Page 1

Introduction
System Overview
This manual was written to help you start using this product
as quickly and smoothly as possbile. Inside you will find
the necessary explanations to solve most problems. In
order for this reference material to be of greatest use, refer
to the “expanded table of contents” to find relevant topics.
This board incorporates the system , I/O , and PCI IDE
into one board that provides a total PC solution. The
mainboard, Intel Celeron/Coppermine PII/PIII processor base
PC ATX system, support single processors with ISA Bus,
PCI Local Bus, and AGP Bus to support upgrades to your
system performance. It is ideal for multi-tasking and fully
supports MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT , Windows ME,
Windows 2000 , Novell, OS/2, Windows95/98 , UNIX ,
SCO UNIX etc.
This manual also explains how to install the mainboard for
operation, and how to setup your CMOS configuration with
the BIOS setup program.
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /1Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /1
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /1
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /1Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /1
Page 2

1.Motherboard Description
1.1 Features
1.1.1 Hardware
CPU
-Socket 370 for Intel Celeron/PIII Processor.
-Intel FC-PGA/PPGA Celeron Processors
300MHz~800MHz or higher processor with 66/100MHz
FSB.
-Intel FC-PGA Pentium III Processors 500MHz~1GHz
or higher processor with 100/133MHz FSB.
-VIA Cyrix III Processor with 100/133MHz FSB.
Chipset
-North Bridge System Chipset : Intel 815 support a 66/
100/133 FSB.
-South Bridge System Chipset : Intel ICH2.
Biggest memory capacity
6M815E is equipped with two DIMM socket to support
(8MB to 512MB) 168 pin 3.3v SDRAM SPD(Special
Presence Detect).
Maximum memory up to 512MB.
AGP for fast VGA solution
-AGP specification compliant.
-AGP 66 MHz 3.3v for 1X/2X/4X device support.
Bus Slot
-Provide three 32 bit PCI slots.
-Provide one AGP slot and one CNR.
On-Board IDE
-An IDE controller on the ICH2 chipset provides IDE HDD/
CD-ROM with PIO, Bus Master and Ultra DMA 33/66/
100 operation modes.
-Can connect up to four IDE devices.
2 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description2 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
2 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
2 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description2 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 3

On-Board Peripherals
-1 floppy port supports 2 FDD with 360K,720K,1.2M,
1.44M and 2.88M byte.
-2 serial ports (COM1+COM2 ).
-4 USB ports.
-1 VGA ports.
-1 parallel port supports EPP/ECP mode(LPT1).
Audio
-ICH chip integrated.
-AC’97 CODEC on board .
BIOS
- The mainboard BIOS provides “Plug & Play” BIOS which
detects the peripheral devices and expansion cards of the
board automatically.
- The mainboard provides a Desktop Management Interface
(DMI) function which records your mainboard
specifications.
- BIOS support CD-ROM, SCSI, LAN BOOT, Temperature
sensor, Wake on modem, LAN, Alarm Bus CLK setup with
BIOS.
Hardware Monitor Function
-CPU Fan Speed Monitor.
-CPU Temperature Monitor.
-System Voltage Monitor.
WOL (Wake On LAN) & WOM (Wake On MODEM)
Supports system power up from LAN ring up and Modem
ring up.
Support Ring on by modem/Alarm on
Support System power up from Modem ring up or timer
of System. Required enabled in Ring on by modem and
Alarm on in BIOS.
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /3Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /3
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /3
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /3Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /3
Page 4

Display Cache:
-1*AIMM.
-Support 4MB (1M*16 or 2M*32) PC 133 SDRAM .
Intel Accelerated Hub Architecture :
Features a dedicated high speed hub link between the ICH2
and GMCH with a bandwidth of 266MB/sec-twice the maximum bandwidth of the PCI bus.
CNR Support :
Two Communication and Networking Riser(CNR) slots
provide interface to support very affordable multichannel
audio,V.90 analog modem, Home PNA, 10/100 Ethernet
networking,USB hub, as well as future technologies such
as XDSL .
Suspend and Go :
Suspend-to-RAM (STR) provides maximum power savings
as an alternative to leaving the computer ON and Quickstart
so that you do not have to wait for a long time for system
boot.
Dual Function Power Button :
Through BIOS, the power button can be defined as the
“Stand by” button or as the Soft-Off button.
Integrated Graphics :
Controller supports 3D hyper pipelined architecture,
parallel data processing and compression, precise pixel
interpolation, full 2D hardware acceleration, and motion
video acceleration.
4 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description4 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
4 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
4 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description4 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 5

1.1.2 Software
BIOS
-AWARD legal BIOS.
-Supports APM 1.2.
-Supports USB Function.
-Supports ACPI.
Operation System
-Offers the highest performance for MS-DOS, Windows,
Windows NT, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Novell, OS/2,
Windows95/98, UNIX, SCO UNIX etc.
1.1.3 Attachments
-HDD UDMA 66/100 Cable.
-FDD Cable.
-Flash Memory Written for BIOS Update.
-COM2 Cable.
-Fully Setup CD Driver built in Utility(Ghost, Anitivirus,
Adobe Acrobat...).
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /5Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /5
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /5
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /5Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /5
Page 6

1.2 Motherboard Installation
1.2.1 Layout of Motherboard
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
Intel
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
GAME1
AGP SLOT
FAN2
PCI1
PCI2
I/O CHIP
CNR SLOT
CHASS1
6 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description6 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
6 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
6 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description6 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
PCI3
CMOS1
DIMM1
Intel
FAN3
DIMM2
1
BIOS
PAN E L1
FWH2
Page 7

1.3 Motherboard Connectors
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
1
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
Printer
GAME1
Intel
DIMM1
DIMM2
8
12
2
3
FAN2
AGP SLOT
PCI1
Intel
19
4,5
I/O CHIP
CNR SLOT
13
1.Back Pannel I/O Connectors1.Back Pannel I/O Connectors
1.Back Pannel I/O Connectors
1.Back Pannel I/O Connectors1.Back Pannel I/O Connectors
3.Front COM2 Connector3.Front COM2 Connector
3.Front COM2 Connector
3.Front COM2 Connector3.Front COM2 Connector
5.Wake-On Modem Connector5.Wake-On Modem Connector
5.Wake-On Modem Connector
5.Wake-On Modem Connector5.Wake-On Modem Connector
7.Fan Connectors(Fan1/2/3)7.Fan Connectors(Fan1/2/3)
7.Fan Connectors(Fan1/2/3)
7.Fan Connectors(Fan1/2/3)7.Fan Connectors(Fan1/2/3)
9.IDE Connectors9.IDE Connectors
9.IDE Connectors
9.IDE Connectors9.IDE Connectors
11.Front USB2 Connector11.Front USB2 Connector
11.Front USB2 Connector
11.Front USB2 Connector11.Front USB2 Connector
13.Chassic Connector(CHASS1)13.Chassic Connector(CHASS1)
13.Chassic Connector(CHASS1)
13.Chassic Connector(CHASS1)13.Chassic Connector(CHASS1)
15.CPU Freq. Selection(JCLK1)15.CPU Freq. Selection(JCLK1)
15.CPU Freq. Selection(JCLK1)
15.CPU Freq. Selection(JCLK1)15.CPU Freq. Selection(JCLK1)
17.AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1)17.AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1)
17.AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1)
17.AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1)17.AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1)
18.CMOS Function Selection(CMOS1)18.CMOS Function Selection(CMOS1)
18.CMOS Function Selection(CMOS1)
18.CMOS Function Selection(CMOS1)18.CMOS Function Selection(CMOS1)
19.Support Smart Panel(FWH2,LPT2,JGP1)(option)19.Support Smart Panel(FWH2,LPT2,JGP1)(option)
19.Support Smart Panel(FWH2,LPT2,JGP1)(option)
19.Support Smart Panel(FWH2,LPT2,JGP1)(option)19.Support Smart Panel(FWH2,LPT2,JGP1)(option)
CHASS1
PCI2
PCI3
CMOS1
19
2.CD Audio-In Connector2.CD Audio-In Connector
2.CD Audio-In Connector
2.CD Audio-In Connector2.CD Audio-In Connector
4.Wake-On LAN Connector4.Wake-On LAN Connector
4.Wake-On LAN Connector
4.Wake-On LAN Connector4.Wake-On LAN Connector
6.Front Panel Connector6.Front Panel Connector
6.Front Panel Connector
6.Front Panel Connector6.Front Panel Connector
8.Floppy Connector8.Floppy Connector
8.Floppy Connector
8.Floppy Connector8.Floppy Connector
10.IR Connector10.IR Connector
10.IR Connector
10.IR Connector10.IR Connector
12.ATX Power Connector12.ATX Power Connector
12.ATX Power Connector
12.ATX Power Connector12.ATX Power Connector
14.SB-LINK Connector14.SB-LINK Connector
14.SB-LINK Connector
14.SB-LINK Connector14.SB-LINK Connector
16.Speaker Selection(WATCH1)16.Speaker Selection(WATCH1)
16.Speaker Selection(WATCH1)
16.Speaker Selection(WATCH1)16.Speaker Selection(WATCH1)
BIOS
FAN3
7
1118
FWH2
15
9
14
16
1
10
17
PAN EL 1
6
19
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /7Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /7
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /7
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /7Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /7
Page 8

