the slot.
This situation is the same as if a line card were inserted into a system that
was previously unoccupied. The line card is initialised without
configuration. No configuration from the current configuration file is
applied.
3. Line Card 1 is removed after being configured via a boot configuration and
the slot is left empty.
Page 14

14 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
The switch’s configuration maintains the swapped-out settings. These
result in error messages on start-up, but do not affect the functioning of the
switch. The configuration can be manually edited to remove the swapped
sections that no longer apply.
4. Line Card 1 has been configured and then removed before the configuration
was saved using the create config command. The user then wishes to enter
this command, while keeping the previous configuration of the line card
that has been hot swapped out.
When the create config command is entered, the switch retains the
configuration of the line card that has been hot swapped out. For example,
if the original configuration included the command add vlan=”V2”
port=1.1-2.4, the show config dynamic command would display the
following configuration even though ports 1.1-1.8 no longer exist:
#
# vlan configuration
#
add vlan="v2" port=1.1-1.8
add vlan="v2" port=2.1-2.4
If the switch is then restarted, some of the commands fail and the resulting
dynamic configuration is:
#
# vlan configuration
#
add vlan="v2" port=2.1-2.4
#
# vlan swapped out port configuration
add vlan="v2" port=1.1-1.8
This situation is potentially problematic because the switch has been
restarted before the line card was hot swapped back in. The remaining
examples describe possible ramifications.
5. (continuing from the end of Example 4) The switch is powered down and a
different type of line card (for example, a 48-port line card) is inserted into
slot 1. The switch is then powered up.
Ports 1.1-1.8 are configured as they were for the original 8-port line card.
The remaining ports are added to the default VLAN.
Ultimately the line card is initialised to match as many of the commands
that were previously configured as possible (some settings such as port
speed are not possible).
6. (continuing from the end of Example 4) A line card is inserted into slot 1,
and the configuration saved by using the command:
create config
The line card is initialised without configuration because the commands
stored in the swapped out configuration that refer to this slot are all
removed when the user creates a configuration.
Before the new line card was inserted, the configuration displayed by the
show config dynamic command would have been:
#
# vlan configuration
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 15

Hardware Reference 15
#
add vlan="v2" port=2.1-2.4
#
# vlan swapped out configuration
add vlan="v2" port=1.1-1.8
After the new line card is inserted and the create config command is
entered, the show config dynamic command displays the following
configuration:
#
# vlan configuration
#
add vlan="v2" port=2.1-2.4
7. (continuing from the end of Example 4) The wrong line card is accidentally
inserted into slot 1. The user realises the mistake and removes the line card.
The user has also already made further configuration changes, and saves
the configuration by using the command:
create config
Because the line card that was inserted by accident has been hot swapped,
creating a configuration removes the commands stored in the swapped-out
configuration. When the correct line card is inserted, it is initialised without
configuration.
To avoid loss of the swapped-out configuration in this situation, insert the
correct line card, and restart the SwitchBlade. Then make the other
configuration changes and create the configuration.
Physical and Operating Specifications
This section provides an overview of the SwitchBlade’s physical and operating
specifications.
AT-SB4108 SwitchBlade 8 Card Chassis
Dimensions
• Height: 666 mm (15U rack occupancy)
• Width: 440 mm (excluding rack-mounting brackets). Suitable for 19
inch racks
• Depth: 392.5 mm (539 mm if a cable manager is attached)
• Chassis 8 weight: 19 kg (empty chassis)
C613-03060-00 REV H
• Chassis 8 loaded Weight: 34 to 63.5 kg (depending on the configuration)
Environmental Conditions
• Operating temperature range: 0 to 40º C (32 to 104º F)
• Storage temperature range: -25 to 70º C (-13 to 158º F)
• Relative humidity range: 5 to 95% non-condensing
Page 16

16 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Regulatory Standards
• EMC: EN55022 class A, FCC class A, and VCCI class I
• Immunity testing to EN55024: EN61000-4 levels 2 (ESD), 3
(susceptibility), 4 (fast transients), 5 (power surge), 6 (RF immunity),
and 11 (Voltage dips and sags; EN61000-3 levels 2 (Harmonics), and 3
(Flicker)
• Safety: UL60950, CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-00, EN60950, ACA TS001
Power Supply Options
For PSU specifications and maximum current loads, see “AT-SB4161 & 2
SwitchBlade Power Supply Units” on page 19. The number of PSUs
required depends on the particular configuration selected.
Note: Because certain chassis models contain additional circuitry to control power
supply switching, the voltage ranges specified for the chassis can differ from those
separately specified for the power supply.
AC models
• AT-SB4108-00 Triple AC Feed (100 to 240) V AC, (50 to 60) Hz
input
• AT-SB4108-60 Dual AC Feed (200 to 240) V AC, (50 to 60) Hz
input
DC models
• 48 V DC. Operating voltage range (40 to 60) V DC
• Accepts positive or negative earthing (grounding)
LEDs
• System status LEDs on each switch controller
• Port LEDs on each line card
• Power supply status LEDs on each PSU and switch controller
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Configuration and Management Ports (AT-SB4211 switch controller)
• Standard DB9 female RS-232 connector for configuration and low-level
management (on switch controller)
• 10/100 TX RJ-45 port for switch management (on switch controller)
See “AT-SB4211 and AT-SB4211 V2, Switch Controller” on page 22 for more
information on management ports
Mounting System
• 19 inch rack mounting
• Front rack-mounting brackets incorporated in chassis. Mid or rear
mounting brackets optional
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 17

Hardware Reference 17
Expansion Bays
• Two switch controller bays
• Eight line card bays
• Three power supply bays
• One fan tray bay (compatible with the AT-SB4152 fan tray)
Alarm Relays
• Two relays (Major and Minor) each located on the rear panel
• Normally open and normally closed contacts
• Software configurable for a range of environmental and operational
events
• Suitable for use with DC alarm circuits (12 V DC 1.0 A or 48 V DC 0.5 A)
• See “Alarm Relays and Monitoring” on page 32 for more information
Backplane Links and Bus Connections
• A SwitchBlade chassis contains two controller bays each capable of
housing a switch controller card. See “Switching Performance and
Characteristics” on page 10 for more information.
• 33MHz 64 bit PCI routing and control bus links are present on all switch
controller and line card bays. This bus provides a high performance
communication channel between switch controller CPUs, and also
allows high speed routing between line cards that have WAN interfaces
Cable Management System
• Optional manager can be fitted to the fan tray front panel
• Cable manager supports up to four cable-management loops
Earth/Ground Point
• An earth/ground point is provided on the chassis’s rear panel. This
point can be used to bond the cha ssis to earth/ground. Even if this point
is used, earth/ground leads of AC and DC power supplies must still be
connected
AT-SB4104 SwitchBlade 4 Slot Chassis
Dimensions
• Height: 400 mm 9U rack occupancy
• Width: 440 mm (excluding rack-mounting brackets). Suitable for 19
inch rack
C613-03060-00 REV H
• Depth: 345 mm
• Chassis 4 (AC) weight: 13 kg (empty chassis)
• Chassis 4 (DC) weight: 13 kg (empty chassis)
• Chassis 4 loaded weight: 23 kg to 45 kg (depending on the
configuration)
Page 18

18 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Environmental Conditions
• Operating temperature range: (0 to 40) ºC, (32 to 104) ºF
• Storage temperature range: (-25 to +70) ºC, (-13 to +158) ºF
• Relative humidity range: 5 to 95% non-condensing
Regulatory Standards
• EMC: EN55022 class A, FCC class A, and VCCI class I
• Immunity testing to EN55024: EN61000-4 levels 2 (ESD), 3
(susceptibility), 4 (fast transients), 5 (power surge), 6 (RF immunity),
and 11 (Voltage dips and sags; EN61000-3 levels 2 (Harmonics), and 3
(Flicker)
• Safety: UL60950, CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-00, EN60950, ACA TS001
Power Supply Options
For PSU specifications and maximum current loads, see “AT-SB4161 & 2
SwitchBlade Power Supply Units” on page 19. The number of PSUs
required depends on the particular configuration selected, i.e. the number
of line cards, controller cards installed. Consult your authorised Allied
Telesis distributor or reseller for more information.
Note: Because certain chassis models contain additional circuitry to control power
supply switching, the voltage ranges specified for the chassis can differ from those
separately specified for the power supply.
AC models
• Universal (110 to 240) V AC, (50 to 60) Hz input
DC models
• 48 V DC, (40 to 60) V DC operating range
• Accepts positive or negative earthing (grounding)
LEDs
• System status LEDs on each switch controller
• Port LEDs on each line card
• Power supply status LEDs on each PSU and switch controller
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Configuration and Management Ports (AT-SB4211 switch controller)
• Standard DB9 female RS-232 connector for configuration and low-level
management (on switch controller)
• 10/100TX RJ-45 port for switch management (on switch controller)
See “AT-SB4211 and AT-SB4211 V2, Switch Controller” on page 22 for more
information on management ports
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 19

