Page 1

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
LAN
• LAN IP – Use the LAN menu to configure the LAN IP address
for the Wireless Barricade and to enable the DHCP server for
dynamic client address allocation.
• Set a period for the lease time if required. For home networks
this may be set to Forever, which means there is no time limit
on the IP address lease.
• IP Address Pool – A dynamic IP start address may be
specified by the user, e.g. 192.168.2.100 (default value).
Once this start IP address has been assigned, IP addresses
running from 192.168.2.100 to 192.168.2.199 will be part of
the dynamic IP address pool. IP addresses from 192.168.2.2
to 192.168.2.99, and 192.168.2.200 to 192.168.2.254 will be
available as static IP addresses.
Remember not to include the address of the Wireless Barricade
in the client address pool. Also remember to configure your client
PCs for dynamic IP address allocation.
44
Page 2

Advanced Setup
Wireless
To configure the Wireless Barricade as a wireless access point
for wireless clients (either stationary or roaming), all you need to
do is define the radio channel, the Service Set identifier (SSID),
and encryption options.
Channel and SSID
You must specify a common radio channel and SSID (Service
Set ID) to be used by the Wireless Barricade and all of your
wireless clients. Be sure you configure all of your clients to the
same values.
ESSID: The Service Set ID. This should be set to the same value
as other wireless devices in your network. (Default: SMC.)
Note: The SSID is case sensitive and can consist of up to 32
alphanumeric characters.
45
Page 3

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
Transmission Rate: Set the data rate transmitted
from the Wireless Barricade. The lower the data
rate, the longer the transmission distance.
(Default: Fully Automatic.)
Basic Rate: The highest rate specified is the rate the
Wireless Barricade will use when transmitting
broadcast/multicast and management frames.
Available options are: 1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps.
(Default: 2Mbps.)
Channel: The radio channel through which the Wireless
Barricade communicates with PCs in its BSS.
(Default: Auto)
Note: The available channel settings are limited by local
regulations.
Encryption
If you are transmitting sensitive
data across wireless channels,
you should enable Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
encryption. Encryption requires you to use the same set of
encryption/decryption keys for the Wireless Barricade and all of
your wireless clients. You can choose between standard 64-bit or
the more robust 128-bit encryption.
46
Page 4

Advanced Setup
You may automatically generate encryption keys or manually
enter the keys. For automatic 64-bit security, enter a passphrase
and click Generate. Four keys will be generated (as shown
below). Choose a key from the dropdown list or accept the
default key. Automatic 128-bit security generates a single key.
47
Page 5

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
If you use encryption, configure the same keys used for the
Wireless Barricade on each of your wireless clients. Note that
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protects data transmitted
between wireless nodes, but does not protect any transmissions
over your wired network or over the Internet.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
From this section you can configure the Address Mapping, Virtual
Server, and Special Application features that provide control over
the port openings in the Wireless Barricade’s firewall. This
section can be used to support several Internet based
applications such as VPN
Address Mapping
Allows one or more public IP addresses to be shared by multiple
internal users. Enter the Public IP address you wish to share into
the Global IP field. Enter a range of internal IPs that will share the
global IP.
48
Page 6

Advanced Setup
Virtual Server
If you configure the Wireless Barricade as a virtual server,
remote users accessing services such as Web or FTP at your
local site via public IP addresses can be automatically redirected
to local servers configured with private IP addresses. In other
words, depending on the requested service (TCP/UDP port
number), the Wireless Barricade redirects the external service
request to the appropriate server (located at another internal IP
address).
For example, if you set Type/Public Port to TCP/80 (HTTP or
Web) and the Private IP/Port to 192.168.2.2/80, then all HTTP
requests from outside users will be transferred to 192.168.2.2 on
port 80. Therefore, by just entering the IP Address provided by
the ISP, Internet users can access the service they need at the
local address to which you redirect them.
The more common TCP service ports include:
HTTP: 80, FTP: 21, Telnet: 23, and POP3: 110.
49
Page 7

