Page 1

AT-ANC10S/2
10 Gigabit Network Interface Card
Installation and User’s Guide
613-002022 Rev. C
Page 2

Copyright 2018 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis and the Allied Telesis logo are trademarks of Allied Telesis, Incorporated. All other product names, company names,
logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document without prior
written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied Telesis, Inc. be liable for
any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related
to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has been advised of, known, or should have known, the
possibility of such damages.
Page 3
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards
This product meets the following standards.
Federal Communications Commission Interference Statement
Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer Name: Allied Telesis, Inc.
Declares that the product: NetExtreme II Family Adapter
Model Numbers: AT-ANC10S/2
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device must not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. End users must
follow the specific operating instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
IEEE802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to channels 1 through 11.
Industry Canada
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances
(RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment
This Allied Telesis RoHS-compliant product conforms to the European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous
Substances (RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Allied Telesis ensures RoHS conformance by requiring
supplier Declarations of Conformity, monitoring incoming materials, and maintaining manufacturing process controls.
3
Page 4

RFI Emissions FCC Class B, EN55022 Class B, VCCI Class B, C-TICK, CE
Immunity EN55024
Electrical Safety EN60950-1 (TUV), UL 60950-1 (
Laser Safety EN60825
CULUS
)
4
Page 5
Translated Safety Statements
Important: The symbol indicates that a translation of the safety statement is available in a PDF
document titled “Translated Safety Statements” on our web site at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support.
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

Contents
Preface ............................................................................................................................................................13
Safety Symbols Used in this Document .....................................................................................................14
Contacting Allied Telesis............................................................................................................................15
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter ..................................................................................... 17
Functional Descriptions..............................................................................................................................18
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Physical Description .......................................................................................19
Features.....................................................................................................................................................21
Adaptive Interrupt Frequency ..............................................................................................................21
ASIC with Embedded RISC Processor................................................................................................21
Supported Operating Environments .................................................................................................... 21
Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware ..............................................................................................................23
Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment ................................................................................................ 24
Reviewing Safety Precautions ...................................................................................................................25
Pre-Installation Checklist............................................................................................................................27
Installing the Standard Bracket on the Adapter..........................................................................................28
Installing the Network Adapter Card ..........................................................................................................30
Installing SFP+ Transceivers in the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter ......................................................................34
Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software ...................................................................35
Overview .................................................................................................................................................... 36
Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment ................................................................................................... 37
Enabling the MBA Driver ..................................................................................................................... 37
Disabling the MBA Driver ....................................................................................................................37
Setting Up the BIOS ............................................................................................................................ 37
Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server .....................................................38
Chapter 4: Installing the Linux Drivers ........................................................................................................ 39
Overview .................................................................................................................................................... 40
bnx2x Driver Limitations ...................................................................................................................... 40
Packaging............................................................................................................................................40
Installing Linux Driver Software..................................................................................................................41
Installing the Source RPM Package ....................................................................................................41
Building the Driver from the Source TAR File......................................................................................42
Unloading the Linux Driver .................................................................................................................. 43
Patching PCI Files (Optional) .............................................................................................................. 44
Network Installations ...........................................................................................................................44
Setting Optional Properties for the bnx2x Driver .................................................................................44
Checking the bnx2x Driver Defaults .................................................................................................... 45
Checking Driver Messages..................................................................................................................46
Teaming with Channel Bonding...........................................................................................................46
Statistics .....................................................................................................................
Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers .................................................................................................47
Supported Versions of Microsoft Windows ................................................................................................48
Installing the Windows Driver Software......................................................................................................49
Using the Installer................................................................................................................................50
.........................46
7
Page 8

Contents
Using Silent Installation....................................................................................................................... 54
Removing the Device Drivers .................................................................................................................... 57
Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties .................................................................................................... 59
Advanced Features ................................................................................................................................... 60
Accessing the Advanced Tab .................................................................................................................... 62
Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 ......................... 62
Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2012 ....................................................................... 63
Modifying the Advanced Properties........................................................................................................... 65
Chapter 7: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability ............................................................................. 75
Installing CIM............................................................................................................................................. 76
Loading the CIM Libraries ................................................................................................................... 77
Installing SNMP ......................................................................................................................................... 79
BASP Subagent .................................................................................................................................. 79
BASP Extensible-Agent ...................................................................................................................... 79
Loading the SNMP Libraries ............................................................................................................... 80
Chapter 8: Installing Management Applications ........................................................................................ 83
Installing Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 and Related Management Applications .......................... 84
Checking .NET Framework Requirements.......................................................................................... 84
Using the Installer ............................................................................................................................... 85
Using the Silent Install Option............................................................................................................. 85
Modifying Management Applications......................................................................................................... 88
Repairing Management Applications......................................................................................................... 89
Removing Management Applications ........................................................................................................ 90
Chapter 9: Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................................... 91
Checking Hardware Diagnostics ............................................................................................................... 92
Checking Port LEDs .................................................................................................................................. 93
Consulting the Troubleshooting Checklist ................................................................................................. 94
Checking the Current Drivers.............................................................................................................. 94
Running a Cable Length Test ............................................................................................................. 95
Testing Network Connectivity.............................................................................................................. 95
Solving Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V Issues .................................................................... 97
Single Network Adapter ...................................................................................................................... 97
Teamed Network Adapters ................................................................................................................. 98
Removing the Device Drivers.............................................................................................................. 98
Preparing an Answer File.................................................................................................................... 98
Solving Broadcom Boot Agent and Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) Issues .................... 100
Solving Miscellaneous Issues.................................................................................................................. 102
Chapter 10: User Diagnostics .................................................................................................................... 105
Overview.................................................................................................................................................. 106
System Requirements ............................................................................................................................. 107
Performing Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................... 108
Diagnostic Test Descriptions ................................................................................................................... 111
Appendix A: Technical Specifications ...................................................................................................... 117
Physical Specifications ............................................................................................................................ 117
Environmental Specifications .................................................................................................................. 117
Power Specifications ............................................................................................................................... 118
Performance Specification....................................................................................................................... 118
Appendix B: Cleaning Fiber Optic Connectors ........................................................................................ 119
Using a Cartridge-Type Cleaner.............................................................................................................. 120
Using a Swab .......................................................................................................................................... 122
8
Page 9

Figures
Figure 1: AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter ......................................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 2: AT-ANC10S/2 Faceplate...................................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 3: Package Contents of the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter................................................................................................. 24
Figure 4: Removing the Low-profile Bracket........................................................................................................................ 28
Figure 5: Installing the Standard Bracket............................................................................................................................. 29
Figure 6: Removing the PC Cover....................................................................................................................................... 31
Figure 7: Removing the Faceplate From PCIe Slot ............................................................................................................. 31
Figure 8: Inserting the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket ................................................................................................. 32
Figure 9: Securing the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket................................................................................................. 33
Figure 10: Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard Page.................................................................. 51
Figure 11: License Agreement Page ................................................................................................................................... 52
Figure 12: Ready to Install the Program Page..................................................................................................................... 53
Figure 13: InstallShield Wizard Completed Page ................................................................................................................ 54
Figure 14: Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Search Box .................................................................... 62
Figure 15: Device Manager Window.................................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 16: Windows Server 2012 Desktop .......................................................................................................................... 64
Figure 17: Windows Server 20112 Run Window................................................................................................................. 64
Figure 18: BACS CIM Option Window................................................................................................................................. 78
Figure 19: BACS SNMP Option Window............................................................................................................................. 81
Figure 20: Ferrule in an SC Connector Plug...................................................................................................................... 119
Figure 21: Unclean and Clean Ferrule............................................................................................................................... 119
Figure 22: Cartridge Cleaner ............................................................................................................................................. 120
Figure 23: Rubbing the Ferrule Tip on the Cleaning Surface ............................................................................................ 120
Figure 24: Lint-Free and Alcohol-Free Swabs................................................................................................................... 122
Figure 25: Cleaning a Recessed Ferrule........................................................................................................................... 122
9
Page 10

List of Figures
10
Page 11

Tables
Table 1. Network Adapter Card ..........................................................................................................................................18
Table 2. Network Link and Activity LEDs ............................................................................................................................20
Table 3. Linux Driver for the AT-ANC10S/2 Network Adapter ............................................................................................40
Table 4. Linux Driver Packaging .........................................................................................................................................40
Table 5. Default Values for the bnx2x Driver ......................................................................................................................45
Table 6. Supported Versions of Microsoft Windows ...........................................................................................................48
Table 7. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows Supported by the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter ..........................................60
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows ............................................................................................................65
Table 9. Linux Module Size ................................................................................................................................................95
Table 10. uediag Command Options ................................................................................................................................108
Table 11. Diagnostic Tests ...............................................................................................................................................111
Table 12. AT-ANC10S/2 Physical Specifications .............................................................................................................117
Table 13. Environmental Specifications ............................................................................................................................117
Table 14. Operating Voltages and Maximum Power Consumption ..................................................................................118
11
Page 12

List of Tables
12
Page 13

Preface
This guide contains instructions on how to install and configure the
AT-ANC10S/2 adapter.
The Preface discusses the following topics:
“Safety Symbols Used in this Document” on page 14
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 15
13
Page 14

Preface
Note
Caution
Warning
Warning
Safety Symbols Used in this Document
This document uses the following conventions:
Notes provide additional information.
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
Laser warnings inform you that an eye or skin hazard exists due to
the presence of a Class 1 laser device.
14
Page 15

Contacting Allied Telesis
If you need assistance with this product, you may contact Allied Telesis
technical support by going to the Support & Services section of the Allied
Telesis web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. You can find links for
the following services on this page:
24/7 Online Support — Enter our interactive support center to
search for answers to your product questions in our knowledge
database, to check support tickets, to learn about RMAs, and to
contact Allied Telesis technical experts.
USA and EMEA phone support — Select the phone number that
best fits your location and customer type.
Hardware warranty information — Learn about Allied Telesis
warranties and register your product online.
Replacement Services — Submit a Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) request via our interactive support center.
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Documentation — View the most recent installation and user
guides, software release notes, white papers, and data sheets for
your products.
Software Downloads — Download the latest software releases for
your managed products.
For sales or corporate information, go to www.alliedtelesis.com/
purchase and select your region.
15
Page 16

