Page 1

61200350L1-1A
July 1998
Router Option Module
1200350L1
USER MANUAL
Page 2

Trademark Information:
OpenView is a registered trademark of Hewlett-Packard Company.
SunNet Manager is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Netview is a registered trademark of IBM.
IQ View is a trademark of ADTRAN.
901 Explorer Boulevard
P.O. Box 140000
Huntsville, AL 35814-4000
Phone: (256) 963-8000
© 1998 ADTRAN, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Printed in USA.
Page 3

ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual is arranged so you can quickly and easily find the information you need. The following is an overview of the contents
of this manual:
• Chapter 1, Introduction, familiarizes you with an over view of
the Router Option Module.
• Chapter 2, Installation, describes the installation of the Router
Option Module connectors.
• Chapter 3, Operation, explains how to operate your Router
Option Module using the terminal interface.
• Chapter 4, Configuration Overview, explains how to access
the Router Option Module configuration menu.
• Chapter 5, Statistics, describes how to access statistical information from the Router Option Module.
• Chapters 6, Diagnostics, explains how to access the Router
Option Module diagnostic features.
• Chapter 7, Utility Menu, explains how the Router Option
Module’s embedded utilities manage and test the network
and facilitate software upgrades.
• Appendix A, Pinouts, provides pinouts for the Router Option
Module connectors.
• Appendix B, Specifications, contains product specifications
and features.
• Appendix C, Log Messages, contains messages of events that
occur.
• Appendix D, SNMP, explains the simple network management protocol and how it works.
• Appendix E, Terminal Mode Commands, describes how the
Terminal Mode Commands work.
Page 4
Notes provide additional useful information.
Cautions signify information that could prevent service interruption.
Warnings provide information that could prevent
damage to the equipment or endangerment to human life.
Page 5

FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE STATEMENT:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio frequencies. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Shielded cables must be used with this unit to ensure compliance
with Class A FCC limits.
Change or modifications to this unit not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
CANADIAN EMISSIONS REQUIREMENTS
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio
noise emissions from digital apparatus as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled "Digital Apparatus,"
ICES-003 of the Department of Communications.
Cet appareil nuerique respecte les limites de bruits radioelectriques applicables aux appareils numeriques de Class A prescrites dans la norme sur le materiel brouilleur: "Appareils
Numeriques," NMB-003 edictee par le ministre des Communications.
Page 6

CANADIAN EQUIPMENT LIMITATIONS
Notice: The Canadian Industry and Science Canada label identifies certified equipment. This certification means that the equipment meets certain telecommunications network protective,
operational, and safety requirements. The Department does not
guarantee the equipment will operate to the user's satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is permissible to be connected to the facilities of the local telecommunications company. The equipment must also be installed using an
acceptable method of connection. In some cases, the company's
inside wiring associated with a single line individual service may
be extended by means of a certified connector assembly (telephone extension cord). The customer should be aware that compliance with the above conditions may not prevent degradation of
service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an authorized
Canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any
repairs or alterations made by the user to this equipment, or
equipment malfunctions, may give the telecommunications company cause to request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical
ground connections of the power utility, telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system, if present, are connected together. This precaution may be particularly important in rural
areas.
Users should not attempt to make such connections themselves, but should contact the appropriate electric inspection
authority, or an electrician, as appropriate.
The Load Number (LN) assigned to each terminal device denotes
the percentage of the total load to be connected to a telephone
loop which is used by the device, to prevent overloading. The termination on a loop may consist of any combination of devices
subject only to the requirement that the total of the Load Numbers
of all devices does not exceed 100.
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction ............................................................................. 1-1
Product Overview ......................................................................................... 1-1
Basic Functions of Router Option Module................................................. 1-1
LAN Bridge ...................................................................................... 1-1
IP Router........................................................................................... 1-1
IPX Router ........................................................................................ 1-1
Network Address Translation (NAT) .......................................... 1-2
PPP or Frame Relay ........................................................................ 1-2
Routing and Bridging with the Router
Option Module............................................................................................... 1-2
Factory Default ................................................................................ 1-2
Bridging ............................................................................................ 1-2
IP Routing......................................................................................... 1-2
IPX Routing ...................................................................................... 1-3
Concurrent Routing and Bridging .............................................................. 1-3
Network Address Translation Mode (NAT) ............................................. 1-3
Warranty and Customer Service ................................................................. 1-4
Chapter 2. Installation ............................................................................... 2-1
Unpack, Inspect, Power Up.......................................................................... 2-1
Receipt Inspection ......................................................................................... 2-1
ADTRAN Shipments Include........................................................ 2-1
Installation ...................................................................................................... 2-2
Placement of the Option Module ................................................................ 2-2
Power Connection ......................................................................................... 2-3
Attaching the Plug-On Board ...................................................................... 2-3
Control............................................................................................................. 2-4
10BaseT............................................................................................................ 2-4
Chapter 3. Operation .................................................................................. 3-1
Front Panel...................................................................................................... 3-1
Terminal Menu Structure ............................................................................. 3-1
Main Menu Options........................................................................ 3-1
Configuration Menu ................................................................ 3-2
Status Menu .............................................................................. 3-3
Test Menu.................................................................................. 3-3
Logs Menu ................................................................................ 3-3
Utilities Menu ........................................................................... 3-3
Navigating the Terminal Menus ................................................................. 3-4
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
vii
Page 8

Table of Contents
General Layout............................................................................................... 3-4
Menu Path....................................................................................................... 3-4
Moving Around ............................................................................................. 3-4
Reading Menu Options .................................................................. 3-5
Navigating the Keyboard............................................................... 3-5
Session Management ...................................................................... 3-6
Configuration................................................................................... 3-7
Security Levels ............................................................................................... 3-8
Chapter 4. Configuration Overview ....................................................... 4-1
Configuration Menu...................................................................................... 4-1
Configuration/System Info.......................................................................... 4-1
System Name ............................................................................ 4-2
System Location ....................................................................... 4-2
System Contact ......................................................................... 4-2
Firmware Revision................................................................... 4-2
System Uptime ......................................................................... 4-2
Date/Time................................................................................. 4-2
Configuration/WAN .................................................................................... 4-3
WAN/DSO Rate.............................................................................. 4-3
WAN/L2 Protocol (also available via Front Panel)............ 4-3
Configuration/IP ........................................................................................... 4-4
IP/IP Address (also available via Front Panel) ................... 4-4
IP/Subnet Mask (also available via Front Panel) ................ 4-4
IP/Default Gateway (also available via Front Panel)......... 4-4
IP/Static Routes............................................................................... 4-5
Static Routes/Active................................................................ 4-5
Static Routes/IP Address........................................................ 4-5
Static Routes/Subnet Mask .................................................... 4-5
Static Routes/Gateway ........................................................... 4-5
Static Routes/Hops.................................................................. 4-5
Static Routes/Private............................................................... 4-5
IP/IP Router ................................................................................................... 4-6
IP Router/Mode .............................................................................. 4-6
IP/RIP ............................................................................................... 4-6
RIP/Mode ................................................................................. 4-6
RIP/Protocol............................................................................. 4-6
RIP/Method.............................................................................. 4-6
RIP/Direction ........................................................................... 4-6
RIP/V2 Secret ........................................................................... 4-7
IP/NAT ..................................................................................... 4-7
NAT/DHCP Mode .................................................................. 4-7
NAT/DHCP Renewal Time ................................................... 4-7
viii
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 9

Table of Contents
NAT/Web Server ..................................................................... 4-7
NAT/Default IP........................................................................ 4-7
IP/DNS.............................................................................................. 4-8
DNS/Domain Name ................................................................ 4-8
DNS/Server 1............................................................................ 4-8
DNS/Server 2............................................................................ 4-8
IP/UDP Relay................................................................................................. 4-8
UDP Relay/Mode ............................................................................ 4-8
UDP Relay/UDP Relay List ........................................................... 4-9
UDP Relay List/Relay Address.............................................. 4-9
UDP Relay List/UDP Port Type ............................................ 4-9
UDP Relay List/UDP Port 1, UDP Port 2, UDP Port 3 ....... 4-9
IP/Proxy ARP ........................................................................... 4-9
Configuration/IPX ....................................................................................... 4-10
IPX/Mode ................................................................................ 4-10
IPX/Network .......................................................................... 4-10
IPX/Frame Type ..................................................................... 4-11
IPX/Seed Status ...................................................................... 4-11
IPX/RIP Timer ........................................................................ 4-12
IPX/SAP Timer....................................................................... 4-12
Configuration/Bridge ................................................................................. 4-13
Bridge/Mode.................................................................................. 4-13
Bridge/WAN IP Bridge ................................................................ 4-14
WAN IP Bridge/Network ..................................................... 4-14
WAN IP Bridge/Netmask..................................................... 4-14
WAN IP Bridge/Triggered ................................................... 4-14
WAN IP Bridge/Proxy ARP ................................................. 4-14
Bridge/WAN IPX Bridge ............................................................. 4-14
WAN IPX Bridge/Network .................................................. 4-15
WAN IPX Bridge/Frame Type............................................. 4-15
WAN IPX Bridge/Seed Status .............................................. 4-15
WAN IPX Bridge/Triggered................................................. 4-15
Bridge/Spanning Tree .................................................................. 4-15
Spanning Tree/Mode............................................................. 4-15
Spanning Tree/Priority ......................................................... 4-16
Spanning Tree/Maximum Age ............................................ 4-16
Spanning Tree/Hello Time ................................................... 4-16
Spanning Tree/Forward Delay ............................................ 4-16
Spanning Tree/LAN Port...................................................... 4-16
LAN Port/Active.................................................................... 4-16
LAN Port/Path Cost .............................................................. 4-16
LAN Port/Priority.................................................................. 4-17
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
ix
Page 10

Table of Contents
Spanning Tree/Bridge Group 1 .................................................. 4-17
Bridge Group 1/Active ......................................................... 4-17
Bridge Group 1/Path Cost.................................................... 4-17
Bridge Group 1/Priority ....................................................... 4-17
Spanning Tree/Bridge Group 2 .................................................. 4-17
Bridge Group 2/Active ......................................................... 4-17
Bridge Group 2/Path Cost.................................................... 4-17
Bridge Group 1/Priority ....................................................... 4-17
Bridge/Address Table.................................................................. 4-18
Address Table/Aging ........................................................... 4-18
Address Table/Forward Policy ........................................... 4-18
Configuration/Security .............................................................................. 4-19
Security/Authentication....................................................... 4-19
Security/Radius Server ................................................................ 4-19
Radius Server/Primary Server ............................................ 4-20
Radius Server/Secondary Server ........................................ 4-20
Radius Server/UDP Port ...................................................... 4-20
Radius Server/Secret............................................................. 4-20
Radius Server/Retry Count.................................................. 4-20
Security/PPP.................................................................................. 4-21
Security/Filter Defines................................................................. 4-22
Filter Defines/MAC Filter Defines...................................... 4-22
Filter Defines /Pattern Filter Defines.................................. 4-23
Filter Defines/IP Filter Defines............................................ 4-23
Filter Defines /IPX Filter Defines ........................................ 4-24
Frame Relay ............................................................................ 4-26
Frame Relay/Maintenance Protocol ................................... 4-27
Frame Relay/Polling Frequency.......................................... 4-27
Frame Relay/DLCI Mapping............................................... 4-27
DLCI Mapping/Active ......................................................... 4-29
DLCI Mapping/DLCI ........................................................... 4-29
DLCI Mapping/IP Map ........................................................ 4-29
IP Map/Active........................................................................ 4-29
IP Map/IARP.......................................................................... 4-29
IP Map/Far-End IP Address ................................................ 4-29
IP Map/IP Netmask .............................................................. 4-29
IP Map/Link IP Address ...................................................... 4-30
IP Map/RIP Protocol............................................................. 4-30
IP Map/RIP Method.............................................................. 4-30
IP Map/RIP Direction ........................................................... 4-31
DLCI Mapping/IPX Map ..................................................... 4-31
IPX Map/Active ..................................................................... 4-31
x
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 11

Table of Contents
IPX Map/IARP ....................................................................... 4-31
IPX Map/Link Network ........................................................ 4-31
DLCI Mapping/Bridge Map................................................. 4-32
Bridge Map/Active ................................................................ 4-32
Bridge Map/Bridge Group ................................................... 4-32
DLCI Mapping/Filters........................................................... 4-32
Configuration/PPP Profile ......................................................................... 4-35
PPP Profile/Authentication ......................................................... 4-35
Authentication/Tx Method................................................... 4-36
Authentication/Tx Username .............................................. 4-36
Authentication/Tx Password ............................................... 4-36
Authentication/Rx Username .............................................. 4-36
Authentication/Rx Password ............................................... 4-36
PPP Profile/IP ................................................................................ 4-36
IP/Mode................................................................................... 4-37
IP/NAT.................................................................................... 4-37
IP/Route .................................................................................. 4-37
Route/IP/Net ......................................................................... 4-37
Route/Netmask ...................................................................... 4-37
Route/Force IP........................................................................ 4-37
IP/RIP.............................................................................................. 4-38
RIP/Mode ................................................................................ 4-38
RIP/Protocol ........................................................................... 4-38
RIP/Method ............................................................................ 4-38
RIP/Direction.......................................................................... 4-38
RIP/Triggered......................................................................... 4-39
PPP Profile/IPX ............................................................................. 4-39
IPX/Mode ................................................................................ 4-39
IPX/Remote Network............................................................ 4-39
IPX/Triggered......................................................................... 4-39
IPX/Type 20 Packets.............................................................. 4-39
PPP Profile/Bridge ........................................................................ 4-40
Bridge/Mode........................................................................... 4-40
PPP Profile/PPP............................................................................. 4-40
PPP/VJ Compression............................................................. 4-40
PPP/Max Config .................................................................... 4-41
PPP/Max Timer...................................................................... 4-41
PPP/Max Failure .................................................................... 4-41
PPP Profile/Filters......................................................................... 4-41
Filters/WAN-to-LAN (In)..................................................... 4-41
Filters/In Exceptions.............................................................. 4-42
Filters/LAN-to-WAN (Out).................................................. 4-43
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
xi
Page 12