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
Special Applications
Some applications, such as Internet gaming, videoconferencing,
Internet telephony and others, require multiple connections.
These applications cannot work with Network Address
Translation (NAT) enabled. If you need to run applications that
require multiple connections, use the following screen to specify
the additional public ports to be opened for each application.
Specify the public port number normally associated with an
application in the Trigger Port field. Set the protocol type to TCP
or UDP, then enter the ports that the application requires. The
ports may be in the format 7, 11, 57, or in a range, e.g., 72-96, or
a combination of both, e.g., 7, 11, 57, 72-96.
For a full list of ports and the services that run on them, see
www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers.
50
Page 8
Advanced Setup
Firewall
the Wireless Barricade firewall can provide access control of
connected client PCs, block common hacker attacks, including IP
Spoofing, Land Attack, Ping of Death, IP with zero length, Smurf
Attack, UDP port loopback, Snork Attack, TCP null scan, and
TCP SYN flooding. The firewall does not significantly affect
system performance, so we advise leaving it enabled to protect
your network users.
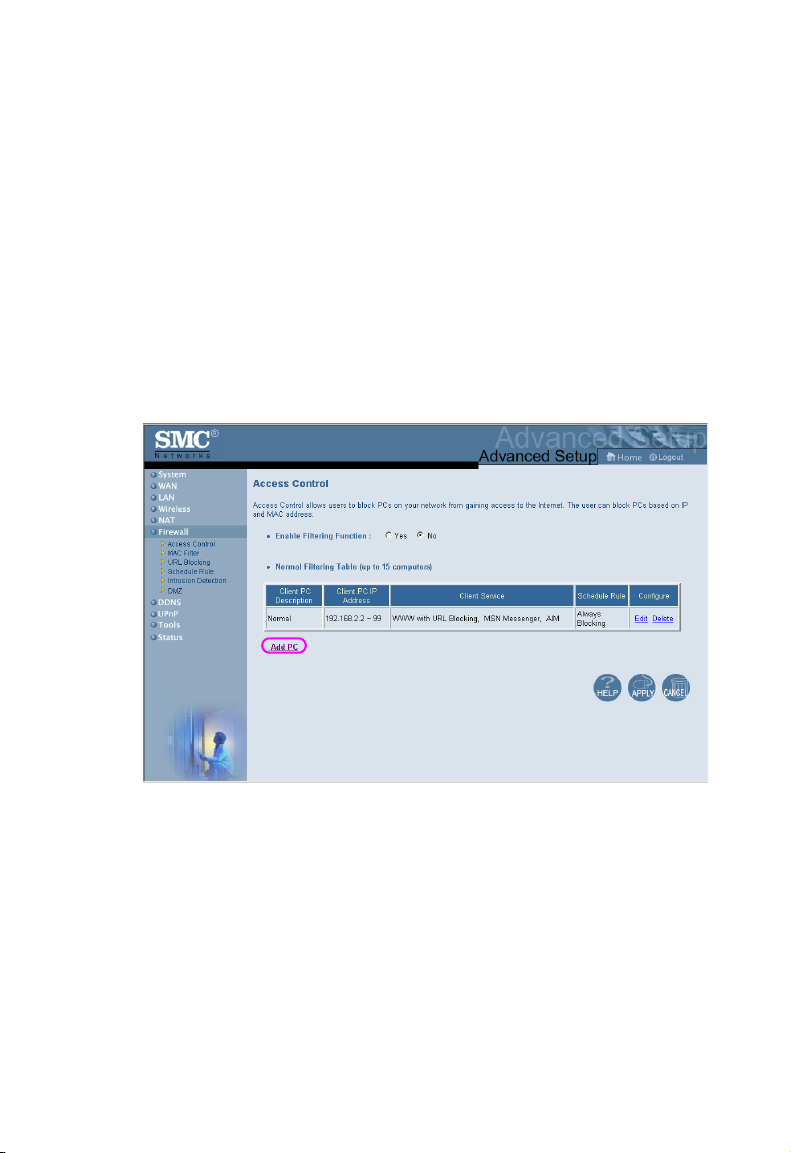
Access Control
Using this option allows you to specify different privileges based
on IP address for the client PCs.
51
Page 9
Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
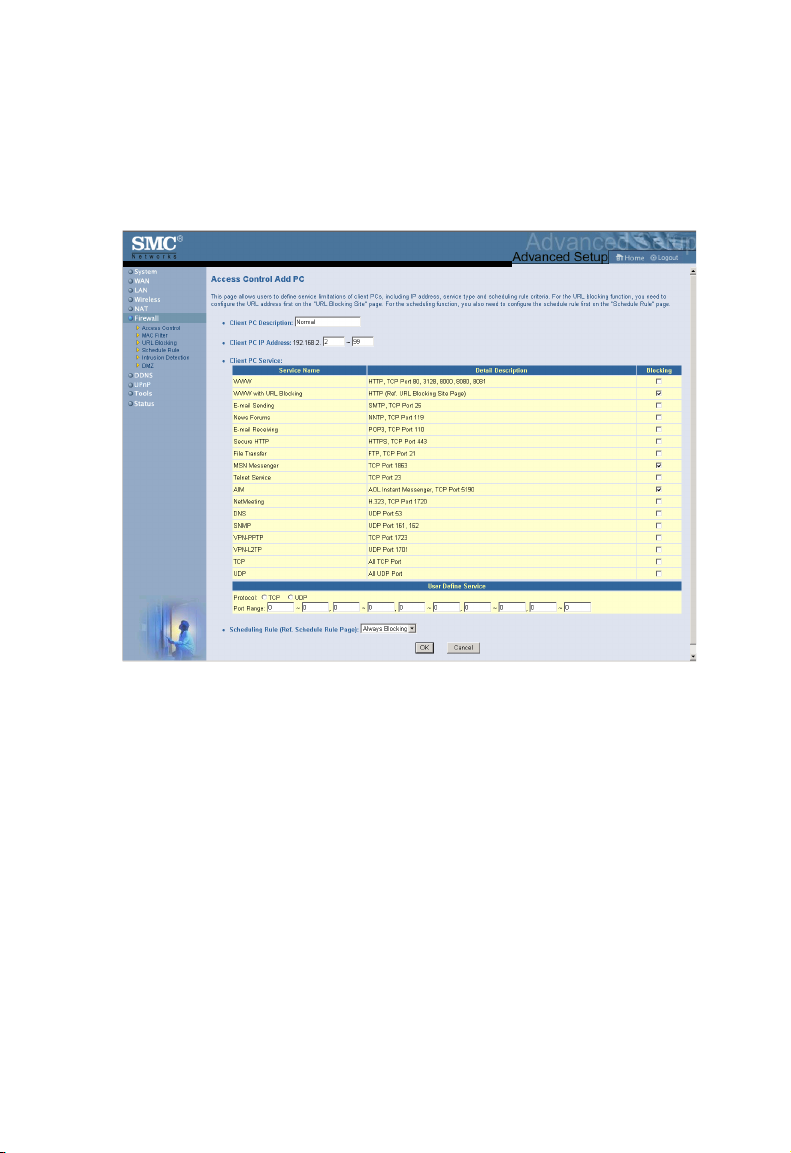
Note: Click on Add PC and define the appropriate settings for
client PC services (as shown in the following screen).
52
Page 10