Preface
16
Page 17

Chapter 1
Introducing the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
This chapter provides an introduction to the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter and discusses the following topics:
“Functional Descriptions” on page 18
“Features” on page 21
17
Page 18
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Note
Functional Descriptions
The AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter is a new class of 10 Gigabit Ethernet
(10GbE) interface controller that is based on the Broadcom 57810 10Gb
network controller. It can perform accelerated Ethernet data networking
and storage networking simultaneously for all popular protocols used in
the data center, and includes features such as:
Data Center Bridging
SR-IOV
Enterprise networks that use multiple protocols and multiple network
fabrics benefit from the NICs ability to combine data communications,
storage, and clustering over a single Ethernet fabric and to boost server
CPU processing performance and memory utilization while alleviating I/O
bottlenecks.
The basic characteristics of the adapter is listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Network Adapter Card
Adapter Number of Slots Speed
AT-ANC10S/2 Two slots for SFP+
transceivers
The maximum operating distances of the SFP+ slots on the adapter
depend on the transceivers. Contact your Allied Telesis sales
representative for a list of supported transceivers for the adapter.
As part of the company’s green range, the adapter is engineered to reduce
power consumption. It incorporates centralized power management
features that automatically place idle circuitry into a lower power mode to
save energy.
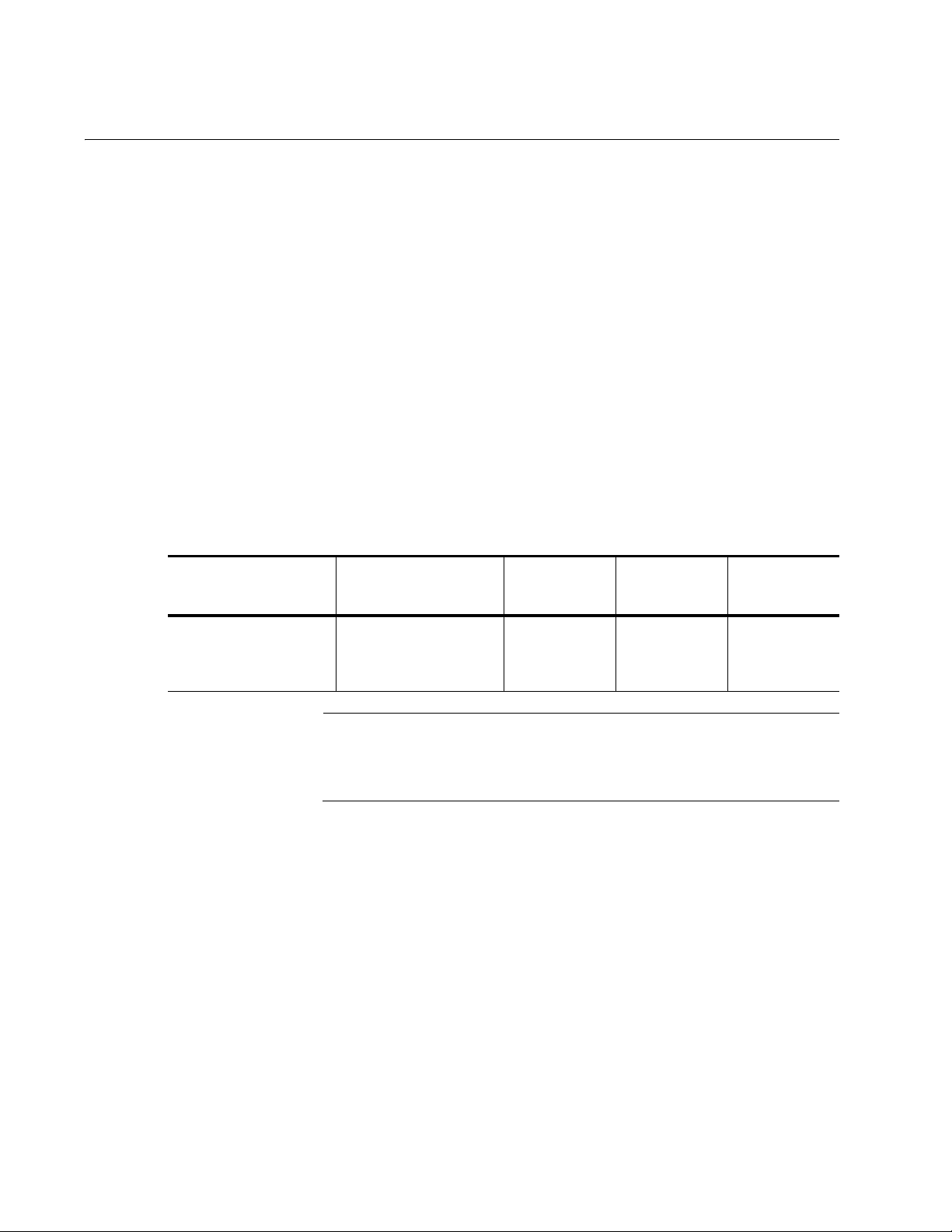
The AT-ANC10S/2 adapter, shown in Figure 1 on page 19, has two slots
for SFP+ modules that operate at 10 Gbps in full duplex mode. You cannot
change the speed or duplex mode of the transceiver slots. The maximum
operating distance of an SFP+ slot will vary depending on the SFP+
transceiver and type of fiber optic cabling.
Maximum
Distance
10 Gbps Varies by
SFP+
transceiver
Bus
Connector
PCIe x8
The adapter has an PCIe x8 motherboard bus connector.
18
Page 19
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 1. AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
AT-ANC10S/2
Adapter Physical
Description
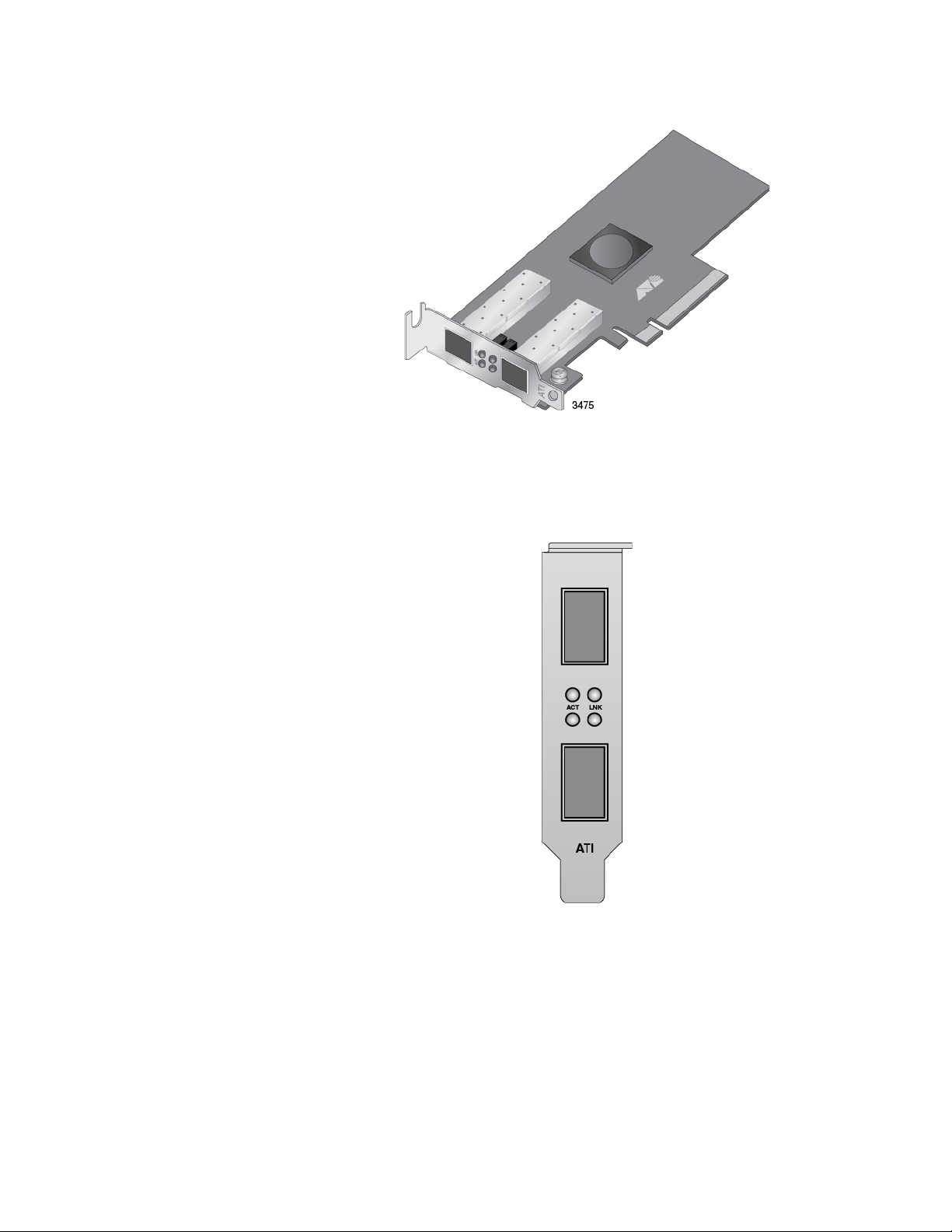
The faceplate on the AT-ANC10S/2 adapter, shown in Figure 2 on page
19, has two slots for SFP+ transceivers, and four LEDs.
Figure 2. AT-ANC10S/2 Faceplate
The LEDs for the SFP+ slots are described in Table 2 on page 20.
19
Page 20
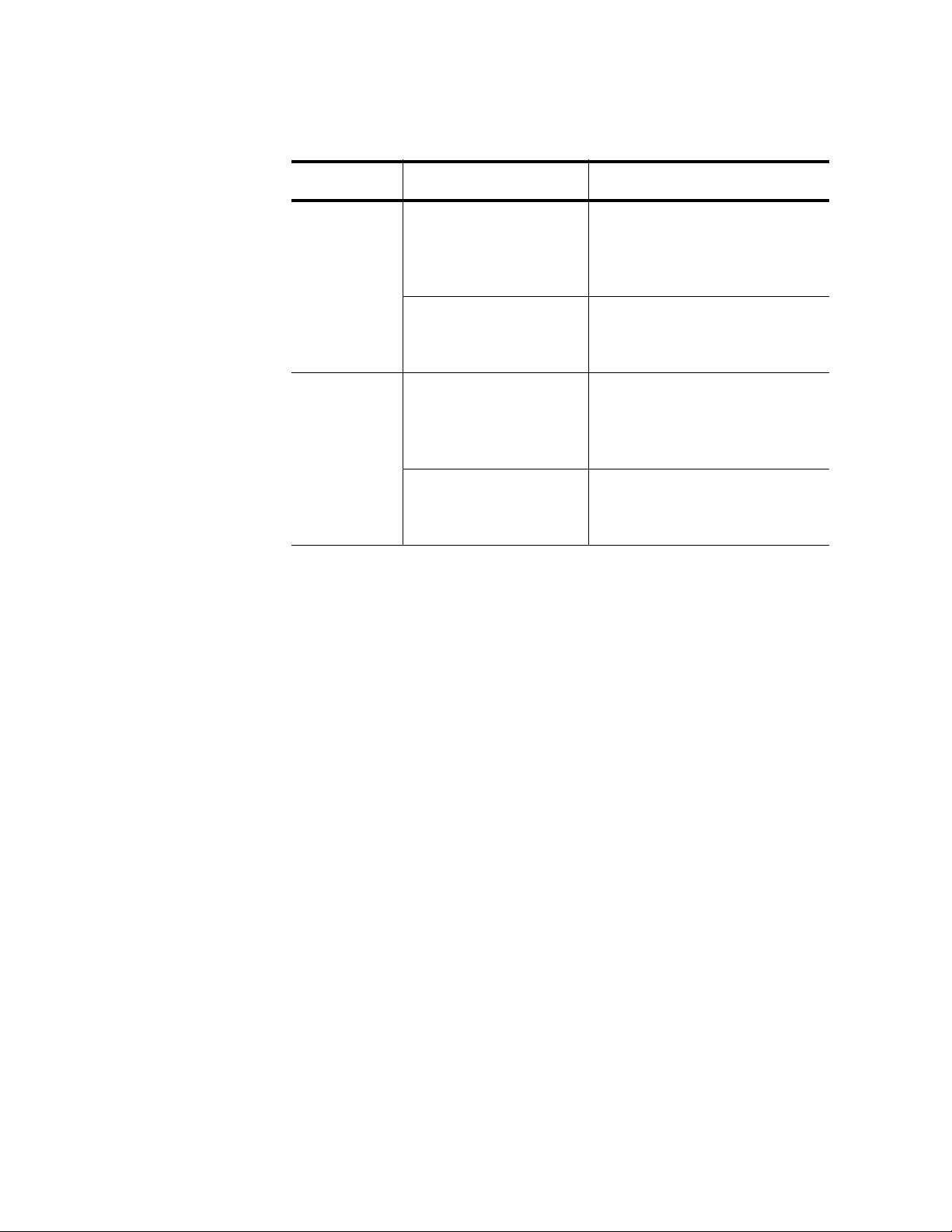
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Port LED LED State Network State
ACT LED Off The slot is empty or the
LNK LED Off The slot is empty or the
Table 2. Network Link and Activity LEDs
transceiver in the slot is not
transmitting or receiving
network traffic.
Blinking The transceiver in the slot is
transmitting or receiving
network traffic.
transceiver has not
established a link to a remote
device.
Steady On The transceiver has
established a link to a remote
device.
20
Page 21

