Page 1

Reference Guide
Agilent Technologies
Electronic Calibration Modules
RF Two-P ort
85091C 85092C 85093C
85096C 85098C 85099C
RF Four-Port
N4431B
Microwave Two-Port
N4690B N4691B N4692A
N4693A N4694A N4696B
Microwave Four-Port
N4432A N4433A
Agilent Part Number: N4693-90001
Printed in USA
Print Date: March 2006
Supersedes: February 2006
© Copyright Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2000–2006
Page 2

WARRANTY STA TEMENT
THE MA TERIAL CONT AINED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED “AS IS,” AND IS SUBJECT
TO BEING CHANGED, WITHOUT NOTICE, IN FUTURE EDITIONS. FURTHER, TO THE
MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, AGILENT DISCLAIMS ALL
WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL AND
ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. AGILENT SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ERRORS OR FOR INCIDENTAL
OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING, USE, OR
PERFORMANCE OF THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN.
SHOULD AGILENT AND THE USER HAVE A SEPARATE WRITTEN AGREEMENT WITH
WARRANTY TERMS COVERING THE MATERIAL IN THIS DOCUMENT THAT CONFLICT
WITH THESE TERMS, THE WARRANTY TERMS IN THE SEPARATE AGREEMENT WILL
CONTROL.
DFARS/Restricted Rights Notice
If software is for use in the per formance of a U.S. Government prime contract or
subcontract, Software is delivered and licensed as “Commercial computer software” as
defined in DFAR 252.227-7014 (June 1995), or as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR
2.101(a) or as “Restricted computer sof tware” as defined in FAR 52.227-19 (June 1987) or
any equivalent agency regulation or contract clause. Use, duplication or disclosure of
Software is subject to Agilent Technologies’ standard commercial l icense terms, and
non-DOD Departments and Agencies of the U.S. Government will receive no greater than
Restricted Rights as defined in FAR 52.227-19(c)(1-2) (June 1987) . U.S. Government users
will receive no greater than Limited Rights as defined in FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987) or
DFAR 252.227-7015 (b)(2) (November 1995), as applicable in any technical data.
Certification
Agilent T echnol ogies, Inc. certifies that this p roduct met its publi shed sp ecific atio ns at the
time of shipment from the factory. Agilent Technologies, Inc . further certifies that its
calibration measurements are traceable to the United States National Institute of
Standards and Technology, to the extent allowed by the Institute's calibration facility, and
to the calibration facilities of other Int ernational Standards Organization members.
ii
Page 3

Assistance
Product maintenance agreements and other cus tomer assistanc e agreements are a vailable
for Agilent Technologies, Inc. products. For information about these agreements and for
other assistance, contact Agilent. Refer to “Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15.
Safety and Regulatory Information
The safety a n d regulator y informati o n p e rtaining to th i s product is l ocated in the s e ction
“Safety and Regulatory Information” on page 1-18.
Safety Notes
The following safety notes are used in this manual. Familiarize yourself with each of the
notes and its meaning before operating this instrument. All pertinen t saf ety notes for
using this product are located in “Safety and Regulatory Information” on page 1-18
WARNING Warning denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure which, if
not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in injury or loss
of life. Do not proceed beyond a warning note until the indicated
conditions are fully understood and met.
CAUTION Caution denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure that, if not
correctly performed or adhered to, could result in damage to or destruction of
the instrument. Do not proceed beyond a caution sign until the indicated
conditions are fully understood and met .
Technology Licenses
The hardware and / or software described in this document are furnished under a license
and may be used or copied only in accordance with the terms of such license.
iii
Page 4

Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation
To print copies of documentation from the Web, download the PDF file from the Agilent
web site:
•Go to http://www.agilent.com. En t e r the docume n t’s pa rt nu mber (loca t ed on the titl e
page) in the Search box.
• Click Search.
• Click on the hyperlink for the document.
• Click the printer icon located in the tool bar.
iv
Page 5

Contents
1 General Information
Manual Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Prerequisite Knowledge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Accuracy of Electronic Calibration versus Mechanical Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Models and Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
8509x Modules (RF Two-Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
N4431B Modules (RF Four-Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
N469xA/B Modules (Microwave Two-Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-8
8506x Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-10
N4432A and N4433A Modules (Microwave Four-Port) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-11
Compatible Network Analyzers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-13
Service and Recertification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-14
Contacting Agilent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 -15
Returning Devices to Agilent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-16
Recertification of ECal Modules. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-17
Safety and Regulatory Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-18
Safety Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-18
Installation Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-18
Instrument Markings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-19
Compliance Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-20
2 Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Inspecting ECal Module Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Inspect the Kit Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Record the Serial Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Verify Electrical Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Equipment Required but Not Supplied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
8509x Series Kit Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
8509x Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
N4431B Series Kit Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
N4431B Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
N469xA/B Series Kit Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-4
N469xA/B Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
N4432A and N4433A Series Kit Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
N4432A Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
N4433A Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Operating and Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
ESD Damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Connector Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Input Power Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
Handling and Storage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-9
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-10
Connect ECal Module to PNA or ENA Analyzer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-10
Connect ECal Module to VNA Analyzer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-12
Table of Contents Contents-v
Page 6

Contents
3 Operating the ECal Module
Setting Up a Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Required Procedure for All Calibrations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Calibration Types Available . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
When to Correct for Isolation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Calibration Methods for Non-Insertable Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Performing a Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Validating a Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Why Validate a Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Measure Known Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Perform ECal Confidence Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
4 Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Electrostatic Discharge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Visual Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Look for Obvious Defects and Damage First . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Inspect the Mating Plane Surfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Inspect Female Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-4
Cleaning Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Cleaning Coax Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Cleaning Precision 7 mm Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Gaging Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Connector Gage Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
When to Gage Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Recognizing Gage Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Reading the Connector Gage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Gaging Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-13
Making Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
3.5 mm, 2.92 mm, 2.4 mm, 1.85 mm, Type-N, 7-16, and Type-F Devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
7 mm Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-15
Final Connection Using a Torque Wrench . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-16
Separating Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-18
Handling and Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-19
5 Specifications and Characteristics
Specifications: Terminology and Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Environmental Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Operating Temperature and Accuracy Enhancement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Barometric Pressure and Relative Humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Characteristic Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-4
8509x Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
N4431B (3.5 mm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
N4431B (Type-N 50 Ω). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
N4432A (Type-N 50 Ω). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
N4433A (3.5 mm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
N469xA/B Series. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Mechanical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
Pin Depth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
Contents-vi Table of Contents
Page 7

Contents
Type-N Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-12
Typical Pin Depth Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-14
Supplemental Mechanical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-17
Measurement Uncertainty Calculator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-18
Download the Vector Network Analyzer Uncertainty Calculator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-18
6 Replaceable Parts
Description of This Chapter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
7 mm Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
Type-N (50 ohm) Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-3
3.5 mm Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-4
7-16 Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-5
2.92 mm Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-6
2.4 mm Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
1.85 mm Modules and Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Type-N (75 ohm) Modules and Accessories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-9
Type-F Modules and Accessories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-10
Other ECal Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-11
Table of Contents Contents-vii
Page 8

Contents
Contents-viii Table of Contents
Page 9

1 General Information
1-1
Page 10

General Information
Manual Overview
Manual Overview
The purpose of this manual is to help you use your Electronic Calibration (ECal) module
confidently and effectively. ECal is a precision, single-connection calibration technique
which uses fully traceable and verifiable electronic standards. Each module has unique
S-parameter data that is stored in the module's memory. During calibration, ECal
transfers this data to the network analyzer to calculate the error terms for your network
analyzer.
This manual provides instructions for operating and maintai ning your ECal module. Also
included are calibration procedures (for supported analyzers), mechanical specifications,
and replaceable parts available for each model.
RF Modules
The 8509x and N4431B series provide two-port and four-port calibration solutions with
operating frequencies starting at 300 kHz and ending as high as 13.5 GHz.
Microwave Modules
The N469xA and N469xB series (which replace the 8506x seri es) an d the N4432A and
N4433A series provide two-port and four-port calibration solutions with operating
frequencies starting as low as 300 kHz and ending as high as 67 GHz.
Prerequisite Knowledge
This manual assumes you are trained in proper connector care. Because an accurate
calibration depends on the integrity and c leanliness of the connector interface, a damaged
connector will invalidate the calibration achieved with that module. Refer to the
“Principles of Microwave Connector Care Quick Reference Card” located at the back of this
manual.
Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface
In this manual, adapters, ECal modules, and gage masters are referred to by way of their
interface connector. For example:
• A female adapter has a female interface.
• A male adapter has a male interface.
A connector gage is referred to by way of the connector it measures. For example:
• A male connector gage has a female interface so it can measure male devices.
• A female connector gage has a male interface so it can measure female devices .
Accuracy of Electronic Calibration versus Mechanical Calibration
As the numb er of DUT test port s increases, the re quired number of calib r ation
measurements also increases. Thi s boosts the probability of bad connections and bad
calibrations when mechanical calibratio n stand ards are used rather than ECal. Also, test
port cable repeatability and stability errors are amplified by the increased number of
1-2 Chapter 1
Page 11

General Information
Manual Overview
connections and disconnections. To per form an SOLT 4-port calibration, a minimum of
twelve 1-port standards and three 2-p ort (thru) standards are measured, requiring a total
of eighteen connections. The same calibration using a 4-port ECal module (N4431B,
N4432A and N4433A) requires only four connections .
Ignoring connection related errors, the following table compares the accuracy of ECal
versus mechanical calibration in various calibration options.
Table 1-1 Accuracy of ECal versus Mechanical Calibration
Mechanical Calibration Type ECal Thru
Type
1-Port; calibration constant (not
NA Reflection ++
Measurement ECal Mechanical
Calibration
data-based) SOL
1-Port; short, open, sliding load NA Reflection +
1-Port; data-based, expanded NA Reflection +
2-Port TRL All types Reflection
Transmission
characterized Reflection
Transmission
≥ 2-Port; calibration constant
SOL; flush Thru
a
internal
unknown
external flush
Reflection
Transmission
a
Reflection
Transmission
≥ 2-Port; calibration constant
SOL; unknown Thru
characterized Reflection
Transmission
internal
unknown
Reflection
Transmission
++
++
++
+
++
++
==
++
++
++
++
≥ 2-Port; data-based, expanded,
flush Thru
a
≥ 2-Port; data-based, expanded,
unknown Thru
characterized Reflection
Transmission
internal
unknown
external flush
Reflection
Transmission
a
Reflection
Transmission
characterized Reflection
Transmission
internal
unknown
Reflection
Transmission
+
++
+
+
+
+
+
++
+
+
++ better; + slightly better; = same
a. Flush thru should NOT be used when the test port connectors are not the same type as
the calibration standards. SMA and 3.5 mm connectors are mateable but are NOT the
same type.
Chapter 1 1-3
Page 12

General Information
Models and Options
Models and Options
This section provides the model number, operating characteristics and connector options
available with Agilent RF and microwave ECal modules. You can order ECal modules by
selecting the model number followed by the desired options.
8509x Modules (RF Two-Port)
ECal modules from this series are available wit h the connector types and fr equency ranges
shown in Table 1-2 on page 1-5. Mixed connector options allow you to conf igure the module
with a different connector type at each port (as shown in Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-1 Model 85092C Option M0F
Figure 1-2 Model 85092C Op tion 104, 201
1-4 Chapter 1
Page 13

Table 1-2 8509x Modules
General Information
Models and Options
Model
Number
Connector
Type
Operating
Frequency
Port A and B Option
-m- and -f- -m- and -m- -f- and -f-
85091C 7 mm 300 kHz to 9 GHz No Connector Option
85091-60004
85092C
Type-N 50 ohm 300 kHz to 9 GHz M0F
85092-60008
Mixed
300 kHz to 9 GHz See Table 1-3
connector types
00M
85092-60009
85092-60004
– see Table 1-3
85093C
3.5 mm 300 kHz to 9 GHz M0F
85093-60008
Mixed
300 kHz to 9 GHz See Table 1-3
connector types
00M
85093-60009
85092-60004
– see Table 1-3
85096C Type-N 75 ohm 300 kHz to 3 GHz M0F
85096-60007
7-16 300 kHz to 7.5 GHz M0F
85098C
Mixed
300 kHz to 7.5 GHz See Table 1-3
85098-60007
connector types
00M
85096-60008
00M
85098-60008
85092-60004
– see Table 1-3
00F
85092-60010
00F
85093-60010
00F
85096-60009
00F
85098-60009
85099C Type-F 300 kHz to 3 GHz M0F
85099-60009
Table 1-3 8509x Mixed Connector Options
Model
Number
85092C Type-N 50Ω 103 104 3.5 mm 201 202
85093C 3.5 mm 101 102 Type-N 50Ω 203 204
85098C
a. Limits ECal module high frequency to 7.5 GHz.
Other Options Description
00A Adds one -m- to -m- and one -f- to -f- adapter.
UK6 Adds commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
Port A Option Port B Option
Type -f- -m- Type -f- -m- Type -f- -m-
7-16
a
105 106 3.5 mm 201 202 Type-N 50Ω 203 204
00M
85099-60010
a
7-16
a
7-16
00F
85099-60011
205 206
205 206
Chapter 1 1-5
Page 14

General Information
Models and Options
N4431B Modules (RF Four-Port)
NOTE The N4431A is no longer available for purchase, but may be returned to
Agilent for service and recertification.
ECal modules from this series are available wit h the connector types and fr equency ranges
shown in Table 1-4. Mixed connector options (shown in Table 1-5) allow you to configure
the module with a different connector type at each port.
Figure 1 -3 Model N443 1B Op tio n 010
Table 1-4 N4431B Modules
Model
Number
N4431B N4431-60007 Type-N 50Ω -f- 300 kHz to
Module
Number
N4431-60006 3.5 mm -f- 300 kHz to
N4431-60008 Mixed connector types – see
Connector Type Port
A,B,C,D
Table 1-5 on page 1-7
Operating
Frequency
13.5 GHz
13.5 GHz
300 kHz to
13.5 GHz
Option
010
020
See Table 1-5
on page 1-7
1-6 Chapter 1
Page 15