Advanced Setup
MAC Filtering Table
The MAC Filtering feature of the Wireless Barricade allows you to
control access to your network to up to 32 clients based on the
MAC (Media Access Control) Address of the client machine. This
ID is unique to each network adapter. If the MAC address is
listed in the table, that client machine will have access to the
network.
53
Page 11

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
URL Blocking
To configure the URL Blocking feature, use the table below to
specify the websites (www.somesite.com) and/or keywords you
want to filter on your network.
To complete this configuration, you will need to create or modify
an access rule in “Access Control” on page 51. To modify an
existing rule, click the Edit option next to the rule you want to
modify. To create a new rule, click on the Add PC option.
From the Access Control Add PC section check the option for
WWW with URL Blocking in the Client PC Service table to filter
out the websites and keywords specified below.
Use the above screen to block access to Web sites or to Web
URLs containing the keyword specified in the table.
54
Page 12

Advanced Setup
Schedule Rule
The Schedule Rule feature allows you to configure specific rules
based on Time and Date. These rules can then be used to
configure more specific Access Control.
Enables Schedule-based Internet access control.
1. Click Add Schedule Rule.
2. Define the settings for the schedule rule (as shown on the
following screen).
3. Click OK and then click the APPLY button to save your
settings.
55
Page 13

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
56
Page 14

Advanced Setup
Intrusion Detection
Firewall Configuration
• SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) and Anti-DoS firewall
protection (Default: Enabled) – the Wireless Barricade’s
Intrusion Detection feature limits access for incoming traffic at
the WAN port. When the SPI feature is turned on, all incoming
packets will be blocked.
• Discard Ping from WAN (Default: Enabled)
– Prevents a PING on the Wireless Barricade’s WAN port from
being routed to the network.
E-Mail Alert Configuration
• When hackers attempt to enter your network, we can alert
you by e-mail – Enter your E-mail address. Specify your
SMTP and POP3 servers, user name, and password.
57
Page 15

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
If you have a client PC that cannot run an Internet application
properly from behind the firewall, then you can open the client up
to unrestricted two-way Internet access. Enter the IP address of
a DMZ host to this screen. Adding a client to the DMZ may
expose your local network to a variety of security risks, so only
use this option as a last resort.
58
Page 16

Advanced Setup
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) Settings
Domain Name is a series of alphanumeric strings separated by
periods, that is the address of a network connection and that
identifies the owner of the address.
Dynamic DNS provides users on the Internet with a method to tie
their domain name(s) to computers or servers. DDNS allows your
domain name to follow your IP address automatically by having
your DNS records changed when your IP address changes.
The Server Configuration section automatically opens the port
options checked in the Virtual Server section. Simply enter in the
IP Address of your server, such as a web server, and then click
on the port option HTTP Port 80 so users can access your server
from the WAN connection (Internet).
59
Page 17

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
This DNS feature is powered by TZO.com. With a DDNS
connection you can host your own web site, email server, FTP
site, and more at your own location even if you have a dynamic
IP address. (Default: Disable)
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) Setting
Enable UPnP by checking ON in the screen above. UPnP allows
the device to automatically:
• dynamically join a network
• obtain an IP address
• convey its capabilities and learn about the presence and
capabilities of other devices.(Default: OFF)
60
Page 18

Advanced Setup
Tools
Use the Tools menu to backup the current configuration, restore
a previously saved configuration, restore factory settings, update
firmware, and reset the Wireless Barricade.
Tools - Configuration Tools
• Backup – saves the Wireless Barricade’s configuration to a
file.
• Restore – restores settings from a saved backup configuration
file.
• Restore to factory defaults – restores the Wireless Barricade
settings back to the factory default original.
61
Page 19

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
Tools - Firmware Upgrade
Use this screen to update the firmware or user interface to the
latest versions. Download the upgrade file from the SMC Web
site (www.smc.com) and save it to your hard drive. In the
Upgrade Target field, choose Firmware. Then click Browse to
look for the previously downloaded file. Click APPLY. Check the
Status page Information section to confirm that the upgrade
process was successful.
62
Page 20

Advanced Setup
Tools - Reset
Click APPLY to reset the Wireless Barricade. The reset will be
complete when the power LED stops blinking.
Note: If you use the Reset button on the front panel, the
Wireless Barricade performs a power reset. If the
button is held depressed for over five seconds, all the
LEDs will illuminate and the factory settings will be
restored.
63
Page 21

