Page 1

PXI-7931
4x8 2-Wire Matrix Module
User’s Manual
Recycled Paper
Page 2

© Copyright 2004 ADLINK Technology Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Manual Rev. 1.00: June 28, 2004
Part Number: 50-17009-100
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in
order to improve reliability, design, and function and does not represent a
commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special,
incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use
the product or documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such
damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All
rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any
mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form without prior written
permission of the manufacturer.
Trademarks
NuDAQ
®
, NuIPC®, NuDAM®, NuPRO® are registered trademarks of ADLINK
Technology Inc. Other product names mentioned herein are used for
identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered
trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 3
Getting Service from ADLINK
Customer Satisfaction is top priority for ADLINK Technology Inc. If you need
any help or service, please contact us.
ADLINK TECHNOLOGY INC.
Web Site http://www.adlinktech.com
Sales & Service Service@adlinktech.com
TEL +886-2-82265877 FAX +886-2-82265717
Address 9F , No. 166, Jian Yi Road, Chungho City, Taipei, 235 Taiwan
Please email or FAX your detailed information for prompt, satisfactory, and
consistent service.
Detailed Company Information
Company/Organization
Contact Person
E-mail Address
Address
Country
TEL FAX
Web Site
Questions
Product Model
OS:
Computer Brand:
M/B: CPU:
Environment
Detail Description
Chipset: BIOS:
Video Card:
NIC:
Other:
Suggestions for ADLINK
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction...............................................................1
1.1 Features............................................................................... 1
1.2 Applications........................................................................ 2
1.3 Specifications...................................................................... 2
1.4 Software Support ................................................................ 3
Chapter 2 Installation................................................................. 5
2.1 Contents.............................................................................. 5
2.2 Unpacking........................................................................... 5
2.3 Mechanical Drawing........................................................... 6
2.4 Installing the switch module into a PXI Platform............... 6
Chapter 3 Signal Connection.....................................................9
3.1 PXI-7931 Topology ............................................................ 9
3.2 PXI-7931 Pin assignment & Description.......................... 10
3.3 TB-6231 T erminal Board.................................................. 11
Chapter 4 Operation Theorem ................................................ 21
4.1 Hardware Block Diagram.................................................21
4.2 Operation Mode................................................................22
4.3 Handshaking ..................................................................... 22
4.4 Trigger Bus ....................................................................... 26
4.5 Star Trigger ....................................................................... 27
4.6 Auxiliary Digital I/O......................................................... 28
4.7 Hot-Swap .......................................................................... 29
4.8 Emergency Shutdown.......................................................29
4.9 Watchdog T imer................................................................ 30
Warranty Policy........................................................................33
Table of Contents • i
Page 6

How to Use This Manual
This User Manual is designed to assist users in the installation of the ADLINK
PXI-7931, 4x8 2-Wire Matrix PXI Switch module.
Chapter 1 Introduction
Gives an outline and overview of ADLINK switch modules’
features, specifications, and applications.
Chapter 2 Installation
Describes how to install a switch module into a PXI chassis. For
software library and utilities installation, please refer to the
Software Users’ Guide.
Chapter 3 Signal Connection
Shows the pin assignments and terminal board connection of the
switch module.
Chapter 4 Operation Theorem
Describes function blocks on ADLINK switch modules and
operation instructions.
ii • How to use this Manual
Page 7
1
Introduction
ADLINK PXI-7931 is a matrix module with 32 cross-point 2-wire relays (DPDT,
2 Form C). The default configuration of the PXI-7931 is a 4-group 2x4 2-wire
matrix. With the termination board, TB-6231, users can flexibly choose one of
the configurations: one 4x8, two 4x4, one 2x16, two 2x8, and four 2x4. Any
contact of the PXI-7931 can connect to other contacts at the same bank,
individually, or in combination. The PXI-7931 matrix module simplifies wiring
and makes it easy to change the internal connection path.
The contact position of the relays can be changed either by direct software
commands or by following the instructions previously stored in the on-board
scan list. The scan list advances upon the trigger from external measurement
devices, such as a DMM. The scan list can also advance when the scan-delay
timer expires. PXI trigger functions are supported and software programmable.
Multiple modules can be synchronized without additional field wiring.
1.1 Features
• PXI specifications Rev. 2.0 compliant
• 3U Eurocard form factor, CompactPCI compliant (PICMG 2.0 R3.0)
• PICMG 2.1 R2.0 CompactPCI Hot-Swap
• 32 DPDT (2 Form C) non-latching relays
• Contact rating
• 2A switching, 2A carrying
• 220V
• 200 operations per second
• 1k-sample scanlist for deterministic scanning
• Provides handshaking signals to trigger external instruments
• Programmable emergency shutdown function and Watchdog timer for
safety critical applications
• Eight auxiliary 3.3 V/TTL digital inputs/outputs with 5V tolerance
• Supports PXI backplane triggers to synchronize multiple modules
• Fully software programmable
, 125VAC
DC
specifications compliant
Introduction • 1
Page 8

