Advanced Linear Devices Inc ALD500RAU-20SEI, ALD500RAU-20SE, ALD500RAU-20QEI, ALD500RAU-20QE, ALD500RAU-20PEI Datasheet
...
ADVANCED |
|
LINEAR |
ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R |
DEVICES, INC. |
PRECISION INTEGRATING ANALOG PROCESSOR
WITH PRECISION VOLTAGE REFERENCE
APPLICATIONS
•4 1/2 digits to 5 1/2 digits plus sign measurements
•Precision analog signal processor
•Precision sensor interface
•High accuracy DC measurement functions
•Portable battery operated instruments
•Computer peripheral
•PCMCIA
FEATURES
•Resolution up to 18 bits plus sign bit and over-range bit
•Accuracy independent of input source impedances
•Accurate on-chip voltage reference
•Tempco as low as 10 ppm/°C guaranteed
•Chip select - power down mode
•High input impedance of 1012 Ω
•Inherently filters and integrates any external noise spikes
•Differential analog input
•Wide bipolar analog input voltage range ±3.5V
•Automatic zero offset compensation
•Low linearity error - as low as 0.001% typical
•Fast zero-crossing comparator - 1μs
•Low power dissipation - 6mW typical
•Automatic internal polarity detection
•Low input current - 2pA typical
•Optional digital control from a microcontroller, an ASIC, or a dedicated digital circuit
•Flexible conversion speed vs. resolution trade-off
BENEFITS
•Low cost, simple functionality
•Wide dynamic signal range
•Very high noise immunity
•Automatic compensation and cancellation of error sources
•Easy to use to acquire bipolar signals
•Up to 19 bit (18 bit + sign bit) single conversion or 21 bit (20 bit + sign bit) multiple conversion and noise performance
•Inherently linear and stable with temperature and component variations
PIN CONFIGURATION
|
|
ALD500R |
|
|
IB |
|
|
|
CS |
1 |
|
20 |
||
CINT |
|
|
|
V+ |
2 |
|
19 |
||
V- |
|
|
|
DGND |
3 |
|
18 |
||
CAZ |
|
|
|
COUT |
4 |
|
17 |
||
BUF |
|
|
|
B |
5 |
|
16 |
||
AGND |
|
|
|
A |
6 |
|
15 |
||
C-REF |
|
|
|
V+IN |
7 |
|
14 |
||
C+REF |
|
|
|
V-IN |
8 |
|
13 |
||
|
|
|
|
V+REF |
N/C |
9 |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
||
N/C |
10 |
|
11 |
V-REF |
|
|
|
||
QE, PE, SE PACKAGE
* N/C pin is connected internally. Connect to V-.
Ordering Information
Resolution |
Endpoint |
Voltage Reference |
|
Package Type |
|
Operating |
|
||
|
Linearity |
Accuracy/Tempco |
|
|
|
|
Temperature |
||
|
|
|
|
20L PDIP |
20L SOIC |
20L QSOP |
20LCDIP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16 bit |
0.015% |
0.5% 50ppm/C |
ALD500R-50PE |
ALD500R-50SE |
ALD500R-50QE |
|
0°C to 70°C |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 bit |
0.01% |
0.3% |
20ppm/C |
ALD500RA-20PE |
ALD500RA-20SE |
ALD500RA-20QE |
|
0°C to 70°C |
|
18 bit |
0.005% |
|
|
ALD500RAU-20PE |
ALD500RAU-20SE |
ALD500RAU-20QE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 bit |
0.01% |
0.2% |
10ppm/C |
ALD500RA-10PE |
ALD500RA-10SE |
ALD500RA-10QE |
|
0°C to 70°C |
|
18 bit |
0.005% |
|
|
ALD500RAU-10PE |
ALD500RAU-10SE |
ALD500RAU-10QE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17 bit |
0.01% |
0.3% |
20ppm/C |
ALD500RA-20PEI |
ALD500RA-20SEI |
ALD500RA-20QEI |
|
-40°C to +85°C |
|
18 bit |
0.005% |
|
|
ALD500RAU-20PEI |
ALD500RAU-20SEI |
ALD500RAU-20QEI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 bit |
0.005% |
0.3% |
20ppm/C |
|
|
|
ALD500RAU-20DE |
-55°C to +125°C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Contact factory for customized voltage reference voltage levels, accuracy and tempco specifications.