General Information
Models and Options
Table 1-5 N4431B Mixed Connector Options
Connector Type Port A Option Port B Option Port C Option Port D Option
3.5 mm -f- 101 201 301 401
3.5 mm -m- 102 202 302 402
Type-N 50Ω -f- 103 203 303 403
Type-N 50Ω -m- 104 204 304 404
7-16 -f7-16 -m-
a
a
105 205 305 405
106 206 306 406
a. Limits ECal module high frequency to 7.5 GHz.
Other Options Description
UK6 Adds commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
Chapter 1 1-7
Page 16

General Information
Models and Options
N469xA/B Modules (Microwave Two-Port)
NOTE The N4690/1/6A are no longer available for purchase, but may be ret urned to
Agilent for service and recertification.
ECal modules from this series are available wit h the connector types and fr equency ranges
shown in Table 1-6. Mixed connector options are not av ailable with this series.
Figure 1-4 Model N4693A Option M0F
1-8 Chapter 1
Page 17

Table 1-6 N469xA/B Modules
General Information
Models and Options
Model
Number
N4690B Type-N 50Ω 300 kHz to 18 GHz M0F 00M 00F
N4691B 3.5 mm 300 kHz to 26.5 GHz M0F 00M 00F
N4692A 2.92 mm 10 MHz to 40 GHz M0F 00M 00F
N4693A 2.4 mm 10 MHz to 50 GHz M0F 00M 00F
N4694A 1.85 mm 10 MHz to 67 GHz M0F 00M 00F
Connector
Type
Operating
Frequency
Port A and B Option
-m- and -f- -m- and -m- -f- and -f-
Module Part Number
N4690-60004 N4690-60005 N4690-60006
Module Part Number
N4691-60004 N4691-60005 N4691-60006
Module Part Number
N4692-60001 N4692-60002 N4692-60003
Module Part Number
N4693-60001 N4693-60002 N4693-60003
Module Part Number
N4694-60001 N4694-60002 N4694-60003
N4696B 7 mm 300 kHz to 18 GHz No Connector Option
Module Part Number
N4696-60004
Other Options Description
00A Adds one -m- to -m- and one -f- to -f- adapter (not available with N4696B).
UK6 Adds commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
Chapter 1 1-9
Page 18

General Information
Models and Options
8506x Modules
ECal modules in this series are no longer available for purchas e, but may be returned to
Agilent for service and recertification. The 8506x series has been replaced by the
N469xA/B series. See “N469xA/B Modules (Microwave Two-Port)” on page 1-8.
Figure 1-5 Model 85062B
Table 1-7 8506x Modules
Model
Number
85060B 7 mm 1 to 18 GHz
85062B 3.5 mm 1 to 26.5 GHz
85064B Type-N 50Ω 1 to 18 GHz
Connector
Type
Operating
Frequency
8506xA series modules with serial numbers below 800 need to be retrofitted for operation
with the 85097B VNA interface kit. The retrofitting must be done by a qualified Agilent
Technologies service office. See “Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15.
1-10 Chapter 1
Page 19

General Information
N4432A and N4433A Modules (Microwave Four-Port)
N4432A and N4433A Modules (Microwave Four-Port)
ECal modules from this series are available wit h the connector types and fr equency ranges
shown in Table 1-8. Mixed connector options (shown in Table 1-9) allow you to configure
the module with a different connector type at each port.
Figure 1-6 Model N4433A Option 010
Table 1-8 N4432A and N4433A Modules
Model
Number
N4432A N4432-60003 Type-N 50Ω -f- 300 kHz to 18 GHz 020
N4433A N4433-60003 3.5 mm -f- 300 kHz to 20 GHz 010
Module
Number
N4432-60005 Mixed connector types – see
N4433-60004 Mixed connector types – see
Connector Type Port
A,B,C,D
Table 1-9 on page 1-12
Table 1-10 on page 1-12
Operating
Frequency
300 kHz to 18 GHz See Table 1-9
300 kHz to 20 GHz See
Option
on page 1-12
Table 1-10 on
page 1-12
Chapter 1 1-11
Page 20

General Information
N4432A and N4433A Modules (Microwave Four-Port)
Table 1-9 N4432A Mixed Connector Options
Connector Type Port A Option Port B Option Port C Option Port D Option
3.5 mm -f-
3.5 mm -m-
a
a
101 201 301 401
102 202 302 402
Type-N 50Ω -f- 103 203 303 403
Type-N 50Ω -m- 104 204 304 404
a. Frequency range of ECal module limited by other connectors.
Other Options Description
UK6 Adds commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
1A7 Adds ISO 17025 compliant calibration.
A6J Adds ANSI Z540 compliant calibration.
Table 1-10 N4433A Mixed Connector Options
Connector Type Port A Option Port B Option Port C Option Port D Option
3.5 mm -f- 101 201 301 401
3.5 mm -m- 1 02 202 302 402
Other Options Description
UK6 Adds commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
1A7 Adds ISO 17025 compliant calibration.
A6J Adds ANSI Z540 compliant calibration.
1-12 Chapter 1
Page 21

General Information
Compatible Network Analyzers
Compatible Network Analyzers
ECal modules operate with the following network analyzer models, as shown in Table 1-11.
Not all ECal module and network analyzer combinations have the same features or
capabilities. See your network analyzer user guide or online Help.
Table 1-11 Compatible Network Analyzers
Network
Analyzers
8509xC
N4431B
ECal Module Series
a
N4432/3A N469xA/B
8753/8720-Series Network Analyzers
8719ES/ET
8720ES/ET
8722ES/ET
8753ES/ET
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
c
c
c
c
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
c
c
c
c
No
No
No
No
PNA Network Analyzers
E8356/7/8A Yes Yes
E8801/2/3A Yes Yes
N3381/2/3A Yes Yes
E8362/3/4A Yes Yes
E8362/3/4B Yes Yes
E8361A Yes Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
N5230A Yes Yes Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Interface
Required
b
8506x
d
d
d
d
e
e
e
e
e
e
e
Yes 85097B
Yes 85097B
Yes 85097B
Yes 85097B
No USB
No USB
No USB
No USB
No USB
No USB
No USB
ENA Network Analyzers
E5070/1A/B Yes Y es
Yes
Yes No USB
E5061/2A Yes Yes Yes Yes No USB
a. Only ports A and B available when operated with 8753/8720-series analyzers.
b. 8506x modules are no longer available for purchase.
c. 8753/8720-series firmware revision 7.68 or higher required.
d. 8753/8720-series firmware revision 7.74 or higher and adapter cable (part no.
8121-1047) required.
e. PNA firmware revision 3.0 or higher required with N4692/3A, and N4694A.
NOTE For 8753 network analyzers, RF ECal modules (8509x) may be used below 300 kHz.
However, calibration accuracy is not specified. The display t race connecting the two
points on either side of the 300 kHz boundary may misrepresent actual performance.
Chapter 1 1-13
Page 22

General Information
Service and Recertification
Service and Recertification
If your ECal module requires service or recertifi cation, contact the Agilent office nearest
you for information about where to send i t. The perf ormance of your ECal mo dule can only
be verified by specially manufactured equipment and calibration s tand ards from Agilent.
1-14 Chapter 1
Page 23

General Information
Service and Recertification
Contacting Agilent
Assistance with test and measurements needs and information on finding a local Agilent
office are available on the Web at:
http://www.agilent.com/find/assist
If you do not have access to the Internet, please contact your Agilent field engineer.
NOTE In any correspondence or telephone conversation, refer to the Agilent product
by its model number and full serial number. With this information, the
Agilent representative can determine whether your product is still within its
warranty period.
Chapter 1 1-15
Page 24

General Information
Service and Recertification
Returning Devices to Agilent
If you are returning the product to Agilent, please include a service tag (located near the
end of this manual) on which you provide the following information:
• your company name and address
• a technical contact person within your company, and the person’s complete telephone
number including country code and area code
• the model number and serial number of the ECal module
• type of service required
• a detailed description of the problem and how the device was being used when the
problem occurred (such as calibration or measurement)
NOTE When transporting the module, use original or comparable packaging.
1-16 Chapter 1
Page 25

General Information
Service and Recertification
Recertification of ECal Modules
The suggested interval for recertification is 12 months. After reviewing the results of the
initial recertification, you may es tablish a shorter interval that reflects greater use and
wear of the module.
Where to Send a Module for Recertification
Contact Agilent for information on where to send your kit for recertification. See
“Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15. Refer to “Returning Devices to Agilent” o n page 1-16 for
instructions on the preparation of returning the device.
How Agilent Verifies Your ECal Module
Agilent verifies the specifications of these devices as follows:
1. The residual microwave error terms of the test sys tem are verified with precision
airlines and shorts or low frequency resistance that are directly traced to the National
Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The airline and short c haract eri stics are
developed from mechanical measurements. The mechanical measurements and
material properties are carefully modeled to give very accurate electrical
representation. The mechanical measurement s are then traced to NIST through
various plug and ring gages and other mechanical measurements.
2. Each module is electrically tested on this system to the specifi cation listed in Chapte r 5,
“Specifications and Characteristics.”
These two steps establish a traceable link to NIST for Agilent to the extent allowed by the
institute’s calib ration facility. The specifications d ata provided for the module are t raceable
to NIST through Agilent Technologies.
What Is Provided with a Recertification
• a new calibra t i on st i cke r a ff i x e d to th e m od u l e
• a certificate of calibration
• a list of United States National Institut e of Standa rds and Technology (NIST) traceable
numbers
• a calibration report for each traceable module listing measured values, specifications,
and uncertainties
• a new set of S-parameter data (embedded in module memory) if the old set of
S-parameters data no longer allows for a calibratio n that me ets all performance
specifications
Agilent Technologies offers different types of calibration for the recertification of the
module. For more information, contact Agilent. See “Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15.
Chapter 1 1-17
Page 26

General Information
Safety and Regulatory Information
Safety and Regulat o ry Inf ormation
Review this section to familiarize yourself with safety markings and instructions before
you operate the ECal module. This produc t has been designed and tested in accordance
with international standards.
WARNING The WARNING notice denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a
procedure, practice, or the like, that, if not correctly performed or
adhered to, could result in personal injury. Do not proceed beyond a
WARNING notice until the indicated conditions are fully understood
and met.
CAUTION The CAUTION noti ce denotes a hazard. It calls attention to an operating
procedure, practice, or the like, that, if not correctly performed or adhered to,
could result in damage to the product or loss of important data. Do not
proceed beyond a CA UTION notice until the indicated conditions are fully
understood and met.
Safety Notices
WARNING To prevent electrical shock, discon nect from instrument before
cleaning. Use a dry cloth or one slightly dampened with water to
clean the external case parts. Do not attempt to clean internally.
WARNING If this product is not used as specified, the protection provided by
the equipment could be impaired. This product must be used in a
normal condition (in which all means for protection are intact) only.
Installation Notices
CAUTION This product is designed for use in INSTALLATION CATEGORY II and
POLLUTION DEGREE 2, per IEC 1010 and 664 respectively.
CAUTION When installing the product in a cabinet, the convection in and out of the
product must not be restricted. The ambient temperature (outside the
cabinet) must be less than the maximum operating temperature of the s ystem
by 4 °C for every 100 watts dissipated in the cabinet. If the total power
dissipated in the cabinet is greater than 800 w atts, then forced convection
must be used.
1-18 Chapter 1
Page 27

Instrument Markings
When you see this symbol on your instrument, you should
!
1SM1-A This text indicates that the instrument is an Industrial
refer to the instrument’s instruction manual for important
information.
This symbol indicates hazardous voltages.
The laser radiation symbol is marked on products that have
a laser output.
This symbol indicates that the instrument requires
alternating current (ac) input.
The CE mark is a registered trademark of the European
Community. If it is accompanie d by a year, it indicates th e
year the design was proven.
The CSA mark is a registered trademark of the Canadian
Standards Association.
Scientific and Medical Group 1 Class A product (CISPER
11, Clause 4).
General Information
Safety and Regulatory Information
This symbol indicates that the power line switch is ON.
This symbol indicates that the power line switch is OFF or
in STANDBY position.
The C-Tick mark is a registered trademark of the
Australian Spectrum Management Agency.
This product complies with the WEEE Directive
(2002/96/EC) marking requirements. The affixed label
indicates that you must not discard this electrical/
electronic product in domestic household waste.
Product Category: With reference to the equipment types in
the WEEE Directive Annex I, this product is classed as a
"Monitoring and Control instrumentation" product.
Do not dispose in domestic household waste.
To return unwanted products, contact your local Agilent
office, or see http://www.agilent.com /envi ronment/p rod uct/
for more information.
Chapter 1 1-19
Page 28

General Information
Safety and Regulatory Information
Compliance Notices
This product has been designated and tested in accordance with the standards in the
Declaration of Conformity (see below), and has bee n supp lied in a safe condition. The
documentation contains information and warnings that must be followed by the user to
ensure safe operation and to maintain the product in a safe conditions.
Compliance IEC 61000-4-4: 1995 (electrical transients) and IEC 61000-4-2: 1995
(electrostatic discharge): Passes using Criterion C.
Calibration cycle may be interrupted by power line transients applied to external power
supply or by electrostatic discharge applied to module. Normal function is restored by
power-cycling the module.
Compliance with Canadian EMC Requirements
This ISM device complies with Canadian ICES-001.
Cet appareil ISM est conforme a la norme NMB du Canada.
Declaration of Conformity
A declaration of conformity is on file for the PNA models, and a copy is available upon
request.
1-20 Chapter 1
Page 29