Features
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
The following features apply to the AT-ANC10S/2 adapter:
Dual 10 Gbps MAC on the AT-ANC10S/2 adapter
TCP segmentation offload
PXE v2.1 remote boot
Receive side scaling (RSS) for IPv4 and IPv6
Statistics gathering (SNMP MIB II)
Comprehensive diagnostic and configuration software suite
ACPI compliant power management
Virtual LANs-802.1q VLAN tagging
Jumbo frames (up to 9 KB). The OS and link partner must support
jumbo frames.
MSI, MSI-X
Adaptive
Interrupt
Frequency
ASIC with
Embedded RISC
Processor
LiveLink™
PCI Express x8 v3.0, 8 GTps-compliant
PCI Express x8 v2.0, 5 GTps-compliant
PCI Express x8 v1.1, 2.5 GTps-compliant
Smart Load Balancing Teaming
IEEE Std 802.3ad teaming
The adapter driver intelligently adjusts host interrupt frequency based on
traffic conditions to increase overall application throughput. When traffic is
light, the adapter driver interrupts the host for each received packet,
minimizing latency. When traffic is heavy, the adapter issues one host
interrupt for multiple, back-to-back incoming packets, preserving host CPU
cycles.
The core control for the ANC10S/2 network adapter resides in a tightly
integrated, high-performance ASIC. The ASIC includes a RISC processor.
This functionality provides the flexibility to add new features to the card
and adapts it to future network requirements through software downloads.
This functionality also enables the adapter drivers to exploit the built-in
host offload functions on the adapter as host operating systems are
enhanced to take advantage of these functions.
Supported
Operating
Environments
The ANC10S/2 network adapter has software support for the following
operating systems:
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
21
Page 22

Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012 and 2012 R2 Hyper-V
Linux
Solaris x86
ESX Server (VMware)
Citrix XenServer
(32-bit and 64-bit extended)
22
Page 23

Chapter 2
Installing the Hardware
This chapter describes how to install the AT-ANC10S/2 in a PC and
discusses the following topics:'
“Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment” on page 24
“Reviewing Safety Precautions” on page 25
“Pre-Installation Checklist” on page 27
“Installing the Standard Bracket on the Adapter” on page 28
“Installing the Network Adapter Card” on page 30
“Installing SFP+ Transceivers in the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter” on
page 34
23
Page 24

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
AT-ANC10S/2
adapter with preinstalled low profile
bracket.
Standard bracket.
Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment
The AT-ANC10S/2 adapter comes with two brackets: a pre-installed lowprofile bracket and a standard bracket. Refer to Figure 3.
24
Figure 3. Package Contents of the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Inform your network supplier of any missing or damaged items. If you
need to return the adapter, you must pack it in the original (or equivalent)
packing material or the warranty will be voided. See “Contacting Allied
Telesis” on page 15.
Page 25

Reviewing Safety Precautions
Note
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Note
Please review the following safety precautions before you begin to install a
network adapter card.
The indicates that a translation of the safety statement is
available in a PDF document titled “Translated Safety Statements”
on the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/
software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to
view the current list of documents.
This is a Class 1 Laser product. L1
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
The fiber optic ports contain a Class 1 Laser device. When the ports
are disconnected, always cover them with the provided plug.
Exposed ports may cause skin or eye damage. L4
Do not stare into the laser beam. L2
Do not look directly at the fiber optic cable ends or inspect the cable
ends with an optical lens. L6
Do not work on this equipment or cables during periods of lightning
activity. E2
All Countries: Install this product in accordance with local and
National Electric Codes. E8
25
Page 26

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Warning
The adapter is being installed in a system that operates with
voltages that can be lethal. Before you remove the cover of your
system, you must observe the following precautions to protect
yourself and to prevent damage to the system components.
- Remove any metallic objects or jewelry from your hands and
wrists.
- Make sure to use only insulated or nonconducting tools.
- Verify that the system is powered OFF and unplugged before
accessing internal components.
- Installation or removal of adapters must be performed in a staticfree environment.
The use of a properly grounded wrist strap or other personal
antistatic devices and an antistatic mat is strongly recommended.
E39
26
Page 27

Pre-Installation Checklist
Note
Before installing the adapter card, perform the following procedure:
1. Verify that your system is using the latest BIOS.
2. If your system is active, shut it down.
3. When the system shutdown is complete, power OFF and unplug the
power cord.
4. Holding the adapter card by the edges, remove it from its shipping
package and place it on an antistatic surface.
5. Check the adapter for visible signs of damage, particularly on the
card’s edge connector.
Do not install a damaged adapter. If the adapter is damaged, report
it to Allied Telesis. See “Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 15.
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
27
Page 28
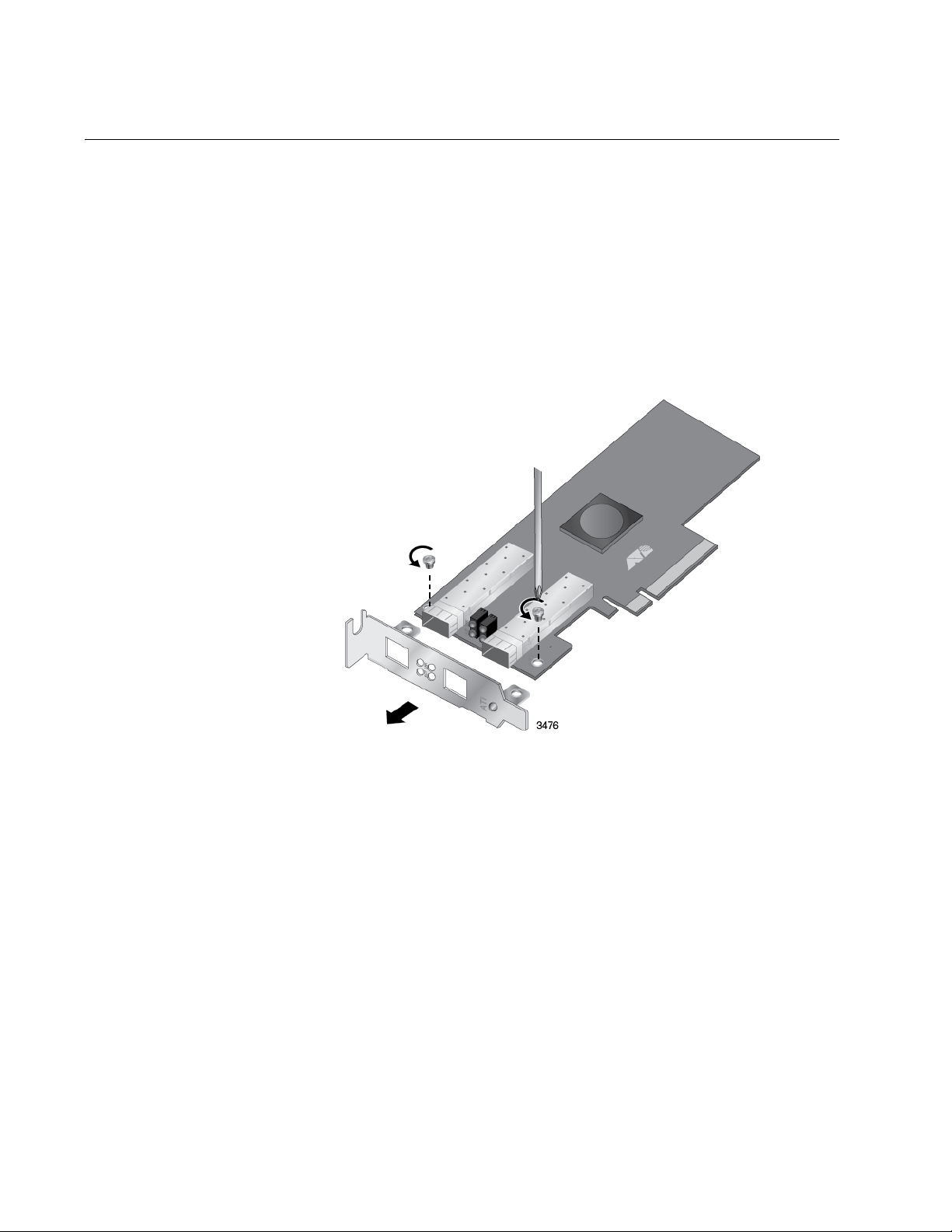
Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Installing the Standard Bracket on the Adapter
If you are installing AT-ANC10S/2 adapter in a computer that requires a
standard bracket, you must replace the pre-installed low profile bracket on
the adapter with the standard bracket. To install the standard bracket,
perform the following procedure:
To replace the low-profile bracket with the standard bracket, do the
following:
1. Remove the screws that attach the bracket to the adapter. See
Figure 4.
28
Figure 4. Removing the Low-profile Bracket
2. Fit the standard bracket onto the adapter as shown in Figure 5 on
page 29 and secure with the two screws.
Page 29
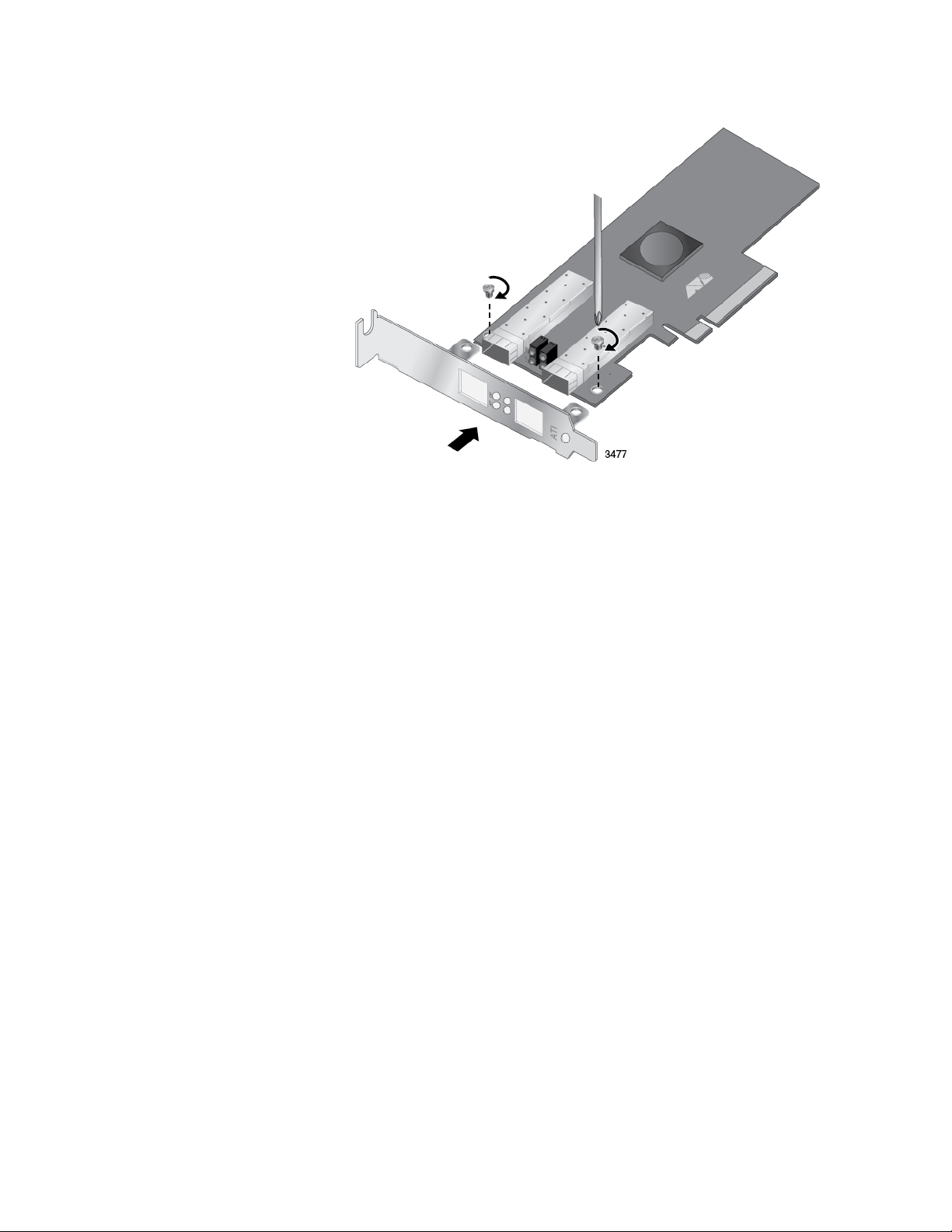
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 5. Installing the Standard Bracket
29
Page 30

