Page 1

VDSL2/GigE
Wireless 11n
Gateway
Model #: T1200H, T2200H
User Manual
Ver 1.0
Solutions for the Digital Life
™
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction 1
Minimum System Requirements 1
Features 2
Getting to Know the Gateway 3
Using the Home Screen 7
Accessing the Home Screen 7
Icon Bar 9
General Information 10
Connection Status 11
Home Network 12
Firewall/Diagnostics 13
Configuring Wireless Settings 14
Accessing Wireless Settings 14
Basic Settings 16
Advanced Settings 19
WPS 21
Wireless MAC Authentication 23
Wireless Distribution System 24
Configuring Firewall Settings 26
Accessing Firewall Settings 26
Firewall 28
IPv6 Firewall 29
Port Forwarding 30
Applications 31
DMZ Hosting 32
IPv6 DMZ Hosting 33
UPnP 34
Configuring Advanced Setup 35
Accessing Advanced Setup 35
Services Blocking 37
Website Blocking 38
Scheduling Access 39
DSL Bonding Settings (T2200H only) 40
WAN IP Addressing 41
IPv6 LAN Settings 42
DHCP Reservation 43
LAN IP and DHCP Settings 44
i
i
Page 3

Table of Contents
IPv6 WAN Settings 45
Dynamic DNS 46
DNS Host Mapping 48
Port Bridging 49
HPNA Settings 49
Admin Password 50
Storage Service 51
Rebooting the Gateway 51
Restoring Factory Default Settings 52
Speed Test 53
Ping Test 54
TCP Dump Debug 55
Iperf Test 56
IPv6 Ping Test 57
Traceroute 58
IPv6 Traceroute 59
Time Zone 59
Language Settings 60
HPNA Diagnostics 61
DNS Cache 62
IGMP Settings 63
Upgrade History 63
SIP ALG 64
Tool Box 64
DLNA 65
xDSL Diagnostics 65
Viewing the Gateway’s Status 66
Accessing Status Tables 66
Connection Status 68
Line 1/Line 2 Status 69
WAN Ethernet Status 70
Routing Table 70
Firewall Status 71
NAT Table 71
Wireless Status 72
Modem Utilization 74
LAN Status 75
ARP Table 75
Interface Statistics 76
Multicast Statistics 76
System Log 77
ii
ii
Page 4

Table of Contents
Specifications 78
General 78
Wireless Operating Range 79
LED Indicators 79
Environmental 79
Notices 80
Regulatory Compliance Notices 80
Modifications 80
GPL (General Public License) 81
Limited Warranty 82
iii
Page 5
Introduction
1
Thank you for choosing the VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway. With its powerful
wireless N radio, gigabit Ethernet switch, and WAN port, as well as its dual-core
processor and support for HPNA, the Gateway will propel you to new speeds as
you traverse the Internet. We are sure the Gateway will provide you with years of
hassle-free performance.
Minimum System Requirements
• Active ADSL2+ service
• Computer with a 10 Mbps or 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet connection
• Microsoft Windows 2000, XP, Vista; Mac OS 7.1+, 8.0+, 9.0+, OS X+
1
Page 6

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
• Internet Explorer 4.0 or higher (5.x+ recommended) or Netscape Navigator
4.0 or higher (4.7+ recommended)
• TCP/IP network protocol installed on each computer
Features
• Gigabit Ethernet (WAN and LAN)
• VDSL 2 access technology (backward compatible to ASDL2+/ASDL2)
• HPNA coax support
• Optional Java Virtual Machine and Java Runtime software
• TR-069 support with remote management
• TR-064 local management
• 64-, 128-, and 256-bit WEP/WPA/WPA2 wireless LAN security
• IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard compliance
• Four 10/100/1000 Base-T Ethernet ports (LAN)
• One 10/100/1000 Base-T Ethernet ports (WAN)
• DHCP server option
• MAC address cloning
• QoS support, including diffserv and random early detection
• PPPoE support
• External Radius support
• Web-based configuration support
• FTP firmware upgradeable
• Web download support
• 802.11b/g/n support
2
Page 7

Chapter 1 Introduction
• WPS support
• Advanced firewall
• ALG
Getting to Know the Gateway
This section contains a quick description of the Gateway’s lights, ports, etc.
The Gateway has several indicator lights (LEDs) and a button on its front panel,
and a series of ports and switches on its rear panel.
Front Panel
The front panel of the Gateway features 11 LEDs: Power, DSL, Internet, WAN
Ethernet, Internet, Ethernet (4), Wireless, USB, and WPS Push Button.
Power
The Power LED displays the Gateway’s current status. If the Power LED glows
steadily green, the Gateway is receiving power and fully operational. When the
Power LED is rapidly flashing, the Gateway is initializing. If the Power LED is
glows red when the Power cord is plugged in, the Gateway has suffered a critical
error and technical support should be contacted. If the Power LED is flashing
red, the Gateway is performing a firmware update.
DSL
The DSL LED illuminates when the Gateway is connected to an ADSL line. If
the DSL LED is flashing, the Gateway is in training for DSL service.
Internet
When the Internet LED glows steadily, the Gateway is connected to the DSL
provider. When it flashes, data traffic is passing across the Gateway.
3
Page 8

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
WAN Ethernet
When the WAN Ethernet LED glows steadily, the Gateway is connected to an
Ethernet WAN. When it flashes, it signifies that data traffic is traveling across
the connection.
LAN Ethernet
The LAN Ethernet LEDs illuminate when the Gateway is connected to another
device via one of its LAN Ethernet ports. When one of the LAN Ethernet LEDs
flashes, data traffic is passing across the corresponding connection.
HPNA
The HPNA LED illuminates when the Gateway is connected to another device
via its HPNA port. When it flashes, data traffic is passing across the connection.
USB
The USB LED illuminates when a USB device is connected via the Gateway’s
USB port. This port is not currently operational, but may be enabled in a future
firmware update.
Wireless
The Wireless LED illuminates when the Gateway is connected wirelessly, assuming the Gateway’s Wireless feature is turned on.
WPS Button
The WPS button activates WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) on the Gateway. To use
WPS, press the WPS button on the Gateway, then, within two minutes, press the
WPS button on a device you wish to connect to the Gateway’s wireless network.
The device will automatically join the Gateway’s wireless network. Repeat for
other wireless devices.
4
Page 9

Chapter 1 Introduction
Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Gateway features 8 ports (Phone, HPNA, LAN Ethernet,
WAN Ethernet, USB, and Power), as well as a Reset button.
DSL Port (Single on T1200H; Dual on T2200H)
The DSL port is used to connect the Gateway to a DSL line connection.
HPNA Port
The HPNA port is used to connect the Gateway to an HPNA connection via
coaxial cable.
LAN Ethernet Ports (4)
The LAN Ethernet ports are used to connect computers to the Gateway via
Ethernet cable. The Ethernet ports are 10/100/1000 Mbps auto-sensing ports,
and either a straight-through or crossover Ethernet cable can be used when connecting to the ports.
WAN Ethernet Port
The WAN Ethernet port is used to connect the Gateway to a WAN via an
Ethernet cable.
USB Port
The USB port is used to connect the Gateway to a USB device. This port is not
currently operational, but may be enabled in a future firmware update.
Reset Button
Depressing the Reset button for 5 seconds will restore the Gateway’s factory
default settings. The reset process will start after releasing the button.
5
Page 10

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Power Port
The Power port is used to connect the Power cord to the Gateway.
WARNING! Do not unplug the Power cord from the Gateway
during the reset process. Doing so may result in permanent damage
to the Gateway.
6
Page 11
Using the Home Screen
This chapter gives a short overview of the Home screen of the Gateway’s firmware,
including explanations of the Home screen’s sections and links.
Accessing the Home Screen
To access the Home screen:
1. Open a Web browser. In the “Address” text box, type:
http://192.168.1.254
then press Enter on the keyboard.
2
7
Page 12
VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
2. The Gateway’s Home screen appears.
3. Enter the username “admin” and the password (printed on the label located on the
bottom of the Gateway) in the Username and Password text boxes at the top right side
of the screen, then click Login.
8
Page 13
Chapter 2 Home Screen
4. You can now access all of the Home screen’s options.
Icon Bar
At the top of the Home screen is the Icon Bar. Here, you can quickly access the
other four main sections of the Gateway’s firmware by clicking on the appropriate
icon: Status (see chapter 6 for more details); Wireless Setup (see chapter 3 for more
details), Firewall (see chapter 4 for more details); and Advanced Setup (see chapter
5 for more details). Clicking Home in any other firmware screen generates the
Home screen.
9
Page 14