2 Preparing to Use the ECal Module
2-1
Page 30

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Inspecting ECal Module Kit
Inspecting ECal Module Kit
Inspect the Kit Contents
Verify the case and its contents are not damaged and that all p arts ar e includ ed (s ee it ems
listed in T able 2- 2, Table 2-3, and Table 2-4). If the case or any device appears damaged, or
if the shipment is incomplete, contact Agilent . Agilent will arrange for repair or
replacement of incomplete or damaged shipments without waiting for settlement from the
transportation company. See “Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15.
Record the Serial Number
ECal modules are individually serialized. Record the se rial number and the date of initial
use as a reminder for annual recertification. See “Recertification of ECal Modules” on
page 1-17.
Table 2-1 Table for Tracking ECal Module Serial Numbers
Module Number Serial Number Date
Verify Electrical Performance
To verify electrical performance of the module, see “Validating a Calibration” on page 3-7.
Equipment Required but Not Supplied
VNA Interface Kit (85097B)
The VNA Interface Kit allows you to connect an ECal module to supported vector network
analyzers. Microw ave ECal modules (N469xA/B series) require an adapter cable
(part no. 8121-1047) to operat e wit h the 85097B. The adapter cable is included as an
option with the interfa ce kit or can be ordered separately. Refer t o Chapter 6 , “Replaceable
Parts.”
Pin Depth Gages
Gages for measuring recession or protrusion are not provided in the kit. See Chapter 6 ,
“Replaceable Parts.” or contact Agilent to order gages and other tes t accessories.
2-2 Chapter 2
Page 31

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
8509x Series Kit Contents
8509x Series Kit Contents
The following table lists the items in each 8509x kit. The ECal module listed in the table
with each kit describes a unit having a male and female connector (Option M0F). See
Table 1-2 on page 1-5 for the part number of other configurations.
Table 2-2 8509x Kit Contents
Qty Description Part No. Qty Description Part No.
85091C 85096C
1 RF Module, 7 mm 85091-60004 1 RF Module, Type-N 75 ohms 85096-60007
1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
1 Extractor, 7 mm Collet 5060-0370
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001 1 RF Module, 7-16 85098-60007
85092C 1 Torque Wrench 1 1/16”, 2.2 N-m 8710-2175
1 RF Module, Type-N 50 ohms 85092-60008 1 Open-end Wrench 15/16” 8710-2174
1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
85093C 1 RF Module, Type-F 85099-60009
1 RF Module, 3.5 mm 85093-60008 1 Type F Wrench 8710-1841
1 Torque Wrench 20 mm, 0.9 N-m 8710-1764 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765 1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
85098C
85099C
8509x Options
• Option 00M configures the module with two male connectors.
• Option 00F configures the module with two female connectors.
• Option M0F configures the module with one male connector and one female connector.
• Option 00A adds one -m- to -m- and one -f- to -f adapter (not av ailable with 85091C).
• Option UK6 adds a commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
Chapter 2 2-3
Page 32

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
N4431B Series Kit Contents
N4431B Series Kit Contents
NOTE The N4431A is no longer available for purchase, but may be returned to
Agilent for service and recertification.
The following table lists the items in each N4431B kit. Option 010 is configu red with
3.5 mm -f- connectors on all ports and Option 020 is configured with type-N -f- connectors
on all ports. See Table 1-5 on page 1-7 for other configurations available.
Table 2-3 N4431B Kit Contents
Qty Description Part No. Qty Description Part No.
N4431B Option 010 N4431B Option 020
1 RF Module, 3.5 mm N4431-60003
or
N4431-60006
1 Torque Wre nch 20 mm, 0.9 N-m 8710-1764 1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766
1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
a. Shipped only with N4431B.
1 RF Module, Type-N 50 ohms N4431-60004
or
a
-N/A
N4431-60007
N4431B Options
• Option 010 configures the module with 3.5 mm -f- connectors on all ports.
• Option 020 configures the module with Type-N 50 ohm -f- connectors on all ports.
• Option UK6 adds a commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
N469xA/B Series Kit Contents
a
-
NOTE The N4690/1/6A are no longer available for purchase, but may be ret urned to
Agilent for service and recertification.
The following table lists the items in each N469xA/B kit. The ECal module li sted in the
table with each kit describes a unit having a male and female connect or (Option M0F). See
Chapter 6 , “Replaceable Parts,” for the part number of other configurations.
2-4 Chapter 2
Page 33

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
N469xA/B Series Kit Contents
Table 2-4 N469xA/B Kit Contents
Qty Description Part No. Qty Description Part No.
N4690B N4693A
1 Microwave Module, Type-N
N4690-60001
1 Microwave Module, 2.4 mm
a
N4693-60001
or
N4690-60004
1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766 1 Torque Wrench 20 mm, 0.9
1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to 9/16” 8710-1770 1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001 1 Spanner Wrench 08513-20014
N4691B 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Microwave Module, 3.5 mm
N4691-60001
b
N-m
9/16”
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
a
8710-1764
8710-1770
or
N4691-60004
1 Torque Wrench 20 mm, 0.9
N-m
1 Torque wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765 1 Microwave Module, 1.85 mm N4694-60001
1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to 9/16” 8710-1770 1 Torque Wrench 20 mm, 0.9
1 Spanner Wrench 08513-20014 1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to
8710-1764 N4694A
b
8710-1764
N-m
8710-1770
9/16”
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001 1 Spanner Wrench 08513-20014
N4692A 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Microwave Module, 2.92 mm N4692-60001 1 R eference Gui de N4693 -90001
1 Torque Wrench 20 mm, 0.9
N-m
1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765 1 Microwave Module, 7 mm
8710-1764
N4696B
N4696-60001
a
or
N4696-60004
1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to 9/16” 8710-1770 1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766
1 Spanner Wrench 08513-20014 1 Open-End Wrench, 1/2 to
9/16”
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506 1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001 1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
8710-1770
b
a. Shipped only with the “A” model.
b. Shipped only with the “B” model.
Chapter 2 2-5
Page 34

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
N4432A and N4433A Series Kit Contents
N469xA/B Options
• Option 00M configures the microwave module with two male connectors.
• Option 00F configures the microwave module with two female connectors.
• Option M0F configures the module with one male connector and one female connector.
• Option 00A adds one -m- to -m- and one -f- to -f- adap ter (not supplied with N4696B).
• Option UK6 adds a commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
N4432A and N4433A Series Kit Contents
The following tables list the items in each N4432A and N4433A kit. For the N4432A kit,
Option 020 is configured with type-N 50 Ohm -f- conne ctors on all ports. For the N4433A
kit, Option 010 is configured with 3.5 mm -f- connectors on all ports. See Table 1-9 on
page 1-12 and Table 1-10 on page 1-12 for other configurations available.
Table 2-5 N4432A Kit Contents
Qty Description Part No.
N4432A Option 020
1 Microwave Module, Type-N
50 Ohm -f1 Torque Wrench 3/4”, 1.3 N-m 8710-1766
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
N4432-60003
Table 2-6 N4433A Kit Contents
Qty Description Part No.
N4433A Option 010
1 Microwave Module, 3.5 mm -f- N4433-60003
1 Torque Wre nc h 20 mm, 0.9 N-m 8710-1764
1 Torque Wrench 5/16”, 0.9 N-m 8710-1765
1 USB A-B Cable, 1.8 m 8121-0506
1 Reference Guide N4693-90001
2-6 Chapter 2
Page 35

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
N4432A and N4433A Series Kit Contents
N4432A Options
• Option 020 configures the module with Type-N 50 ohm -f- connectors on all ports.
• Option UK6 adds a commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
• Option 1A7 adds ISO 17025 compliant calibration.
• Option A6J adds ANSI Z540 compliant calibration.
N4433A Options
• Option 010 configures the module with 3.5 mm -f- connectors on all ports.
• Option UK6 adds a commercial calibration certificate with measured data.
• Option 1A7 adds ISO 17025 compliant calibration.
• Option A6J adds ANSI Z540 compliant calibration.
Chapter 2 2-7
Page 36

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Operating and Safety Precautions
Operating and Safety Precautions
Observe the following guidelines before connecting or operating your ECal module.
ESD Damage
Protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) is important while handling and
operating your ECal module. Static electricity can build up on your body and can easily
damage sensitive components when discharged. Static discharges too small to be felt can
cause permanent damage to the unit. To prevent damage from ESD:
• Use a grounded antistatic mat in front of your test equipment and wear a grounded
wrist strap attached to it when handling or operating the ECal module.
• Wear a heel strap when working in an area with a conductive floor.
• Ground yourself before you clean, inspect, or make a connection to an ECal module .
You can, for example, grasp the grounded outer shell of the analyzer test port or cable
connector briefly.
• Avoid touching the center conductor of the test ports.
For more information about preventing ESD, see “Electrostatic Discharge” on page 4-2.
Connector Care
Because connectors can become defective due to wear during normal use, all connectors
should be inspected and maintained to maximize their service life.
• Inspect the mating surface each time a co n n e ction is made. Meta l pa r ti cl e s fr o m
connector threads often find their way onto the mating surface when a connection is
made or disconnected.
• Clean dirt and contamination from the connector mating surface and threads. This
simple step can extend the service life of the connector and improve the quality of your
calibration and measurements.
• Gage connectors periodically. This not only provides assurance of proper mechanical
tolerances, and thus connector performance, but can also indicate situations where the
potential for damage to another connector may exist.
You should apply connector care to all devices used in the measurement setup. For more
detailed information, see “Visual Inspection” on page 4-3.
CAUTION ECal modules can be damaged if you a pply excessive torque to the c onnectors .
See Ta ble 4-1 on page 4-18 for required torque settings.
2-8 Chapter 2
Page 37

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Operating and Safety Precautions
Input Power Level
Before perfo r m i n g a c al ibration, ma ke su re the input pow e r and DC levels do not exceed
the values indicated in Table 2-7.
Table 2-7 Input Power Limits
Parameter
8509x N443xA/B N469xA/B
Maximum Input Power +20.0 dBm +20.0 dBm +10.0 dBm
Maximum DC Level
Applied to Test Port
± 20 Volts ± 3 Volts ± 10 Volts
ECal Module Series
Operating Temperature
The temperature of the ECal module must be within the following temperature range to
meet the operating specifications.
• 8509x Series: +20 °C to +30 °C
• N443xA/B Series: +20 °C to +30 °C
• N469xA/B Series: +20 °C to +26 °C
For more details, see “Environmental Specifications” on page 5-3.
Handling and Storage
Handle and store the ECal modules with great care. Their continued performance and
accuracy depend upon maintaining the precise mechanical tolerances of the connectors.
When the modules and adapters ar e no t in use, replace their protecti ve end caps. F or more
informatio n , r ef er to “Handling and Storage” on page 4-19.
Chapter 2 2-9
Page 38

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
ECal modules connect to PNA or ENA network analyzers with the USB cable (supplied
with the kit). VNA analyzers require the 85097B VNA Interface Kit.
You can connect (or disconnect) ECal modules when the analyzer is on or off, but should
avoid doing so while data transfer is in progress.
TIP Modules that have completed a cal ibration may remain con n e cted to the
analyzer (with the USB cable or 85097B Interface Kit).
Connect ECal Module to PNA or ENA Analyzer
ECal modules are controlled and p owered by th e analyzer through a U SB cable . When you
connect the module to the analyzer, the analyzer automatically recognizes the type of
module, frequency range, and connector type.
CAUTION Exercise the necessary ESD precautions before connecting the ECal module
to the analyzer. See “Electrostatic Discharge” on page 4-2.
To connect ECal module to the PNA or ENA network analyzer:
1. Connect one end of the USB cable to the ECal module as shown in Figure 2-1 on
page 2-11.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to the USB port on the front or rear panel of the
analyzer (as shown in Figure 2-2 on page 2-11). Depending on available USB ports, two
or more ECal modules may be connected to the analyzer.
3. The LED (on the module) indicates WAIT until the ECal module reaches operating
temperature.
2-10 Chapter 2
Page 39

Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
Figure 2-1 USB Connection to Module
Figure 2-2 USB Connection to PNA or ENA Analyzer
Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Chapter 2 2-11
Page 40

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
Connect ECal Module to VNA Analyzer
VNA network analyzers require the 85097B Interface Kit, which supplies power and
allows data transfer between the analyzer and the ECal module.
The interface kit contains an interface unit, power supply, and cables to connect the
interface unit to the analyzer and the ECal module.
An adapter cable, supplied with Option 100, is required to connect microwave ECal
modules (N469xA/B series) to the interface uni t. This cable may al so be ordered s eparately.
For more information about the 85097B, refer to “Other ECal Accessories” on page 6-11.
CAUTION Exercise the necessary ESD precautions before connecting the ECal module
to the analyzer. See “Electrostatic Discharge” on page 4-2.
To connect ECal module to the VNA network analyzer:
1. Connect interface unit to VNA:
a. Connect one end of the DB25 to DB25 cable to the connector on the interface unit
labeled “DB25 Interface to Parallel Interface on Network Analyzer.”
b. Connect the other end of the cable to the connector labeled “PARALLEL PORT” on
the rear panel of the VNA.
CAUTION Connecting the DB25 cable to any other connector on the analyzer WILL
cause damage.
2. Connect an RF Module:
a. Connect one end of the DB25 to DB25 cable to the parallel port connector on the
ECal module. See Figure 2-3 on page 2-13.
b. Connect the other end of the cable to the connector on the interface unit labeled
“DB25 Interface to ECal M o d ul e A ” or “D B25 Interface to ECal Module B.” See
Figure 2-4 on page 2-13. Two ECal modules may be connected at the same time.
3. Connect a Microwave Module (requires adapter cable, part no. 8121-1047):
a. Connect the miniature (36-pin) connector on the adapter cable to the parallel port
connector on the ECal module. See Figure 2-3 on page 2-13.
b. Connect the DB25 connector on the adapter cable to the connector on the interfac e
unit labeled “DB25 Interface to ECal Module A” or “DB25 Interface to ECal Module
B.” See Figure 2-4 on page 2-13.
4. Connect the interface power supply to the interface unit and then connect to AC power.
NOTE The LED on the ECal module indicates W AIT until the unit reac hes operating
temperature.
2-12 Chapter 2
Page 41

Figure 2-3 Parallel Port Connection to Module
Figure 2-4 Interface Connections to VNA Analyzer
Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
Chapter 2 2-13
Page 42

Preparing to Use the ECal Module
Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module
2-14 Chapter 2
Page 43