1.3.1 Front Panel Connector(PANEL1)
PANEL1 Connector
RSTSW
IDE
KBLOCK
PWLED
+
PBTN
+
1
EXTSMI
+
SPKR
2
+
+
GRNLED
Speaker Connector (SPKR)
An offboard speaker can be installed onto the motherboard as a
manufacturing option. An offboard speaker can be connected to
the motherboard at the front pannel connector. The speaker
(onboard or offboard) provides error beep code information during the Power Self-Test when the computer cannot use the video
interface. The speaker is not connected to the audio subsystem
and does not receive output from the audio subsystem.
Hard Drive LED Connector (IDE)
This connector supplies power to the cabinet IDE activity LED.
Read and write activity by devices connected to the Primary or
Secondary IDE connectors will cause the LED to light up.
SMI Suspend Switch Lead (EXTSMI)
This allows the user to manually place the system into a suspend
mode or Green mode where systematic activity will be instantly
decreased to save electricity and expand the life of certain components when the system is not in use. This 2-pin connector
(see the figure below) connects to the case-mounted suspend
switch. If you do not have a switch for the connector, you may
use the “Turbo Switch” instead since it does not have a function.
SMI is activated when it detects a short to open moment. It may
require one or two pushes depending on the position of the
switch. Wake-up can be controlled by settings in the BIOS but
the keyboard will always allow wake-up (the SMI lead cannot
wake-up the system). If you want to use this connector, the
"Suspend Switch" in the Power Management Setup of the BIOS
SOFTWARE section should be on the default setting of Enable.
8 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description8 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
8 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
8 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description8 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 9

ATX Power Switch (PBTN)
The system power is controlled by a momentary switch
connected to this lead. Pushing the button once will switch
the system ON. The system power LED lights when the
system's power is on .
Power LED Lead (PWLED)
The system Power LED lights when the system power is on.
Keyboard Lock (KBLOCK)
The header is for setting keyboard locked.
SMI LED Lead (GRNLED)
The system SMI LED lights when the system suspend is on.
Reset Switch Lead (RSTSW)
The connector can be connected to a momentary SPST type
switch that is normally open. When the switch is closed, the
motherboard resets and runs the POST.
1.3.2 Floppy Disk Connector(FDC1)
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon
cable. After connecting the single end to the board, connect
the two plugs on the other end to the floppy drives.
1.3.3 Hard Disk Connectors(IDE1/IDE2)
These connectors support the provided IDE hard disk ribbon
cable. After connecting the single end to the board, connect
the two plugs at the other end to your hard disk.
If you install two hard disks, you must configure the second
drive to Slave mode by setting its jumper settings. BIOS now
supports SCSI device or IDE CD-ROM boot up (see "HDD
Sequence SCSI/IDE First" & "Boot Sequence" in the BIOS
Features Setup of the BIOS SOFTWARE) (Pin 20 is removed
to prevent inserting in the wrong orientation when using
ribbon cables with pin 20 plugged) .
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /9Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /9
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /9
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /9Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /9
Page 10

1.3.4 ATX 20-pin Power Connector(PW1)
This connector supports the power button on-board. Using
the ATX power supply, functions such as Modem Ring Wake-
Up and Soft Power Off are supported on this motherboard .
This power connector supports instant power-on
functionality, which means that the system will boot up
instantly when the power connector is inserted on the board.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 3.3V 11 3.3V
2 3.3V 12 -12V
3 GND 13 GND
4 5V 14 PS-ON
5 GND 15 GND
6 5V 16 GND
7 GND 17 GND
8 PW-OK 18 -5V
9 5V_SB 19 5V
10 12V 20 5V
1.3.5 Infrared Connector(IR1)
After the IrDA interface is configured, files can be
transferred from or to portable devices such as laptops,
PDAS, and printers using application software.
10 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description10 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
10 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
10 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description10 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 11

1.4 Back Pannel Connectors
(
)
(
(
Printer) Port
Parallel
PS/2 Mouse
(25-pin Female)
GAME) Port
MIDI/
(15-pin Female)
VGA
PS/2 Keyboard
(6-pin Female)
COM1
Serial Port
9-pin Male
SPEAKER
LINE IN
1.4.1 PS/2 Mouse /Keyboard CONN.
The motherboard provides a standard PS/2 mouse / Keyboard
mini DIN connector for attaching a PS/2 mouse. You can
plug a PS/2 mouse / Keyboard directly into this connector.
1.4.2 USB Connectors: USB1/2
The motherboard provides a OHCI(Open Host Controller
Interface)Universal Serial Bus Roots for attaching USB
devices such as a keyboard, mouse and other USB devices.
You can plug the USB devices directly into this connector.
Pin Signal
1 +5v
2 USBP0-(USBP1-)
3 USBP0+(USBP1+)
4 GND
1.4.3 VGA Interface Connector:VGA(15 Pin)
This connector is for output to VGA-compatible devices.
MIC
VGA
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /11Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /11
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /11
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /11Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /11
Page 12

Front Two USB Connectors:USB2
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
GAME1
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
USB 2
CNR SLOT
VCC
P2-
P2+
GND
GND
FAN2
Intel
DIMM1
DIMM2
AGP SLOT
PCI1
Intel
1
PCI2
FAN3
BIOS
PAN EL 1
FWH2
PCI3
CMOS1
1
2
3
4
5
6
GND
7
GND
8
P3+
9
P3-
10
VCC
12 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description12 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
12 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
12 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description12 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 13

1.5 Serial and Parallel Interface Ports
This system comes equipped with two serial ports and one
parallel port. Both types of interface ports will be explained
in this chapter.
The Serial Interfaces:COM1/COM2
The serial interface port is sometimes refered to as an RS-
232 port or an asynchronous communication port. Mice,
printers, modems and other peripheral devices can be
connected to a serial port. The serial port can also be used
to connect your computer system. If you wish to transfer
the contents of your hard disk to another system it can be
accomplished by using each machine’s serial port.
COM1
COM2
1
The serial port on this system have one 9-pin connector.
Some older computer systems and peripherals used to be
equipped with only a 25-pin connector. Should you need to
connect your 9-pin serial port to an older 25-pin serial port,
you can purchase a 9-to-25 pin adapter.
Signal DB9 Pin DB25 Pin
DCD 1 8
RX 2 3
TX 3 2
DTR 4 20
GND 5 7
DSR 6 6
RTS 7 4
CTS 8 5
RI 9 2 2
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /13Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /13
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /13
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /13Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /13
Page 14

USB1
COM1
FAN 1
Printer
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
Intel
GAME1
DIMM1
DIMM2
AGP SLOT
COM2
FAN2
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
CNR SLOT
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
CMOS1
Intel
FAN3
BIOS
FWH2
Parallel Interface Port
Unlike serial ports, parallel interface ports have been
standardized and should not present any difficulty interfacing
peripherals to your system. Sometimes called a Centronics port,
the parallel port is almost exclusively used with printers. The
parallel port on your system has a 25-pin, DB 25 connector(see
picture below).
PS/2 Mouse
Parallel (Printer) Port
(25-pin Female)
MIDI/(GAME) Port
(15-pin Female)
1
PAN EL 1
VGA
PS/2 Keyboard
(6-pin Female)
14 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description14 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
14 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
14 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description14 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
COM1
Serial Port(9-pin Male)
SPEAKER
MIC
LINE IN
Page 15