Rev. 1.01 © 1999 Advanced Linear Devices, Inc., 415 Tasman Drive, Sunnyvale, California 94089-1706 Tel: (408) 747-1155, Fax: (408) 747-1286 http://www.aldinc.com
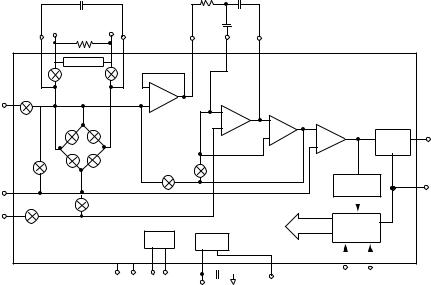
FIGURE 1. ALD500R Functional Block Diagram
|
|
|
CREF |
|
|
|
|
RINT |
CINT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+REF |
|
V-REF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(12) |
RREF |
(11) |
|
|
|
CAZ |
|
CINT |
|
|
|
|
RREF = 100KΩ |
C+REF |
|
|
C-REF |
BUF |
|
CAZ |
|
|
|
||||
CB = 0.1µF |
(8) |
|
|
|
|
(7) |
|
(5) |
|
(4) |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
REFINT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
SWR |
SWR |
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
SWIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
V+IN |
|
|
|
|
|
Buffer |
|
|
Integrator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||
(14) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SW- |
|
SW+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
R |
R |
|
|
|
|
+ |
- |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comp1 |
Level |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
Comp2 |
COUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shift |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ |
(17) |
|
|
SWAz |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SW+R |
SW-R |
|
SWS |
SWAZ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polarity |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DGND |
||
AGND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Detection |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(18) |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SWIN |
|
|
SWG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
V-IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog |
Phase |
|
|
|
(13) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Switch |
Decoding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REF |
|
|
|
Control |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bias |
|
Logic |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
Signals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSS VDD |
N/C N/C |
|
|
|
A |
B |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
CB |
|
CS |
(15) |
(16) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
(3) |
(19) |
(10) (9) |
|
IB |
|
(20) |
Control Logic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R are integrating dual slope analog processors, designed to operate on ±5V power supplies for building precision analog-to-digital converters. The ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R feature specifications suitable for 18 bit/17 bit/16 bit resolution conversion, respectively. Together with three capacitors, two resistors, and a digital controller, a precision Analog to Digital converter with auto zero can be implemented. The digital controller can be implemented by an external microcontroller, under either hardware (fixed logic) or software control. For ultra high resolution applications, up to 23 bit conversion can be implemented with an appropriate digital controller and software.
The ALD500R series of analog processors accept differential inputs and the external digital controller first counts the number of pulses at a fixed clock rate that a capacitor requires to integrate against an unknown analog input voltage, then counts the number of pulses required to deintegrate the capacitor against a known internal reference voltage. This unknown analog voltage can then be converted by the microcontroller to a digital word, which is translated into a high resolution number, representing an accurate reading. This reading, when ratioed against the reference voltage, yields an accurate, absolute voltage measurement reading.
The ALD500R analog processors consist of on-chip digital control circuitry to accept control inputs, integrating buffer amplifiers, analog switches, and voltage comparators and a highly accurate, ultra-stable voltage reference. It functions in four operating modes, or phases, namely auto zero, integrate, deintegrate, and integrator zero phases. At the end of a conversion, the comparator output goes from high to low when the integrator crosses zero during deintegration. ALD500R analog processors also provide direct logic interface to CMOS logic families.
GENERAL THEORY OF OPERATION
Dual-Slope Conversion Principles of Operation
The basic principle of dual-slope integrating analog to digital converter is simple and straightforward. A capacitor, CINT, is charged with the integrator from a starting voltage, VX, for a fixed period of time at a rate determined by the value of an unknown input voltage, which is the subject of measurement. Then the capacitor is discharged at a fixed rate, based on an external reference voltage, back to VX where the discharge time, or deintegration time, is measured precisely. Both the integration time and deintegration time are measured by a digital counter controlled by a crystal oscillator. It can be demonstrated that the unknown input voltage is determined by the ratio of the deintegration time and integration time, and is directly proportional to the magnitude of the external reference voltage.