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
General Information
The next section of the Home screen is the General Information section.
This section is divided into three subsections: Summary, Product Info, and
Login Status.
Summary
The Summary subsection contains four status lines. Broadband displays the status
of the Gateway’s broadband connection (connected or disconnected). Wireless
displays the status of the Gateway’s wireless network (enabled or disabled), and also
whether any wireless devices are connected to the network. System Up Time displays the length of time the Gateway has gone between reboots. DSL Link Up Time
displays how long the DSL link has been active.
Product Info
The Summary subsection contains four information lines. Model# displays the
model number of the Gateway. Serial# displays the serial number of the Gateway.
MAC Address displays the Gateway’s MAC address. Firmware Version displays the
Gateway’s firmware version number.
Login Status
The Login Status subsection displays whether you have logged into the Gateway’s
firmware. If not, enter your user name and password in the appropriate text boxes.
If you are logged in, you can log out by clicking Log Out.
10
Page 15
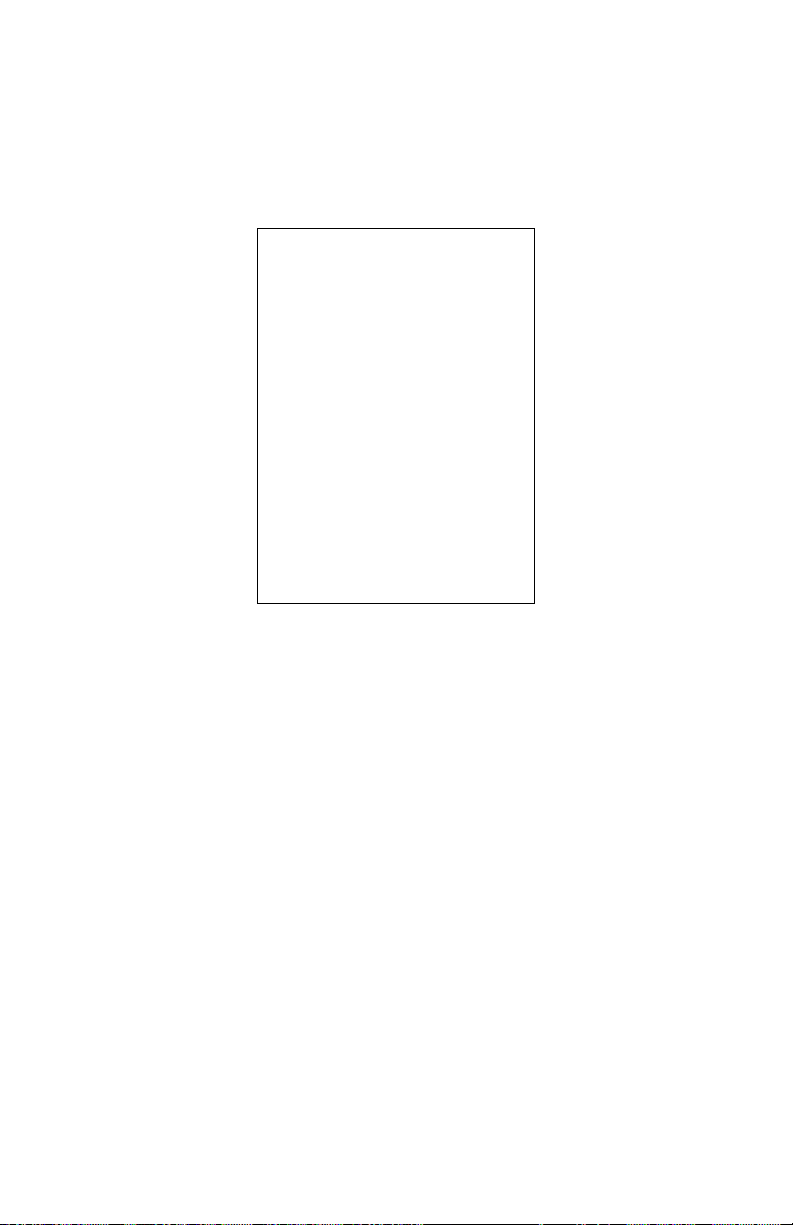
Chapter 2 Home Screen
Connection Status
This subsection of the Home screen displays the status of various parameters
regarding the Gateway’s wired and wireless networks.
This section contains two subsections: WAN Connection Status and Wireless.
WAN Connection Status
The WAN Connection Status subsection contains a number of status lines that
pertain to the Gateway’s WAN (Internet) connection: WAN Type, Dynamic/Static
(type of IP address used), Modem IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway,
Lease Time Remaining, DNS Address #1, and DNS Address #2.
Wireless
The Summary subsection contains three information lines. SSID displays the name
of the Gateway’s wireless network. Security displays whether the wireless network
has security enable. Security Type displays the type of security enabled.
11
Page 16
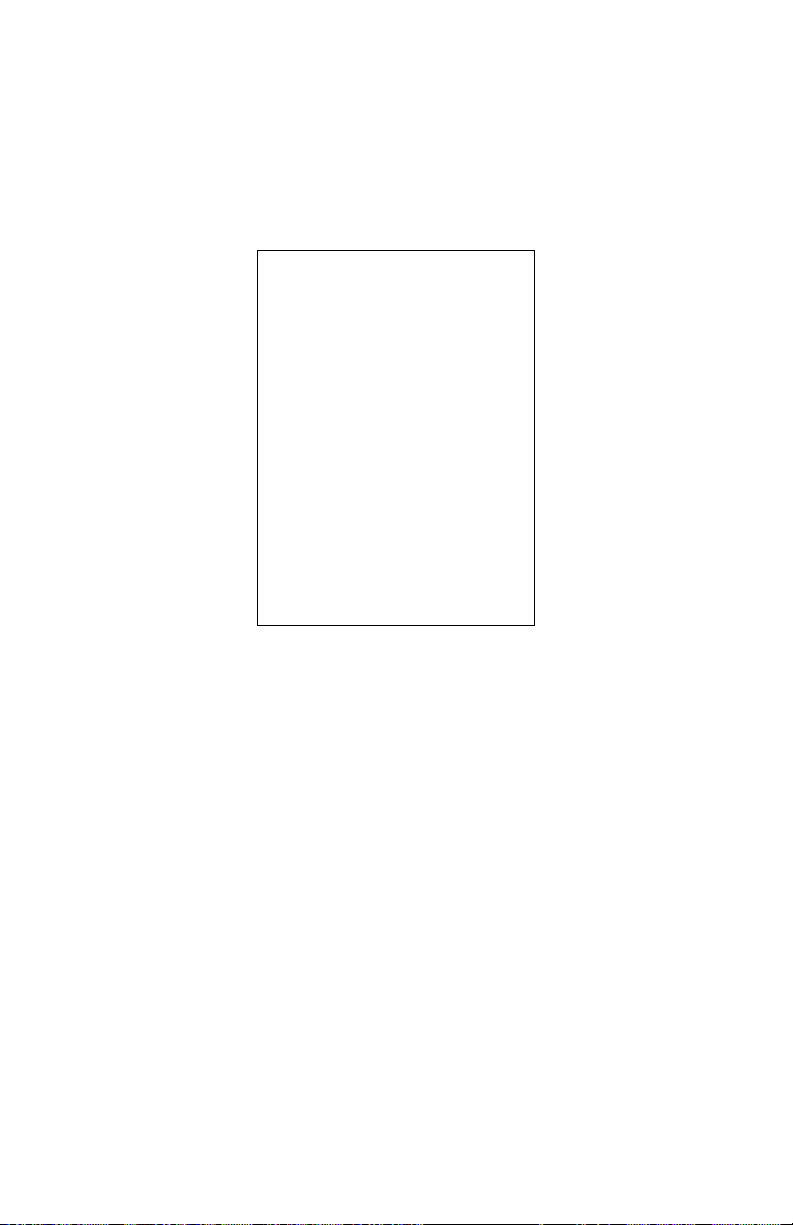
VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Home Network
This section of the Home screen details the devices connected to the Gateway’s
networks (either wired or wireless). Information provided includes the device’s IP
address and the speed of the connection.
12
Page 17
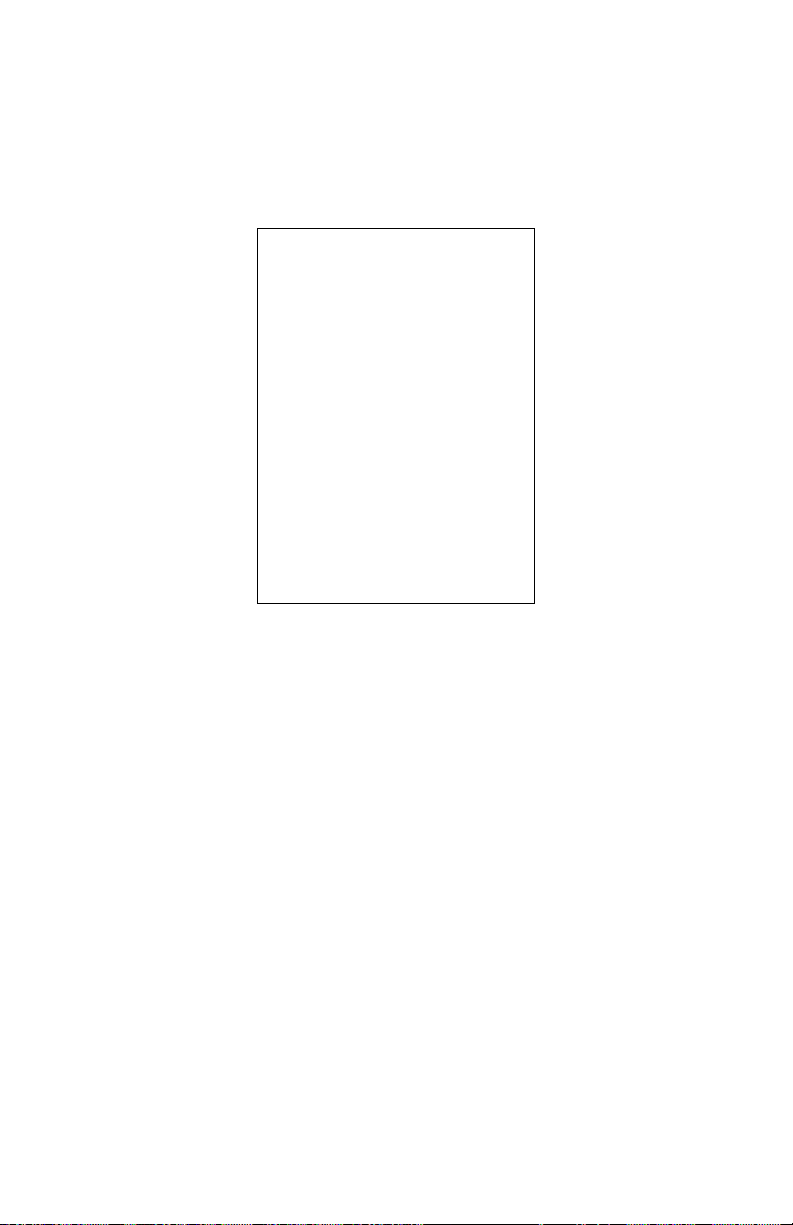
Chapter 2 Home Screen
Firewall/Diagnostics
This subsection of the Home screen displays the status of various parameters
regarding the Gateway’s firewall, as well as list of diagnostics tests.
This section contains two subsections: Firewall and Diagnostics.
Firewall
The Firewall subsection contains a number of status lines that pertain to the
Gateway’s firewall security: UPnP Setting, Firewall (type of firewall used), and
Blocking/Filtering. For more information about the Gateway’s firewall settings, see
chapter 4 of this manual.
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics subsection contains six links to commonly used diagnostics
tools: Ping; Traceroute ; Wireless Reset; Device Reboot; Factory Reset; and DHCP
Release/Renew.
13
Page 18

