ACT CT2556-FP, CT2556, CT2555-FP, CT2555, CT2554-FP Datasheet
...
F
E
I
D
C
E
R
T
A
E
R
O
F
L
E
X
L
A
B
S
I
N
C
.
www.aeroflex.com
Advanced Integrated MUX (AIM) Hybrid
Features
CT2553 / 2554 / 2555 / 2556
FOR MIL-STD-1553
■ Second Source Compatible to the BUS-61553
■ Complete Integrated MUX Including:
•
Low Power Dual Transceiver
•BC/RTU/MT Protocol
•8K x 16 Shared Ram
•Interrupt Logic
■ Compatible with MIL-STD- 1750 and other Standard CPUs
■ DIP or Flatpack Hybrid
■ Minimizes CPU Overhead
■ Provides Memory Mapped 1553 Interface
■ On-Line & Off-Line Self-Test
■ PCs Development Tools Available
■ SEAFAC Tested
■ MIL-PRF-38534 compliant circuits available
■ DESC SMD #5962–88692 Pending
■ Packaging – Hermetic Metal
•
78 Pin, 2.1" x 1.87" x .25" Plug-In type package
•82 Lead, 2.2" x 1.61" x .18" Flat package
CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY
ISO
9001
I
General Description
Aeroflex’s CT2553 Advanced Integrated Mux (AIM) Hybrid is a complete MIL-STD-1553 Bus
Controller (BC), Remote Terminal Unit (RTU), and Bus Monitor (MT) device. Packaged in a single
78 pin DIP package, the CT2553 contains dual low-power transceivers, complete BC/RTU/MT
protocol logic, a MIL-STD-1553-to-host interface unit and an 8K x 16 RAM.
Using an industry standard dual transceiver and standard status and control signals, the CT2553
simplifies system integration at both the MIL-STD-1553 and host processor interface levels.
All 1553 operations are controlled through the CPU access to the shared 8K x 16 RAM. To ensure
maximum design flexibility, memory control lines are provided for attaching external RAM to the
CT2553 Address and Data Buses and for disabling internal memory; the total combined memory
space can be expanded to 64K x16. All 1553 transfers are entirely memory-mapped; thus the CPU
interface requires minimal hardware and/or software support.
The CT2553 operates over the full military -55°C to +125°C temperature range. Available screened
to MIL-STD883, the CT2553 is ideal for demanding military and industrial microprocessor to 1553
interface applications. See "Ordering Information" (last sheet) for CT2554, CT2555 & CT2556.
eroflex Circuit Technology – Data Bus Modules For The Future © SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
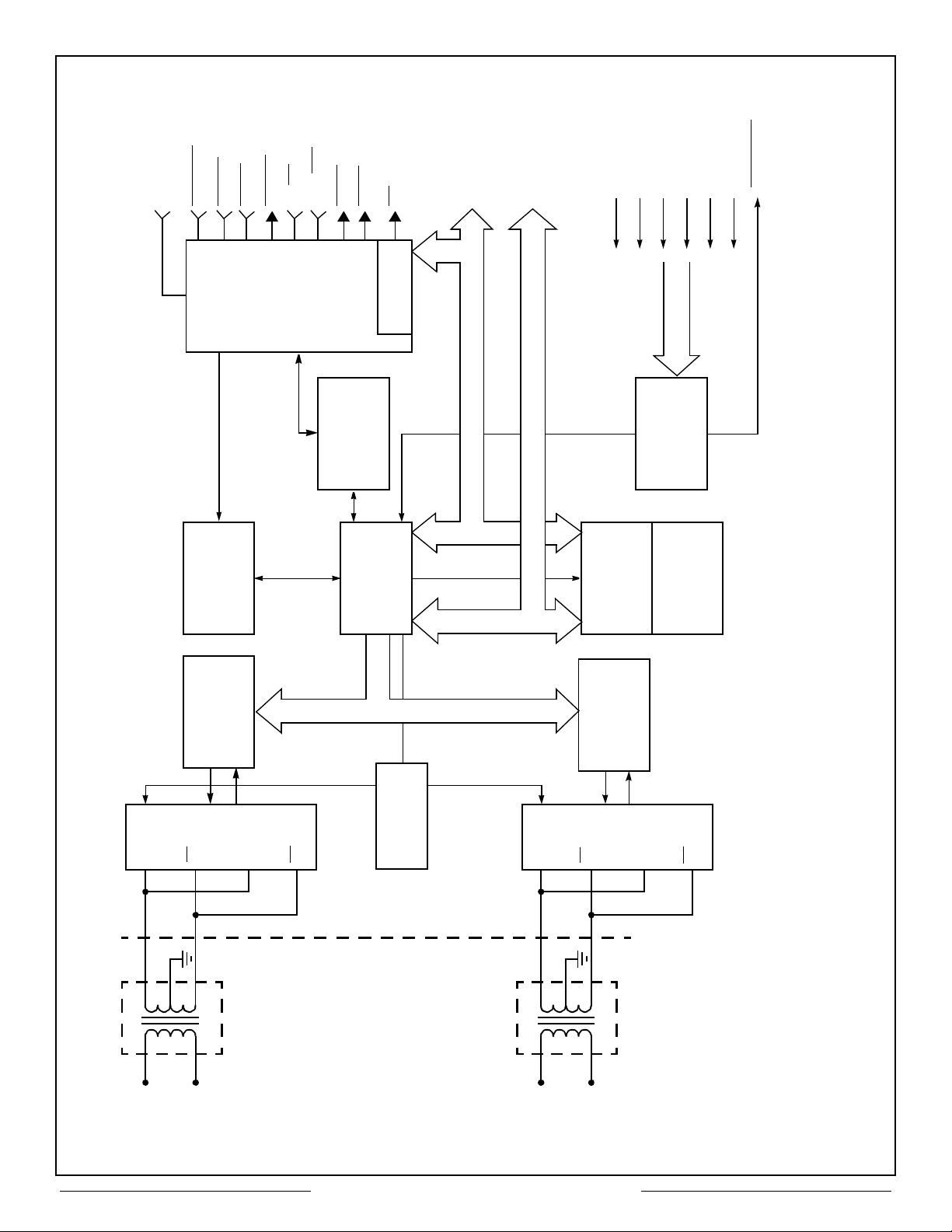
Figure 1 – CT2553 Block Diagram
RTADR2
RTADR0
RTADR4
RTADR3
RTADR1
RTADRP
TRANSCEIVER B
1
2
34
8
DATA
BUS A
1
2
34
8
TRANSFORMER B
DATA
BUS B
TRANSCEIVER A
RT ADDR
RTPARERR
INT
EXTLD
EXTEN
MEM/REG
RD/WR
READYD
STRBD
SELECT
MSTRCLR
CLOCK IN
Q1553-2
Q1553-2
TRANSFORMER A
CHANNEL A
DECODER
ENCODER/
MEMORY
TIMING
CONTENTION
RESOLVER
CHANNEL B
DECODER
ENCODER/
RX
RX
TX
TX
INH
RX
RX
TX
TX
INH
TIMEOUT
768µs
8K X 16
SHARED RAM
RAM
PARITY
CHECKER
CPU
TIMING
INTERRUPT
GENERATOR
PROTOCOL
CONTROLLER
A15 - A00
D15 - D00
Note: The Watch-Dog Time Out (768µs TYP.) is built in.
