Allegro A3054SU-30, A3054SU-29, A3054SU-28, A3054SU-27, A3054SU-26 Datasheet
...
3054
MULTIPLEXED
TWO-WIRE
HALL-EFFECT SENSOR ICs
The A3054KU and A3054SU Hall-effect sensors are digital magnetic sensing ICs capable of communicating over a two-wire power/
signal bus. Using a sequential addressing scheme, the device responds to a signal on the bus and returns the diagnostic status of the
IC, as well as the status of each monitored external magnetic field.
As many as 30 sensors can function on the same two-wire bus. This
IC is ideal for multiple sensor applications where minimizing the wiring
harness size is desirable or essential.
Each device consists of high-resolution bipolar Hall-effect switching circuitry, the output of which drives high-density CMOS logic
stages. The logic stages decode the address pulse and enable a
response at the appropriate address. The combination of magneticfield or switch-status sensing, low-noise amplification of the Halltransducer output, and high-density decoding and control logic is made
possible by the development of a new sensor DABiC™ (digital analog
bipolar CMOS) fabrication technology. The A3054SU is an improved
replacement for the original UGN3055U.
These unique magnetic sensing ICs are available in two temperature ranges; the A3054SU operates within specifications between
-20°C and +85°C, while the A3054KU is rated for operation between
-40°C and +125°C. Alternative magnetic and temperature specifications are available on special order. Both versions are supplied in
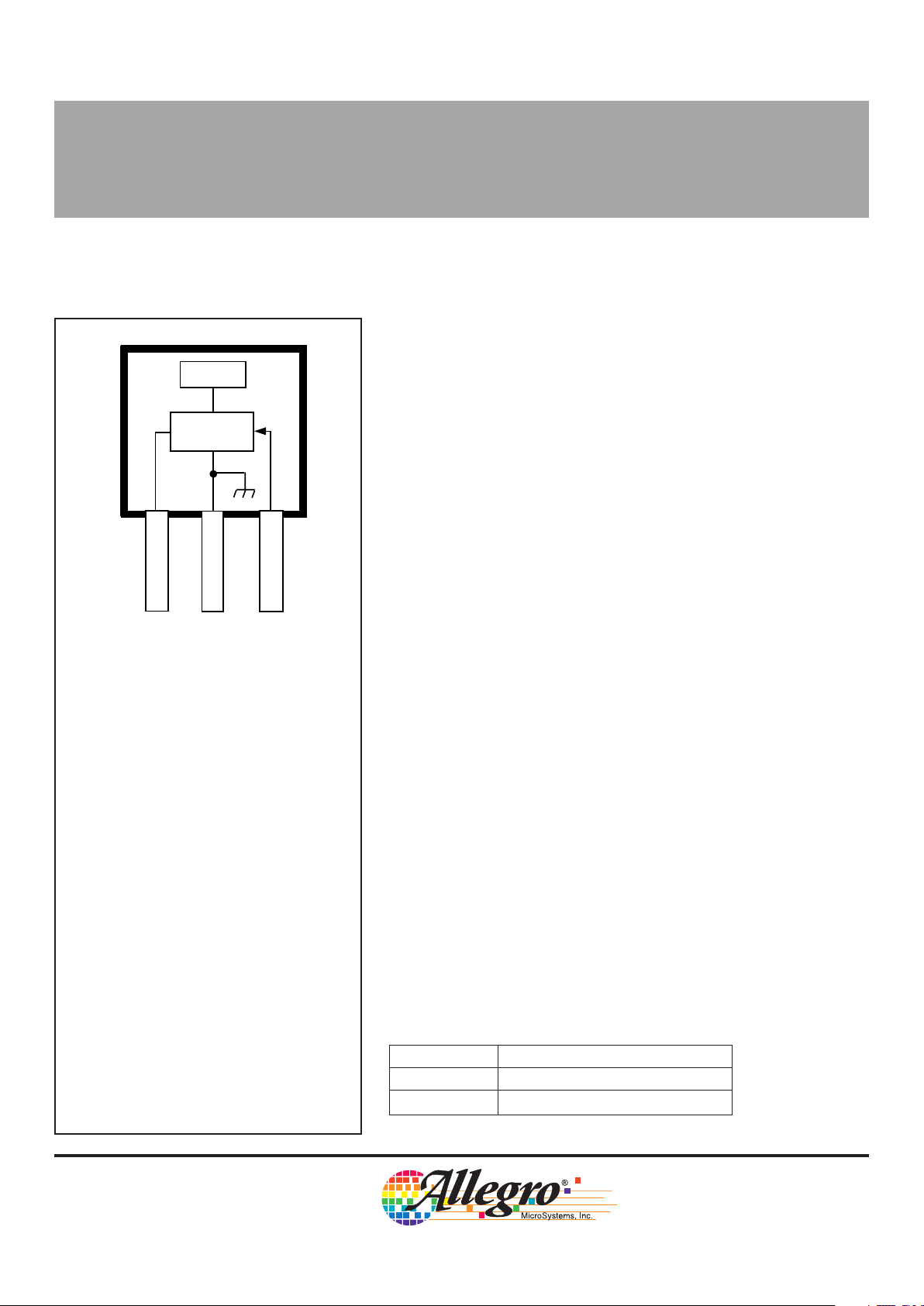
0.060" (1.54 mm) thick, three-pin plastic SIPs. Each device is clearly
marked with a two-digit device address (XX).
