Page 1

CRT Monitor
Service Guide
Diamond View Model
1995SL
November 2000
Distributed by
Mitsubishi Electric Australia Pty. Ltd.
A.B.N. 58 001 215 792
348 Victoria Road
RYDALMERE NSW 2116
Australia
Telephone 1300 651 808
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright ã 1996 by the Company. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language or
computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical,
chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the Company.
Disclaimer
The Company makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to
the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any
particular purpose. Further, the Company reserves the right to reserve this publication and to make
changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation of the Company to notify any
person of such revision or changes.
ii
Page 3

Section
Diamond View CRT Monitor
1995SL
Manual Contents
1. Engineering Specifications
2. Circuit Operation Theory
3. Alignment procedure
4. Trouble Shooting
5. Parts List
6. Schematic Diagrams
7. Assembly
iii
Page 4

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Table of Contents
0. Introduction :.....................................................................................................................................3
1. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................3
1.1 Power Supply.......................................................................................................................3
1.2 Signal Interface....................................................................................................................3
1.3 Scan Range.........................................................................................................................4
1.4 Video Performance..............................................................................................................4
1.5 Timings ................................................................................................................................4
2.ENVIRONMENT & RELIABILITY ......................................................................................................5
3.CRT CHARACTERISTICS ................................................................................................................5
4.FRONT OF SCREEN ........................................................................................................................6
4.1 Geometry.............................................................................................................................6
4.2 Sharpness Crispness...........................................................................................................6
4.3 Light Quality.........................................................................................................................6
4.4 Image Stability .....................................................................................................................7
5. USER CONTROLS...........................................................................................................................8
5.1 Basic....................................................................................................................................8
5.2 Advanced.............................................................................................................................8
6. MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS...............................................................................................8
6.1 Dimension............................................................................................................................8
6.2 Weight..................................................................................................................................9
6.3 Plastic ..................................................................................................................................9
6.4 Carton..................................................................................................................................9
7. Pallet & Shipment.............................................................................................................................10
7.1 Dimension............................................................................................................................10
7.2 Shipping Container ..............................................................................................................10
7.3 Air Transport Container .......................................................................................................11
8. CERTIFICATION..............................................................................................................................11
9. Appendix...........................................................................................................................................12
Table 1 - DDC Table..................................................................................................................12
Table 2 - CRT Blemish & Scratch Spec ....................................................................................21
Table 3 - OSD Menu..................................................................................................................21
Table 4- Geometry Fig...............................................................................................................22
Fig.1 Linearity Measurements
Fig.2 General Pincushion Measurements
Fig.3 Trapezoid Measurements
................................................................................22
................................................................23
.................................................................................24
1
Page 5

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Fig.4 Picture Distortion & Phase Measurements
Fig.5 TCO 99 Pincushion Measurements
Fig.6 TCO 99 Barreling Measurements
Table 5 - TCO 99 Spec..............................................................................................................28
A. Ecology
B. CRT Display
.....................................................................................................................28
.............................................................................................................29
................................................................26
...................................................................27
.................................................25
2
Page 6
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
0. Introduction :
The subject model is designed for a value line 19” color monitor. It has the following figures :
0.26mm dot pitch , short length CRT, 176MHz video bandwidth ,1600X1200 max resolution.
Low radiation TCO99 standard,
ISO 14000 certificated green design. (Refer Table 5)
Optional items : E2000 USB.
1. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1.1 Power Supply
Voltage Universal input full range 90~264VAC /47~63Hz
Input Current 90 ~ 264VAC 4.0 Arms
Power consumption On < 120 W max
DPMS Standby < 15 W
Suspend < 5W
Off < 5 W
Inrush Current 220VAC/50Hz 50 Amp peak
Leakage Current 264 VAC/50Hz < 3.5mA
Hi-Pot 1. 1500VAC, 100mA, 1
sec
2. Ground test : 30A,
1sec
Power cord Length : 1800 mm Color : Flint Gray
1.2 Signal Interface
Pin assignment 5V on Pin 9
Condition Spec
w/o damage
< 0.1 ohm
Condition
Spec
OK
N.A
9
9
9
LED : Green
9
LED : Amber
9
LED : Amber Blink
9
LED : Amber Blink
9
Cold start
9
9
(in-line test)
9
KC-003
OK
N.A
9
Remark
(in-lab test)
Remark
Video input Level / Impedance 700mV / 75 Ohm
Sync input Level TTL-Positive/Negative
Impedance 50 Ohm on H-sync cable 9
Signal Cable D-Sub 1.5mm +/- 20mm
BNC
Color Flint Gray
9
9
9
9
9
0.7μs<H-sync width<25%
of H period 2s<V-sync
width< 400μs
3
Page 7
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
1.3 Scan Range
Horizontal 30 ~ 95 KHz
Vertical 50~ 160 Hz
1.4 Video Performance
Dot Rate 176 MHz
Max. Resolution 1600 x 1200
Rise time/Fall time 6ns
Video Ringing 10% max
Sag 5% max
Bandwidth -3db 176 MHz
DDC Version DDC1/2B
EDID Ver 1 ,Rev 2
1.5 Timings
Preset mode No. : 9 User mode No. : 20
Condition Spec
Spec
OK
N.A
9
9
OK: Positive performance
N. A.
: Not applicable for this set
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
see table 1
9
Remark
Remark
Preset
VGA400 640x400 31.47KHz/70Hz
VGA480 640x480 31.47KHz/59.94Hz
6448A 640X480 37.5KHz/75Hz
6448B 640X480 43.269KHz/85Hz
SVGA4 800x600 46.88KHz/75Hz
SVGA3 800x600 48.09KHz/72.01Hz
SVGA5 800x600 53.67KHz/85Hz
Apple 16”
UVGA2 1024x768 56.476KHz/70.069Hz
UVGA7 1024x768 60.023KHz/75.029Hz
Super MAC 19 1024x768 60.24KHz/75Hz 9
UVGA8 1024x768 68.68KHz/85Hz
WS2 1280x1024 64.317KHz/60.392Hz
WS7 1280x1024 79.98KHz/75Hz
WS8 1280x1024 91.15KHz/85Hz
Resolution Fh (KHz) / Fv (Hz)
832x624 49.71KHz/74.533Hz
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
Sync polarity H/V
-/+
-/-
+/+
+/+
+/+
+/+
+/+
+/+
VESA1600 1600x1200 93.75KHz/75Hz
VESA 1600X1200 81.25KHz/65Hz
9
9
+/+
4
Page 8

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
2.ENVIRONMENT & RELIABILITY
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Condition Spec
Operation Temp./Humidity
Non- Operation Temp./Humi.
Altitude Operating condition 0~3048m (10,000ft)
Non-operating condition 0~12,192m (40,000ft)
Vibration Package, Non-Operating 5~26.6Hz/0.6G
50~500 Hz/1.5G
Un-package, Non-
Operating
Drop (With packing) PKG. 18.2~27.2 Kg Drop Height 61 cm
Electrostatic Discharge
Acoustical Noise < 40 dB/A
Power Line Transient
IEC801-2 standard Contact:8KV, Air:15KV
IEC801-4,IEC1000-4-4 Coupling clamp 0 ~ 4KV
IEC1000-4-5 (Surge)
IEC1000-4-12 (100KHz
+5 ~ +40℃/ 20~90% R.H.
-20~ +60℃/ 10~90% R.H.
5~100/0.015g2/Hz
Common:2KV,Differential:1KV
Common:3KV,Differential:1KV
OK
N.A
9
Non-condensing
9
Non-condensing
9
Without packing
9
With packing
9
26.6~50Hz/1.5G
9
9
100~200/-6db/oct
9
9
9
9
9
9
Remark
200~0.038g2/Hz
0.5~8KV tip table no
blanking
ringwave)
MTBF Demonstration 90% confidence level > 200,000 Hrs
MTBF Prediction
MIL-217F
> 40,000 Hrs
CRT Life 78% degradation > 10000 Hrs
9
Excluding the CRT
9
9
3.CRT CHARACTERISTICS
Spec
CRT Vender Philips Shadow mask
Technology FST
Coating Anti-glare/Anti-
OK
N.A
9
9
9
static/Anti-reflection
Dot pitch 0. 26m m
Phosphor P22
Light transmittance 52.3%
Viewable size >18”
Deflection angle 95 deg
9
9
9
9
9
Remark
Blemishes and scratches
1 trio missing,as approval
see table 2
5
Page 9
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
4.FRONT OF SCREEN
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
sheet
4.1 Geometry
Magnetic Environment Northern Hemisphere H = 0 + 0.05
V = +0.45 +
0.05
Southern Hemisphere H = 0 + 0.05
V = -0.45 +
0.05
Equatorial H = 0 + 0.05
V = 0 +
0.05
Size Hor. 360 + 4 mm
Ver. 270 + 4 mm
Centering Hor. & Ver. |A-B|,|C-D|< 4 mm
Geometric Distortion
Top/Bottom Barrel/pincushion
Side Barrel/pincushion
< 1.35 mm
1.8 mm
<
Hor./Ver. Trapezoid < 3.0mm
Tilt < 1.2 mm
Orthogonal < 2 mm
S-curve < 0.5 mm within 40mm
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
Remark
Linearity Hor. & Ver. < 5 %
4.2 Sharpness
Crispness
“
Focus
Mis-convergence Center < 0.15 mm
Moire Over 18Ft-L no visible moire
Swing not permitted
Reverse character(white
background and black
characters) /20 Ft-L at ful l-white
Jitter DIN 66234 T2 < 0.1mm
4.3 Light Quality
Condition Spec
White Balance Full white center
(Brit. cut-off & Cont.
max.)
Purity W,R,G,B
X max-X min & Y max-Y min
e,w,m” at cut-off and
1280*1024@85Hz
resolution
A <
0.3mm ,B< 0.4mm
x = 0.283 +
y = 0.297 +
0.010
0.010
< 0.015
9
(Xmax-Xmin)/( Xmax+Xmin)*100
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
OK
N.A
9
@ SVGA1280x1024
9
Remark
The distance of watch is
30cm from eyes t o screen
”
”
Remark
79.98KHz75Hz
“
6
Page 10
MEA 1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Color Tracking
Max Brightness with ABL
Max Brightness no ABL
Brightness Uniformit y
Brightness cut off
Full white pattern
3” Block
Full white pattern
Raster light O/P Bright./Cont. Max. 0.5 ~ 1.5Ft-L
Contrast ratio Max/Min 5:1
4.4 Image Stability
H/V regulation < 1 mm per side at cut-
x, y (nominal) + 0.015
30Ft-L(Cut-off)
40Ft-L (Cut-off )
70% (center to corner)
>
9
9
9
9
9
9
OK
N.A
9
Remark
“
“
“
“
“
“
off
Flicker No flicker
Ringing
No visible DY Hor. Video ringing
9
9
7
Page 11
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
5. USER CONTROLS
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
5.1 Basic
Power Switch
Contrast
Brightness
H Size
H Position
V Size
V Position
Barrel/Pincushion
Parallelogram
Trapezoid
5.2 Advanced
OSD position
Color Gain
Corner
Function Spec
Function Spec
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
OK
N.A
9
See Table 3
9
9
Remark
Remark
Pin-balance
Tilt
Color Temp. C1~C5
9300K,6500K,5500K,7100K,1150
0K
Manual Degauss
Recall
Languages 5 languages
Mis-Convergence adj.
Moire adj.
D-sub/BNC switch
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
6. MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS
6.1 Dimension
Spec
Bezel opening 324x 243 mm
Monitor w/o Stand W x H x D mm 455x 406.5 x 416 mm
OK
N.A
9
9
Remark
Monitor w Stand W x H x D mm 455x 476.5 x 416 mm
9
8
Page 12
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Carton Box W x H x D mm 575 x 522 x 536 mm
Tilt and Swivel range Tilt : -5/+15 deg r ee
9
9
Swivel:- 45/ +45 degrees
6.2 Weight
Spec
Monitor (Net) 19 Kg
Monitor w
23 Kg
OK
N.A
9
9
Remark
packaging(Gross)
6.3 Plastic
Flammability UL 94-5V
Heat deflection To
UV stability
Resin PC+ABS
Texture RE-6625
Color Light Gray
6.4 Carton
Spec
75 ℃mini
Delta E<1.5 after 300Hr Xted
test
Spec
OK
N.A
9
9
9
9
9
9
OK
N.A
Remark
Remark
Color Kraft
Material A B Flute
Compression strength 610 KGF
Burst Strength 23 KGF/cm 2
Stacked quantity 5 Layers(max)
9
9
9
9
9
9
Page 13
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
7. Pallet & Shipment
7.1 Dimension
Transport Type Pallet A Pallet B Pallet C
Shipping Pallet Length 1150
Dimension(mm) Width 1072
Height 130
Air Transport Pallet Length 1072
Dimension(mm) Width 1150
Height 130
x
x
x
x
x
x
X
X
X
X
X
X
7.2 Shipping Container
Stowing Type Quantity of
products (sets)
(Every container) (Every Pallet) (Every Container)
20' 160 Pallet A: 16 Pallet A: 10
With pallet 40' 352 Pallet A: 16 Pallet A: 22
Quantity of Products
(sets)
Pallet B:
x Pallet B: x
Quantity of pallet
(sets)
Pallet B: X Pallet B: X
20' 160 X X
X X
Without pallet 40' 352 X X
X X
10
Page 14
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
7.3 Air Transport Container
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Container Type Quantity of products
(sets)
(Every container)
Container
3048 * 2286 * 2438
Pallet B: 8 Pallet B: 2
80
Quantity of Products
(sets)
(Every Pallet)
Pallet A: 16 Pallet A: 4
Quantity of pallet
(sets)
(Every Container)
8. CERTIFICATION
Condition Spec
Environment Green design Doc. 715-C49
OK
N.A
9
ISO14000
Remark
Requirement
Blue Angel German Standard
E-2000 Switzerland
NUTEK Swedish Standard
EPA USA Standard
EN61000-3-2
9
9
Option
9
9
9
Harmonics
TCO92/95
TCO99
PC-Monitor Microsoft Windows PC98/99
DPMS VESA
DDC 1/2B Version 3.0
USB Internal
Safety UL (USA) UL 1950 3rd edition
CSA (Canada) C22.2 No. 950-M95
DNSF EN60950
IEC950 +A1+A2+A3+A4
9
9
9
9
9
9
Option
9
9
9
9
EN60950 +A1+A2+A3+A4
9
11
Page 15