Hardware Reference 19
Mounting System
• 19 inch rack mounting
• Front rack-mounting brackets incorporated in chassis. Mid or rear
mounting brackets optional
Expansion Bays
• Two switch controller bays
•Four line card bays
• Two power supply bays
• One fan tray bay (compatible with the AT-SB4151 fan tray)
Alarm Relays
• Two relays on rear panel
• Normally open and normally closed contacts
• Software configurable for a range of conditions
• See “Alarm Relays and Monitoring” on page 32 for more information
Backplane Links and Bus Connections
• A SwitchBlade chassis contains two controller bays each capable of
housing a switch controller card. See “Switching Performance and
Characteristics” on page 10 for more information.
• 33 MHz 64 bit PCI routing and control bus links all switch controller
and line card bays. This bus provides a high performance
communication channel between switch controller CPUs, and also
allows high speed routing between line cards that have WAN
interfaces.
Earth/Ground Point
• An earth/ground point is provided on the chassis’s rear panel. This
point can be used to bond the cha ssis to earth/ground. Even if this point
is used, earth/ground leads of AC and DC power supplies must still be
connected.
AT-SB4161 & 2 SwitchBlade Power Supply Units
For guidelines on how many PSUs are required for a particular configuration,
see “How Many PSUs do You Need?” on page 33.
LEDs
C613-03060-00 REV H
• Three LEDs indicate power supply status (input, output, and fan status)
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Power Supply Specifications
Weight
• 3.6 kg
Page 20

20 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Cooling
•Built-in fan
• Monitoring of PSU fans for stalled or slow speed
LEDs
• Three LEDs indicate power supply status (input, output, and fan status)
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Electrical Specifications Per Chassis Type
Eight Slot Triple Feed AC Chassis (SB4108-00)
• (100 to 240) V AC (50 to 60) Hz input
For a fully loaded chassis with eight line cards and a fan tray installed
• Maximum continuous current draw for each active PSU, 4 A at 240 V,
8 A at 120 V (due to load sharing, redundant PSUs do not add to the
total continuous current drawn).
• Maximum inrush current for each PSU (cold start), 75 A at 240 V, 37 A
at 120 V.
Eight Slot Dual Feed AC Chassis (SB4108-60)
• 200 V to 240 V AC (50 to 60) Hz input
For a fully loaded chassis with eight line cards and a fan tray installed
• Maximum continuous current draw for each active power feed, 8Aat
240 V, 16 A at 120 V.
• Maximum inrush current for each power feed (cold start), 150 A at
240 V, 75 A at 120 V.
Four Slot Dual Feed AC Chassis (SB4104-00)
• 100 V to 240 V AC (50 to 60) Hz input
For a fully loaded chassis with eight line cards and a fan tray installed
• Maximum continuous current draw for each active power feed, 8A at
240 V, 16 A at 120 V.
• Maximum inrush current for each PSU (cold start), 75 A at 240V, 37 A at
120V.
Eight Slot Dual Feed DC Chassis (SB4108-80)
Fully loaded chassis with four line cards and a fan tray installed
• Maximum continuous current draw for each active power feed, 30A
within the rated input voltage range.
• Maximum inrush current for each PSU (cold start), A within the rated
input voltage range.
• Accepts positive or negative earthing (grounding)
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 21

Hardware Reference 21
Four Slot Dual Feed DC Chassis (SB4104-80)
Fully loaded chassis with four line cards and a fan tray installed
• Maximum continuous current draw for each active power feed, 15A
within the rated input voltage range.
• Maximum inrush current for each PSU (cold start), A within the rated
input voltage range.
• Accepts positive or negative earthing (grounding)
AT-SB4152 Fan Tray (For SwitchBlade 8)
Weight
• 3.5 kg
Compatibility
• For use with the 8 card chassis, AT-SB4108
Fans
• Each fan tray includes six fans
Fault Indicators
• Switch controller LEDs indicate fan and switch overheating faults
• Message triggers can send messages to designated users or terminals
AT-SB4151 Fan Tray (For SwitchBlade 4)
Weight
• 2.0 kg
Compatibility
• For use with the 8 card chassis, AT-SB4104
Fans
• Each fan tray includes four fans
Fault Indicators
C613-03060-00 REV H
• Switch controller LEDs indicate fan and switch overheating faults
• Messages triggers can send messages to designated users or terminals
Page 22

22 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
AT-SB4211 and AT-SB4211 V2, Switch Controller
Weight
AT-SB4211 V2
SWITCH CONTROLLER
STATUS
POWER
MASTER
FAULT
• 2.5 kg
LEDs
• Three system status and fault LEDs, and two LEDs to indicate status of
the ETH0 management port (link activity, full/half-duplex, and
collisions)
For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What They
Mean” on page 47.
Switching Core
• Two Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) switch chips per
switch controller
• Non-blocking L2 and L3 IP Switching (may require two switch
controllers to be installed for some chassis configurations)
• 104 k entry forwarding address database
• 128 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer
Processing Core
• 500 MHz PowerPC Processor
• 1 Mbyte of external L2 cache
MANAGEMENT
E10 / 100 BASE-T
L/A
D/C
100M
FULL DUP
HALF DUP
10M
COLLISION
ACTIVITY
L/A
D/C
ETH0
MANAGEMENT
RS-232
ASYN0
RESET
AT-SB4211 V2
Line Card
• 256 MBytes Synchronous DRAM
• 64 bit memory width
• 32 MBytes flash memory
• 512 kBytes Non-volatile Storage SRAM (NVRAM)
• Battery backed real time clock (RTC)
Asynchronous Serial Configuration Port
•Up to 115 kbps
• Standard DB9 female RS-232 connector
• Hardware or software flow control
10/100BASE-TX Management Port
• 10/100BASE-TX MDI port with RJ-45 connector
• LEDs indicate link activity, full/half-duplex, and collisions
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 23

Hardware Reference 23
AT-SB4215 Bandwidth Expander
The bandwidth expander card achieves the performance of the dual
controller configuration, without incurring the cost of a second controller
AT-SB4215
card.
The bandwidth expander card is used in controller slot B to utilise unused
internal ports, i.e. those ports that would normally be assigned to line
cards 5 to 8 on the 8 slot chassis. This achieves the same level of
performance as using two controller cards. It does not, however, provide
the redundancy obtained by the dual controller card configuration.
Weight
• 2.3 kg
Compatibility
• Can only be used in slot B of the SwitchBlade 4 card chassis (AT-SB4104)
Functionality
• Maximises the bandwidth available.
• Has no external ports, interfaces or LEDs
AT-SB4215
Bandwidth
Expander
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 24

24 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
A
AT-SB4311 and AT-SB4311 V2 48-Port (RJ-45) Fast Ethernet Line Card
AT-SB4311 V2
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
AUTO MDI / MDI-X
Weight
1
3
• 2.2 kg
Ports
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
27
• 48 auto-negotiating 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX ports
• Auto MDI/MDI-X negotiation as default (MDI-X if negotiation is
disabled)
• RJ-45 connectors
LEDs
• Single (switchable) dual-mode LED per port
• Indicates full/half duplex, collisions, and link activity and bps speed
(10/100)
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Switching
• Two ASIC switch chips operating in Layer 3 mode
• 40 k entry forwarding address database
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
D/C
L/A
FULL
HALF
D/C
COLL
T-SB4311 V2
Line Card
29
31
• Support for protocol-based VLANS and MAC address learning
• 128 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
33
35
PCI bus
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
37
39
41
43
45
47
L/A
100M
10M
ACT
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 25

Hardware Reference 25
A
AT-SB4352 and AT-SB4352 V2 32-Port (MT-RJ) Fast Ethernet Line Card
AT-SB4352 V2
100 BASE-FX / MT-RJ
L/A
D/C
117
L/A
D/C
218
L/A
D/C
319
L/A
D/C
420
L/A
D/C
521
L/A
D/C
622
L/A
D/C
723
L/A
D/C
824
L/A
D/C
925
L/A
D/C
1026
L/A
D/C
Weight
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
• 2.2 kg
Ports
• Thirty-two 100BASE-FX ports
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
• MT-RJ connectors
LEDs
• Two per port
• Indicate full/half duplex, collisions, and link activity
L/A
D/C
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
L/A
D/C
Switching
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
• Two ASIC switch chips operating in Layer 3 mode
• 40 k entry forwarding address database
• Support for protocol-based VLANS and MAC address learning
• 128 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
PCI bus
1127
L/A
D/C
D/C
1228
L/A
D/C
D/C
1329
L/A
D/C
D/C
1430
L/A
D/C
D/C
1531
L/A
D/C
D/C
1632
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
DO NOT STARE
INTO BEAM
L/A
D/C
LINK
FULL DUP
HALF DUP
ACTIVITY
COLLISION
T-SB4352 V2
Line Card
L/A
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
L/A
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
L/A
L/A
L/A
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 26

