ACT CT2566-FP, CT2566 Datasheet
CT2566
www.aeroflex.com
F
E
I
D
C
E
R
T
A
E
R
O
F
L
E
X
L
A
B
S
I
N
C
.
MIL-STD-1553 to Microprocessor
Interface Unit
Features
• Second Source Compatible to the BUS-66300
• PGA Version available, (second source to the BUS-66312)
• Compatible with MIL-STD-1750 CPUs
• Compatible with MOTOROLA, INTEL, and ZILOG CPUs
• Compatible with Aeroflex’s CT2565 BC/RT/MT and CT2512 RT
• Minimizes CPU overhead
• Signal controls for shared memory implementation
• Transfers complete messages to shared memory
• Provides memory mapped 1553 interface
• Packaging – Hermetic Metal
• 78 Pin, 2.1" x 1.87" x .25" PGA type package
• 82 Lead, 2.2" x 1.61 x .18" Flat Package
Description
Aeroflex CT2566 MIL-STD-1553 to Microprocessor Interface Unit simplifies the CPU to 1553 Data
Bus interface. The CT2566 provides an interface by using RAM allowing the CPU to transmit or
receive 1553 traffic simply by accessing the memory. All 1553 message transfers are entirely
memory or I/O mapped. The CT2566 supports 1553 interface devices such as Aeroflex's CT2512
dual RT or the CT2565 dual BC, RT, and MT. The CT2566 operates over the full military -55°C to
+125°C temperature range.
CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
ISO
9001
I
MSTRCLR
SELECT
STRBD
READYD
RD/
WR
MEM/
REG
EXTEN
EXTLD
INT
CLOCK IN
MEMORY
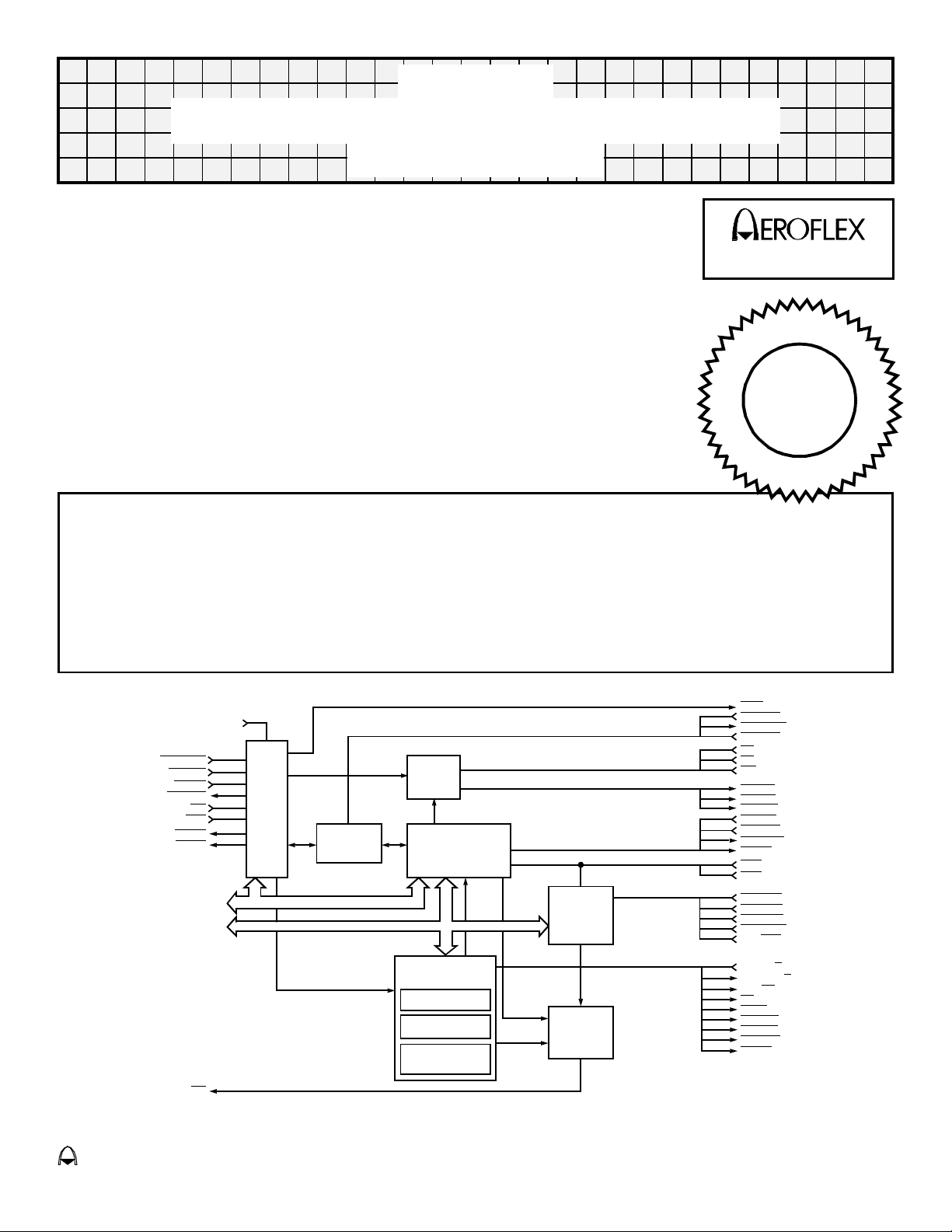
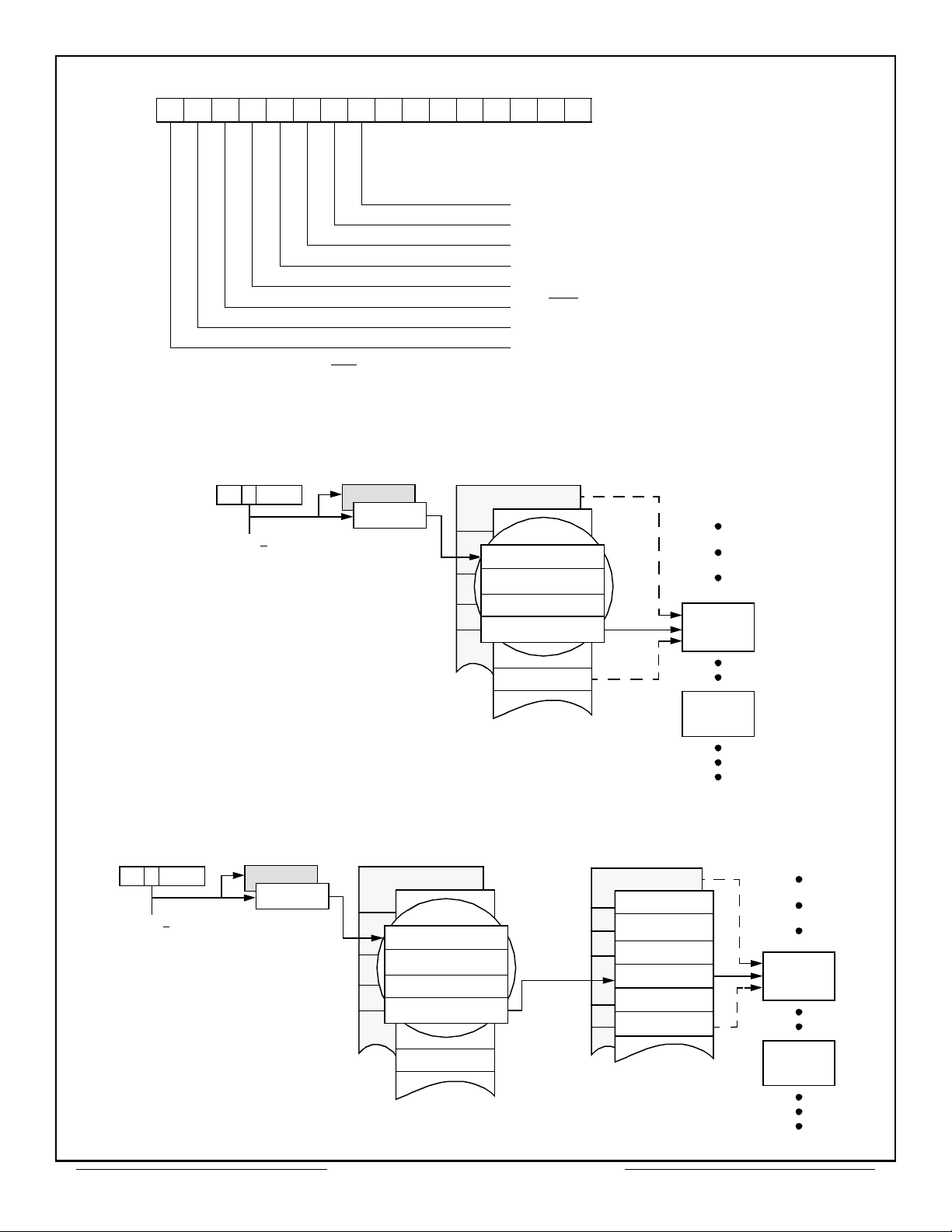
CPU
TIMING
A15-A00
D15-D00
CONTENTION
RESOLVER
TIMING
MICROCODE
CONTROLLER
OPERATION
CONTROL
REGISTERS
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
START / RESET
REGISTER
INTERRUPT
MASK
REGISTER
Figure 1 – Functional Block Diagram
BLOCK
STATUS
WORD
INTERRUPT
GENERATOR
IOEN
BUSREQ
BUSGRNT
BUSACK
CS
OE
WR
MEMCS
MEMOE
MEMWR
ADRINC
NBGRNT
BCSTART
TAGEN
EOM
SOM
MSGERR
TIMEOUT
STATERR
LOOPERR
CHB/
CHA
CTLINB/
CTLOUTB/
RTU/
BC
MT
DBAC
SSBUSY
SSFLAG
SVCREQ
RESET
A
A
eroflex Circuit Technology – Data Bus Modules For The Future © SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99