Table of Contents
Filters/Out Exceptions .......................................................... 4-43
Configuration/Management ..................................................................... 4-44
Management/Telnet..................................................................... 4-44
Telnet/Server Access............................................................. 4-44
Telnet/User List ..................................................................... 4-44
User List/Name ..................................................................... 4-45
User List/Authen Method .................................................... 4-45
User List/Password............................................................... 4-45
User List/Idle Time ............................................................... 4-45
User List/Level ...................................................................... 4-45
Management/SNMP .................................................................... 4-45
SNMP Access.......................................................................... 4-46
SNMP/Communities ............................................................ 4-46
Communities/Name ............................................................. 4-46
Communities/Privilege ........................................................ 4-46
Communities/Manager IP ................................................... 4-46
SNMP/Traps .......................................................................... 4-46
Traps/Manager Name .......................................................... 4-46
Traps/Manager IP ................................................................. 4-46
Management/Maint Port............................................................. 4-47
Maint Port/Password Protect .............................................. 4-47
Maint Port/Password............................................................ 4-47
Maint Port/Baud Rate........................................................... 4-47
Maint Port/Data Bits ............................................................. 4-47
Maint Port/Parity .................................................................. 4-47
Maint Port/Stop Bits ............................................................. 4-48
Configuration/Terminal Mode ................................................................. 4-48
Chapter 5. Statistics .................................................................................... 5-1
Status Menu .................................................................................................... 5-1
Status/Sessions .............................................................................................. 5-2
Sessions/PPP Session ..................................................................... 5-2
Sessions/DLCI Table ...................................................................... 5-3
Sessions/Spanning Tree................................................................. 5-4
Status/ARP Cache ......................................................................................... 5-4
Status/Bridge Table ...................................................................................... 5-5
Status/IP Routes ............................................................................................ 5-5
Status/IPX Routes ......................................................................................... 5-7
Status/IPX Servers ........................................................................................ 5-8
Status/WAN Stats......................................................................................... 5-8
Status/LAN Stats........................................................................................... 5-9
Status/IP Stats.............................................................................................. 5-10
Viewing Statistical Information
xii
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 13

Table of Contents
(Front Panel Interface) ................................................................................. 5-11
Router Statistics Available on Front Panel ............................................... 5-11
Status .............................................................................................. 5-11
Chapter 6. Diagnostics ...............................................................................6-1
Test Menu ........................................................................................................ 6-1
Test Menu/Echo Request.............................................................................. 6-1
Logs Menu....................................................................................................... 6-2
Logs/Syslog Host........................................................................................... 6-3
Logs/PPP Log................................................................................................. 6-3
PPP Log/Active ............................................................................... 6-3
PPP Log/Wrap................................................................................. 6-3
PPP Log/Level ................................................................................. 6-3
PPP Log/View ................................................................................. 6-3
PPP Log/Clear ................................................................................. 6-3
Logs/Connection Log.................................................................................... 6-4
Connection Log/Active .................................................................. 6-4
Connection Log/Wrap.................................................................... 6-4
Connection Log/Level .................................................................... 6-4
Connection Log/View .................................................................... 6-4
Connection Log/Clear .................................................................... 6-4
Logs/Network Log ........................................................................................ 6-4
Network Log/Active....................................................................... 6-4
Network Log/Wrap ........................................................................ 6-5
Network Log/Level ........................................................................ 6-5
Network Log/View ......................................................................... 6-5
Network Log/Clear......................................................................... 6-5
Chapter 7. Utility Menu .............................................................................7-1
Terminal Mode ............................................................................................... 7-1
Utilities Menu ................................................................................................. 7-1
Utilities/Ping .................................................................................................. 7-2
Utilities/Telnet Client ................................................................................... 7-2
Utilities/Upgrade Menu ............................................................................... 7-2
Upgrade/Transfer Method ............................................................ 7-3
Upgrade/TFTP Host ....................................................................... 7-3
Upgrade/Filename .......................................................................... 7-3
Upgrade/Status ............................................................................... 7-3
Upgrade/Start Transfer .................................................................. 7-3
Upgrade/Abort Transfer ................................................................ 7-4
Upgrade/TFTP Server .................................................................... 7-4
Utilities/Exit ................................................................................................... 7-4
Front Panel ...................................................................................................... 7-4
Software Revision ............................................................................ 7-4
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
xiii
Page 14

Table of Contents
CMD Mode....................................................................................... 7-4
Appendix A. Pinouts .............................................................................. . A-1
Appendix B. Specifications .................................................................... B-1
Ethernet Interface (LAN) ........................................................ B-1
Display....................................................................................... B-1
Environmental.......................................................................... B-1
Physical...................................................................................... B-1
Power ......................................................................................... B-1
Agency Approvals ................................................................... B-1
Appendix C. Log Messages ................................................................... . C-1
PPP Log Messages........................................................................................ C-1
Call Log Messages ........................................................................................ C-5
Network Log Messages ............................................................................... C-6
Appendix D. SNMP ............................................................................... . D-1
Understanding SNMP.................................................................................. D-1
SNMP Components:..................................................................................... D-1
Network Manager .......................................................................... D-1
Agent................................................................................................ D-1
MIB ................................................................................................... D-2
SNMP Embedded Agent ............................................................................. D-3
Communities................................................................................... D-3
Traps................................................................................................. D-3
Appendix E. Terminal Mode Commands ............................................ E-1
Menu Commands .......................................................................................... E-1
Key Words ...................................................................................................... E-2
Additional Commands ................................................................................. E-3
Download/Uploading Configuration........................................................ E-3
Index....................................................................................................... Index-1
xiv
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 15

List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Installing the Option Module .................................................. 2-2
Figure 2-2. Attaching the Plug-On Board ................................................. 2-3
Figure 2-3. Router Option Module Rear Panel ......................................... 2-4
Figure 3-1. Top Level Terminal Menu ....................................................... 3-2
Figure 3-2. Router Option Module Front Panel Menu Structure .......... 3-9
Figure 4-1. Configuration/System Info Screen ........................................ 4-1
Figure 4-2. Configuration/Frame Relay Screen ....................................... 4-3
Figure 4-3. Configuration/IP Screen ......................................................... 4-4
Figure 4-4. Configuration/IPX Screen ..................................................... 4-10
Figure 4-5. Configuration/Bridge Screen ............................................... 4-13
Figure 4-6. Configuration/Security Screen ............................................. 4-19
Figure 4-7. Configuration/PPP Profile Screen ....................................... 4-35
Figure 4-8. Configuration/Management Screen .................................... 4-44
Figure 5-1. Status Screen .............................................................................. 5-1
Figure 6-1. Test Screen ................................................................................. 6-1
Figure 6-2. Logs Screen ................................................................................ 6-2
Figure 7-1. Utilities Screen ........................................................................... 7-1
Figure 7-2. System Statistics Screen ........................................................... 7-4
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
xv
Page 16

List of Figures
xvi
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 17

List of Tables
Table A-1: Pin Assignments for Control Connector ............................... A-1
Table A-2: 10BaseT Ethernet ...................................................................... A-1
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
xvii
Page 18

List of Tables
xviii
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 19

Chapter 1
Introduction
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The ADTRAN Router Option Module installs in the option slot of
the TSU muliplexer family of products and provides integrated rout-
ing capability access frame relay or point-to-point networks.
Basic Functions of Router Option Module
The Router Option Module provides the following basic functions:
LAN Bridge
Bridging provides a point-to-point connection between two local
area networks (LANs). The bridge learning function scans the
source and destination media access control (MAC) addresses of all
packets on its LAN and determines which packets should be trans-
mitted over the T1 link. Applications include connectivity between
single users or small offices to corporate LANs. The Router Option
Module uses the Spanning Tree Algorithm (IEEE 802.1d-ISO/
IEC10038), which provides a loop-free topology and redundancy.
IP Router
The Router Option Module can function as an IP router using the
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) for advertising and learning
routes among other routers. Static routes may also be entered into
the routing table.
IPX Router
IPX routers and services can be exchanged between the Router Op-
tion Module and other devices using RIP and Service Advertising
Protocol (SAP). Watch dog serialization filtering and spoofing can
permit the ISDN to be idle during no application traffic periods.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
1-1
Page 20

Chapter 1: Introduction
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Single networks can connect to the Internet with this function. The
Router Option Module translates outgoing IP packets over the T1 to
the IP router at the Internet Service Provider. Popular Internet applications are supported.
PPP or Frame Relay
The layer 2 protocol used to transfer packets can be PPP or Frame
Relay (RFC 1490). PPP allows a point-to-point connection, whereas
Frame Relay can provide up to ten permanent virtual circuits.
Routing and Bridging with the Router
Option Module
The Router Option Module is a Router and Transparent Learning
Bridge. Its features can be easily configured and used, once several
basic concepts are understood.
Factory Default
The Router Option Module comes from the factory configured for
MAC Bridging, IP routing, and IPX routing with no filters or connection information defined. An IP address of 10.0.0.1 with a network mask of 255.255.255.0 is preloaded. The factory default layer 2
configuration is PPP, which provides the least amount of reconfiguration due to its negotiation-oriented nature.
Bridging
IP Routing
1-2
In Bridge Mode, the Router Option Module can be used to connect
two LAN segments. In this mode, all protocols are supported because they are transported across the T1 link at the MAC layer. The
Spanning Tree Algorithm can be used to guarantee a loop-free topology. MAC- save addresses are “learned” by each Router Option
Module to prevent non-WAN packets from being bridged.
The Router Option Module operates as an IP router when the Con-
figuration/IP/IP Router/Mode option is configured to On. In PPP
mode, the Router Option Module uses an IP unnumbered WAN in-
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 21
terface. The IP address and mask assigned to the unit’s LAN inter-
face apply to all routing and IP operations for the unit.
In Frame Relay mode, each PVC can be specified as numbered or
unnumbered links. If a default gateway is specified on the network
of the Ethernet interface, the unit attempts to reach the gateway
through that interface. If no default gateway is specified (i.e.,
0.0.0.0.), the WAN interface becomes the default gateway (recom-
mended for remote applications when there are no other routers on
the remote LAN).
IPX Routing
Network routes and services are learned and advertised using No-
vell’s RIP and SAP.
Concurrent Routing and Bridging
The Router Option Module can route IP and IPX as well as bridge
nonIP/IPX packets simultaneously. The PPP profile will, by default,
negotiate PPP network protocols to support the transmission and
reception of IP, IPX, and Bridge packets. If the PPP peer does not ac-
cept a protocol, the Router Option Module will fall back to any com-
bination of routing and bridging.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Network Address Translation Mode (NAT)
NAT is a special mode of operation in which the Router Option
Module obtains a dynamically assigned IP address from the peer
router (typically an Internet Service Provider). This allows a net-
work of computers to appear as a single IP address.
NAT is enabled if the layer 2 protocol is PPP and the PPP profile has
the IP parameter NAT set to Yes, or the layer 2 protocol is Frame Re-
lay and a DLCI mapping has the IP MAP/NAT parameter set to
Yes.
The network computer’s IP stack may use DHCP to request an IP
address, default gateway address, and domain name server ad-
dresses from the Router Option Module.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
1-3
Page 22