Configuring the Wireless Barricade Router
Status
The Status screen displays WAN/LAN connection status,
firmware, and hardware version numbers, illegal attempts to
access your network, as well as information on DHCP clients
connected to your network.
The following items are included on this screen:
Section Description
INTERNET Displays WAN connection type and status.
Wireless Barricade Displays system IP settings, as well as DHCP and Firewall
status.
INFORMATION Displays the number of attached clients, the firmware
Security Log Displays illegal attempts to access your network.
Save Click on this button to save the security log file.
Clear Click on this button to delete the access log.
Refresh Click on this button to refresh the screen.
DHCP Client Log Displays information on all DHCP clients on your network.
versions, the physical MAC address for each media
interface, as well as the hardware version and serial number.
64
Page 22

TROUBLESHOOTING
The information outlined in this section describes some useful
steps for getting your computer and the Wireless Barricade
Router online.
A. Verify your connection to the Wireless Barricade
If you are unable to access the Wireless Barricade’s web-based
administration pages then you may not be properly connected or
configured. The screen shots in this section were taken on a
Windows 2000 machine, but the same steps will apply to
Windows 95/98/Me/XP.
To determine your TCP/IP configuration status please follow the
steps below:
1. Click Start then choose Run.
2. Type cmd or command to open a DOS prompt.
3. In the DOS window, type ipconfig and verify the information
that is displayed.
4. If your computer is setup for DHCP, then your TCP/IP
configuration should be similar to the information displayed:
• IP Address: 192.168.2.X (x is number between 100 and 199)
• Subnet: 255.255.255.0
• Gateway: 192.168.2.1
65
Page 23

Troubleshooting
If you have any other IP address information listed see below.
If you have an IP address that starts with 169.254.XXX.XXX then
see the next section.
If you have another IP address configured, then see section C.
B. I am getting an IP Address that starts with
169.254.XXX.XXX
If you are getting this IP Address, then you need to check that
you are properly connected to the Wireless Barricade.
Confirm that you have a good link light on the Wireless Barricade
for the port this computer is connected to. If not, please try
another cable.
If you have a good link light, please open up a DOS window as
described in the previous section and type ipconfig/renew.
If you are still unable to get an IP Address from the Wireless
Barricade, reinstall your network adapter. Please refer to your
adapter manual for information on how to do this.
66
Page 24

Troubleshooting
C. I have another IP Address displayed
If you have another IP address listed then the PC may not be
configured for a DHCP connection. Please refer to “Configuring
Client TCP/IP” on page 11 for information.
Once you have confirmed your computer is configured for DHCP,
then please follow the steps below.
1. Open a DOS window as described above.
2. Type ipconfig/release.
3. Then type ipconfig/renew.
67
Page 25

Troubleshooting
D. The 10/100 LED does not light after a connection is made.
1. Check that the host computer and hub are both powered on.
2. Be sure the network cable is connected to both devices.
3. Verify that Category 5 cable is used if you are operating at
100 Mbps, and that the length of any cable does not exceed
100 m (328 ft).
4. Check the network card connections.
5. The 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX hub/switch port, network card,
or cable may be defective.
68
Page 26

SPECIFICATIONS
Below is an outline of the Technical Specifications for the
SMC7004VWBR
Standards
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.11b
LAN Interface
4 - RJ-45 10/100 Mbps Auto MDI/MDI-X ports
WAN Interface
1- RJ-45 10/100 Mbps Auto MDI/MDI-X port
Management
Web management
Advanced Features
Dynamic IP Address Configuration – DHCP, DNS
Firewall – Client privileges, hacker prevention and logging
Virtual Private Network – PPTP, L2TP, IPSec pass-through
Indicator Panel
Power, WLAN, WAN (Link, Activity), LAN (Link/Activity,
10/100 Mbps)LAN: Link/Activity, 10/100 (Mbps)
Temperature
Operating: 0 to 40 °C (32 to 104 °F)
Storage: -20 to 70 °C (-4 to 158 °F)
Dimensions
130 x 85 x 32 mm (5.12 x 3.35 x 1.26 in.)
Weight
370 g (13.05 oz)
Input Power
9 V (1 A)
69
Page 27