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
73/23/EEC
CB (Nordics)
TUV/GS EN60950
CCIB (China)
EIAJ/JEIDA (Japan)
NOM (Mexico)
IAA (Korea)
EMC CE Mark 89/336/EEC
FCC (USA) Class B
EN55022 Class B
CISPR 22 Class B
VCCI (Japan) Class B
BCIQ (Taiwan)
C-Tick (Australia) AS3548
RRL (Korean)
X- Ray Requirement DHHS (21 CFR) USA X- Ray Standard
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
DNHW
PTB German X- Ray standard
MPRII
MPRIII
Ergonomics ZH1/618 German ergonomic
ISO 9241-3 -7 & 8
9
9
9
9
9
9
9. Appendix
Table 1 - DDC Table
DDC1/2B Table
Address Data Description
00 00
01 FF
02 FF
12
Page 16
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
03 FF Header
04 FF
05 FF
06 FF
07 00
08 06 ID Manufacturer Name = MEA
09 09
0A 03 ID Product Code = 1995SL
0B 99 (Vender Assigned code)
0C 00 ID Serial Number
0D 00
0E 00
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
0F 00
10 * Week of Manufacture (0-53),use 0 if n/a
11 * Year of Manufacture (year - 1990)
12 01 EDID version
13 03 Revision
14 6C Video Input Define
15 24 Max. H. Image Size 360 (cm)
16 1B Max. V. Image Size 270 (cm)
17 A9 (gamma*100) - 100 , gamma = 2.75 (Data in Note 3)
18 EA DPMS
19 2C Red Green Bits Rx1Rx0Rxy1Ry0Gx1Gx0Gy1Gy0
1A 24 Blue White Bits Bx1Bx0By1By0Wx1Wx0Wy1Wy0
1B A0 Red x bit9-2
1C 56 Red y bit9-2 (Data in Note 3)
1D 47 Green x bit9-2
1E 9A Green y bits9-2
1F 26 Blue x bit9-2
20 12 Blue y bit9-2
21 48 White x bit9-2
22 4C White y bit9-2
Address Data Description
23 AF Established Timing I
13
Page 17
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
24 CF Established Timing II
25 00 Established Timing III
26 A9 Standard Timing Identification
27 45 #1 1600x1200 / 65Hz
28 45 #2 800x600 / 85Hz
29 59
2A 61 #3 1024x768 / 85Hz
2B 59
2C 01
2D 01
2E 01
2F 01
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
30 01 #6
31 01
32 01 #7
33 01
34 01 #8
35 01
36 86 Detailed Timing Description # 1
37 3D WS8 1280x1024 91.15k/85Hz
38 00
39 C0
3A 51
3B 00
3C 30
3D 40
3E 40
3F A0
40 13
41 00
42 68
43 0E
44 11
45 00
14
Page 18
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
46 00
47 00
Address Data Description
48 00 Detailed Timing Description # 2
49 00
4A 00
4B FC Monitor Name
4C 00 MEA 1995SL
4D 41
4E 43
4F 45
50 52
51 20
52 47 G
53 39 9
54 39 9
55 31 1
56 0A
57 20
58 20
59 20
5A 00 Detailed Timing Description # 3
5B 00
5C 00
5D FD Range Limit: Vertical refresh rate 50Hz~160Hz
5E 00 Horizontal frequency 30KHz~95KHz
5F 32
60 A0
61 1E
62 5F
63 11
64 00
65 0A
66 20
15
Page 19
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
67 20
68 20
69 20
6A 20
6B 20
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
16
Page 20
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Address Data Description
6C 00 Detailed Timing Description # 4
6D 00
6E 00
