Page 1

Web Interface User Guide
Allied Telesyn
AT-AR256E
Rev. 1.0
4-Port ADSL Router
Page 2

1. Introduction................................................................................................................ 4
1.1 Main Features...................................................................................................... 4
2. Your Gateway at a Glance...................................................................................... 6
2.1 Ports and Buttons ................................................................................................ 6
2.2 LED Descript ion ................................................................................................. 6
3. Installing Your ADSL Router................................................................................... 7
4. Setting Up Your ADSL Router................................................................................ 8
4.1 Log into Your ADSL Router .............................................................................. 8
4.2 Quick Start .......................................................................................................... 8
4.3 Setup (For Advance User) ................................................................................... 9
4.3.1 Wide Area Network Connection............................................................... 10
4.3.2 Local Area Network Connection.............................................................. 10
4.4 Configuring the WAN....................................................................................... 10
4.4.1 New Connection........................................................................................ 11
4.4.2 Modify an Existing Connection ................................................................ 17
4.4.3 Modem Setup ............................................................................................ 17
4.5 Configuring the LAN ........................................................................................ 17
4.5.1 Enable/Disable DHCP............................................................................... 18
4.5.2 Changing the ADSL Router IP Address ................................................... 19
4.5.3 Firewall/NAT Services ............................................................................. 20
4.6 Advanced (For Advance User Only) ................................................................ 20
4.6.1 UPnP ......................................................................................................... 20
4.6.2 Port Forwarding ........................................................................................ 21
4.6.3 Advanced Security.................................................................................... 22
4.6.4 Access Control.......................................................................................... 24
4.6.5 LAN Clients .............................................................................................. 24
4.6.6 MAC Address Filters ................................................................................ 24
4.6.7 Multicast.................................................................................................... 25
4.6.8 Static Routing............................................................................................ 26
4.6.9 Dynamic Routing...................................................................................... 27
4.7 Tools.................................................................................................................. 28
4.7.1 System Commands.................................................................................... 28
4.7.2 User Management ..................................................................................... 29
4.7.3 Update Firmware....................................................................................... 29
4.7.4 Ping Test ................................................................................................... 30
4.7.5 Modem Test .............................................................................................. 30
4.8 Status ................................................................................................................. 30
4.8.1 Network Statistics ..................................................................................... 30
4.8.2 Connection Status ..................................................................................... 31
4.8.3 DHCP Clients............................................................................................ 31
4.8.4 Modem Status ........................................................................................... 31
4.8.5 Product Information.................................................................................. 31
4.8.6 System Log............................................................................................... 31
5. Appendix A: Troubleshooting ............................................................................... 32
5.1 The ADSL Router Is Not Functional ................................................................ 32
- 2 -
Page 3

5.2 I Can’t Connect To The ADSL Router. ............................................................ 32
5.3 The DSL Link LED Continues To Blink But Does Not Stop ........................... 32
5.4 The DSL Link LED Is Always Off ................................................................... 33
6. ADSL Router Terms............................................................................................... 34
- 3 -
Page 4

1. Introduction
The AT-AR256E 4-Port ADSL Router is the perfect high speed WAN bridge/router. This fullfeatured product is specifically designed to connect to the Internet , and directly connect to your
local area network via high speed 10/100Mbps Ethernet. The ADSL router also has full NAT
firewall and DMZ services to block unwanted users from accessing your network.
For gaming users, the ADSL router is already pre-configured for several low latency game ports.
Just click on the game you are playing online and the rest is done for you.
The ADSL router is fully compatible with all computers. As long as your computer has a Ethernet
interface and is running a TCP /IP stack, the computer can have high speed WAN access. So,
plug in the ADSL router (refer to Quick Installation Guide), configure it (per your ISP’s
requirements) and enjoy fast Internet access like never before.
1.1 Main Features
ADSL/ATM Support
• ANSI T1.413 issue 2, ITU -T G.992.1 (G.dmt) and G.992.2 (G.lite) compliant
• ADSL2, ADSL2+ , RE-ADSL Ready
• Rate Adaptive modem at 32Kbps steps
• Dynamic Adaptive Equalisation to improve Carrier’s service area
• Bridge Tap Mitigation support
• ATM Layer with Traffic shaping QoS Support (UBR, CBR, VBR-rt, VBR-nrt)
• AAL ATM Attributes – AAL5
• Multiple PVC up to 8 support
• Spectral compatibility with POTS
• F5 OAM Loopback/Send and Receive
Encapsulation Support
• RFC2684 Bridge and Routed LLC and VC Mux support
• RFC2364 PPPoA Client support
• RFC2516 PPPoE Client support
• RFC2225/RFC1577 Classical IP Support
• Transparent Bridge Support
• PAP/CHAP/MS-CHAP for Password Authentication Support
Network Support
• Static IP, Dynamic RIP routing support
• IP/TCP/UDP/ICMP/ARP/RARP Application Support
• Network Address Translation (NAT)
• Port Mapping/Forwarding
• Easy setup of Port Forwarding rules for popular Games/Application
• NAT Application Level Gateway for popular applications
• DHCP Server/Relay/client
• DNS Relay Agent
• DMZ support
• Single Session IPsec and PPTP/L2TP VPN pass-through support
• PPP Always on with configurable timeout
• PPP Dial on Demand
• Universal Plug and Play Support
- 4 -
Page 5

Management Support
• Web Based HTTP management GUI
• TFTP/FTP Support for Firmware Upgrade
• Web Based Firmware Upgrade (Local)
• Soft Factory Reset Button via Web GUI
• Telnet/CLI (Read Only)
• Syslog Support
• Firmware upgradeable for future feature enhancement
Security Support
• NAT for basic Firewall support
• Packet Filtering Firewall Support
• Stateful Packet Inspection Support
• Protection against Denial of Service attacks
• Password Authentication to Modem
External Connectors
• 1 x RJ-11 Telephone socket for ADSL
• 4 x RJ-45 for 10/100Base-T Ethernet (Auto MDI/MDI-X)
• 1 x DC Jack for Power Input
• 1 x Factory Default Reset Button
• 1 x On/Off Power Switch
- 5 -
Page 6

2. Your Gateway at a Glance
The AT-AR256E 4-Port ADSL Router has several ports and LEDs. Let’s take a look at them.
2.1 Ports and Buttons
Reset to Factory Defaults: The reset to factory defaults feature will set the ADSL router back to
its factory default configuration. If you had forgotten the login password, you may need to place
the ADSL router into its factory default settings. Note that while the ADSL router is resetting, you
will loose the ability to communicate with the ADSL router via the web interface. To reset the
ADSL router, simply press the reset button for about 10 seconds. The ADSL router will be reset
to its factory defaults and after about 30 ~ 40 seconds the ADSL router will become operational
again.
Local Area Network (LAN) ports: Connect to Ethernet network devices such as computers ,
hubs, switches or routers. The AT-AR256E has an integral 4-port switch with auto MDI/MDI-X
feature which support s both straight and crossover cables.
DC input: This is where you connect the power adapter. Make sure to observe the proper power
requirements. The required power is 9 volts. Use the power adapter provided.
DSL port: This is the WAN interface that connec ts directly to your telephone wall socket.
2.2 LED Description
1. POWER
Lights up when power is supplied to the ADSL router.
2. ETH/ACT
Lights up when the Ethernet cable is properly connected from your Ethernet network card to
the ADSL router.
Flickers when the ADSL router is transmitting/receiving data.
3. DSL
Lights up when the ADSL connection is established.
Flickers when the ADSL router is trying to establish a connection to your ADSL Provider.
4. INTERNET
Lights up when the PPP connection is established.
- 6 -
Page 7