3054
MULTIPLEXED TWO-WIRE
HALL-EFFECT SENSOR ICs
FEATURES
■ Complete Multiplexed Hall-Effect ICs with
Simple Sequential Addressing Protocol
■ Allows Power and Communication Over a
Two-Wire Bus (Supply/Signal and Ground)
■ Up to 30 Hall-Effect Sensors Can Share a Bus
■ Sensor Diagnostic Capabilities
■ Magnetic-Field or Switch-Status Sensing
■ Low Power of DABiC Technology Favors
Battery-Powered and Mobile Applications
■ Ideal for Automotive, Consumer, and Industrial Applications
Always order by complete part number:
Part Number Operating Temperature Range
A3054KU-XX -40°C to +125°C
A3054SU-XX -20°C to +85°C
where XX = address (01, 02, … 29, 30).
Pinning is shown viewed from branded side.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
at T
A
= +25°C
Supply Voltage, V
BUS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 V
Magnetic Flux Density, B . . . . . . . Unlimited
Operating Temperature Range, T
A
A3054KU . . . . . . . . . . . -40°C to +125°C
A3054SU . . . . . . . . . . . . -20°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range,
TS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -55°C to +150°C
Package Power Dissipation,
PD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 635 mW
Data Sheet
27680.1
Dwg. PH-005
1
BUS
GROUND
32
SWITCH IN
X
LOGIC
3054
MULTIPLEXED
TWO-WIRE
HALL-EFFECT SENSOR ICs
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Power Supply Voltage V
BUS
——15 V
Signal Current I
S
DUT Addressed, B > 300 G 12 15 20 mA
Quiescent Current I
QL
V
BUS
= 6 V — 1.5 2.5 mA
I
QH
V
BUS
= 9 V — 1.4 2.5 mA
∆I
Q
I
QL
– I
QH
— 100 300 µA
Address Range Addr Factory Specified 1 — 30 —
Clock Thresholds V
CLH
LOW to HIGH — — 8.5 V
V
CHL
HIGH to LOW 6.5 — — V
V
CHYS
Hysteresis — 0.8 — V
Max. Clock Frequency* f
CLK
50% Duty Cycle 2.5 — — kHz
Address LOW Voltage V
L
V
RST
6.0 V
CHL
V
Address HIGH Voltage V
H
V
CLH
9.0 V
BUS
V
Reset Voltage V
RST
2.5 3.5 5.5 V
Propagation Delay* t
plh
LOW to HIGH 10 20 30 µs
t
phl
HIGH to LOW — 5.0 10 µs
Pin 3-2 Resistance R
SWH
DUT Addressed, B < 5 G — 50 — kΩ
R
SWL
DUT Addressed, B > 300 G — 200 — Ω
Pin 3-2 Output Voltage V
SWH
DUT Addressed, B < 5 G — 3.9 — V
V
SWL
DUT Addressed, B> 300 G — 30 — mV
MAGNETIC CHARACTERISTICS over operating temperature range.
Limits
Characteristic Symbol Test Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Units
Magnetic Threshold† B
OP
Turn-On 50 150 300 G
B
RP
Turn-Off 5.0 100 295 G
Hysteresis B
HYS
B
OP
– B
RP
5.0 50 — G
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS over operating temperature range.
Typical Data is at TA = +25°C and is for design information only.
*This parameter, although warranteed, is not production tested.
†Alternative magnetic switch point specifications are available on special order. Please contact the factory.
W
Copyright © 1995 Allegro MicroSystems, Inc.