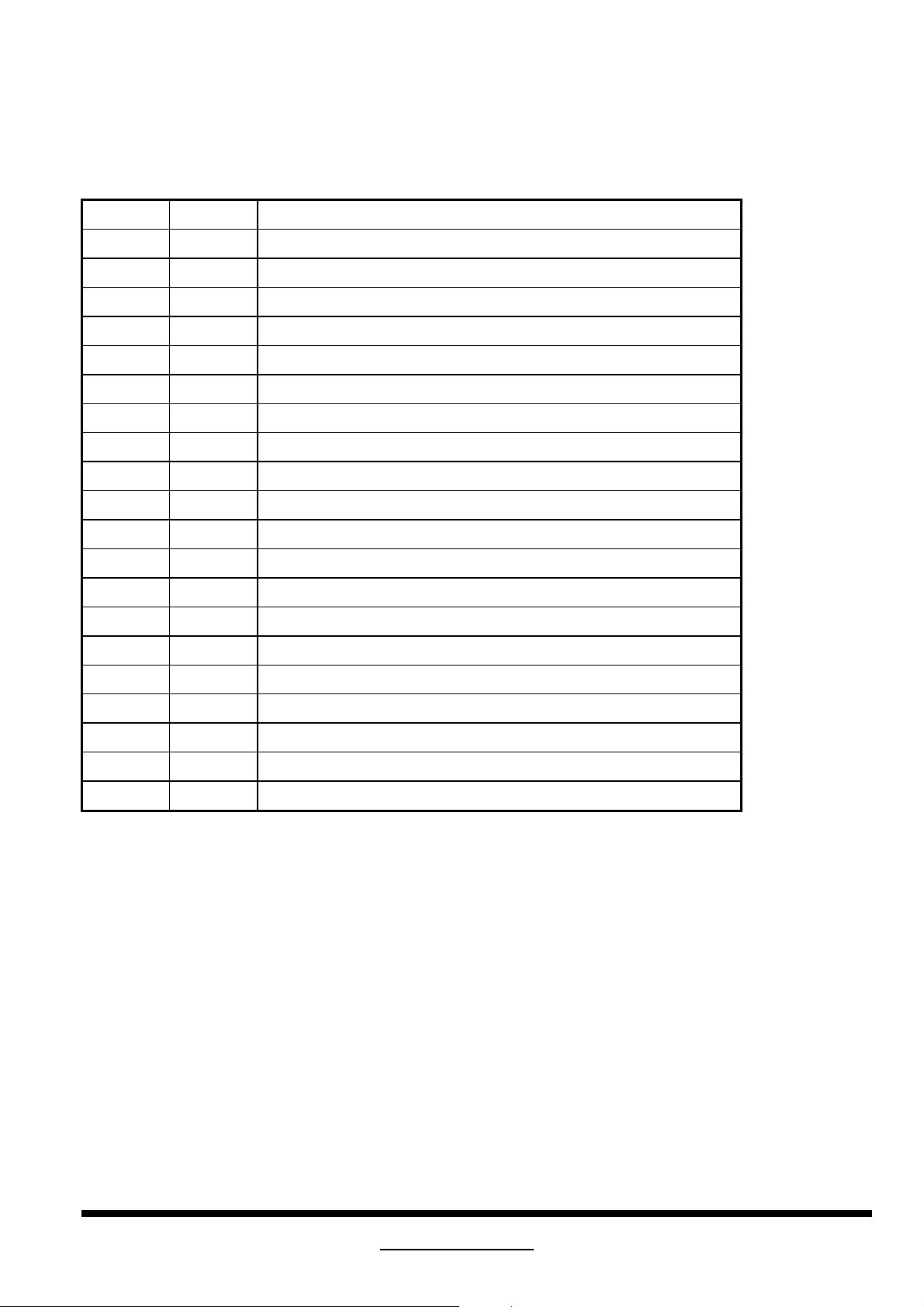
6F FF Serial number.
70 00 PS: Example :
71 32 Monitor serial number in description from 71 to 75 is 23456
72 33 ASCII data string in descriptor until 0A end.
73 34 20 is mean Null string.
74 35
75 36
76 0A
77 20
78 20
79 20
7A 20
7B 20
7C 20
7D 20
7E 00 Extension Flag
7F * Check sum
Serial number format : MEA
Bar code ID of model name : 7C
17
Page 21
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Note 1
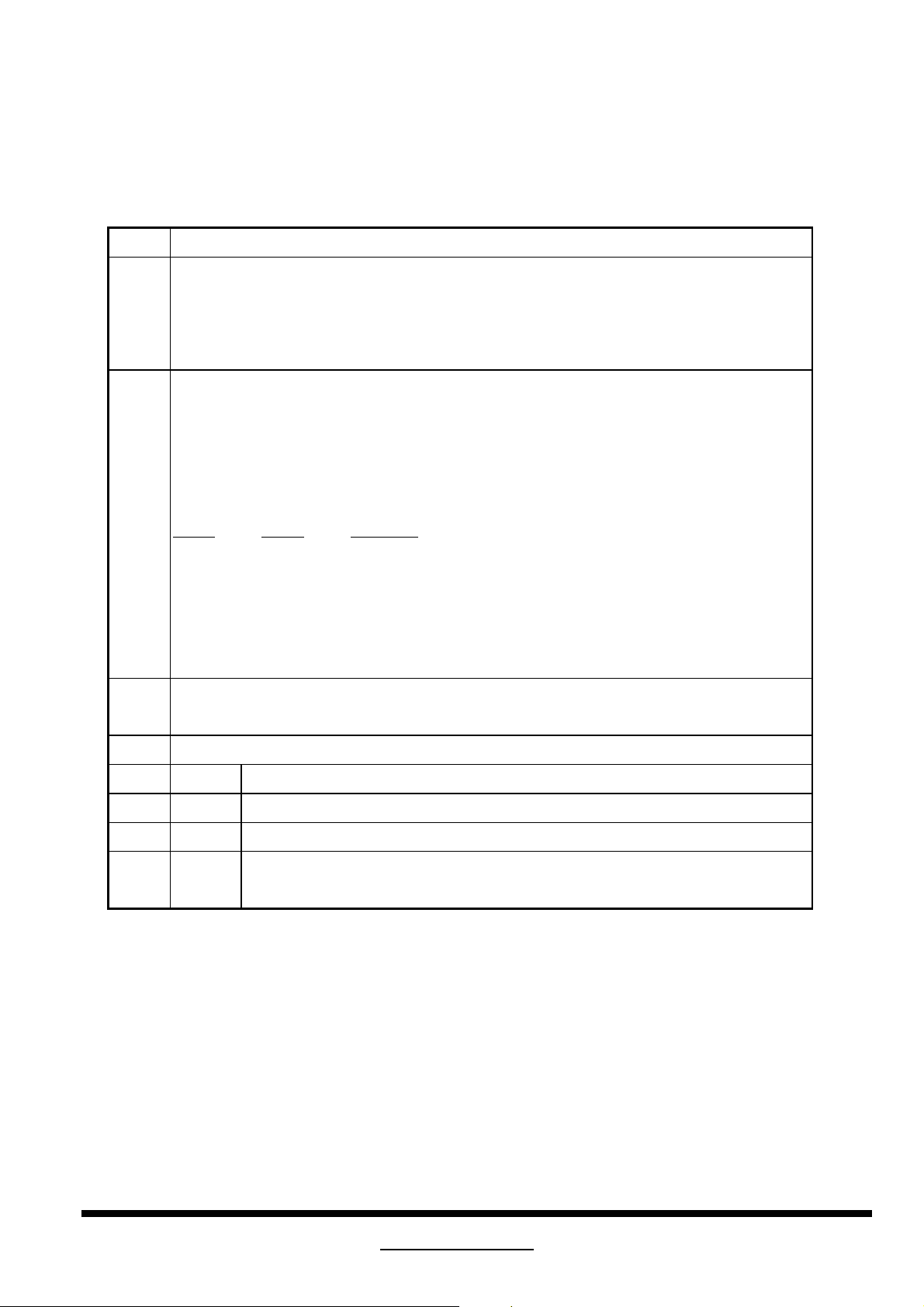
Bit Description
7 Analog / Digital Input : Defines usage of the rest if the byte as "analog input" or digital
input". Analog=0, Digital=1 . If input is described as analog, the following definitions apply to
bits 6-0.
6:5 Signal Level Standard (6:5) : Refer to the following bit definitions. Identified by the level of
reference white volts above blank, followed by the level of the sync tips in volts below
blank.
Bit 6
Bit 5 Operation
0 0 0.700V/0.300V (1.000V p-p)
0 1 0.714V/0.286V (1.000V p-p)
1 0 1.000V/0.400V (1.400V p-p)
1 1 0.700V/0.000V (0.700V P-P)
4 Setup: If set, the display is set to expect a blank-to-black setup or pedestal per the
appropriate signal level standard.
3:0 Sync Inputs (See Bit Operation below)
3 Separate Sync
2 Composite Sync (on H Sync line)
1 Sync on Green Video
0 Serration of the V.Sync Pulse is required when composite sync or sync-on-
green video is used
18
Page 22
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
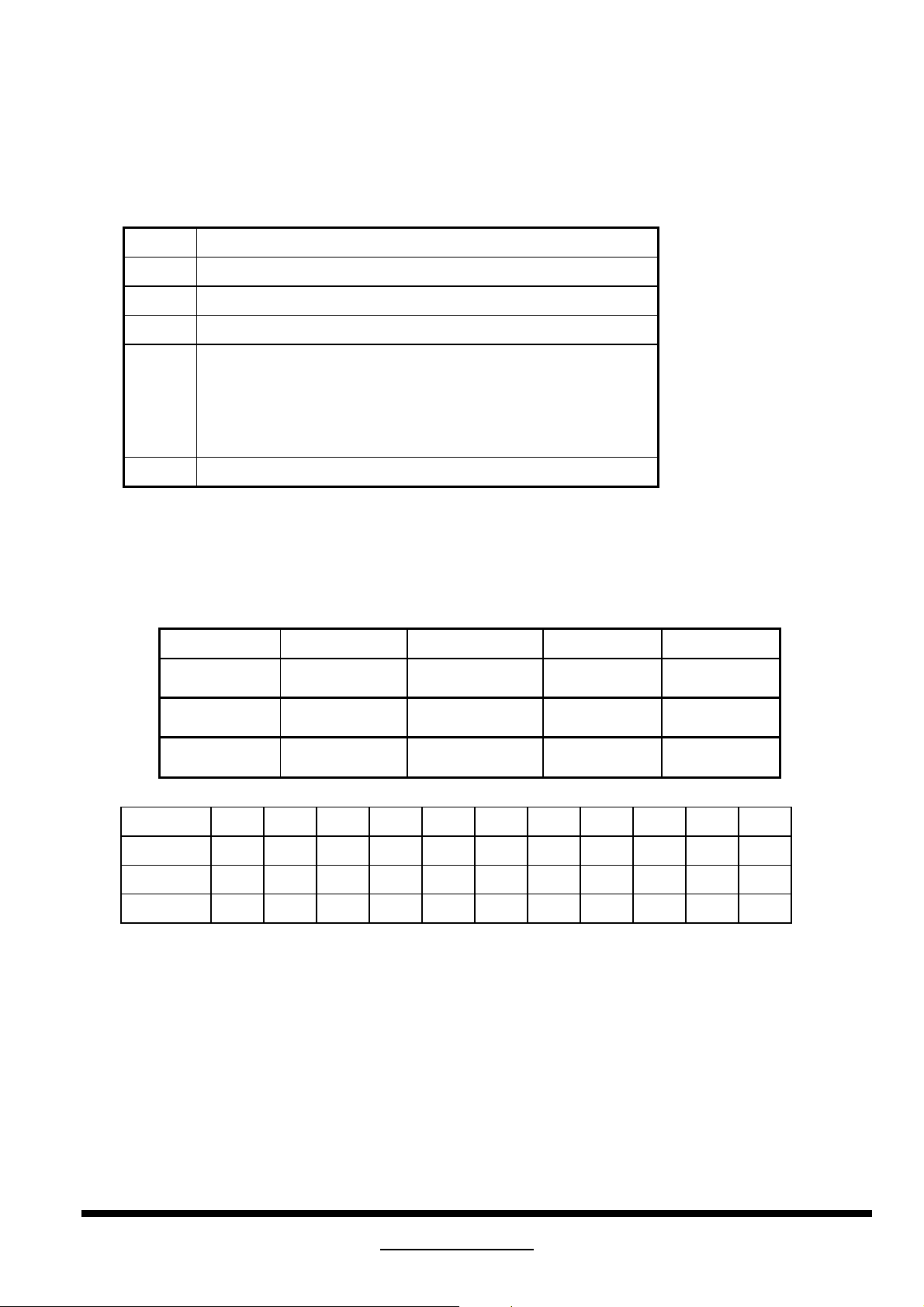
Note 2
Bit 7 Stand-by
Bit 6 Suspend
Bit 5 Active off
Bit 4-3 Display Type
0,0 - Monochrome/gray scale display
0,1 - RGB color display
1,0 - Non-RGB multicolor display (example:RGY)
1,1 - Undefined.
Bit 2-0 Reserved. Set at 00h until defined.
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Note 3
CRT Vender Red (x/y) Green (x/y) Blue (x/y) Gamma
Philip 0.615/0.350 0..290/0.610 0.155/0.065 2.75
Hitachi 0.625/0.333 0.285/0.605 0.150/0.065 2.76
Matsushita 0.535/0.350 0.285/0.605 0.152/0.068 2.90
CRT vender 17 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F 20 21 22
Philips AF 64 A4 9D 59 4A 9C 27 10 48 4C
Hitachi B0 0F 64 A0 57 48 9A 26 10 48 4C
Matsushita BE DF D4 88 55 48 9A 26 11 48 4C
19
Page 23
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
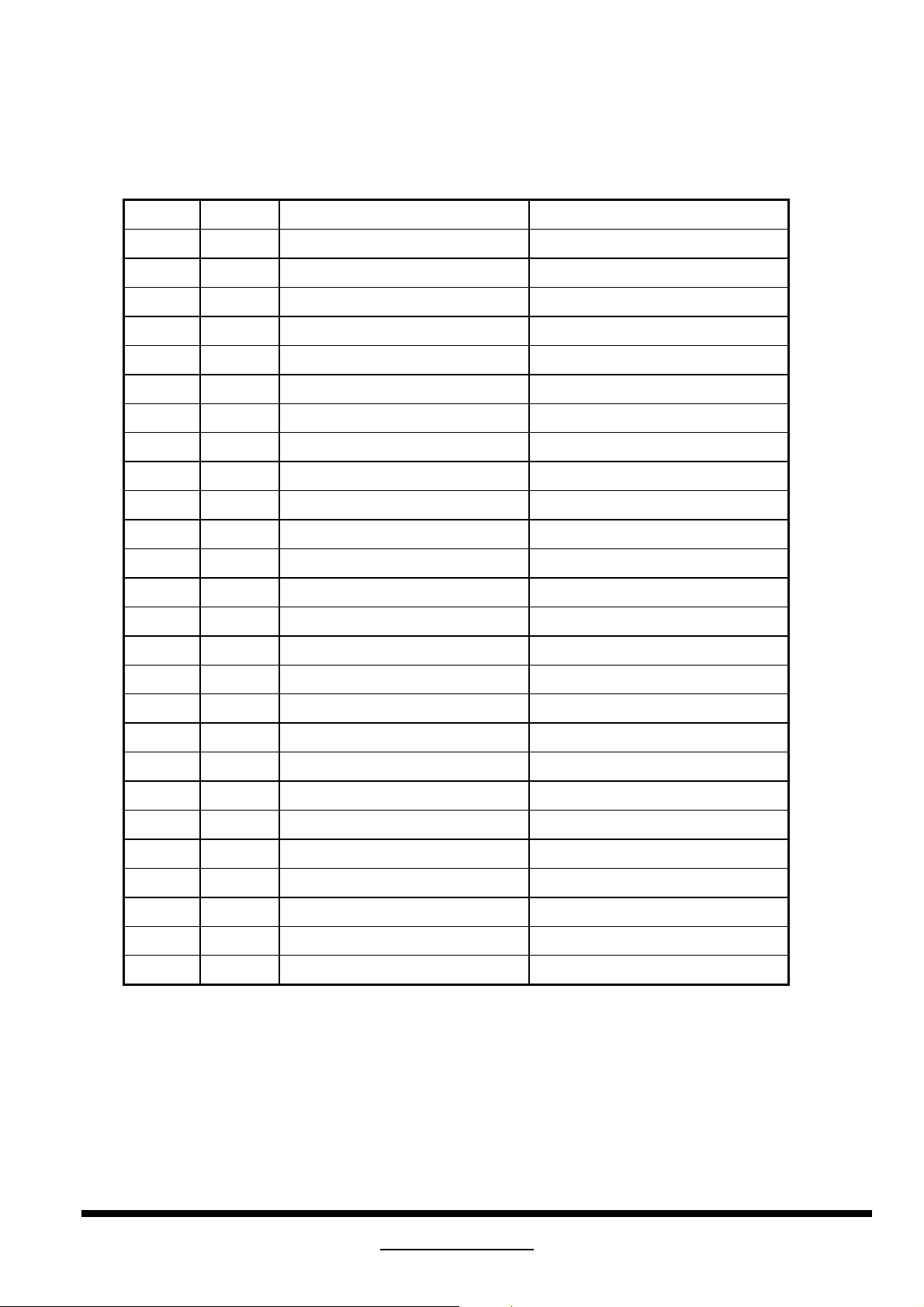
Note 4
Byte 1 bit Established Timings 1 Source
7 640*400 @ 70Hz (720x400) (VGA, MEA)
6 720*400 @ 88Hz (XGA2, MEA)
5 640*480 @ 60Hz (VGA, MEA)
4 640*480 @ 67Hz (Mac II, Apple)
3 640*480 @ 72Hz (VESA)
2 640*480 @ 75Hz (VESA)
1 800*600 @ 56Hz (VESA)
0 800*600 @ 60Hz (VESA)
Byte 2 bit Established Timings II
7 800*600 @ 72Hz (VESA)
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
6 800*600 @ 75Hz (VESA)
5 832*624 @ 75Hz (Mac II, Apple)
4 1024*768 @ 87Hz (interlaced) (MEA)