Chapter 1: Introduction
Warranty and Customer Service
ADTRAN will replace or repair this product within five years from
the date of shipment if it does not meet its published specifications
or fails while in service. For detailed warranty, repair, and return
information refer to the ADTRAN Equipment Warranty and Repair
and Return Policy Procedure.
Return Material Authorization (RMA) is required prior to returning
equipment to ADTRAN.
For service, RMA requests, or further information, contact one of the
numbers listed on the inside back cover of this manual.
1-4
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 23
Chapter 2
UNPACK, INSPECT, POWER UP
Receipt Inspection
Carefully inspect the option module for any shipping damage. If
damage is suspected, file a claim immediately with the carrier and
contact ADTRAN Customer and Product Service (CAPS). If possi-
ble, keep the original shipping container for use in shipping the
Router Option Module for repair or for verification of damage dur-
ing shipment.
ADTRAN Shipments Include
The following items are included in ADTRAN shipments of the
Router Option Module:
• Router option module
• The user manual
• A modular 8-position to 8-position cable for 10-BaseT port
• An 8-position modular to 8-position modular cable and a modular to female DB-25 adapter for access to the Control Port.
Installation
The ADTRAN Router Option Module MIB is available from ADTRAN in
the support section of the ADTRAN Web page at www.adtran.com.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
2-1
Page 24
Chapter 2: Installation
INSTALLATION
Placement of the Option Module
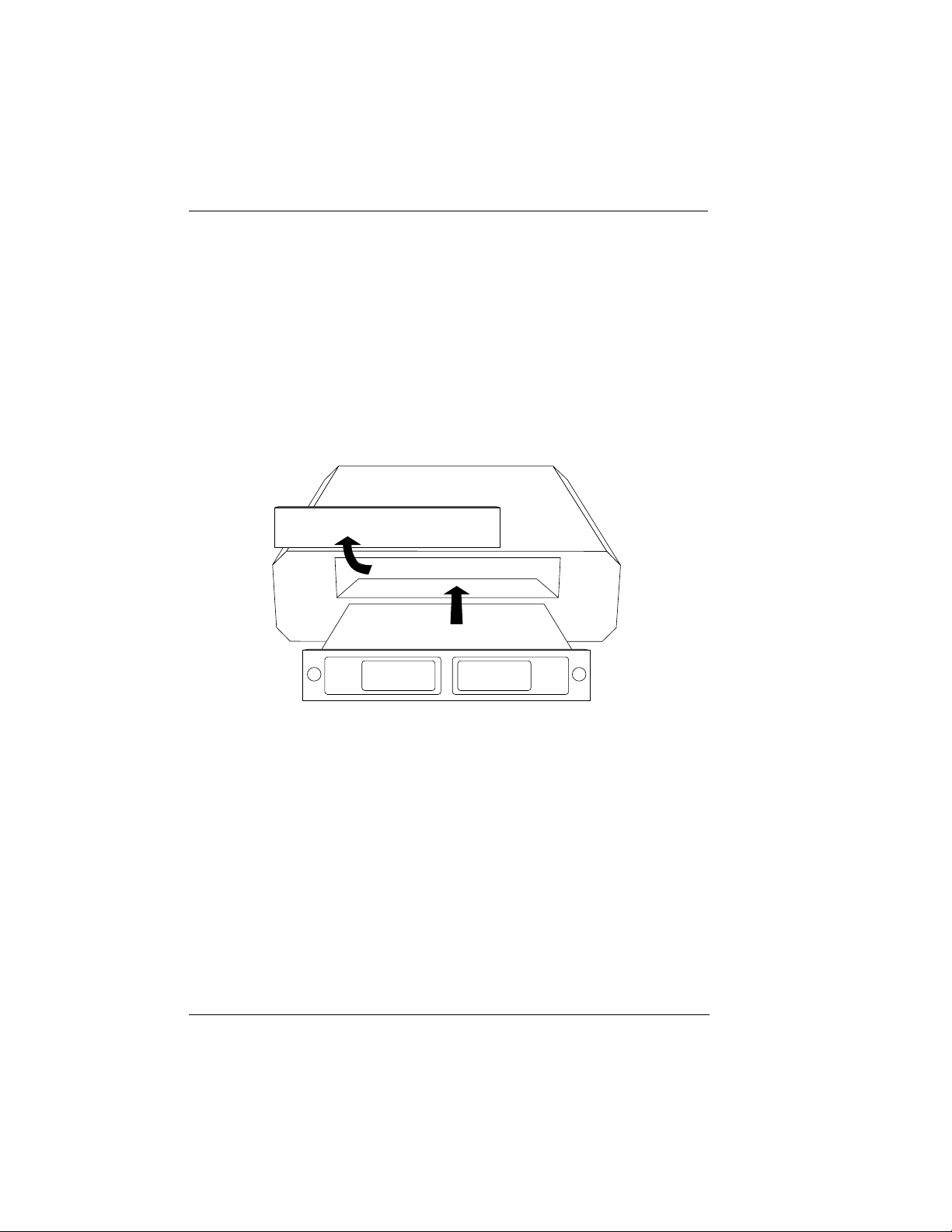
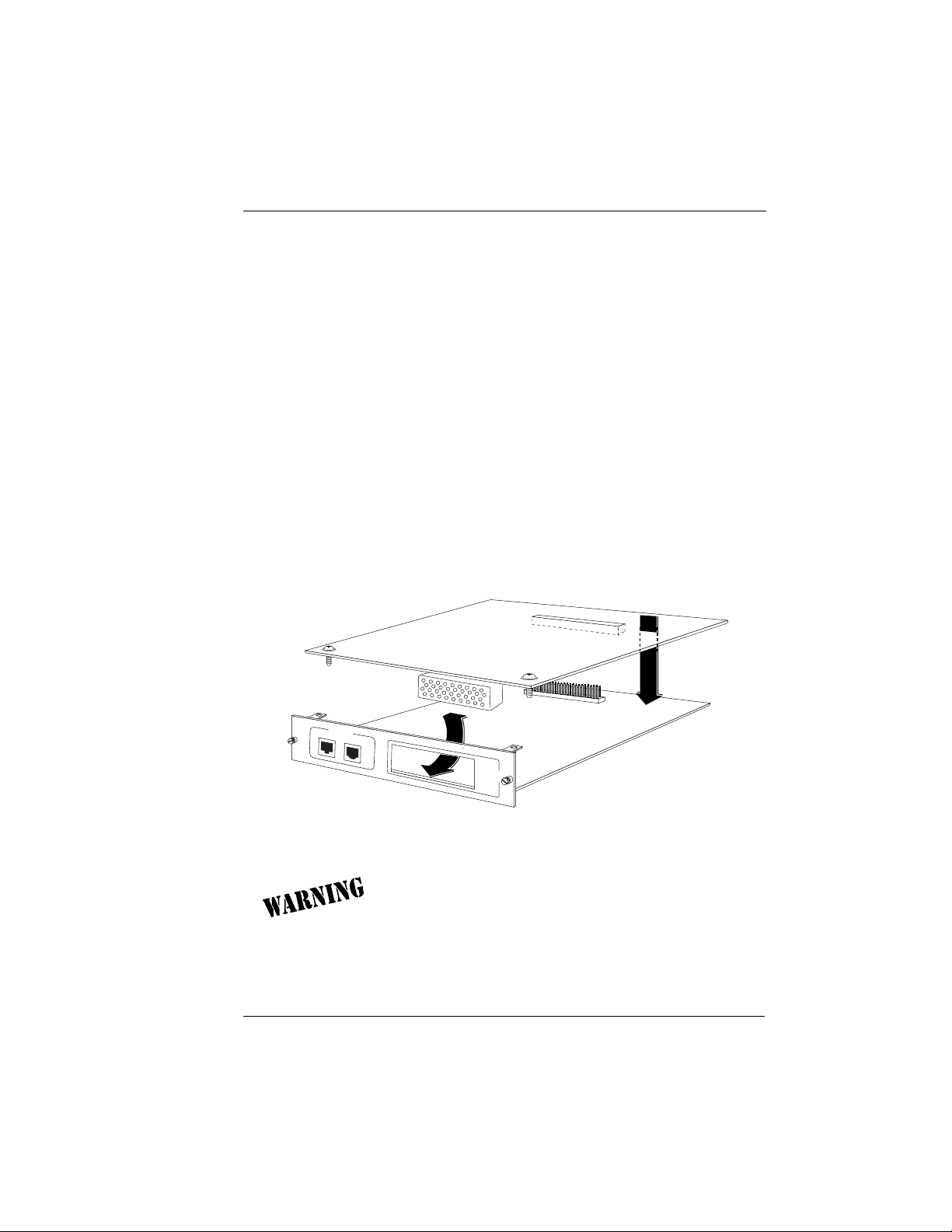
Figure 2-1 shows the proper placement of the option module. Perform the following steps to install the option module.
1. Remove the cover plate from the TSU/TDU unit rear panel.
2. Slide the option module into the rear panel of the TSU/TDU unit
until it is positioned firmly against the front of the unit.
3. Fasten the thumbscrews at both edges of the option module.
Cover Plate
TSU/HSU
UNIT
Option Module
2-2
Figure 2-1.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Installing the Option Module
Page 25
Power Connection
Each option module derives power from the base TSU/TDU unit.
Power to the TSU/TDU is supplied by a captive eight-foot power
cord.
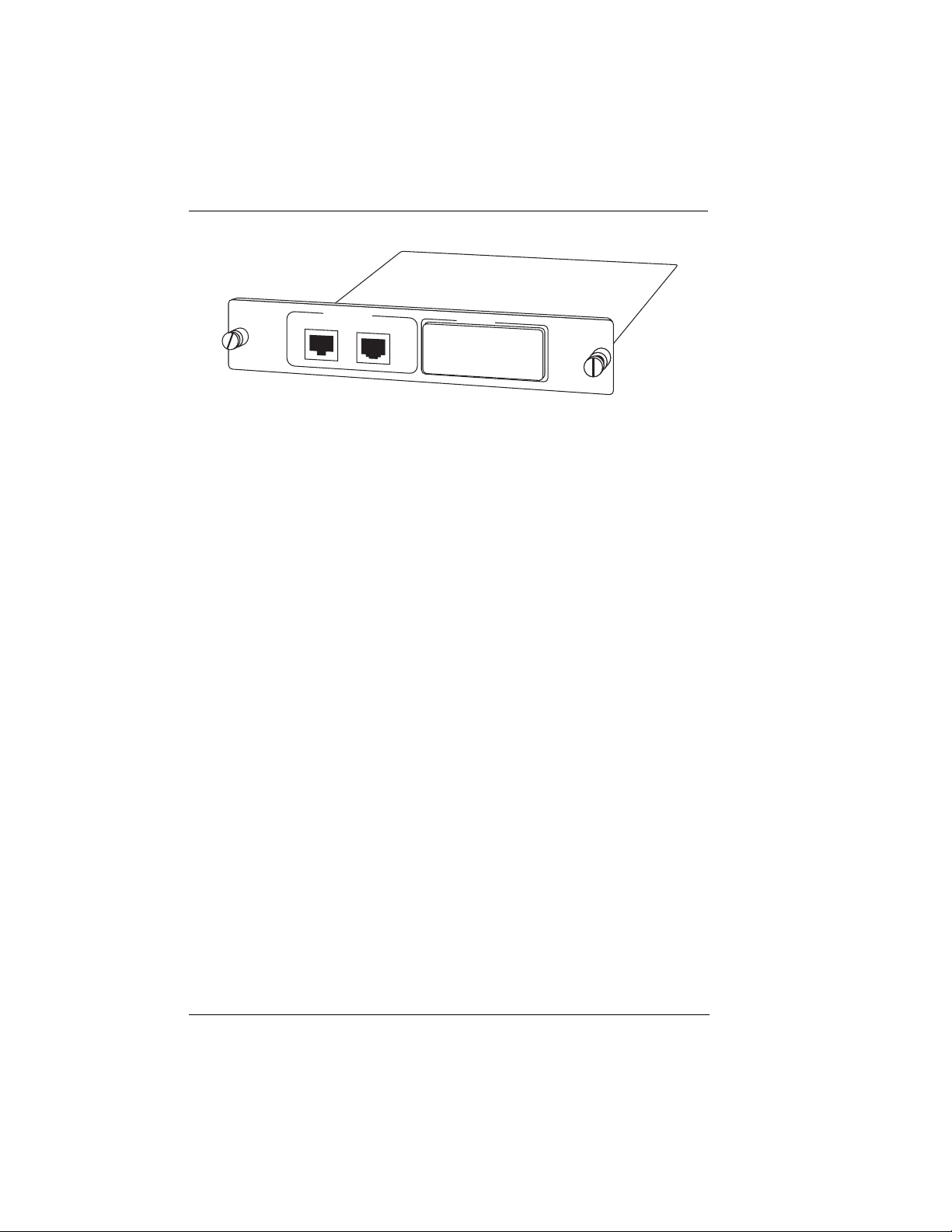
Attaching the Plug-On Board
Figure 2-2 shows the proper attachment of a plug-on board to the option module. Perform the following steps to install the plug-on
board:
1. Hold the plug-on board above the option module.
2. Using a downward and right-to-left motion, slip the V.35 Connector plug into opening in the option module back panel.
3. Moving the plug-on board downward, secure the connection of
the header pins at the front of the boards.
4. Install the two 4-40 screws at both edges of the option module.
Chapter 1: Introduction
ROUTER
X.1
CONTROL
10 BASE T
NX 56/64
PORT X.1
V.35
Figure 2-2.
Attaching the Plug-On Board
The connection of the header pins between the option module
and the plug-on board must be visually verified. Severe damage of the equipment can result from an improper connection.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
2-3
Page 26
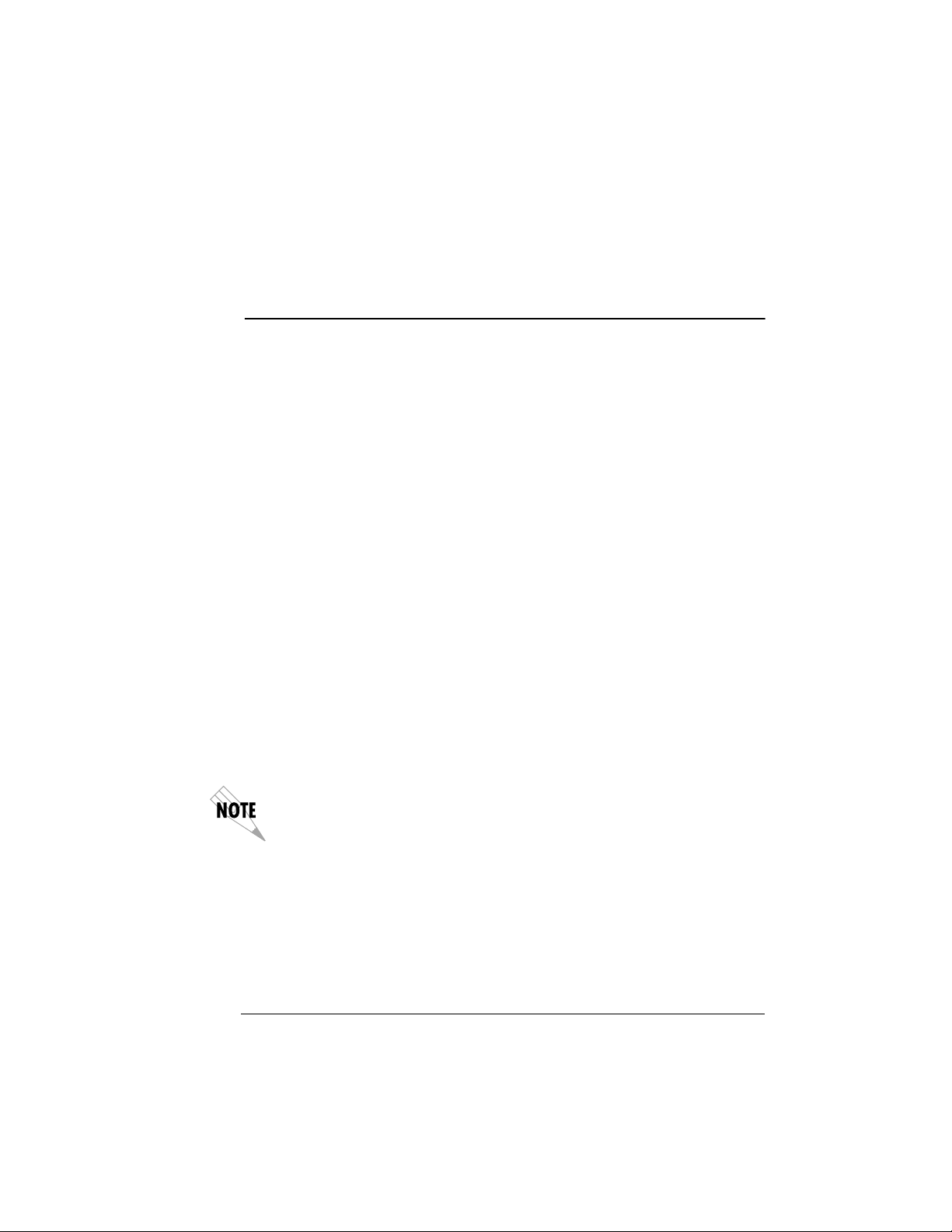
Chapter 2: Installation
CONTROL
HOT
REPLACEABLE
ROUTER
X.1
10 BASE T
PORT X.2
Control
The Router Option Module has an 8-pin modular jack labeled CONTROL. The control port provides connection to a VT 100 EIA-232
compatible interface. An 8-foot cable with adapter connector provides a standard DB-25 EIA-232 interface. See Appendix A: Pinouts
for the control port’s pin assignments. A description of the operation of this port is covered in Chapter 3: Operation.
10BaseT
The 10BaseT Port allows connection to a Local Area Network
(LAN). The 8-pin modular cable included with the Router Module
can be used to connect the 10BaseT port to an Ethernet AVB.
Figure 2-3.
Router Option Module Rear Panel
2-4
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 27
Chapter 3
FRONT PANEL
Refer to the TSU Product Manual for a description of front panel operation.
Terminal Menu Structure
The Router Option Module uses a multilevel menu structure containing both menu items and data fields. All menu operations and
data display in the terminal menu window. The Router Option Module is shipped in the Factory Default configuration. Connect any VT
100 or VT 220 type terminal emulator to the Maintenance port. The
default rate is 9600 baud 8-N-1. The terminal emulator can flow off
the Router Option Module using software flow control. Hardware
flow control is not used.
The opening menu (the Main menu, or top-level menu) is the access
point to all other operations. Each Main menu item has several functions and submenus to identify and access specific parameters.
Figure 3-1 on page 3-2 shows the top-level terminal menu.
Operation
In order to edit items in the terminal menus, you must have the appropriate
security level. Each menu description in this section indicates the required
security level required for write access. The maintenance port is always at
security level 0, giving full access to all configuration items.
Main Menu Options
The Main menu contains the following options.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
3-1
Page 28
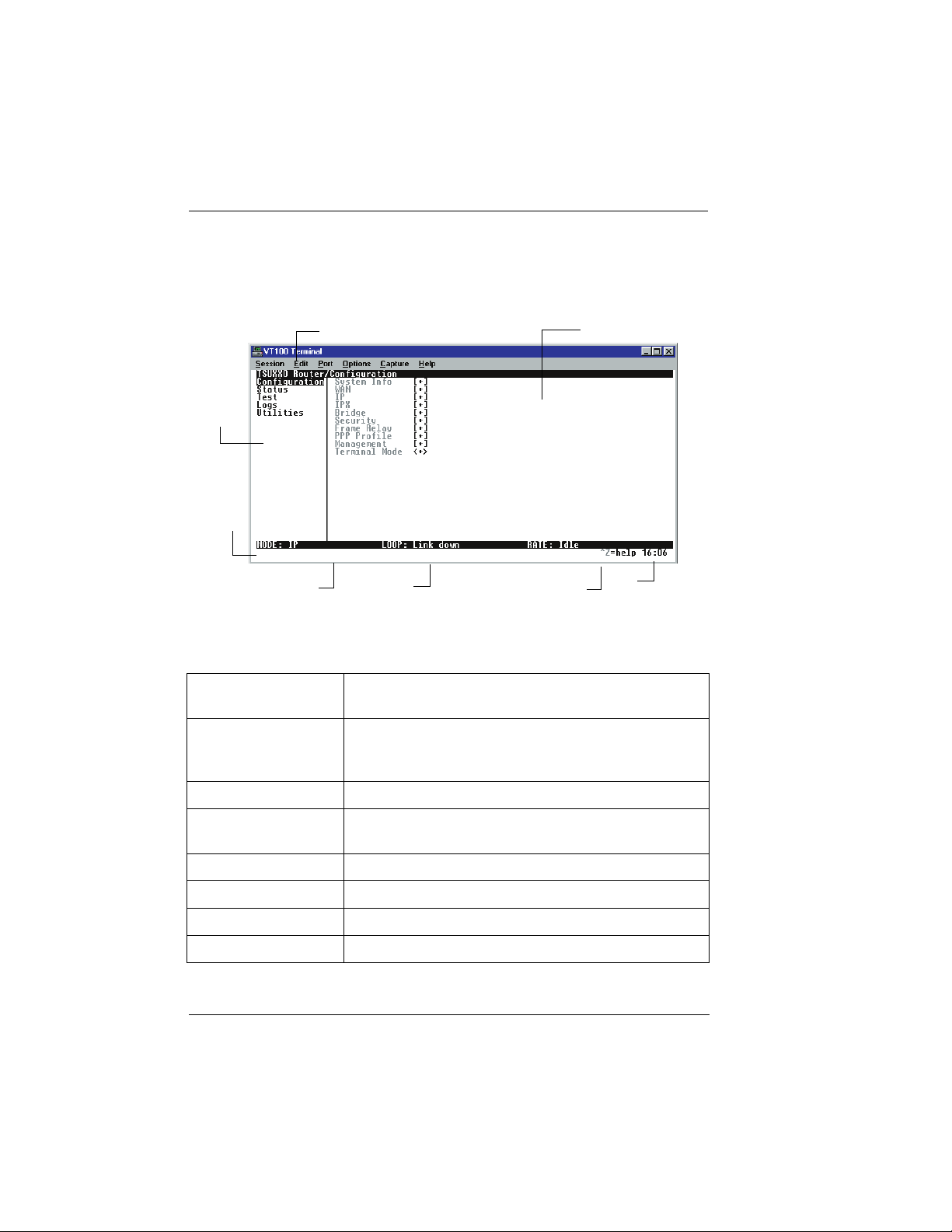
Chapter 3: Operation
Configuration Menu
The Configuration menu provides options to set up the operational
configuration for the Router Option Module. See Chapter 4, Configu-
ration Overview, for detailed information on the available options.
8
7
1
2
6
45
3
1. Menu Path Describes the current position in the terminal menu
structure.
2. Right Pane Lists available submenus. Additional submenus
available through this pane are indicated by the [+]
and [DATA] symbols.
3. System Time Displays the current time.
4. Navigation Help Displays list of characters you can use to navigate the
terminal menus. Press Control-Z
5. Rate Status Displays current rate of connection.
6. Loop Status Displays current status of T1.
7. Mode Describes current operating mode.
8. Left Pane Lists available menus.
Figure 3-1.
3-2
Top Level Terminal Menu
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 29
Chapter 3: Operation
Status Menu
The Status menu provides options to review and monitor the status
of the Router Option Module system. See Status Menu on page 5-1
for detailed information on the available options.
Test Menu
The Test menu can be used for performing diagnostic testing of the
Router Option Module. See Test Menu on page 6-1 for detailed infor-
mation on the tests available.
Logs Menu
The Logs menu can be used for viewing the operational logs for the
Router Option Module. See the Logs Menu on page 6-2 for detailed
information on the available options.
Utilities Menu
The Utilities menu provides tools for system diagnostics and upgrading the Router Option Module. See Utilities Menu on
page 7-1 for detailed information on the available options.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
3-3
Page 30
Chapter 3: Operation
NAVIGATING THE TERMINAL MENUS
The following sections provide information on how to navigate
through the terminal menus.
General Layout
When you first start a terminal mode session, the Top Level Terminal
Menu screen displays, as shown in Figure 3-1 on page 3-2. The screen
is divided into left and right panes. The left pane shows the current
list of submenus, while the right pane shows the contents of a selected submenu.
Menu Path
The top line of the display shows this session’s current position
(path) in the menu tree. Figure 3-1 on page 3-2 shows the top menu
level with the cursor on the Configuration submenu, so the path display shows Router/Configuration.
Moving Around
Use the following keys to navigate the menu:
3-4
If you want to... Press...
Move the cursor from the left pane
to the right pane.
Move the cursor from the right
pane back to the left pane.
Move around within each pane. Up and Down Arrows
Activate a menu. Enter Key
Travel back up the menu. Left Arrow Key or
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Tab Key or
Right Arrow Key
Tab Key or
Left Arrow Key
Escape Key
Page 31