Configuring Wireless Settings
This chapter explains the options provided in the Wireless section of the Gateway’s
firmware, including setting up wireless security and WPS.
Accessing Wireless Settings
To access the Wireless screens:
1. Open a Web browser. In the “Address” text box, type:
http://192.168.1.254
then press Enter on the keyboard.
3
14
Page 19
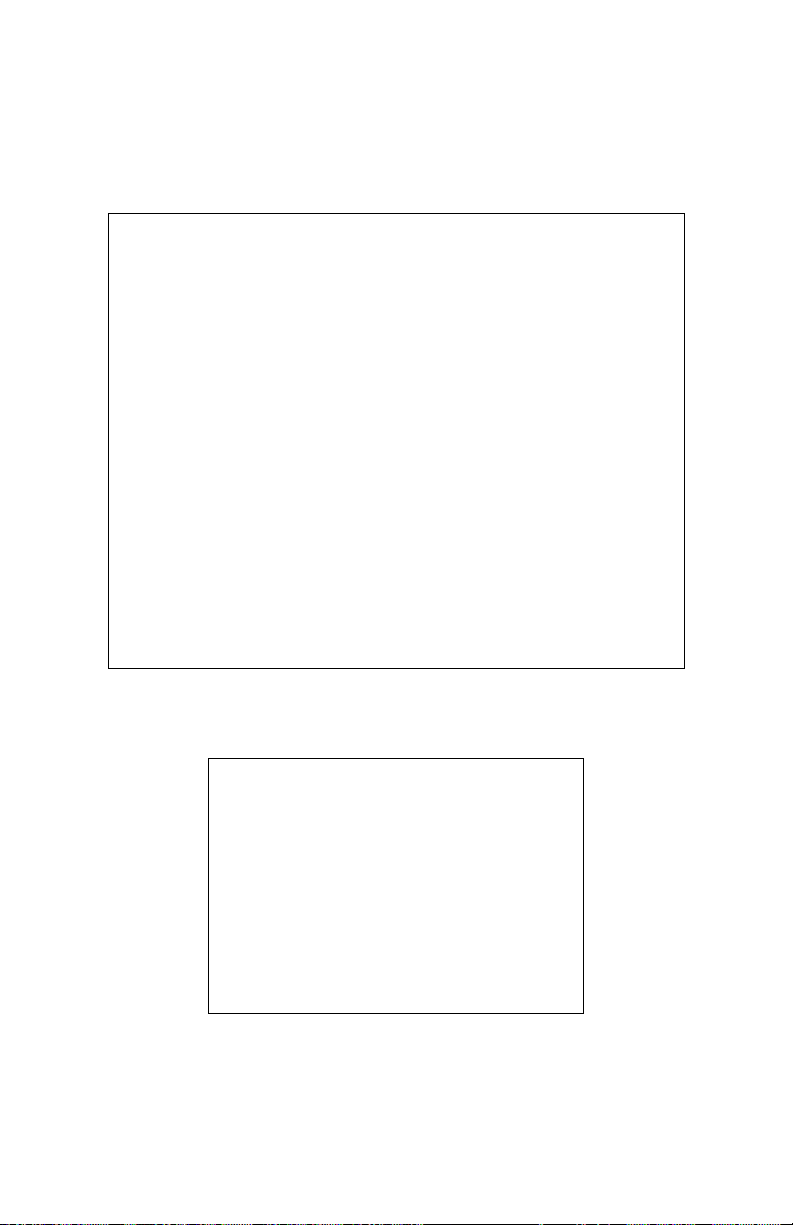
Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
2. The Gateway’s Home screen appears. Enter your user name and password,
then click the Wireless Setup icon from the row of icons at the top of
the screen.
3. The Wireless Settings screen appears, with various options listed in the menu
on the left side of the screen.
15
Page 20
VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Basic Settings
Click Basic Settings from any Wireless screen to generate the Basic Settings
screen. This screen displays a series of settings relating to the core functionality of
the Gateway’s wireless capabilities.
Wireless Radio
Click in the Enable radio button to activate the Gateway’s wireless radio. Clicking
in the Disable radio button turns off the wireless radio.
Select SSID
Select an ISP-configured SSID (wireless network name) from the drop-down list.
SSID State
Enable or disable this option, which activates the Gateway’s ability to use multiple
SSIDs, by clicking in the appropriate radio button.
16
Page 21
Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
SSID Guest
Enable or disable this option, which activates the Gateway’s ability to host a guest
SSID, by clicking in the appropriate radio button. Setting up a guest SSID allows
the user to provide a separate network on the Gateway that can access the Internet,
but does not allow access to devices (printers, other computers, etc.) connected
to the Gateway’s main network. Guest SSID networks are usually created to allow
temporary access to the Internet to one-time users.
SSID Broadcast
Click in the Enable radio button to activate SSID broadcasting, which allows any
computer searching for available wireless networks to detect this network (however, if this network is protected with some form of wireless security, they will not
be able to join the network unless they know the security password). Clicking in
the Disable radio button turns off SSID broadcasting.
SSID Name
If applicable, enter the name of the Gateway’s wireless network in this text box.
Security
There are four choices available in this drop-down list:
WPA/WPA2
This form of wireless security is the default setting on the Gateway. When selected, you can select the WPA Type (WPA orWPA2-Personal, WPA Personal, or
WPA2-Personal), Encryption Type (AES, TKP, or Both), and whether to use the
Gateway’s automatically generated default key/passphrase, or create one of your
own, then click Apply to save your changes.
17
Page 22
VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
WEP
WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy. To use WEP, select it from the
Security drop-down list, then select the Authentication Type (Open or Shared).
Finally, select whether to use the Gateway’s automatically generated default key/
passphrase, or create one of your own (the more keys used, the stronger the
security), then click Apply to save your changes.
WEP + 802.1x
802.1x WEP is a robust security protocol that uses port control with dynamically
changing encryption keys automatically updated over the network. 802.1x WEP
uses a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in Service) server for authentication purposes. This server must be physically connected to the Gateway. Also,
the user must enable the RADIUS client embedded in the Gateway.
1. Enter the RADIUS server IP address in the Radius Server IP text box.
2. Enter the RADIUS server’s port number in the Radius Port text box.
18
Page 23
Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
3. Enter the RADIUS server’s shared secret in the Radius Key text box.
4. Enter the group key interval in the Group Key Interval text box.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
Off
Selecting Off from the Security drop-down list leaves the Gateway’s wireless network completely open, allowing anyone to join the network.
Advanced Settings
Click Advanced Settings from any Wireless screen to generate the Advanced
Settings screen.
These settings should only be adjusted by experienced technical users who are
extremely familiar with wireless networking concepts. After making any changes in
this screen, click Apply to save them.
19
Page 24