3054
MULTIPLEXED
TWO-WIRE
HALL-EFFECT SENSOR ICs
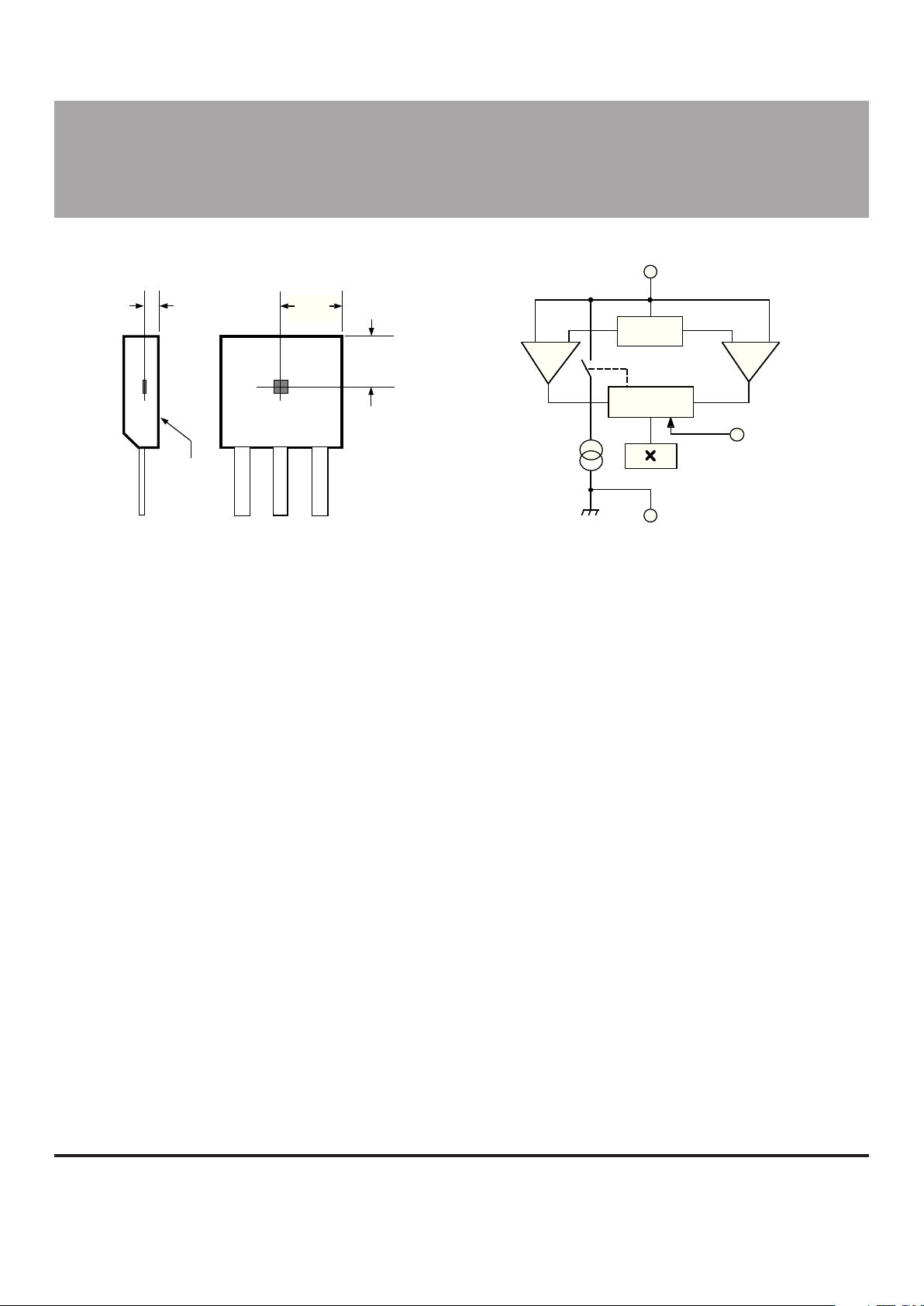
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAMSENSOR LOCATION
(±0.005” [0.13 mm] die placement)
CLOCK
Dwg. FH-009
BUS
SWITCH IN
(OPTIONAL)
GROUND
CMOS LOGIC
REG
COMP COMP
RESET
1
3
2
1 32
Dwg. MH-002-10A
0.015"
0.38 mm
NOM
BRANDED
SURFACE
ACTIVE AREA DEPTH
0.073"
1.85 mm
A
0.090"
2.29 mm
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Sensor Address
Each bus sensor has a factory-specified predefined
address. At present, allowable sensor addresses are
integers from 01 to 30.