2
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
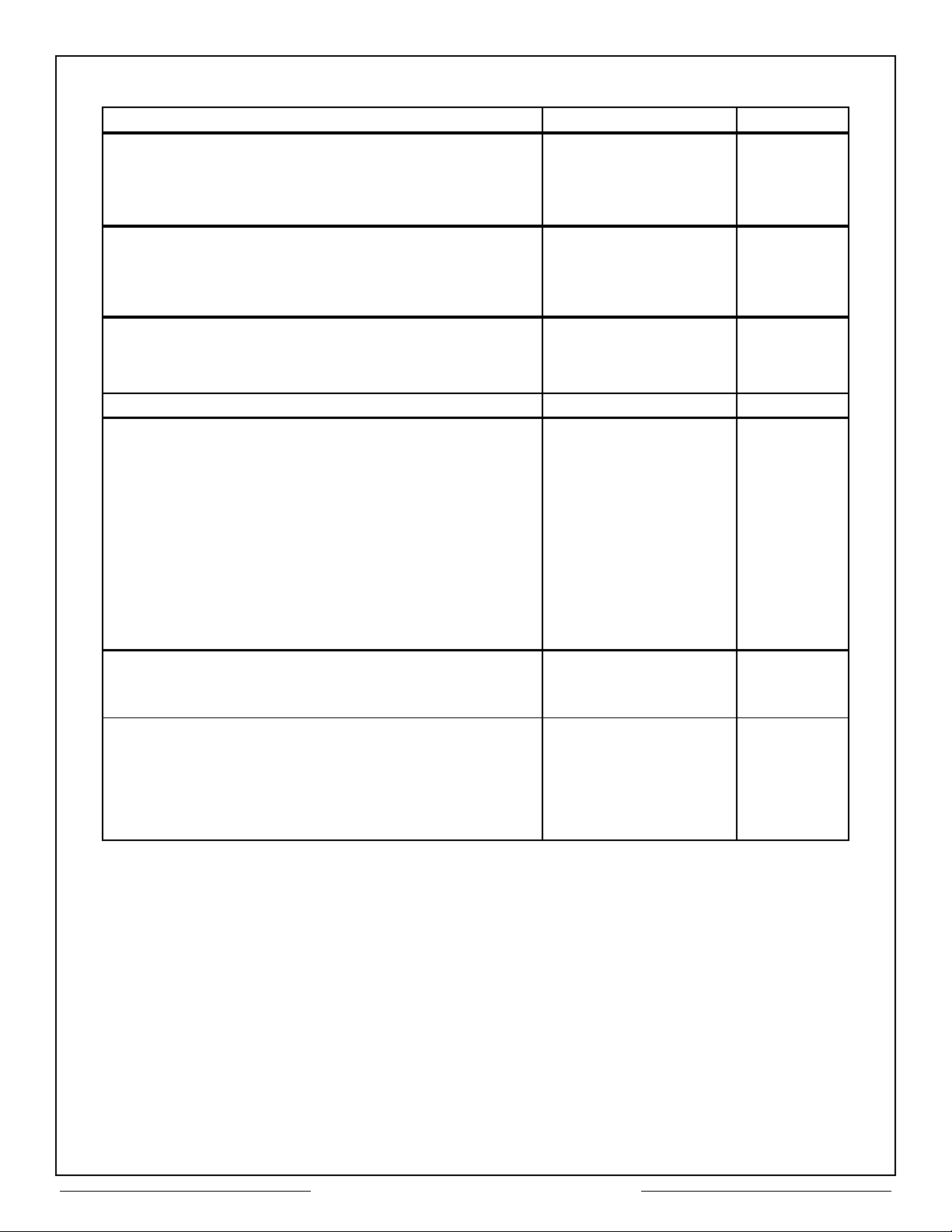
Values at nominal Power Supply Voltages unless otherwise specified
PARAMETER VALUE UNITS
Receiver
Differential Input Voltage 40 max Vp-p
Differential Input
Impedance 7 min KΩ
CMRR 40 min db
Transmitter (Direct Coupled)
Differential Output Voltage 6.0 min, 9.0 max Vp-p
Output Rise and Fall Times 100 min, 300 max nsec
Output Offset Voltage ±90 max mV
Logic*
V
IH
V
IL
2.2 min V
0.8 max V
Clock 16 MHZ
Power Supplies
+5V (Logic) +5±5% V
-15VA (Channel A Transceiver) -15±10% V
-15VB (Channel B Transceiver) -15±10% V
+5VA (Channel A) +5±5% V
+5VB (Channel B) +5±5% V
Current Drain* (Total Package) (TYP)/max
+5V (Idle) (85)/170 mA
-15V (Idle) (45)/80 mA
+5V (25% Duty Cycle) (85)/170 mA
-15V (25% Duty Cycle) (80)/130 mA
Temperature Range
Operating (Case)
Storage
Physical Characteristics
Size
78 pin DDIP 2.1 x 1.87 x 0.25
82 pin flatpack 2.19 x 1.6 x 0.175
* See Table 7 for pin loading characteristics.
Table 1 – CT2553 Specifications
GENERAL
The CT2553 is a complete MIL-STD-1553 bus
interface unit containing dual low-power
transceivers; Bus Controller (BC), Remote
Terminal (RTU), and Bus Monitor (MT) protocol
logic; 8K x 16-bit pseudo dual port RAM; and
memory management arbitration control circuitry.
The host processor interface consists of standard
control and interrupt signals, memory expansion
capability and non-multiplexed address and data
buses.
Control of the CT2553 is accomplished entirely
through the use of three internal registers and the
−55 to +125 °C
−65 to +150 °C
in
(53 x 47.5 x 6.4)
(mm)
in
(55.6 x 40.6 x 4.34)
(mm)
shared RAM. Transfers to and from the CT2553
are executed on a word-by-word basis ensuring
minimal wait time if contention occurs.
The specific mods of operation (1553
BC/RTU/MT) is software programmable. Memory
is configured into unique control and data block
areas based on the 1553 mode of operation.
External registers are also supported by the
CT2553 for manipulation of user data. In addition,
the CT2553 provides dynamic, online and
software initiated self-test capabilities.
3

Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
INTERFACING
The CT2553 is compatible with most common
microprocessors including, but not limited to, the
Motorola 680 x 0, the Intel 808x, Zilog Z800x and
MIL-STD-1750 processors.