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Note
Note
Warning
Installing the Network Adapter Card
The following installation instructions apply to most systems. For details
about performing the tasks on your particular system, refer to the manuals
that were supplied with your system.
This procedure requires a Phillips-head screw.
The AT-ANC10S/2 adapter requires a PCIe x8 PC.
The adapter is being installed in a system that operates with
voltages that can be lethal. Before you remove the cover of your
system, you must observe the following precautions to protect
yourself and to prevent damage to the system components.
- Remove any metallic objects or jewelry from your hands and
wrists.
- Make sure to use only insulated or nonconducting tools.
- Verify that the system is powered OFF and unplugged before
accessing internal components.
- Installation or removal of adapters must be performed in a staticfree environment.
The use of a properly grounded wrist strap or other personal
antistatic devices and an antistatic mat is strongly recommended.
E39
To install the adapter, do the following:
1. Review the “Pre-Installation Checklist” on page 27 and “Reviewing
Safety Precautions” on page 25.
Before installing the adapter, verify that the computer is powered OFF
and that the power cord is unplugged from the power outlet. You
should also be sure to follow all proper electrical grounding
procedures.
30
2. Remove the system cover. Refer to Figure 6 on page 31.
Page 31

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Figure 6. Removing the PC Cover
3. Select an empty, non-shared PCIe slot and remove the faceplate.
If you cannot locate or do not know how to find an appropriate PCIe
slot, refer to the documentation that came with your system.
Keep the faceplate in a safe place. You may need it for future use. See
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Removing the Faceplate From PCIe Slot
31
Page 32

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Caution
4. Remove the network adapter card from the shipping package and
store the packaging material in a safe location.
5. Applying even pressure at both corners of the card, push the adapter
card until it is firmly seated in the appropriate PCIe slot. Refer to
Figure 8. Make sure the card is securely seated.
Figure 8. Inserting the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket
Do not use excessive force when seating the card, because this
may damage the system or adapter. If the card resists seating,
remove it from the system, realign it, and try again. E47
6. Secure the network adapter card to the chassis with a Phillips-head
screw (not provided). See Figure 9 on page 33.
32
Page 33

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 9. Securing the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket
7. Replace the system’s cover and secure it with the screws removed in
step 2.
8. Go to “Installing SFP+ Transceivers in the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter” on
page 34.
9. Power on the system.
33
Page 34

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Warning
Warning
Note
Note
Installing SFP+ Transceivers in the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Here are the guidelines to installing and cabling SFP+ transceivers in the
AT-ANC10S/2 adapter:
SFP+ transceivers can be hot-swapped while the adapter is
powered on. However, you should always disconnect the fiber
optic cables first before removing a transceiver.
You should install a transceiver in the adapter before connecting
the fiber optic cable.
Fiber optic transceivers are dust sensitive. Always keep the plug in
the optical bores when a fiber optic cable is not installed, or when
you store the transceiver. When you do remove the plug, keep it
for future use.
Unnecessary removal and insertion of a transceiver can lead to
premature failure.
The connector on the fiber topic cable should fit snugly into the port
on the adapter, and the tab should lock the connector into place.
Do not remove the dust cover from a fiber optic port until you are
ready to connect a fiber optic cable. Dust contamination can
adversely affect the operation of a fiber optic port.
A transceiver can be damaged by static electricity. Be sure to
observe all standard electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions,
such as wearing an antistatic wrist strap, to avoid damaging the
device. E86
The fiber optic ports contain a Class 1 laser device. When the ports
are disconnected, always cover them with the provided plug.
Exposed ports may cause skin or eye damage. L4
The cable specifications for the SFP+ transceivers are found in the
installation guides that ship with the devices.
34
For information about cleaning a fiber optic connector on the
AT-ANC10S adapter, see Appendix B “Cleaning Fiber Optic
Connectors” on page 119.
Page 35

Chapter 3
Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
This chapter provides information about how to install the Broadcom Boot
Agent Driver Software and discusses the following topics:
“Overview” on page 36
“Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment” on page 37
“Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server”
on page 38
35
Page 36

Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
Overview
The AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter supports Preboot Execution
Environment (PXE). Multi-Boot Agent (MBA) is a software module that
allows your network computer to boot with the images provided by remote
servers across the network. The Broadcom MBA driver complies with PXE
2.1 code.
The MBA module operates in a client/server environment. A network
consists of one or more boot servers that provide boot images to multiple
computers through the network. The Broadcom implementation of the
MBA module has been tested successfully in the following environments:
Linux Red Hat PXE Server. Broadcom PXE clients are able to
remotely boot and use network resources (NFS mount, and so
forth) as well as perform Linux installations. In the case of a remote
boot, the Linux universal driver binds seamlessly with the
Broadcom Universal Network Driver Interface (UNDI) and provides
a network interface in the Linux remotely-booted client
environment.
Intel APITEST. The Broadcom PXE driver passes all API
compliance test suites.
Windows Deployment Service (WDS). For Windows Server
2003 SP2, RIS was replaced by WDS, which offers a Broadcom
PXE client to install Windows operating systems, including
Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008
R2.
36
Page 37

Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment
Note
Note
Setting up a Multiple Boot Agent (MBA) in a client environment involves
the following procedures:
“Enabling the MBA Driver” on page 37
“Disabling the MBA Driver” on page 37
“Setting Up the BIOS” on page 37
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Enabling the
MBA Driver
Disabling the
MBA Driver
To enable MBA, perform the following procedure:
1. Power on the system with the card installed.
2. When prompted, enter CTRL-S to enter the NIC setup menu.
3. Set the pre-boot to PXE, which is the default setting.
To disable MBA, perform the following procedure:
1. Power on the system with the card installed.
2. When prompted, enter CTRL-S to enter the NIC setup menu.
3. Set the pre-boot to None.
If you set PXE to None on all the ports on the adapter, you will not be
able to access the CTRL-S prompt and NIC setup menu.
The message prompting you to press CTRL+S is displayed only
once even if the computer has more than one AT-ANC10S Interface
Adapter. After you press CRTL+S, the Broadcom Comprehensive
Control Manager displays all the Broadcom devices that are
installed in the computer and that you can configure.
Setting Up the
BIOS
To boot from the network with the MBA, make the MBA enabled adapter
the first bootable device under the BIOS. This procedure depends on the
system BIOS implementation. Refer to the user manual for the system
BIOS implementation for instructions.
37
Page 38

Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution has PXE Server support. It
allows users to remotely perform a complete Linux installation over the
network. The distribution comes with the boot images boot kernel
(vmlinuz) and initial ram disk (initrd), which are located on the Red Hat
disk#1:
/images/pxeboot/vmlinuz
/images/pxeboot/initrd.img
Refer to the Red Hat documentation for instructions on how to install PXE
Server on Linux.
However, the Initrd.img file distributed with some Red Hat Enterprise Linux
distributions does not have a Linux network driver for the AT-ANC10S/2
network adapter. These distributions require a driver disk for drivers that
are not part of the standard distribution. You download the driver software
files from the Allied Telesis web site.
38
Page 39

Chapter 4
Installing the Linux Drivers
The procedures in this chapter explain how to install the Linux drivers for
the adapter.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Overview” on page 40
“Installing Linux Driver Software” on page 41
39
Page 40

Chapter 4: Installing the Linux Drivers
Overview
This chapter discusses the Linux drivers for the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter and describes how to install them. For a description of the drivers,
see Table 3.
Table 3. Linux Driver for the AT-ANC10S/2 Network Adapter
Linux Driver Description
bnx2x Indicates the Linux drivers for the AT-ANC10S/
2 network adapter. The bnx2x driver is the
networking driver.
bnx2x Driver
Limitations
The current version of the driver has been tested on 2.4.x kernels (starting
from 2.4.24) and all 2.6.x kernels. The driver may not compile on kernels
older than 2.4.24.
Testing is concentrated on i386 and x86_64 architectures. Only limited
testing has been done on other architectures. You may need to make
minor changes to some source files and the Makefile on some kernels.
Packaging The Linux driver is released in the packaging formats shown in Table 4.
The NetXtreme2 package contains the bnx2x (10 Gb network adapter)
and drivers for source RPM and compressed tar.
Table 4. Linux Driver Packaging
Format
Source RPM Netxtreme2-version.src.rpm
Compressed TAR Netxtreme2-version.tar.gz
Supplemental TAR Netxtreme2_sup-version.tar.gz
Identical source files to build the driver are included in both RPM and TAR
source packages. The supplemental tar file contains additional utilities
such as patches and driver diskette images for network installation.
bnx2x Driver
40
Page 41

Installing Linux Driver Software
Note
Note
There are two ways to install the Linux driver software — from the Source
RPM Package or by building the driver from the source TAR file. See the
following sections:
“Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 41
“Building the Driver from the Source TAR File” on page 42
If a bnx2x driver is loaded and you update the Linux kernel, you
must recompile the driver module if it was installed using the source
RPM or the TAR package.
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Installing the
Source RPM
Package
The procedure in this section describes how to install the Source RPM
Package.
To install the Source RPM Package, do the following:
1. Enter the following command:
rpm -ivh netxtreme2-version.src.rpm
2. Change the directory to the RPM path and build the binary driver for
your kernel (the RPM path is different for each Linux distribution):
cd /usr/src/
rpm -bb SPECS/netxtreme2.spec
or
rpmbuild -bb SPECS/netxtreme2.spec (for RPM version
4.x.x)
The error message error: cannot create %sourcedir /
usr/src/redhat/SOURCES is displayed if the rpm-build package
is not installed. To resolve the problem, locate the rpm-build
package on the Linux installation media and install it using the
following command:
rpm -ivh rpm-build-version.arch.rpm
Then complete the installation of the source RPM.
redhat,OpenLinux,turbo,packages,rpm
...
3. Install the newly built package which includes the driver and man
page:
41
Page 42

Chapter 4: Installing the Linux Drivers
rpm -ivh RPMS/i386/bnx2x-
If you are installing over an existing distribution that may already
contain an older version of the driver, the —force option is needed.
Depending on the kernel, the driver is installed to one of the following
paths:
For 2.4.x kernels
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/net/bnx2x.o
For 2.6.x kernels:
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/net/
bnx2x.ko
4. To load the driver, enter one of the following commands:
insmod bnx2x
or
modprobe bnx2x
version
.arch.rpm
Building the
Driver from the
Source TAR File
To configure the network protocol and address, refer to the documentation
provided with your operating system.
This procedure describes how to build the bnx2x Linux driver from the
Source TAR file.
Building the bnx2x Driver
To build the bnx2x Linux driver from the Source TAR file, do the following:
1. Create a directory and extract the TAR files to the following directory:
tar xvzf netxtreme2-
2. Build the driver bnx2x.ko (or bnx2x.o) as a loadable module for the
running kernel. Enter the following commands:
cd bnx2xmake
3. Test the driver by loading it (if necessary, first unload the existing
driver). Enter the following commands:
version
version
/src
.tar.gz
42
rmmod bnx2x
insmod bnx2x.o
modprobe crc32 && insmod bnx2x.o
Page 43

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
or, for Linux 2.6 kernels:
rmmod bnx2x
insmod bnx2x.ko
4. Install the driver and man page by entering the following command:
make install
See the “Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 41 for the
location of the installed driver.
To configure the network protocol and address after building the driver,
refer to the manuals supplied with your operating system.
Unloading the
Linux Driver
You can unload, or remove, the Linux Driver from an RPM or TAR
installation. See the following:
“Unloading the Driver from an RPM Installation” on page 43
“Unloading the Driver from a TAR Installation” on page 43
Unloading the Driver from an RPM Installation
This section describes how to unload, or remove, a Linux driver from an
RPM installation.
On 2.6 kernels, it is not necessary to bring down the eth# interfaces
before unloading the driver module.
To unload the driver, use ifconfig to bring down all eth# interfaces
opened by the driver, and then enter:
rmmod bnx2x
If the driver was installed using the rpm command, enter the following
command to remove it:
rpm -e netxtreme2
Unloading the Driver from a TAR Installation
If the driver was installed using make install from the tar file, manually
delete the bnx2x.o or bnx2x.ko driver file from the operating system. See
“Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 41 for the location of the
installed driver.
43
Page 44