26 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
AT-SB4412 and AT-SB4412 V2 24-Port Gigabit (RJ-45) Ethernet Line Card
AT-SB4412 V2
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
Weight
• 2.4 kg
Ports
• Twenty four auto-negotiating, or manually configurable, ports:
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T - all able to operate in either full
duplex or half duplex mode
• Auto MDI/MDI-X as default (MDI-X if auto-negotiation is disabled)
• RJ-45 connectors
Where this card is used to replace the 8 port AT-SB4411, a general rule is to
first use the centre 8 ports shown within the dotted line. This is to equally
distribute the traffic across the card’s two ASIC switch instances and their
connections to the intercard backplane. However, where heavy traffic is
anticipated between ports that are both connected to this card, we
recommend that these ports be grouped within the same switch instance.
This will maximise throughput by locally switching the heavy traffic, and
minimise traffic flow across the backplane. Ports 1 to 12 share one switch
instance (and its backplane connections), whilst ports 13 to 24 share the
other.
LEDs
L/A
D/C
L/A
D/C
AT-SB4412 V2
Line Card
Each port contains two LEDs, a D/C (duplex/collisions) LED, and a L/A
(link speed/activity) LED. Their operation is shown below:
L/A
• Steady Green display indicates that negotiation has completed between
both ends of the link and communication at 1 Gbps has been
established.
• Steady Amber display indicates that negotiation has completed between
both ends of the link and communication at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps has
been established.
• Flashing Green display indicates that the link is actively transmitting data
at 1 Gbps.
• Flashing Amber display indicates that the link is actively transmitting
data at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
D/C
• Steady Green display indicates the link is operating in full duplex mode.
• Steady Amber display indicates the link is operating in half duplex mode.
• Flashing Amber display indicates that the link is detecting collisions applies only to the half duplex mode.
Switching
• Two ASIC switch chips operating in Layer 3 mode and at wire speed.
• 40 k-entry, CAM based, L2/L3 forwarding address database.
• VLAN support, based on: protocol, port, IP subnet, and MAC address.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 27

Hardware Reference 27
• 64 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer, enabling traffic bursting to be
absorbed.
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
PCI bus.
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 28

28 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
AT-SB4442 V2 24-Port Gigabit (SFP) Ethernet Line Card
Weight
AT-SB4442 V2
• 2.4 kg
Ports
• Twenty four full duplex SFP ports. SFP ports can be 1000BASE-T
copper, or 1000BASE (SX, LX, ZX) fibre, depending on the SFP used.
• Auto MDI/MDI-X as default (MDI-X if auto-negotiation is disabled).
Where this card is used to replace an 8 port card, a general rule is to first
use the centre 8 ports shown within the dotted line. This is to equally
distribute the traffic across the card’s two ASIC switch instances and their
connections to the intercard backplane. However, where heavy traffic is
anticipated between ports that are both connected to this card, we
recommend that these ports be grouped within the same switch instance.
This will maximise throughput by locally switching the heavy traffic, and
minimise traffic flow across the backplane. Ports 1 to 12 share one switch
instance (and its backplane connections), whilst ports 13 to 24 share the
other.
LEDs
One per port that indicates the following conditions:
• Steady amber glow:
With a fibre SFP inserted - this indicates that the SFP is fitted into the
port connection.
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
DO NOT STARE
INTO BEAM
SFP
INSTALLED
LINK
FAULTACT
T-SB4442 V2
Line Card
• Flashing amber glow indicates that the SFP is not functioning correctly.
• Steady green glow:
With a copper SFP inserted - this indicates that negotiation has
completed between both ends of the link and communication at 1 Gbps
has been established.
With a fibre SFP inserted - this indicates that the SFP is able to send and
receive a light signal from the connection at the far end of the link.
• Flashing green indicates that there is data activity over the connection.
Switching
• Two ASIC switch chips operating in Layer 3 mode and at wire speed.
• 40 k-entry, CAM based, L2/L3 forwarding address database.
• VLAN support, based on: protocol, port, IP subnet, and MAC address.
• 64 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer, enabling traffic bursting to be
absorbed.
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
PCI bus.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 29

Hardware Reference 29
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 30

30 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
AT-SB4441 and AT-SB4441 V2, 8-GBIC Line Card
Weight
AT-SB4441 V2
GBIC
1000BASE-X GBIC
L/A
• 2.2 kg
1
Ports
• Eight 1000BASE ports
L/A
GBIC
• Compatible with copper (1000BASE-T) and fibre (1000BASE-SX and
1000BASE-LX) GBICs
2
• Compatible with RJ-45, SC, and LC connectors
• For use with Ethernet 5 V GBIC connectors
L/A
GBIC
LEDs
3
L/A
GBIC
4
• Two per port
• Indicate link activity, half duplex, and GBIC status
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Switching
L/A
GBIC
5
L/A
GBIC
• ASIC switch chip operating in Layer 3 mode
• 40 k-entry forwarding address database
• Support for protocol-based VLANS and MAC address learning
• 64 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer
6
L/A
GBIC
7
L/A
GBIC
8
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
DO NOT STARE
INTO BEAM
L/A
GBIC
LINK
ENABLED
HALF DUP
DISABLED
FAULT
ACTIVITY
AT-SB4441 V2
Line Card
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
PCI bus
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 31
Hardware Reference 31
AT-SB4541 V2, 1-port 10GBASE-R Gigabit Ethernet Line Card
AT-SB4541 V2
10GBASE-R
Weight
• 2.2 kg
Ports
• One 10BASE-GE port
• Compatible with 10GE XFP-LR connectors
LEDs
• Indicates XFP connection and operational status
• Indicates link operational status and activity
• For a complete list of LEDs and their functions, see “LEDs and What
They Mean” on page 47
Switching
• Two ASIC switch chips operating in Layer 3 mode
• 40 k entry forwarding address database
• Support for protocol-based VLANS and MAC address learning
• 64 MByte RAMBUS packet buffer
XFP
L/A
CLASS 1
LASER PRODUCT
DO NOT STARE
INTO BEAM
L/A
XFP
LINK
ENABLED
DISABLED
ACTIVITY
NOT READY
AT-SB4541 V2
Line Card
• Either 33 MHz or 40 MHz, depending on the speed of the master card’s
PCI bus
Note: The suffix V2 indicates the card's silicon revision level. Certain enhanced
features, such as LACP, will only run on cards with a V2 revision level. You can also
display the silicon revision of a line card by executing the show switch instance
command (V2 revision level cards are displayed as K1). Refer to the Switching Chapter
of your SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on using this command.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 32

32 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Alarm Relays and Monitoring
This section provides an introduction to the SwitchBlade’s alarm and
monitoring capabilities. All SwitchBlade chassis have two alarm relays on their
rear panel, and extensive software-based logging, SNMP trap, and trigger
monitoring capability.
Alarm Relays
The SwitchBlade’s two alarm relays (“Major” and “Minor”) can be configured
to operate when a number of different environmental and operational events
occur. Users can choose which relay (major or minor) operates for a specific
event. The relays do not operate by default, they will only operate if
specifically configured to do so.
The relays are designed to operate in DC circuits. When placed in these circuits
the relays can operate external alarm devices such as small alarms, lights, or
larger relays. If connecting the relays to a 12VDC circuit, they can switch 1
amp. If connecting the relays to a 48VDC circuit, they can switch 0.5 amp. The
relays have normally open (N/O) and normally closed (N/C) contact options.
Connecting the relays to an AC circuit is likely to damage the relays and switch.
Table 1 on page 32 lists the events that can operate alarms. Refer to
“Environmental Monitoring” on page 4-15 of Chapter 4, Configuring and
Monitoring the System for information on configuring alarm relays, including
complete command descriptions.
ALARM RELAYS
MINOR ALARM
N/O N/C
COMMON
12 VDC
48 VDC
Table 1: Alarm and monitoring events.
Event Description
Fan tray presence Initiates an alarm event if a fan tray is removed for more
than 20 seconds. Initiates a monitoring event when a fan
tray is removed.
Fan tray fan status Initiates alarm and or monitoring events when a fan tray fan
fault is detected.
Fixed CPU high temperature Initiates alarm and or monitoring events if CPU temperature
rises above 90º C (194º F). Temperature is measured at the
master switch controller CPU and slave switch controller
CPU.
Settable CPU Temperature Initiates alarm and or monitoring events if CPU temperature
rises above a value defined by the user. Temperature is
measured at the master switch controller CPU and slave
switch controller CPU.
MAJOR ALARM
N/O N/C
COMMON
, 1A
, 0.5A
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 33

Hardware Reference 33
Table 1: Alarm and monitoring events.
Event Description
Power Supply Unit status Initiates alarm and or monitoring events when a Power
Supply Unit fault is detected.
Power Supply Unit fan status Initiates alarm and or monitoring events when a PSU fan
fault is detected.
Port status Initiates alarm and or monitoring events when a specified
port goes down.
Command port (Asyn 0) status Initiates alarm and or monitoring events when a user logs
into Asyn 0 on the master switch controller.
Monitoring
In addition to operating an alarm, the events listed in Table 1 on page 32 can
also be monitored. Users can configure monitored events to generate any
combination of SNMP traps, logging events, and triggers. Monitoring does not
occur by default, users must configure each event that is to be monitored. The
SwitchBlade Software Reference has more information on monitoring, including
complete command descriptions.
How Many PSUs do You Need?
The number of PSU’s required depends on the chassis type and the particular
configuration selected, i.e. the number of line cards, controller cards installed.
Consult your authorised Allied Telesis distributor or reseller for more
information.
For PSU specifications and maximum current loads, see “AT-SB4161 & 2
SwitchBlade Power Supply Units” on page 19.
Online Documentation
This section provides a step-by-step guide to accessing online documentation.
Adobe Acrobat Reader must be installed to view online documentation.
Accessing the CD-ROM and Online Documentation
Follow these steps to access the CD-ROM and online documentation:
C613-03060-00 REV H
1. Insert the Documentation and Tools CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
2. If the CD-ROM browser does not appear.
Select "Run" from the Start Menu (Windows 95, 98, 2000 or NT 4.0).
Type d:\start.exe (where d: is the CD-ROM drive letter) and click OK.
3. To view a document.
Page 34