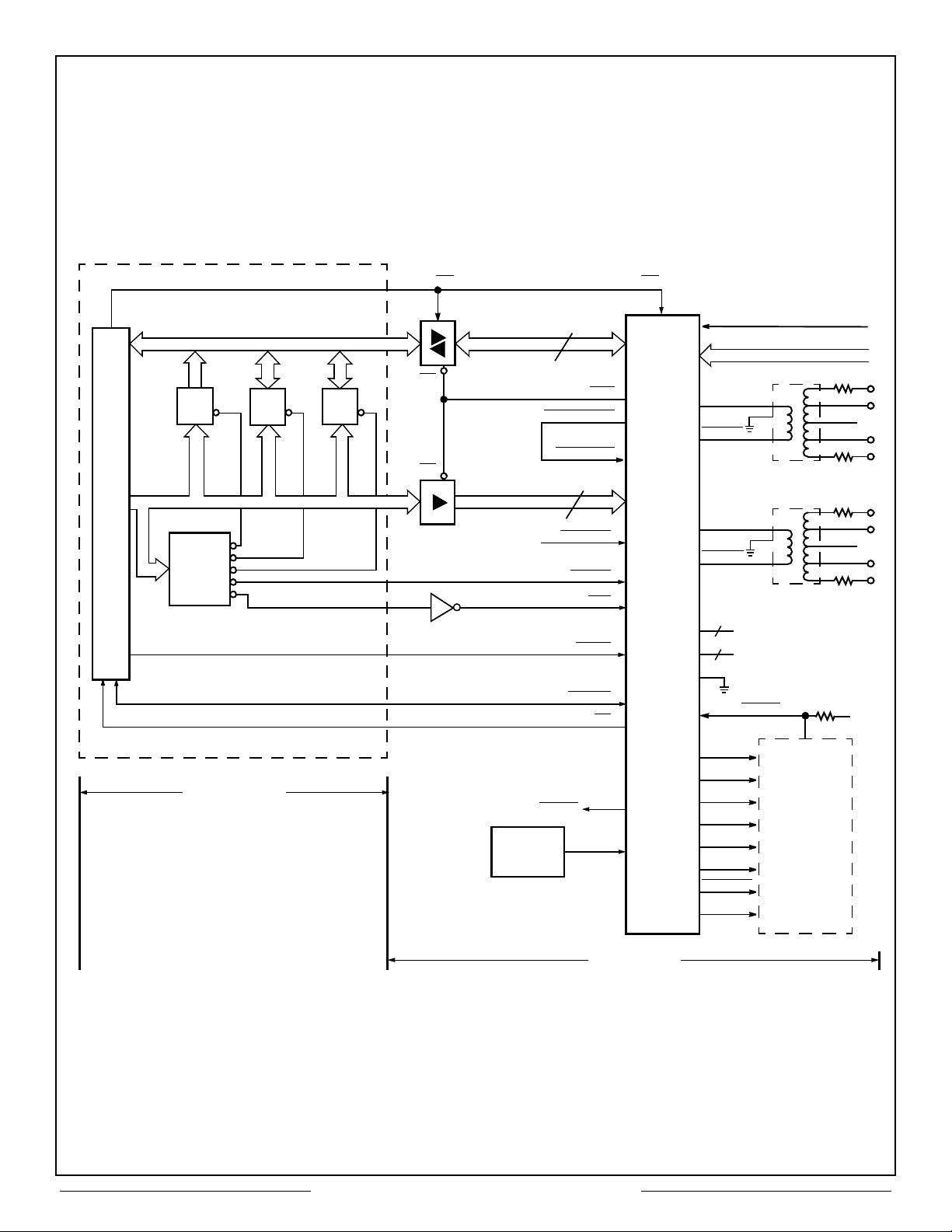
Interfacing the CT2553 to the MIL-STD-1553
Data Bus requires two Q1553-2 pulse
transformers and an external 16 MHz clock (See
Figure 2). Tri-state buffers are used to isolate the
CPU's data and address lines.
External RAM can be used instead of or in
conjunction with the CT2553's internal 8K x 16
bits. The external RAM used by the CT2553 can
be any standard static memory with an access
time of <
55ns. The external RAM can be
expanded to 64K x 16.
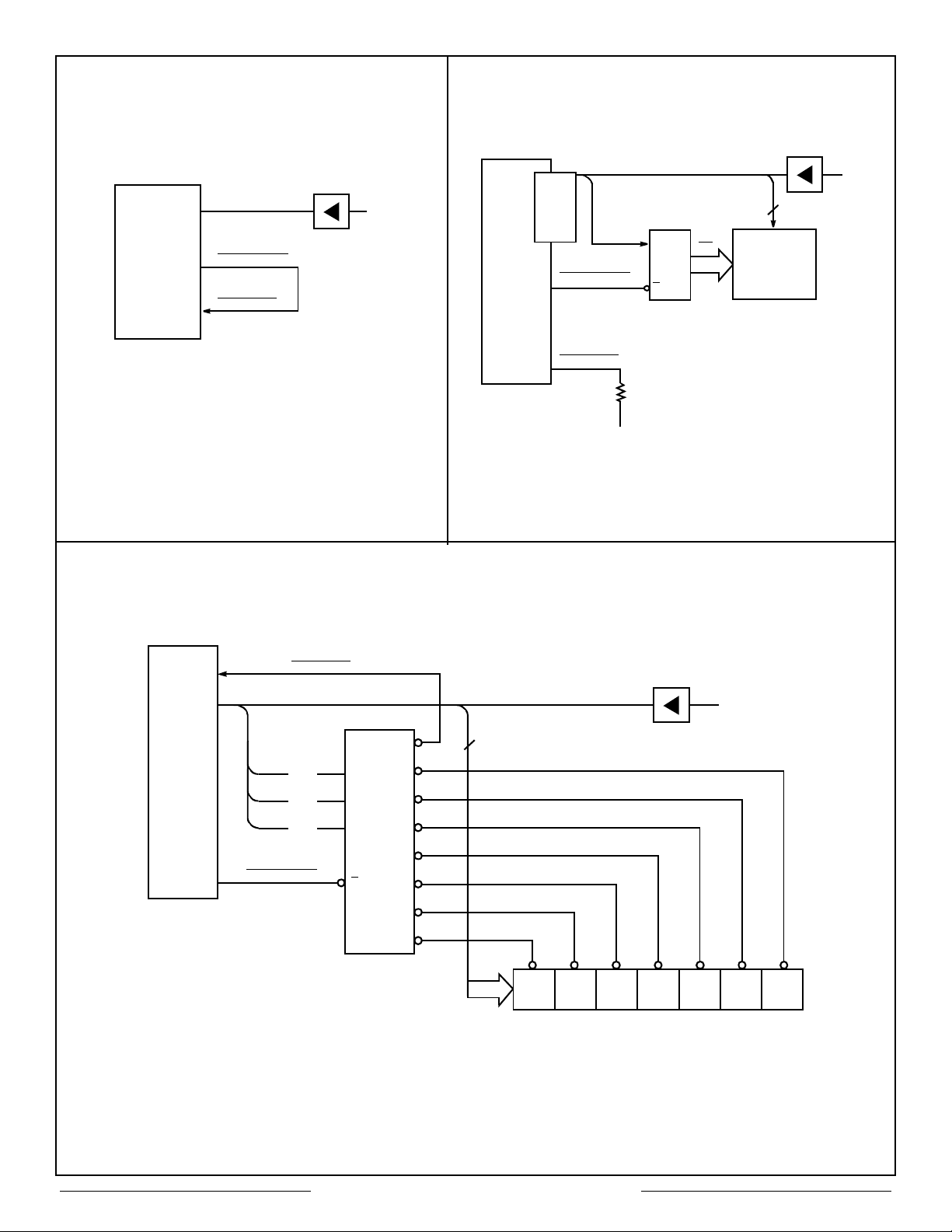
Two control signals, MEMENA-IN
MEMENMA-OUT
(pin 31) are provided in
(pin 69) and
addition to the standard memory I/O signals for
internal/external memory access control (See
Figures 3-5. MEMEN-OUT
and MEMEN-IN
should be tied together for Internal Memory Only
configuration. Memory CS
signals can be
generated for configurations using external
memory.
set to the appropriate logic level (0 for area A or 1
for area B). Internal circuitry ensures that the
swapping of Current Area Status does not occur
during an ongoing message transfer (See
Configuration Register).
