Page 1

Megabit Modem
Megabit Modem
MM701F User Manual
Version 1.x
Page 2

C
opyrig
ht
February 2002
©Copyright 2002 ADC DSL Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Information contained inthis document is company privateto ADC DSL Systems, Inc.,and shall not be modified,used,
copied, reproduced or disclosed in whole or in part without the written consent of ADC.
Trademark Information
ADC is a registered trademark of ADC Telecommunications, Inc.
Avidia and MegabitModem are registered trademarks and StarGazer, SwitchWare, and Skyrocket are trademarks of
ADC DSL Systems, Inc. No right, license, or interest to such trademarks is granted hereunder, and you agree that no
such right, license, or interest shall be asserted by you with respect to such trademark.
Other product names mentioned in this practice are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Disclaimer of Liability
Contents herein are currentas of the date of publication. ADC reserves the right to changethe contents without prior
notice. In no event shall ADC be liable for any damages resulting from loss of data, loss of use, or loss of profits, and
ADC further disclaimsany andallliability for indirect, incidental, special, consequentialor other similar damages.This
disclaimer of liability applies to all products, publications and services during and after the warranty period.
Specific Disclaimer for High-risk Activities
This product is not designed or intended for use in high-risk activities including, without restricting the generality of
the foregoing, on-line control of aircraft, air traffic, aircraft navigationor aircraft communications; orin the design,
construction, operation or maintenance of any nuclear facility. ADC (including its affiliates) and its suppliers
specifically disclaim any express or implied warranty of fitness for such purposes or any other purposes.
ii MM701F User Manual
Page 3

ABOUT THIS USER MANUAL
Use this manual to set up the MM701F modem. It provides instruction on:
• installing the modem
• configuring the modem
• monitoring the modem
• maintaining the modem
DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS
Notes contain information about special circumstances.
Cautions indicate the possibility of equipment damage or personal injury.
About This User Manual
MM701F User Manual iii
Page 4

Product C ertifications
PRODUCT CERTIFICATIONS
FCC CLASS BCOMPLIANCE
This equipmenthas been tested andfound tocomplywith the limits fora Class B digitaldevice,
pursuant topart15 of theFCCRules. These limitsaredesigned to provide reasonableprotection
againstharmfulinterference ina residential installation.This equipmentgenerates, uses andcan
radiateradiofrequency energyand,if not installedand used inaccordance with theinstructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipmentdoes cause harmful interference toradioor television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver
is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
UL
This product meets all safety requirements per UL-1950 standard.
CE
This product meets all EMC and safety requirements per EN 300 386-2 and IEC 950
(EN60950).
iv MM701F User Manual
Page 5

Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1: Overview ...............................................................................................................1
Verify Shipping Package Contents......................................................................................2
System Requirements..........................................................................................................2
What To Do Next ................................................................................................................2
Chapter 2: Installing the Modem ...........................................................................................3
Setting the MDI/MDI-X Switch..........................................................................................4
Connecting the Cables.........................................................................................................5
Checking LED Indications ..................................................................................................6
What To Do Next ................................................................................................................7
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser....................................................9
Setting Up the PC..............................................................................................................10
Configuring the Web Browser ...........................................................................................12
Accessing the Modem Web Pages.....................................................................................15
Managing the System ........................................................................................................16
Configuring the WAN .......................................................................................................23
Configuring the LAN ........................................................................................................27
Managing DSL ..................................................................................................................30
Saving Changes ................................................................................................................. 39
Rebooting the Modem .......................................................................................................40
Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet................................41
Connecting to the Console Port.........................................................................................42
Setting Up a Telnet Session...............................................................................................44
Setting Up the WAN .........................................................................................................45
Managing DSL ..................................................................................................................52
Restoring Factory Defaults................................................................................................59
Saving the Current Configuration .....................................................................................60
MM701F User Manual v
Page 6

Table of Contents
Updating System Software ................................................................................................61
Viewing System Information.............................................................................................62
Rebooting the Modem .......................................................................................................63
Appendix A: Specifications....................................................................................................65
Overview............................................................................................................................66
Data Specifications ............................................................................................................67
Hardware Specifications....................................................................................................71
Appendix B: Technical Assistance and Returns ..................................................................75
Technical Support..............................................................................................................75
World Wide Web...............................................................................................................75
Appendix C: Glossary.............................................................................................................77
vi MM701F User Manual
Page 7
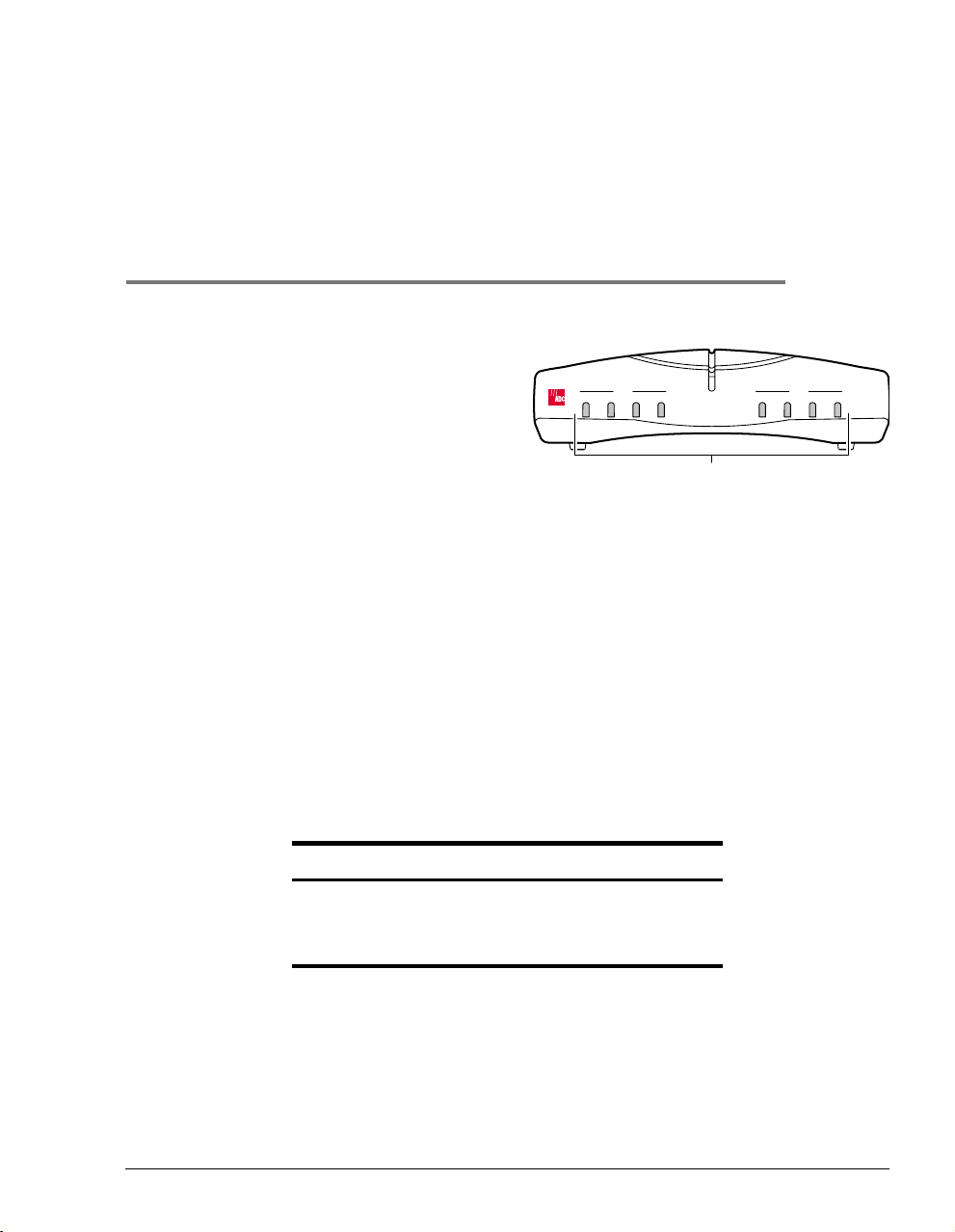
OVERVIEW
The MM701F is a versatile, high speed
modem that connects your LAN to one or
more service providers. It employs ADSL
technology for asymmetric rates up to 7.552
Mbps over single-pair wiring and allows for
multiple management options, including an
easy to use Web-based interface. In addition,
the MM701F supports 32 simultaneousBridge/Router or PPP sessions to the same or different
service providers over its ADSL WAN interface. For sizeable deployment, the MM701F
provides the ability to download pre-defined configuration files to the flash memory instead of
manually defining each and every value for all modems.
The MM701Falsoincludes several usefulprotocols and services.If you require IPaddresses to
be served dynamically on your LAN, use the built-in DHCPserver.Ifyouneed to update your
modem software, use the built-in TFTP client. If you require private IP addresses and n eed to
translate them into public IP addresses, use the built-in NAT function. If you need to exchange
IP routing information with another device, configure and implement RIP. For a complete list
of features, see Appendix A.
Use this guide to install and configure your MM701F. Before installation, verify your shipping
package contents and system requirements as described in the sections listed below.
LAN DSL
PWR
Status LEDs
1
RXTXSYNCCOLRXTXLINK
MAR
Section Page
Verify Shipping Package Contents 2
System Requirements 2
What To Do Next 2
MM701F User Manual 1
Page 8

Verify Shipping Package Contents
VERIFY SHIPPING PACKAGE CONTENTS
As you unpack the modem, inspect the contents for damage. If the equipment was damaged in
transit, report it to the shipping company and to your sales representative.
Check the contents of the package for the following:
• MM701F modem unit
• 6 Vdc power supply
• Ethernet cable
• phone cord with RJ-11 connectors
• console cable and DB-9 console port adapter
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
You needthefollowing hardware and softwaretocomplete the installation andconfigurationof
the MM701F:
• PC with an Ethernet NIC Card (10 Mbps Half Duplex) and serial port
• TCP/IP protocol stack installed (see your operating system documentation)
• Web browser installed such as Internet Explorer
• Ethernet hub/switch (optional)
• Terminal emulation program (such as HyperTerminal)
®
Version 4.0 or higher
WHAT TO DO NEXT
After you have verified the shipping package contents and system requirements, you are now
ready to install the modem as explained in Chapter 2 on page 3.
2 MM701F User Manual
Page 9
INSTALLING THE MODEM
Perform the following installation procedures to install the modem:
Section Page
Setting the MDI/MDI-X Switch 4
Connecting the Cables 5
Checking LED Indications 6
What To Do Next 7
2
MM701F User Manual 3
Page 10
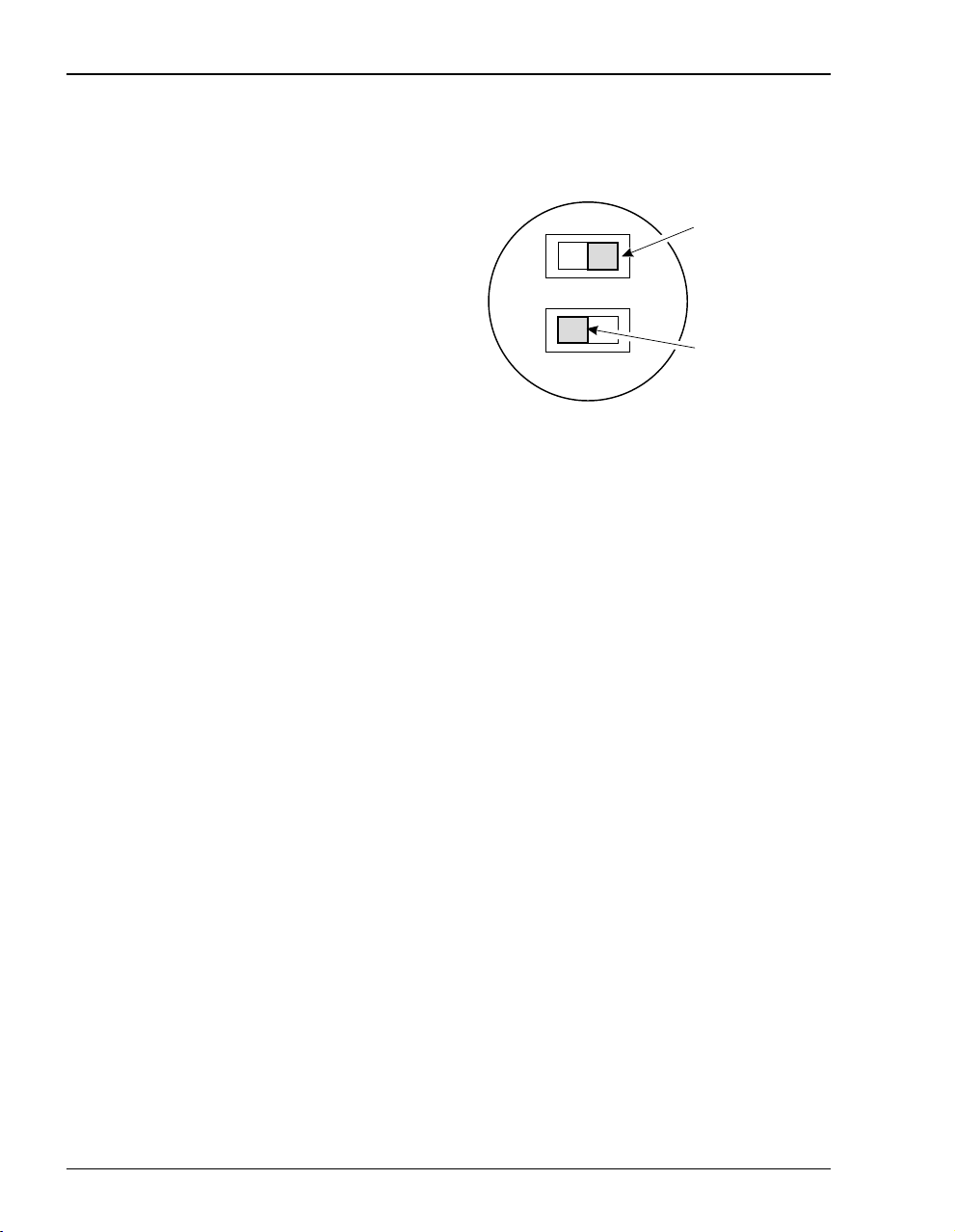
Setting the MDI/MDI-X Switch
SETTING THE MDI/MDI-X SWITCH
The MDI/MDI-X switch located on the modem
rear panel allows you to connect a netw ork
device (such as a PC, hub, switch, or router) to
the modem 10Base-T port.
Set the MDI/MDI-X switch for the 10Base-T
port to:
• MDI-Xwhenconnectingtoanetwork
device such as a PC with an Ethernet NIC
card with a MDI port.
• MDI when connecting to a device such as a
hub, switch, or router with a MDI-X port.
MDI
For connection to
devices such as
a PC
MDI-X
For connection to
devices such as
a Hub
4 MM701F User Manual
Page 11
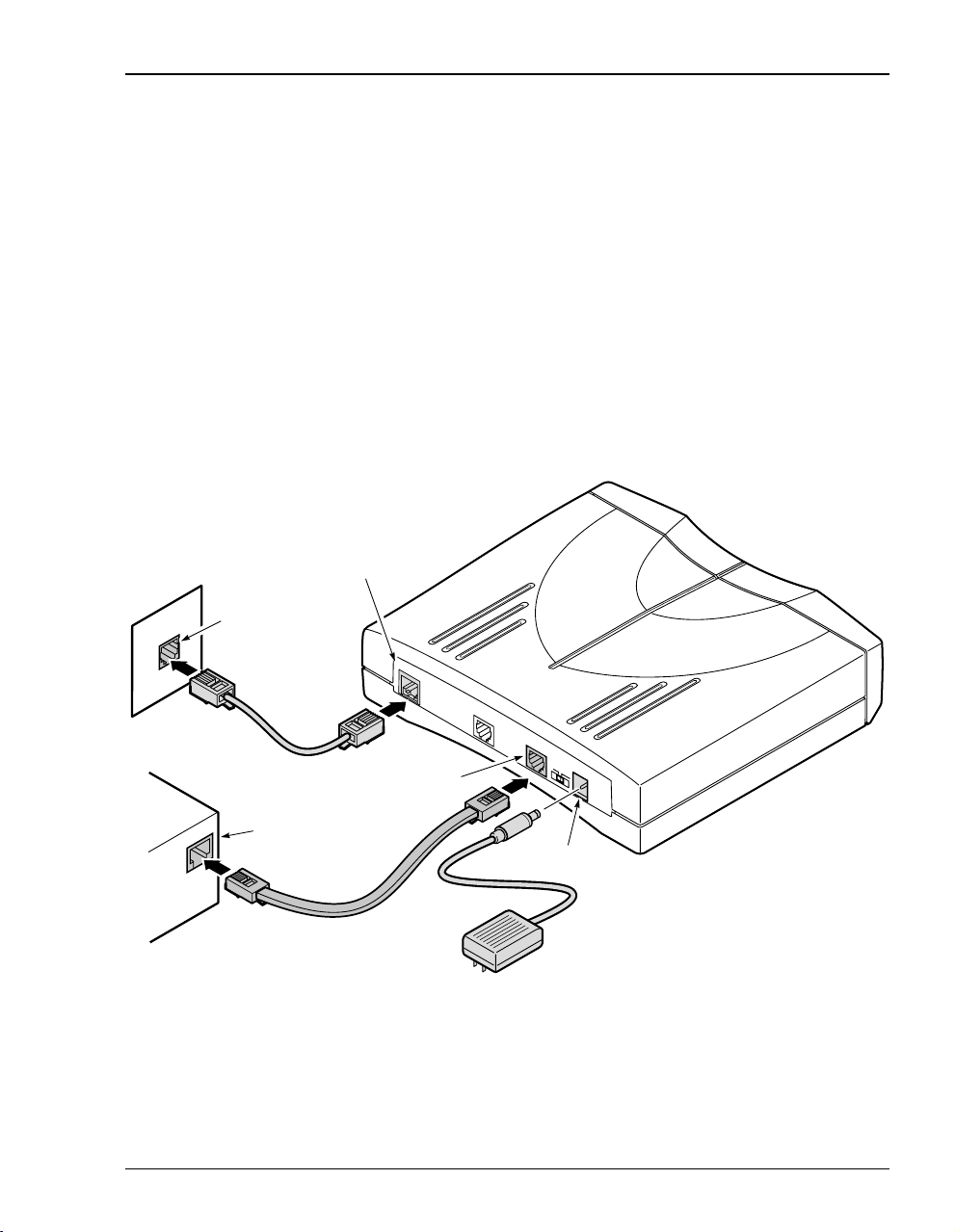
Chapter 2: Installing the Modem
CONNECTING THE CABLES
After you’ve verified the shipping package contents, follow this procedure to physically set up
your modem:
1 Turn off your computer.
2 Connect the cables to the modem rear panel as shown below.
• grey phone cable for the DSL line port
• black cable for the 10Base-T port
• power cable for the modem Power connector
See “Connecting to the Console Port” on page 42 for connecting the console cabling.
DSL line
port
Wall jack with
ADSL service
DSL LINE
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
1
0
B
A
S
E
-
T
POWER
MDI
MDI-X
Power
connector
PC, hub or other
network device
10Base-T
port
MM701F User Manual 5
Page 12