34 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Click on the document title.
4. To navigate around PDF documents.
Use the toolbar buttons, keyboard shortcuts, or commands from the
Document menu to page through the document.
Click on a bookmark, thumbnail or hypertext link to jump to a specific
section or topic.
Use the Search command to search for keywords or phrases.
For more information about using the Adobe Acrobat Reader, select
"Reader Guide" from the Help menu.
5. To install any of the tools included on the CD-ROM.
Click on a link in the Welcome screen.
AT-TFTP Server
This section provides information on how to access and use AT-TFTP Server.
AT-TFTP Server can be used to transfer configuration files as well as to
download software versions.
To use AT-TFTP Server, follow these steps:
1. If AT-TFTP Server has not yet been installed.
Install it now from the SwitchBlade Documentation and Tools CD-ROM.
Choose AT-TFTP Server from the Start > Programs > Allied Telesis >
AT-TFTP Server menu.
2. To set preferences for the AT-TFTP Server.
Select "Options" from the File menu to display the "Set Preferences" dialog
box.
The "Default file transfer directory" field specifies the directory that ATTFTP Server will read from or write to for file requests that do not include a
directory specification.
To prevent unauthorised access to private directories, enter a path name in
the "Restrict to directory" field. AT-TFTP Server will use only the specified
directory, even if file requests contain references to other directories.
Select "Read only" to prevent files being written to the PC. To use the PC to
archive scripts created using the switch's CREATE CONFIG command,
select "Read Write".
Make any required changes and click "OK".
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 35

Hardware Reference 35
3. To load a file from AT-TFTP Server to the Switch.
On a terminal connected to the master switch controller’s RS-232 ASYN0,
type the command:
LOAD METHOD=TFTP FILE=filename SERVER=ipadd DEST=FLASH
where filename is the name of the file to download and ipadd is the IP
address of the PC running AT-TFTP Server.
4. To save a TFTP Server log.
Select "Save As" from the File menu.
TFTP requests are logged to the AT-TFTP Server main window.
Switch Start-up
This section outlines the log in and start-up procedures for your switch.
Although the switch will perform basic switching operations without being
configured, you will need to go through these log in and start-up procedures if
you wish to configure the switch and access its full layer 3 switching
capabilities.
Before you can log in, the switch’s chassis must have at least one power supply
unit, one fan tray, and one switch controller installed.
C613-03060-00 REV H
To log In
To log in you must first connect the master switch controller to a terminal or
PC. This can be done using the switch controller’s RS-232 ASYN0. Tw o
terminal cables suitable for use with ASYN0 are supplied with each chassis.
If two switch controllers are installed, and the switch has not yet been connected to a
power supply, the switch controller in Bay A will assume master controller status. In all
cases the master controller is the controller whose Master LED is lit.
Page 36

36 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Using the supplied terminal cable, or a cable you have made by following
the instructions in “Useful Cables” on page 41, connect your terminal or
PC to the RS-232 ASYN0 on the master switch controller.
Set the communication parameters on your terminal or terminal emulation
program to:
• Baud rate: 9600
• Data bits: 8
•Parity: None
•Stop bits: 1
• Flow control: Hardware
See “Using Windows Terminal and Hyperterminal” on page 59 for more
information on configuring emulation software.
Ensure that the chassis’s stand-by switch is in the Run position and that the
switch controller is receiving power.
After the switch controller has booted, the log in prompt appears. If the log
in prompt doesn’t appear, press [Enter] two or three times.
When the switch boots for the first time it automatically creates an account
with manager privileges. The account has the log in name “manager” and
the password is “friend”.
At the log in prompt, enter the log in name and password.
Log in: manager
Password: friend
The switch’s command prompt appears and you can now configure the
switch using the command line interface.
Change the password as soon as possible. Leaving the manager account with
the default password is a serious security risk. Make sure that you remember
the new password as there is no way to retrieve it if it is lost.
Use the following command to change the account password:
set password
See the SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information on configuring
the switch.
To access help
Before help is used for the first time, the help files must be defined.
To define the files, enter:
set help=help-filename
where help-filename is the name of a help file stored in flash.
To see a list of files stored in flash, enter:
show file
Help files have an HLP extension.
To display a list of help topics, enter:
help
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 37

Hardware Reference 37
To display help on a specific topic, enter:
help topic
Alternatively, type a question mark (?) at the end of a partially completed
command to see a list of valid options.
Start-up Procedures
When the switch starts up following either a power cycle or an operatorinitiated reboot (using the Reset button or RESTART command), a series of
start-up messages is sent to the terminal or PC connected to RS-232 ASYN0
(Figure 2 on page 37).
Figure 2: Switch start-up messages.
INFO: Self tests beginning.
INFO: RAM test beginning.
PASS: RAM test, 262144k bytes found.
INFO: BBR tests beginning.
PASS: BBR test, 512k bytes found.
INFO: Self tests complete
INFO: Downloading switch software.
Force EPROM download (Y) ?
INFO: Initial download succeeded
INFO: Executing configuration script <boot.cfg>
INFO: Switch startup complete
Manager >
After the self tests are complete, the manager is given the option of forcing a
mandatory boot from the EPROM (Flash) release. The message:
Force EPROM download (Y)?
is displayed on the terminal or PC connected to ASYN0 and the switch pauses.
If a key is not pressed within a few seconds, the start-up process will continue
and all steps in the sequence will be executed. Pressing selected keys on the
terminal immediately after the “Force EPROM download” message is
displayed will change the switch start-up process (Table 2 on page 37).
Table 2: Switch start-up sequence keystrokes.
Pressing key... Forces the switch to...
[Y] Load the EPROM release, with no patch.
[S] Start with the default configuration. Any boot script is ignored.
[Ctrl/D] Enter diagnostics mode.
During the start-up process the switch will generate four different types of
messages. All messages are preceded by one of the words INFO, PASS, FAIL,
or ERROR. The significance of these words is shown in Table 3 on page 38.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 38

38 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Table 3: Switch start-up message classes.
Message Meaning
INFO An action will be taken by the system.
PASS A test has been completed successfully.
ERROR An error message that a test has failed, but the system will continue to
operate.
FAIL An error message that a fatal error condition has caused the system to
halt in an unrecoverable fashion.
The possible messages and their meanings are:
INFO: Self tests beginning.
The code loader tests are about to begin.
INFO: RAM test beginning.
The RAM tests are about to begin.
PASS: RAM test, 262144k bytes found.
The RAM test passed, and the indicated amount of memory was found
and will be used by the switch.
ERROR: RAM test 5. Error address = 00345678.
A RAM test failed, at the given address. In the example, it was the fifth
test run. The RAM test repeats until it passes, so a number of messages
like this may appear. This fault means that the memory system is faulty.
If the fault continues, contact your authorised Allied Telesis distributor
or reseller immediately.
INFO: BBR tests beginning.
The BBR battery tests are about to begin.
PASS: BBR test. Battery OK.
The BBR battery tests passed.
ERROR: BBR Battery low.
The BBR battery test failed, indicating that the battery is running low.
The BBR battery will need to be replaced. Contact your authorised
Allied Telesis distributor or reseller.
PASS: BBR test, 512k bytes found.
The BBR size/location test passed, with the indicated amount of BBR
found.
FAIL: BBR test. Error address = 12345678.
The BBR size/location test failed at the given location. The test at this
location failed, indicating the end of memory, but a valid location was
discovered in the 255 long words following this location. The BBR
system will need to be replaced. Contact your authorised Allied Telesis
distributor or reseller.
FAIL: BBR test, only 16k bytes found.
The BBR size/location test completed, but only the displayed amount
of memory was found. This amount is less than the minimum required
to run the switch software.
INFO: Self tests complete.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 39

Hardware Reference 39
The start-up tests have finished.
INFO: Downloading switch software.
The process of downloading the switch software and vector table from
ROM is about to begin.
ERROR: Code load retried.
FAIL: Code load failed.
The load of the code from ROM to RAM failed. The load is retried a
number of times. Each time a failure occurs, the ERROR message is
displayed. If the maximum number of attempts is reached, the FAIL
message is displayed.
INFO: Initial download succeeded.
The start-up tests and download are complete, and the switch software
is about to be started. If the default install is a compressed release, the
release will now be decompressed. This may take a few seconds.
INFO: Downloading compressed release. This may take up to 1
minute...
INFO: Loading software into memory. This may take up to 1
minute...
The main switch software is about to be loaded into RAM. If the release
is a compressed release, the release will be decompressed.
INFO: Executing configuration script <script-name>
The configuration commands stored in <script-name> are being
executed. If an error is found in the script, one or more ERROR
messages will be displayed.
INFO: Switch startup complete.
The start-up process is complete and the switch will now perform basic
switching operations. Further configuration will be necessary if you wish to
access the switch’s full layer 3 switching capabilities. See the SwitchBlade
Software Reference for detailed information on configuring the switch.
Management Interfaces
This section introduces the switch controller’s RS-232 Terminal Port (ASYN0)
and RJ-45 port (ETH0), including their pin assignments.
RS-232 Terminal Port (ASYN0)
C613-03060-00 REV H
The RS-232 ASYN0 Terminal Port can be used to connect the switch to a
management device for initial configuration and switch management tasks.
This allows the switch’s software to be accessed from a terminal, a PC running
terminal emulation software, or from a remote location via a modem
connection. You can also use ASYN0 to establish a network connection from a
remote site using SLIP and a modem.
ASYN0 has a DCE female socket. This allows the use of a straight-through
cable when connecting the switch to a terminal or PC. Output from the SHOW
ASYN command will, however, still have a DTE perspective. The internal DTE
pin roles are listed in Table 4 on page 40. See “Useful Cables” on page 41 for
more information on suitable cables to use with ASYN0.
Page 40