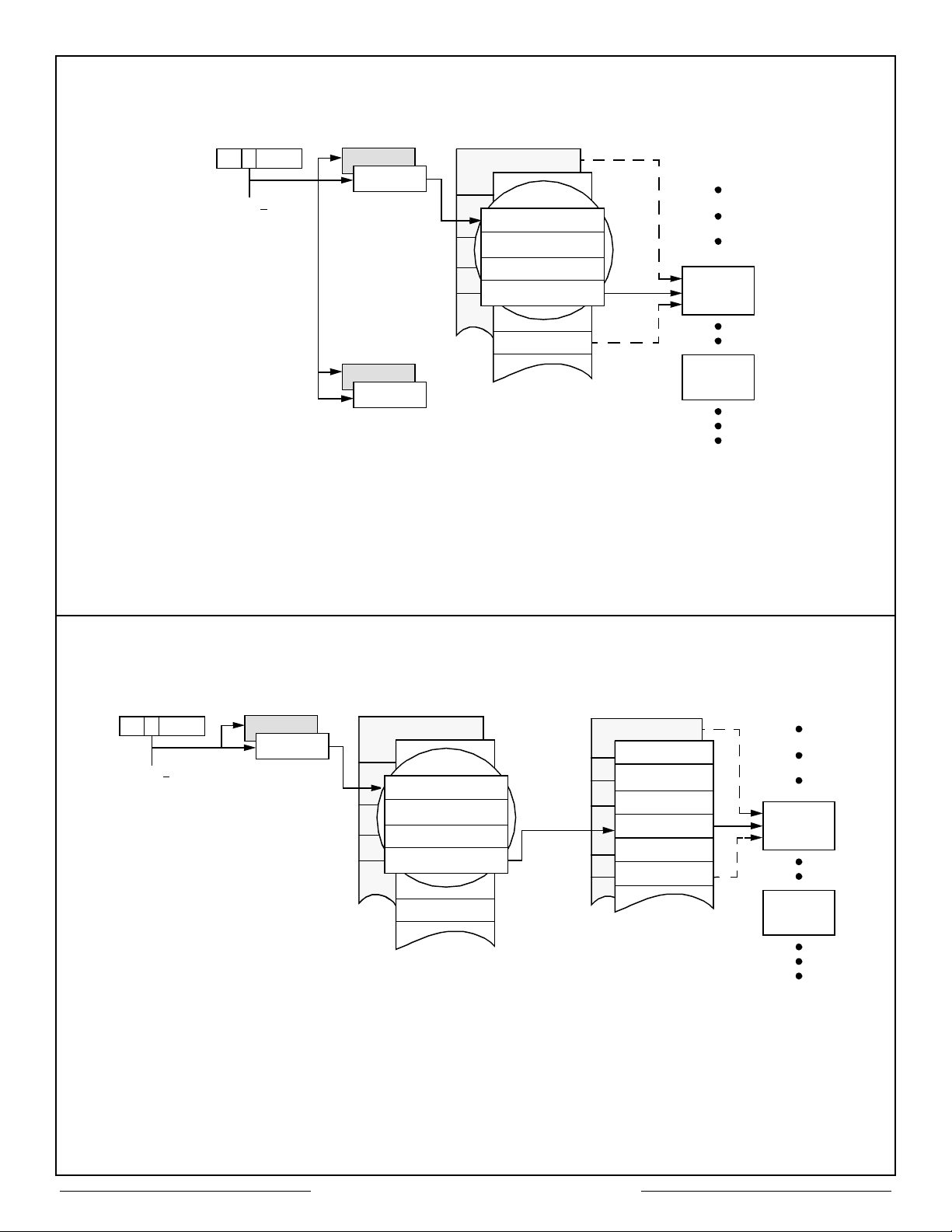
DESCRIPTOR STACK (BC/RTU). The
DESCRIPTOR STACK (DS) is divided into 64
entries. Each stack entry contains four words
which refer to one 1553 message. The Block
Status Word (BSW) indicates the physical bus on
which the message was received (RTU mode),
reports whether or not an error was detected
during message transfer and indicates message
completion (See Figure 8).
The user-supplied Time Tag word is loaded at the
start of a message transfer and is updated at the
end of the transfer (See Time Tagging).
MEMORY MANAGEMENT
Memory can be configured to support two AREAs
(A and B), each with an independent sequential
stack and pointers for manipulating 1553
message and control data. The CPU can access
the shared RAM while 1553 message transfers
are taking place. Arbitration of the RAM is
automatically implemented in a manner
transparent to the subsystem (See Figures
28-31). Variable Length DATA BLOCKS are also
stored in the shared RAM and can be addressed
by setting pointers residing in Area A, Area B or
both.
For BC/RTU operation, each area contains a
Descriptor Stack and Stack Pointer (See Figures
6 and 7). BC operation further maintains a
Message Count for each area (number of 1553
messages per frame). RTU operation maintains a
data block address Look-Up Table for each area.
MT operation utilizes a single Stack Pointer to
indicate the starting address for storage of
received words and associated identification
Words.
CURRENT AREA ASSIGNMENT/SWAPPING.
Current area status (currently available to the
1553 terminal) is Software programmable by the
host; the unassigned area automatically assumes
non-current area status. Both areas are always
addressable by the host. Swapping of the Current
Area can be done following message transfers for
user operations such as exception handling or
multiple buffering of 1553 data.
The host selects the Current Area by writing to
the CT2553’s Configuration Register with bit 13
4
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
CPU
ROM
ADDRESS
DECODER
RAM
I/O
RD/WR
)
(OE
)
(54LS04)
(DIR)
(54LS245)
(SEE NOTE 1)
(54LS244)(OE
DATA
16
D0 - D15
MEMENA-OUT
MEMENA-IN
ADDRESS 13
A0 - A12
A0 - A12
POR
(SEE NOTE 2)
MSTRCLR
MEM/REG
IOEN
SELECT
STRBD
RD/WR
73
31
69
CT2553
71
74
33
34
36
RTADP
51
RTADDRESS
8
40
78
TX/RX-A
TX/RX-A
1
2
3
7
6
5
4
+
–
BUS-25679
8
20
59
TX/RX-B
TX/RX-B
1
2
3
7
6
5
4
+
–
BUS-25679
3
+5V
2
-15V
HOST PROCESSOR
READYD
INT
75
72
12
13
15
MEMOE
30
52
54
16MHz
CLOCK
32
53
57
XX
17
1553 INTERFACE
Figure 2 – CT2553 Example Interconnection
SA/MC-0
SA/MC-1
SA/MC-2
SA/MC-3
SA/MC-4
T/R
BCSTRCV
LMC
ILLCMD
ILLEGALIZATION
PROM
(OPTIONAL)
+5V
5
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
ADDRESS BUS
CPU
CT2553
31
69
ADDRESS BUS
MEMENA OUT
MEMENA IN
CPU
CT2553
MEMENA OUT
31
MEMENA IN
69
+5V
ADDRESS
DECODER
10K
CS
E
16
64K x 16
STATIC RAM
Figure 3 – Internal Memory Only Figure 4 – External Memory Only
CT2553
69
31
MEMENA IN
A13
A14
A15
MEMENA OUT
A
B
C
E
ADDRESS
DECODER
ADDRESS BUS
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
13
8K
8K
8K
x
x
16
16
56 x 16K STATIC RAM MAX
8K
x
16
x
16
8K
16
CPU
8K
x
8K
x
x
16
16
Figure 5 – Configuration Using Both Internal and External Memory
6
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
CURRENT
AREA B/
A
STACK
POINTERS
01315
*
MESSAGE
COUNTER
DESCRIPTOR
STACKS
BLOCK STATUS WORD
**
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
MESSAGE
BLOCK ADDR
*
* Note:
STACK POINTERS and MESSAGE COUNTERS are switched via the
CONFIGURATION REGISTER under external CPU control.