1.6 CPU Installation
1.6.1 CPU Installation Procedure:Socket 370
1. Pull the lever sideways away from the socket then raise
the lever to a 90-degree angle.
2. Locate Pin 1 in the socket and look for the white dot or
cut edge in the CPU. Match Pin 1 with the white dot/cut
edge then insert the CPU.
3. Press the lever down to complete the installation.
4. Make sure the spec of the heatsink is good enough.
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
GAME1
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
FAN2
CNR SLOT
Intel
DIMM1
DIMM2
AGP SLOT
PCI1
Intel
1
Notch
PCI2
FAN3
BIOS
PAN EL 1
FWH2
PCI3
CMOS1
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /15Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /15
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /15
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /15Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /15
Page 16

1.6.2 CPU Frequency Selection:JCLK1
Overclocking is operating a CPU/Processor beyond its specified
frequency.JCLK1 jumper is used for overclocking.
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
CPUCPU
CPU
CPUCPU
6666
66
6666
100100
100
100100
133133
133
133133
AutoAuto
Auto
AutoAuto
(default)(default)
(default)
(default)(default)
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
SDRAMSDRAM
SDRAM
SDRAMSDRAM
100100
100
100100
100100
100
100100
133133
133
133133
AutoAuto
Auto
AutoAuto
GAME1
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
PCICLKPCICLK
PCICLK
PCICLKPCICLK
33.333.3
33.3
33.333.3
33.333.3
33.3
33.333.3
33.333.3
33.3
33.333.3
33.333.3
33.3
33.333.3
FAN2
CNR SLOT
1-2 1-2
1-2
1-2 1-2
ON ON
ON
ON ON
OFF OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
ON ON
ON
ON ON
OFF OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
AGP SLOT
3-4 3-4
3-4
3-4 3-4
ON ON
ON
ON ON
ON ON
ON
ON ON
OFF OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
OFF OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
Intel
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
CMOS1
DIMM1
OFFOFF
OFF
OFFOFF
ONON
ON
ONON
DIMM2
Intel
FAN3
1
BIOS
PAN EL 1
FWH2
16 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description16 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
16 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
16 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description16 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 17

1.7 Jumper Setting
A jumper has two or more pins that can be covered by a
plastic jumper cap, allowing you to select different system
options.
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
FAN1
Connector
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
FAN 2
Connector
WOL1
WOM1
Intel
GAME1
DIMM1
DIMM2
AGP SLOT
FAN2
PCI1
Intel
PCI2
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
CHASS1
Connector
CNR SLOT
PCI3
CMOS1
CMOS1
BIOS
FAN3
FAN 3
Connector
FWH2
1.7.1 CPU/System Fan Connector: Fan1/2/3
1
2
3
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
11
1
11
22
2
22
33
3
33
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
GroundGround
Ground
GroundGround
+12VDC+12VDC
+12VDC
+12VDC+12VDC
SignalSignal
Signal
SignalSignal
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /17Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /17
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /17
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /17Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /17
PAN EL 1
SB LINK
WATCH1
1
STRAP1
Page 18

1.7.2 Wake-On Modem Header: WOM1
1
3
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
11
1
11
22
2
22
33
3
33
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
5VSB5VSB
5VSB
5VSB5VSB
GroundGround
Ground
GroundGround
SignalSignal
Signal
SignalSignal
1.7.3 Wake-On LAN Header: WOL1
1
3
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
11
1
11
22
2
22
33
3
33
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
5VSB5VSB
5VSB
5VSB5VSB
GroundGround
Ground
GroundGround
SignalSignal
Signal
SignalSignal
1.7.4 CMOS Function Select: CMOS1
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
1-21-2
1-2
1-21-2
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
Normal (Default)Normal (Default)
Normal (Default)
Normal (Default)Normal (Default)
2-32-3
2-3
2-32-3
Clear CMOSClear CMOS
Clear CMOS
Clear CMOSClear CMOS
NOTE:
(Please follow the procedure below to clear CMOS data.)
(1)Remove the AC power line.(2)CMOS1(2-3)Closed.(3)Wait
five seconds.(4)CMOS1(1-2) Closed.(5)AC Power on.(6)Re-
set your desired password or clear CMOS data.
18 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description18 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
18 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
18 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description18 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 19

1.7.5 SPEAKER Selection: WATCH1
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
ONON
ON
ONON
OFFOFF
OFF
OFFOFF
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
No Reboot onNo Reboot on
No Reboot on
No Reboot onNo Reboot on
timeouttimeout
timeout
timeouttimeout
Normal(default),Normal(default),
Normal(default),
Normal(default),Normal(default),
Reboot on timeoutReboot on timeout
Reboot on timeout
Reboot on timeoutReboot on timeout
1.7.6 SB-LINK Connector
The motherboard provides one infrared SB-LINK feature
connector for support PCI sound cards.
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
11
1
11
22
2
22
33
3
33
44
4
44
55
5
55
66
6
66
1 2
56
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
REQ#REQ#
REQ#
REQ#REQ#
GNDGND
GND
GNDGND
NCNC
NC
NCNC
GNT#GNT#
GNT#
GNT#GNT#
GNDGND
GND
GNDGND
SERIRQSERIRQ
SERIRQ
SERIRQSERIRQ
1.7.7 Chassic Intrusion Connector: CHASSIC1
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
11
1
11
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
CHASICHASI
CHASI
CHASICHASI
22
2
22
GNDGND
GND
GNDGND
1.7.8 AC97 Serial data out: STRAP1
PinPin
Pin
PinPin
ONON
ON
ONON
OFFOFF
OFF
OFFOFF
AssignmentAssignment
Assignment
AssignmentAssignment
Force CPU to safeForce CPU to safe
Force CPU to safe
Force CPU to safeForce CPU to safe
modemode
mode
modemode
Normal(default),Normal(default),
Normal(default),
Normal(default),Normal(default),
Use registerUse register
Use register
Use registerUse register
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /19Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /19
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /19
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /19Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /19
Page 20

1.8 DRAM Installation
1.8.1 DIMM
DRAM Access Time: 3.3V Unbuffered SDRAM/ PC66/
PC100 and PC133 Type required.
DRAM Type: 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, 256MB
, 512MB DIMM Module.(168 pin)
Bank Memory module
DIMM 1 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, 256MB,512MB
( Bank 0-1 ) 168 pin, 3.3v SDRAM
DIMM 2 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, 256MB,512MB
( Bank 2-3 ) 168 pin, 3.3v SDRAM
Total System Memory(Max 512MB)
1.8.2 How to install a DIMM Module
1. The DIMM socket has a “Plastic Safety Tab” and the DIMM
memory module has an asymmetrical notch”, so the DIMM
memory module can only fit into the slot in one direction.
2. Push the tabs out. Insert the DIMM memory modules
into the socket at a 90-degree angle then push down
vertically so that it will fit into place.
3. The Mounting Holes and plastic tabs should fit over the
edge and hold the DIMM memory modules in place.
88 pins 60 pins 20 pins
168Pin DIMM Socket168Pin DIMM Socket
168Pin DIMM Socket168Pin DIMM Socket
168Pin DIMM Socket
20 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description20 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
20 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
20 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description20 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 21

1.9 Audio Subsystem
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
Intel
JACK1
CDIN1
CDIN2
JACK2
JACK3
GAME1
AGP SLOT
FAN2
PCI1
PCI2
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
CNR SLOT
PCI3
CMOS1
1.9.1 CD Audio-In Connectors: CDIN1/CDIN2
Pin CDIN1 Assignment
1 CD-L
2 GND
3 GND
4 CD-R
Pin CDIN2 Assignment
1 GND
2 CD-L
3 GND
4 CD-R
DIMM1
Intel
FAN3
DIMM2
1
BIOS
PAN EL 1
FWH2
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /21Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /21
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /21
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /21Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /21
Page 22

1.10 Smart Panel Onboard Connector (option)
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
Intel
GAME1
DIMM1
AGP SLOT
FAN2
PCI1
LPT2
Intel
PCI2
I/O CHIP
CHASS1
CNR SLOT
PCI3
FAN3
CMOS1
JGP1 FWH2
Note:
The motherboard provides for Smart Panel. If you refer POST
Error Code or Smart Panel function, please refer to
Smart Panel (SPM815E ) manual.
DIMM2
1
BIOS
PAN EL 1
FWH2
22 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description22 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
22 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
22 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description22 / Chapter 1 Motherboard Description
Page 23