40 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Figure 3: RS-232 Terminal Port Pin Numbers.
Pin 5
Pin 9
DB9 Female Pin View
Table 4: Internal DTE pin roles .
Pin Role
2TXD
3RXD
4CD
5GND
6DTR
7CTS
8RTS
Pin 1
Pin 6
RJ-45 Management Port (ETH0)
Caution. Do not plug a phone jack into any RJ-45 port. Doing so could damage
the switch. Use only twisted pair cables with RJ-45 connectors.
The switch controller’s 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX RJ-45 ETH0 port can be used
to establish a connection to a dedicated network management LAN. ETH0 is
not a switch port.
ETH0 has a default IP address of 192.168.242.242 and a mask of 255.255.255.0.
For instructions on changing the IP address, see the “Graphical User Interface”
section in the “Operations” chapter of the SwitchBlade Software Reference.
As a security precaution, change the default IP address as soon as possible.
If another device on your network already uses 192.168.242.242, do not connect
ETH0 to the network until you have changed its default address.
A twisted pair straight-through cable with RJ-45 connectors should be used
with ETH0. SeeTable 6 on page 41 list the cables described in this section.
“Useful Cables” on page 41 for more information on suitable cables to use with
ETH0.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 41

Hardware Reference 41
With 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX cables, pins 1 and 2 are used for transmitting
data, while pins 3 and 6 are used for receiving data. Table 5 on page 41 lists the
RJ-45 Pin assignments.
Table 5: RJ-45 Pin assignments.
Pin Number Assignment
1TX+
2TX-
3RX+
6RX-
1. The “+” and “-” signs represent the polarity of the wires that make up each wire pair.
1
Useful Cables
This section describes how to make management, test, and network cables for
use with the switch’s RS-232 (ASYN0) and RJ-45 interfaces.
RS-232 Terminal and Modem Cables
Table 6 on page 41 list the cables described in this section.
Table 6: Terminal and modem cable descriptions.
Cable type Description
RS-232 DB9 male to female terminal cable Figure 4 on page 42
RS-232 DB9 male to male modem cable Figure 5 on page 42
Figure 4 on page 42, and Figure 5 on page 42 show how to wire cables to
connect a standard VT100 compatible terminal, or a modem, to the switch
controller’s RS-232 Terminal Port.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 42

42 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Figure 4: Pin wiring diagram for a standard DB9 male to female terminal cable.
DB9 Male
(to switch/DCE)
Not connected
→ (TXD)
← (RXD)
← (CD)
(GND)
→ (DTR)
← (CTS)
→ (RTS)
← (RING)
Pin 1
Pin 6
DB9 Male Pin View
Notes:
(1) → Output from switch; ← Input to switch.
(2) Cable version 1.0.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Pin 5
Cable
Pin 9
DB9 Female
(to PC/terminal/DTE)
(DCD)
1
(RXD)
2
(TXD)
3
(DTR)
4
(GND)
5
(DSR)
6
(RTS)
7
(CTS)
8
(RING)
9
Pin 5
Pin 9
DB9 Female Pin View
Pin 1
Pin 6
DB9MDB9Fsw
Figure 5: Pin wiring diagram for a DCE RS-232 Terminal Port (DB9 female
connector) male to male modem cable.
DB9 Male
(to switch/DCE)
Not connected
→ (TXD)
← (RXD)
← (CD)
(GND)
→ (DTR)
← (CTS)
→ (RTS)
(RING)
Pin 1
Pin 6
DB9 Male Pin View
Pin 5
Pin 9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Cable
DB9 Male
(to modem/DCE)
3 (TXD)
2 (RXD)
1 (DCD)
5 (GND)
4 (DTR)
8 (CTS)
7 (RTS)
9
6
Not connected
Pin 5
Pin 9
DB9 Male Pin View
Pin 6
Pin 1
Notes:
(1) → Output from switch; ← Input to switch
(2) Cable version 1.0.
DB9MDB9Fsw
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 43

Hardware Reference 43
More information on pin assignments for the RS-232 Terminal Port can be
found in “Management Interfaces” on page 39.
Cables for RJ-45 Ethernet LAN Interfaces
For all 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX (10/100BASE) and 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/
1000BASE-T (10/100/1000BASE) connections, a twisted pair cable with RJ-45
connectors must be used. 10/100BASE connections require at least two pairs to
be used, while 10/100/1000 connections require four pairs.
Table 7 on page 43 lists the cables used for network connections and testing of
RJ-45 interfaces.
Table 7: Cables for RJ-45 LAN interfaces.
Purpose Interface type Cable type Pairs Pin assignment
Network 10/100BASE Crossover or straight through Two or four Table 9 on page 44 or
Table 8 on page 43
Network 10/100/1000BASE Straight through Four Table 10 on page 44
Test 10/100BASE Crossover Two or four Table 9 on page 44
orTable 11 on page 45
Test 10/100/1000BASE Crossover or straight through Four Table 11 on page 45 or
Table 10 on page 44
Pin assignments
For twisted pair cables each pair is identified by two different colours. For
example, one wire might be red, and the other red with a white stripe. An RJ-45
connector must be fitted to both ends of the cable.
Caution. Do not plug a phone jack into any RJ-45 port. Doing so could damage
the switch. Use only twisted pair cables with RJ-45 connectors.
10/100BASE straight-through cable
If a twisted pair cable is to join two 10/100BASE network ports and only one of
the ports has an internal crossover (only one port is labelled with an “X”), the
two pairs should be straight through, as listed in Table 8 on page 43.
Table 8: RJ-45 Pin assignments, two pair straight through cable.
End 1 End 2
1 (TX+) 1 (TX+)
2 (TX-) 2 (TX-)
3 (RX+) 3 (RX+)
6 (RX-) 6 (RX-)
C613-03060-00 REV H
10/100BASE crossover cable
If a twisted pair cable is used to join two 10/100BASE network ports and either
both ports are labelled with an “X” or neither port is labelled with an “X”, a
crossover should be used. This cable is also used, in conjunction with the
Page 44

44 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
software test facility, to test 10/100BASE network and management ports.
Table 9 on page 44 lists the RJ-45 crossover wiring pin assignments.
Table 9: RJ-45 Pin assignments, two pair crossover cable.
End 1 End 2
1 (TX+) 3 (TX+)
2 (TX-) 6 (TX-)
3 (RX+) 1 (RX+)
6 (RX-) 2 (RX-)
1000BASE straight-through cable
For 1000BASE network connections, all four pairs are used and the cable is
wired in a straight-through configuration. This cable can also be used, in
conjunction with the software test facility, to test 1000BASE network ports.
Table 10 on page 44 lists the pin assignments.
Table 10: Pin assignments, 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ-45 four pair straight-through
1
.
cable
End 1 End 2
Pin Pair Pin Pair
1 Pair 1+ 1 Pair 1+
2 Pair 1- 2 Pair 1-
3 Pair 2+ 3 Pair 2+
6 Pair 2- 6 Pair 2-
4 Pair 3+ 4 Pair 3+
5 Pair 3- 5 Pair 3-
7 Pair 4+ 7 Pair 4+
8 Pair 4- 8 Pair 4-
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 45

Hardware Reference 45
1000BASE crossover cable
For 1000BASE test cables, all four pairs are used and the cable is wired in a
crossover configuration. This cable can also be used, in conjunction with the
software test facility, to test 10/100BASE network ports. Table 11 on page 45
lists the pin assignments.
Table 11: Pin assignments, 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ-45 four pair crossover cable1.
End 1 End 2
Pin Pair Pin Pair
1 Pair 1+ 1 Pair 2+
2 Pair 1- 2 Pair 2-
3 Pair 2+ 3 Pair 1+
6 Pair 2- 6 Pair 1-
4 Pair 3+ 4 Pair 4+
5 Pair 3- 5 Pair 4-
7 Pair 4+ 7 Pair 3+
8 Pair 4- 8 Pair 3-
1. This cable can also be used with 10/100BASE interfaces.
Test Facility
This section introduces the Test Facility. The Test Facility is built into all
SwitchBlade software. For detailed information on operating the Test Facility,
see the Test Facility chapter of the SwitchBlade Software Reference.
Any interfaces being tested are dedicated to the Test Facility. The Test Facility
can be thought of as a specialised interface module like PPP or Frame Relay.
Ethernet LAN Port Tests
A crossover cable is required to run an Ethernet LAN test. See “Useful Cables”
on page 41 for details of how to make a suitable cable. To start the test, loop a
crossover cable between any two RJ-45 line card ports and enter:
ENABLE TEST INT=ALL
All interfaces connected by crossover cables are tested. Test results are
displayed with the command:
C613-03060-00 REV H
SHOW TEST INT
which produces a display like that shown in Figure 6 on page 46. A more
detailed output (with frame counts) can be displayed with the command:
SHOW TEST COUNT
which is shown in Figure 7 on page 46.
Page 46