Checking LED Indications
CHECKING LED INDICATIONS
Your service provider sets up the ADSL parameters for your service. The MM701F must have
the DSL SYNC LED lit before you can connect sessions with your service provider.
The table below describes LED indications for all operational modes. LEDs on the MM701F
front panel provide continual status at-a-glance for network connections.
LED State Description
POWER On green MM701F has power.
Off MM701F does not have power.
Ethernet
LINK On green A PC, hub, or other network device is connected to the MM701F
Off No device is connected to the MM701F 10Base-T interface.
TX Flashing green MM701F is transmitting data to devices on the LAN.
Off MM701F is not transmitting data to the LAN.
RX Flashing green MM701F is receiving data from devices on the LAN.
Off MM701F is not receiving data from the LAN.
COL Flashing green Ethernet packet collisions are occurring on the LAN.
Off No Ethernet packet collisions are occurring.
SYNC On green DSL transceiver is synchronized (connected) and in normal operation
Flashing green Slow flashing green indicates that the DSL transceiver is in a start-up
Off DSL transceiver is not detecting a transceiver at the far end and is not
TX Flashing green MM701F is transmitting data over the DSL connection.
Off MM701F is not transmitting data over the DSL connection.
RX Flashing green MM701F is receiving data over the DSL connection.
Off MM701F is not receiving data over the DSL connection.
MAR On green DSL margin is above the preset margin value.
Off DSL margin is at or below the preset margin value.
10Base-T interface.
DSL
mode.
or handshaking sequence. Fast flashing green indicates the DSL
transceiver is in training sequence.
connected.
6 MM701F User Manual
Page 13

Chapter 2: Installing the Modem
WHAT TO DO NEXT
After you have installed the modem, determine which method to use to manage the modem:
• To manage the modem through the Web interface using your Web browser
(recommended), refer to Chapter 3 “Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser” on
page 9.
• To manage the modem through the command-line interfaceusing the modem console port
or by a telnet session, refer to Chapter 4 “Managing the Modem Using the Console Port &
Telnet” on page 41.
MM701F User Manual 7
Page 14

What To Do Next
8 MM701F User Manual
Page 15
MANAGING THE MODEM USING A
WEB BROWSER
You can manage the MM701F using a Web browser, console port, or a telnet session.
All of the MM701F features and functionality are accessible through the Web interface. In
contrast, there are some features not supported through the console port. For example, you can
enable or disable spanning tree through the Web interface, but not through the console port or
telnet. The same principle applies for deleting a WAN session and selecting ATM VBR as a
quality of service.
To prevent losing your configuration changes, be sure to save them as described in “Saving
Changes” on page 39.
Refer to the following sections to take advantage of the Web interface:
Section Page
Setting Up the PC 10
Configuring the Web Browser 12
Accessing the Modem Web Pages 15
Managing the System 16
Configuring the WAN 23
Configuring the LAN 27
Managing DSL 30
Saving Changes 39
Rebooting the Modem 40
3
MM701F User Manual 9
Page 16
Setting Up the PC
SETTING UPTHEPC
To access the modem Web interface, connect your PC to the same LAN IP subnet as the
MM701F. The default LAN IP subnet for the modem is 10.0.0.0 with a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0. In addition, the modem uses 10.0.0.1 as its default LAN IP address.
However, if you have an existing subnettoaccommodate the modem, change the IP address of
the modem from thecommand-lineinterfaceas described in “Setting Up the LAN”on page 48.
If your PC cannot connect to the modem, set your PC Ethernet NIC card for 10 Mbps
half-duplex transmission (not auto-detect).
The following is an example of how to set up a PC running Microsoft Windows 98.
1 From the Windows desktop, click
Control Panel dialog.
the
2 From the
3 From the
Control Panel dialog, double-click the Network icon.
Configuration tab, double-click TCP/IP.
Start, Settings, Control Panel to open
10 MM701F User Manual
Page 17
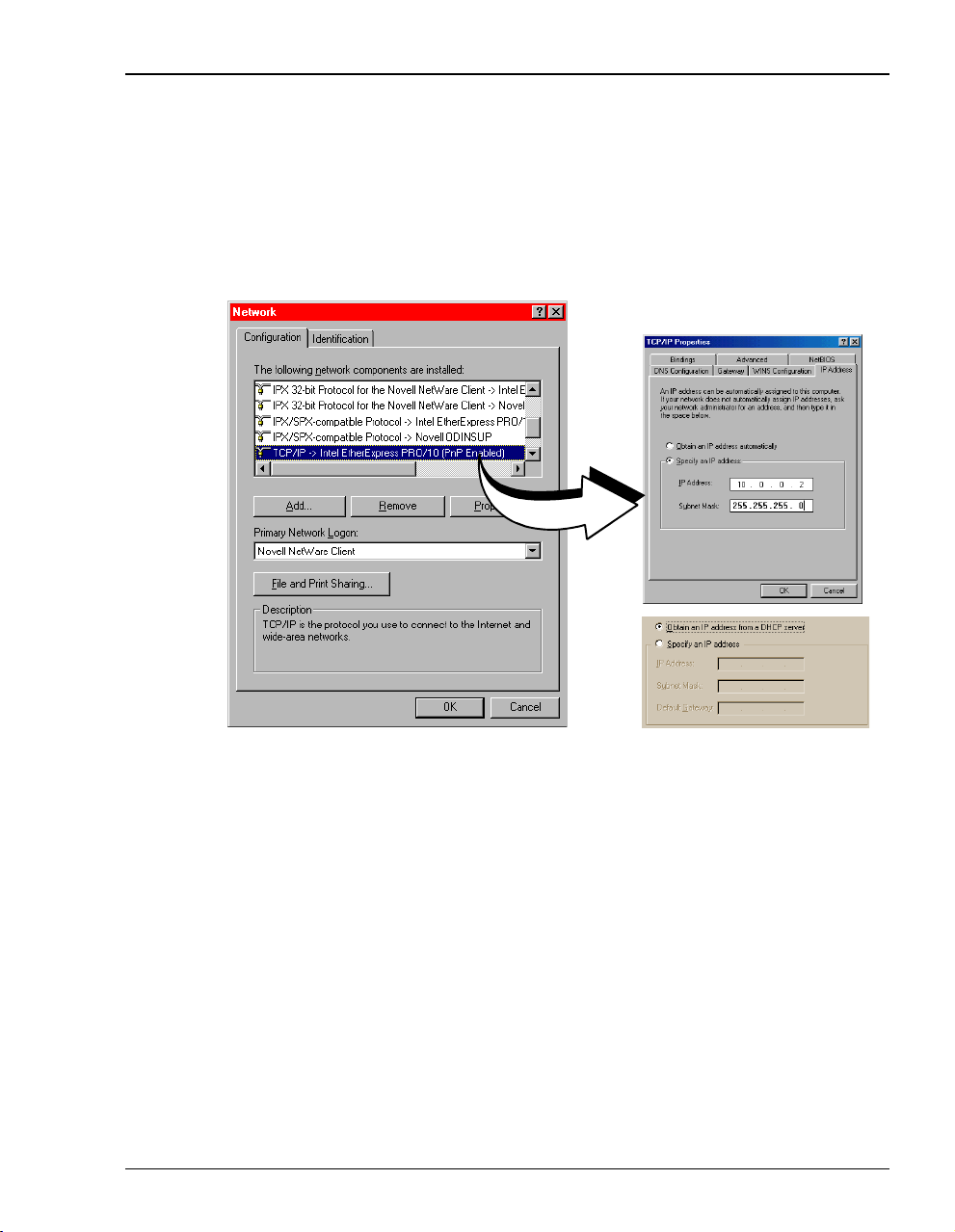
4 Do one of the following:
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
• If DHCP server has not been enabled on the modem (default), select
address
.
• If DHCP server has been enabled on the modem, select
automatically
andskiptostep6.
Obtain an IP address
Specify an IP
5 Enter
IP Address and Subnet Mask. The default modem LAN IP address is 10.0.0.1 with a
subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Use an IP address foryourPC betweentherange of10.0.0.2
to 10.0.0.254.
6 Click
7 Click
8 Click
MM701F User Manual 11
OK to close the TCP/IP Properties dialog.
OK to close the Network dialog.
OK to restart the computer.
Page 18