3 Operating the ECal Module
3-1
Page 44

Operating the ECal Module
Setting Up a Calibration
Setting Up a Calibration
Use the following procedure as a starting point for calibrating the network analyzer with
an ECal module. For more detailed information about adjusting the settings of your
analyzer, refer to the appropriate user guide or online Help.
Required Procedure for All Calibrations
For all calibration types, complete the following steps:
1. Connect an ECal module to the analyzer having the appropriate frequency range and
connector type. See “Connecting and Disconnecting ECal Module” on page 2-10.
2. Allow the module to warm up for 15 minutes (20 minutes for a four-port module) or
until the module indicates READY.
3. Set up the analyzer and the device unde r test (DUT) in the measurement configurat ion.
Select the frequency, power, sweep and other stimulus settings.
4. View the response (uncorrected) and opt imize the analyzer settings as needed.
5. Remove the DUT from the measurement ports and connect the ECal module.
6. Select the desired calibration type and perform the calibration.
7. Remove the ECal module and re-connect the DUT.
CAUTION Excessive torque can damage ECal module connectors. See Table 4-1 on
page 4-18 for the required torque setting for each connector type.
3-2 Chapter 3
Page 45

Operating the ECal Module
Setting Up a Calibration
Calibration Types Available
The following table contains the calibration types and advanced settings available for all
compatible network analyzers:
Table 3-1 Calibration Types and Advanced Settings Available
Network Analyzer Series
Calibration Types
1-Port Reflection Yes Yes Yes
Full 2-Port Yes Yes Yes
Full 2-Port (with isolation)
Full 3-Port Yes Yes —
Full 4-Port Yes Yes —
Advanced Settings
Adapter Removal Yes No No
Flush (zero length) THRU Yes
Unknown THRU
User-Characterization Yes
a. 8509xC only.
b. Available in mid-2006.
c. Unknown THRU setting is not available with E8801/2/3A analyzers.
d. User-Characterization available with firmware revision A.03.50 (February 2003).
a
PNA ENA 8753/8720 Series
Yes Yes Yes
Yes
b
No
c
No No
d
Yes
Yes
No
When to Correct for Isolation
Correction for isolation is a consideration when measuring high-loss devices such as saw
filters or diplexers . When maximum dynamic range is required, correction fo r isolation can
remove the errors due to crosstalk (bet ween test ports) for transmission measurements.
When you include isolation with a two, three, or four-port calibration, the analyzer
automatically applies averaging to reduce noise in the measurement. Without averaging,
you will have noise in the measurement of the crosstalk, and could raise the noise floor
when the analyzer uses this in its error correction.
The analyzer system isolation is normally sufficient for most measurements, and
correction for it is usually unnecessary. As long as crosstalk is below the noise floor, it is
best NOT to correct for isolation using ECal. As of PNA firmware release 4.26, measuring
isolation as part of the ECal process is no longer supported.
Chapter 3 3-3
Page 46

Operating the ECal Module
Setting Up a Calibration
Calibration Methods for Non-Insertable Devices
A "non-insertable" device means that the measurement ports cannot be connected together
to establish a THRU connection during calibration for transmission. Because the module
typically forms the THRU path, you can use one of the following methods to perform a
calibration for non-insertabl e devices:
Configure ECal Module the Same as Device
The simplest way to calibrate for non- insertable devices is to configure an ECal module
with the same connector types as the DUT. RF ECal modules can be configured with mixed
connector s to m a tch th e co nnector typ e s on th e D UT. Refer to “Models and Options” on
page 1-4. You can also configure the module with different co nnector types by performing a
User-Characterization (see below).
Use Adapter Removal Calibration
Adapter removal provides an accurate way to calibrate for non-insertable devices, but
requires extra calibration steps to characterize th e adapter. The adapter type used for this
calibration must be -m- to -m- or -f- to -f- and have the same connector type as the module.
In addition, the module must have a male connector on one test port and a female
connector on the other test port (o f the same connector type).
Use Unknown Thru Calibration
Unknown Thru calibration is currently available with all PNA network analyzers except
the E8801/2/3A. It is easy to perform and can be used on any two ports when using a
multiport PNA. It causes minimal cable movement if the Thru standard has the same
footprint as the DUT. In fact, the DUT can often be the Thru standard. A 1-P ort calibr ation
is performed on the both ports . The unknown Thru is conne cted between the two po rts and
measured. Next, the user must confirm the Estimated Delay. This requires knowing the
phase response to within 1/4 wavelength. If the phase response is unknown, the Delay
value can be measured independently and entered in the dialog box.
Perform a User-Characterization
Normally, when you perform a calibration with an ECal module, the error terms for a
calibration are computed using the factory char acterization (data) stored in the module.
User-Characterization allows you change the characterization of the module in two ways:
• Change the connector configuration: allows you to add an adapter or fixture to the test
port of the module and embed the effects into the characterization of the module. The
result of the new characterizatio n extends the reference plane from one or more of the
module’s test po rts to those on the adapter (or fixture).
• Modify the state settings: allows you to s pecify the number of d ata points (1601 max.) or
other stimulus settings the module uses to perform a calibration.
When you perform a User-Characterization, the factory characterization data remains
stored in the module’s memory. At calibration, you can select the factory characterization
or any of the user-defined characterizations stored in the module . The module can store up
to five user-defined character i z at i ons (in addition to the fact o ry characteri z a tion data).
User-Charac terization is currently available with PNA and ENA network analyzers.
3-4 Chapter 3
Page 47

Operating the ECal Module
Setting Up a Calibration
NOTE To perform a User-Char acterization, a calibration kit (having the same
connector type as the new reference plane) is required .
Chapter 3 3-5
Page 48

Operating the ECal Module
Performing a Calibration
Performing a Calibration
For detailed information on performing a calibration using a VNA, ENA or PNA series
network analyzer, refer to the appropriate user guide or online Help.
• To view the ENA or PNA online Help, press the Help key on the front panel of the
network analyzer.
• To view an online VNA user guide, use the following steps:
1. Go to http://www.agilent.com.
2. Enter your VNA model number (Ex: 8753ES) in the Search box and click Search.
3. Look in the left column for the heading Refine by Type of Content, and click on
Manuals & Guides.
4. In the left column, click on User Guide.
5. In the right column, click on the title/hyperlink for the User Guide PDF you want to
view. If the User Guide you want to view isn’t listed on the Web page that is seen
initially, click on the More hyperlin k (if displayed).
CAUTION Do not perform a calibration procedure unless you have cleaned and visually
inspected all connectors and have taken the necessary ESD precautions.
3-6 Chapter 3
Page 49

Operating the ECal Module
Validating a Calibration
Validating a Calibration
Once a calibration has been performed, its performance should be checked before making
device measurements.
Why Validate a Calibration
There are several sources of error that can invalidate a calibration:
• bad cables
• dirty or worn connectors
• operator error
• measurement uncertainties from interpolation
Measure Known Standards
Measuring known devices, other than calibration standards, is a way of verifying that the
network analyzer system is operating properly. Verification kits use accurately known
standards with well-defined magnitude and phase response. These kits include precision
airlines, mismatch airlines, and precision fixed attenuato rs. Traceable measurement data
is shipped with each kit on disk and verification kits may be re-certified by Agilent. For
information about ordering verification kits, see “Contacting Agilent” on page 1-15.
Perform ECal Confidence Check
ECal Confidence Check is a simple way to check the accuracy of a calibration (performed
with mechanical standards or an ECal module). The confidence check allows you to
measure an impedance state in the ECal module, called the confidence state, and compare
it with factory measured data (of the same confidence state). ECal Confidence Check
overlays the two traces so that the differences between the stored state and the measured
state can be easily viewed.
Before performing a confidence chec k, the analyzer must be calibrated and the calibration
type should be appropriate for the parameter being checked. For exampl e, you cannot
measure the confidence state with S22 if an S11 1-port calibration is active.
NOTE ECal Confidence Check is not available with ENA-L series network
analyzers.
For detailed information on performing an ECal Confidence Check using a VNA, ENA or
PNA series network analyzer, refer to the appropriate user guide or online Help.
• To view the ENA or PNA online Help, press the Help key on the front panel of the
network analyzer.
• To view an online VNA user guide, use the following steps:
1. Go to http://www.agilent.com.
Chapter 3 3-7
Page 50

Operating the ECal Module
Validating a Calibration
2. Enter your VNA model number (Ex: 8753ES) in the Search box and click Search.
3. Look in the left column for the heading Refine by Type of Content, and click on
Manuals & Guides.
4. In the left column, click on User Guide.
5. In the right column, click on the title/hyperlink for the User Guide PDF you want to
view. If the User Guide you want to view isn’t listed on the Web page that is seen
initially, click on the More hyperlin k (if displayed).
3-8 Chapter 3
Page 51

4 Use, Maintenance, and Care of the
Devices
4-1
Page 52

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic Discharge
Protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) is essential while connecting, inspecting,
or cleaning devices attached to static-sensitive circuits (such as those found in network
analyzers and ECal modules).
Static electricity can build up on your body and can easily damage sensitive internal
circuit elements when discharged. Static discharges too small to be felt can cause
permanent da mage. Devices such a s ca l i b ra t i on co mponents and devices unde r test
(DUTs), can also carry an electrostatic charge. To prevent damage to network analyzer
components and devices:
• always wear a grounded wrist strap having a 1 MΩ resistor in series with it when
handling components and devices or when making connections to the test set.
• always use a grounded, conductive table mat while making connections.
• always wear a heel strap when working in an area with a conductive floor. If you are
uncertain about the conductivity of your floor, wear a heel strap.
• always ground yourself before you clean, inspect, or make a connection to a
static-sensitive device or te st po rt. You can, for example, grasp the grounded outer s hel l
of the test port or cable connector briefly.
• always ground the center conductor of a test cable before making a connection to the
analyzer test port or other static-sensitive device. This can be done as follows:
1. Connect a short (from your calibration kit) to one end of the cable to s hort the center
conducto r to th e ou ter conductor.
2. While wearing a grounded wrist strap, grasp the outer shell of the cable connec tor.
3. Connect the other end of the cable to the test port.
4. Remove the short from the cable.
For parts numbers for ESD protection supplies, refer to “Other ECal Accessories” on
page 6-11.
Figure 4-1 ESD Protection Using Mat, Wrist Strap, and Grounded Power Cord
4-2 Chapter 4
Page 53

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Visual Inspection
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection and, if necessary, cleaning should be done every time a connection is
made. Metal particles from the connector threads may fall into the connector when it is
disconnected.
CAUTION Devices with damaged connectors should immediately be discard ed or c learly
marked and set aside for repair. A damaged device will in turn damage any
good conne ct or to which it is a ttached. Try to determine the cause of the
damage before connecting a new, undamaged connector in the same
configuration.
In some cases, magnification is necessary to see damage on a connector. Not all defects
that are visible only under magnification will affect the electrical performance of the
connector. Use the following guidelines when evaluating the integrity of a connector.
Look for Obvious Defects and Damage First
Examine the connectors first for obvious defects and damage: badly worn plating on the
connector interface , deformed threads, or bent, broken, or misaligned ce nter conductors.
What Causes Connector Wear?
Connector wear is caused by connecting and disconnecting the devic es. The more use the
device gets, the faster it wears and degrades. The wear is greatly accelerated when
connectors are not kept clean, or are not properly connected. This is especially true with
electrically characterized devices such as ECal modules. ECal modules should have a long
life if their use is on the order of a few times per week.
The test port connectors on the network analyzer may have many connections each day,
and are therefore more subject to wear. It is recommended that an adapter be used as a
test port saver to minimize the wear on the connectors. Replace devices with worn
connectors.
Inspect the Mating Plane Surfaces
Uniform contact between the connectors at all points on their mating plane surfaces is
required for a good connection. See Figure 4-2 for an example of locations of mating plane
surfaces. Look especially for deep scratches or dents, and for dirt and metal particles on
the connector mating plane surfaces. Also look for signs of damage due to excessive or
uneven wear or misalignment.
Chapter 4 4-3
Page 54

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Inspect Female Connectors
Figure 4-2 Type-N Connector Pin Depth and Mating Surfaces
Light burnishing of the mating plane surfaces is normal, and is evident as light scratches
or shallow circular marks distributed more or less uniformly over the mating plane
surface. Other small defects and cosmetic imperfections are also normal. None of these
affect electrical or mechanical performance. If a connector shows deep scratches or dents,
particles clinging to the mating plane sur faces, or uneven wear, clean and inspect it again.
Inspect Female Connectors
When using slotless connectors like the 3.5 mm or type-N 50 Ω female con n e ctors, pay
special attention to the contact fingers on the female center conductor. These can be bent
or broken, and damage to them is not always easy to see. A connector with damaged
contact fingers will not make good electrical contact and must be repaired or replaced.
NOTE Due to the tighter mechanical specifications of precision devices , ins pection is
particularly important when you are mating nonprecision to precision
devices.
4-4 Chapter 4
Page 55

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Cleaning Connectors
Cleaning Connectors
Clean connector interfaces prolong connector life and produce more accurate and
repeatable measurements.
NOTE The following cleaning procedure can be used for most coaxial connectors. For
7 mm connectors, ref er to “Cleani ng Precis ion 7 mm Connecto rs” on page 4-7.
WARNING Always use protective eyewear when using compressed air or
nitrogen.
Cleaning Coax Connectors
1. Use compressed Air or Nitrogen
Use compressed air (or nitrogen) to loosen particles on the connector mating plane
surfaces.
You can use any source of clean, dry, low-pressure compressed air or nitrogen that has
an effective oil-vapor filter and liquid cond ensation trap placed just before the outlet
hose.
Ground the hose nozzle to prevent electrostatic discharge, and set the air pressure to
less than 414 kPa (60 psi) to control the velocity of the air stream. High-velocity
streams of compressed air can cause electro static effects when directed into a connector.
These electrostatic effects can damage the device. For additional information refer to
“Electrostatic Discharge” on page 4-2 earlier in this chapter.
WARNING Keep isopropyl alcohol away from heat, sparks, and flame. Store in a
tightly closed container . Isopropyl alcohol is extremely fl ammable. In
case of fire, use alcohol foam, dry chemical, or carbon dioxide; water
may be ineffective.
Use isopropyl alcohol with adequate ventilation and avoid contact
with eyes, skin, and clothing. It caus es skin ir ritati on, may cause eye
damage, and is harmful if swallowed or inhaled. It may be harmful if
absorbed through the skin.
W ash thorough ly after handling. I n case of spill, soak up with sand or
earth. Flush spill area with wa ter.
Dispose of isopropyl alcohol in accordance with all applicable
federal, state, and local environmental regulation.
Chapter 4 4-5
Page 56