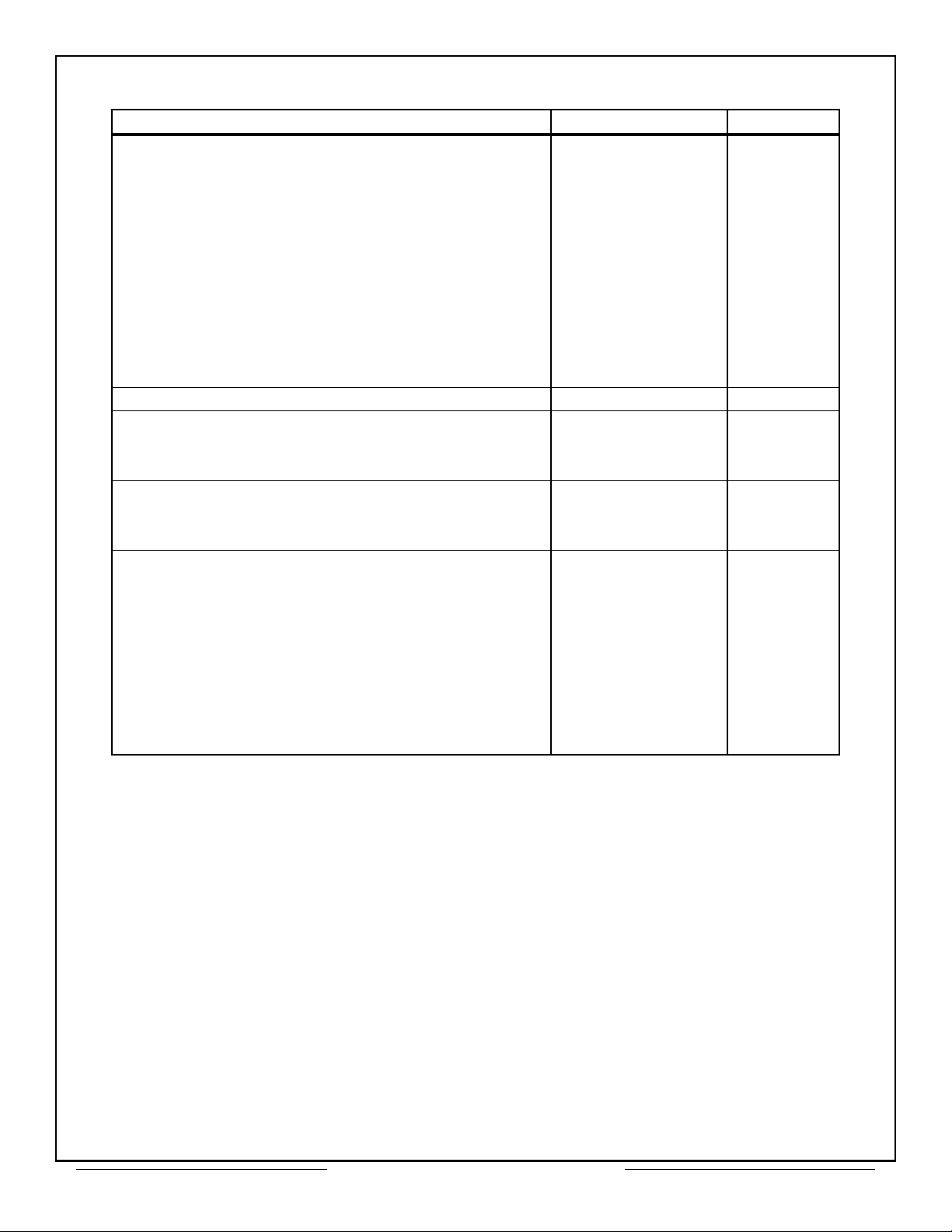
Specifications at Nominal Power Supply Voltages
PARAMETER VALUE UNITS
Logic
I
(With VIH = 2.7V)
IH
(With VIL = 0.0V)
I
IL
I
OH
I
OL
V
IH
V
IL
V
OH
V
OL
−630 µA
−700 µA
4.0 min mA
4.0 mA
2.0 V
0.8 V
3.7 V
0.4 V
Clock 12 MHz
Power Supplies
Voltage
Current Drain
5.0±10% V
10 typ mA
Temperature Range
Operating (Case)
Storage
−55 to +125 °C
−65 to +150 °C
Physical Characteristics
Size
78 pin DIP
82 pin flatpack
2.1 x 1.87 x 0.25
(53 x 47.5 x 6.4)
2.1 x 1.87 x 0.25
(55.6 x 40.6 x 3.71)
in
(mm)
in
(mm)
Weight
78 pin DIP
82 pin flatpack
1 (28) oz (g)
1 (28) oz (g)
Table 1 – Specifications
GENERAL
The CT2566 was designed to perform required
handshaking to the 1553 interface device, storing
or retrieving message(s) from a user supplied
RAM and notifying the CPU that a 1553
transaction has occurred. The CPU uses this
RAM to read the received data as well as to store
messages to be transmitted onto the Bus.
The CT2566 can be used to implement BC, RT,
or MT operation and can be either memory
mapped or I/O mapped to CPU address space.
Registers internal to the CT2566 control its
operation.
The CT2566 can access up to four external,
user supplied registers and can address up to
64K words of RAM. The RAM selected must be a
non-latched static RAM (capable of meeting the
timing constraints for the CT2566). A double
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
buffering architecture is provided to prevent
incomplete or partially updated information from
being transmitted onto the 1553 Data Bus.
The CT2566 requires an external, user supplied
clock.
COMPATIBLE MICROPROCESSOR TYPES
The CT2566 may be used with most common
microprocessors, including, the Motorola 68000
family, the Intel 8080 family, Zilog Z8000
products, and available MIL-STD-1750
processors.
Interfacing the CT2566 to the 1553 Data Bus
requires external circuitry such as Aeroflex’s
CT2565(BC/RT/MT) and ACT4489D
transceivers. Figure 2 shows the interconnection
for these components.