Configuring the Web Browser
CONFIGURING THE WEB BROWSER
To viewthe modem Webpages properly, yourWeb browser musthave the proxiesdisabled and
cache settings enabled to compare the cached document against the network document every
time it is accessed.
The following is an example of how to make the configuration changes using Netscape
Navigator 4.0.
1 Open your Web browser.
2 Click
Edit, Preferences to open the Preferences dialog.
3 From Category, select
compared to document on network
4 From Category, select
5 Click
OK to close the Preferences dialog.
Advanced, click Cache, then select Every time for Document in cache is
.
Advanced, click Proxies, then select Direct connection to the Internet.
12 MM701F User Manual
Page 19
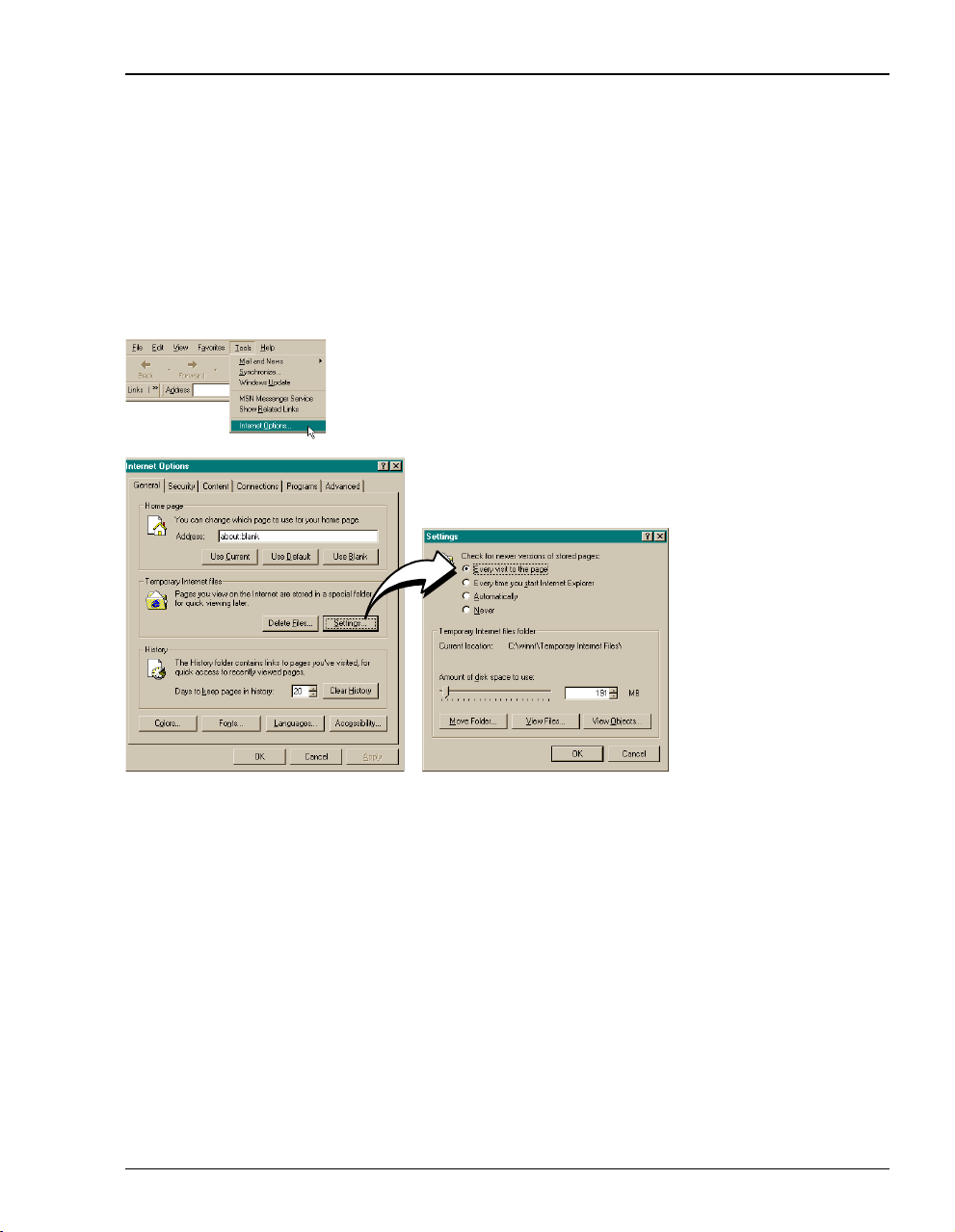
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
The following is an example of how to make the configuration changes using
Internet Explorer 5.5:
1 Open your Web browser.
2 Click
3 In the
4 Select
Tools, Internet Options to open the Internet Options dialog.
Temporary Internet Files section of the dialog, click Settings.
Every visit to the page, then click OK.
MM701F User Manual 13
Page 20
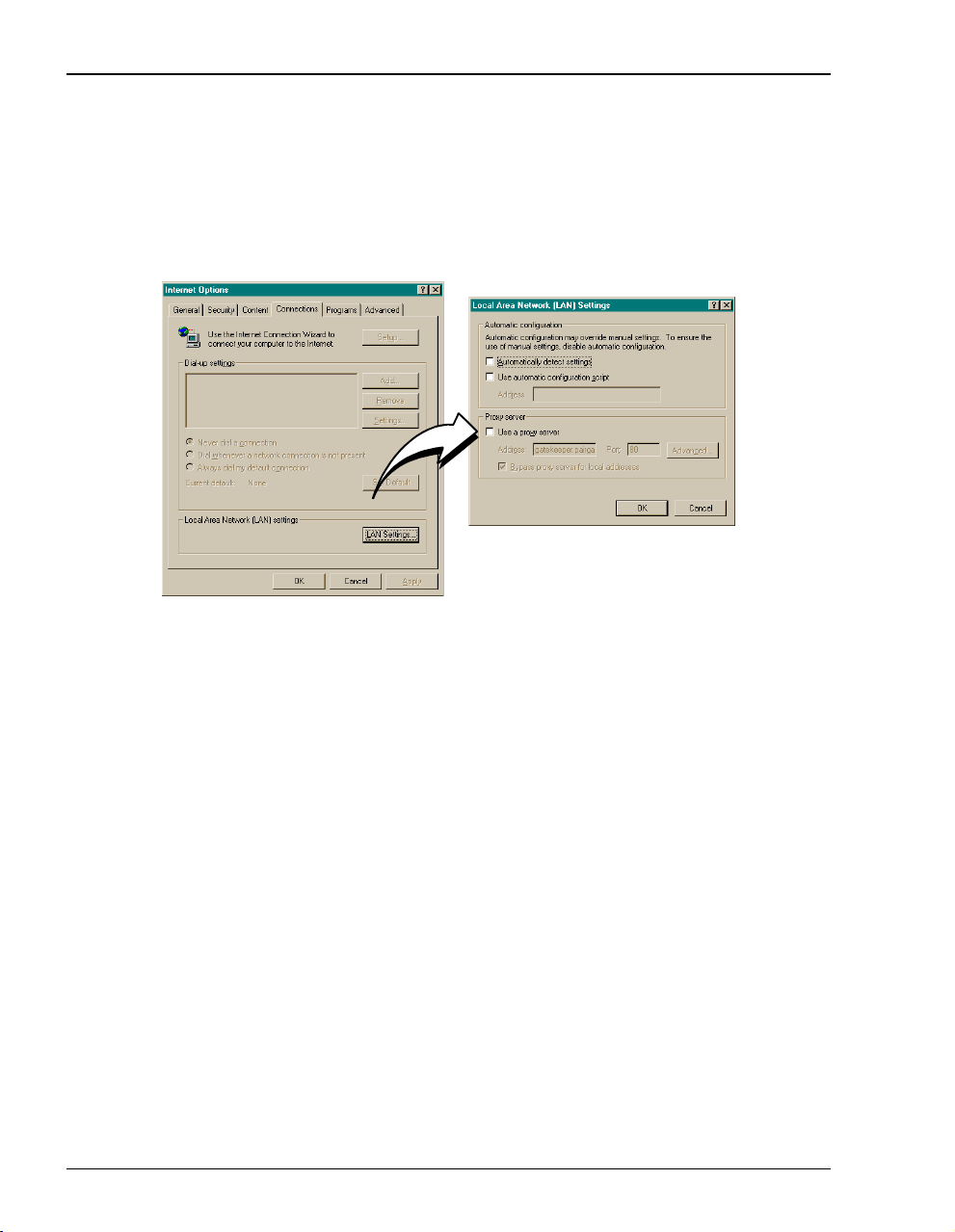
Configuring the Web Browser
5 Click the Connections tab, then click LAN Settings to open the LAN Settings dialog.
6 In the
7 Click
8 Click
Proxy Server section of the dialog, clear the Use a proxy server box.
OK to close the LAN Settings dialog.
OK to close the Internet Options dialog.
14 MM701F User Manual
Page 21
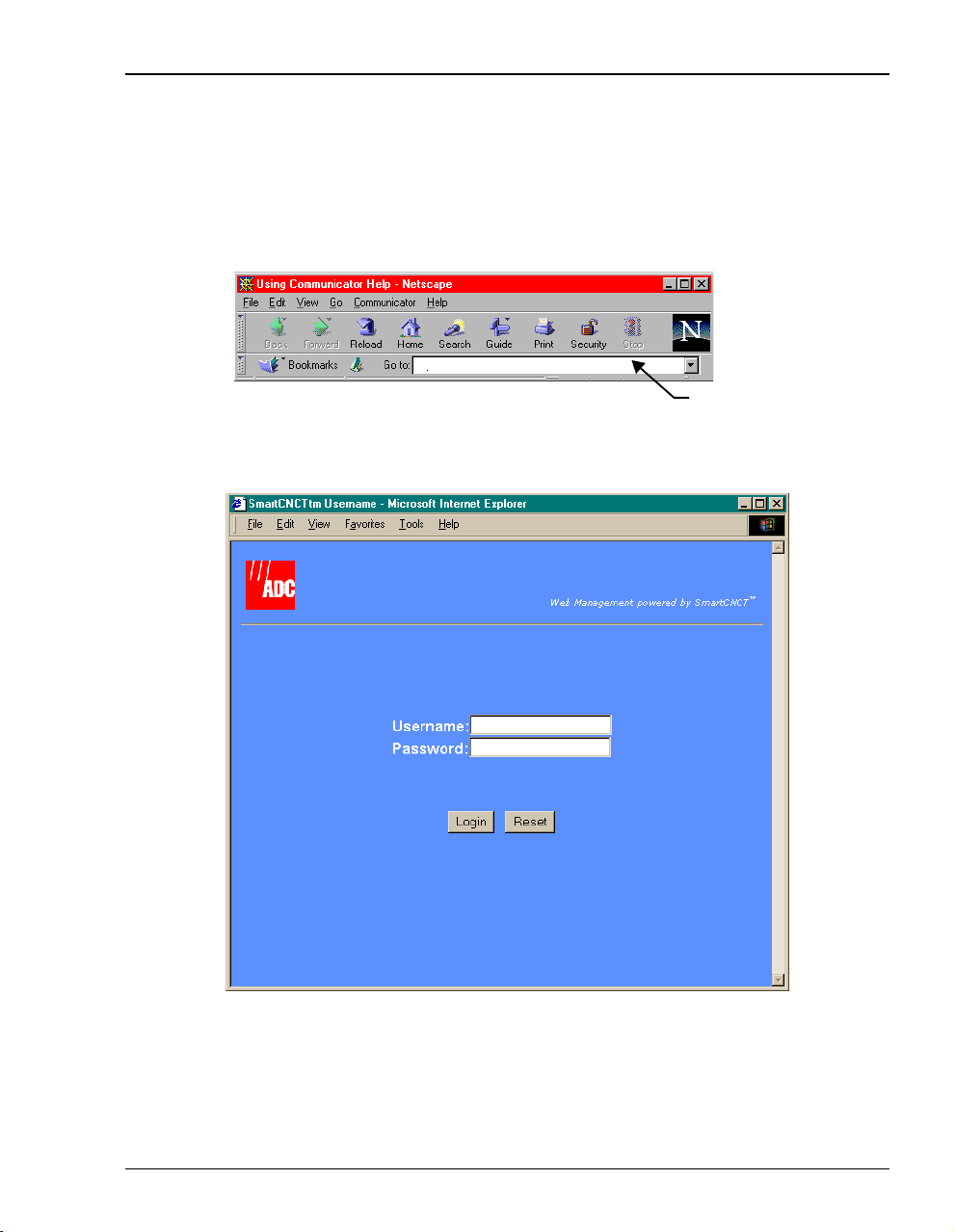
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
ACCESSING THE MODEM WEB PAGES
Type http://10.0.0.1 in the Location Bar field of the Web browser (as shown below), then press
Enter to display the MM701F Web pages.
http://10.0.0.1
Location Bar
The following login screen displays.
This login is for the system administrator responsible for configuring and managing the
MM701F. Enter the default username (
admin)andpassword(password), then click Login.Or,if
you have changed the login username and password, enter the new login username and
password.
MM701F User Manual 15
Page 22

Managing the System
MANAGING THE SYSTEM
The Systempages are designed sothat youcanmanage, update, andtroubleshoot themodemas
a whole. From these pages you can:
• view the overall configuration of the modem
• enable or disable spanning tree
• change the login name and password
• update the modem software and configuration files
• revert back to the default factory values
16 MM701F User Manual
Page 23
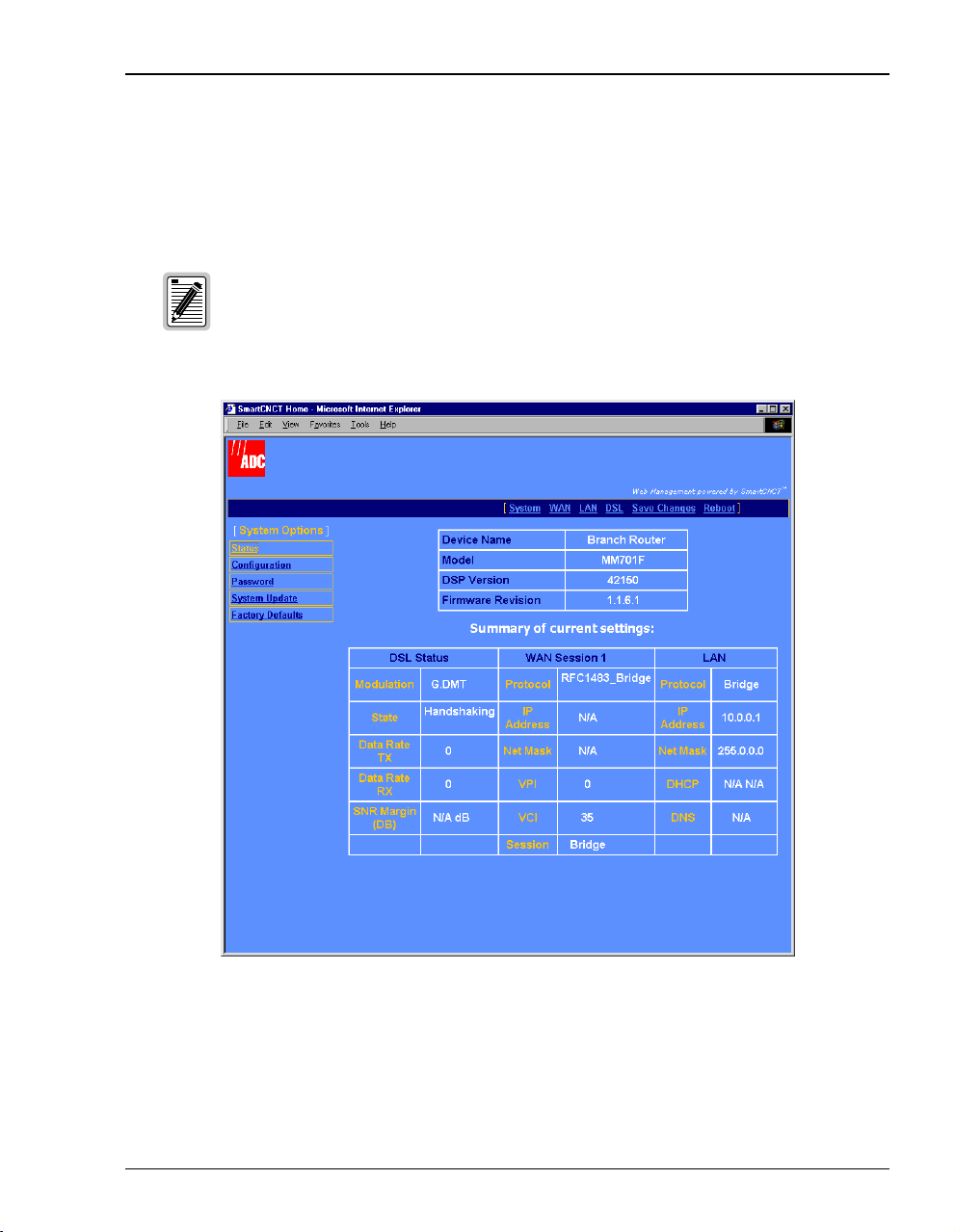
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
View Modem Status
The System Status pageisa read-only summary of the currentmodem configuration. It includes
information about the modem software, DSL configuration values, WAN session settings, and
LAN parameters. Use it as an overview of the modem status.
You cannot change the Device Name.
MM701F User Manual 17
Page 24