3. Installing Your ADSL Router
1. Locate an optimum location for the ADSL router.
2. For connections to the Ethernet and DSL interfaces, please refer to the Quick Installation
Guide.
3. Connect the power adapter. Depending on the type of network, you may want to connect the
power adapter to an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS). Only use the power adapter
supplied with the ADSL router. A different power adapter may damage the product.
Now that the hardware installation is completed, proceed to 4. Setting Up Your ADSL Router
- 7 -
Page 8
4. Setting Up Your ADSL Router
This section will guide you through the ADSL router’s configuration. The ADSL router is shipped
with a standard PPP configuration.
4.1 Log into Your ADSL Router
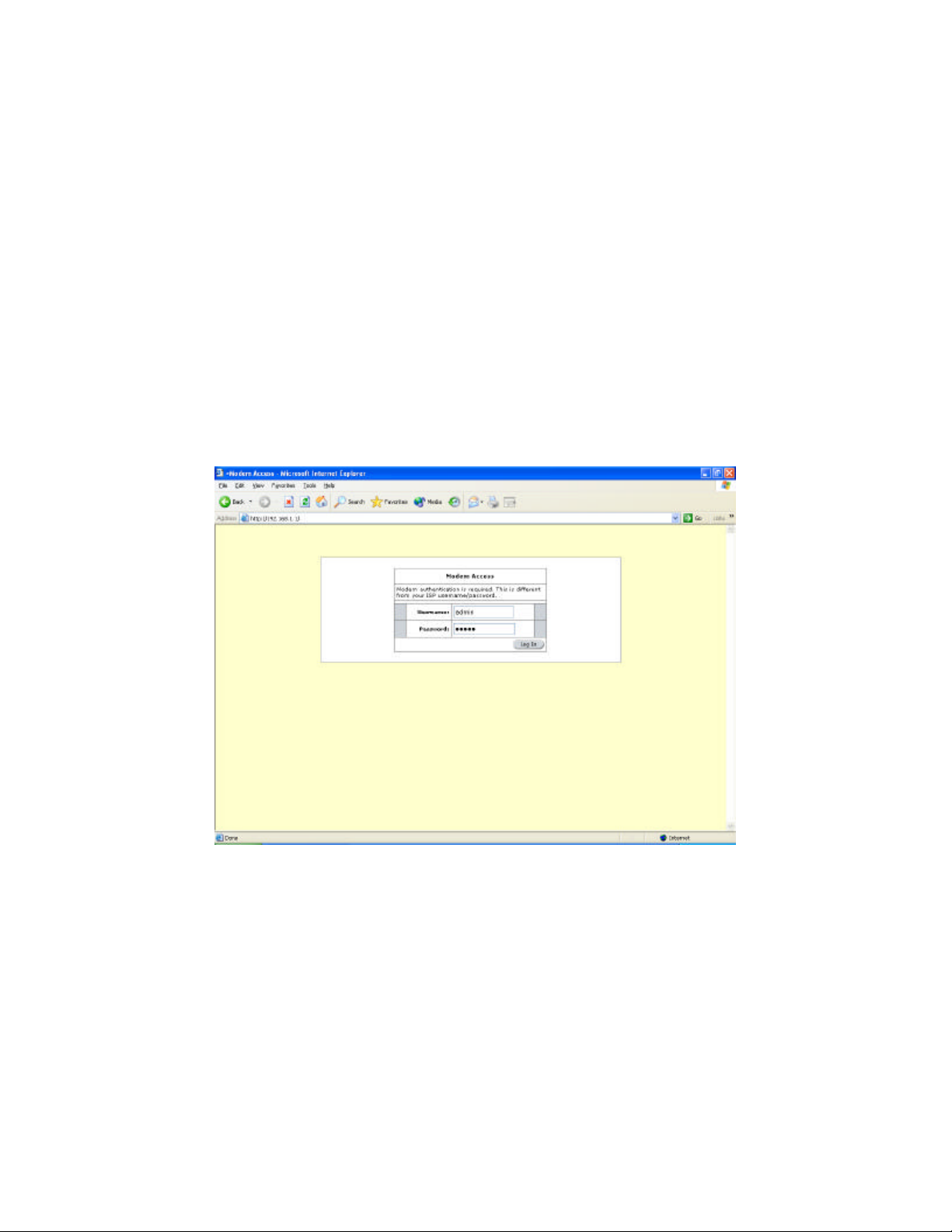
To configure the ADSL router, launch your web browser. You may get an error message at this
point; this is normal. Do not panic! Type the default IP address (192.168.1.1) press the Enter
key and the following page, shown in Figure 1 will appear. The default username is admin
(case-sensitive) and the password is admin (case-sensitive).
Note: Before setting up the ADSL router, make sure you have followed the Quick
Installation Guide. You should have your computers configured for DHCP mode and have
proxies disabled on your browser. If you access the ADSL router and instead of getting a
login page, the browser instead displays a login redirection page, you should check your
browser's setting and verify that JavaScript support is enabled. Also, if you do not get the
page shown in Figure 1, you may need to delete your temporary Internet files (basically
flush the cached web pages).
Figure 1 (Modem Access)
4.2 Quick Start
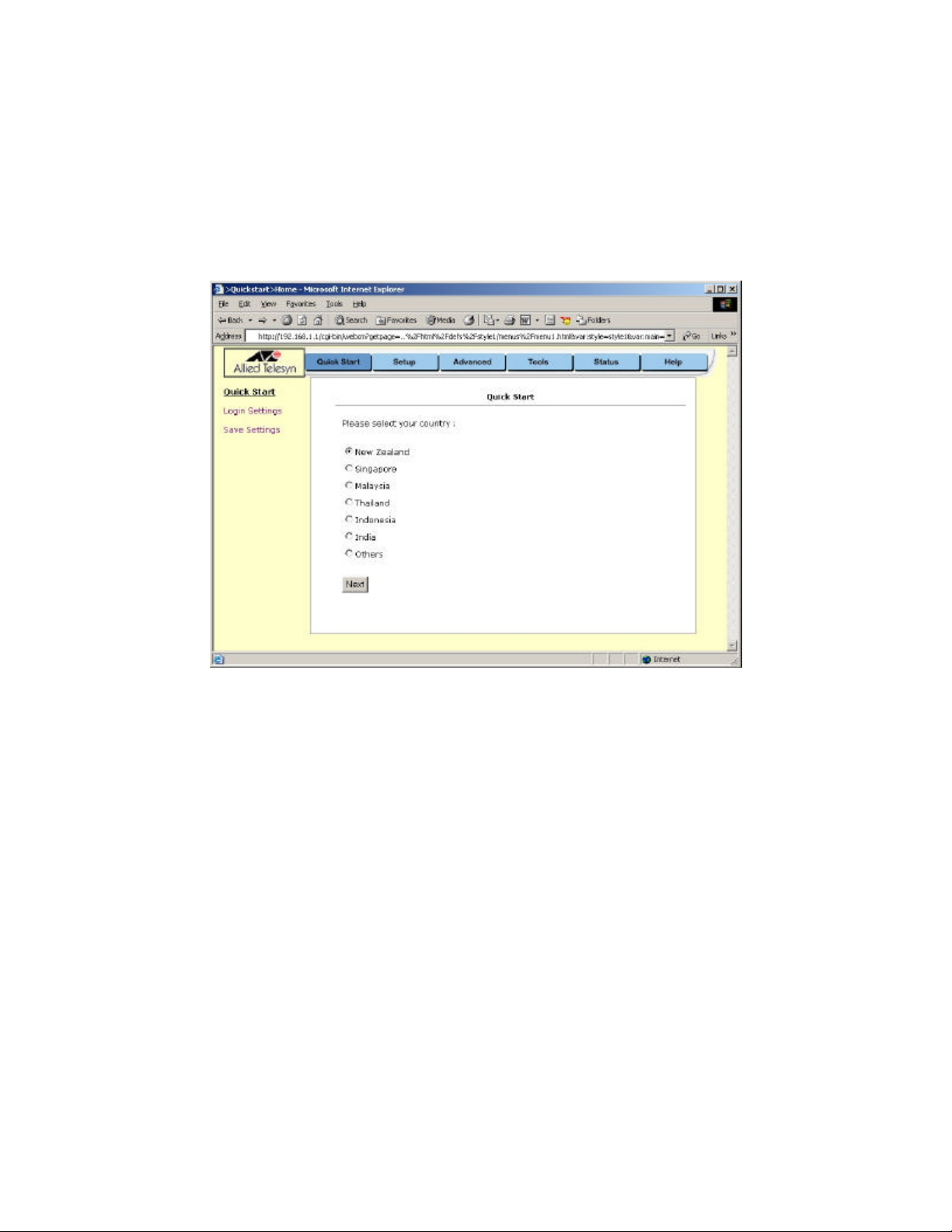
The first page (Figure 2) that appears after the login page is the Quick Start page. Depending on
the country that you reside in, some profiles have been preset for the VPI/VCI and type of
encapsulation. For example, if you reside in New Zealand, click on the button for New Zealand
and then click Next. The next page will display the preset profile of VPI=0, VCI=100 and
encapsulation type is PPPoA VC-MUX. If this is not correct, select Customise Settings and enter
the VPI and VCI values. If the ADSL service is PPPoA or PPPoE, you will also need to enter the
username and password which your ADSL Provider or ISP will supply to you.
- 8 -
Page 9
The Quick Start page is meant for basic users who only require easy and seamless connectivity
to the Internet, without worrying about any other advance configuration setting.
For more advanced setup, please proceed to the next section.
Important:
After clicking on Connect, please be sure to “Save Settings” to register the username / password
or any other changes.
Figure 2 (Quick Start page)
4.3 Setup (For Advance User)
From this page the user can setup the ADSL router (configure the LAN and WAN connections),
configure the advanced configuration options within the ADSL router (security, routing and
filtering), access tools that are helpful for debug purposes, obtain the status of the modem and
view the extensive online help.
To setup the ADSL router with a basic configuration, select Setup. Figure 3 illustrates the setup
page. The page is broken into two subsections, the WAN configuration and the LAN
configuration.
Before configuring the ADSL router, there are several concepts that you should be familiar with
on how your new ADSL router works. Please take a moment to familiarise yourself with these
concepts, as it should make the configuration much easier.
- 9 -
Page 10
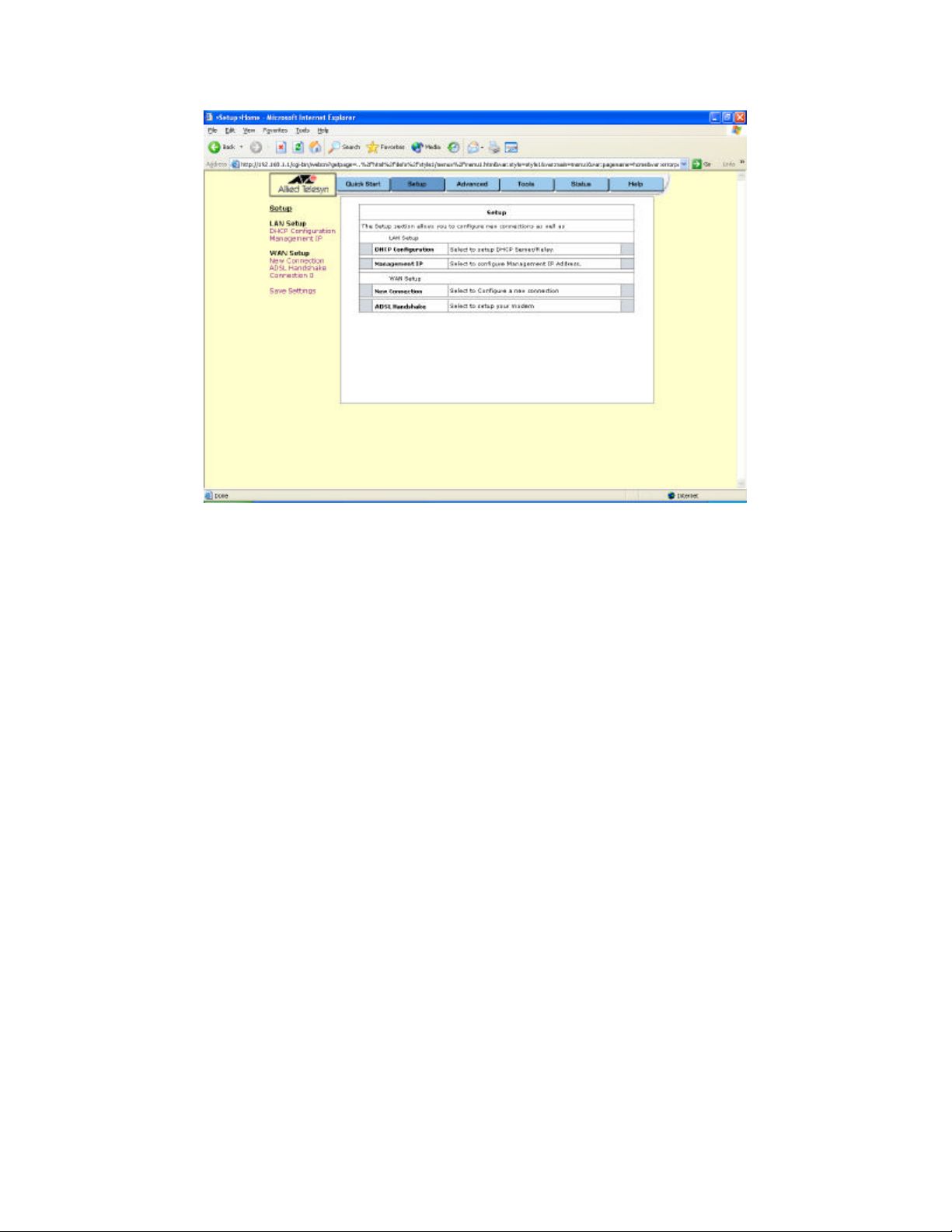
Figure 3 (Setup page)
4.3.1 Wide Area Network Connection
On the other side of the ADSL router is where your Wide Area Network (WAN) connection; also
referred to as a broadband connection. This WAN connection is different for every WAN
provider. Most of the configuration you will perform will be in this area.
4.3.2 Local Area Network Connection
On one side of the ADSL router, you have your own Local Area Network (LAN) connections. This
is where you plug in your local computers to the ADSL router. The ADSL router is normally
configured to automatically provide all the computers on your network with Internet addresses.
4.4 Configuring the WAN
Before the gateway will pass any data between the LAN interface(s) and the WAN interface, the
WAN side of the modem must be configured. Depending on your ADSL Provider or ISP, you will
need some or all of the information outlined below before you can properly configure the WAN:
• Your ADSL VPI and VCI values
• Your ADSL encapsulation type and multiplexing
• Your ADSL training mode (default is MMODE)
• For PPPoA and PPPoE users, you also need these values from your ISP:
• Your username and password
• For RFC 1483 users, you may need these values from your ISP:
• Your ADSL fixed WAN IP address
• Your Subnet Mask
• Your Default Gateway
• Your primary DNS IP address
- 10 -
Page 11
Since multiple users can use the ADSL router, the ADSL router can simultaneously support
multiple connection types; hence, the user must set up different profiles for each connection. The
ADSL router supports the following protocols:
• DHCP
• RFC2364 / PPPoA
• RFC2516 / PPPoE
• Static
• Bridged
• RFC1577 / CLIP
.
4.4.1 New Connection
A new connection is basically a virtual connection. The ADSL router can support up to 8 different
(unique) virtual connections. If you have multiple different virtual con nections, you may need to
utilise the static and dynamic routing capabilities of the modem to pass data correctly.
4.4.1.1 Bridged Gateway Profile and Connection
A pure bridged connection does not assign a IP address to the WAN interface. NAT and firewall
rules are not enabled. This connection method makes the ADSL router act as a hub, and just
passes packets across the WAN interface to the LAN interface.
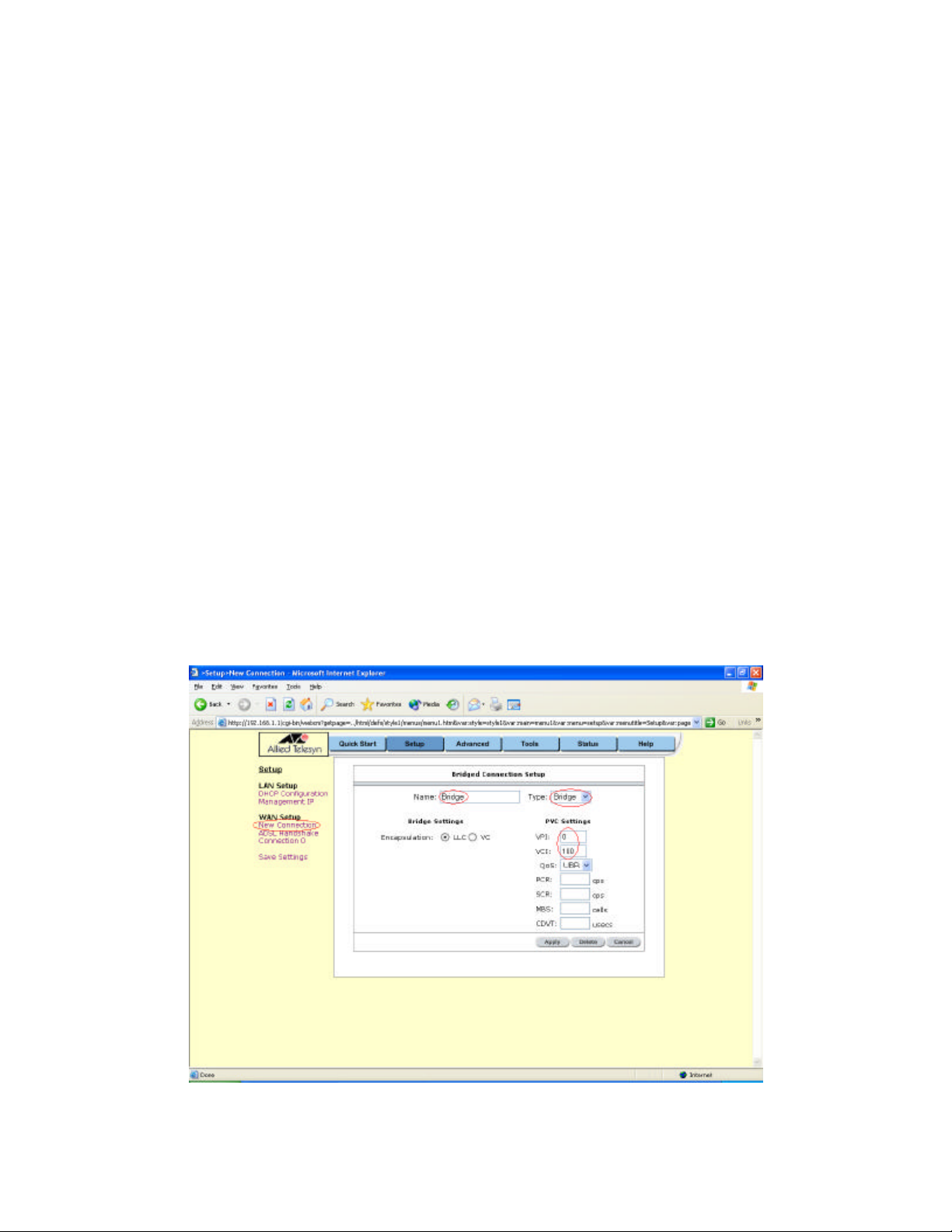
To configure the ADSL router as a bridge, click on Setup and then click on New Connection. The
default PPPoE connection setup is displayed. At the Type field select Bridge and the Bridge
connection setup page is displayed (see Figure 4). Give your Bridge connection a unique name;
the name must not have spaces and cannot begin with numbers. In this case the unique name is
called Bridge. Select the encapsulation type (LLC or VC); if you are not sure, just use the default
mode. Select the VPI and VCI settings; your ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case,
the ADSL Provider is using 0,100. Also select the Quality of Service (QoS); leave the default
value if you are unsure or the ISP did not provide this information.
Figure 4 (Bridge Connection Setup)
- 11 -
Page 12