Specifications
Internet Standards
ARP (RFC 826), IP (RFC 791), ICMP (RFC 792), UDP (RFC
768), TCP (RFC 793), Telnet (RFC 854-859), MD5 (RFC 1321),
BOOTP Extension (RFC 1497), PPP LCP Extension (RFC 1570),
PPPoE (RFC 2516), NAT (RFC 1631), PPP (RFC 1661), HTML
(RFC 1866), HTTP (RFC 1945), CHAP (RFC 1944), DHCP (RFC
2131), PPTP (RFC 2637)
Temperature
Operating (0 to 40 °C), 32 to 104 °F
Storage (- 40 to 70 °C), - 40 to 158 °F
Humidity
5% to 95% (noncondensing)
Compliances
CE Mark
Emissions
FCC Class B
VCCI Class B
Industry Canada Class B
EN55022 (CISPR 22) Class B
C-Tick - AS/NZS 3548 (1995) Class B
Immunity
EN 61000-3-2/3
EN 61000-4-2/3/4/5/6/8/11
Safety
UL 1950
EN60950 (TÜV)
CSA 22.2 No. 950
70
Page 28

Page 29

FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT,CALL:
From U.S.A. and Canada (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
(800) SMC-4-YOU; Phn:(949) 679-8000; Fax: (949) 679-1481
From Europe (8:00 AM - 5:30 PM UK Time)
44 (0) 118 974 8700; Fax:44 (0) 118 974 8701
INTERNET
E-mail addresses:
techsupport@smc.com
european.techsupport@smc-europe.com
Driver updates:
http://www.smc.com/index.cfm?action=tech_support_drivers_downloads
World Wide Web:
http://www.smc.com/
http://www.smc-europe.com/
For Literature or Advertising Response, Call:
U.S.A. and Canada: (800) SMC-4-YOU Fax (949) 679-1481
Spain: 34-93-477-4935 Fax 34-93-477-3774
UK: 44 (0) 118 974 8700 Fax 44 (0) 118 974 8701
France: 33 (0) 41 38 32 32 Fax 33 (0) 41 38 01 58
Italy: 39 02 739 12 33 Fax 39 02 739 14 17
Benelux: 31 33 455 72 88 Fax 31 33 455 73 30
Central Europe: 49 (0) 89 92861-0 Fax 49 (0) 89 92861-230
Switzerland: 41 (0) 1 9409971 Fax 41 (0) 1 9409972
Nordic: 46 (0) 868 70700 Fax 46 (0) 887 62 62
Northern Europe: 44 (0) 118 974 8700 Fax 44 (0) 118 974 8701
Eastern Europe: 34 -93-477-4920 Fax 34 93 477 3774
Sub Saharan Africa: 27-11 314 1133 Fax 27-11 314 9133
North Africa: 34 93 477 4920 Fax 34 93 477 3774
Russia: 7 (095) 290 29 96 Fax 7 (095) 290 29 96
PRC: 86-10-6235-4958 Fax 86-10-6235-4962
Taiwan: 886-2-2659-9669 Fax 886-2-2659-9666
Asia Pacific: (65) 238 6556 Fax (65) 238 6466
Korea: 82-2-553-0860 Fax 82-2-553-7202
Japan: 81-3-5645-5715 Fax 81-3-5645-5716
Australia: 61-2-8875-7887 Fax 61-2-8875-7777
India: 91-22-8204437 Fax 91-22-8204443
If you are looking for further contact information, please visit www.smc.com or
www.smc-europe.com.
Model Number: SMC7004VWBR
38 Tesla
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 679-8000
Pub. # 150000026400E
Revision Number E042003-R01 F 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...