Managing the System
Refer to the following table for a description of the fields:
Parameter Description
Device Name Descriptive role of the modem. This is not configurable.
Model Megabit Modem model number.
DSP Version Version of the Digital Signal Processor of the modem.
Firmware Revision Version number of the image downloaded to the modem.
DSL Status Fields Configuration values specific to ADSL.
Modulation ADSL standard (Multi Mode, T1.413, G.DMT, or G.Lite) in the current configuration.
State Status of the DSL link.
Data Rate TX Rate at which the modem is configured to send data.
Data Rate RX Rate at which the modem is configured to receive data.
SNR Margin (DB) Used to control the front panel LED.
For WAN Session and LAN field descriptions, refer to
• “Configuring the WAN” on page 23 for WAN Session fields.
• “Configuring the LAN” on page 27 for LAN fields.
18 MM701F User Manual
Page 25
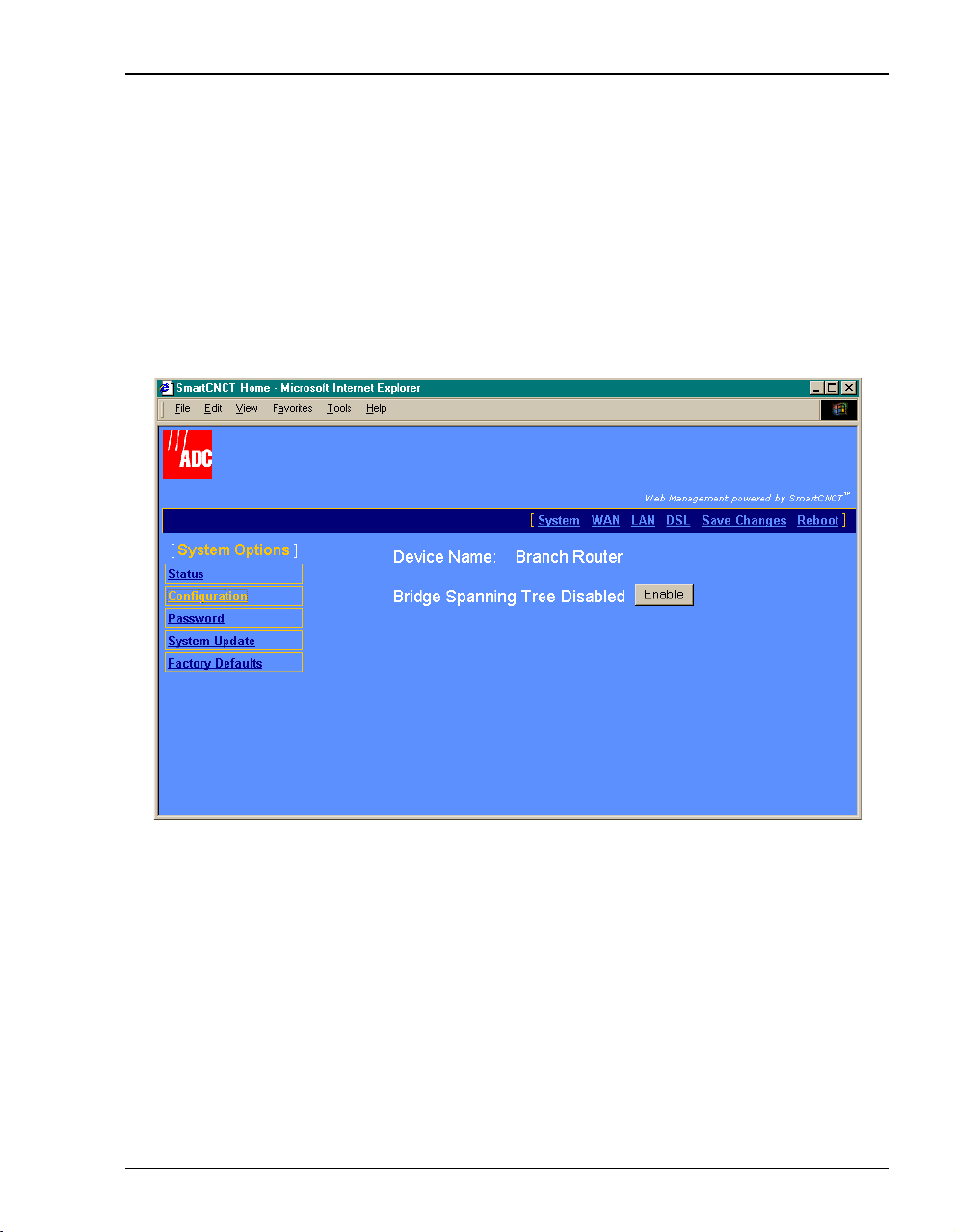
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
Set Spanning Tree
SpanningTreeeliminates loopsina LAN topology,ensuring thatthereis only onepath (or link)
between any two nodeson a network. Use Spanning Tree protocol onlywhen you have already
selected a Bridge session (as described in “Set Up WAN Sessions” on page 23) and when your
LAN has morethan one device (a PConly)on your LAN andthose devices havemore than one
physical path connecting them.
1 Select
System on the menu bar then click Configuration to access the System Configuration
page.
2 Select Enable to activate the Spanning Tree protocol for all bridging sessions.
MM701F User Manual 19
Page 26
Managing the System
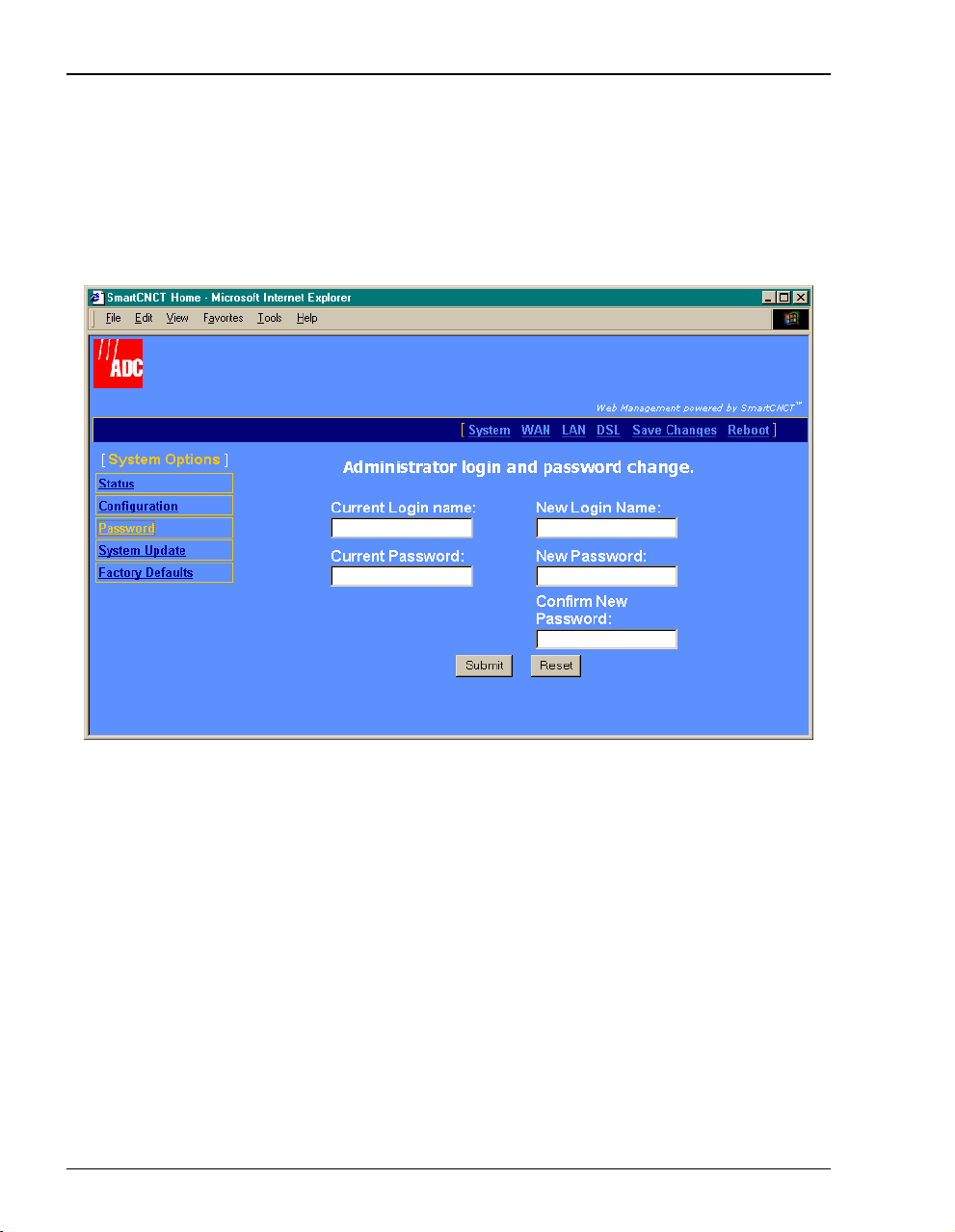
Set Login Name and Password
You can change the login parameters for the system administrator. The default login name is
admin and the default password is password.
1 Select
System on the menu bar then click Password to access the System Password page.
2 Enter the
Current Login name then enter the Current Password.
3 Enter the New Login Name then enter the New Password.
4 Enter the new password again to Confirm New Password.
5 Click
Submit.
Use the new Login Name and Password the next time you login to the MM701F.
20 MM701F User Manual
Page 27
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
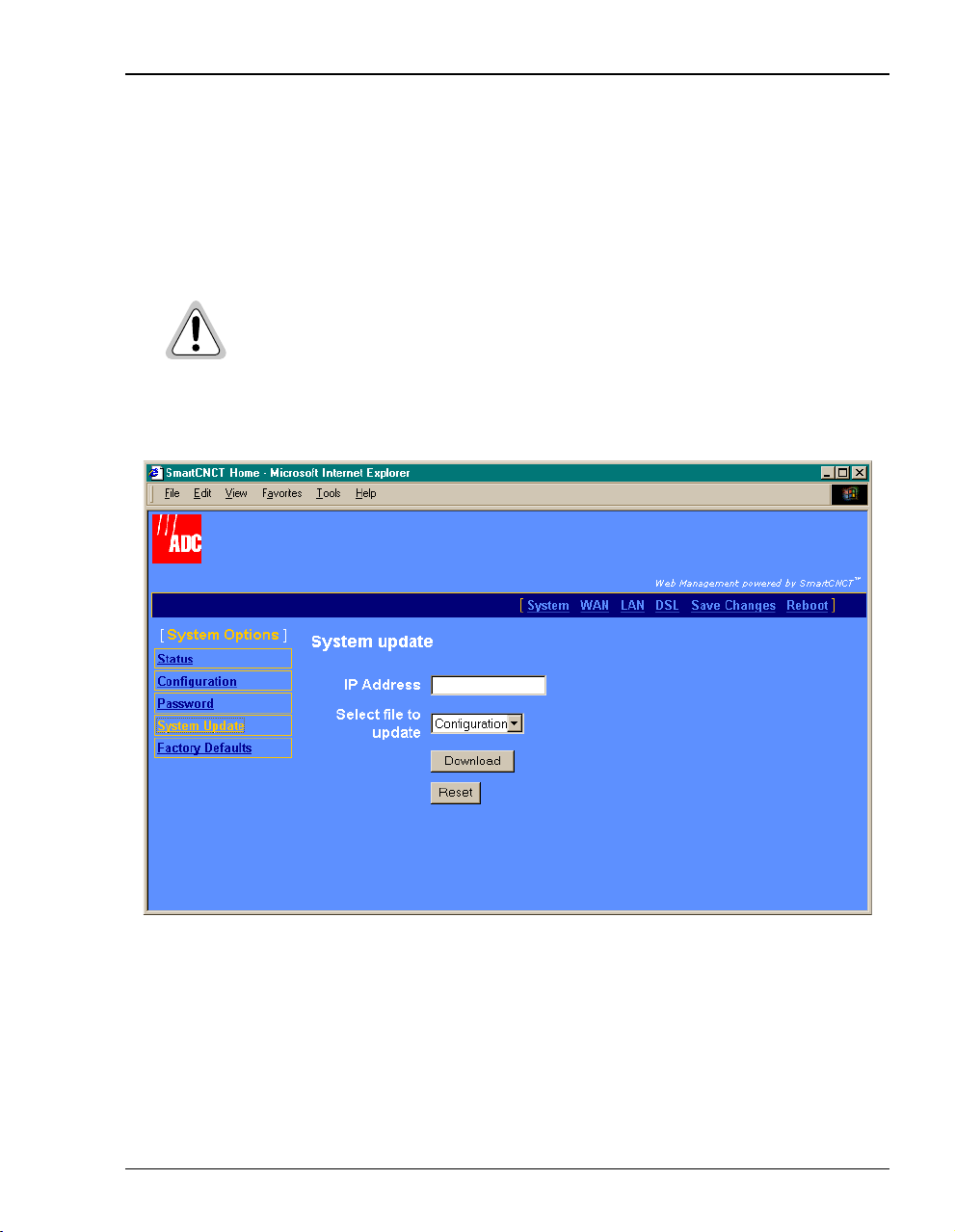
Update System Software
You can upgrade the software on your MM701F. To upgrade, you must specify the IP address
of the server where the new software is stored. The MM701F uses TFTP to download the
software which comprises a configuration file (must be named “celsiancfg”) and an image file
(must be named “image”).
The software update process takes about 90 seconds to complete. After the
update the modem resetsitself. Do not recycle the power during this process.
This will cause permanent image corruption.
1 Click
System on the menu bar, then System Update to access the System Update page.
2 Enter the
IP Address of the server where the firmware image or configuration file is located.
3 From Select file to update, do one of the following:
• select
• select
4 Click
MM701F User Manual 21
Configuration to download the configuration file “celsiancfg”
Image to download the image file “image”
Download to start the file download.
Page 28
Managing the System
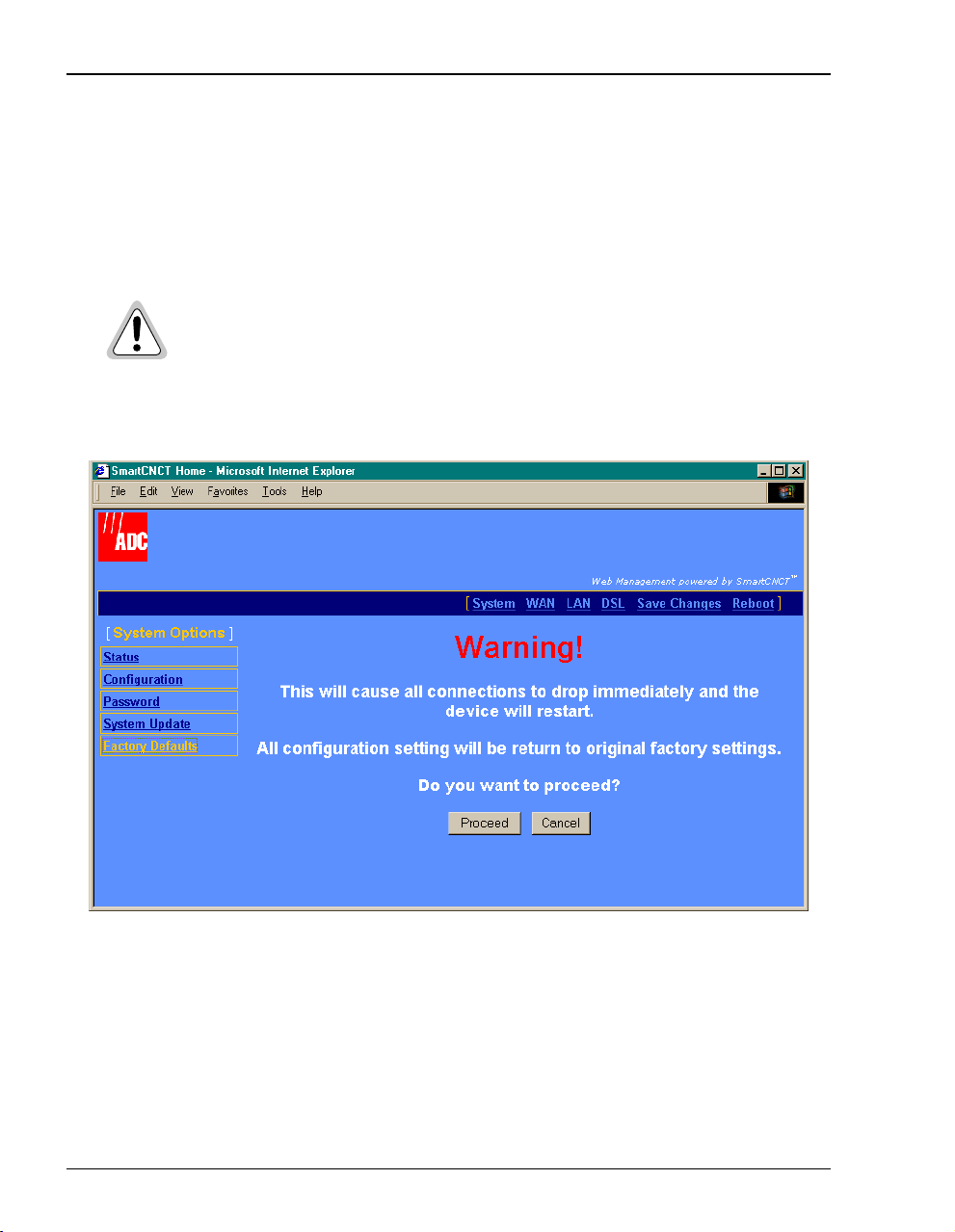
Set to Factory Defaults
When you configure the MM701F, you change the factory default settings to new values. You
can return these parameters to their default values to provide a known starting point if you are
troubleshooting oryou simply wantto configure newparameters.For session defaultvalues,see
“Default Session Parameter Values” on page 70.
Active links are lost when you reset to factory default values.
1 Click
2 Click
System onthemenu bar thenFactory Defaults to accesstheSystem Factory Defaults page.
Proceed if you want to return all values to their original factory values.
3 Click
22 MM701F User Manual
Cancel if you do not want to return all v alues to their original factory values.
Page 29
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
CONFIGURING THE WAN
This configuration sets up the communication between the MM701F and the service provider
for each session you set up.
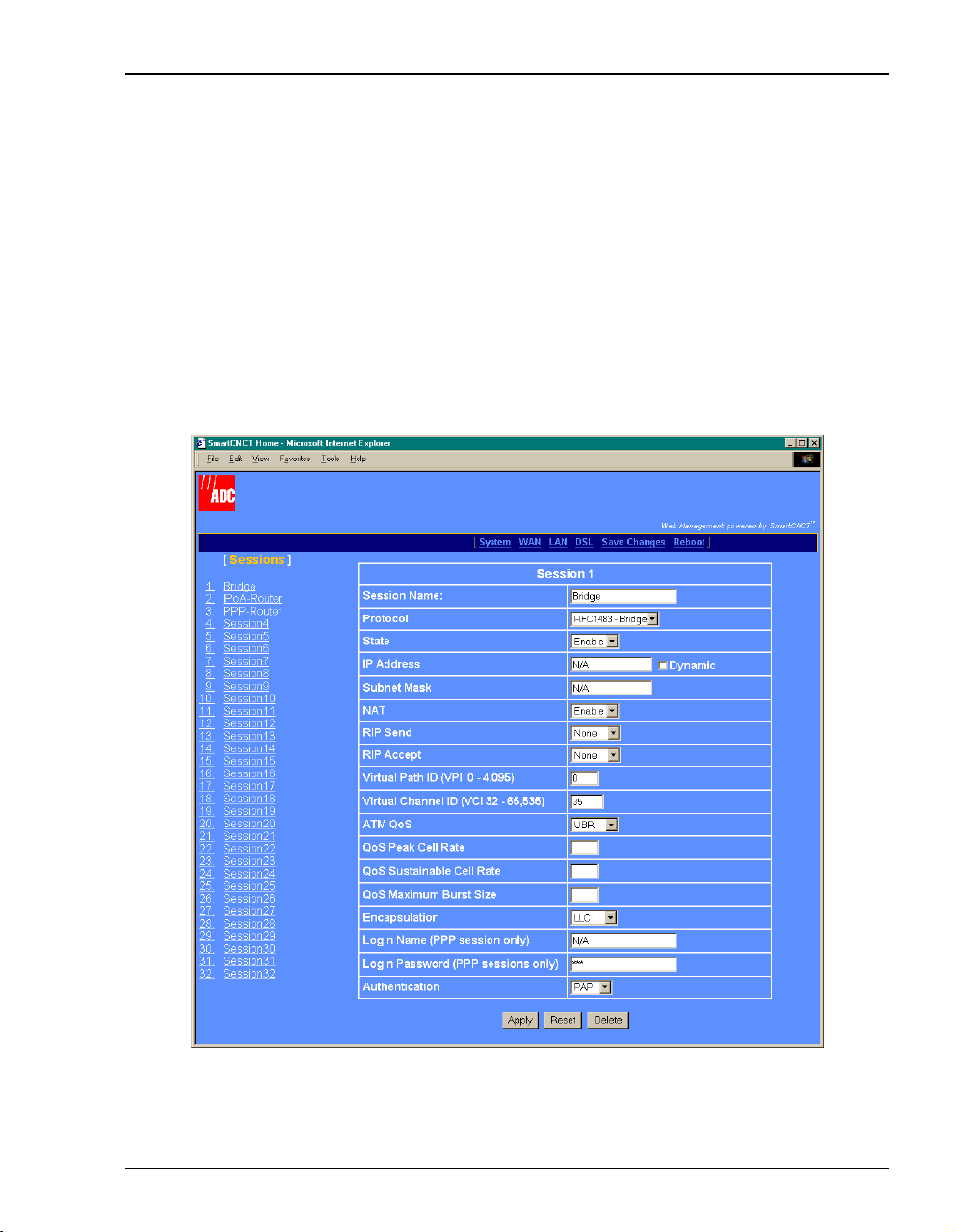
Set Up WAN Sessions
1 Select WAN on the menu bar to access the Session Configuration page.
2 Select a session from the
Session X table (where X equals the Session number).
in the
[Sessions] list. The configuration options for that session appear
MM701F User Manual 23
Page 30