To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you need to click on Save
Settings. At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.1.2 PPPoA Connection Setup
PPPoA is also known as RFC 2364. It is a method of encapsulating PPP packets over ATM cells
which are carried over the ADSL. PPP or Point -to-Point Protocol is a method of establishing a
network connection / session between network hosts. It usually provides a mechanism of
authenticating users. LLC and VC are two different methods of encapsulating the PPP packet.
Contact your ISP to make sure which encapsulation is being supported.
By selecting PPPoA, you are forcing the ADSL router to terminate the PPPoA connection. The
advantage is that the PPPoA termination is done within the ADSL router and not on your
computer; this frees up your computer’s resources and allows multiple users to utilise the PPPoA
connection.
To configure the gateway for PPPoA, click on Setup and then click on New Connection. The
default PPPoE connection setup is displayed. At the Type field select PPPoA and the PPPoA
connection setup page is displayed; Figure 5 illustrates a typical PPPoA configuration. Give your
PPPoA connection a unique name; the name must not have spaces and cannot begin with
numbers. In this case, the unique name is called PPPoA1. Select the encapsulation type (LLC
or VC); if you are not sure, just use the default mode. Select the VPI and VCI settings; your
ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case, the ADSL Provider is using 0,100. Also
select the Quality of Service (QoS); leave the default value if you are unsure or the ISP did not
provide this information.
The following is a description of the different options:
a. Username: The username for the PPPoA access; this is provided by your ADSL
Provider or ISP.
b. Password: The password for the PPPoA access; this is provided by your ADSL
Provider or ISP.
c. On-Demand: Enables on -demand mode. The connection will disconnect if no activity
is detected after the specified idle timeout value.
d. Idle Timeout: Specifies that PPPoA connection should disconnect if the link has no
activity detected for n seconds. This field is used in conjunction with the On -Demand
feature. To ensure that the link is always active, enter a 0 in this field.
e. Keep Alive: When on-demand option is not enabled, this value specifies the time to
wait without being connected to your provider before terminating the connection. To
ensure that the link is always active, enter a 0 in this field.
f. Set Route: Specify this connection as the default route.
g. MRU: Maximum Receive Unit the ADSL connection can receive. It is a negotiated
value that asks the Provider to send packets of no more than n bytes. The maximum
specified value is 1500, although some ADSL Providers/ISPs require a larger value.
The minimum MRU value is 128.
- 12 -
Page 13