2
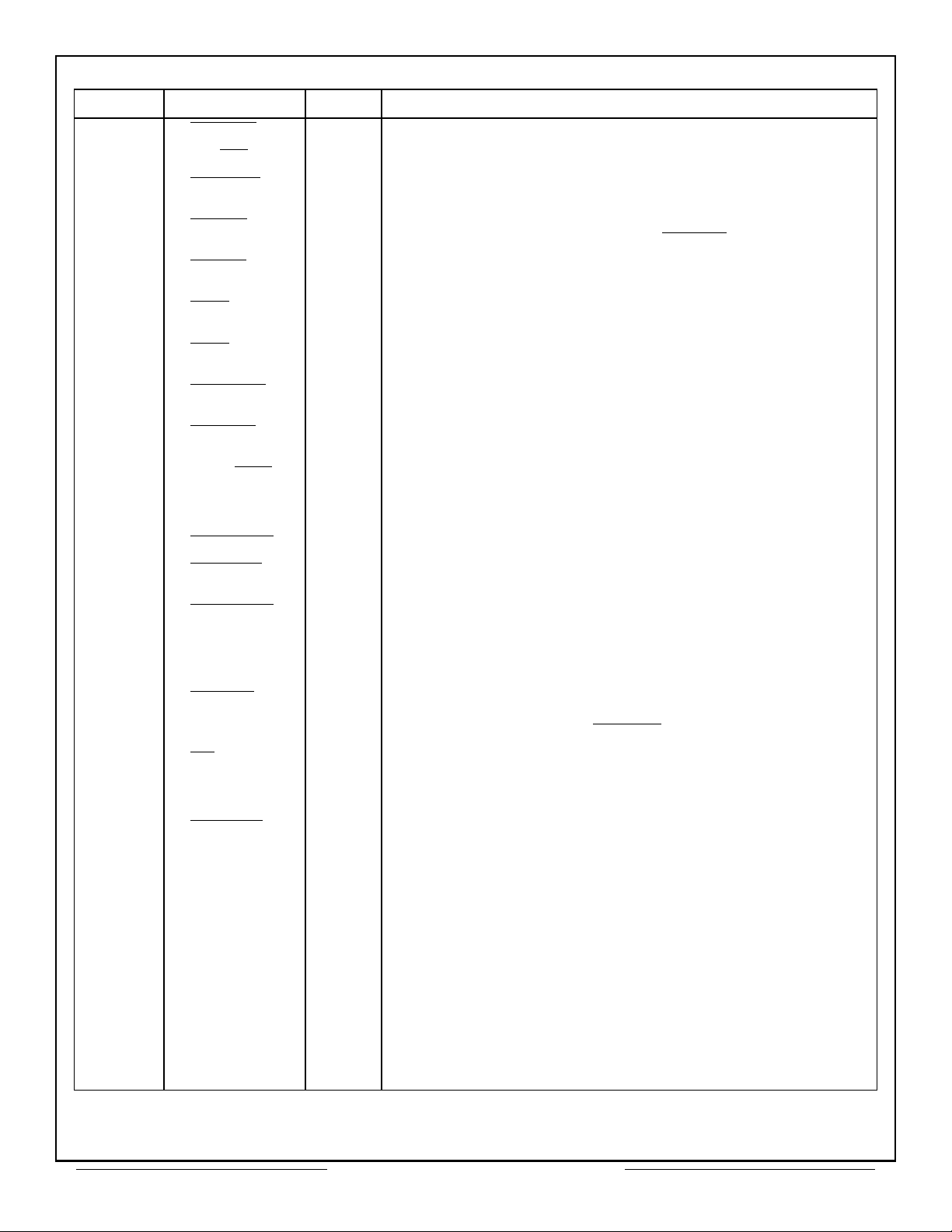
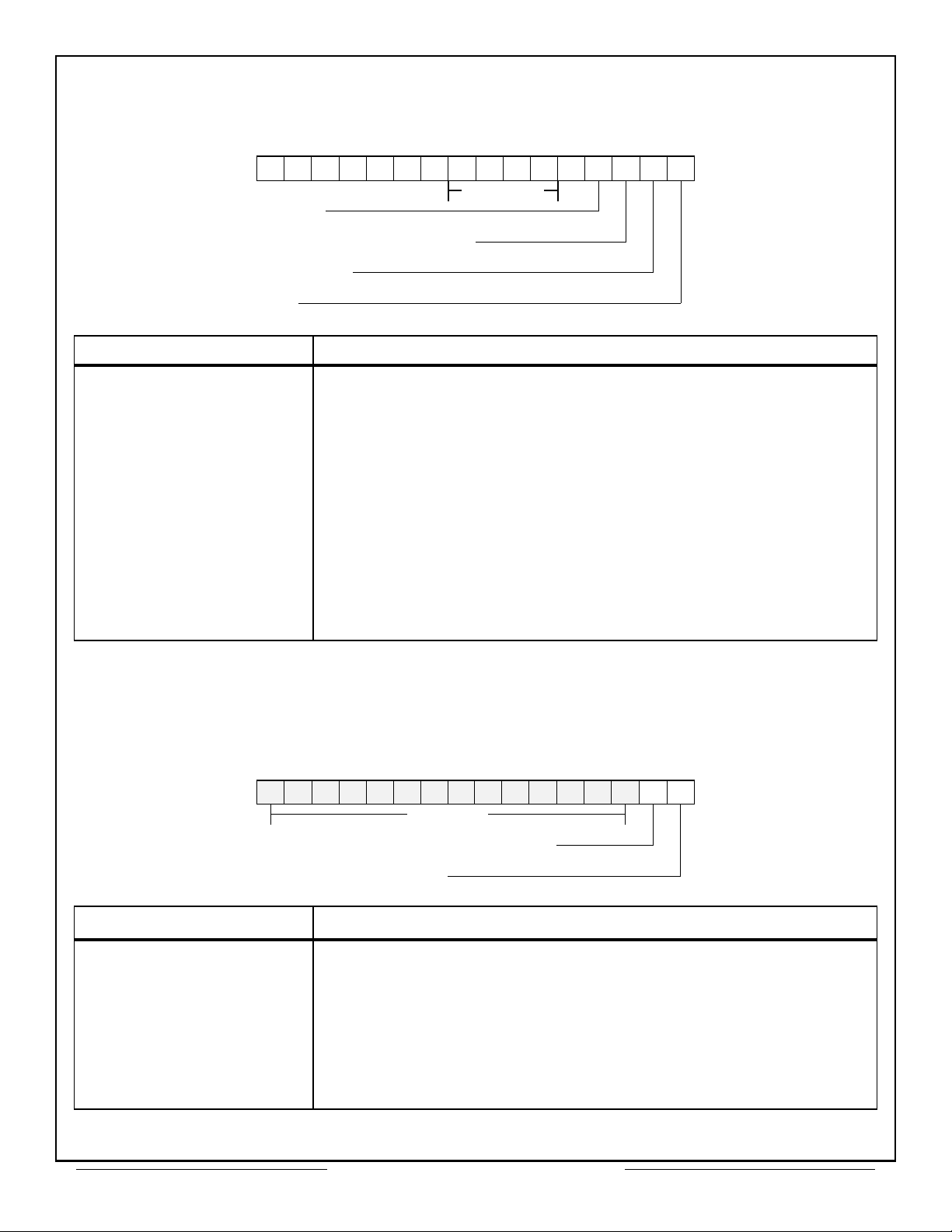
PIN NO. NAME I/O DESCRIPTION
1 SELECT
2 RD/WR
3 READYD
I
I
O
Select. When active, selects CT2566 for operation.
Read/Write. Controls CPU bus data direction.
Ready Data. When active indicates data has been received
from, or is available to the CPU.
4 EXTEN
O
External Enable. Output from CT2566 to enable output from
external devices. Same timing as MEMOE
5 TAGEN
O
Tag Enable. Enables an external time tag counter for
transferring the time tag word into memory.
6 EOM
I
End of Message. Input from 1553 device indicating end of
message.
7 SOM
I
Start of Message. Input from 1553 device indicating start of
message in RTU mode.
8 STATERR
I
Status Error. Input from 1553 device when status word has
either a bit set or unexpected RT address (in BC mode only).
9 ADRINC
I
Address Increment. Sent from 1553 device to increment
address counter following word transfer.