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Cleaning Connectors
2. Clean the Connector Threads
CAUTION Use ONLY isopropyl alcohol to clean connector surfaces. Any other sol ve nt
may damage the insulators, support beads, and seals in the connector.
Never immerse the connector in solvents of any kind. The solvent can become
trapped within the assembly and cause SWR, phase, and insertion loss
problems.
Moisten (don’t soak) a lint-free swab or cleaning cloth with isopropyl alcohol to remove
any dirt or stubborn contaminants that cannot be removed with compressed air or
nitrogen. Refer to “Other ECal Accessories” on page 6-11 for cleaning swabs and other
connector cleaning supplies.
a. Apply a small amount of isopropyl alcohol to a lint-free swab.
b. Cle an th e connecto r th reads.
c. Let the alcoho l evaporate, then blow the threads dry with a gentle stream of clean,
low-pressure compressed air or nitrogen. Always completely dry a connector before
you reassemble or use it.
3. Clean the Mating Plane Surfaces
a. Apply a small amount of isopropyl alcohol to a new lint-free cleaning cloth or swab.
b. Clean the center and outer conductor mating plane surfaces. Refer to Figure 4-2 on
page 4-4. When cleaning a female connector; use short strokes to avoid snagging the
swab on the center conductor contact fingers.
c. Let the alcohol evaporate, then blow the mating plane surface dry with a gentle
stream of clean, low-pressure compres sed air or nitrogen. Always completely dry a
connector before you reassemble or use it.
4. Inspect Each Connector
Inspect the connector to make su re that no particles or residue are present.
4-6 Chapter 4
Page 57

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Cleaning Connectors
Cleaning Precision 7 mm Connectors
You do not have to remove the center conductor collet to clean a prec ision 7 mm connector.
With the Center Collet in Place
1. Dispense a small amount of isopropyl alcohol on the lint free cloth.
2. Retr act the connector sleeve th reads to expo se the connector interfa c e.
3. Gently press the contact end of the connector into the moistened cloth and rotate the
connector. The cloth scrubs away dirt and contaminants on the co nnector interface
without damaging it.
4. Blow the connector dry with a gentle stream of compressed air or nitrogen.
NOTE When not in use, keep the cloth in a plastic bag or box so that it does not
collect dust or dirt.
For Fixed Connec to rs (attached to a device that cannot be freely moved)
1. Fold a lint-free cleaning cloth several times.
2. Moisten the cloth with isopropyl alcohol.
3. Press the moistened cloth against the connector interface and rotate the cloth to clean
the connect or.
4. Blow the connector dry with a gentle stream of compressed air or nitrogen.
Cleaning a Removed Center Collet
Any time you remove the center conductor collet, clean and inspect the interior surfaces as
described in “Cleaning Connectors” on page 4-5.
Chapter 4 4-7
Page 58

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Gaging Connectors
The gages available from Agilent Technologies are intended for preventive maintenance
and troubleshooting purposes only. They are effective in detecting excessive center
conductor protrusion or recession, and conductor damage on DUTs, test accessories, and
ECal module test ports. Do not use the gages for precise pin depth measurements.
Connector Gage Accuracy
The connector gages are only capable of performing coarse measurements. They do not
provide the degree of accuracy necessary to pr ecisely measure the pin depth. This is
partially due to the repeatability uncertainties that are associated with pin-depth
measurements.
With proper technique, the gages are useful in detecting gross pin depth errors on device
connectors. To achieve maximum accuracy, random errors must be reduced by taking the
average of at least three measurements having different gage orientations on the
connector. Even the resultant average can be in error by as much as ±0.0001 inch
(±0.0025 mm) due to systematic (biasing) errors usually resulting from worn gages and
gage masters. The information in “Typical Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14 assumes new
gages and gage masters. Therefore, these systematic errors were not included in the
uncertainty analysis. As the gages endure more use, the systematic errors can become
more significant in the accuracy of the measurement.
The measurement uncertainties are primarily a function of the assembly materials and
design, and the unique interaction each device type has with the gage. Therefore, these
uncertainties can vary among the different devic es.
The observed pin depth limits add in these uncertainties to the typical factory pin depth
values to provide practical limits that can be referenced when using the gages.
When measuring pin depth, the measured value (resultant av erage of three or more
measurements) contains measurement uncertainty and is not necessarily the true value.
Always compare the measured value with the observed pin depth limits (which accou nt for
measurement uncertainties) in “Typical Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14 to ev aluate the
condition of device connectors.
4-8 Chapter 4
Page 59

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
When to Gage Connectors
Gage a connector at the following times:
• Prior to using an ECal module for the first time: record the pin depth measurement so
that it can be compared with future readi ngs . This serve s as a good troublesho oting tool
when you suspect damage may have occurred to the device.
• If either visual inspection or electrical performance suggests that the connector
interface m ay b e ou t of typical ra n g e (d u e to w ear or damag e, fo r example) .
• If a module is used by someone else, or on another system or piece of equipment.
• Initially after every 100 connections , and after that as often as experience suggests.
NOTE W hen using the 7 mm module, you must remove the 7 mm collet before
gaging the pin depth of the co nnectors. Use the collet extractio n too l pr ovide d
in your 7 mm module to remove the collet.
Recognizing Gage Types
A gage is referred to by the sex of the connector it measures. For example , a male gage
measures male connectors and therefore has a corres ponding female connector.
• See Figure 4-3 on page 4-10 for an illustration of a typical gage for 3.5 mm, 2.92mm,
2.4 mm, and 1.85 mm connectors.
• See Figure 4-4 on page 4-11 for an illustration of a typical gage for type-N connectors.
• See Figure 4-5 on page 4-12 for an illustration of a typical gage for 7 mm connectors.
NOTE A 3.5 mm gage set can measure 3.5 mm and 2.92 mm connectors.
A 2.4 mm gage set can measure 2.4 mm and 1.85 mm connectors.
Reading the Connector Gage
The gage dial is divided up into increments of 0.0001 inch (0.002 5 mm) and major divisions
of 0.001 inch (0.0025 mm). For type-N gages, see F igure 4-4 on page 4-11. For each
revolution of the large dial, the smaller dial indicates a change of 0.01 inch (0.025 mm).
Use the small dial as the indicator of mult iples of 0.01 inc h (0.0025 mm). In most connect or
measuring applications, this value will be zero.
When making a measurement, the gage di al indicator wil l travel in o ne of two dir ections . If
the center conductor is recessed fro m the zero reference plane, the indicator will move
counterclockwise to determine the amount of recession, which is read as a negative value.
If center conductor protrudes, the indicator will move clockwise to measure the amount of
protrusion, which is read as a positive value. Refer to “Typical Pin Depth Values” on
page 5-14 for definitions of protrusion and recession.
Chapter 4 4-9
Page 60

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Figure 4-3 Typical Gage: 3.5 mm, 2.92 mm, 2.4 mm and 1.85 mm Connectors
4-10 Chapter 4
Page 61

Figure 4-4 Typical Gage: Type-N Connectors
Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Chapter 4 4-11
Page 62

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Figure 4-5 Typical Gage: 7 mm Connectors
4-12 Chapter 4
Page 63

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Gaging Procedures
Zeroing Connector Gages
For type-N gages, the paired gage master is labeled with an offset value to compensate for
its inaccuracy with its gage. This label appears on the bottom of all type -N gage masters
that have been paired with gages. When se tting a type-N gage with its master, always set
the gage to the master offset value shown on the label, not to the zero, unless that is the
offset value indicated.
The design of the gages used to measure 3.5 mm, 2.92 mm, 2.4 mm, 1.85 and 7 mm
connectors are different than the type-N gage desi gn. The primary difference is that the
type-N gages require an offset to compensate for inaccuracies in the gage masters.
1. Select the proper gage for your connector. Always use gages that are intended for pin
depth measurements. Refer to Chapter 6 , “Replaceable Parts,” Locate the gage model
number listed with the associated connector ty pe.
2. Inspect and clean the gage, gage master, and device to be gaged. Refer to “Visual
Inspection” on page 4-3 and “Cleaning Connectors” on page 4-5.
CAUTION Before continuing, make s ure you are famili ar with the pro per connection and
torque techniques for your connector type. Refer to “Making Connections” on
page 4-15.
3. Wh il e holding th e g a g e by th e barrel, attach the gag e to the gage ma ster. Connec t th e
gage master finger tight. Do not overtighten.
4. Use th e to rque wrench recommend ed for use with y o ur connecto r type to tighten the
connecting nut to the gage master. Refer to Table 4-1 on page 4-18.
5. Type-N: Loosen the dial lock screw on the gage and rotate the gage dial so that the
pointer corresponds to the correction value noted on the gage master. Do not adjust the
gage dial to zero, unless the correction value on the gage master is zero.
3.5mm, 2.4 mm, and 7 mm: The gage pointer should line up exact ly wi th the zero mark
on the gage. If not, adjust the zer o set knob or rotate the gage di al until the gage pointer
lines up exactly with zero.
6. Tighten the dial lock screw and remove the gage master.
7. Attach and torque the gage master once again to verify that the setting is repeatable.
Remove the gage master.
Chapter 4 4-13
Page 64

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Gaging Connectors
Gaging Technique
CAUTION Remove the collet when gaging 7 mm connectors.
1. Connect and torque the device being measured to the gage.
2. Gently tap the barrel of the gage with your finger to settle the gage reading.
3. Type-N and 7mm: Read the gage indicator dial. If the needle has moved clockwise, the
center conductor is protruding by an amount indicated by the black numbers. If the
needle has moved counterclockwise, the center conductor is recessed by an amount
indicated by the red numbers.
3.5 mm and 2.4 mm: Read the gage indicator dial. Read only the black ± signs; not the
red ± signs.
4. For maximum accuracy, measure the connector a minimum of three times and take an
average of the readings. After each measurement, rotate the gage a quarter-turn to
reduce measurement variations that result from the gage or the connector face not
being exactly perpendicular to the center axis.
5. Compare the average reading with the observed pin dept h limits in the tables located in
“Typical Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14 for each type of connector.
4-14 Chapter 4
Page 65

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Making Connections
Making Connections
Good connections are essential for accurate calibrations and measurements and require a
skilled operator. The most common caus e of me asurement error is poor connections.
3.5 mm, 2.92 mm, 2.4 mm, 1.85 m m, Type-N, 7-16, and Type-F Devices
1. Handle the devices at a static-safe work station, only. See “Electrostatic Discharge” on
page 4-2.
2. Carefully align the connectors. The male connector center pin must s lip concentrically
into the contact finger of the female connector.
CAUTION Do not turn the d e v i ce b od y. Only turn the connecto r n u t. Damage to the
center conductor can oc cur if the dev i ce bo dy is twiste d.
3. Push the connectors straight together and tighten the connec tor nut finger tight. Do not
twist or screw the connector together. As the center conductors mate, there is usually a
slight resistance
4. The preliminary connection is tight enough when the mating plane surfaces make
uniform, light contact. Do not overtighten this connection.
A connection in which the outer conductors make gentle contact at all points on both
mating surfaces is sufficient. Very light finger pressure is enough to accomplish this.
5. Make sure the connectors are properly supported. Relieve any side pressure on the
connection from long or heavy devices or cables.
6. Torque the connecti on according to the procedures de scribed in “Final Connect ion Using
a Torque Wrench” on page 4-16.
7 mm Devices
1. Fully extend the connector sleeve on one of the connectors. Spin its knurled connector
nut to make sure the threads are fully extended. Fully retract the sleeve on the other
connector. The extended sleeve creates a cylinder into which the other connector fits.
If one of the connectors is fixed (such as on a test port) , fully extend that connector
sleeve and fully retract the sleeve on the moveable connector.
2. Carefully align the connectors. As you make the actual connection, be sure the
connectors align perfectly.
3. Push the connectors straight together. Do not twist or screw the co n n ectors toget h er.
4. Engage the connector nut (of the connector with the retracted sleeve) over the threads
of the other connector (the connector with the extended sleeve). Turn onl y the connector
nut. Let the connector nut pull the two connectors st raight together.
Chapter 4 4-15
Page 66

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Making Connections
5. Do not overtighten this connection. A connection in which the outer conductors make
gentle contact at all points on both mating surfaces is suff icient. Very light finger
pressure is enough to accomplish this .
6. Make sure the connectors are properly supported. Relieve any side pressure on the
connection from long or heavy devices or cables.
7. Torque the connection according to the procedures described in the foll owing section.
Final Connection Using a Torque Wrench
Using a torque wrench guarantees the connection is not too tight, preve nting possible
connector damage. It also guarantees that al l connections are equally tight.
Use the recom m e n ded torque w r en ch to m a ke a fi n a l co nnection. Table 4-1 on page 4-18
provides information on the to rque wrench re commended f or use with eac h connector type.
1. Turn the connector nut. This may be possible to do by hand if one of the connectors is
fixed (as on a test port). However, it is recommended that you use an open-end wrench
to keep the body of the device from turning.
2. Position both wrenc hes within 90 d egrees of each othe r befor e app lying forc e . Wr enc hes
opposing each other (greater than 90 degrees apart) will cause a lifting action that can
misalign and stress the connections of the device involved . This is esp ecially true when
several devices are connected together . Refer to Figure 4-6.
Figure 4-6 Wrench Positions
4-16 Chapter 4
Page 67