3 1024*768 @ 60Hz (VESA)
2 1024*768 @ 70Hz (VESA)
1 1024*768 @ 75HZ (VESA)
0 1280*1024 @ 75HZ (VESA)
Byte 3 bit Manufacturer's Timings Manufacturer's Specified Timing
7 1152*870 @ 75Hz (Mac II, Apple)
6 Reserved
5 Reserved
4 Reserved
3 Reserved
2 Reserved
1 Reserved
0 Reserved
20
Page 24
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Table 2 - CRT Blemish & Scratch Spec
The following criteria is applied to high-contrast blemishes.
Blemishes
Zone A Zone B
A 1 trio 0 1 1 --- --B (1) 0 0 0 --- ---
C (2) 1 2 2 --- 50
(3) 1 2 2 --- 20
D 1 dot
Red 5 4
Blue 5 4
(1) 3 or more consecutive same color phosphor dots.
(2) 2 consecutive same color phosphor dots.
(3) 2 consecutive different color phosphor dots.
Green 4 2
Allowable No. of Blemishes Allowable
Minimum
Separation
Zone
A
Zone
B
Total
(Zones A & B )
10
50
20
Table 3 - OSD Menu
Please refer to Release 001-C01
21
Page 25
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
X5
Table 4- Geometry Fig.
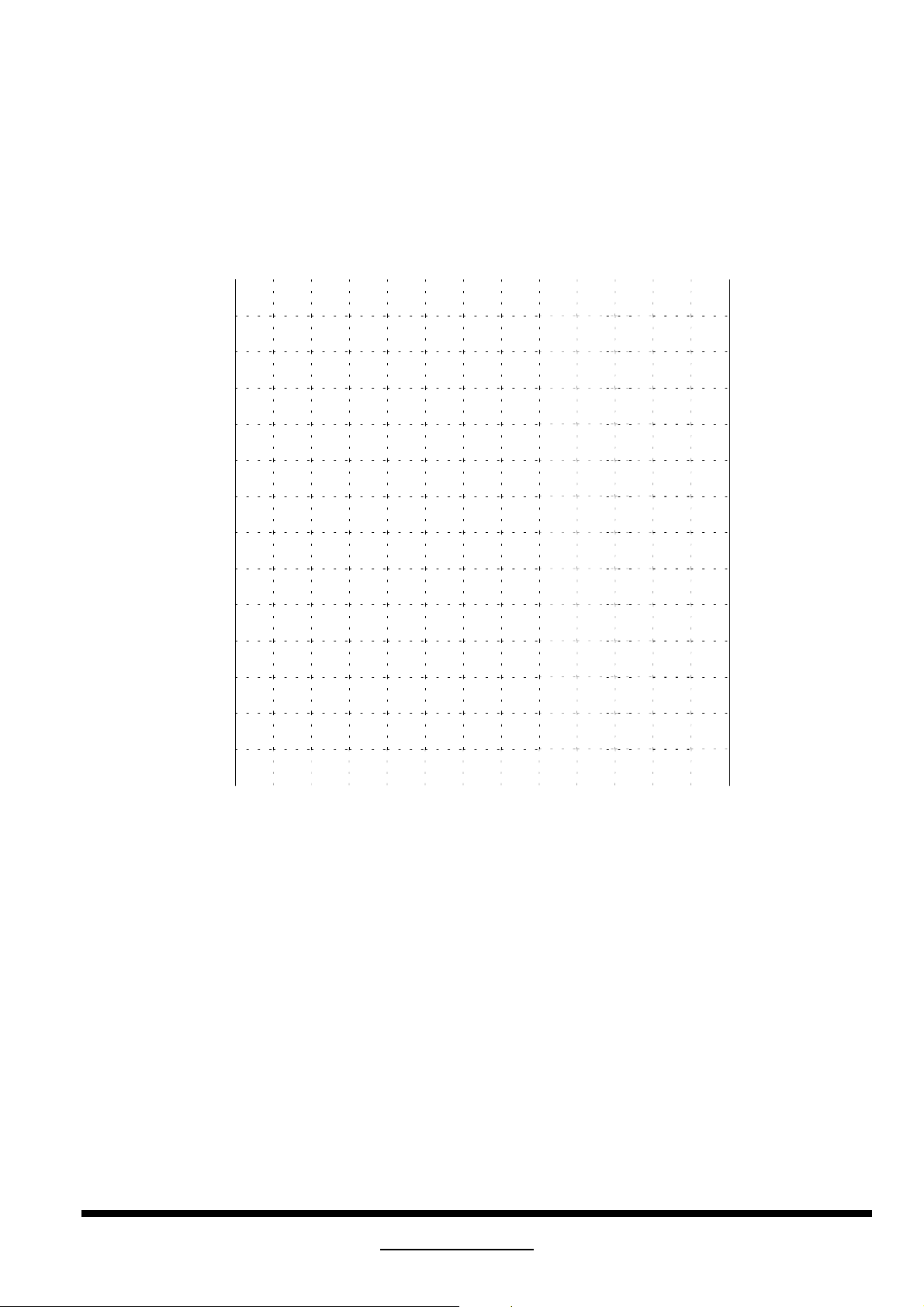
Fig.1 Linearity Measurements
X1 X2 X3 X4 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10X11 ~ X18
Y0
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y1
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y2
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y3
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y4
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y5
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y6
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y7
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y8
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y9
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y10
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y11
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y12
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
Y13
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Xmax - Xmin
------------------- X 100% < 5%
Xmax + Xmin
Ymax - Ymin
------------------- X 100% < 5%
Ymax + Ymin
22
Page 26
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Q
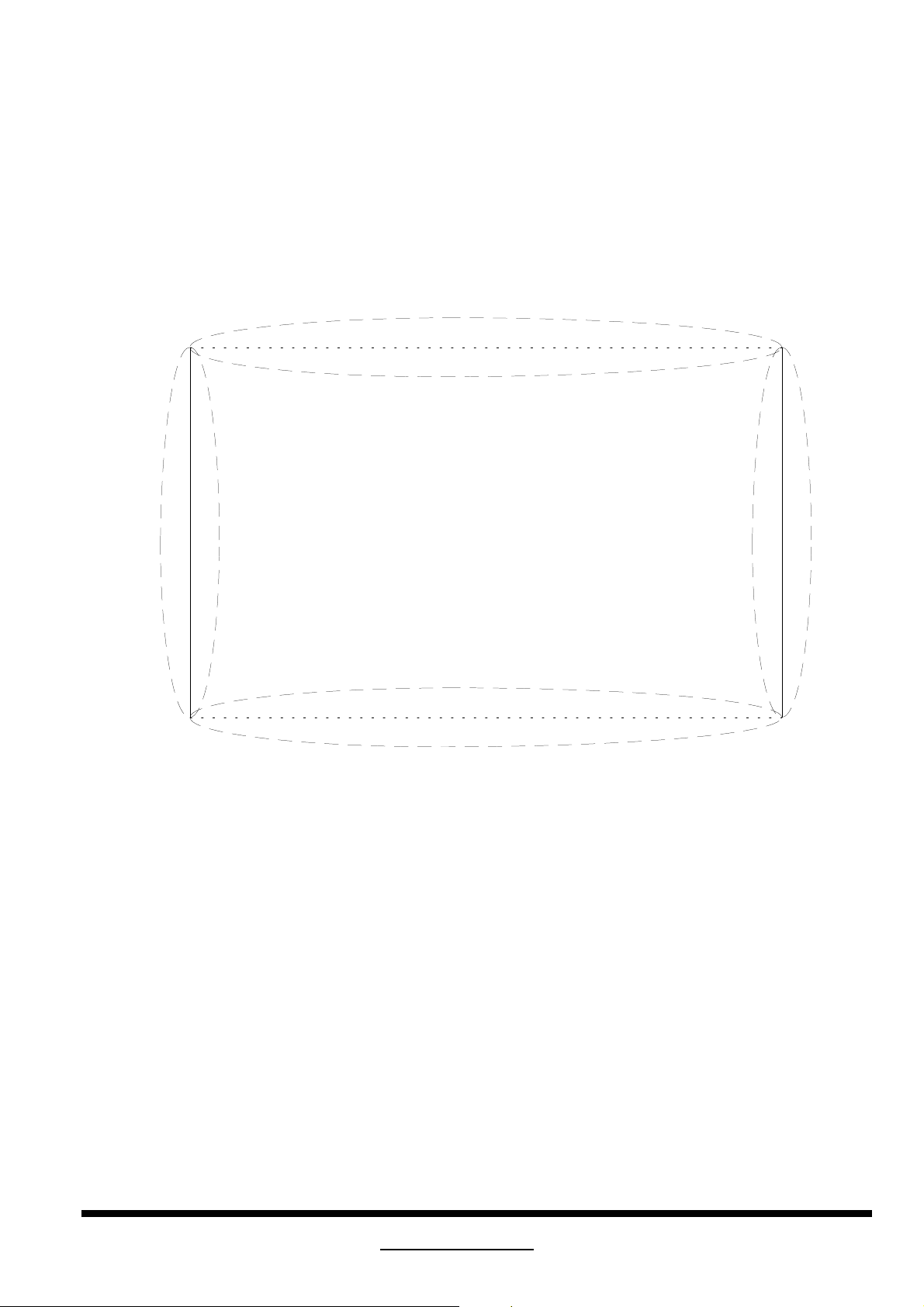
Fig.2 General Pincushion Measurements
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Amm
a1
P
Bmm b1
a2
S
b2
R
A, B represented as display area width and height
Top/Bottom Pincushion = (a1 or a2)
Side Pincushion = (b1 or b2)
Substituted A by (PS + QR)/2
B by (PQ + RS )/2
23
Page 27
1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
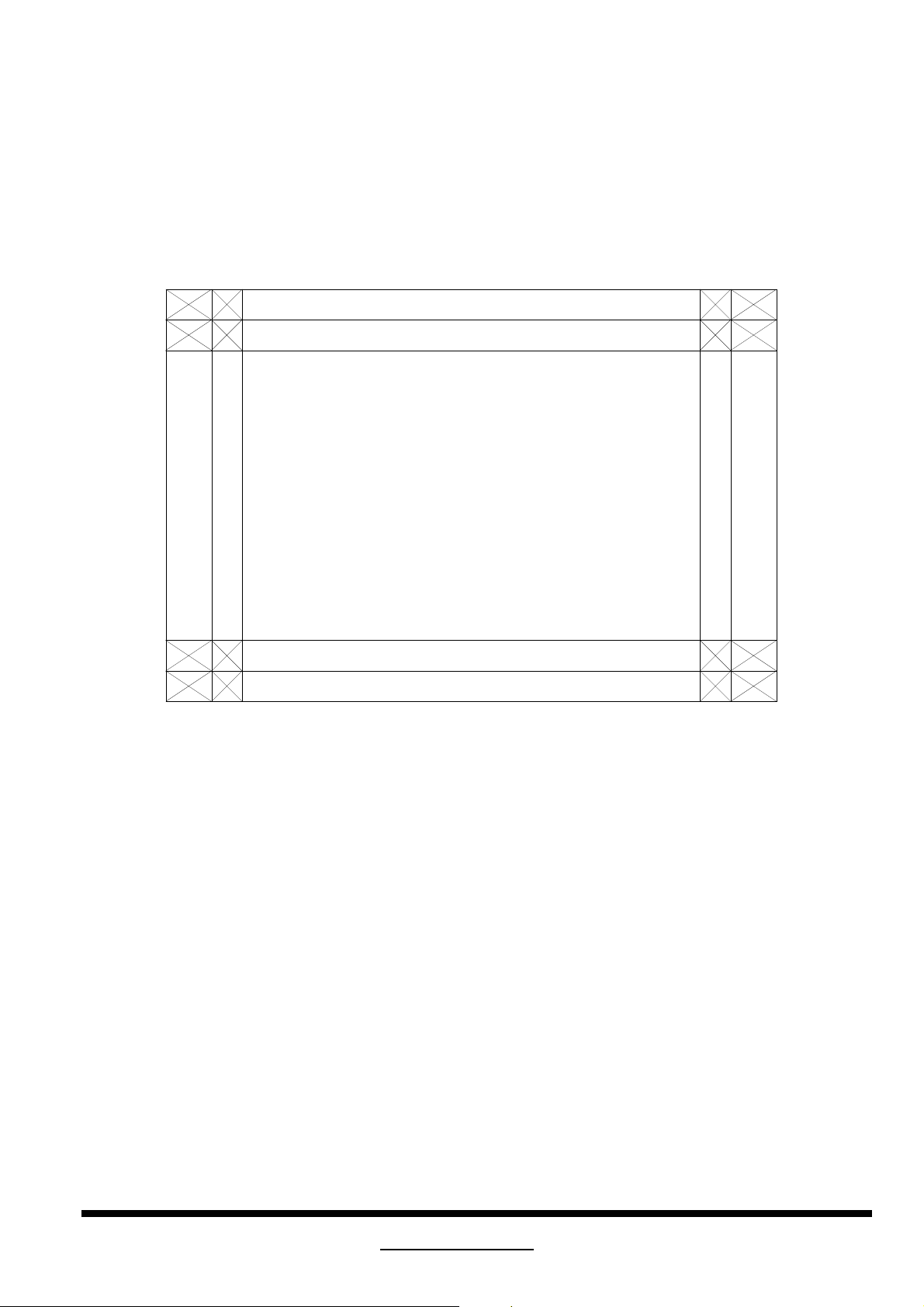
Fig.3 Trapezoid Measurements
2.5
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
2.5
2.5
A
B
2.5
2.5
D
C
2.5
2.5
2.5
* Each of the 4 corners of picture shall fall within the relevant area (F) illustrated up (hatched)
* ABCD is the picture outlines.
24
Page 28