10 MEM/REG
I
Memory/Register. Input from CPU to select memory or
register data transfer.
11 CLOCK IN I
12 LOOPERR
13 BUSREQ
I
I
Clock input; 50% duty cycle, 12MHz, max.
Loop Error. Input from 1553 device if short loop BIT fails.
Bus Request. When active, indicates 1553 device requires
use of the address/data bus.
14 BUSGRNT
O
Bus Grant. Handshake output to 1553 device in response to
BUS REQUEST indicating address/data bus available to
1553 device.
15 Not Used -
16 MEMCS
O
-
Memory Chip Select. Low from CT2566 to enable external
RAM. Used with 4K x 4 RAM type device to read RAM or
used in conjunction with MEMWR
17 OE
I
Output Enable. Input from 1553 device used to enable
memory on the parallel bus.
18 N/C -
19 NBGRNT
I
Not Used.
Low pulse from 1553 device preceding start of received new
protocol sequence. Used with superseding command to reset
DMA in progress.
20 + 5 Volt I
21 D15 I/O
22 D13 I/O
23 D11 I/O
24 D09 I/O
25 D07 I/O
26 D05 I/O
Logic power supply.
Data Bus Bit 15 (MSB).
Data Bus Bit 13.
Data Bus Bit 11.
Data Bus Bit 9.
Data Bus Bit 7.
Data Bus Bit 5.
27 D03 I/O Data Bus Bit 3.
.
to write data into RAM.
Table 2 – Pin Functions (78 Pin DIP)
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
3
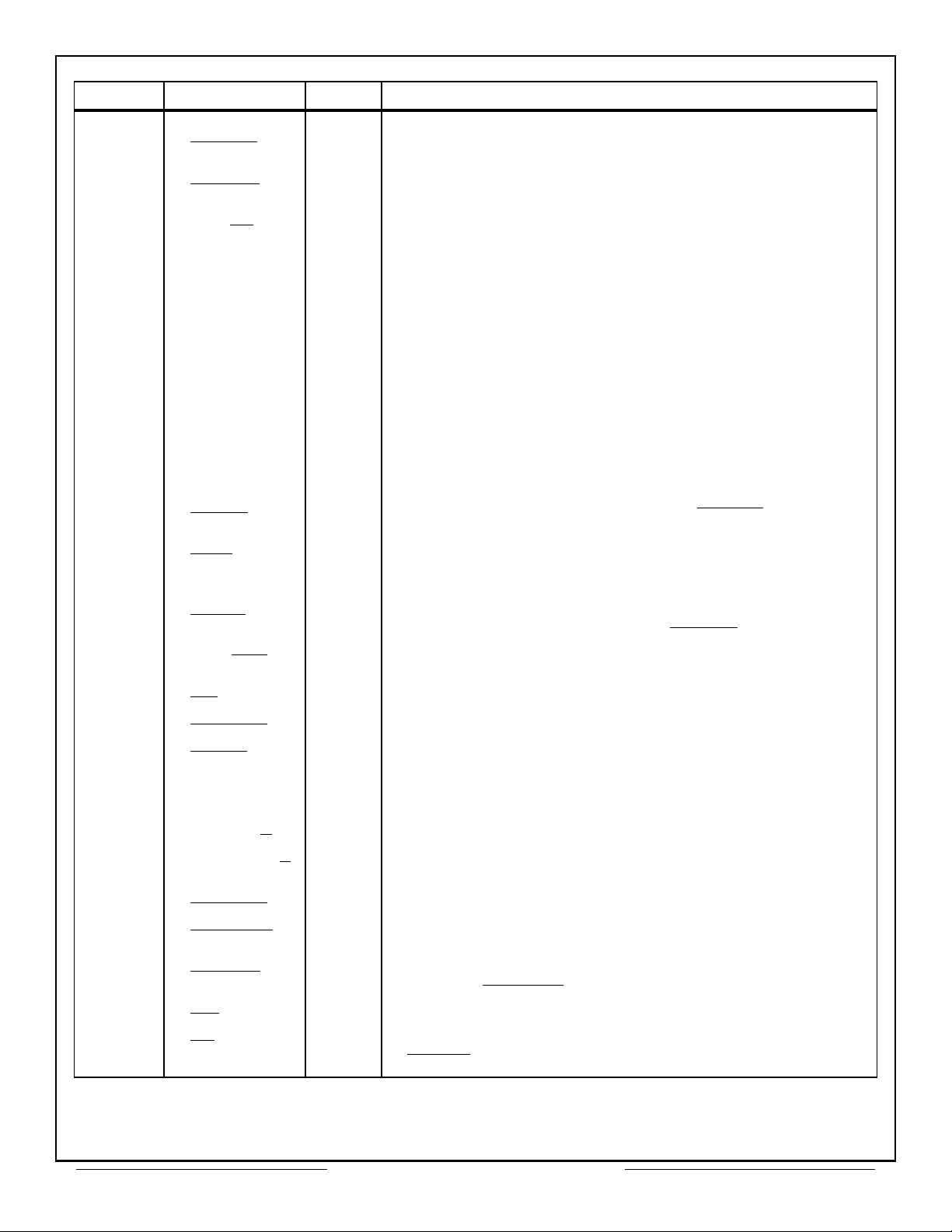
PIN NO. NAME I/O DESCRIPTION
28 D01 I/O Data Bus Bit 1.
29 SSFLAG
O
Subsystem Flag. Output to 1553 device to set RT subsystem
flag status bit.
30 SSBUSY
O
Subsystem Busy. Output to 1553 device to set RT subsystem
busy flag.
31 RTU/BC
O
Output to 1553 device used in conjunction with MT to set
operating mode.
32 A14 O Address Bit 14.
33 A12 O Address Bit 12.
34 A10 O Address Bit 10.
35 A08 O Address Bit 8.
36 A06 O Address Bit 6.
37 A04 O Address Bit 4.
38 A02 I/O Address Bit 2.
39 A00 I/O Address Bit 0 (LSB).
40 GND - Signal Return.
41 STRBD
I
Strobe Data. Used in conjunction with SELECT
data transfer cycle to/from CPU.
42 IOEN
O
Input/Output Enable. Output from CT2566 to enable external
buffers/latches connecting the hybrid to the address/data
bus.
43 EXTLD
O
External Load. Used to load data into external device via the
CT2566 data bus. Same timing as MEMWR
44 CHB/CHA
Input from 1553 in RT mode used to indicate received 1553
message came in either Channel A or B.
to indicate a
.
45 INT
46 BCSTART
47 RESET
48 MSGERR I
49 CTLIN B/A
50 CTLOUT B/A
51 TIMEOUT
52 MSTRCLR
53 BUSACK
54 WR
55 CS
Table 2 – Pin Functions (78 Pin DIP) (Cont.)
O Interrupt. Interrupt pulse line to CPU.
O Bus Controller Start. Outputs to 1553 in initiate BC cycle.
O
Reset. Output to external device from CT2566 consisting of
the OR condition of CPU reset and CPU Master Clear.
Message Error. Input from 1553 device when an error occurs
in message sequence.
I Input to change active memory map area (0 = area A).
O
Output from CT2566 selecting which area is to be active (0 =
area A).
I Input from 1553 device indicating no response time-out.
I
Master Clear. Power-on reset from CPU. Resets DMA in
progress and internal registers to logic “0”.
I
Bus Acknowledge. Input from 1553 device acknowledge
receipt of BUSGRNT
.
I Write. Input from 1553 device for writing data into memory.
I
Chip Select. Input from 1553 device that is routed to
MEMCS
.
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
4
PIN NO. NAME I/O DESCRIPTION
56
MEMOE
O Memory Output Enable. Output from CT2566 to enable
memory output data.
57 MEMWR O
Memory Write. Output pulse from CT2566 to write data bus
data into memory.
58 Not Used - -
59 MT
O
Bus Monitor. Used in conjunction with RTU/BC
operating mode.