Chapter 3: Operation
Reading Menu Options
The following options display throughout the menus.
Menu Option Description
Submenus [+] or [DATA] Menus that display [+] or [DATA]
indicate that more items are available
when selected.
Activation Field <+> Menus that display <+> indicate that
an action is to be taken, such as activating a test.
Editable Data Field A highlighted menu item indicates
that you can enter data in that field.
Read-Only Field An underlined field is a display field
that contains read-only information.
Navigating the Keyboard
You can use different keystrokes to navigate through the terminal
menu.
If you want to... Press...
Activate a pop-up screen with the available keystrokes.
Return to the home screen. H
Jump between two menu items. J
Example
Press J while on a menu item of interest, and you will jump
back to the main screen. Go to another menu item of interest,
Press J, and you will jump back to the screen that was displayed the first time you pressed J. Press J anytime you want
to jump between these items.
Select items. Arrow Keys
Move between the left and right panes. Arrow Keys
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
:
Control-Z
3-5
Page 32

Chapter 3: Operation
If you want to... Press...
Travel back up the menu. Left Arrow Key
Activate an item. Enter
Move into a submenu. Enter
Cancel an edit. Escape
Travel back up the menu. Escape
Dismiss the pop-up help screens. Escape
Move between the left and right panes. Tab
Move to the top of a screen. A
Move to the bottom of a screen. Z
Ascend one menu level. Backspace
Session Management
3-6
If you want to... Press...
Log out of the session. Control-L
Invalidate the password entry and return to the
login screen.
The Password prompt will display.
Refresh the screen.
To save time, only the portion of the screen that
has changed is refreshed. This option should be
necessary only if the display picks up incorrect
characters.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Control-S
Control-R
Page 33

Chapter 3: Operation
Configuration
If you want to... Press...
Restore factory default settings.
F
This setting restores the factory defaults based on
the location of the cursor. Entire submenus can be
factory defaulted.
Copy selected items to the clipboard. (The amount
C
of information you can copy depends on the cursor
location when you press C.)
Example:
If the cursor is over an editable field, only that item is copied. If the
cursor is over the index number of a list, then all of the items in the
row of the list are copied. For example, if the cursor is over the
Numb field in the Frame Relay Mapping screen, all of the information associated with the Map entry is copied.
Paste the item stored in the clipboard, if the infor-
P
mation is compatible. You must confirm all pastes
except those to a single editable field.
For certain types of fields, when you paste information into the field, the value increments by 1.
For certain types of fields, when you paste information into the field, the value decrements by 1.
Insert a new item in a list. I
Example:
To add a new item to the Connection List, press I
while the cursor is over the index number.
Delete a list item. D
Example:
To delete an item from the Connection List, press D
while the index number is active.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
3-7
Page 34

Chapter 3: Operation
Security Levels
Each menu item on the configuration screens has an associated security level. The security level ranges from 0 (highest security level)
to 5 (lowest security level). This level determines whether a Telnet
session can access that menu item. The Telnet session is assigned a
security level set by the user. Passwords can only be accessed at security level 0. The maintenance port is always at security level 0.
The security levels are assigned as follows:
Security
Level No.
Description
0 Access all parameters including passwords
1 Access all parameters except passwords
2 Access all parameters except passwords and
authentication methods
3 Access all parameters except passwords,
authentication methods
4 Access only test and status menus
5 Access status menus only
3-8
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 35

Chapter 3: Operation
TX BYTE
STATUS WAN RX BYTE
RX CRC
TX PCKTS
RX PCKTS
LAN TX ERRORS
RX ERRORS
1) DS0 RATE
CONFIG 1) WAN 2) L2 PROTOCOL
1) IP ADDRESS
2) LAN 2) SUBNET MASK
3) DEF GATEWAY
1) RATE
3) TERMINAL 2) DATA BITS
3) PARITY
4) STOP BITS
UTIL 1) SW REVISION
2) CMD MODE
TEST 1) PING UTILITY 2) NUM PCKTS
Figure 3-2.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
Router Option Module Front Panel Menu Structure
1) HOST ADDRESS
3) START/STOP
4) VIEW RESULTS
3-9
Page 36

Chapter 3: Operation
3-10
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 37

Chapter 4
Configuration Overview
CONFIGURATION MENU
Configuration/System Info
The System Info menu provides basic information about the unit and
displays data fields for editing information. Figure 4-1 displays the
submenus available under this menu item.
Figure 4-1.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
Configuration/System Info Screen
4-1
Page 38

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
System Name
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Provides a user-configurable text string for the name of the Router
Option Module. This name can help distinguish between different
installations. You can enter up to 31 alphanumeric characters in this
field, including spaces and special characters (such as an under bar).
The system name is also used for PPP authentication and IPX service name.
System Location
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Provides a user configurable text string for the location of the Router
Option Module. This helps to keep track of the physical location of
the unit. You can enter up to 31 alphanumeric characters in this
field, including spaces and special characters (such as an under bar).
System Contact
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Provides a user configurable text string for the contact name. This
field can contain a name, phone number, or e-mail address of a person responsible for the Router Option Module. You can enter up to
31 alphanumeric characters in this field, including spaces and special characters (such as an under bar).
4-2
Firmware Revision
Read security: 5
Displays the current firmware revision level of the Router Option
Module. This is a read-only field.
System Uptime
Read security: 5
Displays the length of time the Router Option Module has been running since power up or reset. This is a read-only field.
Date/Time
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Displays the current date and time as programmed in the real-time
clock. This field can be edited. Enter the time in 24-hour format
(such as 23:00:00 to represent 11:00 PM). Enter the date in mm-ddyyyy format.
Example
: 09-30-1998
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 39

Configuration/WAN
The WAN menu is used to set up the ISDN parameters for the Router Option Module. Figure 4-2 shows the WAN menu.
Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Figure 4-2.
Configuration/Frame Relay Screen
WAN/DSO Rate
WAN/L2 Protocol (also available via Front Panel)
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This parameter specifies the layer 2 data link layer transport used.
When selected as PPP (def), the Router Option Module will negotiate PPP over the T1 interface. This would be used mainly for campus wiring applications.
Parameters for controlling the PPP negotiation are in the Configu-
ration/PPP Profile menu. Frame Relay should be selected when the
Router Option Module is connected to a Frame Relay switch. The
Configuration/Frame Relay menu is used for controlling the Frame
Relay parameters.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-3
Page 40

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Configuration/IP
The IP menu is used to set up the IP parameters for the Router Option Module. Any general IP-related configuration item is under
this menu. Figure 4-3 shows the IP menu.
4-4
Figure 4-3.
Configuration/IP Screen
IP/IP Address (also available via Front Panel)
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The IP address assigned to the Router Option Module’s Ethernet
port is set here. This address must be unique within the network.
Factory default is 10.0.0.1.
IP/Subnet Mask (also available via Front Panel)
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The IP network mask to be applied to the Router Option Module’s
Ethernet port is set here. Factory default is 255.255.255.0.
IP/Default Gateway (also available via Front Panel)
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
The default gateway is used by the Router Option Module for sending IP packets whose destination address is not found in the route
table. If this address is all zeros, then the first WAN connection becomes the default gateway.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 41

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP/Static Routes
Static Routes can be inserted under this menu.
Static Routes/Active
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
Adds this static route entry to the IP routing table when set to Yes
(def) and removes it (if it was previously added) if set to No.
Static Routes/IP Address
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
This is the IP address of the host or network address of the device
being routed to.
Static Routes/Subnet Mask
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
This mask determines the bits in the previous IP address that are
used. If this is to be a host route, it must be set to all ones
(255.255.255.255).
Static Routes/Gateway
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
This is the IP address of the router to receive the forwarded IP packet.
Static Routes/Hops
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
This is the number of router hops required to get to the network or
host. Maximum distance is 15 hops.
Static Routes/Private
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
When set to No, the Router Option Module will advertise this static
route using RIP. Otherwise, setting to Yes means that the route is
kept private.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-5
Page 42

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP/IP Router
The IP router is configured under this menu as follows.
IP Router/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When this option is set to On (def), the Router Option Module will
advertise and listen to routes from other IP routers.
If Off, the route table is still used but only static routes are used for
routing IP packets and only the Ethernet port is used. IP packets can
be sent over the WAN, but only when bridged.
IP/RIP
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is supported by the Router
Option Module. The following parameters are required for setting
up the mode on the Ethernet port:
RIP/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This option turns RIP On (def) or Off.
4-6
RIP/Protocol
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Version can be V1 (def) or V2.
RIP/Method
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
• Split Horizon - Only routes not learned on the Ethernet port are
advertised
• Poison Reverse (def) - All routes are advertised, including routes
learned from the Ethernet port. These routes are poisoned.
• None - All routes are advertised, including routes learned from
the Ethernet port. No attempt is made to poison these routes.
RIP/Direction
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
• Tx and Rx (def) - RIP advertisements are transmitted and received on the Ethernet port.
• Tx only - RIP advertisements are transmitted and not received.
• Rx only -RIP advertisements are received but not transmitted
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 43