** Note:
DESCRIPTOR STACKS and DATA BLOCKS have 256 word boundries which
should be observed.
DATA
**
BLOCKS
DATA BLOCK
DATA BLOCK
CONFIGURATION
REGISTER
CURRENT
AREA B/
A
Figure 6 – Use of Descriptor Stack – BC Mode
STACK
POINTERS
01315
*
* Note:
STACK POINTERS and LOOK-UP TABLE are switched via the
CONFIGURATION REGISTER under external CPU control.
** Note:
DESCRIPTOR STACKS and DATA BLOCKS have 256 word boundries which
should be observed.
DESCRIPTOR
STACKS
BLOCK STATUS WORD
RECEIVED COMMAND
**
TIME TAG WORD
RESERVED
WORD
LOOK-UP
TABLE ADDR
LOOK-UP TABLE
(DATA BLOCK ADDR)
*
DATA
**
BLOCKS
DATA BLOCK
DATA BLOCK
Figure 7 – Use of Descriptor Stack – RTU Mode
7
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
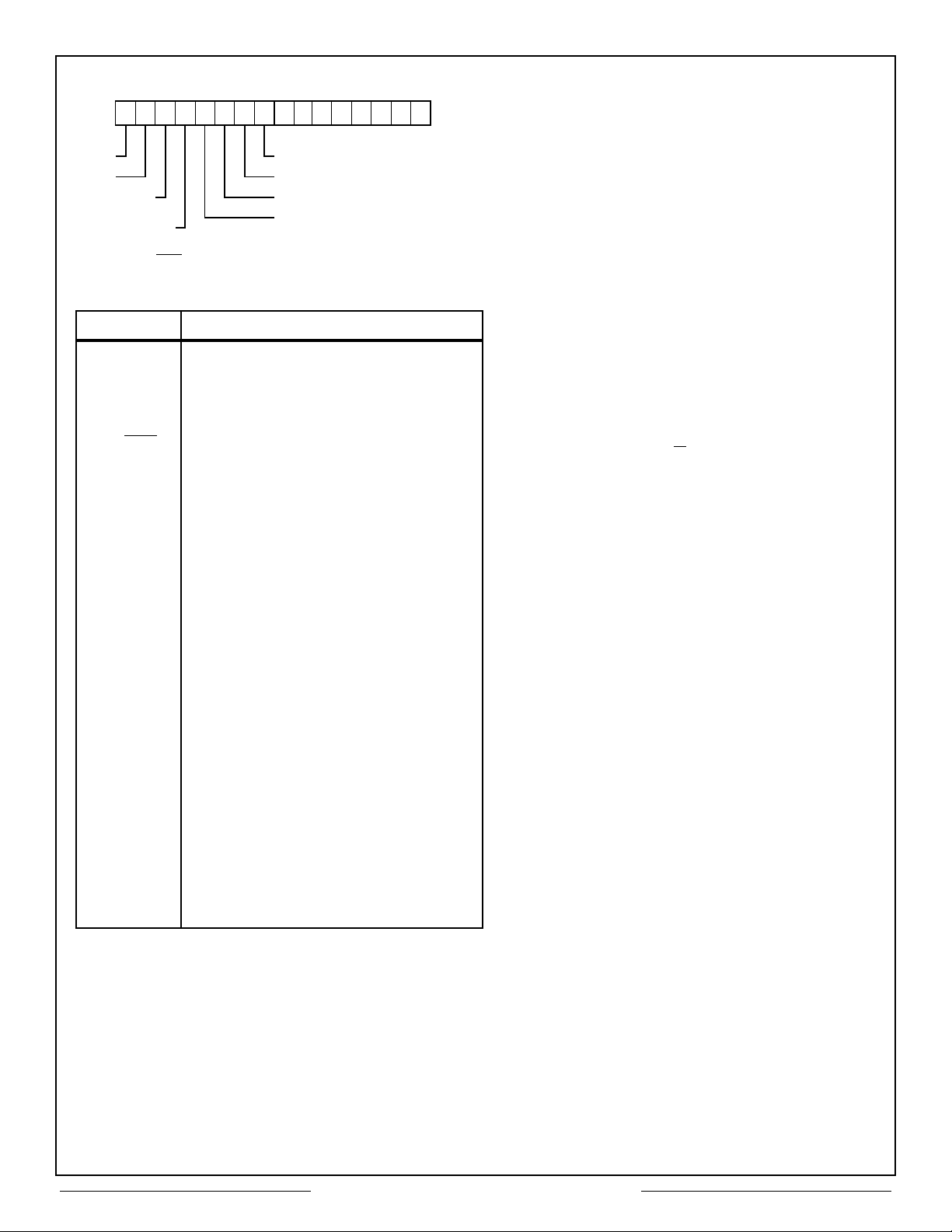
15 8 7 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
EOM LOOP TEST FAIL
SOM RESPONSE TIME OUT (BC ONLY)
CHB/CHA
(RTU ONLY)
ERROR FLAG
Note: In BC operation, the CT2553 always writes the BSW to RAM with
Bit-13. CHB/CHA toggles as per the message control word setting.
FORMAT ERROR
STATUS SET (BC ONLY)
BIT NAME DEFINITION
EOM Set at the completion of a message
transfer regardless of whether any errors
were detected.
SOM Set at the beginning of a message transfer
and Reset upon completion of the transfer.
CHB/CHA
ERROR
FLAG
STATUS SET Set in BC mode to indicate that a status
FORMAT
ERROR
RESPONSE
TIMEOUT
LOOP
TEST FAIL
Set in RTU mode to indicate whether the
message was received on 1553 bus A or
bus B. Toggles to indicate channel, in BC
mode.
Indicates that an error was detected within
the message transfer. The specific error
condition(s) are identified in bits 8-11.
flag bit was set within the received RTU
Status Word or that the RTU address did
not match the associated Command. Set
in BC mode when the message error bit is
set within the received RTU Status Word.
Also set in RTU mode (RT-RT transfer;
CT2553 is acting as the receiving RT)
when the transmitting RTU Status Word
contains an incorrect address. Also, set in
BC or RTU mode if the message violates
MIL-STD-1553 (parity, Manchester, sync
bit count, non-contiguous data or word
count errors).
Set in BC mode if the addressed RTU did
not respond within 14µs. Also set when
acting as a receiving RT (RT-RT transfer) if
the transmitting RT does not respond in
the specified 1553 response time.