60 D14 I/O Data Bus Bit 14.
61 D12 I/O Data Bus Bit 12.
62 D10 I/O Data Bus Bit 10.
63 D08 I/O Data Bus Bit 8.
64 D06 I/O Data Bus Bit 6.
65 D04 I/O Data Bus Bit 4.
66 D02 I/O Data Bus Bit 2.
67 D00 I/O Data Bus Bit 0 (LSB).
68 SVCREQ
O
Service Request. Used to set service request bit in RT Status
Word.
69 DBAC
O
Dynamic Bus Acceptance. Used to set status bit in RT Status
Word.
to set
70 A15 O Address Bit 15 (MSB).
71 A13 O Address Bit 13.
72 A11 O Address Bit 11.
73 A09 O Address Bit 9.
74 A07 O Address Bit 7.
75 A05 O Address Bit 5.
76 A03 O Address Bit 3.
77 A01 I/O Address Bit 1.
78 GND - Chassis Ground.
Table 2 – Pin Functions (78 Pin DIP) (Cont.)
PIN NO. FUNCTION PIN NO. FUNCTION
1 N/C 42 N/C
2 SELECT
3 STRBD
4 RD/WR
5 IOENBL
43 GROUND
44 CHASSIS GROUND
45 A00 (LSB)
46 A01
6 READYD
7 EXTLD
47 A02
48 A03
Table 3 – CT2566FP Pin Functions (82 Pin Flat Package)
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
5
PIN NO. FUNCTION PIN NO. FUNCTION
8 EXTEN 49 A04
9 CHB/CHA
10 TAGEN
11 INT
12 EOM
13 BCSTART
14 SOM
15 RESET
16 STATERR
17 MSGERR
18 ADRINC
19 CTLIN B/A
20 MEM/REG
50 A05
51 A06
52 A07
53 A08
54 A09
55 A10
56 A11
57 A12
58 A13
59 A14
60 A15
61 RTU/BC
21 CTLOUT B/A 62 DBAC
22 CLOCK IN 63 SSBUSY
23 TIMEOUT 64 SVCREQ
24 LOOPERR 65 SSFLAG
25 MSTRCLR 66 D00
26 BUSYREQ
27 BUSACK
28 BUSGRNT
29 WR
67 D01
68 D02
69 D03
70 D04
30 N/C 71 D05
31 CS
32 MEMCS
33 MEMOE
34 OE
35 MEMWR
72 D06
73 D07
74 D08
75 D09
76 D10
36 Not Used 77 D11
37 N/C 78 D12
38 NBGRNT
39 MT
79 D13
80 D14
40 +5V 81 D15
41 N/C 82 N/C
Table 3 – CT2566FP Pin Functions (82 Pin Flat Package) (Cont.)
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
6
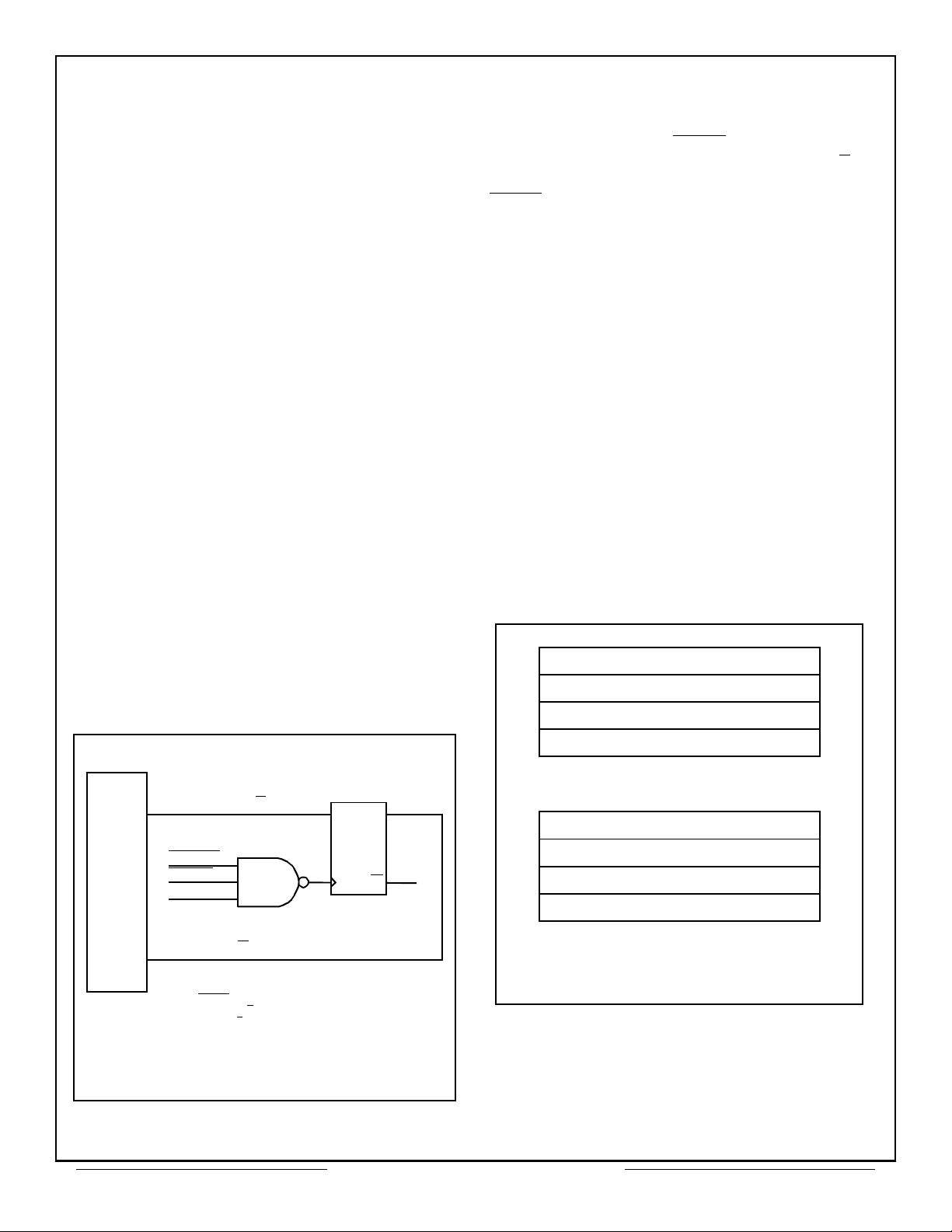
MEMORY MANAGEMENT
BUS-66300
Figure 3 – Synchronized map switching u
the CT2566
The RAM used by the CT2566 can be any standard
static memory with a WRITE STROBE pulse width
requirement less than 70ns. The RAM area is broken
down into pointers, look-up tables, and data blocks. All
1553 operation control is accomplished through the
RAM, including fault monitoring and data block
transfers.
For most applications, a 4K x 16 memory is sufficient
to store the number of messages, but the CT2566 can
access up to 64K words.
DOUBLE BUFFERING
A Double Buffering system is available to prevent
partially updated data blocks from being read by the
CPU or transferred onto the 1553 Data Bus. To use
Double Buffering the CPU must divide the RAM into
two areas: “current” and “non-current”. Two Stack
Pointers, Descriptor Stacks, and Look-Up Tables are
required to be used by the CPU.
The 1553 device has access only to the current area
of RAM, and will use the current Descriptor Stack and
Look-Up Table. While the 1553 device is processing
messages using the current area pointers, the CPU
can be setting up the next set of messages in the
non-current area of RAM.
Once an EOM or BCEOM occurs, the CPU can swap
the current and non-current areas by toggling bit 13 of
the Configuration Register (See register section for
description). The 1553 device will then have access to
the new current area. Meanwhile, the CPU can begin
processing the data received during the previous
transfer or can begin setting up the next set of 1553
messages.
to ensure that the swapping of the current and
non-current areas doesn’t occur while the CT2566 is
processing a message from the 1553 device. During
message processing, the INCMD
CPU’s map area selection is inhibited. CTLIN B/A
is a logic "0" and the
will
be automatically latched back into the CT2566 when
INCMD
and NODT change to a logic "1".