1.10.1 Second BIOS Connector: FWH2 (option)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 VCC 2 NC
3 PCIRST# 4 PCLK_FWH
5 CAD_FWH0 6 P66DTCT
7 CAD_FWH1 8 S66DTCT
9 GND 10 GND
11 CAD_FWH2 12 HINIT#
13 CAD_FWH3 14 FWH_ID0T
15 CAD_FWH4 16 VCC
1.10.2 Parallel Port Connector: LPT2 (option)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 ERD4 2 ERD0
3 ERD5 4 ERD1
5 ERD6 6 ERD2
7 ERD7 8 ERD3
9 GND 10 GND
1.10.3 GPIO Port Connector: JGP1 (option)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 5VSB 2 SLP_S3
3 GP27 4 5VSB(R)
5 GP28 6 SLP_S5
7 GP21 8 5VSB(R)
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /23Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /23
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /23
Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /23Chapter 1 Motherboard Description /23
Page 24

2. BIOS Setup
Introduction
This chapter discusses the Award Setup program built into
the ROM BIOS. The Setup program allows the user to modify
the basic system configuration. This special information is
then stored in battery-backed RAM so that it retains the setup
information when the power is turned off.
The Award BIOS installed in your computer system’s ROM
(Read Only Memory)is a custom version of an industry
standard BIOS. This means that it supports Intel Celeron/
Coppermine PII/PIII Processor. The BIOS provides critical
low-level support for standard devices such as disk drives
and serial and parallel ports.
The rest of this manual is intended to guide you through the
process of configuring your system using Setup.
Plug and Play Support
This AWARD BIOS supports the Plug and Play Version
1.0A specification. ESCD(Extended System Configuration
Data)write is supported.
EPA Green PC Support
This AWARD BIOS supports Version 1.03 of the EPA Green
PC specification.
PCI Bus Support
This AWARD BIOS also supports Version 2.1 of the Intel
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)local bus
specification.
24 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup24 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
24 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
24 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup24 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 25

APM Support
This AWARD BIOS supports Version 1.1&1.2 of the
Advanced Power Management(APM) specification.Power
management features are implemented via the System
Management Interrupt(SMI). Sleep and Suspend power
management modes are supported. Power to the hard disk
drives and video monitors can be managed by this AWARD
BIOS.
DRAM Support
SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) are supported.
Support CPU
This AWARD BIOS supports the Intel Celeron/Coppermine
PII/PIII Processor.
Using Setup
In general, you use the arrow keys to highlight items, press
<Enter>to select, use the <PgUp>and <PgDn>keys to
change entries, press<F1>for help and press <Esc>to quit.
The following table provides more detail about how to
navigate in the Setup program by using the keyboard.
Note:
(BIOS version 1.0 is for reference only. If there is a
change in BIOS version, please use the actual version
on the BIOS.)
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /25Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /25
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /25
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /25Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /25
Page 26

Keystroke Function
Up arrow Move to previous item
Down arrow Move to next item
Left arrow Move to the item on the left(menu bar)
Right arrow Move to the item on the right(menu bar)
Esc Main Menu: Quit without saving changes
Submenus: Exit Current page to the next higher
level menu
Move Enter Move to item you desired
PgUp key Increase the numeric value or make changes
PgDn key Decrease the numeric value or make changes
+Key Increase the numeric value or make changes
-Key Decrease the numeric value or make changes
Esc Key Main menu-Quit and not save changes into
CMOS
Status Page Setup Menu and option Page Setup
Menu-Exit Current page and return to Main
Menu
F1 Key General help on Setup navigation keys.
F5 Key Load previous values from CMOS
F6 Key Load the fail-safe defaults from BIOS default
table
F7 Key Load the optimized defaults
F10 Key Save all the CMOS changes and exit
26 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup26 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
26 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
26 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup26 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 27

2.1 Main Menu
Once you enter AWARD BIOS CMOS Set up Utility, the Main
Menu will appear on the screen. The Main Menu allows you
to select from several setup function. Use the arrow keys to
select among the items and press<Enter> to accept and
enter the sub-menu.
“WARNING”
The information about BIOS defaults on manual (Figure
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14)is just for reference, please
refer to the BIOS installed on the board for updated
information.
◎◎
◎ Figure 1. Main Menu
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
Standard CMOS Features
This setup page includes all the items in standard compatible
BIOS.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /27Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /27
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /27
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /27Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /27
Page 28

Advanced BIOS Features
This setup page includes all the items of the BIOS special
enchanced features.
Advanced Chipset Features
This setup page includes all the items of the Chipset special
enchanced features.
Integrated Peripherals
This selection page includes all the items of the IDE hard
drive and Programmed Input/Output features.
Power Management Setup
This setup page includes all the items of the power manage
ment features.
PnP/PCI Configuration
This setup page includes the user defined or default IRQ
Setting.
PC Health Status
This page shows the hardware Monitor information of the
system.
Frequency / Voltage Control
This setup page controls the CPU's clock and frequency ratio.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Use this menu to load the BIOS default values for the
minimal/stable performance for your system to operate.
28 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup28 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
28 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
28 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup28 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 29

Load Optimized Defaults
These settings are more likely to configure a workable
computer when something is wrong. If you cannot boot the
computer successfully, select the BIOS Setup options and
try to diagnose the problem after the computer boots. These
settings do not provide optional performance.
Set Supervisor Password
Change, set, or, disable password.It allows you to limit
accessto the system and Setup, or just to Setup.
Set User Password
You can specify both a User and a Supervisor password. When
you select either password option, you are prompted for a
1-6 character password. Enter the password and then retype
the password when prompted.
Save & Exit Setup
Save CMOS value changes to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all CMOS value changes and exit setup.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /29Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /29
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /29
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /29Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /29
Page 30

2.2 Standard CMOS Features
This item in the Standard CMOS Setup Menu is divided into
10 categories. Each category includes no, one or more than
one setup items. Use the arrow keys to highlight the item
and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value
you want in each item.
◎◎
◎ Figure 2. Standard CMOS Features
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Date(mm:dd:yy) Tue,Jun 6 2000 Item Help
Time (hh:mm:ss) 11:26:10
IDE Primary Master None
IDE Primary Slave None Change the day,
IDE Secondary Master None month,year
IDE Secondary Master None and century.
Drive A 1.44M,3.5 in
Drive B None
Video EGA/VGA
Halt On All,But Keyboard
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 65472K
Total 1024K
Menu Level
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
30 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup30 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
30 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
30 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup30 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 31

Main Menu Selections
This table shows the selections that you can make on the
Main Menu.
Item Options Description
Date Month DD YYYY Set the system,date. Note that the
‘Day’ automatically changes
when you set the data.
IDE Primary Options are in its sub Press<Enter> to enter the sub menu
Master menu. of detailed.
IDE Primary Options are in its sub Press<Enter> to enter the sub menu
Slave menu. of detailed.
IDE Secondary Options are in its sub Press<Enter> to enter the sub menu
Master menu. of detailed.
IDE Secondary Options are in its sub Press<Enter> to enter the sub menu
Slave menu. of detailed.
Drive A None Select the type of floppy disk drive
Drive B 360K,5.25in installed in your system.
1.2M,5.25in
720K,3.5in
1.44M,3.5in
2.88M,3.5in
Video EGA/VGA Select the default video device.
CGA 40
CGA 80
MONO
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /31Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /31
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /31
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /31Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /31
Page 32

Item Options Description
Halt On All Errors Select the situation in which you
No Errors want the BIOS to stop the POST
All, but Keyboard process and notify.
All, but Diskette
All, but Disk/Key
Base Memory N/A Displays the amount of conventional
memory detected during boot up.
Extended N/A Displays the amount of conventional
Memory memory detected during boot up.
Total N/A Displays the total memory
Memory available in the system.
32 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup32 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
32 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
32 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup32 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 33

2.3 Advanced BIOS Features
◎◎
◎ Figure 3. Advanced BIOS Features
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Advanced BIOS Features
Virus Warning Disabled Item Help
CPU Internal Cache Enabled
External Cache Enabled Menu Level
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking Enabled
Processor Number Feature Enabled Allows you to
Quick Power On Self Test Disabled choose the
First Boot Device Floopy VIRUS warning
Second Boot Device CD-ROM feature for IDE
Third Boot Device HDD-0 Hard Disk boot
Boot Other Device Enabled sector protection.
Swap Floppy Drive Disabled If this function
Boot Up Floppy Seek Enabled is enabled and
Boot Up NumLock Status On someone attempts
Gate A20 Option Fast to w rite data into
Typematic Rate Setting Disabled this area,BIOS
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec) 6 will show a
Typematic Delay (Msec) 25 0 warning message
Security Option Setup on screen and
OS Select For DRAM >64MB Non-OS2 alarm beep
Report No FDD For WIN 95 No
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
Virus Warning
This option allows you to choose the VIRUS Warning
feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector protection. If this
function is enabled and someone attempts to write data into
this area, BIOS will show a warning message on screen and
alarm beep.
The Choices: Disabled(default), Enabled.
CPU Internal Cache
These two categories speed up memory access. However,
it depends on CPU/chipset design.
Enabled(default) Enabled cache.
Disabled Disabled cache.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /33Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /33
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /33
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /33Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /33
Page 34