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
RIP/V2 Secret
Write security: 0; Read security: 0
This is a text string used for authenticating advertised routes.
IP/NAT
The Network Address Translation general parameters are set up
under this menu.
NAT/DHCP Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When this option is set to On, the Router Option Module acts as a
DHCP server and will dynamically assign IP, network mask, default gateway, and DNS addresses to any device which transmits a
broadcast DHCP request. The addresses assigned are based on the
Router Option Module’s own IP address and will be within the
same network. This mode is most commonly used with the NAT
functionality. The default is Off.
NAT/DHCP Renewal Time
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the number of hours that the DHCP server should allow the
device before it is required to send a new DHCP request. The default
is 15 hours. Zero (0) represents an infinite lease.
NAT/Web Server
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the IP address of a web server on the Ethernet network.
When an active NAT connection is made to the Internet, any HTTP,
FTP, or SMTP server requests from the WAN are translated and sent
to this web server.
Normally, communications across NAT must be initiated from the
LAN side of the Router Option Module. Web server allows a single
machine on the NAT side to be accessed from the Internet side of
NAT. This provides outside access to a Web server, mail, or FTP
server.
NAT/Default IP
This is the IP address used by the Router Option Module for Network Address translation when nothing is assigned during the PPP
negotiation when PPP mode is active or when nothing is specified
in the DLCI Mapping Link IP Address.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-7
Page 44

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP/DNS
The Domain Name Server parameters used by the Router Option
Module are specified here. The DNS server addresses can be exchanged between PPP peers. When a connection occurs and IPCP is
negotiated, the Router Option Module will get the DNS server addresses from the PPP peer.
If the configured DNS server addresses (Server 1 and Server 2) are
all zeros, the addresses from the PPP peer are used. In NAT mode,
the PPP peer’s DNS addresses are always used. The DNS addresses set
in Server 1 and Server 2 are offered to a PPP peer, if so requested.
DNS/Domain Name
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is a text string used to represent the domain name used by the
Router Option Module.
DNS/Server 1
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the IP address for the primary DNS device. It is the first server to which domain name requests are sent.
DNS/Server 2
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the IP address for the secondary DNS device. It is used as a
back-up in case the primary address does not respond to the request.
IP/UDP Relay
The Router Option Module can be configured as a relay agent for
UDP broadcast packets. Normally, a router will not forward UDP
broadcast packets. However, many network applications use UDP
broadcasts to configure addresses, host names, and other information. If hosts using these protocols are not on the same network segment as the servers providing the information, the client programs
will not receive a response without enabling the UDP relay agent.
UDP Relay/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When this option is set to On (def), the Router Option Module will
act as a relay agent.
4-8
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 45

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
UDP Relay/UDP Relay List
Up to four relay destination servers can be specified in this list.
UDP Relay List/Relay Address
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the IP address of the server that will receive the relay packet.
UDP Relay List/UDP Port Type
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Standard (def)
The following standard UDP protocols are relayed when set:
• DHCP, TFTP, DNS,
• NTP (NetworkTime Protocol, port 123). NBNS (NetBIOS Name
Server, port 137), NBDG (NetBIOS Datagram, port 138),
• BootP.
Specified
• When set, the UDP port (1 to 65535) can be specified in the UDP
Port columns (up to a maximum of three per server).
UDP Relay List/UDP Port 1, UDP Port 2, UDP Port 3
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
UDP Port 1, UDP Port 2, and UDP Port 3 are used for specifying
UDP ports to be relayed. These fields only apply when UDP Port
Type is set to Specified.
IP/Proxy ARP
Write security: 4; Read security: 5
This feature allows the network portion of a group of addresses to
be shared between several physical network segments. The ARP
protocol itself provides a way for devices to create a mapping between physical (i.e., Ethernet) addresses and logical IP addresses.
Proxy ARP makes use of this mapping feature by instructing a router to answer ARP requests as a “proxy” for the IP addresses behind
one of its ports. The device which sent the ARP request will then
correctly assume that it can reach the requested IP address by sending packets to the physical address that was returned to it. This technique effectively hides the fact that a network has been (further)
subnetted.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-9
Page 46
Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
If this option is set to Yes (def), when an ARP request is received on
the Ethernet port, the address is looked up in the IP routing table. If
the forwarding port is not on the Ethernet port and the route is not
the default route, the Router Option Module will answer the request
with its own hardware address.
If set to No, the Router Option Module will only respond to ARP requests received for its own IP address.
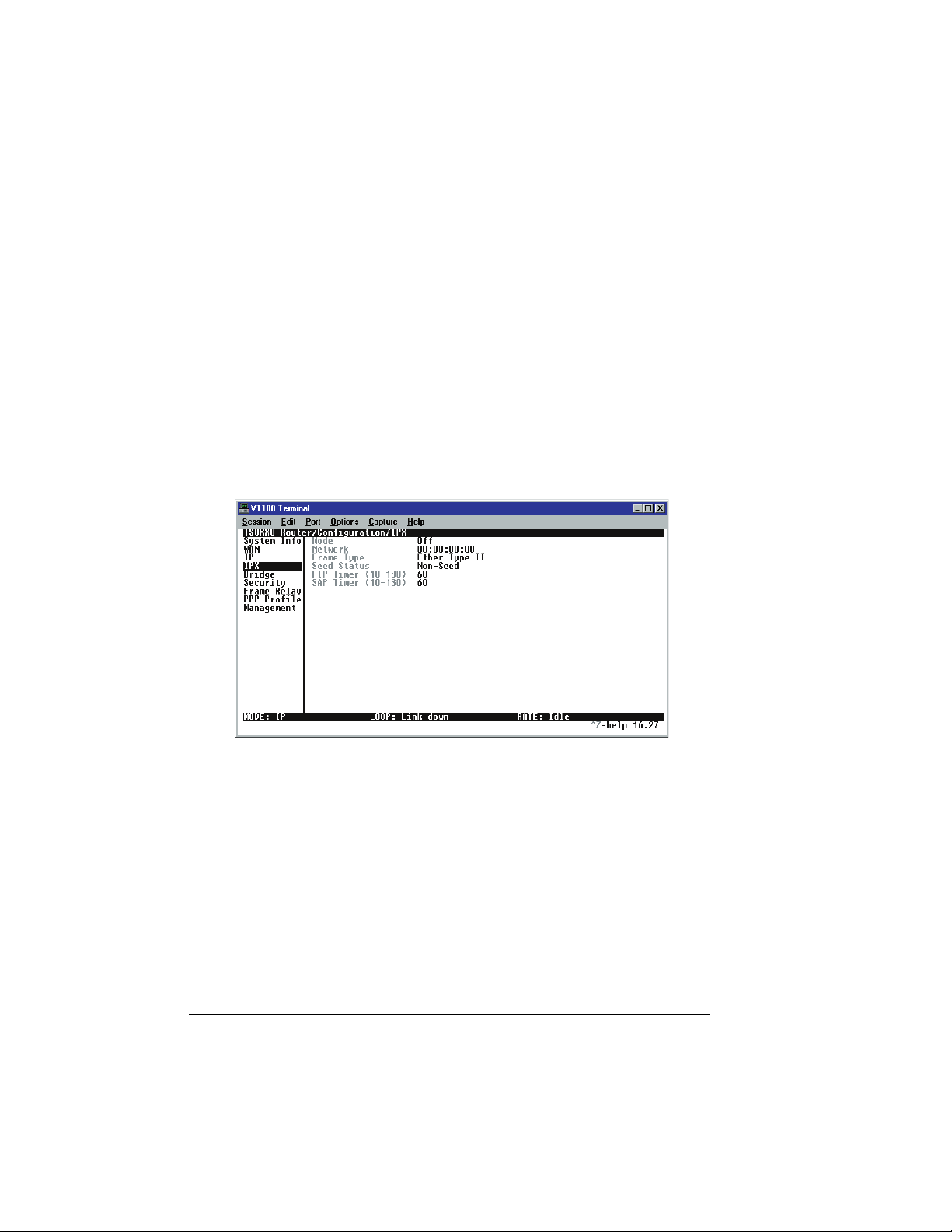
Configuration/IPX
The IPX menu is used to set up the IPX parameters for the Router
Option Module. Any general IPX-related configuration item can be
found under this menu. Figure 4-4 shows the IPX menu.
4-10
Figure 4-4.
Configuration/IPX Screen
IPX/Mode
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When this option is set to On (def), the Router Option Module will
route IPX. Setting it to Off will disable all IPX functionality.
IPX/Network
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The IPX network address for the Ethernet port is set here. This is an
eight-digit hexadecimal value that uniquely identifies the network
segment of the Ethernet port. Accidental selection of an IPX network which is already in use on another network segment may
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 47

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
cause hard-to-diagnose problems. IPX network numbers should be
carefully tracked.
IPX/Frame Type
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The Router Option Module supports all four defined IPX frame
types. The possible frame types are: Ether Type II (def), Ether 802.3
(Raw), Ether 802.2, or Ether SNMP (802.2 SNMP). Only one frame
type can be used at one time.
IPX/Seed Status
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The seed status defines what the Router Option Module is to do
with the network information on the selected frame type during
startup. There are three possible seeding selections specified:
Seeding Selection Description
Seed The Router Option Module will listen for
an IPX network number being sent by
another router (including Novell software
routers residing on servers) on the Ethernet
segment connected to this port and use this
number if it exists. If it doesn’t discover a
number in use, the Router Option Module
will use the configured IPX network number for the Ethernet segment.
Non-Seed (def) The Router Option Module will listen for
an IPX network number being sent by
another router (including Novell software
routers residing on servers) on the Ethernet segment connected to this port and use
this number if it exists. If it doesn’t discover a number in use, the Router Option
Module will wait indefinitely until a number is sent by another router on the Ethernet segment.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-11
Page 48

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Seeding Selection Description
Auto-Seed The Router Option Module will listen for
IPX/RIP Timer
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This value specifies how often the Router Option Module sends out
IPX RIP packets on the network segment attached to the Ethernet
port. The RIP packets sent contain routing information about the
networks for which this Router Option Module is responsible. The
default value is 60 seconds.
IPX/SAP Timer
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This value specifies how often the Router Option Module sends out
IPX SAP (Service Access Protocol) packets on the network segment
attached to the Ethernet port. The SAP packets sent contain information about the services (such as servers, printers, etc.) for which
this Router Option Module is responsible. The default value is 60
seconds.
an IPX network number being sent by
another router (including Novell software
routers residing on servers) on the Ethernet segment connected to this port and use
this number if it exists. If it doesn’t discover a number in use, the Router Option
Module will auto-generate a valid number
using its routing tables.
4-12
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 49

Configuration/Bridge
The Bridge menu is used to set up the bridge parameters for the
Router Option Module. The bridging function runs at the Media Access Control (MAC) level which allows any protocol packets that
run over Ethernet to be forwarded. Bridging can run concurrently
with the IP and IPX routing. However, when packets are bridged
across a WAN connection, the following rules apply:
• When IP routing is active, IP packets (which include ARP packets) are not bridged.
• When IPX routing is active, IPX packets are not bridged.
• The WAN IP Bridge and WAN IPX Bridge menus allow the
WAN connection to bridge packets to the Router Option Module
but get routed as soon as they arrive at the unit.
Figure 4-5 shows the Bridge menu.
Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Figure 4-5.
Configuration/Bridge Screen
Bridge/Mode
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When this option is set to On (def), the Router Option Module
bridge function will be enabled. Setting it to Off will disable all
bridge functionality.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-13
Page 50

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Bridge/WAN IP Bridge
When IP routing is active, the Router Option Module will allow another WAN device to bridge IP packets to itself by using PPP BCP.
Normally, two IP routers would negotiate PPP IPCP to exchange IP
packets.
However, if a device can only support PPP BCP, IP packets are encapsulated by the device as bridge packets. The Router Option
Module can treat the WAN IP Bridge as a virtual Ethernet port connected only to a WAN device which has negotiated PPP BCP. This
menu allows the IP parameters for this virtual Ethernet to be set up.
WAN IP Bridge/Network
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the IP address of the virtual Ethernet port.
WAN IP Bridge/Netmask
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the network mask to be applied to the virtual Ethernet port.
WAN IP Bridge/Triggered
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When set to Yes, only IP RIP updates are sent when the routing table
has changed. When set to No (def), updates are sent periodically.
RIP version, method, and direction are determined by the Ethernet
parameters set in the Configuration/IP/IP Router/RIP menu.
WAN IP Bridge/Proxy ARP
If this option is set to Yes (def), the Router Option Module will
proxy ARP on the bridge IP port. See the section IP/Proxy ARP on
page page 4-9 for an explanation of the proxy ARP function.
Bridge/WAN IPX Bridge
When IPX routing is active, the Router Option Module will allow
another WAN device to bridge IPX packets to it using PPP BCP.
Normally, two IPX routers would negotiate PPP IPXCP to exchange
IPX packets. However, if a device can support only PPP BCP, IPX
packets are encapsulated by the device as bridge packets. The Router Option Module can treat the WAN IPX Bridge as a virtual Ether-
4-14
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 51

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
net port connected only to a WAN device which has negotiated PPP
BCP. This menu allows the IPX parameters for this virtual Ethernet
to be set up.
WAN IPX Bridge/Network
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the network address of the virtual Ethernet port. See IPX/Net-
work on page page 4-10 for explanation of the IPX network number.
WAN IPX Bridge/Frame Type
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the frame type used for the virtual Ethernet port. See IPX/
Frame Type on page page 4-11 for an explanation of the IPX frame
type.
WAN IPX Bridge/Seed Status
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the seed status used for the virtual Ethernet port. See IPX/
Seed Status on page page 4-11 menu for an explanation of the IPX seed
status.
WAN IPX Bridge/Triggered
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When set to Yes, only IPX RIP and SAP updates are sent when the
routing or service table has changed. When set to No (def), updates
are sent at the same rate set for the Ethernet port (see IPX/RIP Timer
and IPX/SAP Timer on page page 4-12).
Bridge/Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol ensures a loop-free topology and provides redundancy. The protocol parameters can be
specifically tuned from their defaults, though most applications require no adjustment.
Spanning Tree/Mode
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When the mode is set to On, the Router Option Module will
participate in the spanning tree protocol between other bridges.
When Off (def), all bridge ports remain permanently open for forwarding.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-15
Page 52

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Spanning Tree/Priority
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This assigns a priority to the Router Option Module that permits the
relative priority of multiple bridges to be managed. The range is 0
to 65535 with a default of 32768.
Spanning Tree/Maximum Age
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the timeout value used by the Router Option Module to test
against the root device. The value is in one-tenth seconds with a
range between 60 (6.0 seconds) and 400 (40.0 seconds). The default
is 200 (20.0 seconds).
Spanning Tree/Hello Time
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the time between the generation of configuration BPDUs
(Bridging Protocol Data Units) by the root bridge. The value is in
one-tenth seconds with a range between 10 (1.0 second) and 100
(10.0 seconds). The default is 20 (2.0 seconds).
Spanning Tree/Forward Delay
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the time spent in the listening and learning state while moving from the blocking state to the forwarding state. The value is in
one-tenth seconds with a range between 40 (4.0 seconds) and 300
(30.0 seconds). The default is 150 (15.0 seconds).
4-16
Spanning Tree/LAN Port
The path cost and priority parameters for the Ethernet port are specified under this menu.
LAN Port/Active
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The Ethernet port can be disabled when set to No. In this mode, no
bridge traffic will be forwarded in or out. Setting to Yes (def) allows
the port to participate in the spanning tree topology.
LAN Port/Path Cost
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the cost of using the Ethernet port in the total cost of the path.
The range is from 1 to 65535 with a default of 100 (for 10 Mbits/second).
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 53