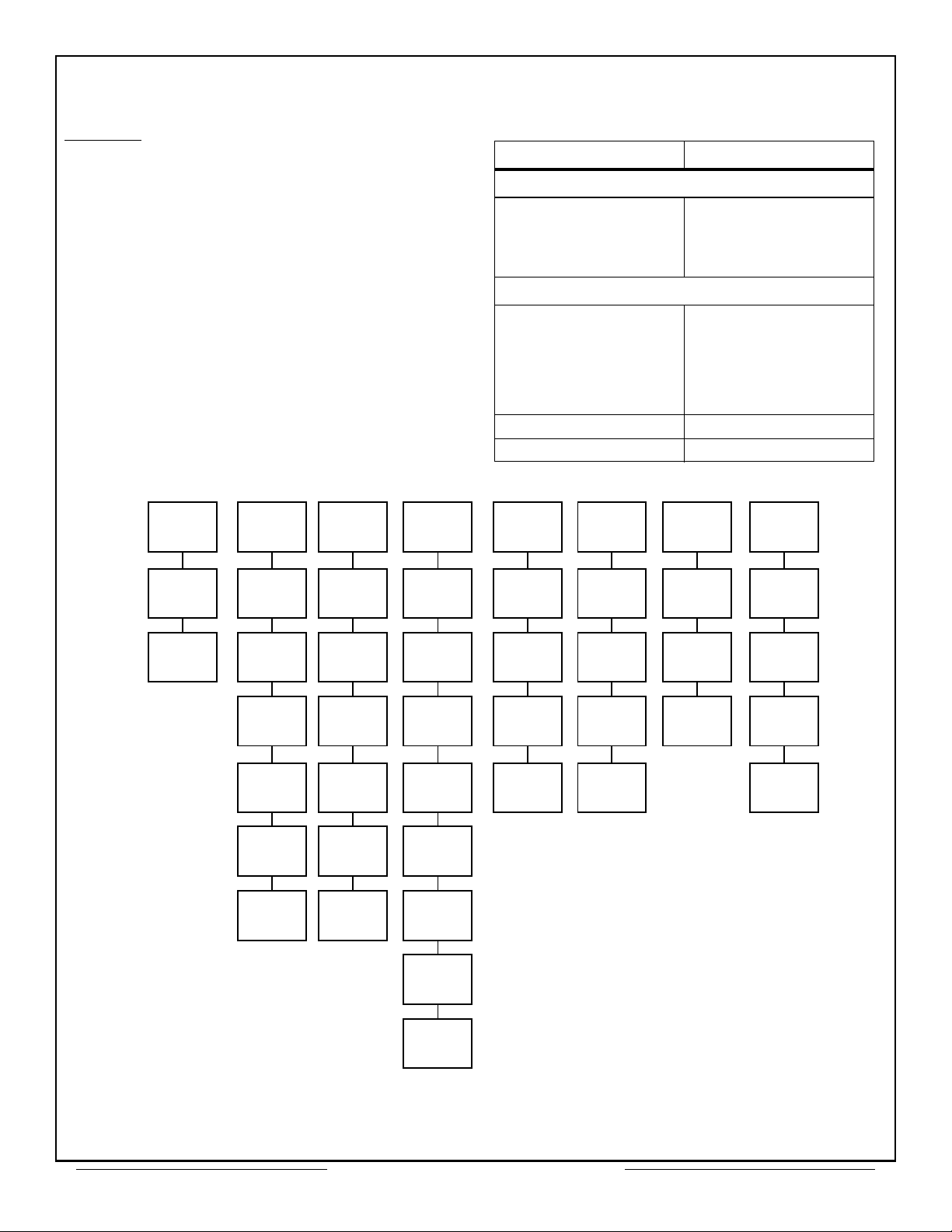
DESCRIPTOR STACK
The CT2566 uses a Descriptor Stack in BC and RTU
modes. Each stack entry contains four words which
refer to one 1553 message (See Figure 4). The Block
Status Word, shown in Figure 5, indicates the physical
bus which received the message (RTU mode), reports
whether or not an error was detected during message
transfer, and indicates whether the message was
completed (SOM replaced with EOM).
The user-supplied Time-Tag word is loaded at the
start of a message transfer and is updated at the end of
the transfer.
The contents of the fourth word in the Descriptor
Stack depends on the operating mode. In BC mode, it
contains the address of the message data block
containing the 1553 message formatted as shown in
Figure 6. In RTU mode, the word contains the received
1553 Command Word as shown in Figure 7.
A Stack Pointer must be initialized by the CPU. The
Descriptor Stack contains 64, four word entries, and
BLOCK STATUS WORD
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
MESSABE BLOCK ADDRESS
50 CTLOUT B/A
INCMD
NODT
12 MHz
49 CTLIN B/A
Notes:
(1) INCMD
(2) CTLOUT B/A
(3) CTLIN B/A
is from the BUS-65600 or BUS-65112.
reflects bit 13 of the Configuration Register.
is used to select the current area.
D Q
LS74
C
Q
An external circuit (shown in Figure 3) can be added
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
BC DESCRIPTION BLOCK
BLOCK STATUS WORD
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
RECEIVED COMMAND WORD
RTU DESCRIPTION BLOCK
Figure 4 – Descriptor Stack Entries
automatically wraps around (the 64th entry is followed
by the first entry). The 1553 device uses the current
area Stack Pointer to determine the address of the
Stack entry to be used for the current 1553 message.
The CT2566 automatically increments the current area
Stack Pointer by four upon the completion of each
7
message regardless of whether or not an error was
External Register
detected during the processing of that message.
LOOK-UP TABLES
In RTU mode a Look-Up Table is provided to allow
the CT2566 to store messages in distinct areas of RAM
based upon the subaddress of the received command
word. See RTU operation for details.
The CT2566 uses the T/R
bits to form a pointer into the “current area” Look-Up
Table. The first 32 words of this table are initialized by
the user with the addresses of the data blocks to be
used for receiving data into subaddress 0,1,2,…31.
The next 32 words are initialized by the user with the
address of the data blocks to be used when
transmitting data from subaddress 0,1,2,…31.
and the five subaddress
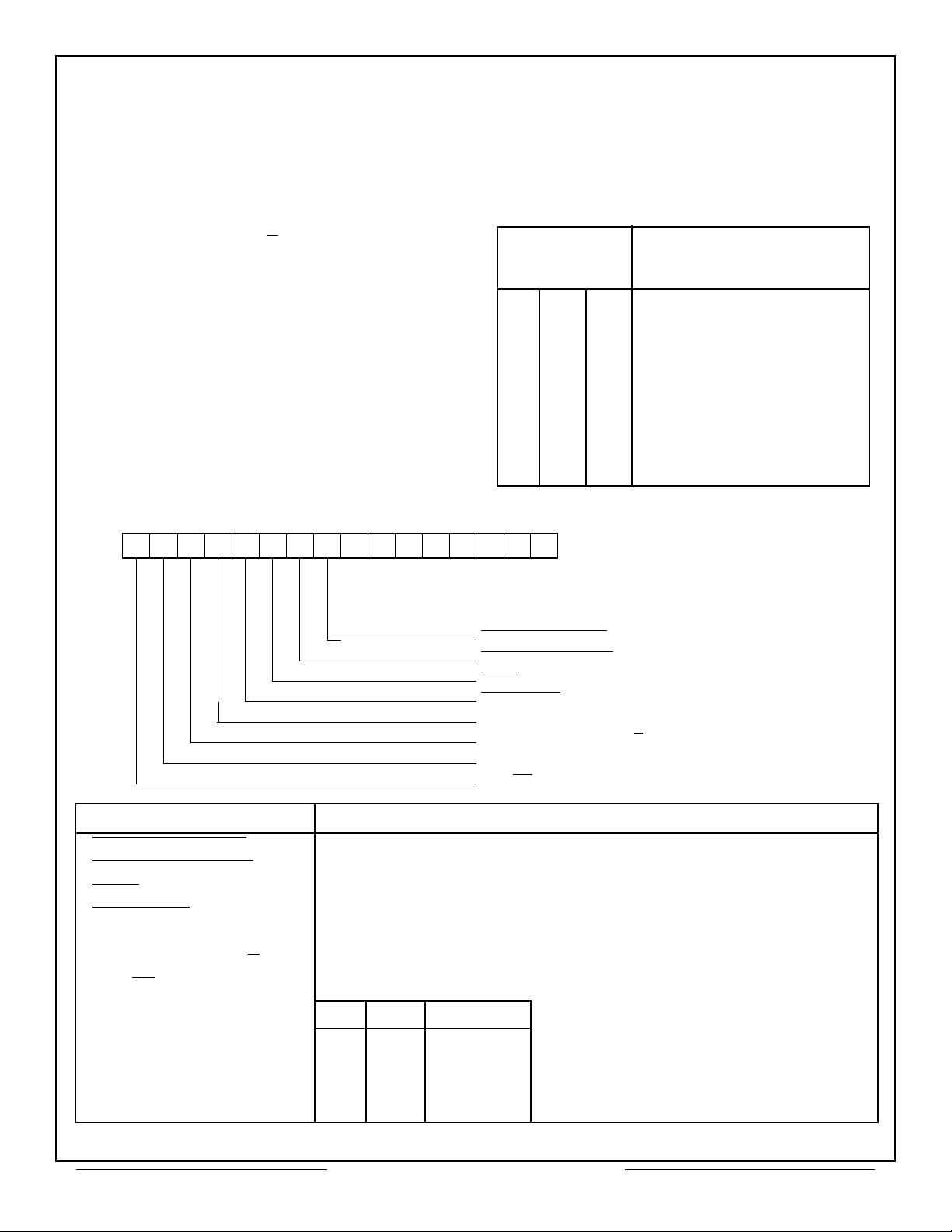
CT2566 REGISTERS
The CT2566 is controlled through the use of three
internal registers: the Interrupt Mask Register,
Configuration Register, and Start/Reset Register. In
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
addition, the CT2566 can access up to four external,
user supplied registers. Possible external register
applications include: defining the RTU address, storing
a CPU Time Tag, and reading a captured Built-In-Test
(BIT) Word from the 1553 interface unit. For further
information, consult factory.