Figure 5 (PPPoA Connection Setup)
To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent , you need to click on Save
Setting s (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.1.3 PPPoE Connection Setup
PPPoE is also known as RFC 2516. It is a method of encapsulating PPP packets over Ethernet.
PPP or Point -to-Point Protocol is a method of establishing a network connection/session between
network hosts. It usually provides a mechanism for authenticating users.
To configure the gateway for PPPoE, click on Setup and then click on New Connection. The
default PPPoE connection setup is displayed. At the Type field select PPPoE and the PPPoE
connection setup page is displayed; Figure 6 illustrates a typical PPPoE configuration. Give your
PPPoE connection a unique name; the name must not have spaces and cannot begin with
numbers. In this case, the unique name is called PPPoE1. Select the encapsulation type (LLC
or VC); if you are not sure, just use the default mode. Select the VPI and VCI settings; your
ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case, the ADSL Provider is using 0,100. Also
select the Quality of Service (QoS); leave the default value if you are unsure or the ISP did not
provide this information.
The following is a description of the different options:
a. Username: The username for the PPPoE access; this is provided by your ADSL
Provider or ISP.
b. Password: The password for the PPPoE access; this is provided by your ADSL
Provider or ISP.
c. On-Demand: Enables on -demand mode. The connection will disconnect if no activity
is detected after the specified idle timeout value.
d. Idle Timeout: Specifies that PPPoE connection should disconnect if the link has no
activity detected for n seconds. This field is used in conjunction with the On -Demand
feature. To ensure that the link is always active, enter a 0 in this field.
- 13 -
Page 14