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
LAN Port/Priority
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The priority adjusts the relative priority of the Ethernet port among
the multiple bridge ports. The range is 0 to 255 with a default of 128.
Spanning Tree/Bridge Group 1
The Bridge Group 1 is either the first PPP BCP connection or part of
multiple DLCI destinations when running Bridge (RFC 1490) over
Frame Relay.
Bridge Group 1/Active
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The Bridge Group 1 port can be disabled when set to No. In this
mode, no bridge traffic will be forwarded in or out. Setting to Yes
(def) allows the port to participate in the spanning tree topology.
Bridge Group 1/Path Cost
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is the cost of using the Bridge Group 1 in the total cost of the
path. The range is from 1 to 65535 with a default of 1302 (for 768
kbits/second).
Bridge Group 1/Priority
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The priority adjusts the relative priority of the Bridge Group 1
among the multiple bridge ports. The range is 0 to 255 with a default of 128.
Spanning Tree/Bridge Group 2
Bridge Group 2 is part of multiple DLCI destinations when running
Bridge (RFC 1490) over Frame Relay.
Bridge Group 2/Active
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This setup is exactly like Bridge Group 1 above.
Bridge Group 2/Path Cost
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This setup is exactly like Bridge Group 1 above.
Bridge Group 1/Priority
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This setup is exactly like Bridge Group 1 above.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-17
Page 54

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Bridge/Address Table
The Router Option Module automatically maintains a table of MAC
addresses detected and associates those addresses with the LAN,
WAN0, or WAN1 port from which they were received. WAN0 represents Bridge Group 1, and WAN1 represents Bridge Group 2. This
menu permits the user to adjust the parameters or rules for the table
as addresses are learned.
Address Table/Aging
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This is the maximum time an idle MAC address remains in the table
before being removed. The value is in minutes and can range from
0 (which means never age) to 65535. The default is 5.
Address Table/Forward Policy
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When this parameter is set to Unknown (def), any bridge packet
with a destination MAC address that is not in the bridge table is forwarded to all other ports. When set to Known, the packet with the
unknown destination MAC address is dropped and is not forwarded.
4-18
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 55

Configuration/Security
The Security menu is used to set up the authentication parameters
needed to authenticate PPP connection. Also, the filter defines are
placed under this menu. Figure 4-6 shows the Security menu.
Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Figure 4-6.
Configuration/Security Screen
Security/Authentication
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
The method used for authenticating the PPP peer is selected here.
The possible values are:
None (def) - No attempt is made to authenticate the PPP peer.
Radius - The Router Option Module will act as a radius client and
authenticate the PPP peer using the radius server. The radius server
parameters must be set up properly for this to work.
PPP Profile - The PPP profile is used to authenticate the PPP peer.
See the Frame Relay section on page 4-26 for more information on au-
thenticating.
Security/Radius Server
The parameters for the radius server are configured in this menu.
The radius server can be used for authenticating a PPP peer (if defined under Security/Authentication) and for Telnet server ses-
sions.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-19
Page 56

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Radius Server/Primary Server
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
This is the IP address of the first RADIUS server that the Router Option Module should attempt to communicate with when authenticating a PPP peer.
Radius Server/Secondary Server
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
This is the IP address of the back-up RADIUS server that the Router
Option Module should attempt to communicate with when the primary server does not respond.
Radius Server/UDP Port
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
This is the UDP port that the Router Option Module should use
when communicating with the RADIUS server. The default is 1645,
which is the commonly used port.
Radius Server/Secret
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
The RADIUS server and Router Option Module share this text
string, which is used by the RADIUS sever to authenticate the Router Option Module that is the RADIUS client. The factory default is
to not use a secret.
4-20
Radius Server/Retry Count
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
This is the number of times the Router Option Module should send
a request packet to the RADIUS server without a response before
giving up.
If the number of attempts to communicate with the primary server
is equal to the retry count, the secondary server (if defined) is tried.
If the secondary server does not respond within the retry count, the
PPP peer (or Telnet session) is not authenticated and is dropped.
The default is 5.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 57

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Security/PPP
Write security: 1; Read security: 2
The PPP peer can be authenticated using three standard methods:
1. PAP (Password Authentication Protocol),
2. CHAP (Challenge Handshake Protocol)
3. EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol).
The strength of the authentication is determined in the following order:
1. EAP
2. CHAP
3. PAP (where EAP is the strongest and PAP is the weakest)
PAP is a clear-text protocol, which means it is sent over the PPP link
in a readable format.
Do not allow highly sensitive passwords to become compromised using this
method.
CHAP and EAP use a one-way hashing algorithm which makes it
virtually impossible to determine the password. EAP has other capabilities which allow more flexibility than CHAP.
The following selections are possible:
PAP, CHAP or EAP (def) - The Router Option Module will ask for
EAP during the first PPP LCP negotiation and allow the PPP peer to
negotiate down to CHAP or PAP.
CHAP or EAP - The Router Option Module will ask for EAP during
the first PPP LCP negotiation and allow the PPP peer to negotiate
down to CHAP but not PAP.
EAP - The Router Option Module will only allow EAP to be negotiated. If the PPP peer is not capable of doing EAP, then the connection will not succeed.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-21
Page 58

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Security/Filter Defines
The Router Option Module can filter packets based on certain parameters within the packet. The method used by the Router Option
Module allows the highest flexibility for defining filters and assigning them to a profile. The filters are set up in two steps:
1. Defining the packet types,
2. Adding them to a list under the PPP profile or DLCI map.
See the section DLCI Mapping/Filters on page 4-32 for information on
how to set up filter profiles. This menu is used to define the individual filter defines based on packet type.
Filter Defines/MAC Filter Defines
Write security: 2; Read security: 3
The MAC filter is applied to bridge packets only. Bridge packets
which are forwarded by the bridge functionality of the Router Option Module are defined here. Up to 32 MAC defines can be specified.
Name Identifies the filter entry
Src Addr 48-bit MAC source address used for compari-
son. (hexadecimal format)
4-22
Src Mask Bits in the MAC source address which are com-
pared. (hexadecimal format)
Dest Addr 48-bit MAC destination address used for com-
parison. (hexadecimal format)
Dest Mask Bits in the MAC destination address used for
comparison. (hexadecimal format)
MAC Type 16-bit MAC type field used for comparison.
(hexadecimal format)
Type Msk Bits in the MAC type field used for comparison.
(hexadecimal format)
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 59

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Filter Defines /Pattern Filter Defines
Write security: 2; Read security: 3
The pattern filter is applied to bridge packets only. That is any pack-
et which is forwarded by the bridge functionality of the Router Option Module. Up to 32 pattern defines can be specified.
Name Identifies the filter entry
Offset Offset from beginning of packet of where to start the
pattern comparison
Pattern 64 bits used for comparison. (hexadecimal format)
Mask Bits in the pattern to be compared.(hexadecimal for-
mat)
Filter Defines/IP Filter Defines
Write security: 2; Read security: 3
The IP filter defines apply to any IP packet, whether it is routed or
bridged. Up to 32 IP defines can be specified.
Name Identifies the filter entry
IP Src IP address compared to the source address.
(dotted decimal format)
Src Mask Bits which are used in the source comparison.
(dotted decimal format)
IP Dest IP address compared to the destination address.
(dotted decimal format)
Dest Mask Bits which are used in the destination compari-
son. (dotted decimal format)
Src Port IP source port number used for comparison.
Range: 0 to 65535. (decimal format)
Src Port
Type of comparison that is performed:
Cmpr
= -- port equal to
not = -- port not equal to
> -- port greater than
< -- port less than
None - the source port is not compared
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-23
Page 60

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Dst Port IP destination port number used for comparison
Range: 0 to 65535. (decimal format)
Dst Port
Cmpr
Type of comparison that is performed:
= -- ports equal to
not = -- port not equal to
> -- port greater than
< -- port less than
None -- the destination port is not compared
Proto Protocol used for comparison.
Range: 0 to 255. (decimal format)
Proto Cmpr Type of comparison that is performed:
= -- protocols equal to
not = -- protocols not equal to
> -- protocols greater than
< -- protocols less than
None -- the protocol is not compared
TCP Est Yes - only when TCP established
No - only when TCP not established
Ignore - ignore TCP flags
Filter Defines /IPX Filter Defines
Write security: 2; Read security: 3
The IPX filter defines apply to any IPX packet whether it is routed
or bridged. Also, any IPX encapsulation type will be accounted for.
Up to 32 IPX defines can be specified.
4-24
Name Identifies the filter entry (15 characters, max)
Src Net 32-bit source network address
Src Mask Bits in the source network address which are com-
pared. (hexadecimal format)
Dest Net 32-bit destination network address
Dest
Mask
Bits in the destination network address which are
compared. (hexadecimal format)
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 61

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Src
Socket
Src
Socket
Comp
16-bit value which is the source socket.
Range:0-65535.
Type of comparison that is performed:
= -- socket equal to
Not = -- socket not equal to
> -- socket greater than
< --socket less than
None -- no comparison is done on source socket
Dest
Socket
Dest
Socket
Comp
16-bit value which is the destination socket. Range
is 0-65535.
Type of comparison that is performed:
= -- socket equal to
Not = -- socket not equal to
> -- socket greater than
< -- socket less than
None -- no comparison is done on destination
socket
Type 8-bit value which is the IPX type
Type
Comp
Type of comparison that is performed:
= -- type equal to
Not = -- type not equal to
> -- type greater than
< -- type less than
None --no comparison is done on IPX type
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-25
Page 62

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Frame Relay
(also available via Front Panel)
Frame Relay is a connection-oriented service requiring circuits to be
configured by your carrier to establish a physical link between two
or more locations. Multiple virtual circuits (which appear as virtual
point-to-point links) can be run through the same physical connection.
There are two types of virtual circuits supported in Frame Relay:
Virtual Circuit Types Description
Permanent Virtual Circuits
(PVC)
PVCs are like dedicated point-to-point
private lines.
Since the physical connection is always
there in the form of a leased line, call
setup and tear down is done by a carrier via a network management system.
Virtually all Frame Relay communication is done using PVCs.
Switched Virtual Circuit
(SVC)
SVCs require setup and tear down and
are generally not available from Frame
Relay carriers.
The Router Option Module supports PVCs only.
The Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) number identifies each
virtual circuit within a shared physical channel.
4-26
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 63

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Frame Relay/Maintenance Protocol
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The Frame Relay maintenance protocol is used on the WAN port.
The maintenance protocol is used to send link status and virtual circuit information between Frame Relay switches and other devices
(such as routers) that communicate with them. Possible choices are
listed below.
Annex D(def) An ANSI standard that is most commonly used
in the US.
Annex A The CCITT European standard.
LMI Used by some carriers in the U.S.
Developed by a vendor consortium and known
as the “consortium” management interface spec-
ification.
Static Select when there is no Frame Relay switch in
the circuit. The DLCIs are assigned in the DLCI
Mapping and must be the same for the device it
will communicate with.
Frame Relay/Polling Frequency
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This parameter is the interval that the Router Option Module polls
the Frame Relay switch using the maintenance protocol selected
above. The Router Option Module is required to poll the Frame Relay switch periodically to determine whether the link is active. The
value is in seconds and ranges from 5 to 30 seconds.
Frame Relay/DLCI Mapping
This menu allows each DLCI to be mapped to a particular protocol.
Each protocol parameter can be individually configured for each
DLCI. By factory default, the DLCI map is empty.
When empty and a maintenance protocol other than static is used,
the Router Option Module will poll the switch to determine which
DLCIs are active. These active DLCIs will attempt to determine the
IP and IPX addresses on the other end of the virtual circuit using Inverse ARP (IARP). If there is a response, the network learned will be
added to the router tables and the virtual circuit will be treated as an
unnumbered interface. Bridge mode is not attempted in this case.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-27
Page 64

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
When more than one DLCI mapping is listed, the Router Option
Module will try to match the DLCIs learned from the Frame Relay
switch with the DLCI values in the map. If there is a match, the protocols specified in the map are used. However, if an active DLCI is
not in the list, the Router Option Module falls back to using IARP as
in the above paragraph to determine the protocols to use with that
particular virtual circuit.
If a static maintenance protocol is used, at least one DLCI mapping
must be specified.
If you want to... Then...
Insert a new profile Press the I key when over the Num col-
umn.
Explanation:
A new inserted profile will always be
set up with the default parameters.
Copy parameters from
Use the copy (C) and paste (P) keys.
an old profile to this
newly inserted profile:
Explanation:
Entire configuration trees can be copied
with this method.
Delete an unused profile Use the D key when the cursor is over
the number in the Num column.
Explanation:
Once deleted, the profile is gone perma-
nently as soon as the Connection List is
saved. Items may be deleted when DEL
appears below the status bar.
4-28
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 65

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
DLCI Mapping/Active
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When this parameter is set to Yes (def), the mapping is used to determine the protocols used. If set to No, the Router Option Module
will ignore the virtual circuit with this DLCI.
DLCI Mapping/DLCI
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This is the DLCI associated with this virtual circuit. This value can
range from 16 to 1007.
DLCI Mapping/IP Map
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This menu represents the IP protocol mapping that is to take place
for this DLCI.
IP Map/Active
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When this is set to Yes (def), the Router Option Module will attempt
to transport IP packets for this DLCI. A setting of No means that no
IP traffic or route will be exchanged.
IP Map/IARP
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When set to Yes (def), the Router Option Module will send Inverse
ARP packets in order to determine the IP address on the other end
of the virtual circuit. If the IARP is responded to, a route is placed
in the IP route table.
When set to No, the route address is to be assigned statically using
the IP Map/Far-End IP Address parameter.
IP Map/Far-End IP Address
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This is the IP address of the device on the other end of the virtual circuit. When this DLCI becomes active, the Router Option Module
will add a route in the IP routing table.
IP Map/IP Netmask
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The IP network mask to apply to the Far-End IP Address and Link
IP Address is specified here.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-29
Page 66

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP Map/Link IP Address
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The virtual circuit may require an IP address to be specified at this
DLCI, or numbered, interface. This address is used by the Router
Option Module to respond to Inverse ARP requests. If this IP address is left as 0.0.0.0, the link is treated as unnumbered and the
Router Option Module responds to the Inverse ARP with its Ethernet IP address.
IP Map/RIP Protocol
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The RIP protocol can be specified per DLCI. The selections are:
Off (meaning no RIP packets are listened to or sent)
V1 (def) (which is RIP version 1)
V2 (which is RIP version 2)
IP Map/RIP Method
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The method of which the RIP protocol is used is specified here:
None All routes in the router table are adver-
tised out this virtual circuit with no modification of the metrics.
4-30
Split
Horizon (def)
Poison
Reverse
Only routes not learned from this particular virtual circuit are advertised.
All routes are advertised, but the routes
learned from this port are “poisoned”
with an infinite metric.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 67