External Cache
This fields allow you to Enable or Disable the CPU’S
“Level 2” secondary cache. Caching allows better
performance.
Enabled(default) Enabled cache.
Disabled Disabled cache.
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
The item allows you to enable/disable CPU L2 Cache ECC
Checking.
The Choices: Enabled(default), Disabled.
Processor Number Feature
The item will show up when you install the Pentium III
processor.
Enabled(default) Pentium Processor Number
Feature.
Disabled Disabled.
Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up Power on self-Test(POST) after
you power up the computer. If it is set to Enable, BIOS
will shorten or skip some check items during POST.
Enabled Enabled quick POST.
Disabled(default) Normal POST.
First/Secondary/Third Boot Device
This BIOS attempts to load the operating system from
the devices in the sequence selected in these items.
The Choices: Floppy, LS120, HDD-0, SCSI, CDROM,
HDD-1, HDD-2, HDD-3, ZIP100, USB-FDD, USB-ZIP,
USB-CDROM, USB-HDD, LAN, Disabled.
Boot Other Device
The Choices: Enabled(default), Disabled.
34 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup34 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
34 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
34 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup34 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 35

Swap Floppy Drive
If the system has two floppy drives, you can swap the
logical drive name assignments.
The Choices: Disabled(default), Enabled.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
Seek disk drives during boot up. Disabled speeds boot-up.
The Choices: Enabled(default), Disabled.
Boot Up NumLock Status
Select power on state for Numlock.
On(default) Numpad is number keys.
Off Numpad is arrow keys.
Gate A20 Option
Select if chipset or keyboard controller should control
Gate A20.
Normal A pin in the keyboard
controller controls Gate A20.
Fast(default) Lets chipset control Gate A20.
Typematic Rate Setting
Enabled Enabled this option to adjust
the keystroke repeat rate.
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Typematic Rate (Char/Sec)
Range between 6(default) and 30 characters per second.
This option controls the speed of repeating keystrokes.
Typematic Delay (Msec)
This option sets the time interval for displaying the first
and the second characters.
The Choices: 250(default), 500, 750, 1000
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /35Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /35
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /35
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /35Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /35
Page 36

Security Option
This category allows you to limit access to the system and
Setup, or just to Setup.
System The system will not boot and
access to Setup will be denied
if the correct password is not
entered in prompt.
Setup(default) The system will boot, but
access to Setup will be denied
if the correct password is not
entered in prompt.
OS Select For DRAM >64MB
Select the operating system that is running with greater
than 64MB of RAM on the system.
The Choices: Non-OS2(default), OS2
Report No FDD For Window 95
No(default) Assign IRQ6 For FDD.
Ye s FDD Detect IRQ6
Automatically.
36 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup36 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
36 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
36 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup36 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 37

2.4 Advanced Chipset Features
This section allows you to configure the system based on
the specific features of the installed chipset. This chipset
manages bus speeds and access to system memory resources,
such as DRAM and external cache. It also coordinates
communications of the PCI bus. It must be stated that these
items should never need to be altered. The default settings
have been chosen because they provide the best operating
conditions for your system. The only time you might
consider making any changes would be if you discovered that
data was lost while using your system.
◎◎
◎ Figure 4. Advanced Chipset Features
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Advanced Chipset Features
SDRAM CAS Latency/Time 3 Item Help
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc 7/9
SDRAM RAS -to- CAS Delay 3 Menu Level
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time 3
System BIOS Cacheable Disabled
Video BIOS Cacheable Disabled
Memory Hole At 15M-16M Disabled
CPU Latency Timer Enabled
Delayed Transaction Enabled
AGP Graphic Aperture Size 64MB
System Memory Frequency Auto
On-Chip Video Window Size 64MB
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /37Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /37
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /37
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /37Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /37
Page 38

SDRAM CAS latency Time
3(default) Slower SDRAM DIMM
Module.
2 Fastest SDRAM DIMM
Module.
SDRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc
7/9(default) Set SDRAM Tras/Trc Cycle
time in 7/9 SCLKs.
5/7 Set SDRAM Tras/Trc Cycle
time in 5/7 SCLKs.
SDRAM RAS -to- CAS Delay
3(default) Set SDRAM RAS -to- CAS
delay 3 SCLKs.
2 Set SDRAM RAS -to- CAS
delay 2 SCLKs.
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time
3(default) Set SDRAM RAS Precharge
Time to 3.
2 Set SDRAM RAS Precharge
Time to 2.
System BIOS Cacheable
When enabled, the access to the system BIOS ROM
address at F0000H-FFFFFFH is cached.
The Choices: Disabled(default), Enabled.
Video BIOS Cacheable
Enabled Enabled Video BIOS
Cacheable.
Disabled(default) Disabled Video BIOS
Cacheable.
38 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup38 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
38 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
38 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup38 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 39

Memory Hole At 15-16M
In order to improve performace, certain space in memory
can be reserved for ISA cards. This memory must be
mapped into the memory's space below 16MB.
The Choices: Diasbled(default), Enabled.
CPU Latency Timer
Enabled(default) Enabled.
Disabled Disabled.
Delayed Transaction
Enabled(default) Slow speed ISA device in
system.
Disabled Disabled.
AGP Graphics Aperture Size
64MB(default) AGP Graphics Aperture Size
is 64 MB.
32MB AGP Graphics Aperture Size
is 32 MB.
System Memory Frequency
Auto(default) System Memory Frequency to
Auto.
100MHZ Set system Memory Frequency
to 100MHZ.
133MHZ Set system Memory Frequency
to 133MHZ.
On-Chip Video Window Size
64MB(default) Set Graphics Aperture Size to
64 MB.
32MB Set Graphics Aperture Size to
32 MB.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /39Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /39
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /39
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /39Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /39
Page 40

2.5 Integrated Peripherals
◎◎
◎ Figure 5. Integrated Peripherals
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Integrated Peripherals
On-Chip Primary PCI IDE Enabled Item Help
On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE Enabled
IDE Primary Master PIO Auto Menu Level
IDE Primary Slave PIO Auto
IDE Secondary Master PIO Auto
IDE Secondary Slave PIO Auto
IDE Primary Master UDMA Auto
IDE Primary Slave UDMA Auto
IDE Secondary Master UDMA Auto
IDE Secondary Slave UDMA Auto
USB Controller Enabled
USB Keyboard Support Disabled
USB Mouse Support Disabled
Init Display First PCI Slot
AC97 Audio Auto
AC97 Modem Auto
IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled
Power On Function Button Only
KB Power On Password Enter
Hot Key Power On Ctrl-F1
Onboard FDC Controller Enabled
Onboard Serial Port 1 3F8/IRQ4
Onboard Serial Port 2 2F8/IRQ3
UART Mode Select Normal
RxD,TxD Active Hi,Lo
IR Transmission Delay Enabled
UR2 Duplex Mode Half
Use IR Pins IR/Rx2Tx2
Onboard Paraller Port 278/IRQ5
Parallel Port Mode SPP
EPP Mode Type EPP1.7
ECP Mode Use DMA 3
Game Port Address 201
Midi Port Adress 330
Midi Port IRQ 10
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
40 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup40 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
40 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
40 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup40 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 41

On-Chip Primary PCI IDE
Enabled(default) Enabled onboard 1st channel
IDE port.
Disabled Disabled onboard 1st channel
IDE port.
On-Chip Secondary PCI IDE
Enabled(default) Enabled onboard 2nd channel
IDE port.
Disabled Disabled onboard 2nd channel
IDE port.
IDE Primary Master PIO(for onboard IDE 1st channel)
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Mode 0~4 Manually set the IDE
Accessing mode.
IDE Primary Slave PIO(for onboard IDE 2nd channel)
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Mode 0~4 Manually set the IDE
Accessing mode.
IDE Secondary Master PIO(for onboard IDE 1st channel)
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Mode 0~4 Manually set the IDE
Accessing mode.
IDE Secondary Slave PIO(for onboard IDE 2nd channel)
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Mode 0~4 Manually set the IDE
Accessing mode.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /41Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /41
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /41
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /41Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /41
Page 42