Chapter 4: Installing the Linux Drivers
Patching PCI
Files (Optional)
This is an optional procedure that describes how to patch PCI files for
identification by other vendors.
For hardware detection utilities, such as Red Hat kudzu, to properly
identify bnx2x supported devices, you may need to update a number of
files containing PCI vendor and device information.
Apply the updates by running the scripts provided in the supplemental tar
file. For example, on Red Hat Enterprise Linux, apply the updates by
entering the following commands:
./patch_pcitbl.sh /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable
pci.updates
/usr/share/hwdata/pcitable.new bnx2x
./patch_pciids.sh /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids
pci.updates
/usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids.new
Next, back up the old files and rename the new files by entering the
following copy commands:
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids /usr/share/hwdata/
old.pci.ids
Network
Installations
Setting Optional
Properties for the
bnx2x Driver
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids.new /usr/share/hwdata/
pci.ids
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable /usr/share/hwdata/
old.pcitable
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable.new /usr/share/hwdata/
pcitable
For network installations through NFS, FTP, or HTTP (using a network
boot disk or PXE), a driver disk that contains the bnx2x driver may be
needed. The driver disk images for the most recent Red Hat and SuSE
versions are included. Boot drivers for other Linux versions can be
compiled by modifying the Makefile and the make environment. Further
information is available from the Red Hat website at www.redhat.com.
The disable_msi optional property can be used as a command line
argument to the insmod or modprobe command. The property can also be
set in the modprobe.conf command. See the man page for more
information.
All other driver settings can be queried and changed using the ethtool
utility. See the ethtool man page for more information. The ethtool
settings do not persist across a reboot or module reload. In addition, you
can put the ethtool commands in a startup script, such as /etc/rc.local, to
44
Page 45

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
preserve the settings across a reboot.
Some combinations of property values may conflict and result in
failures. The driver cannot detect all conflicting combinations.
This property is used to disable Message Signal Interrupts (MSI). The
property is valid only on 2.6 kernels that support MSI. This property cannot
be used on 2.4 kernels. By default, the driver enables MSI if it is supported
by the kernel. It runs an interrupt test during initialization to determine if
MSI is working. If the test passes, the driver enables MSI. Otherwise, it
uses legacy INTx mode. To set the bnx2x driver, enter one of the
following:
insmod bnx2x.ko disable_msi=1
or
modprobe bnx2x disable_msi=1
Checking the
bnx2x Driver
Defaults
The bnx2x driver default values are listed in Table 5:
Table 5. Default Values for the bnx2x Driver
Parameter
Speed 10Gbps Full Duplex
Flow Control Autonegotiation with RX and TX
advertised
MTU 1500 (range is 46–9000)
RX Ring Size 255 (range is 0–4080)
RX Jumbo Ring Size 0 (range 0–16320) adjusted by the
driver based on MTU and RX Ring
Size
TX Ring Size 255 (range is
(MAX_SKB_FRAGS+1)–255).
MAX_SKB_FRAGS varies on
different kernels and different
architectures. On a 2.6 kernel for
x86, MAX_SKB_FRAGS is 18.
Default Value
Coalesce RX Microseconds 18 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce RX Microseconds IRQ 18 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce RX Frames 6 (range is 0–255)
45
Page 46

Chapter 4: Installing the Linux Drivers
Table 5. Default Values for the bnx2x Driver (Continued)
Checking Driver
Messages
Parameter
Coalesce RX Frames IRQ 6 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce TX Microseconds 80 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce TX Microseconds IRQ 80 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce TX Frames 20 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce TX Frames IRQ 20 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce Statistics Microseconds 999936 (approximately 1 second)
(range is 0–16776960 in
increments of 256)
MSI Enabled (if supported by the 2.6
kernel and the interrupt test
passes)
TSO Enabled (on 2.6 kernels)
WoL Not supported.
The following are the most common sample messages that may be logged
in the /var/log/messages file for the bnx2x driver. Use dmesg -n
<level> command to control the level at which messages appear on the
console. Most systems are set to level 6 by default. To see all messages,
set the level higher.
Default Value
Teaming with
Channel Bonding
Statistics You can view detailed statistics and configuration information using the
46
Driver Sign on
NIC Detected
Link Up and Speed Indication
Link Down Indication
MSI enabled successfully
With the Linux drivers, you can team adapters together using the bonding
kernel module and a channel bonding interface. For more information, see
the Channel Bonding information in your operating system documentation.
ethtool utility. See the ethtool man page for more information.
Page 47

Chapter 5
Installing the Windows Drivers
This chapter provides procedures to install and remove the driver software
for all of the Windows Operating Systems supported by the AT-ANC10S/2
adapter. In addition, it describes how to display and change adapter
properties including power management options. This chapter discusses
the following topics:
“Supported Versions of Microsoft Windows” on page 48
“Installing the Windows Driver Software” on page 49
“Removing the Device Drivers” on page 57
47
Page 48

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
Supported Versions of Microsoft Windows
Table 6 lists the versions of Microsoft Windows supported by the adapter.
Table 6. Supported Versions of Microsoft Windows
Version of Microsoft Windows
Operating System
Windows Vista 32/64 -
Windows 7 32/64 -
Windows Server 2003 32/64 -
Windows Server 2008 32/64 Yes
Windows Server 2008 R2 Yes
Windows Server 2012 Yes
Windows Server 2012 R2 Yes
AT-AN C10S/ 2
48
Page 49

Installing the Windows Driver Software
Note
Note
Note
This chapter describes how to install all of the following Windows
Operating Systems:
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2
The Windows driver software for all of the Windows Operating Systems is
available on the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/
support/software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to
display the current list of software drivers.
There are two methods to install the software drivers on all of the Windows
Operating Systems: the Installer and Silent installation. The Installer uses
a graphical interactive mode. The Silent Installation is a command-line
interface for unattended installation. See the following sections:
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
“Using the Installer” on page 50
“Using Silent Installation” on page 54
These instructions are based on the assumption that your adapter
was not factory installed. If your controller was installed at the
factory, the driver software has been installed for you.
Before installing the driver software, verify that the Windows
operating system has been upgraded to the latest version with the
latest service pack applied.
You must physically install a network device driver before the ATANC10S/2 network adapter can be used with your Windows
Operating System. There is no installation CD. You must download
the drivers from the Allied Telesis website at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software. After you have
accessed this website, enter the model number in the Search by
Product Name box and then click Find to view the current list of
documents and drivers.
49
Page 50

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
Using the
Installer
Please read the following information before installing the driver:
Microsoft Windows Operating Systems do not have wizards but
will attempt to install the driver automatically. These processes
should be cancelled. Only the installer should be used to install the
driver.
Do not use any Microsoft Windows wizards to install the driver. All
wizards and informational boxes should be closed or cancelled
before running the installer.
The Installer has a graphical interactive installation mode. To install the
AT-ANC10S/2 driver on a Windows Operating System, do the following:
1. From the driver directory, select the setup.exe file and Run.
The Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard
Page is displayed. See Figure 10 on page 51.
50
Page 51

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 10. Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard
Page
2. Click Next to continue.
The License Agreement Page is displayed. See Figure 11 on page 52.
51
Page 52

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
Figure 11. License Agreement Page
3. After you review the license agreement, click I accept the terms in
the license agreement and then click Next to continue.
The Ready to Install the Program Page is displayed. See Figure 12 on
page 53.
52
Page 53

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 12. Ready to Install the Program Page
4. Click Install.
The InstallShield Wizard Completed Page is displayed. See Figure 13
on page 54.
53
Page 54

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
Note
Using Silent
Installation
Figure 13. InstallShield Wizard Completed Page
5. Click Finish to close the wizard.
6. The installer determines if a system restart is necessary. Follow the
on-screen instructions.
Silent installation provides a command-line silent mode which allows for
unattended installation. This section discusses the various ways to
perform a silent installation on all of the Windows Operating Systems
supported by the AT-ANC10S/2 adapter. See the following sections:
“Performing a Silent Install” on page 55
“Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File” on page 55
“Performing a Silent Upgrade” on page 55
“Performing a Silent Uninstall” on page 55
“Performing a Silent Reinstall” on page 56
All commands are case sensitive.
54
Page 55

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
User must “Run as Administrator” for Vista when using “msiexec” for
“silent” install or uninstall procedures.
For detailed instructions and information about unattended installs,
refer to the Silent.txt file in the DrvInst folder.
Performing a Silent Install
To perform a silent install from within the installer source folder, enter one
of the following:
setup /s /v/qn
or
msiexec /i "BDrv5706.msi" /qn
Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File
To perform a silent install and create a log file at (f:\1testlog.txt), enter:
setup /s /v"/qn /L f:\1testlog.txt"
Performing a Silent Upgrade
To perform a silent upgrade from within the installer source folder, enter:
setup /s /v/qn
Performing a Silent Uninstall
There are two ways to perform a silent uninstall— from the installer source
folder or from the any folder.
In some circumstances, you must reboot your system before uninstallation
can continue. If you used REBOOT=ReallySuppress to suppress the
reboot, the uninstallation may be suspended. In this case, you need to
reboot manually for the uninstallation to continue.
To perform a silent uninstall from within the installer source folder, enter:
msiexec /x "BDrv5706.msi" /qn
To perform a silent uninstall from any folder, enter:
55
Page 56

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
Note
Note
msiexec /x "{F0DA8A3F-1457-419E-96F4-235DD3EF41E1}" /
qn
Performing a Silent Reinstall
To perform a silent reinstall of the same installer, enter:
setup /s /v"/qn REINSTALL=ALL"
The hexadecimal number above may differ from your current
installer. Check the Key name in HKLM\Software\Microsoft\
Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall for the correct hexadecimal
number.
Use REINSTALL switch only if the same installer is already installed
on the system. If you are upgrading an earlier version of the installer,
use setup /s /v/qn as described above.
56
Page 57

Removing the Device Drivers
Note
This section discusses how to remove the device drivers.
Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 provide the
Device Driver Rollback feature that replaces a device driver with one
that was previously installed. However, the complex software
architecture of the AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter may present
problems if the rollback feature is used on one of the individual
components. Therefore, Allied Telesis recommends that changes to
driver versions be made only through the use of a driver installer.
To remove the device drivers, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
2. Click Broadcom NetXtreme II GigE Driver Installer, and then click
Remove. Follow the on screen prompts.
3. Click Yes to restart your system.
- or -
4. Click No to restart your system at a later time.
5. Click OK to acknowledge that the installation has been suspended.
The uninstallation of the driver is postponed until the next restart of
your system.
57
Page 58

Chapter 5: Installing the Windows Drivers
58
Page 59

Chapter 6
Setting Advanced Properties
For all of the Windows operating systems, you access the Windows
Advanced Properties from the Advanced Tab. Although the default values
of the Advanced Properties are appropriate in most cases, you can change
any of the available options to meet the requirements of your system.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Advanced Features” on page 60
“Accessing the Advanced Tab” on page 62
“Modifying the Advanced Properties” on page 65
59
Page 60

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Advanced Features
Table 7 lists the advanced network adapter features in Microsoft Windows
that are supported by the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter. Default values are
marked with an asterisk.
Table 7. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows Supported by the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Feature
Encapsulated Task
Offload
Flow Control Auto*
Interrupt Moderation Disabled
Jumbo Packet 1514*
Large Send Offload
V2 IPv4
Large Send Offload
V2 IPv6
Windows Server
2008 32/64
- - Disabled
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Enabled*
4088
9014
9614
Disabled
Enabled*
Disabled
Enabled*
Windows Server
2008 R2
Auto*
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Disabled
Enabled*
1514*
4088
9014
9614
Disabled
Enabled*
Disabled
Enabled*
Windows Server
2012 and 2012 R2
Enabled*
Auto*
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Disabled
Enabled*
1514*
4088
9014
9614
Disabled
Enabled*
Disabled
Enabled*
Locally Administered
Address
Maximum Number of
RSS Queues
Priority and VLAN Priority/VLAN
Quality of Service - - Disabled
60
No value* No value* No value*
16
2
4
8*
Disabled
Priority/VLAN
Enabled*
Priority Enabled
VLAN Enabled
16
2
4
8*
Priority/VLAN
Disabled
Priority/VLAN
Enabled*
Priority Enabled
VLAN Enabled
16
2
4*
8
Priority/VLAN
Disabled
Priority/VLAN
Enabled*
Priority Enabled
VLAN Enabled
Enabled*
Page 61