Set when the CT2553 does not pass the
Loop Test. See Self Test paragraph.
STACK POINTER. A STACK POINTER (SP) is
maintained at a specified location in shared RAM
for each Descriptor Stack (SP-A: 0100H; SP-B:
0104H). Each Stack Pointer must be initialized by
the CPU to point to the Descriptor Stack Entry to
be used for the first MIL-STD-1553 transmission.
The current area SP is automatically incremented
by four following each message transfer thereby
always pointing to the next Block Status Word.
Note: The Stack Pointer is maintained internally using an
8-BIT REGISTER for the HIGH BYTE and an 8-BIT
COUNTER for the LOW BYTE. The high byte remains
constant (user value) while the low byte will wrap around
from FF(H) to 00(H). For example: a current Stack Pointer
value of 00 FF(H) will increment to 00 00(H) and not
01 00 (H).
LOOK-UP TABLE (RTU). A data block address
Look-Up Table is used to indicate the data blocks
to be used for individual commands. Look-Up is
based upon the T/R
(transmit/receive) and
Subaddress bits of the received 1553 Command
Word. See RTU Operation for detailed operation;
two tables are provided for double buffering in the
RTU mode.
MULTIPLE BUFFERING (BC/RTU). Unused
areas of shared RAM can be used to store
additional stacks, tables, data blocks and/or user
(non 1553-related) data. In this way, multiple data
blocks (RTU) or messages (BC) can be stored for
later use: simply update respective pointers and
initiate the appropriate start conditions. (BC mode
requires SP, message block address and message
count updating while in RTU mode, the SP and
Look-Up Table entry must be updated).
Figure 8 – Descriptor Stack - Block Status
Word
The contents of the fourth word of the stack entry
depends upon the 1553 operating mode selected.
In BC mode, It contains the address of the
associated 1553 message (Data Block). In RTU
mode, it contains the complete (received) 1553
Command Word.
CT2553 REGISTERS
The CT2553 is controlled through the use of three
internal registers: Interrupt Mask Register,
Configuration Register and a Start/Reset Register.
In addition, the CT2553 can access up to four
external, user supplied registers (See Table 2).
Possible external register applications include:
CPU Time Tag storage and RTU Address
assignment (See Figures 9 and 10).
8
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
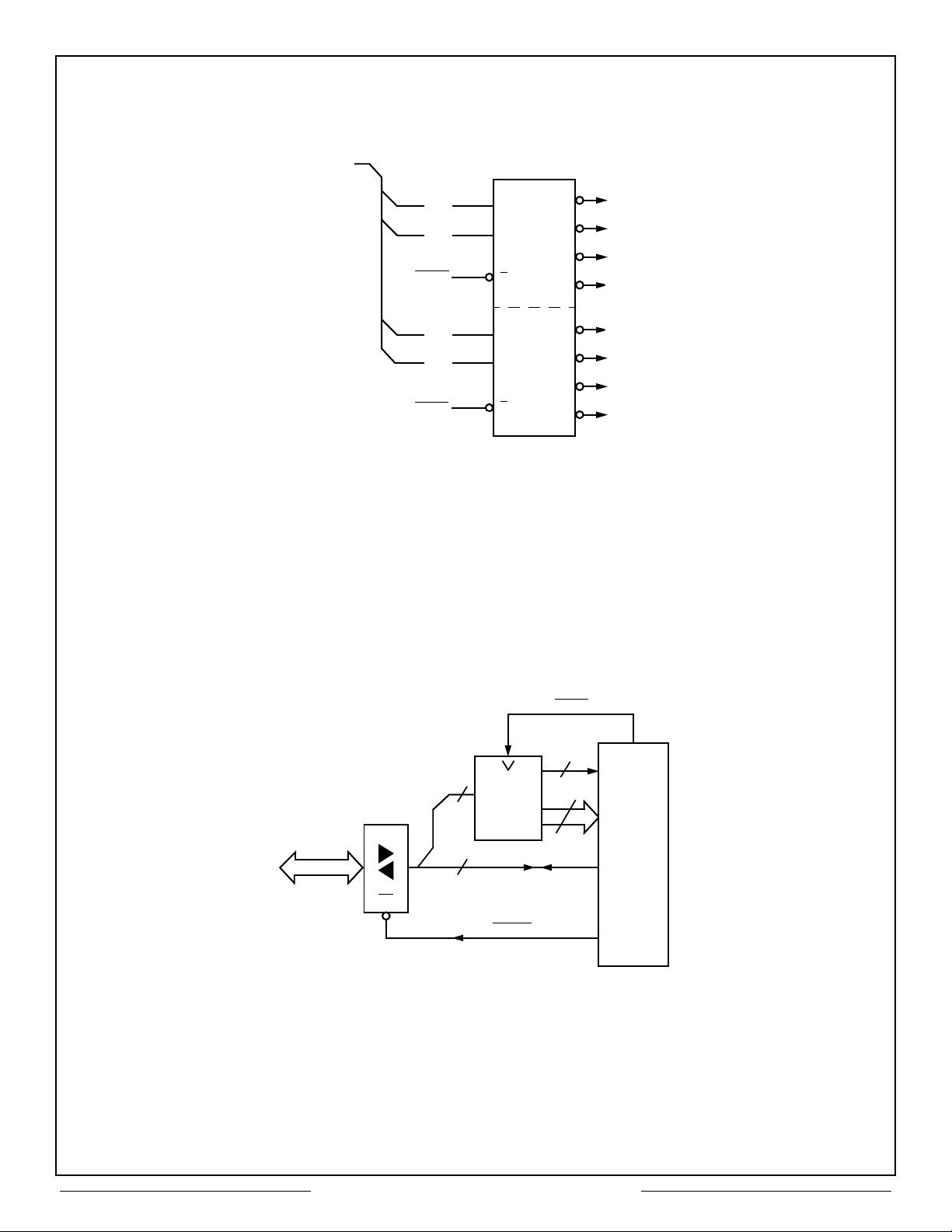
ADDRESS
A00
DECODER
A
{
A01
EXTEN
A00
A01
EXTLD
Note:
A02 of the CT2553 must be set to logic 1 to operate with external registers.