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Compatibility Mode
Allows you to modify the Gateway’s wireless network to allow certain devices
to join, based on the device’s compatibility. Choices include Compatible Mode
(802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n), Balanced Mode (802.11g + n only), Performance
Mode (802.11n only), Legacy Mode (802.11 b + g only), 802.11g only, and
802.11b only.
Maximum Spatial Streams
Spatial streams boost the efficiency of the wireless network, resulting in higher
speeds across the network. However, the more spatial streams you use, the less stable the wireless network connections. Choices include Auto (adjusts spatial streams
automatically), 1, and 2.
Channel Width
Choices include 20 Mhz and 40 Mhz.
Control Channel
Choices include None (20 Mhz channel width only), Lower, and Upper.
MSDU Aggregation, MPDU Aggregation
Enable or disable these options by selecting the appropriate choice from the dropdown lists. They should only be changed if requested by your ISP.
WMM, WMM Power Save
Enable or disable these options by clicking in the appropriate radio buttons.
20
Page 25
Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
Channel
Select the channel at which the Gateway’s wireless network operates. Choices
include channels 1 through 11, and Auto Detect, which allows devices on the network to automatically detect the channel.
Wireless Power Level
Adjust the power of the Gateway’s wireless network signal by selecting a percentage
from 10% to 100% from the drop-down list
WPS
Click WPS in any Wireless screen to generate the WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
screen. WPS provides a simple method of setting up a wireless network by automatically sharing the network key between the Gateway and other wireless devices.
21
Page 26

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
To set up WPS:
1. Enable WPS by clicking in the Enable radio button.
2. Click Apply to save your changes.
3. If connecting a device to the wireless network with a WPS AP PIN, write down
the PIN displayed after Current WPS AP Pin, then enter the PIN in the device’s
WPS AP PIN configuration.
4. If connecting a device to the wireless network with PBC (Push Button
Configuration), click Connect, then press the PBC-compatible button on
the device within two minutes.
5. If the connecting device uses the End Device PIN method, enter the PIN in the
appropriate text box, then enter in the device’s End Device PIN configuration.
22
Page 27
Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
Wireless MAC Authentication
Click MAC address control in any Wireless screen to generate the Wireless MAC
Authentication screen. MAC addresses are alphanumeric designations provided to
every networkable device that act as unique identifiers. Using MAC addresses, you
can allow or deny access to the Gateway’s wireless network to the wireless devices of
your choice.
To set up wireless MAC authentication:
1. Select the SSID from the SSID drop-down menu.
2. Turn on the MAC authentication by clicking in the Enable radio button next to
MAC Authentication.
3. To allow or delete certain devices from the Gateway’s wireless network, click in
the appropriate radio button (Allow device list or Deny device list).
4. Enter the device’s MAC address by either selecting it from the Select MAC
23
Page 28

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Address drop-down list, or manually entering it in the Manually Add MAC
Address text box.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
6. Repeat steps 1-5 to add more devices.
Wireless Distribution System
Click WDS in any Wireless screen to generate the WDS Wireless Distribution
System screen. This screen allows the user to set up a network of access points via
a wireless connection.
To set up WDS:
1. Turn on WDS by clicking in the Enable radio button next to WDS Main Base
Station.
2. Select an access point (remote base station) from the drop-down menu next to
Select Device, or enter the device’s MAC address in the Manually Add MAC
Address text box.
3. Select the type of base station being configured (client station or repeater).
24
Page 29

Chapter 3 Wireless Settings
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
5. Repeat steps 2-4 for additional base stations.
The list of configured base stations will appear at the bottom of the screen, under
WDS Remote Station List.
25
Page 30

Configuring Firewall Settings
This chapter will explain the options provided in the Firewall section of the
Gateway’s firmware, including various firewall options, port forwarding, and
DMZ hosting.
Accessing Firewall Settings
To access the Firewall screens:
1. Open a Web browser. In the Address text box, type:
http://192.168.1.254
then press Enter on the keyboard.
4
26
Page 31

Chapter 4 Firewall
2. The Gateway’s Home screen appears. Enter your user name and password,
then click Firewall from the row of icons at the top of the screen.
3. The Firewall screen appears, with various firewall options listed in the menu
on the left side of the screen.
27
Page 32

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Firewall
Click Firewall from any Firewall screen to generate the Firewall screen. This
screen allows you to configure the firewall settings of the Gateway. If you make
changes in this screen, click Apply at the bottom of the screen to save them.
WAN Ping Block Mode
Click in the Enable radio button next to WAN PING block mode to activate the
WAN Ping Block Mode. This will block all pings originating from the WAN (i.e.,
the Internet) side of the network. Clicking Disable turns off the block mode.
IP Addressing Type
This option is non-configurable and always set to All Dynamic IP Addresses.
28
Page 33

Chapter 4 Firewall
Firewall Security Level
Select the level of firewall security level here, by clicking in the appropriate radio button. None provides no firewall security, while Low, Medium, and High provide different levels of security, as displayed in the Firewall table in the lower part of the screen.
Additionally, after choosing a level of firewall security, you can manually allow (by
clicking in a check box to generate a check mark) or deny (by clicking in a check box
to delete a check mark) selected Internet services listed in the Firewall table.
IPv6 Firewall
Click IPv6 Firewall from any Firewall screen to generate the IPv6 Firewall screen.
This screen allows you to configure the IPv6 firewall settings of the Gateway, and
functions identically to the standard Firewall screen.
29
Page 34