1.2 Applications
• Industrial ON/OFF control
• External high power relay driving and signal switching
• Laboratory automation
• Industrial automation
• Switch contact status sensing
• Limit switch monitoring
• Cooperating with other modules such as A/D and D/A peripherals to
implement a data acquisition and control system
1.3 Specifications
Relay Output
• Number of cross-points: 32 (2-wire)
• Relay type: DPDT (2 Form C), non-latching
• Switching capacity:
• Max. switching current: 2A
• Max. switching voltage: 220V
• Max. switching power: 60VA, 60W
• Failure rate: 10µA, 10mV
• Contact resistance: 100mΩ max.
• Relay set/reset time
• Operate time: 4ms max.
• Release time: 4ms max.
• Bounce time: 1ms max.
• Expected life:
• Mechanical life: 10
• Electrical life: 105 operations min. (2A @ 30VDC, resistive load)
• Data transfer: Programmed I/O
DC
8
operations min.
, 125VAC
DC
Auxiliary Digital I/O
• Numbers of channel: 8 inputs/outputs
• Compatibility: 3.3 V/TTL (5V tolerant)
• Data transfers: programmed I/O
Handshaking Signals
• Programmable polarity
• Logic level: 3.3 V/TTL (5V tolerant)
• Trigger In source: AUX1, PXI trigger bus, PXI star trigger in
• Scanner Advanced destination: AUX0, PXI trigger bus, PXI star trigger
out
Safety functions
2 • Introduction
Page 9
• Emergency shutdown
• Logic level: 3.3 V/TTL (5V tolerant)
• Active with logic low (for AUX2/SHDNn pin)
• Emergency shutdown sources: AUX2/SHDNn, PXI star trigger
input, PXI trigger bus
• Watchdog timer
• Base clock available: 10MHz, fixed
• Counter width: 32-bit
• Watchdog Timer Overflow sources: Onboard 32-bit watchdog
timer, PXI star trigger input, PXI trigger bus
General Specifications
• I/O Connector: 62-pin D-sub male
• Operating temperature: 0 to 55 °C
• Storage temperature: -20 to 70 °C
• Humidity: 5 to 95% non-condensing
• Power requirements (when all relays are activated simultaneously)
+5V +3.3V
1A 400mA
• Dimensions (not including connectors)
• 160 mm x 100 mm
1.4 Software Support
ADLINK's ADL-SWITCH driver package is for Microsoft Windows operating
systems, including Windows 98/ME/NT/2000/XP.
The driver package also provides utilities to test your switch module, as well as
programming samples and source codes in Microsoft Visual Basic and Visual
C/C++.
For other operating systems, please contact ADLINK for more information.
Introduction • 3
Page 10