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Fig.4 Picture Distortion & Phase Measurements
H1
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
A
V1
a1
orthogoal
D1
C D
b2
b1
D2
Tilt
a2
B
PeakTotal
H2
V2
]21|
HH
+−HH
02.0
≤
)21(5.0
]21|
VV
+−VV
02.0
≤
)21(5.0
]21|
DD
+−DD
03.0
≤
)21(5.0
25
Page 29

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
G
Fig.5 TCO 99 Pincushion Measurements
AC
x
x1
∆
∆
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
y1
B
y
∆
x2
Æ Linearity (TCO99) = x1/x or y1/y
Æ
[AC+EG]/2, [AG+CE]/2 represented as display area width and height
Æ
Top/Bottom Pincushion = y1 or y2
Æ
Side Pincushion = x1 or x2
∆
y2
E
26
Page 30

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Fig.6 TCO 99 Barreling Measurements
AC
x1
∆
x
∆
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
y1
y
∆
x2
∆
y2
[AC+EG]/2, [AG+CE]/2 represented as display area width and height
Top/Bottom Pincushion = y1 or y2
Side Pincushion = x1 or x2
Linearity (TCO99) = x1/x or y1/y
EG
27
Page 31

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
Table 5 - TCO 99 Spec
A. Ecology
1 General Criteria
1.1 Manufacturing Processes
1.1.1 Ozone Depleting Substances:
* PCB and any Process shall not use any ozone depleting substance
1.1.2 Chlorinated Solvent:
* PCB and any Process shall not use any Chlorinated Solvent substance
1.2 Environmental Hazards
1.2.1 Mercury and Cadmium in Electronic Components:
*
1.2.2 Flame Retardants in Plastic Components:
*
1.3 Preparation for Recycling:
1.3.1 Labelling of Plastic:
*
1.3.2 Variety of Plastic:
*
1.3.3 Painting of Plastic:
*
*
* All paints, lacquers, vanishes or colour additives used shall be declared by the type and mount.
1.3.4 Metallization of Plastic Housing:
*The plastic housing shall have neither internal nor external metallization.
None of electronic components
Plastic > 25g
Plastic > 25g
Plastic >100g
Plastic > 25g
Mould decoration
shall not contain retardants of organically bound
shall be labelled in accordance with
shall be made from the
shall not be having
(IMD) is not allowed
contain any mercury or cadmium.
ISO11469
same type of plastic material
paint weight >1% of plastic weight
.
.
Chloride or Bromide.
.
28
Page 32

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
B. CRT Display
Part 1: Visual Ergonomic - Legibility
1.3 Linearity: *
1.4 Orthogonality:
* H/V:
1.5.1: Display Luminance: *
1.5.2 Luminance Uniformity: *
1.5.3 Luminance Contrast: *
1.6 Front Frame Reflectance:
* Diffuse reflectance:
* Gloss
1.7.1: Color Temperature Variations:
* Δu'v': <+- 0.01 of White
* 9300
* 7500
* 6500
* 5000
* and actual measured
<= 1%
<= 2%,
<= 30%
o
8500-10250
K:
o
6980-8100
K:
o
6100-6950
K:
o
4700-5350
K:
, (See Fig.5 & Fig.6)
Diagonal:
>=100cd/m
< 1.5:1
> 3:1
> 20%
gloss unit
o
K
o
K
o
K
o
K
Pre-set of Lower CCT should not exceed Higher CCT
<= 3%
2
(80% Loading)
(test at 5% of corner and center)
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
CCT (oK) x,y u’v’
9300 0.283, 0.297 0.189, 0.446
7100 0.304, 0.320 0.195, 0.462
6500 0.313, 0.329 0.198, 0.496
5500 0.333, 0.348 0.204, 0.481
11500 0.272, 0.283 0.186, 0.435
1.7.2: Color Uniformity and Characteristics:
* Δu'v':
<= 0.01
(between any two point of display area (White Color))
Reference White Color Spec. in TCO’99
1976 CIE u’v’ from 1931 CIE x,y
u’= 4x/(-2x+12y+3) v’= 9y/(-2x+12y+3)
29
Page 33

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Part 2: External Alternate Magnetic Fields:
2.1: External Alternating Magnetic Fields: *
Part 3: Emission and Energy Saving
3.1 X-Ray : *
3.2 Electrostatic Potential: *
3.3 Electric Field (AC):
*
*
Note:
3.4 Magnetic Field (AC):
*
*
Note:
3.5 Energy Saving:
* 1st stage: <15W (recover time: 3 sec.)
2nd stage: <5W
* Single stage: <5W (recover time: <3 sec.)
* Monitor
(recover time < 3sec)
Part 4. Acoustic Noise:
4.1 Acoustic Noise (VDUs with fan):
*
*
< 0.5 mR/Hr
Band I < 10V/m (100cd/m
Band II< 1V/m (100cd/m
Shielded Power Cord is not acceptable
Band I < 200 nT (100cd/m
Band II< 25 nT (100cd/m
Shielded Power Cord is not acceptable
with USB Hub
Operating: < 5.5 B
Idle: < 4.8 B
(bels)
<+-0.5KV
: same as above or
(bels)
2,
, “+” Pattern)
2,
, “+” Pattern)
2,
, “+” Pattern)
2,
, “+” Pattern)
< 0.1 mm
(500 mm Viewing Distance; 80Hz, 200nT.)
single stage < 15W
Chapter 1 Engineering Specification
30
Page 34

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
Table of Contents
1995SL System Block Diagram.............................................................................................................3
Switching Power Supply Operation Theory...........................................................................................4
1. General Specification...............................................................................................................4
2. Block Diagram .........................................................................................................................4
3. Circuit Operation Theorem ......................................................................................................5
3.1 RFI FILTER...............................................................................................................5
3.2 Rectifier and filter......................................................................................................5
3.3 switching Element and isolation transformer............................................................6
3.4 Output Rectifier and filter..........................................................................................6
3.5 Control circuit............................................................................................................7
3.6 Feedback circuit........................................................................................................8
3.7 DEGAUSS CIRCUIT.................................................................................................8
3.8 power saving control.................................................................................................8
MEA 1995SL MICROCONTROLLER CIRCUIT OPERATION THEORY..........................................9
1. Introduction..............................................................................................................................9
2. Block diagram..........................................................................................................................9
3.MCU and the peripheral circuit operation theory ......................................................................10
3-1.MCU function............................................................................................................10
3-2.How to detect mode timing.......................................................................................10
3-3.What are the valid key functions for user.................................................................10
3-4.How to memorize the timing and adjusted data .......................................................11
3-5.How to display the OSD menu..................................................................................11
3-6.How to execute the auto alignment function.............................................................11
Deflection Circuit....................................................................................................................................12
[ 1995SL Autosync Deflection Controller Circuit ]........................................................................14
[ Vertical Deflection ]....................................................................................................................14
[ G1 and Spot-killer ]....................................................................................................................15
[ Tilt Circuit ].................................................................................................................................16
[ Horizontal Size Modulation Circuit ]...........................................................................................16
< H-size and East-west PWM generator > .....................................................................16
< H-size Output Circuit >.................................................................................................17
< Top Ringing Elimination Circuit >.................................................................................17
< H-driver Circuit >..........................................................................................................17
< Cs Control Circuit >......................................................................................................18
< H-linearity Control Circuit >..........................................................................................18
[ High Voltage Processing Circuit ] ..............................................................................................19
1
Page 35

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
[ ABL Circuit ]...............................................................................................................................19
[ Dynamic Focus Circuit ].............................................................................................................19
Video Output Circuit...............................................................................................................................20
[ Design Specification ] ................................................................................................................20
[ CRT Specification ]....................................................................................................................20
[ Block Diagram ] .........................................................................................................................20
[ Circuit Descriptions ]..................................................................................................................21
Preamplifier.....................................................................................................................21
CRT Driver (LM2435) .....................................................................................................22
DC Restoration ...............................................................................................................23
2
Page 36

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
1995SL System Block Diagram
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
VGA
signal
source
RS-232
Interface
Yoke
1
Video Amplifier
6
2
3
4
Micro-controller
&
DDC
7
Horizontal & Vertical
Deflection Circuit
9
10
11
12 13
14
19"
CRT
HV
90 - 264 VAC
HV Generation
8
5
Switching
Power Supply
&
Power Saving
3
Page 37

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
Switching Power Supply Operation Theory
1. General Specification
Input Voltage : 90~264VAC (FULL RANGE)
Input Frequency : 47~63Hz
Output Requirement: Output MAX. Load Current
+6.5V 0.7 A
+16.5V 0.8 A
+85V 0.15A
+200V 0.37A
2. Block Diagram
DEGAUSS
CIRCUIT
AC
INPUT
RFI
FILTER
RECTIFIER
&
FILTER
SWITCHING
ELEMENT
ISOLATION
TRANSFOR
-MER
FEEDBACK
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
OUTPUT
RECTIFIER
AND FILTER
OUTPUT
POWER
SAVING
4
Page 38

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
3. Circuit Operation Theorem
3.1 RFI FILTER
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
L
N
FG
R601
430K
1/2W
L602
3
12
C601
4
0.47U
250V
(X)
C602
2200P
250V
(Y)
C603
2200P
250V
(Y)
L603
L604
This circuit designed to inhibit electric and magnetic interference for meet FCC, VDE, VCCI standard
requirements.
3.2 Rectifier and filter
L
~
~
BD601
1
+
+
C612
330U
400V
(EL)
DC OUTPUT
3
4
AC INPUT
-
2
N
When power switch is turn on, the AC voltage is Rectifier and filter by BD601 , C612. The DC output voltage will
be 1.4*(ac input)
5
Page 39