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Port Forwarding
Activating Port Forwarding allows the network to be exposed to the Internet in
certain limited and controlled ways, enabling some applications to work from the
local network (game, voice, and chat applications, for example), as well as allowing
Internet access to servers in the local network. Click Port Forwarding from any
Firewall screen to generate the Port Forwarding screen. This screen allows you to
configure the port forwarding settings of the Gateway. If you make changes in this
screen, click Apply at the bottom of the screen to save them.
To set up port forwarding:
1. Select the LAN device from the Select LAN Device drop-down menu.
2. Enter the LAN IP address in the LAN IP Address text box.
3. Enter the external start port number in the External (WAN) Start Port text
box.
4. Enter the external end port number in the External (WAN) End Port text
box.
5. Enter the internal starting port number in the Internal (LAN) Start Port text
box.
30
Page 35

Chapter 4 Firewall
6. Select a protocol from the Protocol drop-down list box
7. Enter the LAN IP address in the LAN IP Address text box.
8. If applicable, enter the remote port and IP information
9. Click Apply to save your changes.
The list of forwarded ports will be displayed in the Applied Port Forwarding Rules
at the bottom of the screen.
Applications
Click Applications from any Firewall screen to generate the Applications screen.
This screen is an extension of the port forwarding screen, allowing you to quickly
and easily set up commonly-used applications that require port forwarding
To set up a forwarded application:
1. Select a networked device by selecting it from Select Device drop-down list, or
enter its IP address in the Enter IP Address text box.
2. Select the application’s category from the Application Category drop-
down list, or select All to see all the applications provided.
31
Page 36

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
3. Select the application from the Applications drop-down list.
4. If desired, view the rule by clicking the View Rule button. A new screen
appears, listing the application’s port forwarding details. Click Back to return
to the Applications screen.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
6. Repeat steps 1-5 to configure additional applications.
The list of forwarded applications will be displayed in the Forwarded Applications
List at the bottom of the screen.
DMZ Hosting
Click DMZ Hosting from any Firewall screen to generate the DMZ Hosting screen.
The DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) host feature allows one device on the network to
operate outside the firewall to use an Internet service that otherwise would be blocked,
or to expose a networked device to all services without restriction or security.
Caution! A DMZ host is not protected by the firewall and may be
vulnerable to attack. Designating a DMZ host may also put other
computers in the local network at risk. When designating a DMZ
host, consider the security implications and protect it if necessary.
32
Page 37

Chapter 4 Firewall
To designate a local computer as a DMZ host:
1. Click in the Enable radio button to activate DMZ hosting.
2. Select a networked device by selecting it from Select Device drop-down list, or
enter its IP address in the “Enter IP Address” text box.
3. Click Apply to save your changes.
The DMZ host will be displayed in the DMZ Hosted Device table at the bottom of
the screen. Only one device at a time on the Gateway’s network can be designated
as a DMZ host.
IPv6 DMZ Hosting
Click IPv6 DMZ Hosting from any Firewall screen to generate the IPv6 DMZ
Hosting screen. The DMZ (De-Militarized Zone) host feature allows one device on
the network to operate outside the firewall to use an Internet service that otherwise
would be blocked, or to expose a networked device to all services without restriction
or security.
To set up IPv6 DMZ hosting:
1. Enter the last 64 bits of the IPv6 address in the appropriate text box.
2. Click Apply.
33
Page 38

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
The DMZ host will be displayed in the IPv6 DMZ Hosted Device table at the bottom of the screen. Only one device at a time on the Gateway’s network can be designated as a DMZ host.
UPnP
Click UPnP from any Firewall screen to generate the UPnP screen. UPnP (Universal
Plug and Play) allows all supported devices on the Gateway’s network to discover and
interface with each other without additional configuration. To enable UPnP on the
Gateway’s network, click in the Enable radio button, then click Apply.
34
Page 39

Configuring Advanced Setup
This chapter will explain the options provided in the Advanced Setup section of
the Gateway’s firmware, including services blocking, restoring the Gateway to factory default settings, and performing a ping test.
Important! These settings should be configured by an experienced network technician only. Improper configuration can result in the Gateway operating poorly or
not at all.
Accessing Advanced Setup
To access the Advanced Setup screens:
1. Open a Web browser. In the Address text box, type:
http://192.168.1.254
then press Enter on the keyboard.
5
35
Page 40

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
2. The Gateway’s Home screen appears. Enter your user name and password, then
click Advanced Setup from the row of icons at the top of the screen.
3. A Warning screen appears, informing the user that the settings in the
Advanced Setup are for experienced network professionals only. Click Yes . The
Advanced Setup screen appears, with various options listed in the menu on the
left side of the screen.
36
Page 41

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
Services Blocking
Services blocking is used to prevent a device on the Gateway’s network from
accessing particular services available on the Internet, such as receiving email or
downloading files from FTP sites. To set up services blocking on a
networked device:
1. Click Services Blocking from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The Services Blocking screen appears.
2. Select the device on which you wish to block services from the Select Device
drop-down list, or enter the device’s IP address in the Enter IP Address text box.
3. Select a service, or multiple services, to block by clicking in the appropriate
check box below Select service to block.
4. Click Apply to save your changes.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 to block services on another device on the Gateway’s network.
The devices that are blocked from accessing services are listed at the bottom of
the screen.
37
Page 42

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Website Blocking
Website blocking is used to prevent all devices on the Gateway’s network from
accessing particular web sites on the Internet. To set up web site blocking on the
Gateway’s network:
1. Click Website Blocking from the menu on the left side of any Advanced Setup
screen. The Website Blocking screen appears.
2. Enter the web site address of the web site to be blocked in the Website Address
text box.
3. Click Apply to save your changes.
4. Repeat steps 1-3 to block other web sites from being acesssed on the
Gateway’s network.
The web sites blocked from being accessed on the Gateway’s network are listed at
the bottom of the screen.
38
Page 43

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
Scheduling Access
Scheduling access is used to allow a device on the Gateway’s network to access
the Internet at certain times of the day, or certain days of the week, only. During
times not configured in the Scheduling Access screen, the device will not be able to
access the Internet. To set up scheduling access on a networked device:
1. Click Scheduling Access from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The Scheduling Access screen appears.
2. Select the device on which you want to scheduled Internet access from the
Select Device drop-down list, or enter the device’s MAC address in the Enter
MAC Address text box.
3. Select the days of the week during which you want to allow Internet access by
clicking in the appropriate check box below “Select the days of the week…”.
4. If applicable, set the time range during which you want to allow Internet access.
This time range will apply only to the days you activated in step 3.
39
Page 44

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
5. Click Add to create a schedule access.
6. Repeat steps 1-5 to create multiple access schedules for other devices on the
Gateway’s network.
The devices that are configured with an access schedule are listed at the bottom of
the screen.
DSL Bonding Settings (T2200H only)
DSL bonding allows devices the Gateway to use one or both of its DSL lines in
bonded mode. When bonding is disabled, the Gateway only uses a single DSL line.
To configure DSL bonding, click on DSL Bonding Settings in any Advanced screen.
The DSL Bonding Settings screen will appear. There are three options for DSL bonding: Auto, Single, and Bonding. Click in the appropriate button to activate.
40
Page 45

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
WAN IP Addressing
The WAN IP Address screen allows you to manually set up the WAN IP address of
the Gateway. To do this:
1. Click WAN IP Address from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Configuration screen. The WAN IP Address screen appears.
2. Select the type of connection the ISP uses.
Note: Some DSL providers use PPPoE to establish communica-
tion with an end user. Other types of broadband Internet connections (such as fixed point wireless) may use either DHCP or
static IP address. If unsure which connection is present, check
with Telus before continuing.
3. If using PPPoA or PPPoE was selected in step 1, enter the user name and pass-
word in the appropriate text boxes. If the ISP requires no user name or password, click in the “My ISP does not require a username and password”
check box.
41
Page 46