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP Map/RIP Direction
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This parameter allows the direction at which RIP advertisements
are sent and listened to be specified.
Tx and Rx
(def)
RIP advertisements are periodically transmitted
and are listened to on this virtual circuit.
Tx Only RIP advertisements are periodically transmitted
but are not listened to on this virtual circuit.
Rx Only RIP is not transmitted on this virtual circuit but
they are listened to.
DLCI Mapping/IPX Map
This menu represents the IPX protocol mapping that is to take place
for this DLCI.
IPX Map/Active
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When set to Yes
(def), the Router Option Module will attempt to
transport IPX packets for this DLCI.
When set to No, no IP traffic or route will be exchanged.
IPX Map/IARP
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When set to Yes (def), the Router Option Module will send Inverse
ARP packets in order to determine the IPX network on the other end
of the virtual circuit. If the IARP is responded to, a route is placed
in the IPX route table.
When set to No, the IPX network is to be assigned to the link statically using the IPX Map/Link Network parameter.
IPX Map/Link Network
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
This is the IPX network of the link or of the other devices LAN.
When this DLCI becomes active, the Router Option Module will add
a route to this network in the IPX routing table. This address is also
used by the Router Option Module to respond to Inverse ARP requests. If this IPX address is left as 0, the link is treated as unnumbered and the Router Option Module responds to the Inverse ARP
with its Ethernet IP address.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-31
Page 68

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
DLCI Mapping/Bridge Map
This menu is used to permit bridging of packets over this DLCI.
Each DLCI or virtual circuit must be assigned a bridge group. The
bridge group treats all virtual circuits as one circuit. Bridge packets
destined to be transmitted out a particular bridge group are copied
and transmitted individually out each DLCI in the bridge group.
However, incoming bridge packets received from one DLCI are not
retransmitted out the other DLCIs in the same bridge group. Any
device in the bridge group must transmit to each DLCI. This requires a fully meshed circuit, meaning each device has a virtual circuit to each other.
Bridge Map/Active
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
When set to Yes (def), the Router Option Module will bridge packets to and from this DLCI. Bridge packets are any packets that are
not IP or IPX packets except when the router is turned off, in which
case that particular router’s protocol packets are bridged.
When set to No, bridging will not occur.
Bridge Map/Bridge Group
Write security: 3, Read security: 5
The bridge group that this DLCI is part of is specified here as Group
1 or Group 2. These groups correspond to the spanning tree protocols Bridge Group 1 and Bridge Group 2.
4-32
DLCI Mapping/Filters
The Router Option Module can block packets in and out of a PVC
port by use of the filters. They are set up in two steps:
1. Define the types of packets that would be of interest in the Configuration/Security/Filter Defines menu, and
2. Set up the filter type and combination of defines that will cause a
packet block.
Filters/In from PVC
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The packets which come into the Router Option Module via this
PVC can be filtered in three ways:
Disabled (def) - Turns off packet input filtering. No incoming pack-
ets from this PVC are blocked.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 69

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Block All - All incoming packets from this PVC are blocked except
as defined in the Filters/In Exceptions list.
Forward All - All incoming packets from this PVC are not blocked
except as defined in the Filters/In Exceptions list.
Filters/In Exceptions
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is a list of up to 32 filter entries which can be combined using
the operations field. The operations are performed in the order they
appear on the list.
Active Turns this entry active when set to ON
Ty pe Selects the filter define list to reference:
MAC - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/MAC Filter Defines list.
Pattern - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/Pattern Filter Defines list.
IP - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/IP Filter Defines list.
IPX - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/IPX Filter Defines list.
Filter List Name Selects between filters defined in the list.
Next Oper The next operation to use to combine with the next
filter in the list:
End - the last filter to combination.
And - logically AND this filter with the next filter in
the list.
OR - logically OR this filter with the next filter in
the list.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-33
Page 70

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Filters/Out to PVC
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The packets which transmit out this PVC from the Router Option
Module can be filtered in three ways:
Disabled (def) - Turns off packet output filtering. No outgoing
packets to this PVC are blocked.
Block All - All outgoing packets to this PVC are blocked except as
defined in the Filters/Out Exceptions list.
Forward All - All outgoing packets to this PVC are not blocked except as defined in the Filters/Out Exceptions list.
Filters/Out Exceptions
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is a list of up to 32 filter entries. The setup is exactly the same
as the Filter/In Exceptions list.
4-34
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 71

Configuration/PPP Profile
The Router Option Module uses the PPP profile to specify the profile used when connected using PPP. Figure 4-7 shows the PPP profile menu.
Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Figure 4-7.
Configuration/PPP Profile Screen
PPP Profile/Authentication
The authentication menu contains the required parameters for the
authentication of the PPP peer and for being authenticated by the
PPP peer.
Authentication is applied between the Router Option Module and
the PPP peer as follows:
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-35
Page 72

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Authentication/Tx Method
Write security: 2; Read security: 3
This parameter specifies how the Router Option Module is to be authenticated by the PPP peer. There are four possible selections. See
Security/PPP on page page 4-21 for an explanation of the three PPP
standard authentication types.
None (def) The connection will not allow the PPP peer to
authenticate it.
PAP, CHAP or
EAP
The connection can be authenticated using
PAP, CHAP, or EAP.
CHAP or EAP The connection can be authenticated using
CHAP or EAP only.
EAP The connection will only allow authentication
by the peer using EAP.
Authentication/Tx Username
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
This is the username that is used when being authenticated by the
PPP peer.
Authentication/Tx Password
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
This is the password or secret that is used when being authenticated
by the PPP peer.
Authentication/Rx Username
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
This is the username used to authenticate the PPP peer.
Authentication/Rx Password
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
This is the password or secret that is used to authenticate the PPP
peer.
PPP Profile/IP
The IP menu contains the parameters for exchanging IP data with
the PPP peer.
4-36
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 73

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to On (def), this connection profile negotiates PPP IPCP
with the PPP peer for exchanging of IP packets.
IP/NAT
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
The Router Option Module can perform Network Address Translation. This feature is most widely used when connecting to the Internet. The Ethernet network can consist of private network numbers.
When this profile is connected, all IP addresses on the Ethernet side
are translated into the one real IP address negotiated with the PPP
peer (ISP). Multiple stations on the Ethernet side can access the Internet simultaneously. See the section IP/NAT on page page 4-7 for
more global options.
When set to On, the Router Option Module to perform NAT.
When set to Off (def), the unit will route across the connection nor-
mally.
IP/Route
The IP parameters are configured in this menu. Usually the Router Option Module will automatically discover the PPP peer’s networks using PPP
IPCP and/or RIP.
Route/IP/Net
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
The PPP peer’s IP address or network can be set here, if known.
Leaving this at 0.0.0.0 means that the Router Option Module will determine the PPP peer’s IP and network using the PPP IPCP.
Route/Netmask
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This network mask is applied to the IP/NET address for determining the PPP peer’s network. If left as 0.0.0.0, a standard network
mask is used.
Route/Force IP
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to Yes, the Router Option Module will force the PPP peer
to use the IP address in the IP/Net for this profile as its WAN IP ad-
dress. Normally this is set in the No (def) position.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-37
Page 74

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
IP/RIP
The RIP parameters can be adjusted from their defaults under this
menu.
RIP/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to On (def), the Router Option Module will perform RIP
over the WAN connection.
RIP/Protocol
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
The Router Option Module can perform version 1, V1 (def), or ver-
sion 2, V2, of RIP on this WAN connection.
RIP/Method
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Split Horizon Only routes not learned on the WAN con-
Poison Reverse (def) All routes are advertised, including
nection are advertised.
routes learned from the WAN connection. These routes are poisoned.
4-38
None All routes are advertised, including
routes learned from the WAN connection. No attempt is made to poison these
routes
RIP/Direction
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Tx and Rx (def) RIP advertisements are transmitted and
received on the WAN connection.
Tx only RIP advertisements are transmitted and
not received.
Rx only RIP advertisements are received but not
transmitted.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 75

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
RIP/Triggered
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to Yes, only IP RIP updates are sent when the routing table
has changed and learned routes are not “aged.”
When set to No (def), updates are sent periodically.
PPP Profile/IPX
The IPX menu contains the parameters for exchanging IPX data
with the PPP peer.
IPX/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to On (def), the connection profile to negotiate PPP IPXCP
with the PPP peer for exchanging of IPX packets.
IPX/Remote Network
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
A nonzero value in this remote network number will allow the
Router Option Module to add a route to the PPP peer’s network to
the routing table.
The Router Option Module normally will treat the WAN network as
an unnumbered link. This is usually referred to as being a “halfrouter.” However, a PPP peer which wants to assign a network address to the WAN link can do so, in which case the Router Option
Module will go into “full-router” mode.
IPX/Triggered
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to Yes, only IPX RIP and SAP updates are sent when the
routing or service table has changed and learned routes are not
“aged.”
When set to No (def), updates are sent periodically based on the RIP
and SAP timers set in Configuration/IPX/RIP Timer and Configu-
ration/IPX/SAP Timer.
IPX/Type 20 Packets
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
For certain protocol implementations, like NetBIOS, to function in
the NetWare environment, routes must allow a broadcast packet to
be propagated throughout the IPX networks.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-39
Page 76

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
The Type 20 IPX packet is used specifically for this purpose. This
causes special handling of this packet by the Router Option Module.
When a router receives this type of packet, it rebroadcasts it across
all interfaces except the one it is received on and includes the network number of that interface in the data portion of the packet.
The IPX Router Specification from Novell notes that Type 20 packets
should not be propagated across slower links with bandwidths of
less than 1 Mbps (like ISDN). However, when set to Pass (def), the
Router Option Module will allow these packets to propagate over
the WAN connection. This facilitates dial-on-demand applications.
When set to Block, all Type 20 packets are not propagated across the
WAN connection.
PPP Profile/Bridge
The Bridge menu contains the parameters needed for exchanging
bridged packets with the PPP peer.
Bridge/Mode
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to On (def), the Router Option Module will attempt to negotiate PPP BCP with the PPP peer. Bridging can be used even in
route mode only if the PPP peer cannot support certain PPP protocols for that particular routing protocol. See Bridge/WAN IP Bridge
and Bridge/WAN IPX Bridge on page page 4-14 for further details.
PPP Profile/PPP
The Router Option Module supports the IETF standards for the
Point-to-Point Protocol. The PPP state machine running in the Router Option Module can be fine-tuned to support many applications
that can be employed. The configurable items under this menu can
be changed from their default values for special cases.
PPP/VJ Compression
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to On, the Router Option Module will perform TCP/IP
header compression known as Van Jacobson compression to the
PPP peer. Normally, this is not necessary over ISDN connections.
Set to Off (def) to disable it.
4-40
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 77

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
PPP/Max Config
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This value is the number of unanswered configuration requests that
should be transmitted before giving up on a call.
Possible values: 5, 10 (def), 15, 20.
PPP/Max Timer
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
This value is the number of seconds to wait between unanswered
configuration requests.
Possible values: 1 sec, 2 secs (def), 3 secs, 5 secs, 10 secs.
PPP/Max Failure
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
Due to the nature of PPP, configuration options may not be agreed
upon between two PPP peers. This value is the number of configuration requests that should occur before an option is configurationrejected. This allows a connection to succeed that might otherwise
fail.
Possible values: 5 (def), 10, 15, 20.
PPP Profile/Filters
The Router Option Module can block packets in and out of a WAN
port by use of the filters. They are set up in two steps:
1. Define the types of packets that would be of interest in the Con-
figuration/Security/Filter Defines menu,
2. Set up the filter type and combination of defines that will cause a
packet block.
Filters/WAN-to-LAN (In)
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The packets which come into the Router Option Module can be filtered in three ways:
Disabled (def) Turns off packet input filtering. No incoming
packets are blocked.
Block All All incoming packets from the WAN are
blocked except as defined in the Filters/In
Exceptions list.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-41
Page 78

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Forward All All incoming packets from the WAN are not
blocked except as defined in the Filters/In
Exceptions list.
Filters/In Exceptions
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is a list of up to 32 filter entries which can be combined using
the operations field. The operations are performed in the order they
appear on the list.
Active Turns this entry active when set to ON
Ty pe Selects the filter define list to reference:
MAC - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/MAC Filter Defines list.
Pattern - from the Configuration/Security/Filter Defines/Pattern Filter Defines list.
IP - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/IP Filter Defines list.
4-42
IPX - from the Configuration/Security/Filter
Defines/IPX Filter Defines list.
Filter List
Selects between filters defined in the list.
Name
Next Oper The next operation to use to combine with the
next filter in the list:
END - the last filter to combination.
AND - logically AND this filter with the next
filter in the list.
OR - logically OR this filter with the next filter
in the list.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 79

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Filters/LAN-to-WAN (Out)
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
The packets which come out toward the WAN from the Router Option Module can be filtered in three ways:
Disabled (def) Turns off packet output filtering. No outgoing
packets are blocked.
Block All All outgoing packets to the WAN are blocked
except as defined in the Filters/Out Exceptions
list.
Forward All All outgoing packets to the WAN are not blocked
except as defined in the Filters/Out Exceptions
list.
Filters/Out Exceptions
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
This is a list of up to 32 filter entries. The setup is exactly the same
as the Filter/In Exceptions list.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-43
Page 80

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Configuration/Management
The Router Option Module can be managed using Telnet, Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP), or the maintenance port.
See Appendix C for a description of the MIBs supported by the Router Option Module. Each of the three methods can be protected using
authentication. Figure 4-8 shows the Configuration/Management
menu.
Figure 4-8.
Management/Telnet
Any Telnet client application can bring up a session to the Router
Option Module’s Telnet server using the standard Telnet TCP port.
Only one session is supported at a time. All sessions require a user
name and password.
Telnet/Server Access
Write security: 2; Read security: 5
When set to On (def), you can access the Router Option Module via
Telnet.
When set to Off, access is denied.
Telnet/User List
Up to four users can be configured for access to the Router Option
Module. Each user can be assigned a privilege and time-out.
4-44
Configuration/Management Screen
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 81

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
User List/Name
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
A text string of the user name for this session.
User List/Authen Method
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
The user can be authenticated in two ways:
Password Used to authenticate the user
Radius Used for authenticating the user
User List/Password
Write security: 0; Read security: 3
When the authenticating method is Password, this text string is
used for the password.
User List/Idle Time
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
When set to nonzero, the session is automatically logged out when
no activity occurs for this amount of time. The range is 0 to 255 and
is in minutes. The default is 10 minutes, and a setting of 0 will never
time out the session. When a time-out occurs during an edit session,
all changes are saved.
User List/Level
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
This is the security level privilege that is assigned for this user. See
Security Levels for an explanation of what those levels imply. Level
0 is the default.
Management/SNMP
The Router Option Module is an SNMP agent. It can respond to
Get-Requests and generate traps. These two lists set up the manager, communities, and levels. See Appendix D for more information on
SNMP.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-45
Page 82