Configuring the WAN
3 Configurethefollowing parameters foreach session yousetup, as definedi n the following
table.
Parameter Description
Session Name Enter a unique, descriptive identifier for the session. This name can have a maximum
of 15 characters with no spaces.
Protocol Select the message format to be used between the MM701F and the service provider.
You can configure each session with any of the three protocols listed below.
If you select RFC 1483 Bridge or RFC 1483 Router protocol, you only need to set up
one session.
You can, however, configure a combination of RFC 1483 Router/Bridge and PPP
protocols for a multiple session configuration.
• Select RFC 1483-Bridge if the MM701F forwards packets based on MAC
addresses. You can enable Spanning Tree when you select Bridge sessions. See
“Set Spanning Tree” on page 19.
• Select RFC 1483-Router if the MM701F routes packets based on IP addresses.
• Select PPPoA if the MM701F establishes PPP sessions with the service provider.
State Select Enable to activate this session. Select Disable to deactivate this session. You
can set the state for each session. You can also change the state for a session at any
time using this parameter.
IP Address Determine how an IP address is assigned to a session:
• If you selected PPPoA protocol, Dynamic is automatically selected. The service
provider automatically assigns an IP address to this session. The IP address
displays in the box.
• If you selected RFC 1483-Router protocol, you enter the IP address supplied by
the service provider in the box. Do not select Dynamic.
• If you selected RFC 1483-Bridge protocol, do not enter an IP address and do not
select Dynamic.
Subnet Mask Determine how the subnet mask is assigned to a session:
• If you selected PPPoA protocol, the service provider automatically assigns a
Subnet Mask. The Subnet Mask displays in the box.
• If you selected RFC 1483-Router protocol, enter the Subnet Mask supplied by the
service provider in the box.
• If you selected RFC 1483-Bridge protocol, do not enter a Subnet Mask.
NAT Enable or Disable the use of Network Address Translation (NAT) protocol to
translate private IP addresses (addresses on your LAN) to public IP addresses
assigned to each session (see IP Address above in this table for session IP
addresses).
24 MM701F User Manual
Page 31

Parameter Description
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
RIP Send Routing Information Protocol (RIP) dynamically routes packets sent from the
MM701F to the service provider. Select the same RIP version that is used by the
service provider:
• Select Disable if you selected RFC1483 - Bridge protocol.
• Select RIP1 to send broadcast packets from the MM701F.
• Select RIP2 to send multicast packets from the MM701F.
• Select RIP1&RIP2 to send both broadcast and multicast packets from the
MM701F.
RIP Accept To dynamically route packets sent from the service provider to the MM701F, select
the same RIP version that is used by the service provider:
• Select Disable if you chose RFC 1483 Bridge protocol.
• Select RIP1 to receive broadcast packets.
• Select RIP2 to receive multicast packets.
• Select RIP1&RIP2 to receive both broadcast and multicast packets.
Virtual Path ID (VPI) Enter the value (from 0 to 4,095) provided by the service provider. The number
identifies the virtual path that transports ATM cells between the MM701F and the
service provider. This value must match the virtual path identification (VPI) that the
service provider uses for this connection.
Virtual Channel ID (VCI) Enter the value (from 32 to 65,535) provided by the service provider. The number
identifies the virtual channel for this session that transports ATM cells between the
MM701F and the service provider. This value must match the virtual channel
identification (VCI) that the service provider uses for this connection.
ATM QoS Select the ATM Quality of Service supplied by your service provider. The options are:
• UBR (unspecified bit rate)
• VBR-nrt (variable bit rate non-real-time)
• CBR (constant bit rate)
QoS Peak Cell Rate Enter the QoS Peak Cell Rate (PCR) value supplied by your service provider. A PCR
value is required for CBR QoS, but is not used for UBR QoS. PCR is the maximum
rate at which data is transferred on the line, measured in cells per second.
QoS Sustainable Cell
Rate
Enter the QoS Sustainable Cell Rate (SCR) value supplied by your service provider.
Use only for VBR-nrt QoS. SCR is the average rate at which ATM cells are
transferred, measured in cells per second.
QoS Maximum Burst
Rate
Enter the QoS Maximum Burst Rate (MBR) value supplied by your service provider.
Use only for VBR-nrt QoS. MBR is the maximum number of cells that can be
transmitted at the peak cell rate.
Encapsulation Select the encapsulation type that is supplied by the service provider. The options
are:
• VC-MUX—Virtual Channel Multiplexer-based encapsulation allows one protocol
to be run over the session.
• LLC—Logical Link Control allows multiple protocols to be run over the session.
MM701F User Manual 25
Page 32

Configuring the WAN
Parameter Description
Login Name A PPP session requires a Login Name that is supplied by the service provider.
Login Password A PPP session requires a Login Password that is supplied by the service provider.
Authentication Select the authentication protocol provided by your service provider for PPP
sessions. The authentication protocol type must match at the MM701F and the
service provider. The options are:
• PAP—The modem sends authentication requests to the service provider and
authentication occurs only once during the life of the link.
• CHAP—The service provider returns an authentication challenge to the modem
during the authentication.
4 Do one of the following:
• Click
• Click
Apply then save changes as described in “Saving Changes” on page 39.
Reset to undothechangesyou made to the screen. Reset will not work after you
have made changes and Apply has been selected.
• Click Delete to remove the session, then save changes as described in “Saving
Changes” on page 39.
26 MM701F User Manual
Page 33

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
CONFIGURING THE LAN
This configuration sets up the communication between your LAN and the MM701F.
1 Select
LAN on the menu bar to access the LAN Settings page.
MM701F User Manual 27
Page 34

Configuring the LAN
2 Configure the following parameters:
Parameter Description
LAN Protocol Select the message format to be used for your LAN.
• Select Bridge if the LAN forwards packets based on MAC addresses. If you
selected RFC 1483 Bridge protocol for the WAN sessions (page 23), select Bridge
for the LAN traffic.
• Select Router if the LAN routes packets based on IP addresses. If you selected
RFC 1483 Router or PPP protocol for the WAN sessions (page 23), select Router
for the LAN traffic.
IP Address See your LAN administrator for LAN IP addresses.
However, if you want to change the IP address through the Web interface, enter an
IP address for the LAN (10BaseT) port provided by the LAN administrator. Or, you
can use the default IP address for the LAN port which is 10.0.0.1. If you choose to
use the default IP address, ensure that the devices on your LAN are on the same
subnet as the MM701F LAN port.
If you select Client for the DHCP configuration (below in this table), a DHCP server
on your LAN automatically provides the IP address.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask for the LAN (10BaseT) port provided by the LAN
Default Gateway Enter the default IP address for a default gateway that is supplied by the service
DHCP See your LAN administrator for the DHCP selection. You selected whether or not you
DHCP Range Low Enter the IP address supplied by your LAN administrator. This is the lowest IP
DHCP Range High Enter the IP address supplied by your LAN administrator. This is the highest IP
administrator. Or, you can use the default subnet mask for the LAN port which is
255.255.255.0. If you choose to use the default subnet mask, ensure that it allows
devices on your LAN to access the MM701F LAN port.
provider.
wanted to enable DHCP in “Determining IP Addresses” on page 14.
However, if you want to change that DHCP selection through the Web interface,
select one of the following:
• None—DHCP is not enabled.
• Client—The MM701F is a DHCP client and can be served an IP address for the
LAN port by a DHCP server on your LAN.
• Server—The MM701F is a DHCP server and can serve IP addresses to devices
on your LAN. See DHCP Range Low and High for the ranges of IP addresses that
the MM701F can serve.
address value that the MM701F can serve when configured as a DHCP server.
address value that the MM701F can serve when configured as a DHCP server.
28 MM701F User Manual
Page 35

Parameter Description
Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
DHCP Gateway Enter the IP address of the default gateway that is provided by the LAN administrator
DNS Server Enter the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server that is provided by
for devices on the LAN. The MM701F must be configured as a DHCP server and
provides this gateway IP address to requesting DHCP clients (such as PCs) on the
LAN.
either the service provider or the LAN administrator. The MM701F must be
configured as a DHCP server and provides this DNS IP address to requesting DHCP
clients (such as PCs) on the LAN.
The DNS server maps human-readable addresses to IP addresses. A
human-readable address is one such as:
maggie.copro.company.com.
The DNS resolver on the server translates this to a numeric value. This numeric value
is the IP address assigned to a WAN session (see page 23).
3 Click Apply.
4 Save changes as described in “Saving Changes” on page 39.
5 If you enabled DHCP, reboot the modem as described in “Rebooting the Modem” on
page 40 to activate the DHCP parameters.
MM701F User Manual 29
Page 36

Managing DSL
MANAGING DSL
Select either the DSL quick configuration or the advanced configuration as directed by your
service provider.
DSL Quick Configuration
You can configure the MM701F to comply with different standards for DSL transmission. For
the quick configuration, you only select the transmission type.
1 Select DSL on the menu bar then select ADSL Quick Config under [ADSL Options].
30 MM701F User Manual
Page 37

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
2 Select one of t he following options as directed by your service provider:
• Multi Mode: Multi-vendor version of T1.413 line code based off of the ANSI standard.
• T1.413: ANSI standard ADSL line code supporting full-ratetransmission.
• G.DMT: ITU standard ADSL line code supporting full-rate transmission.
• G.lite: ITU standardADSL line code that isa simplified version of G.dmtallowing up to 1.536
Mbps downstream and 512 Kbps upstream.
3 Click Apply.
MM701F User Manual 31
Page 38

Managing DSL
DSL Advanced Configuration
You can configure the MM701F to comply with different standards for ADSL transmission as
well as parameters.
1 Select DSL on the menu bar then select DSL Advanced Config under [ADSL Options].
32 MM701F User Manual
Page 39

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
2 Configure the following parameters as supplied by your service provider:
Parameter Description
ADSL Standard for physical
layer interface
Select from the options:
• ITU G.992.2 G.lite
• ITU G.992.1 G.DMT (default)
• ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
• Multimode
Trellis Encoding Enable or Disable (default) Trellis Encoding. Trellis Encoding allows
for high data speeds and reduces transmission errors.
Bin Overlap Mode Select either FDM (default) or EchoCancellation.
Transmit Power Attenuation Select a value from 0 to 12 decibels (0 is the default).
Coding Gain Select either Auto (default) or a value from 0 to 7 decibels.
Maximum Bits per Bin Select a value from 2 to 15 (14 is the default).
Transmit Start Bin Select a value from 6 to 31 (6 is the default).
Transmit End Bin Select a value from 6 to 31 (31 is the default).
Receive Start Bin Select a value from 6 to 255 (32 is the default).
Receive End Bin Select a value from 6 to 255 (255 is the default).
Maximum Downstream Rate Select a value from 32k to 12000k (12,000 is the default).
SNR Margin Limit Select a value from -64 to 63 (4 is the default).
3 Click
Apply then save changes using “Saving Changes” on page 39.
MM701F User Manual 33
Page 40

Managing DSL
Test DSL
The MM701F has embedded diagnostics used for detecting line problems or as an aid in
troubleshooting line relatedtechnicalproblems.Thesediagnosticsare described in “Testing the
DSL Line” on page 58. These diagnostic programs have significance only to technical support
personnel.
1 Select
DSL on the menu bar then select Spectrum Tests to access the ADSL Test page.
2 Select a test from the menu.
3 Do one of the following:
• Click
• Click
34 MM701F User Manual
Start to begin the test.
Stop to terminate the test.
Page 41

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
View Link Statistics
Use the ATM statistics on the DSL Link Statistics page for troubleshooting and monitoring ATM
traffic.
1 Select DSL on the menu bar then select Link Statistics to access the DSL Link Statistics page.
MM701F User Manual 35
Page 42

Managing DSL
2 View the updated real-time statistics.
ADSL Statistical Parameter Description
Operational State Valid entries are:
Coding Gain (dB) Coding gain is the expected improvement or gain due to
DSP Version The modem DSP code can be upgraded—this is the
Last Failed Shows the last state reached before start-up failed. This is
Local Attenuation (dB Current power attenuation at the modem.
Remote Attenuation (dB) Current remote power attenuation.
Local SNR Margin (dB) Current Signal to Noise (SNA) ratio.
Local Tx Power (dB) Current transmit power attenuation at the modem.
Remote Tx Power (dB) Current remote transmit power attenuation.
RS Frame Count Reed Solomon frame count of forward error corrections on
Downstream Data Rate Actual downstream data bit rate after ATM headers have
Upstream Data Rate Actual upstream data bit rate after ATM headers have been
Total Failure Count Total count of errors including CRC, loss of signal, and
• Handshaking—the transceiver is exchanging or
attempting to exchange information necessary to start
up.
• Training—the transceiver is in the process of starting
up.
• Show Time—the transceiver has started up, trained,
and is capable of passing user data.
trellis/RS coding. It is used to help determine the
downstream connection rate. The larger this value is, the
higher the connection rate will be.
current version that is running on your system.
used for troubleshooting by technicians.
the DSL line.
been removed.
removed.
framing errors.
36 MM701F User Manual
Page 43

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
View Error Counters
Use the ATM statistics on the DSL Error Counters page fortroubleshootingandmonitoring ATM
traffic.
1 Select DSL on the menu bar then select ADSL Counters to access the ADSL Counters page.
MM701F User Manual 37
Page 44

Managing DSL
2 View the statistics.
ADSL Parameter Description
Local RS Interleaved Count of local Reed Solomon forward error correction for
the interleaved data stream.
Local RS Fast Count of local Reed Solomon forward error correction for
fast stream.
Local CRC Interleaved Count of local Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) anomalies
for interleaved data stream.
Local CRC Fast Count of local CRC anomalies for fast data stream.
Local Loss of Signal Count of local loss of signal defects.
Remote RS Interleaved Count of remote Reed Solomon forward error correction
for the interleaved data stream.
Remote RS Fast A Count of remote Reed Solomon forward error correction
for fast stream.
Remote CRC Interleaved Count of remote CRC anomalies for interleaved data
stream.
Remote CRC Fast Count of remote CRC anomalies for fast data stream.
Remote Loss of Signal Count of remote loss of signal defects.
38 MM701F User Manual
Page 45