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Table 7. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows Supported by the AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter
Feature
Receive Buffers
(0=Auto)
Windows Server
2008 32/64
0* to 3000 in
increments of 50
Receive Side Scaling Disabled
Enabled*
Recv Segment
- - Disabled
Coalescing (IPv4)
Recv Segment
- - Disabled
Coalescing (IPv6)
Speed and Duplex 1 Gb-Full
10 Gb-Full*
Windows Server
2008 R2
0* to 3000 in
increments of 50
Disabled
Enabled*
1 Gb-Full
10 Gb-Full*
Windows Server
2012 and 2012 R2
0* to 3000 in
increments of 50
Disabled
Enabled*
Enabled*
Enabled*
1 Gb-Full
10 Gb-Full*
SRIOV - - Disabled
Enabled*
Starting RSS CPU 0* to 63 0* to 63 0* to 63
TCP Connection
Not supported. Not supported. Not supported.
Offload (IPv4)
TCP Connection
Not supported. Not supported. Not supported.
Offload (IPv6)
TCP/UDP Checksum
Offload (IPv4)
TCP/UDP Checksum
Offload (IPv6)
Transmit Buffers
(0=Auto)
Virtual Machine
Queues
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
0* to 5000 in
increments of 50
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
0* to 5000 in
increments of 50
- Enabled*
Disabled
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
Disabled
RX and TX Enabled*
RX Enabled
TX Enabled
0* to 5000 in
increments of 50
Enabled*
Disabled
VLAN ID 0* to 4094 0* to 4094 0* to 4094
61
Page 62

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Accessing the Advanced Tab
To modify the configuration properties of the Windows Operating systems,
you must access the Advanced Tab. Depending on your operating
system, there are several ways to do this. See the following procedures:
“Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2008 or Windows
Server 2008 R2” on page 62
“Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2012” on page 63
Selecting the
Advanced Tab in
Windows Server
2008 or Windows
Server 2008 R2
To select the Advanced Tab in the Windows Server 2008 or Windows
Server 2008 R2 Operating System, do the following:
1. Select the Start button. See Figure 14.
62
Figure 14. Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Search
Box
2. Enter the following command:
mmc devmgmt.msc
Page 63

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
The Device Manager window is displayed. See Figure 15.
Selecting the
Advanced Tab in
Windows Server
2012
Figure 15. Device Manager Window
3. Open the Network Adapters folder.
The list of installed adapters is displayed.
4. Right click on the BCM57810NetXtreme II 10 GigE adapter.
The adapter window is displayed.
5. Select the Advanced tab.
To access the Advanced Tab in the Windows 2012 Server Operating
System, perform the following procedure.
1. Right click on the Windows logo in the bottom left corner of the
Desktop.
See Figure 16 on page 64 for an example of the Windows Server 2012
Desktop.
63
Page 64

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Figure 16. Windows Server 2012 Desktop
2. From the Start Menu, select Run.
The Windows Server 2012 Run window is displayed. See Figure 17.
Figure 17. Windows Server 20112 Run Window
3. Enter the following command in the Run window:
mmc devmgmt.msc
64
The Device Manager window is displayed. See Figure 15 on page 63.
4. Expand the Network Adapters folder.
5. Right click on the Broadcom BCM57810 NetXtreme II 10 GigE and
select Properties from the menu: The adapter window is displayed.
Page 65

Modifying the Advanced Properties
Note
Note
After you have installed the driver software, you can use Table 8 to verify
or change the adapter properties:
After you upgrade the driver software, the Advanced Properties may
change.
The configuration steps in the table may differ slightly if the “Classic
Start Menu” is set on your computer.
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Encapsulated Task
Offload
Flow Control Enables or disables the receipt or
Allows for task offload capabilities
when using Hyper-V Virtualized
Network (HVN) functions
transmission of PAUSE frames.
PAUSE frames allow the network
adapter and a switch to control the
transmit rate. The side that is
receiving the PAUSE frame
momentarily stops transmitting.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and,
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Encapsulated
Task Offload value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Flow Control
value.
65
Page 66

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Interrupt
Moderation
Enables interrupt moderation,
which limits the rate of interrupt to
the CPU during packet
transmission and packet
reception. The disabled option
allows one interrupt for every
packet transmission and packet
reception. Enable is the default
option.
Jumbo Packet Enables the network adapter to
transmit and receive oversized
Ethernet frames that are greater
than 1514 bytes, but less than or
equal to 9000 bytes in length
(9600 bytes for network adapters
that operate at 10 Gbps). This
property requires the presence of
a switch that is able to process
jumbo frames. This property is
only available for the
AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter.
Frame size is set at 1500 bytes by
default. To increase the size of the
received frames, raise the byte
quantity in 500-byte increments.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Interrupt
Moderation value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Jumbo Packet
value.
IPv4 Checksum
Offload
66
Allows configuring checksum
offload for the IPv4 protocol. The
options are listed here:
Disable - Disables checksum
offload.
Rx Enabled - Enables receive
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx Enabled - Enables transmit
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
TX & Rx Enabled (default) Enables transmit and receive
TCP/IP/UDP checks
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired IPv4
Checksum Offload value
Page 67

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Feature Description Configuration Steps
IPv4 Large Send
Offload
IPv6 Checksum
Offload
Normally, the TCP segmentation is
done by the protocol stack. When
you enable the Large Send
Offload property, the TCP
segmentation can be done by the
network adapter. The default
setting for this property is Enabled.
This property is only available for
the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter.
Normally, the checksum function is
computed by the protocol stack.
When you select one of the
Checksum Offload property values
(other than None), the checksum
can be computed by the network
adapter.
Rx Enabled - Enables receive
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx Enabled - Enables transmit
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired IPv4 Large
Send Offload value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired IPv6
Checksum Offload value.
IPv6 Large Send
Offload
Tx/Rx Enabled - (default). Enables
transmit and receive TCP/IP/UDP
checksum offload.
None - Disables checksum
offload.
Normally, the TCP segmentation is
done by the protocol stack. When
you enable the Large Send
Offload property, the TCP
segmentation can be done by the
network adapter. The default
setting for this property is Enabled.
This property is only available for
the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired IPv6 Large
Send Offload value.
67
Page 68

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Jumbo Packet Enables the network adapter to
transmit and receive oversized
Ethernet frames that are greater
than 1514 bytes, but less than or
equal to 9000 bytes in length
(9600 bytes for network adapters
that operate at 10 Gbps). This
property requires the presence of
a switch that is able to process
jumbo frames. This property is
only available for the
AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter.
Frame size is set at 1500 bytes by
default. To increase the size of the
received frames, raise the byte
quantity in 500-byte increments.
Large Send Offload
v2 (IPv4)
Normally, the TCP segmentation is
done by the protocol stack. When
you enable the Large Send
Offload property, the TCP
segmentation can be done by the
network adapter. The default
setting for this property is Enabled.
This property is only available for
the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Enter the desired Jumbo
Packet value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Select the desired Large Send
Offload v2 (IPv4) value.
Large Send Offload
v2 (IPv4)
68
Normally, the TCP segmentation is
done by the protocol stack. When
you enable the Large Send
Offload property, the TCP
segmentation can be done by the
network adapter. The default
setting for this property is Enabled.
This property is only available for
the AT-ANC10S/2 network
adapter.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Select the desired Large Send
Offload v2 (IPv6) value.
Page 69

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Locally
Administered
Address
The Locally Administered Address
is a user-defined MAC address
that is used in place of the MAC
address originally assigned to the
network adapter. Every adapter in
the network must have its own
unique MAC address. This locally
administered address consists of a
12-digit hexadecimal number.
Value - Assigns a unique node
address for the adapter.
Not Present (default) - Uses the
factory-assigned node address on
the adapter.
The appropriate assigned ranges
and exceptions for the locally
administered address include the
following:
The range is 00:00:00:00:00:01 to
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FD.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections, and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Enter the desired network
address value.
Number of RSS
Queues
Do not use a multicast address
(least significant bit of the high
byte = 1).
Do not use all 0s or all Fs.
Allows configuring RSS queues.
For 10 Gbps network adapters,
the RSS queue options are Auto
(default), 2, 4, 8, and 16.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Enter the desired RSS queues
value.
69
Page 70

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Priority and VLAN The options are listed here:
Priority & VLAN Enabled
(default) - Allows for packet
prioritization and VLAN tagging.
Priority & VLAN Disabled Prevents packet prioritization and
VLAN tagging.
Priority Enabled - Allows packet
prioritization only.
VLAN Enabled - Allows VLAN
tagging only.
Quality of Service QoS technologies allow you to
measure bandwidth, detect
changing network conditions (such
as congestion or availability of
bandwidth), and prioritize or
throttle traffic. For example, QoS
technologies can be applied to
prioritize traffic for
latency-sensitive applications
(such as voice or video) and to
control the impact of
latency-insensitive traffic (such as
bulk data transfers).
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and,
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Priority &
VLAN value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and,
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Quality of
Service value.
Receive Buffers
(0=Auto)
70
The number of receive buffers.
Receive buffers are data
segments that allow the network
adapter to allocate receive
packets to memory. For 1 Gbps
adapters, the range of valid
receive buffers is 50 to 5000 in
increments of 1 with 750 receive
buffers as the default value. For 10
Gbps adapters, the range of valid
receive buffers is 0 to 3000 in
increments of 50 with 0 receive
buffers as the default value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Receive
Buffers value.
Page 71

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Receive Side
Scaling
Recv Segment
Coalescing (IPv4)
This parameter allows configuring
network load balancing across
multiple CPUs. The default setting
for this property is Enabled.
When receiving data, the miniport
driver, NDIS, and TCP/IP must all
look at each segment's header
information separately. When
large amounts of data are being
received, this creates a large
amount of overhead. Receive
segment coalescing (RSC)
reduces this overhead by
coalescing a sequence of received
segments and passing them to the
host TCP/IP stack in one
operation, so that NDIS and
TCP/IP need only look at one
header for the entire sequence.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Receive Side
Scaling value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Recv Segment
Coalescing (IPv4) value.
Recv Segment
Coalescing (IPv6)
When receiving data, the miniport
driver, NDIS, and TCP/IP must all
look at each segment's header
information separately. When
large amounts of data are being
received, this creates a large
amount of overhead. Receive
segment coalescing (RSC)
reduces this overhead by
coalescing a sequence of received
segments and passing them to the
host TCP/IP stack in one
operation, so that NDIS and
TCP/IP need only look at one
header for the entire sequence.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Recv Segment
Coalescing (IPv6) value.
71
Page 72

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Speed and Duplex
Mode
The Speed & Duplex property sets
the connection speed and mode to
that of the network. Note that
Full-Duplex mode allows the
adapter to transmit and receive
network data simultaneously.
SRIOV Enables Single-Root I/O
Virtualization which allows virtual
machines to access the network
adapter directly rather than via the
Hypervisor.
Starting RSS CPU Specifies the first logical CPU
number that will be used for
scaling. This value is useful for
excluding CPU? that may already
dedicated to another application of
process. Values up to 63 may be
specified.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Speed &
Duplex value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired SRIOV value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
TCP Connection
Offload (IPv4)
TCP Connection
Offload (IPv6)
72
3. Set the desired Starting RSS
CPU value.
Not supported. 4. Not supported.
Not supported. 5. Not supported.
Page 73

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Feature Description Configuration Steps
TCP/UDP
Checksum Offload
(IPv4)
TCP/UDP
Checksum Offload
(IPv6)
Normally, the checksum function is
computed by the protocol stack.
When you select one of the
Checksum Offload property values
(other than None), the checksum
can be computed by the network
adapter.
Rx Enabled - Enables receive
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx Enabled - Enables transmit
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx/Rx Enabled - (default). Enables
transmit and receive TCP/IP/UDP
checksum offload.
None - Disables checksum
offload.
Normally, the checksum function is
computed by the protocol stack.
When you select one of the
Checksum Offload property values
(other than None), the checksum
can be computed by the network
adapter.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired TCP/UDP
Checksum Offload (IPv4)
value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
Rx Enabled - Enables receive
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx Enabled - Enables transmit
TCP/IP/UDP checksum offload.
Tx/Rx Enabled - (default). Enables
transmit and receive TCP/IP/UDP
checksum offload.
None - Disables checksum
offload.
3. Set the desired TCP/UDP
Checksum Offload (IPv6)
value.
73
Page 74