Figure 9 – Use of External Registers
B
E
A
B
E
READ
{
WRITE
EXTLD
1
6
REGISTER
CPU
DATA BUS
D15 - D00
OE
Figure 10 – Example Configuration Using External Registers
16
IOENBL
5
RTADP
RT ADDR
CT2553
9
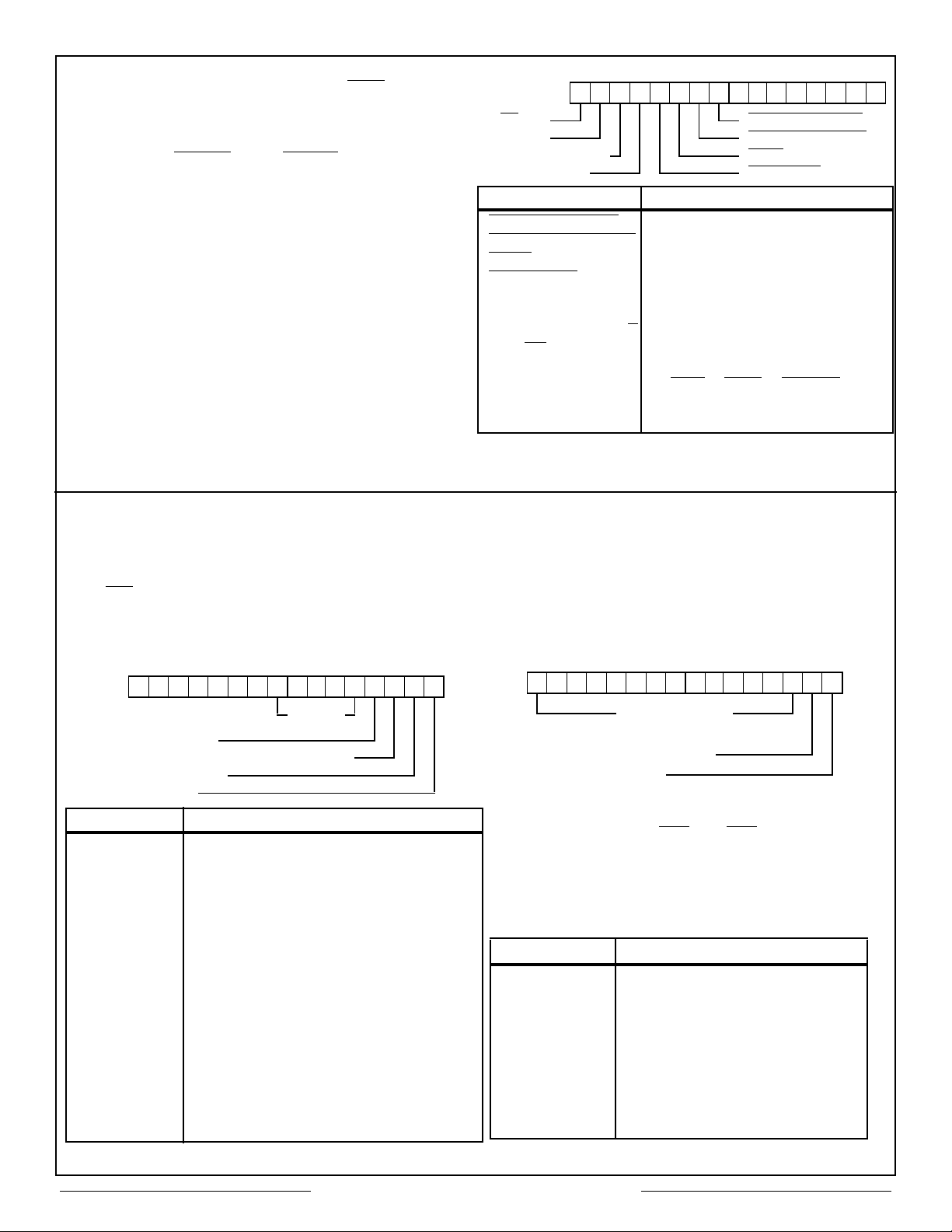
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
CPU TO REGISTER OPERATIONS. The CPU
1 1 Illegal
selects a register by asserting MEM/REG
low and
A2 to a logic 0 (for internal registers) or logic 1 (for
external registers) with A0 and A1 indicating the
appropriate register address (See Figures 28-32).
The signals EXTEN
and EXTLD are used to
access the external registers.
CONFIGURATION REGISTER. The Configuration
Register is a 16-bit read/write register used to
define the 1553 operating mode (BC, RTU, or MT);
define selectable 1553 Status Word bits (RTU
only); select stop-on-error option; and support the
double buffering scheme (See Figure 11).
15 8 7 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
RTU/BC SUBSYSTEM FLAG
MT SERVICE REQUEST
CURRENT AREA B/A BUSY
STOP ON ERROR DB ACCEPT
BIT NAME DEFINITION
SUBYSTEM FLAG
SERVICE REQUEST
BUSY
DB ACCEPT
STOP ON ERROR BC will halt message transfer after
CURRENT AREA B/A
RTU/BC
Note: A logic 0 causes the corresponding bit within the RTU’s status
word to be set to a logic 1.
Sets/resets 1553 Status Word flag.
Sets/resets 1553 Status Word flag.
Sets/resets 1553 Status Word flag.
Sets/resets 1553 Status Word flag.
completing current EOM cycle.
Selects Current Area Pointers.
RTU or BC-MT Operation Select.
BIT15 BIT 14 Operation
0 0 BC
0 1 MT
1 0 RTU
Figure 11 – Configuration Register
INTERRUPT MASK REGISTER (BC/RTU). This
register is a 16-bit read/write register used to
enable/mask interrupt conditions. If an interrupt
condition occurs and the corresponding Interrupt
Register bit has been enabled (set to logic 1) pin
72, INT
will be pulsed low during the respective
End of Message (EOM) cycle (See Figure 12). Not
Used bit locations can optionally be used for
storing user flags.
15 9 8 7 4 3 2 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
NOT
BC EOM
FORMAT ERROR/STATUS SET
NOT USED
EOM
USED
INTERRUPT DEFINITION
EOM End of message. Set by CT2553 in BC or
RTU mode following each 1553 transfer
(regardless of validity).
FORMAT
ERROR/
STATUS SET
BC EOM
Set if one of the following occurs:.
Loop Test Failure: Received word does
not match last word transmitted.
Message Error:
Received message
contained a violation of any of the 1553
message validation criteria (parity, sync,
manchester encoding, bit/word count, etc.)
Time-Out: Expected transmission was
not received during the allotted time.
Status Set:
Received Status Word
contained status bit(s) set or address error.
Bus Controller End of Message. Set by the
CT2553 following transmission of all
messages within the current Message Block
(Current area message count = FFFF).
START/RESET REGISTER. This write-only
register is used to reset the CT2553 and to start
the BC and MT operations, as illustrated in
Figure13.
15 9 8 7 4 3 2 1 0
NOT USED
CONTROLLER START
RESET
START 1 0
RESET 0 1
BIT NAME
CONTROLLER
START
RESET Issued by the CPU to place the
BIT 1 BIT 0
DEFINITION
Issued by the CPU to start
message block transmission (BC
Operation) or to begin reception of
1553 messages (MT Operation).
CT2553 in the power-on condition;
(1) aborts 1553 transfers currently
in progress, and (2) resets
Configuration and Interrupt Mask
Register bits (logic 0).