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Making Connections
3. Hold the torque wrench lightly, at the end of the handle only (beyond the groove). See
Figure 4 -7.
Figure 4-7 Using the Torq ue Wrench
4. Carefully align the connectors. As you make the actual connection, be sure the
connectors align perfectly.
5. Push the connectors straight together. Do not twist or screw the connectors together.
Engage the connector nut over the threads of the other connector. Turn only the
connector nut. Let the connector nut pull the two connectors straight together.
Do not over tighten this connection. A connection in which the outer conductors make
gentle contact at all points on both mating surfaces is suff icient. Very light finger
pressure is enough to accomplish this .
6. Make sure the connectors are properly supported. Relieve any side pressure on the
connection from long or heavy devices or cables.
7. Apply force downward to the wrench handle. This applies torque to the connection
through the wrench.
Do not hold the wrench so tightly that you push the handle straight down along its
length rather than pivoting it, otherwise you apply an unknown amount of torque.
CAUTION You don’t have to fully break the handle of the torque wrench to reach the
specified torque; doing so can cause the handle to kick back and loos en the
connection. Any give at all in the handle is sufficient torque.
8. Tighten the connection just to the torque wrench break point. The wre nch handle gives
way at its internal pivot point. Do not tighten the connection further. See Figure 4-7.
Chapter 4 4-17
Page 68

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Making Connections
Table 4-1 ECal Module Torque Wrench Information
Connector Type
3.5 mm, 2.92 mm,
2.4 mm, 1.85 mm
(test port)
3.5 mm, 2.92 mm,
2.4 mm, 1.85 mm
(adapters)
Type-N 50, 75 Ω 8710-1766 3/4 in 135 N-cm (12 in-lb) ±13.5 N-cm (±1.2 in-lb)
7 mm 8710-1766 3/4 in 135 N-cm (12 in-lb) ±13.5 N-cm (±1.2 in-lb)
7-16 8710-2174 1 1/16 in 226 N-cm (20 in-lb) ±22.6 N-cm (±2 in-lb)
a. Many older Agilent calibration module manuals list different torque tolerances for the
various torque wrenches. The correct torque tolerance for Agilent torque wrenches is
±10% of the torque setting as listed in this table.
Torque Wrench
Part Number
8710-1764 20 mm 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) ±9 N-cm (±0.8 in-lb)
8710-1765 5/16 in 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) ±9 N-cm (±0.8 in-lb)
Wrench
Opening
Torque Setting
Torque Tolerance
a
Separating Connections
To avoid later al (bending) force on the con nector mating pla ne surfaces , alw ays s upport the
devices and connections.
CAUTION Do not turn the device body. Only turn the connector nut. Damage to the
center conductor can oc cur if the dev i ce bo dy is twiste d.
1. Use an open-end wrench or spanner wrench to prevent the device body from turning.
2. Use another open-end wrench to loosen the connector nut.
3. Complete the separation by hand, turning only the connector nut.
4. Pull the connectors straight apart without twisting, rocking, or bending.
4-18 Chapter 4
Page 69

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Handling and Storage
Handling and Storage
• Use the plastic end caps on connectors when not in use.
• Never store modules and adapt ers loose in a box, in a desk, o r in a benc h dra wer. This is
the most common cause of connector damage during storage.
• Keep connectors clean.
• Do not touch mating plane surfaces. Natural skin oils and microscopic particles of dirt
are easily transferred to a connector inte rface and are very difficult to remove.
• Do not set connectors contact-end down on a hard surface. The plating and the mating
plane surfaces can be damaged if the interface comes in contact with any hard surface.
Chapter 4 4-19
Page 70

Use, Maintenance, and Care of the Devices
Handling and Storage
4-20 Chapter 4
Page 71

5 Specifications and Characteristics
5-1
Page 72

Specifications and Characteristics
Specifications: Terminology and Definitions
Specifications: Terminology and Definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to Agilent’s 8509x, N4431B, and N469xA/B
series of ECal modules. Th e definitions are specific to these modules and are not
necessarily valid definitions for oth er Agi l ent Technologies products.
Table 5-1 Specifications and Characteristics Terminology
Terms Definitions
Operating Temperature Range The temperature range over which the ECal modules
maintain conformance to their specifications.
Error-Corrected Temperature
Range
Measurement Calibration This calibration determines the corrections necessary for
Connector Pin Depth Values Pin depth is a relati ve measurement value between t he
Electrical Specifications Warranted performance. Specifications include guard bands
Characteristic Performance A performance parameter that the product is expected to
The allowable network analyzer ambient temperature drift
during measurement calibration and during measurements
when network analyzer correction is turned on. It is also the
range over which the network analyzer maintains its
specified performance while correction is turned on. If this
temperature range is exceeded, the error-corrected
performance of the network analyzer is degraded.
accuracy-enhanced (correction on) measurements.
center conductor and outer conductor mating surfaces. All
references to pin depth in thi s manual treat positive (+)
values as protrusions of the center conductor, and negative
(–) values as recessions of the center conductor. See “Typical
Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14.
to account for the expected statistical distribution,
measurement uncertainties, and changes in performance
due to environmental conditions. Included with Option UK6.
meet before it leaves the factory, but is not verified in the
field and is not covered by the product warranty. A
characteristic includes the same guard bands as a
specification.
Typical Corrected Performance Expected performance of an average unit which does not
include guard bands. It is not covered by the product
warranty.
5-2 Chapter 5
Page 73

Environmental Specifications
Table 5-2 Environmental Specification s for all ECal Modules
Specifications Limits
Temperature
Operating (8509xC series)
Operating (N443xA/B series)
Operating (N469xA/B series)
Storage
Error-corrected range
Altitude
Operation
Storage
a
+20 °C to +30 °C
+20 °C to +30 °C
+20 °C to +26 °C
–40 °C to +70 °C
±1 °C of measurement calibration temperature
< 4,500 meters (15,000 feet)
< 4,500 meters (15,000 feet)
Specifications and Characteristics
Environmental Specifications
Relative Humidity
Operation
Storage
EMI
Conducted Immunity
Radiated Immunity
Radiated Emissions
a. The 85097B VNA interface unit is not warranted for use above 3,000 meters (10,000 feet).
Always Non-Condensing
Up to 80% (at 30 °C maximum dry bulb)
Up to 95% (at 40 °C maximum dry bulb)
IEC 61000-4-6
IEC 61000-4-3
CISPR11
Operating Temperature and Accuracy Enhancement
Because the dimensions of critical components may vary over temperature, certain
electrical characteristics ma y change as well. Thus, the operating temperature is a critical
factor in its performance, and must be stable befor e use. In additi on, excessive air flow can
prevent the ECal module from warming up properly.
Measurement calibration, performanc e verificatio n, and actual device measurements must
be made within ±1 °C of the error-corrected operating temperature range specification of
the network analyzer. If the ambient operating temperature drift of the network analyzer
exceeds the allowable error-corrected temperature range, a new measurement calibration
must be performed to ensure optimum accuracy.
NOTE Avoid prolonged handling of the module, connectors, and cables. Your fingers
are a heat source that can increase the temperature of these devices.
Barometric Pressure and Relative Humidity
Barometric pressure and relative humidity also affec t module performance. The dielectric
constant of the air between the inner and outer conductors of the module changes as the
air pressure and humidity change.
Chapter 5 5-3
Page 74

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
Characteristic Performance
Characteristic performance for RF and microwave ECal modules are provided in the
following tables, which des cribe non-warranted performance that most units exhibit.
8509x Series
Characteristic Performance for 85091C (7 mm)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 1 GHz 1 to 3 GHz 3 to 6 GHz 6 to 9 GHz
Directivity (dB) 52.0 56.0 55.0 45.0
Source Match (dB) 45.0 44.0 41.0 34.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.04 0.04 0.07 0.1
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 47.0 47.0 46.0 39.0
(±dB) 0.06 0.06 0.13 0.23
Characteristic Performance for 85092C (Type-N 50Ω)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 1 GHz 1 to 3 GHz 3 to 6 GHz 6 to 9 GHz
Directivity (dB) 52.0 54.0 52.0 47.0
Source Match (dB) 45.0 44.0 41.0 36.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.07
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 47.0 47.0 44.0 39.0
(±dB) 0.04 0.04 0.07 0.14
Characteristic Performance for 85093C (3.5 mm)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 1 GHz 1 to 3 GHz 3 to 6 GHz 6 to 9 GHz
Directivity (dB) 52.0 52.0 50.5 47.0
Source Match (dB) 44.0 44.0 39.0 34.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.03 0.05 0.07
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 47.0 47.0 44.0 40.0
(±dB) 0.04 0.05 0.07 0.12
5-4 Chapter 5
Page 75

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
Characteristic Performance for 85096C (Type-N 75Ω)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 300 MHz 300 MHz to 1.3 GHz 1.3 to 3 GHz
Directivity (dB) 50.0 48.0 43.0
Source Match (dB) 48.0 45.0 38.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.06 0.1
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 43.0 41.0 39.0
(±dB) 0.08 0.09 0.16
Characteristic Performance for 85098C (7-16)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 1 GHz 1 to 3 GHz 3 to 6 GHz 6 to 7.5 GHz
Directivity (dB) 47.0 50.0 46.0 45.0
Source Match (dB) 43.0 43.0 38.0 37.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.03 0.05 0.06
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 42.0 43.0 41.0 38.0
(±dB) 0.05 0.06 0.08 0.10
Characteristic Performancea for 85099C (Type-F)
Parameter Frequency Range
300 kHz to 300 MHz 300 MHz to 1.3 GHz 1.3 to 3 GHz
Directivity (dB) 50.0 48.0 43.0
Source Match (dB) 48.0 45.0 38.0
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.07 0.15
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match (dB) 43.0 41.0 39.0
(±dB) 0.08 0.10 0.17
a. When mated with male connectors with a 0.77 mm (.030 in) to 0.86 (0.34) pin diameter
Chapter 5 5-5
Page 76

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
N4431B (3.5 mm)
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4431B Option 010
(3.5 mm female connectors on all ports). The data describes performance when measuring
“thru path” A-B , C-D, A-D and B-C.
Characteristic Performance for N4431B Option 010
Parameter
300 kHz
to 1 GHz
Directivity (dB) 57 55 52 50 47
Source Match (dB) 50 47 45 44 43
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.05
Transmission Tracking (±dB) 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.14 0.2
Load Match (dB) 47 46 45 44 42
1 to
3 GHz
Frequency Range
3 to
6 GHz
6 to
8 GHz
8 to
9 GHz
9 to
13.5 GHz
40
32
0.1
0.33
28
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4431B Option 010
(3.5 mm female connectors on all ports). The data describes performance when measuring
“thru path” A-C and B-D.
Characteristic Performance for N4431B Option 010
Parameter
300 kHz
to 1 GHz
Directivity (dB) 57 55 52 50 47
1 to
3 GHz
Frequency Range
3 to
6 GHz
6 to
8 GHz
8 to
9 GHz
9 to
13.5 GHz
40
Source Match (dB) 50 47 45 44 43
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.05
Transmission Tracking (±dB) 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.14
Load Match (dB) 47 46 45 45 43
32
0.1
0.3
29
5-6 Chapter 5
Page 77

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
N4431B (Type-N 50 Ω)
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4431B Option 020
(type-N female connectors on all ports). The data describes performance when measuring
“thru path” A-B , C-D, A-D and B-C.
Characteristic Performance for N4431B Option 020
Parameter
300 kHz
to 1 GHz
Directivity (dB) 55 52 47 44 42
Source Match (dB) 47 43 42 40 39
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06
Transmission Tracking (±dB) 0.07 0.1 0.14 0.2 0.22
Load Match (dB) 47 45 40 38 35
1 to
3 GHz
Frequency Range
3 to
6 GHz
6 to
8 GHz
8 to
9 GHz
9 to
13.5 GHz
40
31
0.11
0.35
26
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4431B Option 020
(type-N female connectors on all ports). The data describes performance when measuring
“thru path” A-C and B-D.
Characteristic Performance for N4431B Option 020
Parameter
300 kHz
to 1 GHz
Directivity (dB) 55 52 47 44 42
1 to
3 GHz
Frequency Range
3 to
6 GHz
6 to
8 GHz
8 to
9 GHz
9 to
13.5 GHz
40
Source Match (dB) 47 43 42 40 39
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06
Transmission Tracking (±dB) 0.07 0.09 0.13 0.15 0.16
Load Match (dB) 47 45 40 38 36
31
0.11
0.32
28
Chapter 5 5-7
Page 78