Chapter 3: Managing the Modem Using a Web Browser
SAVING CHANGES
Use the Save Changes page for saving your current configuration to flash memory. This option
immediately writes all current system configuration to permanent memory (NVRAM). You
cannot selectively write configuration to NVRAM. When you issue the save command, all
current configuration is written to NVRAM.
1 Select
2 Do one of the following:
Save Changes on the menu bar to access the Save Changes page.
• Click
• Click
Save to write the configuration to flash memory.
Cancel to exit the current page without saving your configuration.
MM701F User Manual 39
Page 46

Rebooting the Modem
REBOOTING THE MODEM
Before you reboot the modem, make sure you have saved any configuration changes as
described in “Saving Changes” on page 39.
1 Select Reboot on the menu bar to access the Reboot page.
2 Do one of the following:
• Click
• Click
It is unlikelythat the modem willlockup (no response toanyof your requests throught he Web
interface and command-line interface). In this rare occurrence, power off the modem by
disconnecting the power plug, wait 30 seconds, then reconnect the power. This process allows
the modem to properly reset the power and eliminate the possibility of false values in memory.
However, please note that the preferred method of rebooting is to access the Reboot page as
described in the procedure above.
40 MM701F User Manual
Yes to reboot the modem.
No to cancel the rebooting process.
Page 47

MANAGING THE MODEM USING
THE
You can manage the MM701F using a Web browser, console port, and telnet session.
In comparison,you can manage moreofthe modem’s functionality using a Webbrowserrather
than using the modem console port and telnet access. For example, you can enable or disable
spanning treethroughthe modem Web interface,butnot through the consoleport or telnet. The
same applies for deleting a WAN session and selecting ATM VBR as a quality of service.
However, there are scenarios in which using the command-line interface is preferred over the
Web interface. For example, if you cannot connect to the modem through the DSL line and
10Base-T port, you can still manage the modem through the console port.
The following sections describe how to use the command-line interface:
CONSOLE PORT &TELNET
To prevent losing your configuration changes, save them as described in “Saving the
Current Configuration” on page 60.
Section Page
Connecting to the Console Port 42
Setting Up a Telnet Session 44
Setting Up the WAN 45
Setting Up the LAN 48
Managing DSL 52
Restoring Factory Defaults 59
Saving the Current Configuration 60
Updating System Software 61
Viewing System Information 62
Rebooting the Modem 63
4
MM701F User Manual 41
Page 48

Connecting to the Console Port
DSL LINE
POW
ER
MDI MDI-X
10BASE-T
CONSOLE
CONNECTING TO THE CONSOLE PORT
1 Install the supplied grey console cable between the modem Console port and your PC as
shown below.
PC
9-pin COM
port
Adapter
Grey cable
Console port
2 Using a terminal emulation program, verify the communication settings as follows:
• 9600 baud
• no parity
• 8databits
• no stop bit
• flow control off
42 MM701F User Manual
Page 49

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Currently,Windows includesaterminal emulationprogram calledHyperTerminal. InWindows
98, access it from the Windows desktop by clicking
Start, Programs, Accessories, HyperTerminal.
Once you have established communication, the
Main Menu page displays.
MM701F User Manual 43
Page 50

Setting Up a Telnet Session
SETTING UPATELNET SESSION
Make sure your PC is on the same IP subnetasthemodemas described in “Setting Up the PC”
on page 10. To set up a telnet session, specify the LAN IP address of the modem to establish
communication.Thedefault LAN IP addressis10.0.0.1. If this IPaddress has changed, contact
your network administrator.
You cannot managethemodem through the console port andatelnetsession
at the same time.
Below is an example using the telnet application in Microsoft Windows 98:
1 Click
2 In the
Start, Run to access the Run dialog.
Open box,enter the telnetcommandand IP address(for example: 10.0.0.1)then click
OK to start the Windows telnet client and acces s the password prompt. Enter the telnet
password to access t he
password.
Main Menu page. The default telnet password for the MM701F is
44 MM701F User Manual
Page 51

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
SETTING UPTHEWAN
For Bridge or Router mode you need to set the WAN VPI/VCI as supplied by your service
provider.
1 From the Main Menu, select WAN Setup. The WAN Session screen displays.
.
Session group 1 - 16
1. Session 1 Bridge RFC1483 Bridge (Enabled)
2. Session 2 IPoA-Router RFC1483 Router (Enabled)
3. Session 3 PPP-Router PPPoA (Enabled)
4. Session 4 UNDEFINED
5. Session 5 UNDEFINED
6. Session 6 UNDEFINED
7. Session 7 UNDEFINED
8. Session 8 UNDEFINED
9. Session 9 UNDEFINED
10. Session 10 UNDEFINED
11. Session 11 UNDEFINED
12. Session 12 UNDEFINED
13. Session 13 UNDEFINED
14. Session 14 UNDEFINED
15. Session 15 UNDEFINED
16. Session 16 UNDEFINED
17. Get next group
Select session for editing (Return to exit) ->
The WAN Session screen presents data related to each session defined for yourBridge/Router.
The following table provides a description of the four fields displayed on the WAN Session
screen.
Column Description
1 The session number—Sessions 1-16 are displayed on the first page of the
2 Session name—Up to 15 characters may be entered for a descriptive
3 Session protocol—configured for this session.
4 Session status indicator—enabled or disabled.
MM701F User Manual 45
screen and sessions 17-31 are displayed on a the second page of the WAN
session screen.
name for a session. No spaces are allowed. Use this field to help identify
each of your sessions.
Page 52

Setting Up the WAN
2 Select a session by typing the session number at the Select session for editing prompt to
display the
WAN Session Options screen.
1. Session Name Bridge 10. VPI 0
2. WAN Protocol RFC1483 Bridge 11. VCI 35
3. State Enabled 12. QOS UBR
4. IP Addressing N/A 13. QOS Peak Cell Rate
5. IP Address N/A 14. Encapsulation LLC
6. IP Net Mask N/A 15. Login Name N/A
7. NAT N/A 16. Login Password N/A
8. RIP Send N/A 17. Authentication N/A
9. RIP Accept N/A 18. Apply
Select parameter to edit (Return to exit) ->
3 Type
4 Type
1 to select the Session Name then type a session name.
10 to select the VPI parameters then enter the values s upplied by your service
provider.
5 Type 11 to select the VCI parameters then enter the values supplied by your service
provider.
6 If you are operating in Router mode, you also need to enter the WAN IP address and the
associated WAN IP subnet mask. Both of these values are provided by your service
provider.
7 Type
8 Select
18 to immediately activate the changes that you have made for this session.
Save New System configuration from the Main Menu as described in “Saving the
Current Configuration” on page 60 or the changes will be lost upon reboot or power cycle.
46 MM701F User Manual
Page 53

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Valid values for the parameters shown on the Sessions Options screen are defined in the
following table. Unless there is a special circumstance, the default values for the remaining
parameters should not be changed.
Session Parameter Valid parameter Values
Session Name The name assigned to the session by your service
WAN Protocol RFC1483-Router, RFC1483-Bridge, PPPoA.
State Enable or Disable a session.
IP Addressing Static or Dynamic. Not applicable to bridging.
IP Address WAN IP address supplied by your service provider.
IP Net Mask WAN IP subnet mask supplied by your service provider.
NAT Enable or Disable.
RIP Send Disable, RIP1, RIP2, Rip1&Rip2.
RIP Accept Disable, RIP1, RIP2, Rip1&Rip2.
VPI VPI supplied by your service provider.
VCI VCI supplied by your service provider.
QoS Supplied by your service provider.
QoS Peak Cell Rate Supplied by your service provider.
Encapsulation Select VC-MUX or LLC.
Login Name PPP authentication name supplied by your service
Login Password PPP authentication password supplied by your service
Authentication Select PAP or CHAP.
Apply Apply Settings.
provider—up to 15 characters.
provider.
provider.
MM701F User Manual 47
Page 54

Setting Up the WAN
SETTING UPTHELAN
If you are operating in Router mode and in a LAN environm ent, then you also need to set your
LAN protocol, Ethernet Port IP address, and subnet mask.
If you prefer, you may use the default values of 10.0.0.1 for the Ethernet Port IP Address, and
255.255.255.0 for the subnet mask.
1 From the
2 From the
Main Menu, select LAN Setup. The LAN setup screen displays.
LAN
1. LAN Protocol Bridge
2. IP address 10.0.0.1
3. IP Net Mask 255.255.255.0
4. Default Gateway
5. DHCP None
6. DHCP Range Low Address N/A
7. DHCP Range High Address N/A
8. DHCP Gateway Address N/A
9. DHCP DNS N/A
10. Apply
Select Parameter to edit (Return to exit) ->
LAN Setup menu, select LAN Protocol by typing 1.
3 Do one of the following from the LAN Mode menu:
• Type
1 to select Router.
• Type 2 to select Bridge. You must configure an IP address for the LAN port to use a
Browser or Telnet to manage the MM701F.
4 From the LAN Setup menu, type 2 or 3 toselectIP Address or IP Net Mask (respectively), then
enter the values supplied by your LAN administrator or use the default values.
5 From the LAN Setup menu, type4 to selectDefault Gateway,thenentertheDefault Gateway IP
address supplied by your access provider.
6 From the
LAN Setup menu, type 10 to select Apply. Apply immediately activates the changes
that you have made for this session.
7 From the Main Menu, type 5 to select Save New System Configuration and save these settings.
48 MM701F User Manual
Page 55

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Valid values for the parameters shown on the LAN Setup screen are defined in the following
table.
LAN Parameter Valid parameter Values
LAN Protocol Select the message format to be used for your LAN.
• Select Bridge if the LAN forwards packets based on
MAC addresses. If you selected RFC 1483 Bridge
protocol for the WAN sessions, select Bridge for the
LAN traffic.
• Select Router if the LAN routes packets based on IP
addresses. If you selected RFC 1483 Router or PPP
protocol for the WAN sessions, select Router for the
LAN traffic.
IP address See your LAN administrator for LAN IP addresses.
However, if you want to change the IP address, enter an IP
address for the LAN (10Base-T) port provided by the LAN
administrator. Or, you can use the default IP address for
the LAN port which is 10.0.0.1. If you choose to use the
default IP address, ensure that the devices on your LAN are
on the same subnet as the MM701F LAN port.
If you select Client for the DHCP configuration (below in
this table), a DHCP server on your LAN automatically
provides the IP address.
IP Net Mask Enter the subnet mask for the LAN (10Base-T) port
provided by the LAN administrator. Or, you can use the
default subnet mask for the LAN port which is
255.255.255.0. If you choose to use the default subnet
mask, ensure that it allows devices on your LAN to access
the MM701F LAN port.
Default Gateway Enter the default IP address for a default gateway that is
DHCP See your LAN administrator for the DHCP selection.
supplied by the service provider.
However, if you want to change that DHCP selection
through the Web interface, select one of the following:
• None—DHCP is not enabled.
• Client—The MM701F is a DHCP client and can be
served an IP address for the LAN port by a DHCP server
on your LAN.
• Server—The MM701F is a DHCP server and can serve
IP addresses to devices on your LAN. See DHCP Range
Low and High for the ranges of IP addresses that the
MM701F can serve.
MM701F User Manual 49
Page 56

Setting Up the WAN
LAN Parameter Valid parameter Values
DHCP Range Low Address Enter the IP address supplied by your LAN administrator.
DHCP Range High Address Enter the IP address supplied by your LAN administrator.
DHCP Gateway Address Enter the IP address of the default gateway that is provided
DHCP DNS Enter the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS)
Apply Apply Settings.
SettingUpDHCP
This is the lowest IP address value that the MM701F can
serve when configured as a DHCP server.
This is the highest IP address value that the MM701F can
serve when configured as a DHCP server.
by the LAN administrator for devices on the LAN. The
MM701F must be configured as a DHCP server and
provides this gateway IP address to requesting DHCP
clients (such as PCs) on the LAN.
server that is provided by either the service provider or the
LAN administrator. The MM701F must be configured as a
DHCP server and provides this DNS IP address to
requesting DHCP clients (such as PCs) on the LAN.
The DNS server maps human-readable addresses to IP
addresses. A human-readable address is one such as:
maggie.copro.company.com.
The DNS resolver on the server translates this to a numeric
value.
This procedure is optional. Follow this procedure to enable or disable DHCP on the modem.
From the
Main Menu, select LAN Setup screen and enter values for the following DHCP
parameters:
1 To enableDHCP,select
LAN Setup menu. If DHCP Client is selected, you do not need to configure an IP
on the
address.
2 Type
None disables DHCP.
6 to enter the low range of the DHCP IP addresses as supplied by your LAN
DHCP andtype 2 or3 to choose either Client or Server(respectively)
administrator.
3 Type 7 to enter the high range of the DHCP IP addresses as supplied by your LAN
administrator.
4 Type
8 to enter the default gateway address that is provided to the requesting DHCP
client—only if you are operating in server mode. This IP Address is also available from
your LAN administrator.
50 MM701F User Manual
Page 57

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
5 Type 9 to enter the DNS address that is provided to the requesting DHCP client—only if
you are operating in server mode. This IP Address is also available from your LAN
administrator.
6 Type
10 toselectApply.Apply immediatelyactivatesthe changes thatyou have madefor this
session.
7 From the Main Menu, select Save New System Configuration to save these settings or the
changes will be lost upon reboot or power cycle.
8 If you have enabled DHCP, select Reboot from Main Menu to reboot the router.
SettingUpNAT
This procedure is optional. Follow this procedure to enable or disable NAT for a WAN session.
From the
1 Select the session for which you wish to enable NAT. The
2 From theWAN Sessions Options screen, selectthe NAT optionand type1 or 2 toeither disable
Main Menu, select WAN Setup to access the WAN Sessions page.
displays.
or enable (respectively) NAT.
Session State
1. Disable
2. Enable
Select session NAT (Return to exit) ->
WAN Sessions Options screen
3 From the
Main Menu,type10 to select Apply. Apply immediately activates the changes that
you have made for this session.
4 From the
Main Menu, type 5 to select Save New System Configuration and save these settings.
Otherwise, the changes will be lost upon reboot or power cycle.
.
• If DHCP Client is selected, you do not need to configure an IP address.
• In Bridge mode, you need an IP address for the LAN port to use a Browser
or Telnet to manage the MM701F.
MM701F User Manual 51
Page 58

Managing DSL
MANAGING DSL
Use the DSL menu to manage the DSL line. This menu allows you to:
• view the DSL configuration
• configure the DSL line
• monitor the DSL statistics
• test the DSL line
Main Menu
1. WAN Setup
2. LAN Setup
3. DSL
4. Restore Factory Configuration
5. Save Current Configuration
6. System Update
7. System Information
8. Reboot
Select ->
Viewing the DSL Configuration
1 From the Main Menu,type3 to elect DSL.TheADSL Menu displays.
2 From the
ADSL Menu, type 1 to select ADSL Current Settings. The ADSL Current Setting page
displays.
3 View theDSLconfiguration as describedbythe table shown in“Advanced Configuration”
on page 53.
Configuring the DSL Line
1 From the Main Menu,type3 to select DSL and access the ADSL Menu.
2 From the
• To configurean ADSL standard (G.Lite,G.DMT,T1.413, or Multimode),select
• To configure the advanced features of the modem, select
ADSL Menu, do one of the following:
Configuration Setting
and proceed to “Quick Configuration” on page 53.
and proceed to “Advanced Configuration” on page 53.
Advance Configuration Setting
Quick
52 MM701F User Manual
Page 59

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Quick Configuration
From the ADSL Standard page, select one of the following:
•
Multimode: Multi-vendor version of T1.413 line code based off of the ANSI standard.
•
T1.413: ANSI standard ADSL line code supporting full-rate transmission.
•
G.DMT: ITU standard ADSL line code supporting full-rate transmission.
•
G.lite: ITU standard ADSL line code that is a simplified version of G.dmt allowing up to
1.536 Mbps downstream and 512 Kbps upstream.
Save your changes by selecting Save Current Configuration from the Main Menu as described in
“Saving the Current Configuration” on page 60.
Advanced Configuration
Use the ADSL Advance Configuration Setting page to configure the advanced setting for the DSL
connection.
ADSL Advance Configuration Setting
1. Standard G.DMT
2. Trellis Disable
3. BinOverlapMode FDM
4. TxPwrAtten 0dB
5. CodingGain Auto
6. MaxBitsPerBin 14
7. TxStartBin 6
8. TxEndBin 31
9. RxStartBin 32
10. RxEndBin 255
11. MaxDownstreamRate (Kbps) 12000
12. SNRMarginLimit (dB) 4
13. Apply
Select Parameter to edit (Return to exit) ->
MM701F User Manual 53
Page 60