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
4. Select the IP type. If Single Static IP Address was selected, enter the IP address
in the “Single Static IP” text box. If “Block of Static IP Addresses (Unnumbered
Mode)” was selected, enter the designated gateway IP address and subnet mask
address in the “Modem Address” and “Subnet Mask” text boxes, respectively.
Also, “VIP Mode” can be activated by clicking in the appropriate check box.
VIP mode works in concert with unnumbered mode and allows computers not
assigned a static IP to receive a DHCP LAN side private IP address.
5. Select the DNS type. If static DNS address was selected, enter the primary DNS
address and, optionally, the secondary DNS address in the appropriate
text boxes.
6. If applicable, enter a different MTU value in the MTU text box.
7. Enable or disable IGMP proxy by clicking in the appropriate radio button.
When finished in this screen, click Apply to activate any changes made.
IPv6 LAN Settings
IPv6 LAN Settings allows the user to configure the IPv6 LAN settings on the
Gateway. To configure:
1. Click IPv6 LAN Settings from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The IPv6 screen appears.
2. Select the LAN connection type from the drop-down menu.
42
Page 47

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
3. If applicable, enable EULA support, and enter the subnet number and router
advertisement lifetime values in the appropriate text boxes.
4. Click Apply to save changes.
DHCP Reservation
DHCP reservation allows devices on the Gateway’s network to be permanently
associated with a particular IP address. To set up DHCP reservation on a networked device:
1. Click DHCP Reservation from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The DHCP Reservation screen appears.
2. Select the MAC address of the device on which you want to reserve a perma-
nent DHCP address from the Select MAC Address drop-down list, or enter the
device’s MAC address in the Manually Add MAC Address text box.
3. Select the IP address you want to permanently associate with the device chosen
in step 2 from the IP Address drop-down list, or enter an IP address in the
Manually Add IP Address text box.
43
Page 48

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
4. Click Apply to save changes.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 to reserve IP addresses for other devices on the
Gateway’s network.
The devices with DHCP reserved IP addresses are listed at the bottom of
the screen.
LAN IP and DHCP Settings
The LAN IP and DHCP Settings screen allows you to change the Gateway’s default
LAN IP address, and adjust the DHCP settings. To change the LAN IP:
1. Click LAN IP Settings from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Configuration screen. The LAN IP and DHCP Settings screen appears.
2. Enter the new modem IP address and modem subnet mask in the appropriate
text boxes.
44
Page 49

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
3. Click Apply and Reboot. The Gateway reboots with the new settings.
To change the Gateway’s DHCP settings:
1. Click Enable to activate the Gateway’s DHCP server.
2. Enter the DHCP server’s beginning IP address, ending IP address, and subnet
mask address in the appropriate text boxes.
3. Enter the DHCP server’s lease time period by entering the days, hours, and
minutes in the appropriate text boxes.
4. Set the DNS values by selecting Dynamic or Static (clicking in the appropriate
radio button), then, if needed enter the IP addresses for DNS server 1 and 2.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
IPv6 WAN Settings
To set up the Gateway’s IPv6 WAN settings:
1. Click IPv6 WAN Settings from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The IPv6 WAN Settings screen appears.
45
Page 50

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
2. Click in the button next to Enable to activate.
3. Select the WAN IPv6 connection protocol from the drop-down list.
4. If applicable, activate DHCP 6rd Option Code and enter the 6rd MTU size in
the text box.
5. Click Apply to save change.
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS creates a dynamic IP address that is aliased to a static hostname,
allowing a computer on the network to be more easily accessible from the Internet.
Typically, when connecting to the Internet, the service provider assigns an unused
IP address from a pool of IP addresses, and this address is used only for the duration of a specific connection. Dynamically assigning addresses extends the usable
pool of available IP addresses, while maintaining a constant domain name. This
allows the user to access a device (a camera, for example) from a remote location,
since the device will always have the same IP address.
When using Dynamic DNS, each time the IP address provided by the ISP changes,
the DNS database changes accordingly to reflect the change. In this way, even
though the IP address of the computer changes often, its domain name remains
constant and accessible.
46
Page 51

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
To configure Dynamic DNS:
1. Click Dynamic DNS from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Configuration screen. The Dynamic DNS screen appears.
2. Select the Gateway’s Dynamic DNS account provider from the drop-down list.
3. Enter the Dynamic DNS username and password in the appropriate text boxes.
4. Enter the full Dynamic DNS domain in Dynamic DNS provider text box, or
select one from the drop-down list.
5. Click Apply.
47
Page 52

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
DNS Host Mapping
DNS Host Mapping creates a static host name for the specified IP address. WAN
and LAN addresses are supported. To set up DNS host mapping:
1. Click DNS Host Mapping from the menu on the left side of any Advanced
Setup screen. The DNS Host Mapping screen appears.
2. Enter the DNS host name in the appropriate text box.
3. Enter the IP address in the appropriate text box.
4. Click Apply to save changes.
48
Page 53

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
Port Bridging
Click Port Bridging from any Advanced Configuration screen to generate the
Port1 Bridge screen. This screen allows you to enable port bridging. Click in the
Enable radio button to activate, then click Apply.
HPNA Settings
Click HPNA Settings from any Advanced Configuration screen to generate the
HPNA Settings screen. This screen allows you to enable HPNA (Home Phoneline
Networking Alliance) networking. Click in the Enable radio button to activate,
then click Apply.
49
Page 54

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Admin Password
To change the password that allow access to the Gateway’s firmware screens:
1. Click Admin Password from the menu on the left side of any Advanced Setup
screen. The Admin Password screen appears.
2. Enter the old password in the Old Password text box.
3. Enter a new password in the Admin Password text box.
4. Reenter the new password in the Confirm Your Password text box.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
50
Page 55

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
Storage Service
Click Storage Service to access the Storage Service screen. This screen lists the
storage devices connected to the Gateway, and displays information (type of file
system, total and used space) about the devices.
Rebooting the Gateway
To reboot the Gateway:
1. Click Reboot from the menu on the left side of any Advanced Setup screen.
The Reboot Modem screen appears.
2. Click Reboot to reboot the Gateway. This may take up to one minute.
To reenter the Gateway’s firmware after restarting the Gateway, click the web
browser’s Refresh button.
51
Page 56

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Restoring Factory Default Settings
If the Gateway’s factory default settings need to be restored (to build a new network from the beginning, for example), use the following procedure:
1. Click Restore Defaults in any Advanced Setup screen. The Restore Defaults
screen appears.
2. If you want to restore only the Gateway’s default WAN port settings, click
Restore across from Restore WAN port Settings. The Gateway’s current
WAN port settings will be deleted, and the factory default WAN port settings
restored.
3. If you want to restore only the Gateway’s default wireless settings, click Restore
across from Restore Default Wireless Settings. The Gateway’s current wireless
settings will be deleted, and the factory default wireless settings restored.
4. If you want to restore only the Gateway’s default firewall settings, click Restore
across from Restore Default Firewall Settings. The Gateway’s current firewall
settings will be deleted, and the factory default firewall settings restored.
5. If you want to restore all the Gateway’s default settings, click Restore across
from Restore Modem to Factory Default Settings. All of the Gateway’s current
settings (including wireless and firwall settings) will be deleted, and the factory
default settings restored.
Note: All of the Gateway’s settings and parameters will be
restored to their default values after performing the Restore
Factory Default procedure.
52
Page 57

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
Speed Test
Selecting Speed Test from any Advanced Settings screen generates the Speed Test
screen. Enter a website URL in the appropriate text box, then click Tes t . The connection’s speed results will be displayed.
53
Page 58

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Ping Test
Selecting Ping Test from any Advanced Setup screen generates the Ping Test
screen, which is used to check whether the Gateway is properly connected to the
Internet. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. The results will be
displayed at the bottom of the screen.
54
Page 59

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
TCP Dump Debug
Selecting TCP Dump Debug from any Advanced Setup screen generates the TCP
Dump Debug screen, which is used to debug the Gateway’s TCP (transmission
control protocol) dump. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. This
test is intended for use by experienced technicians only. The results will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
55
Page 60

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Iperf Test
Selecting Iperf Test from any Advanced Setup screen generates the Iperf Test
screen, which is used to check the throughput of the Gateway’s network using TCP
and UDP streams. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Follow
the on-screen instructions to perform the test. The results will be displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
56
Page 61

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
IPv6 Ping Test
Selecting IPv6 Ping Test from any Advanced Setup screen generates the IPv6 Ping
Test screen, which is used to check whether the Gateway is properly connected to
the Internet via IPv6. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. The
results will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
57
Page 62