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
N4432A (Type-N 50 Ω)
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4432A Option 020
(type-N female connectors on all ports).
Characteristic Performance for N4432A Option 020
Parameter
300 kHz
to
10 MHz
Directivity (dB) 45 52 47 41 42
Source Match (dB) 35 41 37 34 34
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.1 0.06 0.1 0.15 0.14
a
Transmission Tracking (±dB)
Load Match (dB)
a
0.082 0.046 0.062 0.089 0.084
39 45 40 36 37
10 MHz
to
5 GHz
Frequency Range
5
to
9 GHz
9
to
13.5 GHz
13.5
to
18 GHz
a. Values based on using the PNA Network Analyzer N5230A Option 240 or 245.
N4433A (3.5 mm)
The characteristic performance in the following table applies to N4433A Option 010
(3.5 mm female connectors on all ports).
Characteristic Performance for N4433A Option 010
Parameter
Frequency Range
300 kHz
to
10 MHz
Directivity (dB) 45 52 47 45 45
Source Match (dB) 36 42 39 37 31
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.1 0.06 0.09 0.10 0.18
a
Transmission Tracking (±dB)
Load Match (dB)
a
0.078 0.045
39 45 41 39 35
10 MHz
to
5 GHz
5
to
9 GHz
0.057
9
to
13.5 GHz
0.069 0.160
13.5
to
20 GHz
a. Values based on using the PNA Network Analyzer N5230A Option 240 or 245.
5-8 Chapter 5
Page 79
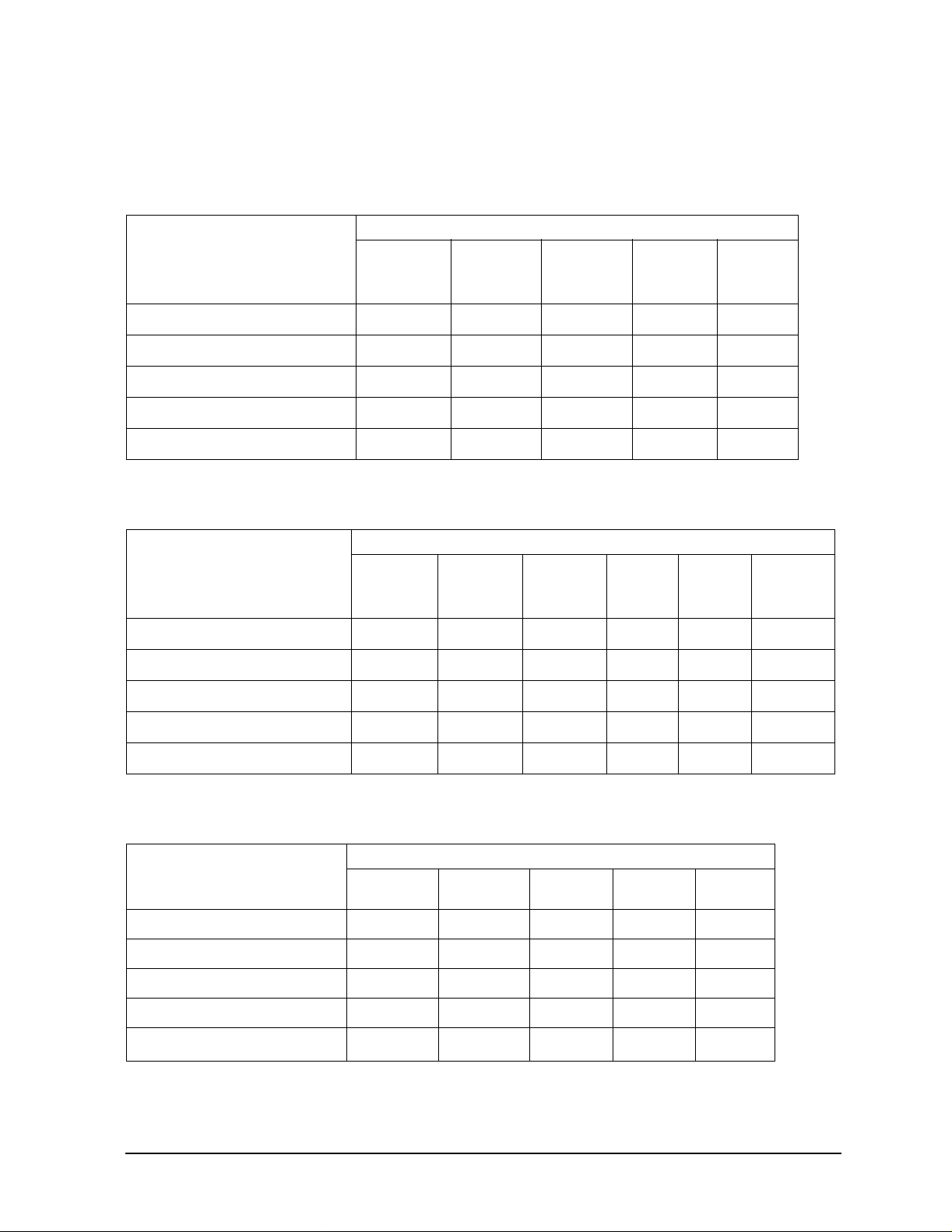
N469xA/B Series
Characteristic Performance for N4690B (Type-N 50 Ω)
Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
Parameter
Directivity (dB)
Source Match (dB)
Reflection Tracking (±dB)
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match w/ ECal Thru (dB)
(±dB)
300 kHz
to 10
MHz
40
35
0.07
0.12
29
Frequency Range
10 to
500 MHz
45 48 46 42
40 43 40 35
0.05 0.03 0.03 0.05
0.08 0.07 0.07 0.12
35 42 41 38
Characteristic Performance for N4691B (3.5 mm)
Parameter
Directivity (dB)
Source Match (dB)
300 kHz
to 10
MHz
41
36
10 to
500
MHz
46 56 54 48 44
41 47 45 44 40
Frequency Range
500 MHz
to 2 GHz
500 MHz
to 2 GHz
2 to
10 GHz
2 to
10 GHz
10 to
20 GHz
10 to
18 GHz
20 to
26.5 GHz
Reflection Tracking (±dB)
Transmission Trac kin g (±dB)
Load Match w/ ECal Thru (dB)
0.06
0.11
31
0.05 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05
0.07 0.05 0.07 0.1 0.12
37 45 49 45 40
Characteristic Performance for N4692A (2.92 mm)
Parameter
10 to
45 MHz
Directivity (dB) 35 45 43 39 38
Source Match (dB) 30 36 35 30 29
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.1 0.08 0.08 0.1 0.1
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match
(dB)
(±dB) 0.1 0.14 0.14 0.2 0.25
27 36 37 33 33
Frequency Range
45 MHz
to 2 GHz
2 to
20 GHz
20 to
30 GHz
30 to
40 GHz
Chapter 5 5-9
Page 80

Specifications and Characteristics
Characteristic Performance
Characteristic Performance for N4693A (2.4 mm)
Parameter Frequency Range
10 to
45 MHz
Directivity (dB) 32 55 49 45 43 41
Source Match (dB) 25 46 42 37 35 30
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.08
Transmission Trac kin g (±dB) 0.10 0.06 0.08 0.11 0.13 0.17
Load Match
(dB)
24 45 42 40 38 36
45 MHz
to 2 GHz
2 to
10 GHz
10 to
20 GHz
20 to
40 GHz
40 to
50 GHz
Characteristic Performance for N4694A (1.85 mm)
Parameter Frequency Range
10 to
45 MHz
Directivity (dB) 33 50 50 46 44 42 41 38
Source Match (dB) 25 38 39 35 34 33 30 27
Reflection Tracking (±dB) 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09
Transmission Trac kin g
(±dB) 0.15 0.07 0.1 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.19 0.25
45 MHz
to 2 GHz
2 to
20 GHz
20 to
30 GHz
30 to
40 GHz
40 to
50 GHz
50 to
60 GHz
60 to
67 GHz
Load Match
(dB)
25 41 44 42 40 38 36 32
Characteristic Performance for N4696B (7 mm)
Parameter Frequency Range
Directivity (dB)
Source Match (dB)
Reflection Tracking (±dB)
Transmission Trac kin g
Load Match
w/ ECal Thru (dB)
(±dB)
300 kHz to
10 MHz
40
35
0.07
0.11
30
10 to
500 MHz
46 45 50 42
40 40 42 36
0.05 0.03 0.03 0.05
0.07 0.04 0.07 0.1
36 40 45 39
500 MHz
to 2 GHz
2 to
10 GHz
10 to
18 GHz
5-10 Chapter 5
Page 81

Specifications and Characteristics
Mechanical Characteristics
Mechanical Characteristics
Mechanical characteristics, such as center conductor protrusion and pin depth, are not
warranted performance specifications. They are, however, important supplemental
characteristics related to the electrical performance of devices. Agilent Technologies
verifies the mechanical characteristics of the devices with special gaging processes and
electrical testing. These processes ensure that the device connectors do not exhibit any
excess center conductor protrusion or improper pin depth when the module leaves the
factory.
“Gaging Connectors” on page 4-8 explains how to use pin-depth gages. Refer to “Typical
Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14 for typical and observed pin depth limits.
Pin Depth
Pin depth is the distance the center conductor mat ing plane differs from being flush with
the outer connector mating plane . The pin dept h of a conn ecto r can be in one of two st ates:
protrusion or recession. The pin depth for a 3.5 mm connector is shown in Figure 5-1,
although the description also applies to 2.92 mm, 2. 4 mm, or 1.85 mm connecto rs. Typical
pin depths for ECal connectors are listed in “Typical Pin Depth Values” on page 5-14.
Protrusion occurs when the center conduct or extends beyond the out er con ductor mating
plane. It reads as a positive value on the connector gage.
Recession occurs when the center conductor is se t back from the outer conductor mating
plane. It reads as a negative value on the gage.
Figure 5-1 Pin Depth for a 3.5 mm Connectors
Chapter 5 5-11
Page 82

Specifications and Characteristics
Mechanical Characteristics
Type-N Characteristics
With type-N and 7-16 connectors, the shoulder position of the male contact pin (not the
position of the tip) defines the position of the center conductor. The male contact pin slides
into the female contact fingers; the inside surfaces of the tip of the female contact fingers
on the sides of the male contact pin provide electrical contact.
Type-N connectors differ from most connector types in that the outer conductor mating
plane is offset from the mating plane of the center conductor (see Figure 5-2). The outer
conductor in the male connector extends in front of the shoulder of the male contact pin.
When you make a connection, this outer conductor fits into a recess in the female outer
conductor behind the plane defined by the tip of the female contact fingers.
Figure 5-2 Pin Depth for Type-N Connectors
Critical Type-N Mechanical Characteristics
CAUTION Never use a type-N connector if the possibility of interference between the
shoulder of the male contact pin and the tip of the female contact fingers
exists.
Irreparable damage will occur if a male 50 Ω type-N connector is mated to a
female 75 Ω type-N connector. If you use both 75 Ω and 50 Ω type-N
connectors, mark the 75 Ω connectors so that they are never accidentally
mated with 50 Ω connectors. The diameter of the center conductor, male
contact pin, and female contact hole are smaller on 75 Ω connectors.
• Minimum protrusion of the female center conductor in front of the outer conductor
mating plane is 5.182 mm or 0.204 inches.
• Maximum protrusion of the female center conductor in front of the outer conductor
mating plane is 5.258 mm or 0.207 inches.
• Minimum recession of the shoulder of the male contact pin behind the outer conductor
mating plane is 5.258 mm or 0.207 inches.
5-12 Chapter 5
Page 83

Specifications and Characteristics
Mechanical Characteristics
• Maximum recession of the shoulder of the male contact pin behind the outer conductor
mating plane is 5.334 mm or 0.210 inches.
In the Agilent precision specification for type-N connec tors, the minimum allowable
recession for the male contact pin shoulder is 0.001 inches less than in the MIL-C-39012,
Class II specification. Agilent T echnologies type-N pin depth gages set “zero” on the gage to
be equal to a nominal 5.258 mm (0.207 inches) offset.
As type-N connectors wear, the protrusion of the female contact-fingers generally
increases. This is due to the wear of the outer conductor mating plane inside the female
connector. It is necessary to check th i s periodica ll y a s it decreases th e to tal center
conductor contact separation.
Chapter 5 5-13
Page 84

Specifications and Characteristics
Typical Pin Depth Values
Typical Pin Depth Values
The pin depth value of each device is not specified, but is an important mechanical
parameter. The electrical performance of the device depends, to some extent, on its pin
depth. The electrical specifications for each module takes into account the effect of pin
depth on the device’s performance. The following tables list the typical pin depths and
measurement uncertainties, and provides observed pin depth limits for the devices. If the
pin depth of a device does not measure within the observed pin depth limits, it may be an
indication that the device fails to meet electrical specification. Refer to Figure 5-1 and
Figure 5 -2 for a visual representation of prope r pin depth (slightly recessed).
NOTE Agilent Technologies does not suppl y pin depth gages for 7-16 connecto rs. The
7-16 module adapter pin dept h is set at 0 to −38.1 micrometers recessed from
the nominal 1.77 mm offset between inner conductor and outer conductor
mating planes.
Table 5-3 Type-N 50 Ω Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Typical Pin Depth
Device
Type-N 50 Ω ECal Mod u le
(85092C, N4431B Opt. 020)
Type-N 50 Ω ECal Mod u le
(N4690B)
Type-N 50 Ω Adapt er
a. Measured fr om a 5.258 mm ( 0.207 inches) nominal offset.
b. Approxi mate ly +2 sig ma to –2 sigma of gage unc ert ain t y base d on studie s per fo rmed at the fac to ry
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–25.4 to –50.8
(–10.0 to –20.0)
–5.1 to –15.2
(–2.0 to –6.0)
0 to –12.7
(0 to –5.0)
a
Measurement
Uncertainty
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
+3.8 to –3.8
(+1.5 to –1.5)
+3.8 to –3.8
(+1.5 to –1.5)
+3.8 to –3.8
(+1.5 to –1.5)
b
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
–21.6 to –54.6
(–8.5 to –21.5)
–1.3 to –19.0
(–0.5 to –7.5)
+3.8 to –16.5
(+1.5 to –6.5)
5-14 Chapter 5
Page 85

Table 5-4 3.5 mm Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Specifications and Characteristics
Typical Pin Depth Values
Device
3.5 mm ECal Module
(85093C, N4431B Opt. 010)
3.5 mm ECal Module
(N4691B)
3.5 mm Adapter
Typical Pin Depth
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–25.4 to –50.8
(–10.0 to –20.0)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
–2.5 to –13.0
(–1.0 to –5.0)
Measurement
Uncertainty
a
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–24.1 to –52.1
(–9.5 to –20.5)
–1.2 to –16.5
(–0.5 to –6.5)
–1.2 to –14.3
(–0.5 to –5.5)
a. Approximately +2 sigma to –2 sigma of gage uncertai nty based on studies per formed at the factory
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
Table 5-5 7 mm Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Device
7 mm ECal Module
(85091C)
Typical Pin Depth
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–25.4 to –50.8
(–10.0 to –20.0)
Measurement
Uncertainty
a
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
–24.1 to –52.1
(–9.5 to –20.5)
7 mm ECal Module
(N4696B)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
+0.6 to –0.6
(+0.25 to –0.25)
–1.9 to –15.9
(–.75 to –6.25)
a. Approximately +2 sigma to –2 sigma of gage uncertai nty based on studies per formed at the factory
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
Table 5-6 2.92 mm Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Device
2.92 mm ECal Module
2.92 mm Adapter
Typical Pin Depth
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
Measurement
Uncertainty
a
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
+1.3 to –1.3
(+0.5 to –0.5)
a. Approximately +2 sigma to –2 sigma of gage uncertai nty based on studies per formed at the factory
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
–1.2 to –16.5
(–0.5 to –6.5)
–1.2 to –16.5
(–0.5 to –6.5)
Chapter 5 5-15
Page 86