Page 11
2
Installation
This chapter describes the installation process for the ADLINK switch module.
Please read the contents of the package and the disassembling information
carefully as they are important in the implementation of the ADLINK switch
module.
2.1 Contents
The package consists of the following items in addition to the User Manual:
• PXI-7931, 4x8 2-Wire Matrix PXI Switch module
• This User Guide
• ADLINK Software CD
• ADL-Switch User’s Guide
If any of these items are missing or broken, please do not hesitate to contact
ADLINK or the dealer from whom the product was purchased. Keep the
shipping materials and carton for future storage or shipping.
2.2 Unpacking
ADLINK switch module contains sensitive electronic components that can be
easily damaged by static electricity. The switch module should be operated on a
grounded anti-static mat. It is strongly recommended that the operator wears an
anti-static wristband, grounded at the same point as the anti-static mat.
Inspect the box for any obvious damage. Check the unit to ensure there are no
shipping and handling damages that may have occurred before proceeding.
After opening, remove the switch module and place it only on a grounded antistatic surface component side up.
Note: DO NOT APPLY POWER TO THE MODULE IF IT HAS BEEN
DAMAGED.
Installation • 5
Page 12
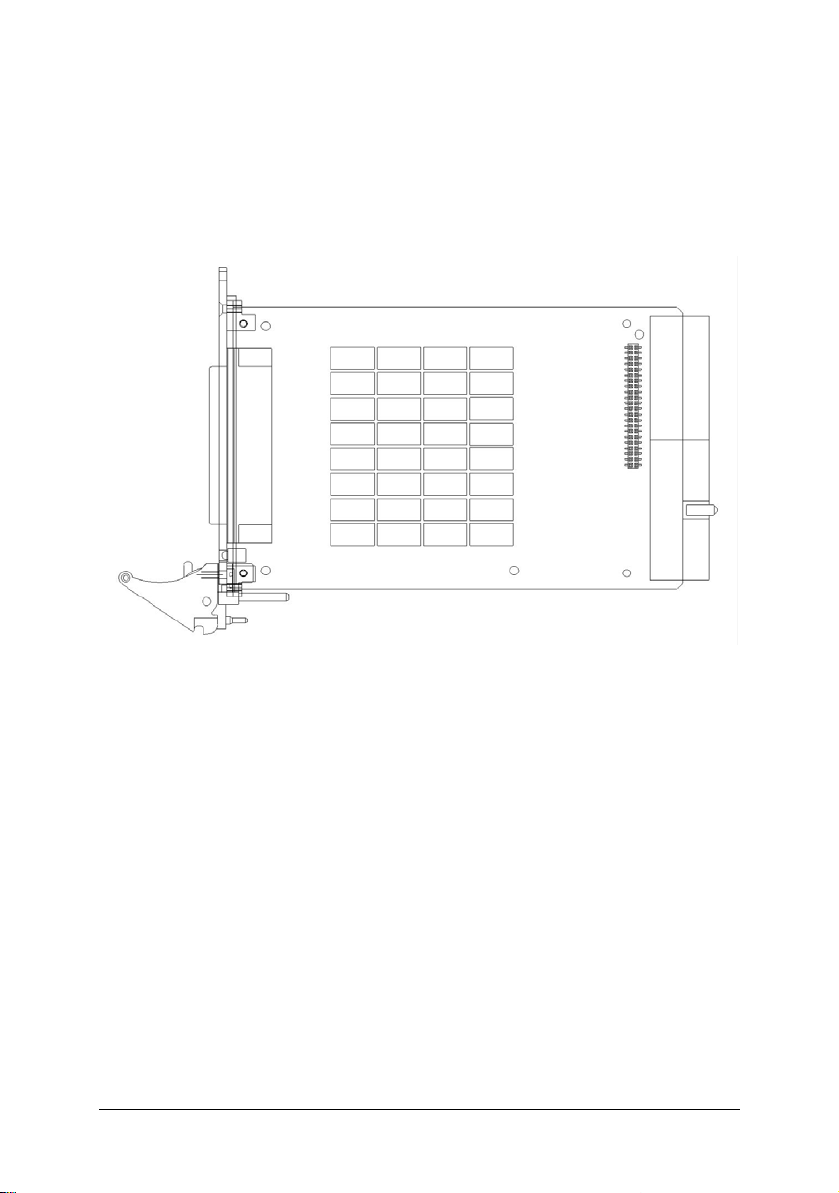
You are now ready to install the PXI-7931.
2.3 Mechanical Drawing
Figure 1: ADLINK Switch Module
ADLINK switch module is packaged in a Eurocard form factor compliant with
PXI Specifications measuring 160 mm in length and 100 mm in height (not
including connectors). A 62-pin connector is located at the front panel for wiring
purposes and the J1/J2 IEC connectors in the rear are used to link the chassis
backplane. With its modular, rugged, and high shock resistant mechanical
features, the switch module functions exceptionally well in any harsh
environment application.
2.4 Installing the switch module into a PXI Platform
To insert the ADLINK PXI switch module, align the module’s edge with the card
guide in the PXI chassis. Slide the switch module into the chassis, until
resistance is felt from the PXI connector. Push the ejector upwards and fully
insert the switch module into the chassis. Once inserted, a “click” can be heard
from the ejector latch. Tighten the screws on the front panel.
6 • Installation
Page 13