Managing DSL
The table below describes each of the parameters displayed in the ADSL Current Settings
screen:
ADSL Parameter Description
Standard May be either ANSI T1.413 Issue 2, ITU G.992.1 (G.dmt),
ITU G.992.2 (G.lite) or Multimode.
Trellis Indicates whether Trellis coding is enabled or disabled.
Trellis Encoding allows for high data speeds and reduces
transmission errors.
BinOverlapMode Valid options are FDM or Echo Cancellation.
TxPwrAtten The current transmit power attenuation level. May range
from 0 dB to 12 dB.
CodingGain Coding Gain refers to the expected improvement or gain
due to trellis coding. It is used to help determine the
downstream connection rate.
MaxBitsPerBin The maximum number of receive bits per bin that can be
selected.
TxStartBin The lowest bin number allowed for the transmit signal.
TxEndBin The highest bin number allowed for the transmit signal.
RxStartBin The lowest bin number allowed for the receive signal.
RxEndBin The highest bin number allowed for the receive signal.
MaxDownstreamRate The maximum downstream transmission rate.
SNRMarginLimit The signal-to-noise ratio limit. This can be set between -64
and +63. The margin LED on the front panel indicates that
the actual SNR is greater than the configured value.
Apply Apply settings.
54 MM701F User Manual
Page 61

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Monitoring the DSL Statistics
Use the ADSL Statistics page to monitor the following types of DSL statistics:
• General Statistics
• Error Counters
Viewing General Statistics
1 From the Main Menu,type3 to select DSL and access the ADSL Menu.
2 Select
3 Select
ADSL Statistics,type4 to access the ADSL Statistics page.
ADSL General Statistics,type1 to access the ADSL General Statistics page.
ADSL General Statistics
1. OperationalState Handshaking
2. CodingGain 0
3. DSP Version 42150
4. LastFailed 0x0000
5. LocalSNRMargin N/A
6. LocalAttenuation 0
7. RemoteAttenuation 0
8. LocalTxPower 0
9. RemoteTxPower 0
10. RSFrameCount N/A
11. DwnstreamDataRate (Kb) 0
12. UpstreamDataRate (Kb) 0
13. TotalFailureCount N/A
Press any key (Return to exit) ->
MM701F User Manual 55
Page 62

Managing DSL
4 View the updated real-time statistics.
ADSL Statistical Parameter Description
OperationalState Valid entries are:
CodingGain (dB) Coding gain is the expected improvement or gain due to
DSP Version The modem DSP code can be upgraded—this is the
LastFailed Shows the last state reached before start-up failed. This is
LocalSNRMargin (dB) Current Signal to Noise (SNA) ratio.
LocalAttenuation (dB Current power attenuation at the IAD.
RemoteAttenuation (dB) Current remote power attenuation.
LocalTxPower (dB) Current transmit power attenuation at the modem.
RemoteTxPower (dB) Current remote transmit power attenuation.
RSFrameCount Reed Solomon frame count of forward error corrections on
DownstreamDataRate (Kb) Actual downstream data bit rate after ATM headers have
UpstreamDataRate (Kb) Actual upstream data bit rate after ATM headers have been
TotalFailureCount Total count of errors including CRC, loss of signal, and
• Handshaking—the transceiver is exchanging or
attempting to exchange information necessary to start
up.
• Training—the transceiver is in the process of starting
up.
• Show Time—the transceiver has started up, trained,
and is capable of passing user data.
trellis/RS coding. It is used to help determine the
downstream connection rate. The larger this value is, the
higher the connection rate will be.
current version that is running on your system.
used for troubleshooting by technicians.
the DSL line.
been removed.
removed.
framing errors.
56 MM701F User Manual
Page 63

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
Viewing Error Counters
1 From the Main Menu, select DSL to access the ADSL Menu.
2 Select
3 Select
ADSL Statistics to access the ADSL Statistics page.
ADSL Counters to access the ADSL Counters page.
ADSL Counters
1. LclRSInterleaved 0
2. LclRSFast 0
3. LclCRCInterleaved 0
4. LclCRCFast 0
5. LclLOS 0
6. RmtRSInterleaved 0
7. RmtRSFast 0
8. RmtCRCInterleaved 0
9. RmtCRCFast 0
10. RmtLOS 0
Press any key (Return to exit) ->
4 View the counters.
ADSL Parameter Description
LclRSInterleaved Count of local Reed Solomon forward error correction for
LclRSFast Count of local Reed Solomon forward error correction for
LclCRCInterleaved Count of local CRC anomalies for interleaved data stream.
LclCRCFast Count of local CRC anomalies for fast data stream.
LclLOS Count of local loss of signal defects.
RmtRSInterleaved Count of remote Reed Solomon forward error correction
RmtRSFast Count of remote Reed Solomon forward error correction
RmtCRCInterleaved Count of remote CRC anomalies for interleaved data
RmtCRCFast Count of remote CRC anomalies for fast data stream.
RmtLOS Count of remote loss of signal defects.
the interleaved data stream.
fast stream.
for the interleaved data stream.
for fast stream.
stream.
MM701F User Manual 57
Page 64

Managing DSL
Testing the DSL Line
The MM701F has embedded diagnostics used for detecting line problems or as an aid in
troubleshooting line related technical problems. These programs are used by technical support
personnel to diagnose problems and determine the appropriate solutions.
1 From the
2 Select
Main Menu, select DSL to access the ADSL Menu.
Hardware/Line Diagnostics to access the ADSL Hardware/Line Diagnostics page.
3 Select a diagnostic test:
•
SpectrumREVERB continuously sends a R-REVERB signal for the CO to measure the
upstream widebandpower.This adjusts the COtransmit power level, its receivergain,
synchronize its receiver, and train its equalizer.
SpectrumMEDLEY continuouslysends a R-MEDLEYsignal (pseudo-randomsignal) for
•
the CO to train its frequency domain equalizer and to estimate upstream S NR.
• SpectrumPILOT continuously sends a R-PILOT signal (single frequency sinusoid) for
the CO to synchronize with the modem.
• None specifies no testing.
These diagnostic programs have significance only to technical support personnel and are not
discussed further in this manual.
58 MM701F User Manual
Page 65

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
RESTORING FACTORY DEFAULTS
When you configure the MM701F, you change the factory default settings to new values. You
can return these parameters to their default values to provide a known starting point if you are
troubleshooting or you simply want to configure new parameters.
Active links may be lost when you reset to factory default values.
1 From the
Configuration
Main Menu, select Restore Factory Configuration to access the Restore Factory
page.
WARNING - This will delete configuration and return to default
1. Continue
2. Cancel
Select (Return to exit) ->
2 Do one of the following:
• Select
• Select
If you restore the factory defaults, savethe changes by selecting
Continue if you want to return all values to their original factory values.
Cancel if you do not want to return all values to their original factory values.
Save Current Configuration from
the Main Menu as described in “Saving the Current Configuration” on page 60.
MM701F User Manual 59
Page 66

Saving the Current Configuration
SAVING THE CURRENT CONFIGURATION
Use the Save Current Configuration page for saving your current configuration to flash memory.
By saving your configuration changes, your changes will not be lost by resetting the modem.
1 From the Main Menu, select Save Current Configuration toaccess the Save Current Configuration
page.
WARNING - This will overwrite configuration
1. Continue
2. Cancel
Select (Return to exit) ->
2 Do one of the following:
• Select
• Select
Continue to write the configuration to flash memory.
Cancel to exit the current page without saving your configuration.
60 MM701F User Manual
Page 67

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
UPDATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE
You can upgrade the firmwareonyourMM701F. To upgrade, you must specifytheIPaddress
of the server where the new firmware is stored.
1 Configure a TFTP server to download the system softw are. The MM701F uses TFTP to
download thefirmware which comprisesaconfiguration file (mustbenamed “celsiancfg”)
and an image file (must be named “image”) located on the TFTP server.
2 From the
3 Type
Main Menu, select System Update to access the System Update page.
System Update
1. IP Address 10.0.0.2
2. File to update CONFIGURATION
3. Update
Select (Return to exit) ->
1 to select IP Address. Configure the IP address of the TFTP server to download the
system software.
4 Type 2 to select File to update. Select the type of file to download.
•
Configuration to download the configuration file “celsiancfg”
•
Image to download the image file “image”
5 Select
Update to begin updating the software.
MM701F User Manual 61
Page 68

Viewing System Information
VIEWING SYSTEM INFORMATION
The System Information page is a read-only summary of the current modem configuration. It
includes information about the firmware release, model, release date, MAC address, and DSP
version. This information is often used by technical support when troubleshooting.
From the
Main Menu, select System Information to access the System Information page.
System Information
1. Firmware Release 1.1.6.1
2. Model MM701F
3. Release date Aug 2 2001
4. MAC address 00:20:A7:A2:01:C0
5. DSP version 42150
Press any key (Return to exit) ->
62 MM701F User Manual
Page 69

Chapter 4: Managing the Modem Using the Console Port & Telnet
REBOOTING THE MODEM
Before you reboot the modem, save configuration changesas describedin “Saving the Current
Configuration” on page 60.
1 From the Main Menu, select Reboot to access the Reboot page.
WARNING - This will reboot without saving configuration
1. Continue
2. Cancel
Select (Return to exit) ->
2 Do one of the following:
• Type
• Type
1 to Continue the reboot process.
2 to Cancel the reboot process.
It is unlikely that the modem will lock up (no response to any of your requests through the Web
interface and command-line interface). In this rare occurrence, power off the modem by
disconnecting the power plug, wait 30 seconds, then reconnect the power. This process allows
the modem to properly reset the power and eliminate the possibility of false values in memory.
However, please note that the preferred method of rebooting is to access the
Reboot page as
described in the above procedure.
MM701F User Manual 63
Page 70

Rebooting the Modem
64 MM701F User Manual
Page 71

SPECIFICATIONS
The MM701F is a DSL CPE modem that takes advantage of ADSL technology by offering
full-rate data transmission at a maximum downstream rate of 7.552 Mbps and a maximum
upstream rate of 928 Kbps. In addition, the MM701F also provides:
sessions for precise control of security, performance and management of users and
•
resources per session. Allowing Service providers to offer additional services and class of
servicefor Internetaccess, privateATMnetworks orconnections toapplication serverslike
video servers or voice gateways.
• self-installation for non-technical users
For further information, reference the following:
Section Page
Overview 66
Data Specifications 67
Hardware Specifications 71
A
MM701F User Manual 65
Page 72

Overview
OVERVIEW
The MM701F provides:
• compliance with full-rate ADSL (ITU G.d mt or ANSI T1.413i2) and ITU G.lite standards
• rates up to 7.552 Mbps downstream/928 kbps upstream for full rate
• rates up to 1.5 Mbps downstream/512 kbps upstream for G.lite
• symmetric rates up to 928 kbps
• RFC 2364 PPP traffic over ATM (AAL5)
• 1483 bridging and routing over ATM
• up to 32 connections set up as PPP Over ATM or RFC 1483 Bridge/Router
• embedded SNMP agent
• DHCP (client and s erver)
• Network and Port Translation (NAPT)
• Web server allowing ease-of-configuration for MM701F through a Web browser
• serial interface for configuration through Telnet or direct connection
• LED reporting status of ADSL and LAN connections
• 10Base-T Ethernet port
66 MM701F User Manual
Page 73

DATA SPECIFICATIONS
DSL Standards
• ADSL (G.dmt, G.lite, T1.413, and Multimode)
ATM standards
• ATM Forum UNI Version 3.1 and UNI Version 4.0
• ITU-T Q.2931, Q.2971 signaling
• ITU I.363.5 ATM Adaptation Layer 5
• ITU I.432 Cell Delineation and HEC
• ITU I.361 ATM Cell Format
• Classes of Service: CBR, UBR, VBR-nrt
• Virtual Circuits: 32 for data
Appendix A: Specifications
Internetworking Features
• PPP: 1332, 1661, 1638, 1570
• NAT and NAPT: 1631
• DHCP Server & Client: 2131, 2132
• Dynamic IP routing, ARP: 826, RIP: 1058, 1723
• TCP/IP: 1112, 1122, 950, 894, 793, 791, 1812
• BOOTP: 951, 1542
• TFTP: 1350
• IP over ATM: 1577, 1755
MM701F User Manual 67
Page 74

Data Specifications
WAN Protocols
• IETF RFC 2364 PPP over AAL5 (VC multiplexing and LLC encapsulation)
• IETF RFC 1483 Multiprotocol encapsulation over AAL5
• IETF RFC 1577 Classical IP over ATM
Security
• PPP authentication - PAP/CHAP: 1334, 1994
• Web and Telnet password
Management
• Embedded SNMPagent,Terminal, Telnet with Webbasedconfiguration and management
tool
• Auto provisioning extensions
• ILMI,OAMF4andF5support
• Concise MIB: 1212, MIB-II: 1213, Traps: 1215, Bridge MIB: 1493
• SNMP MIB: 1471, 1472, 1473, 1474
• SNMP: 1157
• Open DSL
• DSL Forum Auto-Configuration
• Remote Configuration
Software Upgrade
• TFTP download into built-in flash memory
• Remote download (DSLAM support required)
68 MM701F User Manual
Page 75

Appendix A: Specifications
Encapsulation
When you activate R FC 1483 system mode, you can select WAN encapsulation as VC
multiplexing for some sessions and LLC encapsulation for other sessions.
PPP
Authentication
(PAP/CHAP)
Provides authentication of PPP sessions for security through Password and
Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocols (RFC 1994).
Network Address
Translation
Routing Protocol Supports RFC 1724 Routing Information Protocol (RIP and RIP Version 2).
Encapsulation Supports Logical Link Control (LLC) or VC-based multiplexing (RFC 1483).
Static Routes Supports up to 32 static routes.
Address Resolution Supports Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) over the LAN port (RFC 826).
Bridging and Address
Learning
Encapsulation Supports Logical Link Control (LLC) or VC-based multiplexing (RFC 1483).
Spanning Tree Provides Spanning Tree support per IEEE 802.1d.
Network Address Translation (NAT) maps LAN side private IP address to the
public IP address assigned to the 32 virtual channels (RFC 1631). You can map
to two private addresses to each of the 32 sessions for a total of 64 addresses.
Routing
Bridging
Implements a transparent learning bridge with a bridging table of 1024 entries.
RFCs
• RFC 1483 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM (Bridging/Routing)
• RFC 2364 PPP Encapsulation over ATM
• RFC 1994 for PAP/CHAP Authentication
• RFC 1631 IP Network Address Translator (for NAPT)
• RFC 1350 for TFTP client
• RFC 2131 and RFC 2132 for DHCP server and relay protocols (supported only in RFC 1483 Bridging
mode) and extensions, respectively
MM701F User Manual 69
Page 76

Data Specifications
MIBs
• Bridge MIB - 1493
• SNMP MIBs - 1471, 1472, 1473, 1474
• MIB 1213 - MIB II
• MIB 1215 - Trap
Default Session Parameter Values
Session Parameter Bridge IPoA Router PPP-Router
Protocol RFC1483 - Bridge RFC1483 - Router PPPoA
State Enable Enable Enable
IP Address N/A 10.0.0.1 N/A (Dynamic)
Subnet Mask N/A 255.255.255.0 N/A (Dynamic)
NAT Enable Disable Disable
RIP Send None RIP 1& 2 RIP 1 & 2
RIP Accept None RIP 1 & 2 RIP 1 & 2
Virtual Path ID (VPI: 0 - 4095) 0 0 0
Virtual Channel ID (VCI: 32 - 65536) 35 36 38
ATM QoS UBR UBR UBR
QoS Peak Cell Rate (PCR) N/A N/A N/A
QoS Sustainable Cell Rate (SCR) N/A N/A N/A
QoS Maximum Burst Size (MBS) N/A N/A N/A
Encapsulation LLC LLC LLC
Login Name N/A N/A admin
Login Password *** *** password
Authentication PAP PAP CHAP
70 MM701F User Manual
Page 77