IDE Primary Master UDMA
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Disabled Disabled.
IDE Primary Slave UDMA
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Disabled Disabled.
IDE Secondary Master UDMA
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Disabled Disabled.
IDE Secondary Slave UDMA
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
the IDE HDD Accessing mode.
Disabled Disabled.
USB Controller
Enabled(default) Enabled USB Controller.
Disabled Disabled USB Controller.
USB Keyboard Support
Enabled Enabled USB Keyboard
Support.
Disabled(default) Disabled USB Keyboard
Support.
USB Mouse Support
Enabled Enabled USB Mouse Support.
Disabled(default) Disabled USB Mouse Support.
Init Display First
PCI Slot(default) Set Init Display First to PCI
Slot.
Onboard AGP Set Init Display First to
42 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup42 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
42 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
42 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup42 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
onboard AGP.
Page 43

AC 97 Audio
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
onboard Audio.
Disabled Disabled.
AC 97 Modem
Auto(default) BIOS will automatically detect
onboard Modem.
Disabled Disabled.
IDE HDD Block Mode
Enabled(default) Enabled.
Disabled Disabled.
Power On Function
Password Enter from 1 to 7 characters to
set the Keyboard Power On
Password.
Hot Key Hot Key.
Mouse Left Mouse Left.
Mouse Right Mouse Right.
Any Key Any Key.
Button Only(default) Button Only.
Keyboard 98 If your keyboard has an Owner
key button, you can press the
key to power on your system.
KB Power On Password
Enter Enter from 1 to 7 characters to
set the keyboard Power On
Password.
Hot Key Power On First you must choose the
Ctrl-F1(default) Power On by Hot Key function
Ctrl-F2 then Enter from 1 to 8
Ctrl-F3 characters to set the Hot Key
Ctrl-F4 Power On your system.
Ctrl-F5
Ctrl-F6
Ctrl-F7
Ctrl-F8
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /43Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /43
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /43
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /43Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /43
Page 44

Onboard FDC Controller
Enabled(default) Enabled onboard FDC
Controller.
Disabled Disabled onboard FDC
Controller.
Onboard Serial Port1
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first
and second serial ports.
The Choices: 3F8/IRQ4 (default), Auto, (2F8/IRQ3),
(3E8/IRQ4), (2E8/IRQ3), Disabled.
Onboard Serial Port 2
Auto BIOS will automatically setup
the Serial Port 2 address.
3F8/IRQ4 Enabled onboard Serial Port 2
and address is 3F8.
2F8/IRQ3(default) Enabled onboard Serial Port 2
and address is 2F8.
3E8/IRQ4 Enabled onboard Serial Port 2
and address is 3E8.
2E8/IRQ3 Enabled onboard Serial Port 2
and address is 2E8.
Disabled Disabled.
UART Mode Select
This item allows you to select which Infra Red(IR)
function of the onboard I/O chip you wish to use.
The Choices: Normal(default), IrDA, SCR, ASKIR.
44 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup44 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
44 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
44 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup44 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 45

UR2 Duplex Mode
This item allows you to select which Infra Red(IR)
function of the onboard I/O chip you wish to use.
The Choices: Half (default), Full.
Onboard Parallel Port
This item allows you to select the I/O address with which
to access the onboard parallel port controller.
Disabled.
378/IRQ7.
278/IRQ5.(default)
3BC/IRQ7.
Parallel Port Mode
SPP(default) Using Parallel port as Standard
Parallel Port.
EPP Using Parallel port as Ex-
hanced Parallel Port.
ECP Using Parallel port as Ex-
tended Capabilites Port.
ECP+EPP Using Parallel port as
ECP+EPP mode.
Game Port Address
201(default) Set onboard game port to 201.
209 Set onboard game port to 209.
Disabled Disabled.
Midi Port Address
300 Set Midi Port address to 300.
330(default) Set Midi Port address to 330.
Midi Port IRQ
10(default) Set Midi Port IRQ to 10.
5 Set Midi Port IRQ to 5.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /45Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /45
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /45
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /45Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /45
Page 46

2.6 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to configure your
system to most effectively save energy while operating in a
manner consistent with your own style of computer use.
◎◎
◎ Figure 6. Power Management Setup
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Power Management Setup
ACPI Function Enabled Item Help
ACPI Suspend Type S1(POS)
Power Management User Define Menu Level
Video Off Method DPMS
Video Off In Suspend Yes
Suspend Type Stop Grant
Modem Use IRQ 3
Suspend Mode Disabled
HDD Power Down Disabled
Soft-Off by PWR-BTN Instant-Off
Wake Up by PCI Card Disabled
Power On by Ring Enabled
Wake Up On LAN Enabled
USB KB Wake-up From S3 Disabled
CPU Thermal-Throttling 50.0%
Resume by Alarm Disabled
Data (of Month) Alarm 0
Time (of hh:mm:ss) Alarm 0 0 0
**Reload Global Timer Events **
Primary IDE 0 Disabled
Primary IDE 1 Disabled
Secondary IDE 0 Disabled
Secondary IDE 1 Disabled
FDD,COM,LPT Port Disabled
PCI PIRQ[A-D]# Disabled
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
ACPI Function
This item display status of the Advanced Configuration and
Power Management (ACPI).
ACPI Suspend Type
The item allows you to select the suspend type under ACPI
operating system.
S1(POS)(default) Power on Suspend.
S3(STR) Suspend to RAM.
46 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup46 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
46 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
46 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup46 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 47

Power Management
This category allows you to select the type (or degree) of
power saving and is directly related to the following
modes.
1. HDD Power Down.
2. Doze Mode.
3. Suspend Mode.
If you highlight “Press Enter” next to the “Power
Management” label and then press the enter key, it will
take you a submenu with the following options:
Power Management
This option allows you to set each mode individually.
When not disabled, each of the ranges are from 1 min. to 1
hr. except for HDD Power Down which ranges from 1
min. to 15 min. and disable.
The Choices: User Define (default), Min Saving, Max
Saving.
HDD Power Down
By default, this is “Disabled”, meaning that no matter the
mode of the rest of system, the hard drive will remain
ready. Otherwise, you have a range of choices from 1 to 15
minutes or Suspend. This means that you can select to
have your hard disk drive be turned off after a selected
number of minutes or when the rest or the system goes
into a suspend mode.
Disabled(default).
Doze Mode/Suspend Mode
The Doze Mode, and Suspend Mode fields set the Period
of time after each of these modes activates. At Max
Saving, these modes activate sequentially (in the given
order) after one minute; at Min Saving after one hour.
Video Off In Suspend
This field determines when to activate the video off feature
for monitor power management.
The Choices: Yes(default), No
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /47Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /47
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /47
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /47Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /47
Page 48

Video Off Method
This determines the manner in which the monitor is
blanked.
V/H SYNC+Blank This selection will cause the
system to turn off the vertical
and horizontal synchronization
ports and write blanks to the
video buffer.
Blank Screen This option only writes blanks
to the video buffer.
DPMS Support Initial display power
(default) management signaling.
Suspend Type
Stop Grant(default) Set Susped type is stop grant.
PwrOn Suspend Set Suspend type is Power on
Suspend.
Modem Use IRQ
This determines the IRQ, which can be applied in Modem
use.
3(default)
4/5/7/9/10/11/NA
Suspend Mode
Disabled(default) Disabled.
1 min - 1 Hour Set the timer to enter Suspend
Mode.
HDD Power Down
Disabled(default) Disabled.
1 - 15 mins Enabled.
48 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup48 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
48 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
48 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup48 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 49

Soft-Off by PWRBTN
Pressing the power button for more than 4 seconds forces
the system to enter the Soft-Off state when the system has
“hung”.
The Choices: Instant-Off (default), Delay 4 Sec.
Wake Up by PCI card
Enabled Enabled.
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Power On By Ring
Disabled Disabled.
Enabled(default) Enabled.
Wake Up On LAN
Enabled(default) Enabled.
Disabled Disabled.
USB KB Wake Up From S3
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Enabled Enabled.
CPU Termal-Throttling
50.0%(default)
Monitor CPU Temp. will cause system to slow down
CPU Duty Cycle to 12.5% / 25.0% / 37.5% / 62.5% /
70.5% / 87.5%
Resume by Alarm
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Enabled Enabled.
Primary IDE 0/1
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Enabled Enabled monitor Primary IDE
0/1 for Green event.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /49Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /49
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /49
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /49Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /49
Page 50