46 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Figure 6: Example output from the SHOW TEST INT command on an AT-SB4411 with ports 3.1 and 3.2 linked by
a crossover cable.
Board ID Bay Board Name Rev Serial number
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Base 164 AT-SB4411 M1-0 50433214
Duration Details
Interface State Result Type (minutes) Data( %OK ) Control
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth0 testing wait 4 minutes trans 0 - - TP < 1 BAD ( 0.0) ENDEC 0 - - MAC < 1 good(100.0) - .
port3.1 testing wait 4 minutes TP < 1 good(100.0) - .
port3.2 testing wait 4 minutes TP < 1 good(100.0) - .
port3.3 no test - - - - - port3.4 no test - - - - - port3.5 no test - - - - - port3.6 no test - - - - - port3.7 no test - - - - - port3.8 no test - - - - - -
Figure 7: Example output for the SHOW TEST COUNT command.
Board ID Bay Board Name Rev Serial number
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Base 164 AT-SB4411 M1-0 50433214
Duration Frame Counters
Interface State Type (minutes) Tx RxTotal RxGood RxBad
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth0 testing trans 0 000000000 000000000 000000000 000000000
TP < 1 000000047 000000046 000000000 000000046
ENDEC 0 000000000 000000000 000000000 000000000
MAC 0 000000000 000000000 000000000 000000000
port3.1 testing TP < 1 000114290 000114289 000114289 000000000
port3.2 testing TP < 1 000114290 000114289 000114289 000000000
port3.3 no test - - - - - port3.4 no test - - - - - port3.5 no test - - - - - port3.6 no test - - - - - port3.7 no test - - - - - port3.8 no test - - - - - -
Other Interface Tests
Refer to the Test Facility of the SwitchBlade Software Reference for information on
testing other interfaces.
If a test fails, please contact your authorised Allied Telesis distributor or reseller.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 47

Hardware Reference 47
Troubleshooting
This section provides information on how to detect and resolve problems with
the SwitchBlade and its expansion options.
Other sources of useful troubleshooting information are:
■ www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
■ The SwitchBlade Software Reference.
LEDs and What They Mean
The following tables outline how SwitchBlade LEDs report faults and
operational activities.
Switch Controller LEDs
The following LEDs will operate if the switch controller is receiving power.
Table 12: LEDs on the AT-SB4211 Switch Controller.
LED State Function
Power Green The switch controller is receiving power
Master Amber The switch controller is the master controller
Off The switch controller is the slave controller
Fault Red The switch controller or management software
is malfunctioning
2 Flashes
3 Flashes
5 flashes
6 Flashes
Slow flashing at
startup
Rapid flashing at
startup
1
1
1
1
A fan-tray fan has failed
A PSU or PSU fan is malfunctioning
The fan tray has been removed for more than
20 seconds
The switch’s internal temperature has
exceeded the alarm threshold
The SDRAM (DIMM) has not been detected
The SDRAM (DIMM) is not compatible with the
switch
C613-03060-00 REV H
L/A
(Link/Activity)
Green A 100 Mbps management port link is open
Amber A 10 Mbps management port link is open
Flashing green 100 Mbps activity is occurring through the
management port
Flashing amber 10 Mbps activity is occurring through the
management port
Page 48

48 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Table 12: LEDs on the AT-SB4211 Switch Controller. (Continued)
LED State Function
D/C
(Duplex/Collision)
1. Appears on both controller cards.
Green The management port is operating at full-
duplex
Amber The management port is operating at half-
duplex
Flashing Collisions are occurring on the management
port link
Line Card LEDs
The following LEDs will operate if the line card is installed in conjunction with
a properly configured switch controller and at least one functional PSU (or a
DC power supply for DC models)On the AT-SB-L48, one green LED is
provided for each port. The default is for the LED to show link (L/A) activity.
Duplex/Collision activity (D/C) is shown while the LED Mode button (on the
line card’s face-plate) is pressed and held.
Table 13: LEDs on the AT-SB4311 48-port 10/100BASE (RJ-45) Line Card.
LED State Function
L/A
(Default)
Green A 100 Mbps link is open
Flashing green 100 Mbps activity is occurring
Amber A 10 Mbps link is open. The L/A LEDs for ports
1 and 25 briefly light at switch power up or
when the card is hot swapped in
Flashing amber 10 Mbps activity is occurring
D/C
(LED Mode
button pressed)
Table 14: LEDs on the AT-SB4352 32-port 100BASE-FX (MT-RJ) Line Card.
LED State Function
L/A
(Link/Activity)
D/C
(Duplex/Collision)
Green The port is operating at full-duplex
Amber The port is operating at half-duplex
Flashing amber Collisions are occurring
Green A 100 Mbps link is open
Flashing Green 100 Mbps activity is occurring
Amber The L/A LEDs for ports 1 and 17 briefly light at
switch power up or when the card is hot
swapped in
Green The port is operating at full-duplex
Amber The port is operating at half-duplex
Flashing Amber Collisions are occurring
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 49

Hardware Reference 49
Table 15: LEDs on the AT-SB4441 8-port 1000BASE GBIC Line Card.
LED State Function
L/A
(Link/Activity)
GBIC Status Green A GBIC is installed and enabled
Table 16: LEDs on the AT-SB4541 1-port 10GBASE-LR Line Card.
LED State Function
L/A
(Link/Activity)
Green A link is open
Flashing Green Activity is occurring
Amber The port is operating at half-duplex. The L/A
LED for port 1 briefly lights at switch power up
or when the card is hot swapped in
Flashing Amber Half-duplex activity is occurring
Off No link is present
Amber A GBIC is installed but disabled
Flashing Amber A fault is occurring on the link
Off No GBIC is installed
Green A link is open
Flashing Green 10GE activity is occurring
Off No link is present
XFP Green An XFP is installed and enabled
Amber An XFP is installed, but disabled.
Flashing Amber An XFP is not ready, or faulty.
Off No XFP is installed
Power Supply LEDs
Each PSU has the following LEDs.
Table: 17 LEDs on AC and DC variants of the AT-SB4161 PSU .
LED State Function
DC Good Green The PSU is supplying power to the switch
Fan Good Green The PSU’s fan is functioning
Power Present Green The PSU is receiving power from its supply
circuit.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 50

50 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Check these first
1. Check the power cord(s) connection(s).
2. Check that the power supply voltage is stable.
3. Check that the correct data cables are being used and that their connections
are secure.
4. Make sure that other network devices are working properly.
5. Use the SHOW INSTALL command to check that the latest software version
is loaded. See the SwitchBlade Software Reference for more information about
obtaining the latest software version.
6. If the switch is malfunctioning, reboot it by pressing the recessed Reset
button or entering the command RESTART REBOOT. Alternatively, use the
standby switch on the chassis’s rear panel to power OFF and ON the switch.
Some common problems and how to solve them
Link/Activity LED on any port is off
This can indicate:
■ A loose data cable.
■ The device at the other end of the connection is not working properly or is
turned off.
■ The data cable is not wired correctly.
■ The network administrator has manually disabled the port through the
software.
■ The port’s selected transmission mode does not match that of the attached
device.
Perform the following steps in sequence:
1. Make sure the data cable connections are secure.
2. Make sure the device at the other end of the connection is switched on and
working properly.
3. Check that the data cable is wired correctly.
4. If you can, log in and check the port status. See “To log In” on page 35 for
more information on how to log in.
5. If the port is Enabled, make sure the transmission speed matches that of the
connected device (auto-negotiating, full or half-duplex).
If the port is disabled, someone has used the software to manually disable it. You should
find out why the port was disabled before enabling it.
Power LED is off
This can indicate:
■ A loose power cord.
■ A power supply failure.
Perform the following steps in sequence:
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 51

Hardware Reference 51
1. Check that the power cord connections are secure.
2. Check that all switches and circuit protection devices are in the ON position.
3. Ensure that the supply voltage is within the operational range for your
particular chassis type and power supply. Refer to the section, “Physical
and Operating Specifications” on page 15 of this manual.
Fault LED is on
This can indicate:
■ There is a problem with the switch or PSU.
■ The switch or management software is malfunctioning.
■ A hardware fault is preventing switch start-up.
Perform the following steps in sequence:
1. Check “LEDs and What They Mean” on page 47 for descriptions and
explanations of LED flashing sequences.
2. Reset the switch by pressing the recessed RESET button on the front panel.
3. If you were attempting to download software or manage the switch via the
RS-232 Terminal Port, check that connections between the Terminal Port
and local terminal or PC are secure.
If you cannot access the switch’s software because of a faulty RS-232
Terminal Port connection, you can still manage the switch via Telnet or
SNMP until the problem is fixed.
4. Remove the switch controller from the chassis and then re-insert it.
5. Download the latest software version. See the SwitchBlade Software Reference
for more information on how to obtain the latest software version.
Content Addressable Memory (CAM)
CAM is an adaptation of random access memory (RAM) specifically designed
to produce extremely fast look up times. Unlike conventional forms of RAM
whose data content is accessed by referring to specific addresses, CAM
operates by using the content data as addresses. Stored in each CAM location
may be either the required data entity, or an address (in RAM) where it can be
found.
Typically, the content data might be a table of Ethernet addresses and the
required data entities could be either the switch ports to forward each frame to,
or a RAM address where the forwarding port information can be found. The
fast lookup times are achieved because, for each lookup, the entire contents of
the CAM is simultaneously accessed and compared (within the hardware logic
circuitry) with the reference data - a MAC address, for example.
C613-03060-00 REV H
There is a component of CAM (typically 40 K entries) located on each controller
and line card.
Page 52