The major advantages of a dual-slope converter are:
a. Accuracy is not dependent on absolute values of
integration time tINT and deintegration time tDINT, but is dependent on their relative ratios. Long-term clock frequency
variations will not affect the accuracy. A standard crystal controlled clock running digital counters is adequate to generate very high accuracies.
b. Accuracy is not dependent on the absolute values of
RINT and CINT, as long as the component values do not vary through a conversion cycle, which typically lasts less than 1
second.
c.Offset voltage values of the analog components, such as VX, are cancelled out and do not affect accuracy.
d.Accuracy of the system depends mainly on the accuracy and the stability of the voltage reference value.
2 |
Advanced Linear Devices |
ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R |

reference voltage is integrated VREF = Reference Voltage
CINT = Integrating Capacitor value RINT = Integrating Resistor value
Actual data conversion is accomplished in two phases: Input
Signal Integration Phase and Reference Voltage Deintegration
Phase.
The slow conversion speed of the integrating converter provides |
The integrator output is initialized to 0V prior to the start of |
|||||||||||||||
Input Signal Integration Phase. During Input Signal Integration |
||||||||||||||||
inherent noise rejection with at least a 20dB/decade attenuation |
Phase, internal analog switches connect VIN to the buffer |
|||||||||||||||
rate. Interference signals with frequencies at integral multiples |
input where it is maintained for a fixed integration time period |
|||||||||||||||
of the integration period are, theoretically, completely removed. |
(tINT). This fixed integration period is generally determined by |
|||||||||||||||
Integrating converters often establish the integration period to |
a digital counter |
controlled by a crystal oscillator. The |
||||||||||||||
reject 50/60Hz line frequency interference signals. |
application of VIN causes the integrator output to depart 0V at |
|||||||||||||||
The relationship of the integrate and deintegrate (charge |
a rate determined by VIN and a direction determined by the |
|||||||||||||||
polarity of VIN. |
|
|||||||||||||||
and discharge) of the integrating capacitor values are |
|
|
||||||||||||||
shown below: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Reference Voltage Deintegration Phase is initiated |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
. t |
|
|
|
. C |
|
|
|
immediately after tINT, within 1 clock cycle. During |
||
V |
INT |
= V |
X |
- (V |
|
/ R |
INT |
INT |
) |
|
ReferenceVoltage |
Deintegration Phase, internal analog |
||||
|
|
IN |
|
INT |
|
|
|
|
switches connect a reference voltage having a polarity opposite |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(integrate cycle) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1) |
that of VIN to the integrator input. Simultaneously the same |
||||||
V |
|
= V |
|
- (V |
|
. t |
|
|
/ R |
|
. C |
|
) |
digital counter controlled by the same crystal oscillator used |
||
X |
|
|
DINT |
INT |
INT |
above is used to start counting clock pulses. The Reference |
||||||||||
|
|
INT |
REF |
|
|
|
|
Voltage Deintegration Phase is maintained until the comparator |
||||||||
(deintegrate cycle) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
output inside the dual slope analog processor changes state, |
||||||||||
Combining equations 1 and 2 results in: |
|
indicating the integrator has returned to 0V. At that point the |
||||||||||||||
|
digital counter is stopped. The Deintegration time period |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(tDINT), as measured by the digital counter, is directly |
|
VIN / VREF = -tDINT / tINT |
|
|
|
|
(3) |
proportional to the magnitude of the applied input voltage. |
||||||||||
where: |
|
|
Vx |
= |
An offset voltage used as starting voltage |
VINT |
= |
Voltage change across CINT during tINT and |
VIN |
|
during tDINT (equal in magnitude) |
= |
Average, or an integrated, value of input voltage |
|
tINT |
|
to be measured during tINT (Constant VIN) |
= |
Fixed time period over which unknown voltage is |
|
|
|
integrated |
tDINT = |
Unknown time period over which a known |
|
After the digital counter value has been read, the digital counter, the integrator, and the auto zero capacitor are all reset to zero through an Integrator Zero Phase and an Auto Zero Phase so that the next conversion can begin again. In practice, this process is usually automated so that analog-to- digital conversion is continuously updated. The digital control is handled by a microprocessor or a dedicated logic controller. The output, in the form of a binary serial word, is read by a microprocessor or a display adapter when desired.