e. Keep Alive: When on-demand option is not enabled, this value specifies the time to
wait without being connected to your provider before terminating the connection. To
ensure that the link is always active, enter a 0 in this field.
f. Set Route: Specify this connection as the default route.
g. MRU: Maximum Receive Unit the ADSL connection can receive. It is a negotiated
value that asks the Provider to send packets of no more than n bytes. The maximum
specified value is 1500, although some ADSL Providers/ISPs require a larger value.
The minimum MRU value is 128.
h. Enforce MRU: Check this box if you experience problems accessing the Internet over
a PPPoE connection. This feature will force all TCP traffic to conform with PPP
MRU, by changing TCP Maximum Segment Size to PPP MRU.
Figure 6 (PPPoE Connection Setup)
To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent , you need to click on Save
Setting s (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.1.4 DHCP Connection Setup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows the ADSL router to automatically obtain the
IP address from the server. This option is commonly used in situations where IP is dynamically
assigned and is not known prior to assignment.
To configure the ADSL router for a DHCP connection, click on Setup and then click on New
Connection. The default DHCP connection setup is displayed. At the Type field, select DHCP
and the DHCP connection setup page is displayed; Figure 7 illustrates a typical DHCP
configuration. Give your DHCP connection a unique name; the name must not have spaces and
cannot begin with numbers. In this case, the unique name is called DHCP1. Select the
encapsulation type (LLC or VC); if you are not sure, just use the default mode. Select the VPI
and VCI settings; your ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case, the ADSL Provider is
- 14 -
Page 15

using 0,100. Also select the Quality of Service (QoS); leave the default value if you are unsure or
the ISP did not provide this information.
If your ADSL is connected and your ADSL Provider/ISP is supporting DHCP, you can click the
renew button and the gateway will retrieve an IP address, Subnet mask, and Gateway address.
At anytime, you can renew the DHCP address by clicking on the renew button; in most cases ,
you will never have to use this button.
Figure 7 (DHCP Connection Setup)
To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you need to click on Save
Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.1.5 Static Connection Setup
Static is used whenever a known static IP is assigned. The accompanying information such as
the Subnet mask and the gateway should also be specified. Up to three Domain Name Server
(DNS) addresses can also be specified. These servers would enable you to have access to other
web servers. Valid IP address range is from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
To configure the ADSL router for a Static connection, click on Setup and then click on New
Connection. The default Static connection setup is displayed. At the Type field select Static and
the Static connection setup page is displayed; Figure 8 illustrates a typical Stat ic configuration.
Give your Static connection a unique name; the name must not have spaces and cannot begin
with numbers. In this case, the unique name is called STATIC1. Select the encapsulation type
(LLC or VC); if you are not sure, just use the default mode. Select the VPI and VCI settings; your
ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case the ADSL Provider is using 0,35. Also select
the Quality of S ervice (QoS); leave the default value if you are unsure or the ISP did not provide
this information. You can also enable Network Address Translation (NAT) and the Firewall
options. If you are unsure, leave these in the default mode.
- 15 -
Page 16

Based upon the information your A DSL Provider/ISP provided, enter your assigned IP address,
Subnet Mask, Default Gateway (if provided), and Domain Name Service (DNS) values (if
provided). For the static configuration, you can also select a bridge connection or a routed
connection. Since static IP address is typically used to host web servers, you may want to use a
bridge connection.
Figure 8 (Static Connection Setup)
To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent , you need to click on Save
Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.1.6 Classical IP over ATM (CLIP, defined in RFC1577) Connection Setup
The Classical IP over ATM (CLIP) support provides the ability to transmit IP packets over a ATM
network, CLIP support will encapsulate IP in a AAL5 Packet Data Unit (PDU) frame using
RFC1577 and it utilises a ATM aware version of the ARP protocol (ATMARP support only allows
for PVC support; it does not support SVC).
To configure the ADSL router for a CLIP connection, click on Setup and then click on New
Connection. The default CLIP connection setup is displayed. At the Type field select CLIP and
the CLIP connection setup page is displayed; Figure 9 illustrates a typical CLIP configuration.
Give your CLIP connection a unique name; the name must not have spaces and cannot begin
with numbers. In this case, the unique name is called CLIP1. Select the VPI and VCI settings;
your ADSL Provider or ISP will supply these; in this case, the ADSL Provider is using 0,101. Also
select the Quality of Service (QoS); leave the default value if you are unsure or the ISP did not
provide this information. You can also enable Network Address Translation (NAT) and the
Firewall options. If you are unsure, leave these in the default mode.
- 16 -
Page 17

Figure 9 (CLIP Connection Setup)
To complete the connection, you must now click the Apply button. The Apply button will
temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent , you need to click on Save
Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.2 Modify an Existing Connection
To modify an existing connection, click setup and then click the connection you want to modify.
The connections are listed as Connection 0 through Connection 7.
As a note, if you delete the connection, to make the change permanent, you need to click on
Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on Save All.
4.4.3 Modem Setup
To configure the ADSL modulation type, Click setup. Under WAN Setup, select Modem Setup.
This will bring up the modem setup page. Leave the default value if you are unsure or the ADSL
Provider/ISP did not provide this information. For almost all cases, this page should not be
modified.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.5 Configuring the LAN
By default, the ADSL router has DHCP server (LAN side) enabled. If you already have a DHCP
server running on your network, you must disable one of the two DHCP servers; if you plug a
second DHCP server into the network, you will experience network errors and the network will not
function normally.
- 17 -
Page 18