Secondary IDE 0/1
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Enabled Enabled monitor Secondary
IDE 0/1 for Green event.
FDD,COM,LPT Port
Disabled(default) Disabled.
Enabled Enabled monitor FDD, COM,
LPT Port.
PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
Disabled(default) Ignore PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
Active.
Enabled Monitor PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
Active.
50 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup50 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
50 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
50 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup50 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 51
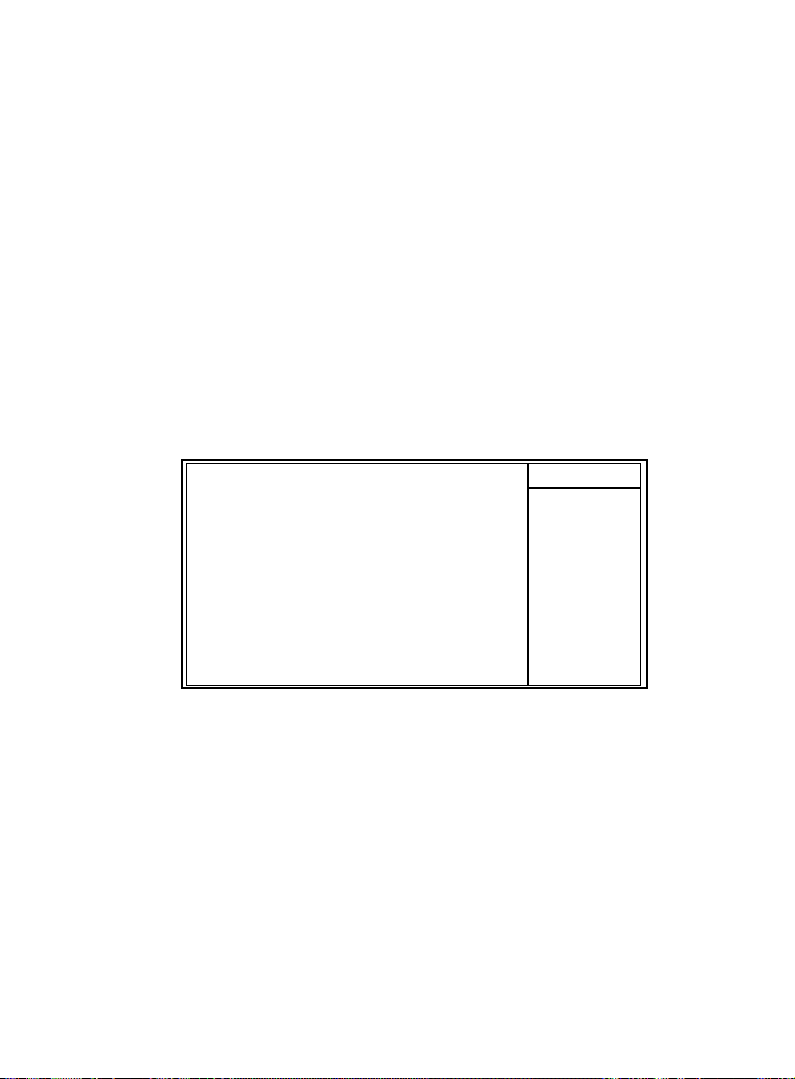
2.7 PnP/PCI Configurations
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system. PCI
or Personal Computer Interconnect,is a system which allows
I/O devices to operate at speeds nearing the speed of the
CPU itself when communicating with its own special
components. This section covers some very technical items
and it is strongly recommended that only experienced uses
make any changes to the default settings.
◎◎
◎ Figure 7. PnP/PCI Configurations
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
PnP/PCI Configurations
Reset Configuration Data Disabled Item Help
Resources Controlled By Auto(ESCD)
IRQ Resources Press Enter Menu Level
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop Disabled When resources
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
are controlled
manually, assign
each system
interrupt a type,
depending on the
type of device
using the
interrupt
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /51Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /51
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /51
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /51Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /51
Page 52

Reset Configuration Data
The system BIOS supports the PnP feature so the system
needs to record which resource is assigned and proceeds
resources from conflict. Every peripheral device has a
node, which is called ESCD. This node records which
resources are assigned to it. The system needs to record
and update ESCD to the memory locations. These
locations (4K) are reserved at the system BIOS. If
Disabled (Default) is chosen, the system’s ESCD will
update only when the new configuration varies from the
last one. If Enabled is chosen, the system is forced to
update ESCDs and then is automatically set to the
“Disabled” mode.
IRQ3 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ4 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ5 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ6 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ7 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ8 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ9 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ10 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ11 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ12 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ13 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ14 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
IRQ15 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-0 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-1 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-2 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-3 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-4 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-5 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-6 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
DMA-7 assigned to:PCI/ISA PnP
52 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup52 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
52 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
52 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup52 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 53

The above settings will be shown on the screen only if
“Manual” is chosen for the resources controlled by
function.
Legacy is the term, which signifies that a resource is
assigned to the ISA Bus and provides for non-PnP ISA
add-on cards. PCI/ISA PnP signifies that a resource is
assigned to the PCI Bus or provides for ISA PnP add-on
cards and peripherals.
Resources Controlled By
By Choosing “Auto” (default), the system BIOS will detect
the system resources and automatically assign the relative
IRQ and DMA channel for each peripheral. By Choosing
“Manual”, the user will need to assign IRQ & DMA for
add-on cards. Be sure that there are no IRQ/DMA and I/O
port conflicts.
IRQ Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each
system interrupt a type, depending on the type of device
using the interrupt.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /53Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /53
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /53
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /53Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /53
Page 54

PCI / VGA Palette Snoop
Choose Disabled or Enabled. Some graphic controllers
which are not VGA compatible take the output from a VGA
controller and map it to their display as a way to provide
boot information and VGA compatibility.
However, the color information coming from the VGA
controller is drawn from the palette table inside the VGA
controller to generate the proper colors, and the graphic
controller needs to know what is in the palette of the VGA
controller. To do this, the non-VGA graphic controller
watches for the write access to the VGA palette and
registers the snoop data. In PCI based systems, the Write
Access to the palette will not show up on the ISA bus if the
PCI VGA controller responds to the Write.
In this case, the PCI VGA controller should not respond to
the Write, it should only snoop the data and permit the
access to be forwarded to the ISA bus. The non-VGA ISA
graphic controller can then snoop the data on the ISA bus.
Unless you have the above situation, you should disable
this option.
Disabled(default) Function Disabled.
Enabled Function Enabled.
54 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup54 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
54 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
54 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup54 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 55

2.8 PC Health Status
◎◎
◎ Figure 8. PC Health Status
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
PC Health Status
CPU Warning Temperature Disabled Item Help
Current System Temp.
Current CPU Temperature Menu Level
Current CPU Fan1 Speed
Current CPU Fan2 Speed
Current CPU Fan3 Speed
VCORE
+3V
+5V
+12V
-12V
VBAT(V)
5VSB(V)
Shut down Temperature Disabled
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
Current Voltage(V) Vcore / VGTL / Vcc3/+-12V/5V/5VSB/
VBAT
Detect system’s voltage status automatically.
((
℃℃
//
℉℉
Current CPU/System Temperature
(
((
This field displays the current CPU temperature,if your
computer contains a monitoring system.
℃
℃℃
))
/
℉
)
//
℉℉
))
Current Fan/Power Fan / System Fan Speed
These field displays the current speed of up to System
Fans,if your computer contains a monitoring system.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /55Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /55
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /55
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /55Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /55
Page 56

CPU Warning Temperature(
Disabled(default) Disabled.
℃℃
//
60
℃
℃℃
℃℃
50
℃
℃℃
℃℃
53
℃
℃℃
℃℃
56
℃
℃℃
℃℃
63
℃
℃℃
℃℃
66
℃
℃℃
℃℃
70
℃
℃℃
Shutdown Temperature(
℉℉
/ 140
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 60 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 122
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 50 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 127
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 53 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 133
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 56 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 145
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 63 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 151
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 66 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 158
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 70 ℃/
//
℉℉
℃℃
℃
℃℃
Disabled(default) Disabled.
℃℃
//
60
65
70
75
℃
℃℃
℃℃
℃
℃℃
℃℃
℃
℃℃
℃℃
℃
℃℃
℉℉
/ 140
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 60 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 149
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 65 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 158
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 70 ℃/
//
℉℉
//
℉℉
/ 167
℉ Monitor CPU Temp.at 75 ℃/
//
℉℉
℃℃
℃)
℃℃
140℉.
122℉.
127℉.
133℉
145℉
151℉
158℉
//
℉℉
/
℉)
//
℉℉
140℉, if Temp.>60 ℃/140℉
system will automatically
power off.
149℉, if Temp.>65 ℃/149℉
system will automatically
power off.
158℉, if Temp.>70 ℃/158℉
system will automatically
power off.
167℉, if Temp.>75 ℃/167℉
system will automatically
power off.
56 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup56 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
56 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
56 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup56 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 57