52 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Switch Controller Card CAM
The switch controller card (SB4211) contains two CAM processor chips. Each
chip contains 8 k entries of content addressable memory (CAM). These entries
contain address locations for the forwarding database of L2/3 addresses and
other similar entries such as VLAN identities. Located alongside each
processor chip are 3 CAM chips that together provide an additional 96 k
entries. Each processor chipset therefore, contains a total of 104 k entries of oncard CAM.
Line Card CAM
Each line card comes with a basic 40 k entries of CAM per switch processor
chip. These entries contain address locations for the forwarding database of
L2/3 addresses and other similar entries such as VLAN identities. Each switch
chip contains 8 k entries of content addressable memory (CAM). Located
alongside each switch chip is a CAM chip that provides an additional 32 k of
CAM entries, thus producing a total of 40 k entries per on-card chipset.
Refer to the card descriptions shown in the “Physical and Operating
Specifications” on page 15 for more information on the above line cards.
Expansion Options
This section provides a brief overview of the expansion options for the
SwitchBlade. Contact your authorised Allied Telesis distributer or reseller for
more information on these products, or visit our Web site at,
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs)
RAM for SwitchBlade switch controllers is provided in the form of two 128
MByte DIMMs. The two DIMMs deliver 256 MBytes of Synchronous DRAM.
To minimise the risk of damage during shipment, DIMMs are not installed on
switch controllers at the factory. Instead, the two 128 MByte DIMMs are
included in a CPU memory pack, which ships with each switch controller.
Installing DIMM
AT-SB4211 switch controllers have two DIMM slots. Both of these slots must be
populated with a 128 MByte DIMM before the switch controller can be used.
Only Allied Telesis supplied DIMMS have been tested and approved for use
with SwitchBlade switch controllers. Using DIMM that has not been approved
may cause unreliable operation and will invalidate the switch controller’s
warranty.
To install a DIMM
1. Prepare the switch controller.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 53

Hardware Reference 53
If the switch controller is installed in a chassis, remove it by following the
instructions in the SwitchBlade Switch Controller Quick Install Guide. The
quick install guide can be found on the CD-ROM shipped with each switch
controller and chassis, and can be downloaded from
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
Lay the switch controller on a flat surface.
2. Prepare the DIMMs.
In an antistatic environment, remove the two DIMMs from their packing
material. Be sure to observe ESD precautions.
Do not attempt to install DIMM without observing correct antistatic
procedures. Failure to do so may damage the DIMM and switch controller. If
you are unsure what the correct procedures are, contact your authorised Allied
Telesis distributor or reseller.
A chassis ground socket is provided on the front vent panel of the SwitchBlade chassis.
This socket is designed to be used in conjunction with an ESD wrist strap.
3. To remove an existing DIMM.
Each DIMM is held in place by two retaining latches, one latch at each end
of the DIMM slot. Release these latches and carefully pull the DIMM from
the DIMM slot.
The location of DIMM slots is shown in Figure 8 on page 53.
4. Align and insert the first DIMM.
Holding a DIMM at an angle of about 30 degrees from horizontal, align the
notches on its connector strips with the notches on an empty DIMM slot
(see Figure 8 on page 53).
Insert the DIMM into the DIMM slot, sliding it along the two DIMM
guides until the retaining latches automatically click into place. The latches
should hold the DIMM firmly in place.
5. Insert the second DIMM.
Repeat Step 4 for the second DIMM.
For the switch to function, both DIMMs must be installed (giving 256 MBytes of
DRAM per switch controller).
Figure 8: Installing DIMM on the AT-SB4211 Switch Controller.
C613-03060-00 REV H
DIMM
DIMM slot
Page 54

54 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Testing DIMM
The switch is unlikely to boot unless the DIMM is correctly installed. The
switch controller’s fault LED will flash slowly if the DIMM is not detected. The
fault LED will flash quickly if the DIMM is not of an acceptable type.
If the switch does boot but you suspect the DIMM is malfunctioning, or if you
hot swapped in a switch controller with new DIMM, enter the command:
SHOW SYSTEM
to display the system information shown in Figure 9 on page 55. In the
output’s memory section there should be an entry showing the size of DRAM.
If the DRAM size is less than the size of DIMM that has been installed, then the
switch has not correctly detected the DIMM. The most likely cause is that the
DIMM connector is not plugged into its slot correctly. Repeat the installation
process, paying particular attention to the DIMM insertion step.
After repeating the installation, use the SHOW SYSTEM command again, and
if the display is still not correct, contact your authorised Allied Telesis
distributor or reseller.
If you have any difficulty with the DIMM at any time, contact your authorised Allied
Telesis distributor or reseller and quote the serial numbers of both the base card on the
switch controller and the DIMM. The switch controller’s serial numbers and revision
details can be read using the SHOW SYSTEM command. It’s a good idea to record this
information for later reference.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 55

Hardware Reference 55
Figure 9: Example output from the SHOW SYSTEM command for a switch controller with DIMM installed.
Switch System Status Time 10:17:43 Date
07-Feb-2002.
Board ID Bay Board Name Rev Serial number
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Base 164 AT-SB4211 M1-0 50433214
Chassis 160 AT-SB4108-00 M1-0 41987310
Blade 171 5 AT-SB4411 M2-0 41362530
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Memory - DRAM :262144 kB FLASH : 32768 kB
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------SysDescription
Allied Telesis AT-SB4211 version 2.4.0-00 22-Aug-2001
SysContact
SysLocation
SysName
SysDistName
SysUpTime
8472 ( 00:01:24 )
Software Version: 2.4.0-00 22-Aug-2001
Release Version : 2.4.0-00 22-Aug-2001
Release built : Feb 7 2002 at 02:08:26
Patch Installed : NONE
Territory : usa
Help File : help.hlp
Configuration
Boot configuration file: Not set
Current configuration: Not set
Security Mode : Disabled
Warning (2048283): No patches found.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 56

56 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Gigabit Interface Converters (GBICs)
The AT-SB4441 line card provides ports for eight GBICs. These are small
hot-swappable plug-in transceivers. By selecting the appropriate GBIC type,
you can match your SwitchBlade ports to their appropriate network interface.
RJ-45 copper, SC and LC fibre GBICs are currently available.
GBIC 1000BASE-T Auto-Negotiation
The 1000BASE-T GBICs operating in the AT-SB4441 line card will provide only
1000 Mbps full-duplex connections. Although these GBICs will participate in
auto-negotiation processes, they will only advertise 1000 Mbps. Half duplex,
10BASE-T, and 100BASE-TX modes are not supported.
While 1000BASE-T GBICs will auto-negotiate at the copper Ethernet level, the
ports will behave as if in fixed 1000 Mbps full-duplex mode. This is because the
SERDES connection used by GBIC ports makes the auto-negotiation invisible
to the switch, and so prevents a successful link negotiation.
The following Allied Telesis GBIC transceivers can be ordered from your
authorisedAllied Telesis reseller.
Model Media Type Description
AT-G8T 1000BASE-T Copper, 100m at 1000Mbps
AT-G8SX-01 1000BASE-X 550m SX, 50µm MM fibre
220m SX, 62.5µm MM fibre
AT-G8LX10 1000BASE-X 10 km LX, 9 µm SM fibre
AT-G8LX25 1000BASE-X 25 km, LX, 9 µm SM fibre
AT-G8LX40 1000BASE-X 40 km, LX, 9 µm SM fibre
AT-G8LX70 1000BASE-X 70 km, LX, 9 µm SM fibre
AT-G8ZX70/wwww
where xxxx is:
1610, 1590, 1570,
1550, 1530, 1510,
1490, 1470, 1450,
1430, 1410, 1390,
1370, 1350, 1330,
1310
1. Both ends of an individual fibre must use GBICs of the same wavelength.
1
1000BASE-ZX CWDM 1610nm to 1310nm (20nm intervals),
70 km, ZX, 9µm SM fibre
Small Form Factor Pluggables (SFPs)
The AT-SB4442 line card provides ports for 24 SFPs. SFPs are miniature
hot-swappable plug-in transceivers. By selecting the appropriate SFP type, 1
Gbps ports can be matched to the appropriate network interface, RJ-45 copper
or LC fibre. The following Allied Telesis SFP transceivers can be ordered from
your Allied Telesis reseller:
Model Media Type Description
AT-SPTX 10/100/1000BASE-T Copper, 100m at 1000Mbps, RJ-45 connector
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 57