4.5.1 Enable/Disable DHCP
To enable or disable DHCP, click setup. Under LAN Setup, select DHCP Configuration. This will
bring up the page shown in Figure 10.
The Start IP Address is where the DHCP server starts issuing IP addresses. This value must be
greater than the ADSL router IP address value. For example, if the ADSL router’s IP addr ess is
192.168.1.1 (default) the n the starting IP address must be 192.168.1. 2 (or higher).
The End IP Address is where the DHCP server stops issuing IP addresses. The ending address
cannot exceed a subnet limit of 254. Hence, the maximum value for our default gateway is
192.168.1.254. If the DHCP server runs out of DHCP addresses, users will not get access to
network resources. If this happens , you can increase the Ending IP address (to the limit of 255)
or reduce the lease time.
The Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed connection to the ADSL
router with their current dynamic IP address. The amount of time is in units of minutes; the
default value is 3600 minutes (60 hours).
Note: If you change the start or end values, make sure the values are still within the same subnet
as the gateway ’s IP address. In other words, if the gateway’s IP address is 192.168.1.1 (default)
and you change the DHCP start/end IP addresses to be 192.168.2.2/192.168.2.100, you will not
be able to communicate with the ADSL router if your computer has DHCP enabled.
Figure 10 (DHCP Configuration)
In addition to the DHCP server feature, the ADSL router supports the DHCP relay function.
When the ADSL router is configured as DHCP server, it assigns the IP addresses to the LAN
clients. When the ADSL router is configured as DHCP relay, it is responsible for forwarding the
requests and respons es negotiating between the DHCP clients and the server. See Figure 11.
- 18 -
Page 19

Figure 11 (Example of a DHCP Relay configuration)
By turning off the DHCP server and relay , the network administrator must carefully configure the
IP address, Subnet Mask and DNS settings of every computer on your network. Do not assign
the same IP address to more than one computer, and the ADSL router must be on the same
subnet as all the other computers.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.5.2 Changing the ADSL Router IP Address
You can change the ADSL router’s IP address by clicking Setup and under LAN Setup, select
Management. This will bring up the page shown in Figure 12.
4.5.2.1 Static IP Address Assignment
The ADSL router’s default IP address and subnet mask are 192.168.1.1/255.255.255.0; this
subnet mask will allow the ADSL router to support 254 users. If you want to support a larger
number of users , you can change the subnet mask; but remember, the DHCP server is defaulted
to only give out 255 IP addresses. Further remember that if you change your gateway’s IP
address and you have DHCP enabled, the DHCP configuration must reside within the same
subnet.
The default gateway is the routing device used to forward all traffic that is not addressed to a
station within the local subnet. Your ISP will provide you with the default gateway address.
Figure 12 shows a default gateway address of 203.125.64.1 because this was the default
gateway defined when the CLIP connection was configured.
The Hostname can be any alphanumeric word that does not contain spaces. The Domain Name
is us ed in conjunction with the Hostname to uniquely identify the gateway. To access the ADSL
router’s web pages, the user can type 192.168.1.1 (the default IP address) or type
AlliedTelesyn.
- 19 -
Page 20

Figure 12 (Management IP )
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.5.3 Firewall/NAT Services
You can enable or disable Firewall and NAT when you are creating a new Connection. By
default, both NAT and Firewall are enable d. Enabling the firewall will allow the router to activate
the Stateful Packet Inspection feature to incoming traffic from the WAN for better security.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6 Advanced (For Advance User Only)
The ADSL router supports a host of advanced features. For basic ADSL router functionality, the
user does not need to utilise these advanced features. The features help with routing, security,
port configuration, and plug-and-play capability.
4.6.1 UPnP
UPnP NAT and Firewall Traversal allow traffic to pass-through the ADSL router for applications
using the UPnP protocol. This feature requires one active ADSL connection. In the presence of
multiple ADSL connections, select the one over which the incoming traffic will be present, for
example the default Internet connection.
- 20 -
Page 21

To enable UPnP, you must first ha ve a WAN connection configured. Once the WAN connection
is configured, click Advanced and under Advanced, select UPnP. This will bring up the page
shown in Figure 13. You must enable UPnP and then select which connection will utilise UPnP.
In this case, the PPPoA connection is enabled.
Figure 13 (UPnP)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.2 Port Forwarding
Using the Port Forwarding page, you can provide local services (for example web hosting) for
people on the Internet or play Internet games. When users send this type of request to your
network via the Internet, the ADSL router will forward those requests to the appropriate computer.
Port forwarding can be used with DHCP assigned addresses but remember that a DHCP address
is dynamic not static. For example, if you were configuring a Net Meeting server, you would want
to assign this server a static IP address so that the IP address is not reassigned. Also remember
that if an Internet user is trying to access an Internet application, they must use the WAN IP
address. The port forwarding will translate the WAN IP address into a LAN IP address.
To configure a service, game or other application, select the external connection (for example the
Internet connection) from the Home page, click Advanced and under Advanced, select Port
Forwarding. Next, select the computer hosting the service and add the corresponding firewall
rule. If you want to add a custom application, select the User category, click New and fill in the
port, protocols and description for your application.
- 21 -
Page 22

For example, if you want to host a Net Meeting session, from the Home page, click Advanced and
under Advanced, select Port Forwarding. First select the IP address for your Net Meeting server.
Next, select the Audio/Video category and add Net Meeting to the applied rules box. To view the
management rules, highlight NetMeeting and select view; this will display the pre-configured
protocols and ports that NetMeeting will use. Now assuming that your WAN connection is
correct, you can run Net Meeting from your server and call users that are on the Internet. If you
know your WAN IP address, users can call you.
Figure 13 (Port Forwarding )
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.3 Advanced Security
In the presence of the firewall, anonymous Internet traffic is blocked. Using the advanced
security features, you can redirect this traffic to a dedicated computer on your local network
(DMZ) or open the access from the Internet to the ADSL router's management ports (web, telnet).
To enable any of the advanced security features, click Advanced and configure the option under
Firewall. Figure 14 illustrates the typical advanced security in Access Cont rol configuration.
- 22 -
Page 23

Figure 14 (Access Control)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.3.1 DMZ Configuration
Setting a computer (on your local network) as a DMZ forwards any network traffic that is not
redirected to another computer via the port forwarding feature to the computer's IP address. This
opens the access to the DMZ comput er from the Internet.
4.6.3.2 Enable Web from WAN
Enabling the Web from WAN on your local network allows Web requests that come from the
Internet to be re -routed to a web server that is on a different subnet. This is different from the
web server rule that is configurable via the port forwarding page. In this case, the web server is
on a different subnet.
4.6.3.3 Enable Remote Telnet
Enabling the Remote Telnet on your local network allows telnet requests that come from the
Internet to be re -routed to a telnet server that is on a different LAN IP subnet. This is different
from the telnet server rule that is configurable via the port forwarding page. In this case, the
telnet server is on a different subnet.
- 23 -
Page 24