2.9 Frequency / Voltage Control
◎◎
◎ Figure 9. Frequency / Voltage Control
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Frequency / Voltage Control
Auto Detect DIMM / PCI CLK Enabled Item Help
Spread Spectrum Disabled
Clock By Slight Adjust 13 3 Menu Level
CPU Clock Ratio X 3
←→↑↓: Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit
F1:General Help F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults
F7:Optimized Defaults
Auto Detect DIMM / PCI CLK
This item allows you to enable/disable auto detect DIMM /
PCI CLOCK.
The Choices: Enabled(default), Disabled.
Clock By Slight Adjust
This item allows you to select the CPU clock from
133MHz to 166MHz, 100MHz to 133MHz or 66MHz to
100MHz depending on the CPU Host Clock .
CPU Clock Ratio
This option will not be shown if you are using a CPU with
the locked ratio.
X3/X3.5/X4/X4.5/X5/X5.5/X6/X6.5/X7/X7.5/X8
Spread Spectrum
This function id designed for the EMI test only.
The Choices: Disabled(default), Enabled.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /57Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /57
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /57
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /57Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /57
Page 58

2.10 Load Fail-Safe Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item, you get a
confirmation dialog box with a message similar to:
◎◎
◎ Figure 10. Load Fail-Safe Defaults
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Pressing ‘Y’ loads the default values that are factory settings
for optimal performance of system operations.
Load Fail-Safe Default (Y/N)? N
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
58 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup58 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
58 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
58 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup58 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 59

2.11 Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item, you get a
confirmation dialog box with a message similar to:
◎◎
◎ Figure 11. Load Optimized Defaults
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Pressing ‘Y’ loads the default values that are factory settings
for optimal performance of system operations.
Load Optimized Default (Y/N)? N
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /59Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /59
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /59
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /59Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /59
Page 60

2.12 Set Supervisor / User Password
◎◎
◎ Figure 12. Set Supervisor / User Password
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
When you select this function, the following message will
appear at the center of the screen to assist you in creating a
password.
Type a password, up to eight characters, and press <Enter>.
The password you type now will clear any previously entered
password from CMOS memory. You will be asked to
confirm the password. Type the password again and press
<Enter>. You may also press <ESC> to abort the selection
and not enter a password. To disable the password, just press
<Enter> when you are prompted to enter a password. A
message will confirm that you wish to disable the password.
Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you
can enter setup freely.
Enter Password:
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
Enter Password
60 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup60 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
60 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
60 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup60 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 61

Password Disabled
If you select “System” at the Security Option of BIOS
Features Setup Menu, you will be prompted for the
password every time when the system is rebooted, or any
time when you try to enter Setup. If you select “Setup” at
the Security Option of BIOS Features Setup Menu, you will
be prompted only when you try to enter Setup.
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /61Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /61
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /61
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /61Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /61
Page 62

2.13 Save & Exit Setup
◎◎
◎ Figure 13. Save & Exit Setup
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Typing “Y” will quit the Setup Utility and save the user setup
value to RTC CMOS RAM.
Typing “N” will return to the Setup Utility.
Save & Exit Setup (Y/N)? Y
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
62 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup62 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
62 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
62 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup62 / Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
Page 63

2.14 Exit Without Saving
◎◎
◎ Figure 14. Exit Without Saving
◎◎
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright(C) 1984-2001 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features Frequency/Voltage Control
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PNP/PCI Configuration Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
Esc : Quit F9 : Menu in BIOS ←→↑↓ : Select Item
F10 : Save & Exit Setup
Typing “Y” will quit the Setup Utility without saving to RTC
CMOS RAM.
Typing “N” will return to the Setup Utility.
Exit Without Saving (Y/N)? Y
Time , Date , Hard Disk Type ...
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /63Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /63
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /63
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /63Chapter 2 BIOS Setup /63
Page 64

Date : / /
Warranty Card/Technical Fault Report
M/B Model No.: Vender
Serial No. :
Date of Purchase:
Hardware Configuration Used :
CPU
RAM (Brand,MB)
Video Card
Hard Drive
Other Card
Diagnostic Software Used :
Fault Description :
Page 65

The 6M815E Mainboard Layout
USB1
FAN 1
COM1
Printer
VGA
JACK1
JACK2
JACK3
GAME1
FAN2
I/O CHIP
CNR SLOT
CHASS1
PANEL1 Connector
IDE
RSTSW
+
GRNLED
KBLOCK
+
EXTSMI
AGP SLOT
+
SPKR
Intel
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
PWLED
CMOS1
DIMM2
DIMM1
Intel
BIOS
FAN3
PBTN
+
1
2
+
1
PAN EL 1
FWH2
Page 66

6M815E
User's Manual Version 1.0
The information presented in this publication has been
carefully prepared to ensure reliability ; however, no
responsibility is assumed for inaccuracies.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
IBM, PC/AT, and PC/XT are trademarks of Interna-
tional Business Machines Corporation.
Socket370 is a trademark of Intel Corporation
AWARD is a registered trademark of Phoenix
Software Inc.
MS-DOS and WINDOWS NT are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Trademarks and/or registered trademarks are the
properties of their respective owners.
i
Page 67

Table of Contents
IntroductionIntroduction
Introduction
IntroductionIntroduction
1. Motherboard Description1. Motherboard Description
1. Motherboard Description
1. Motherboard Description1. Motherboard Description
1.1 Features
1.1.1 Hardware 2
1.1.2 Software 5
1.1.3 Attachments 5
1.2 Motherboard Installation
1.2.1 Layout of Motherboard 6
1.3 Motherboard Connectors
1.3.1 Front Panel Connectors(PANEL1) 8
1.3.2 Floppy Disk Connector(FDC1) 9
1.3.3 Hard Disk Connectors(IDE1/IDE2) 9
1.3.4 ATX 20-pin Power Connector(PW1) 10
1.3.5 Infrared Connector(IR1) 10
1.4 Back Panel Connectors
1.4.1 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard CONN. 11
1.4.2 USB Connectors 11
1.4.3 VGA Interface Connector(VGA) 11
1.5 Serial and Parallel Interface ports 13
1.6 CPU Installation
1.6.1 CPU Installation Product(Socket 370) 15
1.6.2 CPU Frequency Selection(JCLK1) 16
1.7 Jumper Setting
1.7.1 CPU Fan Connector(FAN1/2/3) 17
1.7.2 Wake-On-Modem Header(WOM1) 18
1.7.3 Wake-On-LAN Header(WOL1) 18
1.7.4 CMOS Function Select(CMOS1) 18
1.7.5 SPEAKER Selection(WATCH1) 19
1.7.6 SBLINK Connector 19
1.7.7 Chassic Intrusion Connector(CHASSIC1) 19
1.7.8 AC97 Serial data out(STRAP1) 19
ii
Page 68

Table of Contents
1.8 DRAM Installation
1.8.1 DIMM 20
1.8.2 How to install a DIMM Module 20
1.9 Audio Subsystem
1.9.1 CD-Audio-IN Connectors(CDIN1/CDIN2) 21
1.10 Smart Panel Onboard Connector
1.10.1 Second BIOS Connector(FWH2) 23
1.10.2 Parallel Port Connector(LPT2) 23
1.10.3 GPIO Port Connector(JGP1) 23
2. BIOS Setup2. BIOS Setup
2. BIOS Setup
2. BIOS Setup2. BIOS Setup
2.1 Main Menu 27
2.2 Standard CMOS Features 30
2.3 Advanced BIOS Features 33
2.4 Advanced Chipset Features 37
2.5 Integrated Peripherals 40
2.6 Power Management Setup 46
2.7 PnP/PCI Configurations 51
2.8 PC Health Status 55
2.9 Frequency/Voltage Control 57
2.10 Load Fail-Safe Defaults 58
2.11 Load Optimized Defaults 59
2.12 Set Supervisor/user Password 60
2.13 Save & Exit Setup 62
2.14 Exit Without Saving 63
(option)(option)
(option)
(option)(option)
iii
 Loading...
Loading...