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Traceroute
Selecting Traceroute from any Advanced Setup screen generates the Traceroute
screen, which is used to determine the route taken by packets across a network.
Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. The results will be displayed
at the bottom of the screen.
58
Page 63
Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
IPv6 Traceroute
Selecting IPv6 Traceroute from any Advanced Setup screen generates the IPv6
Traceroute screen, which is used to determine the route taken by packets across a
network via IPv6. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. The results
will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Time Zone
To set the correct time zone on the Gateway:
1. Click Time Zone from the left side of any Advanced Setup screen. The Time
Zone screen appears.
59
Page 64

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
2. Click in the appropriate radio button for your time zone.
3. If daylight saving is currently in effect, click in the Day Light Saving check box
to activate
4. Click Apply to save your settings.
Language Settings
Selecting Language from any Advanced Setup screen generates the Language
screen, which is used to change the language of the Gateway’s GUI. Select a language from the drop-down menu, then click Apply.
60
Page 65

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
HPNA Diagnostics
Selecting HPNA Diagnostics from any Advanced Setup screen generates the
HPNA Diagnostics screen, which is used to test the Gateway’s HPNA (Home
Phoneline Networking Alliance) connections. Follow the on-screen instructions to
perform the test. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. The results
will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
61
Page 66

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
DNS Cache
Selecting DNS Cache from any Advanced Setup screen generates the DNS Cache
screen, which is used to enable/disable the Gateway’s DNS (domain name system)
cache. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Click Apply to
save changes.
62
Page 67

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
IGMP Settings
Selecting IGMP Settings from any Advanced Setup screen generates the IGMP
Configuration screen, which is used to control the Gateway’s IGMP (Internet
Group Management Protocol) settings. Follow the on-screen instructions to perform the test. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Click Apply to
save changes.
Upgrade History
Selecting Upgrade History from any Advanced Setup screen generates the
Upgrade History screen, which displays the Gateway’s firmware upgrade history.
63
Page 68

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
SIP ALG
Selecting SIP ALG from any Advanced Setup screen generates the SIP ALG
screen, which is used to enable/disable the Gateway’s SIP ALG (application-level
gateway) setting. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Click
Apply to save changes.
Tool Box
Selecting To o l B ox from any Advanced Setup screen generates the Tool Box
screen, which includes advanced troubleshooting tools. It is intended for use by
experienced technicians only. Click Apply to save changes.
64
Page 69

Chapter 5 Advanced Setup
DLNA
Selecting DLNA from any Advanced Setup screen generates the DLNA screen,
which is used to enable/disable the Gateway’s DLNA (Digital Living Network
Alliance) settings. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Click
Apply to save changes.
xDSL Diagnostics
Selecting xDSL Diagnostics from any Advanced Setup screen generates the xDSL
Diagnostics screen, which is used to enable diagnostics on all of the Gateway’s DSL
(digital subscriber lines) connections. It is intended for use by experienced technicians only. Click Apply to save changes.
65
Page 70

Viewing the Gateway’s Status
This chapter gives an overview of the various Status tables provided by the
Gateway, which allow you check on various parameters, including xDSL connections, WAN Etherent connection, and wireless status.
Accessing Status Tables
To access the Status screens:
1. Open a web browser. In the Address text box, type:
http://192.168.1.254
then press Enter on the keyboard.
6
66
Page 71

Chapter 6 Status
2. The Gateway’s Home screen appears. Enter your user name and password,
then click Status from the row of icons at the top of the screen.
3. The Status screen appears, with various options for checking the Gateway’s
status listed in the menu on the left side of the screen.
67
Page 72

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Connection Status
Click Connection Status from any Status screen to generate the Connection
Status screen. This table displays various parameters regarding the Internet connection of the Gateway, including broadband and ISP connection status, upstream
rate, least time remaining, and DNS addresses. The only user-configurable option
in the screen is the Release/Renew button, which, when clicked, releases and
renews the Gateway’s IP address.
68
Page 73

Chapter 6 Status
Line 1/Line 2 Status
Click Line 1 Status from any Status screen to generate the Line 1 Status screen.
This table displays various parameters relating to the Line 1 connection of the
Gateway, including VPI, downstream speed, and attenuation. There are no userconfigurable options in this screen, but there is a Clear button at the bottom of the
screen (not shown) that resets all of the statistics back to zero, at which time the
statistics will begin accumulating again.
The Line 2 Status screen is identical to the Line 1 screen, and displays parameters
for the Line 2 connection of the Gateway.
69
Page 74

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
WAN Ethernet Status
Click WAN Ethernet Status from any Status screen to generate the WAN Ethernet
Status screen. This table displays various parameters relating to the WAN Ethernet
connection of the Gateway, including subnet mask, default gateway, and sent packets. There are no user-configurable options in this screen.
Routing Table
Click Routing Table from any Status screen to generate the Routing Table screen.
This screen displays the Gateway’s routing table. There are no user-configurable
options in this screen.
70
Page 75
Chapter 6 Status
Firewall Status
Click Firewall Status from any Status screen to generate the Firewall Status screen.
This table displays the status of the Gateway’s firewall. There are no user-configurable options in this screen. For more details, see chapter 4, Configuring
Firewall Settings.
NAT Table
Click NAT Tabl e from any Status screen to generate the NAT Table screen. This
screen displays the Gateway’s NAT table. There are no user-configurable options in
this screen.
71
Page 76

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Wireless Status
Click Wireless Status from any Status screen to generate the Wireless Status screen.
This table displays the Gateway’s wireless network statistics, including wireless security type, wireless mode, and packets received. If the Gateway is set to use multiple
SSIDs, select the SSID from the drop-down list at the top of the screen. The selected
SSID’s status will be displayed on the lower part of the screen.
72
Page 77

Chapter 6 Status
Advanced Wireless Statistics
Clicking on the “Advanced Wireless Statistics” button at the bottom of the Wireless
Status screen generates the “Advanced Wireless Statistics” screen. From here, the
user can select from a list of fifteen metrics concerning the Gateway, including
packet counters, WMM statistics/counters, and detailed statistics per client. To
display any one of the metrics, click on its name, and a new screen will appear.
Modemstatus Wireless Monitor
Clicking on the “Modemstatus Wireless Monitor” button at the bottom of the
Wireless Status screen generates the “Wireless Monitor” screen. From here, the user
can view real-time statistics specific to clients connected to the Gateway’s wireless
network. To view, select a client from the “Wireless Client” drop-down list. Its
statistics will appear in the lower section of the screen.
73
Page 78

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Modem Utilization
Click Modem Utilizations from any Status screen to generate the Modem Utilization
screen. This table displays the Gateway’s modem statistics, including wireless memory used, LAN TCP settings, and, at the bottom of the screen, a LAN device session
log. There are no user-configurable options in this screen.
74
Page 79

Chapter 6 Status
LAN Status
Click LAN Status from any Status screen to generate the LAN Status screen. This
table displays the Gateway’s LAN (local network) statistics, including Ethernet connections, HPNA link status, and various networked device details. There are no userconfigurable options in this screen.
ARP Table
Click ARP Table from any Status screen to generate the ARP Table screen. This table
displays the Gateway’s addresss resolution protocol (ARP) information. There are no
user-configurable options in this screen.
75
Page 80

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Interface Statistics
Click Interface Statistics from any Status screen to generate the Estimated Interface
Statistics screen. This table displays the Gateway’s various interface statistics, including number of packets and bytes, by connection type. There are no user-configurable options in this screen.
Multicast Statistics
Click Multicast Statistics from any Status screen to generate the Estimated Interface
Statistics screen. This table displays the Gateway’s multicast statistics, including number of joined clients and time out values, by channel. There are no user-configurable
options in this screen.
76
Page 81

Chapter 6 Status
System Log
Click System from any Status screen to generate the System Log screen. The
Gateway’s system log displays all system events that occur while the Gateway is in
operation. A firewall log can be activated from this screen as well (to activate, click
Enable, then Apply).
77
Page 82