Table 2 – Internal Registers Address Definition
CT2566
Address Bits
Definition
A2 A1 A0
0 0 0 Interrupt Mask Register
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
Configuration Register
Not Used
Start/Reset Register (write
only)
External Register
External Register
External Register
1 1 1
SUBSYSTEM FLAG
SERVICE REQUEST
BUSY
DB ACCEPT
STOP ON ERROR
CONTROL AREA BIT B/A
MT
RTU/BC
BIT DEFINITIONS
SUBSYSTEM FLAG
SERVICE REQUEST
BUSY
DB ACCEPT
1553 status word bit.
1553 status word bit.
1553 status word bit.
1553 status word bit.
STOP ON ERROR Causes BC to stop at the end of current data block if an error is detected.
CONTROL AREA B/A
RTU/BC
/MT Operating Mode.
Used for double buffering (See Double Buffering).
Bit 15 Bit 14
Mode
0 0 BC
0 1
1 0
1 1
MT
RTU
ILLEGAL
Figure 8 – Configuration Register
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
8
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
LOOP TEST FAIL
RESPONSE TIME OUT (BC ONLY)
FORMAT ERROR
STATUS SET (BC ONLY)
ERROR FLAG
CHB/CHA
(RTU ONLY)
SOM
EOM
Note: In BC mode Bit 13, CHB/CHA contains a logic "0" regardless of which channel is used.
Figure 5 – Block Status Word
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
CURRENT
AREA B/
A
01315
STACK
POINTERS
Note: User may opt to share memory block(s).
Figure 6 – Use of Descriptor Stack – BC Mode
STACK
POINTERS
01315
DESCRIPTOR
STACKS
DESCRIPTOR
STACKS
BLOCK STATUS WORD
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
MESSAGE
BLOCK ADDR
LOOK-UP TABLE
(DATA BLOCK ADDR)
DATA
BLOCKS
DATA BLOCK
DATA BLOCK
DATA
BLOCKS
(1)
CURRENT
AREA B/
A
Note: (1) User may opt to share memory block(s).
(2) See Figure 19.
BLOCK STATUS WORD
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
RECEIVED COMMAND
WORD
LOOK-UP
TABLE ADDR
(2)
DATA BLOCK
DATA BLOCK
Figure 7 – Use of Descriptor Stack – RTU Mode
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
9
INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER
This register is an eight bit read/write register used to enable the interrupt conditions. All interrupts are enabled
with a logic "1" (See Figure 9).
15 4 3 2 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
NOT USED
BC EOM
FORMAT ERROR/STATUS SET
NOT USED
EOM
INTERRUPT DEFINITION
EOM End of Message. Set by CT2566 (during BC or RTU mode) every time a
1553 message is transferred (regardless of validity).
FORMAT ERROR/
STATUS SET
Set by CT2566 for these conditions:
Loop Test Failure: Last transmitted word did not match received word.
Message Error: Received message contained an address error, one of
eight 1553 status bits set, or 1553 specification violated (parity error,
Manchester error, etc).
Time-Out: Expected transmission was not received during allotted time
Status Set: Received status word contained status bit(s) set or address
error.
BC EOM
Bus Controller End of Message. Set by CT2566 (in BC mode) when all
messages have been transferred.
Figure 9 – Interrupt Mask Register
START/RESET REGISTER
Only two bits of this write only register are used, as illustrated in Figure 10.
15 1 0
NOT USED
CONTROLLER START
RESET
BIT DEFINITION
RESET Issued by the CPU to place the CT2566 in the power-on condition;
Configuration, and Interrupt Mask registers are reset to logic “0”.
CONTROLLER START
Issued by the CPU (BC mode) to start message transmission. The CPU
must first load the number of messages to transfer (256, max) in the
message count location of RAM (area A or B). Value is loaded in 1’s
complement (load FFFE to transmit one message). In MT mode it is
used to begin reception of 1553 messages. Issued by CPU in MT mode
to enable monitor operation.
Figure 10 – Start/Reset Register
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
10
BC Operation
The BC mode is selected by setting the two MSBs of
the Configuration Register to logic "0". This can be done
by writing directly to the register or by issuing a
MSTRCLR
will also clear the Interrupt Mask Register.
BC Initialization.
For BC operation, the user initializes the RAM as
shown in Table 3 and follows the steps in Figure 11, BC
Initialization. The CPU loads the data blocks with 1553
messages (See Figure 12). The first word of each data
block must contain the Control Word (shown in Figure
13) for the message. The starting addresses of the data
blocks are placed in the fourth word of the Descriptor
Stack in the order the messages are to be transmitted
(i.e. the address of the first message is loaded into the
fourth location of the Stack, the address of the second
message is placed into the eighth location, etc). Once
the data blocks and the Descriptor Stack have been
initialized, the CPU loads the current area message
count with the number of messages to transfer (load in
1’s complement).