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
3.3 switching Element and isolation transformer
T601
L608
C614
220P
1KV
ZD650
(OPEN)
(D)
R619
1K
2W
6
1
8
9
R604
82K
3W
D608
RGP10J
R608
22K
L607
(BEAD)
R611
1K
L609
(BEAD)
Q602
FS14SM-12
C616
220P
1KV
R607
0.15
2W
C613
0.01U
1KV
(D)
RGP10J
L606
(BEAD)
D606
RGP10J
D607
(BEAD)
In a flyback converter operated in the discontinuous mode, the energy stored in the flyback transformer
(actually an inductor) must be zero at the beginning and end of each switching period . During the "ON" time,
energy taken from the input is stored in the transformer when the switching transistor turn-off, this stored energy
is all delivered to the output.
3.4 Output Rectifier and filter
The structure of each output is illustrated as below
T601
D1 L1
11
12
10
(SHORT)
16
(SHORT)
13
FR701
(SHORT)
FR702
15
18
FR704
+
C1
+
C2
since the transformer T601 acts as a storing energy inductance, diode D1 and capacitor C1 are to produce a dc
output and additional L1, C2 to suppress high-frequency switching spikes.
6
Page 40

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
3.5 Control circuit
C625
50V (D)
330P
8
R613
33K
C615
1000P
50V
(PE)
R614
100K
+
C617
10U
50V
(EL)
D612
1N4148
D613
1N4148
4
C618
0.01U
50V
(D)
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
R607
0.15
2W
76
VCC OUT
VREF
IC601
UC3842
R/C
C619
0.047U
50V
(D)
R615
47K
IC603
MCR100-3 24V
A
R616
56K
R620
10K
ISSEN
GK
3
GNDFBCOMP
521
ZD602
R622
1K
C627
+
10U
50V
(EL)
+6.5VA
R611
1K
C620
820P
50V
(D)
R738
82
1/2W
4 1
The current mode control IC UC3842 is used in the switching power supply which function of each pin described
as follows.
pin 1 : Error amplifier output pin 5 : Ground
pin 2 : Error amplifier reverse input pin 6 : Output
pin 3 : Current sense pin 7 : VCC
pin 4 : OSC sawtooth pin 8 : Reference Voltage:5V
When power is initially applied to the circuit, capacitor C607 charges through R624, R623, Q601, D609. When
the voltage across C607 reaches a level of 16V, IC601 is turn-on the +5Vdc will be set up at pin8 then R613,
C615 generate a fixed frequency sawtooth wave to pin4, at this time MOSFET will be drived by pin6 with square
wave the pulse width of square wave is decided by pin2 , pin3 is current feedback control, It will to sense
MOSFET current. The D613, D612, R614, C617 are soft start components to avoid the duty too large when
power starts up.
7
Page 41

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
2
5
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
3.6 Feedback circuit
This power supply adopt feedback circuit of +190V. It used IC701 for voltage regulation and IC602 for primarysecondary isolation, The output voltage differential signal will be detected and sensed to the pin2 of UC3842 for
comparison then the duty cycle of MOSFET will be decided to control the output voltage.
R617
1K
3.7 DEGAUSS CIRCUIT
LLLL
2
This circuit has the function of auto degaussing and manual degaussing. When power supply is switched ON it
is auto degaussing stage. When user make the selection of the manual degaussing function in OSD, the
degaussing current will flow through coil to degauss the screen of monitor.
TR602 is a PTCR to control degaussing coil current .
3.8 power saving control
Mode H-sync V-sync LED Power Rating
Normal Normal Normal Green
Stand-by None Normal Orange
Suspend Normal None Orange Flash
Off None None Orange Flash
When the H-sync is none ,the power supply +16.5V output will be cut-off. The power input will be under 15W.
When the V-sync is none, the power supply +6.5V and+16.5V output will be cut-off. The power input will be
under 5W.
When both of the H-sync and V-sync are none, the power supply +6.5V and +16.5V output will be cut-off. The
power input will be under 5W.
342
TR602
9 OHM
CN602
2P
(OPEN)
1
1
RL601
R603
3W
R720
82
1/2W
IC602
TLP721F
+6.5VA
43
+6.5VA
+190V
R730
200K
1/2W
1%
220K
C714
0.1U
50V
(MONO)
R718
470
VR701
500
R717
2.4K
1%
R719
K
R
IC701
TL431
A
D781
1N4148
R787
330
R784
220
1/2W
Q78
H94
D740
1N4148
1
2
Q740
56
H945
NNNN
R741
2.2K
+12V
R740
(OPEN)
DEGAUSS
+
C740
47U
25V
(EL)
100﹪
≦
15W
≦
5W
≦
5W
8
Page 42

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
y
g
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
MEA 1995SL MICROCONTROLLER CIRCUIT OPERATION THEORY
1. Introduction
This model, 1995SL, will support powerful O SD function to help end user fine adjustment. The
Microcontroller circuit of the 1995SL can determine what mode it is by detecting the frequency of
horizontal and vertical synchronous and the polarity of horizontal synchronous, and provide DC
voltages to control the picture and save the adjus ted value into the EEPRO M by using the O SD,
"On Screen Display control", that means the user c an get any information of the picture display or
adjust it and save the status values into the EEPROM by choosing and pressing the proper key
according to the indication of the OSD.
2. Block diagram
The major parts of 1995SL Microcontroller circuit are MCU, EEPROM, and OSD IC. The circuit block
diagram is shown as below.
MCU
(MTV212)
Hsync
Vsync
H-polarity
EEPROM
Preset mode
User saved mode
Reset circuit
12MHz Crystal
Control Panel
4 ke
Left,Ri
circuit
s
ht,Enter,Ex
Detecting the
input signals
of H,Vsync &
H-polarity.
Searching for
the same saved
mode timing
with the input
signals and
get the data.
PWM
output
Degaussing
Blanking
SC0 – SC4
OSD IC
Display OSD
and output
PWM to video
circuit
To deflection
circuit
Checking if th e
valid key be pressed
and do key function.
(UART) External
adjustment
function
PC
RS232
auto alignment
program
9
Page 43

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
3.MCU and the peripheral circuit operation theory:
3-1.MCU function
The MCU is MTV212, it is an 87C51 with PW M output controlled mic rocontroller, after power
on, the reset circuit output a "High" to "Low" signal(>40mS) and the 12MHz crystal oscillated
circuit working , the MCU begin to manages the following functions,
(1) To detect mode and output proper SC0 ~ SC5 to deflection circuit.
(2) To check if there is the same saved mode in the EEPROM and get the data to tr ans f er into
DC voltages by PWM output and RC filter circuits to control the picture, color, contrast and
brightness.
(3) To check if there is the valid key be pressed and do the key function.
(4) To memorize mode timings and any adjustable parameters of the picture into EEPROM.
(5) To output data to OSD IC for making an "on screen display control" menu.
(6) The inner registers and PWM output of MCU can be controlled by the external PC
alignment program.
3-2.How to detect mode timing
Only when the mode timing input is stable, we can adjust the picture and check the horizontal
and vertical sync frequency by the OSD menu, and the mode timing input mean the horizontal
sync signal and the vertical sync signal.
(1) The vertical sync frequency measurement:
We use the base timer, it can generate a count during a f ix ed time, this fixed time is 12/12MHz
and we call it "Time_base", so when the first vertical sync generated, we enable the base timer,
and the next vertical sync generated, we disable the base tim er, and we only need to calculate
how many counts are during a vertical sync period. The formula is
Vertical sync frequency
= FV
= 1 / Vertical sync period
= 1 / [ Counters * (Time_base)]
==> Vertical sync frequency = 1000000 / Counts
(2) The horizontal sync frequency measurement:
We use the event counter for calculating how m any counts are during a long fixed time,
because the vertical sync period is longer than the horizontal sync period, we can enable the
event counter when the first vertical sync generated and disable the event counter when the
next vertical sync generated, this time, we can get the horizontal sync counts during a vertical
sync period.
The formula is Horizontal sync frequency
= FH
= Horizontal sync counts / Vertical sync period
==> Horizontal sync frequency
= Horizontal sync Counts / Vertical sync period
3-3.What are the valid key functions for user
There are four k eys on 1995SL control panel. They are "Left," "Right," "Enter," and "Exit." "Enter" for
entering sub-menu of main menu, "Exit" for esc aping to main menu from sub-menu or leaving O SD menu,
and "Left," "Right" for adjusting the bar value.
Except the OSD basic key functions, the user can only press "Right" for brightness adjustment, or "Left"
for contrast adjustment.
10
Page 44

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
u
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
3-4.How to memorize the timing and adjusted data
The EEPROM of 1995SL is 24C08, it has 1024 bytes memory size and comm unicates with
MCU by two wires of I2C bus, one wire is "SCL," the other is "SDA".
The MCU send clock and data to EEPROM to do "Write" function and send clock and
receive data from EEPROM to do "Read" function by these two wires.
We define three parts of storage area. One is for the storage of the factory preset data,
another is for saving user adjus ted data, the other is f or c ommon settings area where s tored the
data of the OSD color temperature settings, contrast and brightness value .
3-5.How to display the OSD menu
The OSD IC of 1995SL is AP3114 which is developed by vender, it receives the data of the
OSD fonts and attribute what we want to display on the screen from the MCU by 2 wires of
communication, and ex ports OSD window data and PW M volume to the VIDEO c ircuit, the bloc k
diagram is shown as below,
MCU(MTV212)
MCU(MTV112)
(1)Send data to
RAM for OSD
fonts or attribute.
(2)Send data to
Control registers
for PWM ouput
or OSD window
control.
SDA
SCL
OSD IC (MC141542)
Shift receiving
register and decoder.
Control
registers
RAM
Fonts
generator
PWM
output
Output to
the VIDEO circ
ROUT
GOUT
BOUT
FBKGC
VSYNC
HSYNC
(H-BLANK,HBNK)
VCO circuit
3-6.How to execute the auto alignment function
The MCU MTV212 supports the UART function, it has 2 I/O serious ports, one is the receiver, the other is
the transmitter, they are connected with an interface to PC and PC can execute alignment program by
RS232 communication to send the formatted data to the MCU for adjusting any adjustable parameters of
the picture and saving the adjusted values into EEPROM. By this way, we can get the products with the
same quality and reduce the manufacturing time.
11
Page 45

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Deflection Circuit
HUNLOCK
H/H+V
Sync.
Input
VOUT1
VOUT2
Vertical Output
(IC202--TDA8351)
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
G1 & Spot Killer
(Q201,Q202,Q203)
Vertical
Deflection
Yoke
G1
To Video
ABL
(Q382)
To
Video
V Sync.
Input
From
Micro-Controller
I2C control input
BSENS
AutoSync
Deflection
Controller
(IC201-TDA4856)
FOCUS
XRAY
BDRV
BOP
BIN
AFC
HDRV
EW
DRV
HV Feedback
X-Ray
Protection
HV
Generation
Driver
(Q320,323)
V-Focus.
Parabola
(Q324)
Sawtooth wave
Generation
(IC203)
AFC
Extract
(C316,C317)
H-DRIVER
(Q301)
H-Size
PWM
Converter
(Q317)
HV
Output
Circuit
With FBT
(T303)
V-Focus
Parabola
H-Fly Back Pulse
H Output
Circuit
(Q302)
Dynamic
Focus
Mixer
( T304)
H-Focus
Parabola
Horizontal
Deflection
Yoke
HV
26KV
G2
G5-1
G5-2
H-blank
To
Video
12
Page 46

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
TDA4856 is a high performance and efficient solution for auto-sync monitors. Shown as fig. , all functions
are controllable by I2C bus.
TDA4856 provides synchronization processing, horizontal and vertical synchronization with fill auto-sync
capability, a TV/VCR mode and very short settling time after mode changes. External power components are
given a great deal of protection. The IC generates the drive waveforms for DC-couple vertical boosters such as
TDA486X and TDA8351.
TDA4856 provides extended functions e.g. as a flexible B+ controller, an extensive set of geometry control
facilities and a combined output for horizontal and vertical focus signals.
13
Page 47

5SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
[ 1995SL Autosync Deflection Controller Circuit ]
The auto-sync deflection control circuit is shown as fig. R214 and R215 are known as RHBUF and RHREF
which determine fmax and fmin of the horizontal oscillator. For 98e, free-run mode is 28.5KHz and the
frequency range is from 31KHz to 86KHz.
[ Vertical Deflection ]
TDA8351 vertical deflection booster is proper for TDA4856 auto-sync deflection IC. This vertical output circuit is
shown in fig. This vertical driver IC circuit is a bridge configuration. TDA4856 differential output signals VOUT1
and VOUT2 are connected to TDA8351 pin1 and pin2 via DC-couple. The vertical coil is connected between the
output amplifier pin4 and pin7, which are driven in opposite phase. TDA8351 can output current 2.8Ap-p
maximum to drive VDY. It can be calculated by:
IR226*R226 = Icoil*R228
So it will be easy to control Icoil by R226 and R228. R229 is used for thermal compensation for Vsize.
VO(GUARD) at pin8 is used for vertical blanking of the picture tube screen. It is inverted by Q201 to get a 40Vp-
14
Page 48

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
p negative pulse and sent to G1 grid to cancel the vertical retrace line of the raster.
[ G1 and Spot-killer ]
When the monitor power turns off, horizontal and vertical deflection will stop quickly, but the light output still
remains on screen and turns into a light spot at the center screen to destroy the monitor. So monitors need
spot-killer circuits to cut off the light output as fast as possible. Mode changing also needs the blanking function.
G1 voltage level is determined by BRITE from the micro-controller DC control voltage. Users can adjust
brightness from the front panel directly.
When the monitor turns off, Q203 will be cut off and G1 will fall down to -190V quickly and prevents the light spot
from destroying the tube.
15
Page 49

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
[ Tilt Circuit ]
Q204 generates a 12V PWM and the buffer (Q205 and Q206) outputs 0~11VDC to get positive and negative coil
current for tilt.
[ Horizontal Size Modulation Circuit ]
< H-size and East-west PWM generator >
Q207 and Q208 constitute a saw-toothed waveform (IC203 pin2)generator. It takes the PWM from HDRV via
the driver transistor Q301. Q210 acts as a thermal compensation. VR201 preset H-size to assure over-scan at
every preset mode. IC203 pin3 consists of HSIZE (via R257) and East-west waveform (via R203, from IC201
pin11). Then the comparator IC203 takes signals of pin2 and pin3 to generate a control-size PWM.
16
Page 50

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
< H-size Output Circuit >
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
H-output circuit has a positive collect pulse up to 1200V
Q314 acts as a PWM converter for B+ to accept PWM waveform and vary on/off duty.
< Top Ringing Elimina tion Circuit >
L304, R331 and C321 are used to eliminate the ringing at the top of the screen.
< H-driver Circuit >
HDRV signal coming from IC201 pin7 is drived by Q301. T301 is the driver transformer, Q302 the horizontal
output transistor, D303 the damping diode and C305 the tuning capacitor. T301 offers adequate base current of
Q302 from low frequency mode to high frequency mode.
17
Page 51

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
< Cs Control Circuit >
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
The monitor needs several Cs capacitors to obtain good linearity picture from 31K to 86KHz modes. Cs
capacitors include C309 ~ C313. They are switched by IC301 and switch control signals are sent from uC IC801.
The switching truth table is as follows:
< H-linearity Control Circuit >
The monitor use a special linearity coil to get good linearity picture from 31KHz to 86KHz modes. T302 pin3 and
pin4 are control side of linearity. The control signals which comes from uC IC801 are vary by different modes.
R308 and D306 are used to eliminate ringing bar caused by the linearity coil.
18
Page 52

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
[ High Voltage Processing Circuit ]
The high voltage circuit uses two MOSFETs (Q320 and Q323) to drive FBT to generate HV up to 26KV. HVDRV
and BDRV both are from IC201 but are opposite waveforms. HV-FB is the feedback signal for HV compensation
to adjust the duties of HVDRV and BDRV.
[ ABL Circuit ]
When the loading of video increases, the current through R383 increases. And the base voltage of Q382
decreases. So the voltage of ABL to the video board decreases to keep the light output from going up.
[ Dynamic Focus Circuit ]
The monitor uses double focus CRT and it needs vertical and horizontal parabolic focus signals to input to CRT
G3 and G5 grids.
The vertical parabolic signal from IC201 pin32 is amplified by Q324 to obtain about 150Vpp at the collector of
Q324.
The horizontal parabolic signal is taken from Cs capacitors and amplified by T304 to reach about 350Vpp signal
at pin1 of T401 to combine with vertical parabolic signal and get into FBT focus pack.
19
Page 53

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
Video Output Circuit
[ Design Specification ]
Input :
D-sub connector
Sync type :
Separate Sync (H-sync & V-sync)
Pixel rate = 150 MHz
Light output @ 3” block pattern = 35 F.L. min [brightness at cut-off and contrast max]
@ full white pattern = 28 F.L. min [brightness at cut-off and contrast max]
[ CRT Specification ]
Heater voltage = 6.3V
Heater current = 300 mA typical
Cathode spot cut-off voltage = 110V
Max to min cut-off ratio = 1.20
[ Block Diagram ]
R,G,B Drive
Contrast (ABL)
D-Sub Input
M101
R
G
B
H
V
R,G,B
H,V
(to Main BD)
Preamplifier
CRT Driver
IC101
LM1279
R,G,B
IC102
LM2435
R,G,B Bias
Fig. 1 Block Diagram of 7298e Video
R,G,B output
DC Restoration
Q121,Q122
Q141,Q142
Q161,Q162
19"
CPT
Tube
20
Page 54

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
[ Circuit Descriptions ]
Preamplifier
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
IC101 (LM1279) is a high bandwidth preamplifier with OSD mixer.
CONTRAST voltage controls the gain of three guns simultaneously. R, G, B DRIVE voltages control the gains of
these three guns individually to approach the white balance of CRT.
CLAMP signal is used to active low to pull the LM1279 outputs below 0.2V during non-display period.
21
Page 55

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
CRT Driver (LM2435)
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
IC102 (LM2435) contains three wide-bandwidth cascode amplifiers. The parasitic capacitance and
inductance between IC102 outputs and cathodes will also influence the frequency response of IC102.
The diodes and series resistors between cathodes and IC102 output pins are used to protect IC102 during
the tube arcing.
22
Page 56

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
DC Restoration
Chapter 2 Circuit Operation Theory
The amplified video signals are AC couple to cathodes. So a DC restoration circuit is needed to fix their DC
levels. By adjusting R,G,B bias voltages. The raster can be set to specific color temperature.
The control ranges at Q122/Q142/ Q162 emitters are about 80V ~ 53V. Because the blanking pulse at
IC102 output is about 10V, the control range of DC level at cathodes is about 70V ~ 43V.
23
Page 57

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
Preparation for alignment : .......................................................................................................................2
1. B﹢Adjustment...................................................................................................................................... 3
2. HV Adjustment......................................................................................................................................3
3. H-center Adjustment :........................................................................................................................... 3
4. H-size preset :.......................................................................................................................................3
5. Factory setting mode adjustment ......................................................................................................... 3
6. Focus adjustment .................................................................................................................................4
7. Convergence adjustment......................................................................................................................4
8. Color Temperature auto alignment....................................................................................................... 4
9. Clear all of user mode data .................................................................................................................. 5
10. Geometry Specification...................................................................................................................... 5
11. Power Saving Function Check............................................................................................................5
12. Eyelet & Touch up ..............................................................................................................................7
13. Wire dressing:..................................................................................................................................... 9
1
Page 58

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Preparation for alignment :
(I) Setup unit and keep it warm up
(II) Signal mode
Mode Frequency (H/V) Display
1 31.47K / 70 (-/+) 640 * 400 (VGA400)
2 37.50K / 75 (-/-) 640 * 480 (6448A)
3 43.27K / 85 (-/-) 640 * 480 (6448B)
4 46.87K / 75 (+/+) 800 * 600 (SVGA4)
5 53.67K / 85 (+/+) 800 * 600 (SVGA5)
6 60.02K / 75 (+/+) 1024 * 768 (UVGA7)
7 68.68K / 85 (+/+) 1024 * 768 (UVGA8)
8 79.98K / 75 (+/+) 1280 * 1024 (WS7)
9 91.15K / 85 (+/+) 1280 * 1024 (WS8)
10 93.75K / 75 (+/+) 1600 * 1200 (1612E)
at least 30 minutes
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
2
Page 59

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
1. B
a. Input mode
b. Set brightness and contrast in OSD to maximal value.
c. Adjust main board
2. HV Adjustment
a. Input mode
b. Adjust
or 26
3. H-center Adjustment :
a. Input mode
Adjustment
﹢﹢﹢﹢
91K (1280x1024)
VR701
91K (1280x1024)
VR301
±±±±
b. If raster center is near the center of the screen Î plug the CON3 Wire into NONE.
If raster center is near the right side of the screen Î plug the CON3 Wire into LEFT.
If raster center is near the left side of the screen Î plug the CON3 W ire into RIGHT.
to let anode voltage be
0.1KV(for Philips CRT).
91K (1280x1024)
with cross-hatch Pattern.
to main
200V
with cross-hatch pattern.
with raster pattern.
±±±±
0.5V.
±±±±
27
0.1KV (for Hitachi & Samsung CRT)
4. H-size preset :
a. Input mode
b. Use OSD to adjust H-size maximum at factory mode.
c. Adjust
5. Factory setting mode adjustment
1.
H-phase : Set picture to the center of screen
2.
H-Size : Set picture to
3.
V-center : Set picture to the center of screen
4.
V-size : Set picture to
5.
Tilt : L e t tilt ±0.5mm between edge to edge
6.
Pincushion : Set picture to a real rectangular
7.
Unbalance : Set picture to a real rectangular
8.
Trapezoid : Set picture to rectangular or balance of top and bottom
9.
Parallelogram : Set picture to rectangular or balance of top and bottom
10.
Top Corner : Set the line of top corner to a straight line
11.
Bottom Corner: Set the line of bottom corner to a straight line
37.5K (640x480)
VR201
to make H-size
with H-size limit pattern.
just overscreen.
±±±±
350
262
2
mm
±±±±
2
mm
3
Page 60

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
6. Focus adjustment
a. Input mode
b. Adjust V(F2) Focus VR of FBT to make vertical line between center
and corner area of CRT clear.
c. Adjust H(F1) to make horizontal line between center and corner area
of CRT clear.
d. Repeat step b and c to get the best focus.
e. Check focus at input mode 91K (1280x1024) with reverse text-5x7 pattern.
7. Convergence adjustment
a. Input mode
b. Adjust VRs of Yoke and 4-pole , 6-pole to meet specification.
91K (1280x1024)
91K (1280x1024)
with green cross-hatch pattern.
with cross-hatch patterns.
8. Color Temperature auto alignment
[Input mode : 91K/ 85 Hz, WS8]
i) Equipment
a. PC + QUANTUM DATA/CHROMA card
b. RS232 BOX
c. COLOR ANALYZER (CA100)
d. RS232 CABLE (9P) connect RS232 BOX to PC(COM1)
e. CA100 CABLE to PC(COM2)
g. ADJUST PROGRAM for G991
ii) Alignment procedure
a. Press "SPACE BAR " to get raster pattern and set contrast and brightness to
maximum position, adjust the G2 VR such that the max. color of R.G.B color bar on
the monitor is in the mark region.
b. Press "SPACE BAR" to do auto color temperature adjustment and color tracking
c. Press "SPACE BAR" to get 3"-block and finish the adjustment
For TCO99 Color Temperature Alignment:
Item Descriptions x y u’ v’
C1 9300K
C2 6500K
For MPRII Color Temperature Alignment:
Item Descriptions X y
C1 9300K
C2 6500K
283 ± 5 297 ± 5
313 ± 5 329 ± 5
281 ± 5 311 ± 5
313 ± 5 329 ± 5
0.189 0.446
0.198 0.468
4
Page 61