Figure 2: Installing the switch module into a PXI platform
Installation • 7
Page 14

Page 15

3
Signal Connection
3.1 PXI-7931 Topology
Relays on the PXI-7931 are configured into a 4-group 2x4 2-wire matrix. Users
can switch on/off to connect or disconnect any number of rows to any number
of columns in the same bank. This configuration can let user simultaneous
connects one or more input signals to one or more devices. All signal paths on
PXI-7931 are inherently break-before-make.
The TB-6231 is a 2-wire terminal board; each path has two ways (i.e. R0 is
indicated as R0+ and R0-).
Figure 3: 2-wire paths
Signal Connection • 9
Page 16

3.2 PXI-7931 Pin assignment & Description
22. C8+
43. C0+ 23. C8- 1. R0+
44. C0- 24. C9+ 2. R0-
45. C1+ 25. C9- 3. R1+
46. C1- 26. C10+ 4. R1-
47. C2+ 27. C10- 5. R2+
48. C2- 28. C11+ 6. R2-
49. C3+ 29. C11- 7. R3+
50. C3- 30. C12+ 8. R3-
51. C4+ 31. C12- 9. R4+
52. C4- 32. C13+ 10. R4-
53. C5+ 33. C13- 11. R5+
54. C5- 34. C14+ 12. R5-
55. C6+ 35. C14- 13. R6+
56. C6- 36. C15+ 14. R6-
57. C7+ 37. C15- 15. R7+
58. C7- 38. NC 16. R7-
59. NC 39. NC 17. NC
60. AUX3 40. AUX4 18. AUX2/SHDNn
61. AUX6 41. +5V out 19. AUX5
62. AUX7 42. AUX1/TRG_IN 20. GND
21. AUX0/S_ADV
Table 1: Pin Assignment
Signal Name Type Description
C0+ to C15+
C0- to C15R0+ to R7+
R0- to R7-
AUX[7..0] Input/Output
TRG_IN Input Trigger input for handshaking operation
S_ADV Output
SHDNn Input Active-low Emergency Shutdown trigger
+5V out Output
GND Output Ground
NC Not Connected Unused pin
Input/Output
Input/Output
Columns: signals are connected to the
switch module
Rows: signals are connected to the switch
module
Programmable Digital I/O with tri-state
control.
AUX[2..0] are dual function pins used for
triggering, refer to chapter 4 for details.
Scanner Advanced trigger output for
handshaking operation
Unregulated +5V DC Source, maximum
100mA current loading
10 • Signal Connection
Page 17

Table 2: Pin Description
3.3 TB-6231 Terminal Board
Configurations
The TB-6231 is a screw terminal board with D-sub 62-pin female connector.
The terminal board can attach to PXI-7931 directly, or through ADLINK’s
custom-made high-capacity 62-pin D-sub cable.
Users can use the TB-6231 terminal board to make various matrix
configurations. The TB-6231’s default configuration is a 4-group 2x4 matrix
in 2-wire. If other matrix configurations are preferred, users can refer the
table below to short the relative pads.
For example, to use a 2x4 matrix, do not short any pads. To use 2x16 matrix,
short the last 12 pads at the lower-right corner of the table.
2x4 Matrix
This configuration has four independent 2x4 matrices, Bank0 to Bank3, each
with two rows and four columns. The following diagram illustrates the PXI7931 with the TB-6231.
Signal Connection • 11
Page 18

Figure 4: 2x4 Matrix (I)
In this configuration, the TB-6231 would not have any shorted pads.
The grid below shows the names used for software configuration with
corresponding traces to the TB-6231.
12 • Signal Connection
Page 19

Figure 5: 2x4 Matrix (II)
Signal Connection • 13
Page 20

2x8 Matrix
This configuration has two independent 2x8 matrices ranging from Bank0 to
Bank1, each has two rows and eight columns. The following diagram
illustrates the PXI-7931 with the TB-6231 to produce relative paths.
Figure 6: 2x8 Matrix (I)
To use a 2x8 matrix, short the following TB-6231 pads.
The grid below shows the names used for software configuration with
corresponding traces to the TB-6231
14 • Signal Connection
Page 21