HARDWARE SPECIFICATIONS
LED
• Power
• Ethernet: Link, Tx, Rx, Collision
• DSL: Sync, Tx, Rx, Margin
Connectors
• DSL Interface: RJ-11
• 10Base-T: RJ-45
• Console Port: RJ-45 (serial connection to RS-232 for local configuration)
LAN Interface
• 10Base-T (IEEE 802.3i)
Appendix A: Specifications
• Connector: RJ-45 with MDI/MDI-X switch
MM701F User Manual 71
Page 78

Hardware Specifications
WAN Interface
ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line)
Maximum transmission rate:
Downstream
Upstream
Minimum transmission rate to sync 64 kbps
Connector RJ-11
7552 kbps
928 kbps
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
ATM Adaptation Layer AAL5 (ITU I.363.5) - Supports encapsulation and
ATM Layer Attaches or strips the 5-byte header to the 48-byte SAR-PDU.
Cell Format Format complies with ITU I.361 ATM cell format. Cell delineation
Virtual Circuit type Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) per ATM forum UNI Version 3.1.
Maximum Virtual Circuits 32 virtual circuits that can simultaneously connect to service
de-encapsulation of AAL5 Protocol Data Units (PDUs) for
convergence. Segmentation and Reassembly (SAR) layer
segments and reassembles AAL5 PDUs into ATM cells that are
48 byte SAR-PDUs.
Performance is a maximum line rate of 17,812 cells per second
downstream and 2,189 cells per second upstream.
complies with ITU I.432 Cell Delineation and HEC. Cells are fixed
length (53 bytes), including 5 bytes of header and 48 bytes of
payload. Included in the header are the VPI and VCI number.
providers for sessions encapsulated either as PPP or RFC 1483
Bridging/Routing.
72 MM701F User Manual
Page 79

Appendix A: Specifications
Connector Pinouts
The following sections provide the pinout information for the various modem connectors.
DSL Port (RJ-11)
The following table shows the signal on each pin of the DSL port. The connector for this
interface is an RJ-11. See “Connecting the Cables” on page 5 for the location of this port.
Pin Signal
1 Not used
2 No connection
3 Ring
4 Tip
5 No connection
6 Not used
10Base-T Port (RJ-45)
The following table shows the signal on each pin of the 10Base-T port connector when the
switch is in either the MDI or the MDI-X position. The connector for this interface is an RJ-45.
See “Connecting the Cables” on page 5 for the location of this port.
MDI MDI-X Signal Description
1 3 TX+ Transmit Data (+)
2 6 TX- Transmit Data (-)
3 1 RD+ Receive Data (+)
4 4 Not used Not used
5 5 Not used Not used
6 2 RD- Receive Data (-)
7 7 Not used Not used
8 8 Not used Not used
MM701F User Manual 73
Page 80

Hardware Specifications
Console Port (RJ-45)
The following table gives the signal designations and pin numbers for each end of the RJ-45 to
RS-232 cable that is used between the modem Console port (RJ-45) and the PC Serial port
(DB-9).
PC RS-232 Serial Port
(DB-9)
3 3 TxD Transmit Data
5 5 GND Ground
2 6 RxD Receive Data
Modem
Console
(RJ-45)
1 RTS Ground
2 DTR Ground
4 GND Ground
7 DSR Ground
8 CTS Ground
Signal Description
74 MM701F User Manual
Page 81

TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
AND
RETURNS
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Technical support is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week by contacting the ADC Technical
Assistance Center (TAC).
• Telephone: 800.638.0031
714.730.3222
• Fax: 714.730.2400
• Email wsd_support@adc.com
A Customer Service Engineer answers technical assistance calls Monday through Friday
between 7:30AM and5:30PM, PacificTime,excluding holidays.At all othertimes, an on-duty
Customer Service Engineer returns technical assistance calls within 30 minutes.
Refer to the ADC w eb site (see below) for specific warranty information.
WORLD WIDE WEB
B
Avidia product information can be found at http://www. adc.com usinganyWebbrowser.
MM701F User Manual 75
Page 82

Knowledge Base
KNOWLEDGE BASE
The ADC Knowledge Base can help you locate answers to frequently asked questions on a
variety of topics, including:
• troubleshooting
• installation
• configuration
• upgrades
TheKnowledgeBasecanbefoundat:http://www.adc.com/Knowledge_Base/index.jsp using
any Web browser.
76 MM701F User Manual
Page 83

GLOSSARY
10Base-T The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) 802.3 specification for
Ethernet over thin coaxial cable.
C
AAL2 ATM Adaptation Layer 2. Used for compressed voice and video that is intolerant of
AAL5 ATM Adaptation Layer 5. AAL5 has been adopted by the ATM Forum from a Class of
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a high bandwidth, low delay, connection-oriented,
attenuation The dissipation of the power of a transmitted signal as it travels over copper wire,
authentication Security feature offered through PAP and CHAP with PPP sessions.
BER Bit Error Rate is a measure of transmission quality. The ratio of error bits to the total
bps bit-per-second is the number of bits transferred during each second of data
CBR Constant Bit Rate is a Service Class for the modem. It provides constant bit rate data
delay. This layer is used by xDSL technology.
Service called High Speed Data transfer. It typically supports all types of data traffic.
Originally designed to support TCP/IP.
packet-like switching and multiplexing technique that uses 53-byte fixed-size cells to
transmit voice, video and data over a network. ATM layers define how cells are
formatted and provides the transport of the fixed length cells between the modem
and the service provider (or endpoints of the virtual connection).
measured in decibels (dB).
number of bits transmitted.
transmission.
with a timing relationship between the source and the destination. Also, a traffic class
that carries a guaranteed constant bandwidth. Best suited for applications that require
fixed bandwidth, such as uncompressed voice, video and circuit emulation. CBR is a
Quality of Service class defined by the ATM Forum for ATM networks.
cell A fixed-length packet. Also, the unit of data transmission used in ATM. Each ATM cell
MM701F User Manual 77
contains a fixed-size frame (53 bytes) consisting of a five-byte header and a 48-byte
payload.
Page 84

community
string
A text string required for an SNMP trap to be received by a trap receiver(s). Also, a
text string that identifies an SNMP community and is associated with specific access
rights (read-only or read/write).
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check is a method used to verify the accuracy of data
transmission.
downstream
Communications from a service provider to a user.
traffic
encapsulation The inclusion of data in a protocol header prior to transmission, which enables
successful data transmission between different protocol networks.
ES Errored Seconds is the seconds during which errors occur that prevent the payload
from being corrected.
Ethernet A protocol used for LAN traffic, which has a transfer rate of 10 or 100 Mbps.
flash memory Non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed.
gateway A device (generally a router) that provides translation services to allow
communication between two dissimilar networks.
IP Internet Protocol is a TCP/IP protocol that controls packet transmission.
IP address A 32-bit address used in IP routing. The address consists of four octets separated by
decimals. The octets comprise a network section, a subnet section (optional) and a
host section.
LAN Local Area Network is a physically connected group of devices between which data
transmission occurs at high speeds over relatively short distances.
LLC Logical Link Control is an encapsulation protocol for data that you transmit from the
modem over the WAN in 1483 Bridging/Routing mode.
LOF Loss Of Frame is an error indicating that the receiving equipment has lost a frame.
LOS Loss Of Signal is an error indicating that the receiving equipment has lost the signal.
MAC Media Access Control is a physical address associated with a device such as a NIC.
For modem configuration, the MAC is used to map inbound traffic (from a remote IP
address) to an internal (LAN) IP address. Used with 1483 Bridging/Routing Mode.
margin The noise margin in decibels that the modem must achieve with a BER of 10
-7
or
better to successfully complete initialization.
78 MM701F User Manual
Page 85

Appendix C: Glossary
MIB Management Information Base is a set of variables that define the configuration and
status parameters for network management. Network management stations can
retrieve information from and write information to an MIB. The Internet Engineering
Task Force (IETF) specifies standard MIBS for certain types of devices, ensuring any
NMS can manage the devices. Vendors can specify proprietary MIBs for their devices
to fit specific needs.
NAPT Network Address and Port Translation provides the means to map private IP
addresses and TCP/UDP ports to the public IP addresses (proxy addresses) and
TCP/UDP ports that are set up for the PPP sessions. Used with PPP Mode.
NVRAM Non-Volatile Random Access Memory is a medium for storing system configuration
information, so the information is not lost when the system is reset.
octet A TCP/IP term indicating eight bits.
PAP/CHAP Password Authentication Protocol and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
are two ways to authenticate PPP sessions. With PAP, the modem sends
authentication requests to the service provider and authentication occurs only once
during the life of the link.
In CHAP, the service provider returns an authentication challenge to the modem
during authentication. CHAP can be renegotiated during the life of the link. Also, both
the modem and the service provider must support clear text versions of the
password. The CHAP host field must be the same on both ends of the session.
PDU Protocol Data Unit is data as it appears at the interface between a particular sublayer
and the sublayer immediately below.
POTS Plain Old Telephone Service.
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol exists between the hardware layer and the network-layer
interface protocols. It is a widely used protocol for establishing connections on the
Internet. PPP provides the set up and release of connections for each session.
PAP/CHAP provide the authentication for the PPP sessions.
proxy IP address The proxy IP address is the WAN IP address for one of the 32 sessions. The proxy
IP address is used to enter static NAT entries. See IP address.
PVC Permanent Virtual Circuit is a logical connection comprised of a predefined static
route across a packet-switched network that is always in place and always available.
QoS Quality of Service is the configured traffic parameters that are assigned to a virtual
circuit, which specifies how quickly and how accurately data is transferred from the
sender to the receiver.
RFC Request For Comment is a series of notes that contain surveys, measurements, ideas,
techniques, and observations, as well as proposed and accepted TCP/IP protocol
standards. RFCs are available on the Internet.
MM701F User Manual 79
Page 86

RIP Routing Information Protocol allows routers to update the routing tables
automatically (for example with information such as how many hops between
destinations). The version of RIP you select for the session must match the version
supported by the service provider. Versions RIP1 and RIP-1 compatible are used for
broadcast. Version RIP 2 is used for multicast.
SEF Severely Errored Frames is the incoming signal has at least four consecutive errored
framing patterns.
SES Severely Errored Seconds is the seconds during which more than 2,500 bipolar errors
are detected on the line.
session The time during which two computers maintain a communication connection. An
example is a connection configured between the MM550 Integrated Access Device
and the service provider.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol is a protocol that specifies how to send
information between a NMS and managed devices on a network. The managed
devices run a program called an agent. The agent interprets SNMP request and
responds to them. SNMP is used to set device configurations, read device
configurations or read the device status.
Spanning Tree A bridging protocol that detects and prevents loops from occurring in a system
containing multiple bridges.
subnet mask A type of IP address that allows a site to use a single IP address for multiple physical
networks.
TCP Transmission Control Protocol is a transport protocol used to map inbound traffic
(from a remote IP address) to an internal (LAN) IP address. Establishes connection
with remote user before data transmission.
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol is a protocol used for
communications between computers over networks and the internet.
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol is a protocol used to download card images or other files
from an external TFTP server to the NVRAM of any installed cards, or to upload files
from an installed card to an external TFTP server.
trap receivers PCs configured to receive SNMP traps (messages).
traps Autonomous, interrupt-driven, SNMP messages sent from a managed node to a
network management station to indicate that an event has occurred.
UAS UnAvailable Seconds is the number of seconds during which the line is unavailable.
UBR Unspecified Bit Rate is an ATM traffic type used for LAN traffic. When network
congestion occurs, the data is stored in a buffer until it can be sent.
80 MM701F User Manual
Page 87

Appendix C: Glossary
UDP User Datagram Protocol is a transport protocol used to map inbound traffic (from a
remote IP address) to an internal (LAN) IP address. Uses a protocol port number for
the destination at the remote location.
upstream traffic Communications from a user to a service provider.
VCI Virtual Channel Identifier is a 16-bit field addressing identifier in the header of an ATM
cell used to route cell traffic. It identifies a particular VC link for a given VP.
VCMUX Virtual Channel Multiplexer-based encapsulation used for networks with large
numbers of virtual channels making it practical to carry a single protocol per virtual
channel.
VC A Virtual Channel is a logical connection in the ATM network over which ATM cells are
transmitted.
VPI Virtual Path Identifier is an 8-bit field addressing identifier in the header of an ATM
cell that is used to route cell traffic. It identifies a particular VP link.
VP A Virtual Path is a group of VCs carried between two points. The VP provides a means
of bundling traffic traveling in the same direction. VPs are defined by a unique VPI
value.
WAN Wide Area Network is a network consisting of nodes located across a large
geographical area. Also, the connection between a service provider and MM701F
Modem.
MM701F User Manual 81
Page 88

82 MM701F User Manual
Page 89

10Base-T
Numerics
connecting
cables 4
connector pinouts 73
description 77
A
accessing modem web pages 15
adaptation layer 72
ADSL, specifications 72
advanced configuration 53
ATM
adaptation layer 72
cell format 72
description 77
max VCs 72
specifications 72
B
bridging specifications 69
C
cables, connecting 4
cell formats 72
changes,saving 39
configuration file 21
configuration, saving 39, 60
configuring
LAN 27
NAT,CLI 51
, 61
console port 42
connector pinouts 73
console port 74
connecting to 42
managing modem 41
counters, errors 57
D
Data Specifications 67
Default SessionParameter Values 70
defaults
factory 59
settings 22
DHCP 50
downstream 78
DSL
connector pinouts 73
line testing 58
managing 30
monitoring statistics 55
quick configuration 30
testing 34
, 52
E
encapsulation 69
error counters 37, 57
WAN 23
web browser 12
MM701F User Manual 83
Page 90

factory defaults
F
modem
installing 3
restoring 59
setting 22
file
configuration 21
image 21
full duplex 10
general statistics 55
image file 21, 61
installing, modem 3
LAN
configuring 27
setting up 48
troubleshooting 10
, 61
, 61
G
I
L
rebooting 40
modem status, viewing 17
monitoring, DSL statistics 55
, 63
N
NAT
configuring, CLI 51
description 79
setting up 51
network interface card (NIC) 10
O
overview 1
P
package contents 2
password 20
Physical Specifications 71
pinouts 73
login
name 20
PPP, specifications 69
Q
password 20
setting name 20
setting password 20
M
MAC, description 78
managing
DSL 30
, 52
modem 9
system 16
84 MM701F User Manual
, 41
quick configuration 53
R
rebooting, modem 40, 63
requirements 2
restoring, factory defaults 59
RFCs 69
routing, specifications 69
Page 91

saving
S
support 75
system
changes 39
configuration 39
current configuration 60
setting
factory defaults 22
login name 20
password 20
spanning tree 19
setting up
LAN 48
NAT 51
telnet 44
WAN 45
WAN sessions 23
shipping package contents 2
software, updating 21
spanning tree, setting 19
specifications 65
ADSL 72
ATM 72
bridging 69
PPP 69
routing 69
WAN interface 72
, 61
managing 16
requirements 2
updating software 21
viewing information 62
, 61
T
technical specifications 65
technical support 75
telnet
managing modem 41
setting up 44
testing
DSL 34
DSL line 58
TFTP
description 80
updating system software 61
troubleshooting
Ethernet NIC 10
LAN connection 10
no response (lockup) 40
, 63
U
updating system software 21, 61
upstream description 81
statistics
DSL 55
general 55
link 35
subnet mask description 80
MM701F User Manual 85
Page 92

viewing
V
error counters 37
general statistcs 55
link statistics 35
modem status 17
system information 62
, 57
W
WAN
configuring 23
interface specifications 72
setting up 45
setting up sessions 23
warranty 75
web browser, configuring 12
web interface
accessing 15
managing modem 9
86 MM701F User Manual
Page 93

MM701F User Manual 87
Page 94

ADC DSL Systems, Inc.
14402 Franklin Avenue
Tustin, CA 92780
Tel: 714.832.9922
Fax: 714.832.9924
For Technical Assistance:
800.638.0031
714.730.3222
1191789
1191789 Rev A
 Loading...
Loading...