Figure 12 – Interrupt Mask Register
Figure 13 – Start/Reset Register
10
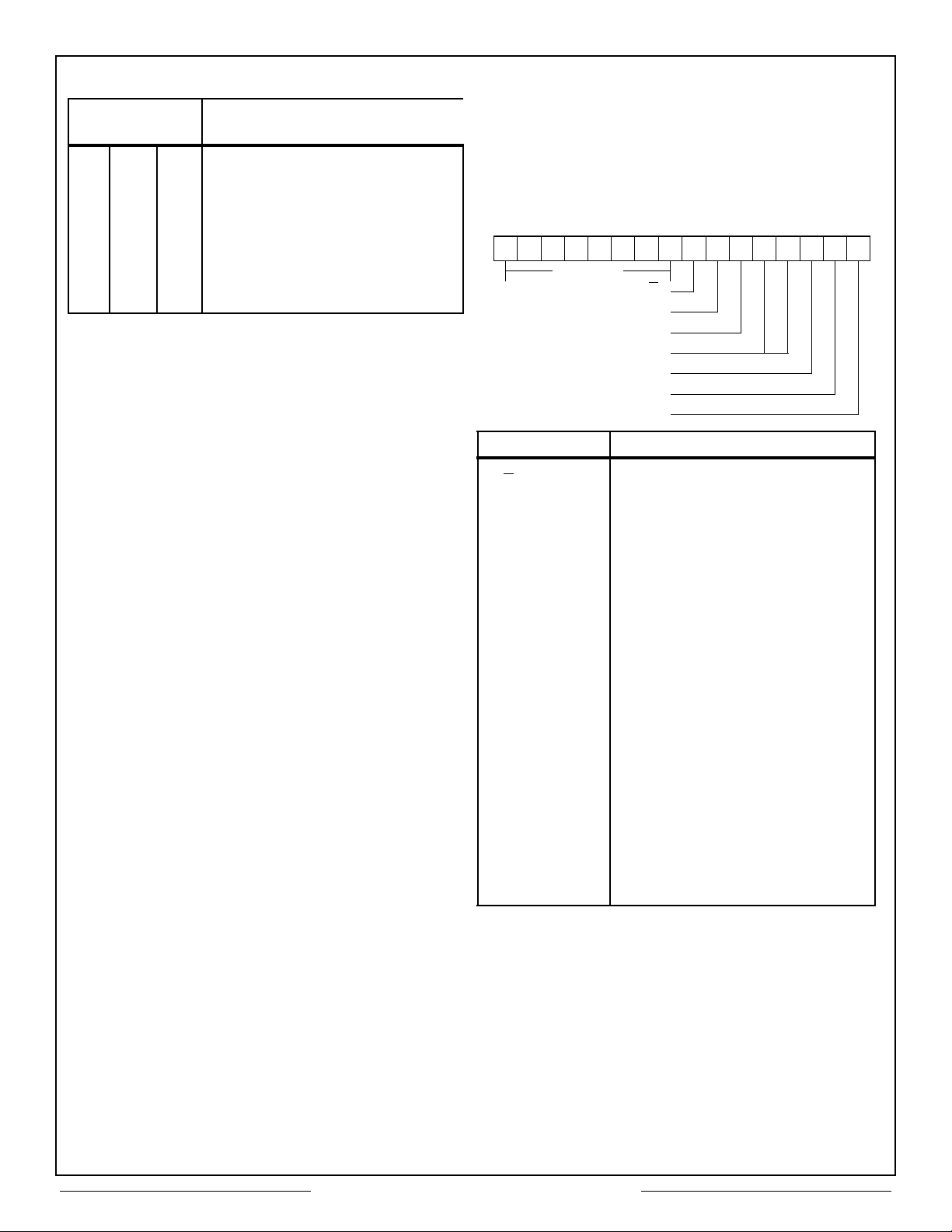
Aeroflex Circuit Technology
SCDCT2553 REV B 8/6/99 Plainview NY (516) 694-6700
Table 2 – CT2553 Register Address Definition
Address Bits
A2 A1 A0
Definition
0 0 0 R/W Interrupt Mask Register
0 0 1 R/W Configuration Register
0 1 0 – Not Used
0 1 1 W Start/Reset Register
1 0 0 R/W * External Register
1 0 1 R/W * External Register
1 1 0 R/W * External Register
1 1 1 R/W
* Note: R/W (read/write) capability is dependent on the user's
decoding implementation (See Figure 9).
* External Register
CONTENTION HANDLING
The CT2553 arbitrates shared RAM (and control
register) accesses between the host CPU and the
internal 1553 protocol logic.
If the host attempts to access the RAM while an
internal 1553 memory cycle is in progress, the
CT1553 will delay the CPU's memory cycle by
inserting wait states via the READYD control
signal until the cycle has been completed. The
maximum delay is 1.8µs.
If the internal 1553 protocol logic attempts to
access the RAM while the host CPU has control of
the memory, the internal 1553 logic will wait until
the host CPU cycle has been completed. To
ensure the integrity of 1553 data transfers, the
host CPU must complete its memory cycle within
1.5µs (See Figures 28-32).
SELF TEST
The CT2553 has two self-test modes: the
automatic, continuous On-Line test and the
software-initiated Off-Line test. In both tests the
Loop Test Fail bit within the Block Status Word will
be set to a logic 1 if a failure is detected.
ON-LINE TEST. The On-Line test occurs in BC
and RTU modes during transmission of each
message onto the 1553 bus. This test wraps
around the last word transmitted, exercising the
1553 protocol logic through the 1553 transceivers.
While operating as a BC, the last word transmitted
is received, decoded, and written back into
memory location immediately following the last
word within the message block. The host CPU can
read and compare this Loop Back Word with the
last word of the message Data Block; these two
words should be identical. This insures data
integrity between the CPU and the CT2553.
While in the RTU mode, the internal 1553 Status
Word will be updated to reflect the result of the self
test. The Status Word's Terminal Flag bit will be
set to a logic 1 if a fault was indicated by the
wrap-around, self-test.
OFF-LINE TEST. The software-initiated Off-Line
test can be executed only when the CT2553 is
configured as a BC. Set the Wrap-Around Test bit
within the BC Control Word to a logic 1 and initiate
any standard message transfer. This inhibits the
1553 transceivers and initiates the standard
wrap-around test (i.e., internal 1553 encoder
output is fed back into the decoder - the word is
then written into memory). See BC Operation and
Figure 14, BC Control Word for more details.
15 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
NOT USED
BUS CHANNEL A/B
OFF-LINE SELF TEST
MASK BROADCAST
NOT USED
MODE CODE
BROADCAST
RT-RT
BIT NAME
BUS CHANNEL
A/B
INITIATE
OFF-LINE SELF
TEST
MASK
BROADCAST (1)
MODE CODE When logic 1, the message is treated
BROADCAST When logic 1, indicates that the
RT-RT When logic 1, the message is treated
Note:
1. MASK BROADCAST XOR BROADCAST BIT in Status Word =
STATUS SET ERROR.
2. When the BC expects the BROADCAST bit set in the Status Word,
a logic 1 will mask the Status Interrupt Error flag.
Determines whether message will be
transmitted on 1553 Bus A or Bus B.
Logic 1 = A, logic 0 = B.
Logic 1 performs internal off-line
transmit/receive test. The last word
of the message is looped back
through the decoder and placed in
RAM. See Self Test paragraph.
When logic 1, prevents Broadcast
RCVD bit of the 1553 Status Word
response from signalling a status
error as a result of a Broadcast
command. (A FORMAT error will be
generated if the BROADCAST bit is
not set on the RTU’s Status Word.)
as a Mode Code. (The Command
Word - Word Count field indicates
Mode Code type.)
message is a Broadcast Command.
(No Status Word is expected.)
as an RT-RT transfer. (The next two
words are Command Words.) Both
Status Word responses are
validated.
DEFINITION
Figure 14 – BC CONTROL WORD
RESET
The CT2553 can be reset by pulsing the
MSTRCLR (pin 71) low or by writing to the
Start/Reset register. After a reset condition has
occurred, the Configuration, Interrupt, and
(internal) Block Status word register outputs are
forced to a logic 0.
11
 Loading...
Loading...