Specifications
General
Model Number(s)
T1200H, T2200H (VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway)
Standards
IEEE 802.3 (10BaseT)
IEEE 802.3u (100BaseTX)
IEEE 802.11 b, g, n (Wireless)
G.dmt
G.lite
t1.413
RFC 1483, 2364, 2516
Protocol
LAN - CSMA/CD
WA N - PPP, DHCP, Static IP
A
WAN
VDSL2 interface
LAN
10/100/1000 RJ-45 switched ports
Speed
LAN Ethernet: 10/100/1000 Mbps auto-sensing
Wireless: 802.11n 300 Mbps optimal (see Wireless Operating Range for details)
Cabling Type
Ethernet 10BaseT: UTP/STP Category 3 or 5
Ethernet100BaseTX: UTP/STP Category 5
78
Page 83

Appendix A Specifications
Wireless Operating Range
Indoors
Up to 91M (300 ft.) @ 300 Mbps
Outdoors
Up to 457M (1500 ft.) @ 300 Mbps
Topology
Star (Ethernet)
LED Indicators
Power, DSL, Internet, Ethernet (WAN/LAN), Ethernet (4), HPNA, USB, Wireless,
and WPS Push Button
Environmental
Power
External, 10V DC, 1.6 A
Certifications
FCC Class B, FCC Class C (part 15, 68), CE Mark Commercial, UL
Operating Temperature
0º C to 40º C (32ºF to 104ºF)
Storage Temperature
-20ºC to 70ºC (-4ºF to 158ºF)
Operating Humidity
10% to 85% non-condensing
Storage Humidity
5% to 90% non-condensing
79
Page 84

Notices
Regulatory Compliance Notices
Class B Equipment
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by implementing one or more of the following measures:
s Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna;
s Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver;
s Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected;
s Consult the dealer or an experienced radio or television technician for help.
Modifications
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made
to this device that are not expressly approved by Actiontec Electronics, Inc., may
void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
80
Page 85

Notices
Declaration of conformity for products marked with the FCC logo – United States
on l y.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference;
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause unwanted operation.
Note: To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance require-
ments, the antenna used for this transmitter must be installed to
provide a separation distance of at least 20 cm from all persons
and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
For questions regarding your product or the FCC declaration, contact:
Actiontec Electronics, Inc.
760 North Mary Ave.
Sunnyvale, CA 94086
United States
Tel: (408) 752-7700
Fax: (408) 541-9005
GPL (General Public License)
This product includes software code developed by third parties, including software
code subject to the enclosed GNU General Public License (GPL) or GNU Lesser
General Public License (LGPL). The GPL Code and LGPL Code used in this product are distributed WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY and are subject to the copyrights of the authors, and to the terms of the applicable licenses included in the
download. For details, see the GPL Code and LGPL Code for this product and the
terms of the GPL and the LGPL, which are available on the Telus web site.
81
Page 86

Limited Warranty
Hardware: Actiontec Electronics, Inc., warrants to the end user (“Customer”) that
this hardware product will be free from defects in workmanship and materials,
under normal use and service, for twelve (12) months from the date of purchase
from Actiontec Electronics or its authorized reseller.
Actiontec Electronics’ sole obligation under this express warranty shall be, at
Actiontec’s option and expense, to repair the defective product or part, deliver to
Customer an equivalent product or part to replace the defective item, or if neither
of the two foregoing options is reasonably available, Actiontec Electronics may,
in its sole discretion, refund to Customer the purchase price paid for the defective product. All products that are replaced will become the property of Actiontec
Electronics, Inc. Replacement products may be new or reconditioned. Actiontec
Electronics warrants any replaced or repaired product or part for ninety (90) days
from shipment, or the remainder of the initial warranty period, whichever is longer.
Software: Actiontec Electronics warrants to Customer that each software program licensed from it will perform in substantial conformance to its program specifications, for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of purchase from Actiontec
Electronics or its authorized reseller. Actiontec Electronics warrants the media containing software against failure during the warranty period. The only updates that
will be provided are at the sole discretion of Actiontec Electronics and will only be
available for download at the Actiontec Web site, www.actiontec.com. Actiontec
Electronics’ sole obligation under this express warranty shall be, at Actiontec
Electronics’ option and expense, to refund the purchase price paid by Customer
for any defective software product, or to replace any defective media with software
which substantially conforms to applicable Actiontec Electronics published specifications. Customer assumes responsibility for the selection of the appropriate applications program and associated reference materials. Actiontec Electronics makes
no warranty or representation that its software products will meet Customer’s
requirements or work in combination with any hardware or applications software
products provided by third parties, that the operation of the software products
will be uninterrupted or error free, or that all defects in the software products
will be corrected. For any third-party products listed in the Actiontec Electronics
software product documentation or specifications as being compatible, Actiontec
Electronics will make reasonable efforts to provide compatibility, except where
82
Page 87

Limited Warranty
the non-compatibility is caused by a “bug” or defect in the third party’s product
or from use of the software product not in accordance with Actiontec Electronics
published specifications or user guide.
THIS ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS PRODUCT MAY INCLUDE OR BE BUNDLED
WITH THIRD-PARTY SOFTWARE, THE USE OF WHICH IS GOVERNED BY A
SEPARATE END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT.
THIS ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS WARRANTY DOES NOT APPLY TO SUCH
THIRD-PARTY SOFTWARE. FOR THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY, PLEASE REFER
TO THE END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT GOVERNING THE USE OF SUCH
SOFTWARE.
Obtaining Warranty Service: Customer may contact Actiontec Electronics
Technical Support Center within the applicable warranty period to obtain warranty service authorization. Dated proof of purchase from Actiontec Electronics or
its authorized reseller may be required. Products returned to Actiontec Electronics
must be pre-authorized by Actiontec Electronics with a Return Merchandise
Authorization (RMA) number marked on the outside of the package, and sent
prepaid and packaged appropriately for safe shipment, and it is recommended that
they be insured or sent by a method that provides for tracking of the package. The
repaired or replaced item will be shipped to Customer, at Actiontec Electronics’
expense, not later than thirty (30) days after Actiontec Electronics receives the
defective product.
Return the product to:
(In the United States)
Actiontec Electronics, Inc.
760 North Mary Avenue
Sunnyvale, CA 94085
83
Page 88

VDSL2/GigE Wireless 11n Gateway
Actiontec Electronics shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, memory data, or Customer data contained in, stored on, or integrated with
any products returned to Actiontec Electronics for repair, whether under warranty
or not.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF AN ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS’ PRODUCT DOES
NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTED ABOVE, CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY FOR
BREACH OF THAT WARRANTY SHALL BE REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND
OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS’ OPTION. TO
THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND
REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, TERMS
OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION
OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES, TERMS OR
CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
SATISFACTORY QUALITY, CORRESPONDENCE WITH DESCRIPTION, AND NON-
INFRINGEMENT, ALL OF WHICH ARE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED. ACTIONTEC
ELECTRONICS NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON
TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE,
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS.
ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY
IF ITS TESTING AND EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT
OR MALFUNCTION IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED
BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE, NEGLECT, IMPROPER
INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPT TO OPEN, REPAIR OR
MODIFY THE PRODUCT, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE
INTENDED USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OTHER HAZARDS, OR ACTS
OF GOD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW,
ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS ALSO EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS
ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR
PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE OR PROFITS,
LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF ITS
PRODUCT, EVEN IF ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER
HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS
84
84
Page 89

Limited Warranty
LIABILITY TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT,OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE
PAID, AT ACTIONTEC ELECTRONICS’ OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN
SHALL FAIL OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Disclaimer: Some countries, states or provinces do not allow the exclusion or
limitation of implied warranties or the limitation of incidental or consequential
damages for certain products supplied to consumers, or the limitation of liability
for personal injury, so the above limitations and exclusions may be limited in their
application to you. When the implied warranties are not allowed to be excluded in
their entirety, they will be limited to the duration of the applicable written warranty.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights which may vary depending on local
law.
Dispute Resolution: The customer may contact the Director of Technical
Support in the event the Customer is not satisfied with Actiontec Electronics’
response to the complaint. In the event that the Customer is still not satisfied with
the response of the Director of Technical Support, the Customer is instructed to
contact the Director of Marketing. In the event that the Customer is still not satisfied with the response of the Director of Marketing, the Customer is instructed to
contact the Chief Financial Officer and/or President.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State
of California, U.S.A., excluding its conflicts of laws and principles, and excluding
the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods.
85
 Loading...
Loading...