2x16 Matrix
Figure 7: 2x8 Matrix (II)
This configuration has one independent 2x16 matrix with two rows and 16
columns. The following diagram illustrates the PXI-7931 with the TB-6231 to
produce relative paths
Signal Connection • 15
Page 22

Figure 8: 2x16 Matrix (I)
To use a 2x16 matrix, short the following eight TB-6231 pads.
The grid below shows the names used for software configuration with
corresponding traces to the TB-6231
Figure 9: 2x16 Matrix (II)
16 • Signal Connection
Page 23

4x4 Matrix
This configuration has two independent 4x4 matrices ranging from Bank0 to
Bank1, each with four rows and four columns. The following diagram
illustrates the PXI-7931 with the TB-6231 to produce relative paths
Figure 10: 4x4 Matrix (I)
To use a 2x16 matrix, short the following 16 TB-6231 pads.
The grid below shows the names used for software configuration with
corresponding traces to the TB-6231
Signal Connection • 17
Page 24

Figure 11: 4x4 Matrix (II)
4x8 Matrix
This configuration has one 4x8 matrix, Bank0, with four rows and eight
columns. The following diagram illustrates the PXI-7931 with the TB-6231 to
produce relative paths
18 • Signal Connection
Page 25

Figure 12: 4x8 Matrix (I)
To use a 2x16 matrix, short the following 24 TB-6231 pads.
The grid below shows the names used for software configuration with
corresponding traces to the TB-6231
Signal Connection • 19
Page 26

Figure 13: 4x8 Matrix (II)
20 • Signal Connection
Page 27

4
Operation Theorem
4.1 Hardware Block Diagram
The ADLINK PXI Switch Module features an onboard FPGA for relay switching
control, trigger control, scanlist storage and sequencing. The PXI triggering and
synchronization functions, such as Star Trigger and Trigger Bus are also
supported. In addition to the Trigger In and Scanner Advanced signals for
external instruments handshaking, the switch module provides eight channels
of programmable digital I/O interface to facilitate general purpose control
applications.
To make full use of the flexible trigger and signaling system on the PXI platform,
the switch module has a built-in signal routing matrix that can exchange signals
between front panel digital I/O, Star Trigger, and Trigger Bus.
Scan Memory
Relay
DIO
Front Connector
Scan-
Trigger-in
Figure 14: Hardware Block Diagram
Relay
Control
Timing
Control
Signal
Routing
Matrix
Trigger
Control
PXI
Interface
Star Trigger In
Star Trigger Out
PXI Trigger Bus
Operation Theorem • 21
PXI Connector
Page 28

4.2 Operation Mode
The ADLINK PXI Switch Module provides two relay operation modes to
accommodate different application requirements.
Direct-update
The Switch Module updates the relay pattern immediately upon receiving a
software command. This mode provides a straightforward control over switch
module with minimal hardware intervention. If relay contact bouncing is of a
concern, users would need to insert software delay.
ADLINK recommends the debounce time to be at least 5ms on the PXI-7931.
Auto-scan
The ADLINK PXI switch module features onboard memory to store user
specified scanlist of up to 1024-entry. In each scanlist entry, users can specify
relay pattern, pattern advancing delay time and criterion.
The switch module can set status bit or generate local interrupt to inform user’s
program whether the pattern has been debounced and advanced to the next
scanlist entry. Users can also specify one-time or cyclic scanning of scanlist
entries.
This operating mode supports trigger signals for instrument handshaking. For
more information on handshaking signals, please refer to section 4.3
.
4.3 Handshaking
In the Auto-scan mode, ADLINK PXI switch module accepts Trigger In and
generates Scanner Advanced signal to synchronize relay switching and
measurements with PXI instruments or external measurement devices.
Trigger In
The Trigger In signal from PXI instruments or external measurement devices
instruct the ADLINK PXI switch module to update the relay pattern according to
the one specified in the scanlist entry.
Users may specify wait-for-trigger instruction in a scanlist entry, to have the
switch module wait for the Trigger In before relay pattern is updated. The
polarity of Trigger In can be set to either rising-edge or falling-edge active.
For more information on scanlist configuration, please refer to the software
programming users’ guide.
22 • Operation Theorem
Page 29