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
9. Clear all of user mode data
After finishing all factory setting , select “Reset to default “at MENU 1 then press enter.
10. Geometry Specification
ITEM DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
1 HORI SIZE
2 VERT SIZE
3 SIDE PIN
4 TOP/BOTTOM PIN
5 SIDE BARREL
6 TOP/BOTTOM BARREL
7 TRAPEZOID
8 VIDEO OFFSET
9 PARALLELOGRAM
350±4 mm
262±4 mm
≦
1.8 mm
≦
1.35 mm
≦
1.8 mm
≦
1.35 mm
≦
3.0 mm
≦
4.0 mm
≦
3.5 mm
11. Power Saving Function Check
a. Input mode 31KHz (VGA400 640 X 400) with full-white pattern.
b. Press both contrast and brightness keys to maximum position.
[Standby Mode]
c. Remove the
The picture will disappear, and the LED indicator is
should be less than
horizontal sync
15W
signal from input, the unit will go into "
amber
.
Standby
. The power consumption
[Suspend Mode]
d. Remove
The picture will disappear, and the LED indicator is
vertical sync
signal from the input, the unit will go into "
amber (blinking)
Suspend
. The power
consumption should be less than 5W.
[Off Mode]
e. Remove
both syncs
from input, the unit will go into "
The picture will disappear, and the LED indicator is
Off
" mode.
amber (blinking)
. The power
consumption should be less than 5W in this case.
f. Input H-sync and V-sync signals in case c, d and e, the unit will recover to normal
state, and the LED indicator is green.
[Override Mode]
" mode.
" mode.
5
Page 62

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
g. Disconnect the signal cable from input ,then power on , the unit will go into
"Override" mode. The OSD windows will show “no signal”, and the LED indicator is
green. The power consumption is normal.
h. Re-connect the signal cable in case g, the unit will recover to normal state, and the
LED indicator is green.
6
Page 63

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
12. Eyelet & Touch up
Eyelet: IC301, Q317 headsink , H & V dy , T303 FBT , C612 , Q602
7
Page 64

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Touch up : T303 FBT , TR602
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
8
Page 65

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
13. Wire dressing:
Right side
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
Top side
9
Page 66

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Back side
Right side Braid wire
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
10
Page 67

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Left side FBT schielding & braid wire
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
Top view FBT wire core
11
Page 68

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Ac GND wire & PCB GND wire
Chapter 3 Alignment Procedure
12
Page 69

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
Table of Contents
0. Introduction..............................................................................................................................2
1. System trouble category.......................................................................................................... 2
2. Trouble shooting for short circuit............................................................................................. 3
3. Trouble shooting for bad geometry.......................................................................................... 4
4.Trouble shooting for no picture................................................................................................. 5
5. Trouble Shooting for bad video................................................................................................ 6
6. Power supply........................................................................................................................... 8
7. Check MCU and OSD for no video output............................................................................... 9
8. Check OSD,MCU for no OSD window .................................................................................... 10
9. Dis-assembly........................................................................................................................... 11
1
Page 70

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
0. Introduction
This 1995SL trouble shooting guide has flow chart and trouble list to show the easy problem
solution for engineers. Please follow this guide and step by step to maintain your 1995SL when
the system is in any trouble.
1. System trouble category
No power
Check SPS
Maintain the G991 all system
Start
Dark
LED
Status
Light
LED
Color
Green
Picture
Status
Flash
Orange
Short circuit
Check all circuits
Power saving
Check
MCU
Bad geometry
Bad geometry
Check
deflection or MCU
circuit
End
Figure.1 Main flow chart for trouble category
Good
No picture
No picture
Check
cathode, G1, G2, HV
voltage
Bad video
Bad video
Check
video or OSD
circuit
2
Page 71

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
2. Trouble shooting for short circuit
Short circuit
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
Fail
Start
Check
**key
components
OK
Remove
+200V,
+85V,+16V,
+12V,+6.5V,
respectively
Check
short circuit
reason on each
Vcc path
** Key components:
Q323,Q320,Q302,Q317,Q301
D308,D303
Damage
Replace
Success
End
Figure.2 Trouble shooting for Short circuit
3
Page 72

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
3. Trouble shooting for bad geometry
Item Status Reason Check Note
1 Ver tical one line Hor. deflection failure R301,R355,R328
2 Hor izontal one line Ver. deflection failure IC202,R227, R228, R233
3 Bad focus Dynamic focus failure Q324,R347,C333,C348,C349,
T304
4 Picture dimension too
large
5 Picture dimension too
large
6 Picture dimension too
small
7 Picture dimension too
small
8 Bad H- linearity Cs switching error IC301,Q305,Q307,Q309,Q311
9 H- linearity unbalance Linear coil malfunction Q310,Q306,Q303,T302,
HV less than 26KV(philips)
27KV(Hitachi&Samsung)
HV feedback circuit f a ilur e VR302,R216
HV greater than
26KV(philips),
27KV(Hitachi&Samsung)
HV feedback circuit f a ilur e VR302,R216
Adjust VR302
Adjust VR302
Q313 or check MCU circuit
SC0~SC4
uC H-LIN
10 Bad V-linearity Ver. circuit failure uC function
11 Asynchronization AFC feedback failure C316,C317,C335,C327
12 Asynchronization Defelction I C failure IC201,C209,C210,R213
13 Spot when power OFF Spot killer circuit failure C219,Q201,Q202,Q203
14 Hor. size too small H-size VR had not been
adjusted
15 Ver. size too small Ver . output abnormal R226,R228,IC202
16 Appear retrace line V-blanking failure IC202,Q201,C219
17 Geometry cannot be
adjusted
18 ABL cannot be adjusted ABL circ uit failure Q381,Q382
19 Tilt cannot be adjusted Tilt circuit or MCU failur e IC801,Q204,Q205,Q206
20 Upper left and right
picture distortion
MCU or defection circuit
failure
H-size RLC filter failur e L304,R331,C321
Adjust VR301
IC801,IC802
4
Page 73

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
4.Trouble shooting for no picture
No picture
Start
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
Check
OSD and
video amplifier
output
No
Abnormal
0 Vp-p output
Connect
to signal
Yes
G1
voltage
Normal
Adjustable -50~-70V
Cathode
voltage
Normal
Adjustable 0 - 55Vp-p
G2
Voltage
Normal
End
Blanking
About -180V
Abnormal
Check
MCU
Check
high voltage
generation
circuit
Figure.3 Trouble shooting for no picture
Item Status Reason Check Note
1 LED ON, but no picture G2 voltage too small Adjust G2
2 LED ON, but no picture No high voltage R332,Q318 ~ Q323
3 LED ON, but no picture X-Ray protection R217,R218,R219,VR301
4 LED ON, but no picture MCU blanking IC801
5 LED ON, but no picture Hor. output mute IC203,Q207,Q208,Q210
6 LED ON, but no picture No video output I C102,IC1901,IC101,IC801
7 LED ON, but no picture CRT heater burn out Replace CRT
5
Page 74

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
5. Trouble Shooting for bad video
Bad video
Start
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
No picture
No picture
Check
Cathode,
G1,G2,HV
Normal
Adjustable 0-4 volts
Check
IC102
video input
Check
ABL circuit
Abnormal
Picture
quality
No video,
but OSD OK
Check
IC101
pin10
0 volt
Check
IC101
ok
ABL
Normal
Video OK, but no OSD
Check OSD,MCU
for no OSD
Check
OSD, MCU
Short
Replace
IC101
Check OSD,MCU
for no video
Check
OSD,MCU
Figure.4 Trouble shooting for bad video
Item Status Reason Check Note
1 No video Short circuit damage IC102,IC101
2 No video Video blank IC101
3 No video Video contrast zero IC1901,IC101
4 Video smear or tilt Check clamp pulse IC101,IC102
5 Bad video quality Check IC101,IC102 IC101,IC102
6
Page 75

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
6 Lack one or more video
color
7 Lack one or more video
color
8 Free run mode OSD
smear
9 No Hor. blanking H-blank failure IC101,D315
10 RGB drive cannot be
adjusted
11 RGB bias cannot not be
adjusted
12 OSD cannot display O SD IC1901
13 Brightness cannot be
adjusted
14 Picture is too bright/dark G2 voltag e too large Adjust G2
Video output path open or
short circuit
Components damage IC102,IC101
No clamp pulse for IC101 IC1901,D315,Q201
OSD IC damage IC1901,IC101
OSD IC damage or DC
restoration circuit fa ilur e
G1 Circuit is abnormal Check G1 circuit
Check open or short circuit
from video input to output
D111,D112,D131,D132,
D151,D152
Q121,Q141,Q161,
Q122,Q142,Q162,IC1901
15 Picture is too bright/dark G1 voltag e too large Q203,Q202
7
Page 76

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
6.Power supply
POWER NO OUTPUT
Replace
F601,BD601
Replace
IC601,Q601
Q603,ZD601
Replace
IC603
ZD602
NO NO
NO
Check
IC601,Q601
Q603,ZD601
ok ?
NO
Check
F601,BD601
ok ?
YES
YES
Check
IC603,ZD602
NO OUTPUT
Check
Q602,R618
R607,R611
YES
Check
IC602 ?
Check
IC701 ?
NO
NO
Replace
Q602,R618
R607,R611
Replace
IC602
Replace
IC701
Check
D701,D702,D703,
D704,D705
YES
Check
FR704
YESYES
Check
Q701,Q702,Q704
Q705 ,Q782
Replace
NO
D701,D702,D703,
D704,D705
NO
Replace
FR704
Replace
NO
Q701,Q702,Q704
Q705,Q782
8
Page 77

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
7. Check MCU and OSD for no video output
Check MCU and OSD
for no video output
Start
Use a preset timing
YES
Check +5V, ok ?
(1) On the Main Board,
(a) IC801 pin5
(b) IC802 pin8
(2) On the video Board,
IC1901 pin6,19
YES
NO
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
Check +5V power
Check F12M=12MHz CLOCK,ok?
(1)On the Main Board
(a) IC801 pin7
(2)IC1901 pin11 ~ pin18 output PWM ?
YES
Check MCU (IC801)
Reset (pin4) = "H" to "L",ok?
YES
Check IC801 (BLANK)= "L",ok?
YES
Check IC802 (EEPROM ),ok?
YES
Check DCLK, DATA, ok?
(1) On the Main Board
(a) SCL (IC801 pin 13)
(b) SDA (IC801 pin 14)
(2) On the VIDEO Board
(a) SCL ( IC1901 pin 10)
(b) SDA ( IC1901 pin 9)
NO
NO
NO
NO
Check F12M CKT
on the Main Board .
on video Board,
check OSD IC pin4 oscillation ?
Check
Reset circuit
Check
IC801 pin 1,12
Check
(1) pin9 (ESDA)
(2) pin10 (ESCL)
(3) IC802 data
( EEPROM)
(Brightness, Contrast)
9
Page 78

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
8. Check OSD,MCU for no OSD window
Check OSD, MCU
for no OSD window
Start
Check +5V, ok?
(1) IC1901(OSD IC) pin 6,19
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
NO
Check +5V power
YES
Check IC1901 (OSD IC) pin 4 have DC 1~3V
with oscillation wave?
YES
Check IC1901(OSD IC) pin20(V-), ok?
YES
Check SCL, SDA INPUT, ok?
NO
NO
NO
Check
pin 2,3,4,5
and the R,C CKT
Check V- circuit
Check R1906 &
R1907
10
Page 79

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
9. Dis-assembly
1. Remove left 2 pcs screw 2. Remove right 2 pcs screw
3. Push backcover 4. Take signal cable cover
5. Remove left & right hook 6. Take base frame
11
Page 80

1995SL CRT Monitor Service Guide
Chapter 4 Trouble Shooting
7. Remove main pcba hook 8. Take main pcba
9. Replacement component
.
12
Page 81

Main Board 1 of 5
Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Page 82

Main Board 2 of 5
Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Page 83

Main Board 3 of 5
Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Page 84

Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Main Board 4 of 5
Page 85

Main Board 5 of 5
Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Page 86

Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Video Board 1 of 2
Page 87

Video Board 2 of 2
Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Page 88

Diamond View CRT Monitor 1995SL
Assy Drawing
 Loading...
Loading...