Hardware Reference 57
Model Media Type Description
AT-SPSX 1000BASE-SX 850nm, 2m to 500m with 50/125 µm MM
fiber, 2m to 275m with 62.5/125 µm MM
fiber, LC connector
AT-SPLX10 1000BASE-LX 1310 nm, 2 m to 10km with 9µm SM fiber,
2m to 550m with 50µm MM fiber, 2m to
550m with 62.5µm MM fiber, LC connector
AT-SPLX40 1000BASE-LX 1310nm SM fiber up to 40km, LC connector
AT-SPLX40/1550 1000BASE-LX 1550nm SM fiber up to 40km, LC connector
AT-SPZX80 1000BASE-ZX 1550nm, 80km with 9µm SM fiber, LC
connector
AT-SPZX80/xxxx 1000BASE-ZX
CWDM
Note:Both ends of an individual CWDM fibre must use SFPs of the same wavelength (xxxx
reference number).
Wavelengths of 1610nm to 1470nm (20nm
intervals) and 1310nm, 80km with 9 micron
SM fibre, LC connector. Where xxxx can
be:1610,1590,1570,1550,1530,1510,1490,
1470.
Small Form Factor Pluggables (XFPs)
The AT-SB4451 line card provides a single XFP port. XFPs are miniature
hot-swappable plug-in transceivers. By selecting the appropriate XFP type, 1
Gbps ports can be matched to the appropriate fibre employed.
The following Allied Telesis XFP transceivers can be ordered from your Allied
Telesis reseller.
Product No. Media Type Description
AT-XPSR 10GBASE-SR 850nm short-haul transmission, 300m with
MMF
AT-XPLRM 10GBASE-LRM 1310 nm short-haul transmission, 300m with
MMF
C613-03060-00 REV H
AT-XPLR 10GBASE-LR 1310nm medium-haul transmission, 10km
with SMF
AT-XPER40 10GBASE-ER 1550nm long-haul transmission, 40km with
SMF
RX and TX terminal locations on SC fibre GBIC ports are the reverse of TX and RX
terminal locations on fixed SC fibre ports. From the GBIC front, the RX terminal is
located on the left and the TX terminal is on the right. Never carry out this check with
the GBIC plugged into the equipment - see the warning that follows this text.
Warning Do not look into fibre cables or their transceivers. Invisible laser
radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibres or connectors.
Page 58

58 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Port, Connector, and Cable Combinations
This section provides cabling guidelines for each line card model.
Table 18: Cable guidelines for line cards.
Model Port Type Connector Type Cable Type
AT-SB4311
Line Card
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX RJ-45 10BASE-T Category 3 or
better
100BASE-TX Category 5
or better
AT-SB4352
line card
AT-SB4411
Line Card
100BASE-FX MT-RJ 50/125 or 62.5/125
micron multimode fibre
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/
RJ-45 CAT5
1000BASE-T
CAT5E
AT-SB4412
Line Card
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/
1000BASE-T
RJ-45 CAT5
CAT5E
AT-SB4441
Line Card
AT-SB4451
Line Card
1000BASE-X Varies with GBIC Refer to GBIC’s user
documentation
1000BASE-SX SC 50/125 micron
multimode fibre
62.5/125 micron
multimode fibre
1
Maximum Cable Length
100m (328ft)
100m (328ft)
Full-duplex 2km (6,600ft)
Half-duplex 412m
(1360ft)
100 to 150m
(328 to 492ft)
200m (656ft)
100 to 150m
(328 to 492ft)
200m (656ft)
Refer to GBIC’s user
documentation
550m (1,804ft)
275m (902ft)
2
3
AT-SB4452
Line Card
1000BASE-SX MT-RJ 50/125 micron
multimode fibre
62.5/125 micron
550m (1,804ft)
275m (902ft)
multimode fibre
AT-SB4461
Line Card
1000BASE-LX SC 9/125 micron
singlemode fibre
3km (1.8mi)
Increasing to 10km (6mi) if
linking two 1000BASE-LX
models
50/125 or 62.5/125
550m (1804ft)
micron multimode fibre
AT-SB4462
Line Card
1000BASE-LX MT-RJ 9/125 micron
singlemode fibre
3km (1.8mi)
Increasing to 10km (6mi) if
linking two 1000BASE-LX
models
50/125 or 62.5/125
550m (1804ft)
micron multimode fibre
1. Refer to the IEEE 802.3 standards for further cable information.
2. Assumes a fibre optic cable rating of 500 Mhz/Km. (Maximum cable length is 500m at a cable rating of 400 Mhz/Km.)
3. Assumes a fibre optic cable rating of 200 Mhz/Km. (Maximum cable length is 220m at a cable rating of160 Mhz/Km.)
2
3
2
2
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 59

Hardware Reference 59
Using Windows Terminal and Hyperterminal
You can use a PC running terminal emulation software as the manager console,
instead of a terminal. There are many terminal emulation applications
available for PCs, but the most readily available are the Terminal and
HyperTerminal applications included in Microsoft Windows 98, 2000, and
XP Professional. In standard Windows installations, HyperTerminal is
available from the Communications submenu.
The key to successful use of terminal emulation software with the switch is to
configure the software and switch with matching communications parameters.
The following procedure can be applied to most terminal emulation programs.
Dialog boxes in the procedure are from Windows 2000 and XP Professional.
To configure Windows HyperTerminal for 2000 and XP Professional
1. Start the program in Windows by doing one of the following:
• Select Programs > Accessories > Communications > HyperTerminal.
• Double-click the Hypertrm.exe icon.
2. In the Connection Description dialog box:
• Enter a name for the connection, such as Admin.
• Select an icon from the scrollable list and click the OK button.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 60

60 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
3. In the “Connect using” field on the Connect To dialog box, select the COM
port on the PC used to connect to the switch. and click the OK button.
4. In the COMn Pro perties di alog box, s et port p arameters as follow s, and clic k
the OK button.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 61

Hardware Reference 61
5. From the main HyperTerminal window, select Properties from the File
menu. Click the Settings tab, and set the Properties dialog box as follows.
6. Click ASCII Setup to display the ASCII Setup dialog box, and ensure the
following options are not selected:
• Echo typed characters locally
• Append line feeds to incoming line ends
Set other parameters as necessary and click the OK buttons on both dialog
boxes to close them.
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 62

62 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
7. Save the current session by selecting Save from the File menu on the main
HyperTerminal window. This creates a connection icon with the name you
assigned in the HyperTerminal group.
To use the configuration, double-click the connection icon. When the
HyperTerminal window appears, press the Enter key several times; the
switch’s login prompt is then displayed.
Restricted Procedures
This section contains procedures that should only be performed by authorised
service personnel. Unauthorised use of procedures in this section may cause
danger of injury from electric shock, damage to the switch, and invalidation of
the product warranty.
If you would like to know more about the procedures outlined in this section,
please contact your authorised Allied Telesis distributor or reseller.
Diagnostics
The switch software includes a set of diagnostic programs. These programs
perform basic level checks of all system components. They do not run in
conjunction with the normal operating code, and require that the system be
totally dedicated to their use. A detailed knowledge of the way the switch
hardware functions is necessary if diagnostics are to be used effectively.
The switch will not perform switching operations if diagnostics are running.
This section is not intended as a guide to the diagnostics software. Diagnostics
are designed to be run by service personnel only. For more information, contact
your authorised Allied Telesis distributor or reseller.
To enable diagnostics mode
1. Connect a terminal to the RS-232 Terminal Port (ASYN0).
Using a terminal cable, connect a terminal to RS-232 (ASYN0) on the
master switch controller. See “Useful Cables” on page 41 for more
information on terminal cables.
Set the terminal communication parameters to the following:
• Baud rate: 9600
• Data bits: 8
•Parity: None
•Stop bits: 1
• Flow control: Hardware
C613-03060-00 REV H
Page 63

Hardware Reference 63
2. Restart the switch.
Restart the switch, either by using a pen or pencil to operate the recessed
reset button on the switch controller’s front panel, or by using the terminal
to log in and enter the command:
RESTART REBOOT
See “To log In” on page 35 for more information on how to log in.
3. Enable diagnostics mode during start-up.
During the switch start-up process, at the prompt:
Force EPROM download (Y)?
press [Ctrl/D] on the terminal to enter diagnostics mode. A banner page will
be displayed on the terminal (Figure 10 on page 63). This can be used to
check that the terminal is correctly connected.
Performing a Full Flash Test or erasing flash will delete all configuration and
release files. Make sure you know how to reload these files before erasing flash
or performing a flash test.
Figure 10: SwitchBlade diagnostics banner page.
* * * Diagnostic Mode * * *
version 16-Mar-98
Main Menu:
0. Restart
1. Full RAM test
2. ROM checksum test
3. Full FLASH test
4. Totally Erase FLASH
5. Battery backed RAM test
Enter selection ==>
To run a diagnostic program, enter the corresponding letter or number (or key).
There are several sub-menus to cover all the available options. Table 19 on
page 63 lists the control keys for diagnostic operations.
Table 19: Basic commands for running the diagnostics.
Key Function
Q Quits any running tests and displays the banner page.
S Prints a summary of test results so far.
C613-03060-00 REV H
A reasonable understanding of the system’s structure is needed to operate
diagnostics and interpret the results.
To restore the switch to normal operation, use a pen or pencil to operate the
recessed reset button on the front panel, or press “0” (zero) to restart.
Page 64

64 SwitchBlade 4000 Series Switch
Contacting Us
With locations covering all of the established markets in North America, Latin
America, Europe, Asia and the Pacific, Allied Telesis provides localized sales
and technical support worldwide. To find our representative nearest you, visit
Allied Telesis on the web at: http://www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software
.
C613-03060-00 REV H
 Loading...
Loading...