Figure 15 illustrates the available signal sources for the Trigger In signal. Signal
names in the solid-line box represent the external (physical) signal on
connectors, and signals in the dotted-line box represents switch module’s
internal signal.
Software Trigger
TRG_IN
Trigger Bus
AUX[7…0]
Star Trigger In
Figure 15: Available signal sources for Trigger In
Trigger In Signal
Scanner Advanced
After updating the relay pattern, the switch module starts its debounce timer
and waits for the relay contacts to settle. When the debounce time elapses, the
switch module will generate a Scanner Advanced signal to notify the PXI
instruments or external measurement devices that the relay contacts have
settled, and ready to take a new measurement.
The waveform, polarity and pulse width of Scanner Advanced signal can also
be software programmed.
For more information on scanlist configuration, please refer to the software
programming users’ guide.
Figure 16 illustrates the available signal destinations for the Scanner Advance d
signal. Signal names in the solid-line boxes represent the external (physical)
signal on connectors, while signals in the dotted-line boxes represent switch
module’s internal signal.
Scanner Adv.
inl
Figure 16: Available signal destinations for Scanner Advanced
S_ADV
Trigger Bus [7…0]
AUX [7...0]
Star Trigger Out
Operation Theorem • 23
Page 30

Handshaking protocol
Figures 17 and 18 depict the relationship between Trigger In, Scanner
Advanced, and relay pattern in handshaking mode. In Figure 17 the Scanner
Advanced is set to pulsating mode.
Trigger In
Scanner Advanced
Relay status
Operation start
Figure 17: Handshaking operation (Scanner Advanced set in pulsating mode)
Trigger In
Scanner Advanced
T
S
T
A1
#0 Pattern #2Pattern #1 Pattern #3 #4
TS
TA1
TS
TA2
TS
TA2
TS
T
TS
A
T
A
Relay status
#0
Pattern #2Pattern #1
Operation start
Figure 18: Handshaking operation (Scanner Advanced set in toggling mode)
24 • Operation Theorem
Pattern #3 #4
Page 31

Once the operation starts and has received a Trigger In signal, the switch
module updates the relay pattern to that specified in the first entry of scanlist.
is the default debounce time for a switch module, i.e. 5ms for PXI-7931. T
T
S
An
is the user specified scan delay time in the scanlist entry, indicating the time
between the relay being debounced and the exact moment that a measurement
device takes a new measurement. The actual delay time would be the greater
of the two times, to guarantee that measurement devices take measurements
after the signal path is fully settled, and the relays switch as close as possible to
their maximum operating speed.
As the scan delay time elapses, the switch module generates Scanner
Advanced signal to inform the measurement device to take a new
measurement.
After the measurement completes, the measurement device will generate
another Trigger In signal to have the switch module update the relay pattern to
that specified in the second entry of scanlist.
The handshaking process will continue, until it reaches the end of the scanlist
(if one-time scanning mode is selected), or when a software scan-abort
command is received.
Connecting, Trigger and Synchronize with External DMM
In this example, Agilent® 33401A 6-1/2 Digital Multimeter (DMM) is used to
demonstrate signal connection for handshaking operation.
The DMM provides two terminals on the rear panel for the handshaking
operation process, Tr i g I n and VM Comp. The Tr i g I n connects to the Scanner
Advanced output on switch module, while the VM Comp to Trigger In. If the
terminal board is used, wire Tr i g I n to TRG_IN on terminal board, and the VM
Comp to S_ADV.
Follow the instructions below to ensure the handshake functions properly:
1. Configure ADLINK PXI switch module’s Tr ig ger In to rising-edge
triggered, Scanner Advanced output in active-low pulsating
mode with pulse width of at least 2us.
2. Configure the DMM to wait for external Trig In before a
measurement, and generate VM Comp after a measurement.
Arm the DMM to wait for the first trigger.
3. Setup the scanlist and auto-scan mode. The first entry in the
scanlist should be set disable wait for the Trigger In, but enable
Scanner Advanced output. Succeeding entries should enable
both Trigg er I n and Scanner Advanced output. Download the
Operation Theorem • 25
Page 32