|
|
CINT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RINT |
INTEGRATOR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VINT |
- |
COMPARATOR |
|
||
ANALOG |
|
|
COUT |
||||
INPUT |
|
+ |
|
+ |
|
|
|
(VIN) |
S1 |
|
|
|
POLARITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DETECTION |
|
VOLTAGE |
SWITCH DRIVER |
PHASE |
|
|
|
||
REF |
|
CONTROL |
CONTROL |
|
|||
REFERENCE |
|
|
|||||
SWITCHES |
|
|
|
|
LOGIC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
POLARITY CONTROL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
INTEGRATOR OUTPUT |
|
|
|
|
A |
B |
|
Vx ≈0 |
VINT = 4.1V MAX |
|
|
|
|
||
|
VIN ≈VFULL SCALE |
|
|
|
MICROCONTROLLER |
|
|
|
VIN ≈1/2VFULL SCALE |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
(CONTROL LOGIC |
|
|
|
tDINT |
|
|
|
|
+ COUNTER) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tINT |
tDINT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 2. Basic Dual-Slope Converter
ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R |
Advanced Linear Devices |
3 |
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply voltage, V+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.2V |
|
Differential input voltage range |
|
|
|
-0.3V to V+ +0.3V |
||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
Power dissipation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
600 mW |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Operating temperature range |
PE, SE package |
|
|
|
|
0°C to +70°C |
||||||
Operating temperature range |
QE package |
|
|
|
|
-55°C to +125°C |
||||||
Storage temperature range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
-65°C to +150°C |
|||||
Lead temperature, 10 seconds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+260°C |
||||
OPERATING ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
T |
A |
= 25°C V+ = +5V V- = -5V (V supply ± 5V) unless otherwise specified; C |
= C |
|
= 0.47μf |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AZ |
REF |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
500RAU |
|
|
500RA |
|
|
500R |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Parameter |
Symbol |
Min Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
Test Conditions |
||||||
Resolution |
|
15 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
μV |
|
Notes 1, 7 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Zero-Scale |
ZSE |
|
|
0.0025 |
|
|
0.003 |
|
|
|
0.005 |
% |
|
0°C to 70°C |
|||
Error |
|
|
|
0.003 |
|
|
0.005 |
|
|
|
0.008 |
% |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
End Point |
ENL |
|
0.001 |
0.005 |
|
0.003 |
0.010 |
|
0.005 |
|
0.015 |
% |
|
Notes 1, 2 |
|||
Linearity |
|
|
|
0.007 |
|
|
0.015 |
|
|
|
0.020 |
|
|
0°C to +70°C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Best Case |
NL |
|
|
0.0025 |
|
0.003 |
0.005 |
|
0.003 |
|
0.008 |
% |
|
Notes 1, 2 |
|||
Straight Line |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Linearity |
|
|
|
0.004 |
|
|
0.008 |
|
|
|
0.015 |
|
|
0°C to +70°C |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Zero-Scale |
TCZS |
|
0.3 |
0.6 |
|
0.3 |
0.7 |
|
0.3 |
|
0.7 |
μV/°C |
0°C to +70°C |
||||
Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Coefficient |
|
|
0.15 |
0.3 |
|
0.15 |
0.35 |
|
0.15 |
|
0.35 |
ppm/°C |
Notes 1, 7 |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Full-Scale |
SYE |
|
0.005 |
|
|
0.008 |
|
|
0.01 |
|
|
|
% |
|
0°C to 70°C |
||
Symmetry Error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
(Rollover Error) |
|
|
0.008 |
|
|
0.010 |
|
|
0.012 |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Full-Scale |
TCFS |
|
1.3 |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
ppm/°C |
0°C to +70°C |
|||
Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 7 |
||
Coefficient |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Input |
IIN |
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
pA |
|
VIN = 0V |
||
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Common-Mode |
CMVR |
VSS+1.5 |
|
VDD-1.5 |
VSS+1.5 |
|
VDD-1.5 |
VSS+1.5 |
|
|
VDD-1.5 |
V |
|
|
|||
Voltage Range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Integrator |
VINT |
VSS+0.9 |
|
VDD-0.9 |
VSS+0.9 |
|
VDD-0.9 |
VSS+0.9 |
|
|
VDD-0.9 |
V |
|
|
|||
Output Swing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Analog Input |
VIN |
VSS+1.5 |
|
VDD-1.5 |
VSS+1.5 |
|
VDD-1.5 |
VSS+1.5 |
|
|
VDD-1.5 |
V |
|
AGND = 0V |
|||
Signal Range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Voltage |
VREF |
VSS+1 |
|
VDD-1 |
VSS+1 |
|
VDD-1 |
VSS+ 1 |
|
|
VDD-1 |
V |
|
|
|||
Reference |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Advanced Linear Devices |
ALD500RAU/ALD500RA/ALD500R |
 Loading...
Loading...