4.6.3.4 Enable Incoming ICMP Ping
Enabling the Incoming Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Ping will allow Echo requests to
come into the gateway. The gateway will respond with a ICMP Echo response message. The
option allows the A DSL Provider or ISP to determine the following:
a. The status of the network.
b. Tracking and isolating hardware and software problems.
c. Testing, measuring and managing networks.
4.6.4 Access Control
Access control can also be called port blocking. Specific types of traffic that is destined to a
selected LAN IP address can be blocked. To enable any of the Access Control features, click
Advanced and under Advanced, select Access Control. A page similar to the port forwarding
page appears. Similar to the port forwarding page, a IP address can be added to a rule. All
Access Control rules have precedence over rules that were added via the port forwarding page.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.5 LAN Clients
To add a LAN client, click Advanced and under Advanced, select LAN Clients. If DHCP is used,
all DHCP clients are automatically assigned. If a fixed IP address server is on the LAN and you
want this server to be visible via the WAN, you must add its IP address. Once the IP address has
been added, you can apply Port Forwarding and Access Control rules to this IP address.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.6 MAC Address Filters
The MAC filtering mechanism provides a way for the users to define rules to allow/deny frames
through the bridge based on source MAC address, destination MAC address and/or frame type.
When bridge filtering is enabled, each frame is examined against the defined filter rules
sequentially, and when a matched is determined, the appropriate filtering action (determined by
the access type selected . . . i.e. allow or deny) is performed. The user should note that the MAC
filter will only examined frames from interfaces that are part of the bridge itself. Twenty filter rules
are supported with MAC filtering. To enable MAC Filters, click Advanced and under Advanced,
select MAC Filters. Figure 15 illustrates a typical Bridge filter configuration.
The User Interface for MAC Filter allows the user to add/edit/delete, as well as, enables the filter
rules. To add rules, simply define the source MAC address, destination MAC address and frame
type with desired filtering type (i.e. allow/deny), and click the “Add” button. The MAC address
must be in the xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx format, with 00 -00-00-00-00-00 as “don’t care”. Blanks can be
used in the MAC address space, and would also be considered as “don’t care”.
To edit/modify an existing filter rule, select the desired rule created previously from “Add” in the
“Edit” select box. The selected filter rule will appear on the top section, as with the “Add” filter
rule. Make the desired change to the MAC address, frame type and/or access type, and click
“Apply”.
To delete filter rule(s), select the filter rule entry to delete in the “Delete” selection box. Note that
multiple deletions are possible. Once all the desired filter rule(s) is/are selected for deletion, click
- 24 -
Page 25

the “Apply” button. The “Select All” select box can also be used to delete the entire filter rule. It
provides a quick method of selecting all filter rules for deletion.
The “Enable MAC Filters” button allows the user to enable or disable MAC filtering. It can be
set/unset during any add/edit/delete operation. It can also be set/unset independently by just
clicking the “Apply” button.
Figure 15 (MAC Filters)
Note: The MAC filter table contains 3 hidden rules. These rules are entered automatically by the
system to ensure the user does not "lock" them out of the system. The first rule allows any and
all ARP frames through the system. The second rule allows all IPv4 frames with the destinat ion
MAC address of the bridge to go through. The third rule allows all IPv4 frames with the source
MAC address of the bridge to go through.
Note: On a Windows based machine, to find a MAC address, at the DOS prompt type ipconfig
/all.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.7 Multicast
Multicasting is a form of limited broadcast. UDP is used to send datagrams to all hosts that
belong to what is called a "host group". A host group is a set of zero or more hosts identified by
the same destination IP address. The following statements apply to host groups.
a. Anyone can join or leave a host group at will.
- 25 -
Page 26

b. There are no restrictions on a host's location.
c. There are no restrictions on the number of members that may belong to a host group.
d. A host may belong to multiple host groups.
e. Non-group members may send UDP datagrams to the host group.
Multicasting is usef ul when data needs to be sent to more than one other device. For instance, if
one device is responsible for acquiring data that many other devices need, then multicasting is a
natural fit. Note that using multicasting as opposed to sending the same data to individual
devices uses less network bandwidth.
To enable Multicasting, click on Advanced and under Advanced, select Multicast. Figure 16
illustrates a typical Multicast configuration.
Figure 16 (Multicast)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.8 Static Routing
If the ADSL router is connected to more than one network, you m ay need to set up a static route
between them. A static route is a pre -defined pathway that network information must travel to
reach a specific host or network. You can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to
access the Internet through the ADSL router.
The New Destination IP is the address of the remote LAN or host to which you want to assign a
static route. Enter the IP address of the host for which you wish to create a static route here. For
a standard Class C IP domain, the network address is the first three fields of the New Destination
IP, while the last field should be 0. The Subnet Mask identifies which portion of an IP address is
the network portion, and which portion is the host portion. For a full Class C Subnet, the Subnet
- 26 -
Page 27

Mask is 255.255.255.0. The Gateway IP address should be the IP address of the gateway device
that allows for contact between the Gateway and the remote network or host. The Hop Count
determines the maximum number of steps between network nodes that data packets will travel.
A node is any device on the network (such as a router or switch).
To enable Static Routing, from the Home page, click Advanced and under Advanced, select
Static Routing. Figure 17 illustrates a typical Static Route.
Figure 17 (Static Routing)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.6.9 Dynamic Routing
Dynamic Routing allows the ADSL router to automatically adjust to physical changes in the
network. The ADSL router, using the RIP protocol, determines the network packets’ route based
on the fewest number of hops between the source and the destination. The RIP protocol
regularly broadcasts routing information to other routers on the network.
The Direction determines the direction that RIP routes will be updated. Selecting In means that
the ADSL router will only incorporate received RIP information. Selecting Out means that the
ADSL router will only send out RIP information. Selecting both means that the ADSL router will
incorporate received RIP information and send out updated RIP information.
The protocol is dependent on the entire net work. Most networks support RIP v1. If RIP v1 is
selected, routing data will be sent in RIP v1 format. If RIP v2 is selected, routing data will be sent
- 27 -
Page 28

in RIP v2 format using subnet broadcasting. If RIP v1 Compatible is selected, routing data will be
sent in RIP v2 format using multicasting.
To enable Dynamic Routing, click Advanced and under Advanced, select Dynamic Routing.
Figure 18 illustrates a typical Dynamic Route.
Figure 18 (Dynamic Routing)
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.7 Tools
The ADSL router supports a host of tools that will allow you to customise and debug the ADSL
router.
4.7.1 System Commands
To make the changes permanent , you need to click on Tools (at the top of the page) and select
System Commands. The following commands are used to configure the gateway:
a. Save all: Click this button in order to permanently save the current configuration of the
ADSL router. If you do restart the system without savin g your configuration, the ADSL
router will revert back to the previously saved configuration.
b. Restart: Use this button to restart the system. If you have not saved your
configurations, the ADSL router will revert back to the previously saved configuration
upon restarting.
NOTE: Connectivity to the unit will be lost. You can reconnect after the unit reboots.
c. Restore Defaults: Use this button to restore factory default configurations.
NOTE: Connectivity to the unit will be lost. You can reconnect after the unit reboots.
- 28 -
Page 29

4.7.2 User Management
You can change the ADSL router’s username and password by clicking on User Management.
From here you can change the login name and password. You can also change the idle timeout;
you will need to log back onto the ADSL router once the timeout expires.
If you forget your password, you can press and hold the reset to factory defaults button for 10
seconds or more. The ADSL router will reset to its factory default configuration and all custom
configurations will be lost.
The Apply button will temporarily save this connection. To make the change permanent, you
need to click on Save Settings (at the side of the page). At the system commands page, click on
Save All.
4.7.3 Update Firmware
You can remotely update the ADSL router’s firmware, clicking on Update Firmware under the
Tools page. This will bring up the page shown in Figure 19. The update file shall be in *.img
format.
To updat e the firmware, click browse, find the firmware file to download. Make sure this is the
correct file. Click on Updat e Firmware (as shown in Figure 19). Once the update is completed,
the ADSL router will reboot. You will need to log back onto the ADSL router after the firmware
update is completed.
The firmware update should tak e about 5 minutes to complete.
Note: Do not re move power from the ADSL router during the firmware update procedure.
Figure 19 (Update Firmware)
- 29 -
Page 30