Chapter 6: Setting Advanced Properties
Feature Description Configuration Steps
Table 8. Advanced Features in Microsoft Windows
Transmit Buffers
(0=Auto)
The number of transmit buffers.
Transmit buffers are data
segments that allow the network
adapter to monitor transmit
packets in the system memory.
The range of valid transmit buffers
is 0 to 5000 in increments of 1 with
1500 transmit buffers as the
default value.
Virtual Machine
Queues
The Virtual Machine Queues
property defines whether the
device has enabled or disabled
the virtual machine queue (VMQ)
feature.
VLAN ID Sets the VLAN ID that will be
added to the packet header to
allow the network adapter to
participate in a virtual network. A
value of 0 means an untagged
packet (no VLAN set).
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Transmit
Buffers value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
3. Set the desired Virtual
Machine Queues value.
1. In Microsoft Windows,
right-click the Network Adapter
in Network Connections and
then click Properties.
2. Click the Configure button and
then the Advanced tab.
74
3. Enter the desired VLAN ID in
the VLAN ID field.
Page 75

Chapter 7
Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability
Both Common Information Model (CIM) and Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) are information models that allow you to monitor and
manage a PC or a network. Both CIM and SNMP are supported on the
Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server
2012 Operating Systems. The CIM standard defines managed elements
and the SNMP standard defines events such as temperature threshold
and power outages which are called traps.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Installing CIM” on page 76
“Installing SNMP” on page 79
75
Page 76

Chapter 7: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability
Installing CIM
The Common Information Model (CIM) is an industry standard defined by
the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF). Microsoft implements
CIM on Windows platforms. Also, Broadcom supports CIM on the
Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server
2012 platforms.
Broadcom's implementation of CIM enables various classes to provide
information through CIM client applications. The Broadcom CIM data
provider provides data only. In addition, you can select your preferred CIM
client software to browse the information exposed by the Broadcom CIM
provider.
The Broadcom CIM provider provides information through the following
classes:
BRCM_NetworkAdapter
BRCM_ExtraCapacityGroup
The BRCM_NetworkAdapter class provides network adapter information
pertaining to a group of adapters including Broadcom and controllers from
other vendors. The BRCM_ExtraCapacityGroup class provides team
configuration for the Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP).
Current implementation provides team information and information about
physical network adapters in the team.
BASP provides information about events through event logs. You can use
either the Event Viewer (provided by Windows Server 2008, Windows
Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server 2012) or CIM to inspect and monitor
these events. The Broadcom CIM provider also provides event information
through the CIM generic event model. The following events are defined by
CIM:
__InstanceCreationEvent
__InstanceDeletionEvent
__InstanceModificationEvent
CIM requires the client application to register the events from the client
application, using queries as examples to receive events properly. See the
following examples:
76
SELECT * FROM __InstanceModificationEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_NetworkAdapter"
SELECT * FROM __InstanceModificationEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_ExtraCapacityGroup"
SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_NetworkAdapter"
Page 77

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation Guide
SELECT * FROM __InstanceDeletionEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_NetworkAdapter"
SELECT * FROM __InstanceCreationEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_ActsAsSpare"
SELECT * FROM __InstanceDeletionEvent
where TargetInstance ISA "BRCM_ActsAsSpare"
For detailed information about these events, see the CIM documentation
at:
www.dmtf.org/sites/default/files/standards/documents/DSP0004V2.3
_final.pdf
Loading the CIM
Libraries
By default, the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite utility does not load the
CIM libraries. You need to select this option.
To load the CIM libraries on your PC, do the following:
1. Download the BACS utility from the Allied Telesis website.
This utility is available from the
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software website. After accessing
the website, enter the model number in the Search by Product Name
box and click Find to view the current list of available files.
2. Download BACS onto your PC.
3. On your PC, open the InstallShield.
Within the BACS utility, there is an option to load the CIM libraries. The
BACS CIM Option Window is displayed. See Figure 18 on page 78.
77
Page 78

Chapter 7: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability
Figure 18. BACS CIM Option Window
4. Select CIM Provider.
5. Select one of the following:
This feature will be installed on local hard drive.
This feature, and all subfeatures, will be installed on local hard
drive.
6. Click Next.
7. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
78
Page 79

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation Guide
Installing SNMP
The BASP version of SNMP has two components that are described in the
following sections:
“BASP Subagent” on page 79
“BASP Extensible-Agent” on page 79
BASP Subagent The BASP subagent, baspmgnt.dll, is designed for the Windows Server
2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server 2012 platforms.
You must install the SNMP service before installing the BASP subagent.
The BASP subagent allows an SNMP manager software to actively
monitor the configuration and performance of the Broadcom Advanced
Server features. The subagent also provides an alarm trap to an SNMP
manager to inform the manager of any changes to the conditions of the
BASP component.
The BASP subagent allows monitoring of the configurations and statistics
of the BASP teams, the physical NIC adapters participating in a team, and
the virtual NIC adapters created as the result of teaming. Non-teamed NIC
adapters are not monitored. The BASP configuration data includes
information such as team IDs, physical-virtual-VLAN-team adapter IDs,
physical-virtual-VLAN-team adapter descriptions, and the MAC addresses
of the adapters.
The statistics include detailed information such as data packets
transmitted and received for the physical-virtual-VLAN-team adapters.
The alarm trap forwards information about the changes in configuration of
the physical adapters participating in a team, such as whether or not the
physical adapter link is up or down and each time the adapter is installed
or removed.
To monitor this information, an SNMP manager must load the Broadcom
BASP MIB database files to allow monitoring of the information described
above. The following files are posted on the Allied Telesis web site:
baspcfg.mib
baspstat.mib
basptrap.mib
BASP
Extensible-Agent
The Broadcom NetXtreme II Gigabit Ethernet Controller Extended
Information SNMP extensible-agent (bcmif.dll) is designed for Windows
Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows Server 2012 SNMP
service. You must install the Windows 2000 Server SNMP service before
installing the extensible-agent.
79
Page 80

Chapter 7: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability
The extensible-agent allows the SNMP manager software to actively
monitor the configurations of the AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter. It
supplements the information already provided by the standard SNMP
Management Network Interface information.
The extensible-agent provides in-depth information about the
AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter including:
MAC address
Bound IP address
IP subnet mask
Physical link status
Adapter state
Line speed
Duplex mode
Memory range
Interrupt setting
Loading the
SNMP Libraries
Bus number
Device number
Function number
To monitor this information, an SNMP manager needs to load the
Broadcom Extended information MIB file to allow monitoring of the
information listed above. See the following procedure.
The monitored workstation requires the installation of the Broadcom
Extended Information SNMP extensible-agent, bcmif.dll, and requires the
Microsoft Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, or Windows
Server 2012 SNMP service to be installed and loaded.
By default, the BACS utility does not load the SNMP libraries. You need to
select this option.
To load the SNMP libraries on your PC, do the following:
1. Download the BACS utility from the Allied Telesis website.
This utility is available from the
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software website. After accessing
the website, enter the model number in the Search by Product Name
box and click Find to view the current list of available files.
80
2. Download BACS onto your PC.
3. On your PC, open the InstallShield.
4. Select SNMP.
Page 81

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation Guide
The BACS SNMP Option Window is displayed. See Figure 18.
Figure 19. BACS SNMP Option Window
5. Select one of the following:
This feature will be installed on local hard drive.
This feature, and all subfeatures, will be installed on local hard
drive.
6. Click Next.
7. Follow the on screen instructions to complete the installation.
81
Page 82

Chapter 7: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability
82
Page 83

Chapter 8
Installing Management Applications
This chapter provides information about prerequisites for installing
management applications as well as procedures instructions. This chapter
discusses the following topics:
“Installing Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 and Related
Management Applications” on page 84
“Modifying Management Applications” on page 88
“Repairing Management Applications” on page 89
“Removing Management Applications” on page 90
83
Page 84

Chapter 8: Installing Management Applications
Note
Note
Note
Installing Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 and Related Management Applications
The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 (BACS 4) software and related
management applications can be installed from the source-file directory or
by using the silent install option. See the following:
“Checking .NET Framework Requirements” on page 84
“Using the Installer” on page 85
“Using the Silent Install Option” on page 85
After you use the source-file directory or the silent install option, the
following features are installed on your system:
Control Suite - Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 (BACS 4).
BASP - Installs Broadcom Advanced Server Program.
SNMP - Installs the Simple Network Management Protocol
subagent.
Checking .NET
Framework
Requirements
CIM Provider - Installs the Common Information Model provider.
Ensure that the Broadcom network adapter(s) is physically installed
in the system before installing BACS 4.
Before installing Broadcom Advance Control Suite 4, verify that
.NET Framework is up to date.
Before you begin the installation, close all applications, windows, or
dialog boxes.
Before you use either the source-file directory or the silent install option,
you must make sure that your system meets the minimum installation
requirements.
Microsoft .NET Framework includes the runtime and associated files
needed to run BACS 4, and must be installed on your system in order for
BACS 4 to operate. Please be sure the .NET Framwwork version for your
operating system is up to date.
84
Page 85

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
Starting BACS 4 without .NET Framework installed on your system
results in an error.
Using the
Installer
The driver software is available for download from the Allied Telesis web
site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. After accessing this website,
enter the model number in the Search by Product Name box and then
click Find to view the current list of available software drivers.
To install the management applications, do the following:
Before starting the installation, verify that .NET Framework is up to
date to ensure optimal performance of BACS 4.
1. Open the MgmtApps folder, select IA32 or x64, and then double-click
Setup.exe to open the InstallShield Wizard.
2. Click Next to continue.
3. After you review the license agreement, click I accept the terms in
the license agreement and then click Next to continue.
4. Select the features you want installed. If you receive a warning
regarding .NET Framework, then press OK to continue installing BACS
4 and manually install .NET Framework when the installation is
completed, or Cancel to quit.
Using the Silent
Install Option
5. Click Next.
6. Click Install.
7. Click Finish to close the wizard.
You can use the silent install option to install from a source folder or any
folder. You can create a log file during the installation procedure. In
addition, you can specify which features you will install on your system.
See the following sections:
“Performing a Silent Install from the Installer Source Folder” on
page 86
“Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File” on page 86
“Performing a Silent Install from any Folder” on page 86
“Performing a Silent Install by Feature on IA32 Platforms” on page 87
“Performing a Silent Install by Feature on AMD64/EM64T Platforms”
on page 87
85
Page 86

Chapter 8: Installing Management Applications
Note
Note
Note
“Performing a Silent Install from Within a Batch File” on page 87
Performing a Silent Install from the Installer Source Folder
To perform a silent install (or upgrade) from within the installer source
folder, enter:
setup /s /v/qn
If performing a silent upgrade, your system may reboot automatically. To
suppress the reboot, enter:
All commands are case sensitive.
User must “Run as Administrator” for Vista when using “msiexec” for
“silent” install/uninstall(s).
setup /s /v"/qn REBOOT=ReallySuppress"
Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File
To perform a silent install and create a log file, enter:
setup /s /v"/qn /L f:\ia32\1testlog.txt"
The 1testlog.txt log file is created at f:\ia32.
Performing a Silent Install from any Folder
To perform a silent uninstall from any folder on the hard drive, enter:
msiexec /x "{26E1BFB0-E87E-4696-9F89-B467F01F81E5}" /
qn
The hexadecimal number above may differ from your current
installer. Check the Key name corresponding with the Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite 4(BACS) application in
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall for the
correct hexadecimal number.
86
Page 87

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
After performing a silent uninstall, it is necessary to reboot the
system before reinstalling this installer. If you do not perform a
reboot, BASP does not install correctly.
Performing a Silent Install by Feature on IA32 Platforms
To perform a silent install by feature on IA32 platforms, enter:
CHM32 or CHM64 installs the BACS help file and must be included
when installing the BACS feature.
Use ADDSOURCE to include any of the features listed below.
setup /s /v"/qn
ADDSOURCE=BACSi32,CHM32,BASPi32,SNMPi32,CIMi32"
Performing a Silent Install by Feature on AMD64/EM64T Platforms
To perform a silent install by feature on AMD64/EM64T platforms, enter:
setup /s /v"/qn
ADDSOURCE=BACSa64,CHMa64,BASPa64,SNMPa64"
Performing a Silent Install from Within a Batch File
To perform a silent install from within a batch file and wait for the install to
complete before continuing with the next command line, enter:
start /wait setup /s /w /v/qn
87
Page 88