Specifications and Characteristics
Typical Pin Depth Values
Table 5-7 2.4 mm Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Device
2.4 mm ECal Module
2.4 mm Adapter
Typical Pin Depth
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
–2.5 to –35.5
(–1.0 to –14.0)
Measurement
Uncertainty
a
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
+0.6 to –0.6
(+0.25 to –0.25)
+0.6 to –0.6
(+0.25 to –0.25)
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–1.9 to –15.9
(–0.75 to –6.25)
–1.9 to –36.6
(–0.75 to –6.25)
a. Approximately +2 sigma to –2 sigma of gage uncertai nty based on studies per formed at the factory
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
Table 5-8 1.85 mm Connector Pin Depth Characteristics
Device
1.85 mm ECal Module
1.85 mm Adapter
Typical Pin Depth
in Micrometers
–4
(10
inches)
–2.5 to –15.2
(–1.0 to –6.0)
–2.5 to –25.5
(–1.0 to –9.8)
Measurement
Uncertainty
a
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
+0.6 to –0.6
(+0.25 to –0.25)
+0.6 to –0.6
(+0.25 to –0.25)
Observed Pin Depth
Limits
in Micrometers
–4
inches)
(10
–1.9 to –15.9
(–0.75 to –6.25)
–1.9 to –25.6
(–0.75 to –5.25)
a. Approximately +2 sigma to –2 sigma of gage uncertai nty based on studies per formed at the factory
using analog gages according to recommended procedures.
5-16 Chapter 5
Page 87

Supplemental Mechanical Characteristics
Supplemental Mechanical Characteristics
Table 5-9 8509x Series Mechanical Characteristics
Characteristic Limits
Net weight with case
Standard 2.7 kilograms (5.9 lbs)
Shipping weight
Standard 4.3 kilograms (9.5 lbs)
Shipping dimensions
Length
Width
Height
55.2 cm (21.75 inches)
36.8 cm (14.50 inches)
27.3 cm (10.75 inches)
Specifications and Characteristics
Table 5-10 N4431B Series Mechanical Characteristics
Characteristic Limits
Net weight with case
Standard 2.9 kilograms (6.3 lbs)
Shipping weight
Standard 4.5 kilograms (9.9 lbs)
Shipping dimensions
Length
Width
Height
55.2 cm (21.75 inches)
36.8 cm (14.50 inches)
27.3 cm (10.75 inches)
Table 5-11 N469xA/B Series Mechanical Characteristics
Characteristic Limits
Net weight with case
Standard 2.7 kilograms (5.9 lbs)
Shipping weight
Standard 4.3 kilograms (9.5 lbs)
Shipping dimensions
Length
Width
Height
Chapter 5 5-17
55.2 cm (21.75 inches)
36.8 cm (14.50 inches)
27.3 cm (10.75 inches)
Page 88

Specifications and Characteristics
Measurement Uncertainty Calculator
Measurement Uncertainty Calculator
This section provides information about d etermining the uncert ainty of the measurement s
on your network analyzer.
Download the Vector Network Analyzer Uncertainty Calculator
You can download a program from Agilent that provides the measurement uncertainty
associated with your vector network analyzer measurement and ECal module . Go to
http://www.agilent.com/find/na_calculator and follow the instructions on the Web
site to downlo a d th e pr o g ra m.
The program uses your Agilent network analyzer model number, your ECal module model
number, and electrical limits to calculate specific uncertainty charts for your network
analyzer. The program is Microsoft
spreadsheet to calculate, graph, and display uncertainty curves.
1
Windows2 based and uses a Microsoft Excel
1. Microsoft is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
2. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
5-18 Chapter 5
Page 89

6 Replaceable Parts
6-1
Page 90

Replaceable Parts
Description of This Chapter
Description of This Chapter
The following tables contain the replaceable part numbers for ECal options and
accessories. Refer to “Inspecting ECal Module Kit” on page 2-2 for the contents of each kit .
To order a part, note the description, Agilent part number, and the quantity desired.
Telephone or send your order to Agilent Technologies. See “Contacting Agilent” on
page 1-15.
7 mm Modules and Accessories
Description Qty Part Number
Wrenches
3/4 in, 135 N-cm (12 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with
7 mm kits)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with N4696B)
Protective End Caps
DB25 multi-pin connector cap
7 mm connector cap
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages and Accessories
7 mm pin depth gage and master 1 85050-80012
Other
7 mm collet extractor tool (supplied with 7 mm kits)
Replacement 7 mm collet
Electronic calibration module reference manual
USB cable, 1.8 meter
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
1
1
as required
as required
as required
1
1
1
1
1
8710-1766
8710-1770
1252-4690
1401-0249
N4693-40002
5060-0370
85050-20001
N4693-90001
8121-0506
8121-1047
6-2 Chapter 6
Page 91

Type-N (50 ohm) Modules and Accessories
Type-N (50 ohm) Modules and Accessories
Replaceable Parts
Description
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
Type-N (50 Ω) female to female adapter
Type-N (50 Ω) male to male adapter
Wrenches
3/4 in, 135 N-cm (12 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with
type-N kits)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with N4690B)
Protective End Caps
DB-25 multi-pin connector cap
Type-N female connector cap
Type-N male connector cap
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages and Accessories
Type-N pin depth gages (male & female gages & masters)
Type-N slotless contact repair kit
Type-N slotless contacts (pkg. of 10)
Type-N slotless contact (1 only)
a
Qty
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
as required
1
1
1
1
Part Number
85054-60037
85054-60038
8710-1766
8710-1770
1252-4690
1401-0225
1401-0214
N4693-40002
85054-60049
85054-60056
85054-60057
85054-60058
Other
Electronic calibration module reference manual
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference
manual)
USB cable A to B 1.8 meter
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. See See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
b
1
1
1
1
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
8121-1047
Chapter 6 6-3
Page 92

Replaceable Parts
3.5 mm Modules and Accessories
3.5 mm Modules and Accessories
Description
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
a
Qty Part Number
3.5 mm female to female adapter
3.5 mm male to male adapter
Wrenches
20 mm, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with all 3.5
mm kits)
5/16 in, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied wit h N4691B,
N4431B, 85093C kits)
Spanner wrench (supplied with N4691B)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with N4691B)
Protective End Caps
DB-25 multi-pin connector cap
3.5 mm connector cap (for module)
3.5 mm female connector cap (for adapter)
3.5 mm male connector cap (for adapter)
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages and Accessories
3.5 mm female pin-depth gage
3.5 mm male pin-depth gage
b
b
3.5 mm repair kit with 10 contacts
3.5 mm slotless contacts (pkg. of 10)
3.5 mm slotless contact (1 only)
1
1
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
as required
as required
1
1
1
1
1
85052-60012
85052-60014
8710-1764
8710-1765
08513-20014
8710-1770
1252-4690
1401-0214
1401-0202
1401-0208
N4693-40002
11752-60105
11752-60106
85052-60049
85052-60050
85052-60051
Other
Electronic calibration modu le refe renc e guid e
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meter
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
1
1
1
1
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
8121-1047
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. A 3.5 mm gage is capable of measuring 3.5 mm and 2.92 mm connectors.
6-4 Chapter 6
Page 93

7-16 Modules and Accessories
Replaceable Parts
7-16 Modules and Accessories
Description
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
7-16 female to female adapter
7-16 male to male adapter
Wrenches
1-1/16 in, 226 N-cm (20 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
15/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with kit)
Protective End Caps
DB-25 multi-pin connector cap
7-16 male connector cap
7-16 female connector cap
Other
Electronic calibration module reference manual
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB Cable, 1.8 meter
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. See See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
a
as required
as required
as required
b
Qty Part Number
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
11906-80016
11906-80015
8710-2175
8710-2174
1252-4690
1401-0417
1401-0418
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
Chapter 6 6-5
Page 94

Replaceable Parts
2.92 mm Modules and Accessories
2.92 mm Modules and Accessories
Description
a
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
2.92 mm female to female adapter
2.92 mm male to male adapter
Wrenches
20 mm, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
5/16 in, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
Spanner wrench (supplied with kit)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with kit)
Protective End Caps
2.92 mm connector cap (for module)
2.92 mm female connector cap (for adapter)
2.92 mm male connector cap (for adapter)
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages
3.5 mm female pin-depth gage
3.5 mm male pin-depth gage
b
b
Other
Qty Part Number
1
1
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
as required
1
1
N4692-60022
N4692-60021
8710-1764
8710-1765
08513-20014
8710-1770
1401-0214
1401-0202
1401-0208
N4693-40002
11752-60105
11752-60106
Electronic calibration module reference manual
c
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meters
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
1
1
1
1
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. A 3.5 mm gage is capable of measuring 3.5 mm and 2.92 mm connectors.
c. See See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
8121-1047
6-6 Chapter 6
Page 95

2.4 mm Modules and Accessories
Replaceable Parts
2.4 mm Modules and Accessories
Description
a
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
2.4 mm female to female adapter
2.4 mm male to male adapter
Wrenches
20 mm, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
5/16 in, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with kit)
Spanner wrench (supplied with kit)
Protective End Caps
2.4 mm connector cap (for module)
2.4 mm female connector cap (for adapter)
2.4 mm male connector cap (for adapter)
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages
2.4 mm female pin-depth gage
2.4 mm male pin-depth gage
b
b
Other
Qty Part Number
1
1
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
as required
1
1
85056-60006
85056-60005
8710-1764
8710-1765
8710-1770
08513-20014
1401-0214
1401-0095
1401-0208
N4693-40002
11752-60107
11752-60108
Electronic calibration module reference manual
c
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meters
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
1
1
1
1
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. A 2.4 mm gage is capable of measuring 2.4 mm and 1.85 mm connectors.
c. See See “Printin g Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
8121-1047
Chapter 6 6-7
Page 96

Replaceable Parts
1.85 mm Modules and Accessories
1.85 mm Modules and Accessories
Description
a
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
1.85 mm female to female adapter
1.85 mm male to male adapter
Wrenches
20 mm, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
5/16 in, 90 N-cm (8 in-lb) torque wrench (supplied with kit)
Spanner wrench (supplied with ki t)
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench (supplied with kit)
Protective End Caps
1.85 mm connector cap (for module)
1.85 mm female connector cap (for adapter)
1.85 mm male connector cap (for adapter)
36-pin connector cap, ESD protected
Gages
2.4 mm female pin-depth gage
2.4 mm male pin-depth gage
b
b
Other
Qty Part Number
1
1
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
as required
1
1
85058-60114
85058-60113
8710-1764
8710-1765
08513-20014
8710-1770
1401-0214
1401-0202
1401-0208
N4693-40002
11752-60107
11752-60108
Electronic calibration module reference manual
c
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meters
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin)
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. A 2.4 mm gage is capable of measuring 2.4 mm and 1.85 mm connectors.
c. See See “Printing C opies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
1
1
1
1
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
8121-1047
6-8 Chapter 6
Page 97

Type-N (75 ohm) Modules and Accessories
Type-N (75 ohm) Modules and Accessories
Replaceable Parts
Description
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
Type-N (75 Ω) female to female adapter
Type-N (75 Ω) male to male adapter
Wrenches
3/4 in, 135 N-cm (12 in-lb) torque wrench
1/2 in to 9/16 in open-ended wrench
Protective End Caps
DB-25 multi-pin connector cap
Type-N male connector cap
Type-N female connector cap
Gages
Type-N (75 ohm) mm pin depth gages (male and female gages
and masters)
Other
Electronic calibration module reference manual
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meters
a
b
Qty Part Number
1
1
1
1
as required
as required
as required
1 85036B
1
1
1
85036-60014
85036-60013
8710-1766
8710-1770
1252-4690
1401-0248
1401-0247
Option K01
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. See See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
Chapter 6 6-9
Page 98

Replaceable Parts
Type-F Modules and Accessories
Type-F Modules and Accessories
Description
Adapters (added with Option 00A)
Type-F female to female adapter
Type-F male to male adapter
Wrenches
Type-F wrench (supplied with kit) 1 8710-1841
Protective End Caps
DB-25 multi-pin connector cap
Type-F male connector cap
Type-F female connector cap
Other
Electronic calibration module reference manual
Connector care quick reference card (part of reference manual)
USB cable, 1.8 meters
a. See “Clarifying the Terminology of a Connector Interface” on page 1-2.
b. See See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
a
b
Qty Part Number
1
1
as required
as required
as required
1
1
1
85039-60002
85039-60006
1252-4690
1401-0297
1401-0296
N4693-90001
08510-90360
8121-0506
6-10 Chapter 6
Page 99

Replaceable Parts
Other ECal Accessories
Other ECal Accessories
Description Qty Part Number
85097B ECal VNA Interface Kit
Interface Unit
Shielded DB25 to DB25 Cables
Adapter cable, DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin) Option 100
Power Supply
Reference Guide
Quick Reference Card
Adapter Cable (connects N469xA/B series modules to 85097B)
DB25 to AMP Champ (36-pin) 1 8121-1047
Cleaning Supplies
Compressed air (235 ml) 1 8500-6659
99.5% isopropyl alcohol (8 oz) 1 8500-0559
99.5% isopropyl alcohol (30 ml) 1 8500-5344
Cleaning swabs 100 9301-1243
Lint-free cleaning cloth 150 9310-4242
ESD Supplies
Grounding wrist strap 1 9300-1367
5 ft Wrist-strap to table-mat grounding cord 1 9300-0980
a
1
3
1
1
1
1
85097-60002
8120-8710
8121-1047
0950-3331
85091-90010
85091-90011
2 x 4 ft conductive table mat with 15 ft ground wire 1 9300-0797
ESD heel strap 1 9300-1126
USB Accessories
USB 4-port hub 1 N4689A
Module Accessories
Rubber foot 1 85060-40001
a. See “Printing Copies of On-Line Documentation” on page iv.
Chapter 6 6-11
Page 100

Replaceable Parts
Other ECal Accessories
6-12 Chapter 6
 Loading...
Loading...