or RESET command. Note that a RESET
Table 3 - Typical BC Memory Map
(4K memory)]
HEX ADDRESS FUNCTION
Fixed Areas
0100 Stack Pointer A
0101 Message Count A
0104 Stack Pointer B
0105 Message Count B
User Defined Areas
0108-013F Not Used
0140-017F Data Block 1
0180-01BF Data Block 2
01C0-01FF Data Block 3
• •
• •
0F00-0FFF Descriptor Stack A
0000-00FF Descriptor Stack B
CONTROL
WORD
BROADCAST
COMMAND
(NO DATA)
BROADCAST
COMMAND
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
BROADCAST
COMMAND
(NO DATA)
CONTROL
WORD
RECEIVE
COMMAND
DATA WORD
1
DATA WORD
2
DATA WORD
LAST
DATA WORD
LAST
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2566
STATUS
RECEIVE
RECEIVE
DATA BLOCK
CONTROL
WORD
TRANSMIT
COMMAND
TRANSMIT
COMMAND
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
STATUS
RECEIVED
DATA WORD
1
DATA WORD
2
DATA WORD
LAST
TRANSMIT
DATA BLOCK
CONTROL
WORD
RECEIVE
COMMAND
TRANSMIT
COMMAND
TRANSMIT
COMMAND
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
STATUS
WORD 1
FROM XMTR
DATA WORD
1 RECEIVED
DATA WORD
2 RECEIVED
LAST DATA
WORD
RECEIVED
CONTROL
WORD
MODE
COMMAND
DATA WORD
DATA WORD
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
STATUS
WORD
MODE CODE
WITH DATA
RECEIVE
DATA BLOCK
FORMAT
CONTROL
WORD
MODE
COMMAND
MODE
COMMAND
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
STATUS
WORD
DATA WORD
RECEIVED
MODE CODE
WITH DATA
TRANSMIT
DATA BLOCK
FORMAT
CONTROL
WORD
MODE
COMMAND
MODE
COMMAND
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
STATUS
WORD
MODE CODE
WITHOUT
DATA
BROADCAST
COMMAND
DATA WORD
1
DATA WORD
2
DATA WORD
LAST
DATA WORD
LOOPED
BACK BY
CT2565
BROADCAST
COMMAND
WITH DATA
STATUS
WORD 2
FROM
RECEIVER
REMOTE
TERMINAL TO
REMOTE
TERMINAL
DATA BLOCK
Figure 12 – BC Message Data Block Formats
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
11
The CPU selects an internal register by asserting
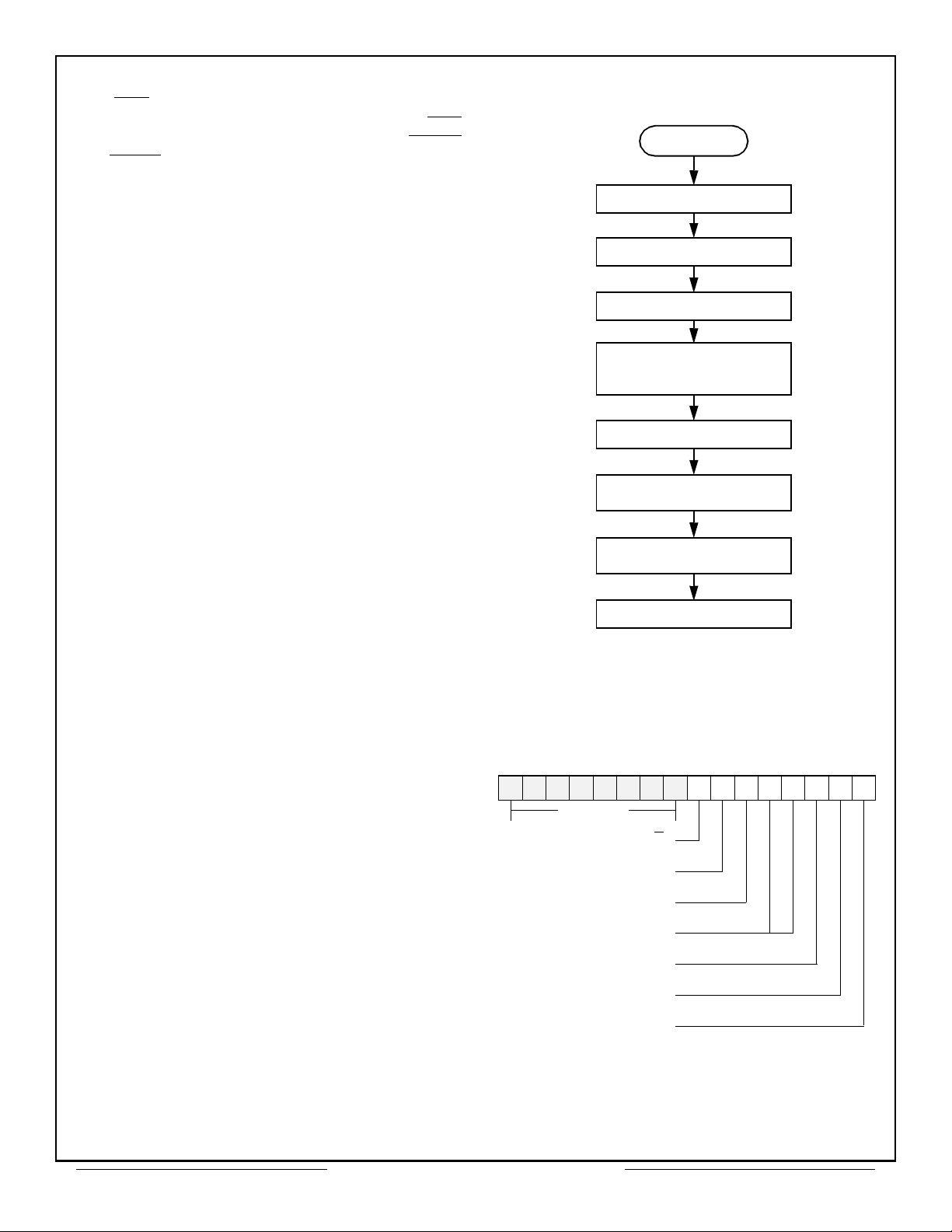
Figure 13 – BC Control Word
MEM/REG
and the A2 bit to logic "0" (See Table 2).
External registers are selected by asserting MEM/REG
logic "0" and A2 bit to a logic "1". The signals EXTEN
and EXTLD are used to read and write from the
external registers (See Figures 26 to 28).
Configuration Register
The Configuration Register is an eight bit read/write
register used to define the 1553 operating mode (BC,
MT, or RTU) and the associated RTU status bits. The
four MSBs define the mode of operation; the four LSBs
define the RTU status bits (See Figure 8).
All bits in the Configuration Register (except bit 12)
will be present on the respective CT2566 output pins to
the 1553 device. The MT bit is inverted at the output.
To begin transferring messages onto the bus, the
CPU must issue a Controller Start Command (See
Figure 14). This is done by setting bit 1 of the
Start/Reset Register to a logic "1". An EOM interrupt
will be generated each time a message transfer has
been completed. A BCEOM will be generated once the
specified number of messages has been transferred
(message counter = FFFF).
A Format Error Status Set Interrupt will be generated
at the end of a message if a timeout condition or error
condition was detected. If the STOP ON ERROR bit in
the Configuration Register is set, the CT2566 will stop
bus transactions until a new Controller Start command
is issued by the CPU. These interrupts may be masked
by the CPU through the Interrupt Mask Register.
1. Reads the Stack Pointer to get the address of the
current Descriptor Stack Entry.
START
ISSUE RESET COMMAND
INITIALIZE STACK POINTER
LOAD MESSAGE COUNTER
LOAD EVERY FOURTH
LOCATION OF STACK WITH
STARTING ADDRESS
LOAD MESSAGES
SET CONFIGURATION
RESISTER TO BC MODE
INITIALIZE INTERRUPT
MASK REGISTER
ISSUE START COMMAND
Figure 11
BC Initialization (under user control)
BC START SEQUENCE
After setting the CONTROLLER START bit in the
Start/Reset Register, the CT2566 takes the following
actions:
1. Reads the Stack Pointer to get the address of the
current Descriptor Stack Entry.
2. Stores an SOM flag in the Block Status Word to
indicate a transfer operation is in progress.
3. Stores the Time Tag if used.
4. Reads the Data Block Address from the fourth
location of the Descriptor Stack and transfers the
Data Block Address into an internal Address
Register.
5. Issues a BCSTART pulse to the associated 1553
device to start the message transfers.
Note that data words are transferred to an from
memory by the associated 1553 interface unit using the
internal Address Register.
BC EOM Sequence.
Upon completion of a 1553 message (valid or invalid)
the 1553 interface unit issues an EOM pulse to the
CT2566 which takes the following actions:
15 8 7 0
NOT USED
BUS CHANNEL A/B
NOT USED
MASK BROADCAST BIT
NOT USED
MODE CODE
BROADCAST
RTU TO RTU
Note: When the BC expects the BROADCAST bit set in the status
word, a logic "1" will mask the status interrupt error flag. A
FORMAT error will be generated if the MASK BROADCAST bit
is not set.
Aeroflex Circuit Technology SCDCT2566 REV B 8/10/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
12
 Loading...
Loading...