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
SNMP Access
Write security: 3; Read security: 5
When set to:
No - SNMP access is denied.
On (def) - the Router Option Module will respond to SNMP manag-
ers based on the following lists.
SNMP/Communities
This list is used to set up to eight SNMP communities’ names that
the Router Option Module will allow. Factory default sets the community “public” with “Get” privileges.
Communities/Name
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
This is a text string for the community name.
Communities/Privilege
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
The access for this manager can be assigned three levels.
None - No access is allowed for this community or manager.
Get - Manager can only read items.
4-46
Get/Set - Manager can read and set items.
Communities/Manager IP
Write security: 1; Read security: 3
This is the IP address of SNMP manager. If set to 0.0.0.0, any SNMP
manager can access the Router Option Module for this community.
SNMP/Traps
The Router Option Module can generate SNMP traps. See Appendix
D for trap types supported. This list allows up to four managers to
be listed to receive traps.
Traps/Manager Name
Write security: 2; Read security: 4
This is the text string describing the name of the entry. It is intended
for easy reference and has no bearing on the SNMP trap function.
Traps/Manager IP
Write security: 2; Read security: 4
This is the IP address of the manager that is to receive the traps.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 83

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Management/Maint Port
The Router Option Module has an EIA-232 connector on the back of
the unit. The setup for that port is under this menu.
Maint Port/Password Protect
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
When set to No, the maintenance port is not password protected.
When set to On (def), the Router Option Module will prompt for a
password upon startup.
Maint Port/Password
Write security: 0; Read security: 1
This is the text string that is used for comparison when password
protecting the maintenance port. By default, no password is entered.
The security level for the maintenance port is always set to 0. This gives
full access to all menus.
Maint Port/Baud Rate
(also available via Front Panel Terminal/Rate)
Write security: 5; Read security: 5
This is the asynchronous rate that the maintenance port will run.
Possible values: 300, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600 (def), 19200, 38400,
57600.
Maint Port/Data Bits
(also available via Front Panel Terminal/Data Bits)
Write security: 5; Read security: 5
This is the asynchronous bit rate that the maintenance port will run.
Possible values: 7 or 8 (def) bits.
Maint Port/Parity
(also available via Front Panel Terminal/Parity)
Write security: 5; Read security: 5
This is the asynchronous parity that the maintenance port will run.
Possible values: None (def), Odd, or Even.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
4-47
Page 84

Chapter 4: Configuration Overview
Maint Port/Stop Bits
(also available via Front Panel Terminal /Stop Bits)
Write security: 5; Read security: 5
This is the stop bit used for the maintenance port.
Possible values: 1 (def), 1.5 or 2.
Configuration/Terminal Mode
This is an activator which places the Router Option Module terminal session into a command prompt mode. All menu options are accessible during this mode. See Appendix E for the command
structure and command list. Type exit to leave the terminal mode
and return to the menus.
4-48
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 85

Chapter 5
STATUS MENU
The Router Option Module’s Status menu contains comprehensive
status and diagnostic information used in verifying configuration
and identifying problems. The menus are divided into protocol
types and sessions. Figure 5-1 shows the Status menu.
Statistics
Figure 5-1.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
Status Screen
5-1
Page 86

Chapter 5: Statistics
Status/Sessions
This menu contains the current status of all dial-in sessions and
spanning tree ports.
Sessions/PPP Session
Read security: 5
This menu reflects the results of PPP negotiations, user name, time
connected, and data rates for the session.
Name Description
PPP Links Reflects LCP layer active
BCP Shows UP if PPP Bridge Control Protocol has
IPCP Shows UP if PPP IP Control Protocol has nego-
IPXCP Shows UP if PPP IPX Control Protocol has
Uptime Displays how long the call has been connected
negotiated successfully
tiated successfully
negotiated successfully
5-2
Tx Pkts Number of packets transmitted
Rx Pkts Number of packets received
Tx Bytes Number of bytes transmitted
Rx Bytes Number of bytes received
Tx Rate Current application data transmission rate
Rx Rate Current application data reception rate
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 87

Chapter 5: Statistics
Sessions/DLCI Table
The status of all virtual circuits is displayed here.
DLCI - The DLCI that is associated with this virtual circuit.
State - The state of the virtual circuit:
State Definition
Inactive The circuit exists but has been deactivated by the
Frame Relay switch.
Exists The circuit exists at this point and should be acti-
vated soon.
Active The circuit is fully active.
Off The circuit has been turned off by the DLCI map-
ping active selection.
Tx Frames Number of Frame Relay packets that have been
transmitted via this DLCI.
Rx Frames Number of Frame Relay packets that have been
received via this DLCI.
Tx Bytes Number of Frame Relay bytes that have been trans-
mitted via this DLCI.
Rx Bytes Number of Frame Relay bytes that have been
received via this DLCI.
IP SubIfc The IP router port assigned for this DLCI. Possible
ports are fr0, fr1, … , fr9. None means that this DLCI
is not used for routing IP.
IPX SubIfc The IPX router port assigned for this DLCI. Possible
ports are fr0, fr1, … , fr9. None means that this DLCI
is not used for routing IPX.
Bridge
Group
The bridge group that this DLCI belongs to (Group 1
or Group 2). None means that this DLCI is not used
for bridging.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
5-3
Page 88

Chapter 5: Statistics
Sessions/Spanning Tree
Read security: 5
When Bridge mode and Spanning Tree mode are active, this reflects
the current state of the LAN and WAN ports. The following can appear:
Name Description
Off Appears when spanning tree mode is disabled
Disabled Port is not connected (for WAN) or disabled in
Listening Port is in the listening state
Learning Port is in the learning state
Forwarding Port is in the forwarding state with the following
Blocking Port is in the blocked state
configuration
possible properties:
root - root port
designated - designated port
Status/ARP Cache
Read security: 5
This lists the contents of the Router Option Module’s ARP table. All
resolved cache entries time out after 20 minutes. Unresolved entries
time out in 3 minutes.
Name Description
ARP Cache/IP Address IP address used for resolving
ARP Cache /MAC Address Ethernet address resolved
ARP Cache/Time Minutes since entry was first
5-4
MAC address
(0=no resolution)
entered
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 89

Status/Bridge Table
Read security: 5
This lists the contents of the Router Option Module’s bridge table.
Name Description
Chapter 5: Statistics
Bridge Cache/MAC
Address
Bridge Cache/Port Port device learned from: LAN,
Bridge Cache/TTL Seconds until address is removed
Status/IP Routes
Read security: 5
This lists the contents of the Router Option Module’s IP router table.
Name Description
IP Routes/IP Address Network or host destination address
IP Routes/Netmask Network mask applied to the destination
IP Routes/Gateway Host or router to receive this packet
IP Routes/Port Port gateway is located on:
Ethernet address for device learned
WAN0, or WAN1
from table
address
local
Sent directly to the Router Option Module
route
eth0
Router Option Module’s ethernet port
wan0
Router Option Module’s first PPP bundle
fr 0 . . . fr 9
Router Option Module is connected up to
10 DLCIs
IP Routes/Use Number of times the Router Option Mod-
ule has referenced the route
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
5-5
Page 90

Chapter 5: Statistics
Name Description
IP Routes/Flags Important tags associated with this route
IP Routes/Hops Number of routers that must go through
IP Routes/TTL Seconds until address is removed from
entry:
H - route is a host route
G - route is a gateway route
D - route learned dynamically from RIP
I - route learned from an ICMP redirect
P - route is private and is not advertised
with RIP
T - route is to a triggered port (updates
only when table changes)
to get to destination. Ranges from 0-15 or
16 for infinite (can’t get there from here).
table or “zombied.” Value of 999 means
route is static.
5-6
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 91

Chapter 5: Statistics
Status/IPX Routes
Read security: 5
This lists the contents of the Router Option Module’s IPX router table.
Name Description
IPX Routes /Network Network destination address
IPX Routes /Gateway Node or Ethernet address of gateway to
receive this packet
IPX Routes /Port Port gateway is located on:
local
Sent directly to the Router Option Module
router
eth0
Router Option Module’s ethernet port
wan0
Router Option Module’s first PPP bundle
fr 0 . . . fr 9
Router Option Module is connected up to
10 DLCIs
IPX Routes /Use Number of times the Router Option Mod-
ule has referenced the route
IPX Routes/Hops Number of routers that must go through to
get to destination. Ranges from 0-15 or 16
for infinite (can’t get there from here).
IPX Routes/Ticks Router-determined value for representing
time packets take to reach the network destination. One tick is equivalent to one-eighteenth of a second.
IPX Routes/TTL Seconds until address is removed from
table. Value of 999 means route is static.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
5-7
Page 92

Chapter 5: Statistics
Status/IPX Servers
Read security: 5
This lists the contents of the Router Option Module’s IPX server ta-
ble.
Name Description
IPX Servers/Type The server type
IPX Servers/Name The server name
IPX Servers/Network The server network address
IPX Servers /Address The servers node address
IPX Servers/Socket The servers socket address
IPX Servers/Hops Number of routers that must go
PX Servers/TTL Seconds until address is removed
through to get to server.
Ranges from 0-15 or 16 for infinite.
from table. Value of 999 means
server is static.
Status/WAN Stats
Read security: 5
This menu contains generic WAN statistics on HDLC hardware
port.
Name Description
Tx Bytes Total number of raw bytes sent out HDLC port 1
Rx Bytes Total number of raw bytes received in HDLC
Rx CRCs Total number of CRC errors detected on HDLC
Clear Counts When activated, clears all WAN stat counts
5-8
port 1
port 1
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 93

Status/LAN Stats
Read security: 5
This menu contains statistics for the Ethernet port.
Name Description
Tx Packets Packets transmitted out the Ethernet port
Rx Packets Packets received from the Ethernet port
Tx Errors Total transmit errors encountered on Ethernet
Chapter 5: Statistics
port
Single Collisions - total single collisions before
successful transmission
Multiple Collisions - total multiple collisions
before successful transmission
Excessive Collisions - total collisions that
resulted in packet being dropped
Deferred Transmissions - total packets deferred
due to collisions
Carrier Sense Errors - total carrier sense errors
encountered (no link integrity)
Rx Errors Total packets received in error and dropped
CRCs - total packets detected with CRC errors
Giants - total packets received that were greater
than 1518 bytes
Runts - total packets received that were less than
64 bytes
Rx Collisions - total collision occurred during
reception
Clear Counts When activated, clears all LAN Stat counts.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
5-9
Page 94

Chapter 5: Statistics
Status/IP Stats
Read security: 5
This menu contains IP statistics that can be useful when diagnosing
problems. All are taken from the SNMP MIB-2 variables.
TCP failed attempts
TCP passive connections
TCP current connections
TCP segments sent
TCP segments received
Total TCP resets
Active TCP connections
Total TCP retransmits
UDP datagrams sent
No application at dest. port
UDP datagrams received
UDP bad packets
ICMP redirected messages
ICMP packet errors
ICMP time-outs received
ICMP messages sent
ICMP messages received
ICMP specif if errors
IP datagrams reassembled
IP datagrams sent
IP datagrams received
Total forwarded datagrams
IP reassembly time-out
Discarded routing entries
Total IP fragments
Failed fragments
IP reassembly failures
Disassembled fragments
Errorfree discards
Routeless discards
Default TTL
Bad IP addresses
Successful fragments
Bad header packets
Sent datagrams to upper layers
Datagrams discarded
Bad protocol discards
Clear Counts - clears all IP stats
5-10
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 95

Viewing Statistical Information
(Front Panel Interface)
To view statistical information:
Step Action Result
1 Select 1)STATUS from the Main menu.
2 Select Port Status.
3 Choose the Router Option Module. A menu appears.
Chapter 5: Statistics
4 From this menu, choose to view:
WAN
LAN
Reset the statistics.
5 Scroll through the remaining screens
using the arrow keys.
The first Statistics
screen appears
Statistic counts are
running totals for the
current day (i.e.,
since 12 AM).
Router Statistics Available on Front Panel
The following information is displayed when the Router module is
selected.
Status
WA N L AN
TX BYTE
RX BYTE
RX CRC
TX PCKTS
RX PCKTS
TX ERRORS
RX ERRORS
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
5-11
Page 96

Chapter 5: Statistics
5-12
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Page 97

Chapter 6
TEST MENU
The Router Option Module’s Test menu contains built-in tests that
can be used to diagnose problems. Figure 6-1 shows the Test menu
screen. The following tests are listed below.
Diagnostics
Figure 6-1.
Test Screen
Test Menu/Echo Request
Write security: 4, Read security: 5
When activated, the echo request test will begin sending continuous
PPP echo request packets to any open LCP ports. Results are displayed on the screen. This test is not used in the Frame Relay mode.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
6-1
Page 98

Chapter 6: Diagnostics
LOGS MENU
The Logs menu contain logs displaying important information
about the running condition of the Router Option Module. The logs
can be set to capture diagnostics of error conditions only by way of
a log level. The levels are divided up as follows:
Level Description
Figure 6-2 shows the Logs menu. The three logs available are listed
after the figure.
0 Fatal event (causes reset)
1 Critical event
2 Error event
3 Warning event
4 Notify event
5 Informational event
6 Debugging event
6-2
Figure 6-2.
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
Logs Screen
Page 99

Logs/Syslog Host
Set this to the IP address or domain name (if DNS configured) of the
sys log host device. All log events are sent to this device.
Logs/PPP Log
Information pertaining to the PPP negotiation and authentication
will be logged here.
PPP Log/Active
When set to Yes (def), PPP events below or equal to this level are
logged.
PPP Log/Wrap
When set to Yes (def), new PPP events will overwrite old PPP events
when the log is full. When set to No, all logging will stop when the
log is full.
PPP Log/Level
In order to log events, they must be at or below this level. Range is
0 to 6. The default is 3.
Chapter 6: Diagnostics
PPP Log/View
This menu displays the log list. The fields are as follows:
Date/Time - Date and time event occurred.
Level - Level associated with this event (0-6).
Message - Text message for this event. If message is too long to fit
on the line, another event appears below it continuing the message.
PPP Log/Clear
This clears the log when activated.
61200350L1-1 Router Option Module User Manual
6-3
Page 100

Chapter 6: Diagnostics
Logs/Connection Log
Information pertaining to the connection over the T1 link.
Connection Log/Active
When set to Yes (def), connection events less than or equal to the log
level are logged into the log.
Connection Log/Wrap
When set to Yes (def), new connection events will overwrite old
connection events when the log is full.
When set to No, all logging will stop when the log is full.
Connection Log/Level
In order to log events, they must be at or below this level. Range is
0 to 6. The default is 3.
Connection Log/View
This menu displays the log list. The fields are as follows:
Date/Time - Date and time event occurred.
Level - Level associated with this event (0-6).
Message - Text message for this event. If message is too long to fit
on the line, another event appears below it continuing the message.
Connection Log/Clear
This clears the log when activated.
Logs/Network Log
Information pertaining to the routing protocols is placed in this log.
Network Log/Active
When set to Yes (def), call events below or equal the log level are
logged into the log.
6-4
Router Option Module User Manual 61200350L1-1
 Loading...
Loading...