LOW-to-HlGH Clock Threshold (V
CLH
)
Minimum voltage required during the positive-going
transition to increment the bus address and trigger a
diagnostic response from the bus sensors. This is also
the maximum threshold of the on-chip comparator that
monitors the supply voltage, V
BUS
.
HlGH-to-LOW Threshold (VHL)
Maximum voltage required during the negative-going
transition to trigger a
signal
current response from the bus
sensors. This is also the maximum threshold of the
on-chip comparator that monitors the supply voltage,
V
BUS
.
Bus HIGH Voltage (VH)
Bus HIGH voltage during addressing. Voltage should
be greater than V
CLH
.
Address LOW Voltage (VL)
Bus LOW voltage during addressing. Voltage should
be greater than V
RST
and less than V
CHL
.
Bus Reset Voltage (V
RST
)
Voltage level while resetting sensors.
Sensor Quiescent Current Drain (IQ)
The current drain of bus sensors when active but not
addressed. IQH is the quiescent current drain when the
sensor is not addressed and is at VH IQL is the quiescent
current drain when the sensor is not addressed and is at
VL. Note that IQL is greater than IQH.
Diagnostic Phase
Period on the bus when the address voltage is at VH.
During this period, a correctly addressed sensor responds
by increasing its current drain on the bus. This response
from the sensor is called the diagnostic response and
the bus current
increase
is called the diagnostic current.
Signal Phase
Period on the bus when the address voltage is at VL.
During this period, a correctly addressed sensor that
detects a magnetic field greater than the magnetic operate point, BOP, responds by maintaining a current drain of
IS on the bus. This response from the sensor is called the
signal response and the bus current is called the signal
current.
Sensor Address Response Current (IS)
Sensor current during the
diagnostic
and the
signal
responses of the bus sensor. This is accomplished by
enabling an internal constant-current source.

3054
MULTIPLEXED
TWO-WIRE
HALL-EFFECT SENSOR ICs
115 Northeast Cutoff, Box 15036
Worcester, Massachusetts 01615-0036 (508) 853-5000
A device may be addressed by changing the supply
voltage as shown in Figure 1. A preferred addressing
protocol is as follows: the bus supply voltage is brought
low (<2.5 V) so that all devices on the bus are reset. The
voltage is then raised to the address LOW voltage (VL) and
the bus quiescent current is measured. The bus is then
toggled between VL and VH (address HIGH voltage), with
each positive transition representing an increment in the
bus address. After each voltage transition, the bus current
may be monitored to check for diagnostic and signal
responses from sensor ICs.
Sensor Addressing
When a sensor detects a bus address equal to its
factory-programmed address, it responds with an increase
in its supply current drain ( IS) during the next HIGH portion
ADDRESSING PROTOCOL
Magnetic Operate Point (BOP)
Minimum magnetic field required to switch ON the
Hall amplifier and switching circuitry of the addressed
sensor. This circuitry is only active when the sensor is
addressed.
Magnetic Release Point (BRP)
Magnetic field required to switch OFF the Hall
amplifier and switching circuitry after the output has been
switched ON. When a device is deactivated by changing
the bus address, all magnetic memory is lost.
Magnetic Hysteresis (B
HYS
)
Difference between the BOP and BRP magnetic field
thresholds.
FIGURE 1
BUS TIMING
SENSOR 03 — DIAGNOSTIC
AND SIGNAL CURRENTS
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS 01
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS 02
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS 04
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS
n
RESET
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS 01
SENSOR 02 —
DIAGNOSTIC CURRENT
DIAGNOSTIC
ADDRESS 03
SENSOR 01
NOT PRESENT
V
H
V
L
V
RST
0
I
S
I
QL
I
QH
0
I
S
0
I
S
n • I
QL
n • I
QH
0
t
phl
t
plh
V
CLH
V
CHL
Dwg. WH-005
BUS
VOLTAGE
SENSOR 02
CURRENT
WITH NO
MAGNETIC
FIELD
SENSOR 03
CURRENT
WITH
MAGNETIC
FIELD
TOTAL
BUS CURRENT
WITH
MAGNETIC
FIELD AT
SENSOR 03
RESET
I
QL
I
QH
SENSOR 01
NOT PRESENT
 Loading...
Loading...