Chapter 8: Installing Management Applications
Modifying Management Applications
To modify the management applications, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Management Programs and then click Change.
3. Click Next to continue.
4. Click Modify to change program features.
5. Click Next to continue.
6. Click on an icon to change how a feature is installed.
7. Click Next.
8. Click Install.
9. Click Finish to close the wizard.
10. Reboot your system to complete the modification of the management
applications.
88
Page 89

Repairing Management Applications
To repair or reinstall the management applications, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Management Programs, and then click Change.
3. Click Next to continue.
4. Click Repair to repair errors in installed applications.
5. Click Next to continue.
6. Click Install.
7. Click Finish to close the wizard.
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 8: Installing Management Applications
Removing Management Applications
To remove all management applications, do the following:
1. In Control panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Management Programs, and then click Remove.
3. Reboot your system to complete the removal of the management
applications.
90
Page 91

Chapter 9
Troubleshooting
This chapter provides troubleshooting information. It discusses the
following topics:
“Checking Hardware Diagnostics” on page 92
“Checking Port LEDs” on page 93
“Consulting the Troubleshooting Checklist” on page 94
“Solving Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V Issues” on
page 97
“Solving Broadcom Boot Agent and Broadcom Advanced Server
Program (BASP) Issues” on page 100
“Solving Miscellaneous Issues” on page 102
Within the chapter there are several references to the Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite 4 User Guide. You can download this manual from
the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software.
After accessing the website, enter the model number in the Search by
Product Name box and then click Find to view the current list of
documents.
91
Page 92

Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
Checking Hardware Diagnostics
Loopback diagnostic tests are available for testing the adapter hardware.
These tests provide access to the adapter internal and external
diagnostics, where packet information is transmitted across the physical
link. For instructions and information on running tests in an MS-DOS
environment, see Chapter 10, “User Diagnostics” on page 105. For
Windows environments, see “Running Diagnostic Tests” in the Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite 4 User Guide which you can download from the
Allied Telesis website.
92
Page 93

Checking Port LEDs
To check the state of the network links and activities on the ports, refer to
Table 2 on page 20:
AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
Note
Consulting the Troubleshooting Checklist
Before you open the cabinet of your server to add or remove the
adapter, see “Reviewing Safety Precautions” on page 25.
The following checklist provides recommended actions to resolve
problems installing or running the AT-ANC10S/2 adapter in your system:
Inspect all cables and connections. Verify that the cable
connections at the network adapter and the switch are attached
properly. Verify that the cable length and rating comply with the
requirements of the SFP+ transceiver.
Check the adapter installation by reviewing “Installing the Network
Adapter Card” on page 30. Verify that the adapter is properly
seated in the slot. Check for specific hardware problems, such as
obvious damage to board components or the PCI edge connector.
Checking the
Current Drivers
Check the configuration settings and change them if they are in
conflict with another device.
Verify that your server is using the latest BIOS.
Try inserting the adapter in another slot. If the new position works,
the original slot in your system may be defective.
Replace the failed adapter with one that is known to work properly.
If the second adapter works in the slot where the first one failed,
the original adapter is probably defective.
Install the adapter in another functioning system and run the tests
again. If the adapter passed the tests in the new system, the
original system may be defective.
Remove all other adapters from the system and run the tests
again. If the adapter passes the tests, the other adapters may be
causing contention.
This section describes how to check that the current drivers are properly
loaded for the Windows and Linux platforms.
Windows
See “Viewing Vital Signs” in the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 User
Guide to view vital information about the adapter, link status, and network
connectivity.
94
Page 95

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
Linux
To verify that the bnx2x.o (or bnx2x.ko) driver is loaded properly, enter:
lsmod
If the driver is loaded, a line similar to one Table 9 is displayed, where size
indicates the size of the driver in bytes, and number is the number of
adapters configured.
Table 9. Linux Module Size
Module Size Used by
BCM5709 size number
Running a Cable
Length Test
Testing Network
Connectivity
For a Windows operating systems, see “Analyzing Cables” in the
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 User Guide for information on
running a cable length test.
This section describes how to test network connectivity for the Windows
and Linux platforms.
When using forced link speeds, verify that both the adapter and the
switch are forced to the same speed.
Windows
In the Windows platforms, use the ping command to test network
connectivity. If the new adapter is the only adapter in the system, you may
test it by having it ping another device on the network. But if the new
adapter is in a system that contains more than one adapter, you instead
should test it by pinging it from another device on your network.
Network connectivity can also be tested using the “Testing the
Network” feature in the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4 User
Guide.
To determine if the network connection is working, do the following:
1. Click Start, and then click Run.
2. Type cmd in the Open box, and then click OK.
95
Page 96

Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
3. If you are performing the ping command at the system where the new
adapter is installed, type ipconfig /all to verify that the new
adapter is operational.
4. Type ping <remote IP address>, and then press Enter. If you
are performing the ping command at the system where the new
adapter is installed, specify the IP address of a remote device the
adapter is to ping. If you are performing the command at another
system, enter the IP address of the new adapter.
The ping statistics that are displayed indicate whether the network
connection is working or not.
Linux
To verify that the Ethernet interface is up and running on a Linux platform,
run ifconfig to check the status of the Ethernet interface. In addition,
you can enter the netstat -i command to check the statistics on the
Ethernet interface. See “Installing Linux Driver Software” on page 41 for
information on ifconfig and netstat.
If the new adapter is the only adapter in the system, you may test it by
having it ping another device on the network. But if the new adapter is in a
system that contains more than one adapter, you instead should test it by
pinging it from another device on your network.
Ping an IP host on the network to verify connection has been established.
From the command line, type ping IP address, and then press Enter.
The ping statistics that are displayed indicate whether or not the network
connection is working.
96
Page 97

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Solving Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V Issues
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V™ is a hypervisor
virtualization system. For detailed information about Hyper-V, refer to the
following website:
www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/hyperv.aspx
This section addresses issues that affect the configuration of the
AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter and teamed adapters when Hyper-V is
used.
Ensure that Integrated Services, which is a component of Hyper-V,
is installed in the guest operating system (child partition) for full
functionality.
Single Network
Adapter
When configuring an AT-ANC10S network adapter for Hyper-V, be aware
of the following:
An adapter that is bound to a virtual network should not be
configured for VLAN tagging through the driver's advanced
properties. Instead, Hyper-V should manage VLAN tagging
exclusively.
Since Hyper-V does not support Jumbo Frames, it is
recommended that this feature not be used or connectivity issues
may occur with the child partition.
The Locally Administered Address (LAA) set by Hyper-V takes
precedence over an address set in the adapter's Advanced
Properties.
In an IPv6 network, a team that supports Checksum Offload (CO)
and Large Send Offload (LSO) and is bound to a Hyper-V virtual
network reports CO and LSO as an offload capability in BACS.
Also, in an IPv6 network, a team that supports CO or LSO and is
bound to a Hyper-V virtual network reports CO or LSO as an
offload capability in BACS. However, in both instances CO and
LSO do not work. This is a limitation of Hyper-V because this
system does not support CO and LSO in an IPv6 network.
97
Page 98

Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
Note
Teamed Network
Adapters
The following Broadcom team types are supported with Hyper-V:
Smart Load Balancing and Failover (configured only for one
primary and one standby)
Link Aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad LACP)
Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC) 802.3ad Draft Static
When configuring a team of AT-ANC10S network adapter on a Hyper-V
system, be aware of the following:
Create the team prior to binding the team to the Hyper-V virtual
network
Create a team only with an adapter that is not already assigned to
a Hyper-V virtual network.
In an IPv6 network, a team that supports Checksum Offload (CO)
and Large Send Offload (LSO) and is bound to a Hyper-V virtual
network reports CO and LSO as an offload capability in BACS.
Also, in an IPv6 network, a team that supports CO or LSO and is
bound to a Hyper-V virtual network reports CO or LSO as an
offload capability in BACS. However, in both instances CO and
LSO do not work. This is a limitation of Hyper-V because this
system does not support CO and LSO in an IPv6 network.
Removing the
Device Drivers
Preparing an
Answer File
To successfully perform VLAN tagging for both the host (parent
partition) and the guest (child partition) with the BASP teaming
software, you must configure the team for tagging. Unlike VLAN
tagging with a single adapter, tagging cannot be managed by
Hyper-V when using BASP software.
Uninstall the device drivers for the network adapter from your system only
through the InstallShield wizard. Uninstalling the device drivers with
Device Manager or any other means may not provide a clean uninstall
which, in turn, may cause the system to become unstable. For information
on uninstalling device drivers, see “Removing the Device Drivers” on
page 57.
When creating an answer file for an unattended installation or for the
System Preparation Tool (Sysprep) utility, you must include the following
lines under the [Unattend] section:
OemPreinstall=Yes
OemPnpDriversPath=Drivers\NIC
This does not include an unattended installation when performed
from a CD-ROM.
98
Page 99

AT-ANC10S/2 Adapter Installation and User’s Guide
Note
The path shown in OemPnpDriversPath can be appended with the
path to other applicable drivers.
For an unattended installation, place the driver files for the network
adapter in the $OEM$\$1\Drivers\NIC directory. For Sysprep, the drivers
are located in Drivers\NIC at the root of the system drive. The driver files
are listed below according to the operating system to be installed:
Windows Server (ia32): bxvbd.inf, bxvbdx.sys, bxvbd.cat,
bxnd.inf, bxnd.cat, bxnd52x.sys, bxndcox.dll, bxdiag.cat,
bxdiag.inf, bxdiagx.sys, wdfcoinstaller01005.dll, and
wUDFUpdate_01005.dll
Windows Server (x64): bxvbd.inf, bxvbda.sys, bxvbd.cat,
bxnd.inf, bxnd.cat, bxnd52a.sys, bxndcoa.dll, bxdiag.cat,
bxdiag.inf, bxdiaga.sys, wdfcoinstaller01005.dll, and
wUDFUpdate_01005.dll
When applying network properties through an answer file for an
AT-ANC10S/2 network adapter where the PnP iD is the identifier, do the
following:
For a BCM57810 Netxtreme II 10GigE - InfId =
"b06bdrv\l2nd&pci_168e14e4"
Currently, the PCI location (PCI bus, device, and function numbers)
method is not supported for a network adapter as an identifier or a network
adapter in the answer file due to a limitation with the Windows operating
system.
99
Page 100

Chapter 9: Troubleshooting
Solving Broadcom Boot Agent and Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) Issues
This section discusses issues with the Broadcom Boot Agent and
Broadcom Advanced Server (BASP) as well as provides solutions.
Problem: Unable to obtain network settings through DHCP using PXE.
Solution: For proper operation, make sure that the Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP) feature is disabled or that portfast mode (for Cisco
switches) is enabled on the port to which the PXE client is connected. For
instance, set spantree portfast 4/12 enable.
Problem: A BASP team in Windows Server 2003 may not function
properly if a team member driver property is modified.
Solution: Due to a limitation in Windows Server 2003, the features of
team members should remain static during the entire life of the team. To
change the characteristics of a team member, remove the team member
from the team, modify the team member, and then the adapter to the team
again. This limitation does not exist in Windows Server 2008 or Windows
Server 2008 R2.
Problem: A system containing an 802.3ad team causes a Netlogon
service failure in the system event log and prevents it from communicating
with the domain controller during boot up.
Solution: Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 326152
(support.microsoft.com/kb/326152/en-us) indicates that Gigabit
Ethernet adapters may experience problems with connectivity to a domain
controller due to link fluctuation while the driver initializes and negotiates a
link with the network infrastructure. The link negotiation is further affected
when the Gigabit adapters are participating in an 802.3ad team due to the
additional negotiation with a switch required for this team type. As
suggested in the Knowledge Base Article above, disabling media sense as
described in a separate Knowledge Base Article 239924
(support.microsoft.com/kb/239924) has shown to be a valid workaround
when this problem occurs.
Problem: The 802.3ad team member links disconnect and reconnect
continuously (applies to all operating systems).
Solution: This is a third-party issue. It is seen only when configuring an
802.3ad team with more than two members on the server and connecting
an HP2524 switch, with LACP enabled as passive or active. The HP
switch shows an LACP channel being brought up successfully with only
two team members. All other team member links disconnect and
reconnect. This issue does not occur with the Cisco Catalyst 6500 switch.
100
 Loading...
Loading...