4.7.4 Ping Test
Once you have the ADSL router configured, it is a good idea to make sure you can ping the
network. You can get to the Ping page under the Tools title, by clicking on Ping Test. Type the
target address that you want to ping. If you have your computer connected to the ADSL router
via the default DHCP configuration, you should be able to Ping the network address 192.168.1.1.
If your ISP has provided their server address, you can try to ping the address. If the pings for
both the WAN and LAN side complete, and you have the proper protocols configured, you should
be able to surf the Internet.
By default when you select ping test, the ADSL router will ping itself 3 times. As shown in Figure
20, the ADSL router passed the Ping test; this basically means that the TCP/IP protocol is up and
running. If this first Ping test does not pass, the TCP/IP protocol is not loaded for some reason;
you should restart the ADSL router.
Figure 20 (Ping Test)
4.7.5 Modem Test
The Modem Test is used to check whether the ADSL router is prope rly connected to the WAN.
This test may take a few seconds to complete. To perform the test, select your connection from
the list and click the Test button. Before running this test, make sure you have a valid ADSL
connection; if the ADSL connec tion is not established, this test will always fail.
Also the DSLAM must support this feature; not all DSLAMs have F4 and F5 support.
4.8 Status
The Status section allows you to view the Status/Statistics of different connections and interfaces .
4.8.1 Network Statistics
Select to view the Statistics of different interfaces - Ethernet/ DSL.
- 30 -
Page 31

4.8.2 Connection Status
Select to view the Status of different connections.
4.8.3 DHCP Clients
Select to view the list of DHCP clients.
4.8.4 Modem Status
Select to view the Status and Statistics of your broadband (A DSL) connection.
4.8.5 Product Information
You can display the ADSL router’s driver and runtime information by going under Status title and
click on Product Information. Figure 21 illustrates the typical product information, which is
provided.
Figure 21 (Product Information)
4.8.6 System Log
You can display the ADSL router’s log by going under the Status title, click System Log. From
here you can view all logged information. Depending upon the severity level, this logged info will
generate log reports to a remote host (if remote logging is enabled).
- 31 -
Page 32

5. Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Below is a list of commonly asked questions. Before calling technical support, please look
through these issues to see if they help to solve you r problem.
5.1 The ADSL Router I s Not Functional
1. Check to see that the power LED is green and the network cables are connected
correctly. Refer to the Quick Installation Guide for more details.
2. Check to see that the ETH/LAN and PPP/WAN LEDs are green.
3. Check to see that the DSL LED is green.
4. Check the settings on your computer. Again, refer to the Quick Installation Guide for
more details.
5. Check the ADSL router’s settings.
6. From your computer, can you PING the ADSL router? Assuming that the ADSL
router has DHCP enabled and your computer is on the same subnet as the gateway,
you should be able to PING the gateway.
7. Can you PING the WAN IP? Your ISP should have provided the IP address of their
server. If you can ping the ADSL router and your protocols are confi gured correctly,
you should be able to ping the ISP’s network. If you cannot PING the ISP’s network,
make sure you are using the correct protocols with the correct VPI/VCI values.
8. Make sure NAT is enabled for your connection. If NAT is disabled, the ADSL router
will not route frames correctly (except in Bridge connection).
5.2 I Can’t Connect To The ADSL Router.
1. Check to see that the power LED is green and that the network cables are connected
correctly; see the Quick Installation Guide for more details.
2. Make sure that your computer and the ADSL router are on the same network
segment. The ADSL router’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1. If you are running a
Windows based computer, you can open a DOS window and type IPCONFIG; make
sure that the network adapter that is connected to the gateway is within the same
192.168.1.x subnet.
3. Also, your computer’s Subnet Mask should match the gateways subnet mask. The
gateway has a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
4. If this still does not work, press the reset button for 10 seconds. This will place the
gateway into its factory defa ult state. Go through the previous configurations again.
5. Make sure NAT is enabled for your connection. If NAT is disabled, the ADSL router
will not route frames correctly (except in Bridge connection).
5.3 The DSL Link LED Continues To Blink And Does Not Stop
1. This means that the ADSL is trying to train but for some reason it cannot establish a
valid connection. The main cause of this is that you are too far away from the central
office. Contact your ADSL Provider for further assistance.
2. Verify that the telephone cable is connected directly to the telephone wall socket and
to the DSL input on the ADSL router.
3. Make sure that for every parallel phone line connected to telephone or fax is installed
with a micro -filter.
Common Problems and Solutions
- 32 -
Page 33

5.4 The DSL Link LED Is Always Off
1. Make sure you have a ADSL service. You should get some kind of information from
your ISP that states that the ADSL service is enabled. You can usually tell if the
service is enabled by listening to the phone line; you will hear some high-pitched
noise. If you do not hear high-pitched noise, contact your ISP.
2. Verify that the telephone cable is connected directly to the telephone wall socket and
the DSL input on the ADSL router.
- 33 -
Page 34

6. ADSL Router Terms
What Is A Firewall?
A firewall is a protection between the Internet and your local network. It acts similarly to the
firewall in your car, protecting the interior of the car from the engine. Your car's firewall has very
small opening that allow desired connections from the engine into the cabin (gas pedal
connection, etc) but if something happens to your engine, you are protected.
The firewall in the ADSL router is very similar. Only the desired connections that you allow are
passed through the firewall. These conn ections are normally originating from the local network;
such as web browsing, checking your email, downloading a file, and playing a game. However, in
some cases, you can allow incoming connections so that you can run programs like a web server.
What Is NAT?
NAT stands for Network Address Translation. Another name for it is Internet Connection Sharing.
What does this mean? Your ISP provides you with a single network address for you to access
the Internet throug h. However, you may have several machines on your local network that want
to access the Internet at the same time. The ADSL router provides NAT functionality that
converts your local network addresses to the single network address provided by your ISP. It
keeps track of all these connections and makes sure that the correct information gets to the
correct local machine.
Occasionally, there are certain programs that don't work well through NAT. Some games and
some specialty applications have a bit of trouble. The ADSL router contains special functionality
to handle the vast majority of these troublesome programs and games. NAT does cause
problems when you want to run a server though. When running a server, please see the DMZ
section below.
What Is A DMZ?
DMZ really stands for Demilitarized Zone. It is a way of separating out part of your local network
so that is more open to the Internet. Suppose that you want to run a web server or a game
server. Normal servers like these are blocked from working by the NAT functionality. The
solution is to "isolate" the single local computer into a DMZ. This makes the single computer look
like it is directly connected to the Internet, and others can access this machine.
Your machine isn't really directly connected to the Internet, and it really has an internal local
network address. When you provide the server’s network address to others, you must provide
the address of the ADSL router. The ADSL router "fakes" the connection to your machine.
You should use the DMZ when you want to run a server that others will access from the Internet.
Internal programs and servers (like print servers, etc) should NOT be connected to the DMZ.
What Is A Gateway?
The Internet is so large that a single network cannot handle all of the traffic and still deliver a
reasonable level of service. To overcome this limitation, the network is broken down into smaller
segments or subnets that can deliver good performance for the stations attached to that segment.
This segmentation solves the problem of supporting a large number of stations but introduces the
problem of getting traffic from one subnet to another.
To accomplish this, devices called routers or gateways are placed between segments. If a
machine wishes to contact another device on the same segment, it transmits to that station
directly using a simple discovery technique. If the target station does not exist on the same
segment as the source station, then the source actually has no idea how to get to the target.
One of the configuration parameters transmitted to each network device is its default gateway.
This address is configured by the network administrators and it informs each personal computer
- 34 -
Page 35

or other network device where to send data if the target station does not reside on the same
subnet as the source. If your machine can reach all stations on the same subnet (usually a
building or a sector within a building) but cannot communicate outside of this area, it is usually
because of an incorrectly configured default gatew ay.
- 35 -
 Loading...
Loading...