scanlist to the switch module afterward.
4. Start auto-scan by sending scan start command to the switch
module.
ADLINK
PXI Switch module
Scanner Advanced Output
(S_ADV)
Trigger Input
(Trig In)
(TRG_IN)
External Trigger Input
Wiring
Agilent 33401A
6-1/2 DMM
Measurement Complete
(VM Comp)
Figure 19: Signal Connection between Switch Module and Agilent DMM
For more information on scanlist configuration, scan mode setup, start, and
stop functions of the auto-scanning process, please refer to the software
programming users’ guide.
4.4 Trigger Bus
PXI specification defines eight bused-lines across slots in a segment. Users
can route various trigger signal to synchronize multiple PXI instruments, and/or
simplify field wiring across multiple ADLINK Switch Modules.
On ADLINK Switch Modules, the trigger bus driver is disconnected from PXI
trigger bus before users’ configuration.
Figure 20 illustrates the available signal destinations for Trigger Bus[7..0].
Signal names in the solid-line boxes represent the external (physical) signals
on connectors while signals in the dotted-line boxes represent the switch
26 • Operation Theorem
Page 33

module’s internal signal.
Software Trigger
Trigger In Signal
Scanner Adv. Signal
AUX [3…2]
Star Trigger In
WDT Overflow
SHDNn
Figure 20: Available signal sources for Trigger Bus[7..0]
Trigger Bus[7..0]
4.5 Star Trigger
The PXI specification defined 13 matched trigger lines to connect to the first 13
PXI peripheral slots on a PXI backplane. Users can route various trigger signal
to synchronize multiple PXI instruments and achieve tight timing control.
On ADLINK Switch Modules, the star trigger driver is disconnected from the PXI
backplane before users’ configuration. The maximum skew between each star
trigger line is controlled to within 1ns.
Note the reverse input voltage protection range is -0.5V to +5.5V. When the
local bus is used on peripheral modules, make sure that the voltage level is
compatible with ADLINK Switch Module.
Figure 21 illustrates the available signal destinations for Star Trigger. Signal
names in the solid-line boxes represent the external (physical) signal on
connectors, while signals in the dotted-line boxes represent the switch module’s
internal signal.
Operation Theorem • 27
Page 34

Software Trigger
Trigger In Signal
Scanner Adv. Signal
Star Trigger Out Trigger Bus [7…0]
AUX [7…0]
WDT Overflow
SHDNn
Figure 21: Available signal sources for Star Trigger
4.6 Auxiliary Digital I/O
The eight auxiliary digital I/O lines on ADLINK Switch Modules provide
versatility to users’ control applications. Each digital I/O line can be input, output
or tri-stated. When in output mode, users can still read back the actual logiclevel on the I/O line. All digital lines are pulled-up to 5V with 10k ohm input
resistance.
Note that AUX[2..0] are dual function pins, driving these pins while enabling
handshaking or emergency shutdown functions, may falsely trigger the Switch
Module or external instruments.
Bus-Switch
and Protection
5VDC
10KΩ
AUX Pin
DO
DI
Tri-state
Control
Feedback from output
Figure 22: Auxiliary Digital I/O Function Block
28 • Operation Theorem
Page 35

4.7 Hot-Swap
The Switch Module can be hot-swapped during hardware failure in noninterruptible or high-availability systems where system shutdown is not an
option.
PXI-7931 incorporates an onboard hot-swap control mechanism. However the
extent of the hot-swap functionality support depends on the operating system
and the PXI platform.
Microsoft Embedded XP
system automatically releases system resources when a switch module is
extracted and recognizes the new device.
To remove a switch module, first release the screws on the front panel then
push down the red latch on the ejector. When the blue LED turns on, the Switch
module is ready to be removed by fully pushing down the ejector.
To insert another switch module, align the module’s edge with the card guide in
the PXI chassis. Slide the switch module into the chassis, until there is
resistance from the PXI connector. Push the ejector up and fully insert the
switch module into the chassis, a click should be heard from the ejector latch.
The blue LED on the front panel of the switch module will switch off when it is
ready for operation. Tighten the screws on the front panel.
Note: Microsoft Windows 2000
PXI-7931 can be hot-swapped by manual control via an additional hot-swap
driver. For the hot-swap driver on Windows 2000 and other operating systems
such as Linux, VxWorks, etc., please contact ADLINK for more information.
®
supports the native hot-swap function. The operating
®
does not natively support hot-swap however,
4.8 Emergency Shutdown
In safety-critical applications, users can enable the emergency shutdown
function on PXI Switch Module, to manually set the relay pattern to preset state.
To access this function, users must first configure the emergency shutdown
function by windows API. Generally the trigger source is on the front panel and
connected to a push button, which pulls the SHDNn pin to logic-low when
activated. When multiple PXI Switch modules are installed in a PXI chassis, the
trigger source can be routed through the PXI Trigger Bus and eliminate field
wiring across multiple devices. Figure 23 illustrates available trigger sources for
emergency shutdown. Signal names in the solid-line boxes represent the
external (physical) signal on connectors and signals in the dotted-line boxes
represent the switch module’s internal signal.
Operation Theorem • 29
Page 36

AUX2/SHDNn
Trigger Bus
Star Trigger In
Shutdown Trigger
Figure 23: Available trigger sources for emergency shutdown
The default relay pattern for emergency shutdown is All-Off on PXI-7931; users
can change the pattern by Windows API.
Upon receiving the emergency shutdown trigger, the Switch Module enters
shutdown mode, and the relay pattern is switched to the preset state. If the
Switch Module is in Auto-scan mode, the updating process would be stopped
immediately; in Direct Update mode where the switch module will not accept
any further update instructions.
To leave emergency shutdown mode, users must call adlSwitch_Recovery in
Windows API. The relay pattern would stay the same as they would in the
emergency shutdown mode, and the scanlist (if set) being rewound to the first
entry.
Note the auxiliary digital I/O function pin AUX2 shares the SHDNn pin; driving
AUX2 to logic-low while the emergency shutdown function is enabled. It will
falsely trigger the Switch Module to enter shutdown mode.
This function is disabled by default. For more information, please refer to the
software programming users’ guide.
4.9 Watchdog Timer
In safety-critical applications, users can enable the watchdog timer function on
PXI Switch Module to automatically set the relay pattern to preset state, in case
the operating system or PXI controller crashes.
To access this function, users must first configure the watchdog timer overflow
trigger source by windows API. Generally the trigger source would come from
the onboard 32-bit watchdog timer. When multiple ADLINK PXI Switch modules
are installed in a PXI chassis, the trigger source can be routed through the PXI
Trigger Bus and eliminate redundant watchdog timer setting on multiple devices.
Figure 24 illustrates the available trigger sources for watchdog timer overflow.
Signal names in the solid-line boxes represent the external (physical) signal on
connectors and signals in the dotted-line boxes represent the switch module’s
internal signal.
30 • Operation Theorem
Page 37

Int. WDTimer
Trigger Bus
Star Trigger In
WDT Overflow
Figure 24:.Available trigger sources for watchdog timer overflow
The watchdog timer overflow interval can be programmed through Windows
API. After enabling the watchdog timer, users must periodically reset the timer
by software command. If the timer is not being reset within the specified interval,
the switch module will generate an overflow signal and set the relay pattern to
the one specified by users.
This function is disabled by default. For more information, please refer to the
software programming users’ guide.
Operation Theorem • 31
Page 38

Page 39

Warranty Policy
Thank you for choosing ADLINK. To understand your rights and enjoy all the
after-sales services we offer, please read the following carefully:
1. Before using ADLINK’s products please read the user manual and follow
the instructions exactly.
2. When sending in damaged products for repair, please attach an RMA
application form.
3. All ADLINK products come with a two-year guarantee, repaired free of
charge.
• The warranty period starts from the product’s shipment date from
ADLINK’s factory.
• Peripherals and third-party products not manufactured by ADLINK
will be covered by the original manufacturers’ warranty.
• End users requiring maintenance services should contact their local
dealers. Local warranty conditions will depend on local dealers.
4. This warranty will not cover repair costs due to:
a. Damage caused by not following instructions.
b. Damage caused by carelessness on the users’ part during product
transportation.
c. Damage caused by fire, earthquakes, floods, lightening, pollution,
other acts of God, and/or incorrect usage of voltage transformers.
d. Damage caused by unsuitable storage environments (i.e. high
temperatures, high humidity, or volatile chemicals.
e. Damage caused by leakage of battery fluid.
f. Damage from improper repair by unauthorized technicians.
g. Products with altered and/or damaged serial numbers.
h. Other categories not protected under our guarantees.
5. Customers are responsible for shipping costs to transport damaged
products to our company or sales office.
6. To ensure the speed and quality of product repair, please download a
RMA application form from our company website:
http://rma.adlinktech.com/policy. Damaged products with attached RMA
forms receive priority.
For further questions, please contact our FAE staff.
ADLINK: service@adlinktech.com
Warranty Policy